10/28/2015. Disclaimer. Disclaimer
|
|
|
- Marilynn Blankenship
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Disclaimer Omnicare, Inc., as a provider of Infusion Pharmacy Services, is committed to the establishment and maintenance of the highest quality of care in infusion therapy services. This Infusion Therapy Education Program ( Program ) has been developed entirely by Omnicare Infusion Services ( Omnicare ) and is not intended to replace your infusion service practice guidelines and nursing requirements. Moreover, the contents of this training are guidance only and do not supersede applicable laws, guidelines and your specific employer s policies, procedures and processes The nature of infusion therapy requires frequent updates. It is the responsibility of the healthcare professionals involved with infusion management to remain current in his/her practice Disclaimer This Program will reference various sources of authority including but not limited to statutes, regulations, standards and treatment guidelines. It is the obligation of every training participant to review these sources of authority and exercise independent skill and judgment in the implementation of this information in the clinical setting. This educational program is not intended to replace good professional judgment by the healthcare provider nor is it intended to supersede the necessity for clinically sound prerogatives of a healthcare organization. Skills validation checklists are available in the Omnicare Nurses Infusion Manual and electronically on Omniview, Omnicare s web portal. Omnicare s provision of these tools are to assist practitioners in providing quality infusion services, however, these tools and guides do not replace independent skills and sound clinical judgment. 1
2 Objectives 1. Define the types of parenteral nutrition 2. Identify the clinical indications for parenteral nutrition 3. Review the components of parenteral nutrition solution 4. List complications of parenteral nutrition 5. Identify appropriate monitoring of patients receiving parenteral nutrition 6. Explain nursing responsibilities related to the administration of parenteral nutrition 7. Discuss administration of premixed formulas Introduction Parenteral nutrition (PN) is the intravenous administration of nutrients needed for metabolic functioning Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) contains glucose, amino acids, lipids, vitamins, electrolytes and minerals Physician/licensed independent practitioner (LIP) must weigh the proposed benefits against the risk of possible complications Introduction The role of the licensed nurse is critical in preventing complications and ensuring the success of therapy A multidisciplinary approach to care of the patient receiving parenteral nutrition is required to achieve positive outcomes and minimize complications. The multidisciplinary team should include the patient, dietitian, infusion pharmacist, physician/lip and nurse 2
3 Definition Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN A highly concentrated form of parenteral nutrition that is given through a central vein Contains a dextrose solution of greater than 10%. Higher glucose concentrations should be administered through a central vascular access device (CVAD) because the high venous flow rate rapidly dissipates the high osmolarity. Indicated for parenteral nutrition needed for more than 7 days Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN) Satisfies all body requirements Can be short term (providing nutrition during critical illness) or long term (providing nutrition for chronic illnesses for months or years) May be a continuous or cyclical infusion (TPN and PPN) - If cyclical, specific tapering schedule must be ordered. - Cyclical PN is usually administered at night - Cyclical must be for patient s convenience, not to meet the needs of facility staffing Definition Peripheral Parenteral Nutrition (PPN) May be administered through a peripheral vein and has a lower concentration of glucose that should not exceed 10%. Higher concentrations of glucose have a higher osmolarity that can cause damage to the peripheral venous endothelium, increasing the risk for venous thrombosis and sclerosis. PPN has fewer calories than TPN and usually the larger percentage of calories are provided by lipids rather than carbohydrates. PPN is indicated for parenteral nutrition needed for less than 7 days. 3
4 Peripheral Parenteral Nutrition (PPN) Parenteral nutrition may be given through a peripheral access device if: o Dextrose concentration is equal to or less than 10% o Amino acid concentration is equal to or less than 5% Short peripheral vascular access sites must be rotated every hours, and as needed. Goals of Parenteral Nutrition The goals of parenteral nutrition therapy include : Preventing unwanted weight loss and skin breakdown Promoting positive nitrogen balance Maintaining visceral and somatic protein stores The patient needs adequate caloric and protein intake to achieve these goals. The Keys to Successful Parenteral Nutrition Therapy Illness and injury promote catabolism and hypermetabolism. The patient is burning calories faster to keep up with his body s demands. If adequate nutrition is not provided, the body will break down lean muscle for glucose, which could slow healing and prolong recovery. Providing adequate nutrition through administration of parenteral nutrition will reduce morbidity and mortality, promote tissue repair, and enhance immune system response. 4
5 Indications for Parenteral Nutrition Patient cannot tolerate oral/enteral nutrition for extended periods Complete bowel rest indicated GI dysfunction number one indication for TPN - Inflammatory bowel disease, short bowel syndrome, pancreatitis, bowel obstruction, fistula, intractable diarrhea, malabsorption Hepatic failure Indications for Parenteral Nutrition Hypermetabolic state (e.g., burns, sepsis) Immunosuppressed states (e.g., AIDS, bone marrow transplants) Delayed wound healing Hyperemesis associated with pregnancy Anorexia Parenteral nutrition is NOT routinely used if patient has an intact GI tract. If the GUT works use it! Parenteral Nutrition Risks Increased risk of infection and metabolic complications PN does not preserve GI tract structure and function Is a patient who has had a stroke, and cannot swallow, a candidate for PN? 5
6 Components of Parenteral Nutrition Solution Water 30 to 40 ml/kg/day Carbohydrates 4-5 grams/kg/day In the form of dextrose (up to 25% dextrose as final concentration) Primary source of energy (calories) Spares protein Components of Parenteral Nutrition Solution Protein In the form of amino acids 1-3 grams/kg/day depending on clinical status Illness and infection increases the body s protein requirements Needed for tissue maintenance, growth and repair Components of Parenteral Nutrition Solution Fats (Lipid Emulsion) Secondary source of energy after carbohydrates May contain triglycerides, egg phospholipids, glycerol, soybean and water 20-30% of calories may be in the form of lipids Prevents essential fatty acid deficiency (EFAD) Concentration of 10-30% Lipids can be mixed with PN solution (3:1 solution) Lipids may be given as a separate infusion Check for allergy to egg or soybean prior to administering lipids/ or solutions containing lipids 6
7 Components of Parenteral Nutrition Solution Electrolytes and Trace Elements (Minerals) Electrolytes play a critical role in all body functions Trace elements are minerals needed for normal metabolism Requirements based on individual needs, lab results (fax to pharmacist) Added by pharmacist Components of Parenteral Nutrition Solution Additives Due to instability, some additives must be added to the solution container by the nurse just prior to administration All additives must be compatible with parenteral nutrition solution Additives added by the nurse may include: Vitamins Insulin Heparin H2 Antagonists Components of Parenteral Nutrition Solution Additives May be in glass ampules (must use filter straw to withdraw from ampules) No more than 3 additives (using no more than 2 punctures into the solution container) may be added by the nurse to a parenteral nutrition solution. If more than 3 additives are ordered consult with the infusion pharmacist for guidance. A transfer device may need to be used. 7
8 Filters Parenteral nutrition solution needs to be filtered Lipids do not require an inline filter if administered separately A 2:1 PN solution (does not contain lipids) only requires a 0.2 micron filter No additional filter required if piggybacking lipids into the lower Y-site of a PN 0.2 micron administration set (note: the Y-site is located below the 0.2 micron filter) If lipids are piggybacked into a higher Y-site above the filter, an administration set containing a 1.2 micron filter must be used Admitting the Parenteral Nutrition Patient PN Admission Criteria The facility must provide the pharmacy with advance notice when a decision is made to accept a patient receiving total parenteral nutrition (TPN) or peripheral (partial) parenteral nutrition (PPN). To ensure safe management of the patient requiring parenteral nutrition, the following information must be obtained prior to admission: Medical necessity for parenteral nutrition Medical history, medical treatments, medication and allergy profiles, laboratory test results, functional status Nutritional habits, food and drug allergies, previous enteral and parenteral treatment, and dietary consult Appropriate vascular access device 8
9 Parenteral Nutrition/Clinimix Initiative Goal To provide a quality PN product to meet the needs of LTC patients Innovative Solution to Current PN Challenges Increased demands for PN in LTC Shortages of many of components of Parenteral Nutrition formula Increased need to provide PN to remote locations Looking more closely at patients that are receiving hydration for extended periods of time and quickly assessing for, and providing, PPN as a solution Advantages of Pre-mixed/Clinimix Commercially prepared under the most stringent sterile compounding practices End-product sterilization Fewer concerns with drug shortages Adverse reactions seen by 56% with commercial vs. 76% with compounded PN1 Advantages of Pre-mixed/Clinimix Reduced ordering complexity for the clinician PN readily available (facilities with high PN utilization may have formulas available in e-kit) Reduced formula manipulations/errors Extended shelf life 9
10 Clinimix vs. Compounded PN Clinimix may not meet the needs of patients that are: Fluid restricted (e.g., hemodialysis) In need of large protein amounts (e.g., burns) In need of electrolyte replacement (e.g., severe electrolyte abnormalities) These patients may benefit from compounded PN Pre-mixed TPN/PPN Solutions Clinimix and Clinimix E Clinimix is a pre-mixed TPN solution containing amino acids and dextrose, the same components that are in customized TPN solutions Clinimix E contains amino acids, dextrose and a standard amount of electrolytes* *(Clinimix E contains (per liter): Na + 35mEq/L, K + 30mEq/L, Mg ++ 5mEq/L, Ca mEq/L, PO 4 15 mmol/l) The first number in the formulation name corresponds to the % amino acids and the second is the dextrose concentration (e.g., Clinimix 4.25/10 = 4.25% Amino Acids and 10% Dextrose) Pre-mixed Clinimix Formulations Sterile, non-pyrogenic, hypertonic solution manufactured in a dual-chamber container One chamber contains sulfite-free amino acids % One chamber contains dextrose 5-25% Add in lipids (3-in-1) or infuse separately (2-in-1) Available with and without electrolytes 1- and 2-liter volumes Central and peripheral formulations Can add in additives such as insulin, vitamins, etc. Dextrose chamber (with or without calcium) Injection port (medications, trace elements, multiple vitamins) Seal Amino acid chamber (with or without electrolytes) Administration port Additive port (lipid) Clinimix [package insert]. Deerfield, IL: Baxter Healthcare Corporation;
11 Pre-mixed TPN/PPN Solutions Administering Clinimix and Clinimix E Prior to administration, the amino acid chamber must be mixed with the dextrose chamber In most cases, the pharmacy will mix the contents in the sterile compounding area and add additional electrolytes and lipids. When this is done, the bag will need to be refrigerated prior to use. Remove from the refrigerator prior to administration (at least one hour per liter). Parenteral Nutrition Orders Verbal orders are not acceptable The attending physician/lip may request that the previous provider s formulation be continued. The pharmacist will use the previous provider s formulation as a template for reducing the formulation to writing and converting ingredient units of measure to match the units of measure on pharmacy label. Fax current hospital parenteral nutrition orders to infusion pharmacy as soon as admission is anticipated Parenteral Nutrition Orders Call infusion pharmacy to verify receipt of orders Pharmacist will reduce hospital orders to writing on TPN/PPN Order Form and fax back to facility The formulation reduced to writing by the pharmacy will NOT be considered a valid order until the physician/lip has reviewed and signed the order, or reviewed and authorized by telephone order 11
12 Parenteral Nutrition Orders Physician/LIP orders should include: Parenteral nutrition solution Additives Volume and rate Continuous or cyclical (if cyclical, specific tapering schedule must be ordered) VAD flush protocol Laboratory monitoring Parenteral Nutrition Orders Physician/LIP orders should include (cont): Daily/weekly weights Vital signs Blood glucose monitoring Intake and output Back-up D 10 W solution or pre-made standard TPN formulation (i.e. Clinimix) in the event of unplanned interruption of TPN solution *D 10 W may be administered through a peripheral access device via an manual flow-control device if an electronic infusion device is not available Parenteral Nutrition Orders Labs: Baseline recommended on admission Blood sampling is not recommended via the lumen used to administer TPN/PPN If the patient has a single-lumen catheter, blood sampling should be drawn by accessing a peripheral vein Fax all lab results to infusion pharmacy as soon as they are available from lab provider. Call pharmacy to verify receipt of results. Adjustments to formula are based on lab results. Abnormal lab results may also indicate presence of PN related complication(s). 12
13 Parenteral Nutrition Orders Weights: - Baseline recommended on admission - Ongoing weights per physician/lip orders or per suggested monitoring - Must be accurate: same time each day, same scale, same clothing, etc. Vital Signs: - Baseline recommended on admission - Per physician/lip orders Parenteral Nutrition Orders Glucose monitoring and insulin coverage using sliding scale: - Glucose monitoring should be performed per physician/lip orders or per suggested monitoring - Orders should also include specific parameters for physician/lip notification - Orders should include specific insulin doses for coverage, if applicable Intake and Output - Per physician/lip orders or per suggested monitoring - Document every shift Suggested PN Monitoring Schedule 13
14 Omnicare PN Prescription Form Completing the PN Prescription Form Fill in the patient demographics Completing the PN Prescription Form Step 1 14
15 Completing the PN Prescription Form Step 2. Select Trace Elements Completing the PN Prescription Form Step 3. Select Lipids Completing the PN Prescription Form Step 4. Select Additional Additives 15
16 Completing the PN Prescription Form Step 5. Select Additional Orders Completing the PN Prescription Form Signatures Assessment of Vascular Access Device (VAD) Identify Type of VAD Location Single vs. multiple-lumen Parenteral nutrition should be administered via a dedicated lumen Tunneled, non-tunneled, PICC, implanted port, peripheral site (for PPN only) Note Date of Insertion Infection control issues Short-term non-tunneled may need to be replaced 16
17 Assessment of Vascular Access Device (VAD) Verification of Tip Placement If CVAD, obtain confirmation of tip placement in superior vena cava (SVC) from party responsible for insertion Must have SVC tip location to be considered CVAD Document tip location in patient s chart Request order for STAT, portable CXR if report/results are not readily available from insertion facility Assessment of Vascular Access Device (VAD) Assessment of Vascular Access Device (VAD) Site Assessment Observe/document any redness, swelling, tenderness, drainage, leaking or other IV related complication If suspected IV related complication exists, take appropriate nursing action Note condition of sutures, if present Measure external catheter length to evaluate for catheter migration (compare to previous measurements) 17
18 Steps to Administration Clean work area using appropriate disinfectant Wash hands Choose a low traffic area free of dust, currents of air and conversation Be as meticulous as possible: remember, when PN is prepared at the pharmacy preparation is done in a clean room under a laminar flow hood Steps to Administration Parenteral nutrition solution should be removed from the refrigerator prior to infusion: ml or less = 1 hour prior to infusion ml = 2 hours prior to infusion ml = 3 hours prior to infusion NEVER use a microwave or warm water bath to warm solution Check expiration date Use containers in numerical order/or per most recent physician/lip order Steps to Administration Inspect container for leaks, discoloration, cloudiness, precipitate or separation of solution ( oiling out or cracking) 18
19 Steps to Administration Compare container label with order sheet Verify the label on the PN container for accuracy with the most current physician/lip order prior to initiating an infusion Steps to Administration (cont) Gather Supplies - Administration set and appropriate filter (0.22 micron vs. 1.2 micron) - Solution container - Additive vials - Safety syringes and needles - Alcohol pads - Filter straw (if drawing additives up from glass ampules) - Additive labels - Appropriate flush solutions based on VAD - Needleless connector - Gloves - Transfer Device when adding more than 2 additives Steps to Administration (cont) Electronic Infusion Device All parenteral nutrition must be administered via an electronic infusion device 19
20 Additives Many additives have limited stability in solution and must be added by the nurse just prior to hanging PN No more than 3 additives (using no more than 2 punctures into the solution container) may be added by the nurse to parenteral nutrition. If more than 3 additives are ordered, consult with infusion pharmacist for guidance. Management of Complications of PN Therapy Management of Complication of PN Therapy 20
21 Management of Complication of PN Therapy Parenteral Nutrition Administration Checklist Documentation Label Solution container Administration set VAD lumens MAR/POS 21
22 Documentation Nursing Progress Notes Date and time Flushing agent(s) Medication additives/solution Volume and rate Tapering schedule, if ordered Site assessment Complications and interventions Patient response to procedure and/or medication Intake and Output Totals Weights Vital Signs Documentation Documentation 22
23 Documentation Documentation Documentation 23
24 Documentation Documentation Documentation 24
25 Preparation and Administration of Parenteral Nutrition Skills Checklist Next Steps Complete Exam with an 80% or above Receive an with your Certificate of Completion Schedule practicum with your local Omnicare Pharmacy, or your employer 25
Jo Kuehn, RN, MSN, CPHQ Jenell Westhoven, RN, BSN
 Jo Kuehn, RN, MSN, CPHQ Jenell Westhoven, RN, BSN Disclosure Information Intravenous Therapy and Parenteral Nutrition Administration: Nursing In- Focus Jo Kuehn, RN, MSN, CPHQ and Jenell Westhoven, RN,
Jo Kuehn, RN, MSN, CPHQ Jenell Westhoven, RN, BSN Disclosure Information Intravenous Therapy and Parenteral Nutrition Administration: Nursing In- Focus Jo Kuehn, RN, MSN, CPHQ and Jenell Westhoven, RN,
PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: PARENTERAL NUTRITION AND INTRAVENOUS FAT EMULSION (ADULT AND PEDIATRICS) Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN II 12/80
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: PARENTERAL NUTRITION AND INTRAVENOUS FAT EMULSION (ADULT AND PEDIATRICS) Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN II 12/80
Chapter 64 Administration of Injectable Medications
 Chapter 64 Administration of Injectable Medications Injectable Medications Injection or intravenous (IV) infusion More invasive than administration by mouth, rectum, or through the skin Common methods
Chapter 64 Administration of Injectable Medications Injectable Medications Injection or intravenous (IV) infusion More invasive than administration by mouth, rectum, or through the skin Common methods
Unit 11. Objectives. Indications for IV Therapy. Intravenous Access Devices & Common IV Fluids. 3 categories. Maintenance Replacement Restoration
 Unit 11 Fluids, Electrolytes and Acid Base Imbalances Intravenous Access Devices & Common IV Fluids Objectives Review the purpose and types of intravenous (IV) therapy. Recall the nursing care related
Unit 11 Fluids, Electrolytes and Acid Base Imbalances Intravenous Access Devices & Common IV Fluids Objectives Review the purpose and types of intravenous (IV) therapy. Recall the nursing care related
Methods of Nutrition Support KNH 406
 Methods of Nutrition Support KNH 406 Malnutrition 30 50% of hospitalized patients 95% of nursing home patients Resulting in reduced quality of life & increased health care costs May be remedied by providing
Methods of Nutrition Support KNH 406 Malnutrition 30 50% of hospitalized patients 95% of nursing home patients Resulting in reduced quality of life & increased health care costs May be remedied by providing
IDPN. A Piece of the Puzzle for Dialysis Patients Nutrition. Toll Free: Toll Free:
 IDPN A Piece of the Puzzle for Dialysis Patients Nutrition Toll Free: 844-633-3448 Toll Free: 844-633-3448 Executive Infusion is pleased to announce our nutritional services which include Intradialytic
IDPN A Piece of the Puzzle for Dialysis Patients Nutrition Toll Free: 844-633-3448 Toll Free: 844-633-3448 Executive Infusion is pleased to announce our nutritional services which include Intradialytic
Central Line Care and Management
 Central Line Care and Management What is a Central Line/ CVAD? (central venous access device) A vascular infusion device that terminates at or close to the heart or in one of the great vessels (aorta,
Central Line Care and Management What is a Central Line/ CVAD? (central venous access device) A vascular infusion device that terminates at or close to the heart or in one of the great vessels (aorta,
IV Fluids. Nursing B23. Objectives. Serum Osmolality
 IV Fluids Nursing B23 Objectives Discuss the purpose of IV Discuss nursing interventions in IV therapy Identify complications of IV therapy Differentiate between peripheral line, central line, and PICC
IV Fluids Nursing B23 Objectives Discuss the purpose of IV Discuss nursing interventions in IV therapy Identify complications of IV therapy Differentiate between peripheral line, central line, and PICC
IV Fluids Nursing B23 Objectives Serum Osmolality 275 to 295 Isotonic
 1 IV Fluids Nursing B23 2 Objectives 3 Serum Osmolality Serum osmolality solute concentration of a solution Higher osmolality means greater pulling power for water Normal serum osmolality is 275 to 295
1 IV Fluids Nursing B23 2 Objectives 3 Serum Osmolality Serum osmolality solute concentration of a solution Higher osmolality means greater pulling power for water Normal serum osmolality is 275 to 295
Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention?
 Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? 1 Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention? Key questions to ask with initial consultation Can the gastrointestinal (GI) tract be utilized? Can the GI tract be
Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? 1 Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention? Key questions to ask with initial consultation Can the gastrointestinal (GI) tract be utilized? Can the GI tract be
Home Total Parenteral Nutrition
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Home Total Parenteral Nutrition This information will help teach you and your caregiver how to give total parenteral nutrition (TPN) at home. You will also receive a copy
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Home Total Parenteral Nutrition This information will help teach you and your caregiver how to give total parenteral nutrition (TPN) at home. You will also receive a copy
Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition
 Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition Carol J Rollins, MS, RD, PharmD, BCNSP Coordinator, Nutrition Support Team The University of Arizona Medical Center www.nutritioncare.org Conflict of Interest None
Drug Shortages with Parenteral Nutrition Carol J Rollins, MS, RD, PharmD, BCNSP Coordinator, Nutrition Support Team The University of Arizona Medical Center www.nutritioncare.org Conflict of Interest None
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Indication See algorithm. Timing Start TPN as indicated on algorithm 1. There is no need to build up TPN volume. The volume of TPN (including lipids) should equate to the total
TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Indication See algorithm. Timing Start TPN as indicated on algorithm 1. There is no need to build up TPN volume. The volume of TPN (including lipids) should equate to the total
Vaxcel Implantable Ports Valved and Non-Valved. A Patient s Guide
 Vaxcel Implantable Ports Valved and Non-Valved A Patient s Guide Vaxcel Implantable Port This pamphlet provides some answers to questions you may have about your implantable port and how to care for it
Vaxcel Implantable Ports Valved and Non-Valved A Patient s Guide Vaxcel Implantable Port This pamphlet provides some answers to questions you may have about your implantable port and how to care for it
Parenteral Nutrition in the Hospitalized Patient: which VAD, which policies? Rob Dawson DNP, MSA, APRN, ACNP-BC, VA-BC USA
 Parenteral Nutrition in the Hospitalized Patient: which VAD, which policies? Rob Dawson DNP, MSA, APRN, ACNP-BC, VA-BC USA Disclosure Consultant, Vascular Access Consultants LLC: Analogic, Inc / BK Ultrasound
Parenteral Nutrition in the Hospitalized Patient: which VAD, which policies? Rob Dawson DNP, MSA, APRN, ACNP-BC, VA-BC USA Disclosure Consultant, Vascular Access Consultants LLC: Analogic, Inc / BK Ultrasound
Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition
 Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition Audis Bethea, Pharm.D. Assistant Professor Therapeutics I December 5 & 9, 2003 Parenteral Nutrition Definition process of supplying nutrients via the intravenous route
Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition Audis Bethea, Pharm.D. Assistant Professor Therapeutics I December 5 & 9, 2003 Parenteral Nutrition Definition process of supplying nutrients via the intravenous route
1/22/2016. Disclaimer. Disclaimer
 Disclaimer Omnicare, Inc., as a provider of Infusion Pharmacy Services, is committed to the establishment and maintenance of the highest quality of care in infusion therapy services. This Infusion Therapy
Disclaimer Omnicare, Inc., as a provider of Infusion Pharmacy Services, is committed to the establishment and maintenance of the highest quality of care in infusion therapy services. This Infusion Therapy
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: INTERMITTENT FLUID AND MEDICATION THERAPY Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN I, LPN II Per Job Description 03/81 8/09
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: INTERMITTENT FLUID AND MEDICATION THERAPY Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN I, LPN II Per Job Description 03/81 8/09
Infusion Skills Competency Checklist To be used at annual skills fair or at any other time for IV Competency
 Employee Profile Infusion Skills Checklist Last Name First Name Middle Initial Employee Number Employee Discipline Check one: RN LPN Per state specific LPN Practice Acts Direct Supervisor s Name: Date
Employee Profile Infusion Skills Checklist Last Name First Name Middle Initial Employee Number Employee Discipline Check one: RN LPN Per state specific LPN Practice Acts Direct Supervisor s Name: Date
Chapter 8 ADMINISTRATION OF BLOOD COMPONENTS
 Chapter 8 ADMINISTRATION OF BLOOD COMPONENTS PRACTICE POINTS Give the right blood product to the right patient at the right time. Failure to correctly check the patient or the pack can be fatal. At the
Chapter 8 ADMINISTRATION OF BLOOD COMPONENTS PRACTICE POINTS Give the right blood product to the right patient at the right time. Failure to correctly check the patient or the pack can be fatal. At the
Central Venous Catheter Care and Maintenance (includes catheter troubleshooting guide)
 Central Venous Catheter Care and Maintenance (includes catheter troubleshooting guide) A Guide for Patients in the Home Phone Number: Nurse/Contact: Central Venous Catheters This manual is a guide for
Central Venous Catheter Care and Maintenance (includes catheter troubleshooting guide) A Guide for Patients in the Home Phone Number: Nurse/Contact: Central Venous Catheters This manual is a guide for
The University of Toledo Medical Center and its Medical Staff
 Name of Policy: Policy Number: Department: 3364-109-GEN-705 Infection Control Medical Staff Hospital Administration Approving Officer: Responsible Agent: Scope: Chair, Infection Control Committee Chief
Name of Policy: Policy Number: Department: 3364-109-GEN-705 Infection Control Medical Staff Hospital Administration Approving Officer: Responsible Agent: Scope: Chair, Infection Control Committee Chief
NOTE: The first appearance of terms in bold in the body of this document (except titles) are defined terms please refer to the Definitions section.
 TITLE PARENTERAL NUTRITION ADMINISTRATION AND MONITORING SCOPE Provincial: Acute Care APPROVAL AUTHORITY Clinical Operations Executive Committee SPONSOR Pharmacy Services, Nutrition Services, and Health
TITLE PARENTERAL NUTRITION ADMINISTRATION AND MONITORING SCOPE Provincial: Acute Care APPROVAL AUTHORITY Clinical Operations Executive Committee SPONSOR Pharmacy Services, Nutrition Services, and Health
Nutrition Therapy. Medical Coverage Policy Enteral/Parenteral EFFECTIVE DATE: POLICY LAST UPDATED: 11/20/2018 OVERVIEW
 Medical Coverage Policy Enteral/Parenteral Nutrition Therapy EFFECTIVE DATE: 01 20 2007 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 11/20/2018 OVERVIEW This policy describes the reimbursement for enteral and parenteral nutrition
Medical Coverage Policy Enteral/Parenteral Nutrition Therapy EFFECTIVE DATE: 01 20 2007 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 11/20/2018 OVERVIEW This policy describes the reimbursement for enteral and parenteral nutrition
Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition in the Home. Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 1.02.01 Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition in the Home Medical Policy Section Durable Medical Equipment Issue Original Policy Date Last Review Status/Date Return to Medical Policy Index
MP 1.02.01 Total Parenteral Nutrition and Enteral Nutrition in the Home Medical Policy Section Durable Medical Equipment Issue Original Policy Date Last Review Status/Date Return to Medical Policy Index
Nutrition Services at a glance
 Nutrition Services at a glance Ragini Raghuveer, MS, RD, LD/N Systems Clinical Nutrition Manager Linette De Armas, RD, LD/N Clinical Dietitian Melissa Lorenzo, RD, LD/N Clinical Dietitian 1 Learning Objectives
Nutrition Services at a glance Ragini Raghuveer, MS, RD, LD/N Systems Clinical Nutrition Manager Linette De Armas, RD, LD/N Clinical Dietitian Melissa Lorenzo, RD, LD/N Clinical Dietitian 1 Learning Objectives
Current concepts in Critical Care Nutrition
 Current concepts in Critical Care Nutrition Dr.N.Ramakrishnan AB (Int Med), AB (Crit Care), MMM, FACP, FCCP, FCCM Director, Critical Care Services Apollo Hospitals, Chennai Objectives Why? Enteral or Parenteral
Current concepts in Critical Care Nutrition Dr.N.Ramakrishnan AB (Int Med), AB (Crit Care), MMM, FACP, FCCP, FCCM Director, Critical Care Services Apollo Hospitals, Chennai Objectives Why? Enteral or Parenteral
If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to to view current policies.
 If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to www.fairview.org/fhipolicies to view current policies. Department Policy Code: D: PC-5555 Entity: Fairview Pharmacy Services
If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to www.fairview.org/fhipolicies to view current policies. Department Policy Code: D: PC-5555 Entity: Fairview Pharmacy Services
ASEPTIC DISPENSING TECHNIQUES/DRUG- NUTRIENT INTERACTIONS
 ASEPTIC DISPENSING TECHNIQUES/DRUG- NUTRIENT INTERACTIONS HARBANS KAUR DHILLON PRESIDENT OF PENSMA KUALA LUMPUR MALAYSIA PENSA 2007 University Malaya Medical Centre Kuala Lumpur ASEPTIC DISPENSING Ppn
ASEPTIC DISPENSING TECHNIQUES/DRUG- NUTRIENT INTERACTIONS HARBANS KAUR DHILLON PRESIDENT OF PENSMA KUALA LUMPUR MALAYSIA PENSA 2007 University Malaya Medical Centre Kuala Lumpur ASEPTIC DISPENSING Ppn
IV therapy. By: Susan Mberenga, RN, MSN. Copyright 2016, 2013, 2010, 2006, 2002 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
 IV therapy By: Susan Mberenga, RN, MSN 1 IV Therapy Types of solutions Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic Caution: Too rapid or excessive infusion of any IV fluid has the potential to cause serious problems
IV therapy By: Susan Mberenga, RN, MSN 1 IV Therapy Types of solutions Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic Caution: Too rapid or excessive infusion of any IV fluid has the potential to cause serious problems
Effect of changing lipid formulation in Parenteral Nutrition in the Newborn Experimental Pathology BSc
 Effect of changing lipid formulation in Parenteral Nutrition in the Newborn Experimental Pathology BSc Word count: 6939 0 CONTENTS Abstract...2 Acknowledgements...3 Introduction...4 Materials and Methods...11
Effect of changing lipid formulation in Parenteral Nutrition in the Newborn Experimental Pathology BSc Word count: 6939 0 CONTENTS Abstract...2 Acknowledgements...3 Introduction...4 Materials and Methods...11
STANDARDIZED PROCEDURE REPROGRAMMING AND REFILLING INTRATHECAL BACLOFEN PUMPS and ACCESSING THE CATHETER ACCESS PORT (Adult,Peds)
 I. Definition The purpose of this procedure is to allow the Advanced Health Practitioner (AHP) to reprogram and refill intrathecal Baclofen pumps, as well as access the catheter access port for those AHPs
I. Definition The purpose of this procedure is to allow the Advanced Health Practitioner (AHP) to reprogram and refill intrathecal Baclofen pumps, as well as access the catheter access port for those AHPs
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter (PICC) Booklet
 Aintree University Hospital FT PICC Booklet: a real world example This local booklet is an example used in the NICE medical technology guidance adoption support resource for SecurAcath for securing percutaneous
Aintree University Hospital FT PICC Booklet: a real world example This local booklet is an example used in the NICE medical technology guidance adoption support resource for SecurAcath for securing percutaneous
Nutrition care plan for surgical patients. Objectives
 Slide 1 Nutrition care plan for surgical patients Surgical Nutrition Training Module Level 1 Philippine Society of General Surgeons Committee on Surgical Training In this session we will discuss the most
Slide 1 Nutrition care plan for surgical patients Surgical Nutrition Training Module Level 1 Philippine Society of General Surgeons Committee on Surgical Training In this session we will discuss the most
Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick Neonatal Pharmacist
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Designation: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Designation: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Dr M Hogan, Maire Cullen ANNP, Una Toland Ward Manager, Sandra Kilpatrick
Central Venous Access Devices. Stephanie Cunningham Amy Waters
 Central Venous Access Devices Stephanie Cunningham Amy Waters 5 Must Know Facts About CVAD s 1) What are CVAD s? 2) What are CVAD s used for? 3) How are these devices put in? 4) What are the complications
Central Venous Access Devices Stephanie Cunningham Amy Waters 5 Must Know Facts About CVAD s 1) What are CVAD s? 2) What are CVAD s used for? 3) How are these devices put in? 4) What are the complications
Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients. Hamdy Amin, Pharm.D., MBA, BCNSP Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
 Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy Amin, Pharm.D., MBA, BCNSP Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Disclosure Information Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy
Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy Amin, Pharm.D., MBA, BCNSP Riyadh, Saudi Arabia Disclosure Information Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition in Hemodialysis Patients Hamdy
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition. in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT. Dzulfikar DLH. Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit
 The Role of Parenteral Nutrition in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Dzulfikar DLH Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Department of Child Health, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjajaran, Hasan
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Dzulfikar DLH Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Department of Child Health, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjajaran, Hasan
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION. Dextrose Injection USP. (Concentrated Dextrose for Intravenous Administration) 50% (500 mg/ml) Fluid and Nutrient Replenisher
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION Dextrose Injection USP (Concentrated Dextrose for Intravenous Administration) 50% (500 mg/ml) Fluid and Nutrient Replenisher Pfizer Canada Inc. 17300 Trans-Canada Highway Kirkland,
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION Dextrose Injection USP (Concentrated Dextrose for Intravenous Administration) 50% (500 mg/ml) Fluid and Nutrient Replenisher Pfizer Canada Inc. 17300 Trans-Canada Highway Kirkland,
Pharmaceutical Services Offered in Hospitals
 Pharmaceutical Services Offered in Hospitals Product Services Research Services Teaching Services Support Services Clinical Services In-patients (hospitalized) Out-patients (ambulatory) In-patients (hospitalized)
Pharmaceutical Services Offered in Hospitals Product Services Research Services Teaching Services Support Services Clinical Services In-patients (hospitalized) Out-patients (ambulatory) In-patients (hospitalized)
TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 19 March Date of the Marketing Authorisation (national procedure): 18 December 1997
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 March 2008 INTRALIPIDE 20 PER CENT, emulsion for infusion 100 ml in Excel container (PE/PP) (CIP: 355 096-5) 250
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 19 March 2008 INTRALIPIDE 20 PER CENT, emulsion for infusion 100 ml in Excel container (PE/PP) (CIP: 355 096-5) 250
ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Central Venous Access Devices
 For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Central Venous Access Devices Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather,
For faculty use only Educator s name Score Date ATI Skills Modules Checklist for Central Venous Access Devices Student s name Date Verify order Patient record Assess for procedure need Identify, gather,
Emergency clamp should always be readily available in case of accidental catheter fracture
 Note: Please see individual policies for further information. Flushing best practice: Always use a 10 diameter syringe or larger when first accessing and when flushing vascular access device (VAD) Use
Note: Please see individual policies for further information. Flushing best practice: Always use a 10 diameter syringe or larger when first accessing and when flushing vascular access device (VAD) Use
MEDICAL POLICY: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition
 POLICY: PG0114 ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE: 02/15/07 LAST REVIEW: 08/14/18 MEDICAL POLICY: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition GUIDELINES This policy does not certify benefits or authorization of benefits, which is
POLICY: PG0114 ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE: 02/15/07 LAST REVIEW: 08/14/18 MEDICAL POLICY: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition GUIDELINES This policy does not certify benefits or authorization of benefits, which is
Home Total Parenteral Nutrition for Adults
 Home Total Parenteral Nutrition for Adults Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.08.007 05/21/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: PPO, HMO, QUEST Integration 05/27/2016 Section: Home
Home Total Parenteral Nutrition for Adults Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.08.007 05/21/1999 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: PPO, HMO, QUEST Integration 05/27/2016 Section: Home
4 PARENTERAL THERAPY
 WOMEN AND NEWBORN HEALTH SERVICE CLINICAL GUIDELINES SECTION A: GUIDELINES RELEVANT TO OBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY 4 PARENTERAL THERAPY 4.11 TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Authorised by: OGCCU Review Team:
WOMEN AND NEWBORN HEALTH SERVICE CLINICAL GUIDELINES SECTION A: GUIDELINES RELEVANT TO OBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY 4 PARENTERAL THERAPY 4.11 TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Authorised by: OGCCU Review Team:
Nutritional intervention in hospitalised paediatric patients. Dr Y.K.Amdekar
 Nutritional intervention in hospitalised paediatric patients Dr Y.K.Amdekar Back to basics Suboptimal nutrient intake is always dangerous in health and more so in disease to feed or not to feed is it a
Nutritional intervention in hospitalised paediatric patients Dr Y.K.Amdekar Back to basics Suboptimal nutrient intake is always dangerous in health and more so in disease to feed or not to feed is it a
Successful IV Starts Revised February 2014
 Successful IV Starts Revised February 2014 Why Intravenous Therapy? Used for access to the body s circulation Indications: Administer fluids, blood, medications, and nutrition Obtain laboratory specimens
Successful IV Starts Revised February 2014 Why Intravenous Therapy? Used for access to the body s circulation Indications: Administer fluids, blood, medications, and nutrition Obtain laboratory specimens
CENTRAL VENOUS ACCESS DEVICES. BETHANY COLTON
 CENTRAL VENOUS ACCESS DEVICES. BETHANY COLTON Aims and Objectives To know what central venous access devices (CVAD) are. Types of CVADS used in haematology. To understand why we use them To know the complications
CENTRAL VENOUS ACCESS DEVICES. BETHANY COLTON Aims and Objectives To know what central venous access devices (CVAD) are. Types of CVADS used in haematology. To understand why we use them To know the complications
Appendix E: Overview of Vascular
 Appendix E: Overview of Vascular 56 Peripheral Short Catheter, less than 3 inches (7.5 cm) in length; over-the-needle catheter is most common. Inserted by percutaneous venipuncture, generally into a hand
Appendix E: Overview of Vascular 56 Peripheral Short Catheter, less than 3 inches (7.5 cm) in length; over-the-needle catheter is most common. Inserted by percutaneous venipuncture, generally into a hand
MANAGEMENT OF INTRAVASCULAR (IV) LINES AND THERAPY. All GCC Countries
 TITLE/DESCRIPTION: MANAGEMENT OF INTRAVASCULAR (IV) LINES AND THERAPY INDEX NUMBER: EFFECTIVE DATE: APPLIES TO: ISSUING AUTHORITY: 01/01/2009 01/01/2013 All GCC Countries GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL CENTRE
TITLE/DESCRIPTION: MANAGEMENT OF INTRAVASCULAR (IV) LINES AND THERAPY INDEX NUMBER: EFFECTIVE DATE: APPLIES TO: ISSUING AUTHORITY: 01/01/2009 01/01/2013 All GCC Countries GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL CENTRE
Parenteral Nutrition in Oncology
 Parenteral Nutrition in Oncology Presenter: Pam Wagner, RD, CNSC Learning Objectives List indications for initiating PN in oncology patients Describe considerations when determining an appropriate candidate
Parenteral Nutrition in Oncology Presenter: Pam Wagner, RD, CNSC Learning Objectives List indications for initiating PN in oncology patients Describe considerations when determining an appropriate candidate
Intravenous Fluid and Drug Therapy
 11 Intravenous Fluid and Drug Therapy OUTLINE Overview Direct Intravenous Injections Continuous Intravenous Injections Solution Additives Calculating IV Components as Percentages Calculating IV Flow Rates
11 Intravenous Fluid and Drug Therapy OUTLINE Overview Direct Intravenous Injections Continuous Intravenous Injections Solution Additives Calculating IV Components as Percentages Calculating IV Flow Rates
CATHETER ACCESS KIT. For use with Prometra Programmable Infusion Systems
 CATHETER ACCESS KIT Caution: Federal (USA) Law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Table of Contents Contents... 3 Description... 3 Indications... 3 Contraindications... 3
CATHETER ACCESS KIT Caution: Federal (USA) Law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Table of Contents Contents... 3 Description... 3 Indications... 3 Contraindications... 3
How to Set Up and Infuse Your TPN
 Page 1 of 10 How to Set Up and Infuse Your TPN Important: Do not change any of the supplies listed here. Keep supplies away from children. Only your home care nurse or persons trained by Fairview Home
Page 1 of 10 How to Set Up and Infuse Your TPN Important: Do not change any of the supplies listed here. Keep supplies away from children. Only your home care nurse or persons trained by Fairview Home
If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to to view current policies.
 If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to www.fairview.org/fhipolicies to view current policies. Department Policy Code: D: PC-5575 Entity: Fairview Pharmacy Services
If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to www.fairview.org/fhipolicies to view current policies. Department Policy Code: D: PC-5575 Entity: Fairview Pharmacy Services
LOUISIANA MEDICAID PROGRAM ISSUED:
 37.12 TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Overview Introduction In This Section This Section explains the LMPBM program s Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN) therapy coverage, limitations, prior authorization, reimbursement
37.12 TOTAL PARENTERAL NUTRITION Overview Introduction In This Section This Section explains the LMPBM program s Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN) therapy coverage, limitations, prior authorization, reimbursement
Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition The Department of Health in England has asked NICE to develop a new guideline on parenteral nutrition in
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition The Department of Health in England has asked NICE to develop a new guideline on parenteral nutrition in
Department Policy. Code: D:PC Entity: Fairview Pharmacy Services. Department: Fairview Home Infusion. Manual: Policy and Procedure Manual
 Entity: Fairview Pharmacy Services Department: Fairview Home Infusion Manual: Policy and Procedure Manual Category: Home Infusion Subject: Midline (Extended Dwell Peripheral) Catheter Care and Management
Entity: Fairview Pharmacy Services Department: Fairview Home Infusion Manual: Policy and Procedure Manual Category: Home Infusion Subject: Midline (Extended Dwell Peripheral) Catheter Care and Management
Managing Fluid, Diet and Medications
 Managing Fluid, Diet and Medications This lesson covers: Fluid and body weight Managing your diet Understanding your medications It is important that you feel comfortable with the information and procedures
Managing Fluid, Diet and Medications This lesson covers: Fluid and body weight Managing your diet Understanding your medications It is important that you feel comfortable with the information and procedures
Curraheen, Co. Cork. Guidelines on the Management and Care of Central Venous Access Devices
 Curraheen, Co. Cork. Guidelines on the Management and Care of Central Venous Access Devices Date re-approved: 27 th Jan 2015. Version No: 2 Revision Due: 2018 Index code: CLIN028 Disclaimer: The information
Curraheen, Co. Cork. Guidelines on the Management and Care of Central Venous Access Devices Date re-approved: 27 th Jan 2015. Version No: 2 Revision Due: 2018 Index code: CLIN028 Disclaimer: The information
IR Central Venous Access [ ] Pre Procedure
![IR Central Venous Access [ ] Pre Procedure IR Central Venous Access [ ] Pre Procedure](/thumbs/90/104119758.jpg) IR Central Venous Access [1050200001] Pre Procedure Case Request/Scheduling Procedure Enter IR Case Request if not already completed (All hospitals except Grant Medical Center) [ ] Case Request IR Lab
IR Central Venous Access [1050200001] Pre Procedure Case Request/Scheduling Procedure Enter IR Case Request if not already completed (All hospitals except Grant Medical Center) [ ] Case Request IR Lab
Chapter 20. Assisting With Nutrition and Fluids
 Chapter 20 Assisting With Nutrition and Fluids Food and water: Are physical needs Basics of Nutrition Are necessary for life A poor diet and poor eating habits: Increase the risk for diseases and infection
Chapter 20 Assisting With Nutrition and Fluids Food and water: Are physical needs Basics of Nutrition Are necessary for life A poor diet and poor eating habits: Increase the risk for diseases and infection
Parenteral Nutrition. What is Parenteral Nutrition? Goals of Parenteral Nutrition
 Parenteral Nutrition Diamond Pharmacy Services What is Parenteral Nutrition? Intravenous feeding that provides a patient with fluids and essential nutrients during a time of gastrointestinal function disruption
Parenteral Nutrition Diamond Pharmacy Services What is Parenteral Nutrition? Intravenous feeding that provides a patient with fluids and essential nutrients during a time of gastrointestinal function disruption
Overview of CVADs. Type of device commonly used. Dwell time Flushing requirement Associated complications. lumens
 Source: Clinical Skills Management of Vascular Access Devices Pre-course handbook. Adapted with permission from NHS Lothian Employee and Education Development Team. Overview of CVADs Type of device Veins
Source: Clinical Skills Management of Vascular Access Devices Pre-course handbook. Adapted with permission from NHS Lothian Employee and Education Development Team. Overview of CVADs Type of device Veins
Procedures/Risks:central venous catheter
 Procedures/Risks:central venous catheter Central Venous Catheter Placement Procedure: Placement of the central venous catheter will take place in the Interventional Radiology Department (IRD) at The Ohio
Procedures/Risks:central venous catheter Central Venous Catheter Placement Procedure: Placement of the central venous catheter will take place in the Interventional Radiology Department (IRD) at The Ohio
CHEMOTHERAPY NETWORK GROUP POLICY FOR ADMINISTRATION OF CYTOTOXIC CHEMOTHERAPY
 CHEMOTHERAPY NETWORK GROUP POLICY FOR ADMINISTRATION OF CYTOTOXIC CHEMOTHERAPY Version 4.0 March 2016 Review date March 2018 Introduction It is the purpose of this policy to provide clear guidelines that
CHEMOTHERAPY NETWORK GROUP POLICY FOR ADMINISTRATION OF CYTOTOXIC CHEMOTHERAPY Version 4.0 March 2016 Review date March 2018 Introduction It is the purpose of this policy to provide clear guidelines that
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION. Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah
 PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah Johor Bahru Malnutrition INTRODUCTION pathologic state of varying severity with clinical features caused
PAEDIATRIC PARENTERAL NUTRITION Ezatul Mazuin Ayla binti Mamdooh Waffa Hospital Sultanah Aminah Johor Bahru Malnutrition INTRODUCTION pathologic state of varying severity with clinical features caused
Clinical Policy: Total Parenteral Nutrition and Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition Reference Number: CP.PHAR.205
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.PHAR.205 Effective Date: 05.16 Last Review Date: 02.18 See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Coding Implications
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.PHAR.205 Effective Date: 05.16 Last Review Date: 02.18 See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Coding Implications
Introduction to Clinical Nutrition
 M-III Introduction to Clinical Nutrition Donald F. Kirby, MD Chief, Section of Nutrition Division of Gastroenterology 1 Things We Take for Granted Air to Breathe Death Taxes Another Admission Our Next
M-III Introduction to Clinical Nutrition Donald F. Kirby, MD Chief, Section of Nutrition Division of Gastroenterology 1 Things We Take for Granted Air to Breathe Death Taxes Another Admission Our Next
Education for Self Administration of Intravenous Therapy HOME IV THERAPY PICC. Portacath
 HOME IV THERAPY PICC Portacath Who To contact Cardio-Respiratory Integrated Specialist Services (CRISS) Office hours 0800 1630 hours Ph: 364 0167 Weekends and after hours, phone Christchurch Hospital operator
HOME IV THERAPY PICC Portacath Who To contact Cardio-Respiratory Integrated Specialist Services (CRISS) Office hours 0800 1630 hours Ph: 364 0167 Weekends and after hours, phone Christchurch Hospital operator
Mary Lou Garey MSN EMT-P MedFlight of Ohio
 Mary Lou Garey MSN EMT-P MedFlight of Ohio Function Prolonged and frequent access to venous circulation Allows for patient to carry on normal life; decrease number of needle sticks Medications, parenteral
Mary Lou Garey MSN EMT-P MedFlight of Ohio Function Prolonged and frequent access to venous circulation Allows for patient to carry on normal life; decrease number of needle sticks Medications, parenteral
HOMES AND SENIORS SERVICES. APPROVAL DATE: February 2011 REVISION DATE: January 2015; July 2018
 POLICY: Page 1 of 6 A resident requiring enteral (tube) feeding as a sole source or adjunctive nutrition support have access to a comprehensive enteral feeding program and receive appropriate support from
POLICY: Page 1 of 6 A resident requiring enteral (tube) feeding as a sole source or adjunctive nutrition support have access to a comprehensive enteral feeding program and receive appropriate support from
Active UMMC Protocols
 UMMC CRRT 2018 Active UMMC Protocols 1. Standard CRRT Protocol PrismaFlex & NxStage CVVH with Fixed Ratio Regional Citrate Anticoagulation 2. No Anticoagulation Protocol PrismaFlex & NxStage CVVH with
UMMC CRRT 2018 Active UMMC Protocols 1. Standard CRRT Protocol PrismaFlex & NxStage CVVH with Fixed Ratio Regional Citrate Anticoagulation 2. No Anticoagulation Protocol PrismaFlex & NxStage CVVH with
Advancing Lives and the Delivery of Health Care. The High-Flow Port Designed for Apheresis
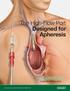 Advancing Lives and the Delivery of Health Care The High-Flow Port Designed for Apheresis Optimized for Long Device Life Bench Tested up to 1,000 Accesses 1 Bard is proud to introduce the first and only
Advancing Lives and the Delivery of Health Care The High-Flow Port Designed for Apheresis Optimized for Long Device Life Bench Tested up to 1,000 Accesses 1 Bard is proud to introduce the first and only
Patient information leaflet. Royal Surrey County Hospital. NHS Foundation Trust. Parenteral Nutrition. Nutrition Support Team (NST)
 Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Parenteral Nutrition Nutrition Support Team (NST) This leaflet gives you information to help you understand what parenteral
Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Parenteral Nutrition Nutrition Support Team (NST) This leaflet gives you information to help you understand what parenteral
Appropriate Use of Enteral Nutrition: Part 1 A Team-Based Approach to. Presented at A.S.P.E.N. s Clinical Nutrition Week January 24, 2012 Orlando, FL
 Appropriate Use of Enteral Nutrition: Part 1 A Team-Based Approach to Overcoming Clinical Barriers Presented at A.S.P.E.N. s Clinical Nutrition Week January 24, 2012 Orlando, FL According to the Commission
Appropriate Use of Enteral Nutrition: Part 1 A Team-Based Approach to Overcoming Clinical Barriers Presented at A.S.P.E.N. s Clinical Nutrition Week January 24, 2012 Orlando, FL According to the Commission
Parenteral Nutrition
 Approved by: Parenteral Nutrition Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures Manual :
Approved by: Parenteral Nutrition Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures Manual :
LIPOSYN III 30% Intravenous Fat Emulsion Pharmacy Bulk Package Not for Direct Infusion.
 LIPOSYN III 30% Intravenous Fat Emulsion Pharmacy Bulk Package Not for Direct Infusion. R x only DESCRIPTION Liposyn III 30% (Intravenous Fat Emulsion) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic fat emulsion for intravenous
LIPOSYN III 30% Intravenous Fat Emulsion Pharmacy Bulk Package Not for Direct Infusion. R x only DESCRIPTION Liposyn III 30% (Intravenous Fat Emulsion) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic fat emulsion for intravenous
Pharmaceutical risk management strategies for parenteral nutrition. J. Eastwood (UK)
 ESPEN Congress Leipzig 2013 Pharmaceutical Session Pharmaceutical risk management strategies for parenteral nutrition J. Eastwood (UK) Pharmaceutical risk management strategies for parenteral nutrition
ESPEN Congress Leipzig 2013 Pharmaceutical Session Pharmaceutical risk management strategies for parenteral nutrition J. Eastwood (UK) Pharmaceutical risk management strategies for parenteral nutrition
Chapter 11. Preparing and Handling Sterile Products and Hazardous Drugs. Paradigm Publishing, Inc. 1
 Chapter 11 Preparing and Handling Sterile Products and Hazardous Drugs Paradigm Publishing, Inc. 1 Preparing Intravenous Products IV route of administration can be used to Reach therapeutic drug serum
Chapter 11 Preparing and Handling Sterile Products and Hazardous Drugs Paradigm Publishing, Inc. 1 Preparing Intravenous Products IV route of administration can be used to Reach therapeutic drug serum
Aseptic Technique and Sterile Compounding
 Aseptic Technique and Sterile Compounding Chapter 12 1 Introduction Hospital technician crucial responsibility: Proper preparation of parenteral products Contamination must be reduced when preparing parenterals
Aseptic Technique and Sterile Compounding Chapter 12 1 Introduction Hospital technician crucial responsibility: Proper preparation of parenteral products Contamination must be reduced when preparing parenterals
A step-by-step preparation guide
 A step-by-step preparation guide For needle and needle-free systems This guide provides detailed instructions on the reconstitution, dilution, and storage of VELETRI. It is intended to be used after your
A step-by-step preparation guide For needle and needle-free systems This guide provides detailed instructions on the reconstitution, dilution, and storage of VELETRI. It is intended to be used after your
BAXTER INITIATES VOLUNTARY NATIONWIDE RECALL OF SELECT LOTS OF IV SOLUTIONS DUE TO THE POTENTIAL FOR LEAKING CONTAINERS AND PARTICULATE MATTER
 FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Media Contact: John O Malley (224) 948-5353 media@baxter.com Investor Contact: Clare Trachtman (224) 948-3085 BAXTER INITIATES VOLUNTARY NATIONWIDE RECALL OF SELECT LOTS OF IV SOLUTIONS
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Media Contact: John O Malley (224) 948-5353 media@baxter.com Investor Contact: Clare Trachtman (224) 948-3085 BAXTER INITIATES VOLUNTARY NATIONWIDE RECALL OF SELECT LOTS OF IV SOLUTIONS
Pharmacy Instructions for Preparation
 MARQIBO (vincristine sulfate LIPOSOME injection) Pharmacy Instructions for Preparation Important Information for Preparation 1 The instructions for the constitution of MARQIBO are provided in each kit.
MARQIBO (vincristine sulfate LIPOSOME injection) Pharmacy Instructions for Preparation Important Information for Preparation 1 The instructions for the constitution of MARQIBO are provided in each kit.
Amanda Hernandez FND Parenteral Nutrition Worksheet October 26, 2011
 Amanda Hernandez FND 430-001 Parenteral Nutrition Worksheet October 26, 2011 1. HP needs TPN because he has short bowel syndrome and his GI tract is not functional. His entire jejunum was and proximal
Amanda Hernandez FND 430-001 Parenteral Nutrition Worksheet October 26, 2011 1. HP needs TPN because he has short bowel syndrome and his GI tract is not functional. His entire jejunum was and proximal
Peel-Apart Percutaneous Introducer Kits for
 Bard Access Systems Peel-Apart Percutaneous Introducer Kits for Table of Contents Contents Page Bard Implanted Ports Hickman*, Leonard*, Broviac*, Tenckhoff*, and Groshong* Catheters Introduction....................................
Bard Access Systems Peel-Apart Percutaneous Introducer Kits for Table of Contents Contents Page Bard Implanted Ports Hickman*, Leonard*, Broviac*, Tenckhoff*, and Groshong* Catheters Introduction....................................
PARENTERAL NUTRITION THERAPY
 UnitedHealthcare Benefits of Texas, Inc. 1. UnitedHealthcare of Oklahoma, Inc. 2. UnitedHealthcare of Oregon, Inc. UnitedHealthcare of Washington, Inc. UnitedHealthcare West BENEFIT INTERPRETATION POLICY
UnitedHealthcare Benefits of Texas, Inc. 1. UnitedHealthcare of Oklahoma, Inc. 2. UnitedHealthcare of Oregon, Inc. UnitedHealthcare of Washington, Inc. UnitedHealthcare West BENEFIT INTERPRETATION POLICY
Understanding Your Medications
 PD Education Booklet 8 Understanding Your Medications What you will learn: Why your medications are important Medications your kidney doctor may prescribe, and what they do Medications that may be added
PD Education Booklet 8 Understanding Your Medications What you will learn: Why your medications are important Medications your kidney doctor may prescribe, and what they do Medications that may be added
Clinical Medical Policy Department Clinical Affairs Division DESCRIPTION
 Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN) [For the list of services and procedures that need preauthorization, please refer to www.mcs.com.pr go to Comunicados a Proveedores, and click Cartas Circulares.] Medical
Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN) [For the list of services and procedures that need preauthorization, please refer to www.mcs.com.pr go to Comunicados a Proveedores, and click Cartas Circulares.] Medical
MANITOBA RENAL PROGRAM
 MANITOBA RENAL PROGRAM SUBJECT Use of Closed Needleless Access Device with Hemodialysis Central Venous Catheters (CVC) SECTION CODE 30.20.04 30.20 Vascular Access AUTHORIZATION Professional Advisory Committee,
MANITOBA RENAL PROGRAM SUBJECT Use of Closed Needleless Access Device with Hemodialysis Central Venous Catheters (CVC) SECTION CODE 30.20.04 30.20 Vascular Access AUTHORIZATION Professional Advisory Committee,
Clinical Policy: Total Parenteral Nutrition and Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.163 Last Review Date: 04/18 See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Coding Implications Revision Log Parenteral
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.163 Last Review Date: 04/18 See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information. Coding Implications Revision Log Parenteral
Your pet s diabetes is manageable
 BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING SYSTEM Your pet s diabetes is manageable Treatment and Monitoring Plan for: Pet s Name: Clinic Name: Primary Vet: Clinic Phone No.: Clinic Email: Emergency Phone No: Today s Date:
BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING SYSTEM Your pet s diabetes is manageable Treatment and Monitoring Plan for: Pet s Name: Clinic Name: Primary Vet: Clinic Phone No.: Clinic Email: Emergency Phone No: Today s Date:
For the use of a registered medical practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only
 For the use of a registered medical practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only Intravenous Fat Emulsion NIRPID * Intravenous fat Emulsion DESCRIPTION: NIRPID * is a stable fat emulsion prepared from
For the use of a registered medical practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only Intravenous Fat Emulsion NIRPID * Intravenous fat Emulsion DESCRIPTION: NIRPID * is a stable fat emulsion prepared from
1/22/2016. Objectives. Vascular Access Devices
 Objectives 1. Discuss selection of appropriate vascular access device based on type and duration of prescribed therapy 2. Demonstrate correct procedure for short peripheral IV insertion including: preparation
Objectives 1. Discuss selection of appropriate vascular access device based on type and duration of prescribed therapy 2. Demonstrate correct procedure for short peripheral IV insertion including: preparation
Home Care Services HomeMed MedEQUIP Michigan Visiting Care Michigan Visiting Nurses Wheelchair Seating Service PROCEDURE
 UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITALS AND HEALTH CENTERS UMHHC-HCS: 253.054 First Approved Date: 3/2010 Home Care Services HomeMed MedEQUIP Michigan Visiting Care Michigan Visiting Nurses Wheelchair Seating
UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN HOSPITALS AND HEALTH CENTERS UMHHC-HCS: 253.054 First Approved Date: 3/2010 Home Care Services HomeMed MedEQUIP Michigan Visiting Care Michigan Visiting Nurses Wheelchair Seating
Intravenous Catheter Complications
 Vascular Access Device-Related Infection Inadequate skin antisepsis prior to VAD insertion Acute onset of fever, chills, and hypotension. No other apparent source of Notify Prescriber immediately Obtain
Vascular Access Device-Related Infection Inadequate skin antisepsis prior to VAD insertion Acute onset of fever, chills, and hypotension. No other apparent source of Notify Prescriber immediately Obtain
