Endocrinology. Learning Outcomes. Cognitive Domain. Psychomotor Domain. ABHES Competencies. Affective Domain
|
|
|
- Elisabeth Butler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 36 Endocrinology Learning Outcomes Cognitive Domain 1. Spell and define key terms 2. Identify abnormal conditions of the thyroid, pancreas, adrenal, and pituitary glands 3. Describe the tests commonly used to diagnose disorders of these endocrine system glands 4. Explain your role in working with patients with endocrine system disorders 5. Identify common pathologies related to each body system 6. Describe implications for treatment related to pathology Psychomotor Domain 1. Manage a patient with a diabetic emergency (Procedure 36-1) 2. Assist physician with patient care 3. Prepare a patient for procedures and/or treatments 4. Practice standard precautions 5. Document patient care 6. Document patient education 7. Practice within the standard of care for a medical assistant Affective Domain 1. Apply critical thinking skills in performing patient assessment and care 2. Use language/verbal skills that enable patients understanding 3. Demonstrate empathy in communicating with patients, family, and staff 4. Use appropriate body language and other nonverbal skills in communicating with patients, family, and staff 5. Demonstrate awareness of the territorial boundaries of the person with whom you are communicating 6. Demonstrate sensitivity appropriate to the message being delivered 7. Demonstrate recognition of the patient s level of understanding in communications 8. Recognize and protect personal boundaries in communicating with others 9. Demonstrate respect for individual diversity, incorporating awareness of one s own biases in areas including gender, race, religion, age, and economic status 10. Apply active listening skills 11. Apply local, state, and federal health care legislation and regulation appropriate to the medical assisting practice setting ABHES Competencies 1. Assist the physician with the regimen of diagnostic and treatment modalities as they relate to each body system 2. Comply with federal, state, and local health laws and regulations 3. Communicate on the recipient s level of comprehension 4. Serve as a liaison between the physician and others 5. Show empathy and impartiality when dealing with patients 6. Document accurately 665
2 666 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant Name: Date: Grade: COG MULTIPLE CHOICE Circle the letter preceding the correct answer: 1. A patient with hypothyroidism must take hormone replacements: a. for as many years as he has had the disease. b. until the conclusion of puberty. c. for his entire life. d. until middle age. e. for 10 years. 2. Diabetics may need supplemental insulin to: a. test blood glucose levels. b. reverse vascular changes. c. reduce the presence of ketones. d. restore pancreatic function. e. control blood glucose levels. 3. One symptom of ketoacidosis is: a. shallow respirations. b. low blood glucose levels. c. overhydration. d. abdominal pain. e. pale, moist skin. 4. Diabetes mellitus affects metabolism of which type of molecule? a. Neurotransmitters b. Carbohydrates c. Hormones d. Vitamins e. Lipids 5. One symptom of type 1 diabetes mellitus is: a. polyuria. b. exophthalmia. c. anorexia. d. weight gain. e. a goiter. 6. Hyperpigmentation of the skin might be an indication of: a. Cushing syndrome. b. Hashimoto thyroiditis. c. Graves disease. d. Addison disease. e. diabetes insipidus. 7. To control gestational diabetes, a blood glucose specimen should be taken from a pregnant woman between: a. 28 and 32 weeks of gestation. b. 24 and 28 weeks of gestation. c. 20 and 24 weeks of gestation. d. 16 and 20 weeks of gestation. e. 12 and 16 weeks of gestation. 8. Cushing syndrome sufferers may experience accelerated: a. Addison disease. b. endocarditis. c. osteoporosis. d. arthritis. e. dementia. 9. Acromegaly results primarily in: a. an increase in bone width. b. muscular atrophy. c. an increase in bone length. d. muscular hypertrophy. e. an increase in bone density.
3 CHAPTER 36 Endocrinology Growth can be stimulated for children with dwarfism by: a. repairs in the pituitary gland. b. administration of growth hormone. c. psychotherapy. d. increased physical activity. e. a high-protein diet. 11. Diabetes inspidus results from a deficiency of: a. adrenocorticotropic hormone. b. anterior pituitary hormones. c. human growth hormone. d. antidiuretic hormone. e. thyroid hormones. 12. Insulin shock is a result of: a. Cushing syndrome. b. Addison disease. c. Graves disease. d. hyperglycemia. e. hypoglycemia. 13. Diabetes mellitus patients need to care for their feet because: a. they regularly develop ingrown toenails. b. their peripheral circulation may be poor. c. they suffer severe joint pain. d. they have weak calves. e. foot pain occurs. 14. Exophthalmia is a protrusion of the: a. thyroid gland. b. pancreas. c. gall bladder. d. eyes. e. liver. 15. Patients taking corticosteroids may be at risk for: a. Cushing disease. b. Addison disease. c. type 2 diabetes mellitus. d. Graves disease. e. Hashimoto thyroiditis. 16. The A1C test determines how well blood glucose has been controlled during the previous: a. 2 to 3 hours. b. 2 to 3 days. c. 2 to 3 weeks. d. 2 to 3 months. e. 2 to 3 years. 17. Gigantism is a disorder of the: a. adrenal glands. b. pancreas. c. liver. d. thyroid. e. pituitary gland. 18. A thyroid scan relies on a radioactive isotope of what element? a. Iodine b. Barium c. Indium d. Bismuth e. Iridium 19. Addison disease is a disorder of the: a. pituitary gland. b. pancreas. c. thyroid. d. adrenal gland. e. salivary glands. 20. Both Graves disease and goiters are examples of: a. hypothyroidism. b. hypoglycemia. c. hyperthyroidism. d. hyperglycemia. e. hypertension.
4 668 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant COG MATCHING Grade: Place the letter preceding the defi nition on the line next to the term. Key Terms Definitions 21. acromegaly a. an enlargement of the thyroid gland 22. Addison disease 23. Cushing syndrome 24. diabetes insipidus 25. dwarfism 26. endocrinologist 27. exophthalmia 28. gigantism 29. glycosuria b. a substance that is produced by an endocrine gland and travels through the blood to a distant organ or gland where it acts to modify the structure or function of that gland or organ c. an adrenal gland disorder that results in an increased production of ACTH from the pituitary glands d. excess quantities of thyroid hormone in tissues e. excessive proliferation of normal cells in the normal tissue arrangement of an organism f. the end products of fat metabolism g. itching h. pronounced hyperthyroidism with signs of enlarged thyroid and exophthalmos i. a type of diabetes in which patients do not require insulin to control blood sugar 30. goiter 31. Graves disease 32. Hashimoto thyroiditis 33. hormones 34. hyperglycemia 35. hyperplasia 36. hypoglycemia 37. insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus 38. ketoacidosis 39. ketones 40. non insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus j. a deficiency in insulin production that leads to an inability to metabolize carbohydrates k. partial or complete failure of the adrenal cortex functions, causing general physical deterioration l. the presence of glucose in the urine m. a disease of the immune system in which the tissue of the thyroid gland is replaced with fibrous tissue n. excessive thirst o. abnormal underdevelopment of the body with extreme shortness but normal proportion; achondroplastic dwarfism is an inherited growth disorder characterized by shortened limbs and a large head but almost normal trunk proportions p. acidosis accompanied by an accumulation of ketones in the body q. excessive size and stature caused most frequently by hypersecretion of the human growth hormone r. deficiency of sugar in the blood s. an unusual protrusion of the eyeballs as a result of a thyroid disorder t. a disorder of metabolism characterized by polyuria and polydipsia; caused by a deficiency in ADH or an inability of the kidneys to respond to ADH 41. polydipsia 42. polyphagia u. excessive excretion and elimination of urine v. hyperfunction of the anterior pituitary gland near the end of puberty that results in increased bone width.
5 CHAPTER 36 Endocrinology polyuria 44. pruritus 45. radioimmunoassay 46. thyrotoxicosis w. the introduction of radioactive substances in the body to determine the concentration of a substance in the serum, usually the concentration of antigens, antibodies, or proteins x. a doctor who diagnoses and treats disorders of the endocrine system and its hormone-secreting glands y. abnormal hunger z. an increase in blood sugar, as in diabetes mellitus COG IDENTIFICATION Grade: 47. Read the following list of symptoms. Are these symptoms representative of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia? Place the prefix hyper on the line preceding the symptoms for hyperglycemia and hypo for hypoglycemia. a. Pale complexion b. Deep respirations c. Moist skin d. Shallow respirations e. Abdominal pain f. Rapid, bounding pulse g. Fruity breath h. Subnormal blood glucose levels COG SHORT ANSWER Grade: 48. When does ketoacidosis occur?
6 670 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant 49. A patient is stunned to learn that she has been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus. She is 43 years old and in excellent health. As a personal trainer and nutritionist, she has always taken good care of her body. What potential cause of type 2 diabetes mellitus might she be overlooking? 50. A patient complains that, lately, his appetite has been ferocious, but he is actually losing weight. He does not understand why this is happening. What do you tell him? 51. Why is it difficult for many sufferers of endocrine disorders to comply with physicians orders? 52. A patient who has been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus explains that a friend told him the disease is sometimes called non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. He asks if this means that he will not need to take insulin. Is he correct? Why, or why not?
7 CHAPTER 36 Endocrinology Who might be at risk for gestational diabetes mellitus? 54. What is the cause of hypoglycemia? 55. How is Addison disease treated? 56. A patient is diagnosed with dwarfism, and the patient s mother is extremely distressed, wondering if certain body parts will grow normally while others will not. She also wonders if her daughter could ever grow normally. What could you tell the mother? 57. What do the fasting glucose test and glucose tolerance test for diabetes mellitus have in common?
8 672 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant 58. What is the purpose of the A1C blood test? 59. Cushing syndrome and Addison disease are both disorders of which gland? 60. Why is it important that patients with diseases of the endocrine system wear a medical alert bracelet or necklace? COG TRUE OR FALSE? Grade: Indicate whether the statements are true or false by placing the letter T (true) or F (false) on the line preceding the statement. 61. Endocrine glands are unlike other glands in the body because they are ductless. 62. Hashimoto thyroiditis is a disease of the endocrine system. 63. Type 1 diabetes mellitus occurs only in children and young adults. 64. Addison disease has no effect on the pituitary gland.
9 CHAPTER 36 Endocrinology 673 COG AFF CASE STUDIES FOR CRITICAL THINKING Grade: 1. A patient is worried that a thyroid function test requires the use of radioactive material. Explain, to the best of your ability, how the test works and why there is no need to be concerned about radiation. If necessary, do additional research on thyroid function tests to prepare your answer. 2. After an examination, a pregnant patient asks why the physician performed a test on her blood glucose level. She says she does not have diabetes. Explain why the physician chose to do the test. 3. Young children are sometimes afflicted with diabetes mellitus. This can be difficult for both the child and the family. What is your perspective of the medical assistant s role in this situation? 4. A patient with hyperthyroidism says she would prefer not to be treated because she has few negative symptoms, and the increased metabolic rate helps keep her thin. How would you respond to this?
10
11 CHAPTER 36 Endocrinology 675 PSY PROCEDURE 36-1 Manage a Patient with a Diabetic Emergency Name: Date: Time: Grade: EQUIPMENT/SUPPLIES: Gloves, blood glucose monitor and strips, fruit juice or oral glucose tablets STANDARDS: Given the needed equipment and a place to work the student will perform this skill with % accuracy in a total of minutes. (Your instructor will tell you what the percentage and time limits will be before you begin.) KEY : 4 = Satisfactory 0 = Unsatisfactory NA = This step is not counted PROCEDURE STEPS SELF PARTNER INSTRUCTOR 1. Wash your hands. 2. Recognize the signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia. 3. Identify the patient and escort him or her into the examination room. 4. Determine if the patient has been previously diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. 5. Ask the patient if he or she has eaten today or taken any medication. 6. Notify the physician about the patient and perform a capillary stick for a blood glucose as directed. 7. Notify the physician with the results of the blood glucose and treat the patient as ordered by the physician. a. Administer insulin subcutaneously to a patient with hyperglycemia. b. Administer a quick-acting sugar, such as an oral glucose tablet or fruit juice, for a patient with hypoglycemia. 8. AFF Explain how to respond to a patient who is developmentally challenged. 9. Be prepared to notify EMS as directed by the physician if the symptoms do not improve or worsen. 10. Document any observations and treatments given.
12 676 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant CALCULATION Total Possible Points: Total Points Earned: Multiplied by 100 = Divided by Total Possible Points = % PASS FAIL COMMENTS: Student s signature Partner s signature Instructor s signature Date Date Date
Hormones by location
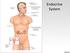 Endocrine System Hormones by location Pineal Gland: Melatonin Feeling of sleepiness Hypothalamus: Hormones that stimulate or inhibit pituitary Temp., hunger, parenting attachment, thirst Pituitary Gland:
Endocrine System Hormones by location Pineal Gland: Melatonin Feeling of sleepiness Hypothalamus: Hormones that stimulate or inhibit pituitary Temp., hunger, parenting attachment, thirst Pituitary Gland:
Diabetic Emergencies. Chapter 15
 Diabetic Emergencies Chapter 15 Diabetes- is a disorder of glucose metabolism or difficulty metabolizing carbohydrates, fats and proteins Full name is diabetes mellitus which refers to the presence of
Diabetic Emergencies Chapter 15 Diabetes- is a disorder of glucose metabolism or difficulty metabolizing carbohydrates, fats and proteins Full name is diabetes mellitus which refers to the presence of
The Endocrine System
 C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013 Endocrine system includes 8 major glands. 1. Pituitary (master gland)
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013 Endocrine system includes 8 major glands. 1. Pituitary (master gland)
Chapter 12 Endocrine System (export).notebook. February 27, Mar 17 2:59 PM. Mar 17 3:09 PM. Mar 17 3:05 PM. Mar 17 3:03 PM.
 Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Scrub In. TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of:
 Scrub In TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: a. Pancreas b. Testes c. Thymus gland d. Thyroid gland Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of: a. Calcium in the blood b. Endorphins
Scrub In TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: a. Pancreas b. Testes c. Thymus gland d. Thyroid gland Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of: a. Calcium in the blood b. Endorphins
Endocrine System. A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine. Endocrine: Exocrine:
 Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Endocrine Glands Glands that secrete their products (HORMONES) into extracellular spaces around cells. The hormones then enter into the bloodstream by diffusing into the capillaries
The Endocrine System Endocrine Glands Glands that secrete their products (HORMONES) into extracellular spaces around cells. The hormones then enter into the bloodstream by diffusing into the capillaries
An Overview Of Diabetes And Endocrinology.
 An Overview Of Diabetes And Endocrinology. Maraveyas Anthony Maraveyas Anthony Department of Academic Oncology Castle Hill Hospital England UK Tel: 01482461318 Research interests Diabetes Endocrinology.
An Overview Of Diabetes And Endocrinology. Maraveyas Anthony Maraveyas Anthony Department of Academic Oncology Castle Hill Hospital England UK Tel: 01482461318 Research interests Diabetes Endocrinology.
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System. Chapter 9
 Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
CHAPTER 50 Endocrine Systems. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 CHAPTER 50 Endocrine Systems Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Endocrine system All the endocrine glands and other organs with hormonesecreting
CHAPTER 50 Endocrine Systems Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Endocrine system All the endocrine glands and other organs with hormonesecreting
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Understand the functions and disorders of the endocrine system
 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3026A: CHILDREN S HEALTH
 J 1 BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3026A: CHILDREN S HEALTH NURSING MANAGEMENT OF ENDOCRINE DYSFUNCTION: THEORETICAL SKILLS and KNOWLEDGE, SCIENTIFIC PRINCIPLES, CRITICAL THINKING, HEALTHCARE PROMOTION,
J 1 BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3026A: CHILDREN S HEALTH NURSING MANAGEMENT OF ENDOCRINE DYSFUNCTION: THEORETICAL SKILLS and KNOWLEDGE, SCIENTIFIC PRINCIPLES, CRITICAL THINKING, HEALTHCARE PROMOTION,
Regula'ng Body Func'on
 Chapter 10 Regula'ng Body Func'on Working closely with your nervous system is the endocrine system, a chemical communication system that regulate many body functions. Exocrine vs Endocrine Exocrine Glands
Chapter 10 Regula'ng Body Func'on Working closely with your nervous system is the endocrine system, a chemical communication system that regulate many body functions. Exocrine vs Endocrine Exocrine Glands
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Learning Objectives. Endocrine System 11/19/2012. Yet to receive Original Copyrite Info 1.
 Chapter 14 Endocrine System Learning Objectives 1. Recognize or write the functions of the endocrine system. 2. Recognize or write the meanings of Chapter 14 word parts and use them to build and analyze
Chapter 14 Endocrine System Learning Objectives 1. Recognize or write the functions of the endocrine system. 2. Recognize or write the meanings of Chapter 14 word parts and use them to build and analyze
The Endocrine System. Lipid-Soluble Hormones. Bio217 Sp14 Unit 5. Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow
 Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Unit V: Endocrine System Disorders Chapter 17 Chap. 17: Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Chap. 18: Alterations
Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Unit V: Endocrine System Disorders Chapter 17 Chap. 17: Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Chap. 18: Alterations
Robert Wadlow and his father
 Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
The Endocrine System 7/6/2015. Outline. Function of the Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
Endocrine Notes Mrs. Laux AP Biology I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones
 I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
Hypothyroidism. Possible cause is iodine deficiency treated by dietary iodine supplements
 Name: Lab Day/Time: Endocrine System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 11 List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes Term Meaning Example Term Meaning Example adeno- gland adenohypophysis insipid- without
Name: Lab Day/Time: Endocrine System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 11 List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes Term Meaning Example Term Meaning Example adeno- gland adenohypophysis insipid- without
I. Provide patient care that is compassionate, appropriate and effective for the prevention and treatment of endocrinologic disorders.
 Endocrinology Curriculum Goal Endocrinology is the diagnosis and care of disorders of the endocrine system. The principal endocrine problems handled by the general internist include goiter, thyroid nodules,
Endocrinology Curriculum Goal Endocrinology is the diagnosis and care of disorders of the endocrine system. The principal endocrine problems handled by the general internist include goiter, thyroid nodules,
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Endocrinology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Endocrinology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing endocrine dysfunction, and in counseling and
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Endocrinology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing endocrine dysfunction, and in counseling and
Endocrine GLANDS: Question:1. Fill in the Blanks.
 Endocrine GLANDS: Question:1 Fill in the Blanks. 1. Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands which are poured in to the blood. 2. Adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline hormone which prepares the body to
Endocrine GLANDS: Question:1 Fill in the Blanks. 1. Hormones are secreted by endocrine glands which are poured in to the blood. 2. Adrenal medulla secretes adrenaline hormone which prepares the body to
Provide preventive counseling to parents and patients with specific endocrine conditions about:
 Endocrinology Description: The resident will become familiar with the diagnosis, management, and treatment of endocrine problems. The resident will evaluate patients with a multitude of endocrine problems,
Endocrinology Description: The resident will become familiar with the diagnosis, management, and treatment of endocrine problems. The resident will evaluate patients with a multitude of endocrine problems,
Endocrinology BLOCK (ENDO 225)
 Attachment 2 (g) Kingdom of Saudi Arabia The National Commission for Academic Accreditation & Assessment COURSE REPORT Endocrinology BLOCK (ENDO 225) 1433-1434 (2012-2013) To be completed by course instructors
Attachment 2 (g) Kingdom of Saudi Arabia The National Commission for Academic Accreditation & Assessment COURSE REPORT Endocrinology BLOCK (ENDO 225) 1433-1434 (2012-2013) To be completed by course instructors
Pulmonary Medicine. 1. Spell and define the key terms 2. Identify the primary defense mechanisms
 CHAPTER 30 Pulmonary Medicine Learning Outcomes Cognitive Domain 1. Spell and define the key terms 2. Identify the primary defense mechanisms of the respiratory system 3. Identify common pathology related
CHAPTER 30 Pulmonary Medicine Learning Outcomes Cognitive Domain 1. Spell and define the key terms 2. Identify the primary defense mechanisms of the respiratory system 3. Identify common pathology related
Endocrine System. Regulating Blood Sugar. Thursday, December 14, 17
 Endocrine System Regulating Blood Sugar Stress results in nervous and hormonal responses. The adrenal glands are located above each kidney. Involved in stress response. Stress Upsets Homeostasis Stress
Endocrine System Regulating Blood Sugar Stress results in nervous and hormonal responses. The adrenal glands are located above each kidney. Involved in stress response. Stress Upsets Homeostasis Stress
PROBLEMS WITH REGULATION AND METABOLISM. Objectives A & P 8/11/2011
 PROBLEMS WITH REGULATION AND METABOLISM Lemone and Burke Chapters 18-20 Objectives Review A & P Recall age related changes Identify diagnostic tests Describe etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestation,
PROBLEMS WITH REGULATION AND METABOLISM Lemone and Burke Chapters 18-20 Objectives Review A & P Recall age related changes Identify diagnostic tests Describe etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestation,
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Disorders
 CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Disorders molecular formula C12H22O11 Major index which describes metabolism of carbohydrates, is a sugar level in blood. In healthy people it is 4,4-6,6 mmol/l (70-110 mg/dl)
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Disorders molecular formula C12H22O11 Major index which describes metabolism of carbohydrates, is a sugar level in blood. In healthy people it is 4,4-6,6 mmol/l (70-110 mg/dl)
Endocrine System. Modified by M. Myers
 Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine system. Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to:
 Name: 1.4 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.3 Responses in the Human -- Endocrine System 1. Say what an Endocrine system is 2. Define the term
Name: 1.4 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.3 Responses in the Human -- Endocrine System 1. Say what an Endocrine system is 2. Define the term
Biology 30. Morinville Community High School. Unit 2: Endocrine System. Name:
 Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
C H A P T E R 1 3 : T H E E N D O C R I N E S Y S T E M
 C H A P T E R 1 3 : T H E E N D O C R I N E S Y S T E M U N I T 1: MAINTA I N I N G DYNAMIC EQ UILIBR IUM II NERVOUS SYSTEM VS. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The nervous system coordinates rapid and precise responses
C H A P T E R 1 3 : T H E E N D O C R I N E S Y S T E M U N I T 1: MAINTA I N I N G DYNAMIC EQ UILIBR IUM II NERVOUS SYSTEM VS. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The nervous system coordinates rapid and precise responses
CHAPTER 12. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK
 CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions)
 ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions) 1. While the nervous system functions very slowly, the endocrine system works very quickly. a. True b. False 2. Hormones that act locally
ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions) 1. While the nervous system functions very slowly, the endocrine system works very quickly. a. True b. False 2. Hormones that act locally
1. Spell and define the key terms 2. List and describe the disorders of the. the urinary system and the male reproductive
 CHAPTER 34 Urology Learning Outcomes Cognitive Domain 1. Spell and define the key terms 2. List and describe the disorders of the urinary system and the male reproductive system 3. Describe and explain
CHAPTER 34 Urology Learning Outcomes Cognitive Domain 1. Spell and define the key terms 2. List and describe the disorders of the urinary system and the male reproductive system 3. Describe and explain
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach - Chapter 27
 Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach - Chapter 27 NURSING CARE OF THE CLIENT: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM NVOC 22C Eliza Rivera-Mitu Mitu,, RN, MSN A Unique System The endocrine system is unique in that
Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach - Chapter 27 NURSING CARE OF THE CLIENT: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM NVOC 22C Eliza Rivera-Mitu Mitu,, RN, MSN A Unique System The endocrine system is unique in that
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs
 9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
Chapter 50 4/9/2015. Care of the Patient with an Endocrine Disorder. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. Endocrine Glands and Hormones cont d
 Chapter 50 Care of the Patient with an Endocrine Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Endocrine Glands and Hormones Pituitary
Chapter 50 Care of the Patient with an Endocrine Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Endocrine Glands and Hormones Pituitary
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
The Endocrine SyStem. COMMUNICATION System
 The Endocrine SyStem COMMUNICATION System Endocrine FACTS The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products (hormones) directly into the bloodstream. The response of hormones is slower
The Endocrine SyStem COMMUNICATION System Endocrine FACTS The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products (hormones) directly into the bloodstream. The response of hormones is slower
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
Endocrine System. The Endocrine Glands
 Endocrine System Working together with the nervous system, the endocrine system helps maintain homeostasis in the body. Where the nervous system uses electric signals, the endocrine system uses chemical
Endocrine System Working together with the nervous system, the endocrine system helps maintain homeostasis in the body. Where the nervous system uses electric signals, the endocrine system uses chemical
Chapter 16: The Endocrine System
 Chapter 16: The Endocrine System Objectives Define the terms endocrine and exocrine. Describe the physiology of hormones including the different types and the mechanisms of their actions. Compare endocrine
Chapter 16: The Endocrine System Objectives Define the terms endocrine and exocrine. Describe the physiology of hormones including the different types and the mechanisms of their actions. Compare endocrine
Ch. 39 Endocrine System
 Ch. 39 Endocrine System The Endocrine System The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products deliver messages throughout the body Hormones Hormones
Ch. 39 Endocrine System The Endocrine System The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products deliver messages throughout the body Hormones Hormones
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
9/11/2012. Chapter 11. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives. Endocrine Emergencies. Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes
 Chapter 11 Endocrine Emergencies Learning Objectives Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes Explain roles of glucagon, glycogen, and glucose in hypoglycemia Learning Objectives Discuss following medications
Chapter 11 Endocrine Emergencies Learning Objectives Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes Explain roles of glucagon, glycogen, and glucose in hypoglycemia Learning Objectives Discuss following medications
Hormones. Regulation. Endocrine System. What Do Endocrine Glands Release (Secrete)? Endocrine System
 Endocrine System Function: Endocrine System - For glands to release products into bloodstream to deliver messages throughout the body. Regulation Is the control & coordination of other life functions to
Endocrine System Function: Endocrine System - For glands to release products into bloodstream to deliver messages throughout the body. Regulation Is the control & coordination of other life functions to
Objectives / Learning Targets: The learner who successfully completes this course will be able to demonstrate understanding of the following concepts:
 Objectives / Learning Targets: The learner who successfully completes this course will be able to demonstrate understanding of the following concepts: Insulin s function in the body. The basics of diabetes
Objectives / Learning Targets: The learner who successfully completes this course will be able to demonstrate understanding of the following concepts: Insulin s function in the body. The basics of diabetes
Endocrine System. True or False
 True or False Endocrine System Some overweight people actually eat very little; their excess weight is caused by glands A woman who becomes anxious and depressed just before menstruating is suffering from
True or False Endocrine System Some overweight people actually eat very little; their excess weight is caused by glands A woman who becomes anxious and depressed just before menstruating is suffering from
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System 26.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Hormones are chemicals produced by the endocrine system that
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System 26.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Hormones are chemicals produced by the endocrine system that
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System. Target Cells: Cells specialized to respond to hormones
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System R. Cummins 1 The Endocrine System Body Coordination This is controlled by the nervous and endocrine systems. The endocrine system is, 1. Slow acting 2. Based on hormones 3. Has a slow
The Endocrine System R. Cummins 1 The Endocrine System Body Coordination This is controlled by the nervous and endocrine systems. The endocrine system is, 1. Slow acting 2. Based on hormones 3. Has a slow
9.2 Hormonal Regulation of Growth
 9.2 Hormonal Regulation of Growth Hormonal Regulation of Growth Pituitary gland regulates growth and development Thyroid gland regulates metabolic rate (exception: some hormones for growth and development)
9.2 Hormonal Regulation of Growth Hormonal Regulation of Growth Pituitary gland regulates growth and development Thyroid gland regulates metabolic rate (exception: some hormones for growth and development)
Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland. Endocrinology
 Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland Endocrinology 5.22 GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Endocrine). Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing endocrine PC, MK, dysfunction,
Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland Endocrinology 5.22 GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Endocrine). Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing endocrine PC, MK, dysfunction,
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine System Functions
 Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine Glands. Comparison of Nervous System and Endocrine System
 Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System. Simple Hormone Pathways
 Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Pathology of the Endocrine System
 Pathology of the Endocrine System นายแพทย ดร.ณตพล ศ ภณ ฐเศรษฐก ล ภาคว ชาพยาธ ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยนเรศวร 4 เมษายน พ.ศ. 2557 Topics Introduction Diseases of the Endocrine glands Pituitary gland
Pathology of the Endocrine System นายแพทย ดร.ณตพล ศ ภณ ฐเศรษฐก ล ภาคว ชาพยาธ ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยนเรศวร 4 เมษายน พ.ศ. 2557 Topics Introduction Diseases of the Endocrine glands Pituitary gland
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology
 Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
9.3 Stress Response and Blood Sugar
 9.3 Stress Response and Blood Sugar Regulate Stress Response Regulate Blood Sugar Stress Response Involves hormone pathways that regulate metabolism, heart, rate and breathing The Adrenal Glands a pair
9.3 Stress Response and Blood Sugar Regulate Stress Response Regulate Blood Sugar Stress Response Involves hormone pathways that regulate metabolism, heart, rate and breathing The Adrenal Glands a pair
Pathophysiology of the th E d n ocr i ne S S t ys em B. Marinov, MD, PhD Endocrine system Central: Hypothalamus
 Pathophysiology of the Endocrine System B. Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department Medical University of Plovdiv Endocrine system Central: Hypothalamus Pituitary Pineal Peripheral Thymus Thyroid Parathyroid
Pathophysiology of the Endocrine System B. Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department Medical University of Plovdiv Endocrine system Central: Hypothalamus Pituitary Pineal Peripheral Thymus Thyroid Parathyroid
Diabetes Emergency Kit
 Diabetes Emergency Kit for: Last updated on / / Courtesy of www.laurenshope.com Diabetes General Information TREATMENT If the child is awake and can swallow, provide sugar immediately. Give 1/2 cup of
Diabetes Emergency Kit for: Last updated on / / Courtesy of www.laurenshope.com Diabetes General Information TREATMENT If the child is awake and can swallow, provide sugar immediately. Give 1/2 cup of
Care of patients with endocrine system disorders
 King Saud University College of Nursing Medical Surgical Department Application of Adult Health Nursing Skills ( NUR 317 ) Care of patients with endocrine system disorders Prepared by Mrs: Alwah M. Alkathiri
King Saud University College of Nursing Medical Surgical Department Application of Adult Health Nursing Skills ( NUR 317 ) Care of patients with endocrine system disorders Prepared by Mrs: Alwah M. Alkathiri
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11
 The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
1 1. LECTURE NOTES FOR UNIT NINE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 Endocrine System 1 1. LECTURE NOTES FOR UNIT NINE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM A. B C. II. HORMONES AND THEIR FUNCTIONS: A. Description of Hormones 1. secretions of endocrine organs
Endocrine System 1 1. LECTURE NOTES FOR UNIT NINE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM I. FUNCTIONS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM A. B C. II. HORMONES AND THEIR FUNCTIONS: A. Description of Hormones 1. secretions of endocrine organs
WK ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. ENDOCRINOLOGY
 WK ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. ENDOCRINOLOGY 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect where possible. 15 Classification. Nomenclature
WK ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. ENDOCRINOLOGY 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect where possible. 15 Classification. Nomenclature
Endocrine part two. Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Clinical Chemistry Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy
 Endocrine part two Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Clinical Chemistry Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Cushing's disease: increased secretion of adrenocorticotropic
Endocrine part two Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Clinical Chemistry Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Cushing's disease: increased secretion of adrenocorticotropic
PATHOLOGY OF ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Peerayut Sitthichaiyakul,, M.D.
 PATHOLOGY OF ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Peerayut Sitthichaiyakul,, M.D. Content Pituitary gland Anterior pituitary gland Hyperpituitarism Hypopituitarism Posteior pituitary gland Posterior pituitary syndrome Thyroid
PATHOLOGY OF ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Peerayut Sitthichaiyakul,, M.D. Content Pituitary gland Anterior pituitary gland Hyperpituitarism Hypopituitarism Posteior pituitary gland Posterior pituitary syndrome Thyroid
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Do Now: 1. Turn in your exit ticket that was due for homework 2. Pg 91: How did they use to test people for Diabetes?
 Do Now: 1. Turn in your exit ticket that was due for homework 2. Pg 91: How did they use to test people for Diabetes? Diabetes a disease in which the pancreas stops producing insulin, the hormone that
Do Now: 1. Turn in your exit ticket that was due for homework 2. Pg 91: How did they use to test people for Diabetes? Diabetes a disease in which the pancreas stops producing insulin, the hormone that
Chapter 21. Human Endocrine System
 Chapter 21 Human Endocrine System Endocrine System Consist of endocrine glands that secrete hormones which regulate a wide range of activities in humans Hormones- are secreted by glands and diffuse directly
Chapter 21 Human Endocrine System Endocrine System Consist of endocrine glands that secrete hormones which regulate a wide range of activities in humans Hormones- are secreted by glands and diffuse directly
Pediatric Endocrine Dysfunction
 Pediatric Endocrine Dysfunction Chapter 52 Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation The endocrine system is composed of various glands located throughout the body. These glands can synthesize
Pediatric Endocrine Dysfunction Chapter 52 Debra Mercer BSN, RN, RRT Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation The endocrine system is composed of various glands located throughout the body. These glands can synthesize
Types of Hormones * OpenStax. 1 Lipid-Derived Hormones (or Lipid-soluble Hormones)
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44766 1 Types of Hormones * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be
OpenStax-CNX module: m44766 1 Types of Hormones * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be
Chapter 13 worksheet
 Name: Chapter 13 worksheet The Endocrine System Please label the: hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland thyroid gland parathyroid gland thymus heart stomach liver adrenal glands kidneys pancreas small
Name: Chapter 13 worksheet The Endocrine System Please label the: hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland thyroid gland parathyroid gland thymus heart stomach liver adrenal glands kidneys pancreas small
Module 2 Endocrine System
 Module 2 Endocrine System Student Name: 1 Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Lesson 5 Total Marks Total Possible Marks 10 8 14 21 16 69 Your Mark Teacher Comments: 2 (10 marks) Lesson 1: Structure and
Module 2 Endocrine System Student Name: 1 Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Lesson 4 Lesson 5 Total Marks Total Possible Marks 10 8 14 21 16 69 Your Mark Teacher Comments: 2 (10 marks) Lesson 1: Structure and
Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes
 Operation of the Endocrine System Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes What is the Endocrine System? The endocrine system is comprised of the hormone producing glands and tissues of the body. Hypothalamus
Operation of the Endocrine System Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes What is the Endocrine System? The endocrine system is comprised of the hormone producing glands and tissues of the body. Hypothalamus
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 29 MAY 2013
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 29 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss the characteristics of hormones. Explain the differences between endocrine and exocrine glands. Look at the location and the functions
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 29 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss the characteristics of hormones. Explain the differences between endocrine and exocrine glands. Look at the location and the functions
Endocrine System Physiology
 M53_MARI0000_00_SE_EX04.qxd 7/15/11 4:32 PM Page 369 4 E X E R C I S E Endocrine System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments Consider covering the following topics to prepare students for the simulation:
M53_MARI0000_00_SE_EX04.qxd 7/15/11 4:32 PM Page 369 4 E X E R C I S E Endocrine System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments Consider covering the following topics to prepare students for the simulation:
Chapter Goal. Learning Objectives 9/12/2012. Chapter 25. Diabetic Emergencies
 Chapter 25 Diabetic Emergencies Chapter Goal Use assessment findings to formulate field impression & implement treatment plan for patients with diabetic emergencies Learning Objectives Describe pathophysiology
Chapter 25 Diabetic Emergencies Chapter Goal Use assessment findings to formulate field impression & implement treatment plan for patients with diabetic emergencies Learning Objectives Describe pathophysiology
Type 1 Diabetes. Insulin
 Type 1 Diabetes Introduction Type 1 diabetes prevents the body from removing sugar from the blood stream normally. Diabetes can lead to serious health problems if it is not treated. Currently, there is
Type 1 Diabetes Introduction Type 1 diabetes prevents the body from removing sugar from the blood stream normally. Diabetes can lead to serious health problems if it is not treated. Currently, there is
Pathology of pituitary gland. By: Shifaa Qa qa
 Pathology of pituitary gland By: Shifaa Qa qa Sella turcica Adenohypophysis (80%): - epithelial cells - acidophil, basophil, chromophobe - Somatotrophs, Mammosomatotrophs, Corticotrophs, Thyrotrophs, Gonadotrophs
Pathology of pituitary gland By: Shifaa Qa qa Sella turcica Adenohypophysis (80%): - epithelial cells - acidophil, basophil, chromophobe - Somatotrophs, Mammosomatotrophs, Corticotrophs, Thyrotrophs, Gonadotrophs
-The process by which organisms maintain, control, and coordinate their internal environment with a constantly changing external environment
 -The process by which organisms maintain, control, and coordinate their internal environment with a constantly changing external environment -It is all of the activities that help to maintain an organism
-The process by which organisms maintain, control, and coordinate their internal environment with a constantly changing external environment -It is all of the activities that help to maintain an organism
The Endocrine Pancreas (Chapter 10) *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m62118 1 The Endocrine Pancreas (Chapter 10) * Ildar Yakhin Based on The Endocrine Pancreas by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m62118 1 The Endocrine Pancreas (Chapter 10) * Ildar Yakhin Based on The Endocrine Pancreas by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
Medically Compromised Patients (Part II)
 Medically Compromised Patients (Part II) Ra ed Salma BDS, MSc, JBOMFS, MFDRCSI Endocrine Disorders I. Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Definition (WHO): - Chronic disease due to absolute or relative lack of insulin
Medically Compromised Patients (Part II) Ra ed Salma BDS, MSc, JBOMFS, MFDRCSI Endocrine Disorders I. Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Definition (WHO): - Chronic disease due to absolute or relative lack of insulin
Endocrine system pathology
 Endocrine system pathology Central endocrine system peripheral endocrine system: thyroid gland parathyroid gland pancreas adrenal glands Thyroid gland. the weight of normal thyroid gland is about 15 grams.
Endocrine system pathology Central endocrine system peripheral endocrine system: thyroid gland parathyroid gland pancreas adrenal glands Thyroid gland. the weight of normal thyroid gland is about 15 grams.
Endocrine system release hormones to regulates physiological process e.g growth, reproduction, metabolism, mentrual cycle, development of secondary
 Endocrine system release hormones to regulates physiological process e.g growth, reproduction, metabolism, mentrual cycle, development of secondary sexual characteristics Consists of endocrine glands which
Endocrine system release hormones to regulates physiological process e.g growth, reproduction, metabolism, mentrual cycle, development of secondary sexual characteristics Consists of endocrine glands which
Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland
 Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland The hypothalamus and pituitary gland form a unit that exerts control over the function of several endocrine glands (thyroid, adrenals, and
Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland The hypothalamus and pituitary gland form a unit that exerts control over the function of several endocrine glands (thyroid, adrenals, and
3. The function of that hormone. In other words, what change does that hormone facilitate.
 Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Estimation of Blood Glucose level. Friday, March 7, 14
 Estimation of Blood Glucose level Importance Diagnosis and treatment of carbohydrate metabolism disorders Monitor the effectivity and response to an ongoing treatment procedure Control mechanism Insulin
Estimation of Blood Glucose level Importance Diagnosis and treatment of carbohydrate metabolism disorders Monitor the effectivity and response to an ongoing treatment procedure Control mechanism Insulin
