The Primary Structure of Pig Liver Thioltransferase
|
|
|
- Marylou Atkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 262, No. 14, Issue of May 15, pp by The Amerian Soiety of Biologial Chemists, In. Printed in U.S.A. The Primary Struture of Pig Liver Thioltransferase Zhong-Ru Gan and William W. Wells$ From the Department of Biohemistry, Mihigan State University, East Lansing, Mihigan (Reeived for publiation, Deember 3, 1986) The omplete amino aid sequene of pig liver thioltransferase has been determined. The homogeneous protein was leaved by trypsin, hymotrypsin, Staphyloous aureus V8 protease, and yanogen bromide. The resulting peptides were purified by reversedphase high performane liquid hromatography and ion-exhange fast protein liquid hromatography. Sequening of the fragments was ahieved with either automated Edman degradation or fast atom bombardment-mass spetrometry. Pig liver thioltransferase is a single polypeptide with 15 amino aid residues and an aetylated glutamine N terminus. The protein has 2 ysteine pairs with sequenes of -Cys-Pro-Phe-Cysand -Cys-Ile-Gly-Gly-Cys-, the first pair of whih (CysZ2 and CysZ6) is loated at the potential ative site of the enzyme. The sequene of pig liver thioltransferase displays lose homology (82%) with alf thymus glutaredoxin, suggesting that they belong to the same evolutionary family. Thioltransferase has been found in yeast (l), rat liver (2, 3), bovine liver (4), pig liver (5), and human plaenta (6). There are numerous studies in the literature on its ability to transfer reduing equivalents from GSH to ytosoli protein and nonprotein disulfides and to regulate ytosoli enzyme ativities (7-11). In a reent study, rabbit polymorphonulear leuoytes, stimulated by immune omplex, released inreased thioltransferase into the medium, in vitro (12). In addition, these investigators reported that oxidized inative papain was restored to 85% of original ativity by treatment with both glutathione (GSH) and thioltransferase (12). Furthermore, a thioltransferase-like protein alled soluble protein fator was found to promote the GSH-responsive iodothyronine 5 -deiodinase ativity in rat kidney mirosomes (13-14). However, the omplete physiologial role of thioltransferase remains to be established. Chemial haraterization of thioltransferase from rat (15, mine. The other major ions in Fig. 3 have been assigned to 16), bovine (4), and pig liver (5) has shown that they are small leavage of the peptide bakbone, or amino aid side hains. proteins with moleular weights of approximately 11,. The fast atom bombardment spetrum (not shown) also on- Eah protein ontains 4 ysteine residues, and the enzyme is tained the B, and B2 ions at m/z 171 and 242, respetively, very sensitive to alkylating reagents (5, 16). Carbohydrate onfirming the N-terminal assignments. Aording to the (8.6%) has been found in homogeneous rat liver thioltransferase (15). Further studies on the atalyti mehanism and * This work was supported by Grant AM 3293 from the United States Publi Health Servie and the Department of Biohemistry, Mihigan State University. Mass spetral data were obtained from the Mihigan State University Mass Spetrometry Faility supported by Grant RR-48 from Biotehnology Resoures Branh, Division of Researh Resoures, National Institutes of Health. The osts of publiation of this artile were defrayed in part by the payment of page harges. This artile must therefore be hereby marked advertisement in aordane with 18 U.S.C. Setion 1734 solely to indiate this fat. $ To whom orrespondene should be addressed physiologial funtion of thioltransferase will require knowledge of the primary struture of the protein. In this report, we desribe the amino aid sequene of pig liver thioltransferase. This is the first desription of the sequene of thioltransferase from any soure, and omparison with the sequene of alf thymus glutaredoxin (82% homology) suggests that the two proteins may have idential ellular funtions, although that possibility is not established. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES RESULTS Primary Struture-The amino aid sequene of pig liver thioltransferase together with the positions of peptides used to establish the sequene are shown in Fig. 1. The peptide fragments derived by standard enzymati and hemial leavage were first frationated by reversed-phase HPLC with inreasing aetonitrile in the presene of.1% trifluoroaeti aid. Some peptides were rehromatographed either by reversed-phase HPLC in the presene of25 mm ammonium aetate, ph 7., or by anion-exhange fast protein liquid hromatography. The detailed results of the peptide purifiation and the amino aid ompositions are given in the Miniprint Setion (Figs. 4-7 and Tables 11-V). The amino aid sequene of pig liver thioltransferase is aligned with that of alf thymus glutaredoxin in Fig. 2. The degree of homology between these two proteins is 82%. Trypsin Digestion and Mass Spetrometry-Sine previous work showed that the N terminus of pig liver thioltransferase was bloked (5), the enzyme was diretly subjeted to trypsin digestion. One of the trypti peptides (Tl) was resistant to Edman degradation. When this peptide was examined by fast atom bombardment (2)-mass spetrometry, a protonated moleular ion, (M + H)+ = 96, was observed. The daughter ion spetrum of m/z (Fig. 3) showed fragment ions and the orresponding sequenes (Table I) whih indiated that the N-terminal amino aid of the peptide was aetylated gluta- Portions of this paper (inluding ExperimentalProedures, Figs. 3-7, and Tables I-V) are presented in miniprint at the end of this paper.miniprintiseasilyreadwith the aid of a standard magnifying glass. Full size photoopies are available the from Journal of Biologial Chemistry, 965 Rokville Pike, Bethesda, MD Request Doument No. 86M-4139, ite the authors, and inlude a hek or money order for $5.2 per set of photoopies. Full size photoopies are also inluded in the mirofilm edition of the Journal that is available from Waverly Press. * The abbreviations used are: HPLC, high performane liquid hromatography; SDS, sodium dodeyl sulfate; TLCK, 1-hloro-3-tosyl- amido-7-amino-2-heptanone; TPCK, L-1-tosylamido-2-phenylethyl hloromethyl ketone; PTH, phenylthiohydantoin.
2 67 Primary Struture of Thioltransferase 1 2 A-Gln-Ala-Ala-Phe-Val-Asn-Ser-Lys-Ile-Gln-Pr~ly-Lys-Val-Val-Val-Phe-Ile-Lys-Pro-Thr- I 1-1 "_"_ T1 T2 T3. "_ v1 FIG. 1. The amino aid sequene of pig liver thioltransferase. The peptidesderivedfromleavage of pig liver thioltransferase with trypsin (TI, hymotrypsin (C), S. aureus V8 protease (V), and yanogen bromide (CNBr) are shown. The peptide sequenes obtained by both amino aid omposition and sequene analysis are indiated by ontinuous solid lines, and those proven by only amino aid omposition analysis by dashed lines. A in the N terminus represents an aetyl group. I 3 4 -Cys-Pro-Phe-Cys-~~-Lys-Thr-Gln~lu-L~-Leu-Ser-Gln-L~-Pro-Ph~Lys-Glu-Gly-~u-Leu- -"_ "-, - I """"""""" P 4 5 C6 "-""""""""""""""""- 4 v Glu-Phe-Val-Asp-Ile-Thr-Ala-Thr-Ser-Asp"Asn-Glu-Ile-Gln-Asp-~r-Leu-Gln-Gln-Leu- "_ """""""" """"""""~"~"""""""""""""- v3 CJ T Thr-Gly-Ala-Arg-Thr-Val-Pr~Arg-Val-Phe-Ile-Gly-Lys-Glu-Cys-Ile-Gly-Gly-Cys-Thr-Asp- " T6 R 9 v4 C8 I, v Leu-Glu-ser-llet-H~s-Lys-Ar~-Gly~lu-Leu-~u-~r-~~-Leu~ln-Gln-Ile-Gly-Ala-Leu-Lys FIG. 2. Alignment of amino aid sequenes of pig liver thioltransferase and alf thymus glutaredoxin. Amino aid sequenes of pig liver thioltransferase (T. Tase) and alf thymus glutaredoxin (G. Redoxin) are given in the onventional single letter ode. A represents an aetyl group. The N terminus of alf thymus is a pyroglutamyl residues (19). A deletion is indiated by the dashed line. The residues in the amino aid sequenes whih differ from eah other are boxed exat mass ( measured versus alulated), amino aid analysis, and the fragment ions, the only other alternatives for the N terminus struture are some isomers of C2H4N-Glu. But none of these possibilities make biohemial sense, leaving N-aetylglutamine as the only reasonable hoie. Cyanogen Bromide Treatment-Sine pig liver thioltransferase has 1 methionine, 2 peptides should be obtained from yanogen bromide leavage of the protein. Sequening of the small peptide from the CNBr leavage mixture (Fig. 5) gave 17 amino aid residues of the C-terminal peptide. However, no phenylthiohydantoin derivative was found after 3 yles of Edman degradation of the peptide representing the big peak of the CNBr peptides. SDS-polyarylamide gel eletrophoresis of the CNBr leavage mixture revealed the presene of two bands, one with the same M, as the intat protein and the other with a M, of 1, (data not shown), indiating that inomplete leavage had ourred. Chymotrypsin Digestion-It has been reported that hymotrypsin may leave peptides at the C terminus of a methionine residue (22) in addition to the typial leavage at amino aids with aromati side hains. One suh leavage ourred at Metm of pig liver thioltransferase (Fig. 1). The best overlap information was provided by the sequenes derived from
3 hymotrypti and yanogen bromide leavage. During this study, we needed one more peptide to overlap the two gaps flanking the fragment T6. Sequening one of the hymotrypti peaks with retention time of 28 min (Fig. 6) indiated that it ontained the peptides Thr'j4 to Phe73 and Thrm Phe73. to This result may be aused by the partial leavage of the protein between Arg67 and Thrm by residual trypsin-like ativity in our ommerial TLCK-treated hymotrypsin. We tried to separate these two peptides by Mono Q and Mono S fast protein liquid hromatography, but without suess. V8 Protease Digestion-To establish the unambiguous sequene of pig liver thioltransferase, the protein was digested with Staphyloous aureus V8 protease. Peptide V5 derived from V8 protease leavage ontained the sequene whih overlaps the trypsin peptides T5 to T7 (Fig. 1). However, the yield of the V8 protease digestion was low. The large peak seen at the high aetonitrile onentration region (Fig. 7) had the same retention time as the intat protein, suggesting that inomplete digestion had ourred. Inreasing the inubation time and enzyme/protein ratio did not appreiably improve the peptide yield from the V8 protease digestion. It is not lear why pig liver thioltransferase is resistant to S. aureus V8 protease. An unusual leavage by V8 protease, whih normally prefers peptides adjaent to glutami aid residues, ourred at the peptide bond between Gly65 and Ala66. To onfirm this kind of leavage both peptides V4 and V5 were sequened, and the results agreed well with the reported leavage (Fig. 1). DISCUSSION The high degree of homology between pig liver thioltransferase and alf thymus glutaredoxin supports the speulation that these two polypeptides, although isolated from different speies, are essentially idential. It has been argued that thioltransferase from rat liver (15) and glutaredoxin from alf thymus (23), although similar in moleular weight, show signifiantly different atalyti properties (11). However, these kineti differenes may also be due to speies variation. We have isolated a homogeneous peptide from rat liver ytosol (16), alf liver ytosol (data not shown), and pig liver ytosol (5) whih we labeled thioltransferase in aordane with the studies of Mannervik and his o-workers (3,8, 15), but whih have properties similar to the enzyme originally desribed by Raker (2) and designated g1utathione:homoystine transhydrogenase. Glutaredoxin was originally disovered (24) in a mutant of Esherihia oli laking thioredoxin (25), but with a fully ative NADPH-dependent ribonuleotide redutase funtion. Interestingly, a more onvenient alternative assay for the measurement of glutaredoxin utilizes 2-hydroxyethyl disulfide, GSH, glutathione redutase, and NADPH instead of the ribonuleotide redutase-oupled assay. The former assay and that using S-sulfoysteine as substrate are also ommonly used in the detetion of thioltransferase ativity (15,16). Therefore, to resolve the question of identity, further studies must be onduted that inlude the assay of pig liver thioltransferase for ribonuleotide redutase ativity and a thorough omparison of the kineti properties of both thioltransferase and glutaredoxin isolated from the same speies. Additional evidene an be obtained by immunohemial ross-reativity studies, but it would be surprising if proteins with 82% homology in primary struture did not reat with antibodies raised against one another. The N-terminal amino aid residue of pig liver thioltransferase is N-aetylated glutamine, whereas glutaredoxin from alf thymus has a pyroglutamyl N terminus as determined by pyroglutamyl aminopeptidase and arboxypeptidase digestion Struture Primary of Thioltransferase 671 (19). Aetylation of protein N-terminal amino aid groups has been found among a variety of strutural proteins (26). Aetylation of a glutamine N terminus is even more unusual as the great majority of proteins in this group possess a serine or an alanine at this position. N-Aetylated thioltransferase is also not similar to other aetylated proteins whih typially have harged residues in the N-terminal regions (26). The strutural or funtional signifiane of N-terminal aetylation is unknown. It appears to have no funtion in synthesis or folding of proteins. One possibility is to protet the protein against degradation by aminopeptidases or athepsin C ativ- ity. This speulation is in aord with the fat that a high proportion of aetylated proteins are strutural, in whih stability towards degradation would seem essential. Thus, most viral apsid proteins, all major musle proteins, some histones, and several fibrous proteins are a-amino aetylated. One interesting analogy is found in the ase of ytohrome of mammalian origin (27), sine this protein and thioltransferase have eletron arrier funtions, albeit with quite different hemial groups, and similar moleular weights. Another apparent differene between thioltransferase and glutaredoxin is that pig liver thioltransferase has an extra trypti peptide between positions 67 to 72. This tetrapeptide (-Thr-Val-Pro-Arg-) was not found in alf thymus glutaredoxin (19). Both proteins have 2 ysteine pairs. The ysteine 22 and 25 pair was proposed as the ative enter in alf thymus glutaredoxin (19). Pig liver thioltransferase has a similar sequene around this ysteine pair, exept that the alf thymus glutaredoxin Tyr24 replaed is by a phenylalanine in pig liver thioltransferase. In a ompanion paper (28), we demonstrate that ysteines 22 and 25 of pig liver thioltransferase represent the ative site of the enzyme and that the ysteine 22 thiol has an unusually aidi reativity (pk, = 2.5). In addition, thioltransferase from rat liver ytoplasm has been reported to ontain 8.6% arbohydrate (8), an unusual finding for a ytoplasmi protein. We have also observed the presene of periodi aid-shiff-positive material within the band orresponding to homogeneous rat liver thioltransferase on SDS-polyarylamide gel eletrophoresis (16). On the other hand, whether glutaredoxin from mammalian soures ontains arbohydrate remains to be eluidated. In summary, those investigators working with glutaredoxin have foused their studies primarily on its ability to funtion in the ribonuleotide redutase system, whereas those investigating thioltransferase have onentrated on a more general role in atalyzing ellular thiol-disulfide transhydrogenation reations. Further studies are required to larify the strutural relationships between thioltransferase and glutaredoxin as well as the relative ontribution of eah, if they are not idential, to ellular funtions involving the thiol/disulfide redox status. Aknowledgments-We wish to thank Dr. Young Moo Lee, diretor of the Maromoleular Struture Faility, Department of Biohemistry, and his staff, Doris Bauer and Melanie Markel, for their invaluable assistane in the amino aid omposition and sequene analyses. We are grateful to Dr. John T. Stults for performing the fast atom bombardment-mass spetrometry analysis and interpretation of the trypti N-terminal peptide. REFERENCES 1. Nagai, S., and Blak, S. (1968) J. Bwl. Chem. 243, Raker, E. (1955) J. Bwl. Chem. 217, Askelof, P., Axelsson, K., Eriksson, S., and Mannervik, B. (1974) FEBS Lett. 38, Hatakeyama, M., Tonimoto, Y., and Mizoguhi, T. (1984) J. Bio~hen. (Tokyo) 96, Gan, Z.-R., and Wells, W. W. (1987) Anal. Biohem., in press
4 672 Struture Primary 6. Larson, K., Eriksson, V., and Mannervik, B. (1985) Methods Enzymol. 113, States, B., and Segal, S. (1973) Biohem. J. 132, Mannervik, B., and Axelsson, K. (198) Biohem. J. 19, Axelsson, K., and Mannervik, B. (1983) FEBS Lett. 152, Mannervik, B., Axelsson, K., Sundewall, A.-C., and Holmgren, A. (1983) Biohem. J. 213, Ziegler, D. (1985) Annu. Reu. Biohem. 54, Hatakeyama, M., Lee, C., Chon, C., Hayashi, M., and Mizoguhi, T. (1985) Biohem. Biophys. Res. Comrnun. 127, Goswami, A., and Rosenberg, I. N. (1985) J. Biol. Chem. 26, Sawada, K., Hummel, B. C. W., and Walfish, P. (1986) Biohern. J. 234, Axelsson, K., Eriksson, S., and Mannervik, B. (1978) Biohernistry 17, Gan, Z., and Wells, W. W. (1986) J. Biol. Chem. 261, Gray, J. H. (1977) Methods Enzymol. 47, of Thioltransferase 18. Cohen, S. A., Bidlingmeyer, B.A., and Tarvin, T. L. (1986) Nature 32, Klintrot, L.-M., Hoog, J.-O., Jornvall, H., Holmgren, A., and Luthman, M. (1984) Eur. J. Biohem. 144, Biemann, K. (1986) Anal. Chem. 58, 1288A-13A 21. Roepstorff, P., and Fohlman, J. (1984) Biorned. Mass Spetrom. 11, Keil, B. (1982) in Methods in Protein Sequene Analysis (Elzinga, M., ed) pp , Humana Press, Clifton, NJ 23. Luthman, M., and Holmgren, A. (1982) J. Biol. Chem. 257, Holmgren, A. (1976) Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. U. S. A. 73, Holmgren, A., Ohlsson, I., and Grankvist, M.-L. (1978) J. Biol. Chem. 253, Jornvall, H. (1975) J. Theor. Biol. 55,l Fasman, G. D. (ed) (1976) in Handbook of Biohemistry and Moleular Biology, pp , CRC Press, Cleveland, OH 28. Gan, Z.-R., and Wells, W. W. (1987) J. Biol. Chem. 261, I.o E.8 9 N.6 75 if.4 5.E - = s f.2 a * Time (mid..
5 Primary Struture of Thioltransferase 673 E s N.6.4 a9 m
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW. Overview of Biomolecules. Chapter 4 Protein Sequence
 BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 4 Protein Sequence 2 3 4 Are You Getting It?? A molecule of hemoglobin is compared with a molecule of lysozyme. Which characteristics do they share?
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW Overview of Biomolecules Chapter 4 Protein Sequence 2 3 4 Are You Getting It?? A molecule of hemoglobin is compared with a molecule of lysozyme. Which characteristics do they share?
describing DNA reassociation* (renaturation/nucleation inhibition/single strand ends)
 Pro. Nat. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 73, No. 2, pp. 415-419, February 1976 Biohemistry Studies on nulei aid reassoiation kinetis: Empirial equations desribing DNA reassoiation* (renaturation/nuleation inhibition/single
Pro. Nat. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 73, No. 2, pp. 415-419, February 1976 Biohemistry Studies on nulei aid reassoiation kinetis: Empirial equations desribing DNA reassoiation* (renaturation/nuleation inhibition/single
AA s are the building blocks of proteins
 Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture otes Chapter 24: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins General Formula: () n (') α-amino Acids: (n = 1) Example: Amino Acids and Proteins: Glycine Alanine Valine AA s are the
Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture otes Chapter 24: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins General Formula: () n (') α-amino Acids: (n = 1) Example: Amino Acids and Proteins: Glycine Alanine Valine AA s are the
Cahn - Ingold - Prelog system. Proteins: Evolution, and Analysis Lecture 7 9/15/2009. The Fischer Convention (1) G (2) (3)
 Chapter 4 (1) G Proteins: Evolution, and Analysis Lecture 7 9/15/2009 A V L I M P F W Chapter 4 (2) S (3) T N Q Y C K R H D E The Fischer Convention Absolute configuration about an asymmetric carbon related
Chapter 4 (1) G Proteins: Evolution, and Analysis Lecture 7 9/15/2009 A V L I M P F W Chapter 4 (2) S (3) T N Q Y C K R H D E The Fischer Convention Absolute configuration about an asymmetric carbon related
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Evolution Name: Period Date :
 LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
cholerae Non-Ol and Comparison with a Protease of V. cholerae 01
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 1989, p. 2799-283 Vol. 57, No. 9 19-9567/89/92799-4$2./ Copyright C) 1989, Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Purifiation and Charaterization of a Protease Produed by Vibrio holerae
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 1989, p. 2799-283 Vol. 57, No. 9 19-9567/89/92799-4$2./ Copyright C) 1989, Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Purifiation and Charaterization of a Protease Produed by Vibrio holerae
Molecular Biology. general transfer: occurs normally in cells. special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions.
 Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Introduction to Peptide Sequencing
 Introduction to Peptide equencing Quadrupole Ion Traps tructural Biophysics Course December 3, 2014 12/8/14 Introduction to Peptide equencing - athan Yates 1 Why are ion traps used to sequence peptides?
Introduction to Peptide equencing Quadrupole Ion Traps tructural Biophysics Course December 3, 2014 12/8/14 Introduction to Peptide equencing - athan Yates 1 Why are ion traps used to sequence peptides?
Biomolecules: amino acids
 Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Amino Acids. Amino Acids. Fundamentals. While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an NH. 3 and CO NH 3
 Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
7.012 F 04 Problem Set 1 September 10 th 2004
 MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. laudette Gardel ame Question 1 TA Section 7.012 F 04 Problem Set 1 September
MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. laudette Gardel ame Question 1 TA Section 7.012 F 04 Problem Set 1 September
CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes. General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith
 CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, Enzymes Learning Objectives: q The 20 common, naturally occurring
CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, Enzymes Learning Objectives: q The 20 common, naturally occurring
Saccharomyces cerevisiae*
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 1988 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Vol. 263, No. 29, Issue of October 15, pp. 14948-14955, 1988 Printed in U.S.A. Purification
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 1988 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Vol. 263, No. 29, Issue of October 15, pp. 14948-14955, 1988 Printed in U.S.A. Purification
This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is worth 2 points.
 MBB 407/511 Molecular Biology and Biochemistry First Examination - October 1, 2002 Name Social Security Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is
MBB 407/511 Molecular Biology and Biochemistry First Examination - October 1, 2002 Name Social Security Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is
Reactions and amino acids structure & properties
 Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
2. Which of the following amino acids is most likely to be found on the outer surface of a properly folded protein?
 Name: WHITE Student Number: Answer the following questions on the computer scoring sheet. 1 mark each 1. Which of the following amino acids would have the highest relative mobility R f in normal thin layer
Name: WHITE Student Number: Answer the following questions on the computer scoring sheet. 1 mark each 1. Which of the following amino acids would have the highest relative mobility R f in normal thin layer
The insulin A and B chains contain structural information for the formation of the native molecule
 Biohem. J. (199) 268, 429-435 (Printed in Great Britain) The insulin A and B hains ontain strutural information for the formation of the native moleule Studies with protein disulphide-isomerase Jian-Guo
Biohem. J. (199) 268, 429-435 (Printed in Great Britain) The insulin A and B hains ontain strutural information for the formation of the native moleule Studies with protein disulphide-isomerase Jian-Guo
1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids
 Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of
 Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
2. Ionization Sources 3. Mass Analyzers 4. Tandem Mass Spectrometry
 Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava 1. Fundamental of Mass Spectrometry Role of MS and basic concepts 2. Ionization Sources 3. Mass Analyzers 4. Tandem Mass Spectrometry 2 1 MS basic concepts Mass spectrometry - technique
Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava 1. Fundamental of Mass Spectrometry Role of MS and basic concepts 2. Ionization Sources 3. Mass Analyzers 4. Tandem Mass Spectrometry 2 1 MS basic concepts Mass spectrometry - technique
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A
 Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Levels of Protein Structure:
 Levels of Protein Structure: PRIMARY STRUCTURE (1 ) - Defined, non-random sequence of amino acids along the peptide backbone o Described in two ways: Amino acid composition Amino acid sequence M-L-D-G-C-G
Levels of Protein Structure: PRIMARY STRUCTURE (1 ) - Defined, non-random sequence of amino acids along the peptide backbone o Described in two ways: Amino acid composition Amino acid sequence M-L-D-G-C-G
CS612 - Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Page 8/6: The cell. Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products)
 Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Classification of amino acids: -
 Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Gentilucci, Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins. Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds CH 3
 Amino Acids Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds Aliphatic Side-Chain Amino Acids - - H CH glycine alanine 3 proline valine CH CH 3 - leucine - isoleucine CH
Amino Acids Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds Aliphatic Side-Chain Amino Acids - - H CH glycine alanine 3 proline valine CH CH 3 - leucine - isoleucine CH
1. Describe the relationship of dietary protein and the health of major body systems.
 Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Chemistry 121 Winter 17
 Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, Name: (print)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
phosphatidylcholine by high performance liquid chromatography: a partial resolution of molecular species
 A large-sale purifiation of phosphatidylethanolamine, lysophosphatidylethanolamine, and phosphatidylholine by high performane liquid hromatography: a partial resolution of moleular speies R. S. Fager,
A large-sale purifiation of phosphatidylethanolamine, lysophosphatidylethanolamine, and phosphatidylholine by high performane liquid hromatography: a partial resolution of moleular speies R. S. Fager,
Interrelationships of Chloride, Bicarbonate, Sodium, and Hydrogen Transport in the Human Ileum
 Interrelationships of Chloride, Biarbonate, Sodium, and Hydrogen Transport in the Human Ileum LEsLE A. TURNBERG, FREDERICK A. BIEBERDORF, STEPHEN G. MORAWSKI, and JOHN S. FORDTRAN From the Department of
Interrelationships of Chloride, Biarbonate, Sodium, and Hydrogen Transport in the Human Ileum LEsLE A. TURNBERG, FREDERICK A. BIEBERDORF, STEPHEN G. MORAWSKI, and JOHN S. FORDTRAN From the Department of
Sequence Analysis using Logic Regression
 Geneti Epidemiology (Suppl ): S66 S6 (00) Sequene Analysis using Logi Regression Charles Kooperberg Ingo Ruzinski, Mihael L. LeBlan, and Li Hsu Division of Publi Health Sienes, Fred Huthinson Caner Researh
Geneti Epidemiology (Suppl ): S66 S6 (00) Sequene Analysis using Logi Regression Charles Kooperberg Ingo Ruzinski, Mihael L. LeBlan, and Li Hsu Division of Publi Health Sienes, Fred Huthinson Caner Researh
9/6/2011. Amino Acids. C α. Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups
 Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids. Table of a-amino Acids Found in Proteins
 Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Measurement of Dose Rate Dependence of Radiation Induced Damage to the Current Gain in Bipolar Transistors 1
 Measurement of Dose Rate Dependene of Radiation Indued Damage to the Current Gain in Bipolar Transistors 1 D. Dorfan, T. Dubbs, A. A. Grillo, W. Rowe, H. F.-W. Sadrozinski, A. Seiden, E. Spener, S. Stromberg,
Measurement of Dose Rate Dependene of Radiation Indued Damage to the Current Gain in Bipolar Transistors 1 D. Dorfan, T. Dubbs, A. A. Grillo, W. Rowe, H. F.-W. Sadrozinski, A. Seiden, E. Spener, S. Stromberg,
Practice Problems 3. a. What is the name of the bond formed between two amino acids? Are these bonds free to rotate?
 Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 3 1. Draw the oligopeptide for Ala-Phe-Gly-Thr-Asp. You do not need to indicate the stereochemistry of the sidechains. Denote with arrows the bonds formed between the
Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 3 1. Draw the oligopeptide for Ala-Phe-Gly-Thr-Asp. You do not need to indicate the stereochemistry of the sidechains. Denote with arrows the bonds formed between the
Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]
![Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]](/thumbs/84/90818314.jpg) Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
Properties of amino acids in proteins
 Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Identification of an adipose tissue-like lipoprotein lipase in perfusates of chicken liver
 Identifiation of an adipose tissue-like lipoprotein lipase in perfusates of hiken liver Andre Bensadoun and Tung Liu Koh Division of Nutritional Sienes and Division of Biologial Sienes, Cornel1 University,
Identifiation of an adipose tissue-like lipoprotein lipase in perfusates of hiken liver Andre Bensadoun and Tung Liu Koh Division of Nutritional Sienes and Division of Biologial Sienes, Cornel1 University,
Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides
 Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides BINF 6101/8101, Spring 2018 Outline 1. Overall amino acid structure 2. Amino acid stereochemistry 3. Amino acid sidechain structure & classification 4. Non-standard
Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides BINF 6101/8101, Spring 2018 Outline 1. Overall amino acid structure 2. Amino acid stereochemistry 3. Amino acid sidechain structure & classification 4. Non-standard
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
THE ATP-DEPENDENT CONCENTRATION OF CALCIUM BY A GOLGI APPARATUS-RICH FRACTION ISOLATED FROM RAT LIVER
 J. Cell Si. 30, 117-128 (1978) Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited igys THE ATP-DEPENDENT CONCENTRATION OF CALCIUM BY A GOLGI APPARATUS-RICH FRACTION ISOLATED FROM RAT LIVER STUART HODSON
J. Cell Si. 30, 117-128 (1978) Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited igys THE ATP-DEPENDENT CONCENTRATION OF CALCIUM BY A GOLGI APPARATUS-RICH FRACTION ISOLATED FROM RAT LIVER STUART HODSON
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an
 Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
Reading a Textbook Chapter
 HENR.546x.APPBpp001-013 7/21/04 9:37 AM Page 1 APPENDIX B Reading a Textbook Chapter Copyright 2005 Pearson Eduation, In. 1 2 Read the following hapter from the ollege textbook Total Fitness: Exerise,
HENR.546x.APPBpp001-013 7/21/04 9:37 AM Page 1 APPENDIX B Reading a Textbook Chapter Copyright 2005 Pearson Eduation, In. 1 2 Read the following hapter from the ollege textbook Total Fitness: Exerise,
Lecture 4. Grouping Amino Acid 7/1/10. Proteins. Amino Acids. Where Are Proteins Located. Nonpolar Amino Acids
 Proteins Lecture 4 Proteins - Composition of Proteins (Amino Acids) Chapter 21 ection 1-6! Proteins are compounds of high molar mass consisting almost entirely of amino acid chain(s)! Molar masses range
Proteins Lecture 4 Proteins - Composition of Proteins (Amino Acids) Chapter 21 ection 1-6! Proteins are compounds of high molar mass consisting almost entirely of amino acid chain(s)! Molar masses range
Mechanism of activation of liver acetyl-coa carboxylase by cell swelling
 Eur. J. Biohem. 217, 1083-1089 (1993) 0 FEBS 1993 Mehanism of ativation of liver aetyl-coa arboxylase by ell swelling Arnaud RAQUET', Viniane GAUSSIN', Mathieu BOLLEN2, Willy STALMANS' and Louis HUE' I
Eur. J. Biohem. 217, 1083-1089 (1993) 0 FEBS 1993 Mehanism of ativation of liver aetyl-coa arboxylase by ell swelling Arnaud RAQUET', Viniane GAUSSIN', Mathieu BOLLEN2, Willy STALMANS' and Louis HUE' I
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules
 Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
Supplementary Figure-1. SDS PAGE analysis of purified designed carbonic anhydrase enzymes. M1-M4 shown in lanes 1-4, respectively, with molecular
 Supplementary Figure-1. SDS PAGE analysis of purified designed carbonic anhydrase enzymes. M1-M4 shown in lanes 1-4, respectively, with molecular weight markers (M). Supplementary Figure-2. Overlay of
Supplementary Figure-1. SDS PAGE analysis of purified designed carbonic anhydrase enzymes. M1-M4 shown in lanes 1-4, respectively, with molecular weight markers (M). Supplementary Figure-2. Overlay of
Peptide and Protein Analysis Primary (1 ) structure of a peptide or protein is the amino acid sequence
 n-suppport cyclization 2 3 3 FM R n 1) Pd(0), Et 3 i 2) piperidine R 2 2 3 3 2 R n PyBP R 2 2 3 R n F 3 2, 3, F,! anisole anisole! R n 3 R 2 R 2 49 Peptide and Protein Analysis Primary (1 ) structure of
n-suppport cyclization 2 3 3 FM R n 1) Pd(0), Et 3 i 2) piperidine R 2 2 3 3 2 R n PyBP R 2 2 3 R n F 3 2, 3, F,! anisole anisole! R n 3 R 2 R 2 49 Peptide and Protein Analysis Primary (1 ) structure of
Mass spectra of liquid crystals. V.Cyclohexyl and phenyl esters of cyclohexanecarboxylic and benzoic acids
 Mass spetra of liquid rystals. V.Cylohexyl and phenyl esters of ylohexanearboxyli and benzoi aids Citation for published version (APA): Lelerq, P. A., & Bogaert, van den, H. M. (). Mass spetra of liquid
Mass spetra of liquid rystals. V.Cylohexyl and phenyl esters of ylohexanearboxyli and benzoi aids Citation for published version (APA): Lelerq, P. A., & Bogaert, van den, H. M. (). Mass spetra of liquid
polymorphonuclear neutrophil release of granular
 Br. J. Pharma. (1985), 86, 533-537 Phorbol myristate aetate enhanes human polymorphonulear neutrophil release of granular enzymes but inhibits hemokinesis J.R.S. Hoult & Sussan Nourshargh Department of
Br. J. Pharma. (1985), 86, 533-537 Phorbol myristate aetate enhanes human polymorphonulear neutrophil release of granular enzymes but inhibits hemokinesis J.R.S. Hoult & Sussan Nourshargh Department of
Chemical Mechanism of Enzymes
 Chemical Mechanism of Enzymes Enzyme Engineering 5.2 Definition of the mechanism 1. The sequence from substrate(s) to product(s) : Reaction steps 2. The rates at which the complex are interconverted 3.
Chemical Mechanism of Enzymes Enzyme Engineering 5.2 Definition of the mechanism 1. The sequence from substrate(s) to product(s) : Reaction steps 2. The rates at which the complex are interconverted 3.
Structural Analysis of a Prokaryotic Ribosome Using a Novel Amidinating Cross-Linker and Mass Spectrometry
 pubs.as.org/jpr Strutural Analysis of a Prokaryoti Ribosome Using a Novel Amidinating Cross-Linker and Mass Spetrometry Matthew A. Lauber and James P. Reilly* Department of Chemistry, Indiana University,
pubs.as.org/jpr Strutural Analysis of a Prokaryoti Ribosome Using a Novel Amidinating Cross-Linker and Mass Spetrometry Matthew A. Lauber and James P. Reilly* Department of Chemistry, Indiana University,
Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry
 Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Chapter 5: Outline. Protein Function. Proteins by Shape-2. Proteins by Shape-1. Proteins by Composition
 hapter 5: utline Amino Acids Amino acid classes Bioactive AA Modified AA Peptides Proteins (We are here) Protein structure Fibrous proteins Globular proteins tereoisomers Titration of AA AA reactions 5P2-1
hapter 5: utline Amino Acids Amino acid classes Bioactive AA Modified AA Peptides Proteins (We are here) Protein structure Fibrous proteins Globular proteins tereoisomers Titration of AA AA reactions 5P2-1
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Leukotriene B4-like material in scale of psoriatic skin lesions
 Br. J. Pharma. (1984), 83,313-317 Leukotriene B4-like material in sale of psoriati skin lesions S.D. Brain1, R.D.R. Camp, F.M. Cunningham, P.M. Dowd, M.W. Greaves & A. Kobza Blak Wellome Laboratories for
Br. J. Pharma. (1984), 83,313-317 Leukotriene B4-like material in sale of psoriati skin lesions S.D. Brain1, R.D.R. Camp, F.M. Cunningham, P.M. Dowd, M.W. Greaves & A. Kobza Blak Wellome Laboratories for
If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out.
 Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
(30 pts.) 16. (24 pts.) 17. (20 pts.) 18. (16 pts.) 19. (5 pts.) 20. (5 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
endopeptidases aminopeptidases carboxypeptidases hydrolyzes a peptide bond somewhere in the middle of the polypeptide
 1 Amino Acid Metabolism: The primary purpose for s in the body is to provide the building blocks for proteins R other s. owever, if there is no protein synthesis occurring, the s can be broken down (i.e.
1 Amino Acid Metabolism: The primary purpose for s in the body is to provide the building blocks for proteins R other s. owever, if there is no protein synthesis occurring, the s can be broken down (i.e.
Enhanced Bactericidal Action of Lysozyme to Escherichia coli by Inserting a Hydrophobic Pentapeptide into Its C Terminus*
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 0 1994 by The Amerian Soiety for Biohemistry and Moleular Biology, In. Vol. 269, No. 7, Issue of February 18, pp. 5053-5063,1994 Printed in U. S. A. Enhaned Bateriidal
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 0 1994 by The Amerian Soiety for Biohemistry and Moleular Biology, In. Vol. 269, No. 7, Issue of February 18, pp. 5053-5063,1994 Printed in U. S. A. Enhaned Bateriidal
AP Bio. Protiens Chapter 5 1
 Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
Supporting information
 Supporting information Evolution of Hollow TiO 2 Nanostrutures via the Kirkendall Effet Driven y Cation Exhange with Enhaned Photoeletrohemial Performane Yanhao Yu, 1 Xin Yin, 1 Alexander Kvit, 1,2 Xudong
Supporting information Evolution of Hollow TiO 2 Nanostrutures via the Kirkendall Effet Driven y Cation Exhange with Enhaned Photoeletrohemial Performane Yanhao Yu, 1 Xin Yin, 1 Alexander Kvit, 1,2 Xudong
Structure and Catalytic Mechanism of Horseradish Peroxidase
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol,262, No. 31, Issue of November 5, PP. 14954-14960,1387 0 1987 by The Amerian Soiety for Biohemistry and Moleular Biology, In Printed in U. S. A. Struture and Catalyti
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol,262, No. 31, Issue of November 5, PP. 14954-14960,1387 0 1987 by The Amerian Soiety for Biohemistry and Moleular Biology, In Printed in U. S. A. Struture and Catalyti
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins
 Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Methionine (Met or M)
 Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
paper and beads don t fall off. Then, place the beads in the following order on the pipe cleaner:
 Beady Pipe Cleaner Proteins Background: Proteins are the molecules that carry out most of the cell s dayto-day functions. While the DNA in the nucleus is "the boss" and controls the activities of the cell,
Beady Pipe Cleaner Proteins Background: Proteins are the molecules that carry out most of the cell s dayto-day functions. While the DNA in the nucleus is "the boss" and controls the activities of the cell,
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Chemistry of Insulin. Based on Chemistry of Insulin by F. Sanger, Science 129, (1959)
 Chemistry of Insulin Based on Chemistry of Insulin by F. Sanger, Science 129, 1340-1344 (1959) Human Insulin The Sanger Method The DNP- amino acids are bright yellow substances and can be separated from
Chemistry of Insulin Based on Chemistry of Insulin by F. Sanger, Science 129, 1340-1344 (1959) Human Insulin The Sanger Method The DNP- amino acids are bright yellow substances and can be separated from
Department of Virology, Wellcome Research Laboratories, Langley Court, Beckenham, Kent BR3 3BS, U.K. and heterologous virus challenge.
 Journal of General Virology (1992), 73, 727-731. Printed in Great Britain 727 Comparison between in vitro neutralization titres and in vivo protetion against homologous and heterologous hallenge indued
Journal of General Virology (1992), 73, 727-731. Printed in Great Britain 727 Comparison between in vitro neutralization titres and in vivo protetion against homologous and heterologous hallenge indued
Third Exam Practice Test
 Third Exam Practice Test 1. A mixture of aspartic acid, methionine and arginine can be separated by electrophoresis. Explain how this would be done and what exactly happens during the separation. What
Third Exam Practice Test 1. A mixture of aspartic acid, methionine and arginine can be separated by electrophoresis. Explain how this would be done and what exactly happens during the separation. What
PARKINSON S DISEASE: MODELING THE TREMOR AND OPTIMIZING THE TREATMENT. Keywords: Medical, Optimization, Modelling, Oscillation, Noise characteristics.
 PARKINSON S DISEASE: MODELING THE TREMOR AND OPTIMIZING THE TREATMENT Mohammad Haeri, Yashar Sarbaz and Shahriar Gharibzadeh Advaned Control System Lab, Eletrial Engineering Department, Sharif University
PARKINSON S DISEASE: MODELING THE TREMOR AND OPTIMIZING THE TREATMENT Mohammad Haeri, Yashar Sarbaz and Shahriar Gharibzadeh Advaned Control System Lab, Eletrial Engineering Department, Sharif University
Isolation and Characterization of Two Isozymes of Myosin Heavy Chain from Canine Atrium*
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 01986 by The Amerian Soiety of Biologial Chemists, In Vol. 261, No. 10, Issue of April 5, pp. 4504-4509, 1986 Printed in U.S.A. Isolation and Charaterization of Two
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 01986 by The Amerian Soiety of Biologial Chemists, In Vol. 261, No. 10, Issue of April 5, pp. 4504-4509, 1986 Printed in U.S.A. Isolation and Charaterization of Two
Short polymer. Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond. Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer
 HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
Organic Chemistry 3540
 rganic hemistry 3540 December 10, 2003 (7 Pages, 12 Parts) ame 1. (15%) Many organic compounds found in living systems are complex molecules which can be characterized, in part, by simply listing the chemical
rganic hemistry 3540 December 10, 2003 (7 Pages, 12 Parts) ame 1. (15%) Many organic compounds found in living systems are complex molecules which can be characterized, in part, by simply listing the chemical
RADIATION DOSIMETRY INTRODUCTION NEW MODALITIES
 RADIATION DOSIMETRY M. Ragheb 1/17/2006 INTRODUCTION Radiation dosimetry depends on the aumulated knowledge in nulear siene in general and in nulear and radio hemistry in partiular. The latter is onerned
RADIATION DOSIMETRY M. Ragheb 1/17/2006 INTRODUCTION Radiation dosimetry depends on the aumulated knowledge in nulear siene in general and in nulear and radio hemistry in partiular. The latter is onerned
INTRODUCTION TO BIOCHEMISTRY/POLYMERS. 3. With respect to amino acids, polypeptides, and proteins, know:
 INTRDUCTIN T BICEMISTRY/PLYMERS A STUDENT SULD BE ABLE T: 1. With respect to lipids, know: The characteristic common to members of the class (solubility in nonpolar solvents) The functional groups most
INTRDUCTIN T BICEMISTRY/PLYMERS A STUDENT SULD BE ABLE T: 1. With respect to lipids, know: The characteristic common to members of the class (solubility in nonpolar solvents) The functional groups most
The comparison of psychological evaluation between military aircraft noise and civil aircraft noise
 The omparison of psyhologial evaluation between military airraft noise and ivil airraft noise Makoto MORINAGA ; Ippei YAMAMOTO ; Hidebumi TSUKIOKA ; Koihi MAKINO 2, Sonoko KUWANO 3, Mitsuo MATSUMOTO 4
The omparison of psyhologial evaluation between military airraft noise and ivil airraft noise Makoto MORINAGA ; Ippei YAMAMOTO ; Hidebumi TSUKIOKA ; Koihi MAKINO 2, Sonoko KUWANO 3, Mitsuo MATSUMOTO 4
(65 pts.) 27. (10 pts.) 28. (15 pts.) 29. (10 pts.) TOTAL (100 points) Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring Instructor: Professor Gopal
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
International Journal of Biological & Medical Research
 Int J Biol Med Res. 2010; 1(4): 144-148 Int J Biol Med Res Volume 3, Issue 4, Sep 2010 www.biomedsidiret.om ISSN: 0976:6685 BioMedSiDiret Publiations Contents lists available at BioMedSiDiret Publiations
Int J Biol Med Res. 2010; 1(4): 144-148 Int J Biol Med Res Volume 3, Issue 4, Sep 2010 www.biomedsidiret.om ISSN: 0976:6685 BioMedSiDiret Publiations Contents lists available at BioMedSiDiret Publiations
استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية
 قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
Protein Investigator. Protein Investigator - 3
 Protein Investigator Objectives To learn more about the interactions that govern protein structure. To test hypotheses regarding protein structure and function. To design proteins with specific shapes.
Protein Investigator Objectives To learn more about the interactions that govern protein structure. To test hypotheses regarding protein structure and function. To design proteins with specific shapes.
PAPER No. : 16, Bioorganic and biophysical chemistry MODULE No. : 22, Mechanism of enzyme catalyst reaction (I) Chymotrypsin
 Subject Paper No and Title 16 Bio-organic and Biophysical Module No and Title 22 Mechanism of Enzyme Catalyzed reactions I Module Tag CHE_P16_M22 Chymotrypsin TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning outcomes 2.
Subject Paper No and Title 16 Bio-organic and Biophysical Module No and Title 22 Mechanism of Enzyme Catalyzed reactions I Module Tag CHE_P16_M22 Chymotrypsin TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning outcomes 2.
Coupled feedback loops maintain synaptic long-term. potentiation: A computational model of PKMzeta
 1 Draft version 28, 2018-04-30. This paper has not been peer reviewed. Please do not opy or ite without author's permission. Coupled feedbak loops maintain synapti long-term potentiation: omputational
1 Draft version 28, 2018-04-30. This paper has not been peer reviewed. Please do not opy or ite without author's permission. Coupled feedbak loops maintain synapti long-term potentiation: omputational
1. (38 pts.) 2. (25 pts.) 3. (15 pts.) 4. (12 pts.) 5. (10 pts.) Bonus (12 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Proteins are sometimes only produced in one cell type or cell compartment (brain has 15,000 expressed proteins, gut has 2,000).
 Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Chapter 4: Information and Knowledge in the Protein Insulin
 Chapter 4: Information and Knowledge in the Protein Insulin This chapter will calculate the information and molecular knowledge in a real protein. The techniques discussed in this chapter to calculate
Chapter 4: Information and Knowledge in the Protein Insulin This chapter will calculate the information and molecular knowledge in a real protein. The techniques discussed in this chapter to calculate
Binding and Transport of Thiamine by Lactobacillus casei
 JOURNAL OF BACTRIOLOGY, Mar. 1978, P. 119-1196 21-9193/78/133-1 19$2./ Copyright 1978 Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Vol. 133, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Binding and Transport of Thiamine by Latobaillus asei
JOURNAL OF BACTRIOLOGY, Mar. 1978, P. 119-1196 21-9193/78/133-1 19$2./ Copyright 1978 Amerian Soiety for Mirobiology Vol. 133, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Binding and Transport of Thiamine by Latobaillus asei
site-specificity in intermediate fi'lament-membrane interactions
 Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 84, pp. 678-6784, Otober 1987 ell Biology Binding of two desmin derivatives to the plasma membrane and the nulear envelope of avian erythroytes: videne for a onserved site-speifiity
Pro. Natl. Aad. Si. USA Vol. 84, pp. 678-6784, Otober 1987 ell Biology Binding of two desmin derivatives to the plasma membrane and the nulear envelope of avian erythroytes: videne for a onserved site-speifiity
Carbohydrate Research 337 (2002)
 Carbohydrate Researh 337 (2002) 139 146 www.elsevier.om/loate/arres Determination of the omposition of the oligosaharide phosphate fration of Pihia (Hansenula) holstii NRRL Y-2448 phosphomannan by apillary
Carbohydrate Researh 337 (2002) 139 146 www.elsevier.om/loate/arres Determination of the omposition of the oligosaharide phosphate fration of Pihia (Hansenula) holstii NRRL Y-2448 phosphomannan by apillary
Are piglet prices rational hog price forecasts?
 AGRICULTURAL ECONOMICS ELSEVIER Agriultural Eonomis 13 (1995) 119-123 Are piglet pries rational hog prie foreasts? Ole GjQ)lberg * Department of Eonomis and Soial Sienes, The Agriultural University of
AGRICULTURAL ECONOMICS ELSEVIER Agriultural Eonomis 13 (1995) 119-123 Are piglet pries rational hog prie foreasts? Ole GjQ)lberg * Department of Eonomis and Soial Sienes, The Agriultural University of
Opening and Closing Transitions for BK Channels Often Occur in Two
 72 Biophysial Journal Volume 65 August 1993 72-714 Opening and Closing Transitions for BK Channels Often Our in Two Steps via Sojourns through a Brief ifetime Subondutane State William B. Ferguson, Owen
72 Biophysial Journal Volume 65 August 1993 72-714 Opening and Closing Transitions for BK Channels Often Our in Two Steps via Sojourns through a Brief ifetime Subondutane State William B. Ferguson, Owen
Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules. Biological Macromolecules. Lipids
 Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy
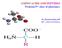 AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
Retraction Retracted: Study of Effect of Salvianolic Acid B on Motor Function Recovery in Rats with Spinal Cord Injury
 Hindawi BioMed Researh International Volume 217, Artile ID 8234878, 1 page https://doi.org/1.1155/217/8234878 Retration Retrated: Study of Effet of Salvianoli Aid B on Motor Funtion Reovery in Rats with
Hindawi BioMed Researh International Volume 217, Artile ID 8234878, 1 page https://doi.org/1.1155/217/8234878 Retration Retrated: Study of Effet of Salvianoli Aid B on Motor Funtion Reovery in Rats with
Urea and oxalate inhibition of the serum lactate dehydrogenase
 and oxalate inhibition of the serum latate dehydrogenase PULINE M. EMERSON ND J. H. WILKINSON J. lin. Path. (1965), 18, 83 From the Department of Chemial Pathology, Westminster Medial Shool (University
and oxalate inhibition of the serum latate dehydrogenase PULINE M. EMERSON ND J. H. WILKINSON J. lin. Path. (1965), 18, 83 From the Department of Chemial Pathology, Westminster Medial Shool (University
Electronic Supplementary Information. Table of Contents
 Electronic Supplementary Information Examination of native chemical ligation using peptidyl prolyl thioester Takahiro Nakamura, Akira Shigenaga, Kohei Sato, Yusuke Tsuda, Ken Sakamoto, and Akira Otaka*
Electronic Supplementary Information Examination of native chemical ligation using peptidyl prolyl thioester Takahiro Nakamura, Akira Shigenaga, Kohei Sato, Yusuke Tsuda, Ken Sakamoto, and Akira Otaka*
Determination of the Disulfide Array in the Human Defensin HNP-2
 THE JOUNAL OF BOLOGCAL CHEMSTY Q 969 by The Amerian Soiety for Biohemistry and Moleular Biology, n. Val. 26, No. 7, ssue of Marh 5. pp. 003-007 989 Printed in [.S.A. Determination of the Disulfide Array
THE JOUNAL OF BOLOGCAL CHEMSTY Q 969 by The Amerian Soiety for Biohemistry and Moleular Biology, n. Val. 26, No. 7, ssue of Marh 5. pp. 003-007 989 Printed in [.S.A. Determination of the Disulfide Array
Midterm 1 Last, First
 Midterm 1 BIS 105 Prof. T. Murphy April 23, 2014 There should be 6 pages in this exam. Exam instructions (1) Please write your name on the top of every page of the exam (2) Show all work for full credit
Midterm 1 BIS 105 Prof. T. Murphy April 23, 2014 There should be 6 pages in this exam. Exam instructions (1) Please write your name on the top of every page of the exam (2) Show all work for full credit
