Accuracy assessment of measuring component position after total ankle arthroplasty using a conventional method
|
|
|
- Chester Dickerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lee et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:115 DOI /s RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Accuracy assessment of measuring component position after total ankle arthroplasty using a conventional method Kyoung-Jai Lee, Shao-Hua Wang, Gun-Woo Lee and Keun-Bae Lee * Abstract Background: This study was to assess the accuracy of measuring the tibial and talar components position and to investigate the outlier rate of each component and predisposing factors related to component malalignment after total ankle arthroplasty (TAA) using a conventional method. Methods: One hundred fifty consecutive primary total ankle arthroplasty were performed using the three-component HINTEGRA prosthesis for ankle end-stage osteoarthritis. Radiographic analysis for the accuracy of component position in coronal and sagittal plane was conducted at postoperative 6 months. Additionally, the accuracy of component position was evaluated according to presence of preoperative deformity or joint incongruency. Results: The mean postoperative coronal angles of the tibial and talar components (α and γ) were 91.9 and The mean postoperative sagittal angles of the tibial and talar components (β and δ angle) were 84.6 and In the coronal plane, 16 (10.7%) tibial components and 15 (10.0%) talar components showed outliers greater than 5. In sagittal plane, 15 (10.0%) tibial components and 29 (19.3%) talar components showed outliers greater than 5. There was no meaningful increase of the outlier rate regarding presence of preoperative deformity or joint incongruency. Conclusions: In conventional method of TAA, the outlier rate of the tibial and talar components was about 10 to 20%, especially, the outlier rate of talar component in sagittal plane was up to 20%. Therefore, careful attention should be paid to implant the talar component in conventional TAA. Keywords: Total ankle arthroplasty, Conventional method, Component position Background Total ankle arthroplasty (TAA) has been widely used for the treatment of end-stage ankle arthritis in recent years and satisfactory results have been reported [1 6]. However, high complication and reoperation rates after TAA have also been reported and still remain unsolved [7 10]. The success of joint arthroplasty depends on many factors, including patient selection, prosthetic design, soft tissue balancing, severity of joint deformity, and component position [11 17]. Among these factors, proper component position is one of the most important factors, which influences the longevity of the implant * Correspondence: kbleeos@jnu.ac.kr Equal contributors Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chonnam National University Medical School and Hospital, 42 Jebongro, Donggu, Gwangju 61469, Republic of Korea and prevents complications. Survivorship was also typically diminished when optimal alignment is not achieved [18 23]. Therefore, ankle prostheses should be aligned in such a way to assure even distribution of forces on the polyethylene liner [24]. Previous studies have reported radiographic outcomes and predisposing factors that increase the risk of postoperative malalignment after hip or knee joint arthroplasty. The malalignment of component has been reported ranges from 4 to 23% after primary total hip arthroplasty. Severe varus deformity and retroversion of the femur can cause incorrect insertion of the stem [25, 26]. In total knee arthroplasty, severe preoperative varus or valgus deformity and femoral bowing are associated with increased risk of alignment problem. Then, the The Author(s) Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Lee et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:115 Page 2 of 7 prevalence of malalignment in total knee arthroplasty has been reported range from 5 to 21% [27 29]. There are several studies about the accuracy assessment of component position following TAA. The rate of malalignment was varied from 0 to 35% after TAA. However, in these studies, the criteria for acceptable alignment of component was not standardized, and there are no comprehensive studies conducted regarding the outlier rates of the tibial and talar components or predisposing factors of incorrect component position following TAA. Therefore, the purpose of the present study was to evaluate the accuracy of component position after conventional TAA and to analyze the predisposing factors that affect outliers by using radiographic analysis. Methods Patient This study was approved by our institutional review board, and informed consent was obtained from all patients. Between January 2005 and December 2011, 153 consecutive TAAs were performed by a single surgeon in 146 patients (153 ankles) with symptomatic end-stage ankle osteoarthritis using cementless mobile-bearing HINTE- GRA prosthesis (Newdeal, SA, Lyon, France). Three patients (3 ankles) were excluded because plain radiographs were not available to measure radiographic parameter. The study cohort consisted of 150 ankles (93 men, 57 women) with a mean age of 61.6 years (42 to 82). Ninety (60%) ankles were diagnosed with posttraumatic ankle arthritis, and 60 (40%) ankles were diagnosed with primary ankle osteoarthritis. Operative technique and postoperative rehabilitation All patients received total ankle arthroplasty by a single surgeon using a longitudinal anterior approach between the anterior tibial tendon and the extensor hallucis longus with the patient in the supine position. After removal of anterior capsular synovial tissue and osteophytes, the tibial cut was made perpendicular to the mechanical axis of tibia in coronal plane and had a posterior slope of 6 in sagittal plane while sparing as much subchondral bone as possible. The talar cut was made parallel to the tibial cut in coronal plane and parallel to the sole, then the medial, lateral, and finally posterior talar cuts were made. After the selected implants were inserted, the alignment, stability, and joint motion were checked clinically, while component position was checked by image intensification. The wound was closed in a standard fashion and a closed suction drain was inserted. All patients followed the same postoperative protocol. In order to keep the foot in a neural position, a short leg splint and non-weight bearing were necessary for the first 2 weeks after surgery. For the next 4 weeks, patient was instructed to start gentle range of motion (ROM) exercise. Progressive weight-bearing ambulation was initiated with ankle-foot orthosis at 6 weeks after surgery. The full weight-bearing ambulation and rehabilitation program, which included stretching of the triceps surae, calf strengthening, and proprioceptive exercise were allowed to start at 8 to 10 weeks after the surgery. The period of immobilization may differ a little whether additional procedures were performed or not. Radiographic evaluations Radiographic examinations including anteroposterior and lateral radiographs of the ankle taken preoperatively, immediate postoperatively, at 3 and 6 months postoperatively, and annually thereafter. With preoperative radiographic analysis, we conducted radiographic analysis after 6 months of operation when the patients were able to perform weight-bearing exercises. For the radiographic analysis, we measured the following by using PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication Systems: Marotech 5.4). We evaluated the accuracy of component position depending on the type of preoperative coronal deformity: varus, neutral, or valgus. Neutral position in coronal plane was defined as within 5 of varus or valgus on anteroposterior radiograph. On preoperative radiograph, 80 (53.3%) ankles showed coronal varus tilting above 5, 28 (18.7%) ankles showed valgus tilting above 5, and 42 (28%) ankles showed coronal tilting below 5 of varus or valgus. Coronal positions of the tibial and talar components were assessed using α and γ angles (Fig. 1a). As done with coronal plane analysis, we evaluated the accuracy of component position depending on preoperative sagittal deformity: extension, neutral, and plantar flexion. The aimed value of the anterior distal tibial angle was 84. Therefore, we defined, a neutral position in sagittal plane as being in the rage of 79 to 89 of the anterior distal tibial angle. On the sagittal plane, 85 (56.7%) ankles showed extension of the distal tibial slope (anterior distal tibial angle <79 ) above 5, 7 (4.7%) ankles showed plantar flexion of the distal tibial slope (anterior distal tibial angle >84 ) above 5, and 58 (38.7%) ankles showed sagittal tilting below 5. Sagittal angular positions of the tibial and talar components were assessed using β and δ angles on postoperative radiographs (Fig. 1b). In addition, we evaluated the congruency of the ankle joint. An ankle was defined as congruent when the difference between the tibial and talar articular surface was less than 5. Accordingly, four categories of deformity were defined: varus-congruent, varusincongruent, valgus-congruent, and valgus-incongruent. Outcomes were defined as excellent when the difference between the postoperative alignment and aimed value was within less than 3, acceptable when more than 3 and less than 5, and outlier when more than
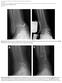
3 Lee et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:115 Page 3 of 7 Fig. 1 The measurement of the angular position of the component. a α and γ are the angles on the anteroposterior view between the longitudinal axis of the tibia and the articulating surface of the tibial and talar components. b β and δ are the angles on the lateral view between the longitudinal axis of the tibia and the articulating surface of the tibial and talar components 5 from aimed value in the coronal-tibial(α), coronaltalar(γ), sagittal-tibia(β), and sagittal-talar(δ) angle. To avoid potential bias, plain radiographs were evaluated by two independent observers who were not involved in the surgical treatment of the patients and who were blinded to the intention of this study. Statistical analysis Descriptive statistics (arithmetic means, standard deviations, and ranges) were calculated with use of standard formulas. The one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test was used to analyze differences in continuous variables such as α, β, γ, and δ angles among three groups. Tukey s honestly significant differences (HSD) was performed was used for post-hoc comparisons. The Fisher s exact test was used to analyze differences in outcomes such as excellent, acceptable, and outlier. A p value of <0.05 was considered significant, and all aspects of the statistical analysis were reviewed by a statistician. Results Accuracy assessment of component position The mean coronal angle of the tibial and talar components (α, γ angle) were 91.9 and 91.3 at 6 months postoperatively (Table 1). In terms of accuracy of component position, 86 (57.3%) and 90 (60.0%) of the tibial and talar components were excellent, and 48 (32.0%) and 45 (30.0%) were acceptable. There were 16 (10.7%) and 15 (10.0%) coronal outliers for the tibial and talar components. The mean sagittal angle of the tibial and talar components (β and δ angle) were 84.6 and 91.7 at 6 months postoperatively (Table 1). Fifteen (10.0%) and 29 (19.3%) outliers for sagittal angle of the tibial and talar components were occurred. Ninety-eight (65.3%) and 76 (50.7%) Table 1 Accuracy of implant position after total ankle arthroplasty a Angle Coronal alignment Sagittal alignment α angle γ angle β angle δ angle 91.9 ± ± ± ± 4.1 Outcomesb a Excellent 86 (57.3%) 90 (60.0%) 98 (65.3%) 76 (50.7%) Acceptable 48 (32.0%) 45 (30.0%) 37 (24.7%) 45 (30.0%) Outlier 16 (10.7%) 15 (10.0%) 15 (10.0%) 29 (19.3%) The values are given as the mean and the standard deviation b The values are given as the number of ankles with the percentage in parentheses α and γ angles are measured on anteroposterior radiographs between the longitudinal axis of the tibia and the articulating surface of the tibial component or talar component β and δ angles are measured on lateral radiographs between the longitudinal axis of the tibia and the articulating surface of the tibial component or talar component The ideal values of α, γ, and δ angles are 90, the ideal value of β angle is 84. Outcomes were defined as excellent when values were within 3, acceptable when within 5, and as outlier when more than 5 from optimum values
4 Lee et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:115 Page 4 of 7 Table 2 Accuracy of implant position after total ankle arthroplasty according to preoperative deformity Preoperative coronal alignment a Preoperative sagittal alignment b Varus (n = 80) Neutral (n = 42) Valgus (n = 28) p value Extension (n = 85) Neutral (n = 58) Flexion (n = 7) α angle a 92.4 ± ± ± β angle a 84.5 ± ± ± Excellent 41 (51.2%) 30 (71.5%) 15 (53.6%) Excellent 52 (61.2%) 41 (70.7%) 5 (71.4%) Acceptable 28 (35.0%) 9 (21.4%) 11 (39.3%) Acceptable 23 (27.0%) 12 (20.7%) 2 (28.6%) Outlier 11 (13.8%) 3 (7.1%) 2 (7.1%) Outlier 10 (11.8%) 5 (8.6%) γ angle a 91.9 ± ± ± δ angle a 91.4 ± ± ± Excellent 43 (53.8%) 29 (69.1%) 18 (64.3%) Excellent 45 (52.9%) 29 (50.0%) 2 (28.6%) Acceptable 26 (32.4%) 10 (23.8%) 9 (32.1%) Acceptable 25 (29.4%) 18 (31.0%) 2 (28.6%) Outlier 11 (13.8%) 3 (7.1%) 1 (3.6%) Outlier 15 (17.7%) 11 (19.0%) 3 (42.8%) a Values are given as the mean and the standard deviation b Values are given as the number of ankles with the percentage in parentheses Neutral is within 5 of tibiotalar angle on anteroposterior radiograph. Varus and valgus ankles are defined as those greater than 5 from optimal values Neutral is within 5 of extension and flexion on lateral radiograph. Extension and flexion ankles are defined as those greater than 5 from optimal values The ideal value of α, γ, and δ angle is 90, that of β angle is 84. Outcome was defined as excellent when values were within 3, acceptable when within 5, and as outlier when more than 5 from optimum value. Outcome values are shown as percentage with the number of ankles in parentheses p value of the tibial and talar components were excellent, and 37 (24.7%) and 45 (45.0%) were acceptable. Predisposing factors for outlier of component position We evaluated the accuracy of implant position depending on preoperative coronal deformity: varus, neutral, and valgus (Table 2). In coronal plane, outliers of the tibial and talar components occurred in 11 (13.8%) ankles of each component in the varus deformity group, 3 (7.1%) of each component in the neutral group, and 2 (7.1%) and 1 (3.6%) in the valgus deformity group. As done with coronal plane analysis, we evaluated the accuracy of implant position depending on preoperative sagittal deformity: extension, neutral, and flexion. In sagittal plane, outliers of the tibial and talar components occurred in 10 (11.8%) and 15 (17.7%) ankles in the extension group, 5 (8.6%) and 11 (19.0%) in the neutral group, and 0 (0.0%) and 3 (42.8%) in the flexion group, respectively. However, there were no meaningful differences between the 3 groups in the accuracy of component position according to preoperative deformity in coronal and sagittal plane. Table 3 Accuracy of implant position after total ankle arthroplasty according to preoperative ankle congruency Varus (n = 80) Valgus (n = 28) Congruent (n = 46) Incongruent (n = 34) p value Congruent (n = 18) Incongruent (n = 10) p value α angle a 92.2 ± ± ± ± Excellent 23 (50.0%) 18 (52.9%) (55.6%) 5 (50.0%) Acceptable 16 (34.8%) 12 (35.3%) 7 (38.9%) 4 (40.0%) Outlier 7 (15.2%) 4 (11.8%) 1 (5.5%) 1 (10.0%) γ angle a 91.7 ± ± ± ± Excellent 26 (56.5%) 17 (50.0%) (61.1%) 7 (70.0%) Acceptable 12 (26.1%) 14 (41.2%) 7 (38.9%) 2 (20.0%) Outlier 8 (17.4%) 3 (8.8%) 1 (10.0%) a Values are given as the mean and the standard deviation b Value are given as the number of ankles with the percentage parentheses α and γ angles are measured on anteroposterior radiographs between the longitudinal axis of the tibia and the articulating surface of the tibial component or talar component β and δ angles are measured on lateral radiographs between the longitudinal axis of the tibia and the articulating surface of the tibial component or talar component The ideal values of α, γ and δ angles are 90, that of β angle is 84. Outcomes were defined as excellent when values were within 3, acceptable when within 5, and as outlier when more than 5 from optimum values
5 Lee et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:115 Page 5 of 7 In addition, presence of joint incongruency did not increase the outlier rate (Table 3). Discussion The most important finding of the present study is that the outlier rate of component was higher than we expected, and the outlier rate of each component in coronal plane is about 10%, but the talar component position in sagittal plane showed the outlier rate up to 20%. Our results highlight a common problem in TAA, which is the lack of repeatability in implantation position, particularly the talar component. Malalignment of component following TAA has been reported in about 0 to 35% of patients, even though components were thought to be appropriately placed at the time of the operation [12, 30]. There are several reports concerning the current radiographic outcomes of TAA [5, 6, 24, 31 34]. Mann et al. [24] analyzed the outcomes of TAA in 84 ankles. The average overall alignment of the tibial component was 3.0 of varus. Fifty seven (78%) ankles had varus tilt averaging 4.6, and 10 (14%) ankles had valgus tilt of the talar component averaging 2.8. Nine (10.7%) outliers occurred in which the tibial component was placed in more than 10 of extension and exceeded 5 of varus. However, Rippstein et al. [6] reported relatively good outcomes after TAA in 240 Mobility ankles. Ninety-three percent of components were correctly centered in the coronal plane, and 97.4% were correctly centered in the sagittal plane. The tibial components were placed on average 2.1 ± 2.9 ( 5.5 to 10.2 ) in the coronal plane. The mean posterior slope was 6.0 ± 3.8 ( 5.8 to 17.1 ). However, there was no comprehensive study concerning the outlier rate of each component or predisposing factors by assessing the accuracy of component after TAA. The present study indicate that outliers rate of the tibial, talar component in coronal plane, and tibial component in sagittal plane showed only about 10.7, 10, and 10%, of cases, but outliers rate of the talar component in sagittal plane occurred in 19.3%. This result suggests that the talar component position intraoperatively is much more difficult than the tibial component position. There are several factors which can affect alignment of the talar component. Firstly, in operative techniques, the component position in the sagittal plane is a very subjective approach and it concerns different types of ankle prosthesis. In this study, distal tibia cutting block was used as a guide for resection of talar dome. So, the talar component position was affected by distal tibial cutting plane. Such problems may be solved by applying separate talar cutting block without considering the tibia in the process, but this is not easy intraoperatively because there is no distinct landmark and anatomy of talus varies much individually. In addition, stabilizing the foot during talar cutting can only be done manually. Therefore, the talar component position tends to vary and easy to be influenced depending upon foot position, particularly in sagittal alignment. Barg and Lundberg et al. [34, 35] also reported that correct position of the talar component is one of the most technically demanding steps in TAA, which is complicated by changes in the original center of rotation of the tibiotalar joint caused by degeneration and concomitant valgus or varus hindfoot deformities. As a result, sagittal malalignment of the talar component is a common complication of TAA. Novel techniques such as computer-assisted surgery or patientspecific instrumentation could be useful solutions to limit component malalignment. Based on our results concerning component position according to the preoperative coronal deformity, varus ankles showed a lower rate of excellent outcomes and a higher rate of outlier than neutral or valgus ankles. Previous studies have reported that for varus ankles with ligament imbalance and asymmetric joint loading. Wood and Haskel [5, 36] reported that the failure of TAA in cases of varus deformity was the result of edge loading on the implant caused by ligament instability and remaining ankle malalignment after the operation. Trincat et al. [37] reported that six (29%) ankles underwent revision surgery to correct residual varus malalignment of the hindfoot. Among them, three failures occurred in incongruent ankles (two varus, one valgus) in which the initial procedure did not provide optimal correction of talar tilt. As the degrees of deformity increase, it is difficult to achieve neutral alignment and easy to remain postoperative malalignment. To achieve neutrally aligned ankle after TAA, it is essential to correct ligament imbalance or hindfoot deformity through additional procedures in index surgery. Therefore, precise check of ligament balancing and proper additional procedures are needed, in order to reduce postoperative malalignment. Our study has some limitations. First, the sample size in neutral and valgus group was relatively small. This may limit our ability to assess outcomes and may evaluate risk factors. Second, we retrospectively reviewed preoperative radiographs, and thus, radiographs were not precisely controlled. It is possible that slight variability of ankle position and rotation influenced assessments the alignment of implant. Finally, this study did not evaluate functional outcomes, which may have been influenced by the component position. Therefore, further studies involving these functional outcomes are required. Conclusions In present study, the outlier rate of components was high as 10 to 20%, especially, the talar component position in sagittal plane showed the outlier rate up to 20% and wider variation. However, presence of preoperative deformity or
6 Lee et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:115 Page 6 of 7 joint incongruency did not increase the outlier rate of component. Therefore, careful attention should be paid when implanting the talar component in sagittal plane and other reliable instrumentation system is necessary to improve the accuracy of component. Abbreviation TAA: Total ankle arthroplasty Acknowledgements Not applicable. Funding Not applicable. Availability of data and materials The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Authors contributions KJL participated in its design and collected the data and wrote the article. SHW involved in the interpretation of the data and helped to write the article. GWL carried out statistical analysis and revised the article. KBL conceived of the study and participated in its design and coordination, carried out the operations and wrote and revised the article. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Ethics approval and consent to participate This study was approved by Chonnam National University Hospital Institutional Review Board. IRB NO: CNUH Consent for publication Consent was obtained from participants with regards to publishing the results of the study in a scientific journal. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Publisher s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Received: 12 April 2017 Accepted: 29 July 2017 References 1. Gougoulias N, Khanna A, Maffulli N. How successful are current ankle replacements?: a systematic review of the literature. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468: Alvine FG, Conti SF. The AGILITY ankle: mid- and long-term results. Orthopade. 2006;35: Hintermann B, Valderrabano V, Dereymaeker G, Dick W. The HINTEGRA ankle: rationale and short-term results of 122 consecutive ankles. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;424: Lee KT, Lee YK, Young KW, Kim HJ, Park SY, Kim JS, et al. Perioperative complications of the MOBILITY total ankle system: comparison with the HINTEGRA total ankle system. J Orthop Sci. 2010;15: Wood PL, Deakin S. Total ankle replacement: the results in 200 ankles. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 2003;85: Rippstein PF, Huber M, Coetzee JC, Naal FD. Total ankle replacement with use of a new three-component implant. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93: Spirt AA, Assal M, Hansen Jr ST. Complications and failure after total ankle arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86: Anderson T, Montgomery F, Carlsson A. Uncemented STAR total ankle prostheses. Three to eight-year follow-up of fifty-one consecutive ankles. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85: Lee KB, Cho YJ, Park JK, Song EK, Yoon TR, Seon JK. Heterotopic ossification after primary total ankle arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93: Primadi A, Xu HX, Yoon TR, Ryu JH, Lee KB. Neurologic injuries after primary total ankle arthroplasty: prevalence and effect on outcomes. J Foot Ankle Res. 2015;8: Deorio JK, Easley ME. Total ankle arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect. 2008;57: Doets HC, Brand R, Nelissen RG. Total ankle arthroplasty in inflammatory joint disease with use of two mobile-bearing designs. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88: Guyer AJ, Richardson G. Current concepts review: total ankle arthroplasty. Foot Ankle Int. 2008;29: Knecht SI, Estin M, Callaghan JJ, Zimmerman MB, Alliman KJ, Alvine FG, et al. The Agility total ankle arthroplasty, Seven to sixteen-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86: Kofoed H, Lundberg-Jensen A. Ankle arthroplasty in patients younger and older than 50 years: a prospective series with long-term follow-up. Foot Ankle Int. 1999;20: Trajkovski T, Pinsker E, Cadden A, Daniels T. Outcomes of ankle arthroplasty with preoperative coronal-plane varus deformity of 10 or greater. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95: Easley ME, Adams Jr SB, Hembree WC, DeOrio JK. Results of total ankle arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93: Fukuda T, Haddad SL, Ren Y, Zhang LQ. Impact of talar component rotation on contact pressure after total ankle arthroplasty: a cadaveric study. Foot Ankle Int. 2010;31: Henricson A, Skoog A, Carlsson A. The Swedish Ankle Arthroplasty Register: an analysis of 531 arthroplasties between 1993 and Acta Orthop. 2007;78: Schutte BG, Louwerens JW. Short-term results of our first 49 Scandinavian total ankle replacements (STAR). Foot Ankle Int. 2008;29: Skyttä ET, Koivu H, Eskelinen A, Ikävalko M, Paavolainen P, Remes V. Total ankle replacement: a population-based study of 515 cases from the Finnish Arthroplasty Register. Acta Orthop. 2010;81: Wood PL, Prem H, Sutton C. Total ankle replacement: medium-term results in 200 Scandinavian total ankle replacements. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 2008; 90: Lee KB, Kim MS, Park KS, Cho KJ, Primadhi A. Effect of anterior translation of the talus on outcomes of three-component total ankle arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14: Mann JA, Mann RA, Horton E. STAR ankle: long-term results. Foot Ankle Int. 2011;32:S Jaffe WL, Hawkins CA. Normalized and proportionalized cemented femoral stem survivorship at 15 years. J Arthroplasty. 1999;14: Ostgaard HC, Helger L, Regnér H, Garellick G. Femoral alignment of the Charnley stem: a randomized trial comparing the original with the new instrumentation in 123 hips. Acta Orthop Scand. 2001;72: Mullaji AB, Shetty GM, Lingaraju AP, Bhayde S. Which factors increase risk of malalignment of the hip-knee-ankle axis in TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013; 471: Ritter MA, Davis KE, Davis P, Farris A, Malinzak RA, Berend ME, et al. Preoperative malalignment increases risk of failure after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95: Heyse TJ, Decking R, Davis J, Boettner F, Laskin RS. Varus gonarthrosis predisposes to varus malalignment in TKA. HSS J. 2009;5: Pyevich MT, Saltzman CL, Callaghan JJ, Alvine FG. Total ankle arthroplasty: a unique design. Two to twelve-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998; 80: Hsu AR, Haddad SL. Early clinical and radiographic outcomes of intramedullary-fixation total ankle arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015; 97: Haytmanek Jr CT, Gross C, Easley ME, Nunley JA. Radiographic outcomes of a mobile-bearing total ankle replacement. Foot Ankle Int. 2015;36: Bonnin M, Gaudot F, Laurent JR, Ellis S, Colombier JA, Judet T. The Salto total ankle arthroplasty: survivorship and analysis of failures at 7 to 11 years. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469: Barg A, Elsner A, Anderson AE, Hintermann B. The effect of threecomponent total ankle replacement malalignment on clinical outcome: pain relief and functional outcome in 317 consecutive patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93:
7 Lee et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:115 Page 7 of Lundberg A, Svensson OK, Németh G, Selvik G. The axis of rotation of the ankle joint. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 1989;71: Haskell A, Mann RA. Ankle arthroplasty with preoperative coronal plane deformity: short-term results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;424: Trincat S, Kouyoumdjian P, Asencio G. Total ankle arthroplasty and coronal plane deformities. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2012;98: Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and we will help you at every step: We accept pre-submission inquiries Our selector tool helps you to find the most relevant journal We provide round the clock customer support Convenient online submission Thorough peer review Inclusion in PubMed and all major indexing services Maximum visibility for your research Submit your manuscript at
Effect of anterior translation of the talus on outcomes of three-component total ankle arthroplasty
 Lee et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:260 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Effect of anterior translation of the talus on outcomes of three-component total ankle arthroplasty Keun-Bae Lee 1*, Myung-Sun
Lee et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:260 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Effect of anterior translation of the talus on outcomes of three-component total ankle arthroplasty Keun-Bae Lee 1*, Myung-Sun
Total ankle replacement in moderate to severe varus deformity of the ankle
 Total ankle replacement in moderate to severe varus deformity of the ankle B. S. Kim, W. J. Choi, Y. S. Kim, J. W. Lee From Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Our study describes the clinical
Total ankle replacement in moderate to severe varus deformity of the ankle B. S. Kim, W. J. Choi, Y. S. Kim, J. W. Lee From Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Our study describes the clinical
What variables influence final range of motion following Total Ankle Arthroplasty. Kevin T. Grosshans MD Mark S. Myerson MD
 What variables influence final range of motion following Total Ankle Arthroplasty Kevin T. Grosshans MD Mark S. Myerson MD Disclosures My disclosure is in the Final AOFAS Mobile App I have no potential
What variables influence final range of motion following Total Ankle Arthroplasty Kevin T. Grosshans MD Mark S. Myerson MD Disclosures My disclosure is in the Final AOFAS Mobile App I have no potential
Design Project. Dr. Kevin O Kelly, TCD
 Design Project Project title: Mentor: Total Ankle Replacement Dr. Kevin O Kelly, TCD Background The ankle joint is a comparatively small joint relative to the weight bearing and torque it must withstand.
Design Project Project title: Mentor: Total Ankle Replacement Dr. Kevin O Kelly, TCD Background The ankle joint is a comparatively small joint relative to the weight bearing and torque it must withstand.
10-year survival of total ankle arthroplasties
 Acta Orthopaedica 2011; 82 (6): 655 659 655 10-year survival of total ankle arthroplasties A report on 780 cases from the Swedish Ankle Register Anders Henricson 1, Jan-Åke Nilsson 2, and Åke Carlsson
Acta Orthopaedica 2011; 82 (6): 655 659 655 10-year survival of total ankle arthroplasties A report on 780 cases from the Swedish Ankle Register Anders Henricson 1, Jan-Åke Nilsson 2, and Åke Carlsson
Total ankle replacement by the Ankle Evolution System
 Total ankle replacement by the Ankle Evolution System MEDIUM-TERM OUTCOME S. S. Morgan, B. Brooke, N. J. Harris From Chapel Allerton Hospital, Leeds, England We present the outcomes in 38 consecutive patients
Total ankle replacement by the Ankle Evolution System MEDIUM-TERM OUTCOME S. S. Morgan, B. Brooke, N. J. Harris From Chapel Allerton Hospital, Leeds, England We present the outcomes in 38 consecutive patients
Total Ankle Replacement
 Protocol Total Ankle Replacement (70177) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/11 Next Review Date: 09/14 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 09/10, 09/11, 09/12, 09/13 The following Protocol contains medical
Protocol Total Ankle Replacement (70177) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/11 Next Review Date: 09/14 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 09/10, 09/11, 09/12, 09/13 The following Protocol contains medical
Residual pain due to soft-tissue impingement after uncomplicated total ankle replacement
 FOOT AND ANKLE Residual pain due to soft-tissue impingement after uncomplicated total ankle replacement B. S. Kim, W. J. Choi, J. Kim, J. W. Lee From Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
FOOT AND ANKLE Residual pain due to soft-tissue impingement after uncomplicated total ankle replacement B. S. Kim, W. J. Choi, J. Kim, J. W. Lee From Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
TOTAL ANKLE REPLACEMENT
 TOTAL ANKLE REPLACEMENT Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and
TOTAL ANKLE REPLACEMENT Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and
Ye-Ran Li, Yu-Hang Gao, Xin Qi *, Jian-Guo Liu, Lu Ding, Chen Yang, Zheng Zhang and Shu-Qiang Li
 Li et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:92 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0588-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Analysis of factors that affect the precision of the radiographic lateral femoral
Li et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:92 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0588-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Analysis of factors that affect the precision of the radiographic lateral femoral
Short Term Clinical and Radiographic Results of the Salto Mobile Version Ankle Prosthesis
 Short Term Clinical and Radiographic Results of the Salto Mobile Version Ankle Prosthesis Dong Dong Wan, MD; Dong woo Shim, MD; Yoo Jung Park, MD; Yeokgu Hwang, MD; Jin Woo Lee, MD, PhD Department of Orthopaedic
Short Term Clinical and Radiographic Results of the Salto Mobile Version Ankle Prosthesis Dong Dong Wan, MD; Dong woo Shim, MD; Yoo Jung Park, MD; Yeokgu Hwang, MD; Jin Woo Lee, MD, PhD Department of Orthopaedic
Poor accuracy of plain radiographic measurements of prosthetic migration and alignment in total ankle replacement
 Braito et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:71 DOI 10.1186/s13018-015-0220-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Poor accuracy of plain radiographic measurements of prosthetic migration
Braito et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:71 DOI 10.1186/s13018-015-0220-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Poor accuracy of plain radiographic measurements of prosthetic migration
Total Ankle Arthroplasty. Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopedics & Sports Medicine the original 2014
 Total Ankle Arthroplasty Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopedics & Sports Medicine the original 2014 Ankle Anatomy The ankle is a hinge or ginglymus joint Made up of the tibia, fibula, & talus
Total Ankle Arthroplasty Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopedics & Sports Medicine the original 2014 Ankle Anatomy The ankle is a hinge or ginglymus joint Made up of the tibia, fibula, & talus
Salto Talaris total ankle arthroplasty: Early clinical results from eighty-one consecutive patients by a single surgeon
 Salto Talaris total ankle arthroplasty: Early clinical results from eighty-one consecutive patients by a single surgeon Kurt Hofmann, MD, Zabrina Shabin, MD, Eric Ferkel, MD, Jeffrey Jockel, MD, Mark Slovenkai,
Salto Talaris total ankle arthroplasty: Early clinical results from eighty-one consecutive patients by a single surgeon Kurt Hofmann, MD, Zabrina Shabin, MD, Eric Ferkel, MD, Jeffrey Jockel, MD, Mark Slovenkai,
The Effect of Hindfoot Stiffness on Osteolysis in Total Ankle Arthroplasty
 The Effect of Hindfoot Stiffness on Osteolysis in Total Ankle Arthroplasty Robert Flavin, MD, Scott Coleman, James Brodsky, MD Baylor University Medical Center The Effect of Hindfoot Stiffness on Osteolysis
The Effect of Hindfoot Stiffness on Osteolysis in Total Ankle Arthroplasty Robert Flavin, MD, Scott Coleman, James Brodsky, MD Baylor University Medical Center The Effect of Hindfoot Stiffness on Osteolysis
Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
Conversion of Pantalar fusion to total ankle replacement: A case Review. Key words: Pantalar fusion, non-union and total ankle replacement
 The Northern Ohio Foot and Ankle Journal Official Publication of the NOFA Foundation Conversion of Pantalar fusion to total ankle replacement: A case Review Author: Bryan Williams DPM 1 and Jonathan Sharpe
The Northern Ohio Foot and Ankle Journal Official Publication of the NOFA Foundation Conversion of Pantalar fusion to total ankle replacement: A case Review Author: Bryan Williams DPM 1 and Jonathan Sharpe
Ankle arthritis is a disabling
 Kelly L. Apostle, MD, FRCSC What role does ankle replacement play in managing pain and disability? Although advances in implant design have contributed to better outcomes in total ankle replacement, ankle
Kelly L. Apostle, MD, FRCSC What role does ankle replacement play in managing pain and disability? Although advances in implant design have contributed to better outcomes in total ankle replacement, ankle
A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients
 Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Clinical Study Accuracy of Implant Placement Utilizing Customized Patient Instrumentation in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 891210, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/891210 Clinical Study Accuracy of Implant Placement Utilizing Customized Patient
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 891210, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/891210 Clinical Study Accuracy of Implant Placement Utilizing Customized Patient
Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Total Ankle Arthroplasty: A Radiographic Outcome Study
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Lee et al. Outcome of Total nkle rthroplasty Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research mie Y. Lee 1 lice S. Ha 1 Jonelle M. Petscavage 2 Felix S. Chew 1 Lee Y,
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Lee et al. Outcome of Total nkle rthroplasty Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research mie Y. Lee 1 lice S. Ha 1 Jonelle M. Petscavage 2 Felix S. Chew 1 Lee Y,
Management of Painful Malleolar Gutters After Total Ankle Replacement
 Management of Painful Malleolar Gutters After Total Ankle Replacement 20 Bernard Devos Bevernage, Paul-André Deleu, Harish V. Kurup, and Thibaut Leemrijse Introduction Total ankle replacement (TAR) is
Management of Painful Malleolar Gutters After Total Ankle Replacement 20 Bernard Devos Bevernage, Paul-André Deleu, Harish V. Kurup, and Thibaut Leemrijse Introduction Total ankle replacement (TAR) is
Health-Related Quality of Life and Functional Outcomes in Ankle Arthritis Patients Based on Treating with and without Total Ankle Replacement Surgery
 Health-Related Quality of Life and Functional Outcomes in Ankle Arthritis Patients Based on Treating with and without Total Ankle Replacement Surgery Chayanin Angthong MD* * Division of Foot and Ankle
Health-Related Quality of Life and Functional Outcomes in Ankle Arthritis Patients Based on Treating with and without Total Ankle Replacement Surgery Chayanin Angthong MD* * Division of Foot and Ankle
Heterotopic ossification after total ankle arthroplasty
 FOOT AND ANKLE after total ankle arthroplasty W. J. Choi, J. W. Lee From Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea We evaluated the incidence of heterotopic ossification following total ankle
FOOT AND ANKLE after total ankle arthroplasty W. J. Choi, J. W. Lee From Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea We evaluated the incidence of heterotopic ossification following total ankle
Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W.
 University of Groningen Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W. Published in: Knee DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.007
University of Groningen Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W. Published in: Knee DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.007
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR
 CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement
 016625 REVISION R INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement CASE STUDY Patient History The patient was a 65-year-old
016625 REVISION R INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement CASE STUDY Patient History The patient was a 65-year-old
Chapter 25 Revision Total Ankle Arthroplasty: Managing Osteolysis and Subsidence
 Chapter 25 Revision Total Ankle Arthroplasty: Managing Osteolysis and Subsidence James A. Nunley, MD Indications A review of 2,240 total ankle arthroplasties (TAAs) from multiple studies with adequate
Chapter 25 Revision Total Ankle Arthroplasty: Managing Osteolysis and Subsidence James A. Nunley, MD Indications A review of 2,240 total ankle arthroplasties (TAAs) from multiple studies with adequate
Total Ankle Arthroplasty for the Treatment of Symptomatic Nonunion following Tibiotalar Fusion
 Total Ankle Arthroplasty for the Treatment of Symptomatic Nonunion following Tibiotalar Fusion W I L L I A M P. H U N T I N G T O N, M. D. W. H O D G E S D A V I S, M. D. R O B E R T B. A N D E R S O N,
Total Ankle Arthroplasty for the Treatment of Symptomatic Nonunion following Tibiotalar Fusion W I L L I A M P. H U N T I N G T O N, M. D. W. H O D G E S D A V I S, M. D. R O B E R T B. A N D E R S O N,
Original Policy Date
 MP 7.01.60 Total Ankle Replacement Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12/2013 Return to Medical Policy Index
MP 7.01.60 Total Ankle Replacement Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12/2013 Return to Medical Policy Index
A Modular S tem-fixed B earing Total Ankle R eplacement: A Two Year Follow Up of 27 Cons ecutive Cas es
 A Modular S tem-fixed B earing Total Ankle R eplacement: A Two Year Follow Up of 27 Cons ecutive Cas es Stephen A. Brigido, DPM, FACFAS Director, Fellowship for Foot and Ankle Reconstruction, Coordinated
A Modular S tem-fixed B earing Total Ankle R eplacement: A Two Year Follow Up of 27 Cons ecutive Cas es Stephen A. Brigido, DPM, FACFAS Director, Fellowship for Foot and Ankle Reconstruction, Coordinated
Presented By Dr Vincent VG An MD BSc (Adv) MPhil Dr Murilo Leie MD Mr Joshua Twiggs BEng Dr Brett A Fritsch MBBS FRACS (Orth) FAOrthA.
 A comparison of kinematic and mechanical alignment with regards to bony resection, soft tissue release, and deformity correction in total knee replacement Presented By Dr Vincent VG An MD BSc (Adv) MPhil
A comparison of kinematic and mechanical alignment with regards to bony resection, soft tissue release, and deformity correction in total knee replacement Presented By Dr Vincent VG An MD BSc (Adv) MPhil
Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 289 296, September 2017 Original Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System Hiroshi TAKAGI 1 2, Soshi ASAI 1, Atsushi
Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 289 296, September 2017 Original Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System Hiroshi TAKAGI 1 2, Soshi ASAI 1, Atsushi
No radiographic difference between patient-specific guiding and conventional Oxford UKA surgery
 DOI 10.1007/s00167-014-2849-0 KNEE No radiographic difference between patient-specific guiding and conventional Oxford UKA surgery Bart Kerens Martijn G. M. Schotanus Bert Boonen Nanne P. Kort Received:
DOI 10.1007/s00167-014-2849-0 KNEE No radiographic difference between patient-specific guiding and conventional Oxford UKA surgery Bart Kerens Martijn G. M. Schotanus Bert Boonen Nanne P. Kort Received:
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up
 Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
Cigna Medical Coverage Policy
 Cigna Medical Coverage Policy Subject Total Ankle Arthroplasty/Replacement Table of Contents Coverage Policy... 1 General Background... 2 Coding/Billing Information... 9 References... 10 Effective Date...
Cigna Medical Coverage Policy Subject Total Ankle Arthroplasty/Replacement Table of Contents Coverage Policy... 1 General Background... 2 Coding/Billing Information... 9 References... 10 Effective Date...
Chapter 24 Alignment in Total Ankle Arthroplasty With Coronal Plane Deformity: Bony and Ligamentous
 Chapter 24 Alignment in Total Ankle Arthroplasty With Coronal Plane Deformity: Bony and Ligamentous Mark E. Easley, MD Indications Total ankle arthroplasty (TAA) is indicated when appropriate nonsurgical
Chapter 24 Alignment in Total Ankle Arthroplasty With Coronal Plane Deformity: Bony and Ligamentous Mark E. Easley, MD Indications Total ankle arthroplasty (TAA) is indicated when appropriate nonsurgical
Ankle Arthritis: Which to Choose Arthrodesis or Arthroplasty
 Review Article Ankle Arthritis: Which to Choose Arthrodesis or Arthroplasty Bajuri MY ( ), Abdullah A Department of Orthopaedics &Traumatology, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre, Jalan Yaacob
Review Article Ankle Arthritis: Which to Choose Arthrodesis or Arthroplasty Bajuri MY ( ), Abdullah A Department of Orthopaedics &Traumatology, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre, Jalan Yaacob
Clinical Policy Bulletin: Total Ankle Arthroplasty
 Go Clinical Policy Bulletin: Total Ankle Arthroplasty Number: 0645 Policy *Please see amendment for Pennsylvania Medicaid at the end of this CPB. Aetna considers total ankle arthroplasty (TAA) using a
Go Clinical Policy Bulletin: Total Ankle Arthroplasty Number: 0645 Policy *Please see amendment for Pennsylvania Medicaid at the end of this CPB. Aetna considers total ankle arthroplasty (TAA) using a
Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick
 Dr Andreas Loefler www.orthosports.com.au 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Dr Andreas Loefler Joint Replacement & Spine Surgery CAS or Navigation in TKA New Software for a Full
Dr Andreas Loefler www.orthosports.com.au 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Dr Andreas Loefler Joint Replacement & Spine Surgery CAS or Navigation in TKA New Software for a Full
Influence of bone morphology and injured ligament of the ankle on ankle stress radiographs
 Influence of bone morphology and injured ligament of the ankle on ankle stress radiographs Gye Wang Lee, MD, Chin Youb Chung, MD, Moon Seok Park, MD Seung Yeol Lee, MD, Myung Ki Chung, MD, Byung Chae Jo,
Influence of bone morphology and injured ligament of the ankle on ankle stress radiographs Gye Wang Lee, MD, Chin Youb Chung, MD, Moon Seok Park, MD Seung Yeol Lee, MD, Myung Ki Chung, MD, Byung Chae Jo,
Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete
 Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete Chair: Maurilio Marcacci, MD Alois Franz "Basic principles and considerations of the Unis" Joao M. Barretto "Sport
Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete Chair: Maurilio Marcacci, MD Alois Franz "Basic principles and considerations of the Unis" Joao M. Barretto "Sport
Peritalar Dislocation After Tibio-Talar Arthrodesis: Fact or Fiction?
 AOFAS Annual Meeting, July 17-20th 2013 Hollywood, Florida Peritalar Dislocation After Tibio-Talar Arthrodesis: Fact or Fiction? Fabrice Colin, MD; Lukas Zwicky, MSc; Alexej Barg, MD; Beat Hintermann,
AOFAS Annual Meeting, July 17-20th 2013 Hollywood, Florida Peritalar Dislocation After Tibio-Talar Arthrodesis: Fact or Fiction? Fabrice Colin, MD; Lukas Zwicky, MSc; Alexej Barg, MD; Beat Hintermann,
Multiapical Deformities p. 97 Osteotomy Concepts and Frontal Plane Realignment p. 99 Angulation Correction Axis (ACA) p. 99 Bisector Lines p.
 Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
2:00 3:00 pm SESSION 6: ANKLE ARTHROPLASTY. Moderators: Steven L. Haddad, MD (Glenview, Illinois)
 2:00 3:00 pm SESSION 6: ANKLE ARTHROPLASTY Moderators: Steven L. Haddad, MD (Glenview, Illinois) John S. Reach, Jr, M.Sc., MD (New Haven, Connecticut) 133 2:00 2:15 pm SESSION 6: Varus, Valgus Whatever!
2:00 3:00 pm SESSION 6: ANKLE ARTHROPLASTY Moderators: Steven L. Haddad, MD (Glenview, Illinois) John S. Reach, Jr, M.Sc., MD (New Haven, Connecticut) 133 2:00 2:15 pm SESSION 6: Varus, Valgus Whatever!
Case Report Navigation-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty for Osteoarthritis with Extra-Articular Femoral Deformity and/or Retained Hardware
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 174384, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/174384 Case Report Navigation-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty for Osteoarthritis with Extra-Articular
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 174384, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/174384 Case Report Navigation-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty for Osteoarthritis with Extra-Articular
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
Unicompartmental Knee Replacement
 Unicompartmental Knee Replacement Results and Techniques Alexander P. Sah, MD California Orthopaedic Association Meeting Laguna Niguel, CA May 20th, 2011 Overview Why partial knee replacement? - versus
Unicompartmental Knee Replacement Results and Techniques Alexander P. Sah, MD California Orthopaedic Association Meeting Laguna Niguel, CA May 20th, 2011 Overview Why partial knee replacement? - versus
Computer Navigation in TKA The role of Robotic Surgery. Christos Yiannakopoulos, M.D., Ph.D.
 Computer Navigation in TKA The role of Robotic Surgery Christos Yiannakopoulos, M.D., Ph.D. Why are TKA failing? 11.8% Sharkley, CORR, 2005 55.6% of revision occurred early (< 2 years) 32% of patients
Computer Navigation in TKA The role of Robotic Surgery Christos Yiannakopoulos, M.D., Ph.D. Why are TKA failing? 11.8% Sharkley, CORR, 2005 55.6% of revision occurred early (< 2 years) 32% of patients
Knee Surg Relat Res 2013;25(1): pissn eissn Knee Surgery & Related Research
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2013;25(1):13-18 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2013.25.1.13 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Comparative Study of Two Techniques for
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2013;25(1):13-18 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2013.25.1.13 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Comparative Study of Two Techniques for
Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with an Ankylosing Knee after Previous Patellectomy
 Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2014;26(3):182-186 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2014.26.3.182 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with
Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2014;26(3):182-186 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2014.26.3.182 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with
pathologic feature of early ankle arthritis.
 Joint space widening may be a paradoxical pathologic Ji-Beom Kim, MD Young Yi, MD Woo-Chun, Lee Seoul Foot & Ankle Center, Dubalo Orthopaedic Clinic. Disclosure NO CONFLICT TO DISCLOSURE Joint space widening
Joint space widening may be a paradoxical pathologic Ji-Beom Kim, MD Young Yi, MD Woo-Chun, Lee Seoul Foot & Ankle Center, Dubalo Orthopaedic Clinic. Disclosure NO CONFLICT TO DISCLOSURE Joint space widening
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Robotic-Arm Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty Demonstrated Greater Accuracy to Plan Compared to Manual Technique
 EPiC Series in Health Sciences Volume 1, 2017, Pages 283 287 CAOS 2017. 17th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Computer Assisted Orthopaedic Surgery Health Sciences Robotic-Arm Assisted Total
EPiC Series in Health Sciences Volume 1, 2017, Pages 283 287 CAOS 2017. 17th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Computer Assisted Orthopaedic Surgery Health Sciences Robotic-Arm Assisted Total
PROPHECY INBONE. Preoperative Navigation Guides
 PROPHECY INBONE Preoperative Navigation Guides Simple. Fast. Accurate. Simple. Fast. Accurate. Prophecy Envision the Results PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Guides have ushered in a new era of total ankle
PROPHECY INBONE Preoperative Navigation Guides Simple. Fast. Accurate. Simple. Fast. Accurate. Prophecy Envision the Results PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Guides have ushered in a new era of total ankle
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA)
 TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
Trainer vs Trainee: Clinical outcome of primary total ankle replacement. Can learning curve be included during training?
 Trainer vs Trainee: Clinical outcome of primary total ankle replacement. Can learning curve be included during training? Kailash Devalia, FRCS (Tr & Orth) Jayasree Ramaskandhan, BPhT, MPT, MSc Malik Siddique,
Trainer vs Trainee: Clinical outcome of primary total ankle replacement. Can learning curve be included during training? Kailash Devalia, FRCS (Tr & Orth) Jayasree Ramaskandhan, BPhT, MPT, MSc Malik Siddique,
ANKLE ARTHRITIS, ARTHRODESIS, & ARTHROPLASTY
 Surgical Management of Ankle Arthritis James J Sferra, MD Allegheny Health Network Director, Division of Foot &Ankle Orthopaedic Institute Allegheny Orthopaedic Associates ANKLE ARTHRITIS, ARTHRODESIS,
Surgical Management of Ankle Arthritis James J Sferra, MD Allegheny Health Network Director, Division of Foot &Ankle Orthopaedic Institute Allegheny Orthopaedic Associates ANKLE ARTHRITIS, ARTHRODESIS,
Extramedullary Tibial Preparation
 Surgical Technique Extramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Extramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 EM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
Surgical Technique Extramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Extramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 EM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
PLEASE SCROLL DOWN FOR ARTICLE
 This article was downloaded by:[universitetsbiblioteket i Bergen] On: 2 November 7 Access Details: [subscription number 7683713] Publisher: Informa Healthcare Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales
This article was downloaded by:[universitetsbiblioteket i Bergen] On: 2 November 7 Access Details: [subscription number 7683713] Publisher: Informa Healthcare Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales
Clinical evaluation of 292 Genesis II posterior stabilized high-flexion total knee arthroplasty: range of motion and predictors
 DOI 10.1007/s00590-014-1467-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical evaluation of 292 Genesis II posterior stabilized high-flexion total knee arthroplasty: range of motion and predictors Mathijs C. H. W. Fuchs Rob
DOI 10.1007/s00590-014-1467-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical evaluation of 292 Genesis II posterior stabilized high-flexion total knee arthroplasty: range of motion and predictors Mathijs C. H. W. Fuchs Rob
Functional and radiological outcome of total knee replacement in varus deformity of the knee
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 4 (2015) pp. 934-938 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Functional and radiological outcome of total knee replacement in varus deformity of the knee Sandesh
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 4 (2015) pp. 934-938 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Functional and radiological outcome of total knee replacement in varus deformity of the knee Sandesh
Overview. Acceptance criteria for all protocols
 X-Ray protocol Overview The Smith & Nephew VISIONAIRE X-Ray protocol is essentially an AP leg length image. The images are preferred to be done erect, but can be done supine if necessary due to the type
X-Ray protocol Overview The Smith & Nephew VISIONAIRE X-Ray protocol is essentially an AP leg length image. The images are preferred to be done erect, but can be done supine if necessary due to the type
JOINT RULER. Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement
 JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference?
 Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference? In this 4 Questions interview, Stephen M. Howell, MD, explains the potential benefits of 3D alignment during total knee replacement. Introduction
Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference? In this 4 Questions interview, Stephen M. Howell, MD, explains the potential benefits of 3D alignment during total knee replacement. Introduction
Torsion bottle, a very simple, reliable, and cheap tool for a basic scoliosis screening
 Romano and Mastrantonio Scoliosis and Spinal Disorders (2018) 13:4 DOI 10.1186/s13013-018-0150-6 RESEARCH Open Access Torsion bottle, a very simple, reliable, and cheap tool for a basic scoliosis screening
Romano and Mastrantonio Scoliosis and Spinal Disorders (2018) 13:4 DOI 10.1186/s13013-018-0150-6 RESEARCH Open Access Torsion bottle, a very simple, reliable, and cheap tool for a basic scoliosis screening
Impact of knee varus and valgus deformity on alignment in lower extremities after total knee arthroplasty (TKA)
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22 (1 Suppl): 83-89 Impact of knee varus and valgus deformity on alignment in lower extremities after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) F. TIAN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22 (1 Suppl): 83-89 Impact of knee varus and valgus deformity on alignment in lower extremities after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) F. TIAN
Sports and Recreational Activities following Total Ankle Replacement
 12 Original Article THIEME Sports and Recreational Activities following Total Ankle Replacement Federico Giuseppe Usuelli 1 Andrea Pantalone 2 Camilla Maccario 1 Matteo Guelfi 2 Vincenzo Salini 2 1 Casco,
12 Original Article THIEME Sports and Recreational Activities following Total Ankle Replacement Federico Giuseppe Usuelli 1 Andrea Pantalone 2 Camilla Maccario 1 Matteo Guelfi 2 Vincenzo Salini 2 1 Casco,
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Total Ankle Replacement Page 1 of 16 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Total Ankle Replacement Professional Institutional Original Effective Date:
Total Ankle Replacement Page 1 of 16 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Total Ankle Replacement Professional Institutional Original Effective Date:
Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini
 Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Duration of Follow-up (mo)
 Page 1 of 7 Fig. E-1 Fig. E-2 Fig. E-1 Medial ankle arthritis with medial translation of the talus and mortise widening. Note the shape of the medial malleolus (white arrow). Fig. E-2 Measurement of mortise
Page 1 of 7 Fig. E-1 Fig. E-2 Fig. E-1 Medial ankle arthritis with medial translation of the talus and mortise widening. Note the shape of the medial malleolus (white arrow). Fig. E-2 Measurement of mortise
Ankle Fusion Rates with Anterior Lock Plates : Is there a Difference Between Plating Systems?
 Ankle Fusion Rates with Anterior Lock Plates : Is there a Difference Between Plating Systems? G. Alex Simpson, DO 1 Sean A. Sutphen, DO 2 Mark A. Prissel, DPM 3 Kyle S. Peterson, DPM 4 Christopher Hyer,
Ankle Fusion Rates with Anterior Lock Plates : Is there a Difference Between Plating Systems? G. Alex Simpson, DO 1 Sean A. Sutphen, DO 2 Mark A. Prissel, DPM 3 Kyle S. Peterson, DPM 4 Christopher Hyer,
Total ankle replacement
 Total ankle replacement THE RESULTS IN 200 ANKLES P. L. R. Wood, S. Deakin From Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, England B etween 1993 and 2000 we implanted 200 cementless, mobile-bearing STAR total ankle
Total ankle replacement THE RESULTS IN 200 ANKLES P. L. R. Wood, S. Deakin From Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, England B etween 1993 and 2000 we implanted 200 cementless, mobile-bearing STAR total ankle
BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENTS
 Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 5, No. 3 (2005) 469 475 c World Scientific Publishing Company BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS
Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 5, No. 3 (2005) 469 475 c World Scientific Publishing Company BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS
Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique
 Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Does Coronal Knee and Ankle Alignment Affect Recurrence of the Varus Deformity after High Tibial Osteotomy?
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 18;3():311-318 https://doi.org/1.579/ksrr.18.35 pissn 3-7 eissn 3-51 Knee Surgery & Related Research Does Coronal Knee and Ankle Alignment Affect Recurrence of the
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 18;3():311-318 https://doi.org/1.579/ksrr.18.35 pissn 3-7 eissn 3-51 Knee Surgery & Related Research Does Coronal Knee and Ankle Alignment Affect Recurrence of the
Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Clinical Results of Lateral Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: Minimum 2-Year Follow-up
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:386-392 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.386 Clinical Results of Lateral Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: Minimum 2-Year Follow-up Kyung Tae
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:386-392 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.386 Clinical Results of Lateral Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: Minimum 2-Year Follow-up Kyung Tae
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
Competence of the Deltoid Ligament in Bimalleolar Ankle Fractures After Medial Malleolar Fixation *
 Competence of the Deltoid Ligament in Bimalleolar Ankle Fractures After Medial Malleolar Fixation * BY PAUL TORNETTA, III, M.D. Investigation performed at Kings County Hospital, New York, N.Y. Abstract
Competence of the Deltoid Ligament in Bimalleolar Ankle Fractures After Medial Malleolar Fixation * BY PAUL TORNETTA, III, M.D. Investigation performed at Kings County Hospital, New York, N.Y. Abstract
The outcome of total ankle replacement
 FOOT AND ANKLE The outcome of total ankle replacement A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS R. Zaidi, S. Cro, K. Gurusamy, N. Siva, A. Macgregor, A. Henricson, A. Goldberg From Royal National Orthopaedic
FOOT AND ANKLE The outcome of total ankle replacement A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS R. Zaidi, S. Cro, K. Gurusamy, N. Siva, A. Macgregor, A. Henricson, A. Goldberg From Royal National Orthopaedic
CLINICAL PAPER / ORTHOPEDIC
 HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
Differences in Walking Mechanics Between Ankle Disarthrodesis and Primary Total Ankle Replacement
 Differences in Walking Mechanics Between Ankle Disarthrodesis and Primary Total Ankle Replacement Robin M. Queen, PhD Abigail L. Carpenter, MS Samuel B. Adams, Jr, MD Mark E. Easley, MD James A. Nunley,
Differences in Walking Mechanics Between Ankle Disarthrodesis and Primary Total Ankle Replacement Robin M. Queen, PhD Abigail L. Carpenter, MS Samuel B. Adams, Jr, MD Mark E. Easley, MD James A. Nunley,
Rotaglide+ TM. Total Knee System Product overview
 Rotaglide+ TM Total Knee System Product overview Rotaglide+ TM Originality Stability History Originally implanted in 1988, Rotaglide+ was the first total knee design to adopt a true mobile bearing philosophy.
Rotaglide+ TM Total Knee System Product overview Rotaglide+ TM Originality Stability History Originally implanted in 1988, Rotaglide+ was the first total knee design to adopt a true mobile bearing philosophy.
Effect of metatarsal osteotomy and open lateral soft tissue procedure on sesamoid position: radiological assessment
 Choi et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:11 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0712-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Effect of metatarsal osteotomy and open lateral soft tissue procedure on sesamoid position:
Choi et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:11 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0712-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Effect of metatarsal osteotomy and open lateral soft tissue procedure on sesamoid position:
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement
 Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Revolution. Unicompartmental Knee System
 Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Benkovich V. Perry T., Bunin A., Bilenko V., Unit for Joint Arthroplasty, Soroka Medical Center Ben Gurion University of Negev Beer
EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Benkovich V. Perry T., Bunin A., Bilenko V., Unit for Joint Arthroplasty, Soroka Medical Center Ben Gurion University of Negev Beer
Overview. Acceptance criteria for all protocols
 X-Ray protocol Overview The Smith & Nephew VISIONAIRE X-Ray protocol is essentially an AP leg length image. The images are preferred to be done erect, but can be done supine if necessary due to the type
X-Ray protocol Overview The Smith & Nephew VISIONAIRE X-Ray protocol is essentially an AP leg length image. The images are preferred to be done erect, but can be done supine if necessary due to the type
STIFFNESS AFTER TKA PRE, PER AND POST OPERATIVE CAUSING FACTORS
 STIFFNESS AFTER TKA PRE, PER AND POST OPERATIVE CAUSING FACTORS Patrick DJIAN INTRODUCTION Stiffness is one of the most common complications following TKR, causing frustration to both the surgeon and the
STIFFNESS AFTER TKA PRE, PER AND POST OPERATIVE CAUSING FACTORS Patrick DJIAN INTRODUCTION Stiffness is one of the most common complications following TKR, causing frustration to both the surgeon and the
Abramsohn Retractor 1
 Abramsohn Retractor 1 Calibrated Femoral Tibial Spreaders Small Medium Large Designed to remain in position, with the femur and tibia separated, without the need of an assistant, and to minimize crushing
Abramsohn Retractor 1 Calibrated Femoral Tibial Spreaders Small Medium Large Designed to remain in position, with the femur and tibia separated, without the need of an assistant, and to minimize crushing
Concept of Tibiotalocalcaneal Fusion with a IIIrd Generation Intramedullary Nail
 June 2006 Page 1 of 6 Concept of Tibiotalocalcaneal Fusion with a IIIrd Generation Intramedullary Nail Thomas Mückley*, M.D., Alexander Petrovitch, M.D., Sebastian Ullm*, Kajetan Klos* Gunther O. Hofmann*
June 2006 Page 1 of 6 Concept of Tibiotalocalcaneal Fusion with a IIIrd Generation Intramedullary Nail Thomas Mückley*, M.D., Alexander Petrovitch, M.D., Sebastian Ullm*, Kajetan Klos* Gunther O. Hofmann*
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine
 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPERS Total Knee Arthroplasty Following High Tibial Osteotomy a Radiological Evaluation Horia ORBAN, MD, PhD; Emil MARES, MD; Mihaela DRAGUSANU, MD; Gabriel
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPERS Total Knee Arthroplasty Following High Tibial Osteotomy a Radiological Evaluation Horia ORBAN, MD, PhD; Emil MARES, MD; Mihaela DRAGUSANU, MD; Gabriel
A Non-CT Based Total Knee Arthroplasty System Featuring Complete Soft-Tissue Balancing
 A Non-CT Based Total Knee Arthroplasty System Featuring Complete Soft-Tissue Balancing Manuela Kunz 1, Matthias Strauss 2, Frank Langlotz 1, Georg Deuretzbacher 2, Wolfgang Rüther 2, and Lutz-Peter Nolte
A Non-CT Based Total Knee Arthroplasty System Featuring Complete Soft-Tissue Balancing Manuela Kunz 1, Matthias Strauss 2, Frank Langlotz 1, Georg Deuretzbacher 2, Wolfgang Rüther 2, and Lutz-Peter Nolte
Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC. Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty 10-15% have Fair to poor Results? Why? The complication rate is 2.567% If It happens To You
Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty 10-15% have Fair to poor Results? Why? The complication rate is 2.567% If It happens To You
Soft Tissue Releases in Valgus Knees
 Soft Tissue Releases in Valgus Knees Ke Xie, MD Steven Lyons, MD Florida Orthopaedic Institute June 17, 2016 Background Valgus deformities make up 10-15% of all primary TKA s performed Restoration of the
Soft Tissue Releases in Valgus Knees Ke Xie, MD Steven Lyons, MD Florida Orthopaedic Institute June 17, 2016 Background Valgus deformities make up 10-15% of all primary TKA s performed Restoration of the
Zenith. Total Ankle Replacement Surgical technique
 Total Ankle Replacement Surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative planning and templating 6 Patient positioning 6 Exposure 6 Saw blades 7 Joint line definition 7 Tibial alignment jig
Total Ankle Replacement Surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative planning and templating 6 Patient positioning 6 Exposure 6 Saw blades 7 Joint line definition 7 Tibial alignment jig
