Primary Posterior Fixation For Tuberculosis Of The Spine
|
|
|
- Chad Adams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 10 Number 1 B Jadav, M Prabhakar Citation B Jadav, M Prabhakar.. The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 10 Number 1. Abstract Tuberculosis of the spine is a very frequent case in the practice of spine surgeons in the developing world, and is set to pose a challenge to the developed world in near future. Only anterior surgery seems to be falling short in potential for correction of the kyphotic deformity as well as of preventing gradual collapse later on. Posterior fixation has shown an excellent potential for correction of deformity and prevention of secondary collapse when combined with anterior reconstruction and fusion in cases of trauma and deformity, and its potential is now being tested worldwide for tuberculous spine. We treated 100 patients with tuberculosis of various spinal levels with different levels of neurological impairments with primary posterior corrective fixation and second stage anterior debridement, decompression and reconstruction and followed them up for an average of 41 months. We didn't face any graft related problems, could mobilize the patient immediate after the surgery and achieved solid fusion in all cases. We faced only 4 un-acceptable adverse events in these cases in form of infection (2), neurological injury (1) and non-fusion (1). The mean preoperative kyphotic angle was 36.6 degrees and correction of a mean of degrees (36.6%) was maintained at final follow up of 41 months. We find that for cases of exudative stage tuberculosis of spine, primary posterior fixation and second stage anterior debridement and reconstruction provides good neurological decompression, early bony fusion and correction and/or prevention of deformity, allows early and better rehabilitation and is a recommendable strategy of surgical treatment for carefully selected patients. INTRODUCTION Mycobacterium Tuberculosis is the most common causative organism for infective spondylitis in developing countries. ( 1 ) While all forms of tuberculosis are rare in the developed countries, its resurgence has been seen in these times of immunodeficiency states and syndromes as well as due to the global migrant population groups from the underdeveloped nations. ( 2 ) Time to diagnosis, early or gradually developed deformities and neurological consequences of the deformity as well as of the disease are the major factors that determine the ultimate outcome for the patient. ( 2, 3 ) Neurological recovery and eradication of tuberculous infection with stabilisation of the spine are the goals of the treatment of the spinal tuberculosis. ( 2 ) Delayed diagnosis is a common problem in developing countries due to lack of access to health care system and in developed countries due to rarity of suspicion. On an average, a patient with spinal tuberculosis is diagnosed at 16 th to 19 th month of the disease process, ( 3 ) by which time the typical kyphotic deformity is usually evident. While the anterior radical debridement surgery and modern chemotherapy have been accepted as ideal treatment for eliminating the infection and healing the bone with fusion ( 4, 5 ), it often leaves behind the kyphotic deformity only partially addressed if at all. This study was aimed at identifying the role and efficacy of treating spinal tuberculosis patients in destructive stage of disease with primary posterior corrective fixation and then anterior debridement and reconstruction. The recently increasing interest into published literature ( 2, 6, 7, 8 ) about posterior fixation in tuberculosis of spine inspired us to share our own experiences with the fraternity. METHODS A total of 100 patients were included in the study with mean age 35.9 years- 52 males and 48 females with tuberculosis of spine with different levels of involvements and neurological status. The patients had been treated from 1997 till December 2006 and data collection was both retrospective as well as prospective. The diagnosis was based on suggestive clinical history; imaging modalities such as plain x-rays, ultrasound of psoas and paravertebral spaces, CT scan of involved levels and/or MRI of involved level with scanning of spine for skip lesions. Diagnosis was confirmed through histopathology of the tissue obtained during anterior surgery. 1 of 9
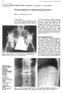
2 All patients included in this study were treated at the active stage of the tuberculous spondylitis. Figure 1 Table 1: Spinal levels involved and neurological status Figure 2 Picture 1: Radiograph showing L1-2 tuberculosis with Kyphosis and anterior destruction of both vertebral bodies The patients received 2-3 weeks of preoperative chemotherapy after being admitted in the special spine unit. Medical and anaesthetic evaluation regarding cardiopulmonary functional status and fitness for surgery and preoperative physiotherapy program including respiratory physiotherapy in view of anterior abdominal, transthoracic or transdiaphragmatic surgery. 2 of 9
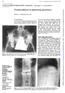
3 Figure 3 Picture 2: Postoperative radiograph showing Steffee instrumentation with good correction of kyphotic deformity and tricortical iliac bone graft in place. Figure 4 Picture 3: A case of L2-3 tuberculosis treated with primary corrective posterior fixation and second stage anterior debridement and fusion at 6 months follow up showing healing of the infection and developing fusion The patients were operated in routine operative list with 1st stage posterior fixation in form of sublaminar wiring and Hartshill rectangle fixation or transpedicular screw, thoracic hook and rod systems extending up to 2 levels on both sides of the lesion. Absence of disease in the adjacent vertebral bodies was confirmed with MRI when pedicle screws fixation was planned in order to avoid putting screws in infected body part; and in turn to avoid risk of providing an innate surface for the infection as well as to avoid unsound fixation in diseased body. No posterior complex decompression or fusion was attempted, neither was a biopsy tried through posterior surgery. 2nd stage anterior debridement, neurological decompression and anterior columns reconstruction was carried out at 1-2 weeks after the first surgery. The major factors dictating the time between the two surgeries were anaesthetist's opinion for fitness for second surgery, availability of crossmatched blood and room on operative schedule. The anterior surgery was carried out with thoracotomy in the levels D2-D11, transdiaphragmatic for D12- L1 and lumbar retroperitoneal for lumbar levels. The paraspinal abscess was drained; debridement of infected bony and soft tissue was done. Neurological decompression was carried out under vision. Bony debridement was carried out till healthy bleeding bone margin was reached and reconstruction was performed with autogenous bone graft from iliac crest or ribs. Iliac crest grafts were used alone or filled into titanium mesh cages, while rib grafts were never used as only graft material; ribs were morsellized and filled into titanium mesh cages. In one case with more than 3 bodies involved, we used a fibula graft. Bone graft substitutes or BMP were not used in any of 3 of 9
4 the cases. Figure 5 Table 2: Method of fixation and graft used Figure 7 Picture 5: MRI of the patient 3 showing 2 bodies involved and debris compressing on the neural tissue. The cephalad body also showing some lytic focus, which prevents us from using pedicle screws for fixation. The patients received local segment nerve blocks for immediate postoperative pain relief and respiratory and bedside physiotherapy were encouraged. The patients were referred for mobilisation and physiotherapy as soon as they were free of the operative pain and received occupational evaluation and therapy according to their neurological status. Figure 6 Picture 4: Another case of L1-2 tuberculosis with minimum Kyphosis 4 of 9
5 Figure 8 Picture 6: Stabilization of the same patient 3 with sublaminar wires and Hartshill rectangle showing good correction of the Kyphosis. The patient later had anterior reconstruction with titanium mesh cage filled with bonegraft Figure 9 Picture 7: Another example of D12-L1 tuberculosis, which shows involvement of D 11 on the MRI that excludes the possibility of using pedicle screw in the D 11 level The patients were followed up at 2 weeks after discharge, and then monthly for 6 months, six monthly or as required later on. The outcome was assessed in the form of mechanical correction achieved by measuring kyphotic angles, neurological recovery in the measure of ASIA (American Spinal Injury Association) scoring system ( 12 ) and fusion status that was suggested by presence or absence of local pain on movement anteroposterior and lateral radiographs and maintenance of correction. RESULTS Mean duration of follow-up months after surgery (range months). 4 patients were lost to follow-up on a long term. Operative blood loss was 300 mls per procedure per patient. Mean angle correction at the last follow-up of all patients degrees (max. 20 degrees) There were no peroperative complications noticed. 2 patients had posterior surgery wound infection at 4 th postoperative day, which was treated with routine wound debridement and antibiotics and healed uneventfully later. Another patient 5 of 9
6 with ASIA A neurology at presentation had severe posterior surgery wound infection that required implant removal in the 4th week after surgery. The patient showed 6 degrees loss of correction after implant removal, and didn't improve in neurological status. 60 patients showed upto 2 ASIA grades improvement in neurology. 6 patients who presented with ASIA A neurology primarily didn't improve at all. One patient had neurological deterioration immediate postoperative after sublaminar wiring and hartshill fixation from ASIA grade B to A. The implants were removed immediately but the patient never had any neurological recovery in next 26 months follow-up. Figure 10 Table 3: Complications encountered Most (81) patients were completely pain free and all had improved pain scores as compared to preoperative status. All but 1 patient had radiological signs of fusion at 12 months post operatively. The patient that didn't show radiological signs of fusion also had significant relief from pain as compared to pre-operative pain scores. The radiological signs of fusion started to appear at 3rd month post anterior surgery follow-up in most patients. 2 patients had signs of lucency around the graft at 3 months, they were sent for ultrasound scans and recurrent abscess was found. The abscess was drained under ultrasound guidance and sent for culture, and both were found to be having tuberculous infection resistant to routine antituberculosis chemotherapy. Revised chemotherapy schedule was arranged in consultation with medical specialists in conjunction with the therapeutic aspiration of abscess. Both patients showed fusion at 8-9 months post surgery. The one patient who had posterior surgical site infection requiring implant removal had lost kyphotic correction, but went on to fuse in kyphotic position anteriorly. The patient was ASIA A at presentation and never improved neurologically, but had healed infection and significant pain relief at 15 months follow-up. The one patient who had worsened after the posterior corrective fixation also had a signal intensity change of the spinal cord matter on the MRI scan. The patient didn't show any improvement in neurology after implant removal. It was assumed that the neurological injury developed due to the mechanical or vascular trauma due to stretching on the neurological tissue which was already involved in tuberculous inflammatory process. 9 patients had decubitus ulcers from the time of presentation, which were of superficial nature and healed with split skin grafting in 3 patients and dressing and rehabilitation in the rest. There were no late neurological deteriorations in any patient. 3 patients died within 12 months of surgery due to unrelated causes. There were no graft related problems like graft displacement, slippage, fracture or subsidence. DISCUSSION Due to the usual late presentation, most TB spine patients present with some degree of kyphosis. Anterior debridement and fusion with structural graft support has been established as recommended surgical treatment for spinal TB, ( 4, 9, 11 ) but it has not been successful in preventing subsequent progressive kyphosis from developing. Only anterior surgery with grafting also has very limited potential for correction of deformity due to adjacent segment bones being too osteoporotic for a good purchase and dispensable forces of correction with anterior instrumentation. Anterior fixation devices bring in the fear of providing innate surface for residual infection and also are not as efficient in correcting and preventing kyphosis as the posterior fixation devices. The residual and progressive kyphosis creates physical and psychological difficulties for the patient including chronic backache and so prevention and correction of kyphotic deformity is an important clinical goal for patients with dorsolumbar tuberculous spines ( 15 ). The patients in this series were all in the active exudative stage of the disease- as established by active destruction and instability of vertebral column with expression of active granulomatous tissue, tuberculous sequestra and pus at the time of anterior surgery. At this stage the correction of kyphotic deformity is mechanically easy to achieve as the kyphosis is not yet rigid enough to require primary anterior release for correction.( 10 ) Posterior correction is partially achieved by positioning the patient in prone position on the Relton-Hall frame, and then using the posterior implant facilities for correction. There are series reported of cases operated with posterior fixation being done after first doing anterior debridement and reconstruction, but we believe that trying to achieve correction after having grafted anteriorly would result in probable destabilization of the graft or loss of compressive forces on graft. Thus the correction would have 6 of 9
7 to be dependant on the amount of correction achievable with only anterior surgery, which might not be as much as that attainable with posterior surgery. Having the spine fixed posteriorly gives the advantages of giving the subsequent anterior graft primary stability and allowing immediate mobilization and rehabilitation of the patient. It may be of concern that with primary fixation in situ the anterior graft material may not have the advantage of compression forces that would hasten fusion, but as most (83) of our patients had fixation with sublaminar wires and Hartshill rectangle system, which allowed some vertical freedom of movement to the spinal column, it provides compression without allowing progressive kyphotic angular deformity. Again as the sublaminar wires are placed in the caudal and cephalad bodies from the apex of the kyphus in the patients, there is no real danger of occupying the already endeared spinal canal. We didn't experience any neurological injury directly attributed to the implant placements. The attained correction at the final follow-up at a mean of 41 months in our series was an average of 36.6% of the original deformity. (Maximum 58.5%) which is significantly more than the correction reported at the final follow up by Kim et al ( 13 ) who reported 55.1% average initial correction but could maintain only 7.5% correction at the final follow up at average 24 month. We didn't face any graft problems like graft fracture, slippage, resorption, or collapse unlike the series by Lifeso et al ( 14 ) who reported these complications in their patients treated with only anterior debridement and fusion. The first stage posterior fixation gave a great mechanical pain relief to the patients early post-operatively which allowed the patients to be mobilized to different extents very soon after the posterior surgery. With this the complications like decubitus ulcers were avoided to a great extent. Again the posterior fixation rendered the anterior reconstruction immediate stability, which allowed important advantage avoiding bed-ridden condition to avoid decubitus ulcers and post-operative pneumonia and other complications of recumbency in the patients. Deep venous thrombosis is anyways uncommon in Indian population and we didn't need to use thromboprophylaxis in any patient. With regular chemotherapy (and 2 patients with modified chemotherapy regime) all patients had their tuberculous infection healed. CONCLUSION Primary posterior corrective fixation with appropriately selected instrumentation and second stage anterior debridement and reconstruction with appropriate chemotherapy gives a good correction and long term maintenance of the deformity with good neurological decompression and early bony healing and allows early and faster rehabilitation when performed for patients with exudative stage of tuberculosis of spine. References 1. Moon MS. Spine update. Tuberculosis of the spine; controversies and a new challenge. Spine. 1997; 22: Ufuk T, Abdullah G, Cagatay O, Azmi H, Unsal D. The role of posterior instrumentation and fusion after anterior radical debridement and fusion in the surgical treatment of spinal tuberculosis: experience of 127 cases. J Spinal Disord Tech 2006: 19: Yao DC, Sartoris DJ. Musculoskeletal tuberculosis. Radiol Clin North Am. 1965; 33: Medical Research Council working party on tuberculosis of the spine. Five year assessment of controlled trials of ambulatory treatment, debridement and anterior spinal fusion in the management of tuberculosis of the spine: studies in Bulawayo (Rhodesia) and in Hong-Kong. J Bone Joint Surg. (Br). 1978; 60: Medical Research Council working party on tuberculosis of the spine. A 10 year assessment of the controlled trials of in-patient and out-patient treatment and of plaster-of-paris jackets for tuberculosis of the spine in children on standard chemotherapy. J Bone Joint Surg (Br). 1985; 67: Wen-Jer Chen, Chi-Chuan Wu, Chi-Hsiung Jung, Lih- Huei Chen, Chi-Chien Niu, Po-Liang Lai. Combined anterior and posterior surgeries in the treatment of spinal tuberculous spondylitis. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 2002; 398: Sundararaj GD, Behera S, Ravi V, Venkatesh K, Cherian VM, Lee V. Role of posterior stabilization in the management of tuberculosis of the dorsal and lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 2003; 85-B: Moon MS, Woo YK, Lee KS, et al. Posterior instrumentation and anterior interbody fusion for tuberculous kyphosis of dorsal and lumbar spine. Spine 1995; 20: Yilmaz C, Selek HY, Gurkan I, et al. Anterior instrumentation for the treatment of spinal tuberculosis. J Bone Joint Surg (Am). 1999; 81: Rajasekaran S. The problem of deformity in spinal tuberculosis. Clin Orthop & Related Research. 2002; 398: Hodgson AR, Stock FE. Anterior spinal fusion for the treatment of tuberculosis of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg. 1960; 42-A: Staas WE Jr, Formal CS, Freedman MK, Fried GW, Schmidt Read ME. Spinal cord injury and spinal cord injury medicine. In: DeLisa JA, Gans BM, eds. Rehabilitation medicine: Principles and practice. Third edition. Philadelphia etc. Lippincott-Raven 1998; Kim BJ, Ko HS, Lim Y, et al. The clinical study of the tuberculous spondylitis. J Korian Orthop Assoc. 1993; 28: Lifeso RM, Weaver P, Harder EH. Tuberculous spondylitis in adults. J Bone Joint Surg (Am). 1985; 67: McLain RF, Isada C. Spinal tuberculosis deserves a place on the radar screen. Cleveland clinic journal of 7 of 9
8 medicine. 2004; 71-7: of 9
9 Author Information Bhavin Jadav, M.S. (Ortho) Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics,, Department of Orthopaedics, B J Medical College and Civil Hospital, Ahmedabad, India., Paraplegia hospital, Ahmedabad, India Mukund M. Prabhakar, M.S. (Ortho) Professor and Head of the department, Department of Orthopaedics, B J Medical College and Civil Hospital, Ahmedabad, India., Paraplegia hospital, Ahmedabad, India 9 of 9
Single stage posterior instrumentation and anterior interbody fusion for tuberculosis of dorsal and lumbar spines
 Original Article interbody fusion for tuberculosis of dorsal Pandey BK 1, Sangondimath GM 2, Chhabra HS 2 1 Department of Orthopaedics, Kathmandu Medical College Teaching Hospital, Sinamangal, Kathmandu,
Original Article interbody fusion for tuberculosis of dorsal Pandey BK 1, Sangondimath GM 2, Chhabra HS 2 1 Department of Orthopaedics, Kathmandu Medical College Teaching Hospital, Sinamangal, Kathmandu,
Surgical Treatment of Thoracic and Lumbar Tuberculosis by Anterior Interbody Fusion and Posterior Instrumentation
 Original Paper Med Princ Pract 2003;12:92 96 DOI: 10.1159/000069113 Received: April 21, 2002 Revised: August 3, 2002 Surgical Treatment of Thoracic and Lumbar Tuberculosis by Anterior Interbody Fusion
Original Paper Med Princ Pract 2003;12:92 96 DOI: 10.1159/000069113 Received: April 21, 2002 Revised: August 3, 2002 Surgical Treatment of Thoracic and Lumbar Tuberculosis by Anterior Interbody Fusion
Long Posterior Fixation with Short Fusion for the Treatment of TB Spondylitis of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine with or without Neurologic Deficit
 Long Posterior Fixation with Short Fusion for the Treatment of TB Spondylitis of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine with or without Neurologic Deficit Shih-Tien Wang MD, Chien-Lin Liu MD 王世典劉建麟 School of Medicine,
Long Posterior Fixation with Short Fusion for the Treatment of TB Spondylitis of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine with or without Neurologic Deficit Shih-Tien Wang MD, Chien-Lin Liu MD 王世典劉建麟 School of Medicine,
To study the outcomes of posterior decompression and fixation of tuberculosis of dorsolumbar spine
 2017; 3(3): 691-695 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 691-695 2017 IJOS wwworthopapercom Received: 15-05-2017 Accepted: 16-06-2017 Dr Manish Shah Assistant Professor, Department of Dr Kushal Suthar Dr Ravindra
2017; 3(3): 691-695 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 691-695 2017 IJOS wwworthopapercom Received: 15-05-2017 Accepted: 16-06-2017 Dr Manish Shah Assistant Professor, Department of Dr Kushal Suthar Dr Ravindra
Comparison of clinical, radiological and functional outcome of short segment V/S long segment posterior fixation of tuberculosis of spine
 2018; 2(4): 104-108 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 104-108 Received: 20-08-2018 Accepted: 21-09-2018 Dr. Mitul Mistry Assistant Professor,
2018; 2(4): 104-108 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 104-108 Received: 20-08-2018 Accepted: 21-09-2018 Dr. Mitul Mistry Assistant Professor,
Tuberculosis Of The Lumbar Spine: Outcomes After Combined Treatment With Short-Course Two-Drug Therapy And Surgery
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 7 Number 1 Tuberculosis Of The Lumbar Spine: Outcomes After Combined Treatment With Short-Course Two-Drug Therapy And Surgery O Karaeminogullari, U Aydinli,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 7 Number 1 Tuberculosis Of The Lumbar Spine: Outcomes After Combined Treatment With Short-Course Two-Drug Therapy And Surgery O Karaeminogullari, U Aydinli,
University of Groningen. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria
 University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
ISPUB.COM. Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay. P Chudgar INTRODUCTION SPINE
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
ASJ. Evaluation of Outcome of Transpedicular Decompression and Instrumented Fusion in Thoracic and Thoracolumbar Tuberculosis. Asian Spine Journal
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2017;11(1):31-36 Transpedicular decompression https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2017.11.1.31 in potts spine Evaluation of Outcome of Transpedicular
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2017;11(1):31-36 Transpedicular decompression https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2017.11.1.31 in potts spine Evaluation of Outcome of Transpedicular
Anterior Surgical Interventions in Spinal Tuberculosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anterior Surgical Interventions in Spinal Tuberculosis Obaid-ur-Rahman, Saleem Ahmad and Tayyab Hussain ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate and compare the effectiveness of the modified Hong
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anterior Surgical Interventions in Spinal Tuberculosis Obaid-ur-Rahman, Saleem Ahmad and Tayyab Hussain ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate and compare the effectiveness of the modified Hong
Preliminary Study of Tuberculosis of the Spine
 Original Articles Preliminary Study of Tuberculosis of the Spine Robert C. Lifeso, MD, FRCS(C)* * Orthopedic Surgeon, Department of Surgery, King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Centre ABSTRACT
Original Articles Preliminary Study of Tuberculosis of the Spine Robert C. Lifeso, MD, FRCS(C)* * Orthopedic Surgeon, Department of Surgery, King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Centre ABSTRACT
Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR Page 1 of 9 INSTABILITY AND DEGENERATIVE DISC CONDITIONS FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY CPT4
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR Page 1 of 9 INSTABILITY AND DEGENERATIVE DISC CONDITIONS FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY CPT4
ASJ. Study of Vertebral Body Replacement with Reconstruction Spinal Cages in Dorsolumbar Traumatic and Koch s Spine. Asian Spine Journal.
 Asian Spine Journal 786 Rohit Anilbhai Clinical Thaker Studyet al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.6.786 Study of Vertebral Body Replacement with Reconstruction Spinal Cages in Dorsolumbar Traumatic
Asian Spine Journal 786 Rohit Anilbhai Clinical Thaker Studyet al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.6.786 Study of Vertebral Body Replacement with Reconstruction Spinal Cages in Dorsolumbar Traumatic
Surgical Treatment of Lower Cervical Tuberculosis With Kyphosis Deformity. Department of Spine, General Hospital of Lanzhou Command, Gansu, China
 Int Surg 2017;102:171 177 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-15-00051.1 Surgical Treatment of Lower Cervical Tuberculosis With Kyphosis Deformity Xu Lan, Jian-Zhong Xu, Xue-Mei Liu, Bao-Feng Ge Department of Spine,
Int Surg 2017;102:171 177 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-15-00051.1 Surgical Treatment of Lower Cervical Tuberculosis With Kyphosis Deformity Xu Lan, Jian-Zhong Xu, Xue-Mei Liu, Bao-Feng Ge Department of Spine,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2): /ISSN: /IJCEM Yi Yang, Hao Liu, Yueming Song, Tao Li
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):1278-1284 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0063093 Case Report Dislocation and screws pull-out after application of an Isobar TTL dynamic stabilisation system at L2/3 in
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):1278-1284 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0063093 Case Report Dislocation and screws pull-out after application of an Isobar TTL dynamic stabilisation system at L2/3 in
3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx. White Paper
 3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx (SLM selective laser melted) Goal of the study: Does the sharx intervertebral cage due to innovative material, new design, and lordotic shape solve some problems
3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx (SLM selective laser melted) Goal of the study: Does the sharx intervertebral cage due to innovative material, new design, and lordotic shape solve some problems
Surgical treatment of tuberculous spondylodiscitis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2012; 1(Suppl 2): 79-85 Surgical treatment of tuberculous spondylodiscitis E. POLA, B. ROSSI, L.A. NASTO, D. COLANGELO, C.A. LOGROSCINO Division
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2012; 1(Suppl 2): 79-85 Surgical treatment of tuberculous spondylodiscitis E. POLA, B. ROSSI, L.A. NASTO, D. COLANGELO, C.A. LOGROSCINO Division
Departement of Neurosurgery A.O.R.N A. Cardarelli- Naples.
 Percutaneous posterior pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic, lumbar and thoraco-lumbar junction (T12-L1) traumatic and pathological spine fractures. Report of 45 cases. G. Vitale, A. Punzo,
Percutaneous posterior pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic, lumbar and thoraco-lumbar junction (T12-L1) traumatic and pathological spine fractures. Report of 45 cases. G. Vitale, A. Punzo,
factor for identifying unstable thoracolumbar fractures. There are clinical and radiological criteria
 NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
Spinal Fusion. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Spinal Fusion North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Spinal Fusion? The spine is made up of a series of bones called vertebrae ; between each vertebra are strong connective tissues
Spinal Fusion North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Spinal Fusion? The spine is made up of a series of bones called vertebrae ; between each vertebra are strong connective tissues
Single-stage approach of posterior debridement, allograft and internal fixation in management of lumbosacral tuberculosis.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (3): 1448-1452 Single-stage approach of posterior debridement, allograft and internal fixation in management of lumbosacral tuberculosis. Jiawen Wu 1, Juanjuan Wang 2, Ming
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (3): 1448-1452 Single-stage approach of posterior debridement, allograft and internal fixation in management of lumbosacral tuberculosis. Jiawen Wu 1, Juanjuan Wang 2, Ming
Posterior. Lumbar Fusion. Disclaimer. Integrated web marketing. Multimedia Health Education
 Posterior Lumbar Fusion Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on. All decisions about surgery must be made in conjunction with your surgeon or
Posterior Lumbar Fusion Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on. All decisions about surgery must be made in conjunction with your surgeon or
FUNCTIONAL OUTCOMES OF TRAUMATIC PARAPLEGIA PATIENTS: DOES SURGERY IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF LIFE?
 FUNCTIONAL OUTCOMES OF TRAUMATIC PARAPLEGIA PATIENTS: DOES SURGERY IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF LIFE? Original Article Orthopaedics R S Bajoria 1, Mahendra Panwar 2, Anand Rao 3, Sameer Gupta 4 1 - Associate
FUNCTIONAL OUTCOMES OF TRAUMATIC PARAPLEGIA PATIENTS: DOES SURGERY IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF LIFE? Original Article Orthopaedics R S Bajoria 1, Mahendra Panwar 2, Anand Rao 3, Sameer Gupta 4 1 - Associate
Key words: Spine, tuberculosis, anterior, surgery, adult. Reprint requests: Prof RN Dunn
 CLINICAL ARTICLE SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Spring 2011 Vol 10 No 3 / Page 43 C L I N I C A L A RT I C L E Anterior-only transthoracic surgery for adult spinal tuberculosis Dr Bryan Riemer MBChB(UCT) Registrar,
CLINICAL ARTICLE SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Spring 2011 Vol 10 No 3 / Page 43 C L I N I C A L A RT I C L E Anterior-only transthoracic surgery for adult spinal tuberculosis Dr Bryan Riemer MBChB(UCT) Registrar,
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:71-77 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.71 More than 5-Year Follow-up Results of Two- Level and Three-Level Posterior Fixations of Thoracolumbar
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:71-77 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.71 More than 5-Year Follow-up Results of Two- Level and Three-Level Posterior Fixations of Thoracolumbar
Behaviour of the kyphotic angle in spinal tuberculosis
 International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2004) 28:110 114 DOI 10.1007/s00264-003-0516-z ORIGINAL PAPER A. K. Jain P. K. Aggarwal A. Arora S. Singh Behaviour of the kyphotic angle in spinal tuberculosis Accepted:
International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2004) 28:110 114 DOI 10.1007/s00264-003-0516-z ORIGINAL PAPER A. K. Jain P. K. Aggarwal A. Arora S. Singh Behaviour of the kyphotic angle in spinal tuberculosis Accepted:
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
ELY ASHKENAZI Israel Spine Center at Assuta Hospital Tel Aviv, Israel
 nterior cervical decompression using the Hybrid Decompression Fixation technique, a combination of corpectomies and or discectomies, in the management of multilevel cervical myelopathy J ORTHOP TRUM SURG
nterior cervical decompression using the Hybrid Decompression Fixation technique, a combination of corpectomies and or discectomies, in the management of multilevel cervical myelopathy J ORTHOP TRUM SURG
Ang Deng, Hong-Qi Zhang, Ming-Xing Tang, Shao-Hua Liu, Qi-Le Gao, Yu-Xiang Wang, Chao-Feng Guo, Xi-Yang Wang
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):3953-3959 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0016644 Original Article One-stage combined posterior and anterior approaches for active tuberculosis of the subaxial cervical
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):3953-3959 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0016644 Original Article One-stage combined posterior and anterior approaches for active tuberculosis of the subaxial cervical
SURGICAL INDICATIONS AND COMPLICATIONS OF CAPENER TECHNIQUE (COSTO-TRANSVERSECTOMY).
 SURGICAL INDICATIONS AND COMPLICATIONS OF CAPENER TECHNIQUE (COSTO-TRANSVERSECTOMY). TRANSVERSECTOMY). Patricia Álvarez González, Javier Pizones Arce, Felisa SánchezS nchez-mariscal, Lorenzo ZúñZ úñiga
SURGICAL INDICATIONS AND COMPLICATIONS OF CAPENER TECHNIQUE (COSTO-TRANSVERSECTOMY). TRANSVERSECTOMY). Patricia Álvarez González, Javier Pizones Arce, Felisa SánchezS nchez-mariscal, Lorenzo ZúñZ úñiga
PATIENT: DOB: TODAY S DATE:
 1. I have been strongly advised to carefully read and consider this operative permit. I realize that it is important that I understand this material. I also understand that if certain sections are not
1. I have been strongly advised to carefully read and consider this operative permit. I realize that it is important that I understand this material. I also understand that if certain sections are not
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine
 A spinal fracture is a serious injury. Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological
A spinal fracture is a serious injury. Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological
POTT'S Disease: a review of 58 cases
 Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 23, No. 4, February, 2010. pp. 200-206 POTT'S Disease: a review of 58 cases Mohammadreza Ehsaei, MD. 1, Fariborz Samini, MD. 2, Gholamreza
Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 23, No. 4, February, 2010. pp. 200-206 POTT'S Disease: a review of 58 cases Mohammadreza Ehsaei, MD. 1, Fariborz Samini, MD. 2, Gholamreza
/ 66 nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide-66 n-ha/pa66
 1425 / 66 / 66 nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide-66 n-ha/pa66 2011 1 10 20 n-ha/pa66 8 12 22 80 51 1 24 4 L 4 5 8 L 5 S 1 9 L 4 S 1 3 3 5 9 3 X CT Oswestry ODI SF-36 20 6 9 7 3 d 3 6 P < 0.01P > 0.05 3 9 4
1425 / 66 / 66 nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide-66 n-ha/pa66 2011 1 10 20 n-ha/pa66 8 12 22 80 51 1 24 4 L 4 5 8 L 5 S 1 9 L 4 S 1 3 3 5 9 3 X CT Oswestry ODI SF-36 20 6 9 7 3 d 3 6 P < 0.01P > 0.05 3 9 4
Thoracic or lumbar spinal surgery in patients with Parkinson s disease -A two-center experience of 32 cases-
 Thoracic or lumbar spinal surgery in patients with Parkinson s disease -A two-center experience of 32 cases- Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto university Hiroaki Kimura,
Thoracic or lumbar spinal surgery in patients with Parkinson s disease -A two-center experience of 32 cases- Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto university Hiroaki Kimura,
Surgical treatment of acute TB spondylitis: indications and outcomes. European Spine Journal, 2013, v. 22 suppl. 4, p. S603-S611
 Title Surgical treatment of acute TB spondylitis: indications and outcomes Author(s) Mak, KC; Cheung, KMC Citation European Spine Journal, 2013, v. 22 suppl. 4, p. S603-S611 Issued Date 2013 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/170210
Title Surgical treatment of acute TB spondylitis: indications and outcomes Author(s) Mak, KC; Cheung, KMC Citation European Spine Journal, 2013, v. 22 suppl. 4, p. S603-S611 Issued Date 2013 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/170210
ISPUB.COM. T Iizuka, S Yamada INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Spine Surgery Volume 2 Number 1 Management Of Symptomatic De Novo Adult Scoliosis Of The Lumbar Spine Caused By Progressive Hemi-Vertebral Compression Fractures Following
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Spine Surgery Volume 2 Number 1 Management Of Symptomatic De Novo Adult Scoliosis Of The Lumbar Spine Caused By Progressive Hemi-Vertebral Compression Fractures Following
Congenital deformity of the spine-therapy. Werner Lack*, Georg Grabmeier**
 Congenital deformity of the spine-therapy Werner Lack*, Georg Grabmeier** *free spine surgeons of Austria, **SMZ-East, Vienna Conservative therapy in clear cases of progression (2 hemi vertebrae, unilateral
Congenital deformity of the spine-therapy Werner Lack*, Georg Grabmeier** *free spine surgeons of Austria, **SMZ-East, Vienna Conservative therapy in clear cases of progression (2 hemi vertebrae, unilateral
Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by vertebral shortening
 Eur Spine J (2002) 11 :8 12 DOI 10.1007/s005860000214 TECHNICAL INNOVATION Alejandro Reyes-Sanchez Luis M. Rosales Victor P. Miramontes Dario E. Garin Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by vertebral
Eur Spine J (2002) 11 :8 12 DOI 10.1007/s005860000214 TECHNICAL INNOVATION Alejandro Reyes-Sanchez Luis M. Rosales Victor P. Miramontes Dario E. Garin Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by vertebral
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 17 Orthopedic Techniques Key Points 2 17.1 Traction Use an appropriate method of traction to treat fractures of the extremities and cervical spine Apply extremity
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 17 Orthopedic Techniques Key Points 2 17.1 Traction Use an appropriate method of traction to treat fractures of the extremities and cervical spine Apply extremity
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
 Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Surgical Treatment Comparisons By: Dr. Alex Rabinovich and Dr. Devin Peterson Options 1. Pedicle Screws versus Hooks 2. Posterior versus Anterior Instrumentation 3. Open
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Surgical Treatment Comparisons By: Dr. Alex Rabinovich and Dr. Devin Peterson Options 1. Pedicle Screws versus Hooks 2. Posterior versus Anterior Instrumentation 3. Open
Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 202 206 Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report RB Winter Clinical Professor,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 202 206 Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report RB Winter Clinical Professor,
POSTERIOR LUMBAR FUSION SURGERY INFORMATION
 POSTERIOR LUMBAR FUSION SURGERY INFORMATION WHAT IS LUMBAR FUSION SURGERY? Spinal fusion is a surgical procedure that joins or fuses 2 or more vertebrae (bones) so that movement no longer occurs between
POSTERIOR LUMBAR FUSION SURGERY INFORMATION WHAT IS LUMBAR FUSION SURGERY? Spinal fusion is a surgical procedure that joins or fuses 2 or more vertebrae (bones) so that movement no longer occurs between
A CASE OF MISMANAGED CERVICAL FRACTURE IN A PATIENT OF ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS
 A CASE OF MISMANAGED CERVICAL FRACTURE IN A PATIENT OF ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS INTRODUCTION Spine fractures occur with minor trauma in patients with ankylosing Spondylitis. They are highly unstable with
A CASE OF MISMANAGED CERVICAL FRACTURE IN A PATIENT OF ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS INTRODUCTION Spine fractures occur with minor trauma in patients with ankylosing Spondylitis. They are highly unstable with
 Introduction Posterior cervical fusion is done through the back posterior of the neck. The surgery joins two or more neck vertebrae into one solid section of bone. The medical term for fusion is arthrodesis.
Introduction Posterior cervical fusion is done through the back posterior of the neck. The surgery joins two or more neck vertebrae into one solid section of bone. The medical term for fusion is arthrodesis.
Advantages of MISS. Disclosures. Thoracolumbar Trauma: Minimally Invasive Techniques. Minimal Invasive Spine Surgery 11/8/2013.
 3 rd Annual UCSF Techniques in Complex Spine Surgery Program Thoracolumbar Trauma: Minimally Invasive Techniques Research Support: Stryker Disclosures Murat Pekmezci, MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF/SFGH
3 rd Annual UCSF Techniques in Complex Spine Surgery Program Thoracolumbar Trauma: Minimally Invasive Techniques Research Support: Stryker Disclosures Murat Pekmezci, MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF/SFGH
Patient Information MIS LLIF. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
 Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine...2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine...2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
Study of functional outcomes of surgical treatment of tuberculosis of spine with debridement and spinal fixation
 2017; 3(1): 389-394 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(1): 389-394 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 15-11-2016 Accepted: 17-12-2016 Dr. Pallav Patel MS Ortho Poojan Orthopaedic Hospital Himmatnagar, Gujarat,
2017; 3(1): 389-394 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(1): 389-394 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 15-11-2016 Accepted: 17-12-2016 Dr. Pallav Patel MS Ortho Poojan Orthopaedic Hospital Himmatnagar, Gujarat,
Yongchun Zhou 1, Weiwei Li 1*, Jun Liu 1, Liqun Gong 1 and Jing Luo 2*
 Zhou et al. BMC Surgery (2018) 18:71 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-018-0405-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Comparison of single posterior debridement, bone grafting and instrumentation with single-stage
Zhou et al. BMC Surgery (2018) 18:71 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-018-0405-4 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Comparison of single posterior debridement, bone grafting and instrumentation with single-stage
Surgical treatment of preschool childhood spinal thoracic tuberculosis: two case reports and technical note
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXII Number 1 2018 January-March Article Surgical treatment of preschool childhood spinal thoracic tuberculosis: two case reports and technical note Mehmet Nuri Erdem, Anas
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXII Number 1 2018 January-March Article Surgical treatment of preschool childhood spinal thoracic tuberculosis: two case reports and technical note Mehmet Nuri Erdem, Anas
Spinal injury. Structure of the spine
 Spinal injury Structure of the spine Some understanding of the structure of the spine (spinal column) and the spinal cord is important as it helps your Neurosurgeon explain about the part of the spine
Spinal injury Structure of the spine Some understanding of the structure of the spine (spinal column) and the spinal cord is important as it helps your Neurosurgeon explain about the part of the spine
MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis
 CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
1105 two (2) vertebrae... 1, add on per additional vertebra
 SPINE STAGE OPERATIONS Staged operations shall be paid at 100% for the first stage and 85% for the second stage. Where the second stage pays a higher fee 100% shall be paid and the first stage shall be
SPINE STAGE OPERATIONS Staged operations shall be paid at 100% for the first stage and 85% for the second stage. Where the second stage pays a higher fee 100% shall be paid and the first stage shall be
Patient Information MIS LLIF. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
 Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine....2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine....2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
Pott s kyphosis. University Affiliated Sixth People s Hospital, 600 Yishan Road, Shanghai , P.
 QJM Advance Access published November 17, 2014 Pott s kyphosis Author Names: Yi Zhang, Yong-Sheng Yu, Zheng-Hao Tang and Guo-Qing Zang Author Affiliations: Department of Infectious Diseases, Shanghai Jiao
QJM Advance Access published November 17, 2014 Pott s kyphosis Author Names: Yi Zhang, Yong-Sheng Yu, Zheng-Hao Tang and Guo-Qing Zang Author Affiliations: Department of Infectious Diseases, Shanghai Jiao
Treatment of Spinal Tuberculosis by Debridement, Interbody Fusion and Internal Fixation via Posterior Approach Only
 89 2016 THE AUTHORS PUBLISHED BY JOHN WILEY &SONS AUSTRALIA, LTD. VIDEO OF ORTHOPAEDIC TECHNIQUE Treatment of Spinal Tuberculosis by Debridement, Interbody Fusion and Internal Fixation via Posterior Approach
89 2016 THE AUTHORS PUBLISHED BY JOHN WILEY &SONS AUSTRALIA, LTD. VIDEO OF ORTHOPAEDIC TECHNIQUE Treatment of Spinal Tuberculosis by Debridement, Interbody Fusion and Internal Fixation via Posterior Approach
Department of Spine Surgery Activity Report-2014
 SKS HOSPITAL I N D I A P R I VAT E LT D., Care to Cure Department of Spine Surgery Activity Report-2014 About SKS Hospital SKS Hospital, started in 1987 as the first multi-speciality hospital in Salem,
SKS HOSPITAL I N D I A P R I VAT E LT D., Care to Cure Department of Spine Surgery Activity Report-2014 About SKS Hospital SKS Hospital, started in 1987 as the first multi-speciality hospital in Salem,
Evaluation of implant stabilization in tubercular Spondylodiscitis: a prospective study
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Maila SK et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Oct;3(10):2647-2653 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20150807
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Maila SK et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Oct;3(10):2647-2653 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20150807
5/27/2016. Stand-Alone Lumbar Lateral Interbody Fusion (LLIF) vs. Supplemental Fixation. Disclosures. LLIF Approach
 Stand-Alone Lumbar Lateral Interbody Fusion (LLIF) vs. Supplemental Fixation Joseph M. Zavatsky, M.D. Spine & Scoliosis Specialists Tampa, FL Disclosures Consultant - Zimmer / Biomet, DePuy Synthes Spine,
Stand-Alone Lumbar Lateral Interbody Fusion (LLIF) vs. Supplemental Fixation Joseph M. Zavatsky, M.D. Spine & Scoliosis Specialists Tampa, FL Disclosures Consultant - Zimmer / Biomet, DePuy Synthes Spine,
Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life
 Original Study Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life Lorenzo Nigro 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Pasquale
Original Study Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life Lorenzo Nigro 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Pasquale
Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia: A Case Series
 C a s e R e p o r t J. of Advanced Spine Surgery Volume 2, Number 2, pp 60~65 Journal of Advanced Spine Surgery JASS Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia:
C a s e R e p o r t J. of Advanced Spine Surgery Volume 2, Number 2, pp 60~65 Journal of Advanced Spine Surgery JASS Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia:
Conservatively Treated Spinal Tuberculosis in Children: Ambulatory Chemotherapy
 Myung-Sang Moon ORIGINL RTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10039-1162 Conservatively Treated Spinal Tuberculosis in Children: mbulatory Chemotherapy Myung-Sang Moon BSTRCT Introduction: To assess the chronological
Myung-Sang Moon ORIGINL RTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10039-1162 Conservatively Treated Spinal Tuberculosis in Children: mbulatory Chemotherapy Myung-Sang Moon BSTRCT Introduction: To assess the chronological
The Neurologic Outcome Of Posterior Fixation Of Thoraco- Lumbar Spine Fractures In A Rural Tertiary Care Centre Without Help Of Image Intensifier
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 4, Issue 6 (Jan.- Feb. 2013), PP 36-40 The Neurologic Outcome Of Posterior Fixation Of Thoraco- Lumbar
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 4, Issue 6 (Jan.- Feb. 2013), PP 36-40 The Neurologic Outcome Of Posterior Fixation Of Thoraco- Lumbar
PART III IN HOSPITAL ON CALL ANESTHESIA COVERAGE
 Anesthesia g) A consultation may not be claimed where the patient is referred to the anesthetist for the sole purpose of providing post-operative Patient Controlled Analgesia. h) Tariff 8406 may not be
Anesthesia g) A consultation may not be claimed where the patient is referred to the anesthetist for the sole purpose of providing post-operative Patient Controlled Analgesia. h) Tariff 8406 may not be
Get back to: my life. Non-fusion treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis
 Get back to: my life Non-fusion treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis Do you have any of these symptoms? numbness, weakness or pain in the lower legs When any of these conditions occur, the spinal nerve,
Get back to: my life Non-fusion treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis Do you have any of these symptoms? numbness, weakness or pain in the lower legs When any of these conditions occur, the spinal nerve,
Surgical Technique INTERSOMATIC CERVICAL CAGE
 R INTERSOMATIC CERVICAL CAGE NEOCIF IMPLANTS NEOCIF is an implant designed to make anterior cervical interbody fusion (ACIF) easier and to remove the need for structural autologous graft. The cage is made
R INTERSOMATIC CERVICAL CAGE NEOCIF IMPLANTS NEOCIF is an implant designed to make anterior cervical interbody fusion (ACIF) easier and to remove the need for structural autologous graft. The cage is made
FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY
 FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY Information for Patients WHAT IS FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY? The foot and the ankle are crucial for human movement. The balanced action of many bones, joints, muscles and tendons
FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY Information for Patients WHAT IS FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY? The foot and the ankle are crucial for human movement. The balanced action of many bones, joints, muscles and tendons
Preliminary Report of Instrumentation in Tuberculous Lumbosacral Spine
 Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1411.004 Preliminary Report of Instrumentation in Tuberculous Lumbosacral Spine, MRCS Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yangon Orthopaedic Hospital, Yangon, Myanmar ABSTRACT
Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1411.004 Preliminary Report of Instrumentation in Tuberculous Lumbosacral Spine, MRCS Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Yangon Orthopaedic Hospital, Yangon, Myanmar ABSTRACT
Posterior wedge osteotomy and debridement for Andersson lesion with severe kyphosis in ankylosing spondylitis
 Liang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:54 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0556-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Posterior wedge osteotomy and debridement for Andersson lesion with severe
Liang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:54 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0556-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Posterior wedge osteotomy and debridement for Andersson lesion with severe
W.-Y. YU, C. LOU, F.-J. LIU, D.-W. HE. Introduction. Abstract. OBJECTIVE: Spinal tuberculosis,
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Clinical efficacy of one stage posterior debridement joint graft fixation for lumbar vertebral fractures in spinal tuberculosis patients with compression
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Clinical efficacy of one stage posterior debridement joint graft fixation for lumbar vertebral fractures in spinal tuberculosis patients with compression
KumaFix fixation for thoracolumbar burst fractures: a prospective study on selective consecutive patients
 Xi an Hong Hui Hospital Xi an, Shaanxi, China KumaFix fixation for thoracolumbar burst fractures: a prospective study on selective consecutive patients Dingjun Hao, Baorong He, Liang Yan Hong Hui Hospital,
Xi an Hong Hui Hospital Xi an, Shaanxi, China KumaFix fixation for thoracolumbar burst fractures: a prospective study on selective consecutive patients Dingjun Hao, Baorong He, Liang Yan Hong Hui Hospital,
Short segment pedicle screw fixation of thoracolumbar fracture: a case series of 33 patients
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Hussain N et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Jul;3(4):681-687 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20172550
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Hussain N et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Jul;3(4):681-687 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20172550
Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy. Case JB. Antonio Castellvi 5/19/2017
 Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy John M. Small MD Florida Orthopedic Institute University South Florida Department Orthopedic Surgery Castellvi Spine May 11, 2017 Case JB 66 y/o male 74 235 lbs Retired police
Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy John M. Small MD Florida Orthopedic Institute University South Florida Department Orthopedic Surgery Castellvi Spine May 11, 2017 Case JB 66 y/o male 74 235 lbs Retired police
Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment of multi-segmental cervical spondylotic myelopathy
 92 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2016; 22(6): 92-96 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.jhmuweb.net/ Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment
92 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2016; 22(6): 92-96 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.jhmuweb.net/ Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment
Objectives. Comprehension of the common spine disorder
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
PARAPLEGIA. B FIG. 6 A, B and C, Same patient three years after spinal grafting shows a most remarkable improvement of spinal deformity and posture.
 16 PARAPLEGIA A B FIG. 6 A, B and C, Same patient three years after spinal grafting shows a most remarkable improvement of spinal deformity and posture. a grotesque deformity of the spine and trunk with
16 PARAPLEGIA A B FIG. 6 A, B and C, Same patient three years after spinal grafting shows a most remarkable improvement of spinal deformity and posture. a grotesque deformity of the spine and trunk with
Treatment Options for Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures
 & Treatment Options for Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures Eldin E. Karaiković¹*, Hector O. Pacheco² 1. Assistant Professor, Northwestern University, and Director of the Spine Center and Lead Physician, Orthopaedic
& Treatment Options for Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures Eldin E. Karaiković¹*, Hector O. Pacheco² 1. Assistant Professor, Northwestern University, and Director of the Spine Center and Lead Physician, Orthopaedic
Curative effect comparison of anterior and posterior approach in debridement combined with bone graft fusion for the treatment of spinal tuberculosis.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (11): 4832-4836 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Curative effect comparison of anterior and posterior approach in debridement combined with bone graft fusion for the treatment
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (11): 4832-4836 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Curative effect comparison of anterior and posterior approach in debridement combined with bone graft fusion for the treatment
Management of Bone and Spinal Cord in Spinal Surgery.
 Management of Bone and Spinal Cord in Spinal Surgery. G. Saló, PhD, MD. Senior Consultant Spine Unit. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Ass. Prof. Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona. Introduction The management
Management of Bone and Spinal Cord in Spinal Surgery. G. Saló, PhD, MD. Senior Consultant Spine Unit. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Ass. Prof. Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona. Introduction The management
A Study of 42 Cases of Pott s Paraplegia with Anterior Spinal Decompression & Stabilisation with Rib Graft Alone
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 7 Ver. VIII (July. 2016), PP 45-49 www.iosrjournals.org A Study of 42 Cases of Pott s Paraplegia
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 7 Ver. VIII (July. 2016), PP 45-49 www.iosrjournals.org A Study of 42 Cases of Pott s Paraplegia
Adult Spinal Deformity Robert Hart. Dept. Orthopaedics and Rehab OHSU
 Adult Spinal Deformity 2010 Robert Hart Dept. Orthopaedics and Rehab OHSU What is Adult Spinal Deformity? Untreated Idiopathic Scoliosis Flat Back Syndrome Adjacent Segment Stenosis Non-Union Degenerative
Adult Spinal Deformity 2010 Robert Hart Dept. Orthopaedics and Rehab OHSU What is Adult Spinal Deformity? Untreated Idiopathic Scoliosis Flat Back Syndrome Adjacent Segment Stenosis Non-Union Degenerative
A Measure to Avoid Pleura Injuries in XLIF at Upper Lumbar Levels
 A Measure to Avoid Pleura Injuries in XLIF at Upper Lumbar Levels Takao Nakajima 1, Yong Kim 2, Masabumi Miyamoto 3 Dept. of Orthop. Surg., Nippon Medical School, Chiba Hokusoh Hospital 1 Dept. of Orthop.
A Measure to Avoid Pleura Injuries in XLIF at Upper Lumbar Levels Takao Nakajima 1, Yong Kim 2, Masabumi Miyamoto 3 Dept. of Orthop. Surg., Nippon Medical School, Chiba Hokusoh Hospital 1 Dept. of Orthop.
Bioactive glass S53P4 in spine surgery -results from a prospective 11-year-follow-up
 Bioactive glass S53P4 in spine surgery -results from a prospective 11-year-follow-up Janek Frantzén M.D., Neurosurgeon Turku University Hospital, Finland ROME SPINE 2011 7.12.2011 1 Clinical Development
Bioactive glass S53P4 in spine surgery -results from a prospective 11-year-follow-up Janek Frantzén M.D., Neurosurgeon Turku University Hospital, Finland ROME SPINE 2011 7.12.2011 1 Clinical Development
Thoracolumbar Spine Trauma: II. Principles of Management
 Thoracolumbar Spine Trauma: II. Principles of Management Jeffrey M. Spivak, MD, Alexander R. Vaccaro, MD, and Jerome M. Cotler, MD Abstract The care of patients with thoracolumbar spine trauma with or
Thoracolumbar Spine Trauma: II. Principles of Management Jeffrey M. Spivak, MD, Alexander R. Vaccaro, MD, and Jerome M. Cotler, MD Abstract The care of patients with thoracolumbar spine trauma with or
POSTERIOR CERVICAL FUSION
 AN INTRODUCTION TO PCF POSTERIOR CERVICAL FUSION This booklet provides general information on the Posterior Cervical Fusion (PCF) surgical procedure for you to discuss with your physician. It is not meant
AN INTRODUCTION TO PCF POSTERIOR CERVICAL FUSION This booklet provides general information on the Posterior Cervical Fusion (PCF) surgical procedure for you to discuss with your physician. It is not meant
SHORT SEGMENT FIXATION THORACOLUMBAR UNSTABLE BURST FRACTURES USING DC PLATES & PEDICLE SCREWS
 STUDY SHORT SEGMENT FIXATION THORACOLUMBAR UNSTABLE BURST FRACTURES USING DC PLATES & PEDICLE SCREWS *Hashem, N.; **A Subai, N. *Faculty of Medicine, Ains Shams University, Egypt ^Department of Orthopedics,
STUDY SHORT SEGMENT FIXATION THORACOLUMBAR UNSTABLE BURST FRACTURES USING DC PLATES & PEDICLE SCREWS *Hashem, N.; **A Subai, N. *Faculty of Medicine, Ains Shams University, Egypt ^Department of Orthopedics,
Clinical Analysis of Minimally Invasive Single-segment Reduction and Internal Fixation in Patients with Thoracolumbar Fractures
 Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research 2018, 2(1): 23-27 Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research Clinical Analysis of Minimally Invasive Single-segment Reduction and Internal Fixation in Patients with
Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research 2018, 2(1): 23-27 Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research Clinical Analysis of Minimally Invasive Single-segment Reduction and Internal Fixation in Patients with
Clinical outcomes of muscle pedicle bone grafting (Meyer's Procedure) in cases of old displaced femur neck fractures: A Study Of 20 Cases
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 10 Number 1 Clinical outcomes of muscle pedicle bone grafting (Meyer's Procedure) in cases of old displaced femur neck fractures: A Study Of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 10 Number 1 Clinical outcomes of muscle pedicle bone grafting (Meyer's Procedure) in cases of old displaced femur neck fractures: A Study Of
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
Management of fractures of the pedicle after instrumentation with transpedicular screws
 Management of fractures of the pedicle after instrumentation with transpedicular screws A REPORT OF THREE PATIENTS F. Lattig, T. F. Fekete, D. Jeszenszky From the Schulthess Clinic, Zürich, Switzerland
Management of fractures of the pedicle after instrumentation with transpedicular screws A REPORT OF THREE PATIENTS F. Lattig, T. F. Fekete, D. Jeszenszky From the Schulthess Clinic, Zürich, Switzerland
Evaluation of Role of Anterior Debridement and Decompression of Spinal Cord and Instrumentation in Treatment of Tubercular Spondylitis
 Asian Spine Journal Vol. 6, No. 3, pp 183~193, 2012 Anterior Debridment Decompression and Instrumentation in Tubercular Spondylitis / 183 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2012.6.3.183 Evaluation of Role of
Asian Spine Journal Vol. 6, No. 3, pp 183~193, 2012 Anterior Debridment Decompression and Instrumentation in Tubercular Spondylitis / 183 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2012.6.3.183 Evaluation of Role of
Missed Traumatic Thoracic Spondyloptosis With no Neurological Deficit: A Case Report and Literature Review
 Trauma Mon. 2016 February; 21(1): e19841. Published online 2016 February 6. doi: 10.5812/traumamon.19841 Case Report Missed Traumatic Thoracic Spondyloptosis With no Neurological Deficit: A Case Report
Trauma Mon. 2016 February; 21(1): e19841. Published online 2016 February 6. doi: 10.5812/traumamon.19841 Case Report Missed Traumatic Thoracic Spondyloptosis With no Neurological Deficit: A Case Report
Prevention of PJF: Surgical Strategies to Reduce PJF. Robert Hart, MD Professor OHSU Orthopaedics Portland OR. Conflicts
 Prevention of PJF: Surgical Strategies to Reduce PJF Robert Hart, MD Professor OHSU Orthopaedics Portland OR Conflicts Consultant Depuy Spine, Medtronic Royalties Seaspine, Depuy Research/Fellowship Support
Prevention of PJF: Surgical Strategies to Reduce PJF Robert Hart, MD Professor OHSU Orthopaedics Portland OR Conflicts Consultant Depuy Spine, Medtronic Royalties Seaspine, Depuy Research/Fellowship Support
MAS TLIF MAXIMUM ACCESS SURGERY TRANSFORAMINAL LUMBAR INTERBODY FUSION AN INTRODUCTION TO
 AN INTRODUCTION TO MAS TLIF MAXIMUM ACCESS SURGERY TRANSFORAMINAL LUMBAR INTERBODY FUSION This booklet is designed to inform you about the Maximum Access Surgery (MAS ) Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody
AN INTRODUCTION TO MAS TLIF MAXIMUM ACCESS SURGERY TRANSFORAMINAL LUMBAR INTERBODY FUSION This booklet is designed to inform you about the Maximum Access Surgery (MAS ) Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody
Vertebral column decancellation for the management of sharp angular spinal deformity
 Eur Spine J (2011) 20:1703 1710 DOI 10.1007/s00586-011-1771-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vertebral column decancellation for the management of sharp angular spinal deformity Yan Wang Lawrence G. Lenke Received:
Eur Spine J (2011) 20:1703 1710 DOI 10.1007/s00586-011-1771-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vertebral column decancellation for the management of sharp angular spinal deformity Yan Wang Lawrence G. Lenke Received:
POSTOPERATIVE COMPLICATIONS IN OPERATED CASES OF PYOGENIC SPONDYLODISCITIS
 Original Article Orthopaedics POSTOPERATIVE COMPLICATIONS IN OPERATED CASES OF PYOGENIC SPONDYLODISCITIS Ravikumar T V 1, Shivprasad M S 2, Yashavatha Kumar 1, Vinay Jain K 3, Mahesh 1 1 -Assistant Professor,
Original Article Orthopaedics POSTOPERATIVE COMPLICATIONS IN OPERATED CASES OF PYOGENIC SPONDYLODISCITIS Ravikumar T V 1, Shivprasad M S 2, Yashavatha Kumar 1, Vinay Jain K 3, Mahesh 1 1 -Assistant Professor,
MISS in Thoracolumbar Fractures
 MISS in Thoracolumbar Fractures Guillem Saló Bru, MD, Phd Spine Unit. Orthopaedic Department. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Associated Professor. Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona. Introduction. The application
MISS in Thoracolumbar Fractures Guillem Saló Bru, MD, Phd Spine Unit. Orthopaedic Department. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Associated Professor. Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona. Introduction. The application
Management of Skip-Lesions in Dialysis-Related Cervical Spondyloarthropathy
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 3 Number 1 Management of Skip-Lesions in Dialysis-Related Cervical Spondyloarthropathy S Chandela, J Llena, J Houten Citation S Chandela, J Llena,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 3 Number 1 Management of Skip-Lesions in Dialysis-Related Cervical Spondyloarthropathy S Chandela, J Llena, J Houten Citation S Chandela, J Llena,
