Don t Miss Causes of Anemia. Reed E. Drews, M.D. Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Boston, MA COPYRIGHT
|
|
|
- Clifford Arnold
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Don t Miss Causes of Anemia Reed E. Drews, M.D. Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Boston, MA
2 Conflicts of Interest UpToDate Section Editor & Author Royalties I do not have other financial relationships with proprietary entities producing health care goods or services
3 Clinical Questions to be Addressed What are don t miss causes of iron deficiency? What are don t miss causes of hemolysis? What are diagnostic challenges in vitamin B12 deficiency? Who should be referred for bone marrow biopsy?
4 Case # 1 A 55-year male chemist develops fatigue 5 years ago at age 50, he had normal screening colonoscopy with visualization of the ileocecal valve and appendiceal orifice With a family history of heart disease, he takes aspirin 81 mg daily and drinks a glass of wine with dinner nightly Family history: no known malignancies or hematologic abnormalities
5 Case # 1 continued Physical exam is entirely normal CBC RBC = 3.80 million/μl (normal, ) Hgb = 10.5 g/dl (normal, ) HCT = 30.8% (normal, 40-52) MCV = 79 fl (normal, 82-98) MCH = 24 pg/rbc (normal, 27-32) MCHC = 34 (31-35) WBC with differential and platelet count are normal Peripheral blood smear (see next slide)
6 Hypochromic, microcytic RBCs, cigars and pencils in IDA
7 Case # 1 continued Serum iron chemistries Iron = 9 μ/dl (normal, ) Calculated TIBC = 460 μ/dl (normal, ) Ferritin = 15 ng/ml (normal, ) Fecal cards obtained at home are heme-positive Colonoscopy is normal to cecum with visualization of appendiceal orifice EGD Gastritis; biopsy negative for H. pylori Duodenum appears normal; biopsy not obtained
8 Case # 1 continued He stops aspirin and begins proton pump inhibitor + non-timed-release formulation ferrous gluconate (27 mg of elemental iron) + ascorbic acid 250 mg Once daily 45 minutes after his evening meal 2 weeks later, he increases his iron regimen to twice daily, once after lunch and once after his evening meal
9 Case # 1 continued 6 weeks later, he returns for re-evaluation He notes persistent fatigue Stools are black but negative for occult blood CBC remains unchanged Ferritin level remains low at 15 ng/ml His primary care physician refers him to a hematologist
10 Case # 1 continued He denies drinking tea or taking calcium supplements with his iron supplement Additional labs: ttg-iga = 112 units
11 Case # 1: Duodenal biopsy shows celiac sprue Celiac sprue should be considered in any patient with IDA and documented impaired iron absorption, even without GI symptoms In 1 study of pts with unexplained IDA, 11 of 93 (12%) were found to have celiac sprue on small bowel biopsy 1 Tissue transglutamic acid-immunoglobulin A Generally increased with active celiac sprue False normal levels in pts with IgA deficiency, which is more common in pts with celiac sprue At EGD, gross macroscopic duodenal findings of celiac sprue can be quite subtle Duodenal biopsies should be obtained routinely at EGD in pts with unexplained IDA, with or without documented impaired iron absorption 2 1 Hershko et al. Haematologica 2005; 90: Ackerman et al. Am J Gastroenterol 1996; 91:2099.
12 Case # 2 55-year old Russian male on disability following work-related injury in metal industry In 2002, underwent Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery for obesity management. He takes supplements of iron & vitb12 In 2010, referred to hematology for iron deficiency anemia with ferritin = 4.7 ng/ml Iron/TIBC = 47/490; vitb12 = 659 pg/ml HGB = 10.9; HCT = 36.7; MCV = 77; MCH = 23.0; MCHC = 29.8; RDW = 18.4 Colonoscopy normal to cecum EGD Congestion and erythema in whole stomach pouch compatible with gastritis Efferent jejunal limb and blind jejunal end Steiner stain of gastric biopsy negative for H. pylori
13 Case # 2 has an oral iron challenge test Following an overnight fast, blood is drawn at time 0, and he swallows 1 ml of ferrous sulfate solution (15 mg of elemental iron) admixed with a glass of orange juice. Blood samples are drawn hourly thereafter. Time (in minutes) Serum iron level (μ/dl) Patient Normal
14 Case # 2 receives parenteral iron Date Ferumoxytol Ferritin HGB HCT MCV MCH MCHC 03/09/ /17/10 03/24/ mg 510 mg /27/ /24/ /26/ mg /26/ /27/ mg /22/ /22/ /30/ mg /27/ /13/
15 Iron Salts versus Polysaccharide-iron Complexes Iron salt formulations (NOT time-release ) Release iron in the duodenum Iron is best absorbed from the duodenum and proximal jejunum Polysaccharide-iron complexes, enteric coated or sustained release capsules (e.g., Niferex 150) Release iron further down GI tract where iron is not absorbed Counterproductive More expensive than simple iron salt tablets
16 Factors Influencing Dietary Iron Absorption Positive factors Ascorbic acid Meat or fish Negative factors Phytate (in bran, oats, rye fiber) Polyphenols (in tea, some vegetables and cereals) Dietary calcium Soy protein Inhibition of gastric acid secretion
17 Optimizing Patient Acceptance in Oral Iron Therapy Administer small doses with or after meals Increase dose amounts as tolerated Once daily for 2 weeks Twice daily thereafter, if tolerated Very few patients tolerate thrice daily iron Administer stool softeners proactively
18 Blood Loss Is the Most Common Cause of Anemia Obvious bleeding Trauma, melena, hematemesis, menometrorrhagia Bleeding that is not always obvious Surgical bleeding, bleeding into the upper thigh or retroperitoneum, factitious bleeding Iatrogenic bleeding Repeated phlebotomy, hemodialysis, blood donation Occult bleeding
19 AGA Definition of Occult Blood Loss The initial presentation of a positive fecal occult blood test result and/or iron deficiency anemia, when there is no evidence of visible blood loss to the patient or physician Zuckerman GR et al. Gastroenterology 2000;118:201
20 When Bleeding Is Not Evident Decreased iron absorption Malabsorption Diet Intravascular hemolysis Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria Malfunctioning heart valves Pulmonary hemosiderosis Anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody disease Erythropoietin administration
21 Considerations when patients do not respond to oral iron supplements Poor patient adherence Oral iron exacerbates symptoms of underlying disease (e.g., inflammatory bowel disease) Continued bleeding Inability to absorb iron preparation Gastric by-pass for obesity Coexisting condition Inflammation (blocking iron utilization) Renal failure (erythropoietin deficiency) Incorrect diagnosis
22
23 Proposed diagnostic workup for unexplained or refractory IDA (Hershko C, Camaschella C. Blood 2014; 123: ) Screening Advanced Response to specific treatment H pylori H pylori IgG antibodies or fecal antigen Urease breath test; gastroscopy and biopsies (optional) Autoimmune gastritis Serum gastrin antiparietal Abs, antiintrinsic factor Abs Gastroscopy and biopsies (recommended) Celiac disease ttg-iga Abs Duodenal biopsy, HLA screening for DQ2 or DQ8 genotypes H pylori eradication NA Gluten-free diet IRIDA Suggestive history and clinical assessment Sequencing of the TMPRSS6 gene NA NA, not applicable; IRIDA, iron refractory iron deficiency anemia
24 Clinical Questions to be Addressed What are don t miss causes of iron deficiency? What are don t miss causes of hemolysis? What are diagnostic challenges in vitamin B12 deficiency? Who should be referred for bone marrow biopsy?
25 Hemolysis: General Approach Congenital vs. acquired Membrane disorders; hemoglobinopathies; enzymopathies Spherocytic vs. non-spherocytic Spherocytes (membrane; immune; phospholipase) Bite cells (oxidant stress; methemoglobin) Schistocytes (fragmentation) Spur cells (liver disease) Malaria; babesiosis Immune vs. non-immune Coombs testing (IgG, C3) Intramedullary vs. extramedullary Intravascular (urine hemosiderin, hemoglobinuria) Extravascular (spleen, RES)
26 Examination of the blood smear is key
27 Microcytic, hypochromic RBCs, targets and sickle forms in S-β + thalassemia
28 Spherocytes in warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia
29 Macrophage Ingesting an IgG-Coated RBC Bessis M. Corpuscles. Atlas of Red Cell Shape. Berlin, Springer- Verlag, 1974
30 RBC aggregates in cold agglutinin disease
31 IgG and IgM Binding RBC Antigens
32 Numerous spherocytes from phospholipase digestion of RBCs in clostridial sepsis
33 Erythrophagocytosis in EBV infection
34 Spur cell hemolytic anemia in liver disease
35 Diagnosis from the blood smear Spherocytes Bite cells Schistocytes
36 Case # 3 24-yo woman develops headaches and fevers. On exam, she appears restless with dysarthric speech. T = F. HCT = 28%; HGB = 9.7 g/dl; MCV = 102 fl WBC = 6.6 K/µL with 55% polys, 3% bands, 30% lymphs, 8% monos, 4% NRBCs Platelets = 5 K/µL; PT = 12.1 sec; aptt = 24.3 sec Retic count = 6.6%; LDH = 546 IU/L; total bili = 1.1 mg/dl; haptoglobin < 20 mg/dl Creatinine = 0.5 mg/dl
37 Schistocytes, NRBC, decreased platelets
38 Thrombotic Microangiopathies (alias Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemias) Disseminated intravascular coagulation Infections Obstetrical disorders Other causes Malignant hypertension Disseminated carcinoma Giant hemangioma TTP Pregnancy Autoimmune disorders HIV E. coli O157:H7, O104:H4 HUS Immunologic vasculitis Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome Mitomycin, ticlopidine, quinine, cyclosporine
39 TTP: Lab Manifestations Red cell fragmentation can be extreme Even to the extent of decreasing red cell mean corpuscular volume (MCV) and artifactually increasing reported platelet counts Serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level is typically extremely high Reflecting hemolysis and tissue damage due to systemic ischemia
40 Pathogenesis of Idiopathic TTP Caused by ADAMTS13 Deficiency Sadler JE. Blood 2008; 112:11-18
41 ADAMTS13 Activity Predicts Relapse Risk Kremer Hovinga JA et al. Blood 2010; 115:
42 ADAMTS13 Assays Assay results for the von Willebrand factor cleaving protease (ADAMTS13) and its inhibitor are not readily available Other reasons for decreased ADAMTS13 activity HIT, severe sepsis, liver cirrhosis, chronic uremia, ITP, DIC, SLE, leukemia, pregnancy, post-op, neonatal age, advanced age
43 Lane DA, Phillippou H, Huntington JA. Directing thrombin. Blood 2005; 106:
44 TTP: Dx and Management Thrombocytopenia and MAHA without another clinically apparent cause (e.g., DIC, malignant hypertension): Warrants suspicion of TTP-HUS and initiation of steroids + plasma exchange Alternative diagnosis: Stop plasma exchange ADAMTS13 activity normal: Stop steroids; debate role of plasma exchange ADAMTS13 inhibitor present: Continue steroids ADMATS13 inhibitor present with refractoryrelapsing TTP: Consider rituximab George JN. How I treat patients with TTP. Blood 2010; 116:
45 Blood 2016; 127:2952.
46 Final Comments Avoid platelet transfusion in patients with TTP except for management of life threatening hemorrhage To date, there is no defined role for monitoring ADAMTS13 activity after recovery
47 Recommended Reading
48
49
50
51 *Disorders that may initially suggest primary TMA.
52
53 Clinical Questions to be Addressed What are don t miss causes of iron deficiency? What are don t miss causes of hemolysis? What are diagnostic challenges in vitamin B12 deficiency? Who should be referred for bone marrow biopsy?
54 Case # 4 A 40-yo woman presents with fatigue and numerous dietary allergies. On exam, she appears thin. HCT = 26.0%; HGB = 9.5 g/dl; MCV = 109 fl WBC = 3.2 K/µL with normal differential Platelets = 143 K/µL Folate (serum) = 2.2 ng/ml (normal, ) Folate (RBC) = 0 Vitamin B 12 = 263 pg/ml (normal, )
55 Case # 4 continued Methylmalonic acid level 612 nmol/l (normal, ) Homocysteine level 52.8 µmol/l (normal, 0-8.9)
56 Case # 5 40-year old lab technician with increasing difficulty focusing and carrying out tasks. HCT, HGB, MCV, WBC, platelets normal Over the next 2 years MCV begins to rise in the normal range, reaching 100 fl HCT and HGB levels remain normal B12 deficiency suspected and replacement therapy begun Neurologic and hematologic improvement
57 Onset of cognitive concerns Dx of B12 deficiency See: Lindenbaum J et al. Neuropsychiatric disorders caused by cobalamin deficiency in the absence of anemia or macrocytosis. N Engl J Med 1988; 318:1720.
58 Normal Macroovalocytes
59 Hypersegmented neutrophil
60 Actions of Cobalamin and Folate From UpToDateÒ
61 From UpToDateÒ
62 Degree of Elevation of MCV Often a clue to whether a vitamin deficiency is present Probability of folate and/or cobalamin deficiency is greater with higher MCVs Normal ( fl), < 25% 115 to 129 fl, 50% > 130 fl, 100% Savage DG et al. Am J Med 1994;96:239
63 Cobalamin Levels > 300 pg/ml Cbl deficiency unlikely (1-5%) pg/ml Borderline result; Cbl deficiency is possible < 200 pg/ml Consistent with Cbl deficiency (specificity, %) May fall during pregnancy without hematologic evidence of deficiency Allen RH. Vitamin B12 metabolism and status during pregnancy, lactation and infancy. AdvExp Med Biol1994; 352:173-86
64 Serum Methylmalonic Acid and Homocysteine Levels Help clarify diagnosis when cobalamin and folate levels are equivocal Serum MMA and homocysteine levels elevated in 98 and 96% of 434 episodes of Cbl deficiency 12 and 91% of 123 episodes of folate deficiency Elevated MMA in all but one folate deficient patient was due to renal insufficiency or hypovolemia Savage DG et al. Am J Med 1994;96:239 Hereditary homocysteinemia can raise serum homocysteine levels
65 Oral Replacement of Cobalamin 2,000 µg daily (NOT time release ) Appears to be as or more effective than parenteral therapy Takes advantage of a second, lower efficiency transport system for Cbl that does not require intrinsic factor or a terminal ileum Requires patient adherence Kuzminski AM et al. Blood 1998;92:1191
66 P <.0005 (Kuzminski AM et al. Blood 1998;92:1191)
67 P <.05 (Kuzminski AM et al. Blood 1998;92:1191)
68
69 Caveats in Testing and Interpretation Role of dietary and vitamin supplements Cobalamin deficiency masked by folate Numerous over-the-counter B 12 supplement choices 2, 25, 50, 100, 1000, and 2000 mcg Not FDA-regulated Role of decreased GFR in determining MMA levels Reliability of assays and clinical labs Other factors influencing RBC mass, MCV, and neurologic symptoms and signs Alcohol
70
71
72 Recommended Reading
73 Clinical Questions to be Addressed What are don t miss causes of iron deficiency? What are don t miss causes of hemolysis? What are diagnostic challenges in vitamin B12 deficiency? Who should be referred for bone marrow biopsy?
74 Bone Marrow Core Biopsy
75 Disorders of Hematopoiesis
76 Peripheral Blood Clues to Myelodysplastic Syndrome Red blood cells Prominent basophilic stippling and other sideroblastic features (e.g., hypochromic, microcytosis) Macro-ovalocytes (reflecting megaloblastic maturation) Tear drops (reflecting myelophthisis) White blood cells Pelgeroid cells, hypogranulation, toxic granulation, Döhle bodies, immature myeloid forms Platelets Giant forms, megakaryoblasts
77 Infiltrative Myelopathies Alias Myelophthisic anemia Leukoerythroblastic anemia Hallmark features include Immature granulocyte precursors in the peripheral blood (bands, metas, myelos) Nucleated red cells Tear drops
78 SEM of Teardrop in Formation
79 Primary myelofibrosis
80 Aplastic Anemia
81 Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance No symptoms No end organ damage related to plasma cell dyscrasia or a related B cell lymphoproliferative disorder No lymphadenopathy, organomegaly, hypercalcemia, renal failure, anemia, bone abnormalities (skeletal survey)* Relatively low paraprotein level (< 3 g/dl) < 10% plasmacytosis in bone marrow Phenomenon of aging *No role for bone scans or PET scans
82 Diagnostic criteria for myeloma Myeloma Serum or urinary monoclonal protein Clonal plasma cell in bone marrow or plasmacytoma End organ damage related to plasma cell dyscrasia Asymptomatic (smoldering) myeloma Serum monoclonal protein 3 g/dl and/or bone marrow plasma cells 10 percent No end organ damage related to plasma cell dyscrasia
83 Bloodline, 1995 by Kiki Smith
Case # 1. RBC Loss. CASE #1 (Continued) Blood Loss Is the Most Common Cause of Anemia. AGA Definition of Occult Blood Loss
 Case # 1 A 42-yo woman with heavy menses presents with rectal bleeding. Except for pallor, exam is normal. HCT = 17.1% (normal, 36-48) HGB = 5.3 g/dl (normal, 12.0-16.0) MCV = 76 fl (normal, 82-98) RBC
Case # 1 A 42-yo woman with heavy menses presents with rectal bleeding. Except for pallor, exam is normal. HCT = 17.1% (normal, 36-48) HGB = 5.3 g/dl (normal, 12.0-16.0) MCV = 76 fl (normal, 82-98) RBC
Evaluation of Anemia. Md. Shafiqul Bari Associate professor (Medicine) SOMC
 Evaluation of Anemia Md. Shafiqul Bari Associate professor (Medicine) SOMC Definition Anemia is operationally defined as a reduction in one or more of the major RBC measurements Hemoglobin concentration
Evaluation of Anemia Md. Shafiqul Bari Associate professor (Medicine) SOMC Definition Anemia is operationally defined as a reduction in one or more of the major RBC measurements Hemoglobin concentration
I. Definitions. V. Evaluation A. History B. Physical Exam C. Laboratory evaluation D. Bone marrow examination E. Specialty referrals
 I. Definitions II. III. Red blood cell life cycle Iron metabolism IV. Causes of anemia A. Kinetic approach 1. decreased production 2. increased destruction 3. blood loss B. Morphologic approach 1. normocytic
I. Definitions II. III. Red blood cell life cycle Iron metabolism IV. Causes of anemia A. Kinetic approach 1. decreased production 2. increased destruction 3. blood loss B. Morphologic approach 1. normocytic
Hematology: Challenging Cases with Your Participation COPYRIGHT
 Hematology: Challenging Cases with Your Participation Reed E. Drews, MD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Question 1 Question 1 64-year-old man is evaluated during
Hematology: Challenging Cases with Your Participation Reed E. Drews, MD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Question 1 Question 1 64-year-old man is evaluated during
Anemia. A case-based approach. David B. Sykes, MD, PhD Hematology, MGH Cancer Center June 8, 2017
 Anemia A case-based approach David B. Sykes, MD, PhD Hematology, MGH Cancer Center June 8, 2017 Recognizing trends Learning Objectives MCV, RDW, Ferritin, LDH, Reticulocytes Managing complex patients 1.
Anemia A case-based approach David B. Sykes, MD, PhD Hematology, MGH Cancer Center June 8, 2017 Recognizing trends Learning Objectives MCV, RDW, Ferritin, LDH, Reticulocytes Managing complex patients 1.
Diagnostic Approach to Patients with Anemia
 J KMA Special Issue Diagnostic Approach to Patients with Anemia Seonyang Park, MD Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine E mail : seonpark@snu.ac.kr J Korean Med
J KMA Special Issue Diagnostic Approach to Patients with Anemia Seonyang Park, MD Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine E mail : seonpark@snu.ac.kr J Korean Med
HAEMATOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF ANEMIA. Sitalakshmi S Professor and Head Department of Clinical Pathology St John s medical College, Bangalore
 HAEMATOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF ANEMIA Sitalakshmi S Professor and Head Department of Clinical Pathology St John s medical College, Bangalore Learning Objectives Laboratory tests for the evaluation of anemia
HAEMATOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF ANEMIA Sitalakshmi S Professor and Head Department of Clinical Pathology St John s medical College, Bangalore Learning Objectives Laboratory tests for the evaluation of anemia
Faculty of Medicine Dr. Tariq Aladily
 Iron deficiency anemia The most common anemia worldwide Only 10% of ingested iron is absorbed Most dietary iron occurs in meat products Absorbed in duodenum Hepcidin By inhibiting ferroportin, hepcidin
Iron deficiency anemia The most common anemia worldwide Only 10% of ingested iron is absorbed Most dietary iron occurs in meat products Absorbed in duodenum Hepcidin By inhibiting ferroportin, hepcidin
Interpreting the CBC. Robert Miller PA Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics and Family Medicine USC Keck School of Medicine Retired
 Interpreting the CBC Robert Miller PA Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics and Family Medicine USC Keck School of Medicine Retired The CBC 3 Cell Lines RBCs WBCs Platelets Assess general health Make
Interpreting the CBC Robert Miller PA Assistant Professor of Clinical Pediatrics and Family Medicine USC Keck School of Medicine Retired The CBC 3 Cell Lines RBCs WBCs Platelets Assess general health Make
Peripheral Blood Smear Examination. Momtazmanesh MD. Ped. Hematologist & Oncologist Loghman General Hospital
 1395 Peripheral Blood Smear Examination Momtazmanesh MD. Ped. Hematologist & Oncologist Loghman General Hospital Peripheral Blood Smear A peripheral blood smear is a snapshot of the cells that are present
1395 Peripheral Blood Smear Examination Momtazmanesh MD. Ped. Hematologist & Oncologist Loghman General Hospital Peripheral Blood Smear A peripheral blood smear is a snapshot of the cells that are present
Taking The Fear Out of Abnormal CBC s Problems of Production, Destruction or loss
 Taking The Fear Out of Abnormal CBC s Problems of Production, Destruction or loss Joanne Eddington, MN, FNP, AOCN Providence Oncology and Hematology Care Clinic - Eastside Blood Cell Abnormalities Abnormalities
Taking The Fear Out of Abnormal CBC s Problems of Production, Destruction or loss Joanne Eddington, MN, FNP, AOCN Providence Oncology and Hematology Care Clinic - Eastside Blood Cell Abnormalities Abnormalities
Does Morphology Matter in 2017
 Does Morphology Matter in 2017 ISLH May 2017 Kathryn Foucar Distinguished Professor Emerita kfoucar@salud.unm.edu Objectives Recognize unique RBC and WBC abnormalities in non-neoplastic disorders Learn
Does Morphology Matter in 2017 ISLH May 2017 Kathryn Foucar Distinguished Professor Emerita kfoucar@salud.unm.edu Objectives Recognize unique RBC and WBC abnormalities in non-neoplastic disorders Learn
Hematopoiesis, The hematopoietic machinery requires a constant supply iron, vitamin B 12, and folic acid.
 Hematopoiesis, 200 billion new blood cells per day The hematopoietic machinery requires a constant supply iron, vitamin B 12, and folic acid. hematopoietic growth factors, proteins that regulate the proliferation
Hematopoiesis, 200 billion new blood cells per day The hematopoietic machinery requires a constant supply iron, vitamin B 12, and folic acid. hematopoietic growth factors, proteins that regulate the proliferation
Lisa B. Weissmann, MD
 Lisa B. Weissmann, MD Anemia- Most common hematologic disorder Evaluation should be orderly Questions to ask Timing - new, old, rapidity of onset Isolated - only anemia, or other cell lines Size of cells
Lisa B. Weissmann, MD Anemia- Most common hematologic disorder Evaluation should be orderly Questions to ask Timing - new, old, rapidity of onset Isolated - only anemia, or other cell lines Size of cells
(anemia) ก hemoglobin concentration, hematocrit deviation 1 1 ก hemoglobin, hematocrit mean corpuscular volume (MCV) 2
 ก ก. ก ก.. ก (anemia) ก hemoglobin concentration, hematocrit ก ก ก 2 Standard deviation 1 1 ก hemoglobin, hematocrit mean corpuscular volume (MCV) 2 Hemoglobin hematocrit MCV (g/dl) (%) (fl) ( ) 0.5-1.9
ก ก. ก ก.. ก (anemia) ก hemoglobin concentration, hematocrit ก ก ก 2 Standard deviation 1 1 ก hemoglobin, hematocrit mean corpuscular volume (MCV) 2 Hemoglobin hematocrit MCV (g/dl) (%) (fl) ( ) 0.5-1.9
Extra Notes 3. Warm. In the core (center) of the body, where the temperature is 37 C.
 Extra Notes 3 *The numbers of the slides are according to the last year slides. Slide 33 Autoimmune hemolytic anemia : Abnormal circulating antibodies that target normal antigen on the RBC and cause lysis.
Extra Notes 3 *The numbers of the slides are according to the last year slides. Slide 33 Autoimmune hemolytic anemia : Abnormal circulating antibodies that target normal antigen on the RBC and cause lysis.
Microcytic Hypochromic Anemia An Approach to Diagnosis
 Microcytic Hypochromic Anemia An Approach to Diagnosis Decreased hemoglobin synthesis gives rise to microcytic hypochromic anemias. Hypochromic anemias are characterized by normal cellular proliferation
Microcytic Hypochromic Anemia An Approach to Diagnosis Decreased hemoglobin synthesis gives rise to microcytic hypochromic anemias. Hypochromic anemias are characterized by normal cellular proliferation
Lisa B. Weissmann, MD
 Lisa B. Weissmann, MD Anemia- Most common hematologic disorder Evaluation should be orderly Questions to ask Timing - new, old, rapidity of onset Isolated - only anemia, or other cell lines Size of cells
Lisa B. Weissmann, MD Anemia- Most common hematologic disorder Evaluation should be orderly Questions to ask Timing - new, old, rapidity of onset Isolated - only anemia, or other cell lines Size of cells
Anemia (3).ms Hemolytic Anemia. Abdallah Abbadi Feras Fararjeh
 Anemia (3).ms4.26.2.18 Hemolytic Anemia Abdallah Abbadi Feras Fararjeh Case 3 24 yr old female presented with anemia syndrome and jaundice. She was found to have splenomegaly. Hb 8, wbc 12k, Plt 212k,
Anemia (3).ms4.26.2.18 Hemolytic Anemia Abdallah Abbadi Feras Fararjeh Case 3 24 yr old female presented with anemia syndrome and jaundice. She was found to have splenomegaly. Hb 8, wbc 12k, Plt 212k,
Year 2003 Paper two: Questions supplied by Tricia
 QUESTION 65 A 36-year-old man presents in a post-ictal state after an observed generalised seizure. Full blood investigation shows: haemoglobin 0 g/l [128-175] mean corpuscular volume (MCV) 106 fl [80-7]
QUESTION 65 A 36-year-old man presents in a post-ictal state after an observed generalised seizure. Full blood investigation shows: haemoglobin 0 g/l [128-175] mean corpuscular volume (MCV) 106 fl [80-7]
Anemia (3).ms4.25.Oct.15 Hemolytic Anemia. Abdallah Abbadi
 Anemia (3).ms4.25.Oct.15 Hemolytic Anemia Abdallah Abbadi Case 3 24 yr old female presented with anemia syndrome and jaundice. She was found to have splenomegaly. Hb 8, wbc 12k, Plt 212k, retics 12%, LDH
Anemia (3).ms4.25.Oct.15 Hemolytic Anemia Abdallah Abbadi Case 3 24 yr old female presented with anemia syndrome and jaundice. She was found to have splenomegaly. Hb 8, wbc 12k, Plt 212k, retics 12%, LDH
Approach to a pale child
 Approach to a pale child Dr. Dafalla Ahmed Babiker Jazan university objectives Definition of anemia Classification and causes Important points in history and physical examination Investigations. Definition
Approach to a pale child Dr. Dafalla Ahmed Babiker Jazan university objectives Definition of anemia Classification and causes Important points in history and physical examination Investigations. Definition
11. An acute leukemia causing. 12. An adult patient presents with acute. 13. Anemia due to renal failure may be
 Hematology Study online at 1. A 23 year old white female has weakness, fatigue and has developed a habit of chewing ice. What are the expected findings in regard to TIBC and Ferritin? 2. A 25 year old
Hematology Study online at 1. A 23 year old white female has weakness, fatigue and has developed a habit of chewing ice. What are the expected findings in regard to TIBC and Ferritin? 2. A 25 year old
3 Ruba hussein Dr. ahmad Dr. ahmad
 3 Ruba hussein Dr. ahmad Dr. ahmad The arrangement of this sheet differs from that of the record. Anemia of peripheral removal in which we are losing hemoglobin and RBCs mass and the two major Causes are:
3 Ruba hussein Dr. ahmad Dr. ahmad The arrangement of this sheet differs from that of the record. Anemia of peripheral removal in which we are losing hemoglobin and RBCs mass and the two major Causes are:
Hematology Unit Lab 1 Review Material
 Hematology Unit Lab 1 Review Material - 2018 Objectives Laboratory instructors: 1. Assist students during lab session Students: 1. Review the introductory material 2. Study the case histories provided
Hematology Unit Lab 1 Review Material - 2018 Objectives Laboratory instructors: 1. Assist students during lab session Students: 1. Review the introductory material 2. Study the case histories provided
General Characterisctics
 Anemia General Characterisctics Definition: anemia is a decrease in red blood cells. Happens due to underproduction, increased destruction or loss of red cells. Diagnosis of anemia: Hgb < 135 (men) Hgb
Anemia General Characterisctics Definition: anemia is a decrease in red blood cells. Happens due to underproduction, increased destruction or loss of red cells. Diagnosis of anemia: Hgb < 135 (men) Hgb
DR V PHILIP CLINICAL HAEMATOLOGY UNIT CHRIS HANI BARAGWANATH ACADEMIC HOSPITAL
 DR V PHILIP CLINICAL HAEMATOLOGY UNIT CHRIS HANI BARAGWANATH ACADEMIC HOSPITAL Rare but fatal disease if unrecognized and untreated Incidence about 1: 1 million in the USA Female preponderance of 2:1 Part
DR V PHILIP CLINICAL HAEMATOLOGY UNIT CHRIS HANI BARAGWANATH ACADEMIC HOSPITAL Rare but fatal disease if unrecognized and untreated Incidence about 1: 1 million in the USA Female preponderance of 2:1 Part
Disorders of Blood Cells & Blood Coagulation
 Disorders of Blood Cells & Blood Coagulation HIHIM 409 WBC count RBC count WBC differential Hemoglobin (HGB) Hematocrit (HCT) % of volume occupied by RBCs CBC Red cell indices Mean cell volume (MCV) average
Disorders of Blood Cells & Blood Coagulation HIHIM 409 WBC count RBC count WBC differential Hemoglobin (HGB) Hematocrit (HCT) % of volume occupied by RBCs CBC Red cell indices Mean cell volume (MCV) average
Updates in the Management of Anemia in Cancer. Taylor M. Ortiz, MD May 19, 2017
 Updates in the Management of Anemia in Cancer Taylor M. Ortiz, MD May 19, 2017 Objectives Recall common causes of anemia in patients with cancer Understand risks/benefits of blood transfusion in patients
Updates in the Management of Anemia in Cancer Taylor M. Ortiz, MD May 19, 2017 Objectives Recall common causes of anemia in patients with cancer Understand risks/benefits of blood transfusion in patients
Collect and label sample according to standard protocols. Gently invert tube 8-10 times immediately after draw. DO NOT SHAKE. Do not centrifuge.
 Complete Blood Count CPT Code: CBC with Differential: 85025 CBC without Differential: 85027 Order Code: CBC with Differential: C915 Includes: White blood cell, Red blood cell, Hematocrit, Hemoglobin, MCV,
Complete Blood Count CPT Code: CBC with Differential: 85025 CBC without Differential: 85027 Order Code: CBC with Differential: C915 Includes: White blood cell, Red blood cell, Hematocrit, Hemoglobin, MCV,
NUTRITIONAL CARE IN ANEMIA
 االله الرحمن الرحيم بسم NUTRITIONAL CARE IN ANEMIA Nutrition Departement Faculty of Medicine University of North Sumatera Definition Deficit of circulating RBC associated with diminished oxygen-carrying
االله الرحمن الرحيم بسم NUTRITIONAL CARE IN ANEMIA Nutrition Departement Faculty of Medicine University of North Sumatera Definition Deficit of circulating RBC associated with diminished oxygen-carrying
Approach to the abnormal CBC
 Approach to the abnormal CBC Robert T. Means, Jr., M.D. Hematology and Blood & Marrow Transplant Division University of Kentucky and VA Medical Center Lexington KY General Considerations Always repeat
Approach to the abnormal CBC Robert T. Means, Jr., M.D. Hematology and Blood & Marrow Transplant Division University of Kentucky and VA Medical Center Lexington KY General Considerations Always repeat
Hematopathology Lab. Third year medical students
 Hematopathology Lab Third year medical students Objectives Identify the lesion Know the specific name of the lesion Know associated disease Know relevant pathologic background Spherocytes: appear small,
Hematopathology Lab Third year medical students Objectives Identify the lesion Know the specific name of the lesion Know associated disease Know relevant pathologic background Spherocytes: appear small,
Dr Anzo William Adiga
 Anemia Dr Anzo William Adiga +256777363201 anzoism2008@gmail.com Definition of Anemia Deficiency in the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood due to a diminished erythrocyte mass. May be due to: Erythrocyte
Anemia Dr Anzo William Adiga +256777363201 anzoism2008@gmail.com Definition of Anemia Deficiency in the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood due to a diminished erythrocyte mass. May be due to: Erythrocyte
Case Report A Puzzle of Hemolytic Anemia, Iron and Vitamin B12 Deficiencies in a 52-Year-Old Male
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Hematology Volume 2013, Article ID 708489, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/708489 Case Report A Puzzle of Hemolytic Anemia, Iron and Vitamin B12 Deficiencies
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Hematology Volume 2013, Article ID 708489, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/708489 Case Report A Puzzle of Hemolytic Anemia, Iron and Vitamin B12 Deficiencies
Deconstructing the CBC
 Deconstructing the CBC Dr. Ann M. Wexler Solano Hematology Oncology September 10, 2017 What Are the Major Components of Blood? Red Blood Cells (also called erythrocytes) White Blood Cells (also called
Deconstructing the CBC Dr. Ann M. Wexler Solano Hematology Oncology September 10, 2017 What Are the Major Components of Blood? Red Blood Cells (also called erythrocytes) White Blood Cells (also called
Dairion Gatot, Soegiarto Ganie, Savita Handayani. Divisi Hematologi & Onkologi Medik Departemen Ilmu Penyakit Dalam FK-USU/RS H.Adam Malik Medan 2009
 HAEMOLYTIC ANAEMIA Dairion Gatot, Soegiarto Ganie, Savita Handayani. Divisi Hematologi & Onkologi Medik Departemen Ilmu Penyakit Dalam FK-USU/RS H.Adam Malik Medan 2009 WHEN BY THEN Hb 9 g% transfusion
HAEMOLYTIC ANAEMIA Dairion Gatot, Soegiarto Ganie, Savita Handayani. Divisi Hematologi & Onkologi Medik Departemen Ilmu Penyakit Dalam FK-USU/RS H.Adam Malik Medan 2009 WHEN BY THEN Hb 9 g% transfusion
HEMATOLOGIC MORPHOLOGY- AECOM HEMATOLOGY COURSE
 Log Out Help current login :lcytryn@montefiore.org HEMATOLOGIC MORPHOLOGY- AECOM HEMATOLOGY COURSE Lawrence Cytryn, M.D. - Course Director 1998 Edward Burns, M.D. Images used by permission within AECOM
Log Out Help current login :lcytryn@montefiore.org HEMATOLOGIC MORPHOLOGY- AECOM HEMATOLOGY COURSE Lawrence Cytryn, M.D. - Course Director 1998 Edward Burns, M.D. Images used by permission within AECOM
Introduction and Approach to Anemia
 2 nd lecture in Hematology by Dr.Alaa Fadhil Alwan Introduction and Approach to Anemia Anemia is defined clinically as a blood hemoglobin or hematocrit value that is below the appropriate reference range
2 nd lecture in Hematology by Dr.Alaa Fadhil Alwan Introduction and Approach to Anemia Anemia is defined clinically as a blood hemoglobin or hematocrit value that is below the appropriate reference range
The primary medical content categories of the blueprint are shown below, with the percentage assigned to each for a typical exam:
 Hematology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified hematologist
Hematology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified hematologist
FBC interpretation. Dr. Gergely Varga
 FBC interpretation Dr. Gergely Varga #1 71 Y/O female, c/o weakness Test Undertaken : FBC (FBC) Sample Type: Whole Blood [ - 26.09.11 14:59] Hb 7.3 g/dl* 12.0-15.5 RBC 3.5 10^12/l * 3.80-5.60 Hct 0.24
FBC interpretation Dr. Gergely Varga #1 71 Y/O female, c/o weakness Test Undertaken : FBC (FBC) Sample Type: Whole Blood [ - 26.09.11 14:59] Hb 7.3 g/dl* 12.0-15.5 RBC 3.5 10^12/l * 3.80-5.60 Hct 0.24
* Renal insufficiencies
 Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Behzad Poopak, DCLS PhD. Tehran medical Branch Islamic Azad university bpoopak@yahoo.com Case Summary Ms. X, a 35-year year-old woman Complained of weakness, low grade
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Behzad Poopak, DCLS PhD. Tehran medical Branch Islamic Azad university bpoopak@yahoo.com Case Summary Ms. X, a 35-year year-old woman Complained of weakness, low grade
Anemia 1: Fourth year Medical Students/ October/21/ 2015/ Abdallah Abbadi.MD.FRCP Professor
 Anemia 1: Fourth year Medical Students/ October/21/ 2015/ Abdallah Abbadi.MD.FRCP Professor Email: abdalla.awidi@gmail.com Main Hematological diseases A- Benign Hematology 1- Anemias 2- Bleeding disorders
Anemia 1: Fourth year Medical Students/ October/21/ 2015/ Abdallah Abbadi.MD.FRCP Professor Email: abdalla.awidi@gmail.com Main Hematological diseases A- Benign Hematology 1- Anemias 2- Bleeding disorders
2. Non- hemolytic anemias 3. Normocytic Normochromic Normocytic Normochromic Blood loss. (MCV<80 fl) (MCV fl) (MCV>100 fl)
 Definition of Anaemia of Anaemias Approach for diagnosis of Red cell disorders any condition resulting from a significant decrease in the total body erythrocyte mass due to decrease of Hb and or RBCs Hemoglobin
Definition of Anaemia of Anaemias Approach for diagnosis of Red cell disorders any condition resulting from a significant decrease in the total body erythrocyte mass due to decrease of Hb and or RBCs Hemoglobin
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient was a five-day-old girl with an elevated unconjugated bilirubin and a weakly positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT). Her CBC showed: WBC = 11.0
Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient was a five-day-old girl with an elevated unconjugated bilirubin and a weakly positive direct antiglobulin test (DAT). Her CBC showed: WBC = 11.0
Drop of Blood Unravels Mysteries. Prof. Salma Afrose Department of Hematology Dhaka Medical College
 Drop of Blood Unravels Mysteries Prof. Salma Afrose Department of Hematology Dhaka Medical College Peripheral Blood Film (PBF) PBF is a laboratory workup that involves cytology of Peripheral blood cell
Drop of Blood Unravels Mysteries Prof. Salma Afrose Department of Hematology Dhaka Medical College Peripheral Blood Film (PBF) PBF is a laboratory workup that involves cytology of Peripheral blood cell
MORPHOLOGY IN ACTION. Description MINI-CASE ONE OBJECTIVES. Differential Diagnosis. Laboratory Results
 MORPHOLOGY IN ACTION Mini-case studies using morphology Bernadette Rodak, MS, MT, SH(ASCP) Professor emeritus Indiana University brodak@iupui.edu Description Mini-case studies will be used to integrate
MORPHOLOGY IN ACTION Mini-case studies using morphology Bernadette Rodak, MS, MT, SH(ASCP) Professor emeritus Indiana University brodak@iupui.edu Description Mini-case studies will be used to integrate
Approach to Anemia PG CME
 Approach to Anemia PG CME 2014 2017 Vikram Mathews Haematology Department Christian Medical College Vellore Definition of Anemia Beutler et al. Blood 2006. Definition of Anemia WHO definition of anemia
Approach to Anemia PG CME 2014 2017 Vikram Mathews Haematology Department Christian Medical College Vellore Definition of Anemia Beutler et al. Blood 2006. Definition of Anemia WHO definition of anemia
HEME 10 Bleeding Disorders
 HEME 10 Bleeding Disorders When injury occurs, three mechanisms occur Blood vessels Primary hemostasis Secondary hemostasis Diseases of the blood vessels Platelet disorders Thrombocytopenia Functional
HEME 10 Bleeding Disorders When injury occurs, three mechanisms occur Blood vessels Primary hemostasis Secondary hemostasis Diseases of the blood vessels Platelet disorders Thrombocytopenia Functional
BONE MARROW PERIPHERAL BLOOD Erythrocyte
 None Disclaimer Objectives Define anemia Classify anemia according to pathogenesis & clinical significance Understand Red cell indices Relate the red cell indices with type of anemia Interpret CBC to approach
None Disclaimer Objectives Define anemia Classify anemia according to pathogenesis & clinical significance Understand Red cell indices Relate the red cell indices with type of anemia Interpret CBC to approach
9/23/2018. Investigation of Hemolysis in the Clinical Laboratory. Objectives. What is hemolysis?
 Investigation of Hemolysis in the Clinical Laboratory Jason Anderson, MPH, MT(ASCP) Field Product Specialist Objectives 1. Define hemolysis. 2. Distinguish between intrinsic and extrinsic hemolysis 3.
Investigation of Hemolysis in the Clinical Laboratory Jason Anderson, MPH, MT(ASCP) Field Product Specialist Objectives 1. Define hemolysis. 2. Distinguish between intrinsic and extrinsic hemolysis 3.
Topic owner: Mollie Grow MD MPH, updated June 2018
 Iron deficiency Anemia UW Pediatrics Outpatient Clinical Guidelines Sources: AAP Clinical Report Diagnosis and Prevention of Iron Deficiency and Iron- Deficiency Anemia in Infants and Young Children (0
Iron deficiency Anemia UW Pediatrics Outpatient Clinical Guidelines Sources: AAP Clinical Report Diagnosis and Prevention of Iron Deficiency and Iron- Deficiency Anemia in Infants and Young Children (0
Anemia In the Insurance Applicant What do the numbers mean?
 Anemia In the Insurance Applicant What do the numbers mean? Lisa Duckett, M.D. Vice President and Medical Director September 12, 2017 Goals of the presentation Develop a consistent way to analyze Complete
Anemia In the Insurance Applicant What do the numbers mean? Lisa Duckett, M.D. Vice President and Medical Director September 12, 2017 Goals of the presentation Develop a consistent way to analyze Complete
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and the Role of ADAMTS-13
 Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and the Role of ADAMTS-13 Mark Cunningham,MD Director, Hematology Laboratory Department of Pathology University of Kansas Medical Center College of American Pathologists
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and the Role of ADAMTS-13 Mark Cunningham,MD Director, Hematology Laboratory Department of Pathology University of Kansas Medical Center College of American Pathologists
The Child with a Hematologic Alteration
 47 The Child with a Hematologic Alteration HELPFUL HINT Review the anatomy and physiology of the hematologic system in an anatomy and physiology textbook. MATCHING KEY TERMS Match the term with the correct
47 The Child with a Hematologic Alteration HELPFUL HINT Review the anatomy and physiology of the hematologic system in an anatomy and physiology textbook. MATCHING KEY TERMS Match the term with the correct
Oral Iron Safe, Effective, and Misunderstood Duke Debates 2017
 Oral Iron Safe, Effective, and Misunderstood Duke Debates 2017 John Strouse, MD, PhD Instructor (temp) Medicine and Pediatrics Director, Adult Sickle Cell Program April 20, 2017 1 Disclosures I have no
Oral Iron Safe, Effective, and Misunderstood Duke Debates 2017 John Strouse, MD, PhD Instructor (temp) Medicine and Pediatrics Director, Adult Sickle Cell Program April 20, 2017 1 Disclosures I have no
namib la UnIVERSITY OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES
 namib la UnIVERSITY OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: SOBBMS LEVEL: 6 COURSE
namib la UnIVERSITY OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: SOBBMS LEVEL: 6 COURSE
QUESTIONS OF HEMATOLOGY AND THEIR ANSWERS
 QUESTIONS OF HEMATOLOGY AND THEIR ANSWERS WHAT IS TRUE AND WHAT IS FALSE? Questions 1 Iron deficiency anemia a) Is usually associated with a raised MCV. b) The MCH is usually low. c) Is most commonly due
QUESTIONS OF HEMATOLOGY AND THEIR ANSWERS WHAT IS TRUE AND WHAT IS FALSE? Questions 1 Iron deficiency anemia a) Is usually associated with a raised MCV. b) The MCH is usually low. c) Is most commonly due
THE UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY
 THE UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY INTRODUCTION TO ANEMIA Third year medical students First semester 2018/2019 Dr. RBC DISORDERS Lecturer: Dr. Tariq Al-Adaily Email: TNALADILY@ju.edu.jo
THE UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY INTRODUCTION TO ANEMIA Third year medical students First semester 2018/2019 Dr. RBC DISORDERS Lecturer: Dr. Tariq Al-Adaily Email: TNALADILY@ju.edu.jo
Things to never miss in the office. Brett Houston MD FRCPC (PYG-5, hematology) Leonard Minuk MD FRCPC
 Things to never miss in the office Brett Houston MD FRCPC (PYG-5, hematology) Leonard Minuk MD FRCPC Presenter Disclosure Faculty / Speaker s name: Brett Houston / Leonard Minuk Relationships with commercial
Things to never miss in the office Brett Houston MD FRCPC (PYG-5, hematology) Leonard Minuk MD FRCPC Presenter Disclosure Faculty / Speaker s name: Brett Houston / Leonard Minuk Relationships with commercial
Comprehensive Review of Clinical Laboratory Tests for Investigating the Etiology of Anemia in the Elderly.
 Comprehensive Review of Clinical Laboratory Tests for Investigating the Etiology of Anemia in the Elderly. December 15, 2017 Dennis J Chapron MS, RPh Medication Safety Pharmacist Saint Francis Hospital
Comprehensive Review of Clinical Laboratory Tests for Investigating the Etiology of Anemia in the Elderly. December 15, 2017 Dennis J Chapron MS, RPh Medication Safety Pharmacist Saint Francis Hospital
Normal Development. Normal Development 10/16/2012. Hematopoietic and Lymph Node Pathology. Red Blood Cell Maturation & Anemias
 Hematopoietic and Lymph Node Pathology Normal Development Red Blood Cell Maturation & Anemias Normal Development Differentiation of Hematopoietic Cells 1 Bone Marrow Bone Marrow Bone Marrow, RBC Precursors
Hematopoietic and Lymph Node Pathology Normal Development Red Blood Cell Maturation & Anemias Normal Development Differentiation of Hematopoietic Cells 1 Bone Marrow Bone Marrow Bone Marrow, RBC Precursors
Types of Anaemias and their Management. S. Moncrieffe, Pharm.D., MPH, Dip.Ed., RPh. PSJ CE Mandeville Hotel April 27, 2014
 Types of Anaemias and their Management S. Moncrieffe, Pharm.D., MPH, Dip.Ed., RPh. PSJ CE Mandeville Hotel April 27, 2014 Objectives At the end of the presentations participants should be able to: 1. Define
Types of Anaemias and their Management S. Moncrieffe, Pharm.D., MPH, Dip.Ed., RPh. PSJ CE Mandeville Hotel April 27, 2014 Objectives At the end of the presentations participants should be able to: 1. Define
Disclosures/COI. Cases in Hematopathology. Outline. Heme Path Findings Not to Miss. Normal Peripheral Smear 6/30/2016
 Disclosures/COI Cases in Hematopathology Vamsi Kota Assistant Professor Department of Hematology & Medical Oncology Leukemia/BMT I have no disclosures or conflicts of interest regarding this presentation.
Disclosures/COI Cases in Hematopathology Vamsi Kota Assistant Professor Department of Hematology & Medical Oncology Leukemia/BMT I have no disclosures or conflicts of interest regarding this presentation.
Hematology Revision. By Dr.AboRashad . Mob
 1 1- Hb A2 is consisting of: a) 3 ά chains and 2 γ chains b) 2 ά chains and 2 β chains c) 2 ά chains and 2 δ chains** d) 2 ά chains and 3 δ chains e) 3 ά chains and 2 δ chains 2- The main (most) Hb found
1 1- Hb A2 is consisting of: a) 3 ά chains and 2 γ chains b) 2 ά chains and 2 β chains c) 2 ά chains and 2 δ chains** d) 2 ά chains and 3 δ chains e) 3 ά chains and 2 δ chains 2- The main (most) Hb found
Anemia 1: Fourth year Medical Students/ Feb/22/ Abdallah Awidi Abbadi.MD.FRCP.FRCPath Professor
 Anemia 1: Fourth year Medical Students/ Feb/22/ 2018 Abdallah Awidi Abbadi.MD.FRCP.FRCPath Professor Email: abdalla.awidi@gmail.com Kidney EPO O2 Sensor Blood vessel Definition: Anemia is operationally
Anemia 1: Fourth year Medical Students/ Feb/22/ 2018 Abdallah Awidi Abbadi.MD.FRCP.FRCPath Professor Email: abdalla.awidi@gmail.com Kidney EPO O2 Sensor Blood vessel Definition: Anemia is operationally
YEREVAN STATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HEMATOLOGY COURSE DESCRIPTION HEMATOLOGY
 1. Module/unit Code II. 1.2. 2. Module/unit Title Hematology 3. Subject Field Internal Diseases Group 4. Faculty/Department General Medicine, Department of Hematology 5. Programme(s) to which the Doctor
1. Module/unit Code II. 1.2. 2. Module/unit Title Hematology 3. Subject Field Internal Diseases Group 4. Faculty/Department General Medicine, Department of Hematology 5. Programme(s) to which the Doctor
INTERELATIONSHIP BETWEEN IDA AND VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY IS NOW ESTABLISHED
 INTERELATIONSHIP BETWEEN IDA AND VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY IS NOW ESTABLISHED Rationale for Combining Iron & Vit-D Vit D deficiency and Iron deficiency Anaemia the two most menacing disorders - are inter-related
INTERELATIONSHIP BETWEEN IDA AND VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY IS NOW ESTABLISHED Rationale for Combining Iron & Vit-D Vit D deficiency and Iron deficiency Anaemia the two most menacing disorders - are inter-related
OBJECTIVES Define anemia and identify the appropriate diagnostic testing necessary to diagnose anemia Discuss various types and causes of anemia Discu
 ANEMIA Marjaana Krieger, MSN, RN, NP-C, AOCNP Advanced Oncology Certified Nurse Practitioner Department of Veterans Affairs/ VA Southern Nevada Healthcare System Hematology/Oncology/Infusion Clinic OBJECTIVES
ANEMIA Marjaana Krieger, MSN, RN, NP-C, AOCNP Advanced Oncology Certified Nurse Practitioner Department of Veterans Affairs/ VA Southern Nevada Healthcare System Hematology/Oncology/Infusion Clinic OBJECTIVES
RBCs Disorders 2. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 RBCs Disorders 2 Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Discuss the classification of anemia into hypochromic-microcytic, normochromicnormocytic and macrocytic. Categorize laboratory test procedures used in the
RBCs Disorders 2 Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Discuss the classification of anemia into hypochromic-microcytic, normochromicnormocytic and macrocytic. Categorize laboratory test procedures used in the
Red cell disorder. Dr. Ahmed Hasan
 Red cell disorder Dr. Ahmed Hasan Things to be learned in this lecture Definition and clinical feature of anemia. Classification of anemia. Know some details of microcytic anemia Question of the lecture:
Red cell disorder Dr. Ahmed Hasan Things to be learned in this lecture Definition and clinical feature of anemia. Classification of anemia. Know some details of microcytic anemia Question of the lecture:
Hematology Case Conference 8/5/03
 Hematology Case Conference 8/5/03 Bone Marrow Case Patient: Emmxxx Lylexxx 74 year old AA female S/P craniotomy for SDH. Pt has Hx of HTN, DM, Crohn s disease, (R) nephrectomy. Bone marrow for abnormal
Hematology Case Conference 8/5/03 Bone Marrow Case Patient: Emmxxx Lylexxx 74 year old AA female S/P craniotomy for SDH. Pt has Hx of HTN, DM, Crohn s disease, (R) nephrectomy. Bone marrow for abnormal
Evaluation of the Inpatient with Anemia
 Evaluation of the Inpatient with Anemia Camila Masias, M.D. Assistant Professor Division of Hematology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Case 1 22 yo woman presents to the ED with fatigue
Evaluation of the Inpatient with Anemia Camila Masias, M.D. Assistant Professor Division of Hematology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Case 1 22 yo woman presents to the ED with fatigue
Evaluation of the Inpatient with Anemia
 Evaluation of the Inpatient with Anemia Camila Masias, M.D. Assistant Professor Division of Hematology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Case 1 22 yo woman presents to the ED with fatigue
Evaluation of the Inpatient with Anemia Camila Masias, M.D. Assistant Professor Division of Hematology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Case 1 22 yo woman presents to the ED with fatigue
Laboratory Techniques. Tehran Medical Branch Islamic Azad University
 Anemia Laboratory Techniques Behzad Poopak, DCLS PhD Tehran Medical Branch Islamic Azad University bpoopak@yahoo.com Learning Objectives Review the anemia as a public health problem Review the lab tests
Anemia Laboratory Techniques Behzad Poopak, DCLS PhD Tehran Medical Branch Islamic Azad University bpoopak@yahoo.com Learning Objectives Review the anemia as a public health problem Review the lab tests
10/1/2016. Iron Deficiency Anemia in Clinical Practice: Evaluation & Treatment Approach. Objectives. Introduction
 Iron Deficiency Anemia in Clinical Practice: Evaluation & Treatment Approach Simi Jesto Joseph, DNP, APN, NP-C Director of Research & Clinical Services/GI NP GI Solutions of IL Objectives To understand
Iron Deficiency Anemia in Clinical Practice: Evaluation & Treatment Approach Simi Jesto Joseph, DNP, APN, NP-C Director of Research & Clinical Services/GI NP GI Solutions of IL Objectives To understand
Chapter 3 Diseases of the Blood and Bloodforming Organs and Certain Disorders Involving the Immune Mechanism D50-D89
 Chapter 3 Diseases of the Blood and Bloodforming Organs and Certain Disorders Involving the Immune Mechanism D50-D89 Presented by Jennifer Kurkulonis 1 FOUR MAJOR TYPES OF BLOOD CELLS White blood cells
Chapter 3 Diseases of the Blood and Bloodforming Organs and Certain Disorders Involving the Immune Mechanism D50-D89 Presented by Jennifer Kurkulonis 1 FOUR MAJOR TYPES OF BLOOD CELLS White blood cells
Approach to the child with anemia. Nittaya Wisanuyothin,MD. Pediatrics Department, Maharat Nakhonratchasima Hospital
 Approach to the child with anemia Nittaya Wisanuyothin,MD. Pediatrics Department, Maharat Nakhonratchasima Hospital Definition of anemia Hb< 2 SD or P2.5 below the mean for a healthy of the same gender
Approach to the child with anemia Nittaya Wisanuyothin,MD. Pediatrics Department, Maharat Nakhonratchasima Hospital Definition of anemia Hb< 2 SD or P2.5 below the mean for a healthy of the same gender
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY BLOOD CELL IDENTIFICATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
Acute Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) in Childhood
 Acute Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) in Childhood Guideline developed by Robert Saylors, MD, in collaboration with the ANGELS team. Last reviewed by Robert Saylors, MD September 22, 2016. Key Points
Acute Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) in Childhood Guideline developed by Robert Saylors, MD, in collaboration with the ANGELS team. Last reviewed by Robert Saylors, MD September 22, 2016. Key Points
Nutritional anaemia. Dr J Potgieter Dept of Haematology NHLS - TAD
 Nutritional anaemia Dr J Potgieter Dept of Haematology NHLS - TAD Classification of anaemia Microcytic, hypochromic MCV < 80fl MCH > 27pg Iron deficiency Anaemia of chronic disease Thalassaemia Lead poisoning
Nutritional anaemia Dr J Potgieter Dept of Haematology NHLS - TAD Classification of anaemia Microcytic, hypochromic MCV < 80fl MCH > 27pg Iron deficiency Anaemia of chronic disease Thalassaemia Lead poisoning
* imagine if the Hb is free ( e.g. hemolysis ) in the plasma what happens?
 In this lecture we will talk about Some characteristics of RBC. Erythrpoiesis : * During fetal & adult life. * its regulation. RBCs : - Appear under the microscope as circular,unnucleated and biconcave
In this lecture we will talk about Some characteristics of RBC. Erythrpoiesis : * During fetal & adult life. * its regulation. RBCs : - Appear under the microscope as circular,unnucleated and biconcave
2013 AAIM Pathology Workshop
 2013 AAIM Pathology Workshop John Schmieg, M.D., Ph.D. None Disclosures 1 Pathology Workshop Objectives Define the general philosophy of reviewing pathology reports Review the various components of Bone
2013 AAIM Pathology Workshop John Schmieg, M.D., Ph.D. None Disclosures 1 Pathology Workshop Objectives Define the general philosophy of reviewing pathology reports Review the various components of Bone
HEMATOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint
 HEMATOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Hematology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that MOC assessments should
HEMATOLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Hematology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that MOC assessments should
Hematologic changes in systemic diseases. Chittima Sirijerachai
 Hematologic changes in systemic diseases Chittima Sirijerachai Systemic diseases Infection Renal diseases Liver diseases Connective tissue diseases Malignancy Anemia of chronic disease (ACD) Chronic infections:
Hematologic changes in systemic diseases Chittima Sirijerachai Systemic diseases Infection Renal diseases Liver diseases Connective tissue diseases Malignancy Anemia of chronic disease (ACD) Chronic infections:
FBC CASES Vernon Louw Clinical Haematology 2010
 FBC CASES Vernon Louw Clinical Haematology 2010 FOR EACH OF THE FOLLOWING PATIENTS, SELECT THE MOST LIKELY FINDING FROM THE ANALYSIS OF THE PERIPHERAL BLOOD. A patient with infectious mononucleosis. A
FBC CASES Vernon Louw Clinical Haematology 2010 FOR EACH OF THE FOLLOWING PATIENTS, SELECT THE MOST LIKELY FINDING FROM THE ANALYSIS OF THE PERIPHERAL BLOOD. A patient with infectious mononucleosis. A
RBCs Disorders 2. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 RBCs Disorders 2 Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Discuss the classification of anemia into hypochromic-microcytic, normochromicnormocytic and macrocytic. Categorize laboratory test procedures used in the
RBCs Disorders 2 Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Discuss the classification of anemia into hypochromic-microcytic, normochromicnormocytic and macrocytic. Categorize laboratory test procedures used in the
Recommendations for Celiac Disease Testing. IgA & ttg IgA
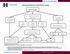 Recommendations for Celiac Disease Testing IgA & ttg IgA IgA Normal ttg IgA Negative IgA >10 mg/dl, but less than age matched range IgA
Recommendations for Celiac Disease Testing IgA & ttg IgA IgA Normal ttg IgA Negative IgA >10 mg/dl, but less than age matched range IgA
Susan Stegman, MD Medical Director AXA Equitable Life May 3, 2016
 Susan Stegman, MD Medical Director AXA Equitable Life May 3, 2016 Underwriting impact Anemia overview Classification of anemia Specific anemia topics Iron deficiency anemia Thalassemia Megaloblastic anemia
Susan Stegman, MD Medical Director AXA Equitable Life May 3, 2016 Underwriting impact Anemia overview Classification of anemia Specific anemia topics Iron deficiency anemia Thalassemia Megaloblastic anemia
HEMOLY L TIC AN A EMIA
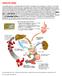 HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA In a healthy person, a red blood cell survives 90 to 120 days in the circulation, so about 1% of human red blood cells break down each day. The spleen (part of the reticulo-endothelial
HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA In a healthy person, a red blood cell survives 90 to 120 days in the circulation, so about 1% of human red blood cells break down each day. The spleen (part of the reticulo-endothelial
Approach To The Evalua4on And Management Of Anemia
 Objec4ves Approach To The Evalua4on And Management Of Anemia Usha Perepu, MD Assistant Professor Hematology/Oncology 9/29/15 Defini4on of anemia Review the causes of anemia Laboratory evalua4on of anemia
Objec4ves Approach To The Evalua4on And Management Of Anemia Usha Perepu, MD Assistant Professor Hematology/Oncology 9/29/15 Defini4on of anemia Review the causes of anemia Laboratory evalua4on of anemia
Hemostatic System - general information
 PLATELET DISORDERS Hemostatic System - general information Normal hemostatic system vessel wall circulating blood platelets blood coagulation and fibrynolysis Bleeding Diathesis inherited or acquired defects
PLATELET DISORDERS Hemostatic System - general information Normal hemostatic system vessel wall circulating blood platelets blood coagulation and fibrynolysis Bleeding Diathesis inherited or acquired defects
Examination Tests from Pathological Physiology. Pavel Maruna et al. Reviewed by: Prof. MUDr. Emanuel Nečas, DrSc. Prof. MUDr. Jaroslav Veselý, CSc.
 Examination Tests from Pathological Physiology Pavel Maruna et al. Reviewed by: Prof. MUDr. Emanuel Nečas, DrSc. Prof. MUDr. Jaroslav Veselý, CSc. Authors: Prof. MUDr. Pavel Maruna, CSc. Doc. MUDr. Martin
Examination Tests from Pathological Physiology Pavel Maruna et al. Reviewed by: Prof. MUDr. Emanuel Nečas, DrSc. Prof. MUDr. Jaroslav Veselý, CSc. Authors: Prof. MUDr. Pavel Maruna, CSc. Doc. MUDr. Martin
Year 2003 Paper two: Questions supplied by Tricia
 QUESTION 93 A 24-year-old woman, who has recently arrived in Australia from Vietnam, presents for evaluation of abnormal menstrual bleeding. There are no abnormalities on examination. Results of investigations
QUESTION 93 A 24-year-old woman, who has recently arrived in Australia from Vietnam, presents for evaluation of abnormal menstrual bleeding. There are no abnormalities on examination. Results of investigations
What is meant by Thrombotic Microangiopathy (TMA)?
 What is meant by Thrombotic Microangiopathy (TMA)? Thrombotic Microangiopathy (TMA) is a group of disorders characterized by injured endothelial cells, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA), with its
What is meant by Thrombotic Microangiopathy (TMA)? Thrombotic Microangiopathy (TMA) is a group of disorders characterized by injured endothelial cells, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA), with its
Thrombotic Microangiopathies
 Thrombotic Microangiopathies ASH/San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium Review James N. George March 14, 2015 Thrombotic Microangiopathies (TMA): Everything you need to know from 5 patient stories Thrombotic
Thrombotic Microangiopathies ASH/San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium Review James N. George March 14, 2015 Thrombotic Microangiopathies (TMA): Everything you need to know from 5 patient stories Thrombotic
DRUG NAME: Eculizumab Brand(s): Soliris DOSAGE FORM/ STRENGTH: 10 mg/ml (300 mg per vial)
 Preamble: A confirmed diagnosis of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (ahus) is required for eculizumab funding. The information below is to provide clinicians with context for how a diagnosis of ahus
Preamble: A confirmed diagnosis of atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (ahus) is required for eculizumab funding. The information below is to provide clinicians with context for how a diagnosis of ahus
Iron deficiency anemia:
 بسم هللا الرمحن الرحمي Before we start: Dr. Malik suggested for the third immunity lecture to be a continuation for the hematology pharmacology. And he will discuss the drugs for treating leukemia and
بسم هللا الرمحن الرحمي Before we start: Dr. Malik suggested for the third immunity lecture to be a continuation for the hematology pharmacology. And he will discuss the drugs for treating leukemia and
