Conservatively Treated Spinal Tuberculosis in Children: Ambulatory Chemotherapy
|
|
|
- Kelley Conley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Myung-Sang Moon ORIGINL RTICLE /jp-journals Conservatively Treated Spinal Tuberculosis in Children: mbulatory Chemotherapy Myung-Sang Moon BSTRCT Introduction: To assess the chronological changes of the disease-related kyphosis after chemotherapy alone, and secondly to clarify the role of growth cartilage in the healed lesion on kyphosis change. Materials and methods: total of 101 children with spinal tuberculosis in various stages of disease processes, aged 2 to 15 years, were the subject materials. They were treated with two different chemotherapy formulas; before 1975, 18 months of triple chemotherapy [isoniazid (INH), paraaminosalicylic acid (PS), and Streptomycin], and from 1976, 12 months of triple chemotherapy (INH, rifampicin, ethambutol, or pyrazinamide). By utilizing the images, the effects of the remaining growth plate cartilage on chronological changes of kyphosis after the initiation of chemotherapy were analyzed. The first assessment at postchemotherapy was at 1 year and at the final discharge time from the follow-up. Results: Complete disk destruction at the initial examination was observed in 2 (5.0%) out of 40 cervical spine, 8 (26.7%) out of 30 dorsal spine, and 6 (19.4%) out of 31 lumbosacral spine. In those cases, kyphosis developed inevitably. In the remainders, the disks were partially preserved or remained intact. mong 101 children, initial kyphosis was maintained in 20 (19.8%), while kyphosis decreased in 14 (13.7%) children, and increased in 67 (66.3%) children with nonrecoverably damaged growth plate. Conclusion: It was possible to predict the fate of the kyphosis at the time of initial treatment, but its predictive accuracy was low. Therefore, finally, it is recommended to be done at the end of chemotherapy. In children, the kyphotic deformity assessment should be continued till the maturity Keywords: Chemotherapy, Children, Kyphosis, Spine, Tuberculosis. How to cite this article: Moon M-S. Conservatively Treated Spinal Tuberculosis in Children: mbulatory Chemotherapy. J Spinal Surg 2018;5(1): Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None 10 Surgeon Department of Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology, Cheju Halla General Hospital, Jeju Province, Republic of Korea Corresponding uthor: Myung-Sang Moon, Surgeon Department of Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology, Cheju Halla General Hospital, Jeju Province, Republic of Korea, Phone: , msmoonos@hotmail.com INTRODUCTION There are numerous previously published papers on spinal tuberculosis, mostly from the tuberculosis prevalent countries, such as India, Northern-frica, Hong Kong, and Korea in the past Good-quality and informative papers are still being published from India. 9,10,15,16 However, pediatric spinal tuberculosis was less dealt in comparison with the adult tuberculosis, and those authors rarely focused on the effect of disk damage on the affected vertebral growth and kyphotic change. 1,2,5,12-16 Children are different from adults in many aspects. child has a growth potential in the growth plate, and high modeling capacity. Therefore, the kyphosis management of the pediatric spinal tuberculosis must be different from the adult. Rajasekaran 9,10 reported the very informative natural course of the pediatric spinal tuberculosis in the late However, they did not discuss the role of the growth cartilage in the lesion which contributed to the column growth. Based on the afore-mentioned information, the current authors designed this retrospective study, utilizing all their previously collected medical records, X-ray, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data. MTERILS ND METHODS Consecutively treated 101 children with various stages of tuberculous disease processes, aged from 2 to 15 years, underwent this study. They were treated at 8 University hospitals and 3 general hospitals during the period 1997 to 2010, and were treated only with the combined antituberculous chemotherapeutics. Forty (39.6%) children had the cervical and cervicodorsal junction lesions, 30 (29.7%) in the dorsal, and 31 (30.7%) in the lumbar and lumbosacral spines. Twenty-six (25.7%) children were under the age of 5 years, 43 (42.5%) with age range from 6 to 10 years, and 32 (31.6%) over 10 years of age. Eighteen (17.8%) children were partially paralytic; 3 in Frankel B, 12 in Frankel C, and 5 in Frankel D. Diagnostic Methods Initial clinical diagnosis was made based on the disease history, complaints, and the physical findings which were augmented later by laboratory and image data, and
2 Conservatively Treated Spinal Tuberculosis in Children finally was reconfirmed by the physical response against chemotherapeutics. For image diagnosis, simple radiograms and MRI were used. The MRI demonstrated more accurately the disk sparing. Thus, great emphasis was placed on the assessment of disk conditions including growth cartilage which was closely related to the regrowth and remodeling of the bony vertebra. This issue was one of the key points. ssessment of the Disease rrest and Heal, and Stability of the Diseased Segment(s) The keys in the assessment were images which were augmented by the clinical symptoms improvement and laboratory data. Disease arrest point is the progress stop time on images in which no further vertebral damage occurs in conjunction with the normalized laboratory data. Disease heal (cure) point is defined when the image and laboratory data of the arrest point are maintained in addition to the radiographic findings, such as bony reformation, modeling, and intercorporal fusion. Diseased segment stability is defined when the same image findings of the arrest point are seen irrespective of corporal fusion. ssessment of Disk Condition at the Lesion Site and Rate of Spontaneous Fusion of the Diseased Segments The disk space becomes narrowed when any part of its component structure is destroyed. Therefore, the assessment of disk space on simple radiographs and MRI is important, and more important is the assessment of the end-plate condition, whether it is irregular, disrupted, and has disappeared. Vertebral growth and shape modeling depend on the growth cartilage. In the case of complete disk disappearance, vertebral regrowth and modeling cannot be anticipated, while the regrowth is possible when the growth cartilage is preserved in spite of some disk space narrowing. ssessment of Changes of Kyphotic Deformity The kyphosis is measured by Cobb angle, utilizing the simple radiograms during chemotherapy: Initiation, arrest, and cure points. Thereafter, the kyphotic change was measured with certain interval in the cases with the decreased and increased kyphosis. The effect of the spontaneously fused bloc vertebrae on kyphosis progress was also assessed. ssessment of the Diseased Segment Stability at the Time Points of rrest and Cure When there was the rapid progress of kyphosis at the fused and unfused arrested and healed vertebral lesion site, the segment was defined unstable. For such a case, a careful observation was carried out. Treatment Protocol For all children, high-calorie protein diet was prescribed when they were hospitalized. However, it was impossible to check it after discharge. For all children, directly observed chemotherapy was practiced under the children s parents and their family members supervision. In all children, a 3-drug regimen was adopted: INH (H), streptomycin (S), and PS (Pa) for 18 months [(3HSPa), 15HPa] was used between 1971 and Since 1976, 3 drugs, isoniazid (H), rifampicin (R), ethambutol (E), or pyrazinamide (Z), for 12 months (12 RHE or 12 RHZ) was adopted. Supplementary immobilization was adopted. Head halter was routinely applied in all cervical cases for 7 to 10 days before definite therapeutic protocol was finalized. Before 1980, Minerva cast in 14 children was applied for 3 months because of the noted cervical instability. Thereafter, four-post cervical brace was applied in 7 children, and halo-shoulder apparatus for 4 months in 12 children. Seven children had no supporting apparatus. RESULTS Laboratory Data Hematologic findings: Erythrocyte sedimentation rate at the initial examination was 41 mm/hour (31 54 mm/ hour) and 14 mm/hour (9 17 mm/hour) at the postchemotherapy 3 months. C-reactive protein (CRP): average CRP at pre- and postchemotherapy 3, 6, 9, and 12 months was 3.9 ( ), 0.5 ( ), 0.05 ( ), 0.06 ( ), and 0.03 mg/dl ( mg/dl). Disk Conditions On images, complete disk destruction was noted in 2 (5.0%) out of 40 cervical tuberculosis, 8 (26.7%) out of 30 dorsal tuberculosis, 6 (19.4%) out of 31 lumbar and lumbosacral tuberculosis. ll 16 (15.0%) children with complete disk destruction were the advanced cases at the initial diagnosis and chemotherapy. Disease rrest and Cure, and the Diseased Segment Stability In some cases, slow drug response was observed in the early stage of drug therapy, but finally, it did not influence the final cure. There was no nonresponder. The Journal of Spinal Surgery, January-March 2018;5(1):
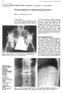
3 Myung-Sang Moon Spontaneous fusion occurred in 5 (12.5%) out of 40 cervical cases, 7 (23.3%) out of 30 dorsal and 4 (12.9%) out of 31 lumbar and lumbosacral cases at the end of chemotherapy. In all, the disease arrest sign was observed at the average postchemotherapy 3 months ( months), and cure was obtained at postchemotherapy 12 months; ll the radiological and laboratory findings of the arrest point were maintained without further change till the cure. dditionally, signs of reformation of destroyed bone were observed. The stability of the diseased segment was maintained till the cure point irrespective of intercorporal fusion status. Kyphotic Curve during Chemotherapy and afterward Cervical tuberculosis (n: 40 cases): mong 40 children with cervical lesion, average initial 10 kyphotic angle was maintained in 8 (20%) children without change, and average 8 kyphosis decreased to 3 in 6 (15%) at the end of treatment. In 26 (65%) children, the initial 8 kyphosis increased to 16 at the cure time (Table 1 and Figs 1 and 2). Dorsal tuberculosis (n: 30 cases): The initial 13 kyphosis was maintained till the end of treatment in 7 (23.3%), and in 4 (13.3%) children, average initial 15 kyphosis decreased to 10 at the end. In 19 (63.3%) children, the average initial 11 kyphosis increased to 23 at the end (Figs 3 and 4). Lumbar and lumbosacral tuberculosis (n: 31 cases): In 5 (16.2%) children, the average initial 5 kyphosis was well maintained till the end of chemotherapy, and in 4 (12.9%), the average initial 12 kyphosis decreased to 4 at the end. In 22 (70.9%) children, the average 14 initial kyphosis increased to 25 at the end (Fig. 5). In summary, among the 101 children, 20 (19.8%) children could maintain the initial kyphosis. The initial Table 1: Changes of tuberculosis kyphosis in each regional level (n: 101 children) Sagittal curve changes (kyphosis) Spine levels Initial 3M 6M 12M 18M 24M 36M (Final) Difference Remarks Cervical (n: 40) Unchanged (n: 8) Decreased (n: 6) Increased (n: 26) Dorsal and dorsolumbar (n: 30) Unchanged (n: 7) Decreased (n: 4) Increased (n: 19) Lumbar and lumbosacral (n: 31) Unchanged (n: 5) Decreased (n: 4) Increased (n: 22) B C D E Figs 1 to E: Tuberculosis of C 3-6 in a 5-year-old boy. () Initial lateral radiograph showing narrowed disk spaces of C 3-4, C 4-5, and C 5-6 with round cervical kyphosis and huge prevertebral soft tissue shadow. Initially, cervical traction was applied in bed for 3 weeks under the cover of the triple chemotherapy which was followed by Minerva cast for 5 weeks. Radiograms taken at postchemotherapy, (B) 18 months, and (C) 36 months are shown in which we can observe the gradual spontaneous correction of kyphosis, visible undestroyed affected disks, and reformation of the diseased vertebral bodies. Radiograms, taken at 4 and 20 years (D, E) after initial chemotherapy, showing the fused C 2 -C 6 block vertebra circumferentially with good spontaneous correction of kyphosis 12
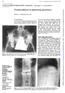
4 Conservatively Treated Spinal Tuberculosis in Children B Figs 2 to D: Tuberculosis of cervical spine at C 5 -C 7 in a 2-year-old paraplegic boy, treated by triple antituberculous chemotherapy (INH, rifampicin, and ethambutol) for 12 months. Serial lateral radiograms taken at initial (), 12 (B), 24 (C), and 36 (D) months are shown. () The initial radiogram shows the almost completely destroyed C6 body with minimum kyphosis. fter chemotherapy, there was no further vertebral body destruction, while slippage of C 5 over C 7 occurred due to facet joint gapping at 12 months (B). However, anterior C 5 slippage was well reduced and stabilized spontaneously at 24 and 36 months (C, D) C D B C a1 b1 Figs 3 to C: Tuberculosis of thoracic spine at D 9 -D 11 in a 5-year-old boy; arrows indicate the lesion. Initial radiograms () show the flattened D 10 vertebral body with mild kyphosis (Cobb angle 18 ), and the disease arrest. Gradual correction of kyphosis (Cobb s angle 10 ) is seen at 12 (B) and 18 (C) months after triple chemotherapy. Intercorporal fusion did not occur The Journal of Spinal Surgery, January-March 2018;5(1): c1
5 Myung-Sang Moon B C D a1 b1 c1 d1 Figs 4 to D: Tuberculosis of L 3 -L 4 in a 7-year-old boy, treated conservatively with triple chemotherapy for 12 months. On initial radiograms, incompletely fused L 3 -L 4 bodies with cystic lesion in anteroinferior part of L 3 body () which was maintained until the last follow-up (B, C, and D). The flattened lumbar curve is seen kyphosis decreased in 14 (13.7%) children, while the initial kyphosis increased in 67 (66.3%) children. This fact evidently suggested that the initial growth plate damage in the advanced spinal tuberculosis hastened the progress of kyphosis, which is an inevitable complication during and after treatment (Table 1). The main cause of the progressive kyphosis was the single-wedged fused bloc or unfused two-wedged vertebrae. Nonfusion was not the main cause of the progressive kyphosis. DISCUSSION The primary objective of the management of the pediatric spinal tuberculosis is not only to cure disease but also to minimize the disease-related complications, such as kyphosis. The management of spinal tuberculosis aims at the prevention of destruction of the infected spinal column maximally, protection of the spinal cord and nerves, hastening the recovery of paralysis, and maintenance of the stability of the diseased segment. 2,3,5-8,11 None of the imaging modalities could solely provide the definite healing points, though all the available measures were mobilized. ll children in the current series presented different disease stages at the initial examination. The selection of the type of management was important. 11 Surgery should be applied only for the complicated tuberculosis. Physicians should assess the growth plate condition in 14
6 Conservatively Treated Spinal Tuberculosis in Children B C a1 b1 c1 Figs 5 to C: Tuberculosis of L 3 -L 5 (initial Cobb angle, 25 ) in a 7-year-old girl, treated with triple chemotherapy for 12 months (, 1). Retrolisthesis of wedged L 4 with increased kyphosis (final Cobb angle, 35 ) is seen, though the disease healed (B, B1, C, C1) the lesion before surgery through the image studies. MRI demonstrated disk sparing and the severity of vertebral destruction. MRI-based observation was the best method for disease assessment. The healing status was defined generally based on the combined clinical and radiological parameters, but improvement on image lagged approximately 3 months behind the clinical improvement in most of the senior author s previous studies. 2,3,11 Until now, there have been controversies regarding the duration of antituberculous treatment (TT) because each individual responded differently to TT even under the same drug formula. Thus, it was needed to evaluate the spinal lesions clinically, hematologically, radiologically, and with contrast MRI to document the healing of the lesion after 8 months of TT and subsequently to decide for the continuation or stoppage of treatment. The current authors did the same practice. When surgery is indicated, gentle, less aggressive debridement of the lesion is the choice to preserve the remaining growth cartilage. 11 The Journal of Spinal Surgery, January-March 2018;5(1):
7 Myung-Sang Moon Prediction of kyphotic change could be possible at the time of initial chemotherapy, but its predictive accuracy was rather low. The change of the kyphosis was primarily not directly related to the drug efficacy, and was rather related to the severity of the growth plate damage at the time of initial chemotherapy. It is acceptable to stop the continuous observation in the noncurve progress form at the end of chemotherapy. However, in the other two forms, follow-up should be continued till deformity fixation. The diseased corporal foci healed in two patterns: fusion and nonfusion. In either case of the current series, the healed original foci did not show sign of instability. s regards the stability of the healed focus, most surgeons were anxious whether the spinal stability could be obtained permanently or not. However, in the current authors series, the stability of the healed diseased segment was well maintained even in the unfused cases. s regards the growth of the fused pediatric bloc vertebral, the British MRC and Schulitz et al reported that in the pediatric spine, there may be progressive kyphosis despite a solid fusion because the continuing growth in the posterior spinal element may create further deformity, and that the anterior fusion alone had the worst prognosis in terms of progressive kyphosis. 1,13 On the contrary, Upadhyay et al 14 showed that a short anterior spinal arthrodesis done at an early age was not associated with the progress of deformity during growth and development from the disproportionate posterior spinal growth. Therefore, they did not recommend a posterior fusion to stop the posterior growth. The current authors supported the former one. 11 The spontaneously fused bloc vertebra during and after chemotherapy becomes stable, but it is not a good news. There may be a possible progressive kyphosis due to continuing posterior element growth and may create further deformity. The spontaneous intercorporal fusion rate during chemotherapy in children is less than 15%, and 85% did not fuse. Thus, it is important to observe the influence of the healed unfused segment on kyphosis. If there is a rapid progress of kyphosis which exceeds over 50 to 60, it should not be allowed because in those cases, the late unrecoverable paralysis develops gradually Those cases with rapidly progressive deformity and unacceptable deformity at the end of chemotherapy need not only the preventive surgery, but also corrective surgery should be carried out. However, we should keep in mind that the undamaged growth disk cartilage in the lesion participates not only in the repairing of the destroyed bony vertebra, but also in the modeling of the spinal column. In all the current children, spinal tuberculosis healed without any drug-related complications in spite of the kyphosis progression even after cure in 67 children (66.3%). However, this high percentile incidence of residual kyphosis was unrelated to the chemotherapy, and was primarily the end-product of the lately discovered advanced disease and treatment delay. Based on the current study results, the early management is stressed under early recognition of the disease by the patients and the healthcare service personnel. Those are the keys not only for the cure of the disease, but also for the reduction of the diseaserelated crippling. Lastly, it is stressed that medicine is the basic curative agent, and that surgery is only the adjuvant therapeutic means for the complicated conditions. lso, a continuous vigilant observation is recommended till growth maturity in children, particularly those who present the evidence of deformity progression. REFERENCES 1. Schulitz KP, Kothe R, Leong JC, Wehling P. Growth changes of solidly fused kyphotic bloc after surgery for tuberculosis. Comparison of four procedures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1997 May;22(10): Moon MS, Kim I, Woo YK, Park YO. Conservative treatment of tuberculosis of the thoracic and lumbar spine in adults and children. Int Orthop 1987;11(4): Moon MS. Tuberculosis of spine. Controversies and a new challenge. Spine 1997 ug;22(15): year assessment of controlled trials of inpatient and outpatient treatment and of plaster-of-paris jackets for tuberculosis of the spine in children on standard chemotherapy. Studies in Masan and Pusan, Korea. Ninth report of the Medical Research Council Working Party on Tuberculosis of the Spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1985 Jan;67(1): Moon MS, Moon YW, Moon JL, Kim SS, Sun DH. Conservative treatment of tuberculosis of the lumbar and lumbosacral spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2002 May;(398): Moon MS, Moon JL, Kim SS, Moon YW. Treatment of tuberculosis of the cervical spine: operative versus nonoperative. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2007 Jul;460: Moon MS, Lee BJ, Kim SS, Lim SF. Evolution of management of spinal deformity: controversial issues and current concept review. J Spinal Surg 2010;2: Moon MS, Kim JM. The effect of mechanical forces on vertebral growth. J Western Pacif Orthop ssoc 1974;11: Rajasekaran S. The problem of deformity in spinal tuberculosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2002 May;(398): Rajasekaran S. The natural history of post-tubercular kyphosis in children. Radiological signs which predict late increase in deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2001 Sep;83(7): Moon MS, Kim SS, Lee BJ, Moon JL. Spinal tuberculosis in children: retrospective analysis of 124 patients. Indian J Orthop 2012 Mar-pr;46(2): Bailey J, Gabriel M, Hodgson R, Shin JS. Tuberculosis of the spine in children. Operative findings and results in one hundred consecutive patients treated by removal of 16
8 Conservatively Treated Spinal Tuberculosis in Children the lesion and anterior grafting. J Bone Joint Surg m 1972 Dec;54(8): Five-year assessments of controlled trials of ambulatory treatment, debridement and anterior spinal fusion in the management of tuberculosis of the spine. Studies in Bulawayo (Rhodesia) and in Hong Kong. Sixth report of the Medical Research Council Working Party on Tuberculosis of the Spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1978 May;60-B(2): Upadhyay SS, Saji MJ, Sell P, Sell B, Hsu LC. Spinal deformity after childhood surgery for tuberculosis of the spine. comparison of radical surgery and debridement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1994 Jan;76(1): Tuli SM. Tuberculosis of the skeletal system: bones, joints, spine and bursal sheaths, 3rd ed. New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Publishers; Jain K, ggarwal PK, rora, Singh S. Behaviour of the kyphotic angle in spinal tuberculosis. Internat Orthop (SICOT) 2004 pr;28: Masini M, Maranho V. Experimental determination of the effect of progressive sharp-angle spinal deformity on the spinal cord. Eur Spine J 1997;6(2): Moon MS, Kim SS, Sihn JC. Tuberculous kyphosis evolving concepts in prevention and treatment. J Musculoskeletal Res 2015 Sep;18(3):1-14. The Journal of Spinal Surgery, January-March 2018;5(1):
Behaviour of the kyphotic angle in spinal tuberculosis
 International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2004) 28:110 114 DOI 10.1007/s00264-003-0516-z ORIGINAL PAPER A. K. Jain P. K. Aggarwal A. Arora S. Singh Behaviour of the kyphotic angle in spinal tuberculosis Accepted:
International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2004) 28:110 114 DOI 10.1007/s00264-003-0516-z ORIGINAL PAPER A. K. Jain P. K. Aggarwal A. Arora S. Singh Behaviour of the kyphotic angle in spinal tuberculosis Accepted:
Tuberculosis Of The Lumbar Spine: Outcomes After Combined Treatment With Short-Course Two-Drug Therapy And Surgery
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 7 Number 1 Tuberculosis Of The Lumbar Spine: Outcomes After Combined Treatment With Short-Course Two-Drug Therapy And Surgery O Karaeminogullari, U Aydinli,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 7 Number 1 Tuberculosis Of The Lumbar Spine: Outcomes After Combined Treatment With Short-Course Two-Drug Therapy And Surgery O Karaeminogullari, U Aydinli,
factor for identifying unstable thoracolumbar fractures. There are clinical and radiological criteria
 NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
Ang Deng, Hong-Qi Zhang, Ming-Xing Tang, Shao-Hua Liu, Qi-Le Gao, Yu-Xiang Wang, Chao-Feng Guo, Xi-Yang Wang
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):3953-3959 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0016644 Original Article One-stage combined posterior and anterior approaches for active tuberculosis of the subaxial cervical
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):3953-3959 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0016644 Original Article One-stage combined posterior and anterior approaches for active tuberculosis of the subaxial cervical
Surgical Treatment of Thoracic and Lumbar Tuberculosis by Anterior Interbody Fusion and Posterior Instrumentation
 Original Paper Med Princ Pract 2003;12:92 96 DOI: 10.1159/000069113 Received: April 21, 2002 Revised: August 3, 2002 Surgical Treatment of Thoracic and Lumbar Tuberculosis by Anterior Interbody Fusion
Original Paper Med Princ Pract 2003;12:92 96 DOI: 10.1159/000069113 Received: April 21, 2002 Revised: August 3, 2002 Surgical Treatment of Thoracic and Lumbar Tuberculosis by Anterior Interbody Fusion
Surgical treatment of acute TB spondylitis: indications and outcomes. European Spine Journal, 2013, v. 22 suppl. 4, p. S603-S611
 Title Surgical treatment of acute TB spondylitis: indications and outcomes Author(s) Mak, KC; Cheung, KMC Citation European Spine Journal, 2013, v. 22 suppl. 4, p. S603-S611 Issued Date 2013 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/170210
Title Surgical treatment of acute TB spondylitis: indications and outcomes Author(s) Mak, KC; Cheung, KMC Citation European Spine Journal, 2013, v. 22 suppl. 4, p. S603-S611 Issued Date 2013 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/170210
Long Posterior Fixation with Short Fusion for the Treatment of TB Spondylitis of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine with or without Neurologic Deficit
 Long Posterior Fixation with Short Fusion for the Treatment of TB Spondylitis of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine with or without Neurologic Deficit Shih-Tien Wang MD, Chien-Lin Liu MD 王世典劉建麟 School of Medicine,
Long Posterior Fixation with Short Fusion for the Treatment of TB Spondylitis of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine with or without Neurologic Deficit Shih-Tien Wang MD, Chien-Lin Liu MD 王世典劉建麟 School of Medicine,
Surgical Treatment of Lower Cervical Tuberculosis With Kyphosis Deformity. Department of Spine, General Hospital of Lanzhou Command, Gansu, China
 Int Surg 2017;102:171 177 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-15-00051.1 Surgical Treatment of Lower Cervical Tuberculosis With Kyphosis Deformity Xu Lan, Jian-Zhong Xu, Xue-Mei Liu, Bao-Feng Ge Department of Spine,
Int Surg 2017;102:171 177 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-15-00051.1 Surgical Treatment of Lower Cervical Tuberculosis With Kyphosis Deformity Xu Lan, Jian-Zhong Xu, Xue-Mei Liu, Bao-Feng Ge Department of Spine,
Pediatric scoliosis. Patient and family guide to understanding
 Patient and family guide to understanding Pediatric scoliosis This brochure is not meant to replace any personal conversations that the patient and family might wish to have with the physician or healthcare
Patient and family guide to understanding Pediatric scoliosis This brochure is not meant to replace any personal conversations that the patient and family might wish to have with the physician or healthcare
Traumatic spondylolisthesis of the axis has been
 Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 60, Number 2 2001-2002 61 Traumatic Spondylolisthesis of the Axis 42 Cases Myung-Sang Moon MD Jeong-Lim Moon MD Young-Wan Moon MD Doo-Hoon Sun MD PhD and Won-Tai
Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 60, Number 2 2001-2002 61 Traumatic Spondylolisthesis of the Axis 42 Cases Myung-Sang Moon MD Jeong-Lim Moon MD Young-Wan Moon MD Doo-Hoon Sun MD PhD and Won-Tai
Preliminary Study of Tuberculosis of the Spine
 Original Articles Preliminary Study of Tuberculosis of the Spine Robert C. Lifeso, MD, FRCS(C)* * Orthopedic Surgeon, Department of Surgery, King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Centre ABSTRACT
Original Articles Preliminary Study of Tuberculosis of the Spine Robert C. Lifeso, MD, FRCS(C)* * Orthopedic Surgeon, Department of Surgery, King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Centre ABSTRACT
University of Groningen. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria
 University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
Single stage posterior instrumentation and anterior interbody fusion for tuberculosis of dorsal and lumbar spines
 Original Article interbody fusion for tuberculosis of dorsal Pandey BK 1, Sangondimath GM 2, Chhabra HS 2 1 Department of Orthopaedics, Kathmandu Medical College Teaching Hospital, Sinamangal, Kathmandu,
Original Article interbody fusion for tuberculosis of dorsal Pandey BK 1, Sangondimath GM 2, Chhabra HS 2 1 Department of Orthopaedics, Kathmandu Medical College Teaching Hospital, Sinamangal, Kathmandu,
To study the outcomes of posterior decompression and fixation of tuberculosis of dorsolumbar spine
 2017; 3(3): 691-695 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 691-695 2017 IJOS wwworthopapercom Received: 15-05-2017 Accepted: 16-06-2017 Dr Manish Shah Assistant Professor, Department of Dr Kushal Suthar Dr Ravindra
2017; 3(3): 691-695 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 691-695 2017 IJOS wwworthopapercom Received: 15-05-2017 Accepted: 16-06-2017 Dr Manish Shah Assistant Professor, Department of Dr Kushal Suthar Dr Ravindra
J Korean Soc Spine Surg 2016 Sep;23(3): Originally published online September 30, 2016;
 Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery Multifocal Extensive Spinal Tuberculosis Accompanying Isolated Involvement of Posterior Elements - A Case Report - Dong-Eun Shin, M.D., Sang-June Lee, M.D., Young
Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery Multifocal Extensive Spinal Tuberculosis Accompanying Isolated Involvement of Posterior Elements - A Case Report - Dong-Eun Shin, M.D., Sang-June Lee, M.D., Young
Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR Page 1 of 9 INSTABILITY AND DEGENERATIVE DISC CONDITIONS FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY CPT4
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR Page 1 of 9 INSTABILITY AND DEGENERATIVE DISC CONDITIONS FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY CPT4
Citation for published version (APA): Jutte, P. C. (2006). Spinal tuberculosis, a Dutch perspective: special reference to surgery s.n.
 University of Groningen Spinal tuberculosis, a Dutch perspective Jutte, Paulus Christiaan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
University of Groningen Spinal tuberculosis, a Dutch perspective Jutte, Paulus Christiaan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
Pott s kyphosis. University Affiliated Sixth People s Hospital, 600 Yishan Road, Shanghai , P.
 QJM Advance Access published November 17, 2014 Pott s kyphosis Author Names: Yi Zhang, Yong-Sheng Yu, Zheng-Hao Tang and Guo-Qing Zang Author Affiliations: Department of Infectious Diseases, Shanghai Jiao
QJM Advance Access published November 17, 2014 Pott s kyphosis Author Names: Yi Zhang, Yong-Sheng Yu, Zheng-Hao Tang and Guo-Qing Zang Author Affiliations: Department of Infectious Diseases, Shanghai Jiao
Factors Influencing the Outcome of Arthrodesis for Congenital Kyphosis and Kyphoscoliosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Factors Influencing the Outcome of Arthrodesis for Congenital Kyphosis and Kyphoscoliosis S Harwant, FRSCSEd., rthopaedic Unit, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 8 th Floor, Grand Seasons Avenue,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Factors Influencing the Outcome of Arthrodesis for Congenital Kyphosis and Kyphoscoliosis S Harwant, FRSCSEd., rthopaedic Unit, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 8 th Floor, Grand Seasons Avenue,
Comparison of clinical, radiological and functional outcome of short segment V/S long segment posterior fixation of tuberculosis of spine
 2018; 2(4): 104-108 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 104-108 Received: 20-08-2018 Accepted: 21-09-2018 Dr. Mitul Mistry Assistant Professor,
2018; 2(4): 104-108 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 104-108 Received: 20-08-2018 Accepted: 21-09-2018 Dr. Mitul Mistry Assistant Professor,
FUNCTIONAL OUTCOMES OF TRAUMATIC PARAPLEGIA PATIENTS: DOES SURGERY IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF LIFE?
 FUNCTIONAL OUTCOMES OF TRAUMATIC PARAPLEGIA PATIENTS: DOES SURGERY IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF LIFE? Original Article Orthopaedics R S Bajoria 1, Mahendra Panwar 2, Anand Rao 3, Sameer Gupta 4 1 - Associate
FUNCTIONAL OUTCOMES OF TRAUMATIC PARAPLEGIA PATIENTS: DOES SURGERY IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF LIFE? Original Article Orthopaedics R S Bajoria 1, Mahendra Panwar 2, Anand Rao 3, Sameer Gupta 4 1 - Associate
There is No Remarkable Difference Between Pedicle Screw and Hybrid Construct in the Correction of Lenke Type-1 Curves
 DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.20522-17.1 Received: 11.04.2017 / Accepted: 12.07.2017 Published Online: 21.09.2017 Original Investigation There is No Remarkable Difference Between Pedicle Screw and Hybrid
DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.20522-17.1 Received: 11.04.2017 / Accepted: 12.07.2017 Published Online: 21.09.2017 Original Investigation There is No Remarkable Difference Between Pedicle Screw and Hybrid
Fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine and thoracolumbar transition
 Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
Idiopathic scoliosis Scoliosis Deformities I 06
 What is Idiopathic scoliosis? 80-90% of all scolioses are idiopathic, the rest are neuromuscular or congenital scolioses with manifest primary diseases responsible for the scoliotic pathogenesis. This
What is Idiopathic scoliosis? 80-90% of all scolioses are idiopathic, the rest are neuromuscular or congenital scolioses with manifest primary diseases responsible for the scoliotic pathogenesis. This
Evaluation of efficacy and clinical outcomes of posterior surgical approach and posterior instrumentation in the management of tuberculosis of spine
 2017; 3(4): 824-829 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(4): 824-829 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 21-08-2017 Accepted: 22-09-2017 Dr. Anil Kumar Chitumallah Assistant Professor, Kamineni Institute of
2017; 3(4): 824-829 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(4): 824-829 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 21-08-2017 Accepted: 22-09-2017 Dr. Anil Kumar Chitumallah Assistant Professor, Kamineni Institute of
MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis
 CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
Anterior Surgical Interventions in Spinal Tuberculosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anterior Surgical Interventions in Spinal Tuberculosis Obaid-ur-Rahman, Saleem Ahmad and Tayyab Hussain ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate and compare the effectiveness of the modified Hong
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anterior Surgical Interventions in Spinal Tuberculosis Obaid-ur-Rahman, Saleem Ahmad and Tayyab Hussain ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate and compare the effectiveness of the modified Hong
Wtrial to compare ambulant short-course
 Short-course chemotherapy for tuberculosis of the spine A COMPARISON BETWEEN AMBULANT TREATMENT AND RADICAL SURGERY - TEN-YEAR REPORT R. Parthasarathy, K. Sriram, T. Santha, R. Prabhakar, P. R. Somasundaram,
Short-course chemotherapy for tuberculosis of the spine A COMPARISON BETWEEN AMBULANT TREATMENT AND RADICAL SURGERY - TEN-YEAR REPORT R. Parthasarathy, K. Sriram, T. Santha, R. Prabhakar, P. R. Somasundaram,
The main causes of cervical radiculopathy include degeneration, disc herniation, and spinal instability.
 SpineFAQs Cervical Radiculopathy Neck pain has many causes. Mechanical neck pain comes from injury or inflammation in the soft tissues of the neck. This is much different and less concerning than symptoms
SpineFAQs Cervical Radiculopathy Neck pain has many causes. Mechanical neck pain comes from injury or inflammation in the soft tissues of the neck. This is much different and less concerning than symptoms
Primary Posterior Fixation For Tuberculosis Of The Spine
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 10 Number 1 B Jadav, M Prabhakar Citation B Jadav, M Prabhakar.. The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery. 2007 Volume 10 Number 1. Abstract
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 10 Number 1 B Jadav, M Prabhakar Citation B Jadav, M Prabhakar.. The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery. 2007 Volume 10 Number 1. Abstract
Spinal Fusion. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Spinal Fusion North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Spinal Fusion? The spine is made up of a series of bones called vertebrae ; between each vertebra are strong connective tissues
Spinal Fusion North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Spinal Fusion? The spine is made up of a series of bones called vertebrae ; between each vertebra are strong connective tissues
PATIENT: DOB: TODAY S DATE:
 1. I have been strongly advised to carefully read and consider this operative permit. I realize that it is important that I understand this material. I also understand that if certain sections are not
1. I have been strongly advised to carefully read and consider this operative permit. I realize that it is important that I understand this material. I also understand that if certain sections are not
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Dr Hesarikia BUMS
 Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Dr. Hesarikia BUMS Subaxial Cervical Spine From C3-C7 ROM Majority of cervical flexion Lateral bending Approximately 50% rotation Ligamentous Anatomy Anterior ALL, PLL, intervertebral
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Dr. Hesarikia BUMS Subaxial Cervical Spine From C3-C7 ROM Majority of cervical flexion Lateral bending Approximately 50% rotation Ligamentous Anatomy Anterior ALL, PLL, intervertebral
Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 202 206 Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report RB Winter Clinical Professor,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 202 206 Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report RB Winter Clinical Professor,
Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life
 Original Study Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life Lorenzo Nigro 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Pasquale
Original Study Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life Lorenzo Nigro 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Pasquale
Single-stage approach of posterior debridement, allograft and internal fixation in management of lumbosacral tuberculosis.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (3): 1448-1452 Single-stage approach of posterior debridement, allograft and internal fixation in management of lumbosacral tuberculosis. Jiawen Wu 1, Juanjuan Wang 2, Ming
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (3): 1448-1452 Single-stage approach of posterior debridement, allograft and internal fixation in management of lumbosacral tuberculosis. Jiawen Wu 1, Juanjuan Wang 2, Ming
Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft. Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD
 Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD Purpose Is lordosis induced by multilevel cortical allograft ACDF placed on
Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD Purpose Is lordosis induced by multilevel cortical allograft ACDF placed on
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma
 Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Pooria Salari, MD Assistant Professor Of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedic Surgery St. Louis University School of Medicine St. Louis, Missouri, USA Initial Evaluation
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Pooria Salari, MD Assistant Professor Of Orthopaedics Department of Orthopaedic Surgery St. Louis University School of Medicine St. Louis, Missouri, USA Initial Evaluation
PARAPLEGIA. B FIG. 6 A, B and C, Same patient three years after spinal grafting shows a most remarkable improvement of spinal deformity and posture.
 16 PARAPLEGIA A B FIG. 6 A, B and C, Same patient three years after spinal grafting shows a most remarkable improvement of spinal deformity and posture. a grotesque deformity of the spine and trunk with
16 PARAPLEGIA A B FIG. 6 A, B and C, Same patient three years after spinal grafting shows a most remarkable improvement of spinal deformity and posture. a grotesque deformity of the spine and trunk with
POTT'S Disease: a review of 58 cases
 Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 23, No. 4, February, 2010. pp. 200-206 POTT'S Disease: a review of 58 cases Mohammadreza Ehsaei, MD. 1, Fariborz Samini, MD. 2, Gholamreza
Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 23, No. 4, February, 2010. pp. 200-206 POTT'S Disease: a review of 58 cases Mohammadreza Ehsaei, MD. 1, Fariborz Samini, MD. 2, Gholamreza
 The spine is made of a column of bones. Each bone, or vertebra, is formed by a round block of bone, called a vertebral body. A bony ring attaches to the back of the vertebral body. When the vertebra bones
The spine is made of a column of bones. Each bone, or vertebra, is formed by a round block of bone, called a vertebral body. A bony ring attaches to the back of the vertebral body. When the vertebra bones
Surgical treatment of tuberculous spondylodiscitis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2012; 1(Suppl 2): 79-85 Surgical treatment of tuberculous spondylodiscitis E. POLA, B. ROSSI, L.A. NASTO, D. COLANGELO, C.A. LOGROSCINO Division
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2012; 1(Suppl 2): 79-85 Surgical treatment of tuberculous spondylodiscitis E. POLA, B. ROSSI, L.A. NASTO, D. COLANGELO, C.A. LOGROSCINO Division
ISPUB.COM. Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay. P Chudgar INTRODUCTION SPINE
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
Spontaneous Resolution of Spinal Canal Deformity After Burst Dispersion Fracture
 779 Spontaneous Resolution of Spinal Canal Deformity After Burst Dispersion Fracture T. M. H. Chakera 1 George Bedbrook C. M. Bradley3 We reviewed the records of 8 patients with 30 burst-dispersion spinal
779 Spontaneous Resolution of Spinal Canal Deformity After Burst Dispersion Fracture T. M. H. Chakera 1 George Bedbrook C. M. Bradley3 We reviewed the records of 8 patients with 30 burst-dispersion spinal
Patient Information MIS LLIF. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
 Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine....2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine....2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
Pediatric cervical spine injuries with neurological deficits, treatment options, and potential for recovery
 SICOT J 2017, 3, 53 Ó The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2017 DOI: 10.1051/sicotj/2017035 Available online at: www.sicot-j.org CASE REPORT OPEN ACCESS Pediatric cervical spine injuries with neurological
SICOT J 2017, 3, 53 Ó The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2017 DOI: 10.1051/sicotj/2017035 Available online at: www.sicot-j.org CASE REPORT OPEN ACCESS Pediatric cervical spine injuries with neurological
Posterior. Lumbar Fusion. Disclaimer. Integrated web marketing. Multimedia Health Education
 Posterior Lumbar Fusion Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on. All decisions about surgery must be made in conjunction with your surgeon or
Posterior Lumbar Fusion Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to make a decision on. All decisions about surgery must be made in conjunction with your surgeon or
ASJ. Evaluation of Outcome of Transpedicular Decompression and Instrumented Fusion in Thoracic and Thoracolumbar Tuberculosis. Asian Spine Journal
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2017;11(1):31-36 Transpedicular decompression https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2017.11.1.31 in potts spine Evaluation of Outcome of Transpedicular
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2017;11(1):31-36 Transpedicular decompression https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2017.11.1.31 in potts spine Evaluation of Outcome of Transpedicular
Spondylolysis. Lysis (Greek λύσις, lýsis from lýein "to separate") refers to the breaking down.
 Spondylolysis Lysis (Greek λύσις, lýsis from lýein "to separate") refers to the breaking down. Thomas J Kishen Spine Surgeon Sparsh Hospital for Advanced Surgeries Bangalore Spondylolysis Defect in the
Spondylolysis Lysis (Greek λύσις, lýsis from lýein "to separate") refers to the breaking down. Thomas J Kishen Spine Surgeon Sparsh Hospital for Advanced Surgeries Bangalore Spondylolysis Defect in the
BJMHR British Journal of Medical and Health Research Journal home page:
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Br J Med Health Res. 2016;3(12) ISSN: 2394-2967 BJMHR British Journal of Medical and Health Research Journal home page: www.bjmhr.com Spinal Stabilization for early mobilization in Pott's
RESEARCH ARTICLE Br J Med Health Res. 2016;3(12) ISSN: 2394-2967 BJMHR British Journal of Medical and Health Research Journal home page: www.bjmhr.com Spinal Stabilization for early mobilization in Pott's
Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by vertebral shortening
 Eur Spine J (2002) 11 :8 12 DOI 10.1007/s005860000214 TECHNICAL INNOVATION Alejandro Reyes-Sanchez Luis M. Rosales Victor P. Miramontes Dario E. Garin Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by vertebral
Eur Spine J (2002) 11 :8 12 DOI 10.1007/s005860000214 TECHNICAL INNOVATION Alejandro Reyes-Sanchez Luis M. Rosales Victor P. Miramontes Dario E. Garin Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by vertebral
The imaging features of spondylolisthesis : what the clinician needs to know
 The imaging features of spondylolisthesis : what the clinician needs to know Poster No.: C-1018 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Educational Exhibit D. Shah 1, C. J. Burke 1, A. C. andi 2, R. Houghton
The imaging features of spondylolisthesis : what the clinician needs to know Poster No.: C-1018 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Educational Exhibit D. Shah 1, C. J. Burke 1, A. C. andi 2, R. Houghton
Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine. Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University
 Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University Objective Anatomy Mechanism and type of injury PE.and radiographic evaluation
Common fracture & dislocation of the cervical spine Theerachai Apivatthakakul Department of Orthopaedic Chiangmai University Objective Anatomy Mechanism and type of injury PE.and radiographic evaluation
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine
 A spinal fracture is a serious injury. Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological
A spinal fracture is a serious injury. Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
SpineFAQs. Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
 SpineFAQs Lumbar Spondylolisthesis Normally, the bones of the spine (the vertebrae) stand neatly stacked on top of one another. The ligaments and joints support the spine. Spondylolisthesis alters the
SpineFAQs Lumbar Spondylolisthesis Normally, the bones of the spine (the vertebrae) stand neatly stacked on top of one another. The ligaments and joints support the spine. Spondylolisthesis alters the
A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spondylolysis. William T. Grant, MD
 A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spondylolysis Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh, PA-C pride themselves
A Patient s Guide to Lumbar Spondylolysis Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh, PA-C pride themselves
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma. Introduction. Anatomic Considerations 7/23/2018
 Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Sheyan J. Armaghani, MD Florida Orthopedic Institute Assistant Professor USF Dept of Orthopedics Introduction Trauma to the cervical spine accounts for 5 of all spine injuries
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Sheyan J. Armaghani, MD Florida Orthopedic Institute Assistant Professor USF Dept of Orthopedics Introduction Trauma to the cervical spine accounts for 5 of all spine injuries
Infantile developmental thoracolumbar kyphosis with segmental subluxation of the spine
 Infantile developmental thoracolumbar kyphosis with segmental subluxation of the spine A. I. Tsirikos, M. J. McMaster From The Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Edinburgh, Scotland We report five children
Infantile developmental thoracolumbar kyphosis with segmental subluxation of the spine A. I. Tsirikos, M. J. McMaster From The Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Edinburgh, Scotland We report five children
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
 Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Surgical Treatment Comparisons By: Dr. Alex Rabinovich and Dr. Devin Peterson Options 1. Pedicle Screws versus Hooks 2. Posterior versus Anterior Instrumentation 3. Open
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Surgical Treatment Comparisons By: Dr. Alex Rabinovich and Dr. Devin Peterson Options 1. Pedicle Screws versus Hooks 2. Posterior versus Anterior Instrumentation 3. Open
A Patient s Guide to Cervical Radiculopathy
 A Patient s Guide to Cervical Radiculopathy 950 Breckinridge Lane Suite 220 Louisville, KY 40223 Phone: 502.708.2940 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It
A Patient s Guide to Cervical Radiculopathy 950 Breckinridge Lane Suite 220 Louisville, KY 40223 Phone: 502.708.2940 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It
LIV selection in selective thoracic fusions
 Russian Research Institute for Traumatology and Orthopedics named after R.R.Vreden, St.Petersburg LIV selection in selective thoracic fusions Ptashnikov D. Professor, The chief of spine surgery & oncology
Russian Research Institute for Traumatology and Orthopedics named after R.R.Vreden, St.Petersburg LIV selection in selective thoracic fusions Ptashnikov D. Professor, The chief of spine surgery & oncology
Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics. Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003
 Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003 Anatomy Dorsal columntouch, vibration Corticospinal tract- UMN Anterior horn-lmn Spinothalamic tractpain, temperature (contralateral)
Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003 Anatomy Dorsal columntouch, vibration Corticospinal tract- UMN Anterior horn-lmn Spinothalamic tractpain, temperature (contralateral)
Clinical Analysis of Minimally Invasive Single-segment Reduction and Internal Fixation in Patients with Thoracolumbar Fractures
 Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research 2018, 2(1): 23-27 Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research Clinical Analysis of Minimally Invasive Single-segment Reduction and Internal Fixation in Patients with
Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research 2018, 2(1): 23-27 Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research Clinical Analysis of Minimally Invasive Single-segment Reduction and Internal Fixation in Patients with
Odontoid process fracture in 2 year old child: a rare case report
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 4 2017 October-December Article Odontoid process fracture in 2 year old child: a rare case report Prajapati Hanuman Prasad, Singh Deepak Kumar, Singh Rakesh Kumar,
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 4 2017 October-December Article Odontoid process fracture in 2 year old child: a rare case report Prajapati Hanuman Prasad, Singh Deepak Kumar, Singh Rakesh Kumar,
An Atypical Case of Lumbar Scheuermann s Disease
 An Atypical Case of Lumbar Scheuermann s Disease Taner Dandinoglu¹, Murat Karadeniz 2, Ozgur Dandin 3 1 Bursa Military Hospital, Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Bursa, Turkey 2 Çorlu
An Atypical Case of Lumbar Scheuermann s Disease Taner Dandinoglu¹, Murat Karadeniz 2, Ozgur Dandin 3 1 Bursa Military Hospital, Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Bursa, Turkey 2 Çorlu
Curative effect comparison of anterior and posterior approach in debridement combined with bone graft fusion for the treatment of spinal tuberculosis.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (11): 4832-4836 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Curative effect comparison of anterior and posterior approach in debridement combined with bone graft fusion for the treatment
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (11): 4832-4836 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Curative effect comparison of anterior and posterior approach in debridement combined with bone graft fusion for the treatment
Segmental Pedicle Screw Fixation for a Scoliosis Patient with Post-laminectomy and Post-irradiation Thoracic Kyphoscoliosis of Spinal Astrocytoma
 Segmental Pedicle Screw Fixation for a Scoliosis Patient with Post-laminectomy and Post-irradiation Thoracic Kyphoscoliosis of Spinal Astrocytoma a* a a a b a a b ʼ 2 ʼ August 2012 Spinal Deformity with
Segmental Pedicle Screw Fixation for a Scoliosis Patient with Post-laminectomy and Post-irradiation Thoracic Kyphoscoliosis of Spinal Astrocytoma a* a a a b a a b ʼ 2 ʼ August 2012 Spinal Deformity with
Spinal injury. Structure of the spine
 Spinal injury Structure of the spine Some understanding of the structure of the spine (spinal column) and the spinal cord is important as it helps your Neurosurgeon explain about the part of the spine
Spinal injury Structure of the spine Some understanding of the structure of the spine (spinal column) and the spinal cord is important as it helps your Neurosurgeon explain about the part of the spine
A.M. REETHA, S. SIVASUBRAMANIAN, R. PARTHASARATHY, P.R. SOMASUNDARAM, R. PRABHAKAR. Tuberculosis Research Centre, Madras
 Five-year Findings of a Comparison of Ambulatory Short Course Chemotherapy with Radical Surgery Plus Chemotherapy for Tuberculosis of the Spine in Madras A.M. REETHA, S. SIVASUBRAMANIAN, R. PARTHASARATHY,
Five-year Findings of a Comparison of Ambulatory Short Course Chemotherapy with Radical Surgery Plus Chemotherapy for Tuberculosis of the Spine in Madras A.M. REETHA, S. SIVASUBRAMANIAN, R. PARTHASARATHY,
Evaluation of Role of Anterior Debridement and Decompression of Spinal Cord and Instrumentation in Treatment of Tubercular Spondylitis
 Asian Spine Journal Vol. 6, No. 3, pp 183~193, 2012 Anterior Debridment Decompression and Instrumentation in Tubercular Spondylitis / 183 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2012.6.3.183 Evaluation of Role of
Asian Spine Journal Vol. 6, No. 3, pp 183~193, 2012 Anterior Debridment Decompression and Instrumentation in Tubercular Spondylitis / 183 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2012.6.3.183 Evaluation of Role of
A Study of 42 Cases of Pott s Paraplegia with Anterior Spinal Decompression & Stabilisation with Rib Graft Alone
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 7 Ver. VIII (July. 2016), PP 45-49 www.iosrjournals.org A Study of 42 Cases of Pott s Paraplegia
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 7 Ver. VIII (July. 2016), PP 45-49 www.iosrjournals.org A Study of 42 Cases of Pott s Paraplegia
RETROLISTHESIS. Retrolisthesis. is found mainly in the cervical spine and lumbar region but can also be often seen in the thoracic spine
 RETROLISTHESIS A retrolisthesis is a posterior displacement of one vertebral body with respect to adjacent vertebrae Typically a vertebra is to be in retrolisthesis position when it translates backward
RETROLISTHESIS A retrolisthesis is a posterior displacement of one vertebral body with respect to adjacent vertebrae Typically a vertebra is to be in retrolisthesis position when it translates backward
Key words: Spine, tuberculosis, anterior, surgery, adult. Reprint requests: Prof RN Dunn
 CLINICAL ARTICLE SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Spring 2011 Vol 10 No 3 / Page 43 C L I N I C A L A RT I C L E Anterior-only transthoracic surgery for adult spinal tuberculosis Dr Bryan Riemer MBChB(UCT) Registrar,
CLINICAL ARTICLE SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Spring 2011 Vol 10 No 3 / Page 43 C L I N I C A L A RT I C L E Anterior-only transthoracic surgery for adult spinal tuberculosis Dr Bryan Riemer MBChB(UCT) Registrar,
Study of functional outcomes of surgical treatment of tuberculosis of spine with debridement and spinal fixation
 2017; 3(1): 389-394 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(1): 389-394 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 15-11-2016 Accepted: 17-12-2016 Dr. Pallav Patel MS Ortho Poojan Orthopaedic Hospital Himmatnagar, Gujarat,
2017; 3(1): 389-394 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(1): 389-394 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 15-11-2016 Accepted: 17-12-2016 Dr. Pallav Patel MS Ortho Poojan Orthopaedic Hospital Himmatnagar, Gujarat,
Scoliosis: Orthopaedic Perspectives
 Scoliosis: Orthopaedic Perspectives Scott B. Rosenfeld, MD Division of Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Texas Children s Hospital Page 0 xxx00.#####.ppt 9/23/2012 8:26:24 AM I have no disclosures Disclosures
Scoliosis: Orthopaedic Perspectives Scott B. Rosenfeld, MD Division of Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Texas Children s Hospital Page 0 xxx00.#####.ppt 9/23/2012 8:26:24 AM I have no disclosures Disclosures
Classification? Classification system should be: Comprehensive Usable Accurate Predictable Able to guide intervention
 Moderator: Dr. P.S. Chandra Dr. Dr Deepak Gupta Classification? Classification system should be: Comprehensive Usable Accurate Predictable Able to guide intervention A precise, comprehensive, ideal
Moderator: Dr. P.S. Chandra Dr. Dr Deepak Gupta Classification? Classification system should be: Comprehensive Usable Accurate Predictable Able to guide intervention A precise, comprehensive, ideal
ASJ. Study of Vertebral Body Replacement with Reconstruction Spinal Cages in Dorsolumbar Traumatic and Koch s Spine. Asian Spine Journal.
 Asian Spine Journal 786 Rohit Anilbhai Clinical Thaker Studyet al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.6.786 Study of Vertebral Body Replacement with Reconstruction Spinal Cages in Dorsolumbar Traumatic
Asian Spine Journal 786 Rohit Anilbhai Clinical Thaker Studyet al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.6.786 Study of Vertebral Body Replacement with Reconstruction Spinal Cages in Dorsolumbar Traumatic
Spine Center. at Stamford Hospital s Orthopedic Institute
 Spine Center at Stamford Hospital s Orthopedic Institute Back pain related to spinal deformity and injury or congenital conditions is a common health complaint, which can be very debilitating. At Stamford
Spine Center at Stamford Hospital s Orthopedic Institute Back pain related to spinal deformity and injury or congenital conditions is a common health complaint, which can be very debilitating. At Stamford
Porcine model for early onset scoliosis created with a posterior mini-invasive method
 E-Poster #P72 Porcine model for early onset scoliosis created with a posterior mini-invasive method WANG Bin, ZHENG Xin, QIU Yong*, QIAN Bang-ping, SUN Xu, ZHU Zezhang, YU Yang Spine surgery, the Affiliated
E-Poster #P72 Porcine model for early onset scoliosis created with a posterior mini-invasive method WANG Bin, ZHENG Xin, QIU Yong*, QIAN Bang-ping, SUN Xu, ZHU Zezhang, YU Yang Spine surgery, the Affiliated
Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis
 35 J. Tokyo Med. Univ., 71 1 35 0 Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis Wuqikun ALIMASI, Kenji ENDO, Hidekazu SUZUKI, Yasunobu SAWAJI, Hirosuke NISHIMURA, Hidetoshi TANAKA,
35 J. Tokyo Med. Univ., 71 1 35 0 Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis Wuqikun ALIMASI, Kenji ENDO, Hidekazu SUZUKI, Yasunobu SAWAJI, Hirosuke NISHIMURA, Hidetoshi TANAKA,
A Very Unusual Case of a Dorsal Heteropagus Twin
 PRG A Very Unusual Case of a Dorsal Heteropagus Twin Nathan David P. Concepcion, MD 1, Bernard F. Laya, DO 1, Eduardo P. Manrique, MD 2 and Faith Caroline D. Bayabos, MD 1 1 Section of Pediatric Radiology,
PRG A Very Unusual Case of a Dorsal Heteropagus Twin Nathan David P. Concepcion, MD 1, Bernard F. Laya, DO 1, Eduardo P. Manrique, MD 2 and Faith Caroline D. Bayabos, MD 1 1 Section of Pediatric Radiology,
Comprehension of the common spine disorder.
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
VAriation. Orthotics and Me (?surgeons) Greg Etherington Spine Surgeon. Orthopaedic & Neurosurgery backgrounds. Subspeciality training
 Orthotics and Me (?surgeons) Greg Etherington Spine Surgeon Orthopaedic & Neurosurgery backgrounds Subspeciality training spine, upper limb, trauma, pelvis. What do you do in spine? Lumbar Cervical Trauma
Orthotics and Me (?surgeons) Greg Etherington Spine Surgeon Orthopaedic & Neurosurgery backgrounds Subspeciality training spine, upper limb, trauma, pelvis. What do you do in spine? Lumbar Cervical Trauma
SPINAL PSEUDOARTHROSIS
 485 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE NO. 3 SPINL PSEUDORTHROSIS COMPLICTION OF NKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS WILLIM MRTEL Fracture of the cervical spine is a recognized complication of advanced ankylosing spondylitis ( 1 ).
485 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE NO. 3 SPINL PSEUDORTHROSIS COMPLICTION OF NKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS WILLIM MRTEL Fracture of the cervical spine is a recognized complication of advanced ankylosing spondylitis ( 1 ).
Selective fusion in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a radiographic evaluation of risk factors for imbalance
 J Child Orthop (2015) 9:153 160 DOI 10.1007/s11832-015-0653-0 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Selective fusion in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a radiographic evaluation of risk factors for imbalance D. Studer
J Child Orthop (2015) 9:153 160 DOI 10.1007/s11832-015-0653-0 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Selective fusion in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a radiographic evaluation of risk factors for imbalance D. Studer
Spinal Deformity: Congenital Scoliosis. A Handbook for Patients
 Spinal Deformity: Congenital Scoliosis A Handbook for Patients Scoliosis Research Society Dedicated to Education, Research and Treatment of Spinal Deformity 555 East Wells Street, Suite 1100 Milwaukee,
Spinal Deformity: Congenital Scoliosis A Handbook for Patients Scoliosis Research Society Dedicated to Education, Research and Treatment of Spinal Deformity 555 East Wells Street, Suite 1100 Milwaukee,
Evaluation of implant stabilization in tubercular Spondylodiscitis: a prospective study
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Maila SK et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Oct;3(10):2647-2653 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20150807
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Maila SK et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Oct;3(10):2647-2653 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20150807
Thoracolumbar fractures. Treatment options. A long trip.
 Thoracolumbar fractures. Treatment options. A long trip. MIS SURGERY. WHY NOT? Murcia. October 5, 2012. Dr. Pedro Cortés García. Spinal Unit. Orthopaedic department. Canary Islands University Hospital
Thoracolumbar fractures. Treatment options. A long trip. MIS SURGERY. WHY NOT? Murcia. October 5, 2012. Dr. Pedro Cortés García. Spinal Unit. Orthopaedic department. Canary Islands University Hospital
A Retrospective Analysis of Management of Tuberculosis of Spine in a Tertiary Care Hospital
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Retrospective Analysis of Management of Tuberculosis of Spine in a Tertiary Care Hospital Prashant N Gedam 1, Prathamesh Kane 2 1. Additional Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, B.Y.L
ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Retrospective Analysis of Management of Tuberculosis of Spine in a Tertiary Care Hospital Prashant N Gedam 1, Prathamesh Kane 2 1. Additional Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, B.Y.L
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
 Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis is characterized by a lateral bending and twisting of the spine. It is the most common spinal deformity affecting adolescents 10 to 16 years
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis is characterized by a lateral bending and twisting of the spine. It is the most common spinal deformity affecting adolescents 10 to 16 years
Scoliosis is considered to be the most common skeletal
 clinical article J Neurosurg Pediatr 19:96 101, 2017 Posterior-only surgical correction of dystrophic scoliosis in 31 patients with neurofibromatosis Type 1 using the multiple anchor point method Ang Deng,
clinical article J Neurosurg Pediatr 19:96 101, 2017 Posterior-only surgical correction of dystrophic scoliosis in 31 patients with neurofibromatosis Type 1 using the multiple anchor point method Ang Deng,
Royal Oak IBFD System Surgical Technique Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF)
 Royal Oak IBFD System Surgical Technique Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF) Preoperative Planning Preoperative planning is necessary for the correct selection of lumbar interbody fusion devices.
Royal Oak IBFD System Surgical Technique Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF) Preoperative Planning Preoperative planning is necessary for the correct selection of lumbar interbody fusion devices.
Computed tomography analysis of L5-S1 fusion in Adult spinal deformity
 Eurospine 2018 Barcelona Computed tomography analysis of L5-S1 fusion in Adult spinal deformity Comparison of whether spinopelvic fixation, ALIF vs PLIF, and cage design Jung-Hee Lee MD, Kyung-Chung Kang
Eurospine 2018 Barcelona Computed tomography analysis of L5-S1 fusion in Adult spinal deformity Comparison of whether spinopelvic fixation, ALIF vs PLIF, and cage design Jung-Hee Lee MD, Kyung-Chung Kang
 Introduction Posterior cervical fusion is done through the back posterior of the neck. The surgery joins two or more neck vertebrae into one solid section of bone. The medical term for fusion is arthrodesis.
Introduction Posterior cervical fusion is done through the back posterior of the neck. The surgery joins two or more neck vertebrae into one solid section of bone. The medical term for fusion is arthrodesis.
INTRODUCTION.
 www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/1.334/jkns.212.51.4.23 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 51 : 23-27, 212 Print ISSN 25-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 212 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical Article
www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/1.334/jkns.212.51.4.23 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 51 : 23-27, 212 Print ISSN 25-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 212 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical Article
