Body composition analysis by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in female diabetics differ between manufacturers
|
|
|
- Lora Weaver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 449±454 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Body composition analysis by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in female diabetics differ between manufacturers Center for Clinical and Basic Research, Ballerup, Denmark, and Steno Diabetes Center, Niels Steensens Vej 2, 2820 Gentofte, Denmark Objective: Comparison of body composition results by two dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) instruments, namely QDR-2000 from Hologic Inc and DPX from Lunar in subpopulations of lean and obese subjects. Design: Cross-sectional study with 85 female diabetics (BMI 18±43 kg/m 2 ) measured with both DXA instruments. Results: The regression lines for fat tissue mass (FTM), FAT% and total body bone mineral content (TBMC), but not lean tissue mass (LTM), were different from the line of identity (P < 0.01). However, the relationships were high (r 2 > 0.95), and the corresponding SEE%'s were low (0.8±4.8%), and were independent of BMI. FTM and FAT% measured by the QDR-2000 were 10% higher, and LTM and TBMC 6% lower, than by DPX (P < 0.001). Conclusions: There were lack of agreements between total body composition results by DPX Lunar, and QDR Hologic Inc. Individual results on the two systems cannot be directly compared. Standardization of body composition measurements by DXA is strongly needed. Descriptors: body composition; dual energy X-ray absorptiometry; diabetes Introduction The advent of dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), which is increasingly used in clinical and research settings, has improved the precision and accuracy of body composition measurements (Mazess et al, 1990; Svendsen et al, 1993; Haarbo et al, 1991; Lukaski, 1993; Fuller et al, 1992). However, there are still matters concerning the comparability and of DXA that are unsolved. The largest manufacturers of DXA, namely Hologic Inc, Norland and Lunar Rad. Corp, use different hardware and software arrangements for their calibration, data collection and analysis, and DXA instruments from the different manufacturers do not seem to offer directly comparable body composition results (Pritchard et al, 1992; Tothill et al, 1994). The few reports of comparisons of body composition results by DXA instruments from the different manufacturers have primarily focused on healthy normal weight volunteers (Pritchard et al, 1992; Tothill et al, 1994). We have previously found that body composition measurements in adults by a Lunar DPX machine were accurate (Svendsen et al, 1993; Haarbo et al, 1991), whereas the in vivo accuracy of body composition measurements in adults by DXA instruments from Hologic Inc and Norland has not been reported yet. The accuracy of body composition measurements by DXA seems to depend on the composition and mass of soft tissue (Laskey et al, 1992; Jebb et al, 1995). Thus, the comparability of body composition results by DXA instruments from different manufacturers may differ with body size and fatness, and may be different in Correspondence: Dr CN Kistorp, Center of Clinical and Basic Research, Ballerup Byvej 222, DK-2750 Ballerup, Denmark. Received 1 November 1996; revised 4 March 1997; accepted 14 March 1997 normal weight, obese and lean people. In order to investigate this, we compared body composition results by DPX (Lunar) with QDR-2000 (Hologic Inc) in subpopulation of more lean subjects, namely female insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) patients, and of more obese subjects, namely female non insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM) patients. Methods With the women wearing light indoor clothes and no shoes, weight was measured to nearest 0.1 kg. Total body composition was measured with two total body DXA scanners, namely DPX (Lunar Radiation Corporation, Madison, WI), software version 3.6y, medium scan mode, extended research analysis, and QDR-2000 X-ray bone densitometer, (Hologic Inc, Waltham, MA, fan beam, software version 5.54A). Regional analysis were made by routine according to the respective operators manual. The measurements were completed on the same day for each subject. Total body bone mineral content (TBMC) and density (TBMD), the total body soft tissue mass (STM) and the fat percentage (FAT%) and the fat (FTM) and lean soft tissue mass (LTM) were measured. The FTM is not solely adipose tissue, but the sum of the fatty elements of the soft tissue. Similarly the LTM is not an anatomical entity, but represents the sum of chemical fat free soft tissue elements. Subjects Eighty- ve female diabetes patients from the Steno Diabetes Center outpatient clinic participated in this study. Thirty-two had NIDDM: age: 56.8 (11.8) y (mean(s.d.)); BMI: 28.9 (5.7) kg/m 2. Fifty-three had IDDM: age: 49.9
2 450 Figure 1 Relationships (left) and lack of agreement (right) between body compositions measurements by DPX (Lunar Radiation Corp) and QDR-2000 (Hologic Inc). Broken lines on the left illustrates the lines of identity. Closed circles, NIDDM patients; triangles, IDDM patients.
3 (14.8) y; BMI: 23.2 (2.9) kg/m 2. All of the subjects were relatively healthy, that is none of the female diabetics suffered from heart failure, renal disease or were using diuretics. The study was carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki II, and with approval of the ethical committee of Copenhagen County. Statistical analysis Linear regression analysis were used to determine the relationship between the two DXA machines. The lack of agreements between QDR and DPX were plotted as a function of the means, according to the statistical procedure of Bland & Altman (1986). Analysis were performed with the SAS computer software package (version 6.0: SAS Institute Inc. Cary NC, 1989). Results The r 2 of the linear regressions between weight measured by a scale weight and the weight calculated by QDR-2000 or DPX were both 0.99, and the corresponding SEE's were 0.7 kg and 0.9 kg, respectively. The mean weight was 0.03 kg higher by QDR-2000 and 0.2 kg lower by DPX than by the scale weight (not signi cantly different from zero). Figure 1 illustrates the linear regressions of FTM, LTM and FAT% and Table 1 gives the relationships between all of the total body components measured by QDR-2000 and DPX. The determination coef cients r 2 were above 0.95 for all comparisons, ranging from 0.95± 0.99, and the corresponding SEE% ranging from 0.8±4.8%. The SEE's of the regression lines were small and were similar along the regression line, that is in lean and obese subjects (Figure 1). Furthermore, there were no signi cant association between the residuals and the size of any of the body components (P > 0.05). The slopes of all the regression lines were signi cantly different from one (P < 0.01), and the regression lines for weight, FTM, FAT%, STM and TBMC were signi cantly different from the line of identity (P < 0.05). There were lack of agreement for all the body components between the DPX and QDR-2000 (Table 1 and Figure 1). Thus the FAT% and FTM measured by the QDR-2000 were about 10% higher (3.7% and 2.5 kg, respectively) and the LTM 5% (2.1 kg) lower than by DPX (P < 0.05). The TBMC and TBMD were 6% and 3.4%, respectively, lower by QDR-2000 than by DPX (P < 0.05). The difference between the two instruments in weight, FTM and STM, but not LTM or FAT%, were signi cantly correlated to the average values of the respective parameters (Table 1 and Figure 1), and for weight, FTM and LTM also with body mass index (BMI) (P < 0.01). The waist to hip ratio (WHR) and the FAT% was signi cantly higher in the NIDDM patients compared to the IDDM (0.91 and 42.5% vs 0.82 and 31.4%, respectively, P < 0.05). Linear regressions revealed that the relationships between DPX and QDR-2000 were independent of weight, BMI and WHR, but were signi cantly (P < 0.05) dependent of the type of diabetes (dummy code: NIDDM:0, IDDM:1) and the FAT%. When both the type of diabetes and the FAT% were entered in the regression models, only the FAT%, but not the type of diabetes, remained signi cant (P < 0.05). Separate linear regression analyses of DPX versus QDR-2000 were performed for all the body components for the IDDM and the NIDDM subpopulation, respectively (Table 2). The regression equations for the IDDM were statistically signi cantly different from those for NIDDM for all the body components (P < 0.01), except for TBMC. However, the determination coef cients remained rather similar, ranging from 0.93±0.99, and the SEE's for the pooled population, and the NIDDM and the IDDM subpopulation, respectively were also quite similar. There was also signi cantly lack of agreement (P < 0.01) for all the body components, (except for weight in IDDM) in both subpopulation between the two DXA instruments (Table 2). The mean differences for all the body components between the two instruments were all signi cantly different in the NIDDM and in the IDDM subpopulation (P < 0.01). Table 3 gives regional comparisons between DPX and Hologic Discussion The present study examined comparability of body composition measurements by two DXA instruments from two 451 Table 1 Linear regressions and lack of agreement between DPX (Lunar Rad. Corp) and QDR-2000 (Hologic Inc) Linear regression Agreement Equation P a SEE r 2 SEE% DPX-QDR (mean 2s.d.) r b Weight (kg) QDR ˆ 1.03DPX P < c d DPX ˆ 0.98QDR STM (kg) QDR ˆ 1.02DPX P < c d DPX ˆ 0.98QDR FTM (kg) QDR ˆ 1.06DPX 1.2 P < c d DPX ˆ 0.93QDR LTM (kg) QDR ˆ 0.95DPX 0.1 NS c 0.16 NS DPX ˆ 1.01QDR Fat% QDR ˆ 0.99DPX 3.9 P < c NS DPX ˆ 0.97QDR TMBC (g) QDR ˆ 1.06DPX P < c d DPX ˆ 0.92QDR TBMD (g/cm 2 ) QDR ˆ 0.98DPX NS c NS DPX ˆ 0.97QDR a Different from the line of identity. b Correlation between the difference of DPX minus QDR and the average value of DPX and QDR. c Signi cantly different from zero (P < 0.05). d P < NS P > 0.05.
4 452 Table 2 Separate linear regressions and lack agreement between DPX (Lunar Rad. Corp) and QDR-2000 (Hologic Inc). For IDDM and NIDDM subpopulations Linear regression Agreement Equation P a SEE r 2 SEE% DPX-QDR (mean 2s.d.) r b Weight (kg) IDDM QDR ˆ 0.99DPX 0.1 NS NS 0.04 NS NIDDM QDR ˆ 1.02DPX NS c d STM (kg) IDDM QDR ˆ 0.99DPX 0.4 NS c 0.09 NS NIDDM QDR ˆ 1.02DPX NS c d FTM (kg) IDDM QDR ˆ 1.02DPX 1.8 P < c NS NIDDM QDR ˆ 1.06DPX 1.4 P < c d LTM (kg) IDDM QDR ˆ 0.99DPX NS c NS NIDDM QDR ˆ 0.91DPX 1.2 NS c 0.46 d Fat% IDDM QDR ˆ 0.95DPX 4.7 P < c 0.08 NS NIDDM QDR ˆ 0.95DPX 6.2 P < c 0.18 NS TMBC (g) IDDM QDR ˆ 1.04DPX P < c d NIDDM QDR ˆ 1.10DPX P < c d TBMD (g/cm 2 ) IDDM QDR ˆ 0.98DPX 7 0 NS c 0.04 NS NIDDM QDR ˆ 1.03DPX 7 0 NS c NS a Different from the line of identity. b Correlation between the difference of DPX minus QDR and the average value of DPX and QDR. c Signi cantly different from zero (P < 0.05). d P < NS P > different manufacturers in populations of rather lean and obese females, namely in NIDDM and IDDM patients, and whether body size or fatness affect this comparability. The correlations between the body composition measurements by QDR-2000 and DPX were high (r 2 > 0.95). However, there were lack of agreements between the two instruments in all the body components measured. Thus, the TBMC and TBMD were signi cantly higher by DPX than by the QDR-2000 (3% and 6%, respectively), which is in accordance with a previous study by Laskey et al (1991). On the other hand, we found that the FAT% measured by DPX was 3.7% lower than by QDR At rst sight these results are not in agreement with previous results. Both Tothill et al (1994) and Pritchard et al (1992) found Table 3 Linear regressions and lack of agreement between DPX Lunar and QDR-2000 Hologic. Regional body composition Linear regression Agreement Equation P a SEE r 2 SEE% DPX-QDR (mean 2s.d.) r b STM (kg) Limb pooled QDR ˆ 0.83DPX 3.7 P < c 0.62 d IDDM QDR ˆ 0.91DPX 1.9 P < c 0.33 d NIDDM QDR ˆ 0.82DPX 3.7 P < c 0.69 d Trunk pooled QDR ˆ 1.18DPX P < c d IDDM QDR ˆ 1.06DPX NS c NIDDM QDR ˆ 1.21DPX P < c FTM (kg) Limb pooled QDR ˆ 0.86DPX 3.3 P < c 0.45 d IDDM QDR ˆ 0.98DPX 2.4 P < c NS NIDDM QDR ˆ 0.83DPX 3.3 P < c 0.54 d Trunk pooled QDR ˆ 1.30DPX P < c d IDDM QDR ˆ 1.10DPX P < NS d NIDDM QDR ˆ 1.38DPX P < c d LTM (kg) Limb pooled QDR ˆ 0.83DPX 0.2 NS c 0.41 d IDDM QDR ˆ 0.85DPX NS c 0.29 NS NIDDM QDR ˆ 0.82DPX 0.2 NS c 0.54 d Trunk pooled QDR ˆ 0.97DPX 1.3 NS c NS IDDM QDR ˆ 1.06DPX70.4 NS c d NIDDM QDR ˆ 0.91DPX 2.3 P < c 0.22 NS Fat% Limb pooled QDR ˆ 0.87DPX 12.9 P < c 0.10 NS IDDM QDR ˆ 0.88DPX 12.1 P < c 0.03 NS NIDDM QDR ˆ 0.74DPX 18.6 P < c 0.26 NS Trunk pooled QDR ˆ 1.21DPX P < NS d IDDM QDR ˆ 1.07DPX P < c d NIDDM QDR ˆ 1.29DPX P < c d a Different from the line of identity. b Correlation between the difference of DPX minus QDR and the average value of DPX and QDR. c Signi cantly different from zero (P < 0.05). d P < NS P > 0.05.
5 Table 4 Difference in Fat% between DXA from Lunar and Hologic Inc. with advancing software and instrument development Lunar Hologic Inc Fat% 453 n DPX QDR-1000 W QDR-2000 W Pencil beam Pencil beam Pencil beam software version software version software version Fan beam software version Diff. a left-right Accumulated diff. b Lunar-Hologic Tothill et al (3.6) 5.35 (5.51p) 3.7% Pritchard et al % 3.6% Mazess et al R±3.6R 0.2% Van Loan et al R±3.6R 72.0% 70.9% Abrahamsen et al % 71.2% A 76.4% Spector et al A 74.3% 75.4% 73.9% The present study y 5.54A 73.7% a Fat% by software version and DXA instrument on the left minus that on the right. b Accumulated difference in Fat% between DPX, software version 3.4 and QDR-2000 W, software version 5.54A, calculated from the reports in the Table. that FAT% measurements by DPX was about 3.7% higher than by the QDR However, when interpreting body composition results by DXA, attention must be given not only to which manufacturer the DXA instrument comes from, but also to the software version, to the generation of the DXA instrument, and to whether pencil or fan beam have been used. New software versions may cause changes in body composition results (Van Loan et al, 1995). For Hologic Inc the introduction of fan beam in QDR-2000 has increased the FAT% signi cantly (Abrahamsen et al, 1995). Table 4 shows the impact of the introduction and development of new software and DXA machines on the difference in measured FAT% between DPX from Lunar and QDR from Hologic. The accumulated effect of the introduction of new software and instruments generations is a shift in the difference in FAT% between DPX and QDR at 3.7% to 73.9%, which is more in accordance with our nding at 73.7%. The fact that the DXA results vary with manufacturer, software version, generation of DXA scanner, scan and beam mode and calibration procedure means that individual results on the two systems cannot be directly compared. The regression equations found were independent of body size (weight, BMI) but were statistically signi cantly dependent on the type of diabetes. A reasonable explanation could be the difference in fat distribution, namely the waist to hip ratio between the IDDM and the NIDDM patients. However, our results suggest that it is the difference in fatness between IDDM and NIDDM that causes this. However, speci c regression equations for the IDDM or NIDDM subpopulation did not improve the r 2 or the SEE's signi cantly as compared to the regression equations for the pooled population of IDDM and NIDDM patients. Thus, to compare body composition results by DPX, software version 3.6y, and by QDR-2000, fan beam and software version 5.54A, the regression equations given in the pooled population can be used (Table 1). These regression equations seem valid in females with a BMI ranging from 18±43 kg/m 2. However, they do introduce an extra nonsystematic error of 0.8±4.8% (SEE%), which must be considered and accounted for when comparing cross-sectional data from different instruments or when using different instruments in longitudinal clinical trials. We nd the results of the differences in the regional body composition results by DPX and Hologic-2000 dif cult to interpret. We do not know the accuracy error with neither DPX or Hologic-2000 of the regional body composition results, as we do it for total body. The optional standard de nitions of the limb and trunk regions seems to be the same by DPX and the Hologic DXA do only measure the soft tissue composition directly in pixels without bone. Thus the trunk with a high bone to non bone pixel ratio (pelvis, spine, ribs and sternum) may have a higher accuracy error than the limbs. On the other hand, the soft tissue composition is not measured if the height of the absorber is too low, as in hands and feet. Discrepancies in the approach to deal with these and related issues may, besides the calibration, cause different accuracy errors and absolute values of the regional body composition results. Interestingly we found the greatest lack of agreement in the FAT% in the limbs, not in the trunk. Conclusions There were lack of agreements ranging from 3±10% between total body composition results by DPX Lunar, and QDR-2000 Hologic Inc. However the determination coef cients were high and SEE's of the linear regressions of the results between the two DXA instruments were small. The manufacturers of the DXA instruments should standardize and intercalibrate their instruments. AcknowledgementsÐWe thank Drs Christian Hassager and Claus Christiansen, Center for Clinical and Basic Research, as well as Dr Hans-Henrik Parving, Steno Diabetes Center, for their valuable help and inspiring discussions. References Abrahamsen B, Gram J, Hansen TB & Beck-Nielsen J (1995): Cross calibration of QDR-2000 and QDR-1000 dual energy X-ray densitometers for bone mineral and soft-tissue measurements. Bone 16, 385± 390. Bland JM & Altman DG (1986): Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet II, 307± 310. Fuller NJ, Laskey MA & Elia M (1992): Assessment of the composition of major body regions by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), with special reference to limb muscle mass. Clin. Physiol. 12, 253±266. Haarbo J, Gotfredsen A, Hassager C & Christiansen C (1991): Validation of body composition by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). Clin. Physiol. 11, 331±341. Jebb SA, Goldberg GR, Jennings G & Elia M (1995): Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry measurements of body composition: effects of depth and tissue thickness, including comparisons with direct analysis. Clin. Sci. 88, 319±324. Laskey MA, Flaxman ME, Barber RW, Trafford S, Hayball MP, Lyttle KD, Crisp AJ & Compston JE (1991): Comparative performance in vitro and in vivo of Lunar DPX and Hologic QDR-1000 dual energy X- ray absorptiometers. Br. J. Radiol. 64, 1023±1029.
6 454 Laskey MA, Lyttle KD, Flaxman ME & Barber RW (1992): The in uence of tissue depth and composition on the performance of the Lunar dual energy X-ray absorptiometer whole-body scanning mode. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 46, 39±45. Lukaski HC (1993): Soft tissue composition and bone mineral status: evaluation by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry. J. Nutr. 123, 438±443. Mazess RB, Barden HS, Bidek JP & Hanson J (1990): Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry for total body and regional bone mineral and soft tissue composition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 51, 1106±1112. Mazess RB, Bisek J, Trempe J & Poutchot S (1991): Effects of tissue thickness on body composition measurements using dual energy X-ray absorptiometry. Madison WI: Lunar Corporation. Pritchard JE, Nowson CA, Strauss BJ, Carlson JS & Kaymakci B (1992): Evaluation of dual energy X-ray absorptiometry as a method of measurement of body fat. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 47, 216±228. SAS Institute Inc (1989): Guide for personal computers, version 6 edition. Gary, North Carolina: SAS Institute Inc. Spector E, LeBlanc A & Shackelford L (1995): Hologic QDR 2000 whole body scans: A comparison of three combinations of scan modes and analysis software. Osteoporosis Int. 5, 440±445. Svendsen OL, Haarbo J, Hassager C & Christiansen C (1993): Accuracy of measurement of body composition by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in vivo. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 57, 605±608. Tothill P, Avenell A, Love J & Reid DM (1994): Comparison between Hologic, Lunar and Norland dual energy X-ray absorptiometers and other techniques used for whole body soft tissue measurements. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 48, 781±794. Van Loan MD, Keim NL, Berg K & Mayclin PL (1995): Evaluation of body composition by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry and two different software packages. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 27, 587±591.
Bone Mineral and Body Composition Measurements: Cross-Calibration of Pencil-Beam and Fan-Beam Dual- Energy X-Ray Absorptiometers*
 JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH Volume 13, Number 10, 1998 Blackwell Science, Inc. 1998 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Bone Mineral and Body Composition Measurements: Cross-Calibration
JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH Volume 13, Number 10, 1998 Blackwell Science, Inc. 1998 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Bone Mineral and Body Composition Measurements: Cross-Calibration
Differences in whole body measurements by DXA-scanning using two Lunar DPX-L machines
 International Journal of Obesity (1999) 23, 764±770 ß 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ijo Short Communication Differences in whole body measurements
International Journal of Obesity (1999) 23, 764±770 ß 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ijo Short Communication Differences in whole body measurements
Cross-calibration of fat and lean measurements by dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry to pig carcass analysis in the pediatric body weight range13
 Cross-calibration of fat and lean measurements by dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry to pig carcass analysis in the pediatric body weight range13 Stephen J Pintauro, Tim R Nagy, Christa M Duthie, and Michael
Cross-calibration of fat and lean measurements by dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry to pig carcass analysis in the pediatric body weight range13 Stephen J Pintauro, Tim R Nagy, Christa M Duthie, and Michael
A multi-center comparison of dual energy X-ray absorptiometers: In vivo and in vitro soft tissue measurement
 European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 312±317 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 A multi-center comparison of dual energy X-ray absorptiometers: In vivo and in vitro
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 312±317 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 A multi-center comparison of dual energy X-ray absorptiometers: In vivo and in vitro
9 Quality Assurance in Bone Densitometry section
 9 Quality Assurance in Bone Densitometry section Introduction Bone densitometry is frequently used to determine an individual's fracture risk at a particular point in time but may also be used to assess
9 Quality Assurance in Bone Densitometry section Introduction Bone densitometry is frequently used to determine an individual's fracture risk at a particular point in time but may also be used to assess
In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in
 1 2 In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in adults: the influence of body mass index 3 4 Running title: Precision of the idxa for the measurement of visceral
1 2 In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in adults: the influence of body mass index 3 4 Running title: Precision of the idxa for the measurement of visceral
Segmental Body Composition Assessment for Obese Japanese Adults by Single-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis with 8-point Contact Electrodes
 Segmental Body Composition Assessment for Obese Japanese Adults by Single-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis with 8-point Contact Electrodes Susumu Sato 1), Shinichi Demura 2), Tamotsu Kitabayashi
Segmental Body Composition Assessment for Obese Japanese Adults by Single-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis with 8-point Contact Electrodes Susumu Sato 1), Shinichi Demura 2), Tamotsu Kitabayashi
Body composition in children and adults by air displacement plethysmography
 European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1999) 53, 382±387 ß 1999 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ejcn Body composition in children and adults by
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1999) 53, 382±387 ß 1999 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ejcn Body composition in children and adults by
Bioelectrical impedance analysis to assess body composition in obese adult women: The effect of ethnicity
 International Journal of Obesity (1998) 22, 243±249 ß 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/98 $12.00 Bioelectrical impedance analysis to assess body composition in obese adult women: The effect
International Journal of Obesity (1998) 22, 243±249 ß 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/98 $12.00 Bioelectrical impedance analysis to assess body composition in obese adult women: The effect
DUAL ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY (DXA) GOLD STANDARD FOR BONE HEALTH AND BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT
 DUAL ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY (DXA) GOLD STANDARD FOR BONE HEALTH AND BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT Prof d-r Slavica Šubeska Stratrova Clinic of Endocrinology, Skopje, Macedonia Definition and classification
DUAL ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY (DXA) GOLD STANDARD FOR BONE HEALTH AND BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT Prof d-r Slavica Šubeska Stratrova Clinic of Endocrinology, Skopje, Macedonia Definition and classification
The Influence of Exogenous Fat and Water on Lumbar Spine Bone Mineral Density in Healthy Volunteers
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.2.289 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 53(2):289-293, 2012 The Influence of Exogenous Fat and Water on Lumbar Spine Bone Mineral Density
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.2.289 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 53(2):289-293, 2012 The Influence of Exogenous Fat and Water on Lumbar Spine Bone Mineral Density
Clinical Densitometry
 Volume 8 Number 3 Fall 2005 ISSN: 1094 6950 Journal of Clinical Densitometry The Official Journal of The International Society for Clinical Densitometry Editor-in-Chief Paul D. Miller, MD HumanaJournals.com
Volume 8 Number 3 Fall 2005 ISSN: 1094 6950 Journal of Clinical Densitometry The Official Journal of The International Society for Clinical Densitometry Editor-in-Chief Paul D. Miller, MD HumanaJournals.com
Does standardized BMD still remove differences between Hologic and GE-Lunar state-of-the-art DXA systems?
 Osteoporos Int (2010) 21:1227 1236 DOI 10.1007/s00198-009-1062-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Does standardized BMD still remove differences between Hologic and GE-Lunar state-of-the-art DXA systems? B. Fan & Y. Lu
Osteoporos Int (2010) 21:1227 1236 DOI 10.1007/s00198-009-1062-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Does standardized BMD still remove differences between Hologic and GE-Lunar state-of-the-art DXA systems? B. Fan & Y. Lu
Location of body fat and body size impacts DXA soft tissue measures: a simulation study
 (2008) 62, 553 559 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954-3007/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/ejcn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Location of body fat and body size impacts DXA soft tissue measures: a simulation
(2008) 62, 553 559 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954-3007/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/ejcn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Location of body fat and body size impacts DXA soft tissue measures: a simulation
Norland Densitometry A Tradition of Excellence
 Norland Densitometry A Tradition of Excellence Norland DXA Bone Density Measurement Osteoporosis is a disease marked by reduced bone strength leading to an increased risk of fractures. About 54 million
Norland Densitometry A Tradition of Excellence Norland DXA Bone Density Measurement Osteoporosis is a disease marked by reduced bone strength leading to an increased risk of fractures. About 54 million
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in Dexa Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Birth Date: 24.7 years Height / Weight: 8.0 cm 79.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 40% 30% 20% 0% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 00 Centile
Birth Date: 24.7 years Height / Weight: 8.0 cm 79.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 40% 30% 20% 0% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 00 Centile
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in Dexa Total Body 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
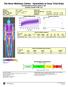 Patient: Obese, Sample Birth Date: 0/Jan/966 44.4 years Height / Weight: 72.0 cm 95.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Referring Physician: DR. SMITH Measured: 07/Jun/200 7:0:52 PM (.40) Analyzed: 02/Apr/203
Patient: Obese, Sample Birth Date: 0/Jan/966 44.4 years Height / Weight: 72.0 cm 95.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Referring Physician: DR. SMITH Measured: 07/Jun/200 7:0:52 PM (.40) Analyzed: 02/Apr/203
Introduction. EG Kamel 1 *, G McNeill 1, TS Han 1, FW Smith 2, A Avenell 3, L Davidson 1 and P Tothill 4
 International Journal of Obesity (1999) 23, 686±692 ß 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ijo Measurement of abdominal fat by magnetic resonance
International Journal of Obesity (1999) 23, 686±692 ß 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ijo Measurement of abdominal fat by magnetic resonance
Multi-Compartment Model (MCM) and Body Composition Measurement Techniques
 White Paper Contents Multi Compartment Model (MCM) 1 Methods comparable to MCM 2 Methods NOT comparable to MCMC 3 References 6 Multi-Compartment Model (MCM) and Body Composition Measurement Techniques
White Paper Contents Multi Compartment Model (MCM) 1 Methods comparable to MCM 2 Methods NOT comparable to MCMC 3 References 6 Multi-Compartment Model (MCM) and Body Composition Measurement Techniques
Suprailiac or Abdominal Skinfold Thickness Measured with a Skinfold Caliper as a Predictor of Body Density in Japanese Adults
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2007, Measurement 213, 51-61Error Characteristics of Skinfold Caliper 51 Suprailiac or Abdominal Skinfold Thickness Measured with a Skinfold Caliper as a Predictor of Body Density
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2007, Measurement 213, 51-61Error Characteristics of Skinfold Caliper 51 Suprailiac or Abdominal Skinfold Thickness Measured with a Skinfold Caliper as a Predictor of Body Density
Bedside methods versus dual energy X-ray absorptiometry for body composition measurement in COPD
 Eur Respir J ; 19: 66 631 DOI: 1.1183/931936..796 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Bedside methods versus dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
Eur Respir J ; 19: 66 631 DOI: 1.1183/931936..796 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Bedside methods versus dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
Understanding Body Composition
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines 7 Understanding Body Composition Objectives Define body composition. Explain why the assessment of body size, shape, and composition is useful. Explain how to perform assessments
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines 7 Understanding Body Composition Objectives Define body composition. Explain why the assessment of body size, shape, and composition is useful. Explain how to perform assessments
DEXA Bone Mineral Density Tests and Body Composition Analysis Information for Health Professionals
 DEXA Bone Mineral Density Tests and Body Composition Analysis Information for Health Professionals PERFORMANCE DEXA is an advanced technology originally used to, and still capable of assessing bone health
DEXA Bone Mineral Density Tests and Body Composition Analysis Information for Health Professionals PERFORMANCE DEXA is an advanced technology originally used to, and still capable of assessing bone health
PhenX Measure: Body Composition (#020300) PhenX Protocol: Body Composition - Body Composition by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (#020302)
 PhenX Measure: Body Composition (#020300) PhenX Protocol: Body Composition - Body Composition by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (#020302) Date of Interview/Examination (MM/DD/YYYY): A downloadable PDF
PhenX Measure: Body Composition (#020300) PhenX Protocol: Body Composition - Body Composition by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (#020302) Date of Interview/Examination (MM/DD/YYYY): A downloadable PDF
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry to Determine Body Composition
 Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Determine Body Composition Description Using low dose x-rays of two different energy levels, whole body dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measures lean tissue
Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Determine Body Composition Description Using low dose x-rays of two different energy levels, whole body dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measures lean tissue
A Pilot Study of Exercise Training to Reduce Trunk Fat in Adults With HIV Associated Fat Redistribution
 A Pilot Study of Exercise Training to Reduce Trunk Fat in Adults With HIV Associated Fat Redistribution Ronenn Roubenoff, Lauren Weiss, Ann McDermott, Tanya Heflin, Gregory J. Cloutier, Michael Wood and
A Pilot Study of Exercise Training to Reduce Trunk Fat in Adults With HIV Associated Fat Redistribution Ronenn Roubenoff, Lauren Weiss, Ann McDermott, Tanya Heflin, Gregory J. Cloutier, Michael Wood and
J EisenkoÈlbl 1, M Kartasurya 1 and K Widhalm 1 * Introduction
 (2001) 55, 423±429 ß 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954±3007/01 $15.00 www.nature.com/ejcn Original Communication Underestimation of percentage fat mass measured by bioelectrical impedance
(2001) 55, 423±429 ß 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954±3007/01 $15.00 www.nature.com/ejcn Original Communication Underestimation of percentage fat mass measured by bioelectrical impedance
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Birth Date: 40.2 years Height / Weight: 158.0 cm 52.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 50% 40% 30% 20% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Birth Date: 40.2 years Height / Weight: 158.0 cm 52.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 50% 40% 30% 20% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Clinical Study Body Fat Mass Assessment: A Comparison between an Ultrasound-Based Device and a Discovery A Model of DXA
 ISRN Obesity Volume 2013, Article ID 462394, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/462394 Clinical Study Body Fat Mass Assessment: A Comparison between an Ultrasound-Based Device and a Discovery A Model
ISRN Obesity Volume 2013, Article ID 462394, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/462394 Clinical Study Body Fat Mass Assessment: A Comparison between an Ultrasound-Based Device and a Discovery A Model
Estimating the Absorbed Dose to Critical Organs During Dual X-ray Absorptiometry
 Estimating the Absorbed Dose to Critical Organs During Dual X-ray Absorptiometry M Mokhtari-Dizaji, PhD 1 A A Sharafi, PhD 2 B Larijani, MD 3 N Mokhlesian, MSc 4 H Hasanzadeh, MS 1 Index terms: Dual X-ray
Estimating the Absorbed Dose to Critical Organs During Dual X-ray Absorptiometry M Mokhtari-Dizaji, PhD 1 A A Sharafi, PhD 2 B Larijani, MD 3 N Mokhlesian, MSc 4 H Hasanzadeh, MS 1 Index terms: Dual X-ray
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 29.5 years Height / Weight: 156.0 cm 57.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 29.5 years Height / Weight: 156.0 cm 57.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
special communication
 special communication Determining bone and total body mineral content from body density and bioelectrical response spectroscopy STEVEN F. SICONOLFI, 1 RANDAL J. GRETEBECK, 2 WILLIAM W. WONG, 3 SHERIL S.
special communication Determining bone and total body mineral content from body density and bioelectrical response spectroscopy STEVEN F. SICONOLFI, 1 RANDAL J. GRETEBECK, 2 WILLIAM W. WONG, 3 SHERIL S.
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 48.2 years Height / Weight: 150.0 cm 72.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 48.2 years Height / Weight: 150.0 cm 72.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 43.4 years Height / Weight: 170.0 cm 66.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 43.4 years Height / Weight: 170.0 cm 66.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
Evaluation of DXA against the four-component model of body composition in obese children and adolescents aged 5 to 21 years
 Europe PMC Funders Group Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Int J Obes (Lond). 2010 April ; 34(4): 649 655. doi:10.1038/ijo.2009.249. Evaluation of DXA against the four-component model
Europe PMC Funders Group Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Int J Obes (Lond). 2010 April ; 34(4): 649 655. doi:10.1038/ijo.2009.249. Evaluation of DXA against the four-component model
Effect of Precision Error on T-scores and the Diagnostic Classification of Bone Status
 Journal of Clinical Densitometry, vol. 10, no. 3, 239e243, 2007 Ó Copyright 2007 by The International Society for Clinical Densitometry 1094-6950/07/10:239e243/$32.00 DOI: 10.1016/j.jocd.2007.03.002 Original
Journal of Clinical Densitometry, vol. 10, no. 3, 239e243, 2007 Ó Copyright 2007 by The International Society for Clinical Densitometry 1094-6950/07/10:239e243/$32.00 DOI: 10.1016/j.jocd.2007.03.002 Original
New bioelectrical impedance formula for patients with respiratory insufficiency: comparison to dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
 Eur Respir J 1998; 12: 960 966 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.98.12040960 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1998 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 New bioelectrical impedance
Eur Respir J 1998; 12: 960 966 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.98.12040960 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1998 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 New bioelectrical impedance
Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies
 Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Femur Bone Measurements Examination Survey Years: 2005 to 2006 SAS Transport File: DXXFEM_D.XPT January 2009 NHANES 2005 2006 Data
Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Femur Bone Measurements Examination Survey Years: 2005 to 2006 SAS Transport File: DXXFEM_D.XPT January 2009 NHANES 2005 2006 Data
Client Sex Facility Birth Date Height Weight Measured ####, #### #### (not specified) #### #### #### ####
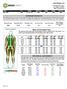 SUMMARY RESULTS This table provides an overview of your total body composition, broken down into total body fat %, total mass, fat tissue, lean tissue, and bone mineral content. These metrics establish
SUMMARY RESULTS This table provides an overview of your total body composition, broken down into total body fat %, total mass, fat tissue, lean tissue, and bone mineral content. These metrics establish
Techniques for Undertaking Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Whole-Body Scans to Estimate Body Composition in Tall and/or Broad Subjects
 International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism, 2012, 22, 313-322 2012 Human Kinetics, Inc. www.ijsnem-journal.com ORIGINAL RESEARCH Techniques for Undertaking Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry
International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism, 2012, 22, 313-322 2012 Human Kinetics, Inc. www.ijsnem-journal.com ORIGINAL RESEARCH Techniques for Undertaking Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry
Whole body and regional body composition analysis by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in cirrhotic patients
 European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 810±814 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Whole body and regional body composition analysis by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 810±814 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Whole body and regional body composition analysis by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
Introduction. Methods
 (2000) 24, 627±632 ß 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0307±0565/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/ijo Overweight and obese children have low bone mass and area for their weight A Goulding 1 *,
(2000) 24, 627±632 ß 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0307±0565/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/ijo Overweight and obese children have low bone mass and area for their weight A Goulding 1 *,
Association of Lean Tissue and Fat Mass with Bone Mineral Content in Children and Adolescents
 Association of Lean Tissue and Fat Mass with Bone Mineral Content in Children and Adolescents Angelo Pietrobelli,* Myles S. Faith,* Jack Wang,* Paolo Brambilla, Giuseppe Chiumello, and Steven B. Heymsfield*
Association of Lean Tissue and Fat Mass with Bone Mineral Content in Children and Adolescents Angelo Pietrobelli,* Myles S. Faith,* Jack Wang,* Paolo Brambilla, Giuseppe Chiumello, and Steven B. Heymsfield*
Bone Mineral Density and Its Associated Factors in Naresuan University Staff
 Naresuan University Journal 2005; 13(3): 13-18 13 Bone Mineral Density and Its Associated Factors in Naresuan University Staff Supawitoo Sookpeng *, Patsuree Cheebsumon, Malinee Dhanarun, Thanyavee Pengpan
Naresuan University Journal 2005; 13(3): 13-18 13 Bone Mineral Density and Its Associated Factors in Naresuan University Staff Supawitoo Sookpeng *, Patsuree Cheebsumon, Malinee Dhanarun, Thanyavee Pengpan
Secular increases in waist ± hip ratio among Swedish women
 International Journal of Obesity (1998) 22, 1116±1120 ß 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/98 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ijo Secular increases in waist ± hip ratio among Swedish
International Journal of Obesity (1998) 22, 1116±1120 ß 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/98 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ijo Secular increases in waist ± hip ratio among Swedish
Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment
 Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott,
Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott,
Evaluation of two foot-to-foot bioelectrical impedance analysers to assess body composition in overweight and obese adolescents
 British Journal of Nutrition (2003), 90, 987 992 q The Authors 2003 DOI: 10.1079/BJN2003983 Evaluation of two foot-to-foot bioelectrical impedance analysers to assess body composition in overweight and
British Journal of Nutrition (2003), 90, 987 992 q The Authors 2003 DOI: 10.1079/BJN2003983 Evaluation of two foot-to-foot bioelectrical impedance analysers to assess body composition in overweight and
This study may not be disseminated, reproduced in whole or in part without the written permission of Roduve Healthcare Solutions.
 This study may not be disseminated, reproduced in whole or in part without the written permission of Roduve Healthcare Solutions. A Randomized Controlled Trial for Roduve Healthcare Solutions on the Efficacy
This study may not be disseminated, reproduced in whole or in part without the written permission of Roduve Healthcare Solutions. A Randomized Controlled Trial for Roduve Healthcare Solutions on the Efficacy
Potassium per kilogram fat-free mass and total body potassium: predictions from sex, age, and anthropometry
 Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 284: E416 E423, 2003. First published October 15, 2002; 10.1152/ajpendo.00199.2001. Potassium per kilogram fat-free mass and total body potassium: predictions from sex, age,
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 284: E416 E423, 2003. First published October 15, 2002; 10.1152/ajpendo.00199.2001. Potassium per kilogram fat-free mass and total body potassium: predictions from sex, age,
Comparison of Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry and Dual Photon Absorptiometry for Bone Mineral Measurements of the Lumbar Spine
 Comparison of Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry and Dual Photon Absorptiometry for Bone Mineral Measurements of the Lumbar Spine HENZ W. WAHNER, M.D., WLLAM L. DUNN, M.Sc, MANUEL L. BROWN, M.D., Section
Comparison of Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry and Dual Photon Absorptiometry for Bone Mineral Measurements of the Lumbar Spine HENZ W. WAHNER, M.D., WLLAM L. DUNN, M.Sc, MANUEL L. BROWN, M.D., Section
Standard Operating Procedure TCRC Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA)
 1. RELEVANCE a. This SOP outlines the instructions to completing Duel Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) including: scanning, analysis, review and filing. 2. SCOPE a. This SOP applies to all TCRC RDs. 3.
1. RELEVANCE a. This SOP outlines the instructions to completing Duel Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) including: scanning, analysis, review and filing. 2. SCOPE a. This SOP applies to all TCRC RDs. 3.
Lateral Vertebral Analysis DXA Body Composition Quality Assurance in DXA
 Strong Bone Asia 2013 Osteoporosis in ASEAN Lateral Vertebral Analysis DXA Body Composition Quality Assurance in DXA Chris Schultz Scientist-in-Charge (Bone Densitometry) Royal Adelaide Hospital, Adelaide,
Strong Bone Asia 2013 Osteoporosis in ASEAN Lateral Vertebral Analysis DXA Body Composition Quality Assurance in DXA Chris Schultz Scientist-in-Charge (Bone Densitometry) Royal Adelaide Hospital, Adelaide,
Obesity Increases Precision Errors in Total Body Dual X-ray Absorptiometry Measurements.
 Obesity Increases Precision Errors in Total Body Dual X-ray Absorptiometry Measurements. 1 K.M.Knapp, 1 J.R.Welsman, 1 S.J.Hopkins, 1 A.Shallcross, 2 I.Fogelman and 2 G.M.Blake 1. University of Exeter,
Obesity Increases Precision Errors in Total Body Dual X-ray Absorptiometry Measurements. 1 K.M.Knapp, 1 J.R.Welsman, 1 S.J.Hopkins, 1 A.Shallcross, 2 I.Fogelman and 2 G.M.Blake 1. University of Exeter,
Fat Mass. Baseline. (lbs) (lbs) Composition Trend: Total. Aug 17. Apr 17. May 17. Jun 17. Jul 17. Measured Date
 Name Sample Report Birth Date: 00/00/000 Height: 74.0 in. Gender Male Age: 54.7 Input Weight: 165.0 lbs. Body Composition Analysis (BCA) DXA or DEXA is a three component model, which means it quantifies
Name Sample Report Birth Date: 00/00/000 Height: 74.0 in. Gender Male Age: 54.7 Input Weight: 165.0 lbs. Body Composition Analysis (BCA) DXA or DEXA is a three component model, which means it quantifies
Effect of hand positioning on idxa precision error for total and regional bone and body
 Effect of hand positioning on idxa precision error for total and regional bone and body composition parameters. Abstract Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) body composition measurements are performed
Effect of hand positioning on idxa precision error for total and regional bone and body composition parameters. Abstract Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) body composition measurements are performed
Is percentage body fat differentially related to body mass index in Hispanic Americans, African Americans, and European Americans?
 Is percentage body fat differentially related to body mass index in Hispanic Americans, African Americans, and European Americans? 1 3 José R Fernández, Moonseong Heo, Steven B Heymsfield, Richard N Pierson
Is percentage body fat differentially related to body mass index in Hispanic Americans, African Americans, and European Americans? 1 3 José R Fernández, Moonseong Heo, Steven B Heymsfield, Richard N Pierson
The use of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry to estimate the dissected composition of lamb carcasses
 Meat Science 73 (2006) 249 257 MEAT SCIENCE www.elsevier.com/locate/meatsci The use of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry to estimate the dissected composition of lamb carcasses J. Mercier a, C. Pomar b,
Meat Science 73 (2006) 249 257 MEAT SCIENCE www.elsevier.com/locate/meatsci The use of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry to estimate the dissected composition of lamb carcasses J. Mercier a, C. Pomar b,
Validation of bioimpedance body composition assessment by TANITA BC-418 in 7 years-
 Validation of bioimpedance body composition assessment by TANITA BC-418 in 7 years- old children vs. Dual X-ray absorptiometry Veronica Luque on behalf to URV Team 18th November 2012 Milano, 10th Bi-annual
Validation of bioimpedance body composition assessment by TANITA BC-418 in 7 years- old children vs. Dual X-ray absorptiometry Veronica Luque on behalf to URV Team 18th November 2012 Milano, 10th Bi-annual
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) to Determine Body Composition. Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 6.01.28 Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) to Determine Body Composition Medical Policy Section Radiology Is12:2013sue 12:2012 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date reviewed
MP 6.01.28 Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) to Determine Body Composition Medical Policy Section Radiology Is12:2013sue 12:2012 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date reviewed
Use of dual X-ray absorptiometry to measure body mass during short- to medium-term trials of nutrition and exercise interventions
 bs_bs_banner Special Article Use of dual X-ray absorptiometry to measure body mass during short- to medium-term trials of nutrition and exercise interventions Christopher PF Marinangeli and Amira N Kassis
bs_bs_banner Special Article Use of dual X-ray absorptiometry to measure body mass during short- to medium-term trials of nutrition and exercise interventions Christopher PF Marinangeli and Amira N Kassis
Estimation of body composition from bioelectrical impedance of body segments : comparison with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
 British Journal of Nutrition (1993), 69, 645-655 645 Estimation of body composition from bioelectrical impedance of body segments : comparison with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry BY S. P. STEWART1, P.
British Journal of Nutrition (1993), 69, 645-655 645 Estimation of body composition from bioelectrical impedance of body segments : comparison with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry BY S. P. STEWART1, P.
Estimates of body composition with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in adults 1 3
 Original Research Communications Estimates of body composition with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in adults 1 3 Chaoyang Li, Earl S Ford, Guixiang Zhao, Lina S Balluz, and Wayne H Giles ABSTRACT Background:
Original Research Communications Estimates of body composition with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in adults 1 3 Chaoyang Li, Earl S Ford, Guixiang Zhao, Lina S Balluz, and Wayne H Giles ABSTRACT Background:
Bone Densitometry Radiation dose: what you need to know
 Bone Densitometry Radiation dose: what you need to know John Damilakis, PhD Associate Professor and Chairman University of Crete, Iraklion, Crete, GREECE Estimation of bone status using X-rays Assessment
Bone Densitometry Radiation dose: what you need to know John Damilakis, PhD Associate Professor and Chairman University of Crete, Iraklion, Crete, GREECE Estimation of bone status using X-rays Assessment
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) to Determine Body Composition
 Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) to Determine Body Composition Policy Number: 6.01.40 Last Review: 4/2018 Origination: 4/2005 Next Review: 4/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) to Determine Body Composition Policy Number: 6.01.40 Last Review: 4/2018 Origination: 4/2005 Next Review: 4/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City
QDR Series. Discovery and Explorer Advanced Health Assessment
 O S T E O P O R O S I S A S S E S S M E N T QDR Series Discovery and Explorer Advanced Health The Hologic QDR Series bone densitometers combine the proven clinical value of bone mineral density (BMD) measurement
O S T E O P O R O S I S A S S E S S M E N T QDR Series Discovery and Explorer Advanced Health The Hologic QDR Series bone densitometers combine the proven clinical value of bone mineral density (BMD) measurement
TigerPrints. Clemson University. Nadia Marie Ghassan Najm Clemson University
 Clemson University TigerPrints All Theses Theses 8-2015 Mathematical Properties that Influence Least Significant Change of Body Composition and Bone Mineral Density Measured by Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry
Clemson University TigerPrints All Theses Theses 8-2015 Mathematical Properties that Influence Least Significant Change of Body Composition and Bone Mineral Density Measured by Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry
Spinal Cord Rehab Program, Toronto Rehabilitation Institute, University Health Network, 520 Sutherland Drive, Toronto, ON, Canada M4G 3V9 2
 Journal of Obesity Volume 212, Article ID 936, 9 pages doi:1.11/212/936 Clinical Study Bioelectrical Impedance and Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Assessments of Changes in Body Composition Following
Journal of Obesity Volume 212, Article ID 936, 9 pages doi:1.11/212/936 Clinical Study Bioelectrical Impedance and Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Assessments of Changes in Body Composition Following
BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES. Abstract. Introduction. Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, UDC :572.
 EXERCISE AND QUALITY OF LIFE Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, 43-48 UDC 796.034.6-051:572.087 Research article BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES Jelena Popadiã Gaãeša *, Otto Barak, Dea Karaba
EXERCISE AND QUALITY OF LIFE Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, 43-48 UDC 796.034.6-051:572.087 Research article BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES Jelena Popadiã Gaãeša *, Otto Barak, Dea Karaba
Medical Policy. MP Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry to Determine Body Composition
 Medical Policy MP 6.01.40 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 6.01.40 Last Review: 09/28/2017 Effective Date: 09/28/2017 Section: Radiology End Date: 09/18/2018 Related Policies 6.01.44 Vertebral Fracture Assessment With
Medical Policy MP 6.01.40 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 6.01.40 Last Review: 09/28/2017 Effective Date: 09/28/2017 Section: Radiology End Date: 09/18/2018 Related Policies 6.01.44 Vertebral Fracture Assessment With
Total and Regional BMD Comparison of Collegiate Male and Female Athletes
 The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2016 Total and Regional BMD Comparison of Collegiate Male and Female Athletes
The University of Akron IdeaExchange@UAkron Honors Research Projects The Dr. Gary B. and Pamela S. Williams Honors College Spring 2016 Total and Regional BMD Comparison of Collegiate Male and Female Athletes
JEPonline Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline
 Estimating Intra-abdominal Fat 1 JEPonline Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline Official Journal of The American Society of Exercise Physiologists (ASEP) ISSN 1097-9751 An International Electronic Journal
Estimating Intra-abdominal Fat 1 JEPonline Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline Official Journal of The American Society of Exercise Physiologists (ASEP) ISSN 1097-9751 An International Electronic Journal
ESPEN Congress Prague 2007
 ESPEN Congress Prague 2007 Nutrition implication of obesity and Type II Diabetes Nutrition support in obese patient Claude Pichard Nutrition Support in Obese Patients Prague, 2007 C. Pichard, MD, PhD,
ESPEN Congress Prague 2007 Nutrition implication of obesity and Type II Diabetes Nutrition support in obese patient Claude Pichard Nutrition Support in Obese Patients Prague, 2007 C. Pichard, MD, PhD,
Body Composition. Chapters 18 and 23
 Body Composition Chapters 18 and 23 Somatotype (Body Type) Soft roundness? endormorphy High muscle mass? mesomorphy Linearity and fragility? ectomorphy Body Composition Methods Height Weight Tables e.g.
Body Composition Chapters 18 and 23 Somatotype (Body Type) Soft roundness? endormorphy High muscle mass? mesomorphy Linearity and fragility? ectomorphy Body Composition Methods Height Weight Tables e.g.
Diagnostische Präzision von DXL im Vergleich zu DXA bei pmp Frauen mit Frakturen
 Diagnostische Präzision von DXL im Vergleich zu DXA bei pmp Frauen mit Frakturen Christian Muschitz II. Medizinische Abteilung mit Rheumatologie, Osteologie & Gastroenterologie Akademisches Lehrkrankenhaus
Diagnostische Präzision von DXL im Vergleich zu DXA bei pmp Frauen mit Frakturen Christian Muschitz II. Medizinische Abteilung mit Rheumatologie, Osteologie & Gastroenterologie Akademisches Lehrkrankenhaus
Adult BMI Calculator
 For more information go to Center for Disease Control http://search.cdc.gov/search?query=bmi+adult&utf8=%e2%9c%93&affiliate=cdc-main\ About BMI for Adults Adult BMI Calculator On this page: What is BMI?
For more information go to Center for Disease Control http://search.cdc.gov/search?query=bmi+adult&utf8=%e2%9c%93&affiliate=cdc-main\ About BMI for Adults Adult BMI Calculator On this page: What is BMI?
Adina Alazraki, MD, FAAP Assistant Professor, Radiology and Pediatrics Emory University School of Medicine Children s Healthcare of Atlanta
 Adina Alazraki, MD, FAAP Assistant Professor, Radiology and Pediatrics Emory University School of Medicine Technical: Patient positioning Performance of the scan Analysis of the data Theoretical: Identification
Adina Alazraki, MD, FAAP Assistant Professor, Radiology and Pediatrics Emory University School of Medicine Technical: Patient positioning Performance of the scan Analysis of the data Theoretical: Identification
Evaluating body fat in girls and female adolescents: advantages and disadvantages of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry 1 4
 Evaluating body fat in girls and female adolescents: advantages and disadvantages of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry 1 4 William W Wong, Albert C Hergenroeder, Janice E Stuff, Nancy F Butte, E O Brian
Evaluating body fat in girls and female adolescents: advantages and disadvantages of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry 1 4 William W Wong, Albert C Hergenroeder, Janice E Stuff, Nancy F Butte, E O Brian
RELIABILITY OF DUAL-ENERGY X-RAY
 RELIABILITY OF DUAL-ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY IN ASSESSING BODY COMPOSITION IN ELITE ATHLETES Alisa Nana BND (Hons) A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
RELIABILITY OF DUAL-ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY IN ASSESSING BODY COMPOSITION IN ELITE ATHLETES Alisa Nana BND (Hons) A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
Introduction. Methods
 International Journal of Obesity (1998) 22, 655±660 ß 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/98 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ijo Sagittal abdominal diameter as a practical predictor
International Journal of Obesity (1998) 22, 655±660 ß 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/98 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ijo Sagittal abdominal diameter as a practical predictor
2013 ISCD Official Positions Adult
 2013 ISCD Official Positions Adult These are the Official Positions of the ISCD as updated in 2013. The Official Positions that are new or revised since 2007 are in bold type. Indications for Bone Mineral
2013 ISCD Official Positions Adult These are the Official Positions of the ISCD as updated in 2013. The Official Positions that are new or revised since 2007 are in bold type. Indications for Bone Mineral
Nutritional Methodology-Body Composition
 Nutritional Methodology-Body Composition An Evaluation of Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry and Underwater Weighing to Estimate Body Composition by Means of Carcass Analysis in Piglets 1 Per Elowsson,*
Nutritional Methodology-Body Composition An Evaluation of Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry and Underwater Weighing to Estimate Body Composition by Means of Carcass Analysis in Piglets 1 Per Elowsson,*
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) to Determine Body Composition
 Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) to Determine Body Composition Policy Number: 6.01.40 Last Review: 4/2014 Origination: 4/2005 Next Review: 4/2015 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) to Determine Body Composition Policy Number: 6.01.40 Last Review: 4/2014 Origination: 4/2005 Next Review: 4/2015 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas
DXA When to order? How to interpret? Dr Nikhil Tandon Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi
 DXA When to order? How to interpret? Dr Nikhil Tandon Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi Clinical Utility of Bone Densitometry Diagnosis (DXA)
DXA When to order? How to interpret? Dr Nikhil Tandon Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi Clinical Utility of Bone Densitometry Diagnosis (DXA)
Obesity Increases Precision Errors in Dual X-ray Absorptiometry Measurements.
 Obesity Increases Precision Errors in Dual X-ray Absorptiometry Measurements. 1 K.M.Knapp, 1 J.R.Welsman, 1 S.J.Hopkins, 2 I.Fogelman and 2 G.M.Blake 1. University of Exeter, Exeter, UK 2. King s College
Obesity Increases Precision Errors in Dual X-ray Absorptiometry Measurements. 1 K.M.Knapp, 1 J.R.Welsman, 1 S.J.Hopkins, 2 I.Fogelman and 2 G.M.Blake 1. University of Exeter, Exeter, UK 2. King s College
Review Comparison of body composition methods: a literature analysis
 European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 495±503 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Review Comparison of body composition methods: a literature analysis M Fogelholm
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 495±503 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Review Comparison of body composition methods: a literature analysis M Fogelholm
Luís B Sardinha, Timothy G Lohman, Pedro J Teixeira, Dartagnan P Guedes, and Scott B Going
 Comparison of air displacement plethysmography with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and 3 field methods for estimating body composition in middle-aged men 1,2 Luís B Sardinha, Timothy G Lohman, Pedro
Comparison of air displacement plethysmography with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and 3 field methods for estimating body composition in middle-aged men 1,2 Luís B Sardinha, Timothy G Lohman, Pedro
UNIT 4 ASSESSMENT OF NUTRITIONAL STATUS
 UNIT 4 ASSESSMENT OF NUTRITIONAL STATUS COMMUNITY HEALTH NUTRITION BSPH 314 CHITUNDU KASASE BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN PUBLIC HEALTH UNIVERSITY OF LUSAKA 1. Measurement of dietary intake 2. Anthropometry 3.
UNIT 4 ASSESSMENT OF NUTRITIONAL STATUS COMMUNITY HEALTH NUTRITION BSPH 314 CHITUNDU KASASE BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN PUBLIC HEALTH UNIVERSITY OF LUSAKA 1. Measurement of dietary intake 2. Anthropometry 3.
Body Composition. Sport Books Publisher 1
 Body Composition Sport Books Publisher 1 The body composition The body composition is affected by the proportions of the body component (bones, muscles, and other tissues) It can be seen that the major
Body Composition Sport Books Publisher 1 The body composition The body composition is affected by the proportions of the body component (bones, muscles, and other tissues) It can be seen that the major
Resting metabolic rate in Italians: relation with body composition and anthropometric parameters
 Acta Diabetol (2000) 37:77-81 Springer-Verlag 2000 ORIGINAL A. De Lorenzo A. Andreoli S. Bertoli G. Testolin G. Oriani P. Deurenberg Resting metabolic rate in Italians: relation with body composition and
Acta Diabetol (2000) 37:77-81 Springer-Verlag 2000 ORIGINAL A. De Lorenzo A. Andreoli S. Bertoli G. Testolin G. Oriani P. Deurenberg Resting metabolic rate in Italians: relation with body composition and
Validation of Body Fat Measurement by Skinfolds and Two Bioelectric Impedance Methods with DEXA The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES-3]
![Validation of Body Fat Measurement by Skinfolds and Two Bioelectric Impedance Methods with DEXA The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES-3] Validation of Body Fat Measurement by Skinfolds and Two Bioelectric Impedance Methods with DEXA The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES-3]](/thumbs/75/72213020.jpg) Original Article Validation of Body Fat Measurement by Skinfolds and Two Bioelectric Impedance Methods with DEXA The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES-3] Sudha Vasudev, Anjana Mohan, Deepa
Original Article Validation of Body Fat Measurement by Skinfolds and Two Bioelectric Impedance Methods with DEXA The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study [CURES-3] Sudha Vasudev, Anjana Mohan, Deepa
The Impact of Recent Technological Advances on the Trueness and Precision of DXA to Assess Body Composition
 nature publishing group The Impact of Recent Technological Advances on the Trueness and Precision of DXA to Assess Body Composition Rebecca J. Toombs 1, Gaele Ducher 1, John A. Shepherd 2 and Mary Jane
nature publishing group The Impact of Recent Technological Advances on the Trueness and Precision of DXA to Assess Body Composition Rebecca J. Toombs 1, Gaele Ducher 1, John A. Shepherd 2 and Mary Jane
Portfolio Requirements and Instructions 2018
 Portfolio Requirements and Instructions 2018 Introduction The purpose of the portfolio is to demonstrate your understanding and practical ability in bone densitometry across four sections. It is to provide
Portfolio Requirements and Instructions 2018 Introduction The purpose of the portfolio is to demonstrate your understanding and practical ability in bone densitometry across four sections. It is to provide
Osteoporosis International. Original Article. Bone Mineral Density and Vertebral Fractures in Men
 Osteoporos Int (1999) 10:265 270 ß 1999 International Osteoporosis Foundation and National Osteoporosis Foundation Osteoporosis International Original Article Bone Mineral Density and Vertebral Fractures
Osteoporos Int (1999) 10:265 270 ß 1999 International Osteoporosis Foundation and National Osteoporosis Foundation Osteoporosis International Original Article Bone Mineral Density and Vertebral Fractures
Body Composition Changes Following a Very Low Calorie Pre-Operative Diet in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery
 Body Composition Changes Following a Very Low Calorie Pre-Operative Diet in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery 03 September 2018 Jonathan Sivakumar, Lynn Chong, Salena Ward, Tom R Sutherland, Michael
Body Composition Changes Following a Very Low Calorie Pre-Operative Diet in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery 03 September 2018 Jonathan Sivakumar, Lynn Chong, Salena Ward, Tom R Sutherland, Michael
Accuracy of DEXA scanning & other methods for determining BMD.
 BMD- Measurement Site Accuracy of DEXA scanning & other methods for determining BMD. Ann Larkin In general, densitometry techniques can be performed in either the axial or the appendicular skeleton, depending
BMD- Measurement Site Accuracy of DEXA scanning & other methods for determining BMD. Ann Larkin In general, densitometry techniques can be performed in either the axial or the appendicular skeleton, depending
TOTAL BODY COMPOSITION
 Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries DEXA TOTAL BODY COMPOSITION www.sportsurgeryclinic.com WHY CHOOSE DEXA TOTAL BODY COMPOSITION? DEXA, short for Dual Energy
Specialists in Joint Replacement, Spinal Surgery, Orthopaedics and Sport Injuries DEXA TOTAL BODY COMPOSITION www.sportsurgeryclinic.com WHY CHOOSE DEXA TOTAL BODY COMPOSITION? DEXA, short for Dual Energy
Evaluation of Bone Mineral Status in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:180-184 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.2.180 Evaluation of Bone Mineral Status in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Babak Pourabbas Tahvildari,
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:180-184 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.2.180 Evaluation of Bone Mineral Status in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Babak Pourabbas Tahvildari,
Introduction. Methods
 International Journal of Obesity (1999) 23, 190±197 ß 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ijo Effects on body weight of strict or liberal adherence
International Journal of Obesity (1999) 23, 190±197 ß 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ijo Effects on body weight of strict or liberal adherence
Healthy percentage body fat ranges: an approach for developing guidelines based on body mass index 1 3
 Healthy percentage body fat ranges: an approach for developing guidelines based on body mass index 1 3 Dympna Gallagher, Steven B Heymsfield, Moonseong Heo, Susan A Jebb, Peter R Murgatroyd, and Yoichi
Healthy percentage body fat ranges: an approach for developing guidelines based on body mass index 1 3 Dympna Gallagher, Steven B Heymsfield, Moonseong Heo, Susan A Jebb, Peter R Murgatroyd, and Yoichi
Differences in body composition between Singapore Chinese, Beijing Chinese and Dutch children
 ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION (2003) 57, 405 409 ß 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954 3007/03 $25.00 www.nature.com/ejcn Differences in body composition between Singapore Chinese, Beijing Chinese
ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION (2003) 57, 405 409 ß 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954 3007/03 $25.00 www.nature.com/ejcn Differences in body composition between Singapore Chinese, Beijing Chinese
