Your prostate: A priority for life
|
|
|
- Hester Morrison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Your prostate: A priority for life A direct report to help every man understand the facts and realities of prostate problems Stop wondering what s normal, when to see your doctor and what the future holds Read on for a no-nonsense guide to the definitions, symptoms, diagnoses & treatment options of prostate problems and take control of your health and your life Ray Collins
2 Introduction Worryingly, two thirds of British men don t have a clue what their prostate gland actually does. If you re not in the know, you won t be aware of the problems that 35,000 men in the UK face every year and most importantly, you won t be able to spot the early warning signs if something goes wrong with your prostate. Remember, prostate problems needn t mean cancer there are other common conditions which are treatable and manageable. That s why it s crucial to know your body and spot the signs when something s not quite right. We blokes are infamous for shying away from seeing a doctor. It s bad enough going in for a repeat prescription, let alone when there s something wrong down there. That s why I m writing this report to give you the facts about prostate problems so you can begin to realise for yourself what s normal and know when you really do need to make that appointment. Don t be scared be prepared, that s what I say. Prostate problems are most common with men over 70 although even golden oldies at 50 are advised to start having regular health checks since it s between these ages that we re most at risk from more aggressive conditions. But who am I to dish out this advice? I m Ray Collins, a health writer dedicated to informing the nation about the latest health news, trends and solutions. The garbage they spin us on the news about our health these days is just preposterous and so contradictory that I ve taken to researching common health complaints myself and feeding back my findings to people who want straight-talking, no-nonsense advice so they can make up their own minds up and take control of their health and their lives. This report is just a stepping stone. If you have prostate problems, there are so many resources out there to help you manage, control and remain positive about the future. From support groups to charities, even the good old NHS. Read on to learn about your prostate what it is, what it does, how to keep it healthy, what obstacles it could throw up and how to overcome them. It will only take a few minutes and could just save your life And remember, if you re at all concerned about your health, please see a medical professional. Yours, Ray Collins
3 Be aware, take care 10 facts every man should know 1. A simple definition of the prostate gland The prostate is a walnut-sized gland in the male reproductive system. The role of the prostate is to make seminal fluid, which is mixed with sperm to make semen. Your prostate is positioned just below your bladder 2. What the prostate gland looks like The prostate is a small gland situated just below the bladder between the root of the penis and the anus In older men with prostate problems it may swell from the size of a walnut to that of a plum If the prostate grows too big, urine flow may be weaker 3. How to know if your prostate is healthy Urine flow is a good indicator of prostate problems. If your once proud stream of urine has dwindled to a feeble trickle, you'll need to see your GP There are a variety of reasons for a change in the pressure of urine flow that are completely normal and just part of the natural ageing process. Symptoms to look out for are getting up more at night to urinate, dribbling before or after urinating, and a weak urine flow
4 Less common symptoms include pain in the testicles, problems getting an erection, pain when ejaculating, pain when passing urine and blood in the urine or semen (hematospermia) 4. Age isn t always a factor Prostate problems are usually most common in men over 70 yet there are conditions which can affect men as young as middle-age. Remember, these conditions are common and manageable and aren t always linked to cancer so it s best to get them checked out by a medical professional so you can treat them accordingly 5. PSA tests If your GP wants to rule out prostate cancer he will probably suggest that you have a PSA test. This is a blood test that measures the level of a protein called Prostate specific antigen (PSA). PSA is produced in the prostate gland and found in small amounts in the blood A raised PSA level can be a warning sign of the presence of prostate cancer. It can also indicate other problems that aren't cancer - three out of four men with a raised PSA level will not have prostate cancer. However, the higher the PSA level, the greater the likelihood of a cancer being present Remember though, that although the PSA test is seen as the best current method for screening, it is often not an absolute measure of accuracy so second opinions may be sought 6. The genetic link Look at your family tree. Has your father, grandfather, uncle or brother had prostate cancer? If this is the case, then you have a greater risk of developing the disease It s hoped that in the future genetic profiling will be developed in order to identify men with a high risk Tell your doctor if any family members have had the disease so you can be given regular blood tests to monitor your PSA 7. Healthy eating does reduce the risk Try to eat six portions of brightly coloured fruit and vegetables a day. Include three portions of oily fish a week, such as salmon, herrings, mackerel or sardines, which are rich in vitamin D and essential fatty acids, omega-3 and omega-6 There is evidence that selenium, a trace mineral, helps lower the risk of prostate cancer by combating cell damage. Selenium is found in broccoli, Brazil nuts, seafood, asparagus, brown rice and onions
5 Selenium can also be taken in supplement form and works best when combined with vitamin E and zinc Mediterranean men have a lower prostate cancer rate and this is believed to be down to a diet rich in fruit and vegetables, garlic, olive oil, fish and tomatoes Tomatoes contain a bright red pigment called lycopene, a powerful carotenoid antioxidant, which helps to repair damaged cells 8. Maintaining a healthy weight is advised There is also a clear link between obesity and cancer putting on those extra cuddly pounds around your waist doubles your risk of dying of cancer Reduce your fat intake and replace saturated fats with monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats Saturated fats are found in found in meat, some margarines, crisps, chips, and many processed foods Lower salt intake and watch your alcohol intake. Avoid too much cured meat such as smoked dishes, or processed hams, as they may contain carcinogens, a substance that may promote or aggravate cancer 9. Keep hydrated with antioxidants Japanese and Chinese men have very low levels of prostate cancer and green tea is thought to be one reason why. This is because it's rich in polyphenols, which have antioxidant properties Alcohol and fizzy drinks are rich in sugar, which can pile on the pounds. Instead, you should try to drink six to eight glasses of water each day to help flush out the kidneys and keep the body hydrated 10. Leading an active lifestyle Exercise helps to balance hormone levels, prevent obesity and boost the immune system. And it's never too late - studies have shown that exercise is still beneficial for men who have been diagnosed with prostate cancer and are receiving treatment for it Since the prostate gland plays a role in the sexual response cycle, it s important for it to release seminal fluid (semen) and some medical professionals recommend ejaculation for relieving prostate distress and as a preventative measure for such conditions
6 Leaflets, advice from your GP, rumours in the pub If you re as confused as I was about prostate problems, read the things you REALLY need to know here Growing older raises your risk of prostate problems. The most common 3 prostate problems are: 1) Prostatitis 2) Benign prostatic hyperplasia 3) Prostate cancer I ll talk through these in more depth shortly, but first, let s look at general changes you should look out for what s normal and what you should monitor. Urinary habits As you get older, you may find you have urinary problems but you don t have to put up with them. If you have a problem in your prostate, your urinary habits may change. This is because your prostate surrounds the tube you pass urine through (your urethra) For some men, problems with passing urine may be an early warning sign that they have a prostate problem. Most men with early prostate cancer do not have urinary symptoms. Remember that not all problems with passing urine lead to the prostate. They could be caused by another health problem such as diabetes or by medication you may be taking. Common symptoms of prostate problems Needing to urinate more often, especially at night Difficulty starting to pass urine Straining or taking a long time to finish urinating A weak flow of urine A feeling that your bladder has not emptied properly Needing to rush to the toilet or dribbling urine
7 Less common symptoms of prostate problems Pain when passing urine Pain when ejaculating Problems getting or keeping an erection Blood in the urine or semen If you have any of the symptoms above, you should make an appointment to see your GP. Now we re going to take a more in-depth look at the 3 most common prostate problems starting with Prostatitis. Prostatitis What is it? Prostatitis is an inflammation or infection of the prostate gland. It does not raise the risk of getting prostate cancer and affects men of all ages. Chronic Prostatitis is the number-one reason men under the age of 50 visit an urologist. Chronic Prostatitis may also be linked to other urinary tract infections. There are three types of Prostatitis: Acute bacterial Prostatitis, Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis and Chronic Nonbacterial Prostatitis. Acute bacterial Prostatitis is a sudden bacterial infection marked by inflammation of the prostate. This is the least common form of Prostatitis but symptoms are usually severe. Symptoms include a fever, chills, nausea and burning when urinating. Left untreated, this condition can lead to low blood pressure and may become fatal. It is usually treated in hospital with intravenous antibiotics, pain relievers and fluids Chronic bacterial Prostatitis is a result of recurrent urinary tract infections that have entered the prostate gland. It is thought to exist for years in some men before producing symptoms. The symptoms are similar to Acute bacterial Prostatitis but are less severe. It s often difficult to find the bacteria in the urine. Treatment includes antibiotics for 4-12 weeks and treatment for pain Chronic Nonbacterial Prostatitis is the most common form of Prostatitis accounting for 90% of cases. The condition is marked by urinary and genital pain for at least 3 of the past 6 months. Patients have no bacteria in their urine but may have other signs of inflammation
8 What causes it? It s not entirely clear how the prostate becomes infected. One theory is that the bacteria that causes Prostatitis may get into the prostate from the urethra by backward flow of infected urine or stools from the rectum In the past, the condition was believed to be a sexually transmitted disease but more recent research suggests that only a small number of cases are passed on through sex There are certain factors that increase your risk of developing Prostatitis however. These include having recently had a medical instrument (such as a urinary catheter) inserted during a medical procedure, engaging in rectal intercourse, having an abnormal urinary tract, having recently had a bladder infection and having an enlarged prostate What are the symptoms? The symptoms of Prostatitis vary you may have no symptoms whatsoever or symptoms may be so sudden and severe that you need emergency care When present, symptoms include: frequent urges to urinate, difficulty urinating, pain or burning during urination, chills and fever, pain in the abdomen, groin or back, pain during sex and blood in the urine How is it diagnosed? If your doctor suspects that you have Prostatitis or another prostate problem, they may refer you to an urologist (a doctor who specializes in diseases of the urinary tract and the male reproductive system) to confirm the diagnosis You will then typically undergo a comprehensive exam, including a digital rectal exam. The doctor will be able to evaluate whether the prostate gland is enlarged or tender. Additional tests such as a prostate fluid analysis for signs of infection, transrectal ultrasound, biopsy or voiding studies may also be carried out How is it treated? The treatment of Prostatitis varies and is usually individual to which type of Prostatitis you have. It s crucial that the correct diagnosis and treatments are carried out. It s also important to make sure your symptoms are not caused by urethritis (inflammation of the urethra) or some other condition that may lead to permanent bladder or kidney damage Treatments include: anti-inflammatory medicines with warm baths, antibiotic medicine for infectious Prostatitis, pain medications, muscle relaxants, surgical removal of the infected portions of the prostrate, stool softeners and prostate massage
9 Most men make a full recovery within 2 weeks How can you prevent it? Although sometimes it can t be completely prevented, avoiding spicy foods, caffeinated or acidic drinks and cycling, staying well hydrated, practicing good general and sexual hygiene have been shown to lessen the chance of developing Prostatitis Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) What is it? In many men, the prostate grows with age and as it does, it compresses the urethra tube. The growth in itself is harmless but the problems it presents can be uncomfortable and frustrating It occurs most often in men over the age of 60. Up to 30% of men in their 70s have BPH which causes them discomfort What causes it? The enlargement of the prostate gland compresses the urethra and so obstructs the urine flow What are the symptoms? Symptoms of BPH include difficulty when urinating, even when the bladder feels full, a weak or interrupted urinary stream, a feeling that the bladder is not completely empty, increased need to urinate, the need to urinate urgently, dribbling of urine after urination and a burning sensation when urinating How is it diagnosed? A doctor can often diagnose BPH by carrying out the following tests: Asking you about your symptoms and filling out a short questionnaire so that they can score the severity of the symptoms, recording your drinking and urination habits over three days, carrying out a rectal examination so they can feel whether the rectum wall is enlarged, taking a urine sample and/or blood test. X-rays including an ultrasound may also be necessary depending on the individual s symptoms
10 How is it treated? Treatment of BPH is only usually necessary if the symptoms are bothersome or complications are present. If there are only minor symptoms, then a monitoring approach may be suitable Your doctor may prescribe you medication if they diagnose BPH. There are two types of medications for this problem: 1) Alpha-blockers: Help to relax muscle fibres within the prostate, reducing the obstruction to the urine flow. They do not reduce the size of the prostate however and side-effects such as dizziness, headaches and drowsiness are common 2) 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors such as finasteride (Proscar) Inhibit the growth of the prostate and decrease the size of the gland. These medicines can take many months to become effective since they rely on physical shrinking Surgery is also an option for BPH. An operation on the prostate will involve the removal of parts of the enlarged tissue. The most common operation is an endoscopic surgical procedure known as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) Surgery has however been linked to side-effects such as erectile dysfunction (in 14% of men after TURP) and urinary incontinence (5%) Although the benefits of surgery are long-lasting, because only part of the prostate is removed, further operations may be needed How can you prevent it? Although sometimes it can t be completely prevented, eating a low-fat diet with plenty of vegetables especially onions and garlic have been shown to lessen the chance of developing Prostatitis Clinic trials have also shown that saw palmetto, nettle root and pumpkin seeds effectively reduced symptoms caused by an enlarged prostrate Prostate cancer What is it? Prostate cancer is a form of cancer which develops in the prostate gland. Early-stage prostate cancer means that cancer cells are found only in your prostate Compared with other cancers, prostate cancer grows slowly. This means that it can take 10 to 30 years before a prostate tumour gets big enough to cause symptoms or for your doctor to find it
11 Most men who develop prostate cancer will die of something other than the condition itself Prostate cancer is most common in men aged 65 or over, although younger men can be diagnosed with it as well. By age 80, more than half of all men have some cancer in their prostate What causes it? The causes of prostate cancer are largely unknown, and for similarly vague reasons the condition is more common in men of African-Caribbean or African descent and less common in men of Asian descent Men with a history of prostate cancer in their family are also at a higher risk of developing it and like with all prostate problems, a healthy lifestyle is advised What are the symptoms? Men with early prostate cancer are unlikely to have any symptoms, as these only occur when the cancer is large enough to put pressure on the urethra (the tube that drains urine from the bladder) However, symptoms can mirror BPH the condition we talked about earlier, so: Difficulty passing urine, passing urine more frequently than usual, pain when passing urine, blood in the urine Secondary cancer in the bones, lungs, lymph nodes and liver can also occur (when the cancer has spread from the prostate to other areas of the body) which is why it is crucial to catch prostate cancer at an early stage How is it diagnosed? Prostate cancer is diagnosed through a series of tests most commonly a urine test, blood test and digital rectal examination. An MRI scan may also be necessary. Your doctor will refer you to an urologist if further investigation is needed How is it treated? Prostate cancer is most often found in early stages. When it is found early, there are a number of treatment choices available The outlook for prostate cancer is generally good. This is because, unlike other cancers, prostate cancer usually develops very slowly. A man can live for decades without having any symptoms or needing any treatment Typical treatments include removing the prostate, hormone therapy and radiotherapy
12 If the cancer spreads from the prostate to other parts of the body (metastasis), typically the bones, it cannot be cured and treatment is focused on prolonging life and relieving symptoms. Approximately 10,000 men die from prostate caner in the UK each year All treatment options carry the risk of side effects including: Loss of libido, inability to obtain or maintain an erection and urinary incontinence. For this reason, many men choose to delay treatment until there is a significant risk that the caner might spread Remember there are a lot of treatment choices, make the one that s right for YOU. Get the opinions of several different doctors and time your time to research your choices and consider your partner too There are organisations and support groups out there and it IS possible to live a full life after prostate cancer Treatment choices will depend on many factors and your prostate cancer risk group will be taken into consideration. Doctors use details about your cancer to place you into a low, medium or high-risk group: Low risk Prostate cancer is not likely to grow or spread for many years Medium risk Prostate cancer is not likely to grow or spread for a few years High risk Prostate cancer may grow or spread within a few years Early stage prostate cancer patients are typically offered the following treatment options. Each come with their own pros and cons so be sure to research them thoroughly before deciding: Active surveillance Closely watching for any sign that the cancer may be growing or changing. This is a good option for early-stage patients as it means you can avoid the side effects and costs of treatments without shortening your life You can change your mind on this treatment and decide to have a different treatment at any time Surgery There are different types of surgery available for men with prostate cancer in good health. These include Open prostatectomy (removing the prostate through a single cut in the abdomen), Laparoscopic surgery (using a laparoscope which is a long slender tube to see and remove the prostate) or
13 Perineal prostatectomy (removing the prostate through an incision between your scrotum and anus) Radiation therapy Radiation therapy uses high doses of radiation energy to treat cancer. This is the best treatment for older men or men who have other health problems. Questions to consider The following questions are common discussions that you may want to think over yourself or talk through with your partner: 1. Which treatment is a good choice for me? 2. What can I expect during the treatment? 3. What are the pros and cons of each treatment? 4. How will this treatment affect our sex life? 5. What about the side effects? 6. Will I be in pain? 7. Will I need further treatments? 8. How long can I expect to live after this treatment? Talk through the options with your doctor too ask questions, know your health history and get a 2 nd or even 3 rd opinion for ultimate peace of mind How can you prevent it? Cut down on meat Prostate cancer - a hormone-based disease - may be strongly linked to the consumption of meat which contains higher levels of hormone-disrupting chemicals. Try to eat meat no more than three times a week. It's best to eat white meat, and lean cuts of red meat with equal portions of fish. Opt for hormone-free organic cuts where possible Don't fry food Diets which are high in dairy products - milk, cheese, butter and saturated animal fats - are also associated with a higher incidence of prostate cancer. Avoid trans-fats, found in margarine, vegetable shortening, and processed vegetable oils. If you are overweight, start a diet to reduce your risk Eat more fruit Eat five to nine daily servings of organic fresh fruit and vegetables. Eat plenty of rich red tomato sauces. Try to include soya in your diet - soya milk, tofu or soya yoghurts. These are all high in antioxidants, which protect our cells against the damaging effects of free radicals and can help prevent cancers
14 Take vitamins Recommended daily supplements for prostate protection include: Vitamin A, C, D and; Selenium and Flaxseed oil Stop smoking Giving up cigarettes will also protect your zinc levels Avoid using garden fertilisers and pesticides Many these contain hormone-disrupting chemicals Exercise Because very little research has been conducted into prostate cancer, the power of exercise, though known to be beneficial in boosting the body's immune system, is still largely uncertain. What scientists do know is that exercise can prevent cancer because it enhances natural immunity by improving circulation, blood pressure and the efficiency and strength of the heart It also improves the antioxidant defences of our cells, which can help to counter the potentially damaging effects of oxidants, and which can lead to the genetic mutations that lie behind the development of cancers Can I still have my steak? Diets that are high in meat, particularly red and processed meats, may increase the risk of prostate cancer. Meat intake has also been associated with high fat intake which may also have cancer-promoting effects. Diets high in meat may also be low in protective fruits and vegetables. Ruminant meats, such as beef and lamb, are also a source of phytanic acid, which has been linked to an increase in the risk of prostate cancer in the case of dairy produce. Red meat is a major source of zinc which promotes testosterone synthesis. A number of studies have compared the relationship between the degree of meat cooking and prostate cancer risk. Meat that is 'well done' and 'very well done' is more likely to increase the risk of prostate cancer. To help prevent and control cancers (including prostate) it is recommended you eat less than 500g (18oz) a week of red meat. However, meat is part of a valuable food group that provides protein to build and repair body tissues, as well as other essential vitamins and minerals, such as iron.
15 There are some other sources of protein such as fish, eggs, soya and pulses, that can substitute for some meat. What about my sex life? It is a physical need, like sleeping or eating, or breathing. For a healthy male, regular release of the prostate fluid is necessary to maintain good prostate health. Orgasm (ejaculation) is much like eating. But, just like eating, if you overdo it, you suffer. If you overdo it all the time, you get weak, and sick, and you die young. It is one of the rhythms of your life. Like your heartbeat, your breathing, your eating, your sleeping... It requires moderation and a regular rhythm for best results. This is something we are not taught as young men. But, it would be a good and important thing to teach. You function best and most healthfully when: Your heartbeat is calm and regular. Your breathing is deep and even. You sleep long enough each night. You eat the right amount on schedule. Doesn't it make sense that the same would hold true for your love life? In a woman, it is easier to see the rhythm the monthly cycle of ovulation and menstruation. BPH will not directly affect your sex drive. You may be having other problems with sex, such as difficulty keeping an erection or pain when you ejaculate, which put you off doing it. It's worth talking these issues through with your partner if you're worried about your relationship suffering. For many Prostatitis sufferers, they may experience sexual dysfunction, including ED, premature ejaculation, loosing gratification and so on. However, not all unpleasant sex result from prostatitis. It can be affected by mood, pressure, and so on. But if you don't have any problem with sexual intercourse while having prostatitis, that doesn't indicates that you're always free from dysfunction. The condition is always changing. Thus, when prostatitis occurs on you, your sexual intercourses would be possibly affected. How sex affects the prostate gland As we all know, when a man is having sex, his prostate gland is congestive because of exciting.
16 Does this indicate that it is harmful to have sex if you prostatitis? No. Prostate fluid is a main ingredient of semen. When a men ejaculates, the prostate fluid expels. This action to help the prostate gland to "detox". Expelled prostate fluid brings away many waste and toxic materials. After the fluid is expelled, more fluid produces. This is like "washing" the gland. What prostatitis sufferers need to notice while having sex 1 If you're an acute prostatitis sufferer, avoid sex till your treatment ends 2 For chronic prostatitis sufferers, don't have too much sexual intercourse it is suggested to control the frequency between 1-3 times per week 3 Before and after having sex, wash your perineum area. A hip bath with warm water helps to eliminate the inflammation 4 If you feel a pain with ejaculation, restrain from having sex 5 Sexual intercourse at each time shouldn't last long. Also the movement shouldn't be intense Prostate cancer and sex Treatment for prostate cancer can cause a variety of side effects. Any of these can affect your sex life, some more than others. Some men get diarrhea during radiotherapy and for some time afterwards. This can be unpleasant and tiring and may put you off wanting to have sex. It will gradually go back to normal after a few weeks though. You may feel too tired to want sex for some time after prostate cancer treatment. Radiotherapy, surgery and hormone treatment can lead to difficulty getting an erection (impotence). Erection difficulties can be temporary or permanent and can be very difficult to come to terms with. You may find it difficult to talk about this with your doctor or with your partner. If you can talk to your doctor or specialist nurse, you may find they have a specialist counsellor or sex therapist you can be referred to.
17 Men also have a cycle The difference is: the time frames in our cycles are much more individual and varied than a woman's. If you are healthy, you produce a certain amount of sperm and semen in a regular period of time. Some men make a lot rather quickly. Some men take a lot longer to make a full supply. Once your body has created a full supply of semen and sperm (specific to each individual) it needs to release it. That is when you get aroused. After you ejaculate, your cycle starts again. The length of that cycle is determined by genetics, age, what you eat, and general health. If you are healthy and enjoy sex within your own personal natural rhythm, you can enjoy sex long into your 80s and 90s without complications. When to see your doctor If you have any of the following symptoms, see a medical professional as soon as possible: Frequent urge to urinate Blood in urine or semen Painful or burning urination Difficulty in urinating Difficulty in having an erection Painful ejaculation Frequent pain or stiffness in lower back, hips, or upper thighs Inability to urinate, or Dribbling of urine
18 Information and support groups: An informative site about prostate problems: NHS prostate resources: Prostate problems in the media: Prostate cancer support association: The British Prostatitis Support Association The Prostate Cancer Charity Cancer Research UK
19 Afterword If you found this report helpful, chances are you ll have a thirst for other health knowledge so why not join my Good Life Letter readers and get two weekly s packed full of fascinating health tips, news, trends and solutions? It s completely free of charge and free from patronising doctors or fitness freaks. What can I say, it s just an enjoyable and informative read written by your average bloke with a passion for keeping the weight off, warding off deadly diseases and ensuring the scamming pharmaceutical companies don t win your trust or your money. Click onto to join in now
The prostate can be affected by three conditions that may cause problems for men as they get older.
 The Prostate Gland The Prostate gland specific to males only, located in the pelvis between the bladder and rectum. It is about the shape and size of a walnut or satsuma and gets bigger as you get older.
The Prostate Gland The Prostate gland specific to males only, located in the pelvis between the bladder and rectum. It is about the shape and size of a walnut or satsuma and gets bigger as you get older.
Trans urethral resection of prostate (TURP)
 Trans urethral resection of prostate (TURP) Information for patients Urology PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST What is the prostate? Only men have a prostate
Trans urethral resection of prostate (TURP) Information for patients Urology PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST What is the prostate? Only men have a prostate
How healthy is your Prostate? - June 2009
 How healthy is your Prostate? - June 2009 Inside this months issue Prostatitis Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Prostate cancer Dietary recommendations Is your Prostate Healthy? The prostate is a small
How healthy is your Prostate? - June 2009 Inside this months issue Prostatitis Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Prostate cancer Dietary recommendations Is your Prostate Healthy? The prostate is a small
PROSTATE CANCER CONTENT CREATED BY. Learn more at
 PROSTATE CANCER CONTENT CREATED BY Learn more at www.health.harvard.edu TALK WITH YOUR DOCTOR Table of Contents Ask your doctor about screening and treatment options. WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? 4 WATCHFUL
PROSTATE CANCER CONTENT CREATED BY Learn more at www.health.harvard.edu TALK WITH YOUR DOCTOR Table of Contents Ask your doctor about screening and treatment options. WHAT IS PROSTATE CANCER? 4 WATCHFUL
Diet, physical activity and your risk of prostate cancer
 Diet, physical activity and your risk of prostate cancer This leaflet is for men who want to find out more about healthy eating and physical activity. A healthy diet and regular exercise are important
Diet, physical activity and your risk of prostate cancer This leaflet is for men who want to find out more about healthy eating and physical activity. A healthy diet and regular exercise are important
Introduction. Growths in the prostate can be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer).
 This information was taken from urologyhealth.org. Feel free to explore their website to learn more. Another trusted website with good information is the national comprehensive cancer network (nccn.org).
This information was taken from urologyhealth.org. Feel free to explore their website to learn more. Another trusted website with good information is the national comprehensive cancer network (nccn.org).
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Definition Prostate gland enlargement is a common condition as men get older. Also called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostate gland enlargement can cause bothersome
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Definition Prostate gland enlargement is a common condition as men get older. Also called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostate gland enlargement can cause bothersome
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
SPECIAL EDITION: Men s Health
 SPECIAL EDITION: Men s Health 1 Heart Health If you re like most Americans, heart health might be something you don t think about very often. You should. The risk of heart disease increases with age and
SPECIAL EDITION: Men s Health 1 Heart Health If you re like most Americans, heart health might be something you don t think about very often. You should. The risk of heart disease increases with age and
Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP)
 Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Patient Information Author ID: SF Leaflet Number: Urol 010 Version: 6 Name of Leaflet: Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Date Produced: March 2018
Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Patient Information Author ID: SF Leaflet Number: Urol 010 Version: 6 Name of Leaflet: Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Date Produced: March 2018
Prostatitis - A straight forward guide to
 Prostatitis - A straight forward guide to inflammation of the prostate and Pelvic Pain Syndrome What is the prostate? Only men have a prostate and it is usually about the size of a walnut. Around the age
Prostatitis - A straight forward guide to inflammation of the prostate and Pelvic Pain Syndrome What is the prostate? Only men have a prostate and it is usually about the size of a walnut. Around the age
Prostate surgery. What is the prostate? What is a TURP? Why is a TURP operation necessary? Deciding to have a TURP operation.
 What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland about the size of a walnut that is only present in men. It is located just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine flows
What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland about the size of a walnut that is only present in men. It is located just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine flows
What do you know about your prostate? Information for Black men
 What do you know about your prostate? Information for Black men Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 1 2 What do you know about your prostate? Did you know that in the UK, about 1 in 4 Black men will get prostate
What do you know about your prostate? Information for Black men Specialist Nurses 0800 074 8383 1 2 What do you know about your prostate? Did you know that in the UK, about 1 in 4 Black men will get prostate
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP)
 Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
What Is Prostate Cancer? Prostate cancer is the development of cancer cells in the prostate gland (a gland that produces fluid for semen).
 What Is Prostate Cancer? Prostate cancer is the development of cancer cells in the prostate gland (a gland that produces fluid for semen). It is a very common cancer in men; some cancers grow very slowly,
What Is Prostate Cancer? Prostate cancer is the development of cancer cells in the prostate gland (a gland that produces fluid for semen). It is a very common cancer in men; some cancers grow very slowly,
TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate
 TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate To learn about a TURP, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm move. It surrounds the urethra
TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate To learn about a TURP, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm move. It surrounds the urethra
ADVICE TO PATIENTS REQUESTING PSA MEASUREMENT FREQUENTLY-ASKED QUESTIONS
 The British Association of Urological Surgeons 35-43 Lincoln s Inn Fields London WC2A 3PE Phone: Fax: Website: E-mail: +44 (0)20 7869 6950 +44 (0)20 7404 5048 www.baus.org.uk admin@baus.org.uk ADVICE TO
The British Association of Urological Surgeons 35-43 Lincoln s Inn Fields London WC2A 3PE Phone: Fax: Website: E-mail: +44 (0)20 7869 6950 +44 (0)20 7404 5048 www.baus.org.uk admin@baus.org.uk ADVICE TO
Prostate Health PHARMACIST VIEW
 Prostate Health PHARMACIST VIEW Prostate Definition Prostate is a gland made of fibromuscular tissue. It is about 4 cm and surrounds the neck of the bladder and the urethra. It produces seminal fluid.
Prostate Health PHARMACIST VIEW Prostate Definition Prostate is a gland made of fibromuscular tissue. It is about 4 cm and surrounds the neck of the bladder and the urethra. It produces seminal fluid.
TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE
 TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE A discussion of the operation and the pre and post operative care You and your doctor have considered the possibility that you have a transurethral resection of
TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF THE PROSTATE A discussion of the operation and the pre and post operative care You and your doctor have considered the possibility that you have a transurethral resection of
ADVICE TO PATIENTS REQUESTING PSA MEASUREMENT
 Frequently-Asked Questions What is the aim of this leaflet? Prostate cancer is a serious condition. The PSA test, which can give an early indication of prostate cancer, is available to you if you want
Frequently-Asked Questions What is the aim of this leaflet? Prostate cancer is a serious condition. The PSA test, which can give an early indication of prostate cancer, is available to you if you want
Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Department of Urology Information for patients
 Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Department of Urology Information for patients i The prostate The prostate is a small gland which is found only in men. It is situated at the base of the bladder
Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Department of Urology Information for patients i The prostate The prostate is a small gland which is found only in men. It is situated at the base of the bladder
Know your prostate A guide to common prostate problems
 Know your prostate A guide to common prostate problems 2 Know your prostate: A guide to common prostate problems About this booklet This booklet is a guide to the prostate what it is, what it does and
Know your prostate A guide to common prostate problems 2 Know your prostate: A guide to common prostate problems About this booklet This booklet is a guide to the prostate what it is, what it does and
Reproduced with the kind permission of Health Press Ltd, Oxford
 Trans Urethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) Department of Urology Where is the Prostate Gland? The prostate gland sits below the bladder which lies behind the pubic bone see diagram below. The urethra
Trans Urethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) Department of Urology Where is the Prostate Gland? The prostate gland sits below the bladder which lies behind the pubic bone see diagram below. The urethra
General information about prostate cancer
 Prostate Cancer General information about prostate cancer Key points Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the prostate. Signs of prostate cancer include
Prostate Cancer General information about prostate cancer Key points Prostate cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the prostate. Signs of prostate cancer include
Saving. Kidneys. Prostate Cancer
 Saving Kidneys 10 Prostate Cancer This booklet will tell you more about the prostate cancer. It will also help you understand this disease in a better way. You will also come to know the causes and treatment
Saving Kidneys 10 Prostate Cancer This booklet will tell you more about the prostate cancer. It will also help you understand this disease in a better way. You will also come to know the causes and treatment
Saving. Kidneys. Benign Prostate Disease
 Saving Kidneys 9 Benign Prostate Disease This booklet will tell you more about the prostate gland. Its functions and benign hyperplasia have been defined in a simple way. Ways to prevent and treat this
Saving Kidneys 9 Benign Prostate Disease This booklet will tell you more about the prostate gland. Its functions and benign hyperplasia have been defined in a simple way. Ways to prevent and treat this
WHY DO WE NEED FAT? It is now known that Omega-3 and Omega- 6 polyunsaturated fats, or good fats, are particularly good for heart health.
 KNOW YOUR FATS WHY DO WE NEED FAT? Fat can contribute positively to our diet, as long as we choose the right types of fats and moderate our intake to the appropriate amounts. Fat has many valuable functions
KNOW YOUR FATS WHY DO WE NEED FAT? Fat can contribute positively to our diet, as long as we choose the right types of fats and moderate our intake to the appropriate amounts. Fat has many valuable functions
Michael van Straten. Preventing Breast Cancer
 Michael van Straten Preventing Breast Cancer This fact sheet is based largely on the most recent information provided by the world famous Mayo Clinic in America. Preventing breast cancer: Lifestyle choices
Michael van Straten Preventing Breast Cancer This fact sheet is based largely on the most recent information provided by the world famous Mayo Clinic in America. Preventing breast cancer: Lifestyle choices
Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP)
 Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Department of Urology Patient Information What What and and where where is the is prostate? the prostate? The prostate is a small gland, about the size of a walnut,
Transurethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Department of Urology Patient Information What What and and where where is the is prostate? the prostate? The prostate is a small gland, about the size of a walnut,
Laser Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP)
 Laser Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Department of Urology Information for patients i Introduction The prostate is a small gland, which is found only in men. It is found at the base of the
Laser Trans Urethral Resection of Prostate (TURP) Department of Urology Information for patients i Introduction The prostate is a small gland, which is found only in men. It is found at the base of the
Notice that the word is pros-tate, although you will occasionally hear pros-trate! Bullet #1: other than skin cancer
 Slide 1 Prostate Cancer American Cancer Society Reviewed March 2016 Slide 2 What we ll be talking about How common is prostate cancer? What is prostate cancer? What causes it? What are the risk factors?
Slide 1 Prostate Cancer American Cancer Society Reviewed March 2016 Slide 2 What we ll be talking about How common is prostate cancer? What is prostate cancer? What causes it? What are the risk factors?
Patient Information. Prostate Tissue Ablation. High Intensity Focused Ultrasound for
 High Intensity Focused Ultrasound for Prostate Tissue Ablation Patient Information CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sell by or on the order of a physician CONTENT Introduction... 3 The prostate...
High Intensity Focused Ultrasound for Prostate Tissue Ablation Patient Information CAUTION: Federal law restricts this device to sell by or on the order of a physician CONTENT Introduction... 3 The prostate...
Prostate Cancer. What you should know
 Prostate Cancer What you should know What is prostate cancer? Prostate cancer happens when the normal cells in the prostate gland grow in an abnormal way to form a mass of cells called a tumour. These
Prostate Cancer What you should know What is prostate cancer? Prostate cancer happens when the normal cells in the prostate gland grow in an abnormal way to form a mass of cells called a tumour. These
Men s Health. A head-to-toe guide on how to look after your body
 Men s Health A head-to-toe guide on how to look after your body Eat healthy to stay healthy Nutrition and disease are closely linked. The food we eat influences our health now and in the future. Below
Men s Health A head-to-toe guide on how to look after your body Eat healthy to stay healthy Nutrition and disease are closely linked. The food we eat influences our health now and in the future. Below
Talking about Prostate Cancer
 Talking about Prostate Cancer Talking about Prostate Cancer If I can avoid going to a doctor, I will but not when we re talking about prostate cancer. Why take chances with a condition that might be serious?
Talking about Prostate Cancer Talking about Prostate Cancer If I can avoid going to a doctor, I will but not when we re talking about prostate cancer. Why take chances with a condition that might be serious?
TYPES OF PROSTATITIS There are three types of prostatitis-type presentations:
 SPECIALIZED UROLOGIC CONSULTANTS, SC 10400 Southwest Hwy 16632 S. 107 th Ct. Chicago Ridge, IL 60453 Orland Park, IL 60467 Tel (708) 423-8706 Tel (708) 349-6350 PROSTATITIS - REVIEW Prostatitis is an inflammation
SPECIALIZED UROLOGIC CONSULTANTS, SC 10400 Southwest Hwy 16632 S. 107 th Ct. Chicago Ridge, IL 60453 Orland Park, IL 60467 Tel (708) 423-8706 Tel (708) 349-6350 PROSTATITIS - REVIEW Prostatitis is an inflammation
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
Prostate Gland Disorders
 Prostate Gland Disorders THE PROSTATE GLAND A male s prostate gland is located in the floor of the pelvis surrounding the urethra between the bladder and the penis. The prostate is positioned immediately
Prostate Gland Disorders THE PROSTATE GLAND A male s prostate gland is located in the floor of the pelvis surrounding the urethra between the bladder and the penis. The prostate is positioned immediately
Should I get screened for prostate cancer? What you should know about the PSA test
 Should I get screened for prostate cancer? What you should know about the PSA test Should I get screened for prostate cancer? What you should know about the PSA test > What is PSA? Prostate-specific antigen
Should I get screened for prostate cancer? What you should know about the PSA test Should I get screened for prostate cancer? What you should know about the PSA test > What is PSA? Prostate-specific antigen
BLADDER PROSTATE PENIS TESTICLES BE YO ND YO UR CA NC ER
 BLADDER PROSTATE PENIS TESTICLES THE PROSTATE IS A SMALL, WALNUT-SIZED GLAND THAT IS PART OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM. IT RESTS BELOW THE BLADDER, IN FRONT OF THE RECTUM AND SURROUNDS PART OF THE URETHRA.
BLADDER PROSTATE PENIS TESTICLES THE PROSTATE IS A SMALL, WALNUT-SIZED GLAND THAT IS PART OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM. IT RESTS BELOW THE BLADDER, IN FRONT OF THE RECTUM AND SURROUNDS PART OF THE URETHRA.
Men. prostate. know about your EASY READ
 Men know about your prostate EASY READ What is in this booklet? To help you understand the messages in this booklet, you may need a carer or friend to read it with you. Where is your prostate gland? 3
Men know about your prostate EASY READ What is in this booklet? To help you understand the messages in this booklet, you may need a carer or friend to read it with you. Where is your prostate gland? 3
Prostate: Know Your Gland
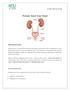 Prostate: Know Your Gland What s prostate cancer? Prostate cancer is a serious disease that affects thousands of men each year who are middle-aged or older. Most prostate cancers occur in men older than
Prostate: Know Your Gland What s prostate cancer? Prostate cancer is a serious disease that affects thousands of men each year who are middle-aged or older. Most prostate cancers occur in men older than
Treating Prostate Cancer
 Treating Prostate Cancer A Guide for Men With Localized Prostate Cancer Most men have time to learn about all the options for treating their prostate cancer. You have time to talk with your family and
Treating Prostate Cancer A Guide for Men With Localized Prostate Cancer Most men have time to learn about all the options for treating their prostate cancer. You have time to talk with your family and
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME
 CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer
 Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer Introduction This leaflet is written for patients and their family. It provides information on prostate cryotherapy for prostate cancer which has not previously
Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer Introduction This leaflet is written for patients and their family. It provides information on prostate cryotherapy for prostate cancer which has not previously
100% Effective Natural Hormone Treatment Menopause, Andropause And Other Hormone Imbalances Impair Healthy Healing In People Over The Age Of 30!
 This Free E Book is brought to you by Natural Aging.com. 100% Effective Natural Hormone Treatment Menopause, Andropause And Other Hormone Imbalances Impair Healthy Healing In People Over The Age Of 30!
This Free E Book is brought to you by Natural Aging.com. 100% Effective Natural Hormone Treatment Menopause, Andropause And Other Hormone Imbalances Impair Healthy Healing In People Over The Age Of 30!
BLADDER HEALTH. Painful Bladder AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION
 BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
About Your Procedure
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION About Your Procedure UroLift This handout describes a UroLift procedure to treat an enlarged prostate. It also gives instructions to follow before and after your procedure.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION About Your Procedure UroLift This handout describes a UroLift procedure to treat an enlarged prostate. It also gives instructions to follow before and after your procedure.
Treating your enlarged prostate gland using holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP)
 Treating your enlarged prostate gland using holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) This leaflet will answer any questions you may have about having holmium laser treatment for your enlarged
Treating your enlarged prostate gland using holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLEP) This leaflet will answer any questions you may have about having holmium laser treatment for your enlarged
Attending for your Prostate Scan
 Attending for your Prostate Scan Patient Information The aim of this booklet is to give you enough information: To help you prepare for your hospital visit To give properly informed consent for the procedure
Attending for your Prostate Scan Patient Information The aim of this booklet is to give you enough information: To help you prepare for your hospital visit To give properly informed consent for the procedure
Mr PHIP No. 1 Prostate cancer: Should I be tested?
 Mr PHIP No. 1 cancer: Should I be tested? Having a large prostate doesn t increase your chances of having prostate cancer. No. 1 / 1 Key points cancer is the most common male cancer after skin cancer.
Mr PHIP No. 1 cancer: Should I be tested? Having a large prostate doesn t increase your chances of having prostate cancer. No. 1 / 1 Key points cancer is the most common male cancer after skin cancer.
Radiotherapy to the prostate
 Radiotherapy to the prostate Information for patients The aim of this leaflet is to provide you with information about the use of external beam radiotherapy in treating prostate cancer, including details
Radiotherapy to the prostate Information for patients The aim of this leaflet is to provide you with information about the use of external beam radiotherapy in treating prostate cancer, including details
(dutasteride/tamsulosin) For the treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
 Combodart (dutasteride/tamsulosin) For the treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) This leaflet is only for use by patients who have been prescribed Combodart. Please see Patient Information Leaflet
Combodart (dutasteride/tamsulosin) For the treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) This leaflet is only for use by patients who have been prescribed Combodart. Please see Patient Information Leaflet
Retropubic Prostatectomy
 2014 Retropubic Prostatectomy Retropubic Prostatectomy What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland that makes a fluid that helps sperm move. It also gives nourishment for the sperm. It is about the size
2014 Retropubic Prostatectomy Retropubic Prostatectomy What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland that makes a fluid that helps sperm move. It also gives nourishment for the sperm. It is about the size
The eatwell plate is based on the Government s Eight Guidelines for a Healthy Diet, which are:
 The eatwell plate The eatwell plate is a pictorial food guide showing the proportion and types of foods that are needed to make up a healthy balanced diet. The plate has been produced by the Food Standards
The eatwell plate The eatwell plate is a pictorial food guide showing the proportion and types of foods that are needed to make up a healthy balanced diet. The plate has been produced by the Food Standards
LIVING WITH. Understanding Your Treatment Options 1510
 Get the Support You Need Having prostate cancer can be hard to cope with. But you don t have to keep your feelings to yourself. Talk with family and friends. Try a prostate cancer support group. Sharing
Get the Support You Need Having prostate cancer can be hard to cope with. But you don t have to keep your feelings to yourself. Talk with family and friends. Try a prostate cancer support group. Sharing
Trans-rectal Ultrasound Scan and Biopsy (TRUSS)
 Trans-rectal Ultrasound Scan and Biopsy (TRUSS) What is the prostate gland? The prostate is a small gland the size of a walnut. It is found at the base of the bladder and surrounds the urethra (water pipe).
Trans-rectal Ultrasound Scan and Biopsy (TRUSS) What is the prostate gland? The prostate is a small gland the size of a walnut. It is found at the base of the bladder and surrounds the urethra (water pipe).
Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC)
 Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
Heart Healthy Living Tips
 Diabetes and Heart Disease Awareness Healthy Living with Diabetes sm and Heart Healthy Living sm Wisconsin Newsletter Fall 2011 Heart Healthy Living Tips What do eating healthy, being active, maintaining
Diabetes and Heart Disease Awareness Healthy Living with Diabetes sm and Heart Healthy Living sm Wisconsin Newsletter Fall 2011 Heart Healthy Living Tips What do eating healthy, being active, maintaining
Prostate Brachytherapy
 Prostate Brachytherapy Radioactive Iodine-125 Seed Implant Treatment Prostate Brachytherapy Information for Patients Introduction This booklet describes the Radioactive Iodine-125 Seed Implant. It is one
Prostate Brachytherapy Radioactive Iodine-125 Seed Implant Treatment Prostate Brachytherapy Information for Patients Introduction This booklet describes the Radioactive Iodine-125 Seed Implant. It is one
Nutrition for sport and exercise. Our Bupa nurses have put together these simple tips to help you eat well for sport and exercise.
 Nutrition for sport and exercise Our Bupa nurses have put together these simple tips to help you eat well for sport and exercise. Whether you re doing a casual workout or training for a major sporting
Nutrition for sport and exercise Our Bupa nurses have put together these simple tips to help you eat well for sport and exercise. Whether you re doing a casual workout or training for a major sporting
THE UROLOGY GROUP
 THE UROLOGY GROUP www.urologygroupvirginia.com 1860 Town Center Drive Suite 150/160 Reston, VA 20190 703-480-0220 19415 Deerfield Avenue Suite 112 Leesburg, VA 20176 703-724-1195 224-D Cornwall Street,
THE UROLOGY GROUP www.urologygroupvirginia.com 1860 Town Center Drive Suite 150/160 Reston, VA 20190 703-480-0220 19415 Deerfield Avenue Suite 112 Leesburg, VA 20176 703-724-1195 224-D Cornwall Street,
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. About Your Surgery DRAFT
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION About Your Surgery Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) This handout describes a transurethral resection of the prostate. It also gives instructions to follow before
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION About Your Surgery Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) This handout describes a transurethral resection of the prostate. It also gives instructions to follow before
PROSTATIC ARTERY EMBOLISATION (PAE) FOR BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA. A Minimally Invasive Innovative Treatment
 PROSTATIC ARTERY EMBOLISATION (PAE) FOR BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA A Minimally Invasive Innovative Treatment What is the prostate? The prostate is an accessory organ of the male reproductive system.
PROSTATIC ARTERY EMBOLISATION (PAE) FOR BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA A Minimally Invasive Innovative Treatment What is the prostate? The prostate is an accessory organ of the male reproductive system.
Radical Prostatectomy
 2014 Radical Prostatectomy Radical Prostatectomy What is a radical prostatectomy? During a radical prostatectomy, the entire prostate gland, the part of the urethra that it surrounds, and the seminal vesicles
2014 Radical Prostatectomy Radical Prostatectomy What is a radical prostatectomy? During a radical prostatectomy, the entire prostate gland, the part of the urethra that it surrounds, and the seminal vesicles
Colorectal Cancer How to reduce your risk
 Prevention Series Colorectal Cancer How to reduce your risk Let's Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Colorectal Cancer How to reduce your risk Colorectal cancer is the third most commonly diagnosed
Prevention Series Colorectal Cancer How to reduce your risk Let's Make Cancer History 1 888 939-3333 cancer.ca Colorectal Cancer How to reduce your risk Colorectal cancer is the third most commonly diagnosed
Heart health and diet. Our Bupa nurses have put together these simple tips to help you eat well and look after your heart.
 Heart health and diet Our Bupa nurses have put together these simple tips to help you eat well and look after your heart. What you eat can have an impact on the health of your heart. Eating a healthy diet
Heart health and diet Our Bupa nurses have put together these simple tips to help you eat well and look after your heart. What you eat can have an impact on the health of your heart. Eating a healthy diet
Heart Healthy Living Tips
 Diabetes and Heart Disease Awareness Healthy Living with Diabetes sm and Heart Healthy Living sm Michigan Newsletter Fall 2011 Heart Healthy Living Tips What do eating healthy, being active, maintaining
Diabetes and Heart Disease Awareness Healthy Living with Diabetes sm and Heart Healthy Living sm Michigan Newsletter Fall 2011 Heart Healthy Living Tips What do eating healthy, being active, maintaining
Having a trans-urethral resection of the prostate (TURP)
 Having a trans-urethral resection of the prostate (TURP) This leaflet gives you information about having a TURP, which is an operation to treat an enlarged prostate gland. It explains the benefits, alternatives
Having a trans-urethral resection of the prostate (TURP) This leaflet gives you information about having a TURP, which is an operation to treat an enlarged prostate gland. It explains the benefits, alternatives
Testing for. Prostate Cancer
 Testing for Prostate Cancer Who this booklet is for: This booklet is to help men who do not have any symptoms decide if they want to be tested. Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find
Testing for Prostate Cancer Who this booklet is for: This booklet is to help men who do not have any symptoms decide if they want to be tested. Prostate cancer affects many men. There are tests to find
Coach on Call. Thank you for your interest in Lifestyle Changes as a Treatment Option. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful.
 It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your UPMC Health Plan
It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your UPMC Health Plan
After Adrenal Cancer Treatment
 After Adrenal Cancer Treatment Living as a Cancer Survivor For many people, cancer treatment often raises questions about next steps as a survivor. Lifestyle Changes After Treatment for Adrenal Cancer
After Adrenal Cancer Treatment Living as a Cancer Survivor For many people, cancer treatment often raises questions about next steps as a survivor. Lifestyle Changes After Treatment for Adrenal Cancer
MANAGING YOUR CHOLESTEROL
 MANAGING YOUR CHOLESTEROL WHAT IS CHOLESTEROL? Cholesterol is a white waxy substance found in every cell of our bodies. It comes from The liver our body makes most of it from the fat we eat in food A little
MANAGING YOUR CHOLESTEROL WHAT IS CHOLESTEROL? Cholesterol is a white waxy substance found in every cell of our bodies. It comes from The liver our body makes most of it from the fat we eat in food A little
SAFETYNET LEARNING TOOLS
 SAFETYNET LEARNING TOOLS Topic: Urinary Tract Infection Use the materials in this document to help others learn more about urinary tract infection. LEARNING TOOLS: 1. How to Say it Guide 2. Recognizing
SAFETYNET LEARNING TOOLS Topic: Urinary Tract Infection Use the materials in this document to help others learn more about urinary tract infection. LEARNING TOOLS: 1. How to Say it Guide 2. Recognizing
Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Form: D-5147 What to Expect When Getting Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer For patients having radiation therapy at Princess Margaret Cancer Centre Read this pamphlet to learn about: The main steps
Form: D-5147 What to Expect When Getting Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer For patients having radiation therapy at Princess Margaret Cancer Centre Read this pamphlet to learn about: The main steps
ABLE TO READ THE LABEL?
 ARE ABLE TO READ THE LABEL? A Consumer s Guide to Navigating Food Labels Food and Drug Safety Program Consumer and Environmental Health Services Phone: 609-826-4935 Fax: 609-826-4990 http://nj.gov/health/eoh/foodweb/
ARE ABLE TO READ THE LABEL? A Consumer s Guide to Navigating Food Labels Food and Drug Safety Program Consumer and Environmental Health Services Phone: 609-826-4935 Fax: 609-826-4990 http://nj.gov/health/eoh/foodweb/
All about the Prostate
 MEN S HEALTH Dr Nick Pendleton January 16 th 2018 All about the Prostate 1 What does it do? Functions of the Prostate 1. Secretes Prostatic Fluid slightly alkaline fluid, 30% of volume of seminal fluid,
MEN S HEALTH Dr Nick Pendleton January 16 th 2018 All about the Prostate 1 What does it do? Functions of the Prostate 1. Secretes Prostatic Fluid slightly alkaline fluid, 30% of volume of seminal fluid,
NHS breast screening Helping you decide
 NHS breast screening Helping you decide 1 What is breast cancer? 2 What is breast screening? 3 Breast screening results 6 Making a choice the possible benefits 9 and risks of breast screening What are
NHS breast screening Helping you decide 1 What is breast cancer? 2 What is breast screening? 3 Breast screening results 6 Making a choice the possible benefits 9 and risks of breast screening What are
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
HOLEP (HOLMIUM LASER ENUCLEATION OF PROSTATE )
 HOLEP (HOLMIUM LASER ENUCLEATION OF PROSTATE ) What does the procedure involve? Removal of obstructing prostate tissue using a telescope and a laser. What are the alternatives to this procedure? Alternatives
HOLEP (HOLMIUM LASER ENUCLEATION OF PROSTATE ) What does the procedure involve? Removal of obstructing prostate tissue using a telescope and a laser. What are the alternatives to this procedure? Alternatives
Bowel health and screening: carers guide. A booklet for carers of people who use easy read materials
 Bowel health and screening: carers guide A booklet for carers of people who use easy read materials Contents Page 3: About this booklet Page 4: What is the bowel? Page 5: Helping someone to have good bowel
Bowel health and screening: carers guide A booklet for carers of people who use easy read materials Contents Page 3: About this booklet Page 4: What is the bowel? Page 5: Helping someone to have good bowel
Prostate Artery Embolisation (PAE)
 Service: Imaging Prostate Artery Embolisation (PAE) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions The team delivering your healthcare want to encourage you to become as involved as possible
Service: Imaging Prostate Artery Embolisation (PAE) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions The team delivering your healthcare want to encourage you to become as involved as possible
TransUrethral Resection for a Bladder Tumour ~ TURBT Women ~
 TransUrethral Resection for a Bladder Tumour ~ TURBT Women ~ To learn about TransUrethral Resection of a Bladder Tumour, you will need to know what these words mean: The bladder stores urine that is made
TransUrethral Resection for a Bladder Tumour ~ TURBT Women ~ To learn about TransUrethral Resection of a Bladder Tumour, you will need to know what these words mean: The bladder stores urine that is made
Just enough of the right sort
 Fats and the heart Just enough of the right sort We all need some fat in our diets, just enough of the right sort to keep our bodies and hearts healthy. In fact, a fat free diet isn t recommended because
Fats and the heart Just enough of the right sort We all need some fat in our diets, just enough of the right sort to keep our bodies and hearts healthy. In fact, a fat free diet isn t recommended because
What You Will Learn to Do. Linked Core Abilities
 Courtesy of Army JROTC U4C1L3 Components of Whole Health Key Words: Balance Behavior Calories Decision Fitness Metabolism Self-discipline What You Will Learn to Do Develop a plan for life-long health Linked
Courtesy of Army JROTC U4C1L3 Components of Whole Health Key Words: Balance Behavior Calories Decision Fitness Metabolism Self-discipline What You Will Learn to Do Develop a plan for life-long health Linked
Treating localised prostate cancer using freezing (cryotherapy) needles in a targeted area of the prostate
 Issue date April 2012 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services NICE interventional procedures guidance advises the NHS on when and how new procedures can be used in clinical
Issue date April 2012 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services NICE interventional procedures guidance advises the NHS on when and how new procedures can be used in clinical
Questions and Answers About the Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Questions and Answers
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Questions and Answers
Sexual Concerns. Mental Health Topics
 Sexual Concerns A lot of people have concerns about their sex life. Common concerns and problems that affect one or both sex partners Talk to your partner about your include: sexual concerns. n Little
Sexual Concerns A lot of people have concerns about their sex life. Common concerns and problems that affect one or both sex partners Talk to your partner about your include: sexual concerns. n Little
Radiotherapy to the prostate
 Radiotherapy to the prostate Radiotherapy A guide for patients and carers Contents When radiotherapy is given... 2 Preparation for planning and treatment... 2 Clinical Nurse Specialist (CNS) Service...
Radiotherapy to the prostate Radiotherapy A guide for patients and carers Contents When radiotherapy is given... 2 Preparation for planning and treatment... 2 Clinical Nurse Specialist (CNS) Service...
A word about incontinence
 A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
Dietary information for people with polycystic kidney disease. Information for patients Sheffield Dietetics
 Dietary information for people with polycystic kidney disease Information for patients Sheffield Dietetics Introduction What is Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD)? PKD is a genetic disorder where your body
Dietary information for people with polycystic kidney disease Information for patients Sheffield Dietetics Introduction What is Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD)? PKD is a genetic disorder where your body
Laser vaporisation of prostate (Green light laser prostate surgery): procedure-specific information
 PATIENT INFORMATION Laser vaporisation of prostate (Green light laser prostate surgery): procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from
PATIENT INFORMATION Laser vaporisation of prostate (Green light laser prostate surgery): procedure-specific information What is the evidence base for this information? This leaflet includes advice from
PROSTATE CANCER SCREENING SHARED DECISION MAKING VIDEO
 PROSTATE CANCER SCREENING SHARED DECISION MAKING VIDEO 1 00:00:00,067 --> 00:00:10,968 2 00:00:10,968 --> 00:00:12,701 So, you were given a decision aid sheet 3 00:00:12,701 --> 00:00:14,567 about prostate
PROSTATE CANCER SCREENING SHARED DECISION MAKING VIDEO 1 00:00:00,067 --> 00:00:10,968 2 00:00:10,968 --> 00:00:12,701 So, you were given a decision aid sheet 3 00:00:12,701 --> 00:00:14,567 about prostate
Radical Cystectomy A Patient s Guide
 Radical Cystectomy A Patient s Guide Introduction The urinary system, which includes the bladder, urethra, ureters, and kidneys, helps maintain stable chemical conditions in the body, stores, and eliminates
Radical Cystectomy A Patient s Guide Introduction The urinary system, which includes the bladder, urethra, ureters, and kidneys, helps maintain stable chemical conditions in the body, stores, and eliminates
STAYING HEART HEALTHY PAVAN PATEL, MD CONSULTANT CARDIOLOGIST FLORIDA HEART GROUP
 STAYING HEART HEALTHY PAVAN PATEL, MD CONSULTANT CARDIOLOGIST FLORIDA HEART GROUP What is Heart Disease Cardiovascular Disease (CVD): Heart or Blood vessels are not working properly. Most common reason
STAYING HEART HEALTHY PAVAN PATEL, MD CONSULTANT CARDIOLOGIST FLORIDA HEART GROUP What is Heart Disease Cardiovascular Disease (CVD): Heart or Blood vessels are not working properly. Most common reason
Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: External Beam Treatment for Prostate Cancer
 Patient & Family Guide 2018 Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: External Beam Treatment for Prostate Cancer www.nscancercare.ca Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: External
Patient & Family Guide 2018 Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: External Beam Treatment for Prostate Cancer www.nscancercare.ca Information for Patients Receiving Radiation Therapy: External
Robotic Prostatectomy - After Surgery
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Robotic Prostatectomy - After Surgery Here are general guidelines for home after your surgery. Your doctor may give you other instructions based on your needs
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Robotic Prostatectomy - After Surgery Here are general guidelines for home after your surgery. Your doctor may give you other instructions based on your needs
Diabetes. What is diabetes?
 Diabetes 966 860 258 www.medcarespain.com doctors@medcarespain.com The incidence of diabetes has reached epidemic proportions. About 350 million people worldwide have diabetes, and according to the World
Diabetes 966 860 258 www.medcarespain.com doctors@medcarespain.com The incidence of diabetes has reached epidemic proportions. About 350 million people worldwide have diabetes, and according to the World
