A guide to completing the Mini Nutritional Assessment MNA
|
|
|
- Ruth Pitts
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A guide to completing the Mini Nutritional Assessment MNA 1149 Last Update 9/10
2 Mini Nutritional Assessment (MNA ) The MNA is a screening and assessment tool that can be used to identify elderly patients at risk of malnutrition. The User Guide will assist you in completing the MNA accurately and consistently. It explains each question and how to assign and interpret the score. Introduction: While the prevalence of malnutrition in the free living elderly population is relatively low, the risk of malnutrition increases dramatically in the institutionalized and hospitalized elderly 1. The prevalence of malnutrition is even higher in cognitively impaired elderly individuals and is associated with cognitive decline. 2 Patients who are malnourished when admitted to the hospital tend to have longer hospital stays, experience more complications, and have greater risks of morbidity and mortality than those whose nutritional state is normal. 3 By identifying patients who are malnourished or at risk of malnutrition either in the hospital or community setting, the MNA allows clinicians to intervene earlier to provide adequate nutritional support, prevent further deterioration, and improve patient outcomes. 4 Mini Nutritional Assessment MNA The MNA provides a simple and quick method of identifying elderly patients who are at risk for malnutrition, or who are already malnourished. It identifies the risk of malnutrition before severe changes in weight or serum protein levels occur. The MNA may be completed at regular intervals in the community and in the hospital or long term care setting. The MNA was developed by Nestlé and leading international geriatricians and remains one of the few validated screening tools for the elderly. It has been well validated in international studies in a variety of settings 5-7 and correlates with morbidity and mortality. INSTRUCTIONS TO COMPLETE THE MNA Before beginning the MNA, please enter the patient s information on the top of the form: Name Gender Age Weight (kg) To obtain an accurate weight, remove shoes and heavy outer clothing. Use a calibrated and reliable set of scales. If applicable: convert pounds (lbs) to kilograms (1kg = 2.2lbs). Height (cm) Measure height without shoes using a stadiometer (height gauge) or, if the patient is bedridden, by knee height or demispan (see Appendices 4 or 5). Convert inches to centimeters (1inch = 2.54cm). Date of screen Last Update 9/10
3 Screening Complete the screen by filling in the boxes with the appropriate numbers. Then, add together the numbers to determine the total score of the screen. If the score is 11 or less, continue on with the assessment to determine the Malnutrition Indicator Score. Key Points Ask the patient to answer the following questions using the suggestions in the shaded areas. If the patient is unable to answer the question, ask the patient s caregiver to answer. Using the patient s medical record or your professional judgment, answer any remaining questions. A Has food intake declined over the past three months due to loss of appetite, digestive problems, chewing or swallowing difficulties? Score 0 = Severe loss of appetite 1 = Moderate loss of appetite 2 = No decrease in food intake Ask patient»» Have you eaten less than normal over the past three months?»» If so, is this because of lack of appetite, chewing, or swallowing difficulties?»» If yes, have you eaten much less than before or only a little less?»» If this is a re-assessment, then rephrase the question: Has the amount of food you have eaten changed since your last assessment? B Weight loss during the last 3 months? Score 0 = Weight loss greater than 3 kg (6.6 pounds) 1 = Does not know 2 = Weight loss between 1 and 3 kg (2.2 and 6.6 pounds) 3 = No weight loss Ask patient / medical record (if long term or residential care)»» Have you lost any weight without trying over the last 3 months?»» Has your waistband gotten looser?»» How much weight do you think you have lost? More or less than 3 kg (or 6 pounds)? Though weight loss in the overweight elderly may be appropriate, it may also be due to malnutrition. When the weight loss question is removed, the MNA loses its sensitivity, so it is important to ask about weight loss even in the overweight Last Update 9/10
4 C Mobility? Score 0 = Bed or chair bound 1 = Able to get out of bed/chair, but does not go out 2 = Goes out Ask patient / Patient s medical record / Information from caregiver»» Are you presently able to get out of the bed / chair?»» Are you able to get out of the house or go outdoors on your own? D Has the patient suffered psychological stress or acute disease in the past three months? Score 0 = Yes 1 = No Ask patient / Patient medical record / Professional judgment»» Have you suffered a bereavement recently?»» Have you recently moved your home?»» Have you been sick recently? E Neuropsychological problems? Score 0 = Severe dementia or depression 1 = Mild dementia 2 = No psychological problems Review patient medical record / Professional judgment / Ask nursing staff or caregiver The patient s caregiver, nursing staff or medical record can provide information about the severity of the patient s neuropsychological problems (dementia). If a patient cannot respond (i.e. one with dementia) or is severely confused, ask the patient s personal or professional caregiver to answer the following questions or check the patient s answers for accuracy (Questions A, B, C, D, G, J, K, L, M, O, P) Last Update 9/10
5 F Body mass index (BMI)? (weight in kg / height in m 2 ) Score 0 = BMI less than 19 1 = BMI 19 to less than 21 2 = BMI 21 to less than 23 3 = BMI 23 or greater Determining BMI BMI is used as an indicator of appropriate weight for height. BMI is calculated by dividing the weight in kg by the height in m 2 (Appendix 1). BMI = weight (kg) height (m 2 ) Before determining BMI, record the patients weight and height on the MNA form. 1. Convert subject s weight to metric using formula 1kg = 2.2lbs. Convert subject s height to metric using formula 1inch = 2.54cm 2. If height has not been measured, please measure using a stadiometer or height gauge (Refer to Appendix 3). 3. If the patient is unable to stand, measure height using indirect methods such as measuring demi-span (half arm span) or knee height (See Appendices 4 and 5). If height cannot be measured either directly or by indirect methods, use a verbal or historical height to calculate a BMI. Verbal height will be the least accurate, especially for bedridden patients and patients who have lost height over the years. 4. Using the BMI chart provided (Appendix 1), locate the patient s height and weight and determine the BMI. It is essential that a BMI is included in the MNA without it the tool is not valid. 5. Fill in the appropriate box on the MNA form to represent the BMI of the patient. 6. To determine BMI for a patient with an amputation, see Appendix 2. The screening section of the questionnaire is now complete. Add the numbers to obtain the screening score. A score of 12 points or greater indicates: Patient is not at nutrition risk. There is no need to complete the rest of the questionnaire. Rescreen at regular intervals. A score of 11 points or less indicates: Patient may be at risk for malnutrition. Please complete the full MNA assessment by answering questions G R Last Update 9/10
6 Assessment G Lives independently (not in a nursing home)? Score 0 = No 1 = Yes Ask patient This question refers to the normal living conditions of the individual. Its purpose is to determine if the person is usually dependent on others for care. For example, if the patient is in the hospital because of an accident or acute illness, where does the patient normally live?»» Do you normally live in your own home, or in an assisted living, residential setting, or nursing home? H Takes more than 3 prescription drugs per day? Score 0 = Yes 1 = No Ask patient / Patient medical record Check the patient s medication record / ask nursing staff / ask doctor / ask patient I Pressure sores or skin ulcers? Score 0 = Yes 1 = No Ask patient / Patient s medical record»» Do you have bed sores? Check the patient s medical record for documentation of pressure wounds or skin ulcers, or ask the caregiver / nursing staff / doctor for details, or examine the patient if information is not available in the medical record Last Update 9/10
7 J How many full meals does the patient eat daily? Score 0 = 1 meal 1 = 2 meals 3 = 3 meals Ask patient / Check food intake record if necessary»» Do you normally eat breakfast, lunch and dinner?»» How many meals a day do you eat? A full meal is defined as eating more than 2 items or dishes when the patient sits down to eat. For example, eating potatoes, vegetable, and meat is considered a full meal; or eating an egg, bread, and fruit is considered a full meal. K Selected consumption markers for protein intake»» At least one serving of dairy products per day? Yes No»» Two or more servings of legumes or eggs per week?»» Yes No Meat, fish or poultry every day? Yes No Ask the patient or nursing staff, or check the completed food intake record»» Do you consume any dairy products (a glass of milk / cheese in a sandwich / cup of yogurt / can of high protein supplement) every day?»» Do you eat beans/eggs? How often do you eat them?»» Do you eat meat, fish or chicken every day? Score 0.0 = if 0 or 1 Yes answer(s) 0.5 = if 2 Yes answers 1.0 = if 3 Yes answers Last Update 9/10
8 L Consumes two or more servings of fruits or vegetables per day? Score 0 = No 1 = Yes Ask the patient / check the completed food intake record if necessary»» Do you eat fruits and vegetables?»» How many portions do you have each day? A portion can be classified as: One piece of fruit (apple, banana, orange, etc.) One medium cup of fruit or vegetable juice One cup of raw or cooked vegetables M How much fluid (water, juice, coffee, tea, milk) is consumed per day? Score 0.0 = Less than 3 cups 0.5 = 3 to 5 cups 1.0 = More than 5 cups Ask patient»» How many cups of tea or coffee do you normally drink during the day?»» Do you drink any water, milk or fruit juice? What size cup do you usually use? A cup is considered ml or 7-8oz. N Mode of Feeding? Score 0 = Unable to eat without assistance * 1 = Feeds self with some difficulty ** 2 = Feeds self without any problems Ask patient / Patient medical record/ information from caregiver»» Are you able to feed yourself? / Can the patient feed himself/herself?»» Do you need help to eat? / Do you help the patient to eat?»» Do you need help setting up your meals (opening containers, buttering bread, or cutting meats)? * Patients who must be fed or need help holding the fork would score 0. ** Patients who need help setting up meals (opening containers, buttering bread, or cutting meats), but are able to feed themselves would score 1 point. Pay particular attention to potential causes of malnutrition that need to be addressed to avoid malnutrition (e.g. dental problems, need for adaptive feeding devices to support eating) Last Update 9/10
9 O Self-View of Nutritional Status Score 0 = Views self as being malnourished 1 = Is uncertain of nutritional state 2 = Views self as having no nutritional problems Ask the patient»» How would you describe your nutritional state? Then prompt Poorly nourished? Uncertain? No problems? The answer to this question depends upon the patient s state of mind. If you think the patient is not capable of answering the question, ask the caregiver / nursing staff for their opinion. P In comparison with other people of the same age, how does the patient consider his/her health status? Score 0.0 = Not as good 0.5 = Does not know 1.0 = As good 2.0 = Better Ask patient»» How would you describe your state of health compared to others your age? Then prompt Not as good as others of your age? Not sure? As good as others of your age? Better? Again, the answer will depend upon the state of mind of the person answering the question. Q Mid-arm circumference (MAC) in cm Score 0.0 = MAC less than = MAC 21 to = MAC 22 or greater Measure the mid-arm circumference in cm as described in Appendix 6. R Calf circumference (CC) in cm Score 0 = CC less than 31 1 = CC 31 or greater Calf circumference should be measured in cm as described in Appendix Last Update 9/10
10 Final Score»» Total the points from the assessment section of the MNA (maximum 16 points).»» Add the assessment and screening scores together to get the total Malnutrition Indicator Score (Maximum 30 points).»» Check the appropriate box indicator.»» If the score is greater than 23.5 points, the patient is in a normal state of nutrition and no further action is required.»» If the score is less than 23.5 points, refer the patient to a dietitian or nutrition specialist for nutrition intervention. Until a dietitian is available, give the patient / caregiver some advice on how to improve nutritional intake such as:»» Increase intake of energy/protein dense foods (e.g. puddings, milkshakes, etc).»» Supplement food intake with additional snacks and milk.»» If diet alone does not improve the patient s nutritional intake, the patient may need oral nutritional supplements.»» Ensure adequate fluid intake ; 6-8 cups / glasses per day. Follow-Up»» Re-screen all patients every three months.»» Please refer results of assessments & re-assessments to dietitian/doctor and record in medical record Last Update 9/10
11 Appendices Appendix Appendix 11 Body Mass Index table Weight (kg) Height (feet & inches) Height (cm) n Underweight n Weight Appropriate n Overweight n Obese Weight (pounds) Source: Adapted from Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults: The Evidence Report. National Institute of Health, National Heart Lung and Blood Institute Last Update 9/10
12 Appendix 2 Determining BMI for amputees To determine the BMI for amputees, first determine the patient s estimated weight including the weight of the missing body part. 8,9»» Use a standard reference (see table) to determine the proportion of body weight contributed by an individual body part.»» Multiple patient s current weight by the percent of body weight of the missing body part to determine estimated weight of missing part.»» Add the estimated weight of the missing body part to patient s current weight to determine estimated weight prior to amputation. Divide estimated weight by estimated body height 2 to determine BMI. Example: 80 year old man, amputation of the left lower leg, 1.72 m, 58 kg 1. Estimate body weight: Current body weight + Proportion for the missing leg 58 (kg) + [58 (kg) x 0.059] = 61.4 kg 2. Calculate BMI: Estimated body weight / body height (m) / 1.72 x 1.72 = 20.8 Weight of selected body components It is necessary to account for the missing body component(s) when estimating IBW. Table: Percent of Body Weight Contributed by Specific Body Parts Body Part Percentage Trunk w/o limbs 50.0 Hand 0.7 Forearm with hand 2.3 Forearm without hand 1.6 Upper arm 2.7 Entire arm 5.0 Foot 1.5 Lower leg with foot 5.9 Lower leg without foot 4.4 Thigh 10.1 Entire leg 16.0 References cited: Malone A., Anthropometric Assessment, In Charney P, Malone E, eds. ADA Pocket Guide to Nutrition Assessment. Chicago, IL: American Dietetic Association; 2004: Osterkamp LK., Current perspective on assessment of human body proportions of relevance to amputees, J Am Diet Assoc. 1995;95: Last Update 9/10
13 Appendix 3 Measuring height using a stadiometer 1. Ensure the floor surface is even and firm. 2. Have subject remove shoes and stand up straight with heels together, and with heels, buttocks and shoulders pressed against the stadiometer. 3. Arms should hang freely with palms facing thighs. 4. Take the measurement with the subject standing tall, looking straight ahead with the head upright and not tilted backwards. 5. Make sure the subjects heels stay flat on the floor. 6. Lower the measure on the stadiometer until it makes contact with the top of the head. 7. Record standing height to the nearest centimeter. Accessed at: Appendix 4 Measurement of Demispan Demispan (half-arm span) is the distance from the midline at the sternal notch to the web between the middle and ring fingers along outstretched arm. Height is then calculated from a standard formula Locate and mark the midpoint of the sternal notch with the pen. 2. Ask the patient to place the left arm in a horizontal position. Calculate height from the formula below: Females Height in cm = (1.35 x demispan in cm) Males Height in cm = (1.40 x demispan in cm) Check that the patient s arm is horizontal and in line with shoulders. 4. Using the tape measure, measure distance from mark on the midline at the sternal notch to the web between the middle and ring fingers. 5. Check that arm is flat and wrist is straight. 6. Take reading in cm. Source: Reproduced here with the kind permission of BAPEN ( British Association for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition ) from the MUST Explanatory Booklet. For further information see ( Last Update 9/10
14 Appendix 5 Measurement of Knee Height Knee height is one method to determine statue in the bed- or chair-bound patient and is measured using a sliding knee height caliper. The subject must be able to bend the knee and the ankle to 90 degree angles. 1. Have the subject bend the knee and ankle of one leg at a 90 degree angle while lying supine or sitting on a table with legs hanging off the side of the table. 2. Place the fixed blade of the knee caliper under the heel of the foot in line with the ankle bone. Place the fixed blade of the caliper on the anterior surface of the thigh about 3.0 cm above the patella. 3. Be sure the shaft of the caliper is in line with and parallel to the long bone in the lower leg (tibia) and is over the ankle bone (lateral malleolus). Apply pressure to compress the tissue. Record the measurement to the nearest 0.1 cm. 4. Take two measurements in immediate succession. They should agree within 0.5 cm. Use the average of these two measurements and the person's chronological age in the country and ethnic group specific equations in the following table. 5. The value calculated from the selected equation is an estimate of the person's true stature. The 95 percent confidence for this estimate is plus and minus twice the SEE value for each equation. Source: Accessed December 12, Using population-specific formula, calculate height from standard formula: Gender & ethnic group Equation: Stature (cm) = Non-Hispanic white men (U.S.) 11 [SEE = 3.74 cm] Non-Hispanic black men (U.S.) 11 [SEE = 3.80 cm] Mexican-American men (U.S.) 11 [SEE = 3.68 cm] Non-Hispanic white women (U.S.) 11 [SEE = 3.98 cm] Non-Hispanic black women (U.S.) 11 [SEE = 3.82 cm] Mexican-American women (U.S.) 11 [SEE = 3.77 cm] Taiwanese men 12 [SEE = 3.86 cm] Taiwanese women 12 [SEE = 3.79 cm] Elderly Italian men 13 [SEE = 4.3 cm] Elderly Italian women 13 [SEE = 4.3 cm] French men 14 [SEE = 3.8 cm] French women 14 [SEE = 3.5 cm] Mexican Men 15 [SEE = 3.31 cm] Mexican Women 15 [SEE = 2.99 cm] Filipino Men 16 Filipino Women 16 Malaysian men 17 [SEE = 3.51 cm] Malaysian women 17 [SEE = 3.40] (1.94 x knee height) (0.14 x age) (1.85 x knee height) (0.14 x age) (1.83 x knee height) (0.16 x age) (1.85 x knee height) (0.21 x age) (1.61 x knee height) (0.17 x age) (1.82 x knee height) (0.26 x age) (1.73 x knee height) (0.11 x age) (1.53 x knee height) (0.16 x age) (1.58 x knee height) (0.23 x age) (1.58 x knee height) (0.23 x age) (2.07 x knee height) (-0.21 x age) (2.2 x knee height) (0.25 x age) (2.17 x knee height) (1.99 x knee height) (0.23 x age) (1.38 x knee height) (0.08 x age) (1.53 x knee height) (0.17 x age) (1.924 x knee height) (2.225 x knee height) Last Update 9/10
15 Appendix 6 Measuring Mid Arm Circumference 1. Ask the patient to bend their non-dominant arm at the elbow at a right angle with the palm up. 2. Measure the distance between the acromial surface of the scapula (bony protrusion surface of upper shoulder) and the olecranon process of the elbow (bony point of the elbow) on the back of the arm. 3. Mark the mid-point between the two with the pen. 4. Ask the patient to let the arm hang loosely by his/ her side. 5. Position the tape at the mid-point on the upper arm and tighten snugly. Avoid pinching or causing indentation. 6. Record measurement in cm. 7. If MAC is less than 21, score = 0. If MAC is 21-22, score = 0.5. If MAC is 22 or greater, score = 1.0. Source: Moore MC, Pocket Guide to Nutrition and Diet Therapy, 1993 Source: PEN Group., A pocket guide to clinical nutrition: Assessment of nutritional status, British Dietetic Association Appendix 7 Measuring Calf Circumference 1. The subject should be sitting with the left leg hanging loosely or standing with their weight evenly distributed on both feet. 2. Ask the patient to roll up their trouser leg to uncover the calf. 3. Wrap the tape around the calf at the widest part and note the measurement. 4. Take additional measurements above and below the point to ensure that the first measurement was the largest. 5. An accurate measurement can only be obtained if the tape is at a right angle to the length of the calf. References 1. Guigoz Y, Vellas B. Garry PJ., Assessing the nutritional status of the elderly: The Mini Nutritional Assessment as part of the geriatric evaluation, Nutr Rev 1996;54:S59-S Fallon C, Bruce I, Eustace A, et al., Nutritional status of community dwelling subjects attending a memory clinic., J Nutr Health Aging 2002;6(Supp): Kagansky N, Berner Y, Koren-Morag N, Perelman L, Knobler H, Levy S., Poor nutritional habits are predictors of poor outcomes in very old hospitalized patients., Am J Clin Nutr 2005;82: Vellas B, Villars H, Abellan G et al., Overview of the MNA It s history and challenges., J Nutr Health Aging 2006;10: Guigoz Y, Vellas J, Garry P (1994)., Mini Nutritional Assessment: A practical assessment tool for grading the nutritional state of elderly patients., Facts Res Gerontol 4 (supp. 2): Guigoz Y., The Mini-Nutritional Assessment (MNA ) review of the literature what does it tell us?, J Nutr Health Aging 2006;10: Murphy MC, Brooks CN, New SA, Lumbers ML., The use of the Mini Nutritional Assessment (MNA) tool in elderly orthopaedic patients., Eur J Clin Nutr 2000;54: Malone A. Anthropometric Assessment. In Charney P, Malone E, eds. ADA, Pocket Guide to Nutrition Assessment., Chicago, IL: American Dietetic Association; 2004: Osterkamp LK., Current perspective on assessment of human body proportions of relevance to amputees., J Am Diet Assoc. 1995;95: Hickson M, Frost G., A comparison of three methods for estimating height in the acutely ill elderly population., J Hum Nutr Diet 2003;6: Chumlea WC, Guo SS, Wholihan K, Cockram D, Kuczmarski RJ, Johnson CL., Stature prediction equations for elderly non-hispanic white, non-hispanic black, and Mexican-American persons developed from NHANES III data., J Am Diet Assoc 1998;98: Cheng HS, See LC, Sheih., Estimating stature from knee height for adults in Taiwan., Chang Gung Med J. 2001;24: Donini LM, de Felice MR, De Bernardini L, et al., Prediction of stature in the Italian elderly., J Nutr Health Aging. 2004;8: Guo SS, Wu X, Vellas B, Guigoz Y, Chumlea WC., Prediction of stature in the French elderly., Age & Nutr. 1994;5: Mendoz-Nunez VM, Sanchez-Rodriguez MA, Cervantes- Sandoval A, et al., Equations for predicting height for elderly Mexican-Americans are not applicable for elderly Mexicans., Am J Hum Biol 2002;14: Tanchoco CC, Duante CA, Lopez ES., Arm span and knee height as proxy indicators for height., J Nutritionist- Dietitians Assoc Philippines 2001;15: Shahar S, Pooy NS., Predictive equations for estimation of statue in Malaysian elderly people., Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2003:12(1): Last Update 9/10
16 1164 Last Update 9/10
Nutritional Assessment of patients in hospital
 Nutritional Assessment of patients in hospital Geoffrey Axiak M.Sc. Nursing (Manchester), B.Sc. Nursing, P.G. Dip. Nutrition & Dietetics Definition of malnutrition Undernutrition can occur as a result
Nutritional Assessment of patients in hospital Geoffrey Axiak M.Sc. Nursing (Manchester), B.Sc. Nursing, P.G. Dip. Nutrition & Dietetics Definition of malnutrition Undernutrition can occur as a result
Guidance on the Measurement and Estimation of Height and Weight
 APPENDIX 4: Guidance on the Measurement and Estimation of Height and Weight Guidance on the Measurement and Estimation of Height and Weight January 2013 Contents Measuring Weight Estimating weight in the
APPENDIX 4: Guidance on the Measurement and Estimation of Height and Weight Guidance on the Measurement and Estimation of Height and Weight January 2013 Contents Measuring Weight Estimating weight in the
Unintended Weight Loss and the Supplement Solution. Nancy Barwick, MS, RD, CD Midwest Regional Dietitian
 Unintended Weight Loss and the Supplement Solution Nancy Barwick, MS, RD, CD Midwest Regional Dietitian Learning Objectives Identify the Resident at nutritional risk. List three problems related to weight
Unintended Weight Loss and the Supplement Solution Nancy Barwick, MS, RD, CD Midwest Regional Dietitian Learning Objectives Identify the Resident at nutritional risk. List three problems related to weight
'Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool'
 BAPEN Advancing Clinical Nutrition 'Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool' MAG Malnutrition Advisory Group A Standing Committee of BAPEN BAPEN is registered charity number 1023927 www.bapen.org.uk 'MUST'
BAPEN Advancing Clinical Nutrition 'Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool' MAG Malnutrition Advisory Group A Standing Committee of BAPEN BAPEN is registered charity number 1023927 www.bapen.org.uk 'MUST'
Appendix 2 Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool ( MUST )
 Malnutrition universal screening tool ( MUST ) 229 Appendix 2 Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool ( MUST ) Reproduced with kind permission of BAPEN from The MUST Report. Nutritional Screening of Adults:
Malnutrition universal screening tool ( MUST ) 229 Appendix 2 Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool ( MUST ) Reproduced with kind permission of BAPEN from The MUST Report. Nutritional Screening of Adults:
MUST and Malnutrition
 MUST and Malnutrition Presenter Housekeeping Northern Devon Healthcare NHS Trust Confidentiality To respect confidentiality within the group unless it is necessary to address a current concern about the
MUST and Malnutrition Presenter Housekeeping Northern Devon Healthcare NHS Trust Confidentiality To respect confidentiality within the group unless it is necessary to address a current concern about the
Assessing Nutritional Risk. Presented by Heather Smart
 Assessing Nutritional Risk Presented by Heather Smart Aims Why we assess nutritional risk. The symptoms of malnutrition Barriers to improved nutrition How we assess nutritional risk. How to use nutritional
Assessing Nutritional Risk Presented by Heather Smart Aims Why we assess nutritional risk. The symptoms of malnutrition Barriers to improved nutrition How we assess nutritional risk. How to use nutritional
Overview of the FITNESSGRAM Body Composition Standards
 body composition Body composition refers to the division of total body weight (mass) into components, most commonly fat mass and fat-free mass. The proportion of total body weight that is fat (referred
body composition Body composition refers to the division of total body weight (mass) into components, most commonly fat mass and fat-free mass. The proportion of total body weight that is fat (referred
Unintended Weight Loss in Older Adults Toolkit Table of Contents 1. Overview of Unintended Weight Loss in Older Adults Toolkit 2. Acronym List 3.
 Unintended Weight Loss in Older Adults Toolkit Table of Contents 1. Overview of Unintended Weight Loss in Older Adults Toolkit 2. Acronym List 3. Referral Process a. Referrals to Registered Dietitian Policy
Unintended Weight Loss in Older Adults Toolkit Table of Contents 1. Overview of Unintended Weight Loss in Older Adults Toolkit 2. Acronym List 3. Referral Process a. Referrals to Registered Dietitian Policy
Leg Ulcer Clinic Discharge Pack. Tissue Viability Service. Luton Tissue Viability Team Luton Treatment Centre 6 Vestry Close Luton LU1 1AR
 Luton Tissue Viability Team Luton Treatment Centre 6 Vestry Close Luton LU1 1AR Tel: 0333 405 0048 Leg Ulcer Clinic Discharge Pack Tissue Viability Service 0361 - June 2018 (v2) June 2018 June 2021 Contents
Luton Tissue Viability Team Luton Treatment Centre 6 Vestry Close Luton LU1 1AR Tel: 0333 405 0048 Leg Ulcer Clinic Discharge Pack Tissue Viability Service 0361 - June 2018 (v2) June 2018 June 2021 Contents
Mini Nutritional Assessment for Hospitalized Patients in King Khalid Hospital at Hail city in Saudi Arabia
 Elderly Health Journal 2016; 2(2): 50-55. Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences, Yazd, Iran Journal Website : http://ehj.ssu.ac.ir Original Article Mini Nutritional Assessment for Hospitalized
Elderly Health Journal 2016; 2(2): 50-55. Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences, Yazd, Iran Journal Website : http://ehj.ssu.ac.ir Original Article Mini Nutritional Assessment for Hospitalized
PREEHCO PROJECT ANTHROPOMETRIC AND MOBILITY TESTING PROCEDURES
 PREEHCO PROJECT ANTHROPOMETRIC AND MOBILITY TESTING PROCEDURES Overview and purpose of anthropometry, and mobility. Functional health is a major determinant of health status and requires survey data. In
PREEHCO PROJECT ANTHROPOMETRIC AND MOBILITY TESTING PROCEDURES Overview and purpose of anthropometry, and mobility. Functional health is a major determinant of health status and requires survey data. In
WHOLE: Wellbeing and Healthy Choices for Older Adults and their Carers
 WHOLE: Wellbeing and Healthy Choices for Older Adults and their Carers Malnutrition in Older Age This dietary information fact sheet is intended for informational purposes only. It is not a substitute
WHOLE: Wellbeing and Healthy Choices for Older Adults and their Carers Malnutrition in Older Age This dietary information fact sheet is intended for informational purposes only. It is not a substitute
DEEP SQUAT. Upper torso is parallel with tibia or toward vertical Femur below horizontal Knees are aligned over feet Dowel aligned over feet
 APPENDIX 9 SCORING CRITERIA DEEP SQUAT Upper torso is parallel with tibia or toward vertical Femur below horizontal Knees are aligned over feet Dowel aligned over feet Upper torso is parallel with tibia
APPENDIX 9 SCORING CRITERIA DEEP SQUAT Upper torso is parallel with tibia or toward vertical Femur below horizontal Knees are aligned over feet Dowel aligned over feet Upper torso is parallel with tibia
Meat. Chicken, steak, fish, beans, pork and veal products are members of the meat group.
 HOW NUTRITION AND FLUID NEEDS CHANGE WITH AGE Food and nutritional needs change as a person gets older and older. The need for a lot of calories decreases when a person gets older. These needs were highest
HOW NUTRITION AND FLUID NEEDS CHANGE WITH AGE Food and nutritional needs change as a person gets older and older. The need for a lot of calories decreases when a person gets older. These needs were highest
Early Mobility in the Coronary Intensive Care Unit (CICU)
 Early Mobility in the Coronary Intensive Care Unit (CICU) Information for patients of the CICU and their caregivers This pamphlet has information about why early mobility in the CICU is important. Early
Early Mobility in the Coronary Intensive Care Unit (CICU) Information for patients of the CICU and their caregivers This pamphlet has information about why early mobility in the CICU is important. Early
Mo-Bility 13. Station 1 Card: How Stable Am I? 1LESSON 3. PROBLEM STATEMENT: How does obesity affect your
 Station 1 Card: How Stable Am I? PROBLEM STATEMENT: How does obesity affect your balance? In this experiment you will test the relationship between the center of gravity of an object and the base of support.
Station 1 Card: How Stable Am I? PROBLEM STATEMENT: How does obesity affect your balance? In this experiment you will test the relationship between the center of gravity of an object and the base of support.
AGREEMENT BETWEEN ESPEN CRITERIA AND MNA IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MALNUTRITION IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH HIP FRACTURE
 AGREEMENT BETWEEN ESPEN CRITERIA AND MNA IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MALNUTRITION IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH HIP FRACTURE Lourdes Evangelista Cabrera 1, Lucía Fernández Arana 1, Victoria Garay Airaghi 1, Esther
AGREEMENT BETWEEN ESPEN CRITERIA AND MNA IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MALNUTRITION IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH HIP FRACTURE Lourdes Evangelista Cabrera 1, Lucía Fernández Arana 1, Victoria Garay Airaghi 1, Esther
Frequently Asked Questions
 Frequently Asked Questions 1. What is BMI? Body Mass Index (BMI) is a number calculated from a child s height and weight. BMI is an inexpensive and easy-to-perform method of screening for weight categories
Frequently Asked Questions 1. What is BMI? Body Mass Index (BMI) is a number calculated from a child s height and weight. BMI is an inexpensive and easy-to-perform method of screening for weight categories
What Should I Eat to Help my Pressure Sore or Wound Heal?
 What Should I Eat to Help my Pressure Sore or Wound Heal? Information for Patients i UHL Nutrition and Dietetic Service UHL Tissue Viability Team Introduction If you have a pressure sore or a large wound
What Should I Eat to Help my Pressure Sore or Wound Heal? Information for Patients i UHL Nutrition and Dietetic Service UHL Tissue Viability Team Introduction If you have a pressure sore or a large wound
FAB55 EXERCISES, 5 WEEKS, 5 MINUTES A DAY
 BANDED SIDE STEP Strengthening Hip Complex Starting Position: Start in a standing position with the strength mini-band placed around your ankles. Your knees, hips and toes should be in-line with each other.
BANDED SIDE STEP Strengthening Hip Complex Starting Position: Start in a standing position with the strength mini-band placed around your ankles. Your knees, hips and toes should be in-line with each other.
Eating Well for Wound Healing
 Eating Well for Wound Healing 2 Introduction The aim of this leaflet is to help you to have the correct diet to enable your wound to heal. What you eat plays an important role in: Looking after your skin
Eating Well for Wound Healing 2 Introduction The aim of this leaflet is to help you to have the correct diet to enable your wound to heal. What you eat plays an important role in: Looking after your skin
Low Back Pain Home Exercises
 Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
Screening for malnutrition in the elderly population: a tool for estimating height from knee height
 Screening for malnutrition in the elderly population: a tool for estimating height from knee height Anil C Mathew 1*, Saranya Sampath 2, Darsana Das 2, M Vijayakumar 3, N Ramakrishnan 4, S L Ravishankar
Screening for malnutrition in the elderly population: a tool for estimating height from knee height Anil C Mathew 1*, Saranya Sampath 2, Darsana Das 2, M Vijayakumar 3, N Ramakrishnan 4, S L Ravishankar
Range of motion and positioning
 Range of motion and positioning Learning guide Why is motion important? Most people take free, comfortable movement for granted. Motion is meant to be smooth and painless. The ligaments, tendons, muscles,
Range of motion and positioning Learning guide Why is motion important? Most people take free, comfortable movement for granted. Motion is meant to be smooth and painless. The ligaments, tendons, muscles,
MACS V56 Physical Exam / Lipodystrophy Form Guidelines. The Physical Exam form is divided into the following main components:
 Physical Exam: The Physical Exam form is divided into the following main components: Vital Signs, Height and Weight (Page 1, Q1-Q5) Physical examination completed by a clinician (Pages 1-4, Q6-Q14) Lipodystrophy
Physical Exam: The Physical Exam form is divided into the following main components: Vital Signs, Height and Weight (Page 1, Q1-Q5) Physical examination completed by a clinician (Pages 1-4, Q6-Q14) Lipodystrophy
1. How many calories do I need to eat if I want to maintain my current weight? Example for a 200 pound athlete who practices for 3 hours per day:
 Nutrition Questions: 1. How many calories do I need to eat if I want to maintain my current weight? Step 1 Calculate your basal metabolic rate (BMR), the minimal number of calories your body needs just
Nutrition Questions: 1. How many calories do I need to eat if I want to maintain my current weight? Step 1 Calculate your basal metabolic rate (BMR), the minimal number of calories your body needs just
Low Back Program Exercises
 Low Back Program Exercises Exercise 1: Knee to Chest Starting Position: Lie on your back on a table or firm surface. Action: Clasp your hands behind the thigh and pull it towards your chest. Keep the opposite
Low Back Program Exercises Exercise 1: Knee to Chest Starting Position: Lie on your back on a table or firm surface. Action: Clasp your hands behind the thigh and pull it towards your chest. Keep the opposite
I. Meeting the Protein Needs of an Athlete A Case Study
 548 Chapter 14 Nutrition: Fitness and Sports I. Meeting the Protein Needs of an Athlete A Case Study Mark is a college student who has been lifting weights at the student recreation center. The trainer
548 Chapter 14 Nutrition: Fitness and Sports I. Meeting the Protein Needs of an Athlete A Case Study Mark is a college student who has been lifting weights at the student recreation center. The trainer
Good Working Positions
 Good Working Positions To understand the best way to set up a computer workstation, it is helpful to understand the concept of neutral body positioning. This is a comfortable working posture in which your
Good Working Positions To understand the best way to set up a computer workstation, it is helpful to understand the concept of neutral body positioning. This is a comfortable working posture in which your
Routine For: Total Hip Arthroplasty - Standard Precautions
 Standard Hip Precautions TOTAL HIP - 4 Ankle Pump not bend your operative hip beyond a 90 degree angle. not sit with your legs crossed or lie on your back with your operative leg crossed over the other
Standard Hip Precautions TOTAL HIP - 4 Ankle Pump not bend your operative hip beyond a 90 degree angle. not sit with your legs crossed or lie on your back with your operative leg crossed over the other
Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises. Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises
 Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction Weight-bearing and resistance exercises have
Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction Weight-bearing and resistance exercises have
PHYSICAL FITNESS TESTING
 PHYSICAL FITNESS TESTING ATHLETIC PLACEMENT PROCESS I PHYSICAL FITNESS TEST: INSTRUCTIONS Curl-ups This activity measures abdominal strength and endurance. Curl-ups Testing Have the student lie on a cushioned,
PHYSICAL FITNESS TESTING ATHLETIC PLACEMENT PROCESS I PHYSICAL FITNESS TEST: INSTRUCTIONS Curl-ups This activity measures abdominal strength and endurance. Curl-ups Testing Have the student lie on a cushioned,
Snow Angels on Foam Roll
 Thoracic Mobilization on Foam Roll Lie on your back with a foam roller positioned horizontally across your mid back, and arms crossed in front of your body. Bend your knees so your feet are resting flat
Thoracic Mobilization on Foam Roll Lie on your back with a foam roller positioned horizontally across your mid back, and arms crossed in front of your body. Bend your knees so your feet are resting flat
Osteoporosis Exercise:
 Osteoporosis Exercise: Balance, Posture and Functional Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction You can help improve and maintain your balance, posture
Osteoporosis Exercise: Balance, Posture and Functional Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction You can help improve and maintain your balance, posture
2017 COS ANNUAL MEETING AND EXHIBITION HOME EXERCISES
 UPPER BODY Push Up From a push up position. Lower whole body down to floor. Press up to return to start position. Maintain abdominal hollow and neutral spinal alignment throughout movement. Note: Perform
UPPER BODY Push Up From a push up position. Lower whole body down to floor. Press up to return to start position. Maintain abdominal hollow and neutral spinal alignment throughout movement. Note: Perform
Resistance Training Program
 Name: Resistance Training Program How to do Resistance Training: Warm up for 5 minutes before resistance training e.g., walk or cycle slowly o Avoid stretching before resistance training Do all exercises
Name: Resistance Training Program How to do Resistance Training: Warm up for 5 minutes before resistance training e.g., walk or cycle slowly o Avoid stretching before resistance training Do all exercises
Nutritional status of Mongolian elderly
 Asian J Gerontol Geriatr 2011; 6: 42 6 Nutritional status of Mongolian elderly COUNTRY REPORT R Oyunkhand 1, E Byambasuren 1, B Batsereedene 2, O Chimedsuren 3, S Byambasuren 4 ABSTRACT Background. Treatment
Asian J Gerontol Geriatr 2011; 6: 42 6 Nutritional status of Mongolian elderly COUNTRY REPORT R Oyunkhand 1, E Byambasuren 1, B Batsereedene 2, O Chimedsuren 3, S Byambasuren 4 ABSTRACT Background. Treatment
Exercise Report For: Augusta James
 Exercise Report For: Optimizing Sport Performance Provided By: Greg Redman BScPT, BScKin, Wave Physiotherapy Phone: 250-763-9283 Fax:, www.wavephysio.ca Page: 1 Stretch hip flexor kneel w/ball Stretch
Exercise Report For: Optimizing Sport Performance Provided By: Greg Redman BScPT, BScKin, Wave Physiotherapy Phone: 250-763-9283 Fax:, www.wavephysio.ca Page: 1 Stretch hip flexor kneel w/ball Stretch
General Principles of Stretching. To be effective, stretching must be done slowly, gently and frequently.
 General Principles of Stretching To be effective, stretching must be done slowly, gently and frequently. Slowly means that while the exercise is being done the muscle being stretched must be moved slowly
General Principles of Stretching To be effective, stretching must be done slowly, gently and frequently. Slowly means that while the exercise is being done the muscle being stretched must be moved slowly
A SELF-COMPLETED NUTRITION SCREENING TOOL FOR COMMUNITY- DWELLING OLDER ADULTS WITH HIGH RELIABILITY: A COMPARISON STUDY
 14 HUHMANN_04 LORD_c 05/03/14 09:39 Page339 A SELF-COMPLETED NUTRITION SCREENING TOOL FOR COMMUNITY- DWELLING OLDER ADULTS WITH HIGH RELIABILITY: A COMPARISON STUDY M.B. HUHMANN 1, V. PEREZ 2, D.D. ALEXANDER
14 HUHMANN_04 LORD_c 05/03/14 09:39 Page339 A SELF-COMPLETED NUTRITION SCREENING TOOL FOR COMMUNITY- DWELLING OLDER ADULTS WITH HIGH RELIABILITY: A COMPARISON STUDY M.B. HUHMANN 1, V. PEREZ 2, D.D. ALEXANDER
Daily Nutrition Checklist Day 22 - Phase 2
 Breakfast Fatlossity Daily Nutrition Checklist Day 22 - Phase 2 Time: Choose 2 Eggs Oatmeal High fiber cereal Skim milk & Hummus Lunch Time: Choose 2 Cold cuts Salad/ High fiber wrap Brown rice Beans or
Breakfast Fatlossity Daily Nutrition Checklist Day 22 - Phase 2 Time: Choose 2 Eggs Oatmeal High fiber cereal Skim milk & Hummus Lunch Time: Choose 2 Cold cuts Salad/ High fiber wrap Brown rice Beans or
Static Back. Instructions: Purpose: Hold this ecise for 05 min. prepared for Pain Free Posture MN
 1 Static Back Hold this ecise for 05 min. 1. Lie on your back with your legs up over a block or chair 2. Place your arms out to the sides at 45 degrees from your body with palms up 3. Relax your upper
1 Static Back Hold this ecise for 05 min. 1. Lie on your back with your legs up over a block or chair 2. Place your arms out to the sides at 45 degrees from your body with palms up 3. Relax your upper
Are you eating & drinking enough?
 Are you eating & drinking enough? A guide to the MUST & GULP screening tools GULP Dehydration Risk Screening Tool To complete GULP, tick the boxes which represent your findings. Add up the total tick scores
Are you eating & drinking enough? A guide to the MUST & GULP screening tools GULP Dehydration Risk Screening Tool To complete GULP, tick the boxes which represent your findings. Add up the total tick scores
Weight and heart and circulatory diseases
 Weight and heart and circulatory diseases YOUR UNDERSTANDING WEIGHT This leaflet is for people who are at increased risk of heart and circulatory diseases because of their weight. Heart and circulatory
Weight and heart and circulatory diseases YOUR UNDERSTANDING WEIGHT This leaflet is for people who are at increased risk of heart and circulatory diseases because of their weight. Heart and circulatory
Stephanie Mansour s. Create New Habits That Stick Year After Year
 Stephanie Mansour s Create New Habits That Stick Year After Year HOW THE CHALLENGE WORKS For 21 days, you re committing (along with hundreds of other women!) to changing your mindset, improving your body
Stephanie Mansour s Create New Habits That Stick Year After Year HOW THE CHALLENGE WORKS For 21 days, you re committing (along with hundreds of other women!) to changing your mindset, improving your body
Making Meals Matter. Tips to feed 6-12 year olds. Healthy eating for your school-age child
 Making Meals Matter Tips to feed 6-12 year olds Healthy eating for your school-age child Your child learns healthy eating from you. Your elementary- school child needs you to guide them and to model healthy
Making Meals Matter Tips to feed 6-12 year olds Healthy eating for your school-age child Your child learns healthy eating from you. Your elementary- school child needs you to guide them and to model healthy
Resistance Training Program
 Name: Resistance Training Program How to do Resistance Training: Warm up for 5 minutes before resistance training e.g., walk or cycle slowly o Avoid stretching before resistance training Do all exercises
Name: Resistance Training Program How to do Resistance Training: Warm up for 5 minutes before resistance training e.g., walk or cycle slowly o Avoid stretching before resistance training Do all exercises
Seated Exercises Information for Patients
 Seated Exercises Information for Patients 1 Seated Exercise These exercises are designed to allow you to exercise and keep your joints moving and strong whilst you maybe using a wheelchair. They can all
Seated Exercises Information for Patients 1 Seated Exercise These exercises are designed to allow you to exercise and keep your joints moving and strong whilst you maybe using a wheelchair. They can all
Malnutrition in Adults: Guidelines for Identification and Treatment
 Malnutrition in Adults: Guidelines for Identification and Treatment Signatures (e.g. chair of the ratifying committee and lay member) and date Signature...date Designation: Signature...date Designation
Malnutrition in Adults: Guidelines for Identification and Treatment Signatures (e.g. chair of the ratifying committee and lay member) and date Signature...date Designation: Signature...date Designation
Exercises for using assistive devices
 Exercises for using assistive devices For individuals who use an assistive device (cane, walker, etc.) please select from the exercises on the following pages. Completing these exercises on a regular basis
Exercises for using assistive devices For individuals who use an assistive device (cane, walker, etc.) please select from the exercises on the following pages. Completing these exercises on a regular basis
Morning EAT Choose an Option from Meal 1. Mid-Morning EAT Choose an Option from Meal 2. daily schedule. Lunch EAT Choose an Option from Meal 3
 One of the secrets to managing your weight is to eat six small meals a day. Keep your metabolism in high gear by feeding your body every few hours! Below is a suggested schedule to follow. Morning EAT
One of the secrets to managing your weight is to eat six small meals a day. Keep your metabolism in high gear by feeding your body every few hours! Below is a suggested schedule to follow. Morning EAT
Thoracic Home Exercise Program
 Home Exercise Program 1. Bridging Laying on your back, knees bent with feet flat on the floor, arms along side resting on the floor, tighten your abdominals to stabilize your low back. Raise your buttocks
Home Exercise Program 1. Bridging Laying on your back, knees bent with feet flat on the floor, arms along side resting on the floor, tighten your abdominals to stabilize your low back. Raise your buttocks
KNEE AND LEG EXERCISE PROGRAM
 KNEE AND LEG EXERCISE PROGRAM These exercises are specifically designed to rehabilitate the muscles of the hip and knee by increasing the strength and flexibility of the involved leg. This exercise program
KNEE AND LEG EXERCISE PROGRAM These exercises are specifically designed to rehabilitate the muscles of the hip and knee by increasing the strength and flexibility of the involved leg. This exercise program
School Visits Fitness Testing
 School Visits Fitness Testing 10m Sprint Test Purpose: To measure an athlete s ability to accelerate Equipment required: timing gates or stop watch, measuring tap - Participant ready s themselves on the
School Visits Fitness Testing 10m Sprint Test Purpose: To measure an athlete s ability to accelerate Equipment required: timing gates or stop watch, measuring tap - Participant ready s themselves on the
Starting Stats. BLOODWORK (Optional. Please consult your physician to have these measurements taken.)
 Starting Stats Record these measurements before you begin the program so you have a baseline from which to assess your progress. Seeing changes in these measurements can help you to stay motivated. If
Starting Stats Record these measurements before you begin the program so you have a baseline from which to assess your progress. Seeing changes in these measurements can help you to stay motivated. If
? do I need to know BEFORE PERFORMING the strength activities?
 ? What 1 2 3 4 do I need to know BEFORE PERFORMING the strength activities? Consult with my doctor to make sure that these strength activities are safe and appropriate for me before my first session. Always
? What 1 2 3 4 do I need to know BEFORE PERFORMING the strength activities? Consult with my doctor to make sure that these strength activities are safe and appropriate for me before my first session. Always
A Body in Motion Stays in Motion. Exercises for Arthritis Prevention. Parts in
 A Body in Motion Stays in Motion Exercises for Arthritis Prevention Parts in Motion A body in motion must stay in motion. It s not just a law of physics it s true about your health as well. No matter your
A Body in Motion Stays in Motion Exercises for Arthritis Prevention Parts in Motion A body in motion must stay in motion. It s not just a law of physics it s true about your health as well. No matter your
Anterior Total Hip Replacement
 Anterior Total Hip Replacement Home Care Instructions Full recovery from your total hip replacement surgery is going to take months. This information will help you understand your recovery and care at
Anterior Total Hip Replacement Home Care Instructions Full recovery from your total hip replacement surgery is going to take months. This information will help you understand your recovery and care at
Copyright Cardiff University
 This exercise programme has been developed by physiotherapists specifically for people with movement disorders. Exercise is not without its risks and this or any other exercise programme has potential
This exercise programme has been developed by physiotherapists specifically for people with movement disorders. Exercise is not without its risks and this or any other exercise programme has potential
Dignity and Nutrition for Older People
 South Gloucestershire Community Health Services Dignity and Nutrition for Older People Lorraine Norris Nutrition and Dietetic Professional Lead South Gloucestershire Community Health November 9th 2011
South Gloucestershire Community Health Services Dignity and Nutrition for Older People Lorraine Norris Nutrition and Dietetic Professional Lead South Gloucestershire Community Health November 9th 2011
Posterior Total Hip Replacement
 Posterior Total Hip Replacement Home Care Instructions Full recovery from your total hip replacement surgery is going to take months. This information will help you understand your recovery and care at
Posterior Total Hip Replacement Home Care Instructions Full recovery from your total hip replacement surgery is going to take months. This information will help you understand your recovery and care at
ICU: Rehabilitation Programme
 Information and exercises ICU: Rehabilitation Programme Introduction During an ICU stay, maintaining a patient s stamina, muscle strength and general movement is very important to their prolonged recovery.
Information and exercises ICU: Rehabilitation Programme Introduction During an ICU stay, maintaining a patient s stamina, muscle strength and general movement is very important to their prolonged recovery.
Edema Exercises. To Improve Drainage
 Edema Exercises To Improve Drainage You will improve your lymph flow by doing a few exercises each day. These exercises are an important part of your home program. They may help you get stronger, too.
Edema Exercises To Improve Drainage You will improve your lymph flow by doing a few exercises each day. These exercises are an important part of your home program. They may help you get stronger, too.
Racquet Sports Training Program
 Racquet Sports Training Program Always consult your physician before beginning any exercise program. The information and advice published or made available through the Orthopaedic and Neurosurgery Specialists,
Racquet Sports Training Program Always consult your physician before beginning any exercise program. The information and advice published or made available through the Orthopaedic and Neurosurgery Specialists,
The eatwell plate is based on the Government s Eight Guidelines for a Healthy Diet, which are:
 The eatwell plate The eatwell plate is a pictorial food guide showing the proportion and types of foods that are needed to make up a healthy balanced diet. The plate has been produced by the Food Standards
The eatwell plate The eatwell plate is a pictorial food guide showing the proportion and types of foods that are needed to make up a healthy balanced diet. The plate has been produced by the Food Standards
Static Flexibility/Stretching
 Static Flexibility/Stretching Points of Emphasis Always stretch before and after workouts. Stretching post-exercise will prevent soreness and accelerate recovery. Always perform a general warm-up prior
Static Flexibility/Stretching Points of Emphasis Always stretch before and after workouts. Stretching post-exercise will prevent soreness and accelerate recovery. Always perform a general warm-up prior
Chapter 9: Exercise Instructions
 RESOURCES RESEARCHERS / MEDICAL HOW TO HELP SPONSORS GEHRIG CONNECTION MEDIA TELETHON MDA.ORG search our site Go MDA/ALS Newsmagazine Current Issue Home> Publications >Everyday Life With ALS: A Practical
RESOURCES RESEARCHERS / MEDICAL HOW TO HELP SPONSORS GEHRIG CONNECTION MEDIA TELETHON MDA.ORG search our site Go MDA/ALS Newsmagazine Current Issue Home> Publications >Everyday Life With ALS: A Practical
The University of North Texas Dining Services White Paper: Wanting to Gain Weight
 The University of North Texas Dining Services White Paper: Wanting to Gain Weight Contents Wanting to Gain Weight What is Underweight? Complications of Being Underweight Possible Causes of Underweight
The University of North Texas Dining Services White Paper: Wanting to Gain Weight Contents Wanting to Gain Weight What is Underweight? Complications of Being Underweight Possible Causes of Underweight
Flexibility and Stretching
 Flexibility and Stretching Stretching before exercise prepares the joints for motion, helps avoid injury and increases the range of motion of the area being stretched. After exercise stretching reduces
Flexibility and Stretching Stretching before exercise prepares the joints for motion, helps avoid injury and increases the range of motion of the area being stretched. After exercise stretching reduces
DIABETES AND CORONARY HEART DISEASE RISK MANAGEMENT
 Lesley Eccott, Community Learning Disability Nurse. November, 2003 DIABETES AND CORONARY HEART DISEASE RISK MANAGEMENT Name D.O.B Address Hospital Number CLDN Diabetic Nurse Consultant Care Manager C.S.W.
Lesley Eccott, Community Learning Disability Nurse. November, 2003 DIABETES AND CORONARY HEART DISEASE RISK MANAGEMENT Name D.O.B Address Hospital Number CLDN Diabetic Nurse Consultant Care Manager C.S.W.
HEALTH EDUCATION CURRICULUM GUIDE
 GRADE 2 Human Body Revised 6/16 2.1 The student will identify the major body systems, healthy food and beverage choices, emotions, and social skills, and explain how each is connected to personal health.
GRADE 2 Human Body Revised 6/16 2.1 The student will identify the major body systems, healthy food and beverage choices, emotions, and social skills, and explain how each is connected to personal health.
Strong and Stable: Exercises for Core, Strength and Balance
 Strong and Stable: Exercises for Core, Strength and Balance Exercise and physical activity before, during and after cancer treatment are important to recovery and general quality of life. Studies show
Strong and Stable: Exercises for Core, Strength and Balance Exercise and physical activity before, during and after cancer treatment are important to recovery and general quality of life. Studies show
Strength and Balance Exercises
 Strength and Balance Exercises LEG EXTENSIONS Purpose: Strengthen the thigh and leg muscles. Starting Position: Sit tall with your feet flat on floor, shoulderwidth apart. You may hold onto the sides of
Strength and Balance Exercises LEG EXTENSIONS Purpose: Strengthen the thigh and leg muscles. Starting Position: Sit tall with your feet flat on floor, shoulderwidth apart. You may hold onto the sides of
Dynamic Flexibility All exercises should be done smoothly while taking care to maintain good posture and good technique.
 Dynamic Flexibility All exercises should be done smoothly while taking care to maintain good posture and good technique. Lying on back: Hip Crossover: Arms out in T position, feet flat on the floor, knees
Dynamic Flexibility All exercises should be done smoothly while taking care to maintain good posture and good technique. Lying on back: Hip Crossover: Arms out in T position, feet flat on the floor, knees
Your guide to bringing in food and beverages
 Your guide to bringing in food and beverages Being in the hospital can be a stressful time. Patients may often eat less than usual or not get enough calories and protein for reasons such as: an increased
Your guide to bringing in food and beverages Being in the hospital can be a stressful time. Patients may often eat less than usual or not get enough calories and protein for reasons such as: an increased
Guideline for the Prescribing of Oral Nutritional Supplements in Adults (NUT2)
 Guideline for the Prescribing of Oral Nutritional Supplements in Adults (NUT2) Author Medicines Optimisation Team, Sunderland CCG Approved by Sunderland Medicines Optimisation and Guideline Group Current
Guideline for the Prescribing of Oral Nutritional Supplements in Adults (NUT2) Author Medicines Optimisation Team, Sunderland CCG Approved by Sunderland Medicines Optimisation and Guideline Group Current
Keeping the Body Healthy!
 Name Hour Food & Nutrition 9 th Grade Keeping the Body Healthy! # Assignment Pts. Possible 1 Create a Great Plate Video 30 2 MyPlate Label & Color 15 3 Color & Food 5 4 6 Basic Nutrients 9 5 Dietary Guidelines
Name Hour Food & Nutrition 9 th Grade Keeping the Body Healthy! # Assignment Pts. Possible 1 Create a Great Plate Video 30 2 MyPlate Label & Color 15 3 Color & Food 5 4 6 Basic Nutrients 9 5 Dietary Guidelines
Information Guide for the 65 Foot Pole Climb Physical Performance Test
 Information Guide for the 65 Foot Pole Climb Physical Performance Test Test Number: 4017 Human Resources Southern California Edison Company REV06042018 1 Introduction The 4017 65 Foot Pole Climb Physical
Information Guide for the 65 Foot Pole Climb Physical Performance Test Test Number: 4017 Human Resources Southern California Edison Company REV06042018 1 Introduction The 4017 65 Foot Pole Climb Physical
How to treat your weight problem
 Behavioral changes for losing weight Changing your behaviors or habits related to food and physical activity is important for losing weight. The first step is to understand which habits lead you to overeat
Behavioral changes for losing weight Changing your behaviors or habits related to food and physical activity is important for losing weight. The first step is to understand which habits lead you to overeat
HEALTH EDUCATION CURRICULUM GUIDE
 GRADE 2 Human Body 2012 2.1 The student will identify the major body systems and explain their connection to personal health. State Standard Descriptive Statement function of the cardiovascular system.
GRADE 2 Human Body 2012 2.1 The student will identify the major body systems and explain their connection to personal health. State Standard Descriptive Statement function of the cardiovascular system.
FIT Start Booklet START CU STO DI AL SERVI CES W ARM U P PRO G RAM
 FIT Start Booklet START CU STO DI AL SERVI CES W ARM U P PRO G RAM Ta b l e o f Co n t e n t s Introduction.. 1 FIT START Movements Swing the Arms. 2 Twist the Body.. 3 Alternate and Sink. 4 Reach and
FIT Start Booklet START CU STO DI AL SERVI CES W ARM U P PRO G RAM Ta b l e o f Co n t e n t s Introduction.. 1 FIT START Movements Swing the Arms. 2 Twist the Body.. 3 Alternate and Sink. 4 Reach and
ESSENTIAL STRETCHES FOR SWIMMERS
 ESSENTIAL STRETCHES FOR SWIMMERS Clare Kersley BSc (Hons) Ost Osteopath & Sports Massage Therapist Notes 1. Stretches should form the 4th part of all your swimming training sessions: Page 1 of 13 Warm
ESSENTIAL STRETCHES FOR SWIMMERS Clare Kersley BSc (Hons) Ost Osteopath & Sports Massage Therapist Notes 1. Stretches should form the 4th part of all your swimming training sessions: Page 1 of 13 Warm
Sportlyzer s Core Exercises
 Sportlyzer s Core Exercises Core training exercises are as important part of your training schedule as your endurance training. You need it to support your everyday running and improve your racing results.
Sportlyzer s Core Exercises Core training exercises are as important part of your training schedule as your endurance training. You need it to support your everyday running and improve your racing results.
WITH DIABETES PRE-TEST
 WITH DIABETES PRE-TEST LIVE HEALTHY GEORGIA SENIORS TAKING CHARGE! CONSENT FORM (WITH DIABETES) I,, agree to participate in the research study titled "Live Healthy Georgia Seniors Taking Charge" conducted
WITH DIABETES PRE-TEST LIVE HEALTHY GEORGIA SENIORS TAKING CHARGE! CONSENT FORM (WITH DIABETES) I,, agree to participate in the research study titled "Live Healthy Georgia Seniors Taking Charge" conducted
Preventing Pressure Ulcers or Bed Sores
 Preventing Pressure Ulcers or Bed Sores Keeping Your Skin Healthy In the Hospital As partners in your care, this brochure will help you, your care givers and care helpers learn how to prevent pressure
Preventing Pressure Ulcers or Bed Sores Keeping Your Skin Healthy In the Hospital As partners in your care, this brochure will help you, your care givers and care helpers learn how to prevent pressure
Preventing Pressure Ulcers or Bed Sores
 Preventing Pressure Ulcers or Bed Sores Keeping Your Skin Healthy In the Hospital As partners in your care, this brochure will help you, your care givers and care helpers learn how to prevent pressure
Preventing Pressure Ulcers or Bed Sores Keeping Your Skin Healthy In the Hospital As partners in your care, this brochure will help you, your care givers and care helpers learn how to prevent pressure
FROZEN SHOULDER REHABILITATION EXERCISES
 FROZEN SHOULDER REHABILITATION EXERCISES Exercise no. 1) Bend forward so that your torso is parallel to the ground, and lean on a stool or table with your healthy arm. Completely relax your sore arm, and
FROZEN SHOULDER REHABILITATION EXERCISES Exercise no. 1) Bend forward so that your torso is parallel to the ground, and lean on a stool or table with your healthy arm. Completely relax your sore arm, and
Do the same as above, but turn your head TOWARDS the side that you re holding on to the chair.
 Stretch 4-6 times per day and hold each stretch for a minimum of 30 seconds. Perform the stretch gently without bouncing. Discuss any problems with your Chiropractor. Sit upright with your head and shoulder
Stretch 4-6 times per day and hold each stretch for a minimum of 30 seconds. Perform the stretch gently without bouncing. Discuss any problems with your Chiropractor. Sit upright with your head and shoulder
Nutrition and Dietetics Patient Information Leaflet
 Dietary advice for people with diabetes Underweight/weight loss Nutrition and Dietetics Patient Information Leaflet How can I make the most of my food? If you want to gain weight, prevent weight loss or
Dietary advice for people with diabetes Underweight/weight loss Nutrition and Dietetics Patient Information Leaflet How can I make the most of my food? If you want to gain weight, prevent weight loss or
Starting position: Lying flat (or if your legs go into spasm - lying with knees bent up and feet flat on floor/bed)
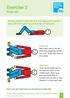 Exercise 2 Knee roll Starting position: Lying flat (or if your legs go into spasm - lying with knees bent up and feet flat on floor/bed) Roll knees over to the left, stretching diagonally across the trunk.
Exercise 2 Knee roll Starting position: Lying flat (or if your legs go into spasm - lying with knees bent up and feet flat on floor/bed) Roll knees over to the left, stretching diagonally across the trunk.
Information Guide for the Structural Mechanic Physical Performance Test
 Information Guide for the Structural Mechanic Physical Performance Test Test Number: 4024 Human Resources Southern California Edison Company REV080717 1 Introduction The 4024 Structural Mechanic Physical
Information Guide for the Structural Mechanic Physical Performance Test Test Number: 4024 Human Resources Southern California Edison Company REV080717 1 Introduction The 4024 Structural Mechanic Physical
Information Guide for the Lineman Physical Performance Test
 Information Guide for the Lineman Physical Performance Test Test Number: 4016 Human Resources Southern California Edison Company REV06042018 1 Introduction The 4016 Lineman Physical Performance Test is
Information Guide for the Lineman Physical Performance Test Test Number: 4016 Human Resources Southern California Edison Company REV06042018 1 Introduction The 4016 Lineman Physical Performance Test is
Elite Health & Fitness Training, Inc. FOOD HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE
 FOOD HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Name: Date: Height: Weight: Age: Sex: Weight History: Have you ever tried to lose weight before or are you currently trying to lose weight? If yes, explain: Do you currently
FOOD HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE Name: Date: Height: Weight: Age: Sex: Weight History: Have you ever tried to lose weight before or are you currently trying to lose weight? If yes, explain: Do you currently
YOUR REHABILITATION AFTER CRITICAL CARE
 YOUR REHABILITATION AFTER CRITICAL CARE Exercise Programme & Exercise Diary Name: Date Commenced: Ref: West Yorkshire Critical Care Network Rehabilitation Group November 2010 CONTENTS PAGE Item Page(s)
YOUR REHABILITATION AFTER CRITICAL CARE Exercise Programme & Exercise Diary Name: Date Commenced: Ref: West Yorkshire Critical Care Network Rehabilitation Group November 2010 CONTENTS PAGE Item Page(s)
TPW 's Upper Back Menu
 TPW 's Upper Back Menu # Sets Reps Duration E-cise 1 1 1 00:10:00 Static Back 2 3 10 Static Back Reverse Presses 3 3 10 Static Back Pullovers 4 1 1 0:01:00 Floor Block 5 1 1 0:02:00 Static Extension Position
TPW 's Upper Back Menu # Sets Reps Duration E-cise 1 1 1 00:10:00 Static Back 2 3 10 Static Back Reverse Presses 3 3 10 Static Back Pullovers 4 1 1 0:01:00 Floor Block 5 1 1 0:02:00 Static Extension Position
Double Knee to Chest. Lying on back with knees slightly bent. Hug both knees to chest
 Double Knee to Chest Lying on back with knees slightly bent Hug both knees to chest Flexion on the Gymnic Ball Lying on stomach over ball Drape body over ball and relax Roll back and forth to stretch out
Double Knee to Chest Lying on back with knees slightly bent Hug both knees to chest Flexion on the Gymnic Ball Lying on stomach over ball Drape body over ball and relax Roll back and forth to stretch out
Presuming all the above symptoms are not present, pain is more likely to be mechanical and caused by a sprain, strain or poor posture.
 Page 1 of 8 View this article online at: patient.info/health/back-pain-exercises Back Pain Exercises Back pain is very common but in most cases is not caused by a serious problem. Most cases of back pain
Page 1 of 8 View this article online at: patient.info/health/back-pain-exercises Back Pain Exercises Back pain is very common but in most cases is not caused by a serious problem. Most cases of back pain
Pressure ulcers can develop in a relatively short time, therefore it is important to prevent them or notice and recognise early signs of damage.
 Preventing Pressure Damage A Guide for Patients and Carers What is pressure damage? A pressure ulcer, (previously often referred to as a bed sore or pressure sore ) is a localised area of damage to the
Preventing Pressure Damage A Guide for Patients and Carers What is pressure damage? A pressure ulcer, (previously often referred to as a bed sore or pressure sore ) is a localised area of damage to the
