Stabilizing Acute Orthopedic Injuries In The Pediatric Patient and Cast Management Principles
|
|
|
- Teresa Manning
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Stabilizing Acute Orthopedic Injuries In The Pediatric Patient and Cast Management Principles Torrie D. Edwards, FNP-C, CPN Department of Orthopedics Cook Children s Physician Network
2 Discussion Topics Purpose of Splinting Splinting and Casting Materials Types of Splints and Their Uses Positioning Basics Risks and Complications Associated with Immobilization Caring for the Immobilized Extremity
3 Why Do We Splint The Injured Extremity?
4 Purpose of Splinting Provide comfort Protect and position the injured extremity Prevent further injury More easily able to accommodate and adjust for swelling Allows for easy visualization of the extremity if needed If high quality and with correct application, it can aid in maintaining optimum injury position that can affect the overall treatment plan
5 Splinting and Casting Materials
6 Prefabricated Splint Injury specific premade splints exist for almost any body location Aluminum and Foam Constructs Soft (Neoprene, elastic) Semi-rigid Rigid (plastic, metal) Good for soft tissue injuries or stabilized fractures with low risk of loss of position
7 Plaster Used for splints and casts Slow setting time Produces less heat More pliable than fiberglass Requires layers More mess than fiberglass
8 Fiberglass Used for splints and casts Quick setting time Little mess Light material Requires less layers than plaster Moldable Can be waterproof if used in conjunction with other waterproof materials
9 Soft Fiberglass Semi-rigid due to incomplete setting Patient has some motion Can be removed without a cast saw Used most commonly for clubfoot casting in infants
10 Encased Fiberglass Fiberglass covered by a felt covering Used for splinting Able to mold in multiple planes Comes either precut or in a roll that can be cut to length Used in conjunction with padding and Ace wrap to secure Commonly referred to as Ortho-Glass
11 Encased Fiberglass
12 ACE Wrap Often used for minor muscle or soft tissue injuries If used correctly, can help control swelling Good reminder to not overuse the extremity Does not provide much support Will not prevent re-injury
13 Magazine, Newspaper, Cardboard Used in emergency settings Immobilize the joint above and below the fracture site Splint the injury prior to moving the patient in order to minimize further damage, unless the patient is in a dangerous setting that requires immediate removal Do not attempt to straighten severely deformed limbs as this may cause further damage
14 Tape Used to stabilize and support the injury or prevent re-injury Provides pain relief by de-loading the painful structure Helps to facilitate normal movement Avoid wrinkles in the tape, as this can result in discomfort and blisters on the skin Apply the tape in angles that are natural to the body Should not be used in place of a rehab program that includes strengthening and proprioception
15 Types of Splints, Their Uses and Positioning Basics
16 Posterior Splint Upper Extremity Used for immobilization of the wrist, forearm, elbow and distal humerus Positioning for Upper Extremities Wrist and forearm in neutral position Elbow at 90 degrees of flexion Splint terminates 2 inches distal to the axilla and palmar crease Humerus have patient lean forward, keeping the humerus vertical to allow axilla access and prevent angulation of the humerus Adequately pad the olecranon due to risk of skin breakdown in this high tension area
17 Posterior Splint Short Leg Immobilization for the foot, ankle, tibia and fibula Positioning for the Short Leg Splint Neutral position of the foot Ankle at 90 degrees Knee flexed at 90 degrees Splint terminates distally at the metatarsal heads and 2 inches distal to the popliteal crease Adequately pad the heel to avoid pressure sores Educate patient on floating the heel when elevating to avoid pressure sores
18 Posterior Splint Long Leg Immobilization of the foot, ankle, tibia, fibula, knee and femur Positioning for the Long Leg Splint Neutral foot position Ankle at 90 degrees Knee is flexed degrees Splint terminates distally at the metatarsal heads and 2 inches distal to the gluteal crease Adequately pad the heel to avoid pressure sores Educate patient on floating the heel when elevating Avoid bunching of the splint material behind the knee keep the leg in the same angle throughout application to avoid this Support the leg with the palms to avoid creating indentations in the splinting materials can result in pressure sores
19 Sugar Tong Splint Long, U shaped splint Named after a utensil used to pick up sugar cubes Immobilization of the wrist, forearm and elbow Positioning for the Sugar Tong Splint Neutral position for wrist and forearm Elbow in 90 degrees of flexion Ulnar and Radial aspects of the splint should not come in contact with one another to allow for possible swelling Splint terminates distally at the metacarpal heads on the dorsal aspect and palmar crease on the volar aspect Avoid positioning to where the patient is able to pronate and supinate
20 Stirrup Splint (U Splint) Splint that has a strap that wraps around the bottom of the foot leaving the heel exposed Immobilization of the foot, ankle, tibia and fibula Positioning for Stirrup Splint Neutral foot position Ankle at 90 degrees Knee flexed at 90 degrees Splint terminates distally at the metatarsal heads and 2 inches distal to the popliteal crease The stirrup portion should terminate 3 inches distal to the popliteal crease on the medial and lateral sides Stirrup should not overlap anteriorly
21 Coaptation Splint Immobilization of midshaft humerus fractures Positioning for Coaptation Splint Humerus resting on torso supported with a sling Elbow flexed to 90 degrees Medial portion of splint should be 2 inches distal from axilla Lateral portion of splint should be 2 inches proximal to the AC joint, well padded and molded Natural tendency is for this fracture to drift into a varus position when in doubt, add a little more valgus positioning to the splint Avoid Radial Nerve Trauma - limit the amount of manipulation and movement to the arm, have the patient lean forward to allow gravity to assist in alignment Document radial nerve function before and after splinting
22 Removable Volar Wrist Brace Used for soft tissue injuries and certain stable wrist fractures Positioning for comfort in rheumatoid arthritis or carpal tunnel Used when transitioning out of a cast
23 Sling Provides support to the collarbone, shoulder or arm after and injury or surgery Positioning For The Sling Elbow at 90 degrees Forearm against the torso Ensure wrist is included in the sling for forearm support Can use a safety pin to help secure the sling in the small child
24 Ankle Brace Used to immobilize ankle injuries, prevent re-injuries and provide support to the joint Types of Ankle Braces Rigid immobilizes the entire ankle Functional or Semi-Rigid Allows for some plantar and dorsiflexion while controlling inversion and eversion The use of an ankle brace in an athlete should not replace a quality rehab program that includes strengthening and proprioception
25 Stirrup Ankle Brace
26 Lace Up Ankle Brace
27 Risks and Complications Associated With Immobilization
28 Thermal Injury Plaster and fiberglass harden by an exothermic reaction which can burn the underlying skin Plaster usually creates more heat than fiberglass Factors That Increase The Risk of Injury: Temperature of the Dip Water keep the temperature below 75 degrees Fahrenheit and check the manufacturers recommendations Number of Layers of Material (>24 ply) the thicker the cast/splint, the more heat produced Too Little Padding less padding allows more heat to reach the skin Pillows/Blankets Under the Cast keeps heat around the limb rather than allowing it to disperse to the surrounding air Applying Several Rolls of Material At Once allow for heat to escape for a few minutes after some rolls applied before applying the remainder
29 Compartment Syndrome Increased pressure within the soft tissue becomes too great that blood cannot flow to the tissue, resulting in necrosis and death of the tissue Emergency that requires immediate treatment Casts and splints by nature will provide some degree of compression to the extremity Casts create higher pressure than a non-circumferential splint Uni-valving a cast can reduce internal pressure by as much as 40% Fiberglass applied under tension creates the highest skin surface pressures Fiberglass applied with stretch-relaxation technique creates the lowest skin surface pressures
30 Compartment Syndrome Signs and Symptoms Pain that is out of proportion to the injury Worsening pain over time that is non-responsive to analgesics Numbness Tingling Swelling Blue/gray color to the skin or nail beds distal to the cast Sluggish capillary refill For very early presentation, loosen or remove the cast/splint
31 Pressure Sores Focal areas of pressure (pressure points) that damages the skin being pressed upon, ultimately resulting in an ulcer Risk Factors Application Technique Do not use fingertips Rough edges can cause pressure sores Excess padding causes cast to be loose and the limb inside can move, resulting in skin irritation from the cast sliding up and down Molding over bony prominences and not molding uniformly Risk Factors Patient Population No or decreased sensation spinal cord injuries, neuropathic or diabetic patients Communication Issues young age, developmental delay, sedated or comatose patients Spastic Limbs cerebral palsy, spina bifida
32 Pressure Sores
33 Wound Infection Inspect extremity being immobilized for the presence of wounds that occurred at time of injury and use caution splinting around these areas Iatrogenic wounds can be caused by abrasions or pressure sores from improperly padding the ends of the splints and casts Wounds with subsequent infection can also be caused by the patient when they attempt to scratch under the cast/splint with a foreign object Can occur if a wet cast goes unreported, causing skin irritation and breakdown
34 Cast Saw Burn If used correctly, the oscillation of the cast saw blade should only cut through rigid material Use an in-and-out drop motion when cutting the cast Never drag the blade across the cast surface The blade can become hot enough to cause full thickness burns More heat produced in a thicker cast Fiberglass creates more heat than plaster Prevention of Cast Saw Burns Good control over the saw to keep it from plunging through the cast Take breaks frequently as the blade becomes hot or use a cool cloth over the blade Can use a protective strip that goes into the cast between the material and the patient s skin. The saw is then used directly over the strip to protect the underlying skin
35 Cast Saw Burn
36 Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Occurs when a blood clots forms in one or more of the deep veins of the body Usually in the legs More common in the adult population than in children The longer the length of immobilization, the higher the risk of DVT development Anticoagulation may be used in high risk patient populations
37 Loss Of Reduction Can occur with both splints and casts Decrease in swelling after the acute phase can result in a more loose fitting cast/splint, resulting in loss of reduction Properly applied and molded casts reduce the risk Weekly in cast x-rays are recommended for unstable fractures until risk of loss of position has abated Cast wedging or modification, re-reduction or operative interventions can be considered for loss of reduction
38 Care of the Immobilized Extremity
39 General Splint and Cast Care Elevate the extremity at a level above the heart in the first hours after the cast is placed and then as needed for swelling Keep the splint/cast dry Do not break or trim cast edges For rough patches, you can apply a band-aid over the site Do not pull out the padding Do not remove the splint or cast yourself unless instructed by the orthopedic provider to do so Do not stick anything inside the cast Do not use powder or lotion under the cast powder can form into clumps that cause skin sores
40 General Splint and Cast Care Check At Least Twice Daily For: Movement and feeling in the fingers or toes and above and below the cast or splint Change in color to fingers or toes Swelling above and below the cast or splint compare with the opposite side Rashes, bruising or red raw areas around cast edges Full activity restrictions unless otherwise specified by the orthopedic provider
41 Splint/Cast Troubleshooting Tips Swelling Evaluate the extremity for blood flow and sensation Elevate the extremity higher than the heart Encourage frequent movement of the fingers or toes while elevated Loosen the splint or the cast Loosen/unwrap the outer bandage layer of the splint, taking care to leave the slab in place Remove the tape and/or widen the space in the cast that is uni-valved or bi-valved Look for indents on the cast that may be causing focal pressure areas If compartment syndrome is suspected, refer to the emergency room immediately Wet Splint/Cast Use a blow dryer on cool setting to blow cool air into the cast Call the Orthopedic Clinic if the padding does not dry within 12 hours or if the extremity was completely submerged in water
42 Splint/Cast Troubleshooting Tips Skin Irritation Apply material to cast edge to create a barrier between the skin and the cast Mole skin Band-Aid Duct tape If concerned for infection or worsening of site, call the orthopedic clinic Itching Decrease activity that would raise body temperature Use a hair dryer on a cool setting and blow cold air into the cast Gently tap on the outside with a pencil Oral Benadryl at night Never stick anything in the cast to scratch Foreign Object in the Cast Call the orthopedic clinic immediately Do not try to retrieve the object yourself
43 When To Call The Orthopedic Clinic Soft spots or cracks in the cast Skin looks raw or red around cast edges Pain that will not go away Numbness/tingling in the fingers or toes Color changes to the fingers or toes Swelling that is not relieved Cast too tight or too loose Odor from the cast Drainage from the cast Burning or stinging sensation Unexplained fevers If you suspect or know that something is in the cast Toes that disappear into the cast Increased fussiness in a young child without an explanation
44 References Baecher, MD, N. B. (2016, March 11). Volar Splinting: Background, Indications, Contraindications. Retrieved from overview Boyd, MD, A., Benjamin, MD, H., & Asplund, MAJ, MC, USA, C. (2009). American Family Physician. Principles of Casting and Splinting, 79(1), Retrieved March 30, 2017, from Brown, S. A., & Radja, F. E. (2015). Orthopaedic immobilization techniques: A step-bystep guide for casting and splinting. Urbana, IL: Sagamore Publishing. Cascade. (2017). BSN Medical Delta-Cast Soft Fiberglass-Free Cast Tape. Retrieved from html Conney Safety. (2017). North Cardboard Arm Splint: 18"L [Cardboard splint]. Retrieved from Cook Children's Medical Center. (2011, December). Fiberglass Cast Care [PDF Document]. Cook Children's Medical Center. (2011, December). Soft Cast Care [PDF Document].
45 References First Aid Product.Com. (2001). 2" x 5 yd Elastic (Ace) Bandage with 2 Fasteners - 1 Each [Ace Wrap]. Retrieved from Physio Works. (2015, March 24). Supportive Taping & Strapping. Retrieved from Gravelee, M.D, J. R., & Van Durme, M.D, D. J. (2007). Braces and Splints for Musculoskeletal Conditions. American Family Physician, 75(3), Retrieved from Reeves, Jr, MD, D. A. (2015, July 27). Ankle Taping and Bracing: Overview, Periprocedural Care, Technique. Retrieved from Takayesu, MD, J. K. (2016, May 31). Splinting Material & Techniques for Broken Bones. Retrieved from
PEDIATRIC CASTING AND SPLINTING HEATHER KONG, M.D. SHRINERS HOSPITAL FOR CHILDREN PORTLAND OCTOBER 7, 2017
 PEDIATRIC CASTING AND SPLINTING HEATHER KONG, M.D. SHRINERS HOSPITAL FOR CHILDREN PORTLAND OCTOBER 7, 2017 DISCLOSURES I have no financial relationship with any company or product discussed in this presentation.
PEDIATRIC CASTING AND SPLINTING HEATHER KONG, M.D. SHRINERS HOSPITAL FOR CHILDREN PORTLAND OCTOBER 7, 2017 DISCLOSURES I have no financial relationship with any company or product discussed in this presentation.
16 th Annual Primary Care & Sports Medicine Symposium January 29th, 2016
 To help protect your privacy, PowerPoint has blocked automatic download of this picture. 16 th Annual Primary Care & Sports Medicine Symposium January 29th, 2016 Excellence in Orthopaedics Through Education
To help protect your privacy, PowerPoint has blocked automatic download of this picture. 16 th Annual Primary Care & Sports Medicine Symposium January 29th, 2016 Excellence in Orthopaedics Through Education
Acute Care Splinting & Casting. FACULTY: Tom Gocke, PA-C Lucy Yang, PA-C
 Acute Care plinting & Casting FACULTY: Tom Gocke, PA-C Lucy Yang, PA-C Disclosure Tom Gocke, M, ATC, PA-C, DFAAPA AAPA Intellectual Property Orthopaedic Educational ervices, Inc. Owner/Royalties/Intellectual
Acute Care plinting & Casting FACULTY: Tom Gocke, PA-C Lucy Yang, PA-C Disclosure Tom Gocke, M, ATC, PA-C, DFAAPA AAPA Intellectual Property Orthopaedic Educational ervices, Inc. Owner/Royalties/Intellectual
CAST CARE. Helping Broken Bones Heal
 CAST CARE Helping Broken Bones Heal When You Need a Cast Are you injured and in need of a cast? Don t worry, you ll get through it. Wearing a cast will help your injured body part heal. Healing takes time,
CAST CARE Helping Broken Bones Heal When You Need a Cast Are you injured and in need of a cast? Don t worry, you ll get through it. Wearing a cast will help your injured body part heal. Healing takes time,
General Cast and Splint Care
 General Cast and Splint Care Casts and splints provide limb support after a fracture or surgery. They may also be used to stretch the muscles in a limb. The cast or splint keeps the arm or leg in the proper
General Cast and Splint Care Casts and splints provide limb support after a fracture or surgery. They may also be used to stretch the muscles in a limb. The cast or splint keeps the arm or leg in the proper
Extremity Injuries and Splinting
 CHAPTER 15 Extremity Injuries and Splinting Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the 3 general types of splints and how to improvise splints with common materials. 2. List the general guidelines for splinting
CHAPTER 15 Extremity Injuries and Splinting Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the 3 general types of splints and how to improvise splints with common materials. 2. List the general guidelines for splinting
AMERICAN RED CROSS FIRST AID RESPONDING TO EMERGENCIES FOURTH EDITION Copyright 2006 by The American National Red Cross All rights reserved.
 Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions
Principles of Casting
 Principles of Casting Trauma Management with Cast Application AADO Dr K B Lee Queen Elizabeth Hospital 3 Nov 2013 Introduction Basic Principles of Fracture Treatment: Reduce (Reduction) Hold (Immobilization)
Principles of Casting Trauma Management with Cast Application AADO Dr K B Lee Queen Elizabeth Hospital 3 Nov 2013 Introduction Basic Principles of Fracture Treatment: Reduce (Reduction) Hold (Immobilization)
Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions
 Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions 1. What is caused by overexerting or tearing of a muscle? p. 375 A.) Dislocation B.) Sprain C.) Fracture *D.)
Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions 1. What is caused by overexerting or tearing of a muscle? p. 375 A.) Dislocation B.) Sprain C.) Fracture *D.)
Orthopedic Injuries and Immobilization.
 Orthopedic Injuries and Immobilization www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz History and Physical Exam Immediately upon presentation with a dislocation or fracture, the neurovascular and circulatory status must be
Orthopedic Injuries and Immobilization www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz History and Physical Exam Immediately upon presentation with a dislocation or fracture, the neurovascular and circulatory status must be
1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles. Striated Skeletal. Smooth
 1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth 3 Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System 4 Skeletal System 5 Skeletal System Functions
1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth 3 Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System 4 Skeletal System 5 Skeletal System Functions
Principles of Casting
 Principles of Casting Trauma Management with Cast Application AADO Dr. WH Yip Queen Elizabeth Hospital 10 th August 2014 Introduction Basic Principles of Fracture Treatment Reduction Immobilization Temporarily
Principles of Casting Trauma Management with Cast Application AADO Dr. WH Yip Queen Elizabeth Hospital 10 th August 2014 Introduction Basic Principles of Fracture Treatment Reduction Immobilization Temporarily
Correcting Joint Contractures
 559 Correcting Joint Contractures CHAPTER 59 In this chapter we discuss different aids used for gradually straightening limbs that have joint contractures. Information on contractures, their causes and
559 Correcting Joint Contractures CHAPTER 59 In this chapter we discuss different aids used for gradually straightening limbs that have joint contractures. Information on contractures, their causes and
9/22/14. ! None. ! Provides non- circumferential support! Accommodates swelling! Useful for acute injuries! Held in place by elastic bandage
 Britt Marcussen, MD Sports Medicine University of Iowa! None! 1. Discuss indications for splinting! 2. Discuss advantages/disadvantages of splints! 3. Go through splinting materials! 4. Discuss casting
Britt Marcussen, MD Sports Medicine University of Iowa! None! 1. Discuss indications for splinting! 2. Discuss advantages/disadvantages of splints! 3. Go through splinting materials! 4. Discuss casting
The Beginning of Better Healing
 The Beginning of Better Healing is available in the following sizes: ILP Interlocking Performance Unique technology offered on the new Single Layer Don t forget to ask your BSN medical representative about
The Beginning of Better Healing is available in the following sizes: ILP Interlocking Performance Unique technology offered on the new Single Layer Don t forget to ask your BSN medical representative about
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Roller Bandages. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-10. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 6-1. Identify the functions of roller bandages.
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Roller Bandages. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 6-1 through 6-10. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 6-1. Identify the functions of roller bandages.
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD
 Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Trauma & Sports Medicine Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UCSF / SFGH History Physical Exam Radiology Treatment History Acute trauma
Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Trauma & Sports Medicine Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UCSF / SFGH History Physical Exam Radiology Treatment History Acute trauma
1.3 Initi t al Tre r at e m at e m n e t Pos P iti t oning of th t e p e ati at en e t an d th t e l e imb m. F gure r 1.4.
 INTRODUCTION Immobilization of injured bones, joints, ligaments, or muscles has been practiced traditionally, if nothing else, because of the comfort that immobilization provides. The types of methods
INTRODUCTION Immobilization of injured bones, joints, ligaments, or muscles has been practiced traditionally, if nothing else, because of the comfort that immobilization provides. The types of methods
Management of Fractures. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 5
 Management of Fractures Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 5 Common methods of fracture immobilization Plaster of Paris (POP): A high quality gypsum The standard method of external splinting
Management of Fractures Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 5 Common methods of fracture immobilization Plaster of Paris (POP): A high quality gypsum The standard method of external splinting
ZOROMED TANGENT INFRA LAB TECH. Orthopedic Rehabilitation Aid Products. Tangent Infra Lab Tech 218 B, Ring Road Mall, Sec 3 Rohini, New Delhi
 TANGENT INFRA LAB TECH ZOROMED Orthopedic Rehabilitation Aid Products Our range of orthopedic rehabilitation products includes Cervical, Knee, Chest, Back, Ankle and Walking aids. We also have healthcare
TANGENT INFRA LAB TECH ZOROMED Orthopedic Rehabilitation Aid Products Our range of orthopedic rehabilitation products includes Cervical, Knee, Chest, Back, Ankle and Walking aids. We also have healthcare
Total Contact Cast System
 Total Contact Cast System Instructions for Use Products Included in Cutimed Off-Loader Select kit Qty Cutimed Cavity Sterile 1 ea. Cutisorb Cotton Gauze 2" x 2" 4 ea. Delta-Lite Conformable Fiberglass
Total Contact Cast System Instructions for Use Products Included in Cutimed Off-Loader Select kit Qty Cutimed Cavity Sterile 1 ea. Cutisorb Cotton Gauze 2" x 2" 4 ea. Delta-Lite Conformable Fiberglass
Lesson 9: Bone & Joint Injuries. Emergency Reference Guide p
 Lesson 9: Bone & Joint Injuries Emergency Reference Guide p. 33-43 Objectives Define strain, sprain, fracture and dislocation List Signs & Symptoms of strain, sprain, fracture & dislocation Demonstrate
Lesson 9: Bone & Joint Injuries Emergency Reference Guide p. 33-43 Objectives Define strain, sprain, fracture and dislocation List Signs & Symptoms of strain, sprain, fracture & dislocation Demonstrate
Kinesiology Tape. Table of contents:
 1 Kinesiology Tape Welcome to the Anuva application center. These application guidelines and general use instructions are intended to be used with Anuve professional quality Kinesiology tape and if followed
1 Kinesiology Tape Welcome to the Anuva application center. These application guidelines and general use instructions are intended to be used with Anuve professional quality Kinesiology tape and if followed
WRIST SPRAIN. Description
 WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
Chapter 30 - Musculoskeletal_Trauma
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 30.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11 12, 19 20, 22 23, 37 30.2 Describe the anatomy of elements of the musculoskeletal system.
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 30.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11 12, 19 20, 22 23, 37 30.2 Describe the anatomy of elements of the musculoskeletal system.
Acute Splinting of Fractures
 Acute Splinting of Fractures Orthopaedic Trauma Todd Horton, MD Holly Pilson, MD Michael Skeen, NP Jacob Nelson, PA C Disclosure Statement We have no financial interest/arrangement or affiliation with
Acute Splinting of Fractures Orthopaedic Trauma Todd Horton, MD Holly Pilson, MD Michael Skeen, NP Jacob Nelson, PA C Disclosure Statement We have no financial interest/arrangement or affiliation with
AADO Trauma Management with Cast Application Kwok Wai Yu APN, O&T, PWH 3 rd November, 2013
 AADO Trauma Management with Cast Application 2013 Kwok Wai Yu APN, O&T, PWH 3 rd November, 2013 *? Fracture, when, how, what type? *? Post operation case,?sg,?flap,?tendon or nerve repair *? General Condition:
AADO Trauma Management with Cast Application 2013 Kwok Wai Yu APN, O&T, PWH 3 rd November, 2013 *? Fracture, when, how, what type? *? Post operation case,?sg,?flap,?tendon or nerve repair *? General Condition:
1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint
 1 Executive Editor: Chris Colton Authors: Mariusz Bonczar, Daniel Rikli, David Ring 1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint Indication All 13-A type fractures, excluding
1 Executive Editor: Chris Colton Authors: Mariusz Bonczar, Daniel Rikli, David Ring 1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint Indication All 13-A type fractures, excluding
OV United Soccer Club
 Preventing disease transmission Place an effective barrier between you and the victim s blood when you give first aid. Examples of such barriers are: the victim s hand, a piece of plastic, clean folded
Preventing disease transmission Place an effective barrier between you and the victim s blood when you give first aid. Examples of such barriers are: the victim s hand, a piece of plastic, clean folded
Everything. You Should Know. About Your Ankles
 Everything You Should Know About Your Ankles How Your Ankle Works The ankle joint is a hinge type joint that participates in movement and is involved in lower limb stability. There are 2 types of motions
Everything You Should Know About Your Ankles How Your Ankle Works The ankle joint is a hinge type joint that participates in movement and is involved in lower limb stability. There are 2 types of motions
Musculoskeletal System
 CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries
 CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
Gwinnett Medical Center. Sports Medicine Program Skills Guide
 Gwinnett Medical Center Sports Medicine Program Skills Guide To find information about this event, including speakers and digital copies of this skills guide, visit: gwinnettmedicalcenter.org/sportsclinics
Gwinnett Medical Center Sports Medicine Program Skills Guide To find information about this event, including speakers and digital copies of this skills guide, visit: gwinnettmedicalcenter.org/sportsclinics
Application of Cast Brace for Post Acute Care of Lower Extremity Fractures
 Application of Cast Brace for Post Acute Care of Lower Extremity Fractures Roy Snelson, C.P.O.*, George Irons, C.P.O.**, and Vert Mooney, M.D.*** The fracture cast brace is designed to allow early ambulation
Application of Cast Brace for Post Acute Care of Lower Extremity Fractures Roy Snelson, C.P.O.*, George Irons, C.P.O.**, and Vert Mooney, M.D.*** The fracture cast brace is designed to allow early ambulation
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation
 A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 2 Introduction When the joint surfaces of an elbow are forced apart, the elbow is dislocated. The elbow is the second most commonly dislocated joint in adults (after
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 2 Introduction When the joint surfaces of an elbow are forced apart, the elbow is dislocated. The elbow is the second most commonly dislocated joint in adults (after
INDEX DR. NICK MARTICHENKO BIO NOTES INTRODUCTION APPLICATIONS AND SOLUTIONS THAT WILL ALLOW YOU TO PLAY BETTER, LONGER AND MORE OFTEN
 01 03 03 05 07 09 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 28 29 INTRODUCTION NOTES INDEX APPLICATIONS AND SOLUTIONS THAT WILL ALLOW YOU TO PLAY BETTER, LONGER AND MORE OFTEN Elbow - Improve wrist range of motion and decreased
01 03 03 05 07 09 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 28 29 INTRODUCTION NOTES INDEX APPLICATIONS AND SOLUTIONS THAT WILL ALLOW YOU TO PLAY BETTER, LONGER AND MORE OFTEN Elbow - Improve wrist range of motion and decreased
P R O D U C T C A T A L O G
 2015 PRODUCT CATALOG AT igo, WE PUT PEOPLE FIRST. Our staff of medical personnel and engineers work tirelessly to take groundbreaking orthopedic technology and turn it into intentionally designed, innovative
2015 PRODUCT CATALOG AT igo, WE PUT PEOPLE FIRST. Our staff of medical personnel and engineers work tirelessly to take groundbreaking orthopedic technology and turn it into intentionally designed, innovative
Injuries to the Extremities
 Injuries to the Extremities KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. List seven signs and symptoms that suggest a serious extremity injury. 2. Describe how to care for injuries to the shoulder, upper arm, and elbow. 3.
Injuries to the Extremities KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. List seven signs and symptoms that suggest a serious extremity injury. 2. Describe how to care for injuries to the shoulder, upper arm, and elbow. 3.
Hands on Sports Therapy KNOWLEDGE REVIEW QUESTIONS 2004 Thomson Learning. Q1: Why are taping and strapping skills important for the sports
 CHAPTER 11 Knowledge Review Q1: Why are taping and strapping skills important for the sports therapist to develop? A1: It is important for the sports therapist to develop taping and strapping skills because
CHAPTER 11 Knowledge Review Q1: Why are taping and strapping skills important for the sports therapist to develop? A1: It is important for the sports therapist to develop taping and strapping skills because
Trauma Department. Caring for Your Cast. Information for patients
 Trauma Department Caring for Your Cast Information for patients You have been prescribed a cast as treatment for your injury. The doctors and nurses will tell you how long you need to wear this cast. This
Trauma Department Caring for Your Cast Information for patients You have been prescribed a cast as treatment for your injury. The doctors and nurses will tell you how long you need to wear this cast. This
Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints. Emergency Medical Response
 Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints Lesson 33: Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints You Are the Emergency Medical Responder You are patrolling the state park where you are the emergency medical responder
Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints Lesson 33: Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints You Are the Emergency Medical Responder You are patrolling the state park where you are the emergency medical responder
COMPLETION PROJECT POSITIONING THE PATIENT IN THE OR Source- Alexander s Care of the Patient in Surgery
 COMPLETION PROJECT POSITIONING THE PATIENT IN THE OR Source- Alexander s Care of the Patient in Surgery Name Date 1. The systems involved with anesthesia, positioning and operative procedures are: a. b.
COMPLETION PROJECT POSITIONING THE PATIENT IN THE OR Source- Alexander s Care of the Patient in Surgery Name Date 1. The systems involved with anesthesia, positioning and operative procedures are: a. b.
Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions
 Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions 1. What do injuries to the shoulder often produce? p. 393 *A.) Anterior dislocation B.) Superior dislocation
Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions 1. What do injuries to the shoulder often produce? p. 393 *A.) Anterior dislocation B.) Superior dislocation
Chapter 28. Wound Care. Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 28 Wound Care Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 28.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe skin tears, circulatory ulcers, and diabetic
Chapter 28 Wound Care Copyright 2019 by Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved. Lesson 28.1 Define the key terms and key abbreviations in this chapter. Describe skin tears, circulatory ulcers, and diabetic
A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome)
 A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome) Introduction The ulnar nerve is often called the funny bone at the elbow. However, there is little funny about injury to
A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome) Introduction The ulnar nerve is often called the funny bone at the elbow. However, there is little funny about injury to
METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures)
 METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures) Description Possible Complications Metatarsal fracture is a broken bone (fracture) in the middle Nonunion (fracture does not heal, particularly
METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures) Description Possible Complications Metatarsal fracture is a broken bone (fracture) in the middle Nonunion (fracture does not heal, particularly
AADO Workshop Trauma Management with Cast Applications 5th July Dr. SHA, Wai-leung Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Tuen Mun Hospital
 AADO Workshop Trauma Management with Cast Applications 5th July 2009 Dr. SHA, Wai-leung Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Tuen Mun Hospital Plaster cast Good method Cheap Safe Safe?? Hazards &
AADO Workshop Trauma Management with Cast Applications 5th July 2009 Dr. SHA, Wai-leung Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Tuen Mun Hospital Plaster cast Good method Cheap Safe Safe?? Hazards &
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
The nomenclature describing the orthosis is basically the same as that suggested for the molded ankle-foot orthosis (2), but the anterior shank enclos
 VACUUM-FORMED ORTHOSES FOR FRACTURE OF THE TIBIA 1 Melvin Stills, C.O. 2 The routine management of fractures of the long bones of the lower limb infers immobilization by use of plaster casts extending
VACUUM-FORMED ORTHOSES FOR FRACTURE OF THE TIBIA 1 Melvin Stills, C.O. 2 The routine management of fractures of the long bones of the lower limb infers immobilization by use of plaster casts extending
Patient and Family Education. Clubfoot Correction. Using casting followed by shoes on a bar (the Ponseti method) What is the cause of clubfoot?
 Patient and Family Education Clubfoot Correction Using casting followed by shoes on a bar (the Ponseti method) The results of treating a child with clubfoot using the Ponseti method are very good. This
Patient and Family Education Clubfoot Correction Using casting followed by shoes on a bar (the Ponseti method) The results of treating a child with clubfoot using the Ponseti method are very good. This
Musculoskeletal Injuries
 Musculoskeletal Injuries KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the four main structures of the musculoskeletal system. 2. List five common signs or symptoms of musculoskeletal injuries. 3. List seven signs
Musculoskeletal Injuries KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the four main structures of the musculoskeletal system. 2. List five common signs or symptoms of musculoskeletal injuries. 3. List seven signs
Instructions for Use
 PRODUCTS Instructions for Use PRODUCTS Andover offers a variety of cohesive flexible bandage options. Why are CoFlex products the Best Bandage Choice? Available latex or latex-free Self-adhering - sticks
PRODUCTS Instructions for Use PRODUCTS Andover offers a variety of cohesive flexible bandage options. Why are CoFlex products the Best Bandage Choice? Available latex or latex-free Self-adhering - sticks
What is arthroscopy? Normal knee anatomy
 What is arthroscopy? Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for examining and repairing the inside of your knee. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which uses an Arthroscope and other specialized
What is arthroscopy? Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for examining and repairing the inside of your knee. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which uses an Arthroscope and other specialized
CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
 WHAT IS CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME? SYMPTOMS Cubital tunnel syndrome is the second most commonly occurring nerve compression in the upper body It is caused by compression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow The
WHAT IS CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME? SYMPTOMS Cubital tunnel syndrome is the second most commonly occurring nerve compression in the upper body It is caused by compression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow The
PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION
 PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION Description For jumping (basketball, volleyball) or contact sports, Patellar dislocation and subluxation are injuries to the protect the patella with supportive devices,
PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION Description For jumping (basketball, volleyball) or contact sports, Patellar dislocation and subluxation are injuries to the protect the patella with supportive devices,
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation
 A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 20295 NE 29th Place, Ste 300 Aventura, FL 33180 Phone: (786) 629-0910 Fax: (786) 629-0920 admin@instituteofsports.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 20295 NE 29th Place, Ste 300 Aventura, FL 33180 Phone: (786) 629-0910 Fax: (786) 629-0920 admin@instituteofsports.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult
 Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Practice Changes I Hope You Make
 Is that Bad? What PCPs (& Parents) Need to Know about Fractures Aharon Z. Gladstein, MD Pediatric Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine Texas Children s Hospital Assistant Professor, Orthopaedics Baylor College
Is that Bad? What PCPs (& Parents) Need to Know about Fractures Aharon Z. Gladstein, MD Pediatric Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine Texas Children s Hospital Assistant Professor, Orthopaedics Baylor College
2452 Lincolnway East Goshen, IN Toll Free: Phone:
 2452 Lincolnway East Goshen, IN 46526 Toll Free: 800.252.4909 Phone: 574.534.3418 Fax: 574.642.4546 E-mail: sales@darenind.com Orthopedic Products Catalog TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Wrist and Forearm Splints
2452 Lincolnway East Goshen, IN 46526 Toll Free: 800.252.4909 Phone: 574.534.3418 Fax: 574.642.4546 E-mail: sales@darenind.com Orthopedic Products Catalog TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Wrist and Forearm Splints
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to: be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Fractures of the Lower Extremities. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: be able to: 4-1. Identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Fractures of the Lower Extremities. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: be able to: 4-1. Identify
Hatfield & McCoy Mine Safety Competition First-Aid Contest JULY 15, Page 1
 Hatfield & McCoy Mine Safety Competition First-Aid Contest JULY 15, 2014 Page 1 PROBLEM Billy is a maintenance person that has been conducting clean-up and service duties on the number one conveyor belt
Hatfield & McCoy Mine Safety Competition First-Aid Contest JULY 15, 2014 Page 1 PROBLEM Billy is a maintenance person that has been conducting clean-up and service duties on the number one conveyor belt
ANKLE SPRAINS. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
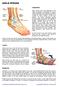 ANKLE SPRAINS Explanation Ankle sprains occur when ligaments in the ankle are partially or completely torn due to sudden stretching, either laterally or medially, or when the ankle is suddenly twisted
ANKLE SPRAINS Explanation Ankle sprains occur when ligaments in the ankle are partially or completely torn due to sudden stretching, either laterally or medially, or when the ankle is suddenly twisted
Property Latmedical, LLC.
 Dr. Goed provides a complete and innovate product portfolio solution to the growing healthcare need within the field of non-invasive orthopedics, sports medicine, bandaging, wound care and compression
Dr. Goed provides a complete and innovate product portfolio solution to the growing healthcare need within the field of non-invasive orthopedics, sports medicine, bandaging, wound care and compression
ANKLE FRACTURES. Contents The Ankle Joint... 3
 Contents The Ankle Joint................................................. 3 What is a fractured ankle?........................................ 4 YOUR GUIDE TO ANKLE FRACTURES What treatment can I receive?.....................................
Contents The Ankle Joint................................................. 3 What is a fractured ankle?........................................ 4 YOUR GUIDE TO ANKLE FRACTURES What treatment can I receive?.....................................
Support Levels. acebrand.com. Product Line Contents. Elastic Bandages, Tape & Underwrap Cold/Hot Therapy Braces & Supports...
 3 Product Line Contents Elastic Bandages, Tape & Underwrap... 4 Cold/Hot Therapy... 7 Braces & Supports...10 Ankle & Foot...10 Knee...14 Elbow...19 Wrist...22 Hand, Thumb & Arm...25 Back...27 Products...30
3 Product Line Contents Elastic Bandages, Tape & Underwrap... 4 Cold/Hot Therapy... 7 Braces & Supports...10 Ankle & Foot...10 Knee...14 Elbow...19 Wrist...22 Hand, Thumb & Arm...25 Back...27 Products...30
Information for Families. Serial Casting
 Information for Families Serial Casting Serial Casting Casting is a treatment used to provide a sustained stretch to tight muscles. Serial casting is when a series of casts are placed on the limb over
Information for Families Serial Casting Serial Casting Casting is a treatment used to provide a sustained stretch to tight muscles. Serial casting is when a series of casts are placed on the limb over
A Patient s Guide to Nursemaid's Elbow in Children. PHYSIO.coza
 A Patient s Guide to Nursemaid's Elbow in Children SANDTON MEDICLINIC 011 706 7495 FAIRWAYS LIFE HOSPITAL 011 875 1827 ST STITHIANS 082 378 9642 JEPPE BOYS HIGH SCHOOL 084 816 5457 JOHANNESBURG, SANDTON@PHYSIO.CO.ZA
A Patient s Guide to Nursemaid's Elbow in Children SANDTON MEDICLINIC 011 706 7495 FAIRWAYS LIFE HOSPITAL 011 875 1827 ST STITHIANS 082 378 9642 JEPPE BOYS HIGH SCHOOL 084 816 5457 JOHANNESBURG, SANDTON@PHYSIO.CO.ZA
Fractures Healing & Management. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4
 Fractures Healing & Management Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4 Fractures Despite their strength, bones are susceptible to fractures. In young people, most fractures result from trauma
Fractures Healing & Management Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4 Fractures Despite their strength, bones are susceptible to fractures. In young people, most fractures result from trauma
Radiographic Positioning Summary (Basic Projections RAD 222)
 Lower Extremity Radiographic Positioning Summary (Basic Projections RAD 222) AP Pelvis AP Hip (Unilateral) (L or R) AP Femur Mid and distal AP Knee Lateral Knee Pt lies supine on table Align MSP to Center
Lower Extremity Radiographic Positioning Summary (Basic Projections RAD 222) AP Pelvis AP Hip (Unilateral) (L or R) AP Femur Mid and distal AP Knee Lateral Knee Pt lies supine on table Align MSP to Center
Essential intervention No. 3 Oedema control KEY OBJECTIVES. Danger
 Essential intervention No. 3 Oedema control KEY OBJECTIVES To know what causes oedema. To know which kind of oedema needs to be referred for emergency surgery and why. To know the effects of oedema on
Essential intervention No. 3 Oedema control KEY OBJECTIVES To know what causes oedema. To know which kind of oedema needs to be referred for emergency surgery and why. To know the effects of oedema on
WEEKEND 2 Elbow. Elbow Range of Motion Assessment
 Virginia Orthopedic Manual Physical Therapy Institute - 2016 Technique Manual WEEKEND 2 Elbow Elbow Range of Motion Assessment - Patient Positioning: Sitting or supine towards the edge of the bed - Indications:
Virginia Orthopedic Manual Physical Therapy Institute - 2016 Technique Manual WEEKEND 2 Elbow Elbow Range of Motion Assessment - Patient Positioning: Sitting or supine towards the edge of the bed - Indications:
Sick Call Screener Course
 Sick Call Screener Course Musculoskeletal System Upper Extremities (2.7) 2.7-2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.46 Utilize the knowledge of musculoskeletal system anatomy while assessing a patient with a musculoskeletal
Sick Call Screener Course Musculoskeletal System Upper Extremities (2.7) 2.7-2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.46 Utilize the knowledge of musculoskeletal system anatomy while assessing a patient with a musculoskeletal
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Traction Splints. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-5. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Identify the purpose of a traction
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 3 Traction Splints. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-5. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 3-1. Identify the purpose of a traction
Orthopaedic Surgery. Wearing a Plaster Cast
 Orthopaedic Surgery Wearing a Plaster Cast The Department of Orthopaedics offers specialist medical and surgical treatments on musculoskeletal disorders, joint replacements, foot and ankle disorders, among
Orthopaedic Surgery Wearing a Plaster Cast The Department of Orthopaedics offers specialist medical and surgical treatments on musculoskeletal disorders, joint replacements, foot and ankle disorders, among
Plaster and Orthopaedic Appliances. Au Wai Kin Tsang Wing Yan Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology PWH
 Plaster and Orthopaedic Appliances Au Wai Kin Tsang Wing Yan Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology PWH Function of Plaster Immobilize of fracture or injured tissue to avoid further damage Maintain
Plaster and Orthopaedic Appliances Au Wai Kin Tsang Wing Yan Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology PWH Function of Plaster Immobilize of fracture or injured tissue to avoid further damage Maintain
DEEP TISSUE FOAM ROLLER MASSAGE GUIDE
 Recover, Recharge, & Renew your body and mind with RE by Empower. Soothe everyday aches & pains; reduce tension & stress; and improve your overall health. DEEP TISSUE FOAM ROLLER MASSAGE GUIDE Three phases
Recover, Recharge, & Renew your body and mind with RE by Empower. Soothe everyday aches & pains; reduce tension & stress; and improve your overall health. DEEP TISSUE FOAM ROLLER MASSAGE GUIDE Three phases
ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT
 ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT Description Possible Complications Pinching of bone or soft tissue, including scar tissue, at the Frequent recurrence of symptoms, resulting in chronically front of the ankle
ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT Description Possible Complications Pinching of bone or soft tissue, including scar tissue, at the Frequent recurrence of symptoms, resulting in chronically front of the ankle
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Ridgegate Pkwy., Suite 309 Lone Tree, Colorado Office: Fax:
 ANKLE SPRAIN What is the ATFL? The ankle joint is made up of the tibia, fibula (bones in the lower leg) and the talus (bone below the tibia and fibula). Ligaments in the ankle connect bone to bone and
ANKLE SPRAIN What is the ATFL? The ankle joint is made up of the tibia, fibula (bones in the lower leg) and the talus (bone below the tibia and fibula). Ligaments in the ankle connect bone to bone and
3 section of the Foot
 TERMINOLOGY 101 How many Bones 3 section of the Foot Bilateral Relating to both Plantar Relating to the bottom or sole Lateral Relating to the outside or farther from the median Medial Relating to the
TERMINOLOGY 101 How many Bones 3 section of the Foot Bilateral Relating to both Plantar Relating to the bottom or sole Lateral Relating to the outside or farther from the median Medial Relating to the
Musculoskeletal Injuries
 Chapter 3 Musculoskeletal Injuries This chapter describes how to recognize and treat injuries to the musculoskeletal system, and the best methods for preventing problems of this nature: Recognize signs
Chapter 3 Musculoskeletal Injuries This chapter describes how to recognize and treat injuries to the musculoskeletal system, and the best methods for preventing problems of this nature: Recognize signs
Mr. Siva Chandrasekaran Orthopaedic Surgeon MBBS MSpMed MPhil (surg) FRACS
 Bunion Surgery Most people with bunions find pain relief with simple treatments to reduce pressure on the big toe, such as wearing wider shoes or using pads in their shoes. However, if these measures do
Bunion Surgery Most people with bunions find pain relief with simple treatments to reduce pressure on the big toe, such as wearing wider shoes or using pads in their shoes. However, if these measures do
Peripheral Vascular Examination. Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment
 Peripheral Vascular Examination Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Competencies 1. Inspection of upper extremity for: size symmetry swelling venous pattern color Texture nail beds Competencies
Peripheral Vascular Examination Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Competencies 1. Inspection of upper extremity for: size symmetry swelling venous pattern color Texture nail beds Competencies
ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE
 ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Achilles tendon rupture is a complete tear of the Achilles tendon. This tendon, sometimes called the heel cord, is the tendon attachment of the calf
ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Achilles tendon rupture is a complete tear of the Achilles tendon. This tendon, sometimes called the heel cord, is the tendon attachment of the calf
Lowe Plastic Surgery (LPS)
 Lowe Plastic Surgery (LPS) PATIENT EDUCATION FOR: CUMULATIVE TRAUMA DISORDER THE PROBLEM: There has been a remarkable increase in what is termed cumulative trauma disorder (CTD) in the last 20 years. Other
Lowe Plastic Surgery (LPS) PATIENT EDUCATION FOR: CUMULATIVE TRAUMA DISORDER THE PROBLEM: There has been a remarkable increase in what is termed cumulative trauma disorder (CTD) in the last 20 years. Other
Range of motion and positioning
 Range of motion and positioning Learning guide Why is motion important? Most people take free, comfortable movement for granted. Motion is meant to be smooth and painless. The ligaments, tendons, muscles,
Range of motion and positioning Learning guide Why is motion important? Most people take free, comfortable movement for granted. Motion is meant to be smooth and painless. The ligaments, tendons, muscles,
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY
 8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
Essential intervention No.1 Health education and self-care KEY OBJECTIVES
 Essential intervention No.1 Health education and self-care Health education bridges the gap between health information and behaviour. The person affected by BU must have the knowledge, skills, resources,
Essential intervention No.1 Health education and self-care Health education bridges the gap between health information and behaviour. The person affected by BU must have the knowledge, skills, resources,
11/5/14. I will try to make this painless. Great, a Fracture, Now What? Objectives. Basics for Fracture Workup. Basics for Fracture Workup
 Great, a Fracture, Now What? I will try to make this painless Mary Greve MS, PA-C Department of Orthopedic Surgery Trauma Team University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Mary-Greve@uiowa.edu Pager 2121 Objectives
Great, a Fracture, Now What? I will try to make this painless Mary Greve MS, PA-C Department of Orthopedic Surgery Trauma Team University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Mary-Greve@uiowa.edu Pager 2121 Objectives
Session 3 or 6: Being Active: A Way of Life.
 Session 3 or 6: Being Active: A Way of Life. You can find the time to be active. Set aside one block of time every day to be active. When can you set aside 20 to 30 minutes to do an activity you like?
Session 3 or 6: Being Active: A Way of Life. You can find the time to be active. Set aside one block of time every day to be active. When can you set aside 20 to 30 minutes to do an activity you like?
SMALL GROUP SESSION 16 January 8 th or 10 th Shoulder pain case/ Touch workshop/ Upper and Lower Extremity Examination
 SMALL GROUP SESSION 16 January 8 th or 10 th Shoulder pain case/ Touch workshop/ Upper and Lower Extremity Examination Suggested Readings: Opatrny L. The Healing Touch. Ann Int Med 2002; 137:1003. http://www.annals.org/cgi/reprint/137/12/1003.pdf
SMALL GROUP SESSION 16 January 8 th or 10 th Shoulder pain case/ Touch workshop/ Upper and Lower Extremity Examination Suggested Readings: Opatrny L. The Healing Touch. Ann Int Med 2002; 137:1003. http://www.annals.org/cgi/reprint/137/12/1003.pdf
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery. By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4
 Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Comprehensive Cast Care Instruction Upper Limb
 Comprehensive Cast Care Instruction Upper Limb Please try to continuously exercise all your joints not covered by your cast: fingers, elbow and shoulder. Regular exercise will significantly reduce post-injury
Comprehensive Cast Care Instruction Upper Limb Please try to continuously exercise all your joints not covered by your cast: fingers, elbow and shoulder. Regular exercise will significantly reduce post-injury
Y: Orthopedic Specialty
 Y: Orthopedic Specialty Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 253 Major Competency Area: Y Priority: One Competency: Y-1 HPA Authorization and Standards Date: September 1, 2005 Y-1-1 Demonstrate
Y: Orthopedic Specialty Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 253 Major Competency Area: Y Priority: One Competency: Y-1 HPA Authorization and Standards Date: September 1, 2005 Y-1-1 Demonstrate
Technical Manual. Transtibial Hand Casting & Modification Version no. 2
 Transtibial Hand Casting & Modification Version no. 2 Introduction The successful fitting of Transtibial prosthesis is dependent on the fit of the hard socket. Appropriate socket design is fundamental
Transtibial Hand Casting & Modification Version no. 2 Introduction The successful fitting of Transtibial prosthesis is dependent on the fit of the hard socket. Appropriate socket design is fundamental
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 1 Fractures and Related Injuries. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraph 1-1 through 1-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 1-1. Identify the signs and
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 1 Fractures and Related Injuries. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraph 1-1 through 1-14. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 1-1. Identify the signs and
Aviation Rescue Swimmer Course
 Aviation Rescue Swimmer Course Primary Survey LT 5.4 December 2003 1 Objectives List the procedures used in a primary survey. Demonstrate primary survey procedures used in a mock trauma (moulage) scenario
Aviation Rescue Swimmer Course Primary Survey LT 5.4 December 2003 1 Objectives List the procedures used in a primary survey. Demonstrate primary survey procedures used in a mock trauma (moulage) scenario
It is also important to make note of your function, as this may be your first indication of improvement.
 Back Pain 1 Management of Back Pain The resolution of pain involves gradually increasing the number of repetitions or resistance of the exercises performed. However, it is important to stay within a range
Back Pain 1 Management of Back Pain The resolution of pain involves gradually increasing the number of repetitions or resistance of the exercises performed. However, it is important to stay within a range
