European Journal of Endocrinology (2007) ISSN
|
|
|
- Clifton Cannon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 European Journal of Endocrinology (2007) ISSN CLINICAL STUDY Superiority of skinfold measurements and waist over waistto-hip ratio for determination of body fat distribution in a population-based cohort of Caucasian Dutch adults Iris J G Ketel, Mariken N M Volman, Jacob C Seidell 1, Coen D A Stehouwer 2, Jos W Twisk 3 and Cornelis B Lambalk Division of Reproductive Medicine, Department of Obstetrics & Gynaecology, de Boelelaan 1117, 1081 HV, room 0Z120, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1 Department of Nutrition and Health, Faculty of Earth and Life Sciences, de Boelelaan 1117, 1081 HV Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2 Department of Internal Medicine, Academic Hospital Maastricht, P. Debyelaan 25, 6229 HX Maastricht, The Netherlands and 3 Department of Public and Occupational Health and Institute for Research in Extramural Medicine of VU University medical centre, de Boelelaan 1117, 1081 HV Amsterdam, The Netherlands (Correspondence should be addressed to C B Lambalk; cb.lambalk@vumc.nl) I J G Ketel and M N M Volman contributed equally to this work Abstract Objective: To determine which anthropometric measurement is the most reliable alternative for fat distribution as measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). Design: Population-based survey carried out in Amsterdam, The Netherlands. Subjects and methods: A total of 376 individuals (200 women) with a mean age of 36.5 years and mean body mass index (BMI) of 24.0 (G3.1) kg/m 2 underwent various anthropometric and DXA measurements of central (CFM) and peripheral fat mass (PFM). Furthermore, for the assessment of apple-shaped body composition, CFM-to-PFM ratio was calculated. Anthropometric measurements were waist and hip circumference, waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), BMI, waist/length and the skinfold thickness of biceps, triceps, suprailiacal (SI), subscapular (SS) and upper leg. We determined whether equations of combined anthropometrics were even more reliable for the assessment of fat mass. Results: In both women and men, reliable alternatives for CFM are central skinfolds and waist (Pearson s correlation (r) R0.8). Peripheral skinfolds are the best predictors of PFM (rr0.8). In contrast, WHR correlated only marginally with any of the DXA measurements. Equations based on several anthropometric variables correlate with CFM even better (R 2 R0.8). CFM-to-PFM ratio has the highest correlation with the ratio (SSCSI)/BMI in women (rz0.66) and waist/length in men (rz 0.71). Equations are reasonable alternatives of CFM-to-PFM ratio (R 2 R0.5). Conclusion: Waist and skinfolds are reliable alternatives for the measurement of body fat mass in a cohort of Caucasian adults. WHR is not appropriate for the measurement of fat distribution. European Journal of Endocrinology Introduction Central fat mass (CFM) is increasingly recognized as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease (1 5) and metabolic disease as well as overall mortality. In contrast, peripheral fat mass (PFM) may independently contribute to a lower risk for cardiovascular disease (4 10). Therefore, measuring fat distribution, i.e. CFM/ PFM ratio, is a topic of great interest, especially population-based cohort studies, in which large numbers of subjects are measured, simple anthropometric measurements are needed to determine fat distribution. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is a well-accepted method and has a good concordance with computed tomography (CT) for the assessment of body fat (11). However, CT and DXA are costly and time consuming. Moreover, these techniques involve exposing the subject to ionizing radiation. As a consequence, the use of these techniques cannot be extended to studies that involve large numbers of subjects. In these kinds of studies, body mass index (BMI, for overall body fatness) and waist-to-hip ratio (WHR, for body fat distribution) are most often used (12). There is doubt whether WHR, which is partly dependent on pelvic skeletal structure and muscle distribution, is a valid anthropometric measure for the assessment of body composition (13 15). Measurement of skinfold thickness in combination with waist circumference may be reasonable alternatives. However, there are no larger studies so far that correlate both skinfold measurements and waist circumference with DXA for determining body fat. Therefore, the purpose of the present study was to assess the predictive value of various simple anthropometric measures of body fat compared with DXA measurements in a population-based cohort of Dutch Caucasian adults. q 2007 Society of the European Journal of Endocrinology DOI: /EJE Online version via
2 656 I J G Ketel, M N M Volman and others EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (2007) 156 Besides the commonly used anthropometric and DXA measures for the estimation of CFM, we had particular interest in ratios. Since CFM is positively and PFM is negatively correlated with cardiovascular disease, the CFM-to-PFM ratio might be a stronger predictor for the assessment of cardiovascular risk. The CFM-to-PFM ratio is known to be associated with increased risk of mortality (16, 17). Furthermore, we analysed a number of skinfold ratios which have been associated with cardiovascular risk factors in previous studies (18 21). In addition, we aimed to develop easy-to-use regression equations consisting of various combinations of anthropometric measurements that predict body fat distribution as measured with DXA. Methods Subjects and design The Amsterdam Growth and Health Longitudinal Study (AGAHLS), which started in 1976, was designed to investigate the development of indicators of growth and health in a cohort of Dutch adolescents. For that purpose, 615 healthy boys and girls were recruited from two secondary schools in and around Amsterdam. All participants were born between 1961 and 1965, and were residents of the Netherlands. In 2000, at a mean age of 36 years, 376 Caucasian subjects (200 women) visited the Vrije Universiteit for assessment of, amongst others, anthropometrics and DXA. More detailed information about the AGAHLS has been described in previous publications (19, 22, 23). The Medical Ethical Committee of the Vrije Universiteit Medical Centre approved the protocol. All subjects gave informed consent. Data collection A whole-body DXA scan was performed using the Hologic QDR-2000 (S/N 2513; Hologic Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). With the use of specific anatomic landmarks, regions of the head, trunk, arms and legs were distinguished as shown in Fig. 1. Total body fat, fat mass of the trunk, legs and arms (kg) were used for analysis. Fat mass of the trunk, further referred to as CFM, includes both the subcutaneous and the visceral fat of this anatomical region. PFM was estimated by the sum of the fat mass of both arms and legs. Furthermore, the CFM-to-PFM ratio was calculated. Anthropometric measurements of body height, body mass, waist-hip and skinfolds were performed according to standard procedures (19). BMI was calculated by dividing body mass (kg) by body height squared (m 2 ). Skinfolds were measured with a Harpenden caliper (Holtain, UK) to the nearest 0.1 mm according to the recommendations of the International Biological Programme (24). Measurements were performed Figure 1 Standard regions of a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry scan. 1, head; 2, trunk; 3, arms; 4, legs. according to standard procedures (25, 26) and with the same instruments throughout the study. Over the entire period of study, one trained examiner performed the measurements of the skinfolds. The DXA and skinfold measurements were done on the same day. The correlation coefficients were calculated for every skinfold. For the single skinfolds, these reproducibility coefficients were R0.8. The following skinfolds were measured: subscapular (SS), suprailiacal (SI), biceps (BI), triceps (TRI) and upper leg (LEG). Two measurements were performed and the mean was used for the analyses. For the assessment of CFM, the skinfolds SS and SI and the sum of these were used. Several combinations of skinfolds were calculated to assess PFM: BICTRICLEG, BICTRI, TRICLEG, BICLEG and LEG. The anthropometrics that
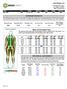
3 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (2007) 156 were correlated best with either central or peripheral fat as measured with DXA were used to calculate CFMto-PFM ratios. In women, the ratio (SSCSI)/BMI, and in men, the ratio waist/(bictri) were calculated. Two other well-known ratios were used for analysis: SS/(SSCTRI) (20) and SS/TRI (18). Furthermore, the best correlated central-to-peripheral skinfold ratio was also analysed (i.e. (SSCSI)/(TRICLEG)). To determine WHR, we measured the circumferences of the waist (at umbilicus height) and hip (at the level of widest circumference over the buttocks) with a flexible steel tape to the nearest 0.1 cm. Statistical analysis Data were analysed with a statistical software package (SPSS 11 for Windows, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Results are given as meansgs.d. The Pearson correlation coefficient (r) was calculated to estimate the predictive value of various anthropometrics. To assess significance, a P!0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. For multiple comparisons, the significance level was adjusted by multiplying the number of comparisons of each DXA measurement according to Bonferroni correction (27). Linear regression analysis was used to develop equations containing anthropometric measurements, which correlate with body fat distribution. The anthropometric measurements of body fat considered were (the combination of) skinfolds, waist or hip circumference, BMI, WHR, waist-to-length ratio, weight and length; and the DXA measurements considered were CFM and CFM-to-PFM ratio. Selection of variables was done in a forward stepwise fashion with strict variable entry (P!0.05) and elimination criteria (PR0.05). Comparing R 2 values of the models obtained from each set assessed the associative value of each set of measurements. Incremental additive value was judged by the increase in R 2 obtained when anthropometric measurements were added to the model. Three types of association models of CFM and CFM-to-PFM ratio were constructed (Table 3). The first type is developed for situations in which skinfold measurements are not available. The second type is the first equation combined with the best associative skinfold. The third equation represents the optimal model. All analyses were performed separately for males and females. Results Characteristics of the study group are presented in Table 1 and Fig. 2. Fourteen women and eight men refused to undergo DXA measurements, resulting in minor loss of subjects. Women Table 2 shows the correlation coefficients regarding the anthropometric indices and DXA measurements for both men and women. CFM is highly correlated with the sum of two skinfolds SSCSI (rz0.82), skinfold SS (rz 0.82), BMI (rz0.82) and waist (rz0.82). BMI has a good correlation with both CFM and PFM. The ratio CFM-to-PFM ratio, determined by DXA, is correlated best with the ratio (SSCSI)/BMI (rz0.66) and SSCSI (rz0.65). The skinfold ratio (SSCSI)/(TRICLEG) has a correlation coefficient of Just as CFM, PFM shows good correlations with anthropometry: BMI (rz0.85), weight (rz0.84), BICTRI (rz0.82) and BICTRIC LEG (rz0.82). In contrast, WHR correlates only marginally with any of the DXA ratios. Men Waist and skinfold for body fatness 657 Just as in women, CFM in men is highly correlated with waist (rz0.85) and the skinfold SSCSI (rz0.84) (Table 2). In contrast to women, waist/length (rz 0.71) has the highest correlation with CFM-to-PFM ratio. Correlations of PFM with anthropometry are slightly lower in men than in women; the best relation is found with the same combination of skinfolds as in women: BICTRICLEG (rz0.78) and BICTRI (rz 0.78). As in women, WHR correlates only marginally with any of the DXA ratios. Table 1 Descriptive statistics for age, height, body mass, body mass index (BMI) and waist-to-hip ratio (WHR). Women (nz200) Men (nz176) Mean S.D. Range Mean S.D. Range Age Height (m) Body mass (kg) BMI (kg/m 2 ) Waist (cm) Hip (cm) WHR DXA, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry; CFM, central fat mass; PFM, peripheral fat mass; S.D., standard deviation.
4 658 I J G Ketel, M N M Volman and others EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (2007) 156 Figure 2 Bar chart of DXA measurements and skinfold thickness in men and women. Values are presented as means; DXA, dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry. $ nz168 men and nz186 women. Linear regression analyses As shown in Table 3, association models consisting of simple anthropometric measurements are a good alternative for the measurement of CFM. The optimal model of CFM in women is a combination of waist, BMI, hip circumference and the skinfold SS, which accounted for 82% of the variance in CFM measured by DXA (R 2 Z0.82). In men, the combination of waist, BMI and SSCSI is the best correlation with CFM (R 2 Z0.83). In both women and men, a reliable model of simple anthropometric measurements, when skinfolds are not available, is the combination of waist and BMI (R 2 Z 0.75 and R 2 Z0.77 respectively). The additional variance explained when the skinfold SS is added to the models was 4 and 5% respectively (R 2 Z0.79 in women and R 2 Z0.82 in men). The optimal model of CFM-to-PFM ratio for women and men is the combination of the following anthropometrics: the waist/ length ratio and the skinfold ratio [(SSCSI)/(TRIC LEG); R 2 Z0.50 and R 2 Z0.56 respectively]. Simple, commonly used anthropometric measurements, such as waist and BMI, account for 30% in women and 38% in men of the variance in CFM-to-PFM ratio measured by DXA. The skinfold ratio (SSCSI)/BMI in women and the skinfold ratio (SSCSI)/(TRICLEG) in men explained a further 17 and 12% of variance respectively (R 2 Z0.47 and R 2 Z0.50 respectively). Discussion The results of this study indicate that in a populationbased cohort of Dutch Caucasians, CFM and PFM Table 2 Correlation between DXA and anthropometric measurements in women and men. CFM CFM/PFM PFM r r r DXA Women Men Women Men Women Men Central anthropometrics SSCSI 0.82* 0.84* 0.65* 0.63* 0.61* 0.73* SS 0.82* 0.80* 0.62* 0.63* 0.64* 0.62* SI 0.72* 0.78* 0.59* 0.56* 0.50* 0.66* Waist 0.82* 0.85* 0.54* 0.66* 0.69* 0.68* Anthropometric ratios (SSCSI)/BMI 0.67* 0.66* 0.39* Waist/(BICTRI) K0.48* K0.24 K0.48* (SSCSI)/(TRICLEG) 0.38* 0.39* 0.62* 0.52* SS/TRI 0.30* 0.39* 0.55* 0.48* K SS/(SSCTRI) 0.31* 0.33* 0.34* 0.46* K BMI 0.82* 0.81* 0.39* 0.59* 0.85* 0.68* WHR * 0.28* 0.29* Waist/length 0.80* 0.82* 0.58* 0.71* 0.64* K0.48* Peripheral anthropometrics BICTRICLEG 0.70* 0.61* * 0.82* 0.78* BICTRI 0.62* 0.52* 0.36* 0.39* 0.82* 0.78* TRICLEG 0.78* 0.70* * 0.73* BICLEG 0.66* 0.59* * 0.74* LEG 0.51* 0.44* * 0.73* Hip circumference 0.78* 0.81* 0.39* 0.57* 0.78* 0.69* Overall anthropometrics Weight 0.77* 0.77* 0.30* 0.44* 0.84* 0.76* Length K0.17 K * r, Pearson s correlation, *P value!0.001, P value!0.05 and not significant; SI, suprailiacal; SS, subscapular; TRI, triceps; BI, biceps; LEG, upper leg; DXA, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry; WHR, waist-to-hip ratio; BMI, body mass index; CFM, central fat mass; PFM, peripheral fat mass.
5 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (2007) 156 Table 3 Association models containing simple anthropometrics correlated with central fat mass and body fat distribution (i.e. central (CFM)-to-peripheral fat mass (PFM) ratio) measured with dualenergy X-. CFM Women K18.53C0.20 waist C0.51 BMI 0.75 K12.90C0.13 waist 0.79 C0.36 BMI C0.23 (SS) K17.67C0.13 waist C0.16 BMI 0.82 C0.11 hip circumferencec0.20 (SS) Men K33.00C0.34 waist C0.48 BMI 0.77 K25.40C0.25 waist C0.32 BMI 0.82 C0.31 (SS) K22.80C0.22 waist 0.83 C0.31 BMI C0.16 (SSCSI) CFM/PFM Women WaistCBMI a 0.30 a K0.21C0.01 waist C0.25 ((SSCSI)/BMI) 0.47 K0.17C1.35 (waist/length) 0.50 C0.37 ((SSCSI)/(TRICLEG)) Men K1.25C0.01 waistc0.04 BMI a 0.38 a K1.17C0.02 waistc0.22 ((SSCSI) 0.50 /(TRICLEG)) K1.42C4.36 (waist/length) 0.56 C0.20 ((SSCSI)/(TRICLEG)) R 2, explained variance. a Not significant. SI, suprailiacal; SS, subscapular; TRI, triceps; BI, biceps; LEG, upper leg; BMI, body mass index. measured by DXA were highly correlated with central and peripheral skinfolds respectively. Waist circumference is a good alternative for the assessment of CFM measured by DXA. In addition, BMI and weight had a good correlation; however, these measurements do not differentiate between central or peripheral fat measured by DXA. The (SSCSI)/BMI ratio in women and the waist/length ratio in men are the best anthropometric alternative for CFM-to-PFM ratio. WHR does not seem appropriate for the DXA measurement of body fat mass. Equations based on several anthropometric variables are correlated with CFM, PFM and CFM-to-PFM ratio even better. For the determination of central adiposity, DXA CFM is most commonly used. Clearly, DXA CFM is related with cardiovascular factors (2, 9, 28). Commonly used standards for defining central versus peripheral adiposity do not yet exist. Central and peripheral measurements and, to a lesser extent, DXA ratios are often used for the determination of fat distribution (2, 4, 5, 9, 29). Due to the importance of body fat distribution, specifically central in relation to peripheral fat, the use of DXA ratios does seem interesting. Moreover, several studies showed correlations of DXA ratios with cardiovascular risk factors (5, 17). DXA derived ratios in this study were aimed at partitioning trunk fat from the remainder of the body. R 2 Waist and skinfold for body fatness 659 The ratio (trunk/(armsclegs)) segments the body into central and peripheral portions. Traditionally, skinfold thickness has been used for the assessment of body composition. Central skinfolds, mainly the SS skinfolds (30), are positively linked to cardiovascular risk factors in contrast to peripheral skinfolds, which are negatively related to cardiovascular disease (31, 32). Skinfold ratios have been widely used for the assessment of fat distribution (17, 19, 20, 33) and correlate well with several factors of cardiovascular disease (18). Our study shows that these skinfold ratios are moderately correlated with CFM-to-PFM ratio, as measured with DXA. As far as we know, the specific skinfold ratio (SSCSI)/BMI, which we found to be the best anthropometric alternative for CFM-to-PFM ratio, has not yet been correlated with cardiovascular disease. The possible usefulness in the context of a relationship with cardiovascular disease needs to be shown in future studies. So far, each of the individual parameters of which this ratio consists is related to cardiovascular risk factors. Weight, which is easy to measure and investigator independent, does not make any differentiation between CFM and PFM. Moreover, weight alone does not represent a person s body fat mass, if one is not taking length into account. BMI, WHR and waist circumference are all markers of body composition and therefore considered as predictive measurements for cardiovascular disease. BMI, a ratio of weight and length, is often used and assumed to represent the degree of body fat (and muscle in adolescents), but does not capture body fat distribution (34). In particular, WHR is considered the traditional anthropometric technique for assessing CFM-to-PFM ratio (12). It is widely used and established in cross-sectional (35), longitudinal (36) and intervention studies, and it is a robust predictor of disease risk and mortality (35, 37, 38). In this context, WHR, rather than BMI, has therefore recently been recommended for the assessment of body fatness (38). However, in the present study, we could not validate WHR against DXA data for the distribution of body fat. The likely explanation for this is that WHR, being largely dependent on pelvic bone structures, contains variability that makes differentiation between distribution of fat and fat-free tissues less accurate and thus less reliable (39, 40). In this context, the importance of waist instead of WHR has recently been recognized (29, 41, 42). Remarkably, the waist circumference, however, is not always a stronger predictor of cardiovascular risk than the WHR (34). In the present study, the waist indeed showed good relation with CFM. Skinfolds and waist circumference are easy to perform in daily practice, cost effective, non-invasive, non-time consuming and widely applicable, especially for large cohort studies. Moreover, with respect to skinfolds, different sites of the body can be measured, which is an advantage in the assessment of body fat distribution.
6 660 I J G Ketel, M N M Volman and others EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (2007) 156 A limitation of the present study is that mostly lean persons (BMI%25) were measured (151 women and 101 men), who might not have an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases because of their weight. However, people with a BMI in the normal weight range can still be at increased risk of metabolic disturbances if their WHR or waist circumference is increased. To obtain an impression as to whether the results could be applicable to an overweight population, the analyses were done on a subset of individuals (BMI between 25 and 30, nz99 (36 women)). Just as in the entire cohort, in overweight women, DXA CFM was highly correlated with central skinfolds (SSCSI; rz0.84). Peripheral skinfolds were correlated slightly less with DXA PFM (BICTRI; rz0.69), whereas the skinfolds ratios were correlated slightly higher with DXA ratio ((SSCSI)/(TRICLEG); rz0.72). In overweight men, DXA CFM was highly correlated with waist circumference (rz0.83). Of the skinfold measurements, SSCSI had the highest correlation rz0.69. The waist/length ratio in men was again the best anthropometric alternative for CFM-to-PFM ratio (rz0.69). As in the entire cohort, WHR does not seem appropriate for the measurement of body fat mass distribution (r%0.4). Since our study was underrepresented for the purpose of the prediction of body fat distribution in an obese population (BMI O30), this needs further investigation. Another limitation of the study is that the study group was Caucasian. Ethnic variation of body fat distribution is well known. Black women, for example, have more bone and muscle mass, but less fat as a percentage of body weight than white women, after controlling for ethnic differences in age, body weight and height (43). Therefore, heterogeneity of waist circumference (44) and skinfold (45) cut-off points have been reported. Conclusions derived from the present study should only be used in Caucasian populations. It should be noticed that our results are applicable on a population level. Since DXA is expressed in kilograms and skinfolds in millimetres, the Bland Altman analysis with standardized S.D. of DXA and anthropometrics, to circumvent problems with different units of the measurements, will not gain more information than Pearson s correlation (46). In conclusion, our study suggests that for predicting central and peripheral body fat mass, anthropometric measurements such as waist circumference and skinfolds are good alternatives in large epidemiological studies that do not allow application of DXA or CT. In daily practice, for the assessment of CFM-to-PFM ratio, the ratio (SSCSI)/ BMI in women and the waist/length in men are the best alternatives. According to our study, WHR should not be used to determine fat distribution. These findings might improve the prediction of diabetes and cardiovascular risk in men and women in future studies. Therefore, longitudinal data must be collected to establish the value of waist circumference and skinfold thickness. References 1 Ferreira I, Twisk JW, van Mechelen W, Kemper HC, Seidell JC & Stehouwer CD. Current and adolescent body fatness and fat distribution: relationships with carotid intima-media thickness and large artery stiffness at the age of 36 years. Journal of Hypertension Ferreira I, Snijder MB, Twisk JWR, van Mechelen W, Kemper HCG, Seidell JC & Stehouwer CDA. Central fat mass versus peripheral fat and lean mass: opposite (adverse versus favorable) associations with arterial stiffness? The Amsterdam Growth and Health Longitudinal Study Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism Kaplan NM. The deadly quartet. Upper-body obesity, glucose intolerance, hypertriglyceridemia, and hypertension. Archives of Internal Medicine Tanko LB, Bagger YZ, Alexandersen P, Larsen PJ & Christiansen C. Peripheral adiposity exhibits an independent dominant antiatherogenic effect in elderly women. Circulation Tanko LB, Bagger YZ, Alexandersen P, Larsen PJ & Christiansen C. Central and peripheral fat mass have contrasting effect on the progression of aortic calcification in postmenopausal women. European Heart Journal Seidell JC, Perusse L, Despres JP & Bouchard C. Waist and hip circumferences have independent and opposite effects on cardiovascular disease risk factors: the Quebec Family Study. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition Snijder MB, Dekker JM, Visser M, Yudkin JS, Stehouwer CD, Bouter LM, Heine RJ, Nijpels G & Seidell JC. Larger thigh and hip circumferences are associated with better glucose tolerance: the Hoorn Study. Obesity Research Snijder MB, Dekker JM, Visser M, Bouter LM, Stehouwer CD, Kostense PJ, Yudkin JS, Heine RJ, Nijpels G & Seidell JC. Associations of hip and thigh circumferences independent of waist circumference with the incidence of type 2 diabetes: the Hoorn Study. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition Snijder MB, Dekker JM, Visser M, Bouter LM, Stehouwer CD, Yudkin JS, Heine RJ, Nijpels G & Seidell JC. Trunk fat and leg fat have independent and opposite associations with fasting and postload glucose levels: the Hoorn Study. Diabetes Care Van Pelt RE, Evans EM, Schechtman KB, Ehsani AA & Kohrt WM. Contributions of total and regional fat mass to risk for cardiovascular disease in older women. American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism E1023 E Glickman SG, Marn CS, Supiano MA & Dengel DR. Validity and reliability of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for the assessment of abdominal adiposity. Journal of Applied Physiology Egger G. The case for using waist to hip ratio measurements in routine medical checks. Medical Journal of Australia Dobbelsteyn CJ, Joffres MR, MacLean DR & Flowerdew G. A comparative evaluation of waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio and body mass index as indicators of cardiovascular risk factors. The Canadian Heart Health Surveys. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders Ho SY, Lam TH, Janus ED & the Hong Kong Cardiovascular Risk Factor Prevalence Study Steering Committee. Waist to stature ratio is more strongly associated with cardiovascular risk factors than other simple anthropometric indices. Annals of Epidemiology von Eyben FE, Mouritsen E, Holm J, Montvilas P, Dimcevski G, Suciu G, Helleberg I, Kristensen L & von Eyben R. Intra-abdominal obesity and metabolic risk factors: a study of young adults. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders
7 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (2007) Krakauer JC, Franklin B, Kleerekoper M, Karlsson M & Levine JA. Body composition profiles derived from dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, total body scan, and mortality. Preventive Cardiology Taaffe DR, Lewis B & Marcus R. Regional fat distribution by dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry: comparison with anthropometry and application in a clinical trial of growth hormone and exercise. Clinical Science van Lenthe FJ, van Mechelen W, Kemper HC & Twisk JW. Association of a central pattern of body fat with blood pressure and lipoproteins from adolescence into adulthood. The Amsterdam Growth and Health Study. American Journal of Epidemiology te Velde SJ, Twisk JW, van Mechelen W & Kemper HC. Birth weight, adult body composition, and subcutaneous fat distribution. Obesity Research van Lenthe FJ, Kemper HC, van Mechelen W & Twisk JW. Development and tracking of central patterns of subcutaneous fat in adolescence and adulthood: the Amsterdam Growth and Health Study. International Journal of Epidemiology van Lenthe FJ, Kemper HC, van Mechelen W, Post GB, Twisk JW, Welten DC & Snel J. Biological maturation and the distribution of subcutaneous fat from adolescence into adulthood: the Amsterdam Growth and Health Study. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders Kemper HC, Snel J, Verschuur R & Storm-van Essen L. Tracking of health and risk indicators of cardiovascular diseases from teenager to adult: Amsterdam Growth and Health Study. Preventive Medicine Kemper HC, van Mechelen W, Post GB, Snel J, Twisk JW, van Lenthe FJ & Welten DC. The Amsterdam Growth and Health Longitudinal Study. The past ( ) and future (1997-?) International Journal of Sports Medicine (Suppl 3) S140 S Weiner JS & Lourie JA. Human Biology, A Guide to Field Methods. IBP Handbook No. 9 Oxford: Blackwell, van Lenthe FJ. The development of a central pattern of body fat from adolescence into adulthood; The Amsterdam Growth and Health Longitudinal Study Amsterdam: Vrije Universiteit. Thesis/Dissertation. 26 Weiner JS & Lourie JA. Human Biology, A Guide to Field Methods IBP Handbook Oxford: Blackwell, Bland JM & Altman DG. Multiple significance tests: the Bonferroni Method. BMJ Snijder MB, Henry RM, Visser M, Dekker JM, Seidell JC, Ferreira I, Bouter LM, Yudkin JS, Westerhof N & Stehouwer CD. Regional body composition as a determinant of arterial stiffness in the elderly: The Hoorn Study. Journal of Hypertension Taylor RW, Keil D, Gold EJ, Williams SM & Goulding A. Body mass index, waist girth, and waist-to-hip ratio as indexes of total and regional adiposity in women: evaluation using receiver operating characteristic curves. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition Donahue RP & Abbott RD. Central obesity and coronary heart disease in men. Lancet Blair SN, Ludwig DA & Goodyear NN. A canonical analysis of central and peripheral subcutaneous fat distribution and coronary heart disease risk factors in men and women aged years. Human Biology Yarnell JW, Patterson CC, Thomas HF & Sweetnam PM. Central obesity: predictive value of skinfold measurements for subsequent ischaemic heart disease at 14 years follow-up in the Caerphilly Study. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders Katz JR, Taylor NF, Goodrick S, Perry L, Yudkin JS & Coppack SW. Central obesity, depression and the hypothalamo-pituitary adrenal axis in men and postmenopausal women. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders Snijder MB, van Dam RM, Visser M & Seidell JC. What aspects of body fat are particularly hazardous and how do we measure them? International Journal of Epidemiology Azizi F, Esmaillzadeh A, Mirmiran P & Ainy E. Is there an independent association between waist-to-hip ratio and cardiovascular risk factors in overweight and obese women? International Journal of Cardiology Shimokata H, Andres R, Coon PJ, Elahi D, Muller DC & Tobin JD. Studies in the distribution of body fat. II. Longitudinal effects of change in weight. International Journal of Obesity Hoefle G, Saely CH, Aczel S, Benzer W, Marte T, Langer P & Drexel H. Impact of total and central obesity on vascular mortality in patients undergoing coronary angiography. International Journal of Obesity Yusuf S, Hawken S, Ounpuu S, Bautista L, Franzosi MG, Commerford P, Lang CC, Rumboldt Z, Onen CL, Lisheng L, Tanomsup S, Wangai P Jr, Razak F, Sharma AM & Anand SS. Obesity and the risk of myocardial infarction in 27,000 participants from 52 countries: a case-control study. Lancet Fuller NJ, Laskey MA & Elia M. Assessment of the composition of major body regions by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), with special reference to limb muscle mass. Clinical Physiology Weststrate JA, Deurenberg P & van Tinteren H. Indices of body fat distribution and adiposity in Dutch children from birth to 18 years of age. International Journal of Obesity Zimmet P, Hodge A, Nicolson M, Staten M, de Court M, Moore J, Morawiecki A, Lubina J, Collier G, Alberti G & Dowse G. Serum leptin concentration, obesity, and insulin resistance in Western Samoans: cross sectional study. BMJ Chan DC, Watts GF, Barrett PH & Burke V. Waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio and body mass index as predictors of adipose tissue compartments in men. QJM Gasperino J. Ethnic differences in body composition and their relation to health and disease in women. Ethnicity and Health Misra A, Wasir JS & Vikram NK. Waist circumference criteria for the diagnosis of abdominal obesity are not applicable uniformly to all populations and ethnic groups. Nutrition Asthana S, Gupta VM & Mishra RN. Screening for obesity in affluent females: body mass index and its comparison with skin fold thickness. Indian Journal of Public Health Douglas G Altman. Practical Statistics for Medical Research. London: Chapman & Hall, Received 11 October 2006 Accepted 20 March 2007 Waist and skinfold for body fatness 661
BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES. Abstract. Introduction. Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, UDC :572.
 EXERCISE AND QUALITY OF LIFE Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, 43-48 UDC 796.034.6-051:572.087 Research article BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES Jelena Popadiã Gaãeša *, Otto Barak, Dea Karaba
EXERCISE AND QUALITY OF LIFE Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, 43-48 UDC 796.034.6-051:572.087 Research article BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES Jelena Popadiã Gaãeša *, Otto Barak, Dea Karaba
CHAPTER 9. Anthropometry and Body Composition
 CHAPTER 9 Anthropometry and Body Composition 9.1 INTRODUCTION Ageing is characterized by reduction in fat free mass (FFM), primarily via loss of muscle mass, loss of bone mineral in women, redistribution
CHAPTER 9 Anthropometry and Body Composition 9.1 INTRODUCTION Ageing is characterized by reduction in fat free mass (FFM), primarily via loss of muscle mass, loss of bone mineral in women, redistribution
Associations of hip and thigh circumferences independent of waist circumference with the incidence of type 2 diabetes: the Hoorn Study 1 3
 Associations of hip and thigh circumferences independent of waist circumference with the incidence of type 2 diabetes: the Hoorn Study 1 3 Marieke B Snijder, Jacqueline M Dekker, Marjolein Visser, Lex
Associations of hip and thigh circumferences independent of waist circumference with the incidence of type 2 diabetes: the Hoorn Study 1 3 Marieke B Snijder, Jacqueline M Dekker, Marjolein Visser, Lex
Broadening Course YPHY0001 Practical Session II (October 11, 2006) Assessment of Body Fat
 Sheng HP - 1 Broadening Course YPHY0001 Practical Session II (October 11, 2006) Assessment of Body Fat REQUIRED FOR THIS PRACTICAL SESSION: 1. Please wear short-sleeve shirts / blouses for skin-fold measurements.
Sheng HP - 1 Broadening Course YPHY0001 Practical Session II (October 11, 2006) Assessment of Body Fat REQUIRED FOR THIS PRACTICAL SESSION: 1. Please wear short-sleeve shirts / blouses for skin-fold measurements.
ANTHROPOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS OF SOME LIMB AND BODY CIRCUMFERENCES IN MALES AND FEMALES WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE BALKAN SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE OF BIOLOGY IN PLOVDIV (BULGARIA) FROM 19 TH TILL 21 ST OF MAY 2005 (EDS B. GRUEV, M. NIKOLOVA AND A. DONEV), 2005 (P. 159 164) ANTHROPOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS
PROCEEDINGS OF THE BALKAN SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE OF BIOLOGY IN PLOVDIV (BULGARIA) FROM 19 TH TILL 21 ST OF MAY 2005 (EDS B. GRUEV, M. NIKOLOVA AND A. DONEV), 2005 (P. 159 164) ANTHROPOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS
Broadening Course YPHY0001 Practical Session III (March 19, 2008) Assessment of Body Fat
 Sheng HP - 1 Broadening Course YPHY0001 Practical Session III (March 19, 2008) Assessment of Body Fat REQUIRED FOR THIS PRACTICAL SESSION: 1. Please wear short-sleeve shirts / blouses. Shirts / blouses
Sheng HP - 1 Broadening Course YPHY0001 Practical Session III (March 19, 2008) Assessment of Body Fat REQUIRED FOR THIS PRACTICAL SESSION: 1. Please wear short-sleeve shirts / blouses. Shirts / blouses
An evaluation of body mass index, waist-hip ratio and waist circumference as a predictor of hypertension across urban population of Bangladesh.
 An evaluation of body mass index, waist-hip ratio and waist circumference as a predictor of hypertension across urban population of Bangladesh. Md. Golam Hasnain 1 Monjura Akter 2 1. Research Investigator,
An evaluation of body mass index, waist-hip ratio and waist circumference as a predictor of hypertension across urban population of Bangladesh. Md. Golam Hasnain 1 Monjura Akter 2 1. Research Investigator,
Body Composition. Sport Books Publisher 1
 Body Composition Sport Books Publisher 1 The body composition The body composition is affected by the proportions of the body component (bones, muscles, and other tissues) It can be seen that the major
Body Composition Sport Books Publisher 1 The body composition The body composition is affected by the proportions of the body component (bones, muscles, and other tissues) It can be seen that the major
Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment
 Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott,
Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott,
Suprailiac or Abdominal Skinfold Thickness Measured with a Skinfold Caliper as a Predictor of Body Density in Japanese Adults
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2007, Measurement 213, 51-61Error Characteristics of Skinfold Caliper 51 Suprailiac or Abdominal Skinfold Thickness Measured with a Skinfold Caliper as a Predictor of Body Density
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2007, Measurement 213, 51-61Error Characteristics of Skinfold Caliper 51 Suprailiac or Abdominal Skinfold Thickness Measured with a Skinfold Caliper as a Predictor of Body Density
Understanding Body Composition
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines 7 Understanding Body Composition Objectives Define body composition. Explain why the assessment of body size, shape, and composition is useful. Explain how to perform assessments
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines 7 Understanding Body Composition Objectives Define body composition. Explain why the assessment of body size, shape, and composition is useful. Explain how to perform assessments
Assessing Overweight in School Going Children: A Simplified Formula
 Journal of Applied Medical Sciences, vol. 4, no. 1, 2015, 27-35 ISSN: 2241-2328 (print version), 2241-2336 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2015 Assessing Overweight in School Going Children: A Simplified Formula
Journal of Applied Medical Sciences, vol. 4, no. 1, 2015, 27-35 ISSN: 2241-2328 (print version), 2241-2336 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2015 Assessing Overweight in School Going Children: A Simplified Formula
In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in
 1 2 In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in adults: the influence of body mass index 3 4 Running title: Precision of the idxa for the measurement of visceral
1 2 In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in adults: the influence of body mass index 3 4 Running title: Precision of the idxa for the measurement of visceral
Obesity in Moscow School Age Students: Prevalence, Ageand Gender- Related Features
 Food and Public Health: 2011; 1(1): 1-5 DOI: 10.5923/j.fph.20110101.01 Obesity in Moscow School Age Students: Prevalence, Ageand Gender- Related Features D. N. Gazina, K. G. Gurevich * Moscow State University
Food and Public Health: 2011; 1(1): 1-5 DOI: 10.5923/j.fph.20110101.01 Obesity in Moscow School Age Students: Prevalence, Ageand Gender- Related Features D. N. Gazina, K. G. Gurevich * Moscow State University
Adult BMI Calculator
 For more information go to Center for Disease Control http://search.cdc.gov/search?query=bmi+adult&utf8=%e2%9c%93&affiliate=cdc-main\ About BMI for Adults Adult BMI Calculator On this page: What is BMI?
For more information go to Center for Disease Control http://search.cdc.gov/search?query=bmi+adult&utf8=%e2%9c%93&affiliate=cdc-main\ About BMI for Adults Adult BMI Calculator On this page: What is BMI?
NJPPP RESEARCH ARTICLE WAIST-RELATED ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASURES: SIMPLE AND USEFUL PREDICTORS OF CORONARY HEART DISEASE IN WOMEN
 NJPPP National Journal of Physiology, Pharmacy & Pharmacology DOI: 10.5455/njppp.2015.5.010820142 http://www.njppp.com/ RESEARCH ARTICLE WAIST-RELATED ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASURES: SIMPLE AND USEFUL PREDICTORS
NJPPP National Journal of Physiology, Pharmacy & Pharmacology DOI: 10.5455/njppp.2015.5.010820142 http://www.njppp.com/ RESEARCH ARTICLE WAIST-RELATED ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASURES: SIMPLE AND USEFUL PREDICTORS
Differences in body composition between Singapore Chinese, Beijing Chinese and Dutch children
 ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION (2003) 57, 405 409 ß 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954 3007/03 $25.00 www.nature.com/ejcn Differences in body composition between Singapore Chinese, Beijing Chinese
ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION (2003) 57, 405 409 ß 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954 3007/03 $25.00 www.nature.com/ejcn Differences in body composition between Singapore Chinese, Beijing Chinese
3/25/2010. Age-adjusted incidence rates for coronary heart disease according to body mass index and waist circumference tertiles
 Outline Relationships among Regional Adiposity, Physical Activity, and CVD Risk Factors: Preliminary Results from Two Epidemiologic Studies Molly Conroy, MD, MPH Obesity Journal Club February 18, 2010
Outline Relationships among Regional Adiposity, Physical Activity, and CVD Risk Factors: Preliminary Results from Two Epidemiologic Studies Molly Conroy, MD, MPH Obesity Journal Club February 18, 2010
Abdominal volume index and conicity index in predicting metabolic abnormalities in young women of different socioeconomic class
 Research Article Abdominal volume index and conicity index in predicting metabolic abnormalities in young women of different socioeconomic class Vikram Gowda, Kripa Mariyam Philip Department of Physiology,
Research Article Abdominal volume index and conicity index in predicting metabolic abnormalities in young women of different socioeconomic class Vikram Gowda, Kripa Mariyam Philip Department of Physiology,
Visceral Fat in Prepubertal Children: Influence of Obesity, Anthropometry, Ethnicity, Gender, Diet, and Growth
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF HUMAN BIOLOGY 11:201 207 (1999) Visceral Fat in Prepubertal Children: Influence of Obesity, Anthropometry, Ethnicity, Gender, Diet, and Growth MICHAEL I. GORAN* Division of Physiology
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF HUMAN BIOLOGY 11:201 207 (1999) Visceral Fat in Prepubertal Children: Influence of Obesity, Anthropometry, Ethnicity, Gender, Diet, and Growth MICHAEL I. GORAN* Division of Physiology
A study of waist hip ratio in identifying cardiovascular risk factors at Government Dharmapuri College Hospital
 Original Research Article A study of waist hip ratio in identifying cardiovascular risk factors at Government Dharmapuri College Hospital M. Arivumani * Assistant Professor of General Medicine, Government
Original Research Article A study of waist hip ratio in identifying cardiovascular risk factors at Government Dharmapuri College Hospital M. Arivumani * Assistant Professor of General Medicine, Government
Procedures for taking physical measurements
 Procedures for taking physical measurements Dr Diane Cooper PhD Exercise physiology and metabolism Partner in True Fitness Coordinator & lecturer on BSc Sports Science, AIT Metabolic researcher on European
Procedures for taking physical measurements Dr Diane Cooper PhD Exercise physiology and metabolism Partner in True Fitness Coordinator & lecturer on BSc Sports Science, AIT Metabolic researcher on European
# % & (!) +,. / !( : 0 ( (;9 +/ ((8
 ! # % & (!) +,. / 0 1 2 3 4 + 5.667 8 19!( : 0 ( (;9 +/ ((8 < Do we need to think beyond BMI for estimating population level health risks? Green, MA (Corresponding author), Research Associate, School of
! # % & (!) +,. / 0 1 2 3 4 + 5.667 8 19!( : 0 ( (;9 +/ ((8 < Do we need to think beyond BMI for estimating population level health risks? Green, MA (Corresponding author), Research Associate, School of
The Indian subcontinent is undergoing epidemiological transition, as noncommunicable
 22 Journal of the association of physicians of india vol 63 january, 2015 Original Article Correlation and Comparison of Various Anthropometric Measurements of Body Fat Distribution and Sagittal Abdominal
22 Journal of the association of physicians of india vol 63 january, 2015 Original Article Correlation and Comparison of Various Anthropometric Measurements of Body Fat Distribution and Sagittal Abdominal
A Pilot Study of Exercise Training to Reduce Trunk Fat in Adults With HIV Associated Fat Redistribution
 A Pilot Study of Exercise Training to Reduce Trunk Fat in Adults With HIV Associated Fat Redistribution Ronenn Roubenoff, Lauren Weiss, Ann McDermott, Tanya Heflin, Gregory J. Cloutier, Michael Wood and
A Pilot Study of Exercise Training to Reduce Trunk Fat in Adults With HIV Associated Fat Redistribution Ronenn Roubenoff, Lauren Weiss, Ann McDermott, Tanya Heflin, Gregory J. Cloutier, Michael Wood and
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 48.2 years Height / Weight: 150.0 cm 72.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 48.2 years Height / Weight: 150.0 cm 72.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Birth Date: 40.2 years Height / Weight: 158.0 cm 52.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 50% 40% 30% 20% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Birth Date: 40.2 years Height / Weight: 158.0 cm 52.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 50% 40% 30% 20% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
1 From the Institute of Health Sciences, Faculty of Earth and Life Sciences,
 Sagittal abdominal diameter: no advantage compared with other anthropometric measures as a correlate of components of the metabolic syndrome in elderly from the Hoorn Study 1 3 Janine Mukuddem-Petersen,
Sagittal abdominal diameter: no advantage compared with other anthropometric measures as a correlate of components of the metabolic syndrome in elderly from the Hoorn Study 1 3 Janine Mukuddem-Petersen,
Body composition. Body composition models Fluid-metabolism ECF. Body composition models Elemental. Body composition models Anatomic. Molnár Dénes.
 Body composition models Fluid-metabolism Fat Body composition ECF Molnár Dénes BCM ICF ICS ECS FFM Body composition models Anatomic Fat NSMST SM Body composition models Elemental Miscellaneous Calcium
Body composition models Fluid-metabolism Fat Body composition ECF Molnár Dénes BCM ICF ICS ECS FFM Body composition models Anatomic Fat NSMST SM Body composition models Elemental Miscellaneous Calcium
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 43.4 years Height / Weight: 170.0 cm 66.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 43.4 years Height / Weight: 170.0 cm 66.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION
 (2004) 58, 888 893 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954-3007/04 $30.00 www.nature.com/ejcn ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION Waist circumference, body mass index, hip circumference and waist-to-hip
(2004) 58, 888 893 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954-3007/04 $30.00 www.nature.com/ejcn ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION Waist circumference, body mass index, hip circumference and waist-to-hip
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in Dexa Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Birth Date: 24.7 years Height / Weight: 8.0 cm 79.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 40% 30% 20% 0% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 00 Centile
Birth Date: 24.7 years Height / Weight: 8.0 cm 79.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 40% 30% 20% 0% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 00 Centile
Understanding & Interpreting Body Composition Measures
 BODY COMPOSITION Understanding & Interpreting Body Composition Measures Body composition = component of health-related fitness & = component of metabolic fitness Unlike other health-related fitness Not
BODY COMPOSITION Understanding & Interpreting Body Composition Measures Body composition = component of health-related fitness & = component of metabolic fitness Unlike other health-related fitness Not
Effect of Physical Training on Body Composition in Moscow Adolescents
 Effect of Physical Training on Body Composition in Moscow Adolescents Elena Godina, Irena Khomyakova, Arsen Purundzhan, Anna Tretyak and Ludmila Zadorozhnaya Institute and Museum of Anthropology, Moscow
Effect of Physical Training on Body Composition in Moscow Adolescents Elena Godina, Irena Khomyakova, Arsen Purundzhan, Anna Tretyak and Ludmila Zadorozhnaya Institute and Museum of Anthropology, Moscow
Bedside methods versus dual energy X-ray absorptiometry for body composition measurement in COPD
 Eur Respir J ; 19: 66 631 DOI: 1.1183/931936..796 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Bedside methods versus dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
Eur Respir J ; 19: 66 631 DOI: 1.1183/931936..796 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Bedside methods versus dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
What Is Body Composition?
 Chapter Six What Is Body Composition? Body composition is the body s relative amounts of fat mass and fat-free mass Body fat includes two categories: Essential fat is crucial for normal body functioning
Chapter Six What Is Body Composition? Body composition is the body s relative amounts of fat mass and fat-free mass Body fat includes two categories: Essential fat is crucial for normal body functioning
The Impact Of Adiposity And Insulin Resistance On Endothelial Function In Middle-Aged Subjects
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Cardiovascular Research Volume 1 Number 1 The Impact Of Adiposity And Insulin Resistance On Endothelial Function In Middle-Aged Subjects L Zhu, K Liu Citation L Zhu, K
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Cardiovascular Research Volume 1 Number 1 The Impact Of Adiposity And Insulin Resistance On Endothelial Function In Middle-Aged Subjects L Zhu, K Liu Citation L Zhu, K
Cut-Off Values of Visceral Fat Area and Waist-to-Height Ratio: Diagnostic Criteria for Obesity-Related Disorders in Korean Children and Adolescents
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.1.99 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 53(1):99-105, 2012 Cut-Off Values of Visceral Fat Area and Waist-to-Height Ratio: Diagnostic
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.1.99 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 53(1):99-105, 2012 Cut-Off Values of Visceral Fat Area and Waist-to-Height Ratio: Diagnostic
BMI may underestimate the socioeconomic gradient in true obesity
 8 BMI may underestimate the socioeconomic gradient in true obesity Gerrit van den Berg, Manon van Eijsden, Tanja G.M. Vrijkotte, Reinoud J.B.J. Gemke Pediatric Obesity 2013; 8(3): e37-40 102 Chapter 8
8 BMI may underestimate the socioeconomic gradient in true obesity Gerrit van den Berg, Manon van Eijsden, Tanja G.M. Vrijkotte, Reinoud J.B.J. Gemke Pediatric Obesity 2013; 8(3): e37-40 102 Chapter 8
Opposite Contributions of Trunk and Leg Fat Mass with Plasma Lipase Activities: The Hoorn Study
 Opposite Contributions of Trunk and Leg Fat Mass with Plasma Lipase Activities: The Hoorn Study Griët Bos,* Marieke B. Snijder,* Giel Nijpels,* Jacqueline M. Dekker,* Coen D.A. Stehouwer,* Lex M. Bouter,*
Opposite Contributions of Trunk and Leg Fat Mass with Plasma Lipase Activities: The Hoorn Study Griët Bos,* Marieke B. Snijder,* Giel Nijpels,* Jacqueline M. Dekker,* Coen D.A. Stehouwer,* Lex M. Bouter,*
Impact of infant feeding on growth trajectory patterns in childhood and body composition in young adulthood
 Impact of infant feeding on growth trajectory patterns in childhood and body composition in young adulthood WP10 working group of the Early Nutrition Project Peter Rzehak*, Wendy H. Oddy,* Maria Luisa
Impact of infant feeding on growth trajectory patterns in childhood and body composition in young adulthood WP10 working group of the Early Nutrition Project Peter Rzehak*, Wendy H. Oddy,* Maria Luisa
Validation of bioimpedance body composition assessment by TANITA BC-418 in 7 years-
 Validation of bioimpedance body composition assessment by TANITA BC-418 in 7 years- old children vs. Dual X-ray absorptiometry Veronica Luque on behalf to URV Team 18th November 2012 Milano, 10th Bi-annual
Validation of bioimpedance body composition assessment by TANITA BC-418 in 7 years- old children vs. Dual X-ray absorptiometry Veronica Luque on behalf to URV Team 18th November 2012 Milano, 10th Bi-annual
WORLDWIDE, THE PREVAlence
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Relation of Impaired Fasting and Postload Glucose With Incident Type 2 Diabetes in a Dutch Population The Hoorn Study Femmie de Vegt, PhD Jacqueline M. Dekker, PhD Agnes Jager, MD,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Relation of Impaired Fasting and Postload Glucose With Incident Type 2 Diabetes in a Dutch Population The Hoorn Study Femmie de Vegt, PhD Jacqueline M. Dekker, PhD Agnes Jager, MD,
Relationship of Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference and Waist-Stature Ratio with Body Fat of the Indian Gorkha Population
 Mal J Nutr Relationship 19(2): 185 of BMI, - 192, WC 2013 and WSR with Body Fat of the Indian Gorkha Population 185 Relationship of Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference and Waist-Stature Ratio with Body
Mal J Nutr Relationship 19(2): 185 of BMI, - 192, WC 2013 and WSR with Body Fat of the Indian Gorkha Population 185 Relationship of Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference and Waist-Stature Ratio with Body
Relationship Among Three Field Methods of Estimating Percent Body Fat in Young Adults
 Relationship Among Three Field Methods of Estimating Percent Body Fat in Young Adults A O AKINPELU Department of Physiotherapy, College of Medicine, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria CA GBIRI Department
Relationship Among Three Field Methods of Estimating Percent Body Fat in Young Adults A O AKINPELU Department of Physiotherapy, College of Medicine, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria CA GBIRI Department
Body mass index, waist circumference and waist:hip ratio as predictors of cardiovascular risk a review of the literature
 (2010) 64, 16 22 & 2010 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0954-3007/10 $32.00 www.nature.com/ejcn REVIEW Body mass index, waist circumference and waist:hip ratio as predictors of cardiovascular
(2010) 64, 16 22 & 2010 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0954-3007/10 $32.00 www.nature.com/ejcn REVIEW Body mass index, waist circumference and waist:hip ratio as predictors of cardiovascular
Understanding Body Composition
 Understanding Body Composition Chapter 7 Body Composition n Body composition is the ratio between fat and fat-free mass n Fat-free mass includes all tissues exclusive of fat (muscle, bone, organs, fluids)
Understanding Body Composition Chapter 7 Body Composition n Body composition is the ratio between fat and fat-free mass n Fat-free mass includes all tissues exclusive of fat (muscle, bone, organs, fluids)
DUAL ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY (DXA) GOLD STANDARD FOR BONE HEALTH AND BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT
 DUAL ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY (DXA) GOLD STANDARD FOR BONE HEALTH AND BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT Prof d-r Slavica Šubeska Stratrova Clinic of Endocrinology, Skopje, Macedonia Definition and classification
DUAL ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY (DXA) GOLD STANDARD FOR BONE HEALTH AND BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT Prof d-r Slavica Šubeska Stratrova Clinic of Endocrinology, Skopje, Macedonia Definition and classification
CORRELATION OF PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS WITH BODY FAT PERCENTAGE IN YOUNG INDIVIDUALS
 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2008; 52 (4) : 383 388 CORRELATION OF PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS WITH BODY FAT PERCENTAGE IN YOUNG INDIVIDUALS ANURADHA R. JOSHI*, RATAN SINGH AND A. R. JOSHI Department of Physiology,
Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2008; 52 (4) : 383 388 CORRELATION OF PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS WITH BODY FAT PERCENTAGE IN YOUNG INDIVIDUALS ANURADHA R. JOSHI*, RATAN SINGH AND A. R. JOSHI Department of Physiology,
Anthropometry: What Can We Measure & What Does It Mean?
 Anthropometry: What Can We Measure & What Does It Mean? Anne McTiernan, MD, PhD Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center Seattle, Washington, U.S.A. I have no conflicts to disclose. Anthropometry in Human
Anthropometry: What Can We Measure & What Does It Mean? Anne McTiernan, MD, PhD Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center Seattle, Washington, U.S.A. I have no conflicts to disclose. Anthropometry in Human
Body composition analysis by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in female diabetics differ between manufacturers
 European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 449±454 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Body composition analysis by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in female diabetics
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 449±454 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Body composition analysis by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in female diabetics
JEPonline Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline
 Estimating Intra-abdominal Fat 1 JEPonline Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline Official Journal of The American Society of Exercise Physiologists (ASEP) ISSN 1097-9751 An International Electronic Journal
Estimating Intra-abdominal Fat 1 JEPonline Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline Official Journal of The American Society of Exercise Physiologists (ASEP) ISSN 1097-9751 An International Electronic Journal
Abdominal fat distribution (subcutaneous vs. visceral abdominal fat compartments): correlation with gender, age, BMI and waist circumference
 Abdominal fat distribution (subcutaneous vs. visceral abdominal fat compartments): correlation with gender, age, BMI and waist circumference Poster No.: C-934 Congress: ECR 202 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Abdominal fat distribution (subcutaneous vs. visceral abdominal fat compartments): correlation with gender, age, BMI and waist circumference Poster No.: C-934 Congress: ECR 202 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Obesity and the Metabolic Syndrome in Developing Countries: Focus on South Asians
 Obesity and the Metabolic Syndrome in Developing Countries: Focus on South Asians Anoop Misra Developing countries, particularly South Asian countries, are witnessing a rapid increase in type 2 diabetes
Obesity and the Metabolic Syndrome in Developing Countries: Focus on South Asians Anoop Misra Developing countries, particularly South Asian countries, are witnessing a rapid increase in type 2 diabetes
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 29.5 years Height / Weight: 156.0 cm 57.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 29.5 years Height / Weight: 156.0 cm 57.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
Body Composition Monitors - Model HBF-361
 Products - Weight Management / Model HBF-361 Measures weight and more! For ideal weight management, know you body composition- body fat percentage, visceral fat level, subcutaneous fat and skeletal muscle
Products - Weight Management / Model HBF-361 Measures weight and more! For ideal weight management, know you body composition- body fat percentage, visceral fat level, subcutaneous fat and skeletal muscle
Association between Raised Blood Pressure and Dysglycemia in Hong Kong Chinese
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online June 12, 2008 Raised Blood Pressure and Dysglycemia Association between Raised Blood Pressure and Dysglycemia in Hong Kong Chinese Bernard My Cheung,
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online June 12, 2008 Raised Blood Pressure and Dysglycemia Association between Raised Blood Pressure and Dysglycemia in Hong Kong Chinese Bernard My Cheung,
Fitness and Wellness 12th Edition Hoeger TEST BANK Full download at:
 Fitness and Wellness 12th Edition Hoeger TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/fitness-wellness-12th-edition-hoeger-testbank/ Fitness and Wellness 12th Edition Hoeger SOLUTIONS
Fitness and Wellness 12th Edition Hoeger TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/fitness-wellness-12th-edition-hoeger-testbank/ Fitness and Wellness 12th Edition Hoeger SOLUTIONS
Interpretation Guide. What you are made of? Find out with - Vital Body Scan NZ Ltd. Mobile Body Composition Analysis
 Interpretation Guide Vital Body Scan NZ Ltd What you are made of? Find out with - Vital Body Scan NZ Ltd Mobile Body Composition Analysis Interpreting your results Total Body Water (TBW) TBW is all the
Interpretation Guide Vital Body Scan NZ Ltd What you are made of? Find out with - Vital Body Scan NZ Ltd Mobile Body Composition Analysis Interpreting your results Total Body Water (TBW) TBW is all the
Evaluation of body fat in fatter and leaner 10-y-old African American and white children: the Baton Rouge Children s Study 1 3
 Original Research Communications Evaluation of body fat in fatter and leaner 10-y-old African American and white children: the Baton Rouge Children s Study 1 3 George A Bray, James P DeLany, David W Harsha,
Original Research Communications Evaluation of body fat in fatter and leaner 10-y-old African American and white children: the Baton Rouge Children s Study 1 3 George A Bray, James P DeLany, David W Harsha,
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
 University of Pretoria etd Mentz, N (2003) 171 CHAPTER 4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION The primary aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of an eight-week programme of electrical muscle stimulation (EMS)
University of Pretoria etd Mentz, N (2003) 171 CHAPTER 4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION The primary aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of an eight-week programme of electrical muscle stimulation (EMS)
IMPACT OF SELECTED MINOR GAMES ON PHYSIOLOGICAL FACTORS AND RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN OBESITY; AMONG SCHOOL STUDENTS
 184 IMPACT OF SELECTED MINOR GAMES ON PHYSIOLOGICAL FACTORS AND RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN OBESITY; AMONG SCHOOL STUDENTS INTRODUCTION PRADEEP.C.S*; AJEESH.P.T**; ARUN.C.NAIR*** *Lecturer in Physical Education,
184 IMPACT OF SELECTED MINOR GAMES ON PHYSIOLOGICAL FACTORS AND RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN OBESITY; AMONG SCHOOL STUDENTS INTRODUCTION PRADEEP.C.S*; AJEESH.P.T**; ARUN.C.NAIR*** *Lecturer in Physical Education,
Pathophysiology Department
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE - PLOVDIV Pathophysiology Department 15A Vasil Aprilov Blvd. Tel. +359 32 602311 Algorithm for interpretation of submaximal exercise tests in children S. Kostianev 1, B. Marinov
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE - PLOVDIV Pathophysiology Department 15A Vasil Aprilov Blvd. Tel. +359 32 602311 Algorithm for interpretation of submaximal exercise tests in children S. Kostianev 1, B. Marinov
Downloaded from ijem.sbmu.ac.ir at 20: on Sunday February 24th 2019
 ( ) ( ). :. :. - -.. -. ( ) %/ :. SPSS %/. %/. %/ :.(r= / p
( ) ( ). :. :. - -.. -. ( ) %/ :. SPSS %/. %/. %/ :.(r= / p
The Relationship of BMI, Fat Percentage, and Waist-Hip Ratio to Physical Fitness Factors in Female Students
 J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res., 3(3)1273-1278, 2013 2013, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-4304 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com The Relationship of BMI, Fat Percentage, and Waist-Hip
J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res., 3(3)1273-1278, 2013 2013, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-4304 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com The Relationship of BMI, Fat Percentage, and Waist-Hip
Obesity and Breast Cancer in a Multiethnic Population. Gertraud Maskarinec, MD, PhD University of Hawaii Cancer Center, Honolulu, HI
 Obesity and Breast Cancer in a Multiethnic Population Gertraud Maskarinec, MD, PhD University of Hawaii Cancer Center, Honolulu, HI Background Breast cancer incidence remains lower in many Asian than Western
Obesity and Breast Cancer in a Multiethnic Population Gertraud Maskarinec, MD, PhD University of Hawaii Cancer Center, Honolulu, HI Background Breast cancer incidence remains lower in many Asian than Western
Timing and tempo of first year growth in relation to cardiovascular and metabolic risk profile in early adulthood
 Note: for non-commercial purposes only Timing and tempo of first year growth in relation to cardiovascular and metabolic risk profile in early adulthood Anita Hokken-Koelega Professor of Pediatric Endocrinology
Note: for non-commercial purposes only Timing and tempo of first year growth in relation to cardiovascular and metabolic risk profile in early adulthood Anita Hokken-Koelega Professor of Pediatric Endocrinology
Temporal Trends in the Prevalence and Extent of Overweight among 9-11 Year-Old Australians:
 CHAPTER 8 Temporal Trends in the Prevalence and Extent of Overweight among 9-11 Year-Old Australians: 1985- Jim Dollman and Amanda Pilgrim INTRODUCTION There are reports of increasing overweight and obesity
CHAPTER 8 Temporal Trends in the Prevalence and Extent of Overweight among 9-11 Year-Old Australians: 1985- Jim Dollman and Amanda Pilgrim INTRODUCTION There are reports of increasing overweight and obesity
UNIT 4 ASSESSMENT OF NUTRITIONAL STATUS
 UNIT 4 ASSESSMENT OF NUTRITIONAL STATUS COMMUNITY HEALTH NUTRITION BSPH 314 CHITUNDU KASASE BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN PUBLIC HEALTH UNIVERSITY OF LUSAKA 1. Measurement of dietary intake 2. Anthropometry 3.
UNIT 4 ASSESSMENT OF NUTRITIONAL STATUS COMMUNITY HEALTH NUTRITION BSPH 314 CHITUNDU KASASE BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN PUBLIC HEALTH UNIVERSITY OF LUSAKA 1. Measurement of dietary intake 2. Anthropometry 3.
Relationship of Waist Circumference and Lipid Profile in Children
 International Journal of Biomedical Science and Engineering 2015; 3(3): 44-48 Published online May 28, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijbse) doi: 10.11648/j.ijbse.20150303.12 ISSN: 2376-7227
International Journal of Biomedical Science and Engineering 2015; 3(3): 44-48 Published online May 28, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijbse) doi: 10.11648/j.ijbse.20150303.12 ISSN: 2376-7227
Fat Mass. Baseline. (lbs) (lbs) Composition Trend: Total. Aug 17. Apr 17. May 17. Jun 17. Jul 17. Measured Date
 Name Sample Report Birth Date: 00/00/000 Height: 74.0 in. Gender Male Age: 54.7 Input Weight: 165.0 lbs. Body Composition Analysis (BCA) DXA or DEXA is a three component model, which means it quantifies
Name Sample Report Birth Date: 00/00/000 Height: 74.0 in. Gender Male Age: 54.7 Input Weight: 165.0 lbs. Body Composition Analysis (BCA) DXA or DEXA is a three component model, which means it quantifies
Client Sex Facility Birth Date Height Weight Measured ####, #### #### (not specified) #### #### #### ####
 SUMMARY RESULTS This table provides an overview of your total body composition, broken down into total body fat %, total mass, fat tissue, lean tissue, and bone mineral content. These metrics establish
SUMMARY RESULTS This table provides an overview of your total body composition, broken down into total body fat %, total mass, fat tissue, lean tissue, and bone mineral content. These metrics establish
Volume 7, Issue 1, January 2018, e-issn:
 Volume 7, Issue 1, January 2018, www.ijfans.com e-issn: 2320-7876 e-issn 2320-7876 www.ijfans.com Vol. 7, No. 1, January 2018 All Rights Reserved Research Paper Open Access ASSESSMENT OF NUTRITIONAL ANTHROPOMETRY
Volume 7, Issue 1, January 2018, www.ijfans.com e-issn: 2320-7876 e-issn 2320-7876 www.ijfans.com Vol. 7, No. 1, January 2018 All Rights Reserved Research Paper Open Access ASSESSMENT OF NUTRITIONAL ANTHROPOMETRY
Do Measures of Body Fat Distribution Provide Information on the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in Addition to Measures of General Obesity?
 Epidemiology/Health Services/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Do Measures of Body Fat Distribution Provide Information on the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in Addition to Measures of General
Epidemiology/Health Services/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Do Measures of Body Fat Distribution Provide Information on the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in Addition to Measures of General
CHAPTER 3 DIABETES MELLITUS, OBESITY, HYPERTENSION AND DYSLIPIDEMIA IN ADULT CENTRAL KERALA POPULATION
 CHAPTER 3 DIABETES MELLITUS, OBESITY, HYPERTENSION AND DYSLIPIDEMIA IN ADULT CENTRAL KERALA POPULATION 3.1 BACKGROUND Diabetes mellitus (DM) and impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) have reached epidemic proportions
CHAPTER 3 DIABETES MELLITUS, OBESITY, HYPERTENSION AND DYSLIPIDEMIA IN ADULT CENTRAL KERALA POPULATION 3.1 BACKGROUND Diabetes mellitus (DM) and impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) have reached epidemic proportions
An Evaluation of Candidate Definitions of the Metabolic Syndrome in Adult Asian Indians
 Metabolic Syndrome/Insulin Resistance Syndrome/Pre-Diabetes O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E An Evaluation of Candidate Definitions of the Metabolic Syndrome in Adult Asian Indians ANOOP MISRA, MD 1 JASJEET
Metabolic Syndrome/Insulin Resistance Syndrome/Pre-Diabetes O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E An Evaluation of Candidate Definitions of the Metabolic Syndrome in Adult Asian Indians ANOOP MISRA, MD 1 JASJEET
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in Dexa Total Body 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Patient: Obese, Sample Birth Date: 0/Jan/966 44.4 years Height / Weight: 72.0 cm 95.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Referring Physician: DR. SMITH Measured: 07/Jun/200 7:0:52 PM (.40) Analyzed: 02/Apr/203
Patient: Obese, Sample Birth Date: 0/Jan/966 44.4 years Height / Weight: 72.0 cm 95.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Referring Physician: DR. SMITH Measured: 07/Jun/200 7:0:52 PM (.40) Analyzed: 02/Apr/203
Changes and clinical significance of serum vaspin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes
 Changes and clinical significance of serum vaspin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes L. Yang*, S.J. Chen*, G.Y. Yuan, D. Wang and J.J. Chen Department of Endocrinology, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu
Changes and clinical significance of serum vaspin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes L. Yang*, S.J. Chen*, G.Y. Yuan, D. Wang and J.J. Chen Department of Endocrinology, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu
Location of body fat and body size impacts DXA soft tissue measures: a simulation study
 (2008) 62, 553 559 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954-3007/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/ejcn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Location of body fat and body size impacts DXA soft tissue measures: a simulation
(2008) 62, 553 559 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954-3007/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/ejcn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Location of body fat and body size impacts DXA soft tissue measures: a simulation
European Journal of Physical Education and Sport, 2016, Vol.(13), Is. 3
 Copyright 2016 by Academic Publishing House Researcher Published in the Russian Federation European Journal of Physical Education and Sport Has been issued since 2013. ISSN: 2310-0133 E-ISSN: 2310-3434
Copyright 2016 by Academic Publishing House Researcher Published in the Russian Federation European Journal of Physical Education and Sport Has been issued since 2013. ISSN: 2310-0133 E-ISSN: 2310-3434
Santosh Metgud 1, Charleen D Silva * 2, Anand Heggannavar 3. Access this Article online. Quick Response code. Original Research Article
 Original Research Article EFFECT OF 30 DAYS ABDOMINALS CHALLENGE VERSUS 30 DAYS PLANKS CHALLENGE ON WAIST CIRCUMFERENCE AND ABDOMINAL SKIN FOLD MEASUREMENTS IN HEALTHY YOUNG INDIVIDUALS: RANDOMIZED CLINICAL
Original Research Article EFFECT OF 30 DAYS ABDOMINALS CHALLENGE VERSUS 30 DAYS PLANKS CHALLENGE ON WAIST CIRCUMFERENCE AND ABDOMINAL SKIN FOLD MEASUREMENTS IN HEALTHY YOUNG INDIVIDUALS: RANDOMIZED CLINICAL
Metabolic Syndrome in Asians
 Metabolic Syndrome in Asians Alka Kanaya, MD Asst. Professor of Medicine, UCSF Asian CV Symposium, November 17, 2007 The Metabolic Syndrome Also known as: Syndrome X Insulin Resistance Syndrome The Deadly
Metabolic Syndrome in Asians Alka Kanaya, MD Asst. Professor of Medicine, UCSF Asian CV Symposium, November 17, 2007 The Metabolic Syndrome Also known as: Syndrome X Insulin Resistance Syndrome The Deadly
University of Groningen. The epidemiology of abdominal adiposity De Lucia Rolfe, Emanuella
 University of Groningen The epidemiology of abdominal adiposity De Lucia Rolfe, Emanuella IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
University of Groningen The epidemiology of abdominal adiposity De Lucia Rolfe, Emanuella IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
Understanding Clinical Assessment Using The Edmonton Obesity Staging System
 Understanding Clinical Assessment Using The Edmonton Obesity Staging System Arya M Sharma, MD. PhD, FRCPC Research Chair for Obesity Research & Management University of Alberta Medical Director Alberta
Understanding Clinical Assessment Using The Edmonton Obesity Staging System Arya M Sharma, MD. PhD, FRCPC Research Chair for Obesity Research & Management University of Alberta Medical Director Alberta
Fetal and Infant Growth and Glucose Tolerance in the Hertfordshire Cohort Study
 Fetal and Infant Growth and Glucose Tolerance in the Hertfordshire Cohort Study A Study of and Born Between 1931 and 1939 David I.W. Phillips, Peter Goulden, Holly E. Syddall, Avan Aihie Sayer, Elaine
Fetal and Infant Growth and Glucose Tolerance in the Hertfordshire Cohort Study A Study of and Born Between 1931 and 1939 David I.W. Phillips, Peter Goulden, Holly E. Syddall, Avan Aihie Sayer, Elaine
This is a digitised version of a dissertation submitted to the University of Bedfordshire. It is available to view only.
 Title The Validity of Two Compartment Model Methods of Body Composition as Compared to Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Asian Indian Versus Caucasian Males Name Ben Davies This is a digitised version of a
Title The Validity of Two Compartment Model Methods of Body Composition as Compared to Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Asian Indian Versus Caucasian Males Name Ben Davies This is a digitised version of a
Component of Statistics Canada Catalogue no X Health Fact Sheets. Article. Body Composition of Canadian Adults 2007 to 2009.
 Component of Statistics Canada Catalogue no. 82-625-X Health Fact Sheets Article Body Composition of Canadian Adults 2007 to 2009 January 2010 How to obtain more information For information about this
Component of Statistics Canada Catalogue no. 82-625-X Health Fact Sheets Article Body Composition of Canadian Adults 2007 to 2009 January 2010 How to obtain more information For information about this
WAIST-HEIGHT RATIO : A NEW OBESITY INDEX FOR FILIPINOS?
 WAIST-HEIGHT RATIO : A NEW OBESITY INDEX FOR FILIPINOS? Consuelo L. Orense, MSPH, Charmaine A. Duante, RMT, MS Epid.(PH), Ermelita N. Bautista, MPH and Lilibeth P. Dasco, MSAN ABSTRACT The study aimed
WAIST-HEIGHT RATIO : A NEW OBESITY INDEX FOR FILIPINOS? Consuelo L. Orense, MSPH, Charmaine A. Duante, RMT, MS Epid.(PH), Ermelita N. Bautista, MPH and Lilibeth P. Dasco, MSAN ABSTRACT The study aimed
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017
 ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Paediatric specificities of nutritional assessment Body composition measurement in children N. Mehta (US) 39 th ESPEN Congress The Hague, Netherlands Body Composition Measurement
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Paediatric specificities of nutritional assessment Body composition measurement in children N. Mehta (US) 39 th ESPEN Congress The Hague, Netherlands Body Composition Measurement
Are Predictive Equations for Estimating Resting Energy Expenditure Accurate in Asian Indian Male Weightlifters?
 Original Article Are Predictive Equations for Estimating Resting Energy Expenditure Accurate in Asian Indian Male Weightlifters? Mini Joseph, Riddhi Das Gupta 1, L. Prema 2, Mercy Inbakumari 1, Nihal Thomas
Original Article Are Predictive Equations for Estimating Resting Energy Expenditure Accurate in Asian Indian Male Weightlifters? Mini Joseph, Riddhi Das Gupta 1, L. Prema 2, Mercy Inbakumari 1, Nihal Thomas
Comparisons of waist circumferences measured at 4 sites 1 3
 Comparisons of waist circumferences measured at 4 sites 1 3 Jack Wang, John C Thornton, Salina Bari, Bennett Williamson, Dympna Gallagher, Steven B Heymsfield, Mary Horlick, Donald Kotler, Blandine Laferrère,
Comparisons of waist circumferences measured at 4 sites 1 3 Jack Wang, John C Thornton, Salina Bari, Bennett Williamson, Dympna Gallagher, Steven B Heymsfield, Mary Horlick, Donald Kotler, Blandine Laferrère,
Overview of the FITNESSGRAM Body Composition Standards
 body composition Body composition refers to the division of total body weight (mass) into components, most commonly fat mass and fat-free mass. The proportion of total body weight that is fat (referred
body composition Body composition refers to the division of total body weight (mass) into components, most commonly fat mass and fat-free mass. The proportion of total body weight that is fat (referred
Body Mass Index. The table below can be used to assess an adult s status BMI Status.
 Body Mass Index (BMI) is used as a screening tool to identify possible weight problems, however, BMI is not a diagnostic tool. To determine if excess weight is a health risk further assessments are needed
Body Mass Index (BMI) is used as a screening tool to identify possible weight problems, however, BMI is not a diagnostic tool. To determine if excess weight is a health risk further assessments are needed
Sports Performance 15. Section 3.2: Body Composition
 Sports Performance 15 Section 3.2: Body Composition The relative percentage of muscle, fat, bone and other tissue in the body Our primary concern in this unit is body fatness and how it pertains to athletic
Sports Performance 15 Section 3.2: Body Composition The relative percentage of muscle, fat, bone and other tissue in the body Our primary concern in this unit is body fatness and how it pertains to athletic
Distribution and Cutoff Points of Fasting Insulin in Asian Indian Adolescents and their Association with Metabolic Syndrome
 Original Article Distribution and Cutoff Points of Fasting Insulin in Asian Indian Adolescents and their Association with Metabolic Syndrome NK Vikram*, A Misra**, RM Pandey***, Kalpana Luthra****, SP
Original Article Distribution and Cutoff Points of Fasting Insulin in Asian Indian Adolescents and their Association with Metabolic Syndrome NK Vikram*, A Misra**, RM Pandey***, Kalpana Luthra****, SP
Body Composition in Healthy Aging
 Body Composition in Healthy Aging R. N. BAUMGARTNER a Division of Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine, Clinical Nutrition Program, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque, New Mexico
Body Composition in Healthy Aging R. N. BAUMGARTNER a Division of Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine, Clinical Nutrition Program, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque, New Mexico
British Journal of Nutrition
 (21), page 1 of 8 q The Authors 21 doi:1.117/s7114512357 Estimation of percentage body fat in 6- to 13-year-old children by skinfold thickness, body mass index and waist circumference Susi Kriemler 1 *,
(21), page 1 of 8 q The Authors 21 doi:1.117/s7114512357 Estimation of percentage body fat in 6- to 13-year-old children by skinfold thickness, body mass index and waist circumference Susi Kriemler 1 *,
Neck circumference measurement as a screening tool for obesity in children
 International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Yashoda HT et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2017 Mar;4(2):426-430 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Yashoda HT et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2017 Mar;4(2):426-430 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
Measures of Obesity and Cardiovascular Risk Among Men and Women
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 52, No. 8, 2008 2008 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/08/$34.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2008.03.066
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 52, No. 8, 2008 2008 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/08/$34.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2008.03.066
