Osteopenia Of Prematurity Prevention And Treatment
|
|
|
- Warren Strickland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Advanced Nursing Practice Volume 4 Number 2 Osteopenia Of Prematurity Prevention And Treatment B Cross, E Vasquez Citation B Cross, E Vasquez. Osteopenia Of Prematurity Prevention And Treatment. The Internet Journal of Advanced Nursing Practice Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract This paper examines Osteopenia of Prematurity (OOP) in a triplet child born at 24 3/7 weeks gestation. The infant required an extensive hospitalization in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) due to his prematurity. During his hospitalization, he was diagnosised with bronchopulmonary dysplasia, experienced multiple episodes of sepsis, and required long-term total parenteral and diuretic therapy. The differential diagnosis, pathophysiology, and prevention and treatment regarding insufficient bone mineralization in premature infants are discussed. INTRODUCTION Osteopenia of prematurity (OOP) occurs when bone mineral content in an infant is significantly decreased compared to that seen in the fetus or infant of comparable size or gestational age. The incidence seen in very-low-birth-weight infants ((1250 grams) is approximately 30%2. The clinical onset of OOP usually occurs between the sixth and twelfth week postnatally and with infants born less than 28 weeks gestation. 1 OOP affects preterm infants with 1) chronic lung disease; 2) very-low-birth-weight; 3) long-term parenteral nutrition; 4) and use of certain medications (diuretics and corticosteriods) that affect mineral absorption. OOP is the current term used for those infants showing evidence of decreased bone mineralization without radiological signs. The term Rickets is used when there is a chronic disorder of calcium metabolism characterized by radiological evidence of bone demineralization and elevated serum alkaline phosphatase levels. 1 Rickets in newborns was first described in a study in All 668 low-birth-weight infants studied were found to have rickets. 3 During the time of this study, vitamin D deficiency was highly prevalent. Successful use of supplementation of Vitamin D did not start till the next decade. Today, with an increasing number of very-low-birth-weight infants surviving, the main pathogenic factor is an insufficient mineral intake of calcium and phosphorous. 4 CASE HISTORY Infant boy FV was born as triplet C to a para 3 gravida 0 abortion 2 mother. Mother s prenatal history was unremarkable except for the multiple gestation. FV was delivered by cesarean section due to premature labor. The amniotic fluid was clear and odorless. Estimated gestational age was 24 3/7 weeks with Apgar scores of 8 and 8 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. Birth weight was 633 grams. The infant was resuscitated and immediately intubated and placed on mechanically ventilation. He was transferred to the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) for further evaluation and work up. FV s long hospital course was very complex and included the following factors: 1) recurrent episodes of respiratory distress causing long-term need for mechanical ventilation; 2) multiple episodes of infection from multiple organisms ( E-Coli; Coagulase-negative Staph; and Candida Albicans) and from multiple sites (blood, trachea; skin and urinary tract); 3) long-term diuretic therapy (Lasix that was switched to Diurul on day of life 95); 4) long-term parenteral nutrition therapy; 5) corticosteriod therapy; 6) diagnoses of nephrocalcinosis and biliary atresia. Laboratory tests were routinely performed, as per standard of care in the NICU. Figures 1 and 2 demonstrate the significant lab data on calcium, phosphorus and alkaline phosphorus for this infant s hospital stay. After day of life 68, the infant s alkaline phosphorus level maintained a level that was greater than the standard normal range for infants (( 800 IU/L). On day of life 28, his parathyroid hormone level was 122 (normal 12-72). He was started on Vitamin D 400 units per day. Liver function tests were performed on multiple occasions and all were within normal limits for this infant. Total parenteral nutrition (TPN) was initiated on day of life 1 of 5
2 2 through 26. He continued to require intermittent TPN due to episodes of multiple sepsis and possible gastrointestional infection. When he was given oral nutrition, it was either fortified breast milk (4 packets on Enfamil Human Milk Fortifier per100 cc of expressed breast milk) or Premature Enfamil 24 kcal/oz. with Iron. Due to the consistent abnormal laboratory test results and concern for his overall nutrient status, a long extremity X- ray was performed on the 60th day of life. Results of this radiological examination showed questionable bowing of his left tibia. The infant was monitored closely throughout the remainder of his hospitalization to prevent fractures. Moreover, his nutritional status was monitored to promote an increase in his bone mineralization. Table 1 illustrates the sequelae of FV s prematurity and it s effect on his overall health status. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY The body distribution and regulation of the serum concentration of minerals such as calcium, phosphorus and magnesium determines overall bone mineralization. The renal regulation of these minerals is also essential to the ability of the infant to prevent bone demineralization. Chronic diseases (such as bronchopulmonary dysplasia), very low birth weight (( 1250 grams), and the use of long term total parenteral and diuretic therapy contribute to the increasing incidence of OOP and eventual Rickets in the preterm infant. 2 Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body. The average term newborn has accumulated between 20 and 30 grams of elemental calcium, 80% of which are accreted during the third trimester of pregnancy. Approximately 99% of this calcium is located in the skeleton; with only about one-third readily exchangeable with extracellular fluid. 4 The preterm infant is unable to accumulate the same amount as the term infant due to early extrauterine life. The serum calcium exists in three separate fractions that are in dynamic equilibrium: 1) 40% protein-bound calcium (albumin representing the primary binding protein); 2) 10% complexed to a number of anions, such as citrate, phosphate, bicarbonate, and sulfate; and, 3) 50% free ionized calcium (the physiologically active form of calcium). 5 This serum concentration varies significantly in the newborn due to decreases over the first days of life, followed by a gradual increase to adult concentrations by the second or third week of life. As with calcium, approximately 80% of the phosphorus in the term newborn is accumulated during the last trimester of pregnancy with 85% found in the skeleton. The phosphorous plasma concentrations in the newborn are maintained at concentrations greater than adults. Phosphorus is divided between the organic fraction and inorganic phosphate. 4 Of the body s total magnesium content, about 60% is contained in the bone, another 29% in muscle, and the remainder is distributed through the soft tissues. The serum concentrations of magnesium are maintained within relatively tight limits and are essentially the same for newborns, infants, children, and adults. 4 Serum calcium homeostasis is maintained primarily through the interaction of parathyroid hormone (PTH), calcitonin (CT), and vitamin D and their actions on the gastrointestinal tract, kidney, and bone. The kidney plays a very important role in calcium homeostasis. The movement of calcium from the gastrointestinal tract and bone determines the serum calcium concentration, but the kidney establishes homeostasis. The serum concentration of inorganic phosphate appears to be primarily regulated through the kidney by means of the tubular reabsorption of inorganic phosphate. The kidney also appears to be the primary site for regulation of serum magnesium concentration. 1 The loop diuretics (Lasix) have been recognized to increase the urinary excretion of calcium. These agents act at the loop of Henle to inhibit the active reabsorption of sodium and chloride. Since calcium reabsorption in the ascending limb of the loop of Henle is dependent on the active reabsorption of these ions, calcium reabsorption is secondarily inhibited. The resulting hypercalciuria can place the infant at risk for development of nephrocalcinosis, and in very-low-birthweight infants, can further impair an already marginal calcium balance. Chronic administration of thiazide diuretics, which are often used as an alternative to loop diuretics, is also known to increase urinary excretion of calcium. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS The differential diagnosis for osteopenia of prematurity (OOP) versus Rickets is determined by routine and supplementary lab tests and examinations of bone density. OOP can generally be suspected when there is an elevated alkaline phosphatase activity (( 800 IU) or lowered serum phosphorus (<3.5 mg/dl). 1 Moderate increases in the alkaline phosphatase ( IU) can be commonly seen in rapidly growing premature infants and warrants careful 2 of 5
3 monitoring of the infant s mineral intake. The serum calcium level usually remains normal. 2 Supplementary tests include the Vitamin D levels (25- hydroxy-vitamin D and 1,25-hydroxy-vitamin D) and the parathyroid hormone (PTH). These tests reveal an increased level of 1,25-hydroxy-vitamin D and a depressed 25- hydroxy-vitamin D when OOP is present. The PTH will either be normal or high with OOP. 1 Most evaluations for bone demineralization, in premature infants with laboratory tests showing increased alkaline phosphorus, are performed using the standard radiograph of a long bone. This technique, unfortunately, does not detect mild OOP. 3 The radiograph of an infant with Rickets will exhibit: 1) a decrease in the long bone growth; 2) craniotabes; 3) nontraumatic palpable swelling of the costochondral junctions of the rib cage; 4) and, splaying of the metaphyseal ends of the long bones. The presence of Rickets can be definitively assessed by direct evaluation with a bone mineral densinometer. 3 The bone density is calculated by applying a photon beam from a 125-Iodine source to the distal radius. The results are compared to standardized normal bone-density curves for different gestational ages. Since this technique is expensive, it is generally reserved for use as a research tool. OOP with elevated akaline phosphatase, such as Baby Boy F., have the potential for a deficit in body length by 18 months of age. 1 CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS Vigilant observation and evaluation by the health care team in the NICU is critical to prevent and treat OOP. Monitoring the infant s nutritional status on a weekly basis is necessary to optimize bone mineralization. Maintaining calcium/phosphorus ratios of :1. in TPN will minimize bone demineralization during long term parenteral nutrition. Initiating enteral feedings with premature formulas or fortified breast milk as soon as medically stable will promote bone mineralization uptake. Cautious handling of infants at risk for OOP will decrease the potential for fractures. Collaboration with physical therapy for range-of-motion exercises may enhance bone mineralization. However, replication studies evaluating the effect of physical therapy on bone mineralization in these premature infants are needed before physical therapy can be instituted as a standard of care. 4 Figure 1 Table 1 PREVENTION AND TREATMENT Prevention is the best approach to Osteopenia of Prematurity (OOP) and resulting Rickets in the newborn. To prevent OOP, adequate amount and ratio ( :1) of Ca and P intake is needed together with an adequate caloric (> 80 Kcal/kg/d) and nutritional (2.5-3 g/kg/d amino acid and 400 IU/d vitamin D) intake. 4 When weaning from TPN to enteral feeding, high Ca and P content formulas should be used, such as: Similac Special Care, Enfamil Premature, or breast milk with Human Milk Fortifier (HMF). 3 Recommendations for the management of OOP complicated by medical conditions in the premature infant are presented in Table 2. In sum, the premature infant needs more minerals than the term infant to develop appropriate bone mineral accretion. Osteopenia of prematurity (OOP) may result from the necessary care (long term total parenteral and diuretic therapy) required by these premature infants. The outlook for the resolution of OOP depends primarily on the causation for the decrease in bone mineralization. Infants exhibiting TABLE 2 :SUMMARY OF NURSING IMPLICATIONS Prevention and Treatment of Osteopenia of Prematurity Prevention & Treatment 1. Calcium and phosphorous in TPN at a ratio of :1 (calcium=9-10 mg/dl and phosphorous= 6-8 units/l) and initiating enteral feedings as soon as medically possible. 2. Optimizing enteral intake of calcium and 3 of 5
4 phosphorus by adding powdered fortifier to breast milk or using a formula made for premature infants. 3. Switching from Lasix to an anticalciuric diuretic, such as Chlorothiazide IV or PO as soon as medically possible. 4. Limiting the use of Aminophylline and Dexamethazone therapy by switching to Albuterol and weaning steroids as soon as medically possible. 5. Figure 2 Maintaining vitamin D intake of 400-IU per day. 6. Physical therapy (i.e., range-of-motion exercises of the upper and lower extremities) to enhance bone mineralization and bone mineral content in VLBW infants in stable condition. 7. Cautious handling in infants with nutritional rickets to avoid bone fractures. Figure 1: Calcium and Phosphorous Values for Baby Boy F References 1. Berseth, B, Abrams, S. Special Gastrointestional Concerns. In R Ballard, H Taeusch. Avery's Diseases of the Newborn. 7th ed. Philadelphia:W.B. Saunders Co; 1998; Gomella T. Rickets and Disorders of Calcium and Magnesium Metabolism. Neonatology. 4th ed. Stamford, Connecticut: Appleton & Lange; 1999; Backstrom M, Kuusela A, Maki R. Metabolic bone disease of prematurity. In Annuals of Medicine, 1996; 28, Smith S, Kirchhoff K. Metabolic bone disease in verylow-birth-weight infants: assessment, prevention, and treatment by neonatal nurse practitioners. In Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic and Neonatal Nursing, 1997; 26, Naylor K, Eastell R, Shattuck K, Alfrey A, Klein G. Bone turnover in preterm Infants. In Pediatric Research, 1999; 45, Zenk K. Nutritional Osteopenia. In Neonatal Medications & Nutrition: A Comprehensive Guide. Santa Rosa, CA: NICU Ink; 1999; Moyer-Mileur L, Luetkemeier M, Boomer L, Chan G. Effect of physical activity on bone mineralization in premature infants. In Pediatrics, 1995;127, Figure 3 Figure 2: Alkaline Phosphatase Values for Baby Boy F 4 of 5
5 Author Information Bridget K. Cross, RN, BSN Neonatal Nurse Practitioner Student, School of Nursing, The University of Texas-Houston Elias Vasquez, PhD, NP, FAANP Associate Professor of Clinical Nursing, School of Nursing, The University of Texas-Houston 5 of 5
Genetic examination of diseases affecting bone development. and structure in newborns
 Genetic examination of diseases affecting bone development and structure in newborns Examination of molecular genetic markers in osteopenic preterm infants PhD Thesis Simone Funke, MD University of Pécs
Genetic examination of diseases affecting bone development and structure in newborns Examination of molecular genetic markers in osteopenic preterm infants PhD Thesis Simone Funke, MD University of Pécs
Diuretic Use in Neonates
 Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: Diuretic Use in the Neonate http://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcareprofessionals/education/continuing-medical-nursing-education/neonatalnursing-education-briefs/ Diuretics
Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: Diuretic Use in the Neonate http://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcareprofessionals/education/continuing-medical-nursing-education/neonatalnursing-education-briefs/ Diuretics
METABOLIC BONE DISEASE OF PREMATURITY NEONATAL CLINICAL GUIDELINE V3.0
 METABOLIC BONE DISEASE OF PREMATURITY NEONATAL CLINICAL GUIDELINE V3.0 Page 1 of 10 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline To provide guidance on the prevention of metabolic bone disease in the neonate. All
METABOLIC BONE DISEASE OF PREMATURITY NEONATAL CLINICAL GUIDELINE V3.0 Page 1 of 10 1. Aim/Purpose of this Guideline To provide guidance on the prevention of metabolic bone disease in the neonate. All
FIAP, FICN, FAMS, FNNF
 Passport Size Photo Name:- Dr BD Bhatia Qualification:-MD, DCH, FIAP, FICN, FAMS, FNNF Current Designation:- Professor and Head Pediatrics,Heritage Institute of Medical Sciences,Varanasi President elect
Passport Size Photo Name:- Dr BD Bhatia Qualification:-MD, DCH, FIAP, FICN, FAMS, FNNF Current Designation:- Professor and Head Pediatrics,Heritage Institute of Medical Sciences,Varanasi President elect
Minimal Enteral Nutrition
 Abstract Minimal Enteral Nutrition Although parenteral nutrition has been used widely in the management of sick very low birth weight infants, a smooth transition to the enteral route is most desirable.
Abstract Minimal Enteral Nutrition Although parenteral nutrition has been used widely in the management of sick very low birth weight infants, a smooth transition to the enteral route is most desirable.
4/15/2014. Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth. Improving early nutrition. Problem Identification
 Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth Cathy Lee Leon, RN, BSN, MBA, NE-BC California Pacific Medical Center-San Francisco Improving early nutrition Standardized feeding protocol Problem
Nurses Take the Lead to Improve Overall Infant Growth Cathy Lee Leon, RN, BSN, MBA, NE-BC California Pacific Medical Center-San Francisco Improving early nutrition Standardized feeding protocol Problem
(1 280 ± 286) g; (1 436 ± 201) g
 259 ( 100730) : 34 1 800 g 24 (, 11 ) (, 13 ) 50%, 100 ml / (kg d) FM85, ; (30.6 ± 2.9), (1 280 ± 286) g; (31.6 ± 1.9), (1 436 ± 201) g, 81.6%, 34.1 24.6 d [18.9 vs 17.1 g / (kg d), P = 0.364] (1.16 vs
259 ( 100730) : 34 1 800 g 24 (, 11 ) (, 13 ) 50%, 100 ml / (kg d) FM85, ; (30.6 ± 2.9), (1 280 ± 286) g; (31.6 ± 1.9), (1 436 ± 201) g, 81.6%, 34.1 24.6 d [18.9 vs 17.1 g / (kg d), P = 0.364] (1.16 vs
ENTERAL NEEDS OF PRETERM INFANTS
 ENTERAL NEEDS OF PRETERM INFANTS A Capstone Seminar Paper for NTR 690: Seminar in Nutrition Presented to Dr. Rayane AbuSabha Department of Nutrition Sciences Sage Graduate School In Partial Fulfillment
ENTERAL NEEDS OF PRETERM INFANTS A Capstone Seminar Paper for NTR 690: Seminar in Nutrition Presented to Dr. Rayane AbuSabha Department of Nutrition Sciences Sage Graduate School In Partial Fulfillment
Post Discharge Nutrition. Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP
 Post Discharge Nutrition Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential conflicts of interest:
Post Discharge Nutrition Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential conflicts of interest:
NUTRITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
 NUTRITION AIMS To achieve growth and nutrient accretion similar to intrauterine rates To achieve best possible neurodevelopmental outcome To prevent specific nutritional deficiencies Target population
NUTRITION AIMS To achieve growth and nutrient accretion similar to intrauterine rates To achieve best possible neurodevelopmental outcome To prevent specific nutritional deficiencies Target population
Index. B BMC. See Bone mineral content BMD. See Bone mineral density Bone anabolic impact, Bone mass acquisition
 A Acid base balance dietary protein detrimental effects of, 19 Acid base balance bicarbonate effects, 176 in bone human studies, 174 mechanisms, 173 174 in muscle aging, 174 175 alkali supplementation
A Acid base balance dietary protein detrimental effects of, 19 Acid base balance bicarbonate effects, 176 in bone human studies, 174 mechanisms, 173 174 in muscle aging, 174 175 alkali supplementation
Research Article Effects of 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol on Recovery and Resolution of Late Transient Neonatal Hypocalcemia
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology Volume 2010, Article ID 409670, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/409670 Research Article Effects of 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology Volume 2010, Article ID 409670, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/409670 Research Article Effects of 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases
 Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
The Case Begins. The case continued. Necrotizing Enterocolitis
 Bugs, Drugs and Things that go Bump in the Night From ghoulies to ghosties and long leggety beasties & things that go bump in the night, good lord deliver us Old Cornish Prayer Caring for premature infant
Bugs, Drugs and Things that go Bump in the Night From ghoulies to ghosties and long leggety beasties & things that go bump in the night, good lord deliver us Old Cornish Prayer Caring for premature infant
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY
 INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5 10% in first week of life Preterm neonates have more total body water and may lose 10 15% of their weight in
INTRAVENOUS FLUID THERAPY PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5 10% in first week of life Preterm neonates have more total body water and may lose 10 15% of their weight in
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم. Rickets
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Rickets 1 Rickets IS defined as failure of mineralization of growing bone or osteoid tissue due to vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D appear as rickets in children and as oteomalacia
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Rickets 1 Rickets IS defined as failure of mineralization of growing bone or osteoid tissue due to vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D appear as rickets in children and as oteomalacia
HYPERCALCEMIA. Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences
 HYPERCALCEMIA Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences ESSENTIALS OF DIAGNOSIS Serum calcium level > 10.5 mg/dl Serum ionized
HYPERCALCEMIA Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences ESSENTIALS OF DIAGNOSIS Serum calcium level > 10.5 mg/dl Serum ionized
Nutrition in the premie World
 SURVIVAL AND GROWTH NUTRITION ESSENTIALS Nutrition in the premie World DR VISH SUBRAMANIAN MD MRCP (UK) FAAP NEONATAL CRITICAL CARE MERCY CHILDRENS HOSPITAL., SPRINGFIELD MO Prematurity Nutritional Requirements
SURVIVAL AND GROWTH NUTRITION ESSENTIALS Nutrition in the premie World DR VISH SUBRAMANIAN MD MRCP (UK) FAAP NEONATAL CRITICAL CARE MERCY CHILDRENS HOSPITAL., SPRINGFIELD MO Prematurity Nutritional Requirements
The Parathyroid Glands Secrete Parathyroid Hormone, which Regulates Calcium, Magnesium, and Phosphate Ion Levels
 17.6 The Parathyroid Glands Secrete Parathyroid Hormone, which Regulates Calcium, Magnesium, and Phosphate Ion Levels Partially embedded in the posterior surface of the lateral lobes of the thyroid gland
17.6 The Parathyroid Glands Secrete Parathyroid Hormone, which Regulates Calcium, Magnesium, and Phosphate Ion Levels Partially embedded in the posterior surface of the lateral lobes of the thyroid gland
Preterm Dietary Supplements
 Preterm Dietary Supplements Dr Umesh Vaidya IAP Neocon, Mumbai 2015 Preterm VLBW Nutrition : Ideal practice Minimal enteral feeds (10 ml / kg / day) Human breast milk Feed advancement @ 20 ml / kg / day
Preterm Dietary Supplements Dr Umesh Vaidya IAP Neocon, Mumbai 2015 Preterm VLBW Nutrition : Ideal practice Minimal enteral feeds (10 ml / kg / day) Human breast milk Feed advancement @ 20 ml / kg / day
NEONATOLOGY Healthy newborn. Neonatal sequelaes
 NEONATOLOGY Healthy newborn. Neonatal sequelaes Ágnes Harmath M.D. Ph.D. senior lecturer 11. November 2016. Tasks of the neonatologist Prenatal diagnosed condition Inform parents, preparation of necessary
NEONATOLOGY Healthy newborn. Neonatal sequelaes Ágnes Harmath M.D. Ph.D. senior lecturer 11. November 2016. Tasks of the neonatologist Prenatal diagnosed condition Inform parents, preparation of necessary
Hazards and Benefits of Postnatal Steroids. David J. Burchfield, MD Professor and Chief, Neonatology University of Florida
 Hazards and Benefits of Postnatal Steroids David J. Burchfield, MD Professor and Chief, Neonatology University of Florida Disclosures I have no financial affiliations or relationships to disclose. I will
Hazards and Benefits of Postnatal Steroids David J. Burchfield, MD Professor and Chief, Neonatology University of Florida Disclosures I have no financial affiliations or relationships to disclose. I will
Journal of Clinical & Translational Endocrinology
 Journal of Clinical & Translational Endocrinology 2 (2015) 14e20 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Clinical & Translational Endocrinology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jcte
Journal of Clinical & Translational Endocrinology 2 (2015) 14e20 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Clinical & Translational Endocrinology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jcte
PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
PARENTERAL NUTRITION DEFINITION Parenteral nutrition [(PN) or total parenteral nutrition (TPN)] is the intravenous infusion of some or all nutrients for tissue maintenance, metabolic requirements and growth
Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants. Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital
 Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital Objectives Review maintenance fluid & electrolyte requirements in neonates Discuss
Fluid & Electrolyte Balances in Term & Preterm Infants Carolyn Abitbol, M.D. University of Miami/ Holtz Children s Hospital Objectives Review maintenance fluid & electrolyte requirements in neonates Discuss
Sachin Soni DNB Pediatrics
 Sachin Soni DNB Pediatrics Vitamin D physiology Introduction Etiology Clinical feature Radiology Diagnosis Lab Treatment Source: -Fish, liver and oil, - Human milk (30-40 IU/L) - Exposure to sun light
Sachin Soni DNB Pediatrics Vitamin D physiology Introduction Etiology Clinical feature Radiology Diagnosis Lab Treatment Source: -Fish, liver and oil, - Human milk (30-40 IU/L) - Exposure to sun light
Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi
 Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi Outline O Background O Challenges in preterm nutrition O Parenteral Nutrition
Nutrition in the preterm - current menu Dr Heena Hooker Consulting Neonatal Paediatrician Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi Outline O Background O Challenges in preterm nutrition O Parenteral Nutrition
Amani Alghamdi. Slide 1
 Minerals in the body Amani Alghamdi Slide 1 The Minerals Small, naturally occurring, inorganic, chemical elements Serve as structural components Minerals classification The minerals present in the body
Minerals in the body Amani Alghamdi Slide 1 The Minerals Small, naturally occurring, inorganic, chemical elements Serve as structural components Minerals classification The minerals present in the body
Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition The Department of Health in England has asked NICE to develop a new guideline on parenteral nutrition in
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Neonatal parenteral nutrition The Department of Health in England has asked NICE to develop a new guideline on parenteral nutrition in
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES
 INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5-10% Postnatal diuresis is delayed in Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Preterm babies have limited capacity to excrete
INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS PRINCIPLES Postnatal physiological weight loss is approximately 5-10% Postnatal diuresis is delayed in Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Preterm babies have limited capacity to excrete
Accepted Manuscript. Metabolic Bone Disease of Prematurity. Stacy E. Rustico, MD Andrew C. Calabria, MD Samuel J. Garber, MD
 Accepted Manuscript Metabolic Bone Disease of Prematurity Stacy E. Rustico, MD Andrew C. Calabria, MD Samuel J. Garber, MD PII: S2214-6237(14)00021-0 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcte.2014.06.004 Reference: JCTE 18
Accepted Manuscript Metabolic Bone Disease of Prematurity Stacy E. Rustico, MD Andrew C. Calabria, MD Samuel J. Garber, MD PII: S2214-6237(14)00021-0 DOI: 10.1016/j.jcte.2014.06.004 Reference: JCTE 18
Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1
 Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1 The body fluids are solutions of inorganic and organic solutes. The concentration balance of the various components is maintained in order for the cell and tissue
Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1 The body fluids are solutions of inorganic and organic solutes. The concentration balance of the various components is maintained in order for the cell and tissue
Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes
 Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes Malki Miller MS, RD, CNSC Neonatal Dietitian, Maimonides Infants and Children s Hospital Adjunct Lecturer of Human and Pediatric,
Prematurity: Optimizing Growth in the NICU for Later Metabolic Outcomes Malki Miller MS, RD, CNSC Neonatal Dietitian, Maimonides Infants and Children s Hospital Adjunct Lecturer of Human and Pediatric,
Phosphoremia (mmol/l) Calcemia (mmol/l) Postnatal age (days) Postnatal age (days) Urinary Calcium (mg/kg/d) Phosphoremia (mmol/l)
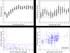 3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
3,0 3,2 Calcemia (mmol/l) 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 Phosphoremia (mmol/l) 3,0 2,8 2,6 2,4 2,2 2,0 1,8 1,6 1,4 1,2 1,6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Postnatal age (days) 1,0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
HUMAN MILK FOR PRETERM INFANTS: ONE SIZE FITS ALL?
 HUMAN MILK FOR PRETERM INFANTS: ONE SIZE FITS ALL? Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Professor and Chief Division of Neonatology Vice Chair, Clinical Research Department of Pediatrics Chair, Augusta University
HUMAN MILK FOR PRETERM INFANTS: ONE SIZE FITS ALL? Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Professor and Chief Division of Neonatology Vice Chair, Clinical Research Department of Pediatrics Chair, Augusta University
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Colecalciferol Meda 800 IU tablet 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each tablet contains colecalciferol (vitamin D 3 ) 800 IU
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Colecalciferol Meda 800 IU tablet 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each tablet contains colecalciferol (vitamin D 3 ) 800 IU
Natpara (parathyroid hormone) Prior Authorization with Quantity Limit Program Summary
 Natpara (parathyroid hormone) Prior Authorization with Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1 Agent Indication Dosing and Administration Natpara (parathyroid hormone) subcutaneous
Natpara (parathyroid hormone) Prior Authorization with Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1 Agent Indication Dosing and Administration Natpara (parathyroid hormone) subcutaneous
Research Roundtable Summary
 Research Roundtable Summary 10 TENTH in a Series of Seminars on MCHB-funded Research Projects Early Cortisol Deficiency and Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia October 18, 1995 Parklawn Building Potomac Conference
Research Roundtable Summary 10 TENTH in a Series of Seminars on MCHB-funded Research Projects Early Cortisol Deficiency and Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia October 18, 1995 Parklawn Building Potomac Conference
DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION
 DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION NAME OF MEDICINE Magnesium Sulfate BP DESCRIPTION DBL Magnesium Sulfate Concentrated Injection is a clear, colourless, sterile solution. Each ampoule contains
DBL MAGNESIUM SULFATE CONCENTRATED INJECTION NAME OF MEDICINE Magnesium Sulfate BP DESCRIPTION DBL Magnesium Sulfate Concentrated Injection is a clear, colourless, sterile solution. Each ampoule contains
lactation normally do not cause any adverse long-term consequences to the maternal skeleton.
 MATRIX Matrix Is The First Choice Product Ever Promotes Bone Health Containing A Unique Combination Of 12 Amino Acid Chelated Active Ingredients Formulated In Palatable Toffee Pieces Which Guarantees The
MATRIX Matrix Is The First Choice Product Ever Promotes Bone Health Containing A Unique Combination Of 12 Amino Acid Chelated Active Ingredients Formulated In Palatable Toffee Pieces Which Guarantees The
PROTOCOL FOR PARENTERAL NUTRITION
 PROTOCOL FOR PARENTERAL NUTRITION Based on; Roberton s textbook of neonatology. 4 th edition. 2005. Sudha Chaudari and Sandeep Kumar.TPN in neonates. Indian Paediatrics. November 2006 Deepak Chawla, Anu
PROTOCOL FOR PARENTERAL NUTRITION Based on; Roberton s textbook of neonatology. 4 th edition. 2005. Sudha Chaudari and Sandeep Kumar.TPN in neonates. Indian Paediatrics. November 2006 Deepak Chawla, Anu
WOMEN S AND INFANT HEALTH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 WOMEN S AND INFANT HEALTH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES SUBJECT/TITLE: Post Discharge Preterm Formula: Neonates Draft June 19, 2009 DATE ESTABLISHED: DATE REVISED: NUMBER: PAGE: 1 of 11 PURPOSE To enhance
WOMEN S AND INFANT HEALTH CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES SUBJECT/TITLE: Post Discharge Preterm Formula: Neonates Draft June 19, 2009 DATE ESTABLISHED: DATE REVISED: NUMBER: PAGE: 1 of 11 PURPOSE To enhance
11/4/10 SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP SAM: PREVENT MALNUTRITION 200. Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure
 Jae H Kim MD PhD Lisa Stellwagen MD Division of Neonatology UC San Diego, Medical Center SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure Jae H. Kim, MD,
Jae H Kim MD PhD Lisa Stellwagen MD Division of Neonatology UC San Diego, Medical Center SUPPORTING PREMATURE INFANT NUTRITION WORKSHOP Workshop: Preventing extrauterine growth failure Jae H. Kim, MD,
Satellite Symposium. Sponsored by
 Satellite Symposium Sponsored by Management of fluids and electrolytes in the preterm infant in the first week of life Pam Cairns St Michaels Hospital Bristol Healthy, term, breast fed babies Limited intake
Satellite Symposium Sponsored by Management of fluids and electrolytes in the preterm infant in the first week of life Pam Cairns St Michaels Hospital Bristol Healthy, term, breast fed babies Limited intake
Nutrition in the NICU ANDI MARKELL RD, LD
 Nutrition in the NICU ANDI MARKELL RD, LD PORTLAND, OREGON ANDI MARKELL NUTRITION CONSULTANT Conflict of Interest I had no conflict of interest until 2015 when I was asked to join the Nutrition Advisory
Nutrition in the NICU ANDI MARKELL RD, LD PORTLAND, OREGON ANDI MARKELL NUTRITION CONSULTANT Conflict of Interest I had no conflict of interest until 2015 when I was asked to join the Nutrition Advisory
Dr Shipa Shah, Lorraine Bell Dietician
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Enteral feeding and use of fortification and supplements in the preterm infant Dr Shipa Shah, Lorraine Bell Dietician Neonatalogy
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate: Enteral feeding and use of fortification and supplements in the preterm infant Dr Shipa Shah, Lorraine Bell Dietician Neonatalogy
Vitamins. Vitamins (continued) Lipid-Soluble Vitamins (A, D, E, K) Vitamins Serve Important Roles in Function of Body
 Vitamins Drugs for Nutritional Disorders Organic substances are needed in small amounts Promote growth Maintain health Vitamins Human cells cannot produce vitamins Exception: vitamin D Vitamins or provitamins
Vitamins Drugs for Nutritional Disorders Organic substances are needed in small amounts Promote growth Maintain health Vitamins Human cells cannot produce vitamins Exception: vitamin D Vitamins or provitamins
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
 Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Professor Joseph HADDAD Pediatric Department Saint George Univ Hosp Balamand Univ Beirut Lebanon
 Nutrition & Growth in Premature Infant Professor Joseph HADDAD Pediatric Department Saint George Univ Hosp Balamand Univ Beirut Lebanon PART ONE : THE GROWTH OF THE PREMATURE INFANT ARE WE ON THE RIGHT
Nutrition & Growth in Premature Infant Professor Joseph HADDAD Pediatric Department Saint George Univ Hosp Balamand Univ Beirut Lebanon PART ONE : THE GROWTH OF THE PREMATURE INFANT ARE WE ON THE RIGHT
Professor Md. Mahtab Uddin Hassan FCPS(Med) MRCP(UK) FRCP(Edin) Professor of Medicine AKMMCH
 Professor Md. Mahtab Uddin Hassan FCPS(Med) MRCP(UK) FRCP(Edin) Professor of Medicine AKMMCH Introduction The sunshine vitamin is a hot topic. Vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency is becoming a global
Professor Md. Mahtab Uddin Hassan FCPS(Med) MRCP(UK) FRCP(Edin) Professor of Medicine AKMMCH Introduction The sunshine vitamin is a hot topic. Vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency is becoming a global
QI: Exclusive Human Milk Diet for Preterm Infants
 QI: Exclusive Human Milk Diet for Preterm Infants Amy B. Hair, MD Assistant s Professor of Program Director of Neonatal Nutrition Program Director of NICU Intestinal Rehab Team Section of Neonatology Department
QI: Exclusive Human Milk Diet for Preterm Infants Amy B. Hair, MD Assistant s Professor of Program Director of Neonatal Nutrition Program Director of NICU Intestinal Rehab Team Section of Neonatology Department
Product Information: Similac Special Care 24 High Protein
 Product Information: Similac Special Care 24 High Protein 1 of 5 A 24 Cal/fl oz iron-fortified feeding for growing, low-birth-weight infants and premature infants who may need extra protein to help support
Product Information: Similac Special Care 24 High Protein 1 of 5 A 24 Cal/fl oz iron-fortified feeding for growing, low-birth-weight infants and premature infants who may need extra protein to help support
Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants
 Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential
Aggressive Nutrition in Preterm Infants Jatinder Bhatia, MD, FAAP Declaration of potential conflicts of interest Regarding this presentation the following relationships could be perceived as potential
Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in Please DO NOT mail or fax this form to the CPQCC Data Center. This form is for internal use ONLY.
 Selection Criteria Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in 2016 To be eligible, you MUST answer YES to at least one of the possible criteria (A-C) A. 401 1500 grams o Yes B. GA range 22 0/7 31 6/7
Selection Criteria Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in 2016 To be eligible, you MUST answer YES to at least one of the possible criteria (A-C) A. 401 1500 grams o Yes B. GA range 22 0/7 31 6/7
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 27 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Fluid Compartments and Fluid In adults, body fluids make up between 55% and 65% of total body mass. Body
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 27 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Fluid Compartments and Fluid In adults, body fluids make up between 55% and 65% of total body mass. Body
Product Information: Similac Special Care 30 With Iron
 Product Information: Similac Special Care 30 With Iron 1 of 5 A 30 Cal/fl oz iron-fortified feeding for growing, low-birth-weight infants and premature infants. Use under medical supervision. First 30-Cal/fl
Product Information: Similac Special Care 30 With Iron 1 of 5 A 30 Cal/fl oz iron-fortified feeding for growing, low-birth-weight infants and premature infants. Use under medical supervision. First 30-Cal/fl
Calcium and Vitamin D Requirements of Enterally Fed Preterm Infants
 Guidance for the Clinician in Rendering Pediatric Care CLINICAL REPORT Calcium and Vitamin D Requirements of Enterally Fed Preterm Infants abstract Bone health is a critical concern in managing preterm
Guidance for the Clinician in Rendering Pediatric Care CLINICAL REPORT Calcium and Vitamin D Requirements of Enterally Fed Preterm Infants abstract Bone health is a critical concern in managing preterm
Comparative study on hypocalcemia and maternal serum calcium level in tertiary care hospital in Chennai
 Original Research Article Comparative study on hypocalcemia and maternal serum calcium level in tertiary care hospital in Chennai V. Ramya 1, Dunnuthala Sreenivasulu Reddy 2*, Shafath Ahmed 3 1 Post Graduate
Original Research Article Comparative study on hypocalcemia and maternal serum calcium level in tertiary care hospital in Chennai V. Ramya 1, Dunnuthala Sreenivasulu Reddy 2*, Shafath Ahmed 3 1 Post Graduate
1.3 Sample Standard of Care from the Medical University of South Carolina
 1.3 Sample Standard of Care from the Medical University of South Carolina Vitamin D Testing and Treatment Protocol MUSC Department of Ob-Gyn, Maternal-Fetal Medicine Division BACKGROUND: A rapidly evolving
1.3 Sample Standard of Care from the Medical University of South Carolina Vitamin D Testing and Treatment Protocol MUSC Department of Ob-Gyn, Maternal-Fetal Medicine Division BACKGROUND: A rapidly evolving
Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE
 Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE I. RELATED TOPICS Integumentary system Cerebrospinal fluid Aqueous humor Digestive juices Feces Capillary dynamics Lymph circulation Edema Osmosis
Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE I. RELATED TOPICS Integumentary system Cerebrospinal fluid Aqueous humor Digestive juices Feces Capillary dynamics Lymph circulation Edema Osmosis
Case Reports. A Rare Cause of Symptomatic Neonatal Hypocalcaemia EKC YAU, AWF CHENG, SY LEE, CB CHOW. Abstract. Key words.
 HK J Paediatr (new series) 2003;8:121-125 Case Reports A Rare Cause of Symptomatic Neonatal Hypocalcaemia EKC YAU, AWF CHENG, SY LEE, CB CHOW Abstract Key words Neonatal hypocalcaemia due to maternal hyperparathyroidism
HK J Paediatr (new series) 2003;8:121-125 Case Reports A Rare Cause of Symptomatic Neonatal Hypocalcaemia EKC YAU, AWF CHENG, SY LEE, CB CHOW Abstract Key words Neonatal hypocalcaemia due to maternal hyperparathyroidism
Osteopenia Versus Rickets in Premature Infants
 Rickets, edited by Francis H. Glorieux. Nestle Nutrition Workshop Series. Vol. 21. Nestec Ltd.. Vevey/Raven Press. Ltd.. New York 1991. Osteopenia Versus Rickets in Premature Infants Jacques Senterre Departement
Rickets, edited by Francis H. Glorieux. Nestle Nutrition Workshop Series. Vol. 21. Nestec Ltd.. Vevey/Raven Press. Ltd.. New York 1991. Osteopenia Versus Rickets in Premature Infants Jacques Senterre Departement
DIAGNOSING X-LINKED HYPOPHOSPHATEMIA (XLH) BIOCHEMICAL TESTING CONSIDERATIONS
 DIAGNOSING X-LINKED HYPOPHOSPHATEMIA (XLH) BIOCHEMICAL TESTING CONSIDERATIONS XLH IS CHARACTERIZED BY CHRONIC HYPOPHOSPHATEMIA XLH is a hereditary, progressive, lifelong disorder. In children and adults,
DIAGNOSING X-LINKED HYPOPHOSPHATEMIA (XLH) BIOCHEMICAL TESTING CONSIDERATIONS XLH IS CHARACTERIZED BY CHRONIC HYPOPHOSPHATEMIA XLH is a hereditary, progressive, lifelong disorder. In children and adults,
GLOSSARY OF TERMS. produced in response to an antigen to bond with and neutralize that antigen / the body's way of destroying foreign invaders
 TERM 24-hour urine acidosis acquired aemia (prefix) albumin alkalosis anemia antibodies antigen autocrine autoimmune basal ganglion bone turnover calcilytic calcimimetic calcitonin Calcitriol Calcium carbonate
TERM 24-hour urine acidosis acquired aemia (prefix) albumin alkalosis anemia antibodies antigen autocrine autoimmune basal ganglion bone turnover calcilytic calcimimetic calcitonin Calcitriol Calcium carbonate
Hypercalcemia. Hypercalcemia: When to Worry, When to Treat! Mineral Metabolism : A Short Course
 Hypercalcemia: When to Worry, When to Treat! Michael A. Levine has no financial relationships to disclose or Conflicts of Interest to resolve. Michael A. Levine, M.D. This presentation will not involve
Hypercalcemia: When to Worry, When to Treat! Michael A. Levine has no financial relationships to disclose or Conflicts of Interest to resolve. Michael A. Levine, M.D. This presentation will not involve
Summary of Product Characteristics
 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Desunin 4000 IU Tablets Summary of Product Characteristics 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each tablet contains colecalciferol (vitamin D 3 ) 4000 IU (equivalent
1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Desunin 4000 IU Tablets Summary of Product Characteristics 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each tablet contains colecalciferol (vitamin D 3 ) 4000 IU (equivalent
Vitamin D: Is it a superhero??
 Vitamin D: Is it a superhero?? Dr. Ashraf Abdel Basset Bakr Prof. of Pediatrics 1 2 History of vitamin D discovery Sources of vitamin D and its metabolism 13 Actions of vitamin D 4 Vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D: Is it a superhero?? Dr. Ashraf Abdel Basset Bakr Prof. of Pediatrics 1 2 History of vitamin D discovery Sources of vitamin D and its metabolism 13 Actions of vitamin D 4 Vitamin D deficiency
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Calcium Sandoz 500 mg, effervescent tablets Calcium Sandoz 1000 mg, effervescent tablets 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Calcium Sandoz 500 mg, effervescent tablets Calcium Sandoz 1000 mg, effervescent tablets 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Product Information: Similac Special Care 24
 Product Information: Similac Special Care 24 1 of 5 A 24 Cal/fl oz iron-fortified feeding for growing, low-birth-weight infants and premature infants. Use under medical supervision. OptiGRO is our exclusive
Product Information: Similac Special Care 24 1 of 5 A 24 Cal/fl oz iron-fortified feeding for growing, low-birth-weight infants and premature infants. Use under medical supervision. OptiGRO is our exclusive
HIJAM-HMF A READY RECKONER HUMAN MILK FORTIFIER 1 gm per Sachet
 HIJAM-HMF A READY RECKONER HUMAN MILK FORTIFIER 1 gm per Sachet To ensure long-term health and development of preterm infants, an early nutritional support is utmost important. Breast milk is undoubtedly
HIJAM-HMF A READY RECKONER HUMAN MILK FORTIFIER 1 gm per Sachet To ensure long-term health and development of preterm infants, an early nutritional support is utmost important. Breast milk is undoubtedly
A.S.P.E.N. Clinical Guidelines: Nutrition Support of Neonatal Patients at Risk for Metabolic Bone Disease
 487216PENXXX10.1177/0148607113487216Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition / Vol. XX, No. X, Month XXXXNehra et al research-article2013 Clinical Guidelines A.S.P.E.N. Clinical Guidelines:
487216PENXXX10.1177/0148607113487216Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition / Vol. XX, No. X, Month XXXXNehra et al research-article2013 Clinical Guidelines A.S.P.E.N. Clinical Guidelines:
David Bruyette, DVM, DACVIM
 VCAwestlaspecialty.com David Bruyette, DVM, DACVIM Disorders of calcium metabolism are common endocrine disorders in both dogs and cats. In this article we present a logical diagnostic approach to patients
VCAwestlaspecialty.com David Bruyette, DVM, DACVIM Disorders of calcium metabolism are common endocrine disorders in both dogs and cats. In this article we present a logical diagnostic approach to patients
ADMISSION/DISCHARGE FORM FOR INFANTS BORN IN 2019 DO NOT mail or fax this form to the CPQCC Data Center. This form is for internal use ONLY.
 1 Any eligible inborn infant who dies in the delivery room or at any other location in your hospital within 12 hours after birth and prior to admission to the NICU is defined as a "Delivery Room Death."
1 Any eligible inborn infant who dies in the delivery room or at any other location in your hospital within 12 hours after birth and prior to admission to the NICU is defined as a "Delivery Room Death."
Role of human milk fortifier on weight gain in very low birth weight babies
 International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Verma GK et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2018 Mar;5(2):353-358 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Verma GK et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2018 Mar;5(2):353-358 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
Resuscitating neonatal and infant organs and preserving function. GI Tract and Kidneys
 Resuscitating neonatal and infant organs and preserving function GI Tract and Kidneys Australian and New Zealand Resuscitation Council Joint Guidelines Outline Emphasis on the infant - PICU Kidney Gastrointestinal
Resuscitating neonatal and infant organs and preserving function GI Tract and Kidneys Australian and New Zealand Resuscitation Council Joint Guidelines Outline Emphasis on the infant - PICU Kidney Gastrointestinal
ENTERAL NUTRITION Identifying risk of patients for enteral feeding problems: Low risk: Moderate risk: High risk:
 ENTERAL NUTRITION Statement of best practice Feeding with mother s own breastmilk is protective against sepsis, NEC and death All mothers should be informed about this and strongly encouraged to express
ENTERAL NUTRITION Statement of best practice Feeding with mother s own breastmilk is protective against sepsis, NEC and death All mothers should be informed about this and strongly encouraged to express
Product Information: Similac Special Care 30
 Product Information: Similac Special Care 30 1 of 5 A 30 Cal/fl oz iron-fortified feeding for growing, low-birth-weight infants and premature infants. First 30-Cal/fl oz ready-to-feed liquid preterm infant
Product Information: Similac Special Care 30 1 of 5 A 30 Cal/fl oz iron-fortified feeding for growing, low-birth-weight infants and premature infants. First 30-Cal/fl oz ready-to-feed liquid preterm infant
Melinda Elliott, MD Senior Director, Clinical Education and Professional Development, Prolacta Bioscience Neonatologist, Pediatrix Medical Group of
 Melinda Elliott, MD Senior Director, Clinical Education and Professional Development, Prolacta Bioscience Neonatologist, Pediatrix Medical Group of Maryland Breast Milk is for Babies, Cows Milk is for
Melinda Elliott, MD Senior Director, Clinical Education and Professional Development, Prolacta Bioscience Neonatologist, Pediatrix Medical Group of Maryland Breast Milk is for Babies, Cows Milk is for
Endocrine Regulation of Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism
 Endocrine Regulation of Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism Huiping Wang ( 王会平 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C516, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208252 Email: wanghuiping@zju.edu.cn
Endocrine Regulation of Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism Huiping Wang ( 王会平 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C516, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208252 Email: wanghuiping@zju.edu.cn
ROLE OF EARLY POSTNATAL DEXAMETHASONE IN RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME
 INDIAN PEDIATRICS VOLUME 35-FEBRUAKY 1998 ROLE OF EARLY POSTNATAL DEXAMETHASONE IN RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME Kanya Mukhopadhyay, Praveen Kumar and Anil Narang From the Division of Neonatology, Department
INDIAN PEDIATRICS VOLUME 35-FEBRUAKY 1998 ROLE OF EARLY POSTNATAL DEXAMETHASONE IN RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME Kanya Mukhopadhyay, Praveen Kumar and Anil Narang From the Division of Neonatology, Department
GESKES/ SSNC Individualized Nutritional Support in the Case of Postnatal Growth Restriction
 Case Presentation for the Course in Clinical Nutrition GESKES/ SSNC Individualized Nutritional Support in the Case of Postnatal Growth Restriction Dr. med. Chantal Cripe-Mamie Division of Neonatology Department
Case Presentation for the Course in Clinical Nutrition GESKES/ SSNC Individualized Nutritional Support in the Case of Postnatal Growth Restriction Dr. med. Chantal Cripe-Mamie Division of Neonatology Department
Calcium Nephrolithiasis and Bone Health. Noah S. Schenkman, MD
 Calcium Nephrolithiasis and Bone Health Noah S. Schenkman, MD Associate Professor of Urology and Residency Program Director, University of Virginia Health System; Charlottesville, Virginia Objectives:
Calcium Nephrolithiasis and Bone Health Noah S. Schenkman, MD Associate Professor of Urology and Residency Program Director, University of Virginia Health System; Charlottesville, Virginia Objectives:
Protein Needs of Preterm Infants: Why Are They So Difficult to Meet?
 Protein in the Feeding of Preterm Infants Bhatia J, Shamir R, Vandenplas Y (eds): Protein in Neonatal and Infant Nutrition: Recent Updates. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 86, pp 121 128, (DOI: 10.1159/000442732
Protein in the Feeding of Preterm Infants Bhatia J, Shamir R, Vandenplas Y (eds): Protein in Neonatal and Infant Nutrition: Recent Updates. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 86, pp 121 128, (DOI: 10.1159/000442732
OMICS Journals are welcoming Submissions
 OMICS Journals are welcoming Submissions OMICS International welcomes submissions that are original and technically so as to serve both the developing world and developed countries in the best possible
OMICS Journals are welcoming Submissions OMICS International welcomes submissions that are original and technically so as to serve both the developing world and developed countries in the best possible
A case of hereditary hypophosphataemic rickets with hypercalciuria (HHRH)
 Case Reports A case of hereditary hypophosphataemic rickets with hypercalciuria (HHRH) M N Lucas 1, Savithri Dias 2 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2006; 35:141-3 (Key words: hereditary hypophosphataemic
Case Reports A case of hereditary hypophosphataemic rickets with hypercalciuria (HHRH) M N Lucas 1, Savithri Dias 2 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2006; 35:141-3 (Key words: hereditary hypophosphataemic
Natpara (parathyroid hormone) Prior Authorization with Quantity Limit Program Summary
 Natpara (parathyroid hormone) Prior Authorization with Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 2 Available Product Indication Dosing and Administration Natpara (parathyroid hormone)
Natpara (parathyroid hormone) Prior Authorization with Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 2 Available Product Indication Dosing and Administration Natpara (parathyroid hormone)
PRACTICE GUIDELINES WOMEN S HEALTH PROGRAM
 C Title: NEWBORN: HYPOGLYCEMIA IN NEONATES BORN AT 35+0 WEEKS GESTATION AND GREATER: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT IN THE FIRST 72 HOURS Authorization Section Head, Neonatology, Program Director, Women s Health
C Title: NEWBORN: HYPOGLYCEMIA IN NEONATES BORN AT 35+0 WEEKS GESTATION AND GREATER: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT IN THE FIRST 72 HOURS Authorization Section Head, Neonatology, Program Director, Women s Health
Hyperparathyroidism. There is however another more potent method to achieve the lowering of PTH in a more natural way.
 Hyperparathyroidism Old Theory The parathyroid glands maintain proper levels of both calcium and phosphorus in your body by turning the secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH) off or on, much like a thermostat
Hyperparathyroidism Old Theory The parathyroid glands maintain proper levels of both calcium and phosphorus in your body by turning the secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH) off or on, much like a thermostat
Intrapartum and Postpartum Management of the Diabetic Mother and Infant
 Intrapartum and Postpartum Management of the Diabetic Mother and Infant Intrapartum Management Women with gestational diabetes who maintain normal glucose levels during pregnancy on diet and exercise therapy
Intrapartum and Postpartum Management of the Diabetic Mother and Infant Intrapartum Management Women with gestational diabetes who maintain normal glucose levels during pregnancy on diet and exercise therapy
Product Information: Similac Advance 20
 Product Information: Similac Advance 20 1 of 7 A 20 Cal/fl oz, nutritionally complete, milk-based, iron-fortified infant formula for use as a supplement or alternative to breastfeeding. No artificial growth
Product Information: Similac Advance 20 1 of 7 A 20 Cal/fl oz, nutritionally complete, milk-based, iron-fortified infant formula for use as a supplement or alternative to breastfeeding. No artificial growth
IJMB ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION /jp-journals
 Bhawna Bhimte, Amrita Vamne ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10054-0027 Metabolic Derangement in Birth Asphyxia due to Cellular Injury with Reference to Mineral Metabolism in Different Stages of Hypoxic-ischemic
Bhawna Bhimte, Amrita Vamne ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10054-0027 Metabolic Derangement in Birth Asphyxia due to Cellular Injury with Reference to Mineral Metabolism in Different Stages of Hypoxic-ischemic
Hypocalcemia 6/8/12. Normal value. Physiologic functions. Nephron a functional unit of kidney. Influencing factors in Calcium and Phosphate Balance
 Normal value Hypocalcemia Serum calcium Total mg/dl Ionized mg/dl Cord blood 9.0 ~ 11.5 5.0 ~ 6.o New born (1 st 24 hrs) 9.0 ~ 10.6 4.3 ~ 5.1 24~ 48 hrs 7.0 ~12.0 4.0 ~4.7 Child 8.8 ~10.8 4.8 ~4.92 There
Normal value Hypocalcemia Serum calcium Total mg/dl Ionized mg/dl Cord blood 9.0 ~ 11.5 5.0 ~ 6.o New born (1 st 24 hrs) 9.0 ~ 10.6 4.3 ~ 5.1 24~ 48 hrs 7.0 ~12.0 4.0 ~4.7 Child 8.8 ~10.8 4.8 ~4.92 There
50% Concentrated Injection
 NAME OF THE MEDICINE. The molecular weight of the compound is 246.5 and the CAS registry number is 10034-99-8. The molecular formula is MgSO4, 7H2O. DESCRIPTION MAGNESIUM SULFATE HEPTAHYDRATE 50% CONCENTRATED
NAME OF THE MEDICINE. The molecular weight of the compound is 246.5 and the CAS registry number is 10034-99-8. The molecular formula is MgSO4, 7H2O. DESCRIPTION MAGNESIUM SULFATE HEPTAHYDRATE 50% CONCENTRATED
WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM
 WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM Attila Miseta Tamás Kőszegi Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2016 1 Average daily water intake and output of a normal adult 2 Approximate contributions to plasma osmolality
WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM Attila Miseta Tamás Kőszegi Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2016 1 Average daily water intake and output of a normal adult 2 Approximate contributions to plasma osmolality
For the use only of Registered Medical Practitioners or a Hospital or a Laboratory OSTOCALCIUM FORTE TABLETS
 For the use only of Registered Medical Practitioners or a Hospital or a Laboratory OSTOCALCIUM FORTE TABLETS Calcium and Phosphorus with Vitamin D3 Tablets QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each
For the use only of Registered Medical Practitioners or a Hospital or a Laboratory OSTOCALCIUM FORTE TABLETS Calcium and Phosphorus with Vitamin D3 Tablets QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each
Ca, Mg metabolism, bone diseases. Tamás Kőszegi Pécs University, Department of Laboratory Medicine Pécs, Hungary
 Ca, Mg metabolism, bone diseases Tamás Kőszegi Pécs University, Department of Laboratory Medicine Pécs, Hungary Calcium homeostasis Ca 1000g in adults 99% in bones (extracellular with Mg, P) Plasma/intracellular
Ca, Mg metabolism, bone diseases Tamás Kőszegi Pécs University, Department of Laboratory Medicine Pécs, Hungary Calcium homeostasis Ca 1000g in adults 99% in bones (extracellular with Mg, P) Plasma/intracellular
Product Information: Similac Advance
 Product Information: Similac Advance 1 of 5 A 19 Cal/fl oz, nutritionally complete, milk-based, iron-fortified infant formula for use as a supplement or alternative to breastfeeding. OptiGRO is our exclusive
Product Information: Similac Advance 1 of 5 A 19 Cal/fl oz, nutritionally complete, milk-based, iron-fortified infant formula for use as a supplement or alternative to breastfeeding. OptiGRO is our exclusive
DECALCITROL- cholecalciferol tablet, coated Pharmin USA, LLC DECALCITROL CHOLECALCIFEROL (VITAMIN D3) 1.25 mg TABLETS (50,000 Units)
 DECALCITROL- cholecalciferol tablet, coated ---------- DECALCITROL CHOLECALCIFEROL (VITAMIN D3) 1.25 mg TABLETS (50,000 Units) HIGH POTENCY SUPPLEMENT* *Warning: Cholecalciferol 50000 IU can be classified
DECALCITROL- cholecalciferol tablet, coated ---------- DECALCITROL CHOLECALCIFEROL (VITAMIN D3) 1.25 mg TABLETS (50,000 Units) HIGH POTENCY SUPPLEMENT* *Warning: Cholecalciferol 50000 IU can be classified
OSTEOMALACIA UPDATE. Nothing to Disclose. Daniel D Bikle, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine University of California and VA Medical Center San Francisco
 OSTEOMALACIA UPDATE Daniel D Bikle, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine University of California and VA Medical Center San Francisco Nothing to Disclose 1 Case History 59 YO WM referred for evaluation of diffuse
OSTEOMALACIA UPDATE Daniel D Bikle, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine University of California and VA Medical Center San Francisco Nothing to Disclose 1 Case History 59 YO WM referred for evaluation of diffuse
Hypophosphatasia. Tom Blevins, MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, TX
 Hypophosphatasia Tom Blevins, MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, TX Hypophosphatasia Case Teeth 57 y/o male with a hyperlipidemia and hypogonadism. Noted to have an alkaline phosphatase of
Hypophosphatasia Tom Blevins, MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, TX Hypophosphatasia Case Teeth 57 y/o male with a hyperlipidemia and hypogonadism. Noted to have an alkaline phosphatase of
