Zhandos Dautovich Kenzhin
|
|
|
- Alice Freeman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 American-Eurasian Journal of Toxicological Sciences 6 (4): , 2014 ISSN IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: /idosi.aejts Comparative Analysis of Heavy Metals (Mn, Zn, Ni, Co, Cr, Sr, Fe, Pb, Cd, Co) Accumulation Ability in Fish Species Sander lucioperca L. and Neogobius melanostomus P. at the Coastal Sea Waters of The Northern and Central Part of Caspian Sea Zhandos Dautovich Kenzhin Karaganda State Medical University (KSMU) 4A, Gogol street 40, , Karaganda, Kazakhstan Abstract: In the work there are described the biological indicators for the Northern and Central parts of Caspian Sea, i.e. Sander lucioperc L. and Neogobius melanostomus P. The purpose of the work is the research of the comparative bioaccumulation ability of one of the most toxic types of the salts of ten heavy metals types in various organs of the above mentioned species of fish. There were applied the methods of spectrophotometry with the usage of induced high-sensitive plasma and gas-liquid chromatography. It has been defined that the species Sander lucioperca L. and Neogobius melanostomus P. can be used in the described region as biological indicators with the purpose of general analytical estimation of the state of the environment pollution by salts of heavy metals. Key words: Caspian Sea Biological Indicators Heavy metals INTRODUCTION physical-and-chemical quality of these elements; it should be noted that many kinds of heavy metals are contained The actual issue of the region is the comparative in tissues and organs of living objects in natural research of the accumulation level, migration and background and take part in the processes of metabolism concentration of one of the most toxic types of heavy and life activity [1]. However, exceeding the values of the metals salts: Mn, Cr, Sr, Zn, Ni, Co, Fe, Pb, Cd, Co, that maximum permissible concentration of one or another kind are following to the intensive anthropogenic activity, in of these elements can cause damage the vital functions of the investigated zones of the Northern and Central parts the organism and in some cases lead to fatal outcome. of Caspian Sea. As a purpose of our studying, there have The research of toxicity of heavy metals and its been chosen the widely-spread in the described studying detailed analysis has been in the spotlight of many region, species of fish - Sander lucioperca L. and researchers for a long time and devoted to the description Neogobius melanostomus P., the both species belong to of the toxic impact of various metals on fish in quite broad one and the same family of perch-like fishes, they are area [2]. Most authors emphasize the high toxicity of widely spread and represent endemics in the studied different heavy metals, especially in the sweet water. points, they spawn and propagate, live actively, migrate Unfortunately, in many works there are given the to considerable distances, occupy similar ecological concentrations of metals that cause the death of niches and habitats. fish during a short term (1-3 hours), defined the toxicity The widely-spread group of the pollutants is of concentrations of each kind of heavy metals represented by associated with human activity (except (4-5 differences for each). The results gained by the Cr and Sr) types of salts of heavy metals that have a author reliably show the existing n toxicity of metals and, toxic effect on living organisms. They are highly toxic and first of all, the high poisonous impact of heavy metals. As remain in basins for a long time. Most kinds of heavy a result of the above-stated, the research of accumulation metals represent complex inorganic compounds, the toxic and migration of heavy metals was one of the foreground impact of which can be caused by anion, or any other tasks in the given research. Corresponding Author: Zhandos Dautovich Kenzhin, Karaganda State Medical University, Karaganda, Kazakhstan Tel: +7 (727) jandos-k@yandex.ru. 123
2 The work had as its own purpose the performance of concentrated nitric acid (HNO 3) was added to the bottles comparative analysis of the soil water sediment in a fume hood. The bottles were properly sealed, placed contamination factor ability and the spread in the in a vessel and put in the microwave apparatus according Northern and Central Caspian Sea species of fish Sander to manufacturer s instruction. The temperature of each lucioperca L. and Neogobius melanostomus P., to sample in the microwave rose to 175 C in approximately 5 accumulate in various organs and tissues, one of the most minutes and remained at same temperature for the toxic for living organisms, the above mentioned types of remaining 5 minutes. At the end of the microwave heavy metals that are associated with intensive program, the vessel was left to cool to room temperature anthropogenic activity and the possibility of usage the before removal from the microwave. After removal from species Sander lucioperc L. and Neogobius the microwave, the bottles were left to cool more for melanostomus P., in monitoring of the investigated area another 2 hours before carefully uncapping in the as well. ventilated fume hood. When it was sufficiently cool, the organ samples were transferred in acid clean volumetric MATERIALS AND METHODS flasks. However, the digested samples contained some Sample Preparation: Several specimens of fishes Sander particulates. The digested samples were was put in lucioperc L. and Neogobius melanostomus P. were centrifuge bottles and placed in Eppendorf centrifuge caught in 4 points of sampling biological objects in the 5702 for 15 minutes at 4.5rpm. The supernatant was investigated place adjacent to Atyrau City in the Northern sufficiently cleared, filtered with Whatman 42 filter paper Caspian Sea region (47 6'4.53"N, 51 54'48.99"E), and transferred into a 50ml volumetric flask and the digest (46 53'46.64"N, 51 38'12.96"E) and Aktau City (47 was diluted to the total volume of 50 ml [3]. 6'4.53"N, 51 54'48.99"E), (43 37'0.77"N, 51 11'41.27"E) on the territory of the Central Caspian Sea, then they were ICP-OES Analysis: A thermos model ICP-OES was used delivered to the laboratory and studied with the usage of for triplicate reading of each blank sample, mixed metal the method of morphometric analysis. The research was standard, nitric acid solution and a fish organs sample realized in summer period from July to August, 2011 extract. The instrument was calibrated and profiled using Then by turns there were taken organs and tissues the mixed calibration standard solution. The system was (gills, reproductive organs and muscle tissue) out of the rinsed for one minute with the deionized water before the caught specimens of fish. Each organ was weighed from analysis of each sample. 1 to 5 g and then prepared for the further analysis. As a control group there were taken the identical species of Statistical Analysis: Statistical differences between fish contained in aquarium in pure running water without particular organs of Sander lucioperc L. è Neogobius any polluting elements and admixtures. melanostomus P., with respect to mean concentrations of elements were evaluated by ANOVA on log-transformed Sample Extraction and Analysis data to obtain a normal distribution of features. Normality Heavy Metals Extractions: Fish organs samples, gills, of analyzed features was checked by Shapiro Wilk s test gonads and muscle tissue were collected and individually and the homogeneity of variances by Bartlett s test. air-dried at room temperature of 21 C to reduce the Statistical confidence was set at p = Fish s ability to moisture content. The fish samples were left to reduce the take up the elements from its environment and moisture content for ten (10) days. Then the samples were translocation rate of the elements within the fish were, homogenized, with a ceramic mortar and pestle and evaluated by the Index Bioaccumulation or Translocation passed through a sieve for particle size reduction. Factor (TF), expressed by the following ratios: metal Since sample results are to be calculated on a dry concentration in gills/metal concentration in muscles and weight basis, a portion of sample was weighed at the same metal concentration in gonads. All statistical calculations time as the portion used for analytical determination. were carried out in using following program [4]. This portion was dried in an oven at temperature of 115 C then allowed to cool in a desiccator before RESULTS weighing. Approximately 0.5g of dried fish sample organ was weighed using an analytical balance and transferred into Concentration of Heavy Metals in the Tested Objects: The results of analysis of the laboratory research on Teflon microwave bottles/containers. 20ml of detection of heavy metals concentration, revealing the 124
3 ranges of concentrations of elements in the water and the elements studied in Atyrau and Aktau groups, sediments from the examined ponds as well as in different between the gills, muscle tissue and gonads as well as to organs of Sander lucioperc L. and Neogobius compare, between the same control groups of fish organs: melanostomus P., are shown in (Tables 1 and 2). gills, muscle tissue and gonads, showed comparatively Transfer factor (TF) was calculated only for those low concentration of all studied metals, not exceeding elements, which were detected in the all fish organs. MPC and experimental groups of fish. On average, transport efficiency from sediment into The following statistical relationships, expressed by the fish organs was higher than this within the fish itself. Pearson s correlation (p<0.05), between chemical The bioaccumulation factor for all the metals analyzed in composition of the marine s fish environment and gonads of Sander lucioperc L. and Neogobius concentrations of the studied elements in the fish were melanostomus P., (gonads/water sediment ratio) was calculated in this study. estimated to exceed 1 confirming an intensive gonads According from (Table 2) it is seen that the greatest uptake of the most studied metals in the having species. ability to accumulation in species Neogobius The highest gonads/water sediment ratio was noted for Sr melanostomus P. was shown by the element Sr; the while the lowest value was calculated for Cd. concentration of this element in the organs is high and Translocation factors for all the elements analyzed in exceeds MPC from 200 to 300 times comparing both with Sander lucioperc L. and Neogobius melanostomus P., the control group of the organisms and the Atyrau were significantly below 1 confirming high gonads population. At (Table 2) there is indicated that retention capacity in respect of the studied elements and concentration of Sr is considerably higher than MPC in low intensity of their transfer to other fish s organs. species that closely contact with the bottom of the sea, Mobility of the metals analyzed within the fish varied in for example in fish Neogobius melanostomus P. There is different parts of an organism. The translocation rate of all also shown the exceeding of the element Cr in the Table 1: The main concentration of heavy metalls in organs of Sander lucioperca L., Atyrau, Northern Caspian sea Gills Control Muscles Control Gonads Control Pb 1.77± ± ± ± ±0.59 Excess, MPC 5.70± ± ± ± ±1.9 MPC 0.31 MPC 0.31 MPC 0.31 MPC 0.31 MPC 0.31 MPC 0.31 MPC 0.31 Cu 0.10± ± ± ± ± ±0.34 Excess, MPC 0.02± ± ± ± ± ±0.09 MPC 5.0 MPC 5.0 MPC 5.0 MPC 5.0 MPC 5.0 MPC 5.0 MPC 5.0 Cd 0.16± ± ± ±0.05 Excess, MPC 1.60± ± ± ±0.5 MPC 0.1 MPC 0.1 MPC 0.1 MPC 0.1 MPC 0.1 MPC 0.1 MPC 0.1 Zn 32.56± ± ± ± ± ±8.92 Excess, MPC 6.51± ± ± ± ±8 3.55±1.77 MPC 5 MPC 5 MPC 5 MPC 5 MPC 5 MPC 5 MPC 5 Fe 82.68± ± ± ± ± ±30.43 Excess, MPC 1.65± ± ± ± ± ±0.60 MPC 50 MPC 50 MPC 50 MPC 50 MPC 50 MPC 50 MPC 50 Ni 6.72± ± ± ± ± ±0.29 Excess, MPC 13.44± ± ± ± ± ±0.7 MPC 0.5 MPC 0.5 MPC 0.5 MPC 0.5 MPC 0.5 MPC 0.5 MPC 0.5 Co 0.30± ± ± ±0.35 Excess, MPC 0.06± ± ± ±0.7 MPC 0.5 MPC 0.5 MPC 0.5 MPC 0.5 MPC 0.5 MPC 0.5 MPC 0.5 Mn 5.20±2,6 3.12± ± ± ±0.9 Excess, MPC 26.04± ± ± ±3.27 9±5.7 MPC 0.2 MPC 0.2 MPC 0.2 MPC 0.2 MPC 0.2 MPC 0.2 MPC 0.2 Sr 13.50± ± ± ± ± ±0.26 Excess, MPC 1.92± ± ± ± ± ±0.031 MPC 7.0 MPC 7.0 MPC 7.0 MPC 7.0 MPC 7.0 MPC 7.0 MPC 7.0 Cr() 0.95± ± ± ± ± ±0.19 Excess, MPC 0.16± ± ± ± ± ±0.03 MPC 6.0 MPC 6.0 MPC 6.0 MPC 6.0 MPC 6.0 MPC 6.0 MPC 6.0 MPC - Maximum permissible concentration a b mg/kg. ND - no detection level 125
4 Table 2: The main concentration of heavy metalls in organs of Neogobius melanostomus P., Aktau, Central Caspian sea Gills Control Muscles Control Gonads Control Pb 17.4± ± ± ± ± ±0.24 Excess, MPC 56.1± ± ± ± ± ±1.10 MPC 0.31 MPC 0.31 MPC 0.31 MPC 0.31 MPC 0.31 MPC 0.31 MPC 0.31 Cu 0.78± ± ± ± ± ±0.3 Excess, MPC 0.15± ± ± ± ± ±0.06 MPC 5.0 MPC 5.0 MPC 5.0 MPC 5.0 MPC 5.0 MPC 5.0 MPC 5.0 Cd 0.14± ± ± ± ± ±0.01 Excess, MPC 1.4± ± ± ± ± ±0.1 MPC 0.1 MPC 0.1 MPC 0.1 MPC 0.1 MPC 0.1 MPC 0.1 MPC 0.1 Zn 4.62± ± ± ± ± ±7.03 Excess, MPC 0.92± ± ± ± ± ±0.94 MPC 5 MPC 5 MPC 5 MPC 5 MPC 5 MPC 5 MPC 5 Fe 35.2± ± ± ± ± ±18.5 Excess, MPC 0.7± ± ± ± ± ±0.06 MPC 50 MPC 50 MPC 50 MPC 50 MPC 50 MPC 50 MPC 50 Ni 5.32± ± ± ± ± ±1.45 Excess, MPC 10.64± ± ± ± ± ±1.64 MPC 0.5 MPC 0.5 MPC 0.5 MPC 0.5 MPC 0.5 MPC 0.5 MPC 0.5 Co 0.2±0.1 1± ± ± ±0.1 Excess, MPC 0.04± ± ± ± ±0.01 MPC 5 MPC 5 MPC 5 MPC 5 MPC 5 MPC 5 MPC 5 Mn ,7± ,7± ,4±2.4 7,14±2.38 2,96±0.98 Excess, MPC 107.1± ,5± ,5± ± ,7± ,8±4.9 MPC 0.2 MPC 0.2 MPC 0.2 MPC 0.2 MPC 0.2 MPC 0.2 MPC 0.2 Sr 172.8± ± ± ± ± ±0.82 Excess, MPC 24.68± ± ± ± ± ±0.15 MPC 7.0 MPC 7.0 MPC 7.0 MPC 7.0 MPC 7.0 MPC 7.0 MPC 7.0 Cr() 6.12± ± ± ± ± ±0.34 Excess, MPC 1.02± ± ± ± ± ±0.05 MPC 6.0 MPC 6.0 MPC 6.0 MPC 6.0 MPC 6.0 MPC 6.0 MPC 6.0 MPC - Maximum permissible concentration a b mg/kg ND - no detection level. organs of the species Neogobius melanostomus P., L. Zn from 4.44 mg/kg to 14 mg/kg. The content Ni at the unlike Sander lucioperca L. The degrees of toxicity Sander lucioperca L., is from mg \kg, to 17.9 mg \kg, of hexa- and trivalent chromium are considerably in comparison with the type Neogobius melanostomus P. different. of the Aktau group. It is probable that such results are connected with The content Pb, in the control group, in comparison sedimentation and storing up of radionuclides on the with the Atyrau group makes from 0 mg \kg, to 5.80 mg\kg, bottom and coastal soil whence they get into the water Mn from 2 mg\kg, to 15.6 mg \kg., Zn from 3.55 mg \kg to and with the food into the organisms of the above 9.10 mg\kg., Ni from1 mg \kg, to 2 mg \kg. species, because the coastal water area of Aktau City At the specie Neogobius melanostomus P. to be places a number of plants of atomic industry. concern on the Aktau group, the excess of identical According to the results of the analysis there was elements in bodies, is characterized by the considerable detected the ability of the species Sander lucioperca L share of the content Pb from 18.7 mg \kg to 56.1 mg \kg, and Neogobius melanostomus P., to store up in their Mn from 35.7 mg\kg to mg\kg, Ni from 6.08 mg \kg to organisms such studied metals as lead (Pb), manganese mg \kg, Zn from 0.92 mg\kg to 4.9 mg\kg in (Mn), nickel (Ni) and zinc (Zn). comparison with the Atyrau group. In the species Sander lucioperca L., sampled near The content of Pb, in the control group, in Atyrau City the exceeding of Pb in organs varies from 3.80 comparison with Aktau group makes from 2.12 mg\kg, to mg/kg to mg/kg, Mn from 9 mg/kg to 26 mg/kg mg\kg, Mn from 14.8 mg\kg, to 37 mg\kg., Zn from Comparative analysis of Zn and Ni concentration showed 2.72 mg\kg to mg\kg., Ni from 5.76 mg\kg, to 9.12 the exceeding in the organs of species Sander lucioperca mg\kg. 126
5 Out of presentation of high toxicity and long Also it s seems to know the sequence of metal bioaccumulation in fabrics of the living organisms, some concentration decreasing in the following order in the metals are microcells to be necessary for metabolic organs of the studied fishes, Sander lucioperc L. Fe processes, but in high density they cause a poisoning. showed the highest concentrations in gonads and also Zn Others Lead (Pb), in the normal, are not met in an in reproductive part, (Table1). Mn was mainly organism and consequently, theoretically, they can be accumulated in the gills and muscle tissue, whereas Ni toxic in any concentration. Toxicity of Lead (Pb) is slightly either in the reproductive, muscles and gills of the studied lower than toxicity of copper and cadmium, (Cu and Cd) fish (Table 1). however it is high enough and in concentration from Whereas sequence of metal concentration decreased mg \l Pb, it is obviously harmful for many kinds of in the following order in the organs of the studied fishes fish. Neogobius melanostomus P. Sr showed the highest It is known that toxicity of Zinc (Zn) is close to concentrations in the muscle and reproductive tissue. Pb toxicity of lead (Pb). The data shows that on degree of shows similar accumulation concentration at gills and harm, metals represent the rather diverse group. For muscle tissue, (Table 2). Mn was mainly accumulated in example, strontium (Sr) is least toxic for fish and can be the muscle tissue, whereas Fe in reproductive tissue joined with the group of less toxic metals Mn and Co (gonads) and gills of the studied fish, (Table 2). Zn also (manganese and cobalt). Copper, lead, cadmium, zinc, showed high accumulation in reproductive tissue nickel (Cu, Pb, Cd, Zn, Ni) and trivalent chrome (Cr ) are (gonads), but low accumulation in gills, whereas Ni, highly toxic for fish. Salts of metals some of this group are mainly accumulated in all organs, Cr showed high extremely toxic for fish, showing their action even at the concentration in same organs gills and muscles. concentration from mg\l. Cadmium (Cd) is a little less toxic and it has damaging influence at the metal DISCUSSION concentration from mg\l. Apparently from the following data, Iron (Fe) shows The mean concentrations of majority of the heavy the greatest ability to accumulate mg/kg for test metals in different organs of Sander Lucioperca L. and objects from Atyrau zone, as shows the second site of the Neogobius Melanostomus P., (Tables 1 & 2) were found research zone in Aktau city, accumulation ability to be relatively low and within the ranges of the mg/kg, the level of the content and excess of the given geochemical background values [5]. Nonetheless, the element remains at the low level in bodies. The content of content of the following elements: Mn, Zn, Ni, Pb and Sr Fe, in control groups, remains at the rather low level and were high in muscles and gills of the studied fish. Other actually, does not exceed the maximum concentration limit organs of both species of the fish were also high in Pb, that is similar to types Sander lucioperca L. and Mn, Zn and Sr. Toxic concentration of Mn was found in Neogobius melanostomus P. (Table 1, Table 2). gills, while Pb exceeded toxicity threshold in the gonads. It is necessary to notice that on the toxicity degree Nonetheless, transfer of some elements from the water iron (Fe) does not represent so high danger both for sediments into the fish organs tissues appeared to be hydrocoles and for a human being, the maximum supply dependent. Statistically significant correlations concentration limit of Fe is 50 mg \kg, in comparison with which were noted between concentrations of the zinc, manganese and lead (Zn, Mn, Pb). It is well-known following metals: Zn, Mn, Pb, Ni and Sr in the water that in an organism of animals iron (Fe) is a part of set of sediments and their content in the below organs of enzymes which participate in oxidation-reduction Sander lucioperca L. and Neogobius melanostomus reactions, mainly in the course of breath. So the high P., suggested that water sediments may be the main concentration of iron as well as other salts of heavy pollution source of these elements for the fish organism. metals, is quite predicted and also thanks to the in the This supports findings, that postulated that the elements leading content of ions of iron in stratum waters arriving taken during the life inhabitant of the fish were mainly to the Caspian sea at oil extracting. Higher concentration became from water sediment derived [6]. of the given metal in organisms collected from bottom Mn is another essential microelement for fishes being sites, are explained by fast transition of dissolved ionic involved in enzyme activity. Water, however seems to be forms Fe (II) and Fe (III) into a deposit in the form of a meaningful source of Mn element for Sander lucioperca various complexes with organic substances. L. and Neogobius melanostomus P., fish species, as 127
6 significant correlation between the content of Mn in the by 42.7% compared to gills and muscles. Zinc mobility water sediments and the sampled fish was noted in this within the fish tissues is low and therefore its study. As far as Ni is concerned, significant, positive translocation ability in the studied organs is reduced. correlations between content of this element in the water Therefore Sander lucioperca L., can be considered as sediments and it s concentration in the gills, muscles and gonads accumulator with regard to Zn, likewise reproductive organs (gonads). Both high content of Mn Neogobius melanostomus P., where concentration of Zn, in the gills and muscles of Sander lucioperca L. and also revealed in higher concentrations, but in lower Neogobius melanostomus P., representing the highest proportion. Zinc showed significant correlations between value compared to the other calculated in this study, the concentration values in the gills and muscles (r = 0.97; suggest availability of this metal to fishes from the water p<0.05) as well as gonads (r=0.71; p<0.05), therefore sediments and noticeable ability of fish for its uptake and reproductive organs (gonads) of studied fishes can be accumulation. The results for Sander Lucioperca L. and used as bio indicator of environmental contamination. Neogobius melanostomus P., studied herein have also Copper is an essential element for many fish species revealed highest Mn concentration in the Neogobius growth and occurs in enzymes of oxidation reduction melanostomus P fish species as well. Nonetheless, the reactions. In the present research, the non-highest highest content of Mn was found in the gills and concentration of Cu was noted again in Sander muscles tissue of Neogobius melanostomus P fish lucioperca L. and Neogobius melanostomus P., species species. The Mn content in gills and muscle tissue of gonads, which have appeared as some kind of Neogobius melanostomus P. was estimated to be 75% accumulative center, for preventing translocation of Cu lower than in gills and muscle tissue of Sander and many other studied heavy metals types, into the lucioperca L. specie. Accumulative factor for the gills and reproductive organs of both fish species. The previous muscle tissue was much higher than that for the findings corresponded that Cu has relatively low mobility reproductive organs (gonads) in both studying species. and being accumulated mainly in reproductive organs [8]. Manganese showed linearly correlated concentrations in In the present research Sander lucioperca L., values for the water sediments and gills, muscle tissues, suggesting Cu (Table 1) were quite similar accumulation of this metal potential use of this organs of in bio indication of trace compared to the Neogobius melanostomus P., presented elements (r = 0.75; p < 0.05). in the (Table 2), indicating relatively similar mobility of Cu Iron (Fe) is vital for the fish development playing a within organs tissue in both mentioned fish species. key role in processes of energy transformations Copper is a vital microelement for many aquatic organisms needed for synthesis and other life process of the cells. and its mobility observed in this study can be explained The analysis carried out herein showed that Fe has been by its active transport to fish organs. The content of Cu accumulated in muscle and gonads of both species to the in the water samples was correlated with its concentration highest extent. Concentration of this element in the in the organs (r = 0.84; p < 0.05) therefore gonads of both Sander lucioperca L. and Neogobius melanostomus P., species, can be used in bio indication of Cu pollution in organs was estimated to be higher than values for both the environment. species from unpolluted water areas [7]. The TF values for Cadmium is a highly toxic and non-essential element iron were estimated to be very low supporting findings, effecting growth, metabolism as well [9]. Results of this which are reported slow translocation of Fe within fish s study show that gills of Sander lucioperca L. and body and its tendency to accumulate in their inner organs Neogobius melanostomus P., can accumulate more higher [8]. amounts of Cd, proportionally to its concentrations in the Zinc is an essential element for many organisms muscle and reproductive tissues (significant, positive growth being actively taken up by the living organisms correlation between the content of Cd in the muscles, during their lifecycle. High gonads/gills/muscles ratio and gonads and the fish s gills) (r=0.72; p<0.05). The content the highest concentration of Zn in abovementioned of Cd in the water sediments was about to 27.4% and its organs, of the studied fish revealed that Zn was easily concentration was below the detection threshold. taken up by the Sander lucioperca L., in compare to The concentrations of Pb, noted in Sander Neogobius melanostomus P. It is likely that the lucioperca L., organs decreasing in the following order: reproductive organs acted as some kind of absorption gonads - muscles - gills, but in second fish organs point, because Zn concentration in gonads was increased Neogobius melanostomus P., the contamination of Pb 128
7 revealed the same concentration in muscles and gills Chromium (Cr ), is an element regarded as toxic tissues, (Table 2), with the lowest concentrations found and mutagenic chemical element for many living in gonads (gills-muscles-gonads). This scheme of Pb organisms. In contamination of Chromium in studied accumulation could be linked to its intensive mobility, organs of Neogobius melanostomus P., were found to pretty similar to mobility of Mn, Zn, Ni and Sr, apparently contain high amounts of Cr,in significantly higher affecting its transport rate within the main fish organs. proportions than in Sander lucioperca L., from point of Lead showed linearly correlated concentrations in water Central Caspian sea waters. Similar high concentrations of sediment and abovementioned organs suggesting Cr in gills and muscles tissues (Table 2) as well as high potential use these organs of Sander lucioperca L. and sea water sediment ratio suggest that Neogobius Neogobius melanostomus P., as a bio indicator of melanostomus P., can be considered a mostly external environmental contamination by metals (r = 0.57; p < 0.05). bodies accumulator for Cr. The analysis also revealed The mobility of Ni in studied fish species varies from that Cr was accumulated predominantly in the being mobile in some aquatic organisms to immobile in reproductive organs of Sander lucioperca L., in compare other water species. In this research, Ni showed similar to previous fish species and the metal content decreased mobile activity in both organisms Sander lucioperca according to the following pattern: gonads, gills and L. and Neogobius melanostomus P., showing a lower muscle tissues. value in all studied organs of Neogobius Strontium is one of the radioactively chemical melanostomus P. (Table 2). Similar results have been elements as well. Strontium - a component of microobtained by other investigators [10]. The concentration of organisms, plants and animals. In marine radiolarians Ni in sea water sediments of the examined reservoir also (acantharians) skeleton is composed of strontium sulfate - was positively correlated with its concentration in organs celestite. Algae contain mg strontium per 100 g of (r = 0.63; p < 0.05). The observed relation suggests a dry matter, terrestrial plants - 2.6, marine animals , possibility of using these organs of Sander lucioperca L. terrestrial animals - 1.4, bacteria Accumulation and Neogobius melanostomus P., in bio indication Strontium various organisms depends not only on its process. type, characteristics, but the ratio among strontium with Regarding Co and its biochemical function, it is not other elements, mainly Ca and P, as well as the adaptation clear whether Co is essential for many water living of the organisms to certain geochemical organisms, including two studied fish species, although environment.animals get Strontium from food and water. there are some evidences of a favorable effect of this Strontium is absorbed with thin and allocated mainly the metal on fish growth. In this research, the maximum large intestine. A number of substances (polysaccharides quantity of this element concentration was found in algae, cation exchange resins) prevent the absorption of muscles, reproductive tissues and gills of Sander strontium. As a result of accumulation ability Sr showed lucioperca L. and it s very low concentration value in all the highest concentration in muscle tissue and organs of Neogobius melanostomus P. The reason for the reproductive organs and the lower percent in gills in high accumulation rate in the muscles could be its big Neogobius melanostomus P., fish species, the immobilization ability in the research area of Northern accumulation result in organs of Sander lucioperca L., Caspian Sea in compare to Central parts of the Sea. Cobalt showed completely different picture, concentration of Sr is also easily taken up by the aquatic organisms through in compare to previous unit, presented lowest the epithelium tissue and can further absorb in internal concentration in all studied organs, in following organs, including reproductive part. This seems to be proportions: gills - muscle tissue gonads, in compare to confirmed by the statistically significant correlation Neogobius melanostomus P. between the content of Co in the sea water sediments and its concentration in the muscle tissue in this study (r = CONCLUSION 0.76; p < 0.05). Other significant correlations found between the content of Co in the sea water and The received results allow making the following reproductive organs (r = 0.70; p < 0.05) and gills (r = 0.55; conclusions: p < 0.05) suggest potential use of Sander lucioperca L. From the resulted complex analysis of accumulation and Neogobius melanostomus P., organs in and migration of salts of heavy metals in fabrics of sorts environmental bio indication of Co contamination. Sander lucioperc L., it is possible make up the degree of 129
8 sequence of accumulation of the given elements: Fe> Zn> REFERENCES Mn> Ni> Pb> Cr> Co> Sr> Cu> Cd and Neogobius melanostomus P., Sr> Pb> Mn> Fe> Zn> Ni> Cr > Cu> 1. Al-Mohanna, M.M., Residues of some heavy Cd> Co. metals in fishes collected from (Red Sea Coast) Jisan, There was revealed excess, as a whole, of elements Saudi Arabia, J. Environ. Biol., 15: Mn, Pb, Zn, Ni, Fe, Sr, Cr 3 + from ten investigated metals. 2. Vardanyan, L.G. and B.S. Ingole, Studies on The content of Fe, Zn, Pb and Ni exceeds the maximum heavy metal accumulation in aquatic organisms from concentration limit in 70% of the investigated test Sevan (Armenia) and Carambolim (India) lake objects and the content of Cu, Co and Cd is less than at systems. Environ. Int., 32: %. Fe shows the greatest accumulative activity (on the 3. Canli, M. and G. Atli, The relationships between average of up to mg/kg), mostly in Sander heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Pb, Zn) levels and the lucioperc L., organs and highest accumulative activity size of six Mediterranean fish species, Environ. of strontium Sr (on the average of up to Pollut., 121: mg/kg), in Neogobius melanostomus P., organs. 4. STATISTICA (Data Analysis Software System), The significant, positive correlations found between Version the content of Mn, Zn, Pb, Ni, Cr, Sr in the studied 5. Kabata-Pendias, A., B.A. Manny and environment and the levels of these elements in the A.B. Mukherjee, Heavy metals in aquatic organs of these fishes indicate the potential use of macrophytes drifting in a large river. Hydrobiologia, Sander lucioperc L. and Neogobius melanostomus P in 219: biomonitoring of environmental contamination with these 6. Ray, S., D.W. McLeese and M.R. Peterson, metals. Accumulation of copper, zinc, cadmium and lead from two contaminated sediments by three marine ACKNOWLEDGMENT invertebrates. A laboratory study//bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. V, 26.(5): The study presented here is part of the dissertation 7. Szymanowska, A., A. Samecka-Cymerman and in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of A.J. Kempers, Heavy Metals in Three Lakes in Ph.D. The author expresses his great appreciation to: West Poland. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe., 43: Institute of Environmental Research and Modern 8. Demirezen, D. and A. Aksoy, Bioaccumulation, Ecological Investigation and Laboratory of Molecular detection and analyses of heavy metal pollution in Biology and Genetics (Al-Faraby Kazakh National sultan marsh and its environment. Water Air Soil University), sponsor help through the project Pollution, 164: Environmental Governance and genetically monitoring in 9. Divan, A.M., de P.L. Oliveira, C.T. Perry, V.L. Atz, the Asian Hydrosphere (Republic of Kazakhstan). Also L.N. Azzarini-Rostirola and M.T. Raya-Rodriguez, thanks the university authorities for the supported Using wild species as indicators for facilities provided to carry out this investigation research. accumulation of emissions from thermal power plant, Candiota, South Brazil. Ecol. Indic., 9: Bonanno, G. and R.L. Giudice, Heavy metal bioaccumulation by the organs of Phragmites australis (common reed) and their potential use as contamination indicators. Ecol. Indic., 10:
Determination of available nutrients in soil using the Agilent 4200 MP-AES
 Determination of available nutrients in soil using the Agilent 4200 MP-AES Application note Agriculture Author Dharmendra Vummiti Agilent Technologies, India Introduction Multielement testing of soil samples
Determination of available nutrients in soil using the Agilent 4200 MP-AES Application note Agriculture Author Dharmendra Vummiti Agilent Technologies, India Introduction Multielement testing of soil samples
VOL. 5, NO. 6, June 2015 ISSN ARPN Journal of Science and Technology All rights reserved.
 VOL. 5, NO. 6, June 2015 ISSN 22-7217 Impact of Cumulative Sediment Deposition by Irrigation Water on Soil and Sugarcane in Savannah Sugar Company Limited; Numan, Adamawa State Nigeria 1 R.P. Ali, 2 H.M.
VOL. 5, NO. 6, June 2015 ISSN 22-7217 Impact of Cumulative Sediment Deposition by Irrigation Water on Soil and Sugarcane in Savannah Sugar Company Limited; Numan, Adamawa State Nigeria 1 R.P. Ali, 2 H.M.
Immobilizing Arsenic in Contaminated Soil Using Humic Mineral Concentrates
 Immobilizing in Contaminated Soil Using Humic Mineral Concentrates Alexander I.Shulgin 1 and D. Joseph Hagerty 2, F. ASCE, PE 1. Research Professor, Chemical Engineering Dept., U. Louisville, Louisville,
Immobilizing in Contaminated Soil Using Humic Mineral Concentrates Alexander I.Shulgin 1 and D. Joseph Hagerty 2, F. ASCE, PE 1. Research Professor, Chemical Engineering Dept., U. Louisville, Louisville,
Assessment of heavy metal contaminants from protein sources.
 Short commentary http://www.alliedacademies.org/food-technology-and-preservation/ Assessment of heavy metal contaminants from protein sources. Zeeshan Umer*, Marriam Wasif, Saif-ur-Rehman Kashif, Saman
Short commentary http://www.alliedacademies.org/food-technology-and-preservation/ Assessment of heavy metal contaminants from protein sources. Zeeshan Umer*, Marriam Wasif, Saif-ur-Rehman Kashif, Saman
Heavy Metal Uptake in Lake Macatawa Fish
 Heavy Metal Uptake in Lake Macatawa Fish Homkes, A., Kreb, R., and Mulcahy, C. Department of Geological and Environmental Sciences, Hope College, Holland, MI 49423, USA The purpose of this study was to
Heavy Metal Uptake in Lake Macatawa Fish Homkes, A., Kreb, R., and Mulcahy, C. Department of Geological and Environmental Sciences, Hope College, Holland, MI 49423, USA The purpose of this study was to
HEAVY METAL RESIDUES OF CHICKEN MEAT AND GIZZARD AND TURKEY MEAT CONSUMED IN SOUTHERN NIGERIA
 Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2008), 11, No 4, 275 280 Short communication HEAVY METAL RESIDUES OF CHICKEN MEAT AND GIZZARD AND TURKEY MEAT CONSUMED IN SOUTHERN NIGERIA Summary C. M. A. IWEGBUE,
Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2008), 11, No 4, 275 280 Short communication HEAVY METAL RESIDUES OF CHICKEN MEAT AND GIZZARD AND TURKEY MEAT CONSUMED IN SOUTHERN NIGERIA Summary C. M. A. IWEGBUE,
Transfer of Some Major and Trace Elements From Phosphate Rock to Super-Phosphate Fertilizers
 Transfer of Some Major and Trace Elements From Phosphate Rock to Super-Phosphate Fertilizers H.I. El-reefy a, A.A. Bin-Jaza b, M.E.Zaied c, and H.M. Badran c,d,* a Hot Laboratories Center, Atomic Energy
Transfer of Some Major and Trace Elements From Phosphate Rock to Super-Phosphate Fertilizers H.I. El-reefy a, A.A. Bin-Jaza b, M.E.Zaied c, and H.M. Badran c,d,* a Hot Laboratories Center, Atomic Energy
Lead and Cadmium Levels in Some Commercially Available Local and Imported Peach Juice Samples in Alkoms City
 Human Journals Research Article September 2018 Vol.:13, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Zaid M. Najah et al. Lead and Cadmium Levels in Some Commercially Available Local and Imported Peach Juice Samples
Human Journals Research Article September 2018 Vol.:13, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Zaid M. Najah et al. Lead and Cadmium Levels in Some Commercially Available Local and Imported Peach Juice Samples
Bottom Ash Data Week 37
 Bottom Ash Data 2018 Week 37 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on October 2, 2018. The data represents bottom ash composite results for
Bottom Ash Data 2018 Week 37 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on October 2, 2018. The data represents bottom ash composite results for
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(2):397-402 Analysis of heavy metals in citrus juice from
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(2):397-402 Analysis of heavy metals in citrus juice from
JORIND 9(2) December, ISSN
 SEQUENTIAL EXTRACTION OF Cu, Cd, Pb AND Zn FROM SOIL AROUND INDUSTRIAL WASTE DUMP SITES IN KADUNA ENVIRON USING SIMPLE AND SEQUENTIAL PROCEDURES. H.A Zakari, D.D. Adams, M Shimbayev, P. Nyam Department
SEQUENTIAL EXTRACTION OF Cu, Cd, Pb AND Zn FROM SOIL AROUND INDUSTRIAL WASTE DUMP SITES IN KADUNA ENVIRON USING SIMPLE AND SEQUENTIAL PROCEDURES. H.A Zakari, D.D. Adams, M Shimbayev, P. Nyam Department
USER SPECIFICATIONS FOR QUINTOLUBRIC 888 Series DESCRIPTION OF THE MOST IMPORTANT PROPERTIES AND THE POSSIBLE VARIATIONS AND TOLERANCES
 USER SPECIFICATIONS FOR QUINTOLUBRIC 888 Series OVERVIEW The QUINTOLUBRIC 888 Series of fluids are based on a synthetic organic ester, which is the main base component, plus a number of selected additives
USER SPECIFICATIONS FOR QUINTOLUBRIC 888 Series OVERVIEW The QUINTOLUBRIC 888 Series of fluids are based on a synthetic organic ester, which is the main base component, plus a number of selected additives
Multi Analyte Custom Grade Solution
 1.0 ACCREDITATION / REGISTRATION INORGANIC VENTURES is accredited to ISO Guide 34, "General Requirements for the Competence of Reference Material Producers" and ISO/IEC 17025, "General Requirements for
1.0 ACCREDITATION / REGISTRATION INORGANIC VENTURES is accredited to ISO Guide 34, "General Requirements for the Competence of Reference Material Producers" and ISO/IEC 17025, "General Requirements for
International Journal of Engineering Research & Science (IJOER) ISSN: [ ] [Vol-2, Issue-12, December- 2016]
![International Journal of Engineering Research & Science (IJOER) ISSN: [ ] [Vol-2, Issue-12, December- 2016] International Journal of Engineering Research & Science (IJOER) ISSN: [ ] [Vol-2, Issue-12, December- 2016]](/thumbs/72/67841640.jpg) Determination of the total chromium in vegetable, rice samples cultivated and marketed along Nhue River Khuat Quang Son 1, Dinh Thi Thu Hien 2, Dao Van Bay 3* 1 PhD student, 2 Graduate student Faculty
Determination of the total chromium in vegetable, rice samples cultivated and marketed along Nhue River Khuat Quang Son 1, Dinh Thi Thu Hien 2, Dao Van Bay 3* 1 PhD student, 2 Graduate student Faculty
DETERMINATION OF SOME HEAVY METALS IN SPINACH AND LETTUCE FROM SELECTED MARKETS IN KADUNA METROPOLIS Z. N.
 DETERMINATION OF SOME HEAVY METALS IN SPINACH AND LETTUCE FROM SELECTED MARKETS IN KADUNA METROPOLIS Z. N. Ali, F.M. Abdulkadir and M. M. Imam Department of Applied Science, College of Science and Technology,
DETERMINATION OF SOME HEAVY METALS IN SPINACH AND LETTUCE FROM SELECTED MARKETS IN KADUNA METROPOLIS Z. N. Ali, F.M. Abdulkadir and M. M. Imam Department of Applied Science, College of Science and Technology,
Mercury, Cadmium and Lead Levels in Three Commercially Important Marine Fish Species of in Sri Lanka
 Sri Lanka J. Aquat. Sci. 15 (2010): 39-43 Mercury, Cadmium and Lead Levels in Three Commercially Important Marine Fish Species of in Sri Lanka B.K.K.K. JINADASA 1*, L.R.S. RAMEESHA 2, E.M.R.K.B. EDIRISINGHE
Sri Lanka J. Aquat. Sci. 15 (2010): 39-43 Mercury, Cadmium and Lead Levels in Three Commercially Important Marine Fish Species of in Sri Lanka B.K.K.K. JINADASA 1*, L.R.S. RAMEESHA 2, E.M.R.K.B. EDIRISINGHE
Bottom Ash Data Week 30
 Bottom Ash Data 2018 Week 30 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on August 14, 2018. The data represents bottom ash composite results for
Bottom Ash Data 2018 Week 30 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on August 14, 2018. The data represents bottom ash composite results for
Edward V. Krizhanovsky, Ph.D., Kamila B. Tursunova
 REPORT ON RESEARCH OF BAE SYNERGY LIQUID PREPARATION INFLUENCE ON MINERAL METABOLISM Edward V. Krizhanovsky, Ph.D., Kamila B. Tursunova Bioenergy Technologies Institute, Sveaborgskaia, 12, Saint- Petersburg,
REPORT ON RESEARCH OF BAE SYNERGY LIQUID PREPARATION INFLUENCE ON MINERAL METABOLISM Edward V. Krizhanovsky, Ph.D., Kamila B. Tursunova Bioenergy Technologies Institute, Sveaborgskaia, 12, Saint- Petersburg,
Introduction of Daehan Salty Mineral Water. It s healthy water similar to body fluids!!!
 Introduction of Daehan Salty Mineral Water It s healthy water similar to body fluids!!! * What is DeepWater (Korean Patent No.: 2003-0078020)? Daehan salty mineral water(deepwater) has 0.9% salinity and
Introduction of Daehan Salty Mineral Water It s healthy water similar to body fluids!!! * What is DeepWater (Korean Patent No.: 2003-0078020)? Daehan salty mineral water(deepwater) has 0.9% salinity and
Test Report No.T JP Date: FEB 22, 2017 Page 1 of 6
 Test Report No.T51710190051JP Date: FEB 22, 2017 Page 1 of 6 JIAN PLASTIC & METAL PRODUCTS LTD NO.3-1, SOUTH GAOBU BLVD, GAOBU TOWN, DONGGUAN CITY, GUANGDONG PROVINCE, CHINA,ZIP CODE:523278 The following
Test Report No.T51710190051JP Date: FEB 22, 2017 Page 1 of 6 JIAN PLASTIC & METAL PRODUCTS LTD NO.3-1, SOUTH GAOBU BLVD, GAOBU TOWN, DONGGUAN CITY, GUANGDONG PROVINCE, CHINA,ZIP CODE:523278 The following
ELEMENTAL COMPOSITION IN VARIOUS THALLUS PARTS OF THREE BROWN SEAWEEDS FROM KARACHI COAST
 Pak. J. Bot., 42(6): 4177-4181, 2010. ELEMENTAL COMPOSITION IN VARIOUS THALLUS PARTS OF THREE BROWN SEAWEEDS FROM KARACHI COAST MUHAMMAD AFZAL RIZVI 1 AND MUSTAFA SHAMEEL 2 1 Hamdard Research Institute
Pak. J. Bot., 42(6): 4177-4181, 2010. ELEMENTAL COMPOSITION IN VARIOUS THALLUS PARTS OF THREE BROWN SEAWEEDS FROM KARACHI COAST MUHAMMAD AFZAL RIZVI 1 AND MUSTAFA SHAMEEL 2 1 Hamdard Research Institute
Bottom Ash Data Week 38
 Bottom Ash Data 2018 Week 38 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on October 4, 2018. The data represents bottom ash composite results for
Bottom Ash Data 2018 Week 38 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on October 4, 2018. The data represents bottom ash composite results for
STANDARD METHODS FOR CHEMICAL ELEMENTS IN FOOD OF ANIMAL ORIGIN
 EN 13804 Performance criteria, general considerations and sample preparation 2013 EN 13805 Pressure digestion 2014 EN 13806 Determination of mercury by cold-vapour atomic absorption spectrometry (CVAAS)
EN 13804 Performance criteria, general considerations and sample preparation 2013 EN 13805 Pressure digestion 2014 EN 13806 Determination of mercury by cold-vapour atomic absorption spectrometry (CVAAS)
Bottom Ash Data Week 17
 Bottom Ash Data 2018 Week 17 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on May 16, 2018. The data represents bottom ash composite results for week
Bottom Ash Data 2018 Week 17 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on May 16, 2018. The data represents bottom ash composite results for week
Bottom Ash Data Week 9
 Bottom Ash Data 2018 Week 9 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on March 26, 2018. The data represents bottom ash composite results for week
Bottom Ash Data 2018 Week 9 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on March 26, 2018. The data represents bottom ash composite results for week
Detection of heavy metals in honey samples using Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS)
 Research Article Open Access Received: November 16, 2017 Accepted: December 22, 2017 Published: December 28, 2017 Detection of heavy metals in honey samples using Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry
Research Article Open Access Received: November 16, 2017 Accepted: December 22, 2017 Published: December 28, 2017 Detection of heavy metals in honey samples using Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry
Bio-accessibility of Trace Metals Using Chemical Fractionation and In Vitro Extraction Methods
 Bio-accessibility of Trace Metals Using Chemical Fractionation and In Vitro Extraction Methods Naomi Waissman Assadian 1 and Juan Pedro Flores Margez 2 Abstract Rural and urban border communities at Paso
Bio-accessibility of Trace Metals Using Chemical Fractionation and In Vitro Extraction Methods Naomi Waissman Assadian 1 and Juan Pedro Flores Margez 2 Abstract Rural and urban border communities at Paso
CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS. tel: fax:
 CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS 300 Technology Drive Christiansburg, VA 24073. USA inorganicventures.com tel: 800.669.6799. 540.585.3030 fax: 540.585.3012 info@inorganicventures.com 1.0 ACCREDITATION / REGISTRATION
CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS 300 Technology Drive Christiansburg, VA 24073. USA inorganicventures.com tel: 800.669.6799. 540.585.3030 fax: 540.585.3012 info@inorganicventures.com 1.0 ACCREDITATION / REGISTRATION
ISSN (Print), ISSN (online) 1 Okeke O.R. and 2 Okeke M.U.
 ESTIMATION OF THE DIETARY INTAKES OF HEAVY METALS BY CHILDREN, ADOLESCENTS, ADULTS AND SENIORS CONSUMING CHICKEN MEATS WITHIN AWKA AND ENUGU METROPOLIS AND ITS ENVIRONS. 1 Okeke O.R. and 2 Okeke M.U. 1
ESTIMATION OF THE DIETARY INTAKES OF HEAVY METALS BY CHILDREN, ADOLESCENTS, ADULTS AND SENIORS CONSUMING CHICKEN MEATS WITHIN AWKA AND ENUGU METROPOLIS AND ITS ENVIRONS. 1 Okeke O.R. and 2 Okeke M.U. 1
Bottom Ash Data Week 49
 Bottom Ash Data 2018 Week 49 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on December 20, 2018. The data represents bottom ash composite results for
Bottom Ash Data 2018 Week 49 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on December 20, 2018. The data represents bottom ash composite results for
Bottom Ash Data Week 40
 Bottom Ash Data 2018 Week 40 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on October 25, 2018. The data represents bottom ash composite results for
Bottom Ash Data 2018 Week 40 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on October 25, 2018. The data represents bottom ash composite results for
Bottom Ash Data Week 1
 Bottom Ash Data 2019 Week 1 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on January 17, 2019. The data represents bottom ash composite results for
Bottom Ash Data 2019 Week 1 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on January 17, 2019. The data represents bottom ash composite results for
by Oguguah, N. M. and Olakolu, F. C. Marine Biology section, Fisheries Resources Department, Nigerian Institute for Oceanography and Marine Research
 Heavy Metal (Pd, Cd, Fe, Zn And Mn) Levels in Shrimp By-Catch SppFrom Industrial Shrimp Trawl Fishery in Nigerian Coastal Waters by Oguguah, N. M. and Olakolu, F. C. Marine Biology section, Fisheries Resources
Heavy Metal (Pd, Cd, Fe, Zn And Mn) Levels in Shrimp By-Catch SppFrom Industrial Shrimp Trawl Fishery in Nigerian Coastal Waters by Oguguah, N. M. and Olakolu, F. C. Marine Biology section, Fisheries Resources
Trace Elements in Manure
 Trace Elements in Manure Purpose: Whenever soil profiles are examined for nutrient trace elements, it has been demonstrated that the metals tend to accumulate in the topsoil. Soil properties affect plant
Trace Elements in Manure Purpose: Whenever soil profiles are examined for nutrient trace elements, it has been demonstrated that the metals tend to accumulate in the topsoil. Soil properties affect plant
Test Report No.T JP Date: FEB 24, 2017 Page 1 of 6
 Test Report No.T51710190071JP Date: FEB 24, 2017 Page 1 of 6 JIAN PLASTIC & METAL PRODUCTS LTD NO.3-1, SOUTH GAOBU BLVD, GAOBU TOWN, DONGGUAN CITY, GUANGDONG PROVINCE, CHINA,ZIP CODE:523278 The following
Test Report No.T51710190071JP Date: FEB 24, 2017 Page 1 of 6 JIAN PLASTIC & METAL PRODUCTS LTD NO.3-1, SOUTH GAOBU BLVD, GAOBU TOWN, DONGGUAN CITY, GUANGDONG PROVINCE, CHINA,ZIP CODE:523278 The following
ANALYSIS OF POTENTIAL CARCINOGENIC CONTAMINANTS IN GRAIN AND VEGETABLES WITH FOCUS ON HEAVY METALS
 ANALYSIS OF POTENTIAL CARCINOGENIC CONTAMINANTS IN GRAIN AND VEGETABLES WITH FOCUS ON HEAVY METALS N. Belc, V. Ionescu, M. Ionescu, E. Iorga and G. Mustatea National R&D Institute for Food Bioresources,
ANALYSIS OF POTENTIAL CARCINOGENIC CONTAMINANTS IN GRAIN AND VEGETABLES WITH FOCUS ON HEAVY METALS N. Belc, V. Ionescu, M. Ionescu, E. Iorga and G. Mustatea National R&D Institute for Food Bioresources,
Leaching Behavior of Coal Combustion Products and the Environmental Implication in Road Construction. Project Progress Report. Jianmin Wang NUTC R201
 Leaching Behavior of Coal Combustion Products and the Environmental Implication in Road Construction Project Progress Report by Jianmin Wang NUTC R21 Disclaimer The contents of this report reflect the
Leaching Behavior of Coal Combustion Products and the Environmental Implication in Road Construction Project Progress Report by Jianmin Wang NUTC R21 Disclaimer The contents of this report reflect the
Speciation Analysis and Removal of Heavy Metals Zn, Cu, Cd from Sludge by Organic Acid
 5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2015) Speciation Analysis and Removal of Heavy Metals Zn, Cu, Cd from Sludge by Organic Acid S.W. SONG 1*, L. WANG
5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2015) Speciation Analysis and Removal of Heavy Metals Zn, Cu, Cd from Sludge by Organic Acid S.W. SONG 1*, L. WANG
CHROMIUM AND ZINC UPTAKE IN ELODEA DENSA AND CERATOPHYLLUM DEMERSUM : APPLICATIONS FOR BIOREMEDIATION
 CHROMIUM AND ZINC UPTAKE IN ELODEA DENSA AND CERATOPHYLLUM DEMERSUM : APPLICATIONS FOR BIOREMEDIATION Jorie Wilson & Dr. James Moore Bioresource Research and Bioresource Engineering, Oregon State University,
CHROMIUM AND ZINC UPTAKE IN ELODEA DENSA AND CERATOPHYLLUM DEMERSUM : APPLICATIONS FOR BIOREMEDIATION Jorie Wilson & Dr. James Moore Bioresource Research and Bioresource Engineering, Oregon State University,
Assessment of Heavy Metals in Trona from Yobe State, Nigeria
 International Journal of Innovative Environmental Studies Research 6(1):10-15, Jan.-Mar., 2018 SEAHI PUBLICATIONS, 2018 www.seahipaj.org ISSN: 2354-2918 Assessment of Heavy Metals in Trona from Yobe State,
International Journal of Innovative Environmental Studies Research 6(1):10-15, Jan.-Mar., 2018 SEAHI PUBLICATIONS, 2018 www.seahipaj.org ISSN: 2354-2918 Assessment of Heavy Metals in Trona from Yobe State,
Soil Conditions Favoring Micronutrient Deficiencies and Responses in 2001
 Soil Conditions Favoring Micronutrient Deficiencies and Responses in 2001 K.A. Kelling and P.E. Speth Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin-Madison Why micronutrients now: Higher yield, therefore
Soil Conditions Favoring Micronutrient Deficiencies and Responses in 2001 K.A. Kelling and P.E. Speth Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin-Madison Why micronutrients now: Higher yield, therefore
Test Report No.T TC Date: JUN 29, 2018 Page 1 of 5
 Test Report No.T31820241114TC Date: JUN 29, 2018 Page 1 of 5 POLYKOTE INK & PAINT (SHENZHEN) LTD. NO. 118, HUANG PU ROAD, SHAJING SUBDISTRICT, BAOAN, SHENZHEN, 518125, CHINA The following samples were
Test Report No.T31820241114TC Date: JUN 29, 2018 Page 1 of 5 POLYKOTE INK & PAINT (SHENZHEN) LTD. NO. 118, HUANG PU ROAD, SHAJING SUBDISTRICT, BAOAN, SHENZHEN, 518125, CHINA The following samples were
Bottom Ash Data Week 8
 Bottom Ash Data 2019 Week 8 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on March 6, 2019. The data represents bottom ash composite results for week
Bottom Ash Data 2019 Week 8 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on March 6, 2019. The data represents bottom ash composite results for week
GB Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE
 Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.268-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Buy True-PDF Auto-delivery. Sales@ChineseStandard.net GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 5009.268-2016
Translated English of Chinese Standard: GB5009.268-2016 www.chinesestandard.net Buy True-PDF Auto-delivery. Sales@ChineseStandard.net GB NATIONAL STANDARD OF THE PEOPLE S REPUBLIC OF CHINA GB 5009.268-2016
Patterns of Trace Metals Accumulation in Different Trophic Levels of Lake Kailana, Jodhpur (India)
 Sengupta, M. and Dalwani, R. (Editors). 28. Proceedings of Taal27: The 12 th World Lake Conference: 373-377 Patterns of Trace Metals Acmulation in Different Trophic Levels of Lake Kailana, Jodhpur (India)
Sengupta, M. and Dalwani, R. (Editors). 28. Proceedings of Taal27: The 12 th World Lake Conference: 373-377 Patterns of Trace Metals Acmulation in Different Trophic Levels of Lake Kailana, Jodhpur (India)
Bottom Ash Data Week 12
 Bottom Ash Data 2019 Week 12 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on April 11, 2019. The data represents bottom ash composite results for
Bottom Ash Data 2019 Week 12 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on April 11, 2019. The data represents bottom ash composite results for
Application note. Determination of metals in soil by microwave plasma - atomic emission spectrometry (MP-AES) using DTPA extraction.
 Determination of metals in soil by microwave plasma - atomic emission spectrometry (MP-AES) using DTPA extraction Application note Agriculture Authors Marília S. Teodoro1, Daniela Schiavo2, Mônica Ferreira
Determination of metals in soil by microwave plasma - atomic emission spectrometry (MP-AES) using DTPA extraction Application note Agriculture Authors Marília S. Teodoro1, Daniela Schiavo2, Mônica Ferreira
RemovalofToxicMetalsContaminatedSoilusingDifferentAmendmentsandSunflowerSpeciesHelianthusAnnuus
 Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: H Environment & Earth Science Volume 16 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: H Environment & Earth Science Volume 16 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Uptake Potential of Some Heavy Metals by Vetiver Grass
 asetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 35 : 46-5 (21) Uptake Potential of Some Heavy Metals by Vetiver Grass Nualchavee Roongtanakiat 1 and Prapai Chairoj 2 ABSTRACT The uptake potential of upland vetiver grass (Vetiveria
asetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 35 : 46-5 (21) Uptake Potential of Some Heavy Metals by Vetiver Grass Nualchavee Roongtanakiat 1 and Prapai Chairoj 2 ABSTRACT The uptake potential of upland vetiver grass (Vetiveria
Analysis of trace elements in nutraceuticals in compliance with USP chapter <2232> Elemental Contaminants in Dietary Supplements
 APPLICATION NOTE 43445 Analysis of trace elements in nutraceuticals in compliance with USP chapter Elemental Contaminants in Dietary Supplements Authors Sanja Asendorf, Application Specialist, Thermo
APPLICATION NOTE 43445 Analysis of trace elements in nutraceuticals in compliance with USP chapter Elemental Contaminants in Dietary Supplements Authors Sanja Asendorf, Application Specialist, Thermo
Seasonal variation of heavy metal concentration in Labeo rohita and Edaphodon kawai fishes of River Yamuna, Allahabad, Utter Pradesh
 IOSR Journal of Environmental Science, Toxicology and Food Technology (IOSR-JESTFT) e-issn: 39-4,p- ISSN: 39-399.Volume 8, Issue 6 Ver. II (Jun. 4), PP 7-34 Seasonal variation of heavy metal concentration
IOSR Journal of Environmental Science, Toxicology and Food Technology (IOSR-JESTFT) e-issn: 39-4,p- ISSN: 39-399.Volume 8, Issue 6 Ver. II (Jun. 4), PP 7-34 Seasonal variation of heavy metal concentration
SPECIAL ASPECTS OF ASSESSING THE ELEMENTAL COMPOSITION OF PHYTOPLANKTON AND SESTON USING NEUTRON ACTIVATION ANALYSIS
 SPECIAL ASPECTS OF ASSESSING THE ELEMENTAL COMPOSITION OF PHYTOPLANKTON AND SESTON USING NEUTRON ACTIVATION ANALYSIS Nekhoroshkov P. S., Frontasyeva M. V. Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, FLNP, SNAAAR
SPECIAL ASPECTS OF ASSESSING THE ELEMENTAL COMPOSITION OF PHYTOPLANKTON AND SESTON USING NEUTRON ACTIVATION ANALYSIS Nekhoroshkov P. S., Frontasyeva M. V. Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, FLNP, SNAAAR
Contribution of Drinking Water to Dietary Requirements of Essential Metals
 Contribution of Drinking Water to Dietary Requirements of Essential Metals Michelle Deveau Water Quality Science Division Health Canada May 7, 2008 Workshop on Health Risk Assessment of Essential Metals
Contribution of Drinking Water to Dietary Requirements of Essential Metals Michelle Deveau Water Quality Science Division Health Canada May 7, 2008 Workshop on Health Risk Assessment of Essential Metals
DISTRIBUTION OF TRACE ELEMENTS IN MUSCLE AND ORGANS OF TILAPIA, OREOCHROMIS NILOTICUS, FROM LAKES AWASSA AND ZIWAY, ETHIOPIA
 , 9-30. ISSN 0-3924 Printed in Ethiopia 2004 Chemical Society of Ethiopia DISTRIBUTION OF TRACE ELEMENTS IN MUSCLE AND ORGANS OF TILAPIA, OREOCHROMIS NILOTICUS, FROM LAKES AWASSA AND ZIWAY, ETHIOPIA Aweke
, 9-30. ISSN 0-3924 Printed in Ethiopia 2004 Chemical Society of Ethiopia DISTRIBUTION OF TRACE ELEMENTS IN MUSCLE AND ORGANS OF TILAPIA, OREOCHROMIS NILOTICUS, FROM LAKES AWASSA AND ZIWAY, ETHIOPIA Aweke
HUMUS AND TRACE ELEMENTS AS AN INDICATORS OF MATERIAL ERODED FROM CARBONATIC CHERNOZEMS SURFACE
 Scientific Papers, UASVM Bucharest, Series A, Vol. LIII, 2010, ISSN 1222-5339 HUMUS AND TRACE ELEMENTS AS AN INDICATORS OF MATERIAL ERODED FROM CARBONATIC CHERNOZEMS SURFACE 22 TAMARA LEAH Nicolae Dimo
Scientific Papers, UASVM Bucharest, Series A, Vol. LIII, 2010, ISSN 1222-5339 HUMUS AND TRACE ELEMENTS AS AN INDICATORS OF MATERIAL ERODED FROM CARBONATIC CHERNOZEMS SURFACE 22 TAMARA LEAH Nicolae Dimo
Heavy Metal Levels in Roadside Soils of some Major Roads in Maiduguri, Nigeria
 IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) e-issn: 78-5736.Volume 6, Issue 6 (Jan. 14), PP 74-78 Heavy Metal Levels in Roadside Soils of some Major Roads in Maiduguri, Nigeria Uwah, E. I., John, K. O.
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) e-issn: 78-5736.Volume 6, Issue 6 (Jan. 14), PP 74-78 Heavy Metal Levels in Roadside Soils of some Major Roads in Maiduguri, Nigeria Uwah, E. I., John, K. O.
ACCUMULATION OF SELENIUM FROM SELENIZED YEAST IN THE CULTIVATED MUSHROOM AGARICUS BISPORUS
 ACCUMULATION OF SELENIUM FROM SELENIZED YEAST IN THE CULTIVATED MUSHROOM AGARICUS BISPORUS MILENA SAVIC 1, BOGDAN DUBLJANIN 1, MILANA KOSTIC 2, IVANA VASILJEVIC 2, MIOMIR NIKSIC* 1 1 Department of Industrial
ACCUMULATION OF SELENIUM FROM SELENIZED YEAST IN THE CULTIVATED MUSHROOM AGARICUS BISPORUS MILENA SAVIC 1, BOGDAN DUBLJANIN 1, MILANA KOSTIC 2, IVANA VASILJEVIC 2, MIOMIR NIKSIC* 1 1 Department of Industrial
10. TRACE ELEMENTS Introduction. Trace Elements Bristol Bay Drainages
 10. TRACE ELEMENTS 10.1 Introduction The trace element studies in the Bristol Bay drainages study areas were conducted to acquire baseline data on naturally occurring constituents in upland soil, terrestrial
10. TRACE ELEMENTS 10.1 Introduction The trace element studies in the Bristol Bay drainages study areas were conducted to acquire baseline data on naturally occurring constituents in upland soil, terrestrial
Copper Removal from the Water Column
 Copper Removal from the Water Column G. Allen Burton and Michelle Hudson School for Environment and Sustainability University of Michigan for the International Copper Association Brussels, Belgium Final
Copper Removal from the Water Column G. Allen Burton and Michelle Hudson School for Environment and Sustainability University of Michigan for the International Copper Association Brussels, Belgium Final
Heavy Metals Effect on the Fertilization and Development of Sea Urchin Embryos
 Heavy Metals Effect on the Fertilization and Development of Sea Urchin Embryos Kristin Parish, Jessica Brown, Renee Cook and Megan Kapp January 2012 Abstract Heavy metal pollution is a prevalent threat
Heavy Metals Effect on the Fertilization and Development of Sea Urchin Embryos Kristin Parish, Jessica Brown, Renee Cook and Megan Kapp January 2012 Abstract Heavy metal pollution is a prevalent threat
Analysis of Organic Fertilizers for Nutrients with AAnalyst 800 Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer
 application Note Atomic Absorption Author Praveen Sarojam, Ph.D. PerkinElmer Global Application Center Mumbai, India Analysis of Organic Fertilizers for Nutrients with AAnalyst 800 Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer
application Note Atomic Absorption Author Praveen Sarojam, Ph.D. PerkinElmer Global Application Center Mumbai, India Analysis of Organic Fertilizers for Nutrients with AAnalyst 800 Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer
Accumulation of Heavy Metals in Soil and Tree Leaves in Heavy Traffic Affected Area of Agra city
 Vol.1 No. 2, 01-05 (2012) Received Aug.2012; Accepted Nov. 2012 Accumulation of Heavy Metals in and Tree in Heavy Traffic Affected Area of Agra city Abstract Sonal Tiwari and Rajesh Dhakarey Department
Vol.1 No. 2, 01-05 (2012) Received Aug.2012; Accepted Nov. 2012 Accumulation of Heavy Metals in and Tree in Heavy Traffic Affected Area of Agra city Abstract Sonal Tiwari and Rajesh Dhakarey Department
Heavy Metal Contamination of Soils around Painted Buildings in Selected Local Governments in Benue and Taraba States of Nigeria
 IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) e-issn: 2278-5736. Volume 6, Issue 4 (Nov. Dec. 2013), PP 40-44 Heavy Metal Contamination of Soils around Painted Buildings in Selected Local Governments in
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) e-issn: 2278-5736. Volume 6, Issue 4 (Nov. Dec. 2013), PP 40-44 Heavy Metal Contamination of Soils around Painted Buildings in Selected Local Governments in
Routine Analysis of Fortified Foods using the Agilent 7800 ICP-MS
 Application Note Trace metals in food Routine Analysis of Fortified Foods using the Agilent 7800 ICP-MS Simple and robust quantitative analysis of 28 elements in food digests using helium mode Author Shuofei
Application Note Trace metals in food Routine Analysis of Fortified Foods using the Agilent 7800 ICP-MS Simple and robust quantitative analysis of 28 elements in food digests using helium mode Author Shuofei
elucidate the role of trace metals in the ecology of the oceans and the
 CHAPTER I I. INTRODUCTION Microalgae acquire nutrients from their environment in order to sustain their growth and division. The classification of nutrients is made on the basis of their quantitative requirements
CHAPTER I I. INTRODUCTION Microalgae acquire nutrients from their environment in order to sustain their growth and division. The classification of nutrients is made on the basis of their quantitative requirements
AVAILABLE Cd CONTENT OF SALT AFFECTED AND NORMAL SOILS OF HALASTRA KALOHORI AREA
 Global NEST Journal, Vol 9, No 3, pp 195-200, 2007 Copyright 2007 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved AVAILABLE Cd CONTENT OF SALT AFFECTED AND NORMAL SOILS OF HALASTRA KALOHORI AREA TH.
Global NEST Journal, Vol 9, No 3, pp 195-200, 2007 Copyright 2007 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved AVAILABLE Cd CONTENT OF SALT AFFECTED AND NORMAL SOILS OF HALASTRA KALOHORI AREA TH.
Elemental analysis in clinical practice
 Elemental analysis in clinical practice Nicholas J Miller FRCPath, Laboratory Director, Biolab Medical Unit, ThermoFisher summer symposium 7 th June 2011, QEII Conference Centre Nutritional Elements Macro
Elemental analysis in clinical practice Nicholas J Miller FRCPath, Laboratory Director, Biolab Medical Unit, ThermoFisher summer symposium 7 th June 2011, QEII Conference Centre Nutritional Elements Macro
Heavy and Trace Elements in Some Brands of Rice Consumed in Delta State, Nigeria
 IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 6, Issue 2 Ver. II (Mar-Apr. 2014), PP 01-05 Heavy and Trace Elements in Some Brands of Rice Consumed in Delta State, Nigeria K. Emumejaye
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 6, Issue 2 Ver. II (Mar-Apr. 2014), PP 01-05 Heavy and Trace Elements in Some Brands of Rice Consumed in Delta State, Nigeria K. Emumejaye
Figure 1. Location of 43 benchmark sites across Alberta.
 1.0 INTRODUCTION This report describes the micronutrient and trace element status of the AESA (Alberta Environmentally Sustainable Agriculture) Soil Quality Benchmark Sites. Previous reports completed
1.0 INTRODUCTION This report describes the micronutrient and trace element status of the AESA (Alberta Environmentally Sustainable Agriculture) Soil Quality Benchmark Sites. Previous reports completed
Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance 1 Terms Balanced ration Carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates Disaccharides Essential nutrients Ether Fat Fat-soluble
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance 1 Terms Balanced ration Carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates Disaccharides Essential nutrients Ether Fat Fat-soluble
Purity Tests for Modified Starches
 Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016 Purity Tests for Modified Starches This monograph was also published in: Compendium
Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016 Purity Tests for Modified Starches This monograph was also published in: Compendium
Evaluation and correlation study of heavy metals load in drinking water and update of water-related disease cases in Ebonyi State from
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC AND INDUSTRIAL RESEARCH 213, Science Huβ, http://www.scihub.org/ajsir ISSN: 2153-649X, doi:1.5251/ajsir.213.4.2.221.225 Evaluation and correlation study of heavy metals load
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC AND INDUSTRIAL RESEARCH 213, Science Huβ, http://www.scihub.org/ajsir ISSN: 2153-649X, doi:1.5251/ajsir.213.4.2.221.225 Evaluation and correlation study of heavy metals load
Contamination of Zinc in Sediments at River Mouths and Channel in Northern Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan
 International Journal of Environmental Science and Development, Vol. 3, No. 6, December 2012 Contamination of Zinc in Sediments at River Mouths and Channel in Northern Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan Cheng-Di
International Journal of Environmental Science and Development, Vol. 3, No. 6, December 2012 Contamination of Zinc in Sediments at River Mouths and Channel in Northern Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan Cheng-Di
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.37 - SOIL.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Plants produce sugars from photosynthesis, but still have many nutritional requirements C, H, and O account for ~95% of a plant s dry weight, and are obtained from CO2 and H2O Vascular
!! www.clutchprep.com Plants produce sugars from photosynthesis, but still have many nutritional requirements C, H, and O account for ~95% of a plant s dry weight, and are obtained from CO2 and H2O Vascular
Trace Toxic Metal Levels in Canned and Fresh Food: A Comparative Study
 Trace Toxic Metal Levels in Canned and : A Comparative Study Zahrah Al-Thagafi 1, Hassan Arida 2, Reham Hassan 1,3 Lecture, Department of Chemistry, Science College, Taif University, 888- Taif, Saudi Arabia
Trace Toxic Metal Levels in Canned and : A Comparative Study Zahrah Al-Thagafi 1, Hassan Arida 2, Reham Hassan 1,3 Lecture, Department of Chemistry, Science College, Taif University, 888- Taif, Saudi Arabia
US EPA SW-846 Method 6010D using the Thermo Scientific icap 7400 ICP-OES Duo
 APPLICATION NOTE 43152 US EPA SW-846 Method 6010D using the Thermo Scientific icap 7400 ICP-OES Duo Authors James Hannan, Application Specialist, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Hemel Hempstead, UK Keywords
APPLICATION NOTE 43152 US EPA SW-846 Method 6010D using the Thermo Scientific icap 7400 ICP-OES Duo Authors James Hannan, Application Specialist, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Hemel Hempstead, UK Keywords
Assessment of Heavy Metals in Rana esculenta Organs from River Guma, Benue State Nigeria
 American Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 4, 496-500 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajac.2013.49063 Published Online September 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajac) Assessment of Heavy Metals in Rana
American Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 4, 496-500 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajac.2013.49063 Published Online September 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajac) Assessment of Heavy Metals in Rana
Research Article. Heavy metals in soil and vegetables in anadrinia region as a result of the use of pesticides, herbicides and fertilizers
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(8):923-927 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Heavy metals in soil and vegetables in anadrinia
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(8):923-927 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Heavy metals in soil and vegetables in anadrinia
Trace Metal Characterization of Soils Using the Optima 7300 DV ICP-OES
 A P P L I C AT I O N N O T E ICP-Optical Emission Spectroscopy Author Praveen Sarojam, Ph.D. PerkinElmer, Inc. Shelton, CT 06484 USA Trace Metal Characterization of Soils Using the Optima 7300 DV ICP-OES
A P P L I C AT I O N N O T E ICP-Optical Emission Spectroscopy Author Praveen Sarojam, Ph.D. PerkinElmer, Inc. Shelton, CT 06484 USA Trace Metal Characterization of Soils Using the Optima 7300 DV ICP-OES
Determination of Heavy Metals in Selected Fish Species found in Kwalkwalawa River, Dundaye. Sokoto State
 IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) e-issn: 2278-5736.Volume 10, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2017), PP 38-42 www.iosrjournals.org Determination of Heavy Metals in Selected Fish Species found in Kwalkwalawa
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) e-issn: 2278-5736.Volume 10, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2017), PP 38-42 www.iosrjournals.org Determination of Heavy Metals in Selected Fish Species found in Kwalkwalawa
BASELINE SURVEY OF TRACE METALS IN CHICKEN AT THE SURROUNDINGS OF THE TUMMALAPALLE URANIUM MINING SITE
 BASELINE SURVEY OF TRACE METALS IN CHICKEN AT THE SURROUNDINGS OF THE TUMMALAPALLE URANIUM MINING SITE Allabaksh Murad Basha 1, Nookala Yasovardhan 1, Suggala V Satyanarayana 1*, Gopireddy V Subba Reddy
BASELINE SURVEY OF TRACE METALS IN CHICKEN AT THE SURROUNDINGS OF THE TUMMALAPALLE URANIUM MINING SITE Allabaksh Murad Basha 1, Nookala Yasovardhan 1, Suggala V Satyanarayana 1*, Gopireddy V Subba Reddy
Application Note novaa 800 D. Determination of Macro and Trace Minerals as well as Toxic Trace Metals in Powdered Milk. Challenge.
 Application Note novaa 800 D Determination of Macro and Trace Minerals as well as Toxic Trace Metals in Powdered Milk Introduction The popularity of milk and dairy products is growing worldwide, resulting
Application Note novaa 800 D Determination of Macro and Trace Minerals as well as Toxic Trace Metals in Powdered Milk Introduction The popularity of milk and dairy products is growing worldwide, resulting
2. is a set of principles intended to help sustain a habitable planet.
 Chapter 2 Tools of the Trade 1 Multiple Choice 2-1 Safe, Ethical Handling of Chemicals and Waste 1. Which of the following statements are TRUE? I Organic solvents, concentrated acids, and concentrated
Chapter 2 Tools of the Trade 1 Multiple Choice 2-1 Safe, Ethical Handling of Chemicals and Waste 1. Which of the following statements are TRUE? I Organic solvents, concentrated acids, and concentrated
Metal concentration of some microelements found in some fruits and vegetables, commonly consumed in Zaria metropolis
 Available online at www.aexpbio.com RESEARCH ARTICLE Annals of Experimental Biology 2015, 3 (2):10-14 ISSN : 2348-1935 Metal concentration of some microelements found in some fruits and vegetables, commonly
Available online at www.aexpbio.com RESEARCH ARTICLE Annals of Experimental Biology 2015, 3 (2):10-14 ISSN : 2348-1935 Metal concentration of some microelements found in some fruits and vegetables, commonly
Determination of Heavy Metals in Canned Dry-Milk and Fish from Supermarkets in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Kefyalew Muleta Tetemke Mehari (PhD)
 Determination of Heavy Metals in Canned Dry-Milk and Fish from Supermarkets in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia Kefyalew Muleta Tetemke Mehari (PhD) 1 PRESENTATION OUT LINE Introduction Objective Material and Methods
Determination of Heavy Metals in Canned Dry-Milk and Fish from Supermarkets in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia Kefyalew Muleta Tetemke Mehari (PhD) 1 PRESENTATION OUT LINE Introduction Objective Material and Methods
Evaluation of the Heavy Metals Level in Selected Industrially Packaged Food Spices
 AASCIT Communications Volume 2, Issue 2 April 10, 2015 online ISSN: 2375-3803 Evaluation of the Heavy Metals Level in Selected Industrially Packaged Food Spices C. T. Onyema Pure and Industrial Chemistry
AASCIT Communications Volume 2, Issue 2 April 10, 2015 online ISSN: 2375-3803 Evaluation of the Heavy Metals Level in Selected Industrially Packaged Food Spices C. T. Onyema Pure and Industrial Chemistry
NUTRIENT AND HEAVY METAL CONTENTS OF HOG MANURE - EFFECT ON SOIL QUALITY AND PRODUCTIVITY
 NUTRIENT AND HEAVY METAL CONTENTS OF HOG MANURE - EFFECT ON SOIL QUALITY AND PRODUCTIVITY G.J. Racz and M.M. Fitzgerald Professor and Research Associate, respectively, Department of Soil Science, University
NUTRIENT AND HEAVY METAL CONTENTS OF HOG MANURE - EFFECT ON SOIL QUALITY AND PRODUCTIVITY G.J. Racz and M.M. Fitzgerald Professor and Research Associate, respectively, Department of Soil Science, University
Matrix Reference Materials - SCP SCIENCE
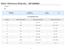 EnviroMAT SS-1 Catalogue No.: 140-025-001 EnviroMAT Contaminated Soil Lot No.: SC0063618 100 g TOTAL DIGESTION VALUES Elements Reference Value (mg/kg) Confidence Interval (mg/kg) Tolerance Interval (mg/kg)
EnviroMAT SS-1 Catalogue No.: 140-025-001 EnviroMAT Contaminated Soil Lot No.: SC0063618 100 g TOTAL DIGESTION VALUES Elements Reference Value (mg/kg) Confidence Interval (mg/kg) Tolerance Interval (mg/kg)
Comparative Analysis of Heavy Metals in Processed Tomato Paste and Fresh Tomatoes Sold in Markets in Ibadan, Nigeria
 The Polytechnic Journal of Science and Technology PJST. Vol. 8. 2013 ISSN: 1115 8336 2013 Journal of Science & Technology Polytechnic Ibadan, Nigeria Comparative Analysis of Heavy Metals in Processed Tomato
The Polytechnic Journal of Science and Technology PJST. Vol. 8. 2013 ISSN: 1115 8336 2013 Journal of Science & Technology Polytechnic Ibadan, Nigeria Comparative Analysis of Heavy Metals in Processed Tomato
COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT
 DATE REPORTED: 11/04/2014 PAGE: 1 Moisture @ 70 C % 53.52 TMECC 03.09-A Dry Matter % 46.48 TMECC 03.09-A Total Nitrogen (N) % 0.76 1.63 TMECC 04.02-D Phosphorus (P) % 0.08 0.17 TMECC 04.03-A Phosphate
DATE REPORTED: 11/04/2014 PAGE: 1 Moisture @ 70 C % 53.52 TMECC 03.09-A Dry Matter % 46.48 TMECC 03.09-A Total Nitrogen (N) % 0.76 1.63 TMECC 04.02-D Phosphorus (P) % 0.08 0.17 TMECC 04.03-A Phosphate
COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT
 DATE REPORTED: 09/14/2015 PAGE: 1 Moisture @ 70 C % 53.88 TMECC 03.09-A Dry Matter % 46.12 TMECC 03.09-A Total Nitrogen (N) % 0.87 1.88 TMECC 04.02-D Phosphorus (P) % 0.10 0.21 TMECC 04.03-A Phosphate
DATE REPORTED: 09/14/2015 PAGE: 1 Moisture @ 70 C % 53.88 TMECC 03.09-A Dry Matter % 46.12 TMECC 03.09-A Total Nitrogen (N) % 0.87 1.88 TMECC 04.02-D Phosphorus (P) % 0.10 0.21 TMECC 04.03-A Phosphate
Understanding a Soil Report
 Understanding a Soil Report AGRONOMY SOIL ANALYSIS 1. Soil ph Soil ph is a measure of the acidity in the soil. An acidic soil has a greater amount of hydrogen (H+) ions and a ph below 7.0. Values above
Understanding a Soil Report AGRONOMY SOIL ANALYSIS 1. Soil ph Soil ph is a measure of the acidity in the soil. An acidic soil has a greater amount of hydrogen (H+) ions and a ph below 7.0. Values above
Heavy metal distribution in Rewa City, MP, India
 International Research Journal of Environmental Sciences ISSN 2319 1414 Heavy metal distribution in soil of Jaypee Cement Industrial Area 2012-13 of Rewa City, MP, India Abstract Mukesh Singh 1, M.K. Bhatnagar
International Research Journal of Environmental Sciences ISSN 2319 1414 Heavy metal distribution in soil of Jaypee Cement Industrial Area 2012-13 of Rewa City, MP, India Abstract Mukesh Singh 1, M.K. Bhatnagar
TEST REPORT ******FOR FURTHER DETAILS, PLEASE REFER TO THE FOLLOWING PAGE(S)******
 NO.: A001T140305209001 Date: Apr 02, 2014 Page 1 of 10 Applicant: TONGLU Penda import and export co., Ltd/Changzhou Penda international trading co., Ltd Address: Dongguan industrial zone, Fenshui town,
NO.: A001T140305209001 Date: Apr 02, 2014 Page 1 of 10 Applicant: TONGLU Penda import and export co., Ltd/Changzhou Penda international trading co., Ltd Address: Dongguan industrial zone, Fenshui town,
Test Report No.: T TY Date: DEC 19, 2018 Page 1 of 10
 Test Report No.: T51810301178TY Date: DEC 19, 2018 Page 1 of 10 GUANGDONG XINYU TECHNOLOGY INDUSTRIAL CO., LTD. LAIMEI INDUSTRIAL ZONE, CHENGHAI DISTRICT, SHANTOU, GUANGDONG The following samples were
Test Report No.: T51810301178TY Date: DEC 19, 2018 Page 1 of 10 GUANGDONG XINYU TECHNOLOGY INDUSTRIAL CO., LTD. LAIMEI INDUSTRIAL ZONE, CHENGHAI DISTRICT, SHANTOU, GUANGDONG The following samples were
SECTION 1: Product and company identification. SECTION 2: Hazards identification
 SECTION 1: Product and company identification 1.1 Product identifier Product Name: Jack s Professional 20-3-19 Petunia FeED Product Number(s): 77770 Product form: powder and prills 1.2 Relevant identified
SECTION 1: Product and company identification 1.1 Product identifier Product Name: Jack s Professional 20-3-19 Petunia FeED Product Number(s): 77770 Product form: powder and prills 1.2 Relevant identified
CENTRE D ETUDE & DE VALORI SATI ON DES ALGUES
 CENTRE D ETUDE & DE VALORI SATI ON DES ALGUES Algae Cal International Las Vega NV 89109 USA February 2007 Presqu Ile de Pen Lan, BP 3 22610 Pleubian tél : 0296229350 fax : 0296228438 algue@cevafr wwwcevafr
CENTRE D ETUDE & DE VALORI SATI ON DES ALGUES Algae Cal International Las Vega NV 89109 USA February 2007 Presqu Ile de Pen Lan, BP 3 22610 Pleubian tél : 0296229350 fax : 0296228438 algue@cevafr wwwcevafr
Mineral Nutrition. Criteria for Essentiality
 Mineral Nutrition Criteria for Essentiality The element is absolutely necessary for supporting normal growth and reproduction. In the absence of essential elements, plants cannot complete their life cycle
Mineral Nutrition Criteria for Essentiality The element is absolutely necessary for supporting normal growth and reproduction. In the absence of essential elements, plants cannot complete their life cycle
The implementation of bioavailability in defining PNEC values for trace metals and metalloids in soil
 Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences Division of Soil and Water Management The implementation of bioavailability in defining PNEC values for trace metals and metalloids in soil Erik Smolders
Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences Division of Soil and Water Management The implementation of bioavailability in defining PNEC values for trace metals and metalloids in soil Erik Smolders
EUROPEAN QUALIFYING EXAMINATION 2006
 EUROPEAN QUALIFYING EXAMINATION 2006 PAPER A CHEMISTRY This paper comprises: * Letter from the applicant 2006/A(Ch)/e/1-6 * Document 1 2006/A(Ch)/e/7 * Document 2 2006/A(Ch)/e/8-10 2006/A(Ch)/e - 1 - LETTER
EUROPEAN QUALIFYING EXAMINATION 2006 PAPER A CHEMISTRY This paper comprises: * Letter from the applicant 2006/A(Ch)/e/1-6 * Document 1 2006/A(Ch)/e/7 * Document 2 2006/A(Ch)/e/8-10 2006/A(Ch)/e - 1 - LETTER
