Review Article A Review of Treatments for Iliotibial Band Syndrome in the Athletic Population
|
|
|
- Percival James
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sports Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID , 6 pages Review Article A Review of Treatments for Iliotibial Band Syndrome in the Athletic Population Corey Beals 1 and David Flanigan 2 1 Department of Surgery, Wexner Medical Center, 395 W. 12th Avenue Columbus, OH 43210, USA 2 Department of Sports Medicine, Wexner Medical Center, 2050 Kenny Road, Suite 3100 Columbus, OH 43221, USA Correspondence should be addressed to David Flanigan; david.flanigan@osumc.edu Received 11 July 2013; Accepted 29 August 2013 Academic Editor: Adrian W. Midgley Copyright 2013 C. Beals and D. Flanigan. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS) is a common injury in runners and other long distance athletes with the best management options not clearly established. This review outlines both the conservative and surgical options for the treatment of iliotibial band syndrome in the athletic population. Ten studies met the inclusion criteria by focusing on the athletic population in their discussion of the treatment for iliotibial band syndrome, both conservative and surgical. Conservative management consisting of a combination of rest (2 6 weeks), stretching, pain management, and modification of running habits produced a 44% complete cure rate, with return to sport at 8 weeks and a 91.7% cure rate with return to sport at 6 months after injury. Surgical therapy, often only used for refractory cases, consisted of excision or release of the pathologic distal portion of the iliotibial band or bursectomy. Those studies focusing on the excision or release of the pathologic distal portion of the iliotibial band showed a 100% return to sport rate at both 7 weeks and 3 months after injury. Despite many options for both surgical and conservative treatment, there has yet to be consensus on onestandardofcare.certaintreatments,bothconservativeandsurgical,inourreviewareshowntobemoreeffectivethanothers; however, further research is needed to delineate the true pathophysiology of iliotibial band syndrome in athletes, as well as the optimal treatment regimen. 1. Introduction Iliotibial band syndrome is a common knee injury caused by inflammation of the distal portion of the iliotibial band (ITB), which results in lateral knee pain. The distal iliotibial band slides over the lateral femoral epicondyle, and during repetitive flexion and extension activities of the knee excessive friction and potential irritation results in pain. Potential risk factors for the development of iliotibial band syndrome include preexisting iliotibial band tightness, high weekly mileage, time spent walking or running on a track, interval training, and muscular weakness of knee extensors, flexors, and hip abductors [1, 2]. Populations who expose their knees to a greater amount of flexion and extension activities, such as athletes, particularly long distance athletes, put themselves at a higher risk for iliotibial band syndrome. Due to the pathophysiology of IT band syndrome, runners have been a group often looked at for prevalence and management of this syndrome. ITB syndrome has been documented to have as high as a 22.2% incidence of all lower extremity injuries in runners [3]. Despite a clear pathophysiology, it is unclear why this syndrome affects some athletes greater than others. Few studies have shown any direct relationship between biomechanical factors and the development of iliotibial bad syndrome [1, 2, 4 6]. Athletes with ITB syndrome typically complain of a sharp or burning pain roughly 2 cm superior to the lateral joint line [3]. The pain may radiate proximally or distally, and in less severe cases, the pain may quickly subside upon cessation of activities. Often pain will occur as activities proceed. It is not uncommon that the athlete will experience popping on the lateral aspect of the knee with activities. ITB syndrome is a clinical diagnosis and most often additional diagnostic studies are not necessary. It should be suspected in overuse and nontraumatic cases of knee pain where rest has not been helpful. Ober s test is one
2 2 Sports Medicine Application of further exclusion criteria (level 4, 5 evidence, non- English, n=11) Potentially relevant studies identified and screened (n = 176) Studies addressing irrelevant topics, not addressing treatment of ITBS (n = 64) Studies discussing treatment of ITBS (n = 112) Studies not specifically addressing athletes (n = 91) Studies specifically addressing athletes (n = 21) Studies reviewed (n = 10) Figure 1: Flow chart displaying search process for review. of numerous physical exam tests often used to assess the tightness of the ITB. If the leg can be passively stretched to a position horizontal but not completely adducted to a table, this constitutes minimal tightness. If the leg can be passively adducted to horizontal at best, this constitutes moderate tightness, and if it cannot be passively adducted to horizontal, this is maximal tightness [7].Popping of the ITB over the lateral femoral condyle can also occur in this position as the knee is brought through range of motion. Palpation over the ITB during this maneuver typically will reproduce pain. History, however, is much more important than physical exam in diagnosis and short-term resolution of symptoms following corticosteroid injection and be both diagnostic and therapeutic. MRI may be of use if there is doubt about the diagnosis as well as to exclude an intra-articular problem such as a lateral meniscal tear; however, isolated ITBFS often does not lead to MRI abnormalities and can be misdiagnosed if a minor but different lesion is present. Two studies revealed that in patients with iliotibial band syndrome, MRI studies have shown that the distal portion of the ITB may thicken, and a bursa deep to the iliotibial band over the lateral epicondyle becomes inflamed and filled with fluid [8, 9]. When the athletic population was isolated, normal, or cystic, poorly defined signal intensities at the distal portion of the ITB predominated. Only in chronic cases was a thickening of the distal ITB at the level of the lateral femoral epicondyle seen [8]. While the majority of patients respond to a nonsurgical, conservative approach, this does not occur for all, and escalation of treatment is necessary. This is especially true in athletes that present with refractory cases, and at this time surgical intervention can be used [3]. Unfortunately, refractory cases can occur quite often, and no treatment has been shown to work best. The purpose of this review is to outline both the conservative and surgical options for treatment of iliotibial band syndrome in athletes. 2. Methods In order to find the most current treatment options for ITB syndrome in athletes, a literature search was conducted in the PubMed database. Criteria for inclusion in this review were papers that primarily (but not exclusively) focused on the athletic population, achieved a level III or greater level of evidence, addressed therapeutic options for ITB syndrome (conservative or surgical), and were written in English. An initial search of iliotibial band syndrome yielded 176 results. After limiting the results to those articles that discussed treatment options, and focused on the athletic population, 10 articles were reviewed. Figure 1 outlines the sequence of the literature search.
3 Sports Medicine 3 Table 1: Conservative treatment. Study Schwellnus et al. [10] Gunter and Schwellnus [11] Pinshaw et al. [12] Fredericson et al. [2] Number of participants Study type 43 runners RCT 18 runners RCT 24 runners 24 (10 M 14 F) injured runners, 30 (16 M 14 F) controls Case series Case series Therapeutic regimen (all groups) Day 0 7: rest ice and medication, daily stretching Days 3, 5, and 7 DTFM No running for 14 days after injection and ice for 30 min every 12 hrs. Softer running shoes, correct leg-length discrepancies, reduce training distance, ice 30 min. BID Injured runners enrolled in a 6-week rehab to strengthen gluteus medius Group specific therapy Group 1: placebo 2: anti-inflammatory (Voltaren) 3: anti-inflammatory/analgesic combo (Myprodol) Group 1: corticosteroid injection (methylprednisolone acetate 40 mg) Group 2: placebo injection Statistically significant (P < 0.05) higher hip abductor torque in control group compared to injured runners. Comparison between groups Group3hadless pain and increased running time/distance from day 0 to 7 Using a visual analogue scale for pain perception, significant (P = 0.01)decrease in pain during running in group 1 Response to treatment was variable, even some who followed treatment judiciously did not benefit After rehab females increased hip abductor torque 34.9%, males 51.4% Outcomes, conclusions All treatments are effective; analgesic/antiinflammatory is superior Local corticosteroid infiltration effectively decreases pain during running in the first 2 wks of treatment of ITBS Group 1 avg. of 53.6% decreases in pain from day 0 to 14 After 8 weeks, 44% were 100% cured, 22% were75%cured,and 34% were 50% or less cured 22/24 athletes were pain-free and able to return to running, with recurrence at 6 months 3. Results 3.1. Conservative Treatment. There are many different conservative treatment modalities for IT band syndrome. Many of these treatment modalities have been geared toward the runner population, and certain guidelines to return to sport (running)havebeensuggested[3]. Table 1 illustrates four studies that outlined conservative treatment modalities. In a randomized controlled trial (RCT), Schwellnus et al. investigated the effect of initial treatment (day 0 7: rest, ice application, and medication) in 43 patients with unilateral ITBS. All subjects received physical therapy consisting of ultrasound, deep transverse friction massages on days 3, 5, and 7 and daily stretching of the IT band. Medication was delivered over the 7 days in a double-blind, placebo-controlled fashion with group 1 taking a placebo anti-inflammatory, group 2 an anti-inflammatory (Voltaren), and group 3 an anti-inflammatory/analgesic (Myprodol). Compared with the other groups, group 3 had less pain during running from day 3 onward, and their running time/distance on the treadmill significantly increased from day 0 to 7 [10]. In another randomized controlled trial, 18 runners with acuteonset ITB syndrome (<14 days duration) were randomly assigned into two groups: group 1 received a corticosteroid injection and group 2 received a placebo injection. Subjects were instructed not to run for 14 days following the injection and to apply ice to the area for 30 minutes every 12 hours. Running pain was significantly decreased in the group that received the corticosteroid injection [11]. In a case series of 196 running injuries, Pinshaw et al. founditbstothethirdmostcommoninjury(12%)behind peripatellar pain syndrome (22%) and posterior tibial stress syndrome (18%). In those with ITBS a four-step conservative approach was used for treatment. These steps included running shoes: change to softer shoes, use of in-shoe support and shoe alterations, and/or removal of the outside heel flare of the shoe for the injured side. Leg-length discrepancies: adapt shoe of the shorter leg by adding material to the midsole to ensure 100% correction at the heel, 50% correction in the mid-sole, and 25% correction at the ball of the foot. Training methods: if appropriate, reduce training distance and decrease running speed and amount of hill running. Also, incorporate a sufficient number of days for recovery. Ice application: apply ice to the injured area for 30 minutes twice aday[12]. Finally, in a case series done at the Stanford Sports Medicine Clinic, 24 runners (10 M, 14 W) with ITBS completed a 6-week rehabilitation program, which consisted of local application of ultrasound with corticosteroid gel for the first two sessions. All patients were instructed to stretch the IT band three times a day, and hip abduction exercises and pelvic drop sets to strengthen the gluteus were increased throughout the program with a goal of 3 sets of 30 repetitions. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs were prescribed until thepatientswerefreeofpainduringdailyactivities.the investigators found a mean increase of 34.9% and 51.4% in the injured leg of the hip abductor torque for females and males, respectively. Twenty-two of the 24 athletes (91.7%) of
4 4 Sports Medicine the athletes were able to return to running at the end of the 6-week program [2]. These four studies demonstrate how diverse conservative treatment for ITBS can be. From clinical experience, rest is the best treatment for the acute cases. This treatment becomes less useful as it becomes a more chronic condition when bursal and periosteal changes have set in. There is limited evidence to support one specific approach to the treatment of ITBS; however, when looking at the desired goal of return to sport, a combination of rest (2 6 weeks), stretching, pain management, and modification of running habits produces a high return to sport rate Surgical Treatment. Surgery is often reserved for refractory cases that have failed other avenues of conservative management. However, in the athletic population, return to sport is a common concern, and multiple, long absences from sport due to trials of various conservative treatment approaches are often not ideal. There are differing viewpoints as to when surgical treatment should be implemented. Martens et al. suggests that conservative treatments should be maintained for an average of 9 months before consideration of surgical intervention [13]. Others have based their decision for surgical intervention on the observation that at 30 degrees flexion, the posterior fibers of the ITB are tighter against the lateral femoral epicondyle than are the more anterior fibers, in which case a surgical release in the posterior fibers is needed to correct the problem [14, 15]. In one study, 36 athletes with a resistant ITBS were treated with a standard arthroscopic technique, limited to the resection of lateral synovial recess. The patients had suffered from ITBS for an average of 18 months (1 7 years). Thirtythree patients (mean age 31.1 years) were available for followup at least 6 months postoperatively. Prior to surgery, all patients had been treated conservatively for at least 6 months with rest, correction of training error, shoe modification, physical therapy and local infiltration with steroids. Thirtytwo patients had good or excellent results based on subjective functionalresultsatfollowup.allpatientswentbacktosports after 3 months. In 2 patients a meniscal lesion was found, which required treatment, and an associated cartilage lesion of the femoral condyle was found in the one patient that reported a fair outcome at followup. The author concluded that arthroscopic resection of the lateral synovial recess in resistant ITBS is a valid option with a consistently good outcome, which also allows excluding or treating other intraarticular pathology [16]. AretrospectivestudyonathletesinNorwaylookedat45 patients who failed conservative management of ITBS. The surgical procedure of choice for these resistant ITBS cases was transection of the posterior half of the iliotibial band whereitpassesoverthelateralepicondyleofthefemur.with a mean age of 27 (14 46) years, 38 (84.4%) had excellent or good results, 6 (13.3%) had fair results, and 1 (2.3%) had a poor result [17]. Return to sport was not documented in this study, but 75.6% of patients reported that they would have the operation again [17]. Bursectomy has also been explored as a surgical treatment option for ITBS. In a recent study a single surgeon performed 11 open iliotibial band bursectomies on 11 patients (7 M, 4 W). Each patient presented with persistent (>6 months) symptoms despite conservative treatment, with an average age at onset of 29 (24 41) years [18]. After a minimum of 20-month followup, all patients were able to return to their preinjury Tegner activity levels, and all reported less pain (11- point visual analogue scale score decreased by 6 points) [18]. Nine of the 11 patients said that knowing what they know now they would have the surgery performed again for the same problem. This population, however, was a mix of athletic and the general population, and the study did not separate out the results of each population. 4. Discussion Iliotibial band syndrome (also called iliotibial band friction syndrome) is a common problem encountered in the knees of athletes, especially endurance athletes whose sport requires repetitive knee flexion. ITBS can often recur in the athletic population, causing significant morbidity and delay in return to sport [19]. There is debate on whether iliotibial band syndrome is truly a friction syndrome where the ITB itself is pathologic or whether a pathologic bursa forms between the ITB and the lateral femoral condyle, causing the pain. This is an important concept because successful surgical treatment of the syndrome must address the underlying pathological causes [18]. Regardless of stance on the pathophysiology, conservative management is the first line of therapy for ITBS. However, both conservative and surgical therapies play a major role in recalcitrant cases. A combination of therapies (rest, pain relief, stretching, strength training, and running habit modification) works best for returning athletes to their preinjury level and reducing their symptoms. However, a systematic regimen involving all aspects of conservative therapy has not been established. A recent systematic review on iliotibial band syndrome in runners concluded that there is limited evidence to support one specific approach to the diagnosis and treatment of ITBS, suggesting that additional research is needed to elucidate an optimal treatment regimen [20]. In our review, conservative therapy alone was found to have a 44% complete cure rate with return to sport at 8 weeks and a 91.7% returntosportrateat6months[2, 12]. ITB syndrome pathophysiology plays a key role in guidingsurgicaltreatments.mostsurgeonswhohavepublishedin theliteratureascribetotheiliotibialfrictionbandsyndrome theory, and numerous procedures that excise or release this supposedly pathologic portion of the ITB have been described. Cortisone injections should still be used first in these scenarios, as ITBS is considered an inflammatory friction syndrome. However, as the duration of symptoms increases and conservative measures fail, surgical treatment may be needed for resolution of symptoms. Three of these procedures have been described above, all in athletes, with a return to sport rate of 100% at an average of 3 months [16] and 7 weeks [13]. One study did not report return to sport rate [17]. Furthermore, Fairclough et al. did not find a
5 Sports Medicine 5 bursa in either the 6 cadaveric specimens they dissected or the 2 symptomatic patients on whom they performed an MRI [21]. In patients with iliotibial band syndrome MRI findings of the ITB can be normal. In a study of 16 patients with ITBS, 31% had a discrete fluid collection medial to the ITB, with a normal looking ITB. However, it was hypothesized that this collection likely arose from chronic inflammation beneath the ITB, resulting in the formation of a secondary or adventitious bursa rather than from the inflammation of an existing primary bursa [22]. There are also those that ascribe to the theory that the ITB itself is not pathological in patients with iliotibial band syndrome, but rather the pain and functional deficits are generated by a pathological bursa that forms beneath the ITB due to compression of that underlying tissue rather than a friction mechanism. In the study performed by Hariri et al. described above, they consistently found what appears to be an inflamed bursa underlying a benign-appearing ITB [18]. This study, however, was not done solely on the athletic population whereas the ones described which favor the friction theory of iliotibial band syndrome were. Surgical intervention is often only utilized after patients have failed conservative management for ITBS, making return to preinjury level a difficult task. Although there are two theories on the pathophysiology of ITBS, when looking at return to sport rate in the athletic population, resection of the lateral synovial recess, after failure of conservative therapy provides an excellent return to sport rate. 5. Conclusion Iliotibial band syndrome is a common cause of lateral knee pain in the athlete, especially runners and other endurance athletes [23]. Both conservative and surgical approaches are viable treatment options, and both need to be considered during treatment planning. While the majority of cases resolve with conservative management, resistant cases are seen in many athletes, requiring surgical intervention. The cases that require surgical intervention are often chronic in nature, and it is important to recognize the duration of symptoms so that surgical treatment can be initiated early. Despite many options for both surgical and conservative treatment, there has yet to be consensus on one standard of care. Further research is needed to delineate the true pathologybehindiliotibialbandsyndromeinathletes,aswell as the optimal treatment regimen. References [1] S. P. Messier, D. G. Edwards, D. F. Martin et al., Etiology of iliotibial band friction syndrome in distance runners, Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, vol.27,no.7,pp , [2]M.Fredericson,C.L.Cookingham,A.M.Chaudhari,B.C. Dowdell, N. Oestreicher, and S. A. Sahrmann, Hip abductor weakness in distance runners with iliotibial band syndrome, Clinical Sport Medicine, vol.10,no.3,pp , [3] M. Fredericson and A. Weir, Practical management of iliotibial band friction syndrome in runners, Clinical Sport Medicine,vol.16,no.3,pp ,2006. [4] S. P. Messier and K. A. Pittala, Etiologic factors associated with selected running injuries, Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, vol. 20, no. 5, pp , [5]J.E.Taunton,M.B.Ryan,D.B.Clement,D.C.McKenzie, D. R. Lloyd-Smith, and B. D. Zumbo, A retrospective casecontrol analysis of 2002 running injuries, British Sports Medicine,vol.36,no.2,pp ,2002. [6]J.W.Orchard,P.A.Fricker,A.T.Abud,andB.R.Mason, Biomechanics of iliotibial band friction syndrome in runners, American Sports Medicine,vol.24,no.3,pp , [7] J. C. Gose and P. Schweizer, Iliotibial band tightness, Journal of Orthopaedic and Sports Physical Therapy, vol.10,no.10,pp , [8] G. Nishimura, M. Yamato, K. Tamai, J. Takahashi, and M. Uetani, MR findings in iliotibial band syndrome, Skeletal Radiology,vol.26,no.9,pp ,1997. [9] E.F.Ekman,T.Pope,D.F.Martin,andW.W.Curl, Magnetic resonance imaging of iliotibial band syndrome, American Sports Medicine,vol.22,no.6,pp ,1994. [10] M. P. Schwellnus, L. Theunissen, T. D. Noakes, and S. G. Reinach, Anti-inflammatory and combined anti-inflammatory/analgesic medication in the early management of iliotibial band friction syndrome: a clinical trial, South African Medical Journal,vol.79,no.10,pp ,1991. [11] P. Gunter and M. P. Schwellnus, Local corticosteroid injection in iliotibial band friction syndrome in runners: a randomised controlled trial, British Sports Medicine, vol.38,no. 3,pp ,2004. [12] R.Pinshaw,V.Atlas,andT.D.Noakes, Thenatureandresponse to therapy of 196 consecutive injuries seen at a runners clinic, South African Medical Journal, vol. 65, no. 8, pp , [13] M.Martens,P.Libbrecht,andA.Burssens, Surgicaltreatment of the iliotibial band friction syndrome, American Sports Medicine,vol.17,no.5,pp ,1989. [14] C. A. Noble, Iliotibial band friction syndrome in runners, American Sports Medicine,vol.8,no.4,pp , [15]C.A.Noble, Thetreatmentofiliotibialbandfrictionsyndrome, British Sports Medicine,vol.13, no.2,pp , [16]F.Michels,S.Jambou,M.Allard,V.Bousquet,P.Colombet, and C. De Lavigne, An arthroscopic technique to treat the iliotibial band syndrome, Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy,vol.17,no.3,pp ,2009. [17] J. O. Drogset, I. Rossvoll, and T. Grøntvedt, Surgical treatment of iliotibial band friction syndrome: a retrospective study of 45 patients, Scandinavian Medicine and Science in Sports,vol.9,no.5,pp ,1999. [18] S. Hariri, E. T. Savidge, M. M. Reinold, J. Zachazewski, and T. J. Gill, Treatmentofrecalcitrantiliotibialbandfrictionsyndrome with open iliotibial band bursectomy: indications, technique, and clinical outcomes, American Sports Medicine, vol.37,no.7,pp ,2009. [19] C. A. Lucas, Iliotibial band friction syndrome as exhibited in athletes, Athletic Training,vol.27, no.3,pp , 1992.
6 6 Sports Medicine [20] M.P.vanderWorp,N.vanderHorst,A.deWijer,F.J.Backx, and M. W. Nijhuis-van der Sanden, Iliotibial band syndrome in runners: a systematic review, Sports Medicine,vol. 42,no.11,pp ,2012. [21] J. Fairclough, K. Hayashi, H. Toumi et al., Is iliotibial band syndrome really a friction syndrome? Science and Medicine in Sport, vol. 10, no. 2, pp , [22] C. Muhle, J. M. Ahn, L. Yeh et al., Iliotibial band friction syndrome: MR imaging findings in 16 patients and MR arthrographic study of six cadaveric knees, Radiology, vol.212,no.1, pp , [23] M. Fredericson and C. Wolf, Iliotibial band syndrome in runners: innovations in treatment, Sports Medicine, vol. 35, no. 5, pp , 2005.
7 MEDIATORS of INFLAMMATION The Scientific World Journal Gastroenterology Research and Practice Diabetes Research International Endocrinology Immunology Research Disease Markers Submit your manuscripts at BioMed Research International PPAR Research Obesity Ophthalmology Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Stem Cells International Oncology Parkinson s Disease Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine AIDS Behavioural Neurology Research and Treatment Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity
Treatment of Iliotibial Band Syndrome. Cameron Goodman & Will Clayton
 Treatment of Iliotibial Band Syndrome Cameron Goodman & Will Clayton Introduction The Iliotibial Band (IT Band) Thick strip of connective tissue connecting several muscles in the thigh The IT band stabilizes
Treatment of Iliotibial Band Syndrome Cameron Goodman & Will Clayton Introduction The Iliotibial Band (IT Band) Thick strip of connective tissue connecting several muscles in the thigh The IT band stabilizes
Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus in an 8-Year-Old Child: Report of a Rare Case
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5263248, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5263248 Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus in an 8-Year-Old Child: Report of a Rare Case Susumu
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5263248, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5263248 Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus in an 8-Year-Old Child: Report of a Rare Case Susumu
Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus Accompanied by Meniscocapsular Separation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 357463, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/357463 Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus Accompanied by Meniscocapsular Separation Aki Fukuda,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 357463, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/357463 Case Report Double-Layered Lateral Meniscus Accompanied by Meniscocapsular Separation Aki Fukuda,
The Iliotibial band syndrome (ITB) is commonly called "runner's knee" and is an inflammatory process in the iliotibial area which is the last section
 The Iliotibial band syndrome (ITB) is commonly called "runner's knee" and is an inflammatory process in the iliotibial area which is the last section of the femoral fascia (or fascia lata). The problem
The Iliotibial band syndrome (ITB) is commonly called "runner's knee" and is an inflammatory process in the iliotibial area which is the last section of the femoral fascia (or fascia lata). The problem
Ilio-Tibial Band Syndrome
 Ilio-Tibial Band Syndrome Ilio-Tibial band syndrome (ITBS) is the most common cause of lateral knee pain in runners and cyclists. It is recognized by the sharp, burning pain that feels almost as if you
Ilio-Tibial Band Syndrome Ilio-Tibial band syndrome (ITBS) is the most common cause of lateral knee pain in runners and cyclists. It is recognized by the sharp, burning pain that feels almost as if you
The Use of a Foot Orthotic in a Runner with Persistent Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome
 The Use of a Foot Orthotic in a Runner with Persistent Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome A Capstone Project for PTY 768 Presented to the Faculty of the Physical Therapy Department Sage Graduate School
The Use of a Foot Orthotic in a Runner with Persistent Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome A Capstone Project for PTY 768 Presented to the Faculty of the Physical Therapy Department Sage Graduate School
Case Report Reverse Segond Fracture Associated with Anteromedial Tibial Rim and Tibial Attachment of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Avulsion Fractures
 Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 9637153, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9637153 Case Report Reverse Segond Fracture Associated with Anteromedial Tibial Rim and Tibial
Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 9637153, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9637153 Case Report Reverse Segond Fracture Associated with Anteromedial Tibial Rim and Tibial
Research Article Relationship between Pain and Medial Meniscal Extrusion in Knee Osteoarthritis
 Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210972, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210972 Research Article Relationship between Pain and Medial Meniscal Extrusion in Knee Osteoarthritis Hiroaki
Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210972, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210972 Research Article Relationship between Pain and Medial Meniscal Extrusion in Knee Osteoarthritis Hiroaki
Anterior Knee Pain in Children. Joseph Chorley, MD Associate Professor, Pediatrics Baylor College of Medicine
 Anterior Knee Pain in Children Joseph Chorley, MD Associate Professor, Pediatrics Baylor College of Medicine Goals and Objectives To learn how to care for patients with chronic knee pain To be able to
Anterior Knee Pain in Children Joseph Chorley, MD Associate Professor, Pediatrics Baylor College of Medicine Goals and Objectives To learn how to care for patients with chronic knee pain To be able to
Mikaela J. Mooney. Clinical Case Report Competition. West Coast College of Massage Therapy. New Westminster. First Place Winner
 Massage Therapists Association of British Columbia Clinical Case Report Competition West Coast College of Massage Therapy New Westminster April 2014 First Place Winner Mikaela J. Mooney Is lengthening
Massage Therapists Association of British Columbia Clinical Case Report Competition West Coast College of Massage Therapy New Westminster April 2014 First Place Winner Mikaela J. Mooney Is lengthening
Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome
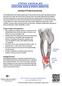 Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon passes
Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon passes
Clinical Study Rate of Improvement following Volar Plate Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Distal Radius Fractures
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2011, Article ID 565642, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/565642 Clinical Study Rate of Improvement following Volar Plate Open Reduction and Internal
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2011, Article ID 565642, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/565642 Clinical Study Rate of Improvement following Volar Plate Open Reduction and Internal
Case Report Detached Anterior Horn of the Medial Meniscus Mimicking a Parameniscal Cyst
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 706241, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/706241 Case Report Detached Anterior Horn of the Medial Meniscus Mimicking a Parameniscal Cyst Shoji Fukuta,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 706241, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/706241 Case Report Detached Anterior Horn of the Medial Meniscus Mimicking a Parameniscal Cyst Shoji Fukuta,
Diagnosis of Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome and Ultrasound Guided Steroid Injection
 Case Report Korean J Pain 2013 October; Vol. 26, No. 4: 387-391 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.4.387 Diagnosis of Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome and Ultrasound
Case Report Korean J Pain 2013 October; Vol. 26, No. 4: 387-391 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.4.387 Diagnosis of Iliotibial Band Friction Syndrome and Ultrasound
The iliotibial band syndrome : MR Imaging findings
 The iliotibial band syndrome : MR Imaging findings Poster No.: P-0081 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: W. Harzallah-Hizem, M. MAATOUK, A. Zrig, R. Salem, W. Mnari, B. Hmida, M. GOLLI;
The iliotibial band syndrome : MR Imaging findings Poster No.: P-0081 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: W. Harzallah-Hizem, M. MAATOUK, A. Zrig, R. Salem, W. Mnari, B. Hmida, M. GOLLI;
Case Report Arthroscopic Microfracture Technique for Cartilage Damage to the Lateral Condyle of the Tibia
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 795759, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/795759 Case Report Arthroscopic Microfracture Technique for Cartilage Damage to the Lateral Condyle of
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 795759, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/795759 Case Report Arthroscopic Microfracture Technique for Cartilage Damage to the Lateral Condyle of
Eisuke Nomura, Hisatada Hiraoka, and Hiroya Sakai. 1. Introduction. 2. Case Report
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1026861, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1026861 Case Report Spontaneous Recurrent Hemarthrosis of the Knee: A Report of Two Cases with a Source
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1026861, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1026861 Case Report Spontaneous Recurrent Hemarthrosis of the Knee: A Report of Two Cases with a Source
Baris Beytullah Koc, 1 Martijn Schotanus, 1 Bob Jong, 2 and Pieter Tilman Introduction. 2. Case Presentation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 7898090, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7898090 Case Report The Role of Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI in a Child with Sport-Induced Avascular
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 7898090, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7898090 Case Report The Role of Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI in a Child with Sport-Induced Avascular
A Patient s Guide to Pes Anserine Bursitis
 A Patient s Guide to Pes Anserine Bursitis 1436 Exchange Street Middlebury, VT 05753 Phone: 802-388-3194 Fax: 802-388-4881 cvo@champlainvalleyortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Pes Anserine Bursitis 1436 Exchange Street Middlebury, VT 05753 Phone: 802-388-3194 Fax: 802-388-4881 cvo@champlainvalleyortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
2. Iliotibial Band syndrome
 2. Iliotibial Band syndrome Iliotibial band (ITB) syndrome (so called runners knee although often seen in other sports e.g. cyclists and hill walkers). It is usually an overuse injury with pain felt on
2. Iliotibial Band syndrome Iliotibial band (ITB) syndrome (so called runners knee although often seen in other sports e.g. cyclists and hill walkers). It is usually an overuse injury with pain felt on
What is Medial Plica Syndrome?
 What is Medial Plica Syndrome? It is a congenital disorder in which the thin wall of fibrous tissue extends from the synovial capsule of the knee. Pain usually occurs when the synovial capsule becomes
What is Medial Plica Syndrome? It is a congenital disorder in which the thin wall of fibrous tissue extends from the synovial capsule of the knee. Pain usually occurs when the synovial capsule becomes
MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS, SHIN SPLINTS
 10 MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS, SHIN SPLINTS What is Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome (MTSS)? Medial tibial stress syndrome (MTSS), commonly encompassed under the umbrella term shin splints, occurs along the bottom
10 MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS, SHIN SPLINTS What is Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome (MTSS)? Medial tibial stress syndrome (MTSS), commonly encompassed under the umbrella term shin splints, occurs along the bottom
Case Report Unusual Bilateral Rim Fracture in Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210827, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210827 Case Report Unusual Bilateral Rim Fracture in Femoroacetabular Impingement Claudio Rafols, Juan
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210827, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210827 Case Report Unusual Bilateral Rim Fracture in Femoroacetabular Impingement Claudio Rafols, Juan
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the
SPORTS MEDICINE OVERUSE MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES FOR
 SPORTS MEDICINE OVERUSE INJURIES: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES FOR THE FAMILY PHYSICIAN DR NG CHUNG SIEN MBBS (SPORE) MSPMED (AUSTRALIA) DFD CAW SENIOR REGISTRAR CHANGI SPORTS MEDICINE CENTRE CHANGI
SPORTS MEDICINE OVERUSE INJURIES: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES FOR THE FAMILY PHYSICIAN DR NG CHUNG SIEN MBBS (SPORE) MSPMED (AUSTRALIA) DFD CAW SENIOR REGISTRAR CHANGI SPORTS MEDICINE CENTRE CHANGI
Introduction. Anatomy
 the patella is called the quadriceps mechanism. Though we think of it as a single device, the quadriceps mechanism has two separate tendons, the quadriceps tendon on top of the patella and the patellar
the patella is called the quadriceps mechanism. Though we think of it as a single device, the quadriceps mechanism has two separate tendons, the quadriceps tendon on top of the patella and the patellar
Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture Dislocation of the Elbow in an Adult
 Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2018, Article ID 5401634, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5401634 Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture
Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2018, Article ID 5401634, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5401634 Case Report Intra-Articular Entrapment of the Medial Epicondyle following a Traumatic Fracture
Case Report Pediatric Transepiphyseal Seperation and Dislocation of the Femoral Head
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 703850, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/703850 Case Report Pediatric Transepiphyseal Seperation and Dislocation of the Femoral Head Mehmet Elmadag,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 703850, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/703850 Case Report Pediatric Transepiphyseal Seperation and Dislocation of the Femoral Head Mehmet Elmadag,
Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 745083, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/745083 Case Report Bilateral Distal Femoral Nailing in a Rare Symmetrical Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Marcos Carvalho,
Case Report A Case of Nonunion Avulsion Fracture of the Anterior Tibial Eminence
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 9648473, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9648473 Case Report A Case of Nonunion Avulsion Fracture of the Anterior Tibial Eminence Satoru Atsumi,
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 9648473, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9648473 Case Report A Case of Nonunion Avulsion Fracture of the Anterior Tibial Eminence Satoru Atsumi,
WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS?
 WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS? If you're finding when you climb out of bed each morning that your first couple steps cause your foot and heel to hurt, this might be a sign of plantar fasciitis. A common condition
WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS? If you're finding when you climb out of bed each morning that your first couple steps cause your foot and heel to hurt, this might be a sign of plantar fasciitis. A common condition
Case Report Bilateral Congenital Agenesis of the Long Head of the Biceps Tendon: The Beginning
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 4309213, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4309213 Case Report Bilateral Congenital Agenesis of the Long Head of the Biceps Tendon: The Beginning
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 4309213, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4309213 Case Report Bilateral Congenital Agenesis of the Long Head of the Biceps Tendon: The Beginning
A Patient s Guide to Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip Iain is a specialist in musculoskeletal imaging and the diagnosis of musculoskeletal pain. This information is provided with the hope that you can
A Patient s Guide to Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip Iain is a specialist in musculoskeletal imaging and the diagnosis of musculoskeletal pain. This information is provided with the hope that you can
Iliotibial Band Syndrome
 Iliotibial Band Syndrome Definition and Home Stretches Edited by Dr. Ryan Lambert-Bellacov Iliotibial Band: Definition The iliotibial band (ITB) is a dense fibrous band running from the lateral pelvis
Iliotibial Band Syndrome Definition and Home Stretches Edited by Dr. Ryan Lambert-Bellacov Iliotibial Band: Definition The iliotibial band (ITB) is a dense fibrous band running from the lateral pelvis
Research Article Reduction of Pain and Edema of the Legs by Walking Wearing Elastic Stockings
 International Vascular Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 648074, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/648074 Research Article Reduction of Pain and Edema of the Legs by Walking Wearing Elastic Stockings
International Vascular Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 648074, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/648074 Research Article Reduction of Pain and Edema of the Legs by Walking Wearing Elastic Stockings
ARTHROSCOPIC LABRAL REPAIR WITH CAPSULAR PLICATION PHYSICAL THERAPY PROTOCOL
 ARTHROSCOPIC LABRAL REPAIR WITH CAPSULAR PLICATION PHYSICAL THERAPY PROTOCOL Jovan R. Laskovski, M.D. Hip Arthroscopy Sports Medicine & Orthopaedic Surgery Crystal Clinic Orthopaedic Center Please use
ARTHROSCOPIC LABRAL REPAIR WITH CAPSULAR PLICATION PHYSICAL THERAPY PROTOCOL Jovan R. Laskovski, M.D. Hip Arthroscopy Sports Medicine & Orthopaedic Surgery Crystal Clinic Orthopaedic Center Please use
Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1834740, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1834740 Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1834740, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1834740 Case Report Multiple Giant Cell Tumors of Tendon Sheath Found within a Single Digit of a 9-Year-Old
Plantar fasciitis occurs when the strong band of tissue that supports the arch of your foot becomes irritated and inflamed.
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition every year.
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition every year.
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT ***
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Hip pain in children may refer to the knee from Legg-Calve-Perthes
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Hip pain in children may refer to the knee from Legg-Calve-Perthes
Case Report Patellofemoral Joint Replacement and Nickel Allergy: An Unusual Presentation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 635082, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/635082 Case Report Patellofemoral Joint Replacement and Nickel Allergy: An Unusual Presentation Farhan
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 635082, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/635082 Case Report Patellofemoral Joint Replacement and Nickel Allergy: An Unusual Presentation Farhan
Hip Injuries & Arthroscopy in Athletes
 Hip Injuries & Arthroscopy in Athletes John P Salvo, MD Sports Medicine Rothman Institute Philadelphia, PA EATA Annual Meeting January, 2011 Hip Injuries & Arthroscopy in Anatomy History Physical Exam
Hip Injuries & Arthroscopy in Athletes John P Salvo, MD Sports Medicine Rothman Institute Philadelphia, PA EATA Annual Meeting January, 2011 Hip Injuries & Arthroscopy in Anatomy History Physical Exam
Case Report A Case Report of Isolated Cuboid Nutcracker Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 3264172, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3264172 Case Report A Case Report of Isolated Cuboid Nutcracker Fracture Takaaki Ohmori, 1,2 Shinichi
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 3264172, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3264172 Case Report A Case Report of Isolated Cuboid Nutcracker Fracture Takaaki Ohmori, 1,2 Shinichi
emoryhealthcare.org/ortho
 COMMON SOCCER INJURIES Oluseun A. Olufade, MD Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopedics and PM&R 1/7/18 GOALS Discuss top soccer injuries and treatment strategies Simplify hip and groin injuries in
COMMON SOCCER INJURIES Oluseun A. Olufade, MD Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopedics and PM&R 1/7/18 GOALS Discuss top soccer injuries and treatment strategies Simplify hip and groin injuries in
A Patient s Guide to Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip. William T. Grant, MD
 A Patient s Guide to Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh, PA-C
A Patient s Guide to Trochanteric Bursitis of the Hip Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh, PA-C
Collected Scientific Research Relating to the Use of Osteopathy with Knee pain including iliotibial band (ITB) friction syndrome
 Collected Scientific Research Relating to the Use of Osteopathy with Knee pain including iliotibial band (ITB) friction syndrome Important: 1) Osteopathy involves helping people's own self-healing abilities
Collected Scientific Research Relating to the Use of Osteopathy with Knee pain including iliotibial band (ITB) friction syndrome Important: 1) Osteopathy involves helping people's own self-healing abilities
Hip Cases from Clinic: Refining your history and physical
 Hip Cases from Clinic: Refining your history and physical Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 11/20/2017 Case #1 Healthy 21 M College
Hip Cases from Clinic: Refining your history and physical Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 11/20/2017 Case #1 Healthy 21 M College
Make sure you have properly fitting running shoes and break these in gradually. Never wear new running shoes for a race or a long run.
 Common Running Injuries We are delighted that you have decided to run in the next Bath Half Marathon and very much hope that you have good running shoes, undertake a regular training programme and don
Common Running Injuries We are delighted that you have decided to run in the next Bath Half Marathon and very much hope that you have good running shoes, undertake a regular training programme and don
HIP INJURY MEDICAL, SCIENTIFIC AND WELFARE COMMITTEE. Lúnasa SLIPPED EPIPHYSIS WHAT IS A SLIPPED FEMORAL EPIPHYSIS?
 HIP INJURY Lúnasa 2013 MEDICAL, SCIENTIFIC AND WELFARE COMMITTEE 1. SLIPPED EPIPHYSIS WHAT IS A SLIPPED FEMORAL EPIPHYSIS? The femoral epiphysis is the ball of the hip joint in a child. In this condition,
HIP INJURY Lúnasa 2013 MEDICAL, SCIENTIFIC AND WELFARE COMMITTEE 1. SLIPPED EPIPHYSIS WHAT IS A SLIPPED FEMORAL EPIPHYSIS? The femoral epiphysis is the ball of the hip joint in a child. In this condition,
A Runner's Guide to ITBS
 A Runner's Guide to ITBS Author: Ann Schofield, P.T., MCSP Iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS) is the most common cause of pain on the outside of the knee in runners, with an incidence as high as 12% of all
A Runner's Guide to ITBS Author: Ann Schofield, P.T., MCSP Iliotibial band syndrome (ITBS) is the most common cause of pain on the outside of the knee in runners, with an incidence as high as 12% of all
A Patient s Guide to Plica Syndrome. William T. Grant, MD
 A Patient s Guide to Plica Syndrome Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh, PA-C pride themselves
A Patient s Guide to Plica Syndrome Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh, PA-C pride themselves
Anatomy Your shoulder is made up of three bones: your upper arm bone (humerus), your shoulder blade (scapula), and your collarbone (clavicle).
 Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great
Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great
Marathon Running & Knee Injuries
 Marathon Running & Knee Injuries Mr Sanjiv Jari Consultant Knee, Lower Limb & Orthopaedic Sports Medicine Surgeon Honorary Clinical Lecturer, University of Manchester. www.thekneedoc.co.uk www.sportmedclinic.com
Marathon Running & Knee Injuries Mr Sanjiv Jari Consultant Knee, Lower Limb & Orthopaedic Sports Medicine Surgeon Honorary Clinical Lecturer, University of Manchester. www.thekneedoc.co.uk www.sportmedclinic.com
Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior Endplate Lesion after Recurrent Disc Herniation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5963924, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5963924 Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5963924, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5963924 Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior
A Gender-Targeted Approach Running Injury Prevention
 Are we comparing apples with apples? A Gender-Targeted Approach Running Injury Prevention Maha Elashi B.Kin Michael Ryan PhD, C Ped (C) Jack Taunton MD Michael Koehl MD, PhD June 23, 1972 Equal Opportunity
Are we comparing apples with apples? A Gender-Targeted Approach Running Injury Prevention Maha Elashi B.Kin Michael Ryan PhD, C Ped (C) Jack Taunton MD Michael Koehl MD, PhD June 23, 1972 Equal Opportunity
Anterior knee pain.
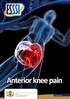 Anterior knee pain What are the symptoms? Anterior knee pain is very common amongst active adolescents and athletes participating in contact sports. It is one of the most common problems/injuries seen
Anterior knee pain What are the symptoms? Anterior knee pain is very common amongst active adolescents and athletes participating in contact sports. It is one of the most common problems/injuries seen
Upper limb injuries II. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Upper limb injuries II Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Capsulitis = inflammatory lesion of the glenohumeral joint capsule leading to: thickening and loss of joint volume painful stiffness of the
Upper limb injuries II Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Capsulitis = inflammatory lesion of the glenohumeral joint capsule leading to: thickening and loss of joint volume painful stiffness of the
APPLICATION OF THE MOVEMENT SYSTEMS MODEL TO THE MANAGEMENT COMMON HIP PATHOLOGIES
 APPLICATION OF THE MOVEMENT SYSTEMS MODEL TO THE MANAGEMENT COMMON HIP PATHOLOGIES Tracy Porter, PT, DPT Des Moines University Department of Physical Therapy Objectives Review current literature related
APPLICATION OF THE MOVEMENT SYSTEMS MODEL TO THE MANAGEMENT COMMON HIP PATHOLOGIES Tracy Porter, PT, DPT Des Moines University Department of Physical Therapy Objectives Review current literature related
Case Report A Rare Case of Traumatic Bilateral Fibular Head Fractures
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2010, Article ID 920568, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2010/920568 Case Report A Rare Case of Traumatic Bilateral Fibular Head Fractures Anastasios Chytas, Antonios Spyridakis, John
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2010, Article ID 920568, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2010/920568 Case Report A Rare Case of Traumatic Bilateral Fibular Head Fractures Anastasios Chytas, Antonios Spyridakis, John
DISTANCE RUNNER MECHANICS AMY BEGLEY
 DISTANCE RUNNER MECHANICS AMY BEGLEY FORM Forward motion is thought to be automatic and hard to change. Changing one thing can cause a chain reaction. Can improve: Balance Strength Flexibility Alignment
DISTANCE RUNNER MECHANICS AMY BEGLEY FORM Forward motion is thought to be automatic and hard to change. Changing one thing can cause a chain reaction. Can improve: Balance Strength Flexibility Alignment
This article is also available in Spanish: Fascitis plantar y protuberancias óseas (topic.cfm?topic=a00702).
 1 of 5 17 Oct 2015 11:04 AM This article is also available in Spanish: Fascitis plantar y protuberancias óseas (topic.cfm?topic=a00702). Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of
1 of 5 17 Oct 2015 11:04 AM This article is also available in Spanish: Fascitis plantar y protuberancias óseas (topic.cfm?topic=a00702). Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of
Iliotibial Band Strain and Force in. Retrospective Iliotibial Band Syndrome. Aspiring Kid, PhD
 Iliotibial Band Strain and Force in Female Runners With and Without Retrospective Iliotibial Band Syndrome Aspiring Kid, PhD FUNCTION OF ILIOTIBIAL BAND Proximally: lateral hip stabilizer Helps prevent
Iliotibial Band Strain and Force in Female Runners With and Without Retrospective Iliotibial Band Syndrome Aspiring Kid, PhD FUNCTION OF ILIOTIBIAL BAND Proximally: lateral hip stabilizer Helps prevent
Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Protocol
 Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Protocol This protocol is a generic outline of the postoperative management for patients undergoing hip arthroscopy. Depending on the exact diagnosis and the procedures performed,
Hip Arthroscopy Rehabilitation Protocol This protocol is a generic outline of the postoperative management for patients undergoing hip arthroscopy. Depending on the exact diagnosis and the procedures performed,
Common Conditions and Injuries of the Knee
 Common Conditions and Injuries of the Knee Iliotibial Band (ITB) Syndrome Ø The ITB is fascia, a connective tissue that gives structure to the body. Its function is to protect the knee from sideways movement
Common Conditions and Injuries of the Knee Iliotibial Band (ITB) Syndrome Ø The ITB is fascia, a connective tissue that gives structure to the body. Its function is to protect the knee from sideways movement
STAIRS. What s Hip: Top 5 Hip Problems in Primary Care. I have no relevant disclosures. Top 5 (or 6) Pathologies. Big 3- Questions to Ask
 I have no relevant disclosures. What s Hip: Top 5 Hip Problems in Primary Care Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery December, 2015
I have no relevant disclosures. What s Hip: Top 5 Hip Problems in Primary Care Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery December, 2015
Case Report Successful Closed Reduction of a Lateral Elbow Dislocation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5934281, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5934281 Case Report Successful Closed Reduction of a Lateral Elbow Dislocation Kenya Watanabe, Takuma
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5934281, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5934281 Case Report Successful Closed Reduction of a Lateral Elbow Dislocation Kenya Watanabe, Takuma
Kanji Mori, Kazuya Nishizawa, Akira Nakamura, and Shinji Imai. 1. Introduction. 2. Case Presentation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 301858, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/301858 Case Report Atraumatic Occult Odontoid Fracture in Patients with Osteoporosis-Associated Thoracic
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 301858, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/301858 Case Report Atraumatic Occult Odontoid Fracture in Patients with Osteoporosis-Associated Thoracic
Overuse Injuries & special skeletal injuries Dr M.Taghavi Director of sport medicine center of olympic academy
 Overuse Injuries & special skeletal injuries Dr M.Taghavi Director of sport medicine center of olympic academy Prevalence of Overuse Injuries 30 to 50% of all sport injuries are from overuse In some sports
Overuse Injuries & special skeletal injuries Dr M.Taghavi Director of sport medicine center of olympic academy Prevalence of Overuse Injuries 30 to 50% of all sport injuries are from overuse In some sports
BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER. Planes of Lumbar Pelvic Femoral (Back, Pelvic, Hip) Muscle Function
 BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER Functional performance of the soccer player reflects functional capability of certain specific muscle and muscle groups of the back, pelvis and hip to work
BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER Functional performance of the soccer player reflects functional capability of certain specific muscle and muscle groups of the back, pelvis and hip to work
Sonographic Evaluation of the Iliotibial Band at the Lateral Femoral Epicondyle
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Sonographic Evaluation of the Iliotibial Band at the Lateral Femoral Epicondyle Does the Iliotibial Band Move? Elena J. Jelsing, MD, Jonathan T. Finnoff, DO, Andrea L. Cheville, MD, Bruce
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Sonographic Evaluation of the Iliotibial Band at the Lateral Femoral Epicondyle Does the Iliotibial Band Move? Elena J. Jelsing, MD, Jonathan T. Finnoff, DO, Andrea L. Cheville, MD, Bruce
5/14/2013. Acute vs Chronic Mechanism of Injury:
 Third Annual Young Athlete Conference: The Lower Extremity February 22, 2013 Audrey Lewis, DPT Acute vs Chronic Mechanism of Injury: I. Direct: blow to the patella II. Indirect: planted foot with a valgus
Third Annual Young Athlete Conference: The Lower Extremity February 22, 2013 Audrey Lewis, DPT Acute vs Chronic Mechanism of Injury: I. Direct: blow to the patella II. Indirect: planted foot with a valgus
Posterior Tibial Tendon Problems
 A Patient s Guide to Posterior Tibial Tendon Problems 2659 Professional Circle Suite 1110 Naples, FL 34119 Phone: 239-596-0100 Fax: 239-596-6737 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Posterior Tibial Tendon Problems 2659 Professional Circle Suite 1110 Naples, FL 34119 Phone: 239-596-0100 Fax: 239-596-6737 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Total Hip Replacement Rehabilitation: Progression and Restrictions
 Total Hip Replacement Rehabilitation: Progression and Restrictions The success of total hip replacement (THR) is a result of predictable pain relief, improvements in quality of life, and restoration of
Total Hip Replacement Rehabilitation: Progression and Restrictions The success of total hip replacement (THR) is a result of predictable pain relief, improvements in quality of life, and restoration of
Tom Eisele, Benedikt M. Muenz, and Grigorios Korosoglou. Department of Cardiology & Vascular Medicine, GRN Hospital Weinheim, Weinheim, Germany
 Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 7376457, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7376457 Case Report Successful Endovascular Repair of an Iatrogenic Perforation of the Superficial
Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 7376457, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7376457 Case Report Successful Endovascular Repair of an Iatrogenic Perforation of the Superficial
The evaluation and management of patients with
 Greater Trochanteric Hip Pain 1.5 ANCC Contact Hours Diane M. Kimpel Chadwick C. Garner Kevin M. Magone Jedediah H. May Matthew W. Lawless In the patient with lateral hip pain, there is a broad differential
Greater Trochanteric Hip Pain 1.5 ANCC Contact Hours Diane M. Kimpel Chadwick C. Garner Kevin M. Magone Jedediah H. May Matthew W. Lawless In the patient with lateral hip pain, there is a broad differential
Illiotibial (IT) Band Syndrome. Author: Anthony J Ross ATC, CSCS, M.Ed.
 Illiotibial (IT) Band Syndrome Author: Anthony J Ross ATC, CSCS, M.Ed. Contents About the Author Background/History Common Signs and Symptoms Treatment Options Sample Program Conclusion Reference Material
Illiotibial (IT) Band Syndrome Author: Anthony J Ross ATC, CSCS, M.Ed. Contents About the Author Background/History Common Signs and Symptoms Treatment Options Sample Program Conclusion Reference Material
Hip Strains. Anyone can experience a hip strain just doing everyday tasks, but strains most often occur during sports activities.
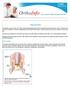 Hip Strains A hip strain occurs when one of the muscles supporting the hip joint is stretched beyond its limit or torn. Strains may be mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the extent of the injury.
Hip Strains A hip strain occurs when one of the muscles supporting the hip joint is stretched beyond its limit or torn. Strains may be mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the extent of the injury.
Bursitis. Other joints are found between the different bones of your fingers and toes. You also have joints that allow your vertebrae to move.
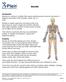 Bursitis Introduction Bursitis is a common condition that causes swelling around muscles and bones. It happens most often in the shoulder, elbow, hip, or knee. Bursitis is usually caused by overusing a
Bursitis Introduction Bursitis is a common condition that causes swelling around muscles and bones. It happens most often in the shoulder, elbow, hip, or knee. Bursitis is usually caused by overusing a
Research Theme. Cal PT Fund Research Symposium 2015 Christopher Powers. Patellofemoral Pain to Pathology Continuum. Applied Movement System Research
 Evaluation and Treatment of Movement Dysfunction: A Biomechanical Approach Research Theme Christopher M. Powers, PhD, PT, FAPTA Understanding injury mechanisms will lead to the development of more effective
Evaluation and Treatment of Movement Dysfunction: A Biomechanical Approach Research Theme Christopher M. Powers, PhD, PT, FAPTA Understanding injury mechanisms will lead to the development of more effective
Factors & Injuries Most Commonly Associated With Distance Running
 Factors & Injuries Most Commonly Associated With Distance Running Paul McKenzie Sports Therapist www.thesportsinjuries-fitnessclinic.co.uk 1 Introduction Despite being an efficient way of improving fitness
Factors & Injuries Most Commonly Associated With Distance Running Paul McKenzie Sports Therapist www.thesportsinjuries-fitnessclinic.co.uk 1 Introduction Despite being an efficient way of improving fitness
Case Report Denosumab Chemotherapy for Recurrent Giant-Cell Tumor of Bone: A Case Report of Neoadjuvant Use Enabling Complete Surgical Resection
 Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 496351, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/496351 Case Report Denosumab Chemotherapy for Recurrent Giant-Cell Tumor of Bone: A Case Report
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 496351, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/496351 Case Report Denosumab Chemotherapy for Recurrent Giant-Cell Tumor of Bone: A Case Report
In comparison to anterior and lateral knee pain, chronic. Semimembranosus Tendinopathy: One Cause of Chronic Posteromedial Knee Pain.
 [ Primary Care ] Semimembranosus Tendinopathy: One Cause of Chronic Posteromedial Knee Pain William E. Bylund, BS,* and Kevin de Weber, MD Context: Semimembranosus tendinopathy (SMT) is an uncommon cause
[ Primary Care ] Semimembranosus Tendinopathy: One Cause of Chronic Posteromedial Knee Pain William E. Bylund, BS,* and Kevin de Weber, MD Context: Semimembranosus tendinopathy (SMT) is an uncommon cause
Case Report Osteolysis of the Greater Trochanter Caused by a Foreign Body Granuloma Associated with the Ethibond Suture after Total Hip Arthroplasty
 Hindawi Volume 2017, Article ID 6082302, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6082302 Case Report Osteolysis of the Greater Trochanter Caused by a Foreign Body Granuloma Associated with the Ethibond Suture
Hindawi Volume 2017, Article ID 6082302, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6082302 Case Report Osteolysis of the Greater Trochanter Caused by a Foreign Body Granuloma Associated with the Ethibond Suture
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Common injuries and how to prevent them
 Common injuries and how to prevent them Sebastian Cormier Msc Physio, Bsc Sports Med, CSCS Chartered Physiotherapist Strength & Conditioning Specialist Overview 1. Very quick recap on understanding your
Common injuries and how to prevent them Sebastian Cormier Msc Physio, Bsc Sports Med, CSCS Chartered Physiotherapist Strength & Conditioning Specialist Overview 1. Very quick recap on understanding your
Strength and Stress Fractures
 Strength and Stress Fractures by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published Jan. 1, 2012 by Dynamic Chiropractor Magazine In any given year, more than one in five runners will sustain a stress fracture (1). In the
Strength and Stress Fractures by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published Jan. 1, 2012 by Dynamic Chiropractor Magazine In any given year, more than one in five runners will sustain a stress fracture (1). In the
Research Article Comparison of Colour Duplex Ultrasound with Computed Tomography to Measure the Maximum Abdominal Aortic Aneurysmal Diameter
 International Vascular Medicine, Article ID 574762, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/574762 Research Article Comparison of Colour Duplex Ultrasound with Computed Tomography to Measure the Maximum
International Vascular Medicine, Article ID 574762, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/574762 Research Article Comparison of Colour Duplex Ultrasound with Computed Tomography to Measure the Maximum
Case Report Combined Effect of a Locking Plate and Teriparatide for Incomplete Atypical Femoral Fracture: Two Case Reports of Curved Femurs
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 213614, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/213614 Case Report Combined Effect of a Locking Plate and Teriparatide for Incomplete Atypical Femoral
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 213614, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/213614 Case Report Combined Effect of a Locking Plate and Teriparatide for Incomplete Atypical Femoral
What s Hip: Common Hip Problems and Kids and Adults
 What s Hip: Common Hip Problems and Kids and Adults Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery I have no relevant disclosures. 2 1 Most
What s Hip: Common Hip Problems and Kids and Adults Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery I have no relevant disclosures. 2 1 Most
Gait Analysis: Qualitative vs Quantitative What are the advantages and disadvantages of qualitative and quantitative gait analyses?
 Gait Analysis: Qualitative vs Quantitative What are the advantages and disadvantages of qualitative and quantitative gait analyses? Basics of Gait Analysis Gait cycle: heel strike to subsequent heel strike,
Gait Analysis: Qualitative vs Quantitative What are the advantages and disadvantages of qualitative and quantitative gait analyses? Basics of Gait Analysis Gait cycle: heel strike to subsequent heel strike,
SHOULDER Highly mobile, so less stable. Abnormalities cloaked within extensive musculature, dx can be difficult Bony abnormalities less common than li
 SPORTS MEDICINE CASES A quick tour of some local joints Featuring gco common o and unusual problems SHOULDER Highly mobile, so less stable. Abnormalities cloaked within extensive musculature, dx can be
SPORTS MEDICINE CASES A quick tour of some local joints Featuring gco common o and unusual problems SHOULDER Highly mobile, so less stable. Abnormalities cloaked within extensive musculature, dx can be
Case Report A Rare Case of Near Complete Regression of a Large Cervical Disc Herniation without Any Intervention Demonstrated on MRI
 Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 832765, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/832765 Case Report A Rare Case of Near Complete Regression of a Large Cervical Disc Herniation without Any Intervention
Case Reports in Radiology, Article ID 832765, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/832765 Case Report A Rare Case of Near Complete Regression of a Large Cervical Disc Herniation without Any Intervention
Prevention and Management of Common Running Injuries. Presented by. Huub Habets (Sports Physiotherapist) Lynsey Ellis (Soft Tissue Therapist)
 Prevention and Management of Common Running Injuries Presented by Huub Habets (Sports Physiotherapist) Lynsey Ellis (Soft Tissue Therapist) Objectives DIALOGUE AND INTERACTION We are not here to preach,
Prevention and Management of Common Running Injuries Presented by Huub Habets (Sports Physiotherapist) Lynsey Ellis (Soft Tissue Therapist) Objectives DIALOGUE AND INTERACTION We are not here to preach,
May 2014 Knife-free Relief for Knee Arthritis More than a million surgeries are
 Knife-free Relief for Knee Arthritis More than a million surgeries are performed every year to help people suffering from arthritis of the knee. While such surgery is sometimes the best option, two studies
Knife-free Relief for Knee Arthritis More than a million surgeries are performed every year to help people suffering from arthritis of the knee. While such surgery is sometimes the best option, two studies
Knee Capsular Disorder. ICD-9-CM: Stiffness in joint of lower leg, not elsewhere classified
 1 Knee Capsular Disorder "Knee Capsulitis" ICD-9-CM: 719.56 Stiffness in joint of lower leg, not elsewhere classified Diagnostic Criteria History: Physical Exam: Stiffness Aching with prolonged weight
1 Knee Capsular Disorder "Knee Capsulitis" ICD-9-CM: 719.56 Stiffness in joint of lower leg, not elsewhere classified Diagnostic Criteria History: Physical Exam: Stiffness Aching with prolonged weight
Iliotibial Band Tendinitis (Runner s Knee)
 Iliotibial Band Tendinitis (Runner s Knee) ANATOMY The iliotibial band (or tract) is a thick band of tissue that starts on the pelvis and upper thigh and passes along the outside of the knee and attaches
Iliotibial Band Tendinitis (Runner s Knee) ANATOMY The iliotibial band (or tract) is a thick band of tissue that starts on the pelvis and upper thigh and passes along the outside of the knee and attaches
Knee Injuries. PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS. Medial Collateral Ligament Sprain
 Knee Injuries PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS Medial Collateral Ligament Sprain Result from either a direct blow from the lateral side in a medial direction or a severe outward twist Greater injury
Knee Injuries PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS Medial Collateral Ligament Sprain Result from either a direct blow from the lateral side in a medial direction or a severe outward twist Greater injury
Research Article Predictive Factors for Medical Consultation for Sore Throat in Adults with Recurrent Pharyngotonsillitis
 International Otolaryngology Volume 2016, Article ID 6095689, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6095689 Research Article Predictive Factors for Medical Consultation for Sore Throat in Adults with
International Otolaryngology Volume 2016, Article ID 6095689, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6095689 Research Article Predictive Factors for Medical Consultation for Sore Throat in Adults with
Post-Op Physical Therapy Protocol for ACL-MCL Reconstruction. Post-Operative Weeks 0-2: Weight-bearing: 1. Non-weightbearing x 4 weeks.
 Adam J. Farber, MD Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic Surgery Board Certified; Fellowship-trained in Sports Medicine & Arthroscopic Surgery P: 480-219-3342; F: 480-219-3271 Post-Op Physical Therapy Protocol
Adam J. Farber, MD Sports Medicine and Orthopaedic Surgery Board Certified; Fellowship-trained in Sports Medicine & Arthroscopic Surgery P: 480-219-3342; F: 480-219-3271 Post-Op Physical Therapy Protocol
Running Injuries. Lower Extremity
 Running Injuries Lower Extremity Causes of Overuse Injuries Repetition Surface/Environment Postural Alignment Improper Biomechanics Poor Footwear/equipment Over-training/improper training Stress Injuries
Running Injuries Lower Extremity Causes of Overuse Injuries Repetition Surface/Environment Postural Alignment Improper Biomechanics Poor Footwear/equipment Over-training/improper training Stress Injuries
