Variation of grain Cd and Zn concentrations of 110 hybrid rice cultivars grown in a low-cd paddy soil
|
|
|
- Verity Beasley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Environmental Sciences 21(2009) Variation of grain Cd and Zn concentrations of 110 hybrid rice cultivars grown in a low-cd paddy soil SHI Jing, LI Lianqing, PAN Genxing Institute of Resource, Ecosystem and Environment of Agriculture, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing , China. shjing1980@yahoo.com.cn Received 01 March 2008; revised 23 April 2008; accepted 23 May 2008 Abstract Enhanced Cd uptake and Zn depletion in rice grains and high potential for food Cd exposure by the high-yielding hybrid cultivars of China had been addressed. A field experiment was conducted in 2006 to determine the difference in grain Cd and Zn between cultivars. Total 110 cultivars including super rice and common hybrid rice cultivars were grown on a single paddy soil (Entic Haplaquept) with a neutral reaction and low total Cd content. Grain Cd and Zn concentrations were determined with graphite atomic adsorption spectrophotometer (GFAAS) and flame atomic adsorption spectrophotometer (AAS) respectively. Wide variation of Cd content in grain was found in a range of mg/kg, while the Zn content in a range of mg/kg among the cultivars. Higher Cd but lower Zn concentration in grains of super rice cultivars was observed compared to the common hybrid ones. A highly significant positive linear correlation of grain Cd/Zn with grain Cd was found for super rice and common hybrid cultivars, meanwhile much higher slope for these hybrid cultivars than the reported non-hybrid cultivars was also observed. Using the limit value of the Chinese chemical guidelines for foods (MOHC and SSC, 2005), calculated potential risk of food Cd exposure with Zn hungry through diet intake was prominent with all the studied 110 hybrid rice cultivars, possessing high potential health problems for rice production in South China using the super rice cultivars. Breeding of genotypes of rice cultivars with low grain Cd and low Cd/Zn ratio is needed for rice production in acidic red soils where Cd bioavailability is prevalently high. Key words: rice cultivar; rice grain; cadmium; zinc; genotype difference DOI: /S (08) Introduction Intake of heavy metals via the soil-crop-food chain has been considered as the predominant pathway of human exposure to potentially toxic heavy metals (Chang et al., 2002). Among the major staple crops, rice is the particular one with high Cd uptake and accumulation (Chaney et al., 2004). Recently, special attention has been paid to Zn- Cd relation in rice as Zn-deficient diets were evidenced to enhance the potential health risk of Cd for animal and even people (Reeves and Chaney, 2004; Liu et al., 2005; Gong and Pan, 2006a). Insufficiency of Zn in human diet may occur with monotonous vegetarian diets in areas with Zn-deficient soils (Chaney et al., 2005). In China, rice is consumed at about 200 kg per capita annually and is produced predominantly in South China where the soils are high in Cd mobility (Wang et al., 2003; Cao et al., 1999) and/or deficient in Zn. However, for meeting the demand by the increasing population and decreasing arable lands, high-yielding hybrid rice or super rice cultivars with high Cd affinity (Wang and Gong, 1996; Wu et al., 1999; Gong et al., 2006b) are under extension in China, which may * Corresponding author. gxpan@njau.edu.cn raise the potential health problems due to increasing of Cd intake and deficiency of Zn. There have been many studies on difference in abilities of crop species to uptake potentially toxic heavy metals in their edible parts (Yu et al., 2006). Even within one species, there are also great genotypic differences in grain concentration (Li et al., 1995; Wu and Zhang, 2002; Liu et al., 2003, 2005). To address the variation in Cd and Zn uptake with the cultivars and screen every cultivar with both low Cd and Cd to Zn ratio, 110 rice cultivars were selected to grow in a single rice paddy soil and the Cd and Zn concentrations in grain were determined for comparison. 1 Rice cultivars Total 110 hybrid rice cultivars of different genotypes were used in the experiment, including 98 common hybrid rice cultivars and 12 super rice cultivars. The growing period of the cultivars was within (155 ± 20) d. The seeds of these cultivars were ordered from rice breeding agencies such as seed companies, breeding institutes of Sichuan, Yunnan, Guangxi of South China. Rice seeds
2 No. 2 Variation of grain Cd and Zn concentrations of 110 hybrid rice cultivars grown in a low-cd paddy soil 169 were submerged in a water bath for about 48 h at room temperature and germinated under moisture condition (seeds were covered with two layers of moist gauze cloth) at 32 C for another 30 h. The germinated seeds were grown in a nursery paddy soil till 3 leaves appearing. Then seedlings were transplanted in the experiment plot. 1.1 Field experiments and soil condition The field experiment was carried out at the Experiment Farm of Nanjing Agricultural University located in Jiangpu, Nanjing, China. Being neutral reaction (Table 1), the soil is classified as Entic Haplaquept (USDA, 1999). Fifty rice seedlings of a single cultivar were transplanted in an area of 2 m 2. The experiment was conducted in triplicate and arranged in a random completely block design (RCBD). A protection row at width of 0.5 m was set around the experimental plots, which had one opening as the inlet and another as the outlet for irrigation water. Fertilizer of N, P, K were applied 3 times during the rice growth: (1) as basal with N, P, and K on the 5th day in advance of seedlings planting, (2) when tillering, and (3) when spiking with only N. The total dressing of N, P, K was applied at 200 kg N/hm 2 as urea, 100 kg P 2 O 5 /hm 2 as calcium magnesium phosphate and 150 kg K 2 O/hm 2 as potassium chloride. All the phosphorus and potassium fertilizer and 60% of N as urea were applied as basal dressing before transplantation. 1.2 Sample preparation, and Cd and Zn determination Whole plant of rice was sampled in triplicate when ripening as removal from the soil randomly from each plot and separated into subsamples of root, shoot, and grain respectively, after washing with deionized water. The subsample was transferred to a paper bag and dried in an air-forced oven at 60 C for 48 h. Dry plant material was ground in a stainless steel blender to pass through a 0.4- mm sieve. All samples were stored at ambient temperature and humidity. Three topsoil samples from the plot were subject to mixed acid digestion (HNO 3 -HClO 4 -HF). A certified reference material of sediment GBW with (0.13 ± 0.04) mg/kg Cd and (97 ± 9) mg/kg Zn was purchased from the National Centre for Certificate Reference Materials, China, and used with all patch of digestions. Dried plant samples were digested in a 4:1 (V/V) mixture of HNO 3 -HClO 4 (Lu, 2000). Ten milliliter of mixed acids was added to 0.75 g of plant sample in a high-walled beaker and allowed to stand for 12 h at 25 C. The samples were then heated in a sand bath at 170 C until clear. After cooling, the solution was diluted to 25 ml with deionized water and filtered through a Xinhua No.11 filter paper (< 0.45 μm, China Xinhua Filter Company). Two certified plant reference materials GBW with (0.14 ± 0.01) mg/kg Cd and (20.6 ± 1.0) mg/kg Zn and GBW with (0.057 ± 0.008) mg/kg Cd, and (26.3 ± 0.9) mg/kg Zn were purchased from the National Centre for Certificate Reference Materials, China, and used respectively with all patches of digestions. The recovery of Cd and Zn were in the range of 81.76% % and 92.02% %, respectively. The total Zn and Cd contents of the digested solutions were determined by flame atomic adsorption spectrophotometry (AAS) and graphite furnace AAS (TAS986, Puxi Analytical Instrument Company, China), respectively. A reagent blank was incorporated within each batch of analytical samples. The chemical reagents used in the analysis were in guaranteed reagent grade. 1.3 Statistical analysis Statistical analysis was conducted using statistical software SPSS. The statistical significance level was defined at P Results and discussion 2.1 Variation of Cd and Zn concentrations in grain The Cd concentration of unpolished rice grain of the 110 cultivars ranged from to mg/kg with a mean of mg/kg. In contrast, the grain Zn contents ranged from to mg/kg with a mean of mg/kg. The variability coefficients of Cd, Zn, and Cd/Zn ratio among the 110 rice cultivars are 51.30%, 24.66%, and 61.08%, respectively (Table 2). Apparently, there is much higher variability with grain Cd than with Zn. Grain Zn concentration here is in higher consistency with the reported results (Pongsakul and Attajarusit, 1999; Marr et al., 1995), although the cultivars were from a diverse Table 1 Physicochemical properties of the topsoil (0 20 cm) ph (H 2 O) Org C (g/kg) CEC (cmol/kg) Available P (mg/kg) Total Cd (mg/kg) Total Zn (mg/kg) CEC: cation exchange capacity of soil. Table 2 Grain concentrations (mg/kg) of Cd and Zn, and the Cd/Zn ratio of 110 rice cultivars Concentration Cd Zn Cd/Zn Maximum (Zhongzheyou-1) (R234) (Teyougui-3) Minimum (J314) (45A/998) (J196) Arithmetic mean Middle value (Jinyou-398, Teyou-559, TianART, P742) (R287, J296) (IIyou-559, Jinyou-398) Standard error Coefficient of variation (%) The number or characters in the brackets are the name of the cultivars while breeded.
3 170 SHI Jing et al. Vol. 21 range of locations, rice varieties, soil conditions. Over half of the cultivars had grain Cd below the mean of mg/kg, and about 10% of the cultivars (including 5 super rice cultivars) had grain Cd over 0.04 mg/kg, as double as the mean value (Fig. 1). Nevertheless, over 12% of the cultivars (14 cultivars) had a grain Cd under 0.0l mg/kg. This result indicates that low Cd cultivars may be screened from common hybrid cultivars but super rice ones. The Chinese State Standard Committee set up 0.2 mg Cd/kg as limit for rice while the Codex Committee draft of provisional maximum level (ML) for Cd in rice grains was 0.4 mg/kg (CCFAC, 2005). In this study, grain Cd concentrations of rice cultivars growing in this neutral paddy soil were all below these two guidelines. The low grain Cd concentrations could be attributed to low soil indigenous Cd and low availability with ph over 6.0. In contrast, Li et al. (2003) reported that Cd concentrations in the rice grain varied in the range of mg/kg of the 57 rice cultivars grown in a paddy soil with ph of 6.54 with total soil Cd content of 0.43 mg/kg. As reported by Wang and Stuane (2003) and Wang et al. (2003), rice grain Cd level could increase a lot when grown in acidic soils such as the red-soil region. Li et al. (2005) reported that grain Cd concentration of common rice cultivars planted in a red soil with ph 4.95 and Cd-spiked treatment were as 14-fold as in a paddy soil with ph 6.54 and non-spiked Cd. Similarly, Gong et al. (2006b) have stated that a hybrid rice cultivar grown in a red earth paddy of ph 5.25 had grain Cd 13-fold as grown in a typical paddy of ph 5.84 and Cd-spiked treatment. In other words, Cd accumulation by 10 folds may be expected when grown in a soil with ph lower by 1 unit and soil Cd level increased by 3 folds. This would infer that such variation of ph and the increase of soil total Cd to the level of mg/kg, is very common in red soil region of China. We assume these 110 hybrid rice cultivars planted in the red soil region as in the case of Li et al. (2005) and Gong et al. (2006b). This would infer that there would be about 10% of the cultivars (including 5 super rice cultivars) grain Cd concentrations over 0.4 mg/kg (ML for Cd by CCFAC). While over 12% of the cultivars (14 common hybrid cultivars, no super rice) grain Cd under 0.1 mg/kg (half of the limit value 0.2 mg/kg by CFCG). About 50% cultivars and, 10 out of total 12 super rice cultivars, had grain Zn below the total mean of mg/kg. A daily dietary intake of Zn could be estimated at 10.7 mg/d assuming the consumption of rice with the mean grain Zn here (19.16 mg/kg), which is close to the Chinese daily intake recommendation (RNI) of Zn at 15 mg/d for adults, but much under the maximum content of Zn (50 mg/kg) proposed by CFSG, suggesting a possible dietary intake deficiency for the monotonous vegetarian diets in China. 2.2 Relationship between Cd and Zn in rice grains Table 3 shows the difference in grain Cd, Zn contents and the ratio of Cd/Zn between the studied two groups of hybrid rice. The super rice cultivars had a significantly higher grain Cd uptake and lower grain Zn uptake than the common hybrid rice cultivars. The calculated mean Cd/Zn ratio in grain was for super rice cultivars and for common hybrid rice cultivars. Mean grain Cd content and Cd/Zn ratio of super rice cultivars were significantly higher than that of common hybrid by 67.86% and 72.43%, respectively. However, no significant difference in rice grain Zn content was observed. A comparison of grain Cd/Zn ratio between hybrid rice and super rice in our experiment revealed limited uptake of Zn by these rice cultivars of high Cd/Zn ratio. A highly significant positive linear correlations of grain Cd/Zn with grain Cd content for super rice and hybrid rice studied was observed (Fig. 2a) in comparison to that of hybrid and conventional rice (Fig. 2b) calculated by Li et al. (2003). The higher slope of the linear regression curve for all the hybrid rice compared to that for conventional rice indicated Zn deficiency is enhanced with super rice cultivars (Gong and Pan, 2006a). Simmons et al. (2003) studied the Cd and Zn level of rice and soybean grains produced in a region of Thailand where soils were contaminated by Zn and Cd in mine area and concluded that rice was a particular crop without increase Zn content and with increased Cd in rice Table 3 Grain Cd and Zn contents and Cd/Zn ratio of the two groups of hybrid rice Cd (mg/kg) Zn (mg/kg) Cd/Zn Super rice ± a ± 2.79 a ± a Hybrid rice ± b ± 4.84 a ± b Different characters in the same column mean significant difference between the two cultivars at P Fig. 1 Distribution of grain Cd and Zn contents of the 110 cultivars.
4 No. 2 Variation of grain Cd and Zn concentrations of 110 hybrid rice cultivars grown in a low-cd paddy soil 171 grain. Similarly, Kukier and Chaney (2002) found that Zn concentrations in rice plants decreased with increased Cd concentrations and the higher plant Zn contents could diminish Cd toxicity symptoms in shoot. While hybrid cultivars had greater uptake of Cd and lower uptake of Zn than the non-hybrid ones, the genotype effect on Zn depletion was considerably striking. The interaction between Cd and Zn on uptake and distribution in crops may impose a public concern. ability of rice to exclude Zn from grain, may have caused underestimation of health risk from soil and rice Cd in China, especially to subsistence rice consumers (Chaney et al., 2005; Wang et al., 2005). In fact, the potential Zn hungry still exists in most countryside (Wang et al., 2006). Assuming rice is consumed for an adult at 206 kg /year, dietary exposure of rice Cd from the super rice and common hybrid rice studied here would amount to 19 and 11 μg/d, respectively. Therefore, hardly health risk may arise from consumption of the hybrid rice grown in this soil as the tolerable daily dietary Cd intake could be as much as 60 μg/d using R f D value (USEPA, 2000). Despite of a moderate Zn content (19.00 mg/kg), in the studied soil, none of the 110 cultivars had grain Zn concentration achieving the maximum permissible limit of 50 mg/kg. The calculated mean adult daily intake of Zn at 11 and 10 mg/d with hybrid rice and super rice cultivars, respectively, lower than the recommended Zn daily intake of 15 mg and especially of 20 mg for pregnant women, suggest a possible Zn deficiency with cultivation of these hybrid rice even in a neutral soil. Therefore, these studied hybrid rice, especially super rice, may impose a potential Zn deficiency in diet for the subsistence diet farmers adults, especially for the pregnant women. 3 Conclusions Fig. 2 Correlation of grain Cd/Zn ratio with grain Cd content in (a) 12 super rice cultivars and 98 hybrid rice cultivars in the same soil and (b) in 110 hybrid rice cultivars and 57 conventional rice cultivars (Li et al., 2003). In addition, significant differences existed in Cd, Zn accumulation and Cd/Zn ratio for rice cultivars and genotypes. For example, the ratio of Cd/Zn varied in wide range of to Whereas, the values were much lower than suggested by Simmons et al. (2003) as a critical value for Cd toxicity to human gut. However, considering the fact that grain Cd content was higher of super rice cultivars than that of hybrid ones and grains of extensive acidic paddy soils with high Cd bioavailability in South China, extension of these high-yielding super rice cultivars in the rice area where Zn is generally deficient (generally mg/kg) may possess a serious problem of Zn-deficiency and Cd toxicity for human health, especially for subsistence rice diet farmers. An insufficient understanding of the agronomy of Cd and Zn, and the Wide range of grain Cd was observed than of Zn among the 110 hybrid rice cultivars grown in a neutral, low Cd content paddy soil. Super rice cultivars exerted significantly higher grain Cd uptake with a higher ratio of Cd/Zn than the common hybrid rice cultivars. Thus, the super rice cultivars may possess a greater risk than those of hybrid ones from Cd exposure and Zn deficiency through dietary intake for human health, especially for subsistence diet farmers in South China where enhanced Cd bioavailability and Zn deficiency occurs due to low ph and poor soil nutrient status. However, a small portion of the common rice cultivars screened here had lower grain Cd and Cd/Zn ratio. This offers an opportunity to conduct a low-cd cultivar breeding and cultivation for a safe highyielding rice production while great care is needed for using super rice in rice production of South China with Cd contaminated and bioavailability enhanced soils. Acknowledgments This work was partially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (No. 2006BAD17B06) and the Ministry of Education of China (No. B200613). Special acknowledgment is given to Dr. R. L. Chaney from USDA for his comments and discussion of potential risk problem for subsistence rice diet farmers. References Cao R L, Jia X K, Zhang J S, The prevention and cure of paddy soil at Cd polluted sites. Agricultural Technology of Tianjin, 16(6):
5 172 SHI Jing et al. Vol. 21 Chaney R L, Angle J S, McIntosh M S, Reeves R D, Li Y M, Brewer E P, Chen K Y, Roseberg R J, Perner H, Synkowski E C, Broadhurst C L, Wang S, Baker A J M, Using hyperaccumulator plants to phytoextract soil Ni and Cd. Naturforschung Journal of Biosciences, 60c: Chaney R L, Reeves P G, Ryan J A, Simmons R W, Welch R M, Angle J S, An improved understanding of soil Cd risk to humans and low cost methods to remediate soil Cd risks. Biometals, 17: Chang A C, Pan G X, Page A L, Asano T, Human Health-related Chemical Guidelines for Reclaimed Water and Sewage Sludge Applications in Agriculture. report.pdf. CCFAC (Codex Committee on Food Additives and Contaminants), Codex Alimentarius Commission Report of the 37th Session of the Codex Committee on Food Additives and Contaminants. the Netherlands. Gong W Q, Pan G X, 2006a. Issues of grain Cd uptake and the potential health risk of rice production sector of China. Science and Technology Review, 24(5): Gong W Q, Li L Q, Pan G X, 2006b. Cd uptake and accumulation in grains by hybrid rice in two paddy soils Interactive effect of soil type and cultivars. Environmental Science, 24(8): Kukier U, Chaney R L, Growing rice grain with controlled cadmium concentrations. Plant Nutrition, 25: Li Y M, Chaney R L, Schneiter A A, Miller J F, Genotypic variation in kernel cadmium concentration in sunflower germplasm under varying soil conditions. Crop Scicience, 35: Li Z W, Li L Q, Pan G X, Chen J, Bioavailability of Cd in a soil-rice system in China: Soil type versus genotype effects. Plant and Soil, 271: Li Z W, Zhang Y L, Pan G X, Li J H, Huang X M, Wang J F, Grain contents of Cd, Cu and Se by 57 rice cultivars and the risk significance for human dietary uptake. Environmental Science, 24(2): Liu J G, Li K Q, Xu J K, Liang J S, Liu X L, Yang J C, Zhu Q S, Interaction of Cd and five mineral nutrients for uptake and accumulation in different rice cultivars and genotypes. Field Crops Research, 83: Liu J G, Zhu Q S, Zhang Z J, Xu J K, Yang J C, Wong M H, Variations in cadmium accumulations among rice cultivars and types and the selection of cultivars for reducing cadmium in the diets. Journal of Scicence Food Agriculture, 85: Lu R K, Methods of inorganic pollutants analysis. In: Soil and Agro-chenmical Analysis Methods. Beijing: Agricultural Science and Technology Press Marr K M, Batten G D, Blakeney A B, Relations between minerals in Australian brown rice. Journal of Scicence Food Agriculture, 68: MOHC and SSC (Ministry of Health of China and State Standardization Committee), Guidelines for Limit Values of Pollutant Contents in Foods. GB rd release of State Standards. Pongsakul P, Attajarusit S, Assessment of heavy metals of soils. Soils Fertilizer, 21: Reeves P G, Channey R L, Marginal nutritional status of zinc, iron, and calcium increases cadmium retention in the duodemum and other organs of rats fed rice-based diets. Environmental Research, 96: Simmons R W, Pongsakul P, Chaney R L, Saiyasitpanich D, Klinphoklap S, Nobuntou W, The relative exclusion of zinc and iron from rice grain in relation to rice grain cadmium as compared to soybean: Implications for human health. Plant and Soil, 257: USDA (United States Department of Agriculture ), Soil taxonomy: A basic system of soil classification for making and interpreting soil surveys. United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service. USEPA (U.S. Environment Protection Agency), Drinking Water Standards and Health Advisories. List of Substance, EPA 822-B , summer Wang H Y, Stuanes A O, Heavy metal pollution in airwater-soil-plant system of Zhuzhou City, Hunan Province, China. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 47: Wang K R, Gong H Q, Comparative study on the difference of the uptake and redistribution of environmental Cd by two generic rices. Agro-Environmental Protection, 15(4): , 176. Wang Q R, Cui Y C, Liu X M, Dong Y T, Christie P, Soil contamination and plant uptake of heavy metals at polluted sites in China. Journal of Environmental Sciences and Health, Part B, 38(5): Wang X L, Sato T, Xing B S, Tao S, Health risks of heavy metals to the general public in Tianjin, China via consumption of vegetables and fish. Science of the Total Environment, 350: Wang Z H, Zhai F Y, He Y N, Hu Y S, Wang H J, Analysis on the changes trend of dietary Zn ingestion in China. Journal of Hygiene Research, 35(4): Wu F B, Zhang G P, Genotypic differences in effect of Cd on growth and mineral concentrations in barley seedlings. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 69: Wu Q T, Chen L, Wang G S, Differences on Cd uptake and accumulation among rice cultivars and its mechanism. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 19(1): Yu H, Wang J L, Fang W, Yuan J G, Yang Z Y, Cadmium accumulation in different rice cultivars and screening for pollution-safe cultivars of rice. Science of the Total Environment, 370:
Effects of Soil Copper Concentration on Growth, Development and Yield Formation of Rice (Oryza sativa)
 Rice Science, 05, 12(2): 125-132 125 http://www.ricescience.org Effects of Soil Copper Concentration on Growth, Development and Yield Formation of Rice (Oryza sativa) XU Jia-kuan 1, 2, YANG Lian-xin 1,
Rice Science, 05, 12(2): 125-132 125 http://www.ricescience.org Effects of Soil Copper Concentration on Growth, Development and Yield Formation of Rice (Oryza sativa) XU Jia-kuan 1, 2, YANG Lian-xin 1,
Effects of Nitrogen Application Level on Rice Nutrient Uptake and Ammonia Volatilization
 Rice Science, 2013, 20(2): 139 147 Copyright 2013, China National Rice Research Institute Published by Elsevier BV. All rights reserved DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6308(13)60117-1 Effects of Nitrogen Application
Rice Science, 2013, 20(2): 139 147 Copyright 2013, China National Rice Research Institute Published by Elsevier BV. All rights reserved DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6308(13)60117-1 Effects of Nitrogen Application
RemovalofToxicMetalsContaminatedSoilusingDifferentAmendmentsandSunflowerSpeciesHelianthusAnnuus
 Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: H Environment & Earth Science Volume 16 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: H Environment & Earth Science Volume 16 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Effect of salinity on Cd and Zn availability
 Symposium no. 33 Paper no. 08 Presentation: poster Effect of salinity on Cd and Zn availability KHOSHGOFTARMENSH A.H., JAAFARI B. and SHARIATMADARI H. Department of Soil Science, College of Agriculture,
Symposium no. 33 Paper no. 08 Presentation: poster Effect of salinity on Cd and Zn availability KHOSHGOFTARMENSH A.H., JAAFARI B. and SHARIATMADARI H. Department of Soil Science, College of Agriculture,
Effect of Humic Acid Application on the Yield and Quality of Flue-Cured Tobacco
 Journal of Agricultural Science; Vol. 6, No. 11; 2014 ISSN 1916-9752 E-ISSN 1916-9760 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Effect of Humic Acid Application on the Yield and Quality of
Journal of Agricultural Science; Vol. 6, No. 11; 2014 ISSN 1916-9752 E-ISSN 1916-9760 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Effect of Humic Acid Application on the Yield and Quality of
Heavy metal pollution of soils and vegetables in the midstream and downstream of the Xiangjiang River, Hunan Province
 J. Geogr. Sci. (2008) 18: 353-362 DOI: 10.1007/s11442-008-0353-5 2008 Science in China Press Springer-Verlag Heavy metal pollution of soils and vegetables in the midstream and downstream of the Xiangjiang
J. Geogr. Sci. (2008) 18: 353-362 DOI: 10.1007/s11442-008-0353-5 2008 Science in China Press Springer-Verlag Heavy metal pollution of soils and vegetables in the midstream and downstream of the Xiangjiang
Bioavailability of Cd to Food Crops in
 Vol. 28, pp. 39-43, /979 Bioavailability of Cd to Food Crops in Relation to Heavy Metal Content of Sludge-Amended Soil by Frank T. Bingham* Results of greenhouse and laboratory experiments on factors influencing
Vol. 28, pp. 39-43, /979 Bioavailability of Cd to Food Crops in Relation to Heavy Metal Content of Sludge-Amended Soil by Frank T. Bingham* Results of greenhouse and laboratory experiments on factors influencing
ABREU Cleide Aparecida de (1), BERTON Ronaldo Severiano (1), KOEKKOEK Edwin Peter Josef (2)
 Scientific registration number: 2207 Symposium number: 25 Presentation : poster Validation of annual and total cumulative loading limits stipulated by USEPA for Zn on oxisol. Validation des apports-limites
Scientific registration number: 2207 Symposium number: 25 Presentation : poster Validation of annual and total cumulative loading limits stipulated by USEPA for Zn on oxisol. Validation des apports-limites
Synergistic Effect of Zinc and Cadmium for Uptake, Accumulation and Growth Responses in Rice (Oryza sativa) Varieties.
 Synergistic Effect of Zinc and Cadmium for Uptake, Accumulation and Growth Responses in Rice (Oryza sativa) Varieties. Dinum Herath, Aruni Weerasinghe, Deepthi Bandara, and Darshani Wijayawardhana Abstract
Synergistic Effect of Zinc and Cadmium for Uptake, Accumulation and Growth Responses in Rice (Oryza sativa) Varieties. Dinum Herath, Aruni Weerasinghe, Deepthi Bandara, and Darshani Wijayawardhana Abstract
Changes in Cooking and Nutrition Qualities of Grains at Different Positions in a Rice Panicle under Different Nitrogen Levels
 Rice Science, 2007, 14(2): 141-148 Copyright 2007, China National Rice Research Institute. Published by Elsevier BV. All rights reserved Changes in Cooking and Nutrition Qualities of Grains at Different
Rice Science, 2007, 14(2): 141-148 Copyright 2007, China National Rice Research Institute. Published by Elsevier BV. All rights reserved Changes in Cooking and Nutrition Qualities of Grains at Different
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(2):397-402 Analysis of heavy metals in citrus juice from
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(2):397-402 Analysis of heavy metals in citrus juice from
Comparison of Delayed Flood and Furrow Irrigation Involving Rice for Nutrient and Arsenic Uptake
 International Journal of Applied Agricultural Research ISSN 0973-2683 Volume 12, Number 2 (2017) pp. 129-136 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Comparison of Delayed Flood and Furrow
International Journal of Applied Agricultural Research ISSN 0973-2683 Volume 12, Number 2 (2017) pp. 129-136 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Comparison of Delayed Flood and Furrow
Use of Soil and Tissue Testing for Sustainable Crop Nutrient Programs
 Use of Soil and Tissue Testing for Sustainable Crop Nutrient Programs Kelly T. Morgan Soil and Water Science Department Southwest Florida Research and Education Center Immokalee 239 658 3400 conserv@ufl.edu
Use of Soil and Tissue Testing for Sustainable Crop Nutrient Programs Kelly T. Morgan Soil and Water Science Department Southwest Florida Research and Education Center Immokalee 239 658 3400 conserv@ufl.edu
Seasonal Changes in Leaf Magnesium and Boron Contents and Their Relationships to Leaf Yellowing of Navel Orange Citrus sinensis Osbeck
 2010 37 81317 1324 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 1, 1,2,* 1 3 2 400712 400716 3 341000 6 P < 0.01 0.9082 0.9063 P > 0.05 S 666.4 A 0513-353X 2010 08-1317-08 Seasonal Changes in Leaf Magnesium and Boron Contents
2010 37 81317 1324 Acta Horticulturae Sinica 1, 1,2,* 1 3 2 400712 400716 3 341000 6 P < 0.01 0.9082 0.9063 P > 0.05 S 666.4 A 0513-353X 2010 08-1317-08 Seasonal Changes in Leaf Magnesium and Boron Contents
Chromium Contaminated Soil
 Chelate Assisted Chromium Uptake by Indian Mustard in Tannery Sludge Contaminated Soil 一 Weimin You, Tianduo Li School of Light Chemistry and Environmental Engineering, Shandong Institute of Light Industry,
Chelate Assisted Chromium Uptake by Indian Mustard in Tannery Sludge Contaminated Soil 一 Weimin You, Tianduo Li School of Light Chemistry and Environmental Engineering, Shandong Institute of Light Industry,
Determination of Five Heavy Metals in White Yam (Dioscorea Rotundata) and Three- Leaved Yam (Dioscorea Dumetorum) from Farms in Khana, Rivers State
 Environment and Pollution; Vol. 4, No. 4; 2015 ISSN 1927-0909 E-ISSN 1927-0917 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Determination of Five Heavy Metals in White Yam (Dioscorea Rotundata)
Environment and Pollution; Vol. 4, No. 4; 2015 ISSN 1927-0909 E-ISSN 1927-0917 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Determination of Five Heavy Metals in White Yam (Dioscorea Rotundata)
VOL. 5, NO. 6, June 2015 ISSN ARPN Journal of Science and Technology All rights reserved.
 VOL. 5, NO. 6, June 2015 ISSN 22-7217 Impact of Cumulative Sediment Deposition by Irrigation Water on Soil and Sugarcane in Savannah Sugar Company Limited; Numan, Adamawa State Nigeria 1 R.P. Ali, 2 H.M.
VOL. 5, NO. 6, June 2015 ISSN 22-7217 Impact of Cumulative Sediment Deposition by Irrigation Water on Soil and Sugarcane in Savannah Sugar Company Limited; Numan, Adamawa State Nigeria 1 R.P. Ali, 2 H.M.
UNDERSTANDING THE INFLUENCE OF SOIL PROPERTIES ON PLANT UPTAKE OF CADMIUM IN NEW ZEALAND AGRICULTURAL SOILS
 Cavanagh, JE, Yi Y, Munir K, Lehto N, Robinson B, Gray C, Geretheran G, Jeyakumar J, Thompson-Morrison H, Anderson C 2017. Understanding the influence of soil properties on plant uptake of cadmium in New
Cavanagh, JE, Yi Y, Munir K, Lehto N, Robinson B, Gray C, Geretheran G, Jeyakumar J, Thompson-Morrison H, Anderson C 2017. Understanding the influence of soil properties on plant uptake of cadmium in New
Effect of Humic Acid and Bacterial Manure on Distribution of Heavy Metals in Different Organs of Maize
 Effect of Humic Acid and Bacterial Manure on Distribution of Heavy Metals in Different Organs of Maize Tao Li, Hongyan Cheng, Kokyo Oh, and Shigeo Hosono Abstract Heavy metal contamination of soil may
Effect of Humic Acid and Bacterial Manure on Distribution of Heavy Metals in Different Organs of Maize Tao Li, Hongyan Cheng, Kokyo Oh, and Shigeo Hosono Abstract Heavy metal contamination of soil may
Efficiency of Arsenic Removal from Soil by Vetiveria zizanioides and Vetiveria nemoralis
 Efficiency of Arsenic Removal from Soil by Vetiveria zizanioides and Vetiveria nemoralis Thares Srisatit 1, Tuearnjai Kosakul 2, and Dusaluk Dhitivara 3 1 Department of Environmental Engineering, Faculty
Efficiency of Arsenic Removal from Soil by Vetiveria zizanioides and Vetiveria nemoralis Thares Srisatit 1, Tuearnjai Kosakul 2, and Dusaluk Dhitivara 3 1 Department of Environmental Engineering, Faculty
Environment, health and risk assessment: a case study of the use of an abandoned municipal waste dump site for agricultural purposes
 African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 4 (11), pp. 1217-1221, November 25 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb ISSN 1684 5315 25 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Environment,
African Journal of Biotechnology Vol. 4 (11), pp. 1217-1221, November 25 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajb ISSN 1684 5315 25 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Environment,
Effects of Bicarbonate and High ph Conditions on Zinc and Other Nutrients Absorption in Rice
 290 Rice Science, 2004, 11(56): 290 296 http://www.ricescience.org Effects of Bicarbonate and High ph Conditions on Zinc and Other Nutrients Absorption in Rice MENG Fanhua, WEI Youzhang, YANG Xiaoe, LIN
290 Rice Science, 2004, 11(56): 290 296 http://www.ricescience.org Effects of Bicarbonate and High ph Conditions on Zinc and Other Nutrients Absorption in Rice MENG Fanhua, WEI Youzhang, YANG Xiaoe, LIN
Mercury, Cadmium and Lead Levels in Three Commercially Important Marine Fish Species of in Sri Lanka
 Sri Lanka J. Aquat. Sci. 15 (2010): 39-43 Mercury, Cadmium and Lead Levels in Three Commercially Important Marine Fish Species of in Sri Lanka B.K.K.K. JINADASA 1*, L.R.S. RAMEESHA 2, E.M.R.K.B. EDIRISINGHE
Sri Lanka J. Aquat. Sci. 15 (2010): 39-43 Mercury, Cadmium and Lead Levels in Three Commercially Important Marine Fish Species of in Sri Lanka B.K.K.K. JINADASA 1*, L.R.S. RAMEESHA 2, E.M.R.K.B. EDIRISINGHE
HEAVY METAL RESIDUES OF CHICKEN MEAT AND GIZZARD AND TURKEY MEAT CONSUMED IN SOUTHERN NIGERIA
 Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2008), 11, No 4, 275 280 Short communication HEAVY METAL RESIDUES OF CHICKEN MEAT AND GIZZARD AND TURKEY MEAT CONSUMED IN SOUTHERN NIGERIA Summary C. M. A. IWEGBUE,
Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2008), 11, No 4, 275 280 Short communication HEAVY METAL RESIDUES OF CHICKEN MEAT AND GIZZARD AND TURKEY MEAT CONSUMED IN SOUTHERN NIGERIA Summary C. M. A. IWEGBUE,
Theories regarding the growing scarcity of rock phosphates for mineral fertilisers
 Theories regarding the growing scarcity of rock phosphates for mineral fertilisers 1. Rock phosphates are becoming scarce 2. Low-cadmium rock phosphates are becoming scarce 3. Secondary phosphates are
Theories regarding the growing scarcity of rock phosphates for mineral fertilisers 1. Rock phosphates are becoming scarce 2. Low-cadmium rock phosphates are becoming scarce 3. Secondary phosphates are
RESPONSE OF TOMATO AND CORN PLANTS TO INCREASING Cd LEVELS IN NUTRIENT CULTURE
 Pak. J. Bot., 37(3): 593--599, 2005. RESPONSE OF TOMATO AND CORN PLANTS TO INCREASING Cd LEVELS IN NUTRIENT CULTURE * NESRIN YILDIZ Department of Soil Science & Plant Nutrition, Faculty of Agriculture,
Pak. J. Bot., 37(3): 593--599, 2005. RESPONSE OF TOMATO AND CORN PLANTS TO INCREASING Cd LEVELS IN NUTRIENT CULTURE * NESRIN YILDIZ Department of Soil Science & Plant Nutrition, Faculty of Agriculture,
INFLUENCE OF DAIRY MANURE APPLICATIONS ON CORN NUTRIENT UPTAKE
 INFLUENCE OF DAIRY MANURE APPLICATIONS ON CORN NUTRIENT UPTAKE A. Moore 1, S. Hines 1, B. Brown 1, M. de Haro Marti 1, C. Falen 1, M. Chahine 1, T. Fife 1, R. Norell 1, and J. Ippolito 2 1 University of
INFLUENCE OF DAIRY MANURE APPLICATIONS ON CORN NUTRIENT UPTAKE A. Moore 1, S. Hines 1, B. Brown 1, M. de Haro Marti 1, C. Falen 1, M. Chahine 1, T. Fife 1, R. Norell 1, and J. Ippolito 2 1 University of
ANALYSIS OF POTENTIAL CARCINOGENIC CONTAMINANTS IN GRAIN AND VEGETABLES WITH FOCUS ON HEAVY METALS
 ANALYSIS OF POTENTIAL CARCINOGENIC CONTAMINANTS IN GRAIN AND VEGETABLES WITH FOCUS ON HEAVY METALS N. Belc, V. Ionescu, M. Ionescu, E. Iorga and G. Mustatea National R&D Institute for Food Bioresources,
ANALYSIS OF POTENTIAL CARCINOGENIC CONTAMINANTS IN GRAIN AND VEGETABLES WITH FOCUS ON HEAVY METALS N. Belc, V. Ionescu, M. Ionescu, E. Iorga and G. Mustatea National R&D Institute for Food Bioresources,
The potential of zinc accumulation in Gynura pseudochina (L.) DC.: study in a tissue culture system Presented Mr. Natthawoot Panitlertumpai
 The potential of zinc accumulation in Gynura pseudochina (L.) DC.: study in a tissue culture system Presented Mr. Natthawoot Panitlertumpai Email: p_natthawoot@yahoo.com (advisor) woranan_n@yahoo.com Phytoremediation
The potential of zinc accumulation in Gynura pseudochina (L.) DC.: study in a tissue culture system Presented Mr. Natthawoot Panitlertumpai Email: p_natthawoot@yahoo.com (advisor) woranan_n@yahoo.com Phytoremediation
Effects of particle sizes of rock phosphate on immobilizing heavy metals in lead zinc mine soils
 Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2014, 14 (2), 258-266 Effects of particle sizes of rock phosphate on immobilizing heavy metals in lead zinc mine soils Z. Zhao 1,2*, G. Jiang 1, R. Mao 1 1
Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2014, 14 (2), 258-266 Effects of particle sizes of rock phosphate on immobilizing heavy metals in lead zinc mine soils Z. Zhao 1,2*, G. Jiang 1, R. Mao 1 1
Important Notices. BASIS CPD Points PN/50971/1516/g
 Chilli pepper results May 2016 1 Important Notices BASIS CPD Points PN/50971/1516/g This document is produced for information only and not in connection with any specific or proposed offer (the Offer )
Chilli pepper results May 2016 1 Important Notices BASIS CPD Points PN/50971/1516/g This document is produced for information only and not in connection with any specific or proposed offer (the Offer )
FROM SOIL ELEMENTS TO FOOD NUTRIENTS: Joyce Kinabo Dept. of Food Science and Technology, Sokoine University, Tanzania
 FROM SOIL ELEMENTS TO FOOD NUTRIENTS: Joyce Kinabo Dept. of Food Science and Technology, Sokoine University, Tanzania All forms of life are directly dependent on plants for food Plant foods contain almost
FROM SOIL ELEMENTS TO FOOD NUTRIENTS: Joyce Kinabo Dept. of Food Science and Technology, Sokoine University, Tanzania All forms of life are directly dependent on plants for food Plant foods contain almost
Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil, Irrigation Water and Vegetables Grown around Kubanni River, Nigeria
 Journal of Physical Science, Vol. 28(1), 49 59, 2017 Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil, Irrigation Water and Vegetables Grown around Kubanni River, Nigeria Nasir Sallau Lawal, * Owolona Agbo
Journal of Physical Science, Vol. 28(1), 49 59, 2017 Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil, Irrigation Water and Vegetables Grown around Kubanni River, Nigeria Nasir Sallau Lawal, * Owolona Agbo
Chapter 1: Overview of soil fertility, plant nutrition, and nutrient management
 Chapter 1: Overview of soil fertility, plant nutrition, and nutrient management Agustin Pagani, John E. Sawyer, and Antonio P. Mallarino / Department of Agronomy, Iowa State University Developed in cooperation
Chapter 1: Overview of soil fertility, plant nutrition, and nutrient management Agustin Pagani, John E. Sawyer, and Antonio P. Mallarino / Department of Agronomy, Iowa State University Developed in cooperation
Inorganic Contaminants
 Inorganic Contaminants Dr Stephen R Smith Dept Civil & Environmental Engineering Page 1 Scope of Presentation Sources and concentrations Qualifying environmental limits Phytotoxicity Dietary intake Grain
Inorganic Contaminants Dr Stephen R Smith Dept Civil & Environmental Engineering Page 1 Scope of Presentation Sources and concentrations Qualifying environmental limits Phytotoxicity Dietary intake Grain
Uptake Potential of Some Heavy Metals by Vetiver Grass
 asetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 35 : 46-5 (21) Uptake Potential of Some Heavy Metals by Vetiver Grass Nualchavee Roongtanakiat 1 and Prapai Chairoj 2 ABSTRACT The uptake potential of upland vetiver grass (Vetiveria
asetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 35 : 46-5 (21) Uptake Potential of Some Heavy Metals by Vetiver Grass Nualchavee Roongtanakiat 1 and Prapai Chairoj 2 ABSTRACT The uptake potential of upland vetiver grass (Vetiveria
Effect of arsenic on plant growth and remediation of arsenic by Cyanobacterial species
 ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Volume VIII: No. 1 2017 [36 45] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Effect of arsenic on plant growth and remediation
ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Volume VIII: No. 1 2017 [36 45] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Effect of arsenic on plant growth and remediation
Speciation Analysis and Removal of Heavy Metals Zn, Cu, Cd from Sludge by Organic Acid
 5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2015) Speciation Analysis and Removal of Heavy Metals Zn, Cu, Cd from Sludge by Organic Acid S.W. SONG 1*, L. WANG
5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2015) Speciation Analysis and Removal of Heavy Metals Zn, Cu, Cd from Sludge by Organic Acid S.W. SONG 1*, L. WANG
FACTORS AFFECTING WATER QUALITY
 TECHNICAL PAPER WATER QUALITY PLANT HEALTH FACTORS Water quality is one of the most important factors affecting plant growth, as unwanted components in water can interfere with nutrient availability and
TECHNICAL PAPER WATER QUALITY PLANT HEALTH FACTORS Water quality is one of the most important factors affecting plant growth, as unwanted components in water can interfere with nutrient availability and
Availability and Spatial Variability of Plant Nutrients in Paddy Fields of Wilgoda Irrigation Scheme in Kurunegala
 Availability and Spatial Variability of Plant Nutrients in Paddy Fields of Wilgoda Irrigation Scheme in Kurunegala D. N. Sirisena, W. M. U. K. Rathnayake and W. M. J. Bandara Rice Research and Development
Availability and Spatial Variability of Plant Nutrients in Paddy Fields of Wilgoda Irrigation Scheme in Kurunegala D. N. Sirisena, W. M. U. K. Rathnayake and W. M. J. Bandara Rice Research and Development
Lead and Cadmium Levels in Some Commercially Available Local and Imported Peach Juice Samples in Alkoms City
 Human Journals Research Article September 2018 Vol.:13, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Zaid M. Najah et al. Lead and Cadmium Levels in Some Commercially Available Local and Imported Peach Juice Samples
Human Journals Research Article September 2018 Vol.:13, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Zaid M. Najah et al. Lead and Cadmium Levels in Some Commercially Available Local and Imported Peach Juice Samples
International Journal of Engineering Research & Science (IJOER) ISSN: [ ] [Vol-2, Issue-12, December- 2016]
![International Journal of Engineering Research & Science (IJOER) ISSN: [ ] [Vol-2, Issue-12, December- 2016] International Journal of Engineering Research & Science (IJOER) ISSN: [ ] [Vol-2, Issue-12, December- 2016]](/thumbs/72/67841640.jpg) Determination of the total chromium in vegetable, rice samples cultivated and marketed along Nhue River Khuat Quang Son 1, Dinh Thi Thu Hien 2, Dao Van Bay 3* 1 PhD student, 2 Graduate student Faculty
Determination of the total chromium in vegetable, rice samples cultivated and marketed along Nhue River Khuat Quang Son 1, Dinh Thi Thu Hien 2, Dao Van Bay 3* 1 PhD student, 2 Graduate student Faculty
By Andrew & Erin Oxford, Bethel
 Chemistry in Plant Nutrition & Growth Objectives Review elements of chemistry and apply them to plant nutrition and growth in an agricultural context. Suggested grade levels 9-12 Alaska Content Standards
Chemistry in Plant Nutrition & Growth Objectives Review elements of chemistry and apply them to plant nutrition and growth in an agricultural context. Suggested grade levels 9-12 Alaska Content Standards
Soil research in Europe with special reference to that in Finland A Review
 Soil research in Europe with special reference to that in Finland A Review Jouko Sippola MTT Agrifood Research Finland, Environmental Research, FIN-31600 Jokioinen, Finland jouko.sippola@surffi.net Abstract
Soil research in Europe with special reference to that in Finland A Review Jouko Sippola MTT Agrifood Research Finland, Environmental Research, FIN-31600 Jokioinen, Finland jouko.sippola@surffi.net Abstract
THE EFFECT OF ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION, ACIDIC RAINS, ALUMINIUM CONTAINING PACKAGING ON THE GROWTH OF WHEAT
 Analele Universităţii din Oradea, Fascicula Protecţia Mediului Vol. XXV, 2015 THE EFFECT OF ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION, ACIDIC RAINS, ALUMINIUM CONTAINING PACKAGING ON THE GROWTH OF WHEAT Szabó-Nagy Andrea*,
Analele Universităţii din Oradea, Fascicula Protecţia Mediului Vol. XXV, 2015 THE EFFECT OF ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION, ACIDIC RAINS, ALUMINIUM CONTAINING PACKAGING ON THE GROWTH OF WHEAT Szabó-Nagy Andrea*,
RESPONSE OF BIO FERTILIZERS IN CONJUNCTION WITH INORGANIC FERTILIZERS IN KHARIF PADDY
 RESPONSE OF BIO FERTILIZERS IN CONJUNCTION WITH INORGANIC FERTILIZERS IN KHARIF PADDY TANDEL, B. B., PATEL, D. D., THANKI, J. D., ARVADIA, M. K. AND JAT, R. A. NAVSARI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY NAVSARI-396
RESPONSE OF BIO FERTILIZERS IN CONJUNCTION WITH INORGANIC FERTILIZERS IN KHARIF PADDY TANDEL, B. B., PATEL, D. D., THANKI, J. D., ARVADIA, M. K. AND JAT, R. A. NAVSARI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY NAVSARI-396
Overview of Chemical Research from Biosolids Land Application
 Overview of Chemical Research from Biosolids Land Application Rufus L. Chaney USDA-Agricultural Research Service Environmental Management and Byproducts Utilization Lab Beltsville, MD California Water
Overview of Chemical Research from Biosolids Land Application Rufus L. Chaney USDA-Agricultural Research Service Environmental Management and Byproducts Utilization Lab Beltsville, MD California Water
Downloaded from jstnar.iut.ac.ir at 21:58 IRDT on Monday May 14th 2018
 / / / *...... (// : // : ).. ( ) ( ) (P ()... ... / / / /..
/ / / *...... (// : // : ).. ( ) ( ) (P ()... ... / / / /..
Importance of fertigation scheduling
 Importance of fertigation scheduling Mr. C K Patel Sr. Manager Agronomy Ck.patel@netafim.com SBU-WEST-NETAFIM 9687696657 Proper fertigation scheduling can maximize the fertilizers use efficiency & Crop
Importance of fertigation scheduling Mr. C K Patel Sr. Manager Agronomy Ck.patel@netafim.com SBU-WEST-NETAFIM 9687696657 Proper fertigation scheduling can maximize the fertilizers use efficiency & Crop
Influence of iron fertilization on cadmium uptake by rice seedlings irrigated with cadmium solution
 Influence of iron fertilization on cadmium uptake by rice seedlings irrigated with cadmium solution Liu, H. J., Zhang, J. L., Christie, P., & Zhang, F. S. (2010). Influence of iron fertilization on cadmium
Influence of iron fertilization on cadmium uptake by rice seedlings irrigated with cadmium solution Liu, H. J., Zhang, J. L., Christie, P., & Zhang, F. S. (2010). Influence of iron fertilization on cadmium
Reuse of Human Urine and Faeces for Crop Production
 XU-GLI GRADUATE CERTIFICATE PROGRAM ON ECOLOGICAL SANITATION Reuse of Human Urine and Faeces for Crop Production May 17, 2009 I Xavier University Ateneo de Cagayan Horacio S. Factura III & PhD Student,
XU-GLI GRADUATE CERTIFICATE PROGRAM ON ECOLOGICAL SANITATION Reuse of Human Urine and Faeces for Crop Production May 17, 2009 I Xavier University Ateneo de Cagayan Horacio S. Factura III & PhD Student,
Cranberry Nutrition: An A Z Guide. Joan R. Davenport Soil Scientist Washington State University
 Cranberry Nutrition: An A Z Guide Joan R. Davenport Soil Scientist Washington State University Soil Derived Plant Essential Elements Macro Micro Nitrogen (N) Phosphorus (P) Sulfur (S) Potassium (K) Calcium
Cranberry Nutrition: An A Z Guide Joan R. Davenport Soil Scientist Washington State University Soil Derived Plant Essential Elements Macro Micro Nitrogen (N) Phosphorus (P) Sulfur (S) Potassium (K) Calcium
Understanding a Soil Report
 Understanding a Soil Report AGRONOMY SOIL ANALYSIS 1. Soil ph Soil ph is a measure of the acidity in the soil. An acidic soil has a greater amount of hydrogen (H+) ions and a ph below 7.0. Values above
Understanding a Soil Report AGRONOMY SOIL ANALYSIS 1. Soil ph Soil ph is a measure of the acidity in the soil. An acidic soil has a greater amount of hydrogen (H+) ions and a ph below 7.0. Values above
5. Plant Physiology/Chemistry Section
 5. Plant Physiology/Chemistry Section The research work/experiments conducted during the year 2014-15 are summarized is under: 1. Influence of potassium fertilizer on the incidence of CLCuV disease and
5. Plant Physiology/Chemistry Section The research work/experiments conducted during the year 2014-15 are summarized is under: 1. Influence of potassium fertilizer on the incidence of CLCuV disease and
Determination of Heavy Metals in Canned Dry-Milk and Fish from Supermarkets in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Kefyalew Muleta Tetemke Mehari (PhD)
 Determination of Heavy Metals in Canned Dry-Milk and Fish from Supermarkets in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia Kefyalew Muleta Tetemke Mehari (PhD) 1 PRESENTATION OUT LINE Introduction Objective Material and Methods
Determination of Heavy Metals in Canned Dry-Milk and Fish from Supermarkets in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia Kefyalew Muleta Tetemke Mehari (PhD) 1 PRESENTATION OUT LINE Introduction Objective Material and Methods
NORTHERN CORRIDORSTANDARD NC 4:2018. Roasted Macadamia Specification
 NORTHERN CORRIDORSTANDARD NC 4:2018 Roasted Macadamia Specification Roasted macadamia Specification 1 Scope This Northern corridor Standard specifies the requirements, methods of sampling and testing for
NORTHERN CORRIDORSTANDARD NC 4:2018 Roasted Macadamia Specification Roasted macadamia Specification 1 Scope This Northern corridor Standard specifies the requirements, methods of sampling and testing for
Biosolids Nutrien Management an Soil Testing. Craig Cogger, Soil Scientis WSU Puyallup
 Biosolids Nutrien Management an Soil Testing Craig Cogger, Soil Scientis WSU Puyallup Nutrient Manageme Meet crop nutrient needs Maintain soil quality Conserve resources Protect water quality -- reduc
Biosolids Nutrien Management an Soil Testing Craig Cogger, Soil Scientis WSU Puyallup Nutrient Manageme Meet crop nutrient needs Maintain soil quality Conserve resources Protect water quality -- reduc
Effects of high concentrations of soil arsenic on the growth of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L) and rape (Brassica napus)
 Effects of high concentrations of soil arsenic on the growth of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L) and rape (Brassica napus) Q.J. Liu 1,2, C.M. Zheng 2, C.X. Hu 1, Q.L. Tan 1, X.C. Sun 1, J.J. Su 1 1 Microelements
Effects of high concentrations of soil arsenic on the growth of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L) and rape (Brassica napus) Q.J. Liu 1,2, C.M. Zheng 2, C.X. Hu 1, Q.L. Tan 1, X.C. Sun 1, J.J. Su 1 1 Microelements
Limitations to Plant Analysis. John Peters & Carrie Laboski Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin-Madison
 Limitations to Plant Analysis John Peters & Carrie Laboski Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin-Madison What is an essential plant nutrient omission of the element will result in abnormal
Limitations to Plant Analysis John Peters & Carrie Laboski Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin-Madison What is an essential plant nutrient omission of the element will result in abnormal
Application Note novaa 800 D. Determination of Macro and Trace Minerals as well as Toxic Trace Metals in Powdered Milk. Challenge.
 Application Note novaa 800 D Determination of Macro and Trace Minerals as well as Toxic Trace Metals in Powdered Milk Introduction The popularity of milk and dairy products is growing worldwide, resulting
Application Note novaa 800 D Determination of Macro and Trace Minerals as well as Toxic Trace Metals in Powdered Milk Introduction The popularity of milk and dairy products is growing worldwide, resulting
The Facts About Phosphorus
 The Facts About Phosphorus An essential element Phosphorus is an important nutrient for both plant and animal growth. In human and animal bones, Phosphorus is present in large quantities. It is also found
The Facts About Phosphorus An essential element Phosphorus is an important nutrient for both plant and animal growth. In human and animal bones, Phosphorus is present in large quantities. It is also found
Interpreting Plant Tissue and Soil Sample Analysis
 Interpreting Plant Tissue and Soil Sample Analysis Dan Fromme Associate Professor-Cotton, Corn, & Grain Sorghum Specialist LSU AgCenter Dean Lee Research & Extension Center Alexandria, Louisiana Fertilization
Interpreting Plant Tissue and Soil Sample Analysis Dan Fromme Associate Professor-Cotton, Corn, & Grain Sorghum Specialist LSU AgCenter Dean Lee Research & Extension Center Alexandria, Louisiana Fertilization
Effect of plant nutrition on turmeric production
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 32 (2012) 166 171 I-SEEC2011 Effect of plant nutrition on turmeric production W. Kulpapangkorn a and S. Mai-leang b a Faculty of Science and
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 32 (2012) 166 171 I-SEEC2011 Effect of plant nutrition on turmeric production W. Kulpapangkorn a and S. Mai-leang b a Faculty of Science and
Journal of Chemical, Biological and Physical Sciences
 JCBPS; Section B; May.2015 July.2015, Vol. 5, No. 3; 2634-2642. E- ISSN: 2249 1929 Journal of Chemical, Biological and Physical Sciences An International Peer Review E-3 Journal of Sciences Available online
JCBPS; Section B; May.2015 July.2015, Vol. 5, No. 3; 2634-2642. E- ISSN: 2249 1929 Journal of Chemical, Biological and Physical Sciences An International Peer Review E-3 Journal of Sciences Available online
SCREENING OF SPRING WHEAT VARIETIES RESISTANT TO SOIL POLUTION WITH HEAVY METALS TO CREATE ECOLOGICALLY PURE PRODUCTION
 Copyright TIIKM ISSN: 2513 2695 online DOI: https://doi.org/10.17501/biotech.2016.1106 SCREENING OF SPRING WHEAT VARIETIES RESISTANT TO SOIL POLUTION WITH HEAVY METALS TO CREATE ECOLOGICALLY PURE PRODUCTION
Copyright TIIKM ISSN: 2513 2695 online DOI: https://doi.org/10.17501/biotech.2016.1106 SCREENING OF SPRING WHEAT VARIETIES RESISTANT TO SOIL POLUTION WITH HEAVY METALS TO CREATE ECOLOGICALLY PURE PRODUCTION
Soil Composition. Air
 Soil Composition Air Soil Included Air Approximately 40 to 60% of the volume of a soil is actually empty space between the solid particles (voids). These voids are filled with air and/or water. The air
Soil Composition Air Soil Included Air Approximately 40 to 60% of the volume of a soil is actually empty space between the solid particles (voids). These voids are filled with air and/or water. The air
The effect of humic acid and fulvic acid on adsorption-desorption behavior of copper and zinc in the yellow soil
 The effect of humic acid and fulvic acid on adsorption-desorption behavior of copper and zinc in the yellow soil Zhantai Wang, Minxia Cao, Wenchang Cai, and Heping Zeng Citation: AIP Conference Proceedings
The effect of humic acid and fulvic acid on adsorption-desorption behavior of copper and zinc in the yellow soil Zhantai Wang, Minxia Cao, Wenchang Cai, and Heping Zeng Citation: AIP Conference Proceedings
Metal concentration of some microelements found in some fruits and vegetables, commonly consumed in Zaria metropolis
 Available online at www.aexpbio.com RESEARCH ARTICLE Annals of Experimental Biology 2015, 3 (2):10-14 ISSN : 2348-1935 Metal concentration of some microelements found in some fruits and vegetables, commonly
Available online at www.aexpbio.com RESEARCH ARTICLE Annals of Experimental Biology 2015, 3 (2):10-14 ISSN : 2348-1935 Metal concentration of some microelements found in some fruits and vegetables, commonly
Genetic and genotype environment interaction effects for the content of seven essential amino acids in indica rice
 Indian Academy of Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE Genetic and genotype environment interaction effects for the content of seven essential amino acids in indica rice J. G. WU 1*, C. H. SHI 1, X. M. ZHANG 1, and
Indian Academy of Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE Genetic and genotype environment interaction effects for the content of seven essential amino acids in indica rice J. G. WU 1*, C. H. SHI 1, X. M. ZHANG 1, and
AVAILABLE Cd CONTENT OF SALT AFFECTED AND NORMAL SOILS OF HALASTRA KALOHORI AREA
 Global NEST Journal, Vol 9, No 3, pp 195-200, 2007 Copyright 2007 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved AVAILABLE Cd CONTENT OF SALT AFFECTED AND NORMAL SOILS OF HALASTRA KALOHORI AREA TH.
Global NEST Journal, Vol 9, No 3, pp 195-200, 2007 Copyright 2007 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved AVAILABLE Cd CONTENT OF SALT AFFECTED AND NORMAL SOILS OF HALASTRA KALOHORI AREA TH.
COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT
 LAB ID: SAMPLE ID: REPORT DATE: SAMPLE TYPE: FEEDSTOCKS COMPOSTING METHOD COUNTY C10462 04/27/2018 Analyte COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT (As is basis) Compost Test 3A (Dry weight basis) ph Soluble Salts Solids
LAB ID: SAMPLE ID: REPORT DATE: SAMPLE TYPE: FEEDSTOCKS COMPOSTING METHOD COUNTY C10462 04/27/2018 Analyte COMPOST ANALYSIS REPORT (As is basis) Compost Test 3A (Dry weight basis) ph Soluble Salts Solids
Utilization of Slop Ash as a Source of Potassium for Corn Grown on the Pakchong Soil Series
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 44 : 17-23 (2010) Utilization of Slop Ash as a Source of Potassium for Corn Grown on the Pakchong Soil Series Pimolsiri Supasatienchai 1, Jongruk Chanchareoook 1 * and Ed Sarobol
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 44 : 17-23 (2010) Utilization of Slop Ash as a Source of Potassium for Corn Grown on the Pakchong Soil Series Pimolsiri Supasatienchai 1, Jongruk Chanchareoook 1 * and Ed Sarobol
Cadmium and Chromium Accumulation in the Tissues of the Chinese Rice Grasshopper, Oxya chinensis
 2011,30(12):2440-2445 Journal of Agro-Environment Science Oxya chinensis 1 1 2 1 1 3 1 1* 1. 030006 2. 030006 3. 030031 Oxya chinensis > > > > > > > > > > 6.798 4 mg kg -1 3.347 7 mg kg -1 P >
2011,30(12):2440-2445 Journal of Agro-Environment Science Oxya chinensis 1 1 2 1 1 3 1 1* 1. 030006 2. 030006 3. 030031 Oxya chinensis > > > > > > > > > > 6.798 4 mg kg -1 3.347 7 mg kg -1 P >
ANALYSIS OF RESPONSE OF DIFFERENT CHELATED ZINC SOURCES ON MICRO AND MACRO NUTRIENTS UPTAKE IN MOONG PLANT AND SEED (VIGNA RADIATA)
 ANALYSIS OF RESPONSE OF DIFFERENT CHELATED ZINC SOURCES ON MICRO AND MACRO NUTRIENTS UPTAKE IN MOONG PLANT AND SEED (VIGNA RADIATA) Jilani A A 1 1 Department of Chemistry, St. John s College, Agra-282003
ANALYSIS OF RESPONSE OF DIFFERENT CHELATED ZINC SOURCES ON MICRO AND MACRO NUTRIENTS UPTAKE IN MOONG PLANT AND SEED (VIGNA RADIATA) Jilani A A 1 1 Department of Chemistry, St. John s College, Agra-282003
Evaluation of AB - DTPA Extractant for Multinutrients Extraction in Soils
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-776 Volume 7 Number 3 (218) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/1.2546/ijcmas.218.73.141
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-776 Volume 7 Number 3 (218) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/1.2546/ijcmas.218.73.141
STANDARD METHODS FOR CHEMICAL ELEMENTS IN FOOD OF ANIMAL ORIGIN
 EN 13804 Performance criteria, general considerations and sample preparation 2013 EN 13805 Pressure digestion 2014 EN 13806 Determination of mercury by cold-vapour atomic absorption spectrometry (CVAAS)
EN 13804 Performance criteria, general considerations and sample preparation 2013 EN 13805 Pressure digestion 2014 EN 13806 Determination of mercury by cold-vapour atomic absorption spectrometry (CVAAS)
International Journal of Advance Research in Engineering, Science & Technology
 Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.542 International Journal of Advance Research in Engineering, Science & Technology e-issn: 2393-9877, p-issn: 2394-2444 Volume 4, Issue 9, September-2017 Critical Limits of Zinc
Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.542 International Journal of Advance Research in Engineering, Science & Technology e-issn: 2393-9877, p-issn: 2394-2444 Volume 4, Issue 9, September-2017 Critical Limits of Zinc
EFFECTS OF ZINC AND BORON ON YIELD, NUTRIENT UPTAKE AND ECONOMICS OF MUSTARD (BRASSICA JUNCEA L.) IN MUSTARD-MAIZE CROPPING SEQUENCE
 Bangladesh J. Bot. 46(2): 817-821, 2017 (June) - Short communication EFFECTS OF ZINC AND BORON ON YIELD, NUTRIENT UPTAKE AND ECONOMICS OF MUSTARD (BRASSICA JUNCEA L.) IN MUSTARD-MAIZE CROPPING SEQUENCE
Bangladesh J. Bot. 46(2): 817-821, 2017 (June) - Short communication EFFECTS OF ZINC AND BORON ON YIELD, NUTRIENT UPTAKE AND ECONOMICS OF MUSTARD (BRASSICA JUNCEA L.) IN MUSTARD-MAIZE CROPPING SEQUENCE
Arsenate Exposure Affects Amino Acids, Mineral Nutrient Status and Antioxidant
 1 Supporting Information 2 3 4 Arsenate Exposure Affects Amino ids, Mineral Nutrient Status and Antioxidant in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Genotypes 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 2 S. Dwivedi, R.D.
1 Supporting Information 2 3 4 Arsenate Exposure Affects Amino ids, Mineral Nutrient Status and Antioxidant in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Genotypes 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 2 S. Dwivedi, R.D.
The 1 th International and The 4 th National Congress on Recycling of Organic Waste in Agriculture April 2012 in Isfahan, Iran
 PERIODIC MUNICIPAL COMPOST AND SEWAGE SLUDGE APPLICATION ON ACCUMULATION OF HEAVY METALS IN SOIL AND PLANTS Ali R. Marjovvi 1,* and Moslehedin Rezaei 1 1 Soil and Water Department, Isfahan Agricultural
PERIODIC MUNICIPAL COMPOST AND SEWAGE SLUDGE APPLICATION ON ACCUMULATION OF HEAVY METALS IN SOIL AND PLANTS Ali R. Marjovvi 1,* and Moslehedin Rezaei 1 1 Soil and Water Department, Isfahan Agricultural
AUTHORS MWANSA MUKUKA DR. CHISHALA BENSON H. DR. MUTITI SAMUEL DR. UCHIDA YOSHITAKA APPSA CONFERENCE 6 TH NOVEMBER, 2017
 EVALUATION OF THE PHYTOREMEDIATION POTENTIAL OF LEMON GRASS (Cymbopogon citratus) AND VETIVER GRASS (Chrysopogon zizanioides) IN LEAD CONTAMINATED SOILS AUTHORS MWANSA MUKUKA DR. CHISHALA BENSON H. DR.
EVALUATION OF THE PHYTOREMEDIATION POTENTIAL OF LEMON GRASS (Cymbopogon citratus) AND VETIVER GRASS (Chrysopogon zizanioides) IN LEAD CONTAMINATED SOILS AUTHORS MWANSA MUKUKA DR. CHISHALA BENSON H. DR.
Thresholds of copper toxicity to lettuce in field-collected agricultural soils exposed to copper mining activities in Chile
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Thresholds of copper toxicity to lettuce in field-collected agricultural soils exposed to copper mining activities in Chile J. Verdejo 1, R. Ginocchio 2,3, S. Sauvé 4, P. Mondaca 1, A.
RESEARCH ARTICLE Thresholds of copper toxicity to lettuce in field-collected agricultural soils exposed to copper mining activities in Chile J. Verdejo 1, R. Ginocchio 2,3, S. Sauvé 4, P. Mondaca 1, A.
Matrix Reference Materials - SCP SCIENCE
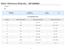 EnviroMAT SS-1 Catalogue No.: 140-025-001 EnviroMAT Contaminated Soil Lot No.: SC0063618 100 g TOTAL DIGESTION VALUES Elements Reference Value (mg/kg) Confidence Interval (mg/kg) Tolerance Interval (mg/kg)
EnviroMAT SS-1 Catalogue No.: 140-025-001 EnviroMAT Contaminated Soil Lot No.: SC0063618 100 g TOTAL DIGESTION VALUES Elements Reference Value (mg/kg) Confidence Interval (mg/kg) Tolerance Interval (mg/kg)
Interaction of Arsenic with Zinc and Organics in a Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivated Field in India
 Research Article TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2005) 5, 646 651 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2005.60 Interaction of Arsenic with Zinc and Organics in a Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivated Field in India
Research Article TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2005) 5, 646 651 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2005.60 Interaction of Arsenic with Zinc and Organics in a Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cultivated Field in India
EFFECT OF ARSENIC ON THE NUTRIENT UPTAKE PATTERN OF AMARANTHUS SAJAL ROY, ZAKIA PARVEEN AND S. M. IMAMUL HUQ*
 Dhaka Univ. J. Biol. Sci. 21(1): 87 96, 2012 (January) EFFECT OF ARSENIC ON THE NUTRIENT UPTAKE PATTERN OF AMARANTHUS SAJAL ROY, ZAKIA PARVEEN AND S. M. IMAMUL HUQ* Bangladesh Australia Centre for Environmental
Dhaka Univ. J. Biol. Sci. 21(1): 87 96, 2012 (January) EFFECT OF ARSENIC ON THE NUTRIENT UPTAKE PATTERN OF AMARANTHUS SAJAL ROY, ZAKIA PARVEEN AND S. M. IMAMUL HUQ* Bangladesh Australia Centre for Environmental
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2013, 5(12): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2013, 5(12):49-53 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Variations in cadmium, mercury and copper accumulation
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2013, 5(12):49-53 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Variations in cadmium, mercury and copper accumulation
Assessment of Secondary and Micro Nutrient Status under Long-Term Fertilizer Experiment on Vertisol
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Joga Rao et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (4): 328-339 (2018) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.3068 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
Available online at www.ijpab.com Joga Rao et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (4): 328-339 (2018) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.3068 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
HEAVY METAL ACCUMULATION IN THE AGRICULTURAL SOIL AROUND IRON-RECYCLING CHAU KHE VILLAGE IN TU SON TOWN, BAC NINH PROVINCE, VIETNAM
 HEAVY METAL ACCUMULATION IN THE AGRICULTURAL SOIL AROUND IRON-RECYCLING CHAU KHE VILLAGE IN TU SON TOWN, BAC NINH PROVINCE, VIETNAM H.T.L. Tra 1, C.T. Son 2, N.T.Hai 3, N.K.Tan 4 1 Department of Land management,
HEAVY METAL ACCUMULATION IN THE AGRICULTURAL SOIL AROUND IRON-RECYCLING CHAU KHE VILLAGE IN TU SON TOWN, BAC NINH PROVINCE, VIETNAM H.T.L. Tra 1, C.T. Son 2, N.T.Hai 3, N.K.Tan 4 1 Department of Land management,
THE EFECTS OF HEAVY METALS, PHOSPHATE, LIME AND SAWDUST ON PLANT GROWTH AND HEAVY METAL ACCUMULATION BY LECTTUCE
 THE EFECTS OF HEAVY METALS, PHOSPHATE, LIME AND SAWDUST ON PLANT GROWTH AND HEAVY METAL ACCUMULATION BY LECTTUCE Nguyen Xuan Cu Department of Pedology and Soil Environment, Faculty of Environmental Sciences,
THE EFECTS OF HEAVY METALS, PHOSPHATE, LIME AND SAWDUST ON PLANT GROWTH AND HEAVY METAL ACCUMULATION BY LECTTUCE Nguyen Xuan Cu Department of Pedology and Soil Environment, Faculty of Environmental Sciences,
Bioavailability based approaches for soil risk assessment of metals: Regional differences arising from distributions of soil chemical properties
 Bioavailability based approaches for soil risk assessment of metals: Regional differences arising from distributions of soil chemical properties EFSA/ECHA Soil Risk Assessment Workshop Wednesday, October
Bioavailability based approaches for soil risk assessment of metals: Regional differences arising from distributions of soil chemical properties EFSA/ECHA Soil Risk Assessment Workshop Wednesday, October
HEAVY METALS CONTAMINATION IN VEGETABLES GROWN IN URBAN AND METAL SMELTER CONTAMINATED SITES IN AUSTRALIA
 HEAVY METALS CONTAMINATION IN VEGETABLES GROWN IN URBAN AND METAL SMELTER CONTAMINATED SITES IN AUSTRALIA ANTHONY GEORGE KACHENKO and BALWANT SINGH Faculty of Agriculture, Food and Natural Resources, Ross
HEAVY METALS CONTAMINATION IN VEGETABLES GROWN IN URBAN AND METAL SMELTER CONTAMINATED SITES IN AUSTRALIA ANTHONY GEORGE KACHENKO and BALWANT SINGH Faculty of Agriculture, Food and Natural Resources, Ross
Improvement of a Peat Soil for Rice Cultivation in Thailand
 Jpn. J. Trop. Agr. 43(2) : 91-96, 1999 Improvement of a Peat Soil for Rice Cultivation in Thailand Tasnee ATTANANDANA, Benjaporn CHAKRANON *, Kazutake KYUMA * 2 and Pojanee MONCHAROEN * 3 Department of
Jpn. J. Trop. Agr. 43(2) : 91-96, 1999 Improvement of a Peat Soil for Rice Cultivation in Thailand Tasnee ATTANANDANA, Benjaporn CHAKRANON *, Kazutake KYUMA * 2 and Pojanee MONCHAROEN * 3 Department of
Uptake of Heavy Metals by Rice Plants in Ranau Valley Paddy Field (Sabah)
 Uptake of Heavy Metals by Rice Plants in Ranau Valley Paddy Field (Sabah) Roslaili Abdul Aziz, Sahibin Abd Rahim, Ismail Sahid, Wan Mohd Razi Idris and Md. Atiqur Rahman Bhuiyan High rainfall during the
Uptake of Heavy Metals by Rice Plants in Ranau Valley Paddy Field (Sabah) Roslaili Abdul Aziz, Sahibin Abd Rahim, Ismail Sahid, Wan Mohd Razi Idris and Md. Atiqur Rahman Bhuiyan High rainfall during the
Plant-Prod is plant productivity. Plant-Prod is the world leader in soluble fertilizers and the partner for growers where high productivity is vital.
 TM Plant-Prod is plant productivity Plant-Prod is the world leader in soluble fertilizers and the partner for growers where high productivity is vital. Table of contents high productivity plant nutrition
TM Plant-Prod is plant productivity Plant-Prod is the world leader in soluble fertilizers and the partner for growers where high productivity is vital. Table of contents high productivity plant nutrition
REVIEW Genotypic Differences in Cadmium Concentration and Distribution of Soybean and Rice
 JARQ 4 (1), 21 3 (26) http://www.jircas.affrc.go.jp REVIEW Genotypic Differences in Cadmium Concentration and Distribution of Soybean and Rice Tomohito ARAO* and Satoru ISHIKAWA Department of Environmental
JARQ 4 (1), 21 3 (26) http://www.jircas.affrc.go.jp REVIEW Genotypic Differences in Cadmium Concentration and Distribution of Soybean and Rice Tomohito ARAO* and Satoru ISHIKAWA Department of Environmental
TRIAZOPHOS (143) First draft prepared by Prof. Dr. Arpad Ambrus, Hungarian Food Safety Office, Budapest, Hungary EXPLANATION
 Triazophos 2023 TRIAZOPHOS (143) First draft prepared by Prof. Dr. Arpad Ambrus, Hungarian Food Safety Office, Budapest, Hungary EXPLANATION Triazophos had been first evaluated by the JMPR for toxicology
Triazophos 2023 TRIAZOPHOS (143) First draft prepared by Prof. Dr. Arpad Ambrus, Hungarian Food Safety Office, Budapest, Hungary EXPLANATION Triazophos had been first evaluated by the JMPR for toxicology
Molluscicide from Tobacco Waste
 Vol. 1, No. 1 Journal of Agricultural Science Molluscicide from Tobacco Waste Rochana Tangkoonboribun (Corresponding author) Agricultural Technology Department Thailand Institute of Scientific and Technological
Vol. 1, No. 1 Journal of Agricultural Science Molluscicide from Tobacco Waste Rochana Tangkoonboribun (Corresponding author) Agricultural Technology Department Thailand Institute of Scientific and Technological
Potassium and Phosphorus as Plant Nutrients. Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients. Potassium is required in large amounts by many crops
 Potassium and Phosphorus as Plant Nutrients Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients Potassium is required in large amounts by many crops Yield K 2 O taken up Crop level/ac in total crop, lb Alfalfa 8 tons
Potassium and Phosphorus as Plant Nutrients Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients Potassium is required in large amounts by many crops Yield K 2 O taken up Crop level/ac in total crop, lb Alfalfa 8 tons
REGISTRATION OF MONOGASTRIC ANIMAL FEED
 REGISTRATION OF MONOGASTRIC ANIMAL FEED Tebogo Banda Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries AFMA workshop for registration and renewals 1 August 2011 1 REGISTRATION REQUIREMENTS A product may
REGISTRATION OF MONOGASTRIC ANIMAL FEED Tebogo Banda Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries AFMA workshop for registration and renewals 1 August 2011 1 REGISTRATION REQUIREMENTS A product may
BIOAG PROJECT FINAL REPORT
 BIOAG PROJECT FINAL REPORT TITLE: Lentil Selection and Management to Reduce Dietary Intake of Arsenic PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR(S): Sanja Roje, Mohammed Islam, Rebecca McGee, Clarice Coyne, Jim Harsh, Julia
BIOAG PROJECT FINAL REPORT TITLE: Lentil Selection and Management to Reduce Dietary Intake of Arsenic PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR(S): Sanja Roje, Mohammed Islam, Rebecca McGee, Clarice Coyne, Jim Harsh, Julia
