Total Ankle Arthroplasty
|
|
|
- Thomas Potter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay estic et al. Total nkle rthroplasty Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from by on 11/26/17 from IP address Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Joseph M. estic 1 Jeffrey J. Peterson 1 James K. DeOrio 1,2 Laura W. ancroft 1 Thomas H. erquist 1 Mark J. Kransdorf 1,3 estic JM, Peterson JJ, DeOrio JK, ancroft LW, erquist TH, Kransdorf MJ Keywords: ankle, ankle arthroplasty devices, arthroplasty, musculoskeletal imaging DOI: /JR Received June 10, 2007; accepted after revision November 1, The opinions and assertions contained herein are the private views of the authors and are not to be construed as official or as reflecting the views of the Department of the rmy or the Department of Defense. J. K. DeOrio is a consultant for Link Orthopedics and Integra, is a consultant for and has a financial interest in INONE Technologies, and is a member of the speakers bureau of Tornier. He was also a member of the design team for the Zimmer total ankle and has been a consultant for the DePuy Orthopedic Company. Presented at the 2007 annual meeting of the merican Roentgen Ray Society, Orlando, FL, where a certificate of merit was awarded. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 4500 San Pablo Rd., Jacksonville, FL ddress correspondence to J. M. estic (bestic.joseph@mayo.edu). 2 Present address: Department of Orthopedics, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC. 3 Department of Radiologic Pathology, rmed Forces Institute of Pathology, Washington, DC. CME This article is available for CME credit. See for more information. JR 2008; 190: X/08/ merican Roentgen Ray Society Postoperative Evaluation of the Total nkle rthroplasty OJECTIVE. The purpose of this article is to review the basic design features of secondgeneration total ankle arthroplasty components and to illustrate the normal and abnormal postoperative imaging features associated with such devices. The usefulness of CT in postoperative evaluation will be highlighted. CONCLUSION. Postoperative evaluation of the total ankle arthroplasty necessitates a familiarity with the various designs currently in use. Radiography serves as an integral component in the postoperative evaluation of such devices, with CT offering further characterization of radiographic abnormalities. T otal ankle arthroplasty was developed to provide an alternative to ankle arthrodesis for the treatment of severe arthrosis, with the inherent advantage of preserving joint motion. Initially introduced with much optimism in the 1970s, cemented first-generation ankle arthroplasties were subsequently found to be plagued with unacceptably high complication rates and were largely abandoned [1, 2]. Enthusiasm for total ankle arthroplasty has been renewed with the development of uncemented second-generation devices, which have addressed many of the initial technical failures through innovative designs and refined surgical techniques. Newer designs require less bone resection, leaving stronger subchondral bone to secure the prosthesis. In addition, mobile-bearing prostheses offer the distinct possibility of less wear and loosening, which is attributable to improved component conformity and minimal constraint. To date, secondgeneration total ankle arthroplasty devices have been reported to have promising intermediate-term results [3, 4]. However, the long-term outcome of total ankle arthroplasty is under continued scrutiny, with recent success tempered by the poor performance of cemented first-generation devices and the realization that complications will and do occur with second-generation devices [3, 5, 6]. Regardless, encouraging results with secondgeneration devices have led to their increasing popularity, with a multitude of total ankle devices to choose from worldwide. Total nkle rthroplasty Devices Effective postoperative imaging evaluation of the total ankle arthroplasty requires an appreciation for basic component design philosophy and a familiarity with the unique features of the various devices in use. Existing second-generation devices incorporate two basic design philosophies namely, three-component (mobile-bearing) and twocomponent (fixed-bearing) designs. Threecom ponent designs are characterized by individual tibial and talar devices, which are separated by a fully conforming mobile polyethylene spacer. Two-component devices have only a single partially conforming articulation between the tibial and talar devices, with the polyethylene spacer fixed to the tibial component. t least 20 different ankle replacement systems are in use worldwide, with new systems in continual development. Examples of commonly used second-generation total ankle arthroplasty devices include the STR (Scandinavian Total nkle Replacement, Waldemar Link) (Fig. 1), the uechel-pappas Total nkle Replacement (Endotec) (Fig. 2), the TNK ankle (Japan Medical Materials) (Fig. 3), and the gility Total nkle System (DePuy) (Fig. 4). Of these devices, only the gility Total nkle was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug dministration (FD) for use in the United States before Since then, three new devices have received FD approval. These include the INONE Total nkle (INONE Technologies, formerly Topez 1112 JR:190, pril 2008
2 Total nkle rthroplasty Downloaded from by on 11/26/17 from IP address Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Orthopedics) (Fig. 5), the Salto Talaris Total nkle (Tornier) (Fig. 6), and the Eclipse Total nkle (Integra Life Sciences Holdings). lthough these devices are FD-approved for use with cement, they are exclusively used offlabel without cement and feature bone ingrowth components. The STR ankle replacement recently received tentative FD approval for use without cement and is expected to be available to surgeons later this year [7]. Imaging of the Total nkle rthroplasty The postoperative evaluation of total ankle arthroplasties consists of serial clinical and radiographic assessment. Imaging is imperative in identifying early postoperative complications, which may not be apparent on clinical examination. Thus, a thorough understanding of the normal and abnormal postoperative imaging features associated with such devices is of considerable value. CT can supplement the postoperative evaluation of total ankle arthroplasty devices by providing a more detailed evaluation of implant components and surrounding osseous change. Routine postoperative radiographs provide valuable information for the orthopedic surgeon concerning the anatomic relationship between osseous structures and implant components and the presence and extent of bone loss or heterotopic bone formation. Most important, radiographs serve to evaluate changes on serial examinations, which may signify the development of postoperative complications. nteroposterior and lateral views of the ankle should ideally be obtained with the patient in the standing position to ensure physiologic positioning. Non weight-bearing lateral radiographs obtained with the ankle in maximal dorsiflexion and plantar flexion can facilitate evaluation of the range of motion. Fluoroscopically positioned views serve to optimize radiographic alignment of the component bone or bone cement interfaces [8]. Perhaps the most important role of imaging in the postoperative evaluation of total ankle arthroplasties is to detect changes in component position, which may signify evidence of component loosening. lthough component migration is often readily apparent, more subtle changes in component angulation or position relative to surrounding osseous structures can be detected by carefully analyzing angular and linear measurements on serial radiographic examinations [9 11] (Fig. 7). lthough such measurements are not routinely made on all follow-up examinations, this information may aid in the detection of subtle abnormalities (especially if there is clinical concern for loosening) and can be used to provide the surgeon with evidence of quantifiable change. n angular change of more than 5 in the measured angle of either component suggests component migration or subsidence [11]. More than 5-mm subsidence of the talar component on lateral view is also considered worrisome for loosening [10]. Component loosening can also manifest as radiolucent lines at the component bone interface. Radiolucent lines greater than 2 mm or a progressive increase in the width or extent of existing radiolucencies is considered significant [8]. It is important to differentiate such radiolucencies from those related to surgical technique, which may surround components in the immediate postoperative setting. To better localize abnormalities about the components, a zonal system (similar to the Gruen classification of the hip) may be used [9, 12, 13]. Using the STR device as a representative example, bone surrounding the tibial component can be divided into distinct zones on the anteroposterior radiograph. Individual zones are demarcated by lines drawn perpendicular to the tibial plate on each side of the cylindric bars, which are seen on end in the anteroposterior projection. Using this system of demarcation yields five zones that span the length of the tibial plate. These five zones are labeled 1 5, medial to lateral. In a similar fashion, the tibial component can be divided into individual zones on the lateral radiograph. gain using the cylindric bars of the tibial plate as a reference, lines are drawn perpendicular to the tibial plate at the anterior and posterior aspects of the cylindric bars now seen in their long axis. Three individual zones are thus demarcated in the lateral projection ( C, anterior to posterior) (Fig. 8). Dividing the components into distinct zones can serve to facilitate effective communication between the radiologist and orthopedic surgeon. In radiographically equivocal or troublesome cases, CT may be used to further characterize or confirm suspected postoperative complications. CT has been shown to be superior to conventional radiography for the early detection and more accurate quantification of periprosthetic radiolucencies [14]. CT technique should be modified to optimize imaging, with attempts made to reduce attenuation and streak artifacts related to metal with a high-attenuation coefficient. The effective energy of the X-ray beam should be increased (kvp 140, ms 200). These adjustments improve the penetration of dense metal and improve the accuracy of projection data. When practical, aligning the axis of the implant so that the X-ray beam traverses the smallest possible cross-sectional area serves to reduce artifacts. rtifacts may be further mini mized with the use of narrow collimation settings [15]. Extended range postprocessing can also be used to decrease metallic streak artifact. standard or smooth reconstruction filter is preferred because metallic artifact is accentuated with the use of a sharp or bone algorithm. If available on individual scanners, the CT scale may be increased (up to 40,000 H) to accommodate the high linear attenuation coefficients of metal, which lie outside the normal range of reconstructed CT attenuations [15]. Thin slice selection and thin collimation are necessary to achieve isotropic imaging, which facilitates multiplanar reformatted imaging in any plane. Postoperative Complications The complex biomechanics of the ankle, with its substantial shearing and axial loading forces, predispose total ankle replacements to a variety of complications. Careful preoperative patient selection and meticulous surgical technique can help to minimize complications associated with total ankle arthroplasty. Such complications may be categorized as intraoperative, early postoperative, or delayed. Intraoperative complications include injury to neurovascular and tendinous structures, malpositioning or improper sizing of prosthetic components, excessive bone resection, and malleolar fractures. Infection (Fig. 9), impaired wound healing, swelling, stress fractures across the medial malleolus, and syndesmotic nonunions (gility Total nkle only) may be observed in the early postoperative period. Delayed postoperative complications include, but are not limited to, deep infection, development of periprosthetic radiolucencies (Fig. 10), aseptic loosening and subsidence (Fig. 11), periprosthetic fractures (Fig. 12), polyethylene wear with osteolysis, spacer migration or fracture (Figs. 13 and 14), heterotopic bone formation, syndesmotic nonunion (gility Total nkle only), and reflex sympathetic dystrophy [5, 6]. mong the more frequent of these complications are wound healing problems, deep infection, polyethylene wear, and aseptic loosening [5, 6]. Failure secondary to loosening is generally considered a major late complication of total ankle arthroplasty [4]. JR:190, pril
3 estic et al. Downloaded from by on 11/26/17 from IP address Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Currently available second-generation total ankle devices share many common characteristics and therefore develop many of the same complications. s a whole, three-component (mobile-bearing) designs are at an increased risk of polyethylene spacer dislocation, albeit unusual, and may generate more wear particles from the two separate articulations. Two-component (fixed-bearing) designs show only partial conformity involving a single articulation, which increases stability but also theoretically increases polyethylene contact stress and wear. The risk of polyethylene spacer dislocation is much lower with two-component designs [2]. Individual design features associated with specific devices often predispose each to unique problems that may be anticipated on follow-up imaging. The three-component STR device shows a relative lack of inversion and eversion, which may result in excessive contact stress (edge loading) on the polyethylene spacer and may transfer an increased load to the prosthesis bone interface [2]. Excessive contact stress increases wear on the polyethylene component, ultimately predisposing to osteolysis. In contrast, the uechel- Pappas ankle uses a fully congruent deepsulcus polyethylene spacer that allows limited inversion and eversion motion with a concomitant reduction in contact stress [2, 16]. Implantation of the uechel-pappas ankle requires violation of the anterior tibial cortex for placement of the tibial component, which may compromise cortical integrity proximal to the implant [2]. In addition, the smaller anteroposterior dimensions of the uechel- Pappas tibial plate in comparison with the anteroposterior dimensions of the resected distal tibia allows bone overgrowth, which may ultimately lead to limitations in range of motion [16] (Fig. 10C). This bone overgrowth often limits motion in the mobile-bearing ankles, essentially converting them to two-piece designs. Nonunion or delayed union of the syndesmotic fusion unique to the gility Total nkle has been associated with migration of the tibial component, ballooning osteolysis, and circumferential radiolucency about the tibial component [12]. gility Total nkle component subsidence or migration frequently involves the talar component [3, 13] (Fig. 11). This may be attributable to the relatively narrow design of the talar component, which only partially covers the cut talar surface [13]. Newer designs incorporate a wider-based talar component in an effort to combat subsidence [7]. The design of the TNK ankle requires removal of a significant amount of bone stock, predisposing this prosthesis to a relatively high rate of subsidence [2]. Limited data are currently available concerning the results of newer total ankle designs. These include three new two-piece designs recently approved for use by the FD: INONE (INONE Technologies), Salto-Talaris (Tornier), and Eclipse (Integra Life Science Holdings) ankles, and a recent recommendation for approval by the FD of the STR mobile-bearing design (Scandinavian Total nkle Replacement, Waldemar Link). Nonetheless, continual advances in both implant design and surgical technique hold much promise for improved outcomes. Conclusion Promising intermediate-term results associated with second-generation devices have made total ankle arthroplasty a viable alternative to ankle arthrodesis. The concomitant increase in popularity of such devices necessitates a familiarity with both normal and abnormal postoperative imaging features. Radiographs serve as an integral component in the postoperative evaluation of the total ankle arthroplasty. The addition of CT to the radiologist s armamentarium can augment postoperative evaluation, specifically when dealing with equivocal radiographic findings. References 1. Sodha S, Wei SY, Okereke E. Evolution of total ankle arthroplasty. Univ Pennsylvania Orthop J 2000; 13: Easley ME, Vertullo CJ, Urban WC, Nunley J. Total ankle arthroplasty. J m cad Orthop Surg 2002; 10: Spirt, ssal M, Hansen ST. Complications and failure after total ankle arthroplasty. J one Joint Surg m 2004; 86: Jackson MP, Singh D. Total ankle replacement. Current Orthopaedics 2003; 17: Conti SF, Wong YS. Complications of total ankle replacement. Clin Orthop 2001; 391: DeOrio JK. Focus on total ankle arthroplasty. Orthopedics 2006; 29: DeOrio JK, Easley ME. Total ankle arthroplasty. In: Instructional course lectures. merican cademy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2008 (in press) 8. erquist TH, DeOrio JK. Reconstructive procedures. In: erquist TH, ed. Radiology of the foot and ankle, 2nd ed. Philadelphia, P: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2000: Knecht SI, Estin M, Callaghan JJ, et al. The gility total ankle arthroplasty: seven to sixteen-year follow-up. J one Joint Surg m 2004; 86: nderson T, Montgomery F, Carlsson. Uncemented STR total ankle prostheses: three to eight-year follow-up of fifty-one consecutive ankles. J one Joint Surg m 2003; 85: Valderrabano V, Hintermann, Dick W. Scandinavian total ankle replacement. Clin Orthop 2004; 424: Pyevich MT, Saltzman CL, Callaghan JJ, lvine FG. Total ankle arthroplasty: a unique design two to twelve-year follow-up. J one Joint Surg m 1998; 80: Kopp FJ, Patel MM, Deland JT, O Malley MJ. Total ankle arthroplasty with the gility prosthesis: clinical and radiographic evaluation. Foot nkle Int 2006; 27: Hanna RS, Haddad SL, Lazarus ML. Evaluation of periprosthetic lucency after total ankle arthroplasty: helical CT versus conventional radiography. Foot nkle Int 2007; 28: Lee MJ, Kim S, Lee S, et al. Overcoming artifacts from metallic orthopedic implants at highfield-strength MR imaging and multidetector CT. RadioGraphics 2007; 27: uechel FF, uechel FF, Pappas MJ. Ten-year evaluation of cementless uechel-pappas meniscal bearing total ankle replacement. Foot nkle Int 2003; 24: JR:190, pril 2008
4 Total nkle rthroplasty Downloaded from by on 11/26/17 from IP address Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 1 STR arthroplasty device (Scandinavian Total nkle Replacement, Waldemar Link) is cementless, three-component (mobile-bearing) design developed by H. Kofoed in Mobile, ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) meniscus (thick black arrow) articulates superiorly with trapezoidal, flat, cobalt chromium tibial plate (white arrow) and inferiorly with longitudinally ridged, convex, cobalt chromium talar component (thin black arrow). Talar component possesses fin (asterisk, ) that inserts caudally into talus. Two characteristic cylindric bars (arrowheads) positioned on superior aspect of tibial component serve to anchor implant in subchondral tibia., Photograph of STR arthroplasty device, oblique lateral view., nteroposterior radiograph of STR arthroplasty device. Fig. 2 uechel-pappas total ankle prosthesis (Endotec). Similar to STR (Scandinavian Total nkle Replacement, Waldemar Link) device, uechel-pappas ankle replacement is cementless, three-component (mobile-bearing) design. Tibial component is stabilized by stem that extends into tibial metaphysis (arrowhead). Ultrahigh-molecularweight polyethylene meniscus (thick arrow) glides along metallic talar component (thin arrow) stabilized by ridge on its undersurface (asterisk) that articulates with corresponding longitudinal groove on talar component. Design allows limited inversion and eversion of ankle joint without loss of congruity and requires minimal talar bone resection., Photograph of uechel-pappas arthroplasty device, frontal view., nteroposterior radiograph of uechel-pappas arthroplasty device. JR:190, pril
5 Downloaded from by on 11/26/17 from IP address Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 3 TNK (Japan Medical Materials) ankle prosthesis is cementless, two-component (fixed-bearing) device used almost exclusively in Japan. This device consists of fused ceramic tibial (thin white arrow) and flat ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene tray (thick white arrow) components that articulate with convex ceramic talar component (black arrow). Several bone fixation methods have been used, including hydroxyapatite-coated beads, fixation screws, and biologic coating. This prosthesis requires large amount of bone resection and has been associated with high rate of subsidence., Photograph of TNK device, oblique frontal view., nteroposterior radiograph of TNK device. Fig. 4 gility Total nkle System (DePuy) has been available for use since 1984, making it longest-used total ankle replacement system in United States. gility ankle is porous-coated, two-piece (fixed-bearing) implant with partially conforming articulation. Modular, concave polyethylene insert (asterisk) locks into tibial component (thin arrow). Talar component (thick arrow) articulates with tibial component with approximately 20 of external rotation. Syndesmotic fusion (double arrowheads, ) increases surface area of tibial component prosthesis bone interface in attempt to resist subsidence while allowing fibula to share portion of load. Failure of syndesmotic fusion is associated with increased rate of failure [8]., Photograph of gility device, oblique frontal view., nteroposterior radiograph of gility device JR:190, pril 2008
6 Total nkle rthroplasty Downloaded from by on 11/26/17 from IP address Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 5 INONE Total nkle (INONE Technologies, formerly Topez Orthopedics) is two-component (fixed-bearing) device with bone ingrowth anchoring stems in both tibial (thin arrow) and talar (arrowhead) components. Polyethylene insert (thick arrow) is attached to tibial component. Modular tibial stem consists of individual segments that can be customized for each patient., Photograph of INONE device, frontal view., nteroposterior radiograph of INONE device. Fig. 6 Salto Talaris Total nkle replacement (Tornier) is two-component (fixed-bearing) device with anatomic design consisting of cobalt chromium tibial (thick arrow) and talar (thin arrow) components. Slide-on ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene insert (asterisk) is attached to tibial component and shows matching articular geometry with talar implant. Tapered fixation plug (arrowhead) on superior aspect of tibial component serves to secure implant against bone surface., Photograph of Salto Talaris device, lateral view., Lateral radiograph of Salto Talaris device. JR:190, pril
7 estic et al. Downloaded from by on 11/26/17 from IP address Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 7 Radiographic measurements for total ankle arthroplasty (illustrated using STR [Scandinavian Total nkle Replacement, Waldemar Link] device). ngular and linear values can be defined to evaluate changes in component alignment and position that may signify component migration [8 10]., nteroposterior view of STR device depicts method of angular evaluation. lpha angle (α) is formed by intersection of lines drawn parallel to flat plate of tibial component and long axis of tibial shaft on anteroposterior view (normal = 90 )., Lateral view of STR device depicts method of angular evaluation. eta angle (β) is formed by intersection of lines drawn parallel to flat plate of tibial component and long axis of tibial shaft (normal = 90 ). Gamma angle (γ) is formed by intersection of line drawn through long axis of talar component with line drawn from posterior talar component through middle of talar neck. Gamma angle in postoperative setting has been shown to range from 11.1 to 33.4, with average measurement of 18.8 [10]. C and D, nteroposterior (C) and lateral (D) views of STR device depict method of linear evaluation of component position. Linear values are established by measuring position of components relative to surrounding osseous structures. Measurement a is perpendicular distance between tip of lateral malleolus and line drawn through base of tibial component. Measurement b is perpendicular distance from anterior aspect of talar component to line intersecting calcaneal tubercle and dorsal aspect of talonavicular joint. Measurement c is perpendicular distance from posterior aspect of talar component to line intersecting calcaneal tubercle and dorsal aspect of talonavicular joint. E and F, Sequential lateral views of STR device depict small change ( 4 ) in gamma angle over course of approximately 3 years. Such angular measurements, although they are often not routinely used, facilitate detection of subtle changes in component position and can be helpful in providing evidence of quantifiable change to surgeon. G, Coronal CT image obtained at time of followup radiograph depicted in F shows thin region of osteolysis involving medial aspect of talar component (arrows). Constellation of findings in this case is concerning for aseptic loosening. Concave undersurface of talar component clearly precludes adequate radiographic evaluation of this region, highlighting usefulness of CT in such circumstances. C D E F G 1118 JR:190, pril 2008
8 Total nkle rthroplasty Downloaded from by on 11/26/17 from IP address Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 8 Zonal system (illustrated with STR [Scandinavian Total nkle Replacement, Waldemar Link] device) offers advantage of more precise localization of abnormalities of components., In anteroposterior projection, tibial component can be divided into five zones by lines drawn perpendicular to tibial plate. Lines are drawn on each side of cylindric bars, yielding five individual zones (1 5, medial to lateral)., In lateral projection, tibial component can be divided into three zones by lines drawn perpendicular to tibial plate. Lines are drawn at anterior and posterior aspects of cylindric bars, yielding three individual zones ( C, anterior to posterior). Fig. 9 Infection in 67-year-old man. Lateral radiograph of STR total ankle (Scandinavian Total nkle Replacement, Waldemar Link) shows several pockets of gas (arrows) in soft tissues of ankle secondary to superficial infection. JR:190, pril
9 estic et al. Downloaded from by on 11/26/17 from IP address Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 10 Periprosthetic lucencies., nteroposterior radiograph of STR total ankle (Scandinavian Total nkle Replacement, Waldemar Link) in 46-year-old woman shows ovoid radiolucency (circled in white) located in zones 4 and 5 of tibial component. t surgery, this radiolucency was found to represent polyethylene osteolysis. Note lateral migration of tibial component with associated remodeling of fibula (white arrow)., Initial postoperative anteroposterior radiograph of STR total ankle in 65-year-old woman shows slight discordance between surgical drill pathways (arrows) and cylindric bars of tibial component. This should not be confused with osteolysis. C, Lateral radiograph of a uechel-pappas total ankle (Endotec) in 41-year-old woman shows well-defined radiolucent region located in anterior tibia just above tibial component plate (arrowhead). Cultures were negative at time of implant removal. Note concomitant subsidence of talar component (black arrow) and prominent heterotopic bone extending into ankle joint around anterior and posterior aspects of tibial plate (white arrows). C 1120 JR:190, pril 2008
10 Total nkle rthroplasty Downloaded from by on 11/26/17 from IP address Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 11 septic loosening., nteroposterior radiograph of STR total ankle (Scandinavian Total nkle Replacement, Waldemar Link) in 46-year-old woman shows marked lateral tibial component migration with extensive surrounding osteolysis (thick black arrow) and remodeling of fibula (thick white arrow). Stress fracture is present in medial malleolus (thin black arrow). Note lateral talar suture anchor (thin white arrow) from prior lateral ligamentous reconstruction., nteroposterior radiograph of gility Total nkle (DePuy) in 65-year-old woman shows marked subsidence and lateral tilt of talar component (black arrow). Large radiolucent focus is evident in medial malleolus (white arrow) with thin region of periprosthetic radiolucency about lateral aspect of tibial component (arrowhead). These changes have developed despite presence of successful syndesmotic fusion (asterisk). oth components were revised within 1 year of this radiograph, with sparse bone ingrowth evident on removal of components. Cultures were negative at time of surgery. Fig. 12 Periprosthetic fracture. lterations in stress distribution related to component size or position may lead to periprosthetic fractures. Malleolar fractures may also occur as result of excessive bone resection or during implantation of prosthesis [5]., Despite presence of medial malleolar screw, periprosthetic fracture (white arrow) can be seen in medial malleolus on anteroposterior radiograph of a STR total ankle (Scandinavian Total nkle Replacement, Waldemar Link) in 75-year-old woman. Note tiny round radiolucency (black arrow) related to wire pins used to secure saw guide during placement of device., Corresponding coronal CT image confirms periprosthetic fracture (arrow) involving medial malleolus. Extension of fracture line to level of tibial component is clearly shown. JR:190, pril
11 estic et al. Downloaded from by on 11/26/17 from IP address Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 13 Migration of polyethylene spacer with ankle subluxation in 72-year-old man., nteroposterior radiograph of STR total ankle (Scandinavian Total nkle Replacement, Waldemar Link) shows ankle subluxation and lateral migration of polyethylene spacer (arrow) with resultant malalignment. Such changes often occur as result of lateral ligamentous instability. Note suture anchor (arrowhead) from lateral ligamentous reconstruction performed at time of STR device placement., Coronal CT scan confirms significant lateral migration of polyethylene spacer (arrow) and facilitates more detailed evaluation of morphology and integrity of polyethylene component. Note loss of normally parallel superior and inferior surfaces of polyethylene spacer due to asymmetric wear medially (asterisk) JR:190, pril 2008
12 Total nkle rthroplasty Downloaded from by on 11/26/17 from IP address Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved C Fig. 14 Fracture of polyethylene component in 69-year-old man., nteroposterior radiograph of STR total ankle (Scandinavian Total nkle Replacement, Waldemar Link) suggests damage to polyethylene spacer, as evidenced by abnormal lateral migration of wire marker embedded in spacer (arrow). and C, xial () and sagittal (C) CT images confirm fractured polyethylene component (asterisk). Note concomitant polyethylene osteolysis in tibia (arrow, C) that predominantly involves posterior aspect of zone. D, Gross photograph of resected fractured polyethylene component. FOR YOUR INFORMTION This article is available for CME credit. See for more information. D JR:190, pril
Design Project. Dr. Kevin O Kelly, TCD
 Design Project Project title: Mentor: Total Ankle Replacement Dr. Kevin O Kelly, TCD Background The ankle joint is a comparatively small joint relative to the weight bearing and torque it must withstand.
Design Project Project title: Mentor: Total Ankle Replacement Dr. Kevin O Kelly, TCD Background The ankle joint is a comparatively small joint relative to the weight bearing and torque it must withstand.
Total Ankle Arthroplasty: A Radiographic Outcome Study
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Lee et al. Outcome of Total nkle rthroplasty Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research mie Y. Lee 1 lice S. Ha 1 Jonelle M. Petscavage 2 Felix S. Chew 1 Lee Y,
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Lee et al. Outcome of Total nkle rthroplasty Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research mie Y. Lee 1 lice S. Ha 1 Jonelle M. Petscavage 2 Felix S. Chew 1 Lee Y,
Total Ankle Arthroplasty. Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopedics & Sports Medicine the original 2014
 Total Ankle Arthroplasty Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopedics & Sports Medicine the original 2014 Ankle Anatomy The ankle is a hinge or ginglymus joint Made up of the tibia, fibula, & talus
Total Ankle Arthroplasty Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopedics & Sports Medicine the original 2014 Ankle Anatomy The ankle is a hinge or ginglymus joint Made up of the tibia, fibula, & talus
Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement
 016625 REVISION R INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement CASE STUDY Patient History The patient was a 65-year-old
016625 REVISION R INVISION Total Ankle Replacement System with PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Revision of a Failed Agility Total Ankle Replacement CASE STUDY Patient History The patient was a 65-year-old
> ZIMMER Total Ankle Arthroplasty. Fabian Krause Inselspital, University of Berne
 Fabian Krause Inselspital, University of Berne 1 > 9/14 > 76 years, female > Posttraumatic end-stage ankle arthrosis > Ankle ROM D/F 10-0-20 2 > 2/15 3 > 1/17 > Ongoing anterior ankle pain, ankle ROM restricted,
Fabian Krause Inselspital, University of Berne 1 > 9/14 > 76 years, female > Posttraumatic end-stage ankle arthrosis > Ankle ROM D/F 10-0-20 2 > 2/15 3 > 1/17 > Ongoing anterior ankle pain, ankle ROM restricted,
ANKLE ARTHRITIS, ARTHRODESIS, & ARTHROPLASTY
 Surgical Management of Ankle Arthritis James J Sferra, MD Allegheny Health Network Director, Division of Foot &Ankle Orthopaedic Institute Allegheny Orthopaedic Associates ANKLE ARTHRITIS, ARTHRODESIS,
Surgical Management of Ankle Arthritis James J Sferra, MD Allegheny Health Network Director, Division of Foot &Ankle Orthopaedic Institute Allegheny Orthopaedic Associates ANKLE ARTHRITIS, ARTHRODESIS,
A Modular S tem-fixed B earing Total Ankle R eplacement: A Two Year Follow Up of 27 Cons ecutive Cas es
 A Modular S tem-fixed B earing Total Ankle R eplacement: A Two Year Follow Up of 27 Cons ecutive Cas es Stephen A. Brigido, DPM, FACFAS Director, Fellowship for Foot and Ankle Reconstruction, Coordinated
A Modular S tem-fixed B earing Total Ankle R eplacement: A Two Year Follow Up of 27 Cons ecutive Cas es Stephen A. Brigido, DPM, FACFAS Director, Fellowship for Foot and Ankle Reconstruction, Coordinated
Competence of the Deltoid Ligament in Bimalleolar Ankle Fractures After Medial Malleolar Fixation *
 Competence of the Deltoid Ligament in Bimalleolar Ankle Fractures After Medial Malleolar Fixation * BY PAUL TORNETTA, III, M.D. Investigation performed at Kings County Hospital, New York, N.Y. Abstract
Competence of the Deltoid Ligament in Bimalleolar Ankle Fractures After Medial Malleolar Fixation * BY PAUL TORNETTA, III, M.D. Investigation performed at Kings County Hospital, New York, N.Y. Abstract
EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Benkovich V. Perry T., Bunin A., Bilenko V., Unit for Joint Arthroplasty, Soroka Medical Center Ben Gurion University of Negev Beer
EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Benkovich V. Perry T., Bunin A., Bilenko V., Unit for Joint Arthroplasty, Soroka Medical Center Ben Gurion University of Negev Beer
Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
JOINT RULER. Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement
 JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE GUIDE
 DANGER indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious injury. WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result
DANGER indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious injury. WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Original Report. Sonography of Ankle Tendon Impingement with Surgical Correlation
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 162.158.89.91 on 08/23/18 from IP address 162.158.89.91. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Monisha Shetty 1 David P. Fessell 1 John E. Femino
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 162.158.89.91 on 08/23/18 from IP address 162.158.89.91. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Monisha Shetty 1 David P. Fessell 1 John E. Femino
LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System.
 LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterior Ankle Arthrodesis Plates. Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP) System. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction
Chapter 25 Revision Total Ankle Arthroplasty: Managing Osteolysis and Subsidence
 Chapter 25 Revision Total Ankle Arthroplasty: Managing Osteolysis and Subsidence James A. Nunley, MD Indications A review of 2,240 total ankle arthroplasties (TAAs) from multiple studies with adequate
Chapter 25 Revision Total Ankle Arthroplasty: Managing Osteolysis and Subsidence James A. Nunley, MD Indications A review of 2,240 total ankle arthroplasties (TAAs) from multiple studies with adequate
Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION
 Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal Fibular
Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal Fibular
Optimum implant geometry
 Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA)
 TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
28 Surgical Technique
 Surgical Technique 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 28 26 Technique described by James L. Guyton, MD Campbell Clinic Memphis, Tennessee James W. Harkess, MD Campbell Clinic Memphis, Tennessee David G. LaVelle,
Surgical Technique 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 28 26 Technique described by James L. Guyton, MD Campbell Clinic Memphis, Tennessee James W. Harkess, MD Campbell Clinic Memphis, Tennessee David G. LaVelle,
Extramedullary Tibial Preparation
 Surgical Technique Extramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Extramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 EM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
Surgical Technique Extramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Extramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 EM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique. Description of Plate
 Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique Description of Plate Merete Medical has designed the PlantarMax; a special Plantar/Medial Locking Lapidus plate which places the plate in the most biomechanically
Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique Description of Plate Merete Medical has designed the PlantarMax; a special Plantar/Medial Locking Lapidus plate which places the plate in the most biomechanically
Bipolar Radial Head System
 Bipolar Radial Head System Katalyst Surgical Technique DESCRIPTION The Katalyst Telescoping Bipolar Radial Head implant restores the support and bearing surface of the radial head in the face of fracture,
Bipolar Radial Head System Katalyst Surgical Technique DESCRIPTION The Katalyst Telescoping Bipolar Radial Head implant restores the support and bearing surface of the radial head in the face of fracture,
Encina Taper Stem. Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA
 Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA 94065 info@stinsonortho.com www.stinsonortho.com Table of Contents Introduction 3 Features 4 Surgical Technique 5 Preoperative
Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA 94065 info@stinsonortho.com www.stinsonortho.com Table of Contents Introduction 3 Features 4 Surgical Technique 5 Preoperative
Total ankle replacement by the Ankle Evolution System
 Total ankle replacement by the Ankle Evolution System MEDIUM-TERM OUTCOME S. S. Morgan, B. Brooke, N. J. Harris From Chapel Allerton Hospital, Leeds, England We present the outcomes in 38 consecutive patients
Total ankle replacement by the Ankle Evolution System MEDIUM-TERM OUTCOME S. S. Morgan, B. Brooke, N. J. Harris From Chapel Allerton Hospital, Leeds, England We present the outcomes in 38 consecutive patients
CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS
 CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Fix single column or both: Always fix both. A study by Svend-Hansen corroborated the poor results associated with isolated medial malleolar fixation in bimalleolar ankle fractures.
CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Fix single column or both: Always fix both. A study by Svend-Hansen corroborated the poor results associated with isolated medial malleolar fixation in bimalleolar ankle fractures.
Zenith. Total Ankle Replacement Surgical technique
 Total Ankle Replacement Surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative planning and templating 6 Patient positioning 6 Exposure 6 Saw blades 7 Joint line definition 7 Tibial alignment jig
Total Ankle Replacement Surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative planning and templating 6 Patient positioning 6 Exposure 6 Saw blades 7 Joint line definition 7 Tibial alignment jig
TIBIAXYS ANKLE FUSION
 TIBIAXYS ANKLE FUSION SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TIBIAXYS Ankle Fusion Plate features Anatomically contoured plates The plates are designed to approximate the patient s bony and soft tissue anatomy The plate designs
TIBIAXYS ANKLE FUSION SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TIBIAXYS Ankle Fusion Plate features Anatomically contoured plates The plates are designed to approximate the patient s bony and soft tissue anatomy The plate designs
Optimizing function Maximizing survivorship Accelerating recovery
 Surgical Technique Optimizing Function Maximizing Survivorship Accelerating Recovery The company believes in an approach to patient treatment that places equal importance on: Optimizing function Maximizing
Surgical Technique Optimizing Function Maximizing Survivorship Accelerating Recovery The company believes in an approach to patient treatment that places equal importance on: Optimizing function Maximizing
Integra. Katalyst Bipolar Radial Head System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 Integra Katalyst Bipolar Radial Head System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Surgical Technique As the manufacturer of this device, Integra does not practice medicine and does not recommend this or any other surgical
Integra Katalyst Bipolar Radial Head System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Surgical Technique As the manufacturer of this device, Integra does not practice medicine and does not recommend this or any other surgical
Talar Dome System Surgical Technique
 Talar Dome System Surgical Technique CAP TALAR DOME RESURFACING HEMIARTHROPLASTY IMPLANT Surgical Technique Guide Description The HemiCAP Contoured Articular Prosthetic incorporates an articular resurfacing
Talar Dome System Surgical Technique CAP TALAR DOME RESURFACING HEMIARTHROPLASTY IMPLANT Surgical Technique Guide Description The HemiCAP Contoured Articular Prosthetic incorporates an articular resurfacing
Clinical. Solutions. Synthes Solutions. Foot and Ankle.
 Clinical Solutions Foot and Ankle. Foot and Ankle. Fractures of the tibial shaft Fractures of the distal fibula Fractures of the distal tibia Fractures and osteotomies of the calcaneus Arthrodesis Fractures,
Clinical Solutions Foot and Ankle. Foot and Ankle. Fractures of the tibial shaft Fractures of the distal fibula Fractures of the distal tibia Fractures and osteotomies of the calcaneus Arthrodesis Fractures,
Clinical Policy Bulletin: Total Ankle Arthroplasty
 Go Clinical Policy Bulletin: Total Ankle Arthroplasty Number: 0645 Policy *Please see amendment for Pennsylvania Medicaid at the end of this CPB. Aetna considers total ankle arthroplasty (TAA) using a
Go Clinical Policy Bulletin: Total Ankle Arthroplasty Number: 0645 Policy *Please see amendment for Pennsylvania Medicaid at the end of this CPB. Aetna considers total ankle arthroplasty (TAA) using a
Revolution. Unicompartmental Knee System
 Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Integra. Salto Talaris Total Ankle Prosthesis PATIENT INFORMATION
 Integra Salto Talaris Total Ankle Prosthesis PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal
Integra Salto Talaris Total Ankle Prosthesis PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
Increasing surgical freedom Restoring patient function
 Increasing surgical freedom Restoring patient function Fracture specific plating solutions for the most common tibia and fibula fractures Frequency of fracture occurrences* 66% 61% 36% 36% 28% 14% 20%
Increasing surgical freedom Restoring patient function Fracture specific plating solutions for the most common tibia and fibula fractures Frequency of fracture occurrences* 66% 61% 36% 36% 28% 14% 20%
PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES
 C H A P T E R 1 2 PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM (The opinions of the author should not be considered as reflecting official policy of the US Army Medical Department.) Pronation-abduction
C H A P T E R 1 2 PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM (The opinions of the author should not be considered as reflecting official policy of the US Army Medical Department.) Pronation-abduction
PLR. Proximal Loading Revision Hip System
 PLR Proximal Loading Revision Hip System The PLR splined revision stem is designed to recreate the natural stresses in the revised femur, where proximal bone may be compromised. PLR Hip System Design Considerations
PLR Proximal Loading Revision Hip System The PLR splined revision stem is designed to recreate the natural stresses in the revised femur, where proximal bone may be compromised. PLR Hip System Design Considerations
Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2, Patrick Smith, M.D. 2, and Larry S. Matthews, M.D. 2
 Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Zimmer Trabecular Metal Ankle Interpositional Spacer and Trabecular Metal Ankle Fusion Spacer
 Zimmer Trabecular Metal Ankle Interpositional Spacer and Trabecular Metal Ankle Fusion Spacer Surgical Technique 2 Zimmer Trabecular Metal Ankle Interpositional Spacer and Trabecular Metal Ankle Fusion
Zimmer Trabecular Metal Ankle Interpositional Spacer and Trabecular Metal Ankle Fusion Spacer Surgical Technique 2 Zimmer Trabecular Metal Ankle Interpositional Spacer and Trabecular Metal Ankle Fusion
Knee Replacement Implants
 Knee Replacement Implants During knee replacement surgery, an orthopaedic surgeon will resurface your damaged knee with artificial components, called implants. There are many different types of implants.
Knee Replacement Implants During knee replacement surgery, an orthopaedic surgeon will resurface your damaged knee with artificial components, called implants. There are many different types of implants.
Intramedullary Tibial Preparation
 Surgical Technique Intramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Intramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 IM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
Surgical Technique Intramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Intramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 IM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
Salto Talaris Total Ankle Prosthesis
 Instructions for Use Salto Talaris Total Ankle Prosthesis Federal (USA) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Important The manufacturer recommends that all personnel responsible
Instructions for Use Salto Talaris Total Ankle Prosthesis Federal (USA) law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. Important The manufacturer recommends that all personnel responsible
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement
 Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Bone Preservation Stem
 TRI-LOCK Bone Preservation Stem Featuring GRIPTION Coating Surgical Technique Implant Geometry Extending the TRI-LOCK Stem heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was
TRI-LOCK Bone Preservation Stem Featuring GRIPTION Coating Surgical Technique Implant Geometry Extending the TRI-LOCK Stem heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was
Types of Plates 1. New Dynamic Compression Plate: Diaphyseal fracture: Radius, Ulna, Humerus, Rarely tibia
 Types of Plates 1. New Dynamic Compression Plate: DCP Diaphyseal fracture: Radius, Ulna, Humerus, Rarely tibia 1. Undercut adjacent to the holes low contact: less stress shield 2. Undercut at the undersurface
Types of Plates 1. New Dynamic Compression Plate: DCP Diaphyseal fracture: Radius, Ulna, Humerus, Rarely tibia 1. Undercut adjacent to the holes low contact: less stress shield 2. Undercut at the undersurface
FIBULAR & SYNDESMOSIS MALUNIONS
 FIBULAR & SYNDESMOSIS MALUNIONS MICHAEL P. CLARE, MD FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE TAMPA, FL USA MORTISE INHERENTLY UNSTABLE LATERAL MALLEOLUS ACTS AS BUTTRESS / POST RESIST LATERAL TRANSLATION OF TALUS
FIBULAR & SYNDESMOSIS MALUNIONS MICHAEL P. CLARE, MD FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE TAMPA, FL USA MORTISE INHERENTLY UNSTABLE LATERAL MALLEOLUS ACTS AS BUTTRESS / POST RESIST LATERAL TRANSLATION OF TALUS
Surgical Technique Guide
 Guide CAUTION: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. INDICATIONS FOR USE The Align Anterior Ankle Fusion Plate is intended to facilitate arthrodesis of the
Guide CAUTION: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. INDICATIONS FOR USE The Align Anterior Ankle Fusion Plate is intended to facilitate arthrodesis of the
EXTENDED TROCHANTERIC OSTEOTOMY SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FPO EXTENSIVELY COATED FIXATION
 EXTENDED TROCHANTERIC OSTEOTOMY SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FPO EXTENSIVELY COATED FIXATION SINCE 1983 PREOPERATIVE PLANNING EXPLANTATION OPTIONS the cement from inside the cement canal until the bone/ cement bond
EXTENDED TROCHANTERIC OSTEOTOMY SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FPO EXTENSIVELY COATED FIXATION SINCE 1983 PREOPERATIVE PLANNING EXPLANTATION OPTIONS the cement from inside the cement canal until the bone/ cement bond
THE P.F.C. SIGMA FEMORAL ADAPTER. Surgical Technique
 THE P.F.C. SIGMA FEMORAL ADAPTER Surgical Technique Contents P.F.C. Sigma Femoral Adapter and Revision Knee Surgery Introduction 2 Preoperative Planning 2 Overview 3 Surgical Technique Preparation of the
THE P.F.C. SIGMA FEMORAL ADAPTER Surgical Technique Contents P.F.C. Sigma Femoral Adapter and Revision Knee Surgery Introduction 2 Preoperative Planning 2 Overview 3 Surgical Technique Preparation of the
Conversion of Pantalar fusion to total ankle replacement: A case Review. Key words: Pantalar fusion, non-union and total ankle replacement
 The Northern Ohio Foot and Ankle Journal Official Publication of the NOFA Foundation Conversion of Pantalar fusion to total ankle replacement: A case Review Author: Bryan Williams DPM 1 and Jonathan Sharpe
The Northern Ohio Foot and Ankle Journal Official Publication of the NOFA Foundation Conversion of Pantalar fusion to total ankle replacement: A case Review Author: Bryan Williams DPM 1 and Jonathan Sharpe
R/F. Can T-smart Tomosynthesis Improve Diagnostic Accuracy on THA Component Stability? 1. Abstract
 R/F Can T-smart Tomosynthesis Improve Diagnostic Accuracy on THA Component Stability? Professor and Chair Dept. of Adult Reconstructive Surgery Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, the 4th Clinical College of PKU
R/F Can T-smart Tomosynthesis Improve Diagnostic Accuracy on THA Component Stability? Professor and Chair Dept. of Adult Reconstructive Surgery Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, the 4th Clinical College of PKU
ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 E C H E L O N P R I M A R Y H I P S Y S T E M P R O D U C T R A T I O N A L E ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY Echelon Primary Total Hip System HIGH OFFSET STANDARD OFFSET Cementless
E C H E L O N P R I M A R Y H I P S Y S T E M P R O D U C T R A T I O N A L E ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY Echelon Primary Total Hip System HIGH OFFSET STANDARD OFFSET Cementless
ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES
 CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
Merete BLP. Surgical Technique. - Bunion Locking Plate - Low Profile Locking Bone Plate System
 Merete BLP - Bunion Locking Plate - Low Profile Locking Bone Plate System Surgical Technique Merete Medical, Inc. 49 Purchase Street Rye, N.Y. 10580 Phone: 914 967-1532 www.merete-medical.com - Surgical
Merete BLP - Bunion Locking Plate - Low Profile Locking Bone Plate System Surgical Technique Merete Medical, Inc. 49 Purchase Street Rye, N.Y. 10580 Phone: 914 967-1532 www.merete-medical.com - Surgical
Hallux Valgus Deformity: Preoperative Radiologic Assessment
 119 Pictorial Essay H............ - Hallux Valgus Deformity: Preoperative Radiologic Assessment David Karasick1 and Keith L. Wapner An estimated 40% of the American adult population experiences foot problems,
119 Pictorial Essay H............ - Hallux Valgus Deformity: Preoperative Radiologic Assessment David Karasick1 and Keith L. Wapner An estimated 40% of the American adult population experiences foot problems,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
SIMITRI STABLE IN STRIDE SURGICAL PROCEDURE
 Copyright 2016 NGD. All rights reserved Neil Embleton, B.Sc., DVM and Veronica Barkowski, DVM Helivet Mobile Surgical Services, Sundre, AB, Canada July 2016 SIMITRI STABLE IN STRIDE SURGICAL PROCEDURE
Copyright 2016 NGD. All rights reserved Neil Embleton, B.Sc., DVM and Veronica Barkowski, DVM Helivet Mobile Surgical Services, Sundre, AB, Canada July 2016 SIMITRI STABLE IN STRIDE SURGICAL PROCEDURE
comprehensive Design Rationale shoulder system Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI TEchnology
 comprehensive shoulder system Design Rationale Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI TEchnology . INTRODUCTION The Comprehensive Shoulder System is an evolutionary design based on the successful
comprehensive shoulder system Design Rationale Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI TEchnology . INTRODUCTION The Comprehensive Shoulder System is an evolutionary design based on the successful
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR
 CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation.
 LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
Aesculap Targon FN. Head Preserving Solution for Medial Femoral Neck Fractures. Aesculap Orthopaedics
 Aesculap Targon FN Head Preserving Solution for Medial Femoral Neck Fractures Aesculap Orthopaedics Targon FN Operating Technique Indications for Targon FN AO 3 B. AO 3 B.2 AO 3 B.3 Undisplaced intracapsular
Aesculap Targon FN Head Preserving Solution for Medial Femoral Neck Fractures Aesculap Orthopaedics Targon FN Operating Technique Indications for Targon FN AO 3 B. AO 3 B.2 AO 3 B.3 Undisplaced intracapsular
CAUTION: Ceramic liners are not approved for use in the United States.
 Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2. Preparation of the Acetabulum 4. Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5.
 Surgical Technique Contents Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5 Cup Positioning 6 Joint Stability 7 Trial sizing and Impaction
Surgical Technique Contents Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5 Cup Positioning 6 Joint Stability 7 Trial sizing and Impaction
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CHI. Cannulated Hemi Implants 1 ST MPJ ARTHROPLASTY
 CHI Cannulated Hemi Implants 1 ST MPJ ARTHROPLASTY SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CHI Cannulated Hemi Implants Design Rationale Pain of the great toe joint often leads to altered lifestyles. The goal of MPJ implant
CHI Cannulated Hemi Implants 1 ST MPJ ARTHROPLASTY SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CHI Cannulated Hemi Implants Design Rationale Pain of the great toe joint often leads to altered lifestyles. The goal of MPJ implant
Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W.
 University of Groningen Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W. Published in: Knee DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.007
University of Groningen Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W. Published in: Knee DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.007
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Zenith. Total Ankle Replacement Surgical technique
 Total Ankle Replacement Surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative planning and templating 6 Patient positioning 6 Exposure 6 Saw blades 7 Joint line definition 7 Tibial alignment jig
Total Ankle Replacement Surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative planning and templating 6 Patient positioning 6 Exposure 6 Saw blades 7 Joint line definition 7 Tibial alignment jig
Duration of Follow-up (mo)
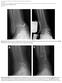 Page 1 of 7 Fig. E-1 Fig. E-2 Fig. E-1 Medial ankle arthritis with medial translation of the talus and mortise widening. Note the shape of the medial malleolus (white arrow). Fig. E-2 Measurement of mortise
Page 1 of 7 Fig. E-1 Fig. E-2 Fig. E-1 Medial ankle arthritis with medial translation of the talus and mortise widening. Note the shape of the medial malleolus (white arrow). Fig. E-2 Measurement of mortise
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?
![Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?](/thumbs/78/78456133.jpg) Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Surgical Technique. Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Ankle Syndesmosis Repair, Operative Technique
 Surgical Technique Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Ankle Syndesmosis Repair, Operative Technique INVISIKNOT Ankle Syndesmosis Repair Surgical Technique The following technique guide was prepared under close
Surgical Technique Foot and Ankle Technique Guide Ankle Syndesmosis Repair, Operative Technique INVISIKNOT Ankle Syndesmosis Repair Surgical Technique The following technique guide was prepared under close
Conversion of Anatomic TSA to RSA
 Conversion of Anatomic TSA to RSA Joseph A. Abboud, M.D. Professor of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Senior Vice-President at the Rothman Institute Philadelphia, PA Disclosures Joseph A. Abboud, MD Depuy Synthes
Conversion of Anatomic TSA to RSA Joseph A. Abboud, M.D. Professor of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Senior Vice-President at the Rothman Institute Philadelphia, PA Disclosures Joseph A. Abboud, MD Depuy Synthes
Locking Radial Head Plates
 Locking Radial Head Plates Locking Radial Head Plates Since 1988, Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopaedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients. Our strategy
Locking Radial Head Plates Locking Radial Head Plates Since 1988, Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopaedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients. Our strategy
Late Results of Total Shoulder Replacement in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 366, pp. 39-45 0 1999 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Late Results of Total Shoulder Replacement in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Jens 0. S@jbjerg,
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 366, pp. 39-45 0 1999 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Late Results of Total Shoulder Replacement in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Jens 0. S@jbjerg,
DESIGN RATIONALE AND SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 DESIGN RATIONALE AND SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ANCHOR PEG GLENOID DESIGN RATIONALE In total shoulder arthroplasty, most cases of clinical and radiographic loosening involve failure of the fixation of the glenoid
DESIGN RATIONALE AND SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ANCHOR PEG GLENOID DESIGN RATIONALE In total shoulder arthroplasty, most cases of clinical and radiographic loosening involve failure of the fixation of the glenoid
Cementless Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement shows reduced radiolucency at one year
 Cementless Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement shows reduced radiolucency at one year H. Pandit, C. Jenkins, D. J. Beard, J. Gallagher, A. J. Price, C. A. F. Dodd, J. W. Goodfellow, D. W. Murray From
Cementless Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement shows reduced radiolucency at one year H. Pandit, C. Jenkins, D. J. Beard, J. Gallagher, A. J. Price, C. A. F. Dodd, J. W. Goodfellow, D. W. Murray From
Shunsaku Nishihara 1, Nobuhiko Sugano 1, Takashi Nishii 1, Hisashi Tanaka 2, Hideki Yoshikawa 1, and Takahiro Ochi 1
 J Orthop Sci (2003) 8:352 360 Comparison of the fit and fill between the Anatomic Hip femoral component and the VerSys Taper femoral component using virtual implantation on the ORTHODOC workstation Shunsaku
J Orthop Sci (2003) 8:352 360 Comparison of the fit and fill between the Anatomic Hip femoral component and the VerSys Taper femoral component using virtual implantation on the ORTHODOC workstation Shunsaku
Knee Surgical Technique
 Knee Surgical Technique COMPASS Universal Hinge by Jimmy Tucker, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgeon Director, Arkansas Sports Medicine, P.A. Little Rock, Arkansas Table of contents Design features 3 Indications
Knee Surgical Technique COMPASS Universal Hinge by Jimmy Tucker, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgeon Director, Arkansas Sports Medicine, P.A. Little Rock, Arkansas Table of contents Design features 3 Indications
Total ankle replacement in moderate to severe varus deformity of the ankle
 Total ankle replacement in moderate to severe varus deformity of the ankle B. S. Kim, W. J. Choi, Y. S. Kim, J. W. Lee From Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Our study describes the clinical
Total ankle replacement in moderate to severe varus deformity of the ankle B. S. Kim, W. J. Choi, Y. S. Kim, J. W. Lee From Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Our study describes the clinical
Exposure EXPOSURE. Exposure - Incision. Extend old incision proximally Expose virgin quadriceps tendon
 Exposure Aaron G Rosenberg MD Professor of Orthopedic Surgery Rush Medical College Chicago, Illinois Exposure - Incision Single incision can be used or modified Multiple longitudinal incisions favor the
Exposure Aaron G Rosenberg MD Professor of Orthopedic Surgery Rush Medical College Chicago, Illinois Exposure - Incision Single incision can be used or modified Multiple longitudinal incisions favor the
Total ankle replacement
 Total ankle replacement THE RESULTS IN 200 ANKLES P. L. R. Wood, S. Deakin From Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, England B etween 1993 and 2000 we implanted 200 cementless, mobile-bearing STAR total ankle
Total ankle replacement THE RESULTS IN 200 ANKLES P. L. R. Wood, S. Deakin From Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, England B etween 1993 and 2000 we implanted 200 cementless, mobile-bearing STAR total ankle
2:00 3:00 pm SESSION 6: ANKLE ARTHROPLASTY. Moderators: Steven L. Haddad, MD (Glenview, Illinois)
 2:00 3:00 pm SESSION 6: ANKLE ARTHROPLASTY Moderators: Steven L. Haddad, MD (Glenview, Illinois) John S. Reach, Jr, M.Sc., MD (New Haven, Connecticut) 133 2:00 2:15 pm SESSION 6: Varus, Valgus Whatever!
2:00 3:00 pm SESSION 6: ANKLE ARTHROPLASTY Moderators: Steven L. Haddad, MD (Glenview, Illinois) John S. Reach, Jr, M.Sc., MD (New Haven, Connecticut) 133 2:00 2:15 pm SESSION 6: Varus, Valgus Whatever!
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending the proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending the proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Ten-Year Evaluation of Cementless Buechel-Pappas Meniscal Bearing Total Ankle Replacement
 FOOT &ANKLE INTERNATIONAL Copyright 2003 by the American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society, Inc. Ten-Year Evaluation of Cementless Buechel-Pappas Meniscal Bearing Total Ankle Replacement Frederick F. Buechel,
FOOT &ANKLE INTERNATIONAL Copyright 2003 by the American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society, Inc. Ten-Year Evaluation of Cementless Buechel-Pappas Meniscal Bearing Total Ankle Replacement Frederick F. Buechel,
Surgical Technique. Fibula Rod System
 Surgical Technique Fibula Rod System Acumed is a global leader of innovative orthopaedic and medical solutions. We are dedicated to developing products, service methods, and approaches that improve patient
Surgical Technique Fibula Rod System Acumed is a global leader of innovative orthopaedic and medical solutions. We are dedicated to developing products, service methods, and approaches that improve patient
Radiographic Assessment of Pediatric Foot Alignment: Self-Assessment Module
 1.5 CME AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Radiographic Assessment of Pediatric Foot Alignment: Self-Assessment Module Mahesh M. Thapa 1,2, Sumit Pruthi 1,2, Felix S. Chew 2 ABSTRACT
1.5 CME AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Radiographic Assessment of Pediatric Foot Alignment: Self-Assessment Module Mahesh M. Thapa 1,2, Sumit Pruthi 1,2, Felix S. Chew 2 ABSTRACT
Fractures of the Ankle Region in the Skeletally Immature Patient. The Salter Classification is Worthless!!
 Fractures of the Ankle Region in the Skeletally Immature Patient. The Salter Classification is Worthless!! Kaye E Wilkins D.V.M,M.D. President's Council/Dielmann Chair in Pediatric Orthopedics Professor
Fractures of the Ankle Region in the Skeletally Immature Patient. The Salter Classification is Worthless!! Kaye E Wilkins D.V.M,M.D. President's Council/Dielmann Chair in Pediatric Orthopedics Professor
Aseptic Revision Total Knee Surgical Techniques. Andrew Ehmke, DO Chicago, IL May 5, 2018
 Aseptic Revision Total Knee Surgical Techniques Andrew Ehmke, DO Chicago, IL May 5, 2018 I have no disclosures relevant to this talk 3 Phases of Revision 1. Exposure Key to the case!! 2. Component Removal
Aseptic Revision Total Knee Surgical Techniques Andrew Ehmke, DO Chicago, IL May 5, 2018 I have no disclosures relevant to this talk 3 Phases of Revision 1. Exposure Key to the case!! 2. Component Removal
Fibula Rod System. Lateral Malleolus Fracture Indications:
 Fibula Rod System Fibula Rod System Since 1988, Acumed has been designing solutions for the demanding situations facing orthopaedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients. Our strategy has been to know
Fibula Rod System Fibula Rod System Since 1988, Acumed has been designing solutions for the demanding situations facing orthopaedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients. Our strategy has been to know
Knee Revision. Portfolio
 Knee Revision Portfolio I use the DePuy Revision Knee System because of its versatility. With this system I can solve nearly any situation I encounter in the OR. Dr. Thomas Fehring, OrthoCarolina Hip and
Knee Revision Portfolio I use the DePuy Revision Knee System because of its versatility. With this system I can solve nearly any situation I encounter in the OR. Dr. Thomas Fehring, OrthoCarolina Hip and
