Retroperitoneal Laparoscopic Surgery: Single Surgeon Experience
|
|
|
- Coleen Stewart
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 european urology supplements 5 (2006) available at journal homepage: Retroperitoneal Laparoscopic Surgery: Single Surgeon Experience Alfredo Aguilera *, Sergio Alonso, Ramón Cansino, Jesús Cisneros, Luis Hidalgo, Javier de la Peña Servicio de Urología, Hospital Universitario La Paz, Madrid, Spain Article info Keywords: Laparoscopic retroperitoneal surgery Renal surgery Adrenal surgery Abstract Objectives: Laparoscopy has become an alternative procedure for various retroperitoneal conditions. It is not easy to learn, and special caution should be taken during its practice because of the presence of large vessels in the surgical field. We report here our 22-mo initial experience with retroperitoneal laparoscopic surgery. Material and methods: The analysed period covers June 2004 to April 2006 (i.e., 22 mo) during which time 128 laparoscopic retroperitoneal surgical procedures were performed. Seventy-eight laparoscopic nephrectomies (43 radical, 16 simple, 14 nephroureterectomies, and 5 in living donors) were performed during this time period. Other types of retroperitoneal laparoscopic surgery were carried out in 50 cases: 10 pyeloplasties, 10 adrenalectomies, 10 partial nephrectomies, 9 retroperitoneal biopsies, 6 stone removals, and 5 cyst marsupialisations. Results: Mean hospital stay was 3.5 d (range: 2 9) for the laparoscopic nephrectomies and 3.3 d (range: 1 7) for the other retroperitoneal laparoscopic surgeries. The conversion rate to open surgery was 1.5% (2 of 128). Conclusions: Learning about renal laparoscopic surgery should be gradual and guided by common sense. The approach to retroperitoneal pathology is technically complex and dangerous because of the presence of the great vessels. The learning curve is long and the potential complications are severe. # 2006 European Association of Urology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. * Corresponding author. P. Castellana 261, Madrid, Spain. Tel ; Fax: address: aaguilera11@yahoo.es (A. Aguilera). 1. Introduction Development and implantation of laparoscopy in urology has been slower as compared with other specialties (general surgery, gynaecology), probably because of the absence of a common condition easily resolved by laparoscopy such as cholecystectomy, ovarian cysts, or tubal ligation. However, there has been an obvious increasing use of this technique in our specialty over the past 10 yr, and while some indications may vary in the future, it may be stated that laparoscopy is here to stay [1] /$ see front matter # 2006 European Association of Urology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. doi: /j.eursup
2 984 european urology supplements 5 (2006) Retroperitoneal laparoscopic surgery is an alternative for a good number of procedures (simple and radical nephrectomy, adrenalectomy, pyeloplasty) and has even exceeded these limits with new indications (living donor extraction, heminephrectomy, retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy). If there is a field that benefits from the advantages of laparoscopy, it is the retroperitoneum. The 2000 review by Janetschek and Marberger [1] provides a list of laparoscopic urologic indications demonstrating this trend. However, the retroperitoneal field is characterised by the presence of large vessels and their branches. This anatomy means that, during plane dissection, if highly anatomic and partly performed by gas, it is essential to remain oriented at all times and to be extremely cautious to avoid a vascular accident that is usually difficult to resolve at laparoscopy. Multiple vascular and intestinal lesions have been reported in the literature [2 5]. After 2 yr in which radical laparoscopic prostatectomy was systematically performed, we started the retroperitoneal surgery program in June Material and methods The period analysed occurred from June 2004 to April 2006 (i.e., a total of 22 mo). A number of conditions were initially rejected because of their greater complexity, including renal tumour excision, radical nephrectomy for tumours greater than 7 cm in size, simple nephrectomy in xanthogranulomatous conditions, adrenalectomy of great masses, or pheochromocytoma. Because of the heterogeneity of indications, we divided the population into complex and less complex procedures (Table 1). We selected the transperitoneal route; it was considered a safer way to start the program because of its advantages of a wider working space and readily identifiable anatomic landmarks compared with the retroperitoneal approach [6,7]. Following our maximum safety principle, we decided to perform the first nephrectomies with manual help using the Gelport (Aesculap), which is a more expensive system than others available in the market (Omniport from Autosuture or LapDisc from Ethicon), but it allows for inserting instruments through the system with no gas loss [8]. After performing 10 nephrectomies, we decided to do without the assisted hand system. The first tumourectomy was performed after 22 retroperitoneal procedures had been completed (12 nephrectomies and 10 diverse surgical procedures). A tumour size greater than 4 cm and a location near the renal hilum were considered contraindications [9 11]. The first transperitoneal extraction from a living donor was carried out after 67 procedures (43 nephrectomies and 24 diverse procedures). In our department, organ extraction from living donors for paediatric receptors has been performed by open surgery since 1984, with a total experience of 63 cases. Table 1 Most common procedures Complex procedure Radical 43 Nephroureter 14 Live donor 5 Partial 10 Pyeloplastia 10 Less complex procedure Simple 16 Adrenalectomy 10 Biopsy 9 Stones 6 Cyst 5 With regards to nephroureterectomy, management of the ureteral time is the most complex part, and several techniques are reported in the literature [12]. In our case, endoscopic deinsertion with early ureteral clipping was performed when the tumour was in the renal pelvis or proximal ureter; below these limits, a bladder cuff was performed by laparoscopy. All surgical procedures were carried out by the same surgeon and assistant. 3. Results 3.1. Nephrectomies During the reported period, 78 laparoscopic nephrectomies (43 radical, 16 simple, 14 nephroureterectomies, and 5 in living donors) were performed in patients with a mean age of 61 yr (range: 22 79) and a mean body mass index (BMI) of 28.1 kg/ m 2 (range: 18 42). Clinical history revealed prior abdominal surgery in 27 (34.6%) cases. Anaesthetic risk score was American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) 1 in 26 patients, ASA 2 in 2, ASA 3 in 23, and ASA 4 in 3 (Table 2). Mean bleeding was 177 ml (range: ), and blood transfusions were required in five (6.4%) cases. However, transfusions were given before surgery in two cases because of hematuria causing anaemia and in a third patient after a radical cystectomy with laparoscopic nephroureterectomy. Mean hospital stay was 3.5 d (range: 2 9). Conversion to open surgery was required in two (2.5%) cases because of a lesion in the superior mesenteric artery requiring an endto-side aortomesenteric bypass and uncontrolled Table 2 Demographic data Laporoscopic nephrectomy Other retroperitoneal surgery Age (yr) (no. [range]) 61 (22 79) 50 (19 79) BMI (kg/m 2 ) (no. [range]) 28 (18 42) 25.2 (20 40) Abdominal surgery 27 (34%) 14 (28%)
3 european urology supplements 5 (2006) bleeding from a lumbar vein, respectively. Open surgical revision attributable to bleeding was needed in two (2.5%) cases: in case no. 5 for a perforating branch of the psoas muscles and in case no. 27 for adrenal gland bleeding. One patient died during surgery from uncontrollable arrhythmia 2 h after the start of the procedure. This patient was a 53-year-old male patient, a heavy smoker with a right kidney tumour, BMI of 34 kg/m 2, cardiologic history, high blood pressure, hypercholesterolemia, and ASA 3 anaesthetic risk. Two surgical wound abscesses also occurred, both in patients with BMI above 30 kg/m 2. Acute kidney failure developed after nephrectomy in four patients, all of them older than 70 yr. Other complications that occurred were controlled by medical management, including acute lung oedema (two cases), angina (one case), toxicoderma (one case), gastric ulcer (one case), and acute gastroenteritis (one case). The pathology study of excised specimens revealed 18 cases of classic renal carcinoma pt1, 1 case of pt2, and 22 cases of pt3. Urothelial carcinoma was pta in 2 cases, pt1 in 6, pt2 in 1, pt3 in 4, and pt4 in 1. An oncocytoma was found as single tumour in 2 patients, and kidneys were atrophic in 16 patients Other retroperitoneal laparoscopic surgeries During this time period, other types of retroperitoneal laparoscopic surgery were carried out in 50 cases: 10 pyeloplasties, 10 adrenalectomies, 10 partial nephrectomies, 9 retroperitoneal biopsies, 6 stone removals, and 5 cyst marsupialisations. Mean patient age was 50 yr (range: 19 79), and mean BMI 25.2 kg/m 2 (range: 20 40). Thirty-five patients were ASA 1, 9 were ASA 2, and 6 were ASA 3. Fourteen of the 50 (28%) patients had a history of abdominal surgery (Table 1). Mean intraoperative bleeding was 85 ml (range: ); heminephrectomies were also responsible for the greatest bleedings. Transfusion was required in two (4%) cases, both heminephrectomies. Mean hospital stay was 3.3 d (range: 1 7), and the longest stay corresponded to a tumour excision complicated by a urinary fistula. No case required conversion to open surgery Open retroperitoneal surgeries During these 20 mo we continued to perform retroperitoneal open surgery in cases not considered amenable to the laparoscopic technique. Thus, 56 nephrectomies were performed: 27 for tumours; 22 simple nephrectomies; 5 extractions from living donors, and 2 nephroureterectomies. Mean patient age was 63 yr (range: 33 83), and mean BMI was 27.3 kg/m 2 (range: 20 39). A history of abdominal surgery was found in 19 of the 56 (33.9%) patients. With regards to anaesthetic risk, there were 13 cases of ASA 1, 24 ASA 2, 17 ASA 3, and 2 ASA 4. Mean surgery time was 170 min (range: ), and tumours with caval thrombi were responsible for the longest procedures. Mean bleeding was 600 ml (range: ), and peroperative or postoperative transfusion was required in 19 (33.9%) patients. Mean hospital stay was 8.8 d (range: 4 15). It should be noted that this series cannot be compared with that of laparoscopic nephrectomies because it comprises cases in which this procedure was rejected because of their complexity (caval thrombus, xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis, big tumour masses). The pathology study of the open nephrectomy specimens revealed 4 conventional kidney tumours pt1, 3 pt2 tumours, 15 pt3 tumours, 3 pt4 tumours, and 2 oncocytomas. One case each of nephroureterectomy was pt2 or pt4 tumour. Among simple nephrectomies, six cases corresponded to polycystic kidneys, seven to xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis, and seven to renal atrophy, and two were emergency procedures performed for multiple trauma with renal hilum involvement. Complications included three surgical wound seromas, one duodenal fistula, one intra-abdominal abscess requiring surgical drainage, one pulmonary thromboembolism, one angina pectoris, one acute renal failure, one pneumonia, one acute gastroenteritis, and one postoperative death (case no. 22, an 83-year-old male with a big left kidney tumour that caused hematuria episodes inducing anaemia; the tumour turned out to be a pt4 conventional kidney tumour). With regards to other types of retroperitoneal surgery, a total of 21 open procedures were performed: 3 adrenalectomies, 3 for retroperitoneal fibroses, 4 partial nephrectomies, 5 for pyeloureteral junction stenoses, 5 for kidney stones (pyelonephrolithotomy), and 1 for a local relapse of a renal carcinoma. Mean patient age was 55.6 yr (range: 21 74), and mean BMI was 26.6 kg/m 2 (range: 23 30). Anaesthetic risk was ASA 1 in 8 cases, ASA 2 in 10 cases, and ASA 3 in 3 cases. A history of abdominal surgery was found in two patients. Mean surgery time was 163 min (range: ), and no patient required postoperative transfusions. Mean hospital stay was 7.8 d (range: 1 17). 4. Discussion Retroperitoneal laparoscopic surgery is a good alternative to the open approach.
4 986 european urology supplements 5 (2006) The two different techniques, transperitoneal and retroperitoneal, have clear characteristics: Whereas the transperitoneal approach provides a better space and orientation, retroperitoneoscopy offers a faster access to the renal hilum and allows for a decreased intestinal manipulation, but demands greater caution with intestinal lesions, generally thermal, that usually go unnoticed. Several studies have compared both approaches, and we agree with the conclusion they usually reached: The surgeon should use the approach with which he or she is more comfortable and experienced [6,13]. Our department chose the transperitoneal approach to start the program on the basis of these reasons. While we have subsequently performed some procedures using retroperitoneoscopy, we think it is a somewhat more complicated approach, particularly with regards to orientation. With regards to use of the manual port, our experience was positive in the early cases. Advantages of this system (a visual reference facilitating learning, touch, bowel loop separation, increased safety preventing vascular lesions, use of incision for specimen removal) are greater than its disadvantages (a somewhat larger incision generally, loss of gas, difficult placement in a small abdomen) [8,14]. However, as experience is gained, having a compromised hand and the increased difficulty for delicate dissection make it convenient to pass to pure laparoscopy. In our experience, the handassisted device has been relegated to laparoscopic organ removal from a living donor. Early contraindications have naturally varied over time so that cases in which laparoscopy is ruled out decrease as experience is gained. Tumour size is a good example of this. Laparoscopic nephrectomy initially was not considered to be indicated for tumours greater than 7 cm because of technical difficulties, while, in the most recent cases, we performed nephrectomies in patients with tumours up to 15 cm in size. In this regard, a review of literature reports in recent years would also show the changes in the criteria for considering tumour size as a contraindication. Thus, although no agreement exists about the maximum size, as early as 2001 various authors proposed the laparoscopic technique for tumours greater than 10 cm [15]. More recently, reference is found to handassisted laparoscopic nephrectomies in tumours greater than 9.5 cm in size, with authors concluding that the tumour limit is directly related to the surgeon s experience [16]. At our department, we currently think that the presence of a tumour thrombus in the vena cava is a contraindication for laparoscopy. This is a controversial subject in the literature. Desai et al. [17] reported a series of 16 cases of tumour thrombi with renal vein involvement (level I involvement) in which renal vein clamping was performed with laparoscopic mechanical suture encircling vein ostium. The thrombus was squeezed out towards the kidney in all cases, and a vena cava opening was not required. This study also discussed an animal model for performing this procedure with caval involvement by the tumour thrombus. In 2002, 2004, and 2005, there were at least three articles reporting hand-assisted right radical nephrectomy in the presence of a caval thrombus: Sundaram et al. [18] and Varkarakis et al. [19] reported cases of patients with tumour thrombi of 1 cm and 2 cm, respectively, in the vena cava in which a hand-assisted transperitoneal approach was used. Whereas in the first case the whole nephrectomy was hand-assisted, with prior embolisation of the renal artery, the four cases of Varkarakis renal vein and vena cava dissections were completely laparoscopic, with no prior embolisation. In their 2005 article, Disanto et al. [20] reported the case of an 87-year-old female patient with a right kidney tumour and a 7-cm-long tumour thrombus resolved by using a hand-assisted retroperitoneoscopic approach. Hand-assisted laparoscopy probably allows for performing this procedure, while undoubtedly demanding and requiring a great experience from the surgical team. In our view, the presence of a tumour thrombus beyond the renal vein is a contraindication to laparoscopy. A history of abdominal surgery was not considered an absolute contraindication. Because of our lower experience with retroperitoneoscopy, we initially decided to attempt the transperitoneal approach in these cases. Conversion to open surgery was not required in any of these procedures, which were all successfully completed. A careful approach is needed, inducing pneumoperitoneum through a minilaparotomy (approximately 2 cm) and placing at least one additional trocar to separate adhesions. In an interesting article, Viterbo et al. [21], in addition to a literature review on laparoscopic complications, reported their series of 48 patients with a history of abdominal radiation therapy and/or surgery undergoing retroperitoneoscopy for renal or adrenal conditions. These results were compared with a series of 30 patients with no such history, and no statistically significant differences were found between the groups (surgery time, bleeding, complications, hospital stay). We agree with their conclusion that retroperitoneoscopy is a good alternative in these patients. However, we think that a certain experience in
5 european urology supplements 5 (2006) the transperitoneal approach is required to learn retroperitoneoscopy. Today, after almost 2 yr of use of retroperitoneal laparoscopic surgery, we retain as absolute contraindications suspected local infiltration of tumour process with vascular or intestinal involvement, xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis, and a caval tumour thrombus. Partial nephrectomy is probably the most demanding indication of the procedure and the one requiring more experience, and should not be performed if intracorporeal suture is not mastered. Highly experienced authors agree with this view in recent publications analysing their series, each consisting of approximately 200 cases and giving very interesting descriptions of the complications found that show the complexity of the procedure [9,22,23]. With regards to laparoscopic organ removal from a living donor, while not so technically demanding as partial nephrectomy, it should not be done until a substantial experience is gained in retroperitoneal laparoscopic surgery because of the complexities involved: It is a procedure affecting two patients, one of them healthy, and the kidney should be removed with no lesions and the maximal vessel length possible. Leventhal et al. [24,25] agreed with these views in several studies, one of which was a review of 500 cases of laparoscopic extraction. As for us, we perform this surgery only on left kidneys for the time being because we think that the length of the right renal vein is too short. In laparoscopic nephroureterectomy, the greatest complications, both technical and in terms of oncologic results, are found with ureter management. In an interesting article, Steinberg et al. [26] reviewed the different possible approaches to the ureter and their oncologic implications: What is the most appropriate approach, and are survival and disease recurrence compromised by any of the procedures? These authors concluded that no procedure currently appears to be superior to the others, and that the surgical oncologic criterion should of course prevail, with additional studies on oncologic results being required. A Gerber and Stockton [27] article based on questionnaires completed by 605 urologists from different countries (United States, Europe, Asia, and Canada) reported that European urologists most frequently perform open surgery, whereas the hand-assisted procedure is more popular among American urologists, and Asian urologists show the greatest preference for retroperitoneoscopy. Most urologists prefer open surgery to manage the ureter in nephroureterectomy. These results should not be regarded as categoric and extrapolative; however, this article demonstrates on the one hand the lack of consensus for ureter management, and on the other hand an ever increasing trend to use laparoscopy in urology (compared with the same study done in 2002), as well as the possible variations with regards to approach and indications depending on the country and surgical school. Whenever a new program is started, it may be expected that a number of complications will occur, but they will then decrease over time as more experience is gained. It is important to be prepared for such complications and to try and resolve them, by laparoscopic means if possible and always without endangering the life of the patient. The most serious complications in our series were a death in a nephrectomy patient because of uncontrolled arrhythmia, an acute stroke 24 h after an adrenalectomy in an 80-year-old female patient, and a lesion in the superior mesenteric artery in a radical nephrectomy requiring conversion to open surgery [28]. There are many references in the literature to complications of laparoscopic surgery, among which special mention should be made to a meta-analysis [29] focusing on renal surgery in which articles published between 1995 and 2004 were analysed. Among the 405 publications reviewed, only 56 met inclusion criteria, and a total of 4859 procedures were therefore analysed. Major and minor complications of the different pure and handassisted renal laparoscopic procedures (radical and simple partial nephrectomy, nephroureterectomy, living donor) were compared. Although difficulties in data collection because of the retrospective nature of the study and the lack of standardisation of complications in the literature were recognised, the authors arrived at some interesting conclusions: Major and minor complication rates were approximately 10% and 2%, respectively; the highest rate of major complications (21%) was associated with partial nephrectomy (need for transfusion and urinoma); and finally, the hand-assisted procedure is associated with a higher rate of incision complications (1.9% vs. 0.2%). 5. Conclusions As stated in the introduction, laparoscopic surgery in urology is obviously not a future project but a reality, and this observation is even clearer in its retroperitoneal application. The development of a retroperitoneal laparoscopic surgery program should be gradual, and it should not be intended
6 988 european urology supplements 5 (2006) to cover all conditions or patients from the beginning. On the other hand, for a program of retroperitoneal laparoscopic surgery to be implemented with the highest guarantee, a sufficiently high volume of patients (at least one procedure weekly) should be available to maintain and develop the skills of the surgical team. We prefer the transperitoneal approach because of its advantages (wider working space and readily identifiable anatomic landmarks). Hand assistance device may be useful in the beginning. As a final conclusion, we think that application of the laparoscopic technique in urology should not be disregarded no matter how difficult and strenuous it may be. Urologists must continue to strive to be in the forefront of surgery and pave the way for other surgical specialties. Our patients will undoubtedly benefit from this progress. References [1] Janetschek G, Marberger M. Laparoscopic surgery in urology. Curr Opin Urol 2000;10: [2] Bishoff JT, Allaf ME, Kirkels W, Moore RG, Kavoussi LR, Schroder F. Laparoscopic bowel injury: incidence and clinical presentation. J Urol 1999;161:887. [3] Gill IS, Kavoussi LR, Clayman RV, et al. Complications of laparoscopic nephrectomy in 185 patients: a multi-institutional review. J Urol 1995;154:479. [4] Fahlenkamp D, Rassweiler J, Fornara P, Frede T, Loening SA. Complications of laparoscopic procedures in urology: experience with 2,407 procedures at 4 German centers. J Urol 1999;162:765. [5] Thiel R, Adams JB, Schulam PG, Moore RG, Kavoussi LR. Venous dissection injuries during laparoscopic urological surgery. J Urol 1996;155:1874. [6] Desai M, Strzempkowski B, Matin SF, Steinberg AP, Meraney AM, Gill IS. Prospective randomized comparison of transperitoneal versus retroperitoneal laparoscopic radical nephretctomy. J Urol 2005;173: [7] Abdelmaksoud A, Biyani CS, Bagheri F, Janetschek G. Laparoscopic approaches in urology. BJU Int 2005;95: [8] Wolf JS. Hand-assisted laparoscopy: pro. Urology 2001;58: [9] Haber G-P, Gill IS. Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy: contemporary technique and outcomes. Eur Urol 2006; 49: [10] Abukora F, Nambirajan T, Albqami N, et al. Laparoscopic nephron sparing surgery: evolution in a decade. Eur Urol 2005;47:488 93, discussion 493. [11] Mita K, Shigeta M, Mutaguchi K, et al. Urological retroperitoneoscopic surgery for patients with prior intraabdominal surgery. Eur Urol 2005;48: [12] Steinberg J, Matin SF. Laparoscopic radical nephroureterectomy: dilemma of the distal ureter. Curr Opin Urol 2004;14:61 5. [13] Sung GT, Gill IS. Anatomic landmarks and time management during retroperitoneoscopic radical nephrectomy. J Endourol 2002;16:165. [14] Wolf Jr JS, Moon TD, Nakada SY. Hand assisted laparoscopic nephrectomy: technical considerations. Tech Urol 1997;3: [15] Gill IS, Merqney AM, Schweizer DK, et al. Laparoscopic radical nephrectomy in 100 patients: a single center experience from the United States. Cancer 2001;92: [16] Malaeb BS, Sherwood JB, Taylor GD, Duchene DA, Broder KJ, Koeneman KS. Hand-assisted laparoscopic nephrectomy for renal masses 9.5 cm: series comparison with open radical nephrectomy. Urol Oncol Semin Original Investig 2005;23: [17] Desai MM, Gill IS, Ramani AP, et al. Laparoscopic radical nephrectomy for cancer with level I renal vein involvement. J Urol 2003;169: [18] Sundaram CP, Rehman J, Lamdman J, et al. Hand assisted laparoscopic radical nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma with inferior vena caval thrombus. J Urol 2002; 168: [19] Varkarakis IM, Bhayanai S, Allaf M, Inagaki T, Gonzalgo M, Jarret T. Laparoscopic-assisted nephrectomy with inferior vena cava tumor thrombectomy: preliminary results. Urology 2004;64: [20] Disanto V, Pansadoro V, Portoghese F, Scalese GA, Romano M. Retroperitoneal laparoscopic radical nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma with infrahepatic vena caval thrombus. Eur Urol 2005;47: [21] Viterbo R, Grenberg R, Al Saleem T, Uzzo R. Prior abdominal surgery and radiation do not complicate the retroperitoneoscopic approach to the kidney or adrenal gland. J Urology 2005;174: [22] Ramani A, Desai M, Steinberg A, et al. Complications of laparoscopic partial nephrectomy in 200 cases. J Urology 2005;173:42 7. [23] Link R, Bhayani S, Allaf M, et al. Exploing the learning curve, pathological outcomes and perioperative morbidity of laparoscopic partial nephrectomy performed for renal mass. J Urol 2005;173: [24] Leventhal J, Deeik R, Joehl J, et al. Laparoscopic live donor nephrectomy is it safe? Transplantation 2000;70: [25] Leventhal J, Kocak B, Salvalaggio P, et al. Laparoscopic donor nephrectomy 1997 to 2003: lessons learned with 500 cases at a single institution. Surgery 2004;136: [26] Steinberg J, Matin SF. Laparoscopic radical nephroureterectomy: dilemma of the distal ureter. Curr Opin Urol 2004; 14:61 5. [27] Gerber GS, Stockton BR. Trends in endourologic practice: laparoscopic radical nephrectomy and nephroureterectomy. J Endourol 2005;19: [28] Saez L, Riera L, Gutierrez M, Aguilera A, Stefanov S, Riera L. Accidental ligation of superior mesenterio artery as a complication of laparoscopic nephrectomy. Angiologia 2005;57:71 7. [29] Pareek G, Hedican S, Gee J, Bruskewitz R, Nakada S. Metaanalysis of the complications of laparoscopic renal surgery: comparison of procedures and techniques. J Urol 2006;175:
Initial Series of Robotic Radical Nephrectomy with Vena Caval Tumor Thrombectomy
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 59 (2011) 652 656 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Case Series of the Month Initial Series of Robotic Radical Nephrectomy with Vena Caval Tumor
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 59 (2011) 652 656 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Case Series of the Month Initial Series of Robotic Radical Nephrectomy with Vena Caval Tumor
Laparoscopic Nephrectomy: New Standard of Care?
 Original Article Laparoscopic Nephrectomy: New Standard of Care? Hong Gee Sim, Sidney K.H. Yip, Chee Yong Ng, Yee Sze Teo, Yeh Hong Tan, Woei Yun Siow and Wai Sam Cheng, Department of Urology, Singapore
Original Article Laparoscopic Nephrectomy: New Standard of Care? Hong Gee Sim, Sidney K.H. Yip, Chee Yong Ng, Yee Sze Teo, Yeh Hong Tan, Woei Yun Siow and Wai Sam Cheng, Department of Urology, Singapore
Retroperitoneoscopic Radical Nephrectomy: Initial Experience
 Retroperitoneoscopic Radical Nephrectomy: Initial Experience A. Hasegan 1, D. Bratu 2, V. Pirvut 1, I. Mihai 1, N. Grigore 1 1 Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu, Department of Urology 2 Lucian Blaga University
Retroperitoneoscopic Radical Nephrectomy: Initial Experience A. Hasegan 1, D. Bratu 2, V. Pirvut 1, I. Mihai 1, N. Grigore 1 1 Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu, Department of Urology 2 Lucian Blaga University
Hand-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy in the Treatment of a Renal Cell Carcinoma with a Level II Vena Cava Thrombus
 Surgical Technique Laparoscopic Excision of an RCC with Level II thrombus International Braz J Urol Vol. 36 (3): 327-331, May - June, 2010 doi: 10.1590/S1677-55382010000300009 Hand-Assisted Laparoscopic
Surgical Technique Laparoscopic Excision of an RCC with Level II thrombus International Braz J Urol Vol. 36 (3): 327-331, May - June, 2010 doi: 10.1590/S1677-55382010000300009 Hand-Assisted Laparoscopic
Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy- the current gold standard
 Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy- the current gold standard Anoop M. Meraney, M.D Director, Urologic Oncology, Helen and Harry Gray Cancer Center, Hartford Hospital and Connecticut Surgical Group. Is it
Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy- the current gold standard Anoop M. Meraney, M.D Director, Urologic Oncology, Helen and Harry Gray Cancer Center, Hartford Hospital and Connecticut Surgical Group. Is it
Organ-Preserving Endoscopic Kidney Cancer Resection
 european urology 50 (2006) 732 737 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Surgery in Motion Organ-Preserving Endoscopic Kidney Cancer Resection Elmar Heinrich, Tobias
european urology 50 (2006) 732 737 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Surgery in Motion Organ-Preserving Endoscopic Kidney Cancer Resection Elmar Heinrich, Tobias
Retroperitoneal Laparoscopic Radical Nephroureterectomy for High Urothelial Tumours
 Retroperitoneal Laparoscopic Radical Nephroureterectomy for High Urothelial Tumours A. Hașegan 1, V. Pîrvuț 1, I. Mihai 1, N. Grigore 1 1 Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu, Faculty of Medicine Clinical
Retroperitoneal Laparoscopic Radical Nephroureterectomy for High Urothelial Tumours A. Hașegan 1, V. Pîrvuț 1, I. Mihai 1, N. Grigore 1 1 Lucian Blaga University of Sibiu, Faculty of Medicine Clinical
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenocarcinoma, pancreatic ductal, laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy for, 61 Adrenal cortical carcinoma, laparoscopic adrenalectomy for, 114
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenocarcinoma, pancreatic ductal, laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy for, 61 Adrenal cortical carcinoma, laparoscopic adrenalectomy for, 114
Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy for Renal Masses 7 Centimeters or Larger
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy for Renal Masses 7 Centimeters or Larger James S. Rosoff, MD, Jay D. Raman, MD, R. Ernest Sosa, MD, Joseph J. Del Pizzo, MD ABSTRACT Objective: To report
SCIENTIFIC PAPER Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy for Renal Masses 7 Centimeters or Larger James S. Rosoff, MD, Jay D. Raman, MD, R. Ernest Sosa, MD, Joseph J. Del Pizzo, MD ABSTRACT Objective: To report
Original Article A novel approach to locate renal artery during retroperitoneal laparoendoscopic single-site radical nephrectomy
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(7):1752-1756 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0000870 Original Article during radical nephrectomy Lixin Shi, Wei Cai, Juan Dong, Jiangping Gao, Hongzhao Li, Shengkun Sun, Qiang
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(7):1752-1756 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0000870 Original Article during radical nephrectomy Lixin Shi, Wei Cai, Juan Dong, Jiangping Gao, Hongzhao Li, Shengkun Sun, Qiang
Retroperitoneoscopic Transureteroureterostomy with Cutaneous Ureterostomy to Salvage Failed Ileal Conduit Urinary Diversion
 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Case Study of the Month Retroperitoneoscopic Transureteroureterostomy with Cutaneous Ureterostomy to Salvage Failed Ileal Conduit
available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Case Study of the Month Retroperitoneoscopic Transureteroureterostomy with Cutaneous Ureterostomy to Salvage Failed Ileal Conduit
Chapter 2. Simple Nephrectomy. Please Give Three Tips for Laparoscopic Simple Nephrectomy. Dr. de la Rosette
 Chapter 2 Simple Nephrectomy Please Give Three Tips for Laparoscopic Simple Nephrectomy............. 39 How Does One Find the Renal Hilum during Transperitoneal Laparoscopic Nephrectomy?.................
Chapter 2 Simple Nephrectomy Please Give Three Tips for Laparoscopic Simple Nephrectomy............. 39 How Does One Find the Renal Hilum during Transperitoneal Laparoscopic Nephrectomy?.................
Long-Term Oncologic Outcome after Laparoscopic Radical Nephroureterectomy for Upper Tract Transitional Cell Carcinoma
 european urology 51 (2007) 1639 1644 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Laparoscopy Long-Term Oncologic Outcome after Laparoscopic Radical Nephroureterectomy for
european urology 51 (2007) 1639 1644 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Laparoscopy Long-Term Oncologic Outcome after Laparoscopic Radical Nephroureterectomy for
Kaiser Oakland Urology
 Kaiser Oakland Urology What is Laparoscopy? Minimally invasive surgical alternative to standard surgery How is Laparoscopy Performed? A laparoscope and video camera are used to visualize internal organs
Kaiser Oakland Urology What is Laparoscopy? Minimally invasive surgical alternative to standard surgery How is Laparoscopy Performed? A laparoscope and video camera are used to visualize internal organs
da Vinci Prostatectomy My Greek personal experience
 da Vinci Prostatectomy My Greek personal experience Vassilis Poulakis MD, PhD, FEBU Ass. Prof. of Urology Director of Urologic Clinic Doctors Hospital Athens Laparoscopy - golden standard in Urology -
da Vinci Prostatectomy My Greek personal experience Vassilis Poulakis MD, PhD, FEBU Ass. Prof. of Urology Director of Urologic Clinic Doctors Hospital Athens Laparoscopy - golden standard in Urology -
Laparoscopic nephrectomy for benign non functioning kidneys
 Review Article Laparoscopic nephrectomy for benign non functioning kidneys Narmada P. Gupta, Gagan Gautam Department of Urology, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India Address for correspondence:
Review Article Laparoscopic nephrectomy for benign non functioning kidneys Narmada P. Gupta, Gagan Gautam Department of Urology, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India Address for correspondence:
Robotic Surgery for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma. Li-Ming Su, MD
 Robotic Surgery for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma Li-Ming Su, MD David A. Cofrin Professor of Urology, Associate Chairman of Clinical Affairs, Chief, Division of Robotic and Minimally Invasive Urologic
Robotic Surgery for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma Li-Ming Su, MD David A. Cofrin Professor of Urology, Associate Chairman of Clinical Affairs, Chief, Division of Robotic and Minimally Invasive Urologic
BJUI. Robotic nephrectomy for the treatment of benign and malignant disease
 . JOURNAL COMPILATION 2008 BJU INTERNATIONAL Laparoscopic and Robotic Urology ROGERS et al. BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Robotic nephrectomy for the treatment of benign and malignant disease Craig Rogers, Rajesh
. JOURNAL COMPILATION 2008 BJU INTERNATIONAL Laparoscopic and Robotic Urology ROGERS et al. BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Robotic nephrectomy for the treatment of benign and malignant disease Craig Rogers, Rajesh
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedures overview of laparoscopic partial nephrectomy 308 Introduction This overview has been
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedures overview of laparoscopic partial nephrectomy 308 Introduction This overview has been
LAPAROSCOPIC NEPHRECTOMY IN INFLAMMATORY RENAL DISEASE: PROPOSAL FOR A STAGED APPROACH
 Clinical Urology LAPAROSCOPIC NEPHRECTOMY IN INFLAMMATORY DISEASE International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology Vol. 31(1): -8, January - February, 5 LAPAROSCOPIC NEPHRECTOMY
Clinical Urology LAPAROSCOPIC NEPHRECTOMY IN INFLAMMATORY DISEASE International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology Vol. 31(1): -8, January - February, 5 LAPAROSCOPIC NEPHRECTOMY
Laparoscopic Surgery. The Da Vinci Robot. Limits of Laparoscopy. What Robotics Offers. Robotic Urologic Surgery: A New Era in Patient Care
 Laparoscopic Surgery Robotic Urologic Surgery: A New Era in Patient Care Laparoscopic technique was introduced in urologic surgery in the 1990s Benefits: Improved recovery time, decreased morbidity Matthew
Laparoscopic Surgery Robotic Urologic Surgery: A New Era in Patient Care Laparoscopic technique was introduced in urologic surgery in the 1990s Benefits: Improved recovery time, decreased morbidity Matthew
PREFACE... V. CONTRIBUTORS... xiii. 1. SURGICAL INCISIONS... 3 J. Stephen Jones
 Contents PREFACE... V CONTRIBUTORS... xiii PART I: THE KIDNEY AND ADRENAL 1. SURGICAL INCISIONS... 3 2. ADRENAL DISEASE: OPEN SURGERY... 17 3. LAPAROSCOPIC ADRENALECTOMY... 23 Mihir M. Desai and Inderbir
Contents PREFACE... V CONTRIBUTORS... xiii PART I: THE KIDNEY AND ADRENAL 1. SURGICAL INCISIONS... 3 2. ADRENAL DISEASE: OPEN SURGERY... 17 3. LAPAROSCOPIC ADRENALECTOMY... 23 Mihir M. Desai and Inderbir
In the past radical nephrectomy necessitated a large
 A Prospective Study of Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy for T1 Tumors Is Transperitoneal, Retroperitoneal or Hand Assisted the Best Approach? Robert B. Nadler,* Stacy Loeb, J. Quentin Clemens, Robert A.
A Prospective Study of Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy for T1 Tumors Is Transperitoneal, Retroperitoneal or Hand Assisted the Best Approach? Robert B. Nadler,* Stacy Loeb, J. Quentin Clemens, Robert A.
Laparoscopic Nephrectomy For Benign and Inflammatory Conditions* T. MANOHAR, M.D., MIHIR DESAI, M.D., and MAHESH DESAI, M.S., FRCS, FRCS ABSTRACT
 JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 21, Number 11, November 2007 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/end.2007.9883 Laparoscopic Nephrectomy For Benign and Inflammatory Conditions* T. MANOHAR, M.D., MIHIR DESAI,
JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 21, Number 11, November 2007 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/end.2007.9883 Laparoscopic Nephrectomy For Benign and Inflammatory Conditions* T. MANOHAR, M.D., MIHIR DESAI,
LAPAROSCOPIC RADICAL NEPHRECTOMY FOR LARGE (GREATER THAN 7 CM, T2) RENAL TUMORS
 0022-5347/04/1726-2172/0 Vol. 172, 2172 2176, December 2004 THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION DOI: 10.1097/01.ju.0000140961.53335.04 LAPAROSCOPIC
0022-5347/04/1726-2172/0 Vol. 172, 2172 2176, December 2004 THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION DOI: 10.1097/01.ju.0000140961.53335.04 LAPAROSCOPIC
Laparoscopic Nephroureterectomy for Upper Tract Transitional Cell Carcinoma: Comparison of Laparoscopic and Open Surgery
 european urology 49 (2006) 332 336 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Laparoscopy Laparoscopic Nephroureterectomy for Upper Tract Transitional Cell Carcinoma:
european urology 49 (2006) 332 336 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Laparoscopy Laparoscopic Nephroureterectomy for Upper Tract Transitional Cell Carcinoma:
Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy for Renal Cell Carcinoma
 Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy for Renal Cell Carcinoma Yoshinari Ono 1,Ryohei Hattori 1,Momokazu Gotoh 1, Tsuneo Kinukawa 2,Shin Yamada 3, and Osamu Kamihira 4 Summary. Laparoscopic radical nephrectomy
Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy for Renal Cell Carcinoma Yoshinari Ono 1,Ryohei Hattori 1,Momokazu Gotoh 1, Tsuneo Kinukawa 2,Shin Yamada 3, and Osamu Kamihira 4 Summary. Laparoscopic radical nephrectomy
Arieh L. Shalhav Is There a Risk in Robotic Nephroureterectomy?
 Arieh L. Shalhav Is There a Risk in Robotic Nephroureterectomy? 80 patients LNU (n = 40) or ONU (n = 40) CSS (p = 0.2), BRFS (p = 0.86), MFS (p = 0.12) similar for the entire cohort Subgroups of pt3 UTUC
Arieh L. Shalhav Is There a Risk in Robotic Nephroureterectomy? 80 patients LNU (n = 40) or ONU (n = 40) CSS (p = 0.2), BRFS (p = 0.86), MFS (p = 0.12) similar for the entire cohort Subgroups of pt3 UTUC
Differences in Left and Right Laparoscopic Adrenalectomy
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER Differences in Left and Right Laparoscopic Adrenalectomy Jocelyn M. Rieder, MD, Alan A. Nisbet, MD, Melanie C. Wuerstle, MD, Viet Q. Tran, MD, Eric O. Kwon, MD, Gary W. Chien, MD ABSTRACT
SCIENTIFIC PAPER Differences in Left and Right Laparoscopic Adrenalectomy Jocelyn M. Rieder, MD, Alan A. Nisbet, MD, Melanie C. Wuerstle, MD, Viet Q. Tran, MD, Eric O. Kwon, MD, Gary W. Chien, MD ABSTRACT
Transperitoneal Laparoscopic Nephrectomy for Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER Transperitoneal Laparoscopic Nephrectomy for Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Grégory Verhoest, MD, Arnaud Delreux, MD, Romain Mathieu, MD, Jean-Jacques Patard, MD, Cécile
SCIENTIFIC PAPER Transperitoneal Laparoscopic Nephrectomy for Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Grégory Verhoest, MD, Arnaud Delreux, MD, Romain Mathieu, MD, Jean-Jacques Patard, MD, Cécile
Single-center comparison of purely laparoscopic, hand-assisted laparoscopic, and open radical nephrectomy in patients at high anesthetic risk
 Single-center comparison of purely laparoscopic, hand-assisted laparoscopic, and open radical nephrectomy in patients at high anesthetic risk Baldwin D D, Dunbar J A, Parekh D J, Wells N, Shuford M D,
Single-center comparison of purely laparoscopic, hand-assisted laparoscopic, and open radical nephrectomy in patients at high anesthetic risk Baldwin D D, Dunbar J A, Parekh D J, Wells N, Shuford M D,
Morbidity Audit and Logbook Tool SNOMED Board Reporting Terms for SET and IMG Urology ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT
 ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT Cystolitholapaxy Cystoscopic removal of foreign body from bladder Cystoscopic removal of ureteric stent Cystoscopy and cystodiathermy Cystoscopy and transurethral biopsy
ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT Cystolitholapaxy Cystoscopic removal of foreign body from bladder Cystoscopic removal of ureteric stent Cystoscopy and cystodiathermy Cystoscopy and transurethral biopsy
Determination of cell viability after laparoscopic tissue stapling in a porcine model
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2005 Determination of cell viability after laparoscopic tissue stapling in a porcine model Ramakrishna Venkatesh
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2005 Determination of cell viability after laparoscopic tissue stapling in a porcine model Ramakrishna Venkatesh
SURGERY, TRANSPLANTATION AND POLYCYSTIC DISEASE. Mr Nick Inston PhD FRCS Consultant Transplant Surgeon Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham
 SURGERY, TRANSPLANTATION AND POLYCYSTIC DISEASE Mr Nick Inston PhD FRCS Consultant Transplant Surgeon Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham What are polycystic kidneys and livers?! Cystic degenerative condition!
SURGERY, TRANSPLANTATION AND POLYCYSTIC DISEASE Mr Nick Inston PhD FRCS Consultant Transplant Surgeon Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham What are polycystic kidneys and livers?! Cystic degenerative condition!
Case Report Left Transperitoneal Adrenalectomy with a Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Surgery Combined Technique: Initial Case Reports
 Volume 2011, Article ID 651380, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/651380 Case Report Left Transperitoneal Adrenalectomy with a Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Surgery Combined Technique: Initial Case Reports Yasuhiro
Volume 2011, Article ID 651380, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/651380 Case Report Left Transperitoneal Adrenalectomy with a Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Surgery Combined Technique: Initial Case Reports Yasuhiro
RADICAL CYSTECTOMY. Solutions for minimally invasive urologic surgery
 RADICAL CYSTECTOMY Solutions for minimally invasive urologic surgery The da Vinci Surgical System High-definition 3D vision EndoWrist instrumentation Intuitive motion RADICAL CYSTECTOMY Maintains the oncologic
RADICAL CYSTECTOMY Solutions for minimally invasive urologic surgery The da Vinci Surgical System High-definition 3D vision EndoWrist instrumentation Intuitive motion RADICAL CYSTECTOMY Maintains the oncologic
Obesity Is an Adverse Factor on Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy for T2 but Not T1 Renal Cell Carcinoma
 Endourology www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/.4/kju.2.52.8.58 Obesity Is an Adverse Factor on Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy for T2 but Not T Renal Cell Carcinoma Se Yun Kwon, Jae Jun Bae, Jung Gon
Endourology www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/.4/kju.2.52.8.58 Obesity Is an Adverse Factor on Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy for T2 but Not T Renal Cell Carcinoma Se Yun Kwon, Jae Jun Bae, Jung Gon
Retroperitoneoscopy: A Versatile Access for Many Urologic Indications
 european urology supplements 5 (2006) 975 982 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Retroperitoneoscopy: A Versatile Access for Many Urologic Indications Dogu Teber,
european urology supplements 5 (2006) 975 982 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Retroperitoneoscopy: A Versatile Access for Many Urologic Indications Dogu Teber,
Financial and Other Disclosures
 Financial and Other Disclosures Off-label use of drugs, devices, or other agents: None Data from IRB-approved human research is not presented I have the following financial interests or relationships to
Financial and Other Disclosures Off-label use of drugs, devices, or other agents: None Data from IRB-approved human research is not presented I have the following financial interests or relationships to
Lower pole approach in retroperitoneal laparoscopic radical nephrectomy: a new approach for the management of renal vascular pedicle
 Yuan et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2018) 16:31 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-018-1324-7 RESEARCH Open Access Lower pole approach in retroperitoneal laparoscopic radical nephrectomy: a new
Yuan et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2018) 16:31 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-018-1324-7 RESEARCH Open Access Lower pole approach in retroperitoneal laparoscopic radical nephrectomy: a new
Oncourology COMPLICATIONS OF PARTIAL NEPHRECTOMY AT OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF RENAL CELL CARCINOMA
 1 Oncourology COMPLICATIONS OF PARTIAL NEPHRECTOMY AT OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF RENAL CELL CARCINOMA Address: Eduard Oleksandrovych Stakhovsky, 03022, Kyiv, Lomonosova Str., 33/43, National Cancer Institute
1 Oncourology COMPLICATIONS OF PARTIAL NEPHRECTOMY AT OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF RENAL CELL CARCINOMA Address: Eduard Oleksandrovych Stakhovsky, 03022, Kyiv, Lomonosova Str., 33/43, National Cancer Institute
Two-handed assisted laparoscopic surgery: Evaluation in an animal model
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Vol. 40 (5): 697-701, September - October, 2014 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.05.16 Two-handed assisted laparoscopic surgery: Evaluation in an animal model Eduardo Sanchez-de-Badajoz,
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Vol. 40 (5): 697-701, September - October, 2014 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.05.16 Two-handed assisted laparoscopic surgery: Evaluation in an animal model Eduardo Sanchez-de-Badajoz,
Laparoscopic Nephroureterectomy with Concomitant Open Bladder Cuff Excision
 Laparoscopic Nephroureterectomy with Concomitant Open Bladder Cuff Excision A Single Center Experience LAPAROSCOPIC UROLOGY Seyed Amir Mohsen Ziaee, Valiollah Azizi, Akbar Nouralizadeh, Shahram Gooran,
Laparoscopic Nephroureterectomy with Concomitant Open Bladder Cuff Excision A Single Center Experience LAPAROSCOPIC UROLOGY Seyed Amir Mohsen Ziaee, Valiollah Azizi, Akbar Nouralizadeh, Shahram Gooran,
Contents SECTION I: ESSENTIALS OF LAPAROSCOPY. Chapter 1: Chronological advances in Minimal Access Surgery
 Contents SECTION I: ESSENTIALS OF LAPAROSCOPY Chapter 1: Chronological advances in Minimal Access Surgery Chapter 2: Laparoscopic Equipments a. Laparoscopic Trolley b. Light cable c. Light source d. Telescope
Contents SECTION I: ESSENTIALS OF LAPAROSCOPY Chapter 1: Chronological advances in Minimal Access Surgery Chapter 2: Laparoscopic Equipments a. Laparoscopic Trolley b. Light cable c. Light source d. Telescope
Minimally invasive surgery in urology oncology. Dr. Tongchai Nakamont 23 Jan 2014
 Minimally invasive surgery in urology oncology Dr. Tongchai Nakamont 23 Jan 2014 Urology oncology Renal cell carcinoma ( RCC) Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) Kidney Ureter Bladder Prostate cancer Urological
Minimally invasive surgery in urology oncology Dr. Tongchai Nakamont 23 Jan 2014 Urology oncology Renal cell carcinoma ( RCC) Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) Kidney Ureter Bladder Prostate cancer Urological
Non-commercial use only
 Surgical Techniques Development 2011; volume 1:e33 Follow-up results of a pure retroperitoneoscopic/extraperi toneal nephroureterectomy for upper tract urothelial tumors Wael Y. Khoder, Stefan Tritschler,
Surgical Techniques Development 2011; volume 1:e33 Follow-up results of a pure retroperitoneoscopic/extraperi toneal nephroureterectomy for upper tract urothelial tumors Wael Y. Khoder, Stefan Tritschler,
LAPAROSCOPIC PARTIAL NEPHRECTOMY FOR CANCER: TECHNIQUES AND OUTCOMES
 Clinical Urology International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology LAPAROSCOPIC PARTIAL NEPHRECTOMY Vol. 31 (2): 100-104, March - April, 2005 LAPAROSCOPIC PARTIAL NEPHRECTOMY
Clinical Urology International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology LAPAROSCOPIC PARTIAL NEPHRECTOMY Vol. 31 (2): 100-104, March - April, 2005 LAPAROSCOPIC PARTIAL NEPHRECTOMY
goire, Bastien Laurence, Hoznek Andras, Vordos Dimitri, Abbou Claude, Salomon Laurent IMRB, Institut Mondor de recherche biomédicale
 Author manuscript, published in "World Journal of Urology 2008;26(6):523-30" DOI :.07/s00345-008-0319-3 Analysis of complications from 600 retroperitoneoscopic procedures of the upper urinary tract during
Author manuscript, published in "World Journal of Urology 2008;26(6):523-30" DOI :.07/s00345-008-0319-3 Analysis of complications from 600 retroperitoneoscopic procedures of the upper urinary tract during
What is Laparoscopy All About?
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage surgical health. All decisions about the management of Laparoscopy must be made in conjunction with your Physician
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage surgical health. All decisions about the management of Laparoscopy must be made in conjunction with your Physician
Complications in robotic surgery!! Review of the literature! RALP, RAPN and RARC!
 Complications in robotic surgery Review of the literature RALP, RAPN and RARC Anna Wallerstedt, MD Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Agenda The importance of reporting surgical complications
Complications in robotic surgery Review of the literature RALP, RAPN and RARC Anna Wallerstedt, MD Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Agenda The importance of reporting surgical complications
Laparoscopic Surgery in Urological Oncology: Brief Overview
 Review Article Laparoscopic Surgery in Urological Oncology International Braz J Urol Vol. 32 (5): 504-512, September - October, 2006 Laparoscopic Surgery in Urological Oncology: Brief Overview Jose R.
Review Article Laparoscopic Surgery in Urological Oncology International Braz J Urol Vol. 32 (5): 504-512, September - October, 2006 Laparoscopic Surgery in Urological Oncology: Brief Overview Jose R.
Rapid communication chronic renal insufficiency after laparoscopic partial nephrectomy and radical nephrectomy for pathologic T1a lesions
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2008 Rapid communication chronic renal insufficiency after laparoscopic partial nephrectomy and radical nephrectomy
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2008 Rapid communication chronic renal insufficiency after laparoscopic partial nephrectomy and radical nephrectomy
Delayed Ureterectomy after Incomplete Nephroureterectomy for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: Pathologic Findings and Outcomes
 ORIGINAL Article Vol. 39 (6): 817-822, November - December, 2013 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2013.06.07 Delayed Ureterectomy after Incomplete Nephroureterectomy for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: Pathologic
ORIGINAL Article Vol. 39 (6): 817-822, November - December, 2013 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2013.06.07 Delayed Ureterectomy after Incomplete Nephroureterectomy for Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: Pathologic
Who are Candidates for Laparoscopic or Open Radical Nephrectomy. Arieh Shalhav
 Who are Candidates for Laparoscopic or Open Radical Nephrectomy Arieh Shalhav Fritz Duda Chair of Urologic Surgery Professor of Surgery and the Comprehensive Cancer Research Center Who are Candidates for
Who are Candidates for Laparoscopic or Open Radical Nephrectomy Arieh Shalhav Fritz Duda Chair of Urologic Surgery Professor of Surgery and the Comprehensive Cancer Research Center Who are Candidates for
Laparoscopic nephrectomy for atrophic kidney due to serious infection: A review of 15 cases
 International Journal of Urology and Nephrology Vol. 2 (2), pp. 048-051, August, 2014. Available online at www.internationalscholarsjournals.org International Scholars Journals Full Length Research Paper
International Journal of Urology and Nephrology Vol. 2 (2), pp. 048-051, August, 2014. Available online at www.internationalscholarsjournals.org International Scholars Journals Full Length Research Paper
Shape the Future of Urological Surgery
 Shape the Future of Urological Surgery THE ROLE OF LAPAROSCOPIC SURGERY IN NEW MILENNIUM Victor Chia-Hsiang Lin, MD Division of Urology, Department of Surgery Chi-Mei Medical Center MY TALK TODAY IS Minimal
Shape the Future of Urological Surgery THE ROLE OF LAPAROSCOPIC SURGERY IN NEW MILENNIUM Victor Chia-Hsiang Lin, MD Division of Urology, Department of Surgery Chi-Mei Medical Center MY TALK TODAY IS Minimal
RAPN. in T1b Renal Masses? A. Mottrie. G. Denaeyer, P. Schatteman, G. Novara
 RAPN in T1b Renal Masses? A. Mottrie G. Denaeyer, P. Schatteman, G. Novara Department of Urology O.L.V. Clinic Aalst OLV Vattikuti Robotic Surgery Institute Aalst Belgium Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma
RAPN in T1b Renal Masses? A. Mottrie G. Denaeyer, P. Schatteman, G. Novara Department of Urology O.L.V. Clinic Aalst OLV Vattikuti Robotic Surgery Institute Aalst Belgium Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma
Laparoscopic Management of Kidney Cancer: Updated Review
 Laparoscopy provides equivalent oncologic outcomes, comparable complication rates, and improved perioperative morbidity compared to standard open surgical techniques for managing kidney cancers. Monique
Laparoscopy provides equivalent oncologic outcomes, comparable complication rates, and improved perioperative morbidity compared to standard open surgical techniques for managing kidney cancers. Monique
Early Experience of Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Nephroureterectomy for Upper Urinary Tract Tumors
 www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2010.51.7.472 Robotics/Laparoscopy Early Experience of Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Nephroureterectomy for Upper Urinary Tract Tumors Ill Young Seo, Hye Min Hong, Il Sang
www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2010.51.7.472 Robotics/Laparoscopy Early Experience of Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Nephroureterectomy for Upper Urinary Tract Tumors Ill Young Seo, Hye Min Hong, Il Sang
The role of hemostatic agents in preventing complications in laparoscopic partial nephrectomy
 362 Central European Journal of Urology O R I G I N A L P A P E R UROLOGICAL ONCOLOGY The role of hemostatic agents in preventing complications in laparoscopic partial nephrectomy Diego M. Carrion 1, Sergio
362 Central European Journal of Urology O R I G I N A L P A P E R UROLOGICAL ONCOLOGY The role of hemostatic agents in preventing complications in laparoscopic partial nephrectomy Diego M. Carrion 1, Sergio
Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Nephrectomy Using Standard Laparoscopic Instruments
 Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Nephrectomy Using Standard Laparoscopic Instruments Our Initial Experience LAPAROSCOPIC UROLOGY Alireza Aminsharifi, Bahman Goshtasbi, Firoozeh Afsar Department of Urology,
Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Nephrectomy Using Standard Laparoscopic Instruments Our Initial Experience LAPAROSCOPIC UROLOGY Alireza Aminsharifi, Bahman Goshtasbi, Firoozeh Afsar Department of Urology,
Urology An introduction to cut up DR J R GOEPEL
 Urology An introduction to cut up DR J R GOEPEL Overview Principles Individual organs Small pieces Partial resections Whole organs Data recording and data sets Principles You are working for the patient
Urology An introduction to cut up DR J R GOEPEL Overview Principles Individual organs Small pieces Partial resections Whole organs Data recording and data sets Principles You are working for the patient
Laparoscopic and Open Partial Nephrectomy: Complication Comparison Using the Clavien System
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER Laparoscopic and Open Partial Nephrectomy: Complication Comparison Using the Clavien System Jennifer E. Reifsnyder, MD, Ranjith Ramasamy, MD, Casey K. Ng, MD, James DiPietro, BS, Benjamin
SCIENTIFIC PAPER Laparoscopic and Open Partial Nephrectomy: Complication Comparison Using the Clavien System Jennifer E. Reifsnyder, MD, Ranjith Ramasamy, MD, Casey K. Ng, MD, James DiPietro, BS, Benjamin
Retroperitoneal Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy for Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Report on 2 Initial Cases
 Yonago Acta medica 2002;45:35 41 Retroperitoneal Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy for Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Report on 2 Initial Cases Tadahiro Isoyama, Takehiro Sejima, Hiroyuki Kadowaki, Shinji Hirakawa
Yonago Acta medica 2002;45:35 41 Retroperitoneal Laparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy for Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Report on 2 Initial Cases Tadahiro Isoyama, Takehiro Sejima, Hiroyuki Kadowaki, Shinji Hirakawa
Experimental Model of Upper-Pole Nephrectomy Using Human Tridimensional Endocasts: Analysis of Vascular Injuries
 JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 25, Number 1, January 2011 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 113 118 DOI: 10.1089=end.2010.0214 Experimental Model of Upper-Pole Nephrectomy Using Human Tridimensional Endocasts:
JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 25, Number 1, January 2011 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 113 118 DOI: 10.1089=end.2010.0214 Experimental Model of Upper-Pole Nephrectomy Using Human Tridimensional Endocasts:
RADICAL CYSTECTOMY. Solutions for minimally invasive urologic surgery
 RADICAL CYSTECTOMY Solutions for minimally invasive urologic surgery The da Vinci Surgical System High-definition 3D vision EndoWrist instrumentation 3D HD Vision 3D HD visualization facilitates accurate
RADICAL CYSTECTOMY Solutions for minimally invasive urologic surgery The da Vinci Surgical System High-definition 3D vision EndoWrist instrumentation 3D HD Vision 3D HD visualization facilitates accurate
Management of Diaphragmatic Injury during Transperitoneal Laparoscopic Urological Procedures
 Clinical Urology Management of Diaphragmatic Injury during Laparoscopy International Braz J Urol Vol. 33 (3): 323-329, May - June, 27 Management of Diaphragmatic Injury during Transperitoneal Laparoscopic
Clinical Urology Management of Diaphragmatic Injury during Laparoscopy International Braz J Urol Vol. 33 (3): 323-329, May - June, 27 Management of Diaphragmatic Injury during Transperitoneal Laparoscopic
Laparoendoscopic Pfannenstiel Nephrectomy using Conventional Laparoscopic Instruments - Preliminary Experience
 Surgical Technique Laparoendoscopic Pfannenstiel Nephrectomy International Braz J Urol Vol. 36 (6): 718-723, November - December, 2010 doi: 10.1590/S1677-55382010000600010 Laparoendoscopic Pfannenstiel
Surgical Technique Laparoendoscopic Pfannenstiel Nephrectomy International Braz J Urol Vol. 36 (6): 718-723, November - December, 2010 doi: 10.1590/S1677-55382010000600010 Laparoendoscopic Pfannenstiel
LAPAROSCOPIC PYELOPLASTY INFORMATION LEAFLET
 LAPAROSCOPIC PYELOPLASTY INFORMATION LEAFLET Laparoscopic Pyeloplasty Page 1 of 8 LAPAROSCOPIC PYELOPLASTY This leaflet has been written to answers questions that you may have about your operation. If
LAPAROSCOPIC PYELOPLASTY INFORMATION LEAFLET Laparoscopic Pyeloplasty Page 1 of 8 LAPAROSCOPIC PYELOPLASTY This leaflet has been written to answers questions that you may have about your operation. If
Patient Selection for Surgery in RCC with Thrombus. E. Jason Abel, M.D.
 Patient Selection for Surgery in RCC with Thrombus E. Jason Abel, M.D. RCC with venous invasion Venous invasion occurs in ~10% of RCC Surgery more complex Increased risk for morbidity Thrombus may be confined
Patient Selection for Surgery in RCC with Thrombus E. Jason Abel, M.D. RCC with venous invasion Venous invasion occurs in ~10% of RCC Surgery more complex Increased risk for morbidity Thrombus may be confined
Retroperitoneoscopic Ablative Renal Surgery in Children: The Feasibility of Using Three Trocars
 Tayfun Oktar, Oner Sanli, Ömer Acar, Tzevat Tefik, Serkan Karakus, Orhan Ziylan LAPAROSCOPIC UROLOGY Retroperitoneoscopic Ablative Renal Surgery in Children: The Feasibility of Using Three Trocars Department
Tayfun Oktar, Oner Sanli, Ömer Acar, Tzevat Tefik, Serkan Karakus, Orhan Ziylan LAPAROSCOPIC UROLOGY Retroperitoneoscopic Ablative Renal Surgery in Children: The Feasibility of Using Three Trocars Department
AN INFORMATION LEAFLET
 LAPAROSCOPIC NEPHRECTOMY AN INFORMATION LEAFLET Written by: Department of Urology May 2011 Stockport: 0161 419 5698 Website: www.stockport.nhs.uk Tameside: 0161 922 6696/6698 Website: www.tameside.nhs.uk
LAPAROSCOPIC NEPHRECTOMY AN INFORMATION LEAFLET Written by: Department of Urology May 2011 Stockport: 0161 419 5698 Website: www.stockport.nhs.uk Tameside: 0161 922 6696/6698 Website: www.tameside.nhs.uk
in Laparoscopy The European Congress of Laparoscopy 2007 Bordeaux, France Palais des Congres
 Challenges 2007 in Laparoscopy The European Congress of Laparoscopy 2007 Some of the most prominent Laparoscopic Urological Surgeons will perform innovative live surgery demonstrating the full spectrum
Challenges 2007 in Laparoscopy The European Congress of Laparoscopy 2007 Some of the most prominent Laparoscopic Urological Surgeons will perform innovative live surgery demonstrating the full spectrum
Atlas of Urologic Surgery
 Atlas of Urologic Surgery Hinman, F ISBN-13: 9781416042105 Table of Contents Section I: Surgical Basics Chapter 1 Surgical Basics Section II: The Urologist at Work Chapter 2 Basic Surgical Techniques Chapter
Atlas of Urologic Surgery Hinman, F ISBN-13: 9781416042105 Table of Contents Section I: Surgical Basics Chapter 1 Surgical Basics Section II: The Urologist at Work Chapter 2 Basic Surgical Techniques Chapter
GUIDELINES ON RENAL CELL CANCER
 20 G. Mickisch (chairman), J. Carballido, S. Hellsten, H. Schulze, H. Mensink Eur Urol 2001;40(3):252-255 Introduction is characterised by a constant rise in incidence over the last 50 years, with a predominance
20 G. Mickisch (chairman), J. Carballido, S. Hellsten, H. Schulze, H. Mensink Eur Urol 2001;40(3):252-255 Introduction is characterised by a constant rise in incidence over the last 50 years, with a predominance
2 Adrenal Disease. Open Surgery. Andrew C. Novick SURGICAL ANATOMY
 Preface More than 125 years have passed since the basic contributions of John Hunter, Crawford Long, and Lord Lister transformed surgery into a sound science as well as a delicate art. Several great surgeons
Preface More than 125 years have passed since the basic contributions of John Hunter, Crawford Long, and Lord Lister transformed surgery into a sound science as well as a delicate art. Several great surgeons
LAPAROSCOPIC NEPHRECTOMY USING A RETROPERITONEAL APPROACH : COMPARISON WITH A TRANSABDOMINAL APPROACH
 LAPAROSCOPIC NEPHRECTOMY USING A RETROPERITONEAL APPROACH : COMPARISON WITH A TRANSABDOMINAL APPROACH Yoshinari One,'" Shinichi Ohshirna, Satoshi Hirabayashi,3 Yukio Hatano,4 Toshibumi Sakakibara,S Hiroaki
LAPAROSCOPIC NEPHRECTOMY USING A RETROPERITONEAL APPROACH : COMPARISON WITH A TRANSABDOMINAL APPROACH Yoshinari One,'" Shinichi Ohshirna, Satoshi Hirabayashi,3 Yukio Hatano,4 Toshibumi Sakakibara,S Hiroaki
UROLOGICAL LAPAROSCOPY MAIN SURGICAL ONCOLOGY PROCEDURES PERFORMED USING LAPAROSCOPY
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 8 (57) No. 2-2015 UROLOGICAL LAPAROSCOPY MAIN SURGICAL ONCOLOGY PROCEDURES PERFORMED USING LAPAROSCOPY I. SCARNECIU 1,2
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 8 (57) No. 2-2015 UROLOGICAL LAPAROSCOPY MAIN SURGICAL ONCOLOGY PROCEDURES PERFORMED USING LAPAROSCOPY I. SCARNECIU 1,2
Laparoscopic Ureterolithotomy: A Comparison Between the Transperitoneal and the Retroperitoneal Approach During the Learning Curve
 JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 23, Number 6, June 2009 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 953 957 DOI: 10.1089=end.2008.0055 Laparoscopic Ureterolithotomy: A Comparison Between the Transperitoneal and the Retroperitoneal
JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 23, Number 6, June 2009 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 953 957 DOI: 10.1089=end.2008.0055 Laparoscopic Ureterolithotomy: A Comparison Between the Transperitoneal and the Retroperitoneal
TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 4 November 2009
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 4 November 2009 EVICEL, solution for sealant Box containing 2 x 1 ml bottles (CIP: 575 463-7) Box containing 2 x 2
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 4 November 2009 EVICEL, solution for sealant Box containing 2 x 1 ml bottles (CIP: 575 463-7) Box containing 2 x 2
Case Report The Role of Laparoscopic Nephrectomy in Pediatric Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 598950, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/598950 Case Report The Role of Laparoscopic Nephrectomy in Pediatric Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis: A
Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 598950, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/598950 Case Report The Role of Laparoscopic Nephrectomy in Pediatric Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis: A
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Eur Urol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2009 March 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Eur Urol. 2008 March ; 53(3): 514 521. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2007.09.047. ROBOTIC PARTIAL NEPHRECTOMY FOR COMPLEX RENAL TUMORS: SURGICAL
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Eur Urol. 2008 March ; 53(3): 514 521. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2007.09.047. ROBOTIC PARTIAL NEPHRECTOMY FOR COMPLEX RENAL TUMORS: SURGICAL
What is the role of partial nephrectomy in the context of active surveillance and renal ablation?
 What is the role of partial nephrectomy in the context of active surveillance and renal ablation? Dogu Teber Department of Urology University Hospital Heidelberg Coming from Heidelberg obligates to speak
What is the role of partial nephrectomy in the context of active surveillance and renal ablation? Dogu Teber Department of Urology University Hospital Heidelberg Coming from Heidelberg obligates to speak
Critical Analysis of Laparoscopic Donor Nephrectomy in the Setting of Complex Renal Vasculature: Initial Experience and Intermediate Outcomes
 JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 23, Number 3, March 2009 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 451 455 DOI: 10.1089=end.2008.0242 Critical Analysis of Laparoscopic Donor Nephrectomy in the Setting of Complex Renal
JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 23, Number 3, March 2009 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 451 455 DOI: 10.1089=end.2008.0242 Critical Analysis of Laparoscopic Donor Nephrectomy in the Setting of Complex Renal
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
THE LATEST STEP FORWARD IN SURGERY. LESS Laparo-Endoscopic Single-Site Surgery
 THE LATEST STEP FORWARD IN SURGERY LESS Laparo-Endoscopic Single-Site Surgery THE ROUTE FROM OPEN SURGERY TO MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY An operation is generally a radical experience for any patient. In
THE LATEST STEP FORWARD IN SURGERY LESS Laparo-Endoscopic Single-Site Surgery THE ROUTE FROM OPEN SURGERY TO MINIMALLY INVASIVE SURGERY An operation is generally a radical experience for any patient. In
Patient Selection for Ablative Therapies. Adrian D Joyce Leeds UK
 Patient Selection for Ablative Adrian D Joyce Leeds UK Therapy Renal Cell Ca USA: 30,000 new cases annually >12,000 deaths RCC accounts for 3% of all adult malignancy 40% of patients will die from their
Patient Selection for Ablative Adrian D Joyce Leeds UK Therapy Renal Cell Ca USA: 30,000 new cases annually >12,000 deaths RCC accounts for 3% of all adult malignancy 40% of patients will die from their
Laparoscopic Radical Removal of the Kidney +/- Ureter
 Who can I contact if I have a problem when I get home? If you experience any problems related to your surgery or admission once you have been discharged home. Please feel free to contact 4A, 4B or 4C ward
Who can I contact if I have a problem when I get home? If you experience any problems related to your surgery or admission once you have been discharged home. Please feel free to contact 4A, 4B or 4C ward
Partial Removal of the Kidney
 Who can I contact if I have a problem when I get home? If you experience any problems related to your surgery or admission once you have been discharged home. Please feel free to contact Ward 4A, 4B or
Who can I contact if I have a problem when I get home? If you experience any problems related to your surgery or admission once you have been discharged home. Please feel free to contact Ward 4A, 4B or
Kidney Donors. Information for
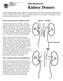 Information for Kidney Donors You have offered to donate a kidney. That is a very generous gift to give. It is not an easy decision to make and it is not an easy thing to do, but it is one of the greatest
Information for Kidney Donors You have offered to donate a kidney. That is a very generous gift to give. It is not an easy decision to make and it is not an easy thing to do, but it is one of the greatest
RESIDENCY TRAINING PROGRAMME IN UROLOGY CERTIFICATION APPLICATION FORM PARTICIPATING INSTITUTE(S)
 Date application Name primary institute RESIDENCY TRAINING PROGRAMME IN UROLOGY CERTIFICATION APPLICATION FORM Name affiliated institute(s) Name Programme Director PARTICIPATING INSTITUTE(S) This form
Date application Name primary institute RESIDENCY TRAINING PROGRAMME IN UROLOGY CERTIFICATION APPLICATION FORM Name affiliated institute(s) Name Programme Director PARTICIPATING INSTITUTE(S) This form
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 57 (2010)
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 57 (2010) 963 969 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Platinum Priority Urothelial Cancer Editorial by Alexandre R. Zlotta on pp. 970 972 of this
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 57 (2010) 963 969 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Platinum Priority Urothelial Cancer Editorial by Alexandre R. Zlotta on pp. 970 972 of this
Guidelines for Laparoscopic Resection of Curable Colon and Rectal Cancer
 SAGES Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons http://www.sages.org Guidelines for Laparoscopic Resection of Curable Colon and Rectal Cancer Author : SAGES Webmaster PREAMBLE The following
SAGES Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons http://www.sages.org Guidelines for Laparoscopic Resection of Curable Colon and Rectal Cancer Author : SAGES Webmaster PREAMBLE The following
ENDOSCOPIC URETERECTOMY DURING NEPHROURETERECTOMY FOR UPPER URINARY TRACT TRANSITIONAL CELL CARCINOMA
 ENDOSCOPIC URETERECTOMY DURING NEPHROURETERECTOMY FOR UPPER URINARY TRACT TRANSITIONAL CELL CARCINOMA Il. Saltirov, Ts. Petkov, G. Georgiev, K.Petkova Department of Urology and Nephrology, Military Medical
ENDOSCOPIC URETERECTOMY DURING NEPHROURETERECTOMY FOR UPPER URINARY TRACT TRANSITIONAL CELL CARCINOMA Il. Saltirov, Ts. Petkov, G. Georgiev, K.Petkova Department of Urology and Nephrology, Military Medical
OUTCOME OF LAPAROSCOPIC DONOR NEPHRECTOMY: OUR INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE
 OUTCOME OF LAPAROSCOPIC DONOR NEPHRECTOMY: OUR INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE Rajaraman Thiagarajan 1, Balaji A. R 2, Ayesha Shaheen 3, Chandramurali Raveendran 4, Subhakanesh S 5, Ashok Kumar R 6, Jessima S
OUTCOME OF LAPAROSCOPIC DONOR NEPHRECTOMY: OUR INSTITUTIONAL EXPERIENCE Rajaraman Thiagarajan 1, Balaji A. R 2, Ayesha Shaheen 3, Chandramurali Raveendran 4, Subhakanesh S 5, Ashok Kumar R 6, Jessima S
Uro-Assiut 2015 Robotic Nephron Sparing Surgery
 Uro-Assiut 2015 Robotic Nephron Sparing Surgery Khaled Fareed, MD, MBA Center for Advanced Laparoscopy, Robotics & Minimally Invasive Surgery Glickman Urological & Kidney Institute Associate Professor,
Uro-Assiut 2015 Robotic Nephron Sparing Surgery Khaled Fareed, MD, MBA Center for Advanced Laparoscopy, Robotics & Minimally Invasive Surgery Glickman Urological & Kidney Institute Associate Professor,
Laparoscopic Partial Nephrectomy with Clamping of the Renal Parenchyma: Initial Experience
 european urology 52 (2007) 1340 1346 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Surgery in Motion Laparoscopic Partial Nephrectomy with Clamping of the Renal Parenchyma:
european urology 52 (2007) 1340 1346 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Surgery in Motion Laparoscopic Partial Nephrectomy with Clamping of the Renal Parenchyma:
Urological procedures in Central Europe and the current reality based on the national registries of Czech Republic, Hungary, and Poland (2012 status)
 327 O R I G I N A L P A P E R UROLOGICAL ONCOLOGY Urological procedures in Central Europe and the current reality based on the national registries of,, and (2012 status) Przemysław Adamczyk 1, Kajetan
327 O R I G I N A L P A P E R UROLOGICAL ONCOLOGY Urological procedures in Central Europe and the current reality based on the national registries of,, and (2012 status) Przemysław Adamczyk 1, Kajetan
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Endourology
 Urology Journal UNRC/IUA Vol. 1, No. 3, 165-169 Summer 2004 Printed in IRAN ORIGINAL ARTICLES Endourology A Comparison between Laparoscopic and Open Pyeloplasty in Patients with Ureteropelvic Junction
Urology Journal UNRC/IUA Vol. 1, No. 3, 165-169 Summer 2004 Printed in IRAN ORIGINAL ARTICLES Endourology A Comparison between Laparoscopic and Open Pyeloplasty in Patients with Ureteropelvic Junction
NEPHRECTOMY AUDIT. OCTOBER 1998-SEPTEMBER 2005 Dr. Sanjeev Bandi MBBS., FRCSI., FRACS(Urology) Mater Misericordiae Hospital, Mackay, Qld 4740
 NEPHRECTOMY AUDIT OCTOBER 1998-SEPTEMBER 2005 Dr. Sanjeev Bandi MBBS., FRCSI., FRACS(Urology) Mater Misericordiae Hospital, Mackay, Qld 4740 This audit has been performed in conjunction with the data requirements
NEPHRECTOMY AUDIT OCTOBER 1998-SEPTEMBER 2005 Dr. Sanjeev Bandi MBBS., FRCSI., FRACS(Urology) Mater Misericordiae Hospital, Mackay, Qld 4740 This audit has been performed in conjunction with the data requirements
