SCROTAL AND TESTICULAR DISEASES. 7 Hydrocele 7 Epididymal cyst 9 Varicocele 9 Cryptorchidism 11 Testicular tumors 13
|
|
|
- Noah Doyle
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Table of Contents Subject Page Scrotal pain Testicular torsion Torsion of the appendages Epididymitis Fournier gangrene 7 Hydrocele 7 Epididymal cyst 9 Varicocele 9 Cryptorchidism 11 Testicular tumors P a g e 1
2 Scrotal Pain Scrotal pain is a condition with a lot of differential diagnoses; Torsion of the testes Torsion of appendages Acute epididymitis. Bleeding or infection in a testicular tumor "tumors per se are usually painless" Fournier gangrene. Trauma Strangulated hernia. Put in your mind that scrotal pain could be a referred pain from the abdomen, for example, a case of appendicitis with long appendix that extends into the pelvis, so you should always examine the abdomen in a patient with scrotal pain. A. Testicular Torsion Coverings of the testis from inside to outside; tunica vaginalis (visceral and parietal), internal spermatic fascia, cremaster muscle (middle spermatic fascia), external spermatic fascia, Dartos muscle, skin. Testicular torsion occurs due to twisting of the spermatic cord and blood supply to the testicles, which causes a sudden severe pain and the scrotum will suddenly increase in size. It is a urological emergency; early diagnosis and treatment are vital to saving the testicles and preserving future fertility. 2/3 of cases are adolescents (peak age at 14), another commonly affected age group is neonates. 1:160 is the lifetime incidence. P a g e 2
3 It has three types; Intravaginal torsion; torsion of the spermatic cord inside the tunica vaginalis, the tunica vaginalis itself is not twisted. It is the commonest overall. Normally, with mature attachments, the tunica vaginalis is attached securely to the posterior lateral aspect of the testicle, and, within it, the spermatic cord is not very mobile. If the attachment of the tunica vaginalis to the testicle is inappropriately high, the spermatic cord can rotate within it, which can lead to intravaginal torsion. This defect is referred to as the bell clapper deformity. Intravaginal torsion most commonly occurs in adolescents. It is thought that the increased weight of the testicle after puberty, as well as sudden contraction of the cremasteric muscles, is the impetus for acute torsion. Extravaginal torsion; the spermatic cord and tunica vaginalis undergo torsion as a unit. Neonates more often have extravaginal torsion. This occurs because the tunica vaginalis is not yet secured to the gubernaculum and, therefore, the spermatic cord, as well as the tunica vaginalis, undergo torsion as a unit. Extravaginal torsion is not associated with bell clapper deformity. This can occur up to months prior to birth and, therefore, is managed differently depending on presentation. In this type of torsion, most of the time there's complete infarction at the time of exploration, This happens because the baby will not tell you he's having severe pain in his testicle, but what happens is that the mother brings him complaining of loud continuous crying. P a g e 3
4 The third type of the torsion is called Isolated Torsion. This happens when the mesoepididymis that connects the testicle to the epididymis is long which causes the testicle to go around itself. This type of course is rare because the prevalence of long mesoepididymis is very low. History - Left : right = 2:1 - Sudden onset of severe pain followed by inguinal and/or scrotal swelling, some cases may suffer of a gradual onset of pain, and a small number of cases will have abdominal pain only. - Could be associated with nausea, anorexia, vomiting and low grade feve, especially in pediatric age group. - Torsion can occur with trauma in about 20% of cases, masturbation is one form of trauma. Physical examination - Tender and swollen testis. - Elevated testis; as the cord is twisted, it becomes shorter. - Horizontal lie. - Redness of the overlying skin. - Loss of cremasteric reflex. Cremaster reflex; scratching the upper medial side of the thigh will stimulate the femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve and ilioinguinal nerve. These synapse in the spinal cord and activates the motor fibers of the genitofemaoral nerve leading to contraction of the cremaster muscle that pulls the epsilateral testis. Management After developing the diagnosis we should send him the Operation Room directly. We don't use ultrasound to detect testicular torsion; - May cause delay, so the possibility to save the testis will be less - More inaccurate in smaller child. - Can give false negative results. - Report will never rule out torsion. If you explore the testis within the first within the first 6 hours, the survival rate will be 85-97%, but after 24 hours, the survival rate will be less than 10%. Note; the time to save the testis varies according to the degree of twisting (in general it is 6 hours), the more the twisting the less time to save the testis. do a small excision, put the testicle in its place and fix the torsion, fixate the testicle very well so we prevent other torsions, and finally we should fixate the other testicle because we will be afraid of torsion in the future to the other testicle too P a g e 4
5 When the testicle gets affected by the torsion, the venous drainage will be the first vascular component to be affected. Following it by few minutes will be the arterial supply, and finally in few hours a complete infarction will occur, and the testicle may become gangrenous if not treated. That's why surgical intervention in cases of testicular torsion should be very fast to prevent any complication. As you know from your previous surgical knowledge, any cut in blood supply to an organ will take only 6 hours before a complete infarction happens and death of the organ starts. For this reason, we shouldn't allow any case of torsion to be left without urgent intervention to correct it. We should remember that the pain is because of venous and then arterial obstruction. This will cause sudden severe pain after movement. That's why you will always face cases where a child was playing with his friends and suddenly he stops playing and feels severe pain in his scrotum. On examining the testicle, you will notice that it is high and tender, with horizontal lie. B. Torsion of appendages The appendages are embryological remnants that are associated with the testicle, epididymis, and vas deferens. The appendages are The superior and inferior aberrans of haller "originate from the body and tail of epididymis". Appendix of the epididymis "from the head of epididymis". Appendix testis "hydatid of morgagni". If one of these appendages become twisted, this will cut off the blood supply and cause ischemia, prolonged torsion will result in the death of the appendix. The peak incidence is below 2-3 years which is below the ages of testicular torsion, and it's important to know that these appendages has no function because they are remnants. 95% of the cases occur in the Hydatid of Morgagni: the appendix of the testis, remnant of mullerian duct, present in the upper pole of the testis and attached to the processus vaginalis. When doing a physical examination we can see (blue dot sign) with the swelling which is palpable dots with blue or black in color. -pain is confined to the upper pole (origin of the appendages) and with time it become indistinguishable from testicular torsion because of scrotal enlargement and the inflammation that spread over the testis P a g e 5
6 C. Torsions Vs epididymitis : - It is frequently difficult to distinguish these two conditions; Because of the edema and pain associated with both acute epididymitis and testicular torsion. Epididymitis usually: - Pain is Gradual because it s inflammation (infection). - Sharp pain (not dull aching). - Epididymitis is might be preceded by UTI (in a lot of cases) or urethral discharge. - Can be associated with fever and turbid urine. Torsion is a vascular pain so: - It s a dull aching (can t be described well). - It s not relived by changing the position. - Spontaneous, can be preceeded by trauma, or physical activity. - Any testicular pain below 20 y age is torsion until proven otherwise. - The patient usually presents with the sudden onset of pain and swelling of the involved testis. The pain may radiate into the groin and lower abdomen. Most appropriate cause Torsion Adolescent who is not sexually active Epididymitis STD (sexual transmitted disease) Onset Sudden Gradual Duration Short Few days Severity More severe Less severe Pattern Constant Intermittent Increasing or decreasing factors Any movement may aggravate the pain Cremaster reflex Loss of cremaster reflex Present Prehn's sign* negative Positive *Prehn's sign: is a medical diagnostic scale which determine if the injured testicles is because of epididymitis or testicular torsion. According to it the physical lifting of the testicles relieves the pain of epididymitis not the pain of testicular torsion. P a g e 6
7 D. Fournier Gangrene A type of necrotizing infection or gangrene that affects the perineum. It is a mixed infection that involves both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Most of the patients are in their 60s or 70s and about half of them are diabetic. The hallmark of the disease is intense pain and tenderness in the genitalia, usually associated with edema of the overlying skin, pruritis may also be present. It progresses till it becomes an obvious gangrene of a portion of genitalia and purulent drainage from wounds. Hydrocele Hydroceles are collection of fluids inside the scrotum that happens for many reasons, and can be classified into: Hydrocele due to patent processus vaginalis, which includes; Primary Vaginal hydrocele, infantile hydrocele, congenital hydrocele, encysted hydrocele of the cord. Processus vaginalis is a pouch of peritoneum that is carried into the scrotum by the descent of the testicle and which in the scrotum forms the tunica vaginalis. In children, patency of the processus vaginalis is the main and commonest cause. In this case the processus, which normally closes and becomes the tunica vaginalis, will fail to close after delivery and it will stay patent, causing fluids from the peritoneum to pass to the scrotum and fill it. P a g e 7
8 Secondary hydrocele to other nearby lesions like inflammations, tumors, traumas and torsion. In adults, the problem lies in the lymphatic drainage of the testicles, where there will be obstruction in the drainage that causes fluids to stay in the scrotum causing the enlargement. Communicating and non-communicating types We can differentiate between the 2 types clinically by asking the patient to lie on his back, and if the hydrocele decreases then it's communicating because the fluids in this case would go to the peritoneal cavity, while in case of non-communicating hydrocele the fluids will stay in the scrotum. Symptoms We should know that the hydrocele is painless and rarely complicated, but we are usually asked to remove it for cosmetic reasons, and because of its heaviness that will make the patient feel uncomfortable. Hydrocele is managed by surgical excision for it to remove the fluids and fix the problem. We do not aspirate the fluids because it will come back, and sometime aspiration will cause infection in the testicle (orchitis) which will end with infertility. P a g e 8
9 in the figure to the left, you can see what happen when using light to transilluminate the hydrocele. in the figure to the right, you can see a case of hydrocele caused by acute epididymitis that blocked the lymphatic drainage of the testicles and caused the accumulation of the fluids. Epididymal Cysts: It occurs at the head of the epididymis, and it usually contains clear fluid. However, if it contains turbid fluid and sperms, then we call it spermatocele. It transilluminate when exposed to light, contrary to the spermatocele which doesn't transilluminate. When we have a young patient with epididymal cyst, we don't advise him to remove it because in surgical excision we might face fibrosis and thus obstruction of the duct, causing infertility. So we delay the operation till the end of fertility period, because this condition is painless and rarely develops any complications. When should we take an action? If the cyst is large and interferes with the patient's life. In this case, we do complete excision not aspiration, because aspirating it puts the patient in risk of recurrence and developing infections. Varicocele: Varicocele is abnormal tortuosity and dilatation of the testicular veins within the spermatic cord due to incompetency of the valves of the venous drainage of the testicles. It is present in about 15-20% of normal fertile male population and 40% of infertile men. Although the majority of men with varicocele are fertile, it is considered as the most common correctable cause of male infertility. This happens because of increased temperature in the scrotal sac due to increased pressure and amount of blood around the testes. The most common effect of it is Asthenospermia, which is decreased motility of the sperms. Decreased sperm density and presence of abnormal forms will follow, and later on the patient may have Azoospermia. P a g e 9
10 90% in the left side, only less than 2 percent is bilateral. It is more common in the left side because the left gonadal vein drains to the renal vein, while the right one drains directly to the inferior vena cava, and so the more perpendicular lie of the left vein makes it more susceptible to be varicose. Because of this, any case of right varicocele should be well investigated for any other causes like renal or retroperitoneal tumors. Symptoms; Dragging like or aching pain in the scrotum Feeling of heaviness in the testicles. Infertility. Atrophy (shrinking) of the testicles. visible or palpable veins described as (bag of worms) Investigations; Renal ultrasound (+/-) CT if suspecting obstructive causes. When to suspect obstructive causes if the varicocele is; Acute onset Doesn't disappear on supine position Palpable abdominal mass Solitary right varicocele. History of RPF. Clinical suspicion of renal tumor (hematuria) Varicoceles grading; 1st grade is when it's small and palpable only on Valsalva maneuver when we ask the patient to cough. 2nd grade is when it's palpable on standing position without coughing 3rd grade you will see it also in standing position. So you should always remember that varicoceles, just like hernias, should be examined in standing position. Treatment Scrotal support Varicocele embolization Varicelectomy P a g e 11
11 Cryptorchidism It is the absence of one or both testis from the scrotum. It is a common condition affecting about 3% of full-term babies, and about 30% of premature infants, with a family history seen in about 10% of cases. A 7% percent incidence rate seen in siblings of boys with undescended testis. Predisposing factors; Prematurity Low birth weight Small size for gestational age Maternal exposure to estrogen during the first trimester Twinning 70% of cases spontaneously descend after 3 months, spontaneous descend after the first year is uncommon. Physical examination It should be performed in a worm room. The patient should be relaxed in a frog-like position. Start the examination by observation, the milk down "palpating from the iliac crest to the scrotum". Examine the scrotum "hypoplastic, bifid, rugae, transposition and pigmentation" Check the penis for any other abnormality "chordee, hypospadiad, and length of stretched penis" Classification Testis in general are either palpable or non-palpable; 1. Palpable testis a. Normal, when the patient is supine (or standing), the testes should be both visible and palpable at the base of scrotum, no manipulation needed to put it there. The ipsilateral hemiscrotum equally well-developed in comparison to the contralateral side. b. Retractile, when the patient is supine (or standing), the testis is not in its normal position at the base of scrotum, but can be located in the inguinal area and normally moved to the base of scrotum where it remains for some minutes without traction. It descends in response to hormonal manipulation (hcg, GnRH) The ipsilateral hemiscrotum is equally developed in comparison to the contralateral side. P a g e 11
12 c. Ectopic testes, these ones have left the path of normal descent, they reside in the superficial inguinal pouch, the perineum, the femoral canal, penopubic area or transversely ectopic. The ipsilateral hemiscrotum is usually smaller than the contralateral side. d. Undescended, located somewhere along the normal path of descent, the ipsilateral hemiscrotum is small 2. Non-palpable a. Canalicular, detected by ultrasound b. Intra-abdominal c. Emergent testis, which lies in the inguinal canal and may sometimes project beyond the superficial inguinal ring but again slips back into the inguinal canal. d. Absent, agenesis "never formed embryologically" or atrophic "which is either unilateral - monorchia- or bilateral anorchia-". We use hormonal test to distinguish bilateral anorchia from bilateral undescended. Complications Using laparoscopy to detect nonpalpable testis carries 100% specificity. On the other hand, MRI and CT scan don't distinguish between the undescended testis and a lymph node, so that the specificity in this case doesn't exceed 80%. One of the most important complications of cryptorchidism is neoplasia. Intra-abdominal testis is more likely to undergo malignancy than inguinal (4times). Orchidopexy (surgery for the testes to put them in their appropriate place) doesn t decrease the risk of malignancy (we only do it for better surveillance of the testes) Hernia (patent processus vaginalis) in 90% of cases Infertility (the process of impaired spermatogensis start for day on in life and become irreversibleat 18 years old) Torsion Associated malformation; Non-urological Cerebral lesion, myelomeningocele, mental retardation (prader-willi syndrome) Urological: epididymal (36-43%) hypospadias up to 9% P a g e 12
13 Management 1. Surgical, common and better 2. Hormonal, no longer used. Note: Very important that the doctor said that we should put the testis in its places at the ages of one year to 1.5 year (possible MCQ). Purpose of treatment Cosmotic Fertility. It doesn't affect the risk of tumor development. Testicular Tumors: They compromise 2% of all male tumors. Its etiology in general is unknown, but we know that patients with cryptorchidism have much higher risk (up to 14 times), patients with intersex problems have higher risk too, and Africans have much lower risk [And of course being a male is the most important risk factor :P ]. Most of the testicular tumors (90-95%) arise from germinal elements, and the rest from non-germinal elements. Neonates will have Embryonal Cell Carcinoma or Yolk Sac Tumor. In young adults we will see teratoma and seminoma, with the former peaking at the age of 27 and the latter at 37. In old ages, after the age of 50 years, we will see lymphomas and seminomas. So knowing the age of the patient is very important to consider the diagnosis. Seminoma is the most common type, crypto-orchidism increases the risk of seminoma up to 50 times. Types of Testicular Tumors: We classify the testicular tumors according to the organ of origin into: Primary, Secondary, or Paratesticular tumors. Primary tumors can be either of a germinal origin (like seminoma, teratoma, combined, or yolk sac tumor), or of a non-germinal origin from other cells in the testes (like interstitial cells tumors or lymphoma). Secondary tumors can come from one of 2 origins: either of a Reticuloendothelial origin, or is a metastasis from another tumor, most commonly RCC. Paratesticular tumors are anything that doesn't involve the testicle in it, but may affect it in other ways. P a g e 13
14 2-3% of testicular tumors are bilateral, and in about 5% of the cases we will have testicular tumor in one side and CIS in the other testes. Mixed tumors of seminoma and teratoma will be seen in about 14% of the cases. Staging When classifying tumors into stages, we will be depending on Royal Marsden System where we have 4 grades of tumors: 1. First stage: There is no metastasis outside the testes to any other organ. stage 1M: As above but with persistently raised AFP & /or b-hcg after orchiectomy 2. Second stage: Metastasis is limited to infra-diaphragmatic and abdominal lymph nodes. IIA: Max. diameter < 2 cm IIB: 2-5 cm IIC: 5 cm 3. Third stage: Metastasis will go also to supra-diaphragmatic lymph nodes (like supraclavicular and thoracic LNs). 4. Fourth stage: Here the metastasis will go other organs other than LNs, like Liver. Tumor Markers Tumor markers are very important for us to help in the diagnosis: 1. Oncofetal substances: AFP & B-hCG AFP is produced by trophoblastic cells, has a half-life of 5-7 hours and has the following features: Increase in cancers of testis, liver, pancreas, lung, pregnancy, benign liver diseases, ataxia & tyrosinemia. Produced by pure embryonal CA, terato CA, Yolk sac tumor, or combined tumors. Indicate presence of a teratomatous element. Not produced by pure choriocarcinoma, or pure seminoma. B-hCG is a glycoprotein with half-life of hours, and has the following features also: Increase in malignancies of liver, pancreas, stomach, lung, breast, kidney, and bladder & marijuana smoker. Increase in all types with choriocarcinoma % of patients with embryonal ca. 5-10% of patients with pure seminoma. 2. Cellular enzymes: LDH, PLAP LDH marks the presence of bulky tissue, PLAP which indicates advanced diseases, and GGT which might be present in seminomas. P a g e 14
15 Clinical Manifestations: % of patients present with painless testicular mass. - Some may present with heavy sensation in the lower abdomen, anal area, or scrotum. - Pain can be due to Epdidymitis or bleeding in the tumor. - 10% of patients come with manifestations of metastasis. - Gynecomastia: as an effect of B-hCG, Androgens & Estrogens. Differential Diagnosis: Epididymo-orchitis Torsion Hydrocele Syphilitic gumma TB Granulomatous orchitis - Spread from the tumor can be either direct, vascular, or through lymphatic drainage. Investigations -CBC, U&E, LFT. -Tumor Markers. -Imaging: - CXR: to exclude metastasis - Ultrasound for the scrotum - CT-scan: Thorax & Abdomen to look for LNs. -Surgical exploration: Trans-inguinal not trans-scortal to prevent spreading tumor cells to the scrotum -No FNA or Tru-cut Biopsy should be done, although some physicians say that performing FNA is not dangerous. Treatment: It's agreed that the basic treatment in cases of testicular tumors is Radical Orchiectomy. After performing the surgery, our next step should be clinically grading the tumor by doing histopathological studies and imaging investigations. It was found that with seminomas, it's usually confined to the testes without any metastasis to other tissues. In non-seminoma germinal cell tumors (NSGCTs), however, recognizable distant metastasis is usually seen in about 60-70% of cases. P a g e 15
16 When classifying the tumors into seminomas and NSGCTs, it was found that seminomas will have much better prognosis. This is due to the fact that they are highly radiosensitive, in addition to the previously mentioned fact of low rate of metastasis. When seminomas metastasize, they mostly go to the liver and lung. In such cases of seminomas, we have to perform inguinal orchiectomy as soon as possible, and then depending on the stage we will continue the treatment. Inguinal approach to the tumor is needed because if we go through the scrotum, we are putting the patient in risk of spreading the tumor cells all over the scrotum. In case staging gave us good prognosis of stage 1 or early stage 2, then abdominal radiotherapy will be the next step. However, if we found out that the grade of the tumor was late grade 2, grade 3, or grade 4, then we should start chemotherapy, with BEP (Bleomycine, Etoposide, and Cis-Platinum) being the drug combination of choice. What should be our aim in treatment? Our main aim of course should be total cure of the patient. We should make sure that we finish the treatment of the patient only when total recovery. Another aim for us should be maintenance of fertility in the patient, especially if he was young. And the third aim is to prevent any future complication in the patient. In cases of NSGCTs, the treatment should be extensive after performing the orchiectomy. Chemotherapy of BEP for 4-6 courses is needed directly after the surgery. Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection (RPLND) is needed also to prevent any metastasis that have reached them and may cause complications. Use of radiotherapy is limited in NSGCTs because the tumor is not sensitive to it. Follow-Up: After finishing treatment and making sure the body of the patient is clear from any metastasized tissue, we should follow him up for 2 years. In the first year after recovery, we should perform a CXR every month to make sure the chest of the patient is clear. In the second year the CXR will be taken every 2 months, and then annually after that. Another follow-up technique should be Abdominal and Chest CT scans perform to look for any metastasis to the LNs or organs. P a g e 16
Scrotal pain and Swelling
 Scrotal pain and Swelling Color index : Important Further explanation Done By: Nada Alamri Editing link Acute Scrotal Pain DDx: 1) Testicular torsion : Twisting and strangulation of the testicle on the
Scrotal pain and Swelling Color index : Important Further explanation Done By: Nada Alamri Editing link Acute Scrotal Pain DDx: 1) Testicular torsion : Twisting and strangulation of the testicle on the
BENIGN & MALIGNANT TESTIS DISEASES. Gary J. Faerber, M.D. Associate Professor, Dept of Urology March 2009 OBJECTIVES
 BENIGN & MALIGNANT TESTIS DISEASES Gary J. Faerber, M.D. Associate Professor, Dept of Urology March 2009 OBJECTIVES 1. Become familiar with the scrotal contents and their anatomical relationship with each
BENIGN & MALIGNANT TESTIS DISEASES Gary J. Faerber, M.D. Associate Professor, Dept of Urology March 2009 OBJECTIVES 1. Become familiar with the scrotal contents and their anatomical relationship with each
M. Al-Mohtaseb. Tala Saleh. Faisal Nimri
 4 5 M. Al-Mohtaseb Tala Saleh Faisal Nimri Inguinal Hernia - An abdominal hernia is the protrusion of part of the abdominal content beyond the normal confines of the abdominal wall through weak points
4 5 M. Al-Mohtaseb Tala Saleh Faisal Nimri Inguinal Hernia - An abdominal hernia is the protrusion of part of the abdominal content beyond the normal confines of the abdominal wall through weak points
حسام أبو عوض. -Dr. Mohammad Muhtasib. 1 P a g e
 5 حسام أبو عوض - -Dr. Mohammad Muhtasib 1 P a g e There are two types of inguinal hernia: direct and indirect. Hernia: protrusion of the small intestine or the greater omentum of the intra-abdominal organs
5 حسام أبو عوض - -Dr. Mohammad Muhtasib 1 P a g e There are two types of inguinal hernia: direct and indirect. Hernia: protrusion of the small intestine or the greater omentum of the intra-abdominal organs
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Gary Faerber, M.D., 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Gary Faerber, M.D., 2011 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Testicular Cancer: Questions and Answers. Testicular cancer is a disease in which cells become malignant (cancerous) in one or both testicles.
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Testicular Cancer: Questions
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Testicular Cancer: Questions
The Acute Scrotum: Sonographic Findings
 The Acute Scrotum: Sonographic Findings 가천의대길병원방사선과 양달모 Gachon Medical School Introduction Many diseases presenting as acute scrotal pain DDx is important for determining the appropriate treatment US with
The Acute Scrotum: Sonographic Findings 가천의대길병원방사선과 양달모 Gachon Medical School Introduction Many diseases presenting as acute scrotal pain DDx is important for determining the appropriate treatment US with
Cardiff MRCS OSCE Courses Testicular Cancer
 Testicular Cancer Scenario: A 40-year-old male presents to the surgical out-patient clinic with a 6-8 week history of a painless lump in his left scrotum. He however complains of a dull ache in the scrotum
Testicular Cancer Scenario: A 40-year-old male presents to the surgical out-patient clinic with a 6-8 week history of a painless lump in his left scrotum. He however complains of a dull ache in the scrotum
Dr Prashant Jain. Sr. Consultant, Pediatric surgery BLK Superspeciality Hospital
 Dr Prashant Jain Sr. Consultant, Pediatric surgery BLK Superspeciality Hospital Acute Scrotum Presentation 0 Pain in scrotal area 0 Scrotal swelling 0 Scrotal redness take him to nearby emergency... Acute
Dr Prashant Jain Sr. Consultant, Pediatric surgery BLK Superspeciality Hospital Acute Scrotum Presentation 0 Pain in scrotal area 0 Scrotal swelling 0 Scrotal redness take him to nearby emergency... Acute
Vikram Dogra, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Urology & BME Department of Imaging Sciences University Of Rochester Medical Center
 Ultrasound of the Scrotum Vikram Dogra, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Urology & BME Department of Imaging Sciences University Of Rochester Medical Center Etiologies of Acute Scrotal Pain Epididymitis/Orchitis
Ultrasound of the Scrotum Vikram Dogra, M.D. Professor of Radiology, Urology & BME Department of Imaging Sciences University Of Rochester Medical Center Etiologies of Acute Scrotal Pain Epididymitis/Orchitis
The case. I m smiling because it hurts
 Brad Sobolewski, MD The case A 7 year old boy has been referred to the ED because his privates hurt The pain has been present for 2 days It is worse when he jumps up and down There is no history of trauma,
Brad Sobolewski, MD The case A 7 year old boy has been referred to the ED because his privates hurt The pain has been present for 2 days It is worse when he jumps up and down There is no history of trauma,
Diagnosis and Management of the Acute Scrotum. AUA update series 2016 volume 35. By Anas Hindawi,Urology Resident Moderated by Dr.
 Diagnosis and Management of the Acute Scrotum AUA update series 2016 volume 35 By Anas Hindawi,Urology Resident Moderated by Dr. Khalid Al Sayyid Introduction The acute onset of pain,tenderness or swelling
Diagnosis and Management of the Acute Scrotum AUA update series 2016 volume 35 By Anas Hindawi,Urology Resident Moderated by Dr. Khalid Al Sayyid Introduction The acute onset of pain,tenderness or swelling
DEFINITION HX & PH/EX
 DEFINITION HX & PH/EX Because of the success of the assisted reproductive techniques (ART), the evaluation of the man is often ignored. The physician should not forget the fact that many causes of male
DEFINITION HX & PH/EX Because of the success of the assisted reproductive techniques (ART), the evaluation of the man is often ignored. The physician should not forget the fact that many causes of male
Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed
 Undescended Testes/Orchiopexy James C.Y. Dunn, MD, PhD, 1 Akemi L. Kawaguchi, MD, 2 and Eric W. Fonkalsrud, MD 1 Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed to prevent the potential complications
Undescended Testes/Orchiopexy James C.Y. Dunn, MD, PhD, 1 Akemi L. Kawaguchi, MD, 2 and Eric W. Fonkalsrud, MD 1 Surgical management of the undescended testis is performed to prevent the potential complications
Undescended Testicle
 What is the normal descending testis? The testicle begins to form just before the second fetal month and starts to look like a testicle around the fourth fetal month. By then it has migrated down from
What is the normal descending testis? The testicle begins to form just before the second fetal month and starts to look like a testicle around the fourth fetal month. By then it has migrated down from
All Men are created. (more or less) Rod Moser, PA, PhD Sutter Roseville Pediatrics Founding President, CAPA
 Rod Moser, PA, PhD Sutter Roseville Pediatrics Founding President, CAPA Balls Stones Family Jewels Meatballs Reece's Pieces Nuts Coconuts Weights Walnuts Gonads / Nads Dumbbells Truffles The sperm factory
Rod Moser, PA, PhD Sutter Roseville Pediatrics Founding President, CAPA Balls Stones Family Jewels Meatballs Reece's Pieces Nuts Coconuts Weights Walnuts Gonads / Nads Dumbbells Truffles The sperm factory
Scrotal Swellings. Dr John Nash GPwSI Urology
 Scrotal Swellings Dr John Nash GPwSI Urology Mode of Presentation Acute Pain Elective Non-acute Pain Acute Painful Presentation Testicular Torsion Torsion of Testicular Appendage ( Hydatid of Morgagni)
Scrotal Swellings Dr John Nash GPwSI Urology Mode of Presentation Acute Pain Elective Non-acute Pain Acute Painful Presentation Testicular Torsion Torsion of Testicular Appendage ( Hydatid of Morgagni)
Good Morning! March 23, 2015
 Good Morning! March 23, 2015 Prep Question You are caring for an 8-year-old girl who was involved in a motor vehiclepedestrian crash. Despite maximal medical and surgical therapy, she developed intractable
Good Morning! March 23, 2015 Prep Question You are caring for an 8-year-old girl who was involved in a motor vehiclepedestrian crash. Despite maximal medical and surgical therapy, she developed intractable
Testicular Malignancies /8/15
 Collecting Cancer Data: Testis 2014-2015 NAACCR Webinar Series January 8, 2015 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching
Collecting Cancer Data: Testis 2014-2015 NAACCR Webinar Series January 8, 2015 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching
Surgical Presentations in Children
 From Gums to Bums: Surgical Presentations in Children Sebastian King Paediatric Colorectal Surgeon From Gums to Bums (and the rest): Surgical Presentations in Children Sebastian King Paediatric Colorectal
From Gums to Bums: Surgical Presentations in Children Sebastian King Paediatric Colorectal Surgeon From Gums to Bums (and the rest): Surgical Presentations in Children Sebastian King Paediatric Colorectal
Inguinal Canal. It is an oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall. Present in both sexes
 Inguinal canal Inguinal Canal It is an oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall Present in both sexes It allows structures to pass to and from the testis to the abdomen in
Inguinal canal Inguinal Canal It is an oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall Present in both sexes It allows structures to pass to and from the testis to the abdomen in
COLOR DOPPLER ULTRASOUND IN EVALUATION OF SCROTAL LESIONS
 COLOR DOPPLER ULTRASOUND IN EVALUATION OF SCROTAL LESIONS Desai Sanjay D Associate Professor, Department of Radiology, RCSM Govt. Medical College, Kolhapur. ABSTRACT: Color Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive,
COLOR DOPPLER ULTRASOUND IN EVALUATION OF SCROTAL LESIONS Desai Sanjay D Associate Professor, Department of Radiology, RCSM Govt. Medical College, Kolhapur. ABSTRACT: Color Doppler ultrasound is a non-invasive,
ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE
 ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE SCROTUM MICHAEL NOMIKOS M.D. F.E.B.U. UROLOGICAL
ESUR SCROTAL AND PENILE IMAGING WORKING GROUP MULTIMODALITY IMAGING APPROACH TO SCROTAL AND PENILE PATHOLOGIES 2ND ESUR TEACHING COURSE NORMAL ANATOMY OF THE SCROTUM MICHAEL NOMIKOS M.D. F.E.B.U. UROLOGICAL
STAGING AND FOLLOW-UP STRATEGIES
 ATHENS 4-6 October 2018 European Society of Urogenital Radiology STAGING AND FOLLOW-UP STRATEGIES Ahmet Tuncay Turgut, MD Professor of Radiology Hacettepe University, Faculty of Medicine Ankara 2nd ESUR
ATHENS 4-6 October 2018 European Society of Urogenital Radiology STAGING AND FOLLOW-UP STRATEGIES Ahmet Tuncay Turgut, MD Professor of Radiology Hacettepe University, Faculty of Medicine Ankara 2nd ESUR
Maldescended testis in Adults. Dr. BG GAUDJI Urologist STEVE BIKO ACADEMIC HOSPITAL
 Maldescended testis in Adults Dr. BG GAUDJI Urologist STEVE BIKO ACADEMIC HOSPITAL Definitions Cryptorchid: testis neither resides nor can be manipulated into the scrotum Ectopic: aberrant course Retractile:
Maldescended testis in Adults Dr. BG GAUDJI Urologist STEVE BIKO ACADEMIC HOSPITAL Definitions Cryptorchid: testis neither resides nor can be manipulated into the scrotum Ectopic: aberrant course Retractile:
أحمد رواجبة- محمود الحربي- أحمد السالمان-
 -6 أحمد رواجبة- محمود الحربي- أحمد السالمان- 1 P a g e The Male Reproductive System The male genital system structures are divided into: Internal structures: 1- Prostate 3-Ejaculatory ducts External structures:
-6 أحمد رواجبة- محمود الحربي- أحمد السالمان- 1 P a g e The Male Reproductive System The male genital system structures are divided into: Internal structures: 1- Prostate 3-Ejaculatory ducts External structures:
Exercise. Discharge Summary
 Exercise Discharge Summary A 32-year-old Brazilian male presented with a 6 month history of right-sided scrotal swelling. Backache was present for 2 months and a history of right epididymitis was present
Exercise Discharge Summary A 32-year-old Brazilian male presented with a 6 month history of right-sided scrotal swelling. Backache was present for 2 months and a history of right epididymitis was present
Inguinal Hernia. Incarcerated hernia
 Inguinal Hernia An inguinal hernia occurs when soft tissue usually part of the membrane lining the abdominal cavity (omentum) or part of the intestine protrudes through a weak point in the abdominal muscles.
Inguinal Hernia An inguinal hernia occurs when soft tissue usually part of the membrane lining the abdominal cavity (omentum) or part of the intestine protrudes through a weak point in the abdominal muscles.
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary Pathology Report Final Diagnosis: Oncology Consult
 Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 31-year-old Brazilian male presented with a 6 month history of right-sided scrotal swelling. Backache was present for 2 months and a history of right epididymitis was
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 31-year-old Brazilian male presented with a 6 month history of right-sided scrotal swelling. Backache was present for 2 months and a history of right epididymitis was
What is Testicular cancer?
 Testicular Cancer What is Testicular cancer? Testicular cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of one or both testicles. The testicles are 2 egg-shaped glands located inside the
Testicular Cancer What is Testicular cancer? Testicular cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of one or both testicles. The testicles are 2 egg-shaped glands located inside the
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary Pathology Report Final Diagnosis: Oncology Consult
 Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 31-year-old Brazilian male presented with a 6 month history of right-sided scrotal swelling. Backache was present for 2 months and a history of right epididymitis was
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 31-year-old Brazilian male presented with a 6 month history of right-sided scrotal swelling. Backache was present for 2 months and a history of right epididymitis was
16:30-18:30 WS #52: Paediatric Forum (120mins - not repeated)
 Dr Kate Gibson Clinical Geneticist Genetic Health Service NZ, Children s Specialist Centre, Christchurch Hospital, Christchurch Dr Antony Bedggood Ophthalmologist Children s Specialist Centre, Christchurch
Dr Kate Gibson Clinical Geneticist Genetic Health Service NZ, Children s Specialist Centre, Christchurch Hospital, Christchurch Dr Antony Bedggood Ophthalmologist Children s Specialist Centre, Christchurch
UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material
 UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material ------------------------------------------------------------------------ The Undescended Testicle What is an Undescended Testicle? The undescended
UCSF Pediatric Urology Child and Family Information Material ------------------------------------------------------------------------ The Undescended Testicle What is an Undescended Testicle? The undescended
What are Varicoceles?
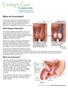 What are Varicoceles? A varicocele is when veins become enlarged inside your scrotum (the pouch of skin that holds your testicles). These veins are called the pampiniform plexus. Ten to 15 of every 100
What are Varicoceles? A varicocele is when veins become enlarged inside your scrotum (the pouch of skin that holds your testicles). These veins are called the pampiniform plexus. Ten to 15 of every 100
DISORDERS OF MALE GENITALS
 Wit JM, Ranke MB, Kelnar CJH (eds): ESPE classification of paediatric endocrine diagnosis. 9. Testicular disorders/disorders of male genitals. Horm Res 2007;68(suppl 2):63 66 ESPE Code Diagnosis OMIM ICD10
Wit JM, Ranke MB, Kelnar CJH (eds): ESPE classification of paediatric endocrine diagnosis. 9. Testicular disorders/disorders of male genitals. Horm Res 2007;68(suppl 2):63 66 ESPE Code Diagnosis OMIM ICD10
Case Based Urology Learning Program
 Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 5 CBULP 2011 021 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
Case Based Urology Learning Program Resident s Corner: UROLOGY Case Number 5 CBULP 2011 021 Case Based Urology Learning Program Editor: Associate Editors: Manager: Case Contributors: Steven C. Campbell,
General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons
 General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons MODULE TITLE: ABDOMINAL WALL, RETROPERITONEUM, UROGENITAL 5-May-2013
General Surgery Curriculum Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, General Surgeons Australia & New Zealand Association of General Surgeons MODULE TITLE: ABDOMINAL WALL, RETROPERITONEUM, UROGENITAL 5-May-2013
Scrotum Kacey Morrison Amanda Baxter Sabrina Tucker July 18, 2006 SCROTUM
 Scrotum Kacey Morrison Amanda Baxter Sabrina Tucker July 18, 2006 SCROTUM 1) Other Names: Scrotum None Testicles Testes (Curry Tempkin, p. 236, 2/3/2) Ductus deferens spermatic cord (Tempkin, p. 279, Anatomy
Scrotum Kacey Morrison Amanda Baxter Sabrina Tucker July 18, 2006 SCROTUM 1) Other Names: Scrotum None Testicles Testes (Curry Tempkin, p. 236, 2/3/2) Ductus deferens spermatic cord (Tempkin, p. 279, Anatomy
Undescended Testicles, Retractile Testicles, and Testicular Torsion
 Undescended Testicles, Retractile Testicles, and Testicular Torsion This guideline, developed by Ashay Patel, D.O., in collaboration with the ANGELS team, on October 14, 2013. Last reviewed by Ashay Patel,
Undescended Testicles, Retractile Testicles, and Testicular Torsion This guideline, developed by Ashay Patel, D.O., in collaboration with the ANGELS team, on October 14, 2013. Last reviewed by Ashay Patel,
Miss Rashmi Singh Consultant urological Surgeon. Men s Health Seminar Parkside Hospital November 2016
 Miss Rashmi Singh Consultant urological Surgeon Men s Health Seminar Parkside Hospital November 2016 Hernia Hydrocele Varicocele Infections Epididymal cyst Testicular Ca Miscellaneous Phimosis Paraphimosis
Miss Rashmi Singh Consultant urological Surgeon Men s Health Seminar Parkside Hospital November 2016 Hernia Hydrocele Varicocele Infections Epididymal cyst Testicular Ca Miscellaneous Phimosis Paraphimosis
GUIDELINES ON TESTICULAR CANCER
 38 (Text updated March 2005) P. Albers (chairman), W. Albrecht, F. Algaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, A. Horwich, O. Klepp, M.P. Laguna, G. Pizzocaro Introduction Compared with other types of cancer
38 (Text updated March 2005) P. Albers (chairman), W. Albrecht, F. Algaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, A. Horwich, O. Klepp, M.P. Laguna, G. Pizzocaro Introduction Compared with other types of cancer
Dr. Syah Mirsya Warli, SpU Dr. Bungaran Sihombing,SpU Div. of Urology, Surgery Dept. Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 Emergency Room Urology Dr. Syah Mirsya Warli, SpU Dr. Bungaran Sihombing,SpU Div. of Urology, Surgery Dept. Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Ref : Clinical Manual of Urology, (Philip M. Hanno
Emergency Room Urology Dr. Syah Mirsya Warli, SpU Dr. Bungaran Sihombing,SpU Div. of Urology, Surgery Dept. Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Ref : Clinical Manual of Urology, (Philip M. Hanno
MEditorial December Kids Urology
 MEditorial December 2012 Kids Urology Most childhood illnesses are in the realm of infections, usually viral, which although sometimes frightening to parents, go away on their own without any major intervention.
MEditorial December 2012 Kids Urology Most childhood illnesses are in the realm of infections, usually viral, which although sometimes frightening to parents, go away on their own without any major intervention.
Role of Colour Doppler Ultrasonography in evaluation of scrotal pain and swelling
 Original Research Article Role of Colour Doppler Ultrasonography in evaluation of scrotal pain and swelling Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Rajnandgaon Chattisghar,
Original Research Article Role of Colour Doppler Ultrasonography in evaluation of scrotal pain and swelling Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Rajnandgaon Chattisghar,
Vascular Related Torsion Venous compression Hemorrhagic infarct Young men At night Very painful Can be reduced Scrotal Masses Testicular Tumors (solid
 Pathology of the Male Reproductive System Testis and Epididymis Failure of Testis to Descend Testis are not always in scrotum at birth. Testes from in abdomen with kidneys Migrate to scrotum May get stuck
Pathology of the Male Reproductive System Testis and Epididymis Failure of Testis to Descend Testis are not always in scrotum at birth. Testes from in abdomen with kidneys Migrate to scrotum May get stuck
The Scrotum & Testes Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi
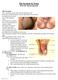 The Scrotum & Testes Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi The Scrotum It is a cutaneous pouch of the anterior abdominal wall. Most layers of the abdominal wall are represented in its structure. It contains the testes
The Scrotum & Testes Prof. Dr. Imran Qureshi The Scrotum It is a cutaneous pouch of the anterior abdominal wall. Most layers of the abdominal wall are represented in its structure. It contains the testes
Diseases of the penis & testis
 Diseases of the penis & testis Done by : Saef B AL-Abbadi Diseases of penis, Condyloma Acuminatum A benign tumor *Tend to recur but only rarely progress into in situ or invasive cancers read this = genital
Diseases of the penis & testis Done by : Saef B AL-Abbadi Diseases of penis, Condyloma Acuminatum A benign tumor *Tend to recur but only rarely progress into in situ or invasive cancers read this = genital
PERSISTANT MULLERIAN DUCT SYNDROME ASSOCIATED WITH TRANSVERSE TESTICULAR ECTOPIA
 PERSISTANT MULLERIAN DUCT SYNDROME ASSOCIATED WITH TRANSVERSE TESTICULAR ECTOPIA Dr. Abdulrahman A. Al-Bassam, FRCS(Ed) Assistant Professor & Consultant Paediatric Surgeon King Khalid University Hospital
PERSISTANT MULLERIAN DUCT SYNDROME ASSOCIATED WITH TRANSVERSE TESTICULAR ECTOPIA Dr. Abdulrahman A. Al-Bassam, FRCS(Ed) Assistant Professor & Consultant Paediatric Surgeon King Khalid University Hospital
-The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - include: I. Germ cell tumors : (95%); all are malignant. II. Sex cord-stromal tumors: from Sertoli or Leydig cells; usually
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - include: I. Germ cell tumors : (95%); all are malignant. II. Sex cord-stromal tumors: from Sertoli or Leydig cells; usually
Wilms' tumor most often occurs in just one kidney, though it can sometimes be found in both kidneys at the same time.
 Wilms' Tumor Wilms' tumor is a rare kidney cancer that primarily affects children. Also known as nephroblastoma, Wilms' tumor is the most common cancer of the kidneys in children. Wilms' tumor most often
Wilms' Tumor Wilms' tumor is a rare kidney cancer that primarily affects children. Also known as nephroblastoma, Wilms' tumor is the most common cancer of the kidneys in children. Wilms' tumor most often
Testicular Cancer. What is testicular cancer? What are the symptoms? Patient Information. Risk factors for testicular cancer.
 Patient Information English 31 Testicular Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is testicular cancer? The testicles (also called the testes ) are part of the male reproductive system
Patient Information English 31 Testicular Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is testicular cancer? The testicles (also called the testes ) are part of the male reproductive system
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL. PHD THESIS UNDESCENDED TESTICLE IN CHILD CLINICAL AND THERAPEUTIC ASPECTS - Abstract -
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL PHD THESIS UNDESCENDED TESTICLE IN CHILD CLINICAL AND THERAPEUTIC ASPECTS - Abstract - SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: Prof. Dr. Ion GEORGESCU PHD
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL PHD THESIS UNDESCENDED TESTICLE IN CHILD CLINICAL AND THERAPEUTIC ASPECTS - Abstract - SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: Prof. Dr. Ion GEORGESCU PHD
THE PATIENT S GUIDE TO VARICOCELE
 The Varicocele Decision Varicoceles are a relatively common problem that can hurt a man's fertility. The good news is that this is a fairly simple problem to fix. Dr. Fisch has treated hundreds of men
The Varicocele Decision Varicoceles are a relatively common problem that can hurt a man's fertility. The good news is that this is a fairly simple problem to fix. Dr. Fisch has treated hundreds of men
Appendix D Answers to the KAP Survey
 From Trainer s Resource Book to accompany Management of Men s Reproductive Health Problems 2003 EngenderHealth Appendix D Answers to the KAP Survey In the answer key that follows: The answers appear in
From Trainer s Resource Book to accompany Management of Men s Reproductive Health Problems 2003 EngenderHealth Appendix D Answers to the KAP Survey In the answer key that follows: The answers appear in
Information for Patients. Testicular Cancer. English
 Information for Patients Testicular Cancer English Table of contents What is testicular cancer?... 3 What are the symptoms?... 3 How is testicular cancer diagnosed?... 3 What is staging?... 4 Stages of
Information for Patients Testicular Cancer English Table of contents What is testicular cancer?... 3 What are the symptoms?... 3 How is testicular cancer diagnosed?... 3 What is staging?... 4 Stages of
Emergent Pediatric Ultrasound. Katharine Dennis, RDMS/RVT Tiffany Schultz, RDMS UNC Health Care Dept of General Ultrasound
 Emergent Pediatric Ultrasound Katharine Dennis, RDMS/RVT Tiffany Schultz, RDMS UNC Health Care Dept of General Ultrasound Introduction Learning Objectives Review common pediatric emergent ultrasound exams
Emergent Pediatric Ultrasound Katharine Dennis, RDMS/RVT Tiffany Schultz, RDMS UNC Health Care Dept of General Ultrasound Introduction Learning Objectives Review common pediatric emergent ultrasound exams
Alex Lam, HMS III. September The Acute Scrotum. Alex Lam, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD. Gillian Lieberman, MD
 September 2002 The Acute Scrotum Alex Lam, Harvard Medical School Year III DDx: : Acute Scrotal Pain & Enlargement PAIN Inflammatory disorder Testicular torsion Testicular infarction Testicular abscess
September 2002 The Acute Scrotum Alex Lam, Harvard Medical School Year III DDx: : Acute Scrotal Pain & Enlargement PAIN Inflammatory disorder Testicular torsion Testicular infarction Testicular abscess
Male genital tract tumors. SiCA. Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital.
 Male genital tract tumors Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital. adenocarcinoma Prostate Cancer most common male cancer in western countries more detected in
Male genital tract tumors Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital. adenocarcinoma Prostate Cancer most common male cancer in western countries more detected in
EAU GUIDELINES ON TESTICULAR CANCER
 EAU GUIDELINES ON TESTICULAR CANCER (Limited text update March 2018) P. Albers (Chair), W. Albrecht, F. Algaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, K. Fizazi, A. Horwich, M.P. Laguna (Vice-chair), N. Nicolai,
EAU GUIDELINES ON TESTICULAR CANCER (Limited text update March 2018) P. Albers (Chair), W. Albrecht, F. Algaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, K. Fizazi, A. Horwich, M.P. Laguna (Vice-chair), N. Nicolai,
Department of Medical Imaging, The Ottawa Hospital. Satheesh Krishna Sabarish Narayanasamy Wael Shabana Adnan Sheikh
 Department of Medical Imaging, The Ottawa Hospital. Satheesh Krishna Sabarish Narayanasamy Wael Shabana Adnan Sheikh Nothing to disclose Common and unusual presentations and manifestations of testicular
Department of Medical Imaging, The Ottawa Hospital. Satheesh Krishna Sabarish Narayanasamy Wael Shabana Adnan Sheikh Nothing to disclose Common and unusual presentations and manifestations of testicular
Quiz 1. Assign Race 1, Race 2 and Spanish Hispanic Origin to the following scenarios.
 Quiz 1 Assign Race 1, Race 2 and Spanish Hispanic Origin to the following scenarios. 1. 62 year old Brazilian female Race 1 Race 2 Spanish/Hispanic Origin 2. 43 year old Asian male born in Japan Race 1
Quiz 1 Assign Race 1, Race 2 and Spanish Hispanic Origin to the following scenarios. 1. 62 year old Brazilian female Race 1 Race 2 Spanish/Hispanic Origin 2. 43 year old Asian male born in Japan Race 1
MALE GENITAL SURGICAL PROCEDURES
 Male Genital Surgical ProceduresDecember 22, 2015 (effective March 1, 201) PENIS Slit of prepuce (complete care) S5 - newborn... 14.35 S58 - infant... 21.50 S59 - adult or child... 30.25 EXCISION Circumcision
Male Genital Surgical ProceduresDecember 22, 2015 (effective March 1, 201) PENIS Slit of prepuce (complete care) S5 - newborn... 14.35 S58 - infant... 21.50 S59 - adult or child... 30.25 EXCISION Circumcision
Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for testicular cancer
 Surgery Illustrated Focus on Details SURGERY ILLUSTRATED SURGICAL ATLASPIZZOCARO and GUARNERI PIZZOCARO and GUARNERI BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for
Surgery Illustrated Focus on Details SURGERY ILLUSTRATED SURGICAL ATLASPIZZOCARO and GUARNERI PIZZOCARO and GUARNERI BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas Inguinal orchidectomy for
Note: The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
Postgraduate Training in Reproductive Health
 SURGICAL TREATMENT OF MALE INFERTILITY Georges A. de Boccard, M.D. Consultant Urologist F.M.H., F.E.B.U. Postgraduate Training in Reproductive Health Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF MALE INFERTILITY Georges A. de Boccard, M.D. Consultant Urologist F.M.H., F.E.B.U. Postgraduate Training in Reproductive Health Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
Common Problems in Urology
 Common Problems in Urology 1. Renal Colic Outline 2. Urinary Retention 3. Acute Scrotum Supanut Lumbiganon, MD. Renal colic The most common urologic emergency O Sudden increase of pressure in the urinary
Common Problems in Urology 1. Renal Colic Outline 2. Urinary Retention 3. Acute Scrotum Supanut Lumbiganon, MD. Renal colic The most common urologic emergency O Sudden increase of pressure in the urinary
Testicular Cancer. J. Richard Auman, MD. James J. Stark, MD. Jerry Singer, MD. September 19, 2008
 Testicular Cancer J. Richard Auman, MD James J. Stark, MD Jerry Singer, MD September 19, 2008 Testicular Cancer From mystery to far-advanced disease: a remarkable case Case Presentation. 23 y. o. male
Testicular Cancer J. Richard Auman, MD James J. Stark, MD Jerry Singer, MD September 19, 2008 Testicular Cancer From mystery to far-advanced disease: a remarkable case Case Presentation. 23 y. o. male
1/3/2008. Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care, 2e Karen Burke, Priscilla LeMone, and Elaine Mohn-Brown
 Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 34 Caring for Male Clients with Reproductive System Disorders Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Testosterone
Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 34 Caring for Male Clients with Reproductive System Disorders Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Testosterone
Suspected testicular cancer
 Suspected testicular cancer Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction Your consultant has informed you that you may have testicular cancer. This leaflet gives the facts about your condition
Suspected testicular cancer Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction Your consultant has informed you that you may have testicular cancer. This leaflet gives the facts about your condition
EAU GUIDELINES ON TESTICULAR CANCER
 EAU GUIDELINES ON TESTICULAR CANCER (Limited text update March 2015) P. Albers (Chair), W. Albrecht, F. Algaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, K. Fizazi, A. Horwich, M.P. Laguna, N. Nicolai, J. Oldenburg
EAU GUIDELINES ON TESTICULAR CANCER (Limited text update March 2015) P. Albers (Chair), W. Albrecht, F. Algaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, K. Fizazi, A. Horwich, M.P. Laguna, N. Nicolai, J. Oldenburg
MANAGEMENT OF UNDESCENDED TESTES IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA M. Maheshwari 1, Roshan Chanchlani 2
 MANAGEMENT OF UNDESCENDED TESTES IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA M. Maheshwari 1, Roshan Chanchlani 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: M. Maheshwari, Roshan Chanchlani. Management of Undescended
MANAGEMENT OF UNDESCENDED TESTES IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA M. Maheshwari 1, Roshan Chanchlani 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: M. Maheshwari, Roshan Chanchlani. Management of Undescended
THE DESCENT OF THE TESTIS
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1964, 39, 605. THE DESCENT OF THE TESTIS BY C. G. SCORER From Hillingdon Hospital, Uxbridge This study is based on observations made on boys at birth, during infancy, and throughout
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1964, 39, 605. THE DESCENT OF THE TESTIS BY C. G. SCORER From Hillingdon Hospital, Uxbridge This study is based on observations made on boys at birth, during infancy, and throughout
EAU GUIDELINES ON TESTICULAR CANCER
 EU GUIDELINES ON TESTICULR CNCER (Limited text update March 2017) P. lbers (Chair), W. lbrecht, F. lgaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, K. Fizazi,. Horwich, M.P. Laguna, N. Nicolai, J. Oldenburg Introduction
EU GUIDELINES ON TESTICULR CNCER (Limited text update March 2017) P. lbers (Chair), W. lbrecht, F. lgaba, C. Bokemeyer, G. Cohn-Cedermark, K. Fizazi,. Horwich, M.P. Laguna, N. Nicolai, J. Oldenburg Introduction
RADIONUCLIDE STUDIES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF PAINFUL TESTICULAR PATHOLOGY
 RADIONUCLIDE STUDIES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF PAINFUL TESTICULAR PATHOLOGY Isabel Roca Vall d'hebron Hospital General Servei de Medicina Nuclear TESTICULAR SCINTIGRAPHY ACUTE TESTICULAR PAIN Differential Diagnosis
RADIONUCLIDE STUDIES IN THE MANAGEMENT OF PAINFUL TESTICULAR PATHOLOGY Isabel Roca Vall d'hebron Hospital General Servei de Medicina Nuclear TESTICULAR SCINTIGRAPHY ACUTE TESTICULAR PAIN Differential Diagnosis
Ultrasound of malignant testicular lesions. Arne Hørlyck Department of Radiology Aarhus University Hospital, Skejby
 Ultrasound of malignant testicular lesions Arne Hørlyck Department of Radiology Aarhus University Hospital, Skejby Testis Ultrasound is fantastic!! Scrotum Extratesticular mass: Benign Intratesticular
Ultrasound of malignant testicular lesions Arne Hørlyck Department of Radiology Aarhus University Hospital, Skejby Testis Ultrasound is fantastic!! Scrotum Extratesticular mass: Benign Intratesticular
Scrotal emergencies Subramaniyan Ramanathan
 Scrotal emergencies Subramaniyan Ramanathan Weill Cornell Medicine, New York (Qatar campus) Hamad medical corporation, Doha, Qatar Disclosure Statement I have no relationships with commercial interests
Scrotal emergencies Subramaniyan Ramanathan Weill Cornell Medicine, New York (Qatar campus) Hamad medical corporation, Doha, Qatar Disclosure Statement I have no relationships with commercial interests
What You Need to Know
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What You Need to Know Facts about male infertility This handout explains what causes male infertility, how it is diagnosed, and possible treatments. Infertility is defined
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What You Need to Know Facts about male infertility This handout explains what causes male infertility, how it is diagnosed, and possible treatments. Infertility is defined
1. Hypogonadism is usually encountered in the following conditions, except
 1. Hypogonadism is usually encountered in the following conditions, except A. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia B. Noonan Syndrome C. Prader-Willi Syndrome D. Bardet-Biedl Syndrome 2. A 6 year old girl with
1. Hypogonadism is usually encountered in the following conditions, except A. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia B. Noonan Syndrome C. Prader-Willi Syndrome D. Bardet-Biedl Syndrome 2. A 6 year old girl with
Collecting Cancer Data: Testis 2/3/11. Collecting Cancer Data: NAACCR Webinar Series 1. Agenda. Fabulous Prizes
 Collecting Cancer Data: Testis February 3, 2011 NAACCR 2010-2011 Webinar Series Agenda Coding moment Race/Hispanic origin Overview Collaborative Stage Treatment Exercises Fabulous Prizes NAACCR 2010-2011
Collecting Cancer Data: Testis February 3, 2011 NAACCR 2010-2011 Webinar Series Agenda Coding moment Race/Hispanic origin Overview Collaborative Stage Treatment Exercises Fabulous Prizes NAACCR 2010-2011
ASYMPTOMATIC COMPLEX TESTICULAR NEOPLASIA ASSOCIATED WITH ORCHIEPIDIDYMITIS. CASE REPORT
 Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2017 vol. 121, no. 4 SURGERY CASE REPORTS ASYMPTOMATIC COMPLEX TESTICULAR NEOPLASIA ASSOCIATED WITH ORCHIEPIDIDYMITIS. CASE REPORT Ș. Iacob 1, R. Vrînceanu 2,3, B.
Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2017 vol. 121, no. 4 SURGERY CASE REPORTS ASYMPTOMATIC COMPLEX TESTICULAR NEOPLASIA ASSOCIATED WITH ORCHIEPIDIDYMITIS. CASE REPORT Ș. Iacob 1, R. Vrînceanu 2,3, B.
Doppler ultrasound of the abdomen and pelvis, and color Doppler
 - - - - - - - - - - - - - Testicular tumors are rare in children. They account for only 1% of all pediatric solid tumors and 3% of all testicular tumors [1,2]. The annual incidence of testicular tumors
- - - - - - - - - - - - - Testicular tumors are rare in children. They account for only 1% of all pediatric solid tumors and 3% of all testicular tumors [1,2]. The annual incidence of testicular tumors
Testicular Cancer. What is cancer?
 What is cancer? Testicular Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide, and die in an orderly fashion. During the early years of a person's life, normal cells
What is cancer? Testicular Cancer The body is made up of trillions of living cells. Normal body cells grow, divide, and die in an orderly fashion. During the early years of a person's life, normal cells
Find Medical Solutions to Your Problems HYDRONEPHROSIS. (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis)
 HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
Acute Scrotal Pain: Clinical Features
 Acute Scrotal Pain: Clinical Features Vincenzo Mirone, Paolo Verze, and Davide Arcaniolo Contents 1 Introduction... 85 2 Torsion... 86 2.1 Extravaginal Torsion... 86 2.2 Intravaginal Torsion... 86 2.3
Acute Scrotal Pain: Clinical Features Vincenzo Mirone, Paolo Verze, and Davide Arcaniolo Contents 1 Introduction... 85 2 Torsion... 86 2.1 Extravaginal Torsion... 86 2.2 Intravaginal Torsion... 86 2.3
COMPLICATIONS OF HERNIA REPAIR
 COMPLICATIONS OF HERNIA REPAIR Stanley Rogers, MD Associate Clinical Professor of Surgery University of Califronia, San Francisco Paré was respected as a hernia specialist, and was known to have elevated
COMPLICATIONS OF HERNIA REPAIR Stanley Rogers, MD Associate Clinical Professor of Surgery University of Califronia, San Francisco Paré was respected as a hernia specialist, and was known to have elevated
Follow this and additional works at: Part of the Other Medical Specialties Commons, and the Surgery Commons
 Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Department of Surgery Hernias Lauren Dudas MD Lehigh Valley Health Network, Lauren.Dudas@lvhn.org Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarlyworks.lvhn.org/surgery
Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Department of Surgery Hernias Lauren Dudas MD Lehigh Valley Health Network, Lauren.Dudas@lvhn.org Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarlyworks.lvhn.org/surgery
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH
 ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
Penis Cancer. What is penis cancer? Symptoms. Patient Information. Pagina 1 / 9. Patient Information - Penis Cancer
 Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 9 Urinary Tract and Perineum Key Points 2 9.1 Urinary Bladder & Urinary Retention Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 9 Urinary Tract and Perineum Key Points 2 9.1 Urinary Bladder & Urinary Retention Acute retention of urine is an indication for emergency drainage of the bladder
Rama Nada. - Ensherah Mokheemer. - Ahmed salman. 1 P a g e
 - 5 - Rama Nada - Ensherah Mokheemer - Ahmed salman 1 P a g e We will continue talking about the urinary bladder The ligaments of the bladder: 1-Median umbilical ligament: Continuous with apex of the bladder
- 5 - Rama Nada - Ensherah Mokheemer - Ahmed salman 1 P a g e We will continue talking about the urinary bladder The ligaments of the bladder: 1-Median umbilical ligament: Continuous with apex of the bladder
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen
 Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
The Good News. The Comprehensive Approach. Examining the Male Patient: Sexually Transmitted Infections. April 25, 2013 Brittany Grier, M.
 Examining the Male Patient: Sexually Transmitted Infections April 25, 2013 Brittany Grier, M.S, PA-C The Good News Learning how to do a proper male exam can provide high yield information in formulating
Examining the Male Patient: Sexually Transmitted Infections April 25, 2013 Brittany Grier, M.S, PA-C The Good News Learning how to do a proper male exam can provide high yield information in formulating
Clinical Diagnosis. your PR.i.VATES.
 your PR.i.VATES Clinical Diagnosis What is an orchidectomy? What to expect after orchidectomy Results and Confirmed Diagnosis What is the lymphatic system? www.yourprivates.org.uk CONTENTS CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS
your PR.i.VATES Clinical Diagnosis What is an orchidectomy? What to expect after orchidectomy Results and Confirmed Diagnosis What is the lymphatic system? www.yourprivates.org.uk CONTENTS CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS
Chapter 11 Guidelines and Best Practice Statements for the Evaluation and Management of Infertile Adult and Adolescent Males with Varicocele
 Chapter 11 Guidelines and Best Practice Statements for the Evaluation and Management of Infertile Adult and Adolescent Males with Varicocele With the continuous growth of medical knowledge and the need
Chapter 11 Guidelines and Best Practice Statements for the Evaluation and Management of Infertile Adult and Adolescent Males with Varicocele With the continuous growth of medical knowledge and the need
Penis Cancer. What is penis cancer? Symptoms. Patient Information. Pagina 1 / 9. Patient Information - Penis Cancer
 Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Patient Information English 31 Penis Cancer The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. What is penis cancer? Cancer is abnormal cell growth in the skin or organ tissue. When this cell growth starts
Title: Quadruple Orchidopexy for Torsion Testis in an Adolescent with Polyorchidism: a Case Report
 Accepted Manuscript Title: Quadruple Orchidopexy for Torsion Testis in an Adolescent with Polyorchidism: a Case Report Author: Hany Ibrahim, Matthew J. Roberts, David Hussey PII: S0090-4295(15)00890-0
Accepted Manuscript Title: Quadruple Orchidopexy for Torsion Testis in an Adolescent with Polyorchidism: a Case Report Author: Hany Ibrahim, Matthew J. Roberts, David Hussey PII: S0090-4295(15)00890-0
Male Genital Cancers in the US in Frequency of Types
 Germ Cell Tumors of the Testis Pathology, Immunohistochemistry, and the Often Confusing Appearance of Their Metastases Charles Zaloudek, MD Department of Pathology UCSF Male Genital Cancers in the US in
Germ Cell Tumors of the Testis Pathology, Immunohistochemistry, and the Often Confusing Appearance of Their Metastases Charles Zaloudek, MD Department of Pathology UCSF Male Genital Cancers in the US in
Acute Groin Pain Following Trauma
 Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Department of Family Medicine Acute Groin Pain Following Trauma Victoria Chen MD Lehigh Valley Health Network, victoria.chen@lvhn.org Follow this and additional
Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Department of Family Medicine Acute Groin Pain Following Trauma Victoria Chen MD Lehigh Valley Health Network, victoria.chen@lvhn.org Follow this and additional
