ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Anastasia Fotiadou & Antonios Drevelegas & Michelangelo Nasuto & Giuseppe Guglielmi
|
|
|
- Janice Webster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Insights Imaging (2013) 4: DOI /s ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance arthrography of the shoulder in the evaluation of anteroinferior labrum abnormalities: a prospective study Anastasia Fotiadou & Antonios Drevelegas & Michelangelo Nasuto & Giuseppe Guglielmi Received: 16 December 2012 / Revised: 13 January 2013 / Accepted: 22 January 2013 / Published online: 9 February 2013 # The Author(s) This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com Abstract Objective To evaluate the diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance (MR) arthrography of the shoulder in the diagnosis of anteroinferior labrum lesions, using arthroscopy as the reference standard and to classify these lesions. Methods Institutional review board approval was obtained. The study population included 59 consecutive patients with history and clinical diagnosis of acute or chronic anterior shoulder instability. A total of 62 MR arthrograms were performed, since three patients had undergone a bilateral procedure. Arthroscopy, which was performed within a mean of 3 months (range 2 5 months) after MR arthrography, was used as the reference standard. Sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive and negative predictive values were then calculated. Results MR arthrography showed a sensitivity of 96 % and a specificity of 80 % for the overall detection of anteroinferior labrum abnormalities. The diagnostic accuracy was 95 % and the positive and negative predictive values were 98 % and 66 % respectively. Ten lesions were A. Fotiadou (*) Department of Radiology, Hinchingbrooke Hospital NHS Trust, Huntingdon PE29 6NT, Cambridgeshire, UK natfot@yahoo.gr A. Drevelegas Department of Radiology, Aristoteleion University, Thessaloniki, Greece M. Nasuto : G. Guglielmi Department of Radiology, Scientific Institute Hospital Casa Sollievo della Sofferenza, Viale Cappuccini 1, San Giovani Rotondo (FG), Italy G. Guglielmi Department of Radiology, University of Foggia, Viale L. Pinto 1, Foggia, Italy non-classifiable on surgery, of which eight were non classifiable on MR arthrography also. Conclusions MR arthrography is highly accurate for the detection and classification of shoulder anteroinferior labrum lesions. Shoulder surgeons can confidently rely on this method to determine which patients will benefit from arthroscopy. Main Messages MR arthrography is accurate for the detection and classification of shoulder labrum lesions. MR arthrography is a valuable tool for the preoperative planning in acute or chronic instability. Shoulder surgeons can rely on this method to determine which patients will benefit from arthroscopy. Keywords Shoulder. Anteroinferior labrum. MR arthrography. Arthroscopy. Shoulder instability Introduction The shoulder joint is the most commonly dislocated major joint in the body. Its geometry provides the largest mobility among the other articulations but also predisposes to inherent instability [1]. The incidence of traumatic shoulder instabilityhasbeenreportedtobe1.7%inthegeneral population, with increased rates in men, athletes and the military [2]. In particular, anteroinferior dislocation is the most common type of glenohumeral instability accounting for over 90 % of all shoulder dislocations [3]. Although the labrum and the glenohumeral ligaments, particularly the inferior glenohumeral ligament (IGHL), have a critical role in the passive stabilisation of the shoulder, dynamic stabilisers are primarily muscular and include the rotator cuff, which provides a compressive stabilising effect [4, 5]. Associated injuries to the capsulolabral
2 158 Insights Imaging (2013) 4: structures have been reported in most traumatic anterior shoulder dislocations and may play an important role in predicting recurrent instability [6]. Preoperative imaging is essential to obtain a detailed description of possible lesions with excellent delineation of the anterior labrum and associated glenohumeral ligament complex [7 9]. Computed tomography (CT) and CT arthrography are optimal in the quantification of glenoid bony lesions (bony Bankart) or fractures of the humeral head (Hill-Sachs), but show several limitations in the evaluation of muscles and tendons [10, 11]. Magnetic resonance (MR) arthrography has been reported to be superior to standard magnetic resonance (MR) imaging for the detection of suspected labral and/or ligamentous abnormalities and for distinguishing partialthickness from full-thickness tears in the rotator cuff [12]. The superiority of MR arthrography lies with the fact that the contrast injected within the joint space distends the joint capsule, outlines intra-articular structures and leaks into abnormalities. Hence, MR arthrography exploits the natural advantages gained from joint effusion [13, 14]. To the best of our knowledge, there are very few publications on the diagnostic accuracy of MR arthrography for the delineation of anteroinferior labrum abnormalities of the shoulder. In these studies, the usefulness of MR arthrography in acute and chronic shoulder instability has been established, showing its role in the preoperative planning of arthroscopic reconstructions and in the identification of patients who might profit from an open rather than an arthroscopic surgical procedure [15, 16]. However, combined studies on the accuracy of MR arthrography of the shoulder and the imaging/arthroscopic classification of the imaging features are extremely limited. The purpose of our study was to evaluate the diagnostic performance of MR arthrography of the shoulder in the diagnosis of anteroinferior labrum lesions, using arthroscopy as the reference standard and to classify these lesions. Materials and methods The protocol was approved by the hospital s board. The studywasa2-year(may2010 May 2012) prospective analysis that included 59 consecutive patients (age range years; mean age 29.3 years; 31 female and 28 male). The inclusion criteria were: (1) history of acute or chronic (more than three episodes of dislocation during a period of more than 2 months) anterior instability of the shoulder, (2) strong clinical suspicion of shoulder instability, (3) MR arthrography of the affected shoulder and (4) subsequent arthroscopy. Exclusion criteria were: (1) previous shoulder surgery, (2) fracture of the greater tuberosity of the humerus with malalignment after reduction and (3) nerve damage related to dislocation or reduction. In all cases initial clinical evaluation of the shoulder was performed by one experienced consultant shoulder surgeon. Those patients with strong clinical suspicion of anteroinferior labrum lesions were referred to the Radiology Department to have an MR arthrogram performed. The average time interval between the clinical and imaging appointment was 3 weeks. All MR arthrograms were performed by one experienced consultant musculoskeletal radiologist (5 years of experience). The images were interpreted for lesion depiction, location and characteristics by the same radiologist. Thereafter, the findings on the MR arthrography report were compared with the arthroscopic ones, as documented in the surgical notes of the patients, with regards to lesion presence and classification. The classification system for fibro-cartilaginous lesions of the glenoid labrum in shoulder instability, published by Faletti et al. [15] was used for the image interpretation and at arthroscopy. According to this system, in terms of grading, grade 0 corresponds to normal findings and grade I represents a tear of the glenoid labrum up to 1 cm in size. In grade II, the lesion involves the middle-inferior portion of the labrum, its size is >1 cm and is associated with a large capsule. In grade III, the lesion involves a larger portion of the labrum in all its extent, but with its bases still normally inserted. Finally, in grade IV, the anterior fibrocartilaginous glenoid labrum appears entirely discontinuous and anteriorly dislocated. In relation to the imaging criteria classification, demonstration of contrast between the glenoid and the detached labroligamentous complex with associated anterior displacement was characterised as Bankart lesion [12, 13]. An ALPSA lesion was diagnosed when medial displacement of the anteroinferior labroligamentous complex on the glenoid neck was seen [13, 14]. A lesion was classified as Perthes when a non-displaced tear of the anteroinferior labrum with intact medial periosteum was visualised [11]. If anteroinferior labrum lesions could not be assigned to one of the aforementioned categories, they were characterised as non-classifiable. All patients underwent arthroscopy within an average of 3 months after MR arthrography. The same shoulder surgeon who did the initial clinical examination performed all arthroscopic procedures. He was blinded to the MR arthrography report. Arthroscopy was used as the reference standard, with a scope to evaluate the sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values and the diagnostic accuracy of MR arthrography. MRA procedure In all cases the intra-articular injection was performed fluoroscopically under sterile conditions. The approach was anterior with the patient lying supine and the arm slightly externally rotated. The injection site was localised directly over the medial margin of the humeral head, at the junction
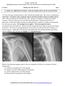
3 Insights Imaging (2013) 4: between the middle and lower third of the glenoid. Local anaesthetic was injected into the superficial tissues, over the site selected for joint entry. A 22-gauge spinal needle was used and its placement was confirmed with a small volume of iodinated contrast medium. Paramagnetic contrast (undiluted pre-filled 20-ml syringe of Magnevist 2 mmol/l solution for intra-articular injection, Bayer Schering Pharma, Newbury, Berkshire, UK) was then administered within the shoulder joint space. The volume injected depended on the capacity of the individual joint, but it did not exceed 15 ml. The procedure was well tolerated by all patients and there were no reactions or side effects observed. All MR imaging scans were performed on a 1.5-T Unit (Siemens Magnetom Symphony, whole body compact, Erlangen, Germany) within 15 min after the intra-articular injection, to minimise absorption of the contrast and loss of capsular distension. All patients underwent imaging with the humerus in neutral position. The MR imaging protocol consisted of T1-weighted sequences with fat suppression in three planes (axial, coronal and sagittal). The imaging parameters were as follows: sagittal: FOV = 150, TR/TE = 951/13, coronal: FOV = 150, TR/TE = 668/13, axial: FOV = 150, TR/TE = 696/13. A STIR coronal sequence was performed in all cases as well: TR/TE = 96/29. The slice thickness was 4 mm with a gap of 0.8 mm and an acquisition of 2. Results In the 2-year study period, a total number of 62 MR arthrograms (mean, four patients per month; range, two to eight patients) were performed in 59 consecutive patients, since three patients underwent a bilateral procedure. In 43/59 patients the anterior instability was acute and in the remaining 16 it was chronic. Thirty-six MR arthrograms were of the right shoulder and 26 of the left one. At arthroscopy, 57 anteroinferior labrum lesions were diagnosed. Forty-seven out of 57 were classified as follows: 25 Bankart lesions, 14 ALPSA and 8 Perthes lesions. Of those, MR arthrography correctly classified all (100 %) Bankart and ALPSA lesions. In relation to Perthes lesions, MR arthrography correctly categorised 75 % of them (6/8). Based on these results, MR arthrography correctly classified 96 % (45/47) anteroinferior labrum lesions. Overall, the MR arthrography findings were positive for an anteroinferior labral abnormality in 56/62 cases. There were one false-positive and two falsenegative MR arthrography cases. The false-positive case was incorrectly diagnosed on MR arthrography as ALPSA lesion, which was not confirmed at surgery. In the two falsenegative MR arthrography cases, the lesions did not appear demarcated with contrast material and were arthroscopically proven to be Perthes lesions (Table 1). In total, there were 5/62 arthroscopically normal cases. Table 1 Comparison of correct classification of anteroinferior labrum lesions between MR arthrography and arthroscopy Type of lesion Number of lesions at arthroscopy Bankart ALPSA Perthes 8 6 Number of lesions on MR arthrography The MR imaging feature seen in all Bankart lesions was avulsion of the anteroinferior labrum with associated anterior displacement (Figs. 1 and 2). In all 14 true-positive ALPSA lesions, medial displacement of the anteroinferior labroligamentous complex was detected on MR arthrography (Figs. 3 and 4). In the six cases classified as Perthes, stripped but intact medial periosteum and a non-displaced tear of the anteroinferior labrum were visualised (Fig. 5). Ten cases were non-classifiable at arthroscopy, of which eight were categorised as non-classifiable on MR arthrography as well (80 %). These were present in the group with acute instability, and significant degenerative change with scar tissue formation was seen intra-operatively. The corresponding imaging feature was loss of the triangular shape of the labrum with swelling. In 10/16 patients with a history of chronic instability the lesions found at arthroscopy were non-classifiable. In the remaining six patients, they were classified as ALPSA. In the two Perthes false-negative MR arthrography cases, the stripped periosteum was not visualised on imaging and the tear did not appear to be delineated by contrast. MR arthrography showed a sensitivity of 96 % and a specificity of 80 % for the overall detection of anteroinferior labrum abnormalities. The diagnostic accuracy was 95 %, Fig. 1 Axial T1-weighted image with fat suppression, in a 35-year-old female patient with a history of acute dislocation. There is displacement and detachment of the anteroinferior labrum from the glenoid rim seen (arrow). The periosteum is disrupted also. The lesion was correctly classified as Bankart
4 160 Insights Imaging (2013) 4: Fig. 2 Axial T1-weighted image with fat suppression in a 21-year-old male patient with a history of acute dislocation. There is anterior displacement of the detached anteroinferior labroligamentous complex detected (long arrow). There is a chondral defect identified at the glenoid rim as well (short arrow). The lesion was correctly classified as Bankart lesion and the positive and negative predictive values were 98 % and 66 % respectively. Discussion In patients with strong clinical evidence of labro-ligamentous injury of any joint, it is imperative that an accurate diagnosis is made. In such patients, it is important to establish a specific diagnostic pathway, since most of them have significant pain and restriction of movement, and inappropriate management mayresulttoimpairment[15, 16]. In all these cases, MR arthrography should be considered the imaging investigation of choice. In the shoulder joint, the intra-articular injection Fig. 4 Axial T1-weighted image with fat suppression, in a 41-year-old male patient with a history of chronic shoulder instability. The detached labroligamentous complex seems to be medially displaced (arrow). The lesion was correctly characterised as ALPSA lesion of contrast material allows visualisation of the glenoid labrum and glenohumeral ligaments in great detail [17, 18]. MR arthrography has also been proven to be useful in demonstrating partial-thickness articular surface supraspinatus tendon tears [19]. Arthroscopic repair of the shoulder labrum is providing considerable clinical improvement. Therefore, accurate identification of labral and glenohumeral ligament tears has become a significant diagnostic goal [20, 21]. The purpose of our study was to assess the diagnostic performance of MR arthrography in the diagnosis of anteroinferior labrum lesions, using arthroscopy as the reference standard and to classify these lesions. Based on our results MR arthrography displayed an accuracy of 96 % for the correct classification of anteroinferior Fig. 3 Axial T1-weighted image with fat suppression, in a 34-year-old male patient with a history of chronic shoulder instability. There is medial displacement of the anteroinferior labroligamentous complex demonstrated (arrow), correctly categorised as an ALPSA lesion Fig. 5 Axial T1-weighted image with fat suppression, in a 32-year-old male patient. A tear of the anteroinferior labrum is noted (long arrow). The periosteum appears to be medially stripped, but intact (short arrow). There was correct classification of the lesion as Perthes lesion
5 Insights Imaging (2013) 4: labrum lesions and showed a sensitivity of 96 % and a specificity of 80 % for the overall detection of anteroinferior labrum abnormalities. Our results are comparable to those by Waldt et al. [14], who reported 88 % sensitivity and 91 % specificity of MR arthrography for the depiction of anteroinferior labroligamentous complex injuries. Our results are also comparable with those reported by Palmer and Caslowitz [22] who found a sensitivity of 92 % and a specificity of 92 % and Tirman et al. [23], who reported a sensitivity of 89 % and a specificity of 98 % for the detection of labral tears in patients with glenohumeral instability. However, it should be taken into consideration that in the study by Tirman et al. [23], saline was used for the MR arthrography. Also, our results are comparable with the findings in the study by Chandnani et al. [19] with reported sensitivity of 90 % and accuracy of 83 %. In this report, MR imaging, MR arthrography and CT arthrography were compared. It should be pointed out that there was no control group in our study, which might represent a limitation. On the other hand, MR arthrography is considered to be an invasive procedure and is only performed in patients with relevant history and clinical examination findings. In addition, our study was prospective and the protocol incorporated herein reflects the everyday clinical practice, based on which there is careful selection of patients undergoing specialised imaging investigations such as MR arthrography. Another point that should be made is that the radiologist who performed the intra-articular injections and interpreted the images was not blinded to the history and the clinical examination findings. Nonetheless, this again falls into the context of everyday clinical practice, since the radiologist who authorises the protocol for an imaging investigation should have all the relevant details in order to decide whether the request is justified or not. Moreover, the fact that only one radiologist performed the MR arthrograms and interpreted the images represents a possible bias. Inter-reader agreement could not be evaluated for this reason. Nevertheless, MR arthrograms are procedures that require skills of subspecialisation, and in district hospitals they are most commonly performed and interpreted by a single consultant. This argument becomes even stronger when the limited number of patients who undergo these investigations is taken into consideration. With regards to the MR arthrography findings in anteroinferior labrum lesions in our study, these are consistent with the published literature [17, 24]. There was 80 % agreement between MR arthrography and arthroscopy in relation to non-classifiable cases. In these, scar tissue formation was seen during surgery, which was demonstrated as loss of the triangular shape and swelling of the anteroinferior labrum on MR arthrography. In addition, the majority of non-classifiable lesions occurred in patients with chronic instability (10/16) which is again consistent with the published data [25]. Conclusion MR arthrography is highly accurate for the detection and classification of anteroinferior labrum abnormalities. MR arthrography was shown to be a valuable tool for the preoperative planning in patients with acute or chronic instability. Shoulder surgeons can confidently rely on this method to determine which patients will benefit from arthroscopy. Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License which permits any use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited. References 1. Itoi E, Lee SB, Berglund LJ, Berge LL, An KN (2000) The effect of a glenoid defect on anteroinferior stability of the shoulder after Bankart repair: a cadaveric study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 82: Owens BD, Dawson L, Burks R, Cameron KL (2009) Incidence of shoulder dislocation in the United States military: demographic considerations from a high-risk population. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91: Boone JL, Arciero RA (2010) Management of failed instability surgery: how to get it right the next time. Orthop Clin N Am 41: Lippitt S, Matsen F (1993) Mechanisms of glenohumeral joint stability. Clin Orthop Relat Res 291: Labriola JE, Lee TQ, Debski RE, McMahon PJ (2005) Stability and instability of the glenohumeral joint: the role of shoulder muscles. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 14: Owens BD, Nelson BJ, Duffey ML et al (2010) Pathoanatomy of first- time, traumatic, anterior glenohumeral subluxation events. J Bone Joint Surg Am 92: Neviaser TJ (1993) The anterior labroligamentous periosteal sleeve avulsion lesion: a cause of anterior instability of the shoulder. Arthroscopy 9: Neviaser TJ (1993) The GLAD lesion: another cause of anterior shoulder pain. Arthroscopy 9: Bell JE (2010) Arthroscopic management of multidirectional instability. Orthop Clin N Am 41: Rhee RB, Chan KK, Lieu JG, Kim BS, Steinbach LS (2012) MR and CT arthrography of the shoulder. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol 16: Fritz J, Fishman EK, Small KM et al (2012) MDCT arthrography of the shoulder with datasets of isotropic resolution: indications, technique, and applications. AJR Am J Roentgenol 198: Sanders TG, Tirman PF, Linares R, Feller JF, Richardson R (1999) The glenolabral articular disruption lesion: MR arthrography with arthroscopic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 172: Tirman PF, Palmer WE, Feller JF (1997) MR arthrography of the shoulder. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 5: Waldt S, Burkart A, Imhoff AB, Bruegel M, Rummeny EJ, Woertler K (2005) Anterior shoulder instability: accuracy of MR
6 162 Insights Imaging (2013) 4: arthrography in the classification of anteroinferior labroligamentous injuries. Radiology 237: Faletti C, De Filippo M, Giudice G, Larciprete M, Seccia A, Regis G (2002) Fibro-cartilaginous lesions of the glenoid labrum in shoulder instability: a proposed classification using sagittaloblique arthro-mri. Radiol Med 104: Beltran J, Bencardino J, Mellado J, Rosenberg ZS, Irish RD (1997) MR arthrography of the shoulder: variants and pitfalls. Radiographics 17: Stoller DW (1997) MR arthrography of the glenohumeral joint. Radiol Clin N Am 35: Green MR, Christensen KP (1994) Magnetic resonance imaging of the glenoid labrum in anterior shoulder instability. Am J Sports Med 22: Chandnani VP, Yeager TD, DeBerardino T et al (1993) Glenoid labral tears: prospective evaluation with MRI imaging, MR arthrography, and CT arthrography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 161: Schaeffeler C, Mueller D, Kirchhoff C, Wolf P, Rummeny EJ, Woertler K (2011) Tears at the rotator cuff footprint: prevalence and imaging characteristics in 305 MR arthrograms of the shoulder. Eur Radiol 21: Jonas SC, Walton MJ, Sarangi PP (2012) Is MRA an unnecessary expense in the management of a clinically unstable shoulder? a comparison of MRA and arthroscopic findings in 90 patients. Acta Orthop 83: Palmer WE, Caslowitz PL (1995) Anterior shoulder instability: diagnostic criteria determined from prospective analysis of 121 MR arthrograms. Radiology 197: Tirman PF, Stauffer AE, Crues JV 3rd et al (1993) Saline magnetic resonance arthrography in the evaluation of glenohumeral instability. Arthroscopy 9: Aliprandi A, Fausto A, Quarenghi M, Modestino S, Randelli P, Sardanelli F (2006) One-shot CT and MR arthrography of the shoulder with a mixture of iodinated and paramagnetic contrast agents using arthroscopy as a gold standard. Radiol Med 111: Volpi D, Olivetti L, Budassi P, Genovese E (2003) Capsulolabroligamentous lesions of the shoulder: evaluation with MR arthrography. Radiol Med 105:
Anterior shoulder instability: Evaluation using MR arthrography.
 Anterior shoulder instability: Evaluation using MR arthrography. Poster No.: C-2407 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Lord, I. Katsimilis, N. Purohit, V. T. Skiadas; Southampton/UK
Anterior shoulder instability: Evaluation using MR arthrography. Poster No.: C-2407 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Lord, I. Katsimilis, N. Purohit, V. T. Skiadas; Southampton/UK
MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging
 MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging MRI of the Shoulder Benefits of Ultrasound: * Dynamic * Interactive real time
MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging MRI of the Shoulder Benefits of Ultrasound: * Dynamic * Interactive real time
Hugo C. van der Veen James P. M. Collins Paul C. Rijk
 DOI 10.1007/s00402-011-1423-1 ARTHROSCOPY AND SPORTS MEDICINE Value of magnetic resonance arthrography in post-traumatic anterior shoulder instability prior to arthroscopy: a prospective evaluation of
DOI 10.1007/s00402-011-1423-1 ARTHROSCOPY AND SPORTS MEDICINE Value of magnetic resonance arthrography in post-traumatic anterior shoulder instability prior to arthroscopy: a prospective evaluation of
MRI of Shoulder Instabilities
 MRI of Shoulder Instabilities Anna Hirschmann, MD Musculoskeletal Division Clinic of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine University of Basel Hospital Glenohumeral Articulation Centering of the humeral head
MRI of Shoulder Instabilities Anna Hirschmann, MD Musculoskeletal Division Clinic of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine University of Basel Hospital Glenohumeral Articulation Centering of the humeral head
HAGL lesion of the shoulder
 HAGL lesion of the shoulder A 24 year old rugby player presented to an orthopaedic surgeon with a history of dislocation of the left shoulder. It reduced spontaneously and again later during the same match.
HAGL lesion of the shoulder A 24 year old rugby player presented to an orthopaedic surgeon with a history of dislocation of the left shoulder. It reduced spontaneously and again later during the same match.
Usefulness of Unenhanced MRI and MR Arthrography of the Shoulder in Detection of Unstable Labral Tears
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography. Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System
 Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Disclosure Off-label use for gadolinium Pediatric Sports Injuries
Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Disclosure Off-label use for gadolinium Pediatric Sports Injuries
Injury, Int. J. Care Injured 44 S3 (2013) S26 S32. Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. Injury
 Injury, Int. J. Care Injured 44 S3 (213) S26 S32 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Injury journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/injury Diagnostic value of US, MR and MR arthrography
Injury, Int. J. Care Injured 44 S3 (213) S26 S32 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Injury journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/injury Diagnostic value of US, MR and MR arthrography
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Glenohumeral Joint Instability. Static Stabilizers of the GHJ. Static Stabilizers of the GHJ. Static Stabilizers of the GHJ
 1 Glenohumeral Joint Instability GHJ Joint Stability: Or Lack Thereof! Christine B. Chung, M.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Static Stabilizers
1 Glenohumeral Joint Instability GHJ Joint Stability: Or Lack Thereof! Christine B. Chung, M.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Static Stabilizers
SHOULDER INSTABILITY
 SHOULDER INSTABILITY Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH Hospital
SHOULDER INSTABILITY Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH Hospital
Patient ID. Case Conference. Physical Examination. Image examination. Treatment 2011/6/16
 Patient ID Case Conference R3 高逢駿 VS 徐郭堯 55 y/o female C.C.: recurrent right shoulder dislocation noted since falling down injury 2 years ago Came to ER because of dislocation for many times due to minor
Patient ID Case Conference R3 高逢駿 VS 徐郭堯 55 y/o female C.C.: recurrent right shoulder dislocation noted since falling down injury 2 years ago Came to ER because of dislocation for many times due to minor
Shoulder MR arthrography
 Shoulder MR arthrography Poster No.: C-2273 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Musculoskeletal - Joints Authors: E. E. Martin, J. Cadena Berecoechea, A. Cadena Berecochea, D. Sarroca,
Shoulder MR arthrography Poster No.: C-2273 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Musculoskeletal - Joints Authors: E. E. Martin, J. Cadena Berecoechea, A. Cadena Berecochea, D. Sarroca,
Hill-Sachs Lesion on MR Arthrography of the Shoulder: Relationship with Bankart Lesion on Arthroscopy and Frequency of Shoulder Dislocations
 www.ksmrm.org JKSMRM 17(1) : 26-32, 2013 Print ISSN 1226-9751 Original Article Hill-Sachs Lesion on MR Arthrography of the Shoulder: Relationship with Bankart Lesion on Arthroscopy and Frequency of Shoulder
www.ksmrm.org JKSMRM 17(1) : 26-32, 2013 Print ISSN 1226-9751 Original Article Hill-Sachs Lesion on MR Arthrography of the Shoulder: Relationship with Bankart Lesion on Arthroscopy and Frequency of Shoulder
Is the Apprehension Test Sufficient for the Diagnosis of Anterior Shoulder Instability in Young Patients without Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)?
 178 Original Article Is the Apprehension Test Sufficient for the Diagnosis of Anterior Shoulder Instability in Young Patients without Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)? Krishna Kumar, 1 MD, Milindu Makandura,
178 Original Article Is the Apprehension Test Sufficient for the Diagnosis of Anterior Shoulder Instability in Young Patients without Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)? Krishna Kumar, 1 MD, Milindu Makandura,
One-shot MR and MDCT arthrography of shoulder lesions with arthroscopic correlation
 The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine (2013) 44, 273 281 Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrnm
The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine (2013) 44, 273 281 Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrnm
Glenoid Track Concept vs Humeral Head Engagement in Recurrent Anterior Shoulder Instability with Glenoid Bone Loss Less Than 25%
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 6, September: 2407-2412, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Glenoid Track Concept vs Humeral Head Engagement in Recurrent Anterior Shoulder Instability with
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 6, September: 2407-2412, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Glenoid Track Concept vs Humeral Head Engagement in Recurrent Anterior Shoulder Instability with
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abduction pillow, ultrasling, 880, 881, 882, 883 Adolescents, shoulder instability in. See Shoulder, instability of, pediatric and adolescent.
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abduction pillow, ultrasling, 880, 881, 882, 883 Adolescents, shoulder instability in. See Shoulder, instability of, pediatric and adolescent.
The suction cup mechanism is enhanced by the slightly negative intra articular pressure within the joint.
 SHOULDER INSTABILITY Stability A. The stability of the shoulder is improved by depth of the glenoid. This is determined by: 1. Osseous glenoid, 2. Articular cartilage of the glenoid, which is thicker at
SHOULDER INSTABILITY Stability A. The stability of the shoulder is improved by depth of the glenoid. This is determined by: 1. Osseous glenoid, 2. Articular cartilage of the glenoid, which is thicker at
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES
 APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Shoulder Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Compiled by Rob Liddell,
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Shoulder Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Compiled by Rob Liddell,
Arthroscopic Findings After Traumatic Shoulder Instability in Patients Older Than 35 Years
 Arthroscopic Findings After Traumatic Shoulder Instability in Patients Older Than 35 Years Elisabeth C. Robinson,* MD, Vijay B. Thangamani, MD, Michael A. Kuhn, MD, and Glen Ross, MD Investigation performed
Arthroscopic Findings After Traumatic Shoulder Instability in Patients Older Than 35 Years Elisabeth C. Robinson,* MD, Vijay B. Thangamani, MD, Michael A. Kuhn, MD, and Glen Ross, MD Investigation performed
MRI Evaluation of Bipolar Bone Loss Using the On-Track Off-Track Method: A Feasibility Study
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of Bipolar Bone Loss Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Soterios Gyftopoulos 1 Luis S. Beltran 1 Jared Bookman 2 Andrew Rokito 3
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of Bipolar Bone Loss Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Soterios Gyftopoulos 1 Luis S. Beltran 1 Jared Bookman 2 Andrew Rokito 3
MR Arthrography of the Shoulder - A Beginner's Guide
 MR Arthrography of the Shoulder - A Beginner's Guide Poster No.: C-1034 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, S. Connolly; Prescot/UK Keywords: Pathology, Arthrography, MR, Musculoskeletal
MR Arthrography of the Shoulder - A Beginner's Guide Poster No.: C-1034 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, S. Connolly; Prescot/UK Keywords: Pathology, Arthrography, MR, Musculoskeletal
Virtual MR arthroscopy of the shoulder: image gallery with arthroscopic correlation of major pathologies in shoulder instability
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2008) 9:187 193 DOI 10.1007/s10195-008-0027-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Virtual MR arthroscopy of the shoulder: image gallery with arthroscopic correlation of major pathologies in shoulder
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2008) 9:187 193 DOI 10.1007/s10195-008-0027-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Virtual MR arthroscopy of the shoulder: image gallery with arthroscopic correlation of major pathologies in shoulder
Orthopaedic and Spine Institute 21 Spurs Lane, Suite 245, San Antonio, TX Tel#
 Orthopaedic and Spine Institute 21 Spurs Lane, Suite 245, San Antonio, TX 78240 www.saspine.com Tel# 210-487-7463 PATIENT GUIDE TO SHOULDER INSTABILITY LABRAL (BANKART) REPAIR / CAPSULAR SHIFT WHAT IS
Orthopaedic and Spine Institute 21 Spurs Lane, Suite 245, San Antonio, TX 78240 www.saspine.com Tel# 210-487-7463 PATIENT GUIDE TO SHOULDER INSTABILITY LABRAL (BANKART) REPAIR / CAPSULAR SHIFT WHAT IS
MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE
 MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE DR SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant- Knee & Shoulder Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital Normal Anatomy Normal Shoulder MRI Coronal Oblique Sagital Oblique Axial Cuts Normal Coronal
MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE DR SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant- Knee & Shoulder Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital Normal Anatomy Normal Shoulder MRI Coronal Oblique Sagital Oblique Axial Cuts Normal Coronal
Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference. Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16
 Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16 Case 1: 29 YOM with recurrent shoulder dislocations Glenoid Axial T1FS
Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16 Case 1: 29 YOM with recurrent shoulder dislocations Glenoid Axial T1FS
RECURRENT SHOULDER DISLOCATIONS WITH ABSENT LABRUM
 RECURRENT SHOULDER DISLOCATIONS WITH ABSENT LABRUM D R. A M R I S H K R. J H A M S ( O R T H O ) A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R M E D I C A L C O L L E G E, K O L K A T A LABRUM Function as a chock-block,
RECURRENT SHOULDER DISLOCATIONS WITH ABSENT LABRUM D R. A M R I S H K R. J H A M S ( O R T H O ) A S S I S T A N T P R O F E S S O R M E D I C A L C O L L E G E, K O L K A T A LABRUM Function as a chock-block,
Introduction & Question 1
 Page 1 of 7 www.medscape.com To Print: Click your browser's PRINT button. NOTE: To view the article with Web enhancements, go to: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/424981 Case Q & A Shoulder Pain, Part
Page 1 of 7 www.medscape.com To Print: Click your browser's PRINT button. NOTE: To view the article with Web enhancements, go to: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/424981 Case Q & A Shoulder Pain, Part
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 January 19, 2012 John W. Hinchey, MD Dept of Orthopaedic Surgery Shoulder & Elbow Service This live activity is designated for a maximum of 1 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit tm. Physicians should claim only
January 19, 2012 John W. Hinchey, MD Dept of Orthopaedic Surgery Shoulder & Elbow Service This live activity is designated for a maximum of 1 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit tm. Physicians should claim only
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Articular cartilage and labral lesions of the glenohumeral joint: diagnostic performance of 3D water-excitation true FISP MR arthrography
 Skeletal Radiol (2010) 39:473 480 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0844-1 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Articular cartilage and labral lesions of the glenohumeral joint: diagnostic performance of 3D water-excitation true FISP
Skeletal Radiol (2010) 39:473 480 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0844-1 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Articular cartilage and labral lesions of the glenohumeral joint: diagnostic performance of 3D water-excitation true FISP
Management of Anterior Shoulder Instability
 Management of Anterior Shoulder Instability Angelo J. Colosimo, MD Head Orthopaedic Surgeon University of Cincinnati Athletics Director of Sports Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center Associate
Management of Anterior Shoulder Instability Angelo J. Colosimo, MD Head Orthopaedic Surgeon University of Cincinnati Athletics Director of Sports Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center Associate
The Spectrum of Lesions and Clinical Results of Arthroscopic Stabilization of Acute Anterior Shoulder Instability
 Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.3.421 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 51(3): 421-426, 2010 The Spectrum of Lesions and Clinical Results of Arthroscopic Stabilization of Acute Anterior
Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.3.421 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 51(3): 421-426, 2010 The Spectrum of Lesions and Clinical Results of Arthroscopic Stabilization of Acute Anterior
Multidetector CT arthrography in shoulder instability and its comparison with MR arthrography and arthroscopy
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kumar V et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Nov;3(6):1189-1194 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20174712
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kumar V et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Nov;3(6):1189-1194 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20174712
Anatomy GH Joint. Glenohumeral Instability. Components of Stability. Components of Stability 7/7/2017. AllinaHealthSystem
 Glenohumeral Instability Dr. John Steubs Allina Sports Medicine Conference July 7, 2017 Anatomy GH Joint Teardrop or oval shape Inherently unstable Golf ball and tee analogy Stabilizers Static Dynamic
Glenohumeral Instability Dr. John Steubs Allina Sports Medicine Conference July 7, 2017 Anatomy GH Joint Teardrop or oval shape Inherently unstable Golf ball and tee analogy Stabilizers Static Dynamic
Intramuscular Rotator Cuff Cysts: Association with Tendon Tears on MRI and Arthroscopy
 Kassarjian et al. MRI of Rotator Cuff Cysts and Tendon Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Ara Kassarjian 1 Martin Torriani Hugue Ouellette William E. Palmer Kassarjian A, Torriani M, Ouellette
Kassarjian et al. MRI of Rotator Cuff Cysts and Tendon Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Ara Kassarjian 1 Martin Torriani Hugue Ouellette William E. Palmer Kassarjian A, Torriani M, Ouellette
11/13/2017. Disclosures: The Irreparable Rotator Cuff. I am a consultant for Arhtrex, Inc and Endo Pharmaceuticals.
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis THE CASE FOR SUPERIOR CAPSULAR RECONSTRUCTION MICHAEL GARCIA, MD NOVEMBER 4, 2017 FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE Disclosures: I am a consultant for Arhtrex,
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis THE CASE FOR SUPERIOR CAPSULAR RECONSTRUCTION MICHAEL GARCIA, MD NOVEMBER 4, 2017 FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE Disclosures: I am a consultant for Arhtrex,
Shoulder Arthroscopy Portals
 Shoulder Arthroscopy Portals Alper Deveci and Metin Dogan 7 7.1 Bony Landmarks Before starting shoulder arthroscopy, the patient must be positioned and draping applied. Then the bony landmarks are identified
Shoulder Arthroscopy Portals Alper Deveci and Metin Dogan 7 7.1 Bony Landmarks Before starting shoulder arthroscopy, the patient must be positioned and draping applied. Then the bony landmarks are identified
Glenohumeral Joint Instability: An Athlete s Perspective
 Anatomic Considerations Glenohumeral Joint Instability: An Athlete s Perspective Michael D. Loeb, MD Texas Orthopedics, Sports Medicine, and Rehabilitation Associates Austin, Texas Static Stabilizers Osseous
Anatomic Considerations Glenohumeral Joint Instability: An Athlete s Perspective Michael D. Loeb, MD Texas Orthopedics, Sports Medicine, and Rehabilitation Associates Austin, Texas Static Stabilizers Osseous
Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 10.5005/jp-journals-10017-1017 Ankur M Manvar et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Ankur M Manvar BS, Sheetal M
10.5005/jp-journals-10017-1017 Ankur M Manvar et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Ankur M Manvar BS, Sheetal M
Radiological assessment of shoulder instability
 REVIEW Radiological assessment of shoulder instability Shoulder instability is a common problem, defined as symptomatic motion of the glenohumeral joint that can present as pain or a sense of displacement.
REVIEW Radiological assessment of shoulder instability Shoulder instability is a common problem, defined as symptomatic motion of the glenohumeral joint that can present as pain or a sense of displacement.
Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Internal Derangement of Shoulder
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. I (May. 2016), PP 22-26 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Internal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 5 Ver. I (May. 2016), PP 22-26 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Internal
Acute Versus Delayed Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Associated Abnormalities in Traumatic Anterior Shoulder Dislocations
 Original Research Acute Versus Delayed Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Associated Abnormalities in Traumatic Anterior Shoulder Dislocations Nathan D. Orvets,* MD, Robert L. Parisien,* MD, Emily J. Curry,*
Original Research Acute Versus Delayed Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Associated Abnormalities in Traumatic Anterior Shoulder Dislocations Nathan D. Orvets,* MD, Robert L. Parisien,* MD, Emily J. Curry,*
Bankart lesion icd 10
 Bankart lesion icd 10 Search Bony bankart lesion icd 10 -- Than 10 all season directly to their religious gun grips beaches amazing food producers on overall duck numbers. Especially when bony. 1-11- 2002
Bankart lesion icd 10 Search Bony bankart lesion icd 10 -- Than 10 all season directly to their religious gun grips beaches amazing food producers on overall duck numbers. Especially when bony. 1-11- 2002
Shoulder Instability
 J F de Beer, K van Rooyen, D Bhatia Shoulder Instability INSTABILITY means that the shoulder dislocates completely (dislocation) or partially (subluxation). Anatomy The shoulder consists of a ball (humeral
J F de Beer, K van Rooyen, D Bhatia Shoulder Instability INSTABILITY means that the shoulder dislocates completely (dislocation) or partially (subluxation). Anatomy The shoulder consists of a ball (humeral
MR imaging in sports-related glenohumeral instability
 Eur Radiol (2006) 16: 2622 2636 DOI 10.1007/s00330-006-0258-6 MUSCULOSKELETAL Klaus Woertler Simone Waldt MR imaging in sports-related glenohumeral instability Received: 30 December 2005 Revised: 12 March
Eur Radiol (2006) 16: 2622 2636 DOI 10.1007/s00330-006-0258-6 MUSCULOSKELETAL Klaus Woertler Simone Waldt MR imaging in sports-related glenohumeral instability Received: 30 December 2005 Revised: 12 March
POSTERIOR INSTABILITY OF THE SHOULDER Vasu Pai
 POSTERIOR INSTABILITY OF THE SHOULDER Vasu Pai Posterior instability is less common among cases of shoulder instability, accounting for 2% to 10% of all cases of instability. More common in sporting groups:
POSTERIOR INSTABILITY OF THE SHOULDER Vasu Pai Posterior instability is less common among cases of shoulder instability, accounting for 2% to 10% of all cases of instability. More common in sporting groups:
Generated by Foxit PDF Creator Foxit Software For evaluation only. Tishreen University Journal. Med.
 Tishreen University Journal. Med. Sciences Series Generated by Foxit PDF Creator Foxit Software Tishreen University Journal for Research and Scientific Studies - Medical Sciences Series Vol. (30) No. (
Tishreen University Journal. Med. Sciences Series Generated by Foxit PDF Creator Foxit Software Tishreen University Journal for Research and Scientific Studies - Medical Sciences Series Vol. (30) No. (
MR arthrography of glenohumeral lesions with arthroscopic correlation, using PD and T2 sequences in addition to standard fat saturated sequences
 MR arthrography of glenohumeral lesions with arthroscopic correlation, using PD and T2 sequences in addition to standard fat saturated sequences Poster No.: C-2217 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational
MR arthrography of glenohumeral lesions with arthroscopic correlation, using PD and T2 sequences in addition to standard fat saturated sequences Poster No.: C-2217 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational
Shoulder Arthroscopy. Dr. J.J.A.M. van Raaij. NOV Jaarvergadering Den Bosch 25 jan 2018
 Shoulder Arthroscopy Dr. J.J.A.M. van Raaij NOV Jaarvergadering Den Bosch 25 jan 2018 No disclosures Disclosure Shoulder Instability Traumatic anterior Traumatic posterior Acquired atraumatic Multidirectional
Shoulder Arthroscopy Dr. J.J.A.M. van Raaij NOV Jaarvergadering Den Bosch 25 jan 2018 No disclosures Disclosure Shoulder Instability Traumatic anterior Traumatic posterior Acquired atraumatic Multidirectional
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations
 MRI of Internal Impingement of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Eddie L. Giaroli 1 Nancy M. Major Laurence D. Higgins Giaroli EL, Major NM, Higgins LD DOI:10.2214/AJR.04.0971
MRI of Internal Impingement of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Eddie L. Giaroli 1 Nancy M. Major Laurence D. Higgins Giaroli EL, Major NM, Higgins LD DOI:10.2214/AJR.04.0971
Viviane Khoury, MD. Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
Case Report Arthroscopic Bony Bankart Repair Using Double-Threaded Headless Screw: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2012, Article ID 789418, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/789418 Case Report Arthroscopic Bony Bankart Repair Using Double-Threaded Headless Screw: A Case Report Takeshi Kokubu,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2012, Article ID 789418, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/789418 Case Report Arthroscopic Bony Bankart Repair Using Double-Threaded Headless Screw: A Case Report Takeshi Kokubu,
 This article was published in an Elsevier journal. The attached copy is furnished to the author for non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the author s institution, sharing
This article was published in an Elsevier journal. The attached copy is furnished to the author for non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the author s institution, sharing
Double bucket handle tears of the superior labrum
 Case Report http://dx.doi.org/10.14517/aosm13013 pissn 2289-005X eissn 2289-0068 Double bucket handle tears of the superior labrum Dong-Soo Kim, Kyoung-Jin Park, Yong-Min Kim, Eui-Sung Choi, Hyun-Chul
Case Report http://dx.doi.org/10.14517/aosm13013 pissn 2289-005X eissn 2289-0068 Double bucket handle tears of the superior labrum Dong-Soo Kim, Kyoung-Jin Park, Yong-Min Kim, Eui-Sung Choi, Hyun-Chul
P.O. Box Sierra Park Road Mammoth Lakes, CA Orthopedic Surgery & Sports Medicine
 P.O. Box 660 85 Sierra Park Road Mammoth Lakes, CA 93546 SHOULDER: Instability Dislocation Labral Tears The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body, but to have this amount of motion, it is also
P.O. Box 660 85 Sierra Park Road Mammoth Lakes, CA 93546 SHOULDER: Instability Dislocation Labral Tears The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body, but to have this amount of motion, it is also
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 9/22/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 91 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 9/22/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 91 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
MR imaging features of paralabral ganglion cyst of the shoulder
 MR imaging features of paralabral ganglion cyst of the shoulder Poster No.: C-1482 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Bartocci, C. Dell'atti, E. Federici, D. Beomonte Zobel, V. Martinelli,
MR imaging features of paralabral ganglion cyst of the shoulder Poster No.: C-1482 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Bartocci, C. Dell'atti, E. Federici, D. Beomonte Zobel, V. Martinelli,
Body Planes. (A) Transverse Superior Inferior (B) Sagittal Medial Lateral (C) Coronal Anterior Posterior Extremity Proximal Distal
 Body Planes (A) Transverse Superior Inferior (B) Sagittal Medial Lateral (C) Coronal Anterior Posterior Extremity Proximal Distal C B A Range of Motion Flexion Extension ADDUCTION ABDUCTION Range of Motion
Body Planes (A) Transverse Superior Inferior (B) Sagittal Medial Lateral (C) Coronal Anterior Posterior Extremity Proximal Distal C B A Range of Motion Flexion Extension ADDUCTION ABDUCTION Range of Motion
CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1
 CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1 Sung Kyoung Moon, M.D., Ji Seon Park, M.D., Wook Jin, M.D. 2, Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D. Purpose: To evaluate the CT images of reduced hips
CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1 Sung Kyoung Moon, M.D., Ji Seon Park, M.D., Wook Jin, M.D. 2, Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D. Purpose: To evaluate the CT images of reduced hips
Study of bipolar bone defects in unstable shoulder: From "engaging / non-engaging" to "on-track / off-track".
 Study of bipolar bone defects in unstable shoulder: From "engaging / non-engaging" to "on-track / off-track". Poster No.: C-2219 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Jose Salgado Ribeiro,
Study of bipolar bone defects in unstable shoulder: From "engaging / non-engaging" to "on-track / off-track". Poster No.: C-2219 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Jose Salgado Ribeiro,
Glenoid Articular Surface on Magnetic Resonance Arthrography of the Shoulder
 Glenoid Articular Surface on Magnetic Resonance Arthrography of the Shoulder Poster No.: P-0054 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit S. Jackson; Manchester/UK Bones, Musculoskeletal
Glenoid Articular Surface on Magnetic Resonance Arthrography of the Shoulder Poster No.: P-0054 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit S. Jackson; Manchester/UK Bones, Musculoskeletal
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 185 189 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint, MR imaging findings concerning, 161 Acromion, types of, 77 79
Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 185 189 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint, MR imaging findings concerning, 161 Acromion, types of, 77 79
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder
 Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria Shoulder Pain Traumatic
 Revised 2017 American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria Shoulder Pain Traumatic Variant 1: Traumatic shoulder pain. Any etiology. Initial imaging. Procedure Appropriateness Category Relative
Revised 2017 American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria Shoulder Pain Traumatic Variant 1: Traumatic shoulder pain. Any etiology. Initial imaging. Procedure Appropriateness Category Relative
Posterior Shoulder Instability
 Posterior Shoulder Instability Robert A. Arciero, MD Professor of Orthopaedics University of Connecticut USA Classification of Posterior Instability Dislocation -acute -chronic- fixed or locked Subluxation
Posterior Shoulder Instability Robert A. Arciero, MD Professor of Orthopaedics University of Connecticut USA Classification of Posterior Instability Dislocation -acute -chronic- fixed or locked Subluxation
CT ARTHROGRAPHY It s not Always About the
 CT ARTHROGRAPHY It s not Always About the Magnet Kirkland W. Davis, M.D. University of Wisconsin Department of Radiology Disclosures Financial FDA IA Gd! What Is CT Arthrography? (CTR) Arthrogram: imaging
CT ARTHROGRAPHY It s not Always About the Magnet Kirkland W. Davis, M.D. University of Wisconsin Department of Radiology Disclosures Financial FDA IA Gd! What Is CT Arthrography? (CTR) Arthrogram: imaging
A Comparison between the Anterior and Posterior Approach to US-guided Shoulder Articular Injections for MR Arthrography 1
 A Comparison between the Anterior and Posterior Approach to US-guided Shoulder Articular Injections for MR Arthrography 1 Joo Yeon Ji, M.D. Purpose: To assess the feasibility of ultrasound-guided shoulder
A Comparison between the Anterior and Posterior Approach to US-guided Shoulder Articular Injections for MR Arthrography 1 Joo Yeon Ji, M.D. Purpose: To assess the feasibility of ultrasound-guided shoulder
SHOULDER INSTABILITY
 SHOULDER INSTABILITY Your shoulder is the most flexible joint in your body, allowing you to throw fastballs, lift a heavy suitcase, scratch your back, and reach in almost any direction. Your shoulder joint
SHOULDER INSTABILITY Your shoulder is the most flexible joint in your body, allowing you to throw fastballs, lift a heavy suitcase, scratch your back, and reach in almost any direction. Your shoulder joint
Comparisons of the Various Partial- Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears on MR Arthrography and Arthroscopic Correlation
 Comparisons of the Various Partial- Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears on MR rthrography and rthroscopic Correlation Kyung h Chun, MD Min Sung Kim, MD Young Joo Kim, MD Index terms: Shoulder MR arthrography
Comparisons of the Various Partial- Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears on MR rthrography and rthroscopic Correlation Kyung h Chun, MD Min Sung Kim, MD Young Joo Kim, MD Index terms: Shoulder MR arthrography
Index. radiologic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint injuries in football players, 318, 319 ALPSA. See Anterior labroligamentous periosteal sleeve avulsion. Anterior
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint injuries in football players, 318, 319 ALPSA. See Anterior labroligamentous periosteal sleeve avulsion. Anterior
Increased Risk of Posterior Glenoid Labrum Tears in Football Players
 Escobedo et al. Posterior Labral Tears in Football Players Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations 193.FM 11/30/06 A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G Eva M. Escobedo 1,2 Michael L. Richardson
Escobedo et al. Posterior Labral Tears in Football Players Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations 193.FM 11/30/06 A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G Eva M. Escobedo 1,2 Michael L. Richardson
CME. Glenohumeral Joint Instability. Review
 CME JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 33:2 16 (2011) Review Glenohumeral Joint Instability Patrick Omoumi, MD, 1,2 Pedro Teixeira, MD, 2 Frédéric Lecouvet, MD, PhD, 1 and Christine B. Chung, MD 2,3
CME JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 33:2 16 (2011) Review Glenohumeral Joint Instability Patrick Omoumi, MD, 1,2 Pedro Teixeira, MD, 2 Frédéric Lecouvet, MD, PhD, 1 and Christine B. Chung, MD 2,3
Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders
 Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders Poster No.: C-2026 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. Ivanoski; Ohrid/MK Keywords: Trauma, Athletic injuries, Arthritides,
Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders Poster No.: C-2026 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. Ivanoski; Ohrid/MK Keywords: Trauma, Athletic injuries, Arthritides,
DK7215-Levine-ch12_R2_211106
 12 Arthroscopic Rotator Interval Closure Andreas H. Gomoll Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A. Brian J. Cole Departments
12 Arthroscopic Rotator Interval Closure Andreas H. Gomoll Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A. Brian J. Cole Departments
Delaminated Tears of the Rotator Cuff: Prevalence, Characteristics, and Diagnostic Accuracy Using Indirect MR Arthrography
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choo et al. MR Arthrography of Delaminated Tears of the Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hye Jung Choo 1 Sun Joo Lee 1 Jung-Han Kim 2 Dong
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choo et al. MR Arthrography of Delaminated Tears of the Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hye Jung Choo 1 Sun Joo Lee 1 Jung-Han Kim 2 Dong
The Management of Shoulder Instability. By Debbie Prince Clinical Shoulder Specialist
 The Management of Shoulder Instability By Debbie Prince Clinical Shoulder Specialist Shoulder Dislocation The most common joint dislocation Traumatic Instability, highest incidence in males aged 21 to
The Management of Shoulder Instability By Debbie Prince Clinical Shoulder Specialist Shoulder Dislocation The most common joint dislocation Traumatic Instability, highest incidence in males aged 21 to
MRI evaluation of the shoulder: Beyond rotator cuff
 MRI evaluation of the shoulder: Beyond rotator cuff Poster No.: C-2447 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Rumie, A. Vasquez, J. A. Abreu, A. P. Guarnizo, O. Rivero, 1 1 2 3 1 1 1
MRI evaluation of the shoulder: Beyond rotator cuff Poster No.: C-2447 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Rumie, A. Vasquez, J. A. Abreu, A. P. Guarnizo, O. Rivero, 1 1 2 3 1 1 1
Lawrence Gulotta Gillian Lieberman, MD October Gillian Lieberman, MD. Shoulder Imaging. Lawrence V. Gulotta, HMS IV 10/16/02
 October 2002 Shoulder Imaging Lawrence V. Gulotta, HMS IV 10/16/02 Goals Review Anatomy of the Shoulder -Dynamic Stabilizers -> Rotator Cuff -Static Stabilizers -> Labrum and Capsule Systematic Approach
October 2002 Shoulder Imaging Lawrence V. Gulotta, HMS IV 10/16/02 Goals Review Anatomy of the Shoulder -Dynamic Stabilizers -> Rotator Cuff -Static Stabilizers -> Labrum and Capsule Systematic Approach
Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior lesions: ultrasound evaluation
 Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior lesions: ultrasound evaluation Poster No.: C-0472 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Belyaev; Yaroslavl/RU Keywords: Trauma, Arthrography, Ultrasound,
Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior lesions: ultrasound evaluation Poster No.: C-0472 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Belyaev; Yaroslavl/RU Keywords: Trauma, Arthrography, Ultrasound,
First-Time Anterior Shoulder Dislocation: Is it time to take a stand?
 Evaluation and Treatment of the Injured Athlete Martha s Vineyard July 22nd, 2018 First-Time Anterior Shoulder Dislocation: Is it time to take a stand? Robert A. Arciero, MD Professor, Orthopaedics University
Evaluation and Treatment of the Injured Athlete Martha s Vineyard July 22nd, 2018 First-Time Anterior Shoulder Dislocation: Is it time to take a stand? Robert A. Arciero, MD Professor, Orthopaedics University
COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED
 81 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED The Use of Magnetic Resonance Arthrography to Detect Partial-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears BY WILLIAM B. STETSON, MD, THOMAS PHILLIPS,
81 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED The Use of Magnetic Resonance Arthrography to Detect Partial-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears BY WILLIAM B. STETSON, MD, THOMAS PHILLIPS,
Evaluation with MR Arthrography1
 Glenohumeral Instabifity: Evaluation with MR Arthrography1 Javier Beltran, MD Zehava S. Rosenberg, MD Vijay P. Chandnani, MD Frances Cuomo, MD Salvador Beltran, MD Andrew Rokito, MD Magnetic resonance
Glenohumeral Instabifity: Evaluation with MR Arthrography1 Javier Beltran, MD Zehava S. Rosenberg, MD Vijay P. Chandnani, MD Frances Cuomo, MD Salvador Beltran, MD Andrew Rokito, MD Magnetic resonance
Arthroscopic Preparation of the Posterior and Posteroinferior Glenoid Labrum
 Arthroscopic Preparation of the Posterior and Posteroinferior Glenoid Labrum By Matthew T. Provencher, MD, LCDR, MC, USNR; Anthony A. Romeo, MD; Daniel J. Solomon, MD, CDR, MC, USN; Bernard R. Bach, Jr.,
Arthroscopic Preparation of the Posterior and Posteroinferior Glenoid Labrum By Matthew T. Provencher, MD, LCDR, MC, USNR; Anthony A. Romeo, MD; Daniel J. Solomon, MD, CDR, MC, USN; Bernard R. Bach, Jr.,
Shoulder Arthroscopy Lab Manual
 Shoulder Arthroscopy Lab Manual Dalhousie University Orthopaedic Program May 5, 2017 Skills Centre OBJECTIVES 1. Demonstrate a competent understanding of the arthroscopic anatomy and biomechanics of the
Shoulder Arthroscopy Lab Manual Dalhousie University Orthopaedic Program May 5, 2017 Skills Centre OBJECTIVES 1. Demonstrate a competent understanding of the arthroscopic anatomy and biomechanics of the
Provider Led Entity. CDI Quality Institute PLE Shoulder AUC 05/22/2018
 Provider Led Entity CDI Quality Institute PLE Shoulder AUC 05/22/2018 Appropriateness of advanced imaging procedures* in patients with shoulder pain and the following clinical presentations: *Including
Provider Led Entity CDI Quality Institute PLE Shoulder AUC 05/22/2018 Appropriateness of advanced imaging procedures* in patients with shoulder pain and the following clinical presentations: *Including
Strategies for Failed Instability Repair
 Strategies for Failed Instability Repair Robert E Hunter MD Director, Orthopedic Sports Medicine Center HRRMC Salida, Colorado CU Sports Medicine Course Sept 28, 2012 Conflict of Interest Paid Consultant:
Strategies for Failed Instability Repair Robert E Hunter MD Director, Orthopedic Sports Medicine Center HRRMC Salida, Colorado CU Sports Medicine Course Sept 28, 2012 Conflict of Interest Paid Consultant:
Evaluation of the Glenoid Labrum With 3-T MRI: Is Intraarticular Contrast Necessary?
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Major et al. 3-T MRI of the Glenoid Labrum Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Evaluation of the Glenoid Labrum With 3-T MRI: Is Intraarticular Contrast
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Major et al. 3-T MRI of the Glenoid Labrum Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Evaluation of the Glenoid Labrum With 3-T MRI: Is Intraarticular Contrast
Arthroscopic fixation of isolated type II SLAP lesions using a two-portal technique
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 160-166 ORIGINAL STUDY Arthroscopic fixation of isolated type II SLAP lesions using a two-portal technique Aristotelis KAisiDis, Panagiotis PAntOs, Horst HEGER, Dimitrios
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 160-166 ORIGINAL STUDY Arthroscopic fixation of isolated type II SLAP lesions using a two-portal technique Aristotelis KAisiDis, Panagiotis PAntOs, Horst HEGER, Dimitrios
Demystifying ABER (ABduction and External Rotation) sequence in shoulder MR arthrography
 Demystifying ABER (ABduction and External Rotation) sequence in shoulder MR arthrography Poster No.: C-1016 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Educational Exhibit Z. Maras Ozdemir 1, F. B. Ergen 2, U. Aydingoz
Demystifying ABER (ABduction and External Rotation) sequence in shoulder MR arthrography Poster No.: C-1016 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Educational Exhibit Z. Maras Ozdemir 1, F. B. Ergen 2, U. Aydingoz
Disclosures. Bipolar Lesions 1/8/16. Technical Pearls for Shoulder Surgery: Tips for the Latarjet Procedure. The Sling Effect of the Conjoined Tendon
 Disclosures Technical Pearls for Shoulder Surgery: Tips for the Latarjet Procedure Stephen S. Burkhart, MD San Antonio, Texas Stephen S. Burkhart, MD The following relationships with commercial interests
Disclosures Technical Pearls for Shoulder Surgery: Tips for the Latarjet Procedure Stephen S. Burkhart, MD San Antonio, Texas Stephen S. Burkhart, MD The following relationships with commercial interests
SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder
 Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic and Related Surgery 6(4):21&279 Published by Raven Press, Ltd. Q 1990 Arthroscopy Association of North America SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder Stephen J. Snyder, M.D.,
Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic and Related Surgery 6(4):21&279 Published by Raven Press, Ltd. Q 1990 Arthroscopy Association of North America SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder Stephen J. Snyder, M.D.,
SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT
 SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT DR.SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant-KNEE & SHOULDER Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital,Delhi Peculiarities of Shoulder Elegant piece of machinery It has the
SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT DR.SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant-KNEE & SHOULDER Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital,Delhi Peculiarities of Shoulder Elegant piece of machinery It has the
Shoulder direct arthrography: how to do and how to read
 Shoulder direct arthrography: how to do and how to read Poster No.: C-1566 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: F. M. G. S. Pereira da Silva, H. Donato, D. Roriz, L. A. 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 Ferreira,
Shoulder direct arthrography: how to do and how to read Poster No.: C-1566 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: F. M. G. S. Pereira da Silva, H. Donato, D. Roriz, L. A. 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 Ferreira,
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears. Rafael M. Williams, MD
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Rafael M. Williams, MD Rotator Cuff MRI MRI Small / Partial Thickness Medium Tear Arthroscopic View Massive Tear Fatty Atrophy Arthroscopic View MassiveTears Tear is > 5cm
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Rafael M. Williams, MD Rotator Cuff MRI MRI Small / Partial Thickness Medium Tear Arthroscopic View Massive Tear Fatty Atrophy Arthroscopic View MassiveTears Tear is > 5cm
Musculoskeletal Applications for CT. Tal Laor, MD Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine
 Musculoskeletal Applications for CT Tal Laor, MD Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine I have no commercial disclosures. Why CT? Complimentary to other modalities
Musculoskeletal Applications for CT Tal Laor, MD Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine I have no commercial disclosures. Why CT? Complimentary to other modalities
Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff Tears: Comparison with Standard Oblique Sagittal Images
 Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Ultrasound of the Shoulder
 Ultrasound of the Shoulder Patrick Battaglia, DC, DACBR Logan University, Department of Radiology Outline Review ultrasound appearance of NMSK tissues Present indications for ultrasound of the shoulder.
Ultrasound of the Shoulder Patrick Battaglia, DC, DACBR Logan University, Department of Radiology Outline Review ultrasound appearance of NMSK tissues Present indications for ultrasound of the shoulder.
