United States Patent (19) Burton
|
|
|
- Gabriella Gilbert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 United States Patent (19) Burton 54 76) (52) 58) (56. METHOD FOR A FLEXBLE STABLIZATION SYSTEM FOR A VERTEBRAL COLUMN Inventor: Appl. No.: 742,923 Charles W. Burton, 148 W. Lake St., Excelsior, Minn Filed: Jun. 10, 1985 Int. Cl'... A61B 17/58 U.S. C /17; 128/69; 128/92 Z; 128/92 YF; 128/92 YM Field of Search /69, 92 B, 92 BB, 128/92 BA, 84 R, 92 YM, 92 YF, 92 YP; 623/17 References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 3,988,783 1/1976 Treace /92 B 4,611,581 9/1986 Steffee /69 FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS /1978 U.S.S.R /69 (11 Patent Number: 4,743,260 (45) Date of Patent: May 10, 1988 OTHER PUBLICATIONS Macey; Mayo Clinic Staff Meeting, pp ; Sep The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, vol. 56B, No. 2, May 1974, pp Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics, pp Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, No. 180, Nov. 1983, pp Miner. Sci. Enging, vol. 5, No. 2, Apr. 1973, pp Primary Examiner-Clyde I. Coughenour Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Merchant, Gould Smith, Edell, Welter & Schmidt 57 ABSTRACT A method for a flexible stabilization system for a verte bral column is disclosed. The device includes a strong, non-metallic stabilization element or elements (18) for providing flexibility. The stabilization elements (18) are secured to the vertebrae (11) and (12) wherein, when secured, the stabilization element or elements stabilize the vertical column while still allowing for flexibility. In a preferred embodiment the stabilization elements are anchored to the vertebrae by a bone screw (15) having an upper shank portion (16) and a lower threaded por tion (17) having segmented area (17c). 5 Claims, 3 Drawing Sheets
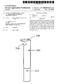
2 U.S. Patent May 10, 1988 Sheet 1 of 3 4,743,260
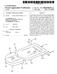
3 U.S. Patent May 10, 1988 Sheet 2 of 3 4,743,260 F. G. 3 F.G. 5 2O 2b 2 ZAOT. 2 siz.
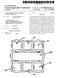
4 U.S. Patent May 10, 1988 Sheet 3 of 3 4,743,260 FIG. O 26 O O O O O OOO) O O OOOOO
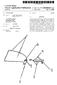
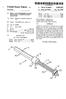
5 1. METHOD FOR A FLEXBLE STABILIZATION SYSTEM FOR A VERTEBRAL COLUMN BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 1. Field of the Invention This invention relates generally to a non-metallic device and method for the stabilization of at least a portion of a vertebral column and more particularly to a device and method for spinal stabilization without fusion. 2. Description of the Prior Art Fusion of vertebral columns by instrumentation de vices and/or bone material is common and a long prac ticed surgical technique. Fusion is the permanent inter nal fixation of part or all of the intervertebral joints, an intervertebral joint being composed of two adjacent vertebrae and their posterior bony elements connected by an intervertebral disc, ligaments, and two facet joint capsules. However, the concept of fusion carries signifi cant and previously unappreciated patient disability. By fusing vertebrae the remaining segments are subject to inordinately high stress and degeneration. In the typical L4-S1 fusion the L3-4 level typically undergoes dra matic degeneration of the disc and zygoapophyseal joints leading to the production of a clinical entity called the "transitional syndrome' often leading to "mechanical-type' pain or actual spinal nerve compres sion. The stress patterns produced by fusion often pro duce clinical problems relating to the sacro-iliac and hip joints. When spine fusions involve mechanical instrumenta tion, significant forces are directly aimed at the support ive sites whether they be bone screws, hooks, etc. This phenomenon usually produces loosening of the points of attachment for the implanted hardware and a result ing loss of support by this instrumentation. Because of this, fusions involving instrumentation are often carried out in conjunction with a bone fusion so as the instru mentation loosens and fails, support can be maintained by growth of the bony counterpart. These combined procedures involve extensive surgery, substantial blood loss and high cost. Following such a procedure, patients are usually disabled for long periods of time. Therefore, the treating of spinal instability by fusion is not optimal. It immobilizes adjacent segments, elimi nating their previous natural ability to move relative to each other. Further, when fusion has taken place with the addition of internal fixation, often the internal fixa tion parts are of a metallic nature. In modern medical practice the presence of dense metallic devices is a significnat liability due to the scattering artifacts gener ated if imaging is attempted. Since the spinal diagnostic procedure of choice is imaging, the presence of signifi cant metallic objects represents a serious diagnostic limitation. The present invention addresses the problems associ ated with the prior art devices and method for treating spinal instability and provides for stabilization, rather than fusion, that is, support with the allowance of some natural movement or flex, and accomplishes this with a minimal amount of metallic components. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The present invention is a device and method for stabilizing a portion of a vertebral column without fu sion. In the preferred form the stabilization device of the present invention is substantially completely or 4,743, completely made of non-metallic materials (e.g. plastic) which are bio-compatible. The vertebral column is composed of segments of adjacent vertebrae, with the first vertebra being adja cent the second vertebra. Each vertebra has a posterior vertebral element which, when removed, leaves first and second pedicles on each of the vertebra. The pres ent device includes a strong non-metallic anchor means for securing the stabilization means to at least one of the pedicles of the first and second vertebrae and means for cooperatively connecting the stabilization means to the anchor means. In a preferred embodiment, the device further includes a means for locking the stabilization means to the anchor means. In a preferred embodiment, the anchor means in cludes an upper shank portion and a lower threaded portion having a screw thread. The lower portion is cooperatively connected to the shank portion. The screw thread has segmented areas, wherein a rotary force may be applied to the shank portion whereby the threaded portion is driven into and secured into the pedicles. The screw thread may have segmented areas, wherein after a period of time the vertebra's bony re growth encompasses the segmented areas to further secure the threaded portion to the pedicles. In a preferred embodiment the stabilization means includes a first stabilization element having first and second openings and a second stabilization element having first and second openings. The anchor means comprises four support members such that one of the support members is secured to each of the pedicles, wherein each of the openings is adapted for being posi tioned around one of the support members. The stabili zation elements may then be aligned along the four support members in either a generally parallel relation ship or in an X shape. Further, a cross support member may be used to further connect the first stabilization element to second stabilization element. The present invention also comprises a surgical method for stabilizing a portion of a vertebral column without fusion. The method includes making an incision to expose the first and second vertebrae. Then, the posterior vertebral elements of each of the vertebrae to be stabilized are removed, leaving first and second pedi cles of the first vertebra and first and second pedicles of the second vertebra. A bone screw is secured into at least one of the pedicles of the first and second verte brae. The bone screw has a threaded bottom portion and an upper shank portion. Then, the stabilization means is cooperatively connected between the bone screw of one of the first pedicles of the first vertebra to the bone screw of one of the first pedicles of the second vertebra. It is understood that screws are not essential, but are a preferred embodiment. Other suitable anchor ing means may be used to anchor the stabilization means to pedicles, such as stapling. It is also understood that multiple segments may be stabilized. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a perspective view showing one embodi ment of the present invention in a partially exploded perspective view. FIG. 2 is a top-plan view of the present invention shown in FIG. 1. FIG. 3 is a perspective view of the bone screw of the present invention.
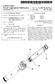
6 3 FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view taken generally along the lines 4-4 of FIG. 3. FIG. 5 is a cross-sectional view of one embodiment of the locking cap as shown in FIG. 1. FIG. 6 is a perspective view of a second embodiment of a locking cap. FIG. 7 is a cross-sectional view taken generally along the lines 7-7 of FIG. 6. FIG. 8 is a partial cross-sectional view showing a bone screw being inserted into a vertebra according to the present invention. FIG. 9 is a side-elevational view of a vertebra before the posterior vertebral elements are removed according to the present invention. FIG. 10 is perspective view of a second embodiment of a bone screw. FIG. 11 is a perspective view of a second embodi ment of a stabilization element. DETALED DESCRIPTION OF A PREFERRED EMBODIMENT Referring to the figures, wherein like numerals repre sent like parts throughout the several views, there is generally illustrated at 10 a device for stabilizing at least a portion of a vertebral column. In FIG. 1, a first verte bra 11 and second vertebra 12 are shown. It should be understood that when first and second vertebrae are used in this application, it is only in reference to verte brae that are adjacent, and not to any specific vertebrae along the vertebral column. Each vertebra has a poste rior element, designated as 13 shown in FIG. 9. When the posterior element 13 is removed from the vertebra, a first and second vertebral pedicle is exposed in each vertebra. FIG. 1 shows the first vertebral pedicle 11a and second vertebral pedicle 11b of the first vertebra 11 and first vertebral pedicle 12a and second vertebral pedicle 12b of the second vertebra 12. If screws are used as anchoring devices, each of the pedicles (11a, 11b, 12a or 12d) that are to be utilized have a hole 14 drilled into the pedicle. A bone screw, generally designated as 15, has an upper shank portion 16, that in a preferred embodiment, has a square cross section to allow for efficient insertion and removal. A lower threaded portion 17 is coopera tively connected to the upper shank portion 16. The threaded portion 17 has an inner shaft 17a and a threaded member 17b. The threaded member 1.7b is a continuous helical member having segmented areas 17c. The threaded member 17 provides a wide flange to give a deep bite when secured in the vertebra. While the segmented areas 17c are shown in FIG. 4 as being pie shaped, and having three per one complete circumfer ence, it is understood that any suitable shape or number of segmented areas may be utilized. The inner shaft 17a and threaded member 17b have a generally consistent diameter throughout, except for a taper towards a point at their bottom end. Preferably, the diameter of the hole 14 is slightly smaller than the diameter of the inner shaft Ta, A stabilization element 18, having a first end 18a and a second end 18b has two openings 19 adapted to being placed over the upper shank 16 of the bone screw 15. A spacer 20 may also be used if the height of the pedicle is not sufficient. The spacer 20 can be inserted between the pedicle and stabilization element 18 to avoid com pression of exiting spinal nerves. In one embodiment, the element 18 is a flat strip. However, it is understood 4,743, that other suitable shapes such as an hour glass shape or dumbbell shape may be used. A locking cap 21, having an opening 21a has a gener ally downwardly depending circumferential member 21b that locks the rod 18 in place. A second embodi ment of a locking cap is shown in FIGS. 6 and 7. The locking cap 22 is similar to the locking cap 21 in that it has an opening 22a and a generally downwardly de pending circumferential member 22b, similar to locking cap 21. However, in addition, there are two skirt mem bers 22c. As will be more fully discussed hereinafter, the skirt members 22c limit parallelogram movement be tween the two stabilization elements 18 when they are in position. The material that the stabilization elements 18 and screws 15 are made of must provide sufficient strength, be bio-compatible, and preferably non-metallic. Some non-reinforced biocompatible plastic polymers indicate a tendency to crack, fissure or shear with repeated flex or stress. A preferred material is a two-phase biocon patible plastic so as to provide adequate strength. Inter nal reinforcement with dissimilar polymers or filaments provide increased strength over that of a single phase plastic, but as the internal diameter of the stabilization element 18 decreases, practical fabrications become a problem. Therefore, it is preferred that internal fibers be used for reinforcement. It is desired that the material used have sufficient strength and flexibility, as well as being bio-compatible. It is known that many fibers have been tested in poly mers and many lightweight and remarkably strong ma terials have resulted. A most innovative reinforced two phase material to date have been created for aeronauti cal use. Although many of these systems are attractive for their physical qualities, they are also marginal or clearly unacceptable from the standpoint of being bi ocompatible. It has been found that carbon fiber rein forced plastic yields adequate strength for constructing the stabilization elements 18. However, it is sometimes preferable that the screws be made of a still stronger materialso as to prevent the screws from being sheared off by the stress of the system. One such material that has been found adequate for the screws 15 is a magna mite graphite fiber or carbon reinforced plastic. The materials used for the stabilization elements 18 and screws 15 are not limited to the above noted plastics, and may also include other suitable solid materials that have the above-noted properties. Also, porous material forms in which the porosity is controlled by the re planineform process may be utilized. Polymers such as silicone, polyethylene, nylon, vinyl, methylmethacy rate, dacrons or teflon may be suitable. In use, only a limited surgical exposure is necessary to perform the operation necessary to incorporate the present invention. Following the removal of the poste rior vertebral elements 13, the exposed pedicles serve as the anchoring media for the bone screws 15. The pedi cles are drilled by appropriate means to create the hole 14. A driving mechanism is placed over the upper shank 16 and the lower portion 17 is screwed completely into the vertebra. The threaded mamber 17b serves to stabis lize the bone screw 15 and the segmented areas 17c are designed to allow bone growth to further stabilize the screw 15 in place. If only two vertebrae are to be stabi lized, it is only necessary for bone screws 15 to be se cured into the pedicles 11a, 11b, 12a and 12b. However, if multiple vertebrae are to be stabilized, the corre sponding pedicles on the third or subsequent vertebrae
7 5 would also have to be provided with a bone screw 15. The stabilization elements 18 are tapped at the appropri ate position and holes 19 are made either by drilling or by a heated rod at the site of the tap. While FIGS. 1 and 2 show that stabilization elements 18 have been placed for a one-level stabilization, the present invention is compatible with stabilizing multiple levels as well as single levels. Further, only one stabilization element 18 may be necessary for some patients. Once the screws 15 are in place, a separator instrument, not shown, may be used to distract the vertebrae, if this desired, and this separation is maintained by the placement of the stabili zation elements 18 over the shank 16 of the bone screw 15. As previously mentioned, if the heighth of the pedi cle is not sufficient, a spacer 20 may be inserted on top of the pedicle. The spacer 20 may be constructed from a softer plastic such as polyurethane or silicone. The procedure is then completed by the application of a locking cap, either 21 or 22, at each of the upper shanks 16 and the removal of any excess shank material above the top of the locking cap 21 or 22. While the device 10 is illustrated in FIGS. 1 and 2 as having a stabilized means having two generally parallel stabilization elements 18, it is understood that the stabili zation means may be other suitable forms such as a single stabilization element 18, or two stabilization ele ments 18 that cross to form an X shape, or two stabiliza tion elements 18 generally parallel having across sup port member to form an H shape. The present invention allows for flexibility and be cause of the flexibility of the system, less disruptive force is applied to the screw 15, or other anchor means, following the application of the system itself. The flexibility of the device 10 has as its lower limit no flexibility. No flexibility would have the same result as fusion and the device 10 provides for at least some flexibility more than fusion. In the preferred embodi ment, the flexibility of the device 10 would stabilize with a degree that substantially equals a normal back. Too much flexibility would render the back non-func tional and not stabilize the back. Any stabilization more than that present in the back of the patient before the procedure would be beneficial. Numerically, the gen eral upper limit of flexibility for the device 10 is shown in the following table for the stabilization means: Stabilization Inch-Pounds for Standard Means Length Deflection of Inch 1" 45 ip ip ip. If locking cap 21 is used, parallelogram movement between the two stabilization elements 18 is possible. That is, there is a possibility of some relative sideways movement of the first vertebra 11 to the second verte bra 12. If locking cap 22 is used, the locking cap 22 will limit the parallelogram movement. This is because the rod 18 is positioned inside of the skirt member 22c such that parallelogram rotation is limited. In addition to anchoring the stabilization element 18 by means of screws 15, it is also envisioned that other suitable methods of anchoring may be used. One such example would be to staple the stabilization element 18 to the pedicles. Another embodiment would include ribbed tabs molded to the stabilization element 18 as an integral part thereof and would be positioned approxi mately the same place where the bone screws 15 would 4,743, be inserted in the previously discussed embodiment. The holes would then be drilled into the pedicles at the appropriate distances and the ribbed tabs could be in serted into the holes and glued in place. The ribbed tabs could be placed at varying distances along the stabiliza tion element in various models and the appropriate length model simply chosen depending upon the spac ing between the vertebraes of the patient. FIGS. 10 and 11 show another embodiment of the present invention wherein it would not be necessary to have an opening in the stabilization rod. The second embodiment of the bone screw 23 has an upper portion 24 and a lower threaded portion 25. The lower threaded portion 25 is similar to the lower threaded section 17 in that the lower portion 25 has a shaft 25a about which is threaded members 25b having segmented areas 25c. The upper portion 24 has a base 24a and two upright mem bers 24b cooperatively connected thereto. The top sur face of the base 24a has a corrugated area 24c. The second embodiment of the stabilization element, designated as 26 has a corrugated upper surface 26a and a corrugated bottom surface 26b. The corrugated sur faces 26a, 26b and 24c could also be described as having a verticle toothed surface. The toothed surface 26b meshes with the toothed surface 24c, thereby prevent ing relative movement between the stabilization ele ment 26 and the bone screw 23. With such a verticle tooth configuration, it is not necessary to create an opening in the stabilization element 26. The uprights 24b are spaced to have a distance between them the approximate width of the stabilization element 26. Therefore the upright members 24b also assist in limit ing relative movement of the stabilization element 26 to the bone screw 23. The present invention represents an important ad vance in spinal stabilization technology. The system provides for limited surgical exposure, limited operat ing time, lower cost and is a simpler operation than fusion. Further, the method is conducive to revision if the status of the patient changes. By allowing some motion in the system, stress on the anchoring device as well as adjacent vertebrae have been reduced. The unique nature of this stabilization system is such that its applicability will not only involve fusion candidates, but will also involve extension to impaired individuals not presently considered to be treatable. Other modifications of the invention will be apparent to those skilled in the art in light of the foregoing de scription. This description is intended to provide spe cific examples of individual embodiments which clearly disclose the present invention. Accordingly, the inven tion is not limited to these embodiments or the use of elements having specific configurations and shapes as presented herein. All alternative modifications and vari ations of the present invention which follows in the spirit and broad scope of the appended claims are in cluded. What is claimed is: 1. A method of stabilizing a portion of a vertebral column without fusion, the vertebral column having a first and second vertebra, the first vertebrae being adja cent the second vertebra, each vertebra having a poste rior vertebral element, said method comprising: (a) making an incision to expose the first and second vertebrae; (b) removing the posterior vertebral element of each of the vertebrae, leaving first and second pedicles
8 4,743,260 7 of the first vertebra and first and second pedicles of the second vertebra; (c) anchoring a strong, non-metallic stabilization means stiff enough to stabilize the vertebral column but flexible enough to permit at least limited nor- 5 mal movement of the vertebral column having a first and second end to the posterior vertebral ele ments of adjacent vertebrae, wherein when an chored said stabilization means stabilizes, without the use of fusion, the vertical column while still 10 providing flexibility so that forces on the stabiliza tion means are dissipated throughout thereby re ducing force concentration. 2. The method of claim 1, further comprising anchor ing a bone screw into at least one of the pedicles of the 15 8 first and second vertebrae, the bone screw having a threaded bottom portion and an upper shank portion and cooperatively connecting said first end of said stabi lization means to said one of the pedicles of the first vertebra and said second end of said stabilization means to said one of the pedicles of the second vertebra. 3. The method of claim 2, wherein the stabilization means comprises a first rod and a second rod and said method comprises anchoring the first and second rods in a generally parallel relationship. 4. The method of claim 1, wherein the stabilizing means is made of a porous material. 5. The method of claim 4, wherein said porous stabi lizing means is produced by the replamineform process
Berry (43) Pub. Date: May 6, (76) Inventor: Bret Berry, Cordova, TN (US) (57) ABSTRACT
 US 20040O88054A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0088054A1 Berry (43) Pub. Date: (54) LATERALLY EXPANDABLE CAGE (52) U.S. Cl.... 623/17.11 (76) Inventor: Bret
US 20040O88054A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0088054A1 Berry (43) Pub. Date: (54) LATERALLY EXPANDABLE CAGE (52) U.S. Cl.... 623/17.11 (76) Inventor: Bret
IIII. United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 11 Patent Number: 5,776,150 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 1998
 United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 54) SUTURE ASSIST DEVICE 75) Inventors: Leo J. Nolan; John P. Measamer, both of Cincinnati; James D. Staley, Jr., Loveland; Robert F. Welch, Maineville, all of Ohio
United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 54) SUTURE ASSIST DEVICE 75) Inventors: Leo J. Nolan; John P. Measamer, both of Cincinnati; James D. Staley, Jr., Loveland; Robert F. Welch, Maineville, all of Ohio
( 12 ) United States Patent
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Ingwer et al. US009907655B2 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 907, 655 B2 ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Mar. 6, 2018 ( 54 ) COMPONENTS FOR ARTIFICIAL JOINTS ( 56 ) References Cited U. S.
( 12 ) United States Patent Ingwer et al. US009907655B2 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 907, 655 B2 ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Mar. 6, 2018 ( 54 ) COMPONENTS FOR ARTIFICIAL JOINTS ( 56 ) References Cited U. S.
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Truax (54) DENTAL UNDERCUT APPLICATION DEVICE AND METHOD OF USE 75) Inventor: Lloyd H. Truax, Rochester, Minn. 73) Assignee: Tru-Tain, Inc., Rochester, Minn. (21) Appl. No.: 782,159
United States Patent (19) Truax (54) DENTAL UNDERCUT APPLICATION DEVICE AND METHOD OF USE 75) Inventor: Lloyd H. Truax, Rochester, Minn. 73) Assignee: Tru-Tain, Inc., Rochester, Minn. (21) Appl. No.: 782,159
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,137,401 B2
 USOO8137401B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,137,401 B2 Stad et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2012 (54) INTERVERTEBRAL DEVICE HAVING (56) References Cited EXPANDABLE ENDPLATES U.S.
USOO8137401B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,137,401 B2 Stad et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2012 (54) INTERVERTEBRAL DEVICE HAVING (56) References Cited EXPANDABLE ENDPLATES U.S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 US 20090287233A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0287233 A1 Huculak (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2009 (54) SMALL GAUGE MECHANICAL TISSUE Publication Classification
US 20090287233A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0287233 A1 Huculak (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 19, 2009 (54) SMALL GAUGE MECHANICAL TISSUE Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160135857A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0135857 A1 Marrero, SR. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) CURVEDTIBIOTALARFUSION NAIL AND Publication Classification
US 20160135857A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0135857 A1 Marrero, SR. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) CURVEDTIBIOTALARFUSION NAIL AND Publication Classification
United States Patent (19) Annoni
 United States Patent (19) Annoni (54. TOOTH TRANSILLUMINATING LIGHT HOLDER 76) Inventor: Jerry D. Annoni, 450 Maple Ave., Vallejo, Calif. 94591 (21) Appl. No.: 427,850 22 Filed: Sep. 29, 1982 51) Int.
United States Patent (19) Annoni (54. TOOTH TRANSILLUMINATING LIGHT HOLDER 76) Inventor: Jerry D. Annoni, 450 Maple Ave., Vallejo, Calif. 94591 (21) Appl. No.: 427,850 22 Filed: Sep. 29, 1982 51) Int.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O1 OO694A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0100694 A1 PELLETER (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) KNEE PILLOW Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
US 2016O1 OO694A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0100694 A1 PELLETER (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) KNEE PILLOW Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,108,510 B2
 US00710851 OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,108,510 B2 Niznick (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 19, 2006 (54) ENDOSSEOUS DENTAL IMPLANT 6,733,291 B1* 5/2004 Hurson... 433,173 20O2/O110784 A1*
US00710851 OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,108,510 B2 Niznick (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 19, 2006 (54) ENDOSSEOUS DENTAL IMPLANT 6,733,291 B1* 5/2004 Hurson... 433,173 20O2/O110784 A1*
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9381093B1 (12) United States Patent Morris et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Jul. 5, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (63) (51) (52) (58) LOCKING DEVICE FOR FXATION MECHANISM OF MEDICAL
USOO9381093B1 (12) United States Patent Morris et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Jul. 5, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (63) (51) (52) (58) LOCKING DEVICE FOR FXATION MECHANISM OF MEDICAL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.690,305 B2
 US0076903 05B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.690,305 B2 Harjula et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 2010 (54) INCREMENT CHARGE FOR 4,408,534 A * 10, 1983 Araki et al.... 102.288 FIN-STABILIZED
US0076903 05B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.690,305 B2 Harjula et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 2010 (54) INCREMENT CHARGE FOR 4,408,534 A * 10, 1983 Araki et al.... 102.288 FIN-STABILIZED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090305855A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0305855A1 Terre (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) ABDOMINAL EXERCISE MACHINE (57) ABSTRACT An abdominal exercise
(19) United States US 20090305855A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0305855A1 Terre (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) ABDOMINAL EXERCISE MACHINE (57) ABSTRACT An abdominal exercise
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,039,574 B2
 US0090395.74B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,039,574 B2 Wilson (45) Date of Patent: May 26, 2015 (54) EXERCISE RING USPC... 482/24, 44 50, 79, 91, 92, 121-128, 482/131, 139 (76) Inventor:
US0090395.74B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,039,574 B2 Wilson (45) Date of Patent: May 26, 2015 (54) EXERCISE RING USPC... 482/24, 44 50, 79, 91, 92, 121-128, 482/131, 139 (76) Inventor:
III. United States Patent (19) Sheiban 5,226,889. Jul. 13, and at least a pair of inflatable balloons carried on the
 United States Patent (19) Sheiban (54) DOUBLE BALLOON CATHETER FOR STENT IMPLANTATION 76 Inventor: Imad Sheiban, Via Sommavalle No. 9, Verona, 37128, Italy (21) Appl. No.: 734,968 (22 Filed: Jul. 24, 1991
United States Patent (19) Sheiban (54) DOUBLE BALLOON CATHETER FOR STENT IMPLANTATION 76 Inventor: Imad Sheiban, Via Sommavalle No. 9, Verona, 37128, Italy (21) Appl. No.: 734,968 (22 Filed: Jul. 24, 1991
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O130094A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0130094A1 Graham (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2005 (54) ORTHODONTIC ACCESSORY ARCH BAR (52) U.S. Cl.... 433/20
(19) United States US 2005O130094A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0130094A1 Graham (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2005 (54) ORTHODONTIC ACCESSORY ARCH BAR (52) U.S. Cl.... 433/20
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8584.853B2 (12) United States Patent Knight et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,584.853 B2 Nov. 19, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FORAN ORTHOPEDCFXATION SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Adam T.
USOO8584.853B2 (12) United States Patent Knight et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,584.853 B2 Nov. 19, 2013 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FORAN ORTHOPEDCFXATION SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Adam T.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,413,232 B1
 USOO6413232B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,413,232 B1 Townsend et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) ORTHOPEDIC KNEE BRACE HAVING AN 5,807,294. A 9/1998 Cawley et al. ADJUSTABLE
USOO6413232B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,413,232 B1 Townsend et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) ORTHOPEDIC KNEE BRACE HAVING AN 5,807,294. A 9/1998 Cawley et al. ADJUSTABLE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,744,043 B2
 USOO774.4043B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Otinger (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 29, 20 (54) CPAP HOSETENDER 6,854,694 B1* 2/2005 Van Etten... 248,75 7,040,581 B2 * 5/2006 Noelke et al.... 248,75
USOO774.4043B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Otinger (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 29, 20 (54) CPAP HOSETENDER 6,854,694 B1* 2/2005 Van Etten... 248,75 7,040,581 B2 * 5/2006 Noelke et al.... 248,75
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 US007052479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,052.479 B2 Drennan (45) Date of Patent: May 30, 2006 (54) TRACTION DEVICE 3,762.405 A * 10/1973 De George... 602/23 3,771,519 A * 11/1973 Haake......
US007052479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,052.479 B2 Drennan (45) Date of Patent: May 30, 2006 (54) TRACTION DEVICE 3,762.405 A * 10/1973 De George... 602/23 3,771,519 A * 11/1973 Haake......
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080082047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0082047 A1 Harmon (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2008 (54) VEIN HOLDER (52) U.S. Cl.... 604/115 (76) Inventor: Stoney
US 20080082047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0082047 A1 Harmon (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2008 (54) VEIN HOLDER (52) U.S. Cl.... 604/115 (76) Inventor: Stoney
Piersch (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 29, 1993
 United States Patent (19) 11) USOO5222902A Patent Number: 5,222,902 Piersch (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 29, 1993 54 INTERLOCKING BLOCKS 3,890,738 6/1975 Bassani... 44.6/1 3,900,985 8/1975 Yoen... 44.6/124
United States Patent (19) 11) USOO5222902A Patent Number: 5,222,902 Piersch (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 29, 1993 54 INTERLOCKING BLOCKS 3,890,738 6/1975 Bassani... 44.6/1 3,900,985 8/1975 Yoen... 44.6/124
United States Patent (19) Hensel
 United States Patent (19) Hensel - 54 75 73 1 51 5 58 56) FLUID BEARNG CONSTRUCTION EMPLOYING THRUST PLATE WITH PRESSURE COMPENSATION PORTS Inventor: Robert J. Hensel, Gaston, Oreg. Assignee: Synektron
United States Patent (19) Hensel - 54 75 73 1 51 5 58 56) FLUID BEARNG CONSTRUCTION EMPLOYING THRUST PLATE WITH PRESSURE COMPENSATION PORTS Inventor: Robert J. Hensel, Gaston, Oreg. Assignee: Synektron
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0039210 A1 Yates et al. US 20090039210A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 12, 2009 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) CPAP HOSE SUPPORT SYSTEM Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0039210 A1 Yates et al. US 20090039210A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 12, 2009 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) CPAP HOSE SUPPORT SYSTEM Inventors:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080040891A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0040891 A1 Tyler (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 21, 2008 (54) EXERCISE EQUIPMENT HANDLE GRIPS Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20080040891A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0040891 A1 Tyler (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 21, 2008 (54) EXERCISE EQUIPMENT HANDLE GRIPS Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 US008556757B2 (12) United States Patent Kilshaw (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2013 (54) BICYCLE GEAR MECHANISM (76) Inventor: Richard J. Kilshaw, Lake Oswego, OR (US) *) Notice: Subject
US008556757B2 (12) United States Patent Kilshaw (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2013 (54) BICYCLE GEAR MECHANISM (76) Inventor: Richard J. Kilshaw, Lake Oswego, OR (US) *) Notice: Subject
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080283526A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0283526 A1 Buchanan (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 20, 2008 (54) ATTACHABLE PACKAGES FOR THIN, (52) U.S. Cl.... 220/234
(19) United States US 20080283526A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0283526 A1 Buchanan (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 20, 2008 (54) ATTACHABLE PACKAGES FOR THIN, (52) U.S. Cl.... 220/234
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 20040121286A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub No: US 2004/0121286 A1 Aravena et al (43) Pub Date: (54) ORGANIC SHAPED INTERFACE FOR Related US Application Data DENTAL
US 20040121286A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub No: US 2004/0121286 A1 Aravena et al (43) Pub Date: (54) ORGANIC SHAPED INTERFACE FOR Related US Application Data DENTAL
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Kesling 54) ORTHODONTIC HOOKASSEMBLY AND APPLIANCE 75 Inventor: Christopher K. Kesling, LaPorte, Ind. 73 Assignee: TP Orthodontics, Inc., LaPorte, Ind. 21 Appl. No.: 852,046 22
United States Patent (19) Kesling 54) ORTHODONTIC HOOKASSEMBLY AND APPLIANCE 75 Inventor: Christopher K. Kesling, LaPorte, Ind. 73 Assignee: TP Orthodontics, Inc., LaPorte, Ind. 21 Appl. No.: 852,046 22
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O230191A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0230191 A1 Frey et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 18, 2004 (54) DISTRACTION AND RETRACTION SYSTEM FOR SPINAL SURGERY
(19) United States US 2004O230191A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0230191 A1 Frey et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 18, 2004 (54) DISTRACTION AND RETRACTION SYSTEM FOR SPINAL SURGERY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,224,174 B1
 USOO6224174B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,224,174 B1 Mu (45) Date of Patent: *May 1, 2001 (54) POSTER DISPLAY APPARATUS 3.817,393 6/1974 Neilsen... 211/50 4,164,309 8/1979 Staats...
USOO6224174B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,224,174 B1 Mu (45) Date of Patent: *May 1, 2001 (54) POSTER DISPLAY APPARATUS 3.817,393 6/1974 Neilsen... 211/50 4,164,309 8/1979 Staats...
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 4,821,355 Burkhardt (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 1989
 United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 4,821,5 Burkhardt () Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 1989 (54) SELF-ADJUSTING ORTHOPEDIC 4,447,922 5/1984 Brochu... 5/434 CERVICAL PLLOW 4,528,705 7/1985 Greenawalt...
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 4,821,5 Burkhardt () Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 1989 (54) SELF-ADJUSTING ORTHOPEDIC 4,447,922 5/1984 Brochu... 5/434 CERVICAL PLLOW 4,528,705 7/1985 Greenawalt...
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014001 1160A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0011160 A1 JOrneus et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 9, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ABUTMENT SYSTEMAND
(19) United States US 2014001 1160A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0011160 A1 JOrneus et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 9, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ABUTMENT SYSTEMAND
(12) United States Patent
 USOO951 0624B2 (12) United States Patent Li et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,510,624 B2 Dec. 6, 2016 (54) DISPOSABLE ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (75) Inventors: Yonghai Li, Shenzhen (CN); Zhongli
USOO951 0624B2 (12) United States Patent Li et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,510,624 B2 Dec. 6, 2016 (54) DISPOSABLE ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (75) Inventors: Yonghai Li, Shenzhen (CN); Zhongli
76 Inventors: late Stella YErin, 5,479,944 1/1996 Petruson /858
 USOO593.1799A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,931,799 Guastella et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 1999 54 PARASEPTAL SPLINT FOR USE IN 4,340,040 7/1982 Straith... 606/204.45 SURGICAL NASAL
USOO593.1799A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,931,799 Guastella et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 3, 1999 54 PARASEPTAL SPLINT FOR USE IN 4,340,040 7/1982 Straith... 606/204.45 SURGICAL NASAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0287886 A1 Patti US 20140287886A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PROTECTOR FOR EXERCISE BAR Applicant:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0287886 A1 Patti US 20140287886A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PROTECTOR FOR EXERCISE BAR Applicant:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,234,797 B1
 USOO6234797B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ura (45) Date of Patent: *May 22, 2001 (54) DENTAL IMPLANT AND METHOD FOR 5,322,443 6/1994 Beaty. INSTALLING THE SAME 5,336,225 8/1994 Zang. 5,338,197
USOO6234797B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Ura (45) Date of Patent: *May 22, 2001 (54) DENTAL IMPLANT AND METHOD FOR 5,322,443 6/1994 Beaty. INSTALLING THE SAME 5,336,225 8/1994 Zang. 5,338,197
(12) United States Patent
 US007094007B2 (12) United States Patent Satran et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 22, 2006 (54) TANGENTIAL CUTTING INSERT AND MILLING CUTTER (75) Inventors: Amir Satran, Kfar Vradim (IL);
US007094007B2 (12) United States Patent Satran et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 22, 2006 (54) TANGENTIAL CUTTING INSERT AND MILLING CUTTER (75) Inventors: Amir Satran, Kfar Vradim (IL);
3, /1973 Sakita /6 thereby providing a cervical Support without requiring
 USOO589 1069A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Moffett (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 1999 54 CERVICAL EXTRACTION COLLAR AND 5,618,263 4/1997 Alivizatos... 602/6 METHOD OF IMMOBILIZING ACERVICAL
USOO589 1069A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Moffett (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 1999 54 CERVICAL EXTRACTION COLLAR AND 5,618,263 4/1997 Alivizatos... 602/6 METHOD OF IMMOBILIZING ACERVICAL
United States Patent (19) James
 United States Patent (19) James 54 DEVICE FOR DISPENSING MEDICAMENTS (75) Inventor: Michael James, Welwyn Garden City, England Allen & Hanburys Limited, London, 73 Assignee: England (21) Appl. No.: 767,518
United States Patent (19) James 54 DEVICE FOR DISPENSING MEDICAMENTS (75) Inventor: Michael James, Welwyn Garden City, England Allen & Hanburys Limited, London, 73 Assignee: England (21) Appl. No.: 767,518
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US006319006B1 (10) Patent N0.: US 6,319,006 B1 Scherer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2001 (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCINGA DRILL 5,967,777 * 10/1999 Klein 5 a1...... 433/75 ASSISTANCE
(12) United States Patent US006319006B1 (10) Patent N0.: US 6,319,006 B1 Scherer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2001 (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCINGA DRILL 5,967,777 * 10/1999 Klein 5 a1...... 433/75 ASSISTANCE
SE CE. E. E. C. alignment.
 USOO6478799B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,478,799 B1 Williamson (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) INSTRUMENTS AND METHODS FOR USE FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS N PERFORMING KNEE SURGERY
USOO6478799B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,478,799 B1 Williamson (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) INSTRUMENTS AND METHODS FOR USE FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS N PERFORMING KNEE SURGERY
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fung (54) DENTAL CROWN 76) Inventor: John Fung, 627 George Street, Sydney, NSW 2000, Australia (21) Appl. No.: 969,186 (22) PCT Filed: Jul. 5, 1991 (86). PCT No.: PCT/AU91/00300
United States Patent (19) Fung (54) DENTAL CROWN 76) Inventor: John Fung, 627 George Street, Sydney, NSW 2000, Australia (21) Appl. No.: 969,186 (22) PCT Filed: Jul. 5, 1991 (86). PCT No.: PCT/AU91/00300
Fixel 45 Date of Patent: May 12, 1992 (54 INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS
 IIIHIIIHIIII United States Patent (19) 11) US51 12333A Patent Number: 5,112,333 Fixel 45 Date of Patent: May 12, 1992 s A N (54 INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL FREIGN PATENT DCUMENTS 76) Inventor: Irving E. Fixel,
IIIHIIIHIIII United States Patent (19) 11) US51 12333A Patent Number: 5,112,333 Fixel 45 Date of Patent: May 12, 1992 s A N (54 INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL FREIGN PATENT DCUMENTS 76) Inventor: Irving E. Fixel,
Imola Lateral IBF System Surgical Technique
 Imola Lateral IBF System Surgical Technique IMOLA CIRCUIT TABLE OF CONTENTS Design Rationale Instructions for Use Surgical Technique 1. Table Mounting 2. Surgical Planning & Targeting 3. Access and Preparation
Imola Lateral IBF System Surgical Technique IMOLA CIRCUIT TABLE OF CONTENTS Design Rationale Instructions for Use Surgical Technique 1. Table Mounting 2. Surgical Planning & Targeting 3. Access and Preparation
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,292,699 B1
 USOO6292699B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,292,699 B1 Simon et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 18, 2001 (54) DIRECT CURRENT STIMULATION OF OTHER PUBLICATIONS SPINAL INTERBODY FXATION DEVICE
USOO6292699B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,292,699 B1 Simon et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 18, 2001 (54) DIRECT CURRENT STIMULATION OF OTHER PUBLICATIONS SPINAL INTERBODY FXATION DEVICE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012.0089051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0089051A1 Draudt et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 12, 2012 (54) BLOOD GLUCOSE METER HAVING INTEGRAL LANCET DEVICE
(19) United States US 2012.0089051A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0089051A1 Draudt et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 12, 2012 (54) BLOOD GLUCOSE METER HAVING INTEGRAL LANCET DEVICE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,461,697 B1
 USOO646.1697B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,461,697 B1 Slat et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) POLYETHYLENE TEREPHTHALATE 4,149,645 A 4/1979 Valyi MULTI-LAYER PREFORM USED
USOO646.1697B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,461,697 B1 Slat et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) POLYETHYLENE TEREPHTHALATE 4,149,645 A 4/1979 Valyi MULTI-LAYER PREFORM USED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201701 65099A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0165099 A1 Buddharaju (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 15, 2017 (54) CONDOM CATHETER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A61F 5/453
(19) United States US 201701 65099A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0165099 A1 Buddharaju (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 15, 2017 (54) CONDOM CATHETER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A61F 5/453
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,916,338 B2
 USOO691.6338B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,916,338 B2 Speziali (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005 (54) SYNTHETIC LEAFLETS FOR HEART VALVE (51) Int. Cl."... A61F 2/06 REPAIR OR REPLACEMENT
USOO691.6338B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,916,338 B2 Speziali (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 12, 2005 (54) SYNTHETIC LEAFLETS FOR HEART VALVE (51) Int. Cl."... A61F 2/06 REPAIR OR REPLACEMENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 2007 O185493A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0185493 A1 Feibel et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 9, 2007 (54) CLAVICULAR BONE PLATE (30) Foreign Application
US 2007 O185493A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0185493 A1 Feibel et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 9, 2007 (54) CLAVICULAR BONE PLATE (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,837,905 B1
 USOO6837905B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,837,905 B1 Lieberman (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 4, 2005 (54) SPINAL VERTEBRAL FUSION IMPLANT 6,106,557 A * 8/2000 Robioneck et al.... 623/17.15
USOO6837905B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,837,905 B1 Lieberman (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 4, 2005 (54) SPINAL VERTEBRAL FUSION IMPLANT 6,106,557 A * 8/2000 Robioneck et al.... 623/17.15
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 20120083881A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0083881 A1 Claybrooks (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 5, 2012 (54) STAND-ALONE ANTERIOR FUSION DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 20120083881A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0083881 A1 Claybrooks (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 5, 2012 (54) STAND-ALONE ANTERIOR FUSION DEVICE (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0265315 A1 Kusogullariet al. US 20120265315A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2012 (54) SHOULDER PROSTHESIS (75) Inventors: Levent
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0265315 A1 Kusogullariet al. US 20120265315A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 18, 2012 (54) SHOULDER PROSTHESIS (75) Inventors: Levent
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,128,575 B1. Sohn (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2006
 US007128575B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,128,575 B1 Sohn (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2006 (54) TOOTHELEVATOR 1,762,888 A 6/1930 Roberts... 433/159 2,030,798 A 2/1936 Krajeski......
US007128575B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,128,575 B1 Sohn (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 31, 2006 (54) TOOTHELEVATOR 1,762,888 A 6/1930 Roberts... 433/159 2,030,798 A 2/1936 Krajeski......
50 3 % % 2. ta. SN & (12) United States Patent US 7, B1. Jun. 10, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.:
 USOO7384414B1 (1) United States Patent Marshall et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,384.414 B1 Jun., 008 (54) SAFETY PEN NEEDLE WITH (75) (73) (*) (1) () (51) (5) (58) (56) NON-INUECTION END
USOO7384414B1 (1) United States Patent Marshall et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,384.414 B1 Jun., 008 (54) SAFETY PEN NEEDLE WITH (75) (73) (*) (1) () (51) (5) (58) (56) NON-INUECTION END
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0174911 A1 Naruse US 2006O174911A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 10, 2006 (54) ELECTRIC DENTAL FLOSS (76) Inventor: Haruhiko Naruse,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0174911 A1 Naruse US 2006O174911A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 10, 2006 (54) ELECTRIC DENTAL FLOSS (76) Inventor: Haruhiko Naruse,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO8623055B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,623,055 B2 Abdou (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 7, 2014 (54) SPINOUS PROCESS FUSION AND (56) References Cited ORTHOPEDICMPLANTS AND METHODS U.S.
(12) United States Patent USOO8623055B2 (10) Patent No.: US 8,623,055 B2 Abdou (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 7, 2014 (54) SPINOUS PROCESS FUSION AND (56) References Cited ORTHOPEDICMPLANTS AND METHODS U.S.
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,166,107 B2. Anderson (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, (54) PERCUTANEOUS TECHNIQUE AND 4,955,908 A 9/1990 Frey et al.
 United States Patent US007166 107B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,166,107 B2 Anderson (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2007 (54) PERCUTANEOUS TECHNIQUE AND 4,955,908 A 9/1990 Frey et al. MPLANT FOR EXPANDING
United States Patent US007166 107B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,166,107 B2 Anderson (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 23, 2007 (54) PERCUTANEOUS TECHNIQUE AND 4,955,908 A 9/1990 Frey et al. MPLANT FOR EXPANDING
Zimmer Trabecular Metal Ankle Interpositional Spacer and Trabecular Metal Ankle Fusion Spacer
 Zimmer Trabecular Metal Ankle Interpositional Spacer and Trabecular Metal Ankle Fusion Spacer Surgical Technique 2 Zimmer Trabecular Metal Ankle Interpositional Spacer and Trabecular Metal Ankle Fusion
Zimmer Trabecular Metal Ankle Interpositional Spacer and Trabecular Metal Ankle Fusion Spacer Surgical Technique 2 Zimmer Trabecular Metal Ankle Interpositional Spacer and Trabecular Metal Ankle Fusion
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 2009.02451 05A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0245105 A1 HO (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2009 (54) METHOD FOR NETWORK TRANSMISSION (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2009.02451 05A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0245105 A1 HO (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2009 (54) METHOD FOR NETWORK TRANSMISSION (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,358,254 B1
 USOO6358254B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,358,254 B1 Anderson (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 19, 2002 (54) METHOD AND IMPLANT FOR EXPANDING 5,722.977 A * 3/1998 Wilhelmy... 606/61 A SPINAL
USOO6358254B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,358,254 B1 Anderson (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 19, 2002 (54) METHOD AND IMPLANT FOR EXPANDING 5,722.977 A * 3/1998 Wilhelmy... 606/61 A SPINAL
Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 6,120,471
![Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 6,120,471 Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 6,120,471](/thumbs/72/66899349.jpg) US006120471A Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 6,120,471 Varn [45] Date of Patent: Sep. 19, 2000 [54] DORSAL RESTING HAND ORTHOSIS 5,637,078 6/1997 Varn..... 602/21 5,746,707 5/1998 Eck.....
US006120471A Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 6,120,471 Varn [45] Date of Patent: Sep. 19, 2000 [54] DORSAL RESTING HAND ORTHOSIS 5,637,078 6/1997 Varn..... 602/21 5,746,707 5/1998 Eck.....
United States Patent (19) Groesch et al.
 United States Patent (19) Groesch et al. 54 DUMMY FOR CAR CRASH TESTING 75) Inventors: Lothar Groesch; Gabriel Netzer, both of Stuttgart; Lothar Kassing, Nufringen, all of Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Groesch et al. 54 DUMMY FOR CAR CRASH TESTING 75) Inventors: Lothar Groesch; Gabriel Netzer, both of Stuttgart; Lothar Kassing, Nufringen, all of Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kimber et al. USOO6565529B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,565,529 B1 (45) Date of Patent: May 20, 2003 (54) TAMPEREVIDENT SYRINGE DESIGN (75) Inventors: Michael Browning Kimber, New South
(12) United States Patent Kimber et al. USOO6565529B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,565,529 B1 (45) Date of Patent: May 20, 2003 (54) TAMPEREVIDENT SYRINGE DESIGN (75) Inventors: Michael Browning Kimber, New South
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Modglin et al. USOO6478759B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) THORACO-LUMBO-SACRAL ORTHOSIS (75) Inventors: Michael D. Modglin, Braselton, GA (US); Paul
(12) United States Patent Modglin et al. USOO6478759B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 12, 2002 (54) THORACO-LUMBO-SACRAL ORTHOSIS (75) Inventors: Michael D. Modglin, Braselton, GA (US); Paul
VLIFT System Overview. Vertebral Body Replacement System
 VLIFT System Overview Vertebral Body Replacement System VLIFT System System Description The VLIFT Vertebral Body Replacement System consists of a Distractible In Situ (DIS) implant, which enables the surgeon
VLIFT System Overview Vertebral Body Replacement System VLIFT System System Description The VLIFT Vertebral Body Replacement System consists of a Distractible In Situ (DIS) implant, which enables the surgeon
72 inventors Maurice Rosman 2,460,895 2/1949 Meany /80
 United States Patent (113,581,741 72 inventors Maurice Rosman 2,460,895 2/1949 Meany - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 128/80 6 Elmwood Ave., 19142; 3,387,305 6/1968 Shafer... 128/80X
United States Patent (113,581,741 72 inventors Maurice Rosman 2,460,895 2/1949 Meany - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 128/80 6 Elmwood Ave., 19142; 3,387,305 6/1968 Shafer... 128/80X
United States Patent (19) 3,787,641 Santori - 45) Jan. 22, 1974
 United States Patent (19) 3,787,641 Santori - 45) Jan. 22, 1974 (54) BoNE CONDUCTION MICROPHONE ASSEMBLY Primary Examiner-Ralph D. Blakeslee 75 Inventor: Charles - M. Santori, San Jose, Calif., Attorney,
United States Patent (19) 3,787,641 Santori - 45) Jan. 22, 1974 (54) BoNE CONDUCTION MICROPHONE ASSEMBLY Primary Examiner-Ralph D. Blakeslee 75 Inventor: Charles - M. Santori, San Jose, Calif., Attorney,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0143905 A1 Goyal et al. US 20170143905A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) NEEDLE-FREE INUECTION GUIDE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0143905 A1 Goyal et al. US 20170143905A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) NEEDLE-FREE INUECTION GUIDE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Jones et al. USOO6833003B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 2004 (54) EXPANDABLE STENT AND DELIVERY SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Donald K. Jones, Lauderhill, FL (US);
(12) United States Patent Jones et al. USOO6833003B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 2004 (54) EXPANDABLE STENT AND DELIVERY SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Donald K. Jones, Lauderhill, FL (US);
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Brown et al. USOO6494.914B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,494.914 B2 Dec. 17, 2002 (54) UNICONDYLAR FEMORAL PROSTHESIS AND INSTRUMENTS (75) Inventors: David Ray Brown,
(12) United States Patent Brown et al. USOO6494.914B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,494.914 B2 Dec. 17, 2002 (54) UNICONDYLAR FEMORAL PROSTHESIS AND INSTRUMENTS (75) Inventors: David Ray Brown,
United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,582,607 Lackman 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 10, 1996
 US005582607A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Lackman 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 10, 1996 (54) HEART VALVE PROSTHESIS ROTATOR 4,982,727 1/1991 Sato... 606/205 v WTH BENDABLE SHAFT AND DRIVE 5,236,450
US005582607A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Lackman 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 10, 1996 (54) HEART VALVE PROSTHESIS ROTATOR 4,982,727 1/1991 Sato... 606/205 v WTH BENDABLE SHAFT AND DRIVE 5,236,450
Sepetka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 3, ) VARIABLE STIFFNESS CATHETER 4,739,768 4/1988 Engelson.
 United States Patent (19) 11 USOO5308342A Patent Number: Sepetka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 3, 1994 54) VARIABLE STIFFNESS CATHETER 4,739,768 4/1988 Engelson. o 4,775,371 10/1988 Mueller, Jr.... 604/280
United States Patent (19) 11 USOO5308342A Patent Number: Sepetka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 3, 1994 54) VARIABLE STIFFNESS CATHETER 4,739,768 4/1988 Engelson. o 4,775,371 10/1988 Mueller, Jr.... 604/280
Patient Information MIS LLIF. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
 Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine...2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine...2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0196770 A1 Klintenstedt et al. US 201701.96770A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) (60) (30) CNTAINER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0196770 A1 Klintenstedt et al. US 201701.96770A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) (60) (30) CNTAINER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 US 2011 0023281A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0023281 A1 Schraga (43) Pub. Date: (54) PEN INJECTION DEVICE CAP WITH Related U.S. Application Data NSSENSECKRELEASE
US 2011 0023281A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0023281 A1 Schraga (43) Pub. Date: (54) PEN INJECTION DEVICE CAP WITH Related U.S. Application Data NSSENSECKRELEASE
United States Patent (19) Andelin et al.
 United States Patent (19) Andelin et al. 54 BONE MARROW BIOPSY NEEDLE AND METHOD FOR USING THE SAME 76 Inventors: John B. Andelin, 4940 140 Ave., N.W., Lot 62, Williston, N. Dak. 58801-8605; Martin T.
United States Patent (19) Andelin et al. 54 BONE MARROW BIOPSY NEEDLE AND METHOD FOR USING THE SAME 76 Inventors: John B. Andelin, 4940 140 Ave., N.W., Lot 62, Williston, N. Dak. 58801-8605; Martin T.
SMAX ling supportinganahaigahadistand
 o US005368046A United States Patent (19) (11 Patent Number: 5,368,046 Scarfone et al. () Date of Patent: Nov. 29, 1994 54 BONE MARROW NEEDLEASSEMBLY 4,513,754 4/1985 Lee... 128/753 4,630,616 12/1986 Tretinyak......
o US005368046A United States Patent (19) (11 Patent Number: 5,368,046 Scarfone et al. () Date of Patent: Nov. 29, 1994 54 BONE MARROW NEEDLEASSEMBLY 4,513,754 4/1985 Lee... 128/753 4,630,616 12/1986 Tretinyak......
The Most Reliable Spinal Solution
 MFG : 09.02.20 REV : 1 4CIS VANE introduces you the reliable pedicle screw The Most Reliable Spinal Solution Non-slip threaded joint Ergonomic design Wedged trapezoid thread Superior locking mechanism
MFG : 09.02.20 REV : 1 4CIS VANE introduces you the reliable pedicle screw The Most Reliable Spinal Solution Non-slip threaded joint Ergonomic design Wedged trapezoid thread Superior locking mechanism
(19) United States (12) Reissued Patent
 (19) United States (12) Reissued Patent Talaber et al. USOORE430O8E (10) Patent Number: (45) Date of Reissued Patent: Dec. 6, 2011 (54) ORTHOPEDIC IMPLANTASSEMBLY (75) Inventors: David J. Talaber, Livermore,
(19) United States (12) Reissued Patent Talaber et al. USOORE430O8E (10) Patent Number: (45) Date of Reissued Patent: Dec. 6, 2011 (54) ORTHOPEDIC IMPLANTASSEMBLY (75) Inventors: David J. Talaber, Livermore,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O130096A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0130096 A1 LaCroce (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 10, 2003 (54) BARBELL WITH PLURAL HAND GRIPPING Publication Classification
US 2003O130096A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0130096 A1 LaCroce (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 10, 2003 (54) BARBELL WITH PLURAL HAND GRIPPING Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005.0020415A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0020415 A1 Reno (43) Pub. Date: (54) ISOMETRIC EXERCISE EQUIPMENT WITH Publication Classification PORTABLE
US 2005.0020415A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0020415 A1 Reno (43) Pub. Date: (54) ISOMETRIC EXERCISE EQUIPMENT WITH Publication Classification PORTABLE
4.5 System. Surgical Technique. This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA.
 4.5 System Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Contents EXPEDIUM 4.5 Spine System 2 Features and Benefits 3 Surgical Technique Extended Tandem Connector 4 Placement
4.5 System Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Contents EXPEDIUM 4.5 Spine System 2 Features and Benefits 3 Surgical Technique Extended Tandem Connector 4 Placement
Thoracolumbar Spine Locking Plate (TSLP) System. A low-profile plating system for anterior stabilization of the thoracic and lumbar spine.
 Thoracolumbar Spine Locking Plate (TSLP) System. A low-profile plating system for anterior stabilization of the thoracic and lumbar spine. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation
Thoracolumbar Spine Locking Plate (TSLP) System. A low-profile plating system for anterior stabilization of the thoracic and lumbar spine. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation
United States Patent (19) Martin
 United States Patent (19) Martin 54 DENTAL INSTRUMENT 76 Inventor: James A. Martin, Wieand Rd., P.O. Box 77, Milford Square, Pa. 18935 21 Appl. No.: 831,321 22 Filed: Feb. 20, 1986 Related U.S. Application
United States Patent (19) Martin 54 DENTAL INSTRUMENT 76 Inventor: James A. Martin, Wieand Rd., P.O. Box 77, Milford Square, Pa. 18935 21 Appl. No.: 831,321 22 Filed: Feb. 20, 1986 Related U.S. Application
BAK/C Cervical Anterior Interbody Fusion System
 Surgical Technique BAK/C Cervical Anterior Interbody Fusion System The Comfortable Choice for Cervical Fusion BAK/C Cervical Surgical Technique 1 The BAK/C Cervical Fusion System is an alternative to conventional
Surgical Technique BAK/C Cervical Anterior Interbody Fusion System The Comfortable Choice for Cervical Fusion BAK/C Cervical Surgical Technique 1 The BAK/C Cervical Fusion System is an alternative to conventional
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160213850A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0213850 A1 LOOF et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 28, 2016 (54) MEDICAMENT DELIVERY DEVICE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20160213850A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0213850 A1 LOOF et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 28, 2016 (54) MEDICAMENT DELIVERY DEVICE Publication Classification
United States Patent (19) Dobben
 United States Patent (19) Dobben 54 ARTIFICIAL HEART VALVE FOR MPLANTATION IN A BLOOD WESSEL (76 Inventor: Richard L. Dobben, 6355 N. 600 West, Michigan City, Ind. 46360 21 Appl. No.: 342,2 (22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Dobben 54 ARTIFICIAL HEART VALVE FOR MPLANTATION IN A BLOOD WESSEL (76 Inventor: Richard L. Dobben, 6355 N. 600 West, Michigan City, Ind. 46360 21 Appl. No.: 342,2 (22 Filed:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 2007025.0167A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0250167 A1 Bray et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 25, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) SPINE IMPLANTS Inventors:
(19) United States US 2007025.0167A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0250167 A1 Bray et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 25, 2007 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) SPINE IMPLANTS Inventors:
IHIH IIII. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,417, Date of Patent: May 23, Kawai et al.
 United States Patent (19) Kawai et al. 54 METHOD FOR EXTRACTING AMARGIN LINE FOR DESIGNING AN ARTIFICIAL CROWN 75) Inventors: Masaharu Kawai, Kanagawa; Katsuya Miyoshi, Tokyo; Masami Baba, Saitama, all
United States Patent (19) Kawai et al. 54 METHOD FOR EXTRACTING AMARGIN LINE FOR DESIGNING AN ARTIFICIAL CROWN 75) Inventors: Masaharu Kawai, Kanagawa; Katsuya Miyoshi, Tokyo; Masami Baba, Saitama, all
OPTIONAL/ADDITIONAL INSTRUMENTS
 20 Elevated 6320-36-22 20 Elevated Rim Liner, 36mm OD x 22mm ID 6320-80-22 20 Elevated Rim Liner, 80mm OD x 22mm ID 6320-42-26 20 Elevated Rim Liner, 42mm OD x 26mm ID 6320-80-26 20 Elevated Rim Liner,
20 Elevated 6320-36-22 20 Elevated Rim Liner, 36mm OD x 22mm ID 6320-80-22 20 Elevated Rim Liner, 80mm OD x 22mm ID 6320-42-26 20 Elevated Rim Liner, 42mm OD x 26mm ID 6320-80-26 20 Elevated Rim Liner,
Patient Information MIS TLIF. Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
 Patient Information MIS TLIF Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques MIS TLIF Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine...2 General Conditions of the Spine...4 6 MIS-TLIF
Patient Information MIS TLIF Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques MIS TLIF Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine...2 General Conditions of the Spine...4 6 MIS-TLIF
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) (11) 4,170,995 Levine et al.. ) Oct. 16, 1979 54 (76) CATHETER CLAMP Inventors: Robert A. Levine, 31 Pilgrim La., Guilford, Conn. 06437; Stephen C. Wardlaw, 128 Sunset Hill Dr.,
United States Patent (19) (11) 4,170,995 Levine et al.. ) Oct. 16, 1979 54 (76) CATHETER CLAMP Inventors: Robert A. Levine, 31 Pilgrim La., Guilford, Conn. 06437; Stephen C. Wardlaw, 128 Sunset Hill Dr.,
Patient Information MIS LLIF. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
 Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine....2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine....2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/ A1. Ditola (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 29, 2010
 US 20100105.528A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0105528A1 Ditola (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 29, 2010 (54) VERTICLE EXERCISE CYCLE Publication Classification (76)
US 20100105.528A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0105528A1 Ditola (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 29, 2010 (54) VERTICLE EXERCISE CYCLE Publication Classification (76)
Valencia Pedicle Screw Surgical Technique
 Valencia Pedicle Screw Surgical Technique VALENCIA CIRCUIT TABLE OF CONTENTS Design Rationale Indications for Use Surgical Technique 1. Pedicle Preparation 2. Screw Insertion 3. Rod Placement 4. Locking
Valencia Pedicle Screw Surgical Technique VALENCIA CIRCUIT TABLE OF CONTENTS Design Rationale Indications for Use Surgical Technique 1. Pedicle Preparation 2. Screw Insertion 3. Rod Placement 4. Locking
EXACTECH SPINE. Operative Technique. Cervical Spacer System. Surgeon focused. Patient driven. TM
 EXACTECH SPINE Operative Technique Cervical Spacer System Surgeon focused. Patient driven. TM ACAPELLA ONE Acapella One Cervical Spacer System is an anterior cervical discectomy and fusion device with
EXACTECH SPINE Operative Technique Cervical Spacer System Surgeon focused. Patient driven. TM ACAPELLA ONE Acapella One Cervical Spacer System is an anterior cervical discectomy and fusion device with
nva Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion System
 nva Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion System 1 IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR PHYSICIANS, SURGEONS, AND/OR STAFF The nv a, nv p, and nv t are an intervertebral body fusion device used in the lumbar spine following
nva Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion System 1 IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR PHYSICIANS, SURGEONS, AND/OR STAFF The nv a, nv p, and nv t are an intervertebral body fusion device used in the lumbar spine following
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0160728A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0160728A1 Blitz et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2011 (54) INTRAMEDULLARY COMPRESSION NAIL AND RELATED METHOD
(19) United States US 2011 0160728A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0160728A1 Blitz et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2011 (54) INTRAMEDULLARY COMPRESSION NAIL AND RELATED METHOD
