Prospective clinical study of a novel biodegradable sub-acromial spacer in treatment of massive irreparable rotator cuv tears
|
|
|
- Ferdinand Barnett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOI /s ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prospective clinical study of a novel biodegradable sub-acromial spacer in treatment of massive irreparable rotator cuv tears Vladimir Senekovic Boris Poberaj Ladislav Kovacic Martin Mikek Eliyahu Adar Assaf Dekel Received: 21 January 2012 / Accepted: 19 March 2012 Springer-Verlag 2012 Abstract Purpose The purposes of this prospective non-randomized study were to conwrm the feasibility of the biodegradable sub-acromial spacer (InSpace ) implantation in patients with massive irreparable rotator cuv tear and to determine the safety prowle and functional results 3 years post-implantation. Methods Twenty patients were implanted with the InSpace device and assessed up to 3 years of postimplantation. Improvement in shoulder function was assessed using Constant score, while ease of use of the system was recorded by surgeons as were device-related adverse events. Results Twenty patients were available for assessment. Implantation was performed arthroscopically in all patients, and a range of deployment time was 2 20 min. The mean V. Senekovic L. Kovacic Department of Traumatology, University Medical Centre Ljubljana, Zaloska 2, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia B. Poberaj Valdoltra Orthopedic Hospital, Jadranska Cesta 31, 6280 Ankaran, Slovenia M. Mikek Center for Orthopedic Surgery and Sports Medicine, Novo Mesto General Hospital, ARTROS, Tehnolonki Park 21, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia E. Adar Department of Orthopedic Surgery, E. Wolfson Medical Center, 62 HaLohamim Street, P.O. Box 5, Holon, Israel A. Dekel (&) Advanced Orthopedic Center, Assuta Medical Center, 20 Habarzel St, Ramat Hachayil, Tel Aviv, Israel dekel.assaf@gmail.com total Constant score increased from 33.4 to 65.4 points at 3 years. There was an improvement of 6.4 points in subjective pain score which commenced at 1 week post-operatively and was sustained until 3 years of follow-up. Also activities of daily living and motions commenced improvement by 9.4 and 7.7 points, respectively. Improvement in power was only evident at 18 months of follow-up but was sustained at 3 years. Conclusions Arthroscopic deployment of a co-polymer biodegradable spacer (balloon) into the sub-acromial space for an irreparable rotator cuv tear was found to be low-risk and simple procedure associated with improvement in shoulder function and low rate of complications. Level of evidence IV; therapeutic case series Keywords Massive irreparable rotator cuv tears Constant score Sub-acromial spacer Arthroscopy Introduction Rotator cuv tears (RCTs) are amongst the commonest tendon injuries seen in orthopaedic patients [1] resulting in signiwcant community-borne pain and disability [2]. Irreparable RCTs are dewned by the size of the tear [3], the presence of tendon retraction, chronicity of the injury [4, 5] and the amount of muscle atrophy and degree of fatty degeneration [6]. In these situations, direct repair at the point of insertion is usually not feasible despite extensive soft-tissue mobilization and release [7]. A range of surgical options are available, including debridement (with or without partial tendon repair), tendon transfer, muscle tendon slide procedures, the utilization of rotator cuv allograft and synthetic graft materials, arthrodesis, reverse arthroplasty or hemiarthroplasty [8 11].
2 The purpose and hypothesis of this Wrst-in-human prospective study was to conwrm that the implantation of biodegradable co-polymer spacer (InSpace ) into the subacromial space of patients with massive irreparable rotator cuv is a simple and safe procedure associated with clinical improvement of shoulder function and low rate of devicerelated adverse events. Materials and methods Study design The study was approved by the hospital Ethical Committee and associated National Competent Authority and was conducted as a clinical part of the product CE mark application. The study was designed as a one-arm, prospective study to assess the feasibility, safety and eycacy of the InSpace sub-acromial spacer system in subjects with massive irreparable tears. Patients were voluntarily (with no compensation on their participation in the study) enrolled in the study after receiving information on other treatment alternatives and signing an informed consent. Patients were considered eligible to participate in the study when diagnosed with irreparable massive rotator cuv tear (conwrmed during arthroscopy), had persistent pain for at least 6 months with documented failure of conservative treatment and presented positive shoulder impingement test at screening. Exclusion criteria included signiwcant shoulder osteoarthritis, prior shoulder surgery, shoulder infection or systemic immune suppression. Primary end-points included pain relief over time, improvement in the range of motion, activities of daily living and shoulder strength using the Constant score [12] that was recorded at each follow-up visit. Patients were clinically assessed pre-operatively for the presence of a fullthickness massive RCT with supplementary imaging using ultrasound, CT arthrography and magnetic resonance (MR) imaging as appropriate [13 15]. Final conwrmation of the RCT size, tendon involvement and reducibility was made during arthroscopy where the surgeon assessed the feasibility of surgical repair. Prospective post-operative assessment of symptoms, complications and/or device-related adverse events was recorded with prospective determination of the Constant score at hospital discharge, 1, 3 and 6 weeks, 3, 6, 18 and 36 months post-operatively. Device placement and biodegradation were assessed by ultrasonographic evaluation at 1 week and 3 and 6 months post-implantation. Device complete absorption and absence of signiwcant device-related complications were conwrmed by shoulder MRI at 3 years post-implantation. InSpace spacer system The InSpace system is a biodegradable spacer (balloon shape) meant for arthroscopic insertion into the sub-acromial space following bursa excision. Animal studies performed in rabbit, canine and swine models conwrmed spacer biocompatibility and safety for in vivo use without any evidence of local or systemic reaction. The pre-shaped spacer is comprised of a co-polymer of poly-l-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone in a 70: 30 ratio, which biodegrades over a period of 12 months [16]. Insertion of the sub-acromial spacer is aided by folding it into a cylindrical shape inside an insertion tube. Once positioned in the sub-acromial space, the spacer is inxated with saline permitting frictionless gliding of the humeral head against the acromion. Surgical technique All operations were performed with the patient in a beachchair position under general anaesthesia using 3 arthroscopic ports (anterior, lateral and posterior or posterolateral). After sub-total removal of the sub-acromial bursa, the tear was debrided and the rotator cuv was assessed by grasping the edges of the tendons with an arthroscopic clamp in an attempt to draw it to the footprint region. A decision was made to insert the sub-acromial spacer when it was deemed that the RCT was irreparable. During the arthroscopic procedure, all patients who presented in this analysis had over 5-cm tear involving the supraspinatus and usually the infraspinatus with tissue quality validated at procedure not adequate for repair (Goutallier grade 3 4). The long head of biceps was found to be torn or ruptured in 13 of cases, while in the remaining 7 cases a biceps tenotomy was done. A schematic representation of the device deployment is shown in Figs. 1 and 2, and spacer size (small, medium or large) is selected based on the surgeon s discretion following measurement of the distance between the lateral border of the acromion and the superior rim of the glenoid as well after dewning the extent of any tear extension. The range of motion is determined by spacer inxation and dexation, and the appropriate inxation volume is left in situ by withdrawing the syringe that enables the spacer sealing (Fig. 2). Statistics Study data were analysed using the SAS version 9.2 (SAS Institute, Cary NC, USA). Data are presented in tabular format where continuous variables are presented as means (SD) for total Constant score (TCS), subjective pain score
3 Δ=31.5 baseline M 6 Y 1.5 Y Fig. 1 Schematic representation of the InSpace deployment and inxation in the sub-acromial space through an insertion tube Δ=6.4 Δ=1 Δ=9.24 Δ=8.1 Δ=7.2 TCS SPS NP ADL ROM Power Fig. 3 Graphical presentation of Constant variables following In- Space spacer insertion. TCS total Constant score, SPS subjective pain score, NP night pain, ROM range of motion, ADL activity of daily living. Δ: presents change in score from baseline to 3 years Fig. 2 Image of InSpace after sealing (SPS; Module A of the CS), activity of daily living (ADL; Module B of the CS), range of motion (ROM; Module C of the CS) and power (Module D of the CS). Categorical variables are presented as counts and percentages, and the change from baseline of the Constant scores was determined using a repeated-measures analysis variance model. s <0.05 were considered statistically signiwcant. Results A total of 20 patients with massive irreparable rotator cuv tear were enrolled in the study between the periods of May and October 2008 (11 men and 9 women; mean age 70.5 years range years). In all evaluated cases, the device was inserted arthroscopically. The mean duration of symptoms prior to surgery was 34.7 months (range 4 95 months) with failure of conservative treatment in all patients. The technique of implantation was recorded as easy and straightforward by all surgeons where the time for implantation ranged from 2 to 20 min and decreased over time while the surgeon gained more experience in the procedure. Three patients did not reach the 3-year follow-up: one patient withdrew consent 6 weeks post implantation due to unsatisfactory outcome and referred to reverse total shoulder arthroplasty, the second patient had improvement in symptoms but refused to continue the participation in the study, and the third patient died during follow-up from cardiac disease not related to the implantation. Figure 3 represents graphically the baseline and followup clinical scoring data of the analysed patients. There was a signiwcant improvement in the subjective pain score (Module A of the Constant score), commencing at 1 week following spacer implantation (95 % CI, ; P = ). This improvement remained statistically signiwcant with a progressive increase throughout the duration of follow-up. At the 3-year visit, the average change reached 6.11 points (95 % CI, ; P < ). Night pain statistically improved beginning at 1 week postsurgery (95 % CI, ; P < ) with a sustained statistically signiwcant improvement through to the 3-year follow-up visit (95 % CI, ; P < ). Improvement in night pain was reported in 12/20 patients (60 %) at the Wrst post-operative week, in 14 (70 %) patients at the 1.5-year visit and sustained at the 3-year follow-up visit. Two patients had no improvement in their total Constant score, and the MR images at 3 years post-implantation of these two patients showed suspected synovitis without cystic formation. Post-surgery images did not reveal any bone cysts or signiwcant synovitis in any of the evaluated patients. No other device- or procedure-related adverse events were noted during the follow-up period. Figure 4a, b presents an example of MR image of the InSpace spacer (balloon) placement at sub-acromial space following 3 and 6 months post-implantation. Table 1 shows the Constant score variables as measured at pre- and post-implantation, while Table 2 shows the changes in these parameters as assessed from baseline over
4 to improve up to the Wnal follow-up at 3 years with a mean change of 31.5 from baseline (95 % CI, ; P < ). Patients reported signiwcant improvement in their activities of daily living beginning at the third week after surgery with continuous increase at 3 years of followup. The range of motion also showed signiwcant improvement beginning at 6 weeks post-surgery and progressively increased throughout the study period. Shoulder power was diycult to evaluate early on in the post-implantation period but showed signiwcant improvement at 1.5 years (95 % CI, ; P = ) which was sustained at 3 years (95 % CI, ; P < ). In all measurable parameters, once an improvement reached signiwcance, it was maintained throughout the follow-up period. Discussion Fig. 4 a MRI section 3 months following InSpace insertion (arrow). b MRI section 6 months following InSpace insertion the 3-year follow-up. Statistically signiwcant changes were evident in TCS assessment at the 6-week follow-up visit (95 % CI, ; P = 0.010), and this change continued This prospective, Wrst-in-human, pilot study has shown clinical safety and eycacy of the InSpace device in a small group of patients with massive irreparable RCTs. The insertion of the device was associated with signiwcant improvement in subjective pain scores and a decrease in reported night pain. The total Constant score showed statistically signiwcant improvement starting at 6 months post- InSpace implantation when 55.5 % of the treated patients showed an improvement of at least 15 points in their TCS, this percentage continues to grow, and 68.8 % of the patients who reached 3 years post-implantation follow-up had an improvement of at least 25 points of their TCS. Shoulder power did not improve until 18 months postimplantation with this improvement being maintained at 3 years of follow-up. The procedure of InSpace insertion was rated by surgeons as easy to use with no demonstrable adverse side evects, except suspected non-clinically signiwcant synovitis in 2 cases. The rotator cuv overs stability by compression of the humeral head into the glenoid, while rotator cuv disruption compromises concavity compression and alters glenohumeral Table 1 Pre-operative and post-operative Constant scores variables [Mean (SD)] Post-op period/(n) TCS SPS (Part A) ADL (Part B) ROM (Part C) Power (Part D) Pre-operative/(20) (13.34) 5.08 (2.76) 7.20 (3.38) (8.95) 0.54 (2.39) Week 1/(20) (12.99) 8.03 (3.62) 8.65 (2.85) (9.32) 0.00 Week 3/(20) (13.04) 7.70 (3.57) 9.75 (4.48) 21.6 (7.75) 1.25 (0.79) Week 6/(20) (15.21) 8.28 (3.94) 9.50 (3.44) (9.91) 0.26 (1.16) Month 3/(17) (14.56) 8.29 (3.59) (3.07) (10.27) 0.00 Month 6/(18) (19.72) 8.92 (4.16) (3.95) (9.68) 3.50 (7.02) Year 1.5/(18) (22.98) (3.85) (4.93) (10.13) 4.99 (7.83) Year 3/(16) (25.23) (3.94) (4.15) (11.89) 7.76 (8.49) TCS total Constant score, SPS subjective pain score, ROM range of motion, ADL activity of daily living
5 Table 2 Change in Constant score variables from pre-operation up to 3 years after InSpace implantation Variable baseline to M3 baseline to M6 baseline to Y1.5 baseline to Y3 TCS < < <.0001 SPS < < <.0001 Night pain 0.65 < < < <.0001 ADL < <.0001 ROM < <.0001 Power N/A N/A <.0001 TCS total Constant score, SPS subjective pain score, ROM range of motion, ADL activity of daily living, N/A not applicable load structure and direction [17, 18]. Optimal sub-acromial decompression aims to restore a smooth coracoacromial arch and to reduce rotator cuv contact pressure while preserving arch function. The deployment of the sub-acromial spacer should achieve these aims by reducing sub-acromial friction during shoulder abduction. The biodegradable sub-acromial spacer, which can be introduced arthroscopically in a short procedure with a good safety prowle, alleviates pain and improves shoulder function by lowering the head of the humerus during spacer inxation, thereby facilitating humeral gliding against the acromion. The biocompatible co-polymer used in the InSpace device mimics the structure of natural extracellular matrices, promoting cell cell and cell matrix interactions because of the balance between its hydrophilic and hydrophobic characteristics consequent upon the variable biodegradation between its softer epsilon-caprolactone and harder L-lactide components [20]. At present, it is unclear exactly how long the spacer remains inxated, nor is it understood why pain and functional scores continue to improve beyond the period of spacer disintegration. Based on the information from histological evaluation following implantation of the spacer in two rabbits when 6 weeks following implantation, the formation of mature connective tissue around the spacer with no signs of active inxammation was observed. It is conceivable that new soft tissue forms in the spacer area and continues to act as a barrier between the humeral head and the acromion providing continued pain relief despite spacer dexation. The reduction in the overall pain score appears almost immediately after insertion, although this may occur in part as a result of debridement and bursectomy [21]. Although there are several surgical procedures that over acceptable outcome results for patients with massive irreparable RCTs such as debridement, tendon transfer, muscle tendon slide procedures, allograft and synthetic graft materials, arthrodesis, reverse arthroplasty or hemiarthroplasty [8 11], there is no consensus or dewnitive guidelines on the preferred surgical option to treat this challenging patient population [19]. The InSpace spacer implantation procedure overs less invasive, simple, low-risk option with minimal morbidity, and its initial success appears in this small study to be sustainable. Longer longitudinal study of this device is justiwed as this technique represents a simple, safe alternative to conventional surgical approaches for massive irreparable RCTs where clinical and functional outcomes have been mixed. This study has several weaknesses. The shoulder functional assessment was based solely on the Constant score, which might be limited in its scope and can be gender biased in regard to power measures [22]. Lack of established protocol for radiographic evaluation modalities makes the comparison between pre- and posttreatment imaging impossible, while having no control group to the procedure makes the results relatively weak and raised the need for further randomized studies to determine the place of the InSpace spacer in the management of massive rotator cuv injury. Conclusions Arthroscopic deployment of a co-polymer biodegradable spacer (balloon) into the sub-acromial space for an irreparable rotator cuv tear was found to be low-risk and simple procedure associated with the improvement in shoulder function and low rate of complications. ConXict of interest In support of their research or preparation of this manuscript, one or more of the authors received grants or outside funding from OrthoSpace Ltd. Also, a commercial entity (OrthoSpace Ltd.) paid or directed, or agreed to pay or direct, benewts to a research fund, foundation, educational institution or other charitable or non-prowt organization with which the authors are ayliated or associated. Dr. Dekel and Dr. Adar have Wnancial interest in the funding company, while other authors have no such interest. References 1. Tonino PM, Gerber C, Itoi E, Porcellini G, Sonnabend D, Walch G (2009) Complex shoulder disorders: evaluation and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 17: CoWeld RH (1985) Rotator cuv disease of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Am 67(6):
6 3. Matthews TJ, Hand GC, Rees JL, Athanasou NA, Carr AJ (2006) Pathology of the torn rotator cuv tendon. Reduction in potential for repair as the tear size increases. J Bone Joint Surg Br 88: Coleman SH, Fealy S, Ehteshami JR et al (2003) Chronic rotator cuv injury and repair model in sheep. J Bone Joint Surg Am 85: Liu X, Manzano G, Kim HT, Feeley BT (2011) A rat model of massive rotator cuv tears. J Orthop Res 29: Goutallier D, Postel JM, Bemageau J et al (1994) Fatty muscle degeneration in cuv ruptures. Pre- and postoperative evaluation by CT scan. Clin Orthop Rel Res 304: Encalada-Diaz I, Cole BJ, MacGillivray JD, Ruiz-Suarez M, Kercher JS, Friel NA, Valero-Gonzalez F (2011) Rotator cuv repair augmentation using a novel polycarbonate polyurethane patch: preliminary results at 12 months follow-up. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 20: Moser M, Jablonski MV, Horodyski M, Wright TW (2007) Functional outcome of surgically treated massive rotator cuv tears: a comparison of complete repair, partial repair and debridement. Orthopedics 30: Aurora A, McCarron J, Ianotti J, Derwin K (2007) Commercially available extracellular matrix materials for rotator cuv repairs: state of the art and future trends. J Should Elbow Surg 16(5 Suppl):S171 S Goldberg SS, Bell JE, Kim HJ, Bak SF, Levine WM, Bigilani LY (2008) Hemiarthroplasty for the rotator cuv-dewcient shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90: CuV D, Pupello D, Virani N, Levy J, Frankle M (2008) Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of rotator cuv dewciency. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90: doi: /jbjs.g Constant CR, Murley AH (1987) A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder. Clin Orthop Rel Res 214: Boes MT, McCann PD, Dines DM (2006) Diagnosis and management of massive rotator cuv tears: the surgeon s dilemma. Instr Course Lect 55: Al-Shawi A, Badge R, Bunker T (2008) The detection of full thickness rotator cuv tears using ultrasound. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90: Morag Y, Jacobson JA, Miller B, De Maeseneer M, Girish G, Jamadar D (2006) MR imaging of rotator cuv injury: what the clinician needs to know. Radiographics 26: Burks CA, Bundy K, Fotuhi P, Alt E (2006) Characterization of 75:25 poly(l-lactide-co-e-caprolactone) thin Wlms for the endoluminal delivery of adipose-derived stem cells to abdominal aortic aneurysms. Tissue Eng 12: doi: /ten Parsons IM, Apreleva M, Fu FH, Woo SL (2002) The evect of rotator cuv tears on reaction forces at the glenohumeral joint. J Orthop Res 20: Kedgley AE, MacKenzie GA, Ferreira LM, Johnson JA, Faber KJ (2007) In vitro kinematics of the shoulder following rotator cuv injury. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 22: Mulieri P, Dunning P, Klein S, Pupello D, Frankle M (2010) Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of irreparable rotator cuv tear without glenohumeral arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92: doi: /jbjs.i Li S, Sun B, Li X, Yuan X (2008) Characterization of electrospun core/shell poly (vinyl pyrrolidone)/poly (L-lactide-co-epsiloncaprolactone) Wbrous membranes and their cytocompatibility in vitro. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 19: Liem D, Lengers N, Dedy N, Poetzl W, Steinbeck J, Marquardt B (2008) Arthroscopic debridement of massive irreparable rotator cuv tears. Arthroscopy 24: Katolik LY, Romeo AA, Cole BJ, Verma NN (2005) Normalization of the Constant score. J Should Elbow Surg 14:
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of inserting a biodegradable subacromial spacer for rotator cuff tears The rotator
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of inserting a biodegradable subacromial spacer for rotator cuff tears The rotator
The massive, irreparable rotator cuff tear is a challenging
 New Solution for Massive, Irreparable Rotator Cuff Tears: The Subacromial Biodegradable Spacer Eugenio Savarese, M.D., Ph.D., and Rocco Romeo, M.D. Abstract: Massive, irreparable rotator cuff tears are
New Solution for Massive, Irreparable Rotator Cuff Tears: The Subacromial Biodegradable Spacer Eugenio Savarese, M.D., Ph.D., and Rocco Romeo, M.D. Abstract: Massive, irreparable rotator cuff tears are
Irreparable Cuff Tear - new treatment modality
 Irreparable Cuff Tear - new treatment modality disclosure Orthospace: consultant stock Options Definition of Irreperable Tear Size? Definition of Irreperable Tear Size? Patient s age/condition? Definition
Irreparable Cuff Tear - new treatment modality disclosure Orthospace: consultant stock Options Definition of Irreperable Tear Size? Definition of Irreperable Tear Size? Patient s age/condition? Definition
Inserting a biodegradable subacromial spacer for rotator cuff tears
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Inserting a biodegradable subacromial spacer for rotator cuff tears The rotator cuff is a group of muscles
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Inserting a biodegradable subacromial spacer for rotator cuff tears The rotator cuff is a group of muscles
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears. Rafael M. Williams, MD
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Rafael M. Williams, MD Rotator Cuff MRI MRI Small / Partial Thickness Medium Tear Arthroscopic View Massive Tear Fatty Atrophy Arthroscopic View MassiveTears Tear is > 5cm
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Rafael M. Williams, MD Rotator Cuff MRI MRI Small / Partial Thickness Medium Tear Arthroscopic View Massive Tear Fatty Atrophy Arthroscopic View MassiveTears Tear is > 5cm
11/13/2017. Disclosures: The Irreparable Rotator Cuff. I am a consultant for Arhtrex, Inc and Endo Pharmaceuticals.
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis THE CASE FOR SUPERIOR CAPSULAR RECONSTRUCTION MICHAEL GARCIA, MD NOVEMBER 4, 2017 FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE Disclosures: I am a consultant for Arhtrex,
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis THE CASE FOR SUPERIOR CAPSULAR RECONSTRUCTION MICHAEL GARCIA, MD NOVEMBER 4, 2017 FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE Disclosures: I am a consultant for Arhtrex,
Management of Massive/Revision Rotator Cuff Tears
 Management of Massive/Revision Rotator Cuff Tears Nikhil N. Verma MD, Director Sports Medicine, Rush University Medical Center, Midwest Orthopedics at Rush, Chicago, IL nverma@rushortho.com I. Anatomy
Management of Massive/Revision Rotator Cuff Tears Nikhil N. Verma MD, Director Sports Medicine, Rush University Medical Center, Midwest Orthopedics at Rush, Chicago, IL nverma@rushortho.com I. Anatomy
Options for the Irreparable RCT 3/9/2018. Your Patient has an Irreparable RC Tear: What Now? Asheesh Bedi, MD
 Your Patient has an Irreparable RC Tear: What Now? Asheesh Bedi, MD Harold and Helen W. Gehring Professor Chief, Sports Medicine & Shoulder Surgery MedSport, Department of Orthopedic Surgery Head Team
Your Patient has an Irreparable RC Tear: What Now? Asheesh Bedi, MD Harold and Helen W. Gehring Professor Chief, Sports Medicine & Shoulder Surgery MedSport, Department of Orthopedic Surgery Head Team
RCR or rtsa? Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis in Patients Older than 65 Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty or Rotator Cuff Repair?
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis in Patients Older than 65 Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty or Rotator Cuff Repair? JESSE W. ALLERT, MD THOMAS SELLERS, MD PETER SIMON, PHD RACHEL CLARK,
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis in Patients Older than 65 Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty or Rotator Cuff Repair? JESSE W. ALLERT, MD THOMAS SELLERS, MD PETER SIMON, PHD RACHEL CLARK,
ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT
 ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH
ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH
Conflict of Interest. New Strategies in Rotator Cuff Repair. Objectives. Learner Outcome
 Conflict of Interest New Strategies in Rotator Cuff Repair Sheri Lankford, BSN, CNOR I hereby certify that, to the best of my knowledge, no aspect of my current personal or professional situation might
Conflict of Interest New Strategies in Rotator Cuff Repair Sheri Lankford, BSN, CNOR I hereby certify that, to the best of my knowledge, no aspect of my current personal or professional situation might
Rotator Cuff Repair Outcomes. Patrick Birmingham, MD
 Rotator Cuff Repair Outcomes Patrick Birmingham, MD Outline Arthroscopic Vs. Mini-open Subjective Outcomes Objective Outcomes Timing Arthroscopic Vs. Mini-open Sauerbrey Arthroscopy 2005 Twenty-six patients
Rotator Cuff Repair Outcomes Patrick Birmingham, MD Outline Arthroscopic Vs. Mini-open Subjective Outcomes Objective Outcomes Timing Arthroscopic Vs. Mini-open Sauerbrey Arthroscopy 2005 Twenty-six patients
Management of arthritis of the shoulder. Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Management of arthritis of the shoulder Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Diagnosis Pain - with activity initially. As disease progresses night pain is common and sleep difficult Stiffness trouble
Management of arthritis of the shoulder Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Diagnosis Pain - with activity initially. As disease progresses night pain is common and sleep difficult Stiffness trouble
3/9/2018. Algorithm for Massive RCT s. Massive Rotator Cuff Tears: When is Reverse TSA the only option?
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears: When is Reverse TSA the only option? Anthony A. Romeo, MD Professor, Department of Orthopedics Head, Section of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Team Physician, Chicago White Sox
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears: When is Reverse TSA the only option? Anthony A. Romeo, MD Professor, Department of Orthopedics Head, Section of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Team Physician, Chicago White Sox
How repaired rotator cuff function influences Constant scoring
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2010) 96, 500 505 ORIGINAL ARTICLE How repaired rotator cuff function influences Constant scoring D. Goutallier a,, J.-M. Postel a, C. Radier b, J. Bernageau
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2010) 96, 500 505 ORIGINAL ARTICLE How repaired rotator cuff function influences Constant scoring D. Goutallier a,, J.-M. Postel a, C. Radier b, J. Bernageau
Diagnosis: Significant atrophy of supraspinatus FATTY INFILTRATION AND CUFF ATROPHY
 Diagnosis Diagnosis: Significant atrophy of supraspinatus FATTY INFILTRATION AND CUFF ATROPHY Degenerative muscular changes associated with rotator cuff tears include fatty infiltration and atrophy. Increased
Diagnosis Diagnosis: Significant atrophy of supraspinatus FATTY INFILTRATION AND CUFF ATROPHY Degenerative muscular changes associated with rotator cuff tears include fatty infiltration and atrophy. Increased
Considerations 3/9/2018. Asheesh Bedi, MD. I have no disclosures or conflicts of interest related to the content of this presentation.
 Radiological Assessment of the Rotator Cuff What predicts outcomes? Asheesh Bedi, MD Harold and Helen W. Gehring Professor Chief, Sports Medicine & Shoulder Surgery MedSport, Department of Orthopedic Surgery
Radiological Assessment of the Rotator Cuff What predicts outcomes? Asheesh Bedi, MD Harold and Helen W. Gehring Professor Chief, Sports Medicine & Shoulder Surgery MedSport, Department of Orthopedic Surgery
Adress correspondence and reprint requests to Hyun Seok Song, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St.Paul s Hospital, The Catholic University of
 Adress correspondence and reprint requests to Hyun Seok Song, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St.Paul s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea 620-56 Jeonnong-dong, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul, Korea
Adress correspondence and reprint requests to Hyun Seok Song, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St.Paul s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea 620-56 Jeonnong-dong, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul, Korea
Shoulder Injuries: Treatments that Work, Do Not Work, and When ENOUGH is Enough? Mark Ganjianpour, M.D. Beverly Hills, CA April 20, 2012
 Shoulder Injuries: Treatments that Work, Do Not Work, and When ENOUGH is Enough? Mark Ganjianpour, M.D. Beverly Hills, CA April 20, 2012 Multiaxial ball and socket Little Inherent Instability Glenohumeral
Shoulder Injuries: Treatments that Work, Do Not Work, and When ENOUGH is Enough? Mark Ganjianpour, M.D. Beverly Hills, CA April 20, 2012 Multiaxial ball and socket Little Inherent Instability Glenohumeral
The Irreparable Rotator Cuff Tear:
 The Irreparable Rotator Cuff Tear: Trauma 101: Shoulder Session #2 Brian Grawe, MD Assistant Professor Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine 5/10/2018 Brian Grawe, MD Assistant Professor Phone Number: 513-558-4516
The Irreparable Rotator Cuff Tear: Trauma 101: Shoulder Session #2 Brian Grawe, MD Assistant Professor Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine 5/10/2018 Brian Grawe, MD Assistant Professor Phone Number: 513-558-4516
AMSER Case of the Month January 2019
 AMSER Case of the Month January 2019 55 yo female presenting with 1 year of shoulder pain without prior trauma Nicholas Bertha, MS4 Drexel University College of Medicine Brandon Schooley, MD Allegheny
AMSER Case of the Month January 2019 55 yo female presenting with 1 year of shoulder pain without prior trauma Nicholas Bertha, MS4 Drexel University College of Medicine Brandon Schooley, MD Allegheny
Shoulder Arthroscopy Portals
 Shoulder Arthroscopy Portals Alper Deveci and Metin Dogan 7 7.1 Bony Landmarks Before starting shoulder arthroscopy, the patient must be positioned and draping applied. Then the bony landmarks are identified
Shoulder Arthroscopy Portals Alper Deveci and Metin Dogan 7 7.1 Bony Landmarks Before starting shoulder arthroscopy, the patient must be positioned and draping applied. Then the bony landmarks are identified
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME
 ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
Rotator Cuff Tears Keys to Universe
 Cuff Tears Current Concepts Associated Pathology Keys to the Universe Anthony Miniaci MD FRCSC Professor of Surgery Cleveland Clinic Sports Health Center Cleveland Clinic Rotator Cuff Tears Keys to Universe
Cuff Tears Current Concepts Associated Pathology Keys to the Universe Anthony Miniaci MD FRCSC Professor of Surgery Cleveland Clinic Sports Health Center Cleveland Clinic Rotator Cuff Tears Keys to Universe
Worker's Compensation Shoulder Practices
 Worker's Compensation Shoulder Practices Aimee S. Klapach Orthopedic Surgeon; Knee, Shoulder, & Sports Medicine Sports & Orthopaedic Specialists, part of Allina Health Minnesota Department of Labor and
Worker's Compensation Shoulder Practices Aimee S. Klapach Orthopedic Surgeon; Knee, Shoulder, & Sports Medicine Sports & Orthopaedic Specialists, part of Allina Health Minnesota Department of Labor and
SHOULDER ANATOMY AND FUNCTION. Disclosure. Case. Learning Objectives MRI. Plan? 3/23/2017 5
 Disclosure Doc, My Shoulder Keeps me Up at Night! Evaluation and Treatment of Atraumatic Shoulder Pain Matthew F. Dilisio, MD Shoulder and Elbow Surgery, CHI Health Orthopedics Assistant Professor, Creighton
Disclosure Doc, My Shoulder Keeps me Up at Night! Evaluation and Treatment of Atraumatic Shoulder Pain Matthew F. Dilisio, MD Shoulder and Elbow Surgery, CHI Health Orthopedics Assistant Professor, Creighton
Rotator Cuff Repair TRENDS OF REPAIRS. Evolution of Arthroscopic Repair. Shoulder Girdle. Rotator Cuff Repair 8/29/2013
 Rotator Cuff Repair Indications, Patient Selection, Outcomes James C. Vailas, M.D. New Hampshire Orthopaedic Center September 14, 2013 New Hampshire Musculoskeletal Institute 20 th Annual Symposium Evolution
Rotator Cuff Repair Indications, Patient Selection, Outcomes James C. Vailas, M.D. New Hampshire Orthopaedic Center September 14, 2013 New Hampshire Musculoskeletal Institute 20 th Annual Symposium Evolution
The Current State of Rotator Cuff Repairs
 Conflict of Interest Slide The Current State of Rotator Cuff Repairs Gerald R. Williams, Jr, MD John M. Fenlin, Jr, MD Professor of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Royalties Depuy: shoulder arthroplasty DJO:
Conflict of Interest Slide The Current State of Rotator Cuff Repairs Gerald R. Williams, Jr, MD John M. Fenlin, Jr, MD Professor of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Royalties Depuy: shoulder arthroplasty DJO:
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy
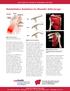 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy Front View Acromion Supraspinatus Back View Supraspinatus Long head of bicep Type I Infraspinatus Short head of bicep
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy Front View Acromion Supraspinatus Back View Supraspinatus Long head of bicep Type I Infraspinatus Short head of bicep
SHOULDER IMPINGEMENT / ROTATOR CUFF TENDONITIS / SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS
 SHOULDER IMPINGEMENT / ROTATOR CUFF TENDONITIS / SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS The terms impingement, rotator cuff tendonitis, and subacromial bursitis, all refer to a spectrum of the same condition. Anatomy The
SHOULDER IMPINGEMENT / ROTATOR CUFF TENDONITIS / SUBACROMIAL BURSITIS The terms impingement, rotator cuff tendonitis, and subacromial bursitis, all refer to a spectrum of the same condition. Anatomy The
STATE OF CONNECTICUT ETHICS BOARD NONE ARTHREX INC ARTHREX INC
 Rationale, Biomechanics,Early Results after Superior Capsular Reconstruction Augustus D Mazzocca MS, MD Director of the New England Musculoskeletal Institute Chairman Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
Rationale, Biomechanics,Early Results after Superior Capsular Reconstruction Augustus D Mazzocca MS, MD Director of the New England Musculoskeletal Institute Chairman Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
Shoulder Ultrasonography as a Diagnostic Tool for Rotator Cuff Disease
 Shoulder Ultrasonography as a Diagnostic Tool for Rotator Cuff Disease Jay D Keener, MD Associate Professor Shoulder and Elbow Service Washington University Disclosure No relevant financial disclosures
Shoulder Ultrasonography as a Diagnostic Tool for Rotator Cuff Disease Jay D Keener, MD Associate Professor Shoulder and Elbow Service Washington University Disclosure No relevant financial disclosures
Two-Year Outcomes Following Biologic Patch Augmentation for the Treatment of Massive Rotator Cuff Tears
 Two-Year Outcomes Following Biologic Patch Augmentation for the Treatment of Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Maximilian Petri, MD Ryan J. Warth, MD Marilee P.Horan, MPH Joshua A. Greenspoon, BSc Peter J. Millett,
Two-Year Outcomes Following Biologic Patch Augmentation for the Treatment of Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Maximilian Petri, MD Ryan J. Warth, MD Marilee P.Horan, MPH Joshua A. Greenspoon, BSc Peter J. Millett,
Anatomy Your shoulder is made up of three bones: your upper arm bone (humerus), your shoulder blade (scapula), and your collarbone (clavicle).
 Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great
Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great
Burwood Road, Concord 160 Belmore Road, Randwick
 www.orthosports.com.au 47 49 Burwood Road, Concord 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Conservative management of subacromial pathology Mel Cusi MBBS, Cert Sp Med, FACSP, FFSEM (UK) Presenting symptoms Shoulder
www.orthosports.com.au 47 49 Burwood Road, Concord 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Conservative management of subacromial pathology Mel Cusi MBBS, Cert Sp Med, FACSP, FFSEM (UK) Presenting symptoms Shoulder
Clinical Outcomes and Complications during the Learning Curve for Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: An Analysis of the First 40 Cases
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:213-217 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.2.213 Clinical Outcomes and Complications during the Learning Curve for Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty:
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:213-217 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.2.213 Clinical Outcomes and Complications during the Learning Curve for Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty:
Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Bilateral Shoulder Pain
 HR J Bilateral Shoulder Pain, p. 64-69 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Bilateral Shoulder Pain Musculoskeletal Eirini D. Savva, Rafaela M. Smarlamaki, Foteini I. Terezaki Department of Radiology, University
HR J Bilateral Shoulder Pain, p. 64-69 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Bilateral Shoulder Pain Musculoskeletal Eirini D. Savva, Rafaela M. Smarlamaki, Foteini I. Terezaki Department of Radiology, University
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Partial repair in irreparable rotator cuff tear: our experience in long-term follow-up
 Acta Biomed 2017; Vol. 88, Supplement 4: 69-74 DOI: 0.23750/abm.v88i4 -S.6796 Mattioli 1885 Original article Partial repair in irreparable rotator cuff tear: our experience in long-term follow-up Enrico
Acta Biomed 2017; Vol. 88, Supplement 4: 69-74 DOI: 0.23750/abm.v88i4 -S.6796 Mattioli 1885 Original article Partial repair in irreparable rotator cuff tear: our experience in long-term follow-up Enrico
How they begin 8/18/15. Arthroscopic Management of Complex RCT. Disclosures in AAOS Database
 Arthroscopic Management of Complex RCT Brian J. Cole, MD, MBA Professor and Vice-Chairman, Department of Orthopedics Chairman, Department of Surgery, Rush OPH Team Physician, Chicago Whites Sox and Bulls
Arthroscopic Management of Complex RCT Brian J. Cole, MD, MBA Professor and Vice-Chairman, Department of Orthopedics Chairman, Department of Surgery, Rush OPH Team Physician, Chicago Whites Sox and Bulls
SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY (TOTAL, HEMI, REVERSE)/ARTHRODESIS
 evicore healthcare. Clinical Decision Support Tool Diagnostic Strategies This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Imaging requests for patients with atypical symptoms or clinical presentations
evicore healthcare. Clinical Decision Support Tool Diagnostic Strategies This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Imaging requests for patients with atypical symptoms or clinical presentations
Massive cuff tears treated with arthroscopically assisted latissimus dorsi transfer. Surgical technique
 Original article Massive cuff tears treated with arthroscopically assisted latissimus dorsi transfer. Surgical technique Vincenzo De Cupis 1, Mauro De Cupis 2 1 I.C.O.T., Latina, Italy 2 Department of
Original article Massive cuff tears treated with arthroscopically assisted latissimus dorsi transfer. Surgical technique Vincenzo De Cupis 1, Mauro De Cupis 2 1 I.C.O.T., Latina, Italy 2 Department of
THE ROTATOR CUFF the science behind the disease
 THE ROTATOR CUFF the science behind the disease Jerome Goldberg www.orthosports.com.au 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick What do we know Many older people have RC tears Many people
THE ROTATOR CUFF the science behind the disease Jerome Goldberg www.orthosports.com.au 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick What do we know Many older people have RC tears Many people
SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT
 SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT DR.SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant-KNEE & SHOULDER Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital,Delhi Peculiarities of Shoulder Elegant piece of machinery It has the
SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT DR.SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant-KNEE & SHOULDER Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital,Delhi Peculiarities of Shoulder Elegant piece of machinery It has the
Acromioplasty. Surgical Indications and Considerations
 1 Acromioplasty Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: Any abnormality that disrupts the intricate relationship within the subacromial space may lead to impingement. Both intrinsic
1 Acromioplasty Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: Any abnormality that disrupts the intricate relationship within the subacromial space may lead to impingement. Both intrinsic
A Patient s Guide to Rotator Cuff Tendinitis or Shoulder Impingement
 A Patient s Guide to Rotator Cuff Tendinitis or Shoulder Impingement Introduction Shoulder pain is a common condition whether due to aging, overuse, trauma or a sports injury. Shoulder pain and injuries
A Patient s Guide to Rotator Cuff Tendinitis or Shoulder Impingement Introduction Shoulder pain is a common condition whether due to aging, overuse, trauma or a sports injury. Shoulder pain and injuries
Degenerative joint disease of the shoulder, while
 Arthroscopic Debridement of the Shoulder for Osteoarthritis David M. Weinstein, M.D., John S. Bucchieri, M.D., Roger G. Pollock, M.D., Evan L. Flatow, M.D., and Louis U. Bigliani, M.D. Summary: Twenty-five
Arthroscopic Debridement of the Shoulder for Osteoarthritis David M. Weinstein, M.D., John S. Bucchieri, M.D., Roger G. Pollock, M.D., Evan L. Flatow, M.D., and Louis U. Bigliani, M.D. Summary: Twenty-five
D Degenerative joint disease, rotator cuff deficiency with, 149 Deltopectoral approach component removal with, 128
 Index A Abduction exercise, outpatient with, 193, 194 Acromioclavicular arthritis, with, 80 Acromiohumeral articulation, with, 149 Acromio-humeral interval (AHI), physical examination with, 9, 10 Active
Index A Abduction exercise, outpatient with, 193, 194 Acromioclavicular arthritis, with, 80 Acromiohumeral articulation, with, 149 Acromio-humeral interval (AHI), physical examination with, 9, 10 Active
The Shoulder. By Patrick Ryan, Bobby Law, Jack Beaty, Alex Newhouse and Chuck Nelson
 The Shoulder By Patrick Ryan, Bobby Law, Jack Beaty, Alex Newhouse and Chuck Nelson Learning Objectives/Agenda Review the anatomy of the shoulder Describe the main diseases of the shoulder Describe the
The Shoulder By Patrick Ryan, Bobby Law, Jack Beaty, Alex Newhouse and Chuck Nelson Learning Objectives/Agenda Review the anatomy of the shoulder Describe the main diseases of the shoulder Describe the
Functional repair in massive immobile rotator cuff tears leads to satisfactory quality of living: results at 3 years follow up.
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Functional repair in massive immobile rotator cuff tears leads to satisfactory quality of living: results at 3 years follow up. P. Arrigoni, C. Fossati, L. Zottarelli, V. Ragone, P. Randelli
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Functional repair in massive immobile rotator cuff tears leads to satisfactory quality of living: results at 3 years follow up. P. Arrigoni, C. Fossati, L. Zottarelli, V. Ragone, P. Randelli
P.O. Box Sierra Park Road Mammoth Lakes, CA Orthopedic Surgery & Sports Medicine
 P.O. Box 660 85 Sierra Park Road Mammoth Lakes, CA 93546 SHOULDER: Instability Dislocation Labral Tears The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body, but to have this amount of motion, it is also
P.O. Box 660 85 Sierra Park Road Mammoth Lakes, CA 93546 SHOULDER: Instability Dislocation Labral Tears The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body, but to have this amount of motion, it is also
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Pathophysiology and Treatment Options. Mike Walton Consultant Shoulder Surgeon Wrightington Hospital
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Pathophysiology and Treatment Options Mike Walton Consultant Shoulder Surgeon Wrightington Hospital Tendon Structure Tendons are mechanically responsible for the transmission
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Pathophysiology and Treatment Options Mike Walton Consultant Shoulder Surgeon Wrightington Hospital Tendon Structure Tendons are mechanically responsible for the transmission
Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair
 Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair CHRISTOPHER S. AHMAD, MD; WILLIAM N. LEVINE, MD; LOUIS U. BIGLIANI, MD Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair offers less pain, quicker recovery, and less stiffness compared
Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair CHRISTOPHER S. AHMAD, MD; WILLIAM N. LEVINE, MD; LOUIS U. BIGLIANI, MD Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair offers less pain, quicker recovery, and less stiffness compared
Ultrasound of the Shoulder
 Ultrasound of the Shoulder Patrick Battaglia, DC, DACBR Logan University, Department of Radiology Outline Review ultrasound appearance of NMSK tissues Present indications for ultrasound of the shoulder.
Ultrasound of the Shoulder Patrick Battaglia, DC, DACBR Logan University, Department of Radiology Outline Review ultrasound appearance of NMSK tissues Present indications for ultrasound of the shoulder.
Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Techniques What should we really be doing?
 COA 2014 Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Techniques What should we really be doing? C. Benjamin Ma, MD Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery University of California, San Francisco Department of
COA 2014 Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Techniques What should we really be doing? C. Benjamin Ma, MD Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery University of California, San Francisco Department of
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Arthroscopic Treatments
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Arthroscopic Treatments Brian D. Busconi, MD Chief of Sports Medicine & Arthroscopy UMass Memorial Medical Center Brian.Busconi@umassmemorial.org Disclosures Consultant Arthrex
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Arthroscopic Treatments Brian D. Busconi, MD Chief of Sports Medicine & Arthroscopy UMass Memorial Medical Center Brian.Busconi@umassmemorial.org Disclosures Consultant Arthrex
Common Shoulder Problems and Treatment Options. Benjamin W. Szerlip D.O. Austin Shoulder Institute
 Common Shoulder Problems and Treatment Options Benjamin W. Szerlip D.O. Austin Shoulder Institute Speaker Disclosure Dr. Szerlip has disclosed that he has no actual or potential conflict of interest in
Common Shoulder Problems and Treatment Options Benjamin W. Szerlip D.O. Austin Shoulder Institute Speaker Disclosure Dr. Szerlip has disclosed that he has no actual or potential conflict of interest in
DK7215-Levine-ch12_R2_211106
 12 Arthroscopic Rotator Interval Closure Andreas H. Gomoll Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A. Brian J. Cole Departments
12 Arthroscopic Rotator Interval Closure Andreas H. Gomoll Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A. Brian J. Cole Departments
WHAT YOU IS BACK WITHIN ARM S REACH
 YOUR TOTAL SHOULDER REPLACEMENT SURGERY STEPS TO RETURNING TO A LIFESTYLE YOU DESERVE WHAT YOU IS BACK WITHIN ARM S REACH Nathan Richardson, MD Orthopedics, Shoulder & Elbow Surgeon Board Certified in
YOUR TOTAL SHOULDER REPLACEMENT SURGERY STEPS TO RETURNING TO A LIFESTYLE YOU DESERVE WHAT YOU IS BACK WITHIN ARM S REACH Nathan Richardson, MD Orthopedics, Shoulder & Elbow Surgeon Board Certified in
DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS
 DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS Lyndon B. Gross M.D. Ph.D. The Orthopedic Center of St. Louis SHOULDER PAIN Third most common musculoskeletal
DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS Lyndon B. Gross M.D. Ph.D. The Orthopedic Center of St. Louis SHOULDER PAIN Third most common musculoskeletal
US finding of the shoulder (with live demonstration) 인제의대상계백병원 안재기
 US finding of the shoulder (with live demonstration) 인제의대상계백병원 안재기 Shoulder US Biceps tendon & Rotator Cuff Long Head of Biceps Tendon Subscapularis tendon Supraspinatus tendon Infraspinatus tendon Teres
US finding of the shoulder (with live demonstration) 인제의대상계백병원 안재기 Shoulder US Biceps tendon & Rotator Cuff Long Head of Biceps Tendon Subscapularis tendon Supraspinatus tendon Infraspinatus tendon Teres
Why are these shoulder replacements called a reverse prosthesis?
 PATIENT GUIDE TO REVERSE PROSTHESIS Edward G. McFarland MD The Division of Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery The Department of Orthopaedic Surgery The Johns Hopkins University Baltimore MD Why are these
PATIENT GUIDE TO REVERSE PROSTHESIS Edward G. McFarland MD The Division of Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery The Department of Orthopaedic Surgery The Johns Hopkins University Baltimore MD Why are these
Shoulder Arthroscopy Curriculum
 ARTHRO Mentor 1 Description All those with an interest in the shoulder should develop a basic level of proficiency and should be able to perform a thorough diagnostic exam, looking from both the anterior
ARTHRO Mentor 1 Description All those with an interest in the shoulder should develop a basic level of proficiency and should be able to perform a thorough diagnostic exam, looking from both the anterior
Cigna Medical Coverage Policies Musculoskeletal Shoulder Arthroplasty (Total, Hemi, Reverse)/Arthrodesis
 Cigna Medical Coverage Policies Musculoskeletal Shoulder Arthroplasty (Total, Hemi, Reverse)/Arthrodesis Effective January 1, 2016 Instructions for use The following coverage policy applies to health benefit
Cigna Medical Coverage Policies Musculoskeletal Shoulder Arthroplasty (Total, Hemi, Reverse)/Arthrodesis Effective January 1, 2016 Instructions for use The following coverage policy applies to health benefit
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES
 APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Shoulder Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Compiled by Rob Liddell,
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Shoulder Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Compiled by Rob Liddell,
Rotator cuff. MR Imaging of the Shoulder: Rotator Cuff. Trauma. Trauma. Trauma. Tendon calcification. Acute. Degenerative. Trauma Calcific tendinitis
 Rotator cuff MR Imaging of the Shoulder: Rotator Cuff Dr. Mini N. Pathria M.D., FRCP(C) Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine San Diego, California Acute Trauma Calcific tendinitis
Rotator cuff MR Imaging of the Shoulder: Rotator Cuff Dr. Mini N. Pathria M.D., FRCP(C) Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine San Diego, California Acute Trauma Calcific tendinitis
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the Shoulder
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the Shoulder
Fully Torn Rotator Cuff Repair
 Fully Torn Rotator Cuff Repair A torn rotator cuff is a common condition that can cause shoulder pain, weakness, and loss of mobility. If the tear is severe enough, surgical intervention is often necessary
Fully Torn Rotator Cuff Repair A torn rotator cuff is a common condition that can cause shoulder pain, weakness, and loss of mobility. If the tear is severe enough, surgical intervention is often necessary
Late Results of Total Shoulder Replacement in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 366, pp. 39-45 0 1999 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Late Results of Total Shoulder Replacement in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Jens 0. S@jbjerg,
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 366, pp. 39-45 0 1999 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Late Results of Total Shoulder Replacement in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Jens 0. S@jbjerg,
Evidence Based Approach to Shoulder Injections
 Evidence Based Approach to Shoulder Injections Bradley Sandella, DO Christiana Care Sports Medicine Joseph Straight, MD First State Orthopaedics Objectives Relevant Anatomy Indications for injections Injection
Evidence Based Approach to Shoulder Injections Bradley Sandella, DO Christiana Care Sports Medicine Joseph Straight, MD First State Orthopaedics Objectives Relevant Anatomy Indications for injections Injection
Management of Humeral Bone Loss in Anterior Shoulder Instability. Scott D. Mair, MD University of Kentucky Sports Medicine
 Management of Humeral Bone Loss in Anterior Shoulder Instability Scott D. Mair, MD University of Kentucky Sports Medicine Disclosure Smith and Nephew Endoscopy fellowship support Importance Bone loss (glenoid
Management of Humeral Bone Loss in Anterior Shoulder Instability Scott D. Mair, MD University of Kentucky Sports Medicine Disclosure Smith and Nephew Endoscopy fellowship support Importance Bone loss (glenoid
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 185 189 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint, MR imaging findings concerning, 161 Acromion, types of, 77 79
Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 185 189 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint, MR imaging findings concerning, 161 Acromion, types of, 77 79
Goals and Objectives for the Orthopaedic Surgery Resident McGill Orthopaedic Sports Medicine and Minimally Invasive (MGH & Shriners) Junior Residents
 Goals and Objectives for the Orthopaedic Surgery Resident McGill Orthopaedic Sports Medicine and Minimally Invasive (MGH & Shriners) Junior Residents The following document is intended to guide you in
Goals and Objectives for the Orthopaedic Surgery Resident McGill Orthopaedic Sports Medicine and Minimally Invasive (MGH & Shriners) Junior Residents The following document is intended to guide you in
Short term results of arthroscopic repair of subscapularis tendon tear
 Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 23, No. 3, November, 2009. pp. 117-121 Short term results of arthroscopic repair of subscapularis tendon tear Hamid Reza Aslani, MD.
Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 23, No. 3, November, 2009. pp. 117-121 Short term results of arthroscopic repair of subscapularis tendon tear Hamid Reza Aslani, MD.
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 9/22/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 91 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 9/22/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 91 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Protocol Shawn Hennigan, MD
 General Information: Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Protocol Shawn Hennigan, MD Reverse or Inverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty (rtsa) is designed specifically for the treatment of glenohumeral (GH)
General Information: Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Protocol Shawn Hennigan, MD Reverse or Inverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty (rtsa) is designed specifically for the treatment of glenohumeral (GH)
Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference. Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16
 Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16 Case 1: 29 YOM with recurrent shoulder dislocations Glenoid Axial T1FS
Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16 Case 1: 29 YOM with recurrent shoulder dislocations Glenoid Axial T1FS
Sonographic Differences in the Appearance of Acute and Chronic Full-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears
 Sonographic Differences in the Appearance of Acute and Chronic Full-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears Sharlene A. Teefey, MD, William D. Middleton, MD, Gregory S. Bauer, MD, Charles F. Hildebolt, DDS, PhD,
Sonographic Differences in the Appearance of Acute and Chronic Full-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears Sharlene A. Teefey, MD, William D. Middleton, MD, Gregory S. Bauer, MD, Charles F. Hildebolt, DDS, PhD,
Patient Presentation. Prevalence of Rotator Cu Tears. By Derek S. Shia, M.D.
 Rotator Cu Tears By Derek S. Shia, M.D. Rotator cu tears are one of the most common orthopedic problems and e ect more than 17 million persons annually in the United States. The rotator cu is an essential
Rotator Cu Tears By Derek S. Shia, M.D. Rotator cu tears are one of the most common orthopedic problems and e ect more than 17 million persons annually in the United States. The rotator cu is an essential
What can Imaging tell us?
 What can Imaging tell us? David Connell FRANZCR, FFSEM (UK) Assoc Professor Dept of Medicine, Nursing & Healthcare Monash University, Melbourne, Australia Assoc Professor Sport & Exercise Medicine Research
What can Imaging tell us? David Connell FRANZCR, FFSEM (UK) Assoc Professor Dept of Medicine, Nursing & Healthcare Monash University, Melbourne, Australia Assoc Professor Sport & Exercise Medicine Research
2015 OPSC Annual Convention. syllabus. February 4-8, 2015 Hyatt Regency Mission Bay San Diego, California
 2015 OPSC Annual Convention syllabus February 4-8, 2015 Hyatt Regency Mission Bay San Diego, California THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 5, 2015: 3:30pm - 4:30pm The Shoulder: 2 View or Not 2 View * Presented by Alexandra
2015 OPSC Annual Convention syllabus February 4-8, 2015 Hyatt Regency Mission Bay San Diego, California THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 5, 2015: 3:30pm - 4:30pm The Shoulder: 2 View or Not 2 View * Presented by Alexandra
Shoulder Arthroscopy Lab Manual
 Shoulder Arthroscopy Lab Manual Dalhousie University Orthopaedic Program May 5, 2017 Skills Centre OBJECTIVES 1. Demonstrate a competent understanding of the arthroscopic anatomy and biomechanics of the
Shoulder Arthroscopy Lab Manual Dalhousie University Orthopaedic Program May 5, 2017 Skills Centre OBJECTIVES 1. Demonstrate a competent understanding of the arthroscopic anatomy and biomechanics of the
06/Μαρ/2013 FUNCTION OF THE ROTATOR CUFF. ARTHROSCOPIC ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR Primarily to stabilize and centralize the humeral head GENERAL GUIDE LINES
 FUNCTION OF THE ROTATOR CUFF ARTHROSCOPIC ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR Primarily to stabilize and centralize the humeral head GENERAL GUIDE LINES Achieved by balancing the force couples in coronal and transverse
FUNCTION OF THE ROTATOR CUFF ARTHROSCOPIC ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR Primarily to stabilize and centralize the humeral head GENERAL GUIDE LINES Achieved by balancing the force couples in coronal and transverse
Latissimus dorsi transfer for primary treatment of irreparable rotator cuff tears
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2002) 2:139 145 Springer-Verlag 2002 ORIGINAL F. Postacchini S. Gumina P. De Santis R. Di Virgilio Latissimus dorsi transfer for primary treatment of irreparable rotator cuff tears
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2002) 2:139 145 Springer-Verlag 2002 ORIGINAL F. Postacchini S. Gumina P. De Santis R. Di Virgilio Latissimus dorsi transfer for primary treatment of irreparable rotator cuff tears
Superior Capsular Reconstruction: Clinical Outcomes After Minimum 2-Year Follow-Up
 An Original Study Superior Capsular Reconstruction: Clinical Outcomes After Minimum 2-Year Follow-Up Alan M. Hirahara, MD, FRCSC, Wyatt J. Andersen, ATC, and Alberto J. Panero, DO Abstract Superior capsular
An Original Study Superior Capsular Reconstruction: Clinical Outcomes After Minimum 2-Year Follow-Up Alan M. Hirahara, MD, FRCSC, Wyatt J. Andersen, ATC, and Alberto J. Panero, DO Abstract Superior capsular
what you is back within LOVE arm s reach find out why the exactech shoulder may be right for you
 TOTAL shoulder REPLACEMENT what you is back within LOVE arm s reach find out why the exactech shoulder may be right for you how does your shoulder work? The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body.
TOTAL shoulder REPLACEMENT what you is back within LOVE arm s reach find out why the exactech shoulder may be right for you how does your shoulder work? The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body.
Rotator cuff injuries are commonly attributed to repetitive
 [ Orthopaedics ] Massive Rotator Cuff Tear in an Adolescent Athlete: A Case Report Kimberly A. Turman, MD,* Mark W. Anderson, MD, and Mark D. Miller, MD Full-thickness rotator cuff tears in the young athlete
[ Orthopaedics ] Massive Rotator Cuff Tear in an Adolescent Athlete: A Case Report Kimberly A. Turman, MD,* Mark W. Anderson, MD, and Mark D. Miller, MD Full-thickness rotator cuff tears in the young athlete
"Stability and Instability of RTSA"
 Orthopedics Update «Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty» Stability and Instability of RTSA A. LÄDERMANN Orthopaedics and Traumatology, La Tour Hospital, Meyrin, Switzerland Orthopaedics and Traumatology,
Orthopedics Update «Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty» Stability and Instability of RTSA A. LÄDERMANN Orthopaedics and Traumatology, La Tour Hospital, Meyrin, Switzerland Orthopaedics and Traumatology,
Mr. Duy Thai Orthopaedic Surgeon, Melbourne VIC
 Mr. Duy Thai Orthopaedic Surgeon, Melbourne VIC International Convention of the Vietnamese Physicians, Dentists and Pharmacists of the Free World Melbourne 8 10 August 2014 Conflict of Interest None Subacromial
Mr. Duy Thai Orthopaedic Surgeon, Melbourne VIC International Convention of the Vietnamese Physicians, Dentists and Pharmacists of the Free World Melbourne 8 10 August 2014 Conflict of Interest None Subacromial
ARTHROSCOPIC DEBRIDEMENT VERSUS OPEN REPAIR FOR ROTATOR CUFF TEARS. From the University of Toronto and the Toronto Hospital, Canada
 ARTHROSCOPIC DEBRIDEMENT VERSUS OPEN REPAIR FOR ROTATOR CUFF TEARS A PROSPECTIVE COHORT STUDY D. J. OGILVIE-HARRIS, ALAIN DEMAZIERE From the University of Toronto and the Toronto Hospital, Canada We compared
ARTHROSCOPIC DEBRIDEMENT VERSUS OPEN REPAIR FOR ROTATOR CUFF TEARS A PROSPECTIVE COHORT STUDY D. J. OGILVIE-HARRIS, ALAIN DEMAZIERE From the University of Toronto and the Toronto Hospital, Canada We compared
Shoulder Joint Replacement
 Shoulder Joint Replacement Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was first performed
Shoulder Joint Replacement Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was first performed
Surgical management of massive rotator cuff tears
 All-Arthroscopic Patch Augmentation of a Massive Rotator Cuff Tear: Surgical Technique Peter N. Chalmers, M.D., Rachel M. Frank, M.D., Anil K. Gupta, M.D., M.B.A., Adam B. Yanke, M.D., Scott W. Trenhaile,
All-Arthroscopic Patch Augmentation of a Massive Rotator Cuff Tear: Surgical Technique Peter N. Chalmers, M.D., Rachel M. Frank, M.D., Anil K. Gupta, M.D., M.B.A., Adam B. Yanke, M.D., Scott W. Trenhaile,
Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders
 Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders Poster No.: C-2026 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. Ivanoski; Ohrid/MK Keywords: Trauma, Athletic injuries, Arthritides,
Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders Poster No.: C-2026 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. Ivanoski; Ohrid/MK Keywords: Trauma, Athletic injuries, Arthritides,
Arthroscopic repair for subacromial incarceration of a torn rotator cuff
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Asia-Pacific Journal of Sports Medicine, Arthroscopy, Rehabilitation and Technology 2 (2015) 90e94 www.ap-smart.com Original article Arthroscopic
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Asia-Pacific Journal of Sports Medicine, Arthroscopy, Rehabilitation and Technology 2 (2015) 90e94 www.ap-smart.com Original article Arthroscopic
POSTSURGICAL STIFFNESS IN ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR
 POSTSURGICAL STIFFNESS IN ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR P.Avanzi, M. Collarile, R. Giovarruscio, C. Zorzi P. Avanzi M.D. Sacro Cuore Don Calabria Hospital Negrar-Italy STIFFNESS IN SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY. restricted
POSTSURGICAL STIFFNESS IN ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR P.Avanzi, M. Collarile, R. Giovarruscio, C. Zorzi P. Avanzi M.D. Sacro Cuore Don Calabria Hospital Negrar-Italy STIFFNESS IN SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY. restricted
Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow.
 Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow. Prepared for The Canadian Orthopaedic Association Contents Executive
Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow. Prepared for The Canadian Orthopaedic Association Contents Executive
Clinical determinants of a durable rotator cuff repair
 13 Surgical Technique and Functional Results of Irreparable Cuff Tears Reconstructed with the Long Head of the Biceps Tendon Osman Guven MD Murat Bezer MD Zeynep Guven MD Kemal Gokkus MD and Cihangir Tetik
13 Surgical Technique and Functional Results of Irreparable Cuff Tears Reconstructed with the Long Head of the Biceps Tendon Osman Guven MD Murat Bezer MD Zeynep Guven MD Kemal Gokkus MD and Cihangir Tetik
Magnetic resonance imaging of painful shoulder arthroplasty
 Magnetic resonance imaging of painful shoulder arthroplasty John W. Sperling, MD, MS, a Hollis G. Potter, MD, b Edward V. Craig, MD, a Evan Flatow, MD, c and Russell F. Warren, MD, a New York, NY Specialized
Magnetic resonance imaging of painful shoulder arthroplasty John W. Sperling, MD, MS, a Hollis G. Potter, MD, b Edward V. Craig, MD, a Evan Flatow, MD, c and Russell F. Warren, MD, a New York, NY Specialized
