Clinical Study Minimal Invasive Percutaneous Fixation of Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Fractures
|
|
|
- Ezra Wilkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2012, Article ID , 6 pages doi: /2012/ Clinical Study Minimal Invasive Percutaneous Fixation of Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Fractures Federico De Iure, Michele Cappuccio, Stefania Paderni, Giuseppe Bosco, and Luca Amendola Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology-Spine Surgery, Ospedale Maggiore C.A. Pizzardi, Largo Nigrisoli 2, Bologna, Italy Correspondence should be addressed to Michele Cappuccio, m.cappuccio73@gmail.com Received 2 March 2012; Accepted 1 June 2012 Academic Editor: Zachary A. Smith Copyright 2012 Federico De Iure et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. We studied 122 patients with 163 fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine undergoing the surgical treatment by percutaneous transpedicular fixation and stabilization with minimally invasive technique. Patient followup ranged from 6 to 72 months (mean 38 months), and the patients were assessed by clinical and radiographic evaluation. The results show that percutaneous transpedicular fixation and stabilization with minimally invasive technique is an adequate and satisfactory procedure to be used in specific type of the thoracolumbar and lumbar spine fractures. 1. Introduction Surgical treatment of thoracic and lumbar spine fractures is based on different factors. Type of fracture, neurological deficit, general conditions, and associated injuries affect both treatment and final result. Although type B and C fractures following AO-Magerl classification [1]requiresurgical treatment, most type A fractures without neurological involvement can be safely treated in a conservative way [2, 3]. Conservative treatment is a demanding procedure for the patient, and the risk of a final deformity has to be considered as a residual kyphosis can consistently worsen the quality of life of the patient. Moreover, some situations rule out the chance for a conservative treatment. In case of polytrauma, claustrophobia, psychological disease, venous disease or previous deep venous thrombosis, obesity, and bronchopulmonary diseases, conservative treatment is not advisable. Attention must also be paid to the fact that younger and active workers refuse the conservative treatment in order to avoid bed rest and an inactive period. A traditional open surgery may be an overtreatment in all these cases, considering blood loss, possible complications, hospital stay, and delayed functional recovery. In this setting, a good option can be a percutaneous minimally invasive surgery (MIS) [4, 5]. This technique is suggested by the authors every time a conservative treatment is not indicated or advisable, and posterior open arthrodesis may represent an overtreatment. 2. Materials and Methods From May 2005 to December 2011, 163 vertebral fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine in 122 patients were stabilized. Eighty-tree patients were males and 39 females, the mean age was 48 years (from 15 to 85). Eighteen patients were polytrauma with an average Injury Severity Score of 25.2 (from 17 to 34). In those patient, percutaneous fixation was also intended to be a damage control procedure. The most frequent location was the thoracolumbar junction (T12-L1). All fractures were classified according to the AO-Magerl classification: the vast majority were type A fractures (A1 and A3), while type B or type C were recorded in a few cases (Table 1). The most frequent construct was the monosegmental one (one level above and one below the fractured vertebra) in 96 cases. A multilevel construction was performed in 26 cases of multiple injuries. Overall, 553 pedicle screws were implanted with a percutaneous technique. In 18 cases, a bone substitute (cement and hydroxyapatite) was introduced in the fractured vertebra to fill the
2 2 Minimally Invasive Surgery Table 1: Fractures distribution according to the type and level. A1 A2 A3 B1 B2 B3 C1 C2 TOT T4 1 1 T T T T T9 3 3 T T T L L L L L TOT anterior gap left after reduction, to better support the anterior column. In one of patients with poor bone stock due to osteoporosis, we used a fenestrated cemented screw, associated with kyphoplasty, to stabilize a T12 type A3 fracture (Figure 1). In one case, the fracture stabilization was associated with a minimally invasive endoscopic-assisted discectomy and interbody fusion for a preexisting symptomatic degenerative disc-disease at the same level. In another case where T11, T12, and L3 type A fractures were associated with L1 and L2 type B fractures, we performed a percutaneous stabilization from T10 to L4 and an L1-L2 arthrodesis with a miniopen approach (Figure 2). In no other case fusion was associated to the MIS. To monotrauma patients with type A1, A2, and A3.1 fractures without significant stenosis of the spinal canal, a conservative option consisting of cast and bed rest was also offered but was rejected in 85% of cases. In all cases, the impairment of the spinal canal was less than 30%, and local kyphosis was less than 20 except in one case. All patients underwent plain radiographs and CT scan preoperatively and immediately postoperatively and were followed over time with systematic clinical and radiographic controls at 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24 months after surgery. 3. Results The average surgical time was 113 minutes (range 35 to 240 minutes), and it was directly related to the number of screws implanted: the average time, reduced to 106 minutes using 4 pedicle screws, becomes 144 minutes with 6 screws and 171 minutes with 8 screws. Blood losses were not assessable intraoperatively. Postoperative analgesia was performed in all cases with a 36-hour lasting elastomeric pump containing an opioid and an NSAID. All monotrauma patients recovered the standing position in the second postoperative day on the average and were discharged on the fifth day. In polytrauma patients has been granted an immediate mobilization in the bed. The mean followup was 38 months, with a minimum of 6 months and a maximum of 72 months. All the cases, except one, have been considered healed after a 6-month control. Radiological examinations confirmed good spontaneous reconstruction of the anterior and posterior columns. Radiographic evaluation was performed through the measurement of the segmental kyphosis and the wedging deformity of the involved vertebral body [6]. Back pain, evaluated by VAS scale was 1.9 points at FU. Clinical evaluation was performed by subjective evaluation of the final results by patients themselves, and every patient was satisfied of surgical procedure. Radiographic evaluation showed a real improvement in the postoperative period (segmental kyphosis: 4.1 preop, 2.2 postop, and 2.7 FU kyphosis of the fractured vertebral segment: 12.2 preop, 5.9 postop, and 8.7 FU), but also a worsening of the segmentary kyphosis in the cases treated with CD Horizon Longitude (6.4 preop, 3.5 postop, and 7.8 FU) if implanted with multiaxial screws. (5.7 preop, 4.8 postop, 9.9 FU) (Table 2). In two patients, one screw was found medial into the spine canal on the postoperative TC, without any clinical consequence. At the beginning of our experience, we planned to remove all implants including L2 or a lower vertebra, no implant above T10 and all the implants in the thoracolumbar junction showing clinical (local pain) or mechanical problems (hardware failure or screws mobilization). We planned hardware removal in the lumbar spine as we were afraid that posterior fixation without fusion in such a mobile part of the spine could lead to hardware failure and consequently to clinical problems. Overall, the instrumentation has been removed in 23 patients (19%), in 5 cases due to a local complication and in 17 cases, as scheduled, because of implantation in the lumbar spine (Figure 3). The average delay from first surgery to implant removal was 9,5 months (range: 6 36). In the 17 patients in which implant removal had been planned, only 3 showed screws mobilization, and only 2 had pain. None of them showed pain or loss of sagittal alignment at six-month followup. 4. Complications The complications were divided according to a temporal order of appearance in intraoperative and postoperative. The latter were divided into early if they appear within one month from the date of surgery and late when they occurred after that period [7]. Depending on the severity, we divided complications into major and minor [8]. Major complications were those involving an increased hospitalization, or a second operation not scheduled. We recorded 12 complications (9.8%) divided into 4 intraoperative (3.3%), 6 early postoperative (4.9%), 2 late postoperative (1.6%). Four complications were minor (3.3%) and 8 major (6.5%).
3 Minimally Invasive Surgery 3 Figure 1: T12 type A3.1 fracture treated with cemented fenestrated screw and kyphoplasty. Table 2: Radiographic evaluation. Segmental kyphosis Vertebral wedging Preop Postop FU Preop Postop FU Sextant + longitude Sextant Longitude Long. polyaxial screws Long. monoaxial screws
4 4 Minimally Invasive Surgery Figure 2: T11, T12, and L3 type A fractures associated with L1 and L2 type B fractures. Percutaneous stabilization from T10 to L4 and L1-L2 arthrodesis with a miniopen approach. Intraoperative complications were all minor, related to mechanical instruments, which lengthened the surgical time but without any consequence for the patients. Early postoperative complications were all major: 4 mechanical, 1 neurological and 1 infectious complication. In 2 patients the screw head disconnected from the stem in the first postoperative day. In one case, the patient was reoperated, while the other had to wear a brace for 3 months postoperatively. In 2 patients we recorded a pullout of the pedicle screws, 15 days and 20 days after surgery respectively. The first case was a 63-year old patient with 2 noncontiguous type A1 fractures (T11 and L1) undergoing MIS from T10 L3 with bilateral pedicle screws in L1. The second case was a patient of 67 years fixed from T12 to L2 for a type A3 L1 fracture. In both cases, we performed the implant removal and a percutaneous augmentation of the vertebral bodies with cement. The neurologic complication was a cauda equina syndrome which appeared in the second postoperative day in a patient treated for a type A L1 fracture by T12 L2 MIS. The patient underwent urgent surgical revision. In that occasion, we found an organized intradural hematoma sleeve enveloping the conus medullaris. We performed a complete removal of the hematoma with a microsurgical technique without finding the source of bleeding. Surprisingly no screw was found in the spinal canal during the revision surgery. The patient was subsequently sent to a rehabilitation center, and he completely regained the neurological functions in 2 months. A 35-year old patient had a Staphylococcus epidermidis infection with surgical wound dehiscence. The patient had
5 Minimally Invasive Surgery 5 Figure 3: Percutaneous minimal invasive removal of the instrumentation. been submitted to MIS for a type A2 T11 fracture. Two and a half after surgery underwent surgical debridement and removal of the instrumentation resulting in healing of the infection. The patient wore a 3-point bodice for further 45 days, and the fracture healed with a residual kyphosis of 18 degrees. Both late postoperative complications were major. In one case there was a nonunion in a patient with an A3 type T12 fracture, with initial kyphosis of 25. Three months after surgery the patient still complained pain during weight bearing, and there was no evidence of healing on the CT scan. The patient underwent anterior fusion by thoracoscopic approach with incomplete pain relief. In the other case, there was an aseptic loosening of the screws in L5 in a young patient of 28 years, treated 3 years earlier by L3 L5 MIS for a B2 type L4 fracture. The patient had been scheduled for instrumentation removal 6 months after surgery, but he refused the operation. The patient underwent minimally invasive removal of fixation, with immediate disappearance of pain. 5. Discussion The choice of treatment of the thoracic and lumbar spine injuries is related to many factors such as the type of fracture, the presence of neurological damage, associated injuries, patient s age, and others more. Conservative treatment of stable vertebral fractures is proposed with success by many authors [2, 3, 9 11], with different techniques: bed rest followed by external orthoses, extension gymnastics, plaster jacket in bed, or stand reduction [12]. Regardless of the methodology adopted, the treatment should be continued for a period of at least 3-4 months during which the patient care and cooperation is mandatory. The problems related to bed rest, particularly in the elderly, are countless, although difficult to calculate. Deep vein thrombosis may affect up to 30% of patients. Obesity, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, venous incompetence, and psychiatric disorders are almost absolute contraindications to conservative treatment. In addition, today more and more patients need to return to their social and working life in a short time; therefore, surgery becomes the simplest way to shortcut recovery. In our experience, only 15% of the patients eligible for MIS opted for a conservative treatment. The rationale for applying MIS in the management of the spine fractures is to reduce the approach-related morbidity associated with the conventional technique: iatrogenic muscle denervation, increased intramuscular pressures, ischemia, pain, and functional impairment. Because of the impossibility to perform a fusion, the minimally invasive percutaneous stabilization has been limited to relatively stable vertebral fractures, involving mainly bone component with a consistent possibility of spontaneous healing after immobilization; the screws and rods implanted acted as an internal fixator, leading to the biological healing of all fractures. Wang et al. comparing two groups of patients with thoracolumbar burst fractures, one treated by instrumented fusion, while the other just fixed without fusion, showed that there were no statistically significant differences in the long term between the two groups with a slight advantage, both for clinical than for radiographic parameters, for the group treated only with fixation without fusion [13]. This study further justifies the minimally invasive approach we have taken. PMMA injection through fenestrated cannulated screws provided additional stability in fixation procedures carried out on osteoporotic vertebral columns without affecting fracture healing. Implant removal remains a controversial key point against this technique as it requires a second surgery and a general anesthesia, adding risks for the patient and costs for the hospital. Nevertheless, the real need for implant removal is probably much lower than that showed in our study as most of the patients who had the implant removed showed no clinical or radiological complications at the time of second surgery. Further studies are required to determinate the real need for hardware removal. The loss of correction, we observed during the followup for the cases treated with multiaxial screws could be explained by the possibility of this type of screws to have slight movement, also after implantation, between the head and the arm of the screw. For this reason, monoaxial screws should be considered for this kind of surgery, when it is possible. There are yet no studies that analyze the complications of MIS in thoracic and lumbar spine fractures. A retrospective study compares two groups of patients treated by MIS (10 patients) and arthrodesis with conventional technique (11 patients), with a minimum followup of 5 years. There is evidence of reduced blood loss for the group treated with MIS, but the study did not consider the complications occurred [14]. The complications in our series are comparable to those reported in the literature for conservative treatment, and much less than with open fusion. 6. Conclusion MIS in the treatment of thoracolumbar and lumbar spine fractures represents a good alternative option to conservative treatment.
6 6 Minimally Invasive Surgery Clinical and functional results are better or comparable, time of recovery is much quicker and the rate of complications is low. Implants need to be removed in case of complications or symptoms referred by the patient. Otherwise system hardware removal is mandatory only when fixation involves L2 or lower segments. An adequate learning curve is important in order to minimize complications. The surgeon should also be confident about the instrumentation to reduce the duration of surgery and radiation exposure. The major complications primarily occur in the immediate postoperative period and can be related both to the implant and to the surgical procedure. The correct surgical indication remains mandatory. Patients should be informed about the potential complications and the possible need for instrumentation removal. References fractures without neurologic deficit, Spine, vol.26,no.9,pp , [12] G. H. Chow, B. J. Nelson, J. S. Gebhard, J. L. Brugman, C. W. Brown, and D. H. Donaldson, Functional outcome of thoracolumbar burst fractures managed with hyperextension casting or bracing and early mobilization, Spine, vol. 21, no. 18, pp , [13] S. T. Wang, H. L. Ma, C. L. Liu, W. K. Yu, M. C. Chang, and T. H. Chen, Is fusion necessary for surgically treated burst fractures of the thoracolumbar and lumbar spine? A prospective, randomized study, Spine, vol. 31, no. 23, pp , [14] M. H. Wild, M. Glees, C. Plieschnegger, and K. Wenda, Fiveyear follow-up examination after purely minimally invasive posterior stabilization of thoracolumbar fractures: a comparison of minimally invasive percutaneously and conventionally open treated patients, Archives of Orthopaedic and Trauma Surgery, vol. 127, no. 5, pp , [1] F. Magerl, M. Aebi, S. D. Gertzbein et al., A comprehensive classification of thoracic and lumbar injuries, European Spine Journal, vol. 3, no. 4, pp , [2] J. Mumford, J. N. Weinstein, K. F. Spratt, and V. K. Goel, Thoracolumbar burst fractures: the clinical efficacy and outcome of nonoperative management, Spine, vol. 18, no. 8, pp , [3] W. J. Shen and Y. S. Shen, Nonsurgical treatment of three-column thoracolumbar junction burst fractures without neurologic deficit, Spine, vol. 24, no. 4, pp , [4] Y. R. Rampersaud, N. Annand, and M. B. Dekutoski, Use of minimally invasive surgical techniques in the management of thoracolumbar trauma: current concepts, Spine, vol. 31, no. 11, supplement, pp. S96 S102, [5] G. Barbanti Brodano, F. De Iure, M. Cappuccio et al., Osteosintesi con tecnica percutanea mininvasiva nel trattamento delle fratture vertebrali toraciche e lombari. Esperienza preliminare, Giot, vol. 33, pp , [6]T.R.Kuklo,D.W.PollyJr.,B.D.Owens,S.M.Zeidman, A.S.Chang,andW.R.Klemme, Measurementofthoracic and lumbar fracture kyphosis: evaluation of intraobserver, interobserver, and technique variability, Spine, vol. 26, no. 1, pp , [7] J. J. Wise, J. S. Fischgrund, H. N. Herkowitz, D. Montgomery, and L. T. Kurz, Complication, survival rates, and risk factors of surgery for metastatic disease of the spine, Spine, vol. 24, no. 18, pp , [8] M. F. McDonnell, S. D. Classman, J. R. Dimar II, R. M. Puno, and J. R. Johnson, Perioperative complications of anterior procedures on the spine, Bone and Joint Surgery Series A, vol. 78, no. 6, pp , [9] H. D. Been, R. W. Poolman, and L. H. Ubags, Clinical outcome and radiographic results after surgical treatment of post-traumatic thoracolumbar kyphosis following simple type Afractures, European Spine Journal, vol. 13, no. 2, pp , [10] E.A.Seybold,C.A.Sweeney,B.E.Fredrickson,L.G.Warhold, and P. M. Bernini, Functional outcome of low lumbar burst fractures: a multicenter review of operative and nonoperative treatment of L3 L5, Spine, vol. 24, no. 20, pp , [11] W. J. Shen, T. J. Liu, and Y. S. Shen, Nonoperative treatment versus posterior fixation for thoracolumbar junction burst
7 MEDIATORS of INFLAMMATION The Scientific World Journal Gastroenterology Research and Practice Diabetes Research International Endocrinology Immunology Research Disease Markers Submit your manuscripts at BioMed Research International PPAR Research Obesity Ophthalmology Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Stem Cells International Oncology Parkinson s Disease Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine AIDS Behavioural Neurology Research and Treatment Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity
Departement of Neurosurgery A.O.R.N A. Cardarelli- Naples.
 Percutaneous posterior pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic, lumbar and thoraco-lumbar junction (T12-L1) traumatic and pathological spine fractures. Report of 45 cases. G. Vitale, A. Punzo,
Percutaneous posterior pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic, lumbar and thoraco-lumbar junction (T12-L1) traumatic and pathological spine fractures. Report of 45 cases. G. Vitale, A. Punzo,
Thoracolumbar fractures. Treatment options. A long trip.
 Thoracolumbar fractures. Treatment options. A long trip. MIS SURGERY. WHY NOT? Murcia. October 5, 2012. Dr. Pedro Cortés García. Spinal Unit. Orthopaedic department. Canary Islands University Hospital
Thoracolumbar fractures. Treatment options. A long trip. MIS SURGERY. WHY NOT? Murcia. October 5, 2012. Dr. Pedro Cortés García. Spinal Unit. Orthopaedic department. Canary Islands University Hospital
Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Kanji Mori, Kazuya Nishizawa, Akira Nakamura, and Shinji Imai. 1. Introduction. 2. Case Presentation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 301858, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/301858 Case Report Atraumatic Occult Odontoid Fracture in Patients with Osteoporosis-Associated Thoracic
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 301858, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/301858 Case Report Atraumatic Occult Odontoid Fracture in Patients with Osteoporosis-Associated Thoracic
Percutaneous Posterior Fixation: A Unique Entity to minimize Further Damage to Patient with Traumatic Spine
 Kaushal R Patel et al RESEARCH ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10039-1129 Percutaneous Posterior Fixation: A Unique Entity to minimize Further Damage to Patient with Traumatic Spine 1 Kaushal R Patel, 2 Jayprakash
Kaushal R Patel et al RESEARCH ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10039-1129 Percutaneous Posterior Fixation: A Unique Entity to minimize Further Damage to Patient with Traumatic Spine 1 Kaushal R Patel, 2 Jayprakash
University of Groningen. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria
 University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
Advantages of MISS. Disclosures. Thoracolumbar Trauma: Minimally Invasive Techniques. Minimal Invasive Spine Surgery 11/8/2013.
 3 rd Annual UCSF Techniques in Complex Spine Surgery Program Thoracolumbar Trauma: Minimally Invasive Techniques Research Support: Stryker Disclosures Murat Pekmezci, MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF/SFGH
3 rd Annual UCSF Techniques in Complex Spine Surgery Program Thoracolumbar Trauma: Minimally Invasive Techniques Research Support: Stryker Disclosures Murat Pekmezci, MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF/SFGH
Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life
 Original Study Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life Lorenzo Nigro 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Pasquale
Original Study Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life Lorenzo Nigro 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Pasquale
Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture: Severe Canal Compromise but Neurologically Intact Cases
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2013;9:101-105 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.101 Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture:
CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2013;9:101-105 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.101 Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture:
Case Report Traumatic Death due to Simultaneous Double Spine Fractures in Patient with Ankylosing Spondylitis
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 590935, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/590935 Case Report Traumatic Death due to Simultaneous Double Spine Fractures in Patient with Ankylosing
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 590935, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/590935 Case Report Traumatic Death due to Simultaneous Double Spine Fractures in Patient with Ankylosing
Clinical Study Percutaneous Cement-Augmented Screws Fixation in the Fractures of the Aging Spine: Is It the Solution?
 BioMed Research International, Article ID 610675, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/610675 Clinical Study Percutaneous Cement-Augmented Screws Fixation in the Fractures of the Aging Spine: Is It the
BioMed Research International, Article ID 610675, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/610675 Clinical Study Percutaneous Cement-Augmented Screws Fixation in the Fractures of the Aging Spine: Is It the
International Journal of Orthopaedics Sciences 2016; 2(4): Dr. Ajay MB and Dr. Vijayakumar AV
 2016; 2(4): 154-159 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2016; 2(4): 154-159 2016 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 10-08-2016 Accepted: 20-09-2016 Dr. Ajay MB Consultant, Orthopedic Surgeon, Puttur, Mangalore, Karnataka,
2016; 2(4): 154-159 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2016; 2(4): 154-159 2016 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 10-08-2016 Accepted: 20-09-2016 Dr. Ajay MB Consultant, Orthopedic Surgeon, Puttur, Mangalore, Karnataka,
Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 456940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/456940 Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion Koshi Ninomiya, Koichi Iwatsuki,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 456940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/456940 Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion Koshi Ninomiya, Koichi Iwatsuki,
Case Report Pediatric Transepiphyseal Seperation and Dislocation of the Femoral Head
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 703850, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/703850 Case Report Pediatric Transepiphyseal Seperation and Dislocation of the Femoral Head Mehmet Elmadag,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 703850, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/703850 Case Report Pediatric Transepiphyseal Seperation and Dislocation of the Femoral Head Mehmet Elmadag,
REFERENCE DOCTOR Thoracolumbar Trauma MIS Options. Hyeun Sung Kim, MD, PhD,
 Thoracolumbar Trauma MIS Options Medical College of Chosun University, Gwangju, South Korea (1994) / Board of Neurosurgery (1999) MEMBERSHIPS & PROFESSIONAL SOCIETIES Korean Neurosurgical Society / Korean
Thoracolumbar Trauma MIS Options Medical College of Chosun University, Gwangju, South Korea (1994) / Board of Neurosurgery (1999) MEMBERSHIPS & PROFESSIONAL SOCIETIES Korean Neurosurgical Society / Korean
Original Article 0Role of Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Transpedicular
 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 30 / No. 4 / October - December 2015 291-298 Original Article 0Role of Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Transpedicular 1Screws in Lumbar Fracture 1 2 Ahmed Elsayed*
Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 30 / No. 4 / October - December 2015 291-298 Original Article 0Role of Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Transpedicular 1Screws in Lumbar Fracture 1 2 Ahmed Elsayed*
KumaFix fixation for thoracolumbar burst fractures: a prospective study on selective consecutive patients
 Xi an Hong Hui Hospital Xi an, Shaanxi, China KumaFix fixation for thoracolumbar burst fractures: a prospective study on selective consecutive patients Dingjun Hao, Baorong He, Liang Yan Hong Hui Hospital,
Xi an Hong Hui Hospital Xi an, Shaanxi, China KumaFix fixation for thoracolumbar burst fractures: a prospective study on selective consecutive patients Dingjun Hao, Baorong He, Liang Yan Hong Hui Hospital,
Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR Page 1 of 9 INSTABILITY AND DEGENERATIVE DISC CONDITIONS FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY CPT4
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR Page 1 of 9 INSTABILITY AND DEGENERATIVE DISC CONDITIONS FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY CPT4
Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture Dislocation of the Elbow in an Adult
 Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2018, Article ID 5401634, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5401634 Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture
Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2018, Article ID 5401634, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5401634 Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Orthop Clin N Am 38 (2007) 463 468 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Andreas Vesalius, in history of spine pathology, 306 Anesthesia/anesthetics for PECD, 329 in minimally
Orthop Clin N Am 38 (2007) 463 468 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Andreas Vesalius, in history of spine pathology, 306 Anesthesia/anesthetics for PECD, 329 in minimally
Case Report A Rare Case of Hypopharyngeal Screw Migration after Spine Stabilization with Plating
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 475285, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/475285 Case Report A Rare Case of Hypopharyngeal Screw Migration after Spine Stabilization with Plating
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 475285, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/475285 Case Report A Rare Case of Hypopharyngeal Screw Migration after Spine Stabilization with Plating
Case Report Unilateral Pedicle Stress Fracture in a Long-Term Hemodialysis Patient with Isthmic Spondylolisthesis
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 426940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/426940 Case Report Unilateral Pedicle Stress Fracture in a Long-Term Hemodialysis Patient with Isthmic
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 426940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/426940 Case Report Unilateral Pedicle Stress Fracture in a Long-Term Hemodialysis Patient with Isthmic
Postero-lateral approach with open view vertebroplasty - eggshell technique
 Romanian Neurosurgery (2013) XX 4: 357-368 357 Postero-lateral approach with open view vertebroplasty - eggshell technique E.Fl. Exergian 1, I.Fl. Luca-Husti 2, D. Şerban 1 1 Spine Surgery Department,
Romanian Neurosurgery (2013) XX 4: 357-368 357 Postero-lateral approach with open view vertebroplasty - eggshell technique E.Fl. Exergian 1, I.Fl. Luca-Husti 2, D. Şerban 1 1 Spine Surgery Department,
Long Posterior Fixation with Short Fusion for the Treatment of TB Spondylitis of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine with or without Neurologic Deficit
 Long Posterior Fixation with Short Fusion for the Treatment of TB Spondylitis of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine with or without Neurologic Deficit Shih-Tien Wang MD, Chien-Lin Liu MD 王世典劉建麟 School of Medicine,
Long Posterior Fixation with Short Fusion for the Treatment of TB Spondylitis of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine with or without Neurologic Deficit Shih-Tien Wang MD, Chien-Lin Liu MD 王世典劉建麟 School of Medicine,
Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by vertebral shortening
 Eur Spine J (2002) 11 :8 12 DOI 10.1007/s005860000214 TECHNICAL INNOVATION Alejandro Reyes-Sanchez Luis M. Rosales Victor P. Miramontes Dario E. Garin Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by vertebral
Eur Spine J (2002) 11 :8 12 DOI 10.1007/s005860000214 TECHNICAL INNOVATION Alejandro Reyes-Sanchez Luis M. Rosales Victor P. Miramontes Dario E. Garin Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by vertebral
Thoracic or lumbar spinal surgery in patients with Parkinson s disease -A two-center experience of 32 cases-
 Thoracic or lumbar spinal surgery in patients with Parkinson s disease -A two-center experience of 32 cases- Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto university Hiroaki Kimura,
Thoracic or lumbar spinal surgery in patients with Parkinson s disease -A two-center experience of 32 cases- Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto university Hiroaki Kimura,
Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia: A Case Series
 C a s e R e p o r t J. of Advanced Spine Surgery Volume 2, Number 2, pp 60~65 Journal of Advanced Spine Surgery JASS Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia:
C a s e R e p o r t J. of Advanced Spine Surgery Volume 2, Number 2, pp 60~65 Journal of Advanced Spine Surgery JASS Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia:
Classification? Classification system should be: Comprehensive Usable Accurate Predictable Able to guide intervention
 Moderator: Dr. P.S. Chandra Dr. Dr Deepak Gupta Classification? Classification system should be: Comprehensive Usable Accurate Predictable Able to guide intervention A precise, comprehensive, ideal
Moderator: Dr. P.S. Chandra Dr. Dr Deepak Gupta Classification? Classification system should be: Comprehensive Usable Accurate Predictable Able to guide intervention A precise, comprehensive, ideal
Asymmetric T5 Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy (PSO) for complex posttraumatic deformity
 Eur Spine J (2013) 22:2130 2135 DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-2942-y OPEN OPERATING THEATRE (OOT) Asymmetric T5 Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy (PSO) for complex posttraumatic deformity Ibrahim Obeid Fethi Laouissat
Eur Spine J (2013) 22:2130 2135 DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-2942-y OPEN OPERATING THEATRE (OOT) Asymmetric T5 Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy (PSO) for complex posttraumatic deformity Ibrahim Obeid Fethi Laouissat
MISS in Thoracolumbar Fractures
 MISS in Thoracolumbar Fractures Guillem Saló Bru, MD, Phd Spine Unit. Orthopaedic Department. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Associated Professor. Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona. Introduction. The application
MISS in Thoracolumbar Fractures Guillem Saló Bru, MD, Phd Spine Unit. Orthopaedic Department. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Associated Professor. Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona. Introduction. The application
Case Report A Rare Case of Near Complete Regression of a Large Cervical Disc Herniation without Any Intervention Demonstrated on MRI
 Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 832765, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/832765 Case Report A Rare Case of Near Complete Regression of a Large Cervical Disc Herniation without Any Intervention
Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 832765, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/832765 Case Report A Rare Case of Near Complete Regression of a Large Cervical Disc Herniation without Any Intervention
Baris Beytullah Koc, 1 Martijn Schotanus, 1 Bob Jong, 2 and Pieter Tilman Introduction. 2. Case Presentation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 7898090, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7898090 Case Report The Role of Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI in a Child with Sport-Induced Avascular
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 7898090, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7898090 Case Report The Role of Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI in a Child with Sport-Induced Avascular
Module 1: Basic Comprehensive Course
 The Hellenic Spine Society organize 5 modules according to the following program, which is based on the Eurospine program Module 1: Basic Comprehensive Course SESSION1: SPINE THE BIGGER PICTURE Evidence
The Hellenic Spine Society organize 5 modules according to the following program, which is based on the Eurospine program Module 1: Basic Comprehensive Course SESSION1: SPINE THE BIGGER PICTURE Evidence
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Nonoperative Treatment of Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Fractures Stadhouder, Agnita; Buskens, Erik; Vergroesen, Diederik A.; Fidler, Malcolm W.; de Nies, Frank; Oner, F. C. Published
University of Groningen Nonoperative Treatment of Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Fractures Stadhouder, Agnita; Buskens, Erik; Vergroesen, Diederik A.; Fidler, Malcolm W.; de Nies, Frank; Oner, F. C. Published
Spine Center. at Stamford Hospital s Orthopedic Institute
 Spine Center at Stamford Hospital s Orthopedic Institute Back pain related to spinal deformity and injury or congenital conditions is a common health complaint, which can be very debilitating. At Stamford
Spine Center at Stamford Hospital s Orthopedic Institute Back pain related to spinal deformity and injury or congenital conditions is a common health complaint, which can be very debilitating. At Stamford
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2): /ISSN: /IJCEM Yi Yang, Hao Liu, Yueming Song, Tao Li
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):1278-1284 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0063093 Case Report Dislocation and screws pull-out after application of an Isobar TTL dynamic stabilisation system at L2/3 in
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):1278-1284 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0063093 Case Report Dislocation and screws pull-out after application of an Isobar TTL dynamic stabilisation system at L2/3 in
Department of Oncologic Surgery, Rizzoli Institute, Bologna, Italy 3
 International Surgical Oncology Volume 2011, Article ID 239230, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/239230 Clinical Study Minimally Invasive Posterior Stabilization Improved Ambulation and Pain Scores in Patients
International Surgical Oncology Volume 2011, Article ID 239230, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/239230 Clinical Study Minimally Invasive Posterior Stabilization Improved Ambulation and Pain Scores in Patients
Royal Oak IBFD System Surgical Technique Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF)
 Royal Oak IBFD System Surgical Technique Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF) Preoperative Planning Preoperative planning is necessary for the correct selection of lumbar interbody fusion devices.
Royal Oak IBFD System Surgical Technique Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF) Preoperative Planning Preoperative planning is necessary for the correct selection of lumbar interbody fusion devices.
factor for identifying unstable thoracolumbar fractures. There are clinical and radiological criteria
 NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
Clinical Analysis of Minimally Invasive Single-segment Reduction and Internal Fixation in Patients with Thoracolumbar Fractures
 Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research 2018, 2(1): 23-27 Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research Clinical Analysis of Minimally Invasive Single-segment Reduction and Internal Fixation in Patients with
Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research 2018, 2(1): 23-27 Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research Clinical Analysis of Minimally Invasive Single-segment Reduction and Internal Fixation in Patients with
Ankle Replacement Surgery
 Ankle Replacement Surgery Ankle replacement surgery is performed to replace the damaged articular surfaces of the three bones of the ankle joint with artificial implants. This procedure is now being preferred
Ankle Replacement Surgery Ankle replacement surgery is performed to replace the damaged articular surfaces of the three bones of the ankle joint with artificial implants. This procedure is now being preferred
Case Report Sacral Emphysematous Osteomyelitis Caused by Escherichia coli after Arthroscopy of the Knee
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1961287, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1961287 Case Report Sacral Emphysematous Osteomyelitis Caused by Escherichia coli after Arthroscopy of
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1961287, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1961287 Case Report Sacral Emphysematous Osteomyelitis Caused by Escherichia coli after Arthroscopy of
INTRODUCTION.
 www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/1.334/jkns.212.51.4.23 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 51 : 23-27, 212 Print ISSN 25-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 212 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical Article
www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/1.334/jkns.212.51.4.23 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 51 : 23-27, 212 Print ISSN 25-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 212 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical Article
3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx. White Paper
 3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx (SLM selective laser melted) Goal of the study: Does the sharx intervertebral cage due to innovative material, new design, and lordotic shape solve some problems
3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx (SLM selective laser melted) Goal of the study: Does the sharx intervertebral cage due to innovative material, new design, and lordotic shape solve some problems
Vertebral Augmentation for Compression Fractures. Scott Magnuson, MD Pain Management of North Idaho, PLLC
 Vertebral Augmentation for Compression Fractures Scott Magnuson, MD Pain Management of North Idaho, PLLC OVCFs are most common type of fragility fracture 20-25% Caucasian women and men over 50 yrs have
Vertebral Augmentation for Compression Fractures Scott Magnuson, MD Pain Management of North Idaho, PLLC OVCFs are most common type of fragility fracture 20-25% Caucasian women and men over 50 yrs have
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine
 A spinal fracture is a serious injury. Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological
A spinal fracture is a serious injury. Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological
Focal Correction of Severe Fixed Kyphosis with Single Level Posterior Ponte Osteotomy and Interbody Fusion
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.653 Focal Correction of Severe Fixed Kyphosis with Single Level Posterior Ponte Osteotomy and Interbody Fusion Seth S. Molloy 1, Faiz U. Ahmad 2, Griffin R.
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.653 Focal Correction of Severe Fixed Kyphosis with Single Level Posterior Ponte Osteotomy and Interbody Fusion Seth S. Molloy 1, Faiz U. Ahmad 2, Griffin R.
Case Report Medial Radial Head Dislocation Associated with a Proximal Olecranon Fracture: A Bado Type V?
 Case Reports in Surgery, Article ID 723756, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/723756 Case Report Medial Radial Head Dislocation Associated with a Proximal Olecranon Fracture: A Bado Type V? Neil Segaren,
Case Reports in Surgery, Article ID 723756, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/723756 Case Report Medial Radial Head Dislocation Associated with a Proximal Olecranon Fracture: A Bado Type V? Neil Segaren,
Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior Endplate Lesion after Recurrent Disc Herniation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5963924, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5963924 Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5963924, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5963924 Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior
5/27/2016. Stand-Alone Lumbar Lateral Interbody Fusion (LLIF) vs. Supplemental Fixation. Disclosures. LLIF Approach
 Stand-Alone Lumbar Lateral Interbody Fusion (LLIF) vs. Supplemental Fixation Joseph M. Zavatsky, M.D. Spine & Scoliosis Specialists Tampa, FL Disclosures Consultant - Zimmer / Biomet, DePuy Synthes Spine,
Stand-Alone Lumbar Lateral Interbody Fusion (LLIF) vs. Supplemental Fixation Joseph M. Zavatsky, M.D. Spine & Scoliosis Specialists Tampa, FL Disclosures Consultant - Zimmer / Biomet, DePuy Synthes Spine,
 Introduction Posterior cervical fusion is done through the back posterior of the neck. The surgery joins two or more neck vertebrae into one solid section of bone. The medical term for fusion is arthrodesis.
Introduction Posterior cervical fusion is done through the back posterior of the neck. The surgery joins two or more neck vertebrae into one solid section of bone. The medical term for fusion is arthrodesis.
Comparison of clinical, radiological and functional outcome of short segment V/S long segment posterior fixation of tuberculosis of spine
 2018; 2(4): 104-108 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 104-108 Received: 20-08-2018 Accepted: 21-09-2018 Dr. Mitul Mistry Assistant Professor,
2018; 2(4): 104-108 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 104-108 Received: 20-08-2018 Accepted: 21-09-2018 Dr. Mitul Mistry Assistant Professor,
If you have a condition that compresses your nerves, causing debilitating back pain or numbness along the back of your leg.
 Below, we have provided some basic information for your benefit. Please use this information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk
Below, we have provided some basic information for your benefit. Please use this information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk
Fenestrated pedicle screws for cement-augmented purchase in patients with bone softening: a review of 21 cases
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2011) 12:193 199 DOI 10.1007/s10195-011-0164-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Fenestrated pedicle screws for cement-augmented purchase in patients with bone softening: a review of 21 cases Luca
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2011) 12:193 199 DOI 10.1007/s10195-011-0164-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Fenestrated pedicle screws for cement-augmented purchase in patients with bone softening: a review of 21 cases Luca
Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy. Case JB. Antonio Castellvi 5/19/2017
 Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy John M. Small MD Florida Orthopedic Institute University South Florida Department Orthopedic Surgery Castellvi Spine May 11, 2017 Case JB 66 y/o male 74 235 lbs Retired police
Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy John M. Small MD Florida Orthopedic Institute University South Florida Department Orthopedic Surgery Castellvi Spine May 11, 2017 Case JB 66 y/o male 74 235 lbs Retired police
Surgical technique. synex. The vertebral body replacement with ratchet mechanism.
 Surgical technique synex. The vertebral body replacement with ratchet mechanism. Table of contents Indications and contraindications 2 Implants 3 Surgical technique 4 Cleaning of instruments 10 Optional
Surgical technique synex. The vertebral body replacement with ratchet mechanism. Table of contents Indications and contraindications 2 Implants 3 Surgical technique 4 Cleaning of instruments 10 Optional
Management Of Posttraumatic Spinal Instability (Neurosurgical Topics, No 3) READ ONLINE
 Management Of Posttraumatic Spinal Instability (Neurosurgical Topics, No 3) READ ONLINE If you are searching for a ebook Management of Posttraumatic Spinal Instability (Neurosurgical Topics, No 3) in pdf
Management Of Posttraumatic Spinal Instability (Neurosurgical Topics, No 3) READ ONLINE If you are searching for a ebook Management of Posttraumatic Spinal Instability (Neurosurgical Topics, No 3) in pdf
Incidence of deep vein thrombosis after major spine surgeries with no mechanical or chemical prophylaxis
 29 29 33 Incidence of deep vein thrombosis after major spine surgeries with no mechanical or chemical prophylaxis Author Institution Sreedharan Namboothiri Kovai Medical Center and Hospitals, Coimbatore,
29 29 33 Incidence of deep vein thrombosis after major spine surgeries with no mechanical or chemical prophylaxis Author Institution Sreedharan Namboothiri Kovai Medical Center and Hospitals, Coimbatore,
Case Report A Case of Nonunion Avulsion Fracture of the Anterior Tibial Eminence
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 9648473, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9648473 Case Report A Case of Nonunion Avulsion Fracture of the Anterior Tibial Eminence Satoru Atsumi,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 9648473, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9648473 Case Report A Case of Nonunion Avulsion Fracture of the Anterior Tibial Eminence Satoru Atsumi,
Short segment pedicle screw fixation for unstable T11-L2 fractures : with or without fusion? A three-year follow-up study
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 822-827 ORIGINAL STUDY Short segment pedicle screw fixation for unstable T11-L2 fractures : with or without fusion? A three-year follow-up study Jin-Ho HWANG, Hitesh N. MODI,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 822-827 ORIGINAL STUDY Short segment pedicle screw fixation for unstable T11-L2 fractures : with or without fusion? A three-year follow-up study Jin-Ho HWANG, Hitesh N. MODI,
Saudi Journal of Medicine (SJM)
 Saudi Journal of Medicine (SJM) Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-3389 (Print) ISSN 2518-3397 (Online) A Comparative Study of Thoracolumbar
Saudi Journal of Medicine (SJM) Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-3389 (Print) ISSN 2518-3397 (Online) A Comparative Study of Thoracolumbar
Case Report Combined Effect of a Locking Plate and Teriparatide for Incomplete Atypical Femoral Fracture: Two Case Reports of Curved Femurs
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 213614, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/213614 Case Report Combined Effect of a Locking Plate and Teriparatide for Incomplete Atypical Femoral
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 213614, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/213614 Case Report Combined Effect of a Locking Plate and Teriparatide for Incomplete Atypical Femoral
Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012
 Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012 Posterior distraction and decompression Secure Fixation and Stabilization Integrated Bone
Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012 Posterior distraction and decompression Secure Fixation and Stabilization Integrated Bone
ACDF. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion. An introduction to
 An introduction to ACDF Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion This booklet provides general information on ACDF. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with
An introduction to ACDF Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion This booklet provides general information on ACDF. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with
Spine: Base to Summit 2018 Beaver Creek, CO ǀ January 18-21, 2018 Program
 THURSDAY, JANUARY 18 6:30 Registration, Breakfast and Exhibits Heritage Hall Foyer/Brown Dempsey Room 4:00 Welcome C. Shaffrey, MD SESSION 1: The Best Technique Is Grouse Mountain Room Mod: R. Haid, MD
THURSDAY, JANUARY 18 6:30 Registration, Breakfast and Exhibits Heritage Hall Foyer/Brown Dempsey Room 4:00 Welcome C. Shaffrey, MD SESSION 1: The Best Technique Is Grouse Mountain Room Mod: R. Haid, MD
A U X I L I A R Y C O N N E C T O R S Surgical Technique
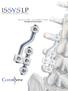 A U X I L I A R Y C O N N E C T O R S Surgical Technique AUXILIARY CONNECTORS ISSYS LP Auxiliary Connectors The ISSYS LP auxiliary connectors were designed to provide medial-lateral variability for the
A U X I L I A R Y C O N N E C T O R S Surgical Technique AUXILIARY CONNECTORS ISSYS LP Auxiliary Connectors The ISSYS LP auxiliary connectors were designed to provide medial-lateral variability for the
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
Evidence Table. Study Type: Randomized controlled trial. Study Aim: To evaluate the safety and efficacy of the X-Stop interspinous implant.
 Evidence Table Clinical Area: Reference: Spinal decompression device for lumbar spinal stenosis Zucherman JF et al. A prospective randomized multi-center study for the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis
Evidence Table Clinical Area: Reference: Spinal decompression device for lumbar spinal stenosis Zucherman JF et al. A prospective randomized multi-center study for the treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis
A Structural Service Plan: Towards Better and Safer Spine Surgeries. Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Tuen Mun Hospital
 A Structural Service Plan: Towards Better and Safer Spine Surgeries Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Tuen Mun Hospital Cheung KK Wong CY Chan Andrew Tse Alfred Chow YY Department of Orthopaedics
A Structural Service Plan: Towards Better and Safer Spine Surgeries Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Tuen Mun Hospital Cheung KK Wong CY Chan Andrew Tse Alfred Chow YY Department of Orthopaedics
SYNEX The vertebral body replacement with ratchet mechanism
 SYNEX The vertebral body replacement with ratchet mechanism Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Image
SYNEX The vertebral body replacement with ratchet mechanism Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Image
Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression and Fusion
 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. 4 / October - December 014 51-56 Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression
Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. 4 / October - December 014 51-56 Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression
Case Report Successful Closed Reduction of a Lateral Elbow Dislocation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5934281, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5934281 Case Report Successful Closed Reduction of a Lateral Elbow Dislocation Kenya Watanabe, Takuma
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5934281, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5934281 Case Report Successful Closed Reduction of a Lateral Elbow Dislocation Kenya Watanabe, Takuma
Comprehension of the common spine disorder.
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
SpineFAQs. Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
 SpineFAQs Lumbar Spondylolisthesis Normally, the bones of the spine (the vertebrae) stand neatly stacked on top of one another. The ligaments and joints support the spine. Spondylolisthesis alters the
SpineFAQs Lumbar Spondylolisthesis Normally, the bones of the spine (the vertebrae) stand neatly stacked on top of one another. The ligaments and joints support the spine. Spondylolisthesis alters the
Spine Surgery: Techniques, Complication Avoidance, and Management. 2 Volume Set
 Spine Surgery: Techniques, Complication Avoidance, and Management. 2 Volume Set Benzel, E ISBN-13: 9781437705874 Table of Contents SECTION 1 - HISTORY 1 - History 2 - History of Spine Instrumentation -
Spine Surgery: Techniques, Complication Avoidance, and Management. 2 Volume Set Benzel, E ISBN-13: 9781437705874 Table of Contents SECTION 1 - HISTORY 1 - History 2 - History of Spine Instrumentation -
Case Report A Case Report of Isolated Cuboid Nutcracker Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 3264172, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3264172 Case Report A Case Report of Isolated Cuboid Nutcracker Fracture Takaaki Ohmori, 1,2 Shinichi
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 3264172, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3264172 Case Report A Case Report of Isolated Cuboid Nutcracker Fracture Takaaki Ohmori, 1,2 Shinichi
FUNCTIONAL OUTCOMES OF TRAUMATIC PARAPLEGIA PATIENTS: DOES SURGERY IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF LIFE?
 FUNCTIONAL OUTCOMES OF TRAUMATIC PARAPLEGIA PATIENTS: DOES SURGERY IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF LIFE? Original Article Orthopaedics R S Bajoria 1, Mahendra Panwar 2, Anand Rao 3, Sameer Gupta 4 1 - Associate
FUNCTIONAL OUTCOMES OF TRAUMATIC PARAPLEGIA PATIENTS: DOES SURGERY IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF LIFE? Original Article Orthopaedics R S Bajoria 1, Mahendra Panwar 2, Anand Rao 3, Sameer Gupta 4 1 - Associate
VAriation. Orthotics and Me (?surgeons) Greg Etherington Spine Surgeon. Orthopaedic & Neurosurgery backgrounds. Subspeciality training
 Orthotics and Me (?surgeons) Greg Etherington Spine Surgeon Orthopaedic & Neurosurgery backgrounds Subspeciality training spine, upper limb, trauma, pelvis. What do you do in spine? Lumbar Cervical Trauma
Orthotics and Me (?surgeons) Greg Etherington Spine Surgeon Orthopaedic & Neurosurgery backgrounds Subspeciality training spine, upper limb, trauma, pelvis. What do you do in spine? Lumbar Cervical Trauma
The vertebral body replacement with ratchet mechanism. Synex. Surgical Technique
 The vertebral body replacement with ratchet mechanism Synex Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use of DePuy Synthes products.
The vertebral body replacement with ratchet mechanism Synex Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use of DePuy Synthes products.
Osteoporotic Compression Fracture of Spine Treated With Posterior Instrumentation and Transpedicular Bone Grafting
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1211.003 Osteoporotic Compression Fracture of Spine Treated With Posterior Instrumentation and Transpedicular Bone Grafting Foead AI, MS Orth, Thanapipatsiri S*, MD, Pichaisak
http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1211.003 Osteoporotic Compression Fracture of Spine Treated With Posterior Instrumentation and Transpedicular Bone Grafting Foead AI, MS Orth, Thanapipatsiri S*, MD, Pichaisak
Role of Posterior Fixation Technique in Surgeries for Pathological Fractures of the Dorsal and Lumbar Spine Secondary to Neoplastic Causes
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 1, March: 293-298, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of Posterior Fixation Technique in Surgeries for Pathological Fractures of the Dorsal and Lumbar Spine
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 1, March: 293-298, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of Posterior Fixation Technique in Surgeries for Pathological Fractures of the Dorsal and Lumbar Spine
Case Report An Undescribed Monteggia Type 3 Equivalent Lesion: Lateral Dislocation of Radial Head with Both-Bone Forearm Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 8598139, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8598139 Case Report An Undescribed Monteggia Type 3 Equivalent Lesion: Lateral Dislocation of Radial
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 8598139, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8598139 Case Report An Undescribed Monteggia Type 3 Equivalent Lesion: Lateral Dislocation of Radial
Patient Information ACDF. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion
 Patient Information ACDF Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Table of Contents Anatomy of the Spine...2-3 General Conditions of the Cervical Spine...4 5 What is an ACDF?...6 How is an ACDF performed?...7
Patient Information ACDF Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Table of Contents Anatomy of the Spine...2-3 General Conditions of the Cervical Spine...4 5 What is an ACDF?...6 How is an ACDF performed?...7
Spinal Fusion. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Spinal Fusion North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Spinal Fusion? The spine is made up of a series of bones called vertebrae ; between each vertebra are strong connective tissues
Spinal Fusion North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Spinal Fusion? The spine is made up of a series of bones called vertebrae ; between each vertebra are strong connective tissues
Patient Information MIS LLIF. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
 Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine....2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine....2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
SHORT SEGMENT FIXATION THORACOLUMBAR UNSTABLE BURST FRACTURES USING DC PLATES & PEDICLE SCREWS
 STUDY SHORT SEGMENT FIXATION THORACOLUMBAR UNSTABLE BURST FRACTURES USING DC PLATES & PEDICLE SCREWS *Hashem, N.; **A Subai, N. *Faculty of Medicine, Ains Shams University, Egypt ^Department of Orthopedics,
STUDY SHORT SEGMENT FIXATION THORACOLUMBAR UNSTABLE BURST FRACTURES USING DC PLATES & PEDICLE SCREWS *Hashem, N.; **A Subai, N. *Faculty of Medicine, Ains Shams University, Egypt ^Department of Orthopedics,
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:71-77 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.71 More than 5-Year Follow-up Results of Two- Level and Three-Level Posterior Fixations of Thoracolumbar
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:71-77 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.71 More than 5-Year Follow-up Results of Two- Level and Three-Level Posterior Fixations of Thoracolumbar
ProDisc-L Total Disc Replacement. IDE Clinical Study.
 ProDisc-L Total Disc Replacement. IDE Clinical Study. A multi-center, prospective, randomized clinical trial. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Indications, Contraindications
ProDisc-L Total Disc Replacement. IDE Clinical Study. A multi-center, prospective, randomized clinical trial. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Indications, Contraindications
Clinical Study Rate of Improvement following Volar Plate Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Distal Radius Fractures
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2011, Article ID 565642, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/565642 Clinical Study Rate of Improvement following Volar Plate Open Reduction and Internal
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2011, Article ID 565642, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/565642 Clinical Study Rate of Improvement following Volar Plate Open Reduction and Internal
Case Report Intra-Articular Osteotomy for Distal Humerus Malunion
 Volume 2009, Article ID 631306, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/631306 Case Report Intra-Articular Osteotomy for Distal Humerus Malunion RenéK.Marti 1 and Job Doornberg 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
Volume 2009, Article ID 631306, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/631306 Case Report Intra-Articular Osteotomy for Distal Humerus Malunion RenéK.Marti 1 and Job Doornberg 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections in Patients with Hydrocephalus
 The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 461896, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/461896 Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections
The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 461896, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/461896 Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections
Augmentable Pedicle Screws for Osteoporotic Bone. Perforated Click X. Surgical Technique
 Augmentable Pedicle Screws for Osteoporotic Bone Perforated Click X Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use of DePuy Synthes
Augmentable Pedicle Screws for Osteoporotic Bone Perforated Click X Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use of DePuy Synthes
Patient Guide to Neck Surgery
 The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Posterior Cervical Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Neck Surgery Posterior Cervical Fusion NexPosure NexPosure MIS Access provides
The following is a sampling of products offered by Zimmer Spine for use in Posterior Cervical Fusion procedures. Patient Guide to Neck Surgery Posterior Cervical Fusion NexPosure NexPosure MIS Access provides
Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus Accompanied by Meniscocapsular Separation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 357463, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/357463 Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus Accompanied by Meniscocapsular Separation Aki Fukuda,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 357463, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/357463 Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus Accompanied by Meniscocapsular Separation Aki Fukuda,
Patient Information MIS TLIF. Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
 Patient Information MIS TLIF Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques MIS TLIF Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine..............................................
Patient Information MIS TLIF Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques MIS TLIF Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine..............................................
22110 vertebral segment; cervical vertebral segment; thoracic vertebral segment; lumbar
 The following codes are authorized by Palladian Health for applicable product lines. Visit palladianhealth.com to request authorization and to access guidelines. Palladian Musculoskeletal Program Codes
The following codes are authorized by Palladian Health for applicable product lines. Visit palladianhealth.com to request authorization and to access guidelines. Palladian Musculoskeletal Program Codes
Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Fractures and Dislocations: Assessment and Classification
 Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Fractures and Dislocations: Assessment and Classification Mark L Prasarn MD University of Texas Dept of Orthopaedic Surgery Houston, Texas Updated 7/2016 Anatomy of the Spine
Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Fractures and Dislocations: Assessment and Classification Mark L Prasarn MD University of Texas Dept of Orthopaedic Surgery Houston, Texas Updated 7/2016 Anatomy of the Spine
Case Report Pulmonary Artery Cement Embolism after a Vertebroplasty
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 582769, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/582769 Case Report Pulmonary Artery Cement Embolism after a Vertebroplasty Anas Nooh, 1,2 Fahad H. Abduljabbar,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 582769, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/582769 Case Report Pulmonary Artery Cement Embolism after a Vertebroplasty Anas Nooh, 1,2 Fahad H. Abduljabbar,
