Osteogenesis Imperfecta: A Case Report and Review of Literature
|
|
|
- Katrina O’Brien’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Case Report Osteogenesis Imperfecta: A Case Report and Review of Literature Edelu BO, Ndu IK 1, Asinobi IN, Obu HA, Adimora GN Departments of Paediatrics, University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital, 1 Enugu State University Teaching Hospital, Enugu, Nigeria Address for correspondence: Dr. Edelu BO, Department of Paediatrics, University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital, Enugu, Nigeria. E mail: onyedelu@yahoo.com Abstract Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a group of rare inherited disorders of connective tissue with the common feature of excessive fragility of bones caused by mutations in collagen. Diagnosis is mainly based on the clinical features of the disorder. We report, the case of a male neonate delivered to a 33 year old para 2 female at University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital, Enugu with no family history suggestive of OI. He had clinical features of a type II OI and severe birth asphyxia. Multidisciplinary management was instituted, but he died on the 7 th day of life. Keywords: Brittle bone disease and fragile bone disease, Fragilitas ossium, Osteogenesis imperfecta, Osteopetrosis idiopathica Introduction Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a group of rare inherited disorders of connective tissue with the common feature of excessive fragility of bones. [1] It is caused by mutations in the collagen, type I, alpha 1 and collagen type I alpha 2 genes, which encode the alpha 1 and the alpha 2 chain of type I procollagen, respectively. [2] Molecular genetic studies have detected more than 150 mutations of these genes. [2] Other mutations have been identified in the leucine proline enriched proteoglycan 1, cartilage associated protein and peptidyl proly lisomerase B genes. [3,4] The incidence is 1:20,000 and occurs in all races and ethnicity. [5] It is mostly inherited as an autosomal dominant disorder, but autosomal recessive forms have been reported. [6,7] The clinical classification by Sillence et al., is the most helpful in prognosis and genetic counseling and it groups OI into four types: Type I OI is mild, type II is perinatal lethal, type III is progressive deforming and type IV is moderately severe. [8] It is characterized by multiple and recurrent fractures, which are intrauterine or perinatal or post natal. Other features include blue sclera, otosclerosis with hearing loss, high arched palate, Quick Response Code: Access this article online Website: DOI: / hyperlaxity of ligaments and skin, dentinogenesis imperfecta (defective dentition), scoliosis and growth retardation. Wormian bones could also be seen on skull X ray. Intelligence is not affected. [3] Diagnosis can be made clinically. Radiographic support and confirmation by collagen analysis of skin fibroblast culture or blood deoxyribonucleic acid analysis may be necessary in some cases. [5,9] This is important for genetic counseling and cases of suspected child abuse. Prenatal diagnosis for at risk pregnancies by fetal ultrasonography in the early 2 nd trimester is possible and enables care. [5,10] There s no cure for OI. Management is multidisciplinary involving mainly surgery, physiotherapy and rehabilitation. However, medical treatment, especially with bisphosphonate have shown good prospects. [3,5,9] This case is being reported because of its rarity, especially among blacks and also, to review the literature to highlight the challenges and advances in its management. Case Report O.E [Figure 1] was a male neonate delivered to a 33 year old para 2 female at University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital, Enugu. He was admitted to the new born special care unit (NBSCU) 10 min after birth for inability to cry at birth, multiple deformities with abnormal body posture. His mother received routine antenatal care and pregnancy was uneventful. Only routine drugs were used during pregnancy. Annals of Medical and Health Sciences Research Mar-Apr 2014 Vol 4 Special Issue 1 1
2 Prenatal ultrasonography detected no fractures or other abnormalities. Onset of labor was spontaneous and lasted about 8 h with spontaneous vertex delivery. Apgar score was four at 10 min. There was no history of the tendency to fractures in the family and no family history of any baby with fracture at birth. On examination in the NBSCU, he was found to be in frog like position with abnormal movement of the left thigh. He was in respiratory distress with acrocyanosis. He had blue grey sclera and micrognathia with a high arched palate. Musculoskeletal system examination revealed pectus excavatum, fixed flexion deformity of the fingers, crepitus of the right humerus and ulnar and both femurs with bilateral talipes equinovarus and micromelia. A diagnosis of severe birth asphyxia in a neonate with OI type II was made. Radiograph revealed fractures of the right humerus, ulna and femur with osteopenia. Treatment was mainly supportive with minimal handling, intermittent suctioning and intra nasal oxygen administration. The parents were counseled and the baby was also reviewed by the orthopaedic surgeons and anesthetist for later surgical intervention when he stabilized. However, he continued to deteriorate until his death on the 7 th day of life. Discussion/Literature Review OI is a rare disorder. It has variously been called osteopsathyrosis idiopathica by Lobstein, fragilitus osseum, hereditary fragility of bone, later brittle bone disease and fragile bone disease, but the current name OI was coined by Vrolik in [11,12] The disorder was first brought to the limelight by the Swede, Olof Jakob Ekman in his doctorate thesis at Uppsala in 1788 as osteomalacia congenital involving three generations. [12,13] Since then, various researchers have tried to describe and classify this disorder into various types: In 1906, Looser, proposed the classification: Congenita and tarda based on time of fractures. [14] Congenita type has fracture in utero and most were either still birth or died soon after. OI congenita was found in children whose parents have no traces of the disease while OI tarda was the hereditary form. In 1975, Bauze et al., [15] describing the clinical, radiological and biochemical features of 42 patients classified OI into three: mild, moderate and severe based on deformity of one or more of the long bones. Mild had no long bone deformity; moderate had minor long bone deformities while severe had severe long bone deformities. One of their arguments is that long bone deformity is a strong prognostic feature and easily recognizable. The most widely acceptable classification was by Sillence et al., [8] in 1979, in which they grouped the disorder into four: Type I; dominantly inherited OI with blue sclera, type II; perinatally lethally deforming OI with crumpled femora, type III; progressively deforming OI with normal sclera and type IV; dominantly inherited OI with normal sclerae. Type I is a mild form with recurrent fractures and blue sclera. It has A and B subtypes depending on the absence or presence of dentinogenesis imperfecta. Fractures are less common after puberty. Type II is autosomal recessive and generally lethal in the newborn period with multiple congenital fractures, micromelia and severe lung disease. Types III and IV represent intermediate phenotypes with type III being the most severe non lethal form causing significant bony deformity secondary to multiple fractures, which can be congenital. Type IV also has subtypes A and B based on the presence of dentinogenesis imperfecta. Over the past few decades, five additional types (V IX) have been identified using histological and molecular findings. [6,7] Plotkin [16] proposed a classification of OI as syndromes secondary to mutations in type I pro collagen genes and syndromes resembling osteogenesis imperfecta as those secondary to mutations other than the type I pro collagen genes. The diagnosis of OI type II in our patient was based on the clinical features of multiple fractures at birth, blue grey sclera, micromelia and radiological evidence of osteopenia. Although, there was no positive family history suggestive of OI or other skeletal malformations, it was noted that sporadic cases were most likely in type II. [8] Akiode et al., in Sagamu, [17] and Akinola et al., in Lagos, [18] both in Western Nigeria reported a single and two cases respectively of female babies based on the clinical findings of multiple fractures, blue sclera and craniotabes at birth with radiological evidence of defective ossification of the skull. Although, reports available, [5,19] show no racial or ethnic variation, the sparseness of reports from Africa and obvious absence of blacks in most of the case reports from other continents may be an indication of low incidence in Africans. It may also be as a result of under reporting due to wide unavailability of facilities for disease confirmation. Although, an autosomal recessive form of type III, which is very rare, has been reported as been relatively more common among South African black population, [20] the etiology is not certain as type I collagen structural genes Colia one and two have not been demonstrated to be mutated in the affected population. [21] There have also been reports of OI in twins from Burundi [22] and more recently Nigeria. [23] Prenatal diagnosis by fetal ultrasonography is possible, [5] but no abnormality was detected in our patient prenatally. Likewise, in the first case earlier reported within the country. The other case, report did not state the ultrasonography findings. It s also possible that the fractures occurred during delivery in both cases since prenatal diagnosis is mainly based on the presence of fractures. Fractures can occur even on minimal stress, but there is no empiric data to prove that caesarean section will improve outcome over vaginal birth even when diagnosed prenatally. [24] However, its poor prognostic course raises an 2 Annals of Medical and Health Sciences Research Mar-Apr 2014 Vol 4 Special Issue 1
3 ethical question of termination of pregnancy on detection. Despite this, advances in technology continue to proffer options for these children. Surgery had been the main stay of management of OI with supportive physiotherapy and rehabilitation. However, the persistent brittleness of the bones with repeated fractures made researchers to seek alternative treatment that will permanently strengthen the bone structure. Medical treatment, though dating back to about two centuries ago, thus started to dominate discussions over the past few decades as an adjunct. Experiments on medical management started as far back as 1897 with Griffith who combined phosphorus, codliver oil, fresh air and exercise. [25] Since then, over 25 different agents including hormones such as pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, androgens, estrogens and calcitonin, vitamins A, C and D as well as mineral agents such as strontium, aluminum, fluoride, magnesium and citrate of sodium hydroxide have been used in attempts to treat OI. [26] Just like in recent years, most of the researchers claimed some benefits for their products but none was recorded to be a success. Almost a century later, Devogelaer et al., [27] introduced the use of bisphosphonates, which appeared to have brought the hope of a successful medical treatment. Their trial was based on the use of the drug in the treatment of other bone disorders like juvenile osteoporosis and Paget disease of the bone. Bisphosphonates (diphosphonates) are derived from pyrophosphate, a naturally occurring agent that slows or stops the naturally occurring process of bone resorption, thereby resulting in increased bone density and strength. Bisphosphonates have evolved over time from its original compound to 2 nd and 3 rd generation aminobisphosphonates such as pamidronate, alendronate and risedronate. Since this first report in 1987, numerous researchers have tried to evaluate the use of bisphosphonates in the treatment of OI using different regimens, with over a hundred publications and still counting. Cyclic IV pamidronate appears to be the most widely reported treatment for children with OI. Most researchers reported increase in bone mineral density as well as reduction in the risk of fracture. [28 30] There are also a report on increased height and weight in children treated with pamidronate. [31] Risedronate has been proposed as a more suitable alternative to pamidronate because of its lower mineral affinity than the other nitrogen containing bisphosphonates such as alendronate and olpadronate. [32] Antoniazzi et al., [33] also demonstrated that a combination of bisphosphonate and growth hormone produced a better result in terms of bone mineral density, lumbar spine projected area and growth velocity than bisphosphonate alone. The aim of these treatments should be to increase bone strength and thus reduce to the barest minimum the rate of fractures as well as prevent deformities of long bone and spine. This should improve the general well being of the affected individuals. However, despite these reports by the various researchers, of improvement in bone mineral density, linear growth, reduced rates of fractures and chronic bone pain, the ultimate goal of treatment is yet to be achieved. There are even concerns on how long treatment should be continued to achieve a sustained result, the safety of prolonged use of bisphosphonates on children, [9,34,35] as well as delay in healing of fractures after osteotomy. [36] Rauch et al., [36] observed very little benefit after 2 to 4 years of therapy. Even the documented weight increase, [31] is a source of concern as it s likely to affect negatively the rate of fractures and effective physical rehabilitation of the patients. Bone marrow transplant as a treatment strategy has been evaluated with documented improvement in linear growth, total body bone mineral content and reduction in fracture rate. [37] The principle behind this success stems from the fact that bone marrow mesenchymal cells could differentiate into a variety of tissues including bone and cartilage. The increased level of osteoblasts resulting from the transplant ultimately increases collagen formation. Although researchers [12] had earlier pointed out that the problem in OI is not a decrease in bone formation, rather an increase in bone resorption, it may be argued that the increased formation of osteoblasts are able to match the rate of resorption, resulting in the effects obtained. The question, like in the use of bisphosphonates, is the issue of long term benefit. There is no doubt that medical treatment has brought about some respite for children with OI, ultimately, a cure for OI is expected to stem from a re engineering or elimination of the mutated gene. The Gene therapy approach is being investigated as potential for future treatments of OI. [38] Until then, palliative treatment remains the only option. Conclusion OI is a rare inherited disorder, especially among blacks. This case has been reported as one of the few cases coming from Figure 1: The newborn while on admission Annals of Medical and Health Sciences Research Mar-Apr 2014 Vol 4 Special Issue 1 3
4 Africa. This report from Nigeria and other reports from other parts of Africa call for more alertness to identify the case of babies who may have OI. The review of literature highlights the challenges in the latest progress in the management. There is still need for further research toward improved morbidity of the disease and possibly a cure. References 1. Smith R. Disorders of the skeleton. In: Weatherall DJ, Ledingham JG, Warrell DA, editors. Oxford Textbook of Medicine. Oxford: Oxford University Press; p Burton BK, Charrow J. Other important single gene disorders. In: Green TP, Franklin WH, Tanz RR, editors. Pediatrics: Just the Facts. Boston: McGraw Hill; p Polousky JD, Eilert RE. Orthopedics. In: Hay WW, Levin MJ, Sondheimer JM, Deterding RR, editors. Current Pediatrics: Diagnosis and Treatment. Vol. 753, 19 th ed. New York: McGraw Hill; p Cabral WA, Chang W, Barnes AM, Weis M, Scott MA, Leikin S, et al. Prolyl 3 hydroxylase 1 deficiency causes a recessive metabolic bone disorder resembling lethal/severe osteogenesis imperfecta. Nat Genet 2007;39: Marini JC. Osteogenesis imperfecta. In: Nelson WE, Behrman RE, Kliegman RM, Arvin AM, editors. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 18 th ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company; p Ward LM, Rauch F, Travers R, Chabot G, Azouz EM, Lalic L, et al. Osteogenesis imperfecta type VII: An autosomal recessive form of brittle bone disease. Bone 2002;31: Glorieux FH, Rauch F, Plotkin H, Ward L, Travers R, Roughley P, et al. Type V osteogenesis imperfecta: A new form of brittle bone disease. J Bone Miner Res 2000;15: Sillence DO, Senn A, Danks DM. Genetic heterogeneity in osteogenesis imperfecta. J Med Genet 1979;16: Rauch F, Glorieux FH. Osteogenesis imperfecta. Lancet 2004;363: Stephens JD, Filly RA, Callen PW, Golbus MS. Prenatal diagnosis of osteogenesis imperfecta type II by real time ultrasound. Hum Genet 1983;64: Brailsford JF. Osteogenesis imperfecta. Br J Radiol 1943;16: Robichon J, Germain JP. Pathogenesis of osteogenesis imperfecta. Can Med Assoc J 1968;99: Carey MC, Fitzgerald O, McKiernan E. Osteogenesis imperfecta in twenty three members of a kindred with heritable features contributed by a non specific skeletal disorder. Q J Med 1968;37: Chawla S. Intrauterine osteogenesis imperfecta in four siblings. Br Med J 1964;1: Bauze RJ, Smith R, Francis MJ. A new look at osteogenesis imperfecta. A clinical, radiological and biochemical study of forty two patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1975;57: Plotkin H. Syndromes with congenital brittle bones. BMC Pediatr 2004;4: Akiode O, Ogunfowora OB, Shonubi A, Bajoma AA, Musa AA, Sotimehin SA. Osteogenesis imperfecta in a Nigerian baby. SICOT Online Report E049; [Last cited on 2012 Aug]. 18. Akinola R, Disu E, Adewale O. Osteogenesis imperfecta: A report of two cases. Internet J Pediatr Neonatol 2008;8(2). 19. Byers PH, Steiner RD. Osteogenesis imperfecta. Annu Rev Med 1992;43: Beighton P, Versfeld GA. On the paradoxically high relative prevalence of osteogenesis imperfecta type III in the black population of South Africa. Clin Genet 1985;27: Wallis GA, Sykes B, Byers PH, Mathew CG, Viljoen D, Beighton P. Osteogenesis imperfecta type III: Mutations in the type I collagen structural genes, COL1A1 and COL1A2, are not necessarily responsible. J Med Genet 1993;30: Armstrong O, Karayuba R, Ngendahayo L, Habonimana E. Osteogenesis imperfecta in monozygotic twins in Burundi. Med Trop (Mars) 1994;54: Fajolu IB, Ezeaka VC, Elumelu OJ, Onabajo OA, Ananti CH, Iroha EO et al. Osteogenesis Imperfecta in a set of Nigerian twins A case report. Internet J Pediatr Neonatol 2012;(14) doi: /2c Cubert R, Cheng EY, Mack S, Pepin MG, Byers PH. Osteogenesis imperfecta: Mode of delivery and neonatal outcome. Obstet Gynecol 2001;97: Albright JA. Systemic treatment of osteogenesis imperfecta. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1981;: Albright JA. Systemic treatment of osteogenesis imperfecta Historic review. Abstract of symposium II on osteogenesis imperfecta. Curr Orthop Pract 1976;116: Devogelaer JP, Malghem J, Maldague B, Nagant de Deuxchaisnes C. Radiological manifestations of bisphosphonate treatment with APD in a child suffering from osteogenesis imperfecta. Skeletal Radiol 1987;16: Plotkin H, Rauch F, Bishop NJ, Montpetit K, Ruck Gibis J, Travers R, et al. Pamidronate treatment of severe osteogenesis imperfecta in children under 3 years of age. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000;85: Glorieux FH, Bishop NJ, Plotkin H, Chabot G, Lanoue G, Travers R. Cyclic administration of pamidronate in children with severe osteogenesis imperfecta. N Engl J Med 1998;339: Falk MJ, Heeger S, Lynch KA, DeCaro KR, Bohach D, Gibson KS, et al. Intravenous bisphosphonate therapy in children with osteogenesis imperfecta. Pediatrics 2003;111: Zeitlin L, Rauch F, Plotkin H, Glorieux FH. Height and weight development during four years of therapy with cyclical intravenous pamidronate in children and adolescents with osteogenesis imperfecta types I, III, and IV. Pediatrics 2003;111: Bishop N, Harrison R, Ahmed F, Shaw N, Eastell R, Campbell M, et al. A randomized, controlled dose ranging study of risedronate in children with moderate and severe osteogenesis imperfecta. J Bone Miner Res 2010;25: Antoniazzi F, Monti E, Venturi G, Franceschi R, Doro F, Gatti D, et al. GH in combination with bisphosphonate treatment in osteogenesis imperfecta. Eur J Endocrinol 2010;163: Castillo H, Samson Fang L, American Academy for Cerebral Palsy and Developmental Medicine Treatment Outcomes Committee Review Panel. Effects of bisphosphonates in children with osteogenesis imperfecta: An AACPDM systematic review. Dev Med Child Neurol 2009;51: Marini JC. Do bisphosphonates make children s bones better 4 Annals of Medical and Health Sciences Research Mar-Apr 2014 Vol 4 Special Issue 1
5 or brittle? N Engl J Med 2003;349: Rauch F, Travers R, Glorieux FH. Pamidronate in children with osteogenesis imperfecta: Histomorphometric effects of long term therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006;91: Horwitz EM, Prockop DJ, Gordon PL, Koo WW, Fitzpatrick LA, Neel MD, et al. Clinical responses to bone marrow transplantation in children with severe osteogenesis imperfecta. Blood 2001;97: Niyibizi C, Wang S, Mi Z, Robbins PD. Gene therapy approaches for osteogenesis imperfecta. Gene Ther 2004;11: How to cite this article: Edelu BO, Ndu IK, Asinobi IN, Obu HA, Adimora GN. Osteogenesis imperfecta: A case report and review of literature. Ann Med Health Sci Res 2014;4:1-5. Source of Support: Nil. Conflict of Interest: None declared. Annals of Medical and Health Sciences Research Mar-Apr 2014 Vol 4 Special Issue 1 5
Osteogenesis Imperfecta In A Set Of Nigerian Twins A Case Report. I Fajolu, V Ezeaka, O Elumelu, O Onabajo, C Ananti, E Iroha, M Egri-Okwaji
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pediatrics and Neonatology Volume 14 Number 1 Osteogenesis Imperfecta In A Set Of Nigerian Twins A Case Report I Fajolu, V Ezeaka, O Elumelu, O Onabajo, C Ananti, E Iroha,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pediatrics and Neonatology Volume 14 Number 1 Osteogenesis Imperfecta In A Set Of Nigerian Twins A Case Report I Fajolu, V Ezeaka, O Elumelu, O Onabajo, C Ananti, E Iroha,
PROTOCOLS. Osteogenesis imperfecta. Principal investigator. Co-investigators. Background
 Osteogenesis imperfecta Principal investigator Leanne M. Ward, MD, FRCPC, paediatric endocrinologist Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Children s Hospital of Eastern Ontario, 401 Smyth Rd., Ottawa
Osteogenesis imperfecta Principal investigator Leanne M. Ward, MD, FRCPC, paediatric endocrinologist Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Children s Hospital of Eastern Ontario, 401 Smyth Rd., Ottawa
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation Vol. 7, Issue 4, October - December 2015
 ASSOCIATION OF BILATERAL RADIOULNAR SYNOSTOSIS WITH OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA TYPE 1 CASE PRESENTATION Valeriu V. Lupu 1, Mirabela Subotnicu 1, Ancuța Ignat 1, Gabriela Păduraru 1 *, Irina Naumcieff 1, Bogdan
ASSOCIATION OF BILATERAL RADIOULNAR SYNOSTOSIS WITH OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA TYPE 1 CASE PRESENTATION Valeriu V. Lupu 1, Mirabela Subotnicu 1, Ancuța Ignat 1, Gabriela Păduraru 1 *, Irina Naumcieff 1, Bogdan
Newborn with Fractures. Payal Patel, M.D. Pediatric Endocrinology Fellow May 22, 2014
 Newborn with Fractures Payal Patel, M.D. Pediatric Endocrinology Fellow May 22, 2014 Chief Complaint 2-day-old F with prenatally dx ed osteogenesis imperfecta (OI). HPI Born via repeat C/S to a 30 yo G3P2
Newborn with Fractures Payal Patel, M.D. Pediatric Endocrinology Fellow May 22, 2014 Chief Complaint 2-day-old F with prenatally dx ed osteogenesis imperfecta (OI). HPI Born via repeat C/S to a 30 yo G3P2
BISPHOSPHONATE THERAPY IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS WITH OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA
 14 CASE PRESENTATIONS BISPHOSPHONATE THERAPY IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS WITH OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA Alina Murgu 1, Roxana Cretu 2, Adnana Jaramani 2, Elena Macsim 3, Ana Maria Chiforeanu 2 1 Department of
14 CASE PRESENTATIONS BISPHOSPHONATE THERAPY IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS WITH OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA Alina Murgu 1, Roxana Cretu 2, Adnana Jaramani 2, Elena Macsim 3, Ana Maria Chiforeanu 2 1 Department of
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Congenita in a nigerian baby
 Osteogenesis Imperfecta Congenita in a nigerian baby O Akiode ( ), OB Ogunfowora, A. Shonubi, AA Bajomo, AA Musa & SA Sotimehin Olabisi Onabanjo University Teaching Hospital, Sagamu, Nigeria. Correspondence:
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Congenita in a nigerian baby O Akiode ( ), OB Ogunfowora, A. Shonubi, AA Bajomo, AA Musa & SA Sotimehin Olabisi Onabanjo University Teaching Hospital, Sagamu, Nigeria. Correspondence:
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. A severe case of osteogenesis imperfecta
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY A severe case of osteogenesis imperfecta October 2016 Pohl C, Kämpfen S, Filges I, Wellmann S, Division of Neonatology (PC, KS, WS), University of Basel Children s Hospital,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY A severe case of osteogenesis imperfecta October 2016 Pohl C, Kämpfen S, Filges I, Wellmann S, Division of Neonatology (PC, KS, WS), University of Basel Children s Hospital,
Bisphosphonate treatment in osteogenesis imperfecta: Which drug, for whom, for how long?
 Annals of Medicine. 2005; 37: 295 302 Bisphosphonate treatment in osteogenesis imperfecta: Which drug, for whom, for how long? FRANK RAUCH & FRANCIS H. GLORIEUX Genetics Unit, Shriners Hospital for Children
Annals of Medicine. 2005; 37: 295 302 Bisphosphonate treatment in osteogenesis imperfecta: Which drug, for whom, for how long? FRANK RAUCH & FRANCIS H. GLORIEUX Genetics Unit, Shriners Hospital for Children
= Developmental disorders of chondro-osseous tissue
 = Developmental disorders of chondro-osseous tissue Common Orthopedic Problems Dwarfism Short Stature Pathologic Short Stature Normal Variant Short Stature Proportionate Short Stature Midget Endocrine/nutritional
= Developmental disorders of chondro-osseous tissue Common Orthopedic Problems Dwarfism Short Stature Pathologic Short Stature Normal Variant Short Stature Proportionate Short Stature Midget Endocrine/nutritional
The Use of Bisphosphonates in Increasing Bone Mineral Density and Decreasing Fracture Occurrence in Children with Osteogenesis Imperfecta
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-8-2014 The Use of Bisphosphonates in Increasing Bone Mineral Density and Decreasing
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-8-2014 The Use of Bisphosphonates in Increasing Bone Mineral Density and Decreasing
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX
 DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
Efficacy of Bisphosphonates in Increasing Bone Mineral Density and Decreasing the Incidence of Fractures in Children with Osteogenesis Imperfecta
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects 8-14-2010 Efficacy of Bisphosphonates in Increasing Bone Mineral Density and Decreasing
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects 8-14-2010 Efficacy of Bisphosphonates in Increasing Bone Mineral Density and Decreasing
THE RISK OF ITERATIVE FRACTURES IN PATIENTS WITH OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA - CASE REPORT
 Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2017 vol. 121, no. 1 SURGERY CASE REPORTS THE RISK OF ITERATIVE FRACTURES IN PATIENTS WITH OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA - CASE REPORT D. Popescu 1*, B. Puha 1, B. Veliceasa
Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2017 vol. 121, no. 1 SURGERY CASE REPORTS THE RISK OF ITERATIVE FRACTURES IN PATIENTS WITH OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA - CASE REPORT D. Popescu 1*, B. Puha 1, B. Veliceasa
Scholars Journal of Medical Case Reports
 Scholars Journal of Medical Case Reports Sch J Med Case Rep 2016; 4(4):265-269 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publishers (SAS Publishers) (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Medical Case Reports Sch J Med Case Rep 2016; 4(4):265-269 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publishers (SAS Publishers) (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Benefits of pamidronate in children with osteogenesis imperfecta: an open prospective study
 Joint Bone Spine 72 (2005) 313 318 http://france.elsevier.com/direct/bonsoi/ Original article Benefits of pamidronate in children with osteogenesis imperfecta: an open prospective study Véronique Forin
Joint Bone Spine 72 (2005) 313 318 http://france.elsevier.com/direct/bonsoi/ Original article Benefits of pamidronate in children with osteogenesis imperfecta: an open prospective study Véronique Forin
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases
 Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names Osteogenesis Imperfecta
NATIONAL COALITION FOR OSTEOPOROSIS AND RELATED BONE DISEASES
 NATIONAL COALITION FOR OSTEOPOROSIS AND RELATED BONE DISEASES Fact Sheet FY 2007 What is the Mission of the Bone Coalition? The National Coalition for Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases is dedicated
NATIONAL COALITION FOR OSTEOPOROSIS AND RELATED BONE DISEASES Fact Sheet FY 2007 What is the Mission of the Bone Coalition? The National Coalition for Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases is dedicated
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Types I-XI
 Beyond the Basics Ksenia Zukowsky, PhD, APRN, NNP-BC Section Editor 3.0 HOURS Continuing Education Osteogenesis Imperfecta Types I-XI Implications for the Neonatal Nurse Jody Womack, RNC-NIC, NNP-BC, MS
Beyond the Basics Ksenia Zukowsky, PhD, APRN, NNP-BC Section Editor 3.0 HOURS Continuing Education Osteogenesis Imperfecta Types I-XI Implications for the Neonatal Nurse Jody Womack, RNC-NIC, NNP-BC, MS
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a genetically determined
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Dysplasia in Children With Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Association With Collagen Type I C-Propeptide Mutations Waleed Kishta, MBBCH, PhD, FRCSC,*w Fahad H. Abduljabbar, MBBS, FRCSC,*z
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Dysplasia in Children With Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Association With Collagen Type I C-Propeptide Mutations Waleed Kishta, MBBCH, PhD, FRCSC,*w Fahad H. Abduljabbar, MBBS, FRCSC,*z
Fracture of mandible during yawning in a patient with osteogenesis imperfecta
 1 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, King George s Medical University, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India 2 King George s Medical University, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India 3 Department of Medicine,
1 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, King George s Medical University, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India 2 King George s Medical University, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India 3 Department of Medicine,
Association between spondylolisthesis and L5 fracture in patients with Osteogenesis Imperfecta
 DOI 10.1007/s00586-014-3737-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Association between spondylolisthesis and L5 fracture in patients with Osteogenesis Imperfecta Pietro Persiani Jole Graci Claudia de Cristo Giovanni Noia
DOI 10.1007/s00586-014-3737-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Association between spondylolisthesis and L5 fracture in patients with Osteogenesis Imperfecta Pietro Persiani Jole Graci Claudia de Cristo Giovanni Noia
Fibrous Dysplasia in Children. Professor Nick Shaw Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK
 Fibrous Dysplasia in Children Professor Nick Shaw Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK Overview What is Fibrous Dysplasia? Clinical Presentations Endocrine Problems Skeletal Problems Treatment Options Fibrous
Fibrous Dysplasia in Children Professor Nick Shaw Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK Overview What is Fibrous Dysplasia? Clinical Presentations Endocrine Problems Skeletal Problems Treatment Options Fibrous
OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA
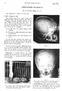 46 SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL V01. I. No. 1 March. 1960 OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA By A. Lim Siew Meng, M.B., B.S. The following is a report of three cases. CASE I (Figures 1-8) This Chinese boy, L.C.S., aged
46 SINGAPORE MEDICAL JOURNAL V01. I. No. 1 March. 1960 OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA By A. Lim Siew Meng, M.B., B.S. The following is a report of three cases. CASE I (Figures 1-8) This Chinese boy, L.C.S., aged
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a heritable disorder
 Height and Weight Development During Four Years With Cyclical Intravenous Pamidronate in Children and Adolescents With Osteogenesis Imperfecta Types I, III, and IV Leonid Zeitlin, MD; Frank Rauch, MD;
Height and Weight Development During Four Years With Cyclical Intravenous Pamidronate in Children and Adolescents With Osteogenesis Imperfecta Types I, III, and IV Leonid Zeitlin, MD; Frank Rauch, MD;
Effects of bisphosphonates in children with osteogenesis imperfecta: an AACPDM systematic review
 DEVELOPMENTAL MEDICINE & CHILD NEUROLOGY REVIEW Effects of bisphosphonates in children with osteogenesis imperfecta: an AACPDM systematic review HEIDI CASTILLO MD 1 LISA SAMSON-FANG MD 2 * ON BEHALF OF
DEVELOPMENTAL MEDICINE & CHILD NEUROLOGY REVIEW Effects of bisphosphonates in children with osteogenesis imperfecta: an AACPDM systematic review HEIDI CASTILLO MD 1 LISA SAMSON-FANG MD 2 * ON BEHALF OF
CYCLIC ADMINISTRATION OF PAMIDRONATE THERAPY IN CHILDREN WITH SEVERE OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA
 CYCLIC ADMINISTRATION OF PAMIDRONATE THERAPY IN CHILDREN WITH SEVERE OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA CYCLIC ADMINISTRATION OF PAMIDRONATE IN CHILDREN WITH SEVERE OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA FRANCIS H. GLORIEUX, M.D.,
CYCLIC ADMINISTRATION OF PAMIDRONATE THERAPY IN CHILDREN WITH SEVERE OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA CYCLIC ADMINISTRATION OF PAMIDRONATE IN CHILDREN WITH SEVERE OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA FRANCIS H. GLORIEUX, M.D.,
Cleidocranial Dysplasia
 BRIEF REPORTS Cleidocranial Dysplasia Anita Sharma Rohtash Yadav Kuldip Ahlawat Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD), is characterized by short stature, typical facial features and variable degree of pan-skeletal
BRIEF REPORTS Cleidocranial Dysplasia Anita Sharma Rohtash Yadav Kuldip Ahlawat Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD), is characterized by short stature, typical facial features and variable degree of pan-skeletal
BMC Pediatrics. Debate Syndromes with congenital brittle bones Horacio Plotkin* Open Access. Abstract
 BMC Pediatrics BioMed Central Debate Syndromes with congenital brittle bones Horacio Plotkin* Open Access Address: Inherited Metabolic Diseases Section, Department of Pediatrics, University of Nebraska
BMC Pediatrics BioMed Central Debate Syndromes with congenital brittle bones Horacio Plotkin* Open Access Address: Inherited Metabolic Diseases Section, Department of Pediatrics, University of Nebraska
Contents available at PubMed Gac Med Mex. 2015;151:152-6
 Contents available at PubMed www.anmm.org.mx PERMANYER Gac Med Mex. 2015;151:152-6 www.permanyer.com 152 GACETA MÉDICA DE MÉXICO Zoledronic acid (zoledronate) in children with osteogenesis imperfecta (OI)
Contents available at PubMed www.anmm.org.mx PERMANYER Gac Med Mex. 2015;151:152-6 www.permanyer.com 152 GACETA MÉDICA DE MÉXICO Zoledronic acid (zoledronate) in children with osteogenesis imperfecta (OI)
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type I Caused by a Novel Mutation in the Start Codon of the COL1A1 Gene in a Korean Family
 100 Available online at www.annclinlabsci.org Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 45, no. 1, 2015 Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type I Caused by a Novel Mutation in the Start Codon of the COL1A1 Gene
100 Available online at www.annclinlabsci.org Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 45, no. 1, 2015 Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type I Caused by a Novel Mutation in the Start Codon of the COL1A1 Gene
Audiologic and Genetic Determination of Hearing Loss in Osteogenesis Imperfecta
 Ghent University Hospital Ghent University Audiologic and Genetic Determination of Hearing Loss in Osteogenesis Imperfecta Swinnen F 1, De Leenheer E 1, Coucke P 2, Cremers C 3, Dhooge I 1 1 Department
Ghent University Hospital Ghent University Audiologic and Genetic Determination of Hearing Loss in Osteogenesis Imperfecta Swinnen F 1, De Leenheer E 1, Coucke P 2, Cremers C 3, Dhooge I 1 1 Department
Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Congenital Defects - Clubfoot (congenital equinovarus) Forefoot is adducted and supinated o Positional equinovarus o Idiopathic congenital equinovarus
Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Congenital Defects - Clubfoot (congenital equinovarus) Forefoot is adducted and supinated o Positional equinovarus o Idiopathic congenital equinovarus
A new COL1A1 mutation in a Greek patient with osteogenesis imperfecta: Response to a low-dose protocol of zoledronic acid and two-year follow-up
 Journal of Research and Practice on the Musculoskeletal System JOURNAL OF RESEARCH AND PRACTICE Case Report A new COL1A1 mutation in a Greek patient with osteogenesis imperfecta: Response to a low-dose
Journal of Research and Practice on the Musculoskeletal System JOURNAL OF RESEARCH AND PRACTICE Case Report A new COL1A1 mutation in a Greek patient with osteogenesis imperfecta: Response to a low-dose
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Peripartal management of a prenatally diagnosed large oral cyst
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Peripartal management of a prenatally diagnosed large oral cyst May 2007 2 Fontana M, Berger TM, Winiker H, Jöhr M, Nagel H, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (FM,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Peripartal management of a prenatally diagnosed large oral cyst May 2007 2 Fontana M, Berger TM, Winiker H, Jöhr M, Nagel H, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (FM,
Radiographic Appearance Of Primary Hyperparathyroidism With Atypical Parathyroid Adenoma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 6 Number 2 Radiographic Appearance Of Primary Hyperparathyroidism With Atypical Parathyroid Adenoma P George, N Philip, B Pawar Citation P George,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Internal Medicine Volume 6 Number 2 Radiographic Appearance Of Primary Hyperparathyroidism With Atypical Parathyroid Adenoma P George, N Philip, B Pawar Citation P George,
Overview. Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases. People Centred Positive Compassion Excellence
 Overview Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Dr Chandini Rao Consultant Rheumatologist Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases Bone Biology Osteoporosis Increased bone remodelling
Overview Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Dr Chandini Rao Consultant Rheumatologist Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases Bone Biology Osteoporosis Increased bone remodelling
Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteoporosis. Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism Ajou University School of Medicine.
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteoporosis Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism Ajou University School of Medicine Yoon-Sok CHUNG WCIM, COEX, Seoul, 27Oct2014 Case 1 71-year old woman Back pain Emergency
Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteoporosis Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism Ajou University School of Medicine Yoon-Sok CHUNG WCIM, COEX, Seoul, 27Oct2014 Case 1 71-year old woman Back pain Emergency
a Genetics Unit, Department of Paediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, University of Received 29 June 2004 Accepted 3 November 2004
 Original article 1 Further delineation of Al-Gazali syndrome (multiple skeletal abnormalities with anterior segment anomalies of the eye and early lethality) in a Malaysian family Meow-Keong Thong a, Lee-Gaik
Original article 1 Further delineation of Al-Gazali syndrome (multiple skeletal abnormalities with anterior segment anomalies of the eye and early lethality) in a Malaysian family Meow-Keong Thong a, Lee-Gaik
A radiological perspective of assessing neonatal respiratory distress syndrome
 Original Research Article A radiological perspective of assessing neonatal respiratory distress syndrome Jayesh Shah 1, Nikhil Parvatkar 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident,
Original Research Article A radiological perspective of assessing neonatal respiratory distress syndrome Jayesh Shah 1, Nikhil Parvatkar 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident,
Esther Briganti. Fetal And Maternal Health Beyond the Womb: hot topics in endocrinology and pregnancy. Endocrinologist and Clinician Researcher
 Fetal And Maternal Health Beyond the Womb: hot topics in endocrinology and pregnancy Esther Briganti Endocrinologist and Clinician Researcher Director, Melbourne Endocrine Associates Associate Professor,
Fetal And Maternal Health Beyond the Womb: hot topics in endocrinology and pregnancy Esther Briganti Endocrinologist and Clinician Researcher Director, Melbourne Endocrine Associates Associate Professor,
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta
 The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
Deficiency of Cartilage-Associated Protein in Recessive Lethal Osteogenesis Imperfecta
 The new england journal of medicine brief report Deficiency of Cartilage-Associated Protein in Recessive Lethal Osteogenesis Imperfecta Aileen M. Barnes, M.S., Weizhong Chang, Ph.D., Roy Morello, Ph.D.,
The new england journal of medicine brief report Deficiency of Cartilage-Associated Protein in Recessive Lethal Osteogenesis Imperfecta Aileen M. Barnes, M.S., Weizhong Chang, Ph.D., Roy Morello, Ph.D.,
CASE 1 WHY IS IT IMPORTANT TO TREAT? FACTS CONCERNS
 4:30-5:15pm Ask the Expert: Osteoporosis SPEAKERS Silvina Levis, MD OSTEOPOROSIS - FACTS 1:3 older women and 1:5 older men will have a fragility fracture after age 50 After 3 years of treatment, depending
4:30-5:15pm Ask the Expert: Osteoporosis SPEAKERS Silvina Levis, MD OSTEOPOROSIS - FACTS 1:3 older women and 1:5 older men will have a fragility fracture after age 50 After 3 years of treatment, depending
Quality of life in children with osteogenesis imperfecta treated with oral bisphosphonates (Olpadronate): a 2-year randomized placebo-controlled trial
 Eur J Pediatr (2007) 166:1155 1161 DOI 10.1007/s00431-006-0399-2 ORIGINAL PAPER Quality of life in children with osteogenesis imperfecta treated with oral bisphosphonates (Olpadronate): a 2-year randomized
Eur J Pediatr (2007) 166:1155 1161 DOI 10.1007/s00431-006-0399-2 ORIGINAL PAPER Quality of life in children with osteogenesis imperfecta treated with oral bisphosphonates (Olpadronate): a 2-year randomized
Bone Stimulators and Their Use in Horses and People
 Bone Stimulators and Their Use in Horses and People New Mexico Supercomputing Challenge Final Report April 2, 2014 Team Number 6 Annunciation Catholic School Team Members Evan Donnelly Moira Donnelly Andreana
Bone Stimulators and Their Use in Horses and People New Mexico Supercomputing Challenge Final Report April 2, 2014 Team Number 6 Annunciation Catholic School Team Members Evan Donnelly Moira Donnelly Andreana
Genetics Questions: There are 15 questions in total. The answers can be found on the accompanying document
 Page 1 Genetics Questions: These questions are aimed at medical and allied health professionals and they are designed to show where genetics has a role in clinical practice. There are 15 questions in total
Page 1 Genetics Questions: These questions are aimed at medical and allied health professionals and they are designed to show where genetics has a role in clinical practice. There are 15 questions in total
Coverage Guidelines. Genetic Testing and Counseling for Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS)
 Coverage Guidelines Genetic Testing and Counseling for Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS) Disclaimer: Please note that Baptist Health Plan Coverage Guidelines may be updated throughout the year. A printed version
Coverage Guidelines Genetic Testing and Counseling for Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS) Disclaimer: Please note that Baptist Health Plan Coverage Guidelines may be updated throughout the year. A printed version
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Diaphyseal Femur Fractures in Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Characteristics and Relationship With Bisphosphonate Treatment
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JBMR Diaphyseal Femur Fractures in Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Characteristics and Relationship With Bisphosphonate Treatment Pamela Trejo, FranScois Fassier, Francis H Glorieux, and Frank
ORIGINAL ARTICLE JBMR Diaphyseal Femur Fractures in Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Characteristics and Relationship With Bisphosphonate Treatment Pamela Trejo, FranScois Fassier, Francis H Glorieux, and Frank
DXA When to order? How to interpret? Dr Nikhil Tandon Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi
 DXA When to order? How to interpret? Dr Nikhil Tandon Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi Clinical Utility of Bone Densitometry Diagnosis (DXA)
DXA When to order? How to interpret? Dr Nikhil Tandon Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi Clinical Utility of Bone Densitometry Diagnosis (DXA)
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type VI: A Form of Brittle Bone Disease with a Mineralization Defect*
 JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH Volume 17, Number 1, 2002 2002 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type VI: A Form of Brittle Bone Disease with a Mineralization
JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH Volume 17, Number 1, 2002 2002 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Osteogenesis Imperfecta Type VI: A Form of Brittle Bone Disease with a Mineralization
Congenital hypothyroidism and your child
 Congenital hypothyroidism and your child Contributed by Sirisha Kusuma. B Consultant Pediatric Endocrinologist Rainbow Children s hospital What is Thyroid? The thyroid is a small butterfly shaped endocrine
Congenital hypothyroidism and your child Contributed by Sirisha Kusuma. B Consultant Pediatric Endocrinologist Rainbow Children s hospital What is Thyroid? The thyroid is a small butterfly shaped endocrine
Hypophosphatasia. Tom Blevins, MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, TX
 Hypophosphatasia Tom Blevins, MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, TX Hypophosphatasia Case Teeth 57 y/o male with a hyperlipidemia and hypogonadism. Noted to have an alkaline phosphatase of
Hypophosphatasia Tom Blevins, MD Texas Diabetes and Endocrinology Austin, TX Hypophosphatasia Case Teeth 57 y/o male with a hyperlipidemia and hypogonadism. Noted to have an alkaline phosphatase of
Yorkshire and Humber Neonatal ODN (South) Clinical Guideline
 Yorkshire and Humber Neonatal ODN (South) Clinical Guideline Title: Author: NEONATAL BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURY Rebecca Musson Date written: January 2011, reviewed January 2016 Review date: January 2019 This
Yorkshire and Humber Neonatal ODN (South) Clinical Guideline Title: Author: NEONATAL BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURY Rebecca Musson Date written: January 2011, reviewed January 2016 Review date: January 2019 This
Genetic examination of diseases affecting bone development. and structure in newborns
 Genetic examination of diseases affecting bone development and structure in newborns Examination of molecular genetic markers in osteopenic preterm infants PhD Thesis Simone Funke, MD University of Pécs
Genetic examination of diseases affecting bone development and structure in newborns Examination of molecular genetic markers in osteopenic preterm infants PhD Thesis Simone Funke, MD University of Pécs
Management of Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
 Background and Prevalence Management of Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Pregestational Diabetes - 8 million women in the US are affected, complicating 1% of all pregnancies. Type II is
Background and Prevalence Management of Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Pregestational Diabetes - 8 million women in the US are affected, complicating 1% of all pregnancies. Type II is
Assessment and Treatment of Osteoporosis Professor T.Masud
 Assessment and Treatment of Osteoporosis Professor T.Masud Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust University of Nottingham University of Derby University of Southern Denmark What is Osteoporosis? Osteoporosis
Assessment and Treatment of Osteoporosis Professor T.Masud Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust University of Nottingham University of Derby University of Southern Denmark What is Osteoporosis? Osteoporosis
Prenatal Ultrasonographic Diagnosis of Proximal Focal Femoral Deficiency
 Prenatal Ultrasonographic Diagnosis of Proximal Focal Femoral Deficiency Ravi D Wadhwa, Madhusudan Dey, Anupam Kapur, Vipin Kumar Fetal Medicine Div, Department of Obstetric and Gynecology, Armed Forces
Prenatal Ultrasonographic Diagnosis of Proximal Focal Femoral Deficiency Ravi D Wadhwa, Madhusudan Dey, Anupam Kapur, Vipin Kumar Fetal Medicine Div, Department of Obstetric and Gynecology, Armed Forces
Vertebral morphometry in children and adolescents with osteogenesis imperfecta: Effect of intravenous pamidronate treatment
 Bone 39 (2006) 901 906 www.elsevier.com/locate/bone Vertebral morphometry in children and adolescents with osteogenesis imperfecta: Effect of intravenous pamidronate treatment Christof Land, Frank Rauch,
Bone 39 (2006) 901 906 www.elsevier.com/locate/bone Vertebral morphometry in children and adolescents with osteogenesis imperfecta: Effect of intravenous pamidronate treatment Christof Land, Frank Rauch,
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS
 OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
APPLICATION FORM FOR FELLOWSHIPS
 APPLICATION FORM FOR FELLOWSHIPS Name of Institution: Shriners Hospital for Children Location: Shriners Hospital for Children 1529 Cedar Avenue Montreal, Quebec H3G 1A6 2C7 Tel: (514) 842 5964 Fax: (514)
APPLICATION FORM FOR FELLOWSHIPS Name of Institution: Shriners Hospital for Children Location: Shriners Hospital for Children 1529 Cedar Avenue Montreal, Quebec H3G 1A6 2C7 Tel: (514) 842 5964 Fax: (514)
BRITTLE BONES, UNBREAKABLE SPIRIT: OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA Subhra Mandal * 1, Prabir Mandal 2, Panchanan Kundu 3.
 Case Report BRITTLE BONES, UNBREAKABLE SPIRIT: OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA Subhra Mandal * 1, Prabir Mandal 2, Panchanan Kundu 3. ABSTRACT International Journal of Anatomy and Research, Int J Anat Res 2015,
Case Report BRITTLE BONES, UNBREAKABLE SPIRIT: OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA Subhra Mandal * 1, Prabir Mandal 2, Panchanan Kundu 3. ABSTRACT International Journal of Anatomy and Research, Int J Anat Res 2015,
Bone mechanics bone strength and beyond
 Bone mechanics bone strength and beyond Tim Arnett Bone Curriculum Symposium 2018 Department of Cell & Developmental Biology University College London Factors affecting bone strength Mass Architectural
Bone mechanics bone strength and beyond Tim Arnett Bone Curriculum Symposium 2018 Department of Cell & Developmental Biology University College London Factors affecting bone strength Mass Architectural
CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE. Dr. Bahar Naghavi
 2 CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE Dr. Bahar Naghavi Assistant professor of Basic Science Department, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran,Iran 3 Introduction Over 4000
2 CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE Dr. Bahar Naghavi Assistant professor of Basic Science Department, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran,Iran 3 Introduction Over 4000
The clinical and radiological assessment of cyclic intravenous pamidronate administration in children with osteogenesis imperfecta
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2004; 46: 322-328 Original The clinical and radiological assessment of cyclic intravenous pamidronate administration in children with osteogenesis imperfecta Pelin Adýyaman,
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2004; 46: 322-328 Original The clinical and radiological assessment of cyclic intravenous pamidronate administration in children with osteogenesis imperfecta Pelin Adýyaman,
Awaisheh. Mousa Al-Abbadi. Abdullah Alaraj. 1 Page
 f #3 Awaisheh Abdullah Alaraj Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 Page *This sheet was written from Section 1 s lecture, in the first 10 mins the Dr. repeated all the previous material relating to osteoporosis from the
f #3 Awaisheh Abdullah Alaraj Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 Page *This sheet was written from Section 1 s lecture, in the first 10 mins the Dr. repeated all the previous material relating to osteoporosis from the
A Genetic Overview of Hypophosphatasia
 A Genetic Overview of Hypophosphatasia A Background in Genetics Cells are the basic building blocks of all living organisms. Our body is composed of trillions of cells. Each of these cells contains deoxyribonucleic
A Genetic Overview of Hypophosphatasia A Background in Genetics Cells are the basic building blocks of all living organisms. Our body is composed of trillions of cells. Each of these cells contains deoxyribonucleic
BONE HEALTH Dr. Tia Lillie. Exercise, Physical Activity and Osteoporosis
 BONE HEALTH Dr. Tia Lillie Exercise, Physical Activity and Osteoporosis Food for thought... How old would you be if you didn t know how old you were? DEFINITION: Osteoporosis Osteoporosis (OP) is a disease
BONE HEALTH Dr. Tia Lillie Exercise, Physical Activity and Osteoporosis Food for thought... How old would you be if you didn t know how old you were? DEFINITION: Osteoporosis Osteoporosis (OP) is a disease
Pediatrics. Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (PKD) Symptoms and Treatment. Definition. Epidemiology of Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency.
 Pediatrics Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (PKD) Symptoms and Treatment See online here Pyruvate kinase deficiency is an inherited metabolic disorder characterized by a deficiency in the enzyme "pyruvate kinase"
Pediatrics Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (PKD) Symptoms and Treatment See online here Pyruvate kinase deficiency is an inherited metabolic disorder characterized by a deficiency in the enzyme "pyruvate kinase"
Case A rare case of polycarpyly in a patient with Ellis - van Creveld syndrome: plain film findings and additional value of MRI.
 Case 12659 A rare case of polycarpyly in a patient with Ellis - van Creveld syndrome: plain film findings and additional value of MRI. M. Mespreuve 1, 2 F. Vanhoenacker 1, 2 F. Malfait 3 D. Mortier 4 G.
Case 12659 A rare case of polycarpyly in a patient with Ellis - van Creveld syndrome: plain film findings and additional value of MRI. M. Mespreuve 1, 2 F. Vanhoenacker 1, 2 F. Malfait 3 D. Mortier 4 G.
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Genetic Counseling I- Introduction II- Motives for genetic counseling requests II-1. Couple before reproduction II-2. Couple at risk III-
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Genetic Counseling I- Introduction II- Motives for genetic counseling requests II-1. Couple before reproduction II-2. Couple at risk III-
NEONATOLOGY Healthy newborn. Neonatal sequelaes
 NEONATOLOGY Healthy newborn. Neonatal sequelaes Ágnes Harmath M.D. Ph.D. senior lecturer 11. November 2016. Tasks of the neonatologist Prenatal diagnosed condition Inform parents, preparation of necessary
NEONATOLOGY Healthy newborn. Neonatal sequelaes Ágnes Harmath M.D. Ph.D. senior lecturer 11. November 2016. Tasks of the neonatologist Prenatal diagnosed condition Inform parents, preparation of necessary
Potential implications of cell therapy for osteogenesis imperfecta
 REVIEW Potential implications of cell therapy for osteogenesis imperfecta Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a brittle-bone disease whose hallmark is bone fragility. Since the disease is genetic, there is
REVIEW Potential implications of cell therapy for osteogenesis imperfecta Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a brittle-bone disease whose hallmark is bone fragility. Since the disease is genetic, there is
Paget s Disease of Bone
 Paget s Disease of Bone Copyright Copyright 2019 American 2019 American Associa7on Associa7on of Clinical of Clinical Endocrinologists Endocrinologists 1 A Common Bone Disorder Paget s disease of bone
Paget s Disease of Bone Copyright Copyright 2019 American 2019 American Associa7on Associa7on of Clinical of Clinical Endocrinologists Endocrinologists 1 A Common Bone Disorder Paget s disease of bone
Hypercalcemia and hypercalciuria during denosumab treatment in children with osteogenesis imperfecta type VI
 J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 2018; 18(1):76-80 Journal of Musculoskeletal and Neuronal Interactions Case Report Article Hypercalcemia and hypercalciuria during denosumab treatment in children with
J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 2018; 18(1):76-80 Journal of Musculoskeletal and Neuronal Interactions Case Report Article Hypercalcemia and hypercalciuria during denosumab treatment in children with
Severity of Hypoxic Ischaemic Encephalopathy in Neonates with Birth Asphyxia
 Journal of Rawalpindi Medical College (JRMC); 2007; (): 8-22 Severity of Hypoxic Ischaemic Encephalopathy in Neonates with Birth Asphyxia Rubina Zulfiqar, Samiya Naeemullah Department of Paediatrics, Holy
Journal of Rawalpindi Medical College (JRMC); 2007; (): 8-22 Severity of Hypoxic Ischaemic Encephalopathy in Neonates with Birth Asphyxia Rubina Zulfiqar, Samiya Naeemullah Department of Paediatrics, Holy
Growth, Development, Nutrition & Ageing Module Year 1 Semester 2 Credits - 4 Duration: 3 weeks (15 days)
 Growth, Development, Nutrition & Ageing Module Year 1 Semester 2 Credits - 4 Duration: 3 weeks (15 days) Concept Objectives Time Dept. in - Charge T / L Activity At the end of the module, the students
Growth, Development, Nutrition & Ageing Module Year 1 Semester 2 Credits - 4 Duration: 3 weeks (15 days) Concept Objectives Time Dept. in - Charge T / L Activity At the end of the module, the students
Anthropometry of patients with osteogenesis imperfecta
 54 Arch Dis Child 1999;8:54 58 Department of Clinical Genetics, Rigshospitalet 46, Blegdamsvej 9, DK-1 Copenhagen, Denmark A M Lund F Skovby Department of Growth and Reproduction, Rigshospitalet 564, Blegdamsvej
54 Arch Dis Child 1999;8:54 58 Department of Clinical Genetics, Rigshospitalet 46, Blegdamsvej 9, DK-1 Copenhagen, Denmark A M Lund F Skovby Department of Growth and Reproduction, Rigshospitalet 564, Blegdamsvej
Download slides:
 Download slides: https://www.tinyurl.com/m67zcnn https://tinyurl.com/kazchbn OSTEOPOROSIS REVIEW AND UPDATE Boca Raton Regional Hospital Internal Medicine Conference 2017 Benjamin Wang, M.D., FRCPC Division
Download slides: https://www.tinyurl.com/m67zcnn https://tinyurl.com/kazchbn OSTEOPOROSIS REVIEW AND UPDATE Boca Raton Regional Hospital Internal Medicine Conference 2017 Benjamin Wang, M.D., FRCPC Division
Significance of radiological appearance of ossific femoral nucleus in diagnosis of developmental hip dysplasia
 Significance of radiological appearance of ossific femoral nucleus in diagnosis of developmental hip dysplasia, MBChB, D Orth, MSc. Abstract: The aim of the study to determine the benefit of delaying appearance
Significance of radiological appearance of ossific femoral nucleus in diagnosis of developmental hip dysplasia, MBChB, D Orth, MSc. Abstract: The aim of the study to determine the benefit of delaying appearance
Clinical Analysis of Femur Shaft Insufficiency Fractures
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:227-233 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.3.227 Clinical Analysis of Femur Shaft Insufficiency Fractures Sang-Bong Ko, MD, Sang-Wook Lee, MD, Chang-Min
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:227-233 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.3.227 Clinical Analysis of Femur Shaft Insufficiency Fractures Sang-Bong Ko, MD, Sang-Wook Lee, MD, Chang-Min
Pathophysiology. Tutorial 1 Genetic Diseases
 Pathophysiology Tutorial 1 Genetic Diseases ILOs Analyze genetic pedigrees and recognize the mode of inheritance of diseases. Differentiate between patterns of inheritance based on the type of the protein
Pathophysiology Tutorial 1 Genetic Diseases ILOs Analyze genetic pedigrees and recognize the mode of inheritance of diseases. Differentiate between patterns of inheritance based on the type of the protein
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم. Rickets
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Rickets 1 Rickets IS defined as failure of mineralization of growing bone or osteoid tissue due to vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D appear as rickets in children and as oteomalacia
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Rickets 1 Rickets IS defined as failure of mineralization of growing bone or osteoid tissue due to vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D appear as rickets in children and as oteomalacia
Intramedullary Rodding and Bisphosphonate Treatment of Polyostotic Fibrous Dysplasia Associated With the. rodding McCune-Albright syndrome.
 Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 22:255 260 2002 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Intramedullary Rodding and Bisphosphonate Treatment of Polyostotic Fibrous Dysplasia Associated With
Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 22:255 260 2002 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Intramedullary Rodding and Bisphosphonate Treatment of Polyostotic Fibrous Dysplasia Associated With
Trebeculae. Step 4. compact bone. Diploë Pearson Education, Inc.
 Trebeculae compact bone Step 4 Diploë Abnormalities in bone growth Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) autosomal dominant, Codon 206: Arg à Hist 1 : 2, 000, 000 endothelial cells à mesenchymal
Trebeculae compact bone Step 4 Diploë Abnormalities in bone growth Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) autosomal dominant, Codon 206: Arg à Hist 1 : 2, 000, 000 endothelial cells à mesenchymal
Good News Santa Monica!
 Children s Hospital Los Angeles Santa Monica is located in the Saint John s Medical Plaza, one block northeast of St. John s Health Center. 1301 20th St., Ste. 460, Santa Monica, CA 90404 Appointments:
Children s Hospital Los Angeles Santa Monica is located in the Saint John s Medical Plaza, one block northeast of St. John s Health Center. 1301 20th St., Ste. 460, Santa Monica, CA 90404 Appointments:
DOWNLOAD OR READ : DISORDERS OF BONE AND MINERAL METABOLISM PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : DISORDERS OF BONE AND MINERAL METABOLISM PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 disorders of bone and mineral metabolism disorders of bone and pdf disorders of bone and mineral metabolism
DOWNLOAD OR READ : DISORDERS OF BONE AND MINERAL METABOLISM PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 disorders of bone and mineral metabolism disorders of bone and pdf disorders of bone and mineral metabolism
Bone Health in Children with Physical Disabilities AACPDM 2014: BRK 10
 Bone Health in Children with Physical Disabilities AACPDM 2014: BRK 10 Steven Bachrach, MD Tessa Gresley-Jones, MN, NP-Paeds Disclosure Information AACPDM 68 th Annual Meeting Sept 10-13, 2014 Speaker
Bone Health in Children with Physical Disabilities AACPDM 2014: BRK 10 Steven Bachrach, MD Tessa Gresley-Jones, MN, NP-Paeds Disclosure Information AACPDM 68 th Annual Meeting Sept 10-13, 2014 Speaker
Permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus. Case Report
 Rawal Medical Journal An official publication of Pakistan Medical Association Rawalpindi Islamabad branch Established 1975 Volume 36 Number 4 October - December 2011 Case Report Permanent neonatal diabetes
Rawal Medical Journal An official publication of Pakistan Medical Association Rawalpindi Islamabad branch Established 1975 Volume 36 Number 4 October - December 2011 Case Report Permanent neonatal diabetes
Submission to the National Institute for Clinical Excellence on
 Submission to the National Institute for Clinical Excellence on Strontium ranelate for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis by The Society for Endocrinology
Submission to the National Institute for Clinical Excellence on Strontium ranelate for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis by The Society for Endocrinology
The Effect of Valvular Heart Diseases on Maternal and Fetal Outcome of Pregnancy Nada Salih Ameen*,Nawfal Fawzi Anwer**
 THE VALVULAR IRAQI POSTGRADUATE HEART DISEASES MEDICAL AND JOURNAL PREGNANCY The Effect of Valvular Heart Diseases on Maternal and Fetal Outcome of Pregnancy Nada Salih Ameen*,Nawfal Fawzi Anwer** ABSTRACT:
THE VALVULAR IRAQI POSTGRADUATE HEART DISEASES MEDICAL AND JOURNAL PREGNANCY The Effect of Valvular Heart Diseases on Maternal and Fetal Outcome of Pregnancy Nada Salih Ameen*,Nawfal Fawzi Anwer** ABSTRACT:
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Invasive Prenatal (Fetal) Diagnostic Testing File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: invasive_prenatal_(fetal)_diagnostic_testing 12/2014 3/2018
Corporate Medical Policy Invasive Prenatal (Fetal) Diagnostic Testing File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: invasive_prenatal_(fetal)_diagnostic_testing 12/2014 3/2018
Effect of Various Degrees of Maternal Hyperglycemia on Fetal Outcome
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Various Degrees of Maternal Hyperglycemia on Fetal Outcome ABSTRACT Shagufta Tahir, Shaheen Zafar, Savita Thontia Objective Study design Place & Duration of study Methodology
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Various Degrees of Maternal Hyperglycemia on Fetal Outcome ABSTRACT Shagufta Tahir, Shaheen Zafar, Savita Thontia Objective Study design Place & Duration of study Methodology
Administration of soluble activin receptor 2B increases bone and muscle mass in a mouse model of osteogenesis imperfecta
 OPEN Citation: Bone Research (215) 3, 1442 doi:1.138/boneres.214.42 ß 215 Sichuan University. All rights reserved 295-47/15 www.nature.com/boneres ARTICLE Administration of soluble activin receptor 2B
OPEN Citation: Bone Research (215) 3, 1442 doi:1.138/boneres.214.42 ß 215 Sichuan University. All rights reserved 295-47/15 www.nature.com/boneres ARTICLE Administration of soluble activin receptor 2B
Chapter 39: Exercise prescription in those with osteoporosis
 Chapter 39: Exercise prescription in those with osteoporosis American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York:
Chapter 39: Exercise prescription in those with osteoporosis American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York:
Visual Vignette EP VISUAL VIGNETTE
 ENDOCRINE PRACTICE Rapid Electronic Article in Press Rapid Electronic Articles in Press are preprinted manuscripts that have been reviewed and accepted for publication, but have yet to be edited, typeset
ENDOCRINE PRACTICE Rapid Electronic Article in Press Rapid Electronic Articles in Press are preprinted manuscripts that have been reviewed and accepted for publication, but have yet to be edited, typeset
Publications of Mr Nigel Kiely FRCS
 Publications of Mr Nigel Kiely FRCS Peer Reviewed McFarlane J, Knight T, Sinha A, Cole T, Kiely N, Freeman R. Exostoses, enchondromatosis and metachondromatosis; diagnosis and management. Acta Orthop Belg.
Publications of Mr Nigel Kiely FRCS Peer Reviewed McFarlane J, Knight T, Sinha A, Cole T, Kiely N, Freeman R. Exostoses, enchondromatosis and metachondromatosis; diagnosis and management. Acta Orthop Belg.
What is Osteoporosis?
 What is Osteoporosis? 2000 NIH Definition A skeletal disorder characterized by compromised bone strength predisposing a person to an increased risk of fracture. Bone strength reflects the integration of
What is Osteoporosis? 2000 NIH Definition A skeletal disorder characterized by compromised bone strength predisposing a person to an increased risk of fracture. Bone strength reflects the integration of
12/13/16. Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD Medical Director, Queens CAC December 14, 2016
 Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD Medical Director, Queens CAC December 14, 2016 Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD, has no financial relationships with any commercial interests. The learner will be able to:! Articulate
Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD Medical Director, Queens CAC December 14, 2016 Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD, has no financial relationships with any commercial interests. The learner will be able to:! Articulate
