28 Orthopedics. Learning Outcomes. Affective Domain. Cognitive Domain. Psychomotor Domain
|
|
|
- Jonas McCarthy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 28 Orthopedics Learning Outcomes Cognitive Domain 1. Spell and define the key terms 2. List and describe disorders of the musculoskeletal system 3. Compare the different types of fractures 4. Identify and explain diagnostic procedures of the musculoskeletal system 5. Discuss the role of the medical assistant in caring for the patient with a musculoskeletal system disorder 6. Describe the various types of ambulatory aids 7. Identify common pathology related to each body system 8. Describe implications for treatment related to pathology Psychomotor Domain 1. Apply an arm sling (Procedure 28-1) 2. Assist physician with patient care 3. Prepare a patient for procedures and/or treatments 4. Document patient care 5. Document patient education 6. Apply cold packs (Procedure 28-2) 7. Practice standard precautions 8. Use a hot water bottle or commercial hot pack (Procedure 28-3) 9. Measure a patient for axillary crutches (Procedure 28-4) 10. Instruct a patient in various crutch gaits (Procedure 28-5) 11. Practice within standard of care for a medical assistant Affective Domain 1. Apply critical thinking skills in performing patient assessment and care 2. Use language/verbal skills that enable patients understanding 3. Demonstrate empathy in communicating with patients, family, and staff 4. Use appropriate body language and other nonverbal skills in communicating with patients, family, and staff 5. Demonstrate awareness of the territorial boundaries of the person with whom you are communicating 6. Demonstrate sensitivity appropriate to the message being delivered 7. Demonstrate recognition of the patient s level of understanding in communications 8. Recognize and protect personal boundaries in communicating with others 9. Demonstrate respect for individual diversity, incorporating awareness of one s own biases in areas including gender, race, religion, age, and economic status 10. Apply active listening skills 11. Apply local, state, and federal health care legislation and regulation appropriate to the medical assisting practice setting 519
2 520 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant ABHES Competencies 1. Assist the physician with the regimen of diagnostic and treatment modalities as they relate to each body system 2. Comply with federal, state, and local health laws and regulations 3. Communicate on the recipient s level of comprehension 4. Serve as a liaison between the physician and others 5. Show empathy and impartiality when dealing with patients 6. Document accurately
3 CHAPTER 28 Orthopedics 521 Name: : Grade: COG MULTIPLE CHOICE Circle the letter preceding the correct answer. 1. The rebound phenomenon happens: a. when the body secretes callus, which fills in fractures and mends damaged bone. b. when the body experiences bulging discs or biomechanical stress as a result of poor posture. c. when the body overcompensates for a muscle sprain by increasing use of unaffected muscles. d. when the body responds to extremes of temperature for long periods of time by exerting an opposite effect. e. when the body releases fat droplets from the yellow marrow of the long bones. 2. In which crutch gait do both legs leave the floor together? a. One-arm gait b. Two-point gait c. Three-point gait d. Four-point gait e. Swing-through gait 3. A fracture that occurs in flat bones (like those of the skull) and results in a fragment being driven below the surface of the bone is called a(n): a. depressed fracture. b. impacted fracture. c. pathological fracture. d. compression fracture. e. spiral fracture. 4. A possible cause of gout is: a. a liver disorder. b. a degenerative strain. c. a diet high in purines. d. the wear and tear on weight-bearing joints. e. the release of fat droplets from the marrow of long bones. Scenario for questions 5 and 6: The physician has determined that a male patient will need to wear a short arm cast on his left arm as part of the treatment for his fracture. The physician asks you to help her apply the cast to the patient. You assemble the items needed to apply the cast. As the physician prepares the limb for casting, you soak the casting material and press it until it is no longer dripping. Then, the physician wraps the affected limb with the material. After the cast has dried, the physician asks you to apply an arm sling to the patient s left arm. 5. How should the physician wrap the patient s affected arm with the soaked casting material? a. From the axilla to mid palm b. From mid palm to the axilla c. From the elbow to mid palm d. From mid palm to the elbow e. From the axilla to the elbow 6. Which of these steps will you follow when applying the arm sling? a. Cover the left arm with soft knitted tubular material. b. Position the hand of the left arm at a 90-degree angle. c. Instruct the patient in various gaits using auxiliary crutches. d. Check the patient s circulation by pinching each of his fingers. e. Insert the elbow of the right arm into the pouch end of the sling. 7. Rheumatoid arthritis is a(n): a. joint failure. b. bone fracture. c. skeletal tumor. d. autoimmune disease. e. spine disorder.
4 522 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant 8. Tendonitis that is caused by calcium deposits is called: a. fibromyalgia. b. iontophoresis. c. hardened tendons. d. calcific tendonitis. e. depository tendonitis. Scenario for questions 9 and 10: A 20-year-old female patient is visiting your office because of pain in her knee. During the patient interview, the patient tells you that she experiences pain when walking down stairs and getting out of bed. You learn that she is very active and is a member of her university s track and field team. 9. What musculoskeletal disorder does this patient have? a. Plantar fasciitis b. Lateral humeral epicondylitis c. Dupuytren contracture d. Chondromalacia patellae e. Ankylosing spondylitis 10. What surgical procedure may need to be performed to repair or remove damaged cartilage if the patient s case is severe? a. Arthrogram b. Arthroplasty c. Arthroscopy d. Phonophoresis e. Electromyography 11. You should not apply cold to: a. open wounds. b. the pregnant uterus. c. acute inflammation. d. the very young and older adults. e. a contusion. 12. Proper cane length calls for the cane to be level with the user s greater trochanter and for the user s elbow to be bent at a: a. 30-degree angle. b. 50-degree angle. c. 60-degree angle. d. 80-degree angle. e. 90-degree angle. 13. A subluxation is a(n): a. dislocation of a facet joint. b. partial dislocation of a joint. c. complete dislocation of a joint. d. dislocation that damages the tendons. e. injury to a joint capsule. 14. How is immobilization during closed reduction achieved? a. Casting b. Surgery c. Exercise d. Splinting e. Ultrasound 15. You and the physician must wear goggles during a cast removal to protect against: a. flying particles. b. dangerous waves. c. unsanitary material. d. bloodborne pathogens. e. disease and infection. 16. If a fat embolus becomes lodged in a patient s pulmonary or coronary vessels, the patient may experience: a. limited mobility. b. pain and swelling. c. a warm sensation. d. an infarction and death. e. swelling and numbness. 17. The most common site of bursitis is the: a. foot. b. wrist. c. elbow. d. shoulder. e. ankle.
5 CHAPTER 28 Orthopedics Your patient has just received a fiberglass leg cast. Which of the following is a sign that proper circulation is present? a. Red, hot toes b. Swollen toes c. Clammy toes d. Cold, blue toes e. Warm, pink toes 19. Osteoporosis is a condition in which the bones lack: a. bursae. b. calcium. c. vitamin D. d. malignancies. e. marrow. 20. Your patient is recovering from a strain in his Achilles tendon. He is unable to use one leg, but he has coordination and upper body strength. Which of the following ambulatory assist devices should this patient use to gain mobility? a. Cast b. Cane c. Sling d. Walker e. Crutches COG MATCHING Grade: Place the letter preceding the defi nition on the line next to the term. Key Terms Definitions 21. ankylosing spondylitis a. introduction of various chemical ions into the skin by means of electrical current b. a deposit of new bone tissue that forms between the healing ends of broken bones 22. arthrogram c. any artificial replacement for a missing body part, such as false teeth or an artificial 23. arthroscopy limb 24. arthroplasty d. a mass of matter (thrombus, air, fat globule) freely floating in the circulatory system 25. bursae e. small sacs filled with clear synovial fluid that surround some joints 26. callus f. a lateral curve of the spine, usually in the thoracic area, with a corresponding curve in the lumbar region, causing uneven shoulders and hips 27. contracture g. an abnormal shortening of muscles around a joint caused by atrophy of the muscles and resulting in flexion and fixation 28. contusion h. an abnormally deep ventral curve at the lumbar flexure of the spine; also known as 29. electromyography swayback i. ultrasound treatment used to force medications into tissues 30. embolus j. surgical repair of a joint 31. goniometer k. an abnormally deep dorsal curvature of the thoracic spine; also known as humpback or hunchback 32. iontophoresis l. an examination of the inside of a joint through an arthroscope 33. kyphosis m. x-ray of a joint 34. lordosis n. an instrument used to measure the angle of joints for range of motion
6 524 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant 35. Paget disease 36. phonophoresis 37. prosthesis 38. reduction 39. scoliosis o. a collection of blood in tissues after an injury; a bruise p. correcting a fracture by realigning the bones; may be closed (corrected by manipulation) or open (requires surgery) q. a stiffening of the spine with inflammation r. a recording of electrical nerve transmission in skeletal muscles s. a degenerative bone disease usually in older persons with bone destruction and poor repair COG MATCHING Grade: Place the letter preceding the condition on the line preceding the ambulatory assist device. Devices Conditions 40. crutches a. Patient A is a 53-year-old female who has recently undergone hip replacement surgery. She is able to walk and needs only slight assistance until she has fully healed from her surgery. 41. cane b. Patient B is a 17-year-old male with a sprained ankle. His condition is temporary, but he needs assistance walking with one affected leg. 42. walker c. Patient C is a 79-year-old female with osteoarthritis. She has trouble maintaining her balance when walking. COG IDENTIFICATION Grade: 43. Complete this chart to show the different types of fractures. Type of Fracture Avulsion Comminuted a. Compound or open Description Tearing away of bone fragments caused by sharp twisting force applied to ligaments or tendons attached to bone Broken end of bone punctures and protrudes through skin b. Damage to bone caused by strong force on both ends of the bone, such as through a fall Depressed Greenstick c. Impacted Fracture of flat bones (typically the skull) which causes bone fragment to be driven below the surface of the bone One bone segment driven into another d. Break is slanted across the axis of the bone
7 CHAPTER 28 Orthopedics 525 Pathological Simple or closed e. Spiral Related to a disease such as osteoporosis, Paget disease, bone cysts, tumors, or cancers Appears as an S-shaped fracture on radiographs and occurs with torsion or twisting injuries f. A fracture at right angles to axis of bone that is usually caused by excessive bending force or direct pressure on bone 44. Complete this chart, which shows the variations of arthritis, the most commonly affected site, and the characteristics of the variation. Disease Affected Site Characteristics Osteoarthritis Weight-bearing joints a. b. Synovial membrane lining of the joint Ankylosing spondylitis (or Marie-Strumpell disease) Usually begins in non-weight-bearing joints, but can spread to many other joints; results in inflammation, pain, stiffness, and crippling deformities c. Rheumatoid arthritis of the spine; results in extreme forward fl exion of the spine and tightness in the hip fl exors d. Joint, usually the great toe An overproduction of uric acid leads to a deposit of uric acid crystals in the joint; results in a painful, hot, inflamed joint; can become chronic 45. Review the list of tasks below and determine which tasks you may be responsible for as a medical assistant working in the clinical area. Place a check mark in the Yes column for those duties you may be responsible for doing and place a check mark in the No column for those tasks that you would not perform. Task Yes No a. Instruct patients on how to use crutches, a cane, a walker, or a wheelchair. b. Inform patients of the potential injury associated with heating pad use. c. Perform arthroplasty to repair or remove cartilage damaged by chondromalacia patellae. d. Assemble the supplies needed to cast a fractured bone. e. Treat tendonitis with a transverse friction massage. f. Help older adult patients avoid hip fractures by reviewing fall-prevention techniques. g. Observe and report signs of a musculoskeletal disorder, such as skin color, temperature, tone, and tenderness. h. Give patients specific and detailed instructions for applying heat or cold at home. i. Identify the type of fracture and decide the method of treatment.
8 526 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant 46. Use the word bank to fill in the blanks in this paragraph about bone tumors. The cause of malignant skeletal tumors is unknown but may be linked to rapid development of during youth. An early sign of bone tumors is bone pain, which is most intense at night. Some bone tumors have the potential to spread to the skin and muscles. Bone tumors are identified by after a bone scan reveals the need for further diagnosis. Treatments include surgery, amputation, and. Word Bank: biopsy bone tissue chemotherapy CT scan osteosarcomas COG SHORT ANSWER Grade: 47. Describe these three abnormal spine curvatures. a. Lordosis: b. Kyphosis: c. Scoliolis: 48. What is the difference between a sprain and a strain? How are they similar? 49. Name four common sites of dislocations. 50. Your patient is complaining of pain in his wrist. You learn that the pain began after he fell from a ladder and used his hand to break his fall. What would be signs that the patient has fractured his arm?
9 CHAPTER 28 Orthopedics What is the difference between a spiral fracture and an avulsion fracture? 52. What test is performed that determines whether back pain results from a herniated intervertebral disc? How is the test done, and what is a positive indicator? 53. Both heat and cold treatments are used to relieve pain, but how do their uses differ? 54. List the five gaits utilized by patients who use crutches to assist them with walking. 55. The physician has just applied a plaster cast to a patient. What instructions and information should you give to the patient regarding her plaster cast?
10 528 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant COG TRUE OR FALSE? Grade: Indicate whether the statements are true or false by placing the letter T (true) or F (false) on the line preceding the statement. 56. Heat, such as heat from a heating pad or hot water bottle, should not be applied to the uterus of a pregnant woman. 57. A greenstick fracture is a partial or incomplete fracture in which only one side of the bone is broken. 58. The swing-through gait is the gait most commonly used to train patients to use crutches. 59. Fibromyalgia is easy to diagnose because the symptoms are constant and centrally located in one joint socket. COG AFF CASE STUDIES FOR CRITICAL THINKING Grade: 1. Deirdre is a 52-year-old patient. She visits the office with a complaint of joint pain. After taking Deirdre s height and weight measurements, you notice that she is 1 1/2 inches shorter than she was just 2 years ago. After speaking with the patient, you learn that she does not exercise. The physician suspects Deirdre may have osteoporosis. What tests might the physician order to confirm his diagnosis? What preventative medicine information might be useful for Deirdre? 2. Maddy, a 9-year-old patient, needs to have her arm put into a cast after it is discovered that she has a greenstick fracture. The physician informs Maddy s mother that he will be using a fiberglass cast to immobilize Maddy s arm. Maddy s mother grows concerned after speaking with the physician. She has heard that fiberglass can be dangerous, and she wonders why the physician does not use a plaster like the cast she received when she was a child with a fractured arm. Explain to Maddy s mother the benefits of a fiberglass cast over a plaster cast, especially when the patient is a young, active child.
11 CHAPTER 28 Orthopedics Your coworker Ben is moving some boxes from the reception area to a closet in the office. As you walk by, you observe him bending his back and lifting a box with extended arms. You know that this method of lifting could lead to serious back problems, so you decide to speak to Ben about avoiding back strain. What should you say to Ben? How would you respond if he laughs and tells you he is fine? 4. A 46-year-old patient has been advised by the physician to avoid using his strained knee. After you secure an ice pack to the patient s knee, you begin to instruct the patient in how to care for his knee at home. While you are speaking, the patient interrupts you saying that he has had this injury before and will just throw a heating pad on there like he has done in the past. How would you respond to the patient?
12
13 CHAPTER 28 Orthopedics 531 PSY PROCEDURE 28-1 Apply an Arm Sling Name: : Time: Grade: EQUIPMENT/SUPPLIES: A canvas arm sling with adjustable straps. STANDARDS: Given the needed equipment and a place to work the student will perform this skill with % accuracy in a total of minutes. (Your instructor will tell you what the percentage and time limits will be before you begin.) KEY : 4 = Satisfactory 0 = Unsatisfactory NA = This step is not counted PROCEDURE STEPS SELF PARTNER INSTRUCTOR 1. Wash your hands. 2. Assemble the equipment and supplies. 3. Greet and identify the patient; explain the procedure. 4. AFF Explain how to respond to a patient who does not speak English. 5. Position the affected limb with the hand at slightly less than a 90 angle. 6. Place the affected arm into the sling with the elbow snugly against the back of the sling, and the arm extended through the sling with the hand and/or fingers protruding out of the opposite end of the sling. 7. Position the strap from the back of the sling around the patient s back, over the opposite shoulder. 8. Secure the strap by inserting the end through the two metal rings on the top of the sling and further bringing the end of the strap back, looping it through the top metal ring only. 9. Tighten the strap so that the patient s arm in the sling is slightly elevated. Make sure the strap coming around the patient s shoulder and neck is comfortable, padding if necessary to prevent friction and pressure areas. 10. Check the patient s level of comfort and distal extremity circulation. 11. Document the appliance in the patient s chart.
14 532 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant CALCULATION Total Possible Points: Total Points Earned: Multiplied by 100 = Divided by Total Possible Points = % PASS FAIL COMMENTS: Student s signature Partner s signature Instructor s signature
15 CHAPTER 28 Orthopedics 533 PSY PROCEDURE 28-2 Apply Cold Packs Name: : Time: Grade: EQUIPMENT/SUPPLIES: Ice bag and ice chips or small cubes, or disposable cold pack; small towel or cover for ice pack; gauze or tape. STANDARDS: Given the needed equipment and a place to work the student will perform this skill with % accuracy in a total of minutes. (Your instructor will tell you what the percentage and time limits will be before you begin.) KEY : 4 = Satisfactory 0 = Unsatisfactory NA = This step is not counted PROCEDURE STEPS SELF PARTNER INSTRUCTOR 1. Wash your hands. 2. Assemble the equipment and supplies, checking the ice bag, if used, for leaks. If using a commercial cold pack, read the manufacturer s directions. 3. Fill a nondisposable ice bag about two-thirds full. a. Press it flat on a surface to express air from the bag. b. Seal the container. 4. If using a commercial chemical ice pack, activate it now. 5. Cover the bag in a towel or other suitable cover. 6. Greet and identify the patient. Explain the procedure. 7. AFF Explain how to respond to a patient who has cultural or religious beliefs that prohibit disrobing. 8. After assessing skin for color and warmth, place the covered ice pack on the area. 9. Secure the ice pack with gauze or tape. 10. Apply the treatment for the prescribed amount of time, but no longer than 30 minutes. 11. During the treatment, assess the skin under the pack frequently for mottling, pallor, or redness. 12. Properly care for or dispose of equipment and supplies. Wash your hands. 13. Document the procedure, the site of the application, the results including the condition of the skin after the treatment, and the patient s reactions.
16 534 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant CALCULATION Total Possible Points: Total Points Earned: Multiplied by 100 = Divided by Total Possible Points = % PASS FAIL COMMENTS: Student s signature Partner s signature Instructor s signature
17 CHAPTER 28 Orthopedics 535 PSY PROCEDURE 28-3 Use a Hot Water Bottle or Commercial Hot Pack Name: : Time: Grade: EQUIPMENT/SUPPLIES: A hot water bottle or commercial hot pack, towel or other suitable covering for the hot pack STANDARDS: Given the needed equipment and a place to work the student will perform this skill with % accuracy in a total of minutes. (Your instructor will tell you what the percentage and time limits will be before you begin.) KEY : 4 = Satisfactory 0 = Unsatisfactory NA = This step is not counted PROCEDURE STEPS SELF PARTNER INSTRUCTOR 1. Wash your hands. 2. Assemble equipment and supplies, checking the hot water bottle for leaks. 3. Fill the hot water bottle about two-thirds full with warm (110 F) water. a. Place the bottle on a flat surface and the opening up; burp it by pressing out the air. b. If using a commercial hot pack, follow the manufacturer s directions for activating it. 4. Wrap and secure the pack or bottle before placing it on the patient s skin. 5. Greet and identify the patient. Explain the procedure. 6. AFF Explain how to respond to a patient who is from a different generation (older) than you are. 7. After assessing the color of the skin where the treatment is to be applied, place the covered hot pack on the area. 8. Secure the hot pack with gauze or tape. 9. Apply the treatment for the prescribed length of time, but no longer than 30 minutes. 10. During treatment, assess the skin every 10 minutes for pallor (an indication of rebound), excessive redness (indicates temperature may be too high), and swelling (indicates possible tissue damage). 11. Properly care for or dispose of equipment and supplies. Wash your hands. 12. Document the procedure, the site of the application, the results including the condition of the skin after the treatment, and the patient s reactions.
18 536 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant CALCULATION Total Possible Points: Total Points Earned: Multiplied by 100 = Divided by Total Possible Points = % PASS FAIL COMMENTS: Student s signature Partner s signature Instructor s signature
19 CHAPTER 28 Orthopedics 537 PSY PROCEDURE 28-4 Measure a Patient for Axillary Crutches Name: : Time: Grade: EQUIPMENT/SUPPLIES: Axillary crutches with tips, pads for the axilla, and hand rests, as needed STANDARDS: Given the needed equipment and a place to work the student will perform this skill with % accuracy in a total of minutes. (Your instructor will tell you what the percentage and time limits will be before you begin.) KEY : 4 = Satisfactory 0 = Unsatisfactory NA = This step is not counted PROCEDURE STEPS SELF PARTNER INSTRUCTOR 1. Wash your hands. 2. Assemble the equipment including the correct-size crutches. 3. Greet and identify the patient. 4. Ensure that the patient is wearing low-heeled shoes with safety soles. 5. Have the patient stand erect. Support the patient as needed. 6. AFF Explain how to respond to a patient who is hearing impaired. 7. While standing erect, have the patient hold the crutches in the tripod position. 8. Adjust the central support in the base. a. Tighten the bolts for safety when the proper height is reached. b. Adjust the handgrips. Tighten bolts for safety. c. If needed, pad axillary bars and handgrips. 9. Wash your hands and record the procedure.
20 538 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant CALCULATION Total Possible Points: Total Points Earned: Multiplied by 100 = Divided by Total Possible Points = % PASS FAIL COMMENTS: Student s signature Partner s signature Instructor s signature
21 CHAPTER 28 Orthopedics 539 PSY PROCEDURE 28-5 Instruct a Patient in Various Crutch Gaits Name: : Time: Grade: EQUIPMENT/SUPPLIES: Axillary crutches measured appropriately for a patient STANDARDS: Given the needed equipment and a place to work the student will perform this skill with % accuracy in a total of minutes. (Your instructor will tell you what the percentage and time limits will be before you begin.) KEY : 4 = Satisfactory 0 = Unsatisfactory NA = This step is not counted PROCEDURE STEPS SELF PARTNER INSTRUCTOR 1. Wash your hands. 2. Have the patient stand up from a chair: a. The patient holds both crutches on the affected side. b. Then the patient slides to the edge of the chair. c. The patient pushes down on the chair arm on the unaffected side. d. Then the patient pushes to stand. 3. With one crutch in each hand, rest on the crutches until balance is restored. 4. Assist the patient to the tripod position. 5. AFF Explain how to respond to a patient who is visually impaired. 6. Depending upon the patient s weight-bearing ability, coordination, and general state of health, instruct the patient in one or more of the following gaits: a. Three-point gait: (1) Both crutches are moved forward with the unaffected leg bearing the weight. (2) With the weight supported by the crutches on the handgrips, the unaffected leg is brought past the level of the crutches. (3) The steps are repeated. b. Two-point gait: (1) The right crutch and left foot are moved forward. (2) As these points rest, the right foot and left crutch are moved forward. (3) The steps are repeated.
22 540 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant c. Four-point gait: (1) The right crutch moves forward. (2) The left foot is moved to a position just ahead of the left crutch. (3) The left crutch is moved forward. (4) The right foot moves to a position just ahead of the right crutch. (5) The steps are repeated. d. Swing-through gait: (1) Both crutches are moved forward. (2) With the weight on the hands, the body swings through to a position ahead of the crutches with both legs leaving the floor together. (3) The crutches are moved ahead. (4) The steps are repeated. e. Swing-to gait: (1) Both crutches are moved forward. (2) With the weight on the hands, the body swings to the level of the crutches with both legs leaving the floor. (3) The crutches are moved ahead. (4) The steps are repeated. 7. Wash your hands and record the procedure CALCULATION Total Possible Points: Total Points Earned: Multiplied by 100 = Divided by Total Possible Points = % PASS FAIL COMMENTS: Student s signature Partner s signature Instructor s signature
Arm Injuries and Disorders
 Arm Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your arms are made up of muscles, joints, tendons and other connective tissue. There are many injuries and disorders that can affect the arm. Some arm injuries and
Arm Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your arms are made up of muscles, joints, tendons and other connective tissue. There are many injuries and disorders that can affect the arm. Some arm injuries and
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms.
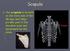 The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
AMERICAN RED CROSS FIRST AID RESPONDING TO EMERGENCIES FOURTH EDITION Copyright 2006 by The American National Red Cross All rights reserved.
 Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
1/3/2008. Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care, 2e Karen Burke, Priscilla LeMone, and Elaine Mohn-Brown
 Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 42 Caring for Clients with Musculoskeletal Trauma Musculoskeletal Trauma Tissue is subjected to more
Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 42 Caring for Clients with Musculoskeletal Trauma Musculoskeletal Trauma Tissue is subjected to more
CAST CARE. Helping Broken Bones Heal
 CAST CARE Helping Broken Bones Heal When You Need a Cast Are you injured and in need of a cast? Don t worry, you ll get through it. Wearing a cast will help your injured body part heal. Healing takes time,
CAST CARE Helping Broken Bones Heal When You Need a Cast Are you injured and in need of a cast? Don t worry, you ll get through it. Wearing a cast will help your injured body part heal. Healing takes time,
Joint Injuries and Disorders
 Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
Joint Injuries and Disorders Introduction A joint is where two or more bones come together. Your joints include the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. There are many types of joint disorders, including
Bursitis. Other joints are found between the different bones of your fingers and toes. You also have joints that allow your vertebrae to move.
 Bursitis Introduction Bursitis is a common condition that causes swelling around muscles and bones. It happens most often in the shoulder, elbow, hip, or knee. Bursitis is usually caused by overusing a
Bursitis Introduction Bursitis is a common condition that causes swelling around muscles and bones. It happens most often in the shoulder, elbow, hip, or knee. Bursitis is usually caused by overusing a
Bone Injuries and Treatment. Fractures and Dislocations
 Bone Injuries and Treatment Fractures and Dislocations Bellwork Research the small bones in the foot and wrist. Draw them in your notes. State Standards 16) Understand principles of and successfully perform
Bone Injuries and Treatment Fractures and Dislocations Bellwork Research the small bones in the foot and wrist. Draw them in your notes. State Standards 16) Understand principles of and successfully perform
Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints. Emergency Medical Response
 Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints Lesson 33: Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints You Are the Emergency Medical Responder You are patrolling the state park where you are the emergency medical responder
Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints Lesson 33: Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints You Are the Emergency Medical Responder You are patrolling the state park where you are the emergency medical responder
1.03 Understand the functions and disorders of the skeletal system
 1.03 Understand the functions and disorders of the skeletal system Bellringer The process of blood cell formation in the red bone marrow of bones is called: a. Erythrocytopenia b. Hemolysis c. hemopoiesis
1.03 Understand the functions and disorders of the skeletal system Bellringer The process of blood cell formation in the red bone marrow of bones is called: a. Erythrocytopenia b. Hemolysis c. hemopoiesis
METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures)
 METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures) Description Possible Complications Metatarsal fracture is a broken bone (fracture) in the middle Nonunion (fracture does not heal, particularly
METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures) Description Possible Complications Metatarsal fracture is a broken bone (fracture) in the middle Nonunion (fracture does not heal, particularly
MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES
 WHAT ARE THEY They are injuries to muscles, nerves, tendons ligaments, joints, cartilage and spinal discs. WHAT KIND OF INJURIES ARE MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES 1. Fractures- -Open -Closed 2. Dislocations
WHAT ARE THEY They are injuries to muscles, nerves, tendons ligaments, joints, cartilage and spinal discs. WHAT KIND OF INJURIES ARE MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES 1. Fractures- -Open -Closed 2. Dislocations
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery. By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4
 Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Chapter 30 - Musculoskeletal_Trauma
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 30.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11 12, 19 20, 22 23, 37 30.2 Describe the anatomy of elements of the musculoskeletal system.
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 30.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11 12, 19 20, 22 23, 37 30.2 Describe the anatomy of elements of the musculoskeletal system.
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM. What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders
 MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
Spine Conditions and Treatments. Your Guide to Common
 Your Guide to Common Spine Conditions and Treatments The spine is made up of your neck and backbone. It allows your body to bend and move freely. As you get older, it is normal to have aches and pains.
Your Guide to Common Spine Conditions and Treatments The spine is made up of your neck and backbone. It allows your body to bend and move freely. As you get older, it is normal to have aches and pains.
Knee arthroscopy. Physiotherapy Department. Patient information leaflet
 Knee arthroscopy Physiotherapy Department Patient information leaflet What is a knee arthroscopy? A knee arthroscopy is a type of keyhole surgery performed through small cuts in the skin. An instrument
Knee arthroscopy Physiotherapy Department Patient information leaflet What is a knee arthroscopy? A knee arthroscopy is a type of keyhole surgery performed through small cuts in the skin. An instrument
Mr. Siva Chandrasekaran Orthopaedic Surgeon MBBS MSpMed MPhil (surg) FRACS
 Sprained Ankle An ankle sprain occurs when the strong ligaments that support the ankle stretch beyond their limits and tear. Ankle sprains are common injuries that occur among people of all ages. They
Sprained Ankle An ankle sprain occurs when the strong ligaments that support the ankle stretch beyond their limits and tear. Ankle sprains are common injuries that occur among people of all ages. They
Musculoskeletal Review. By: Bayly, Jared, Phillip
 Musculoskeletal Review By: Bayly, Jared, Phillip Sprain Tearing of ligament, tissue that may be slight moderate or complete. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Painful condition resulting from compression of
Musculoskeletal Review By: Bayly, Jared, Phillip Sprain Tearing of ligament, tissue that may be slight moderate or complete. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Painful condition resulting from compression of
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
UNDERSTANDING FRACTURE CARE CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, AND TREATMENT
 UNDERSTANDING FRACTURE CARE CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, AND TREATMENT PremierOrtho.com UNDERSTANDING FRACTURE CARE CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, AND TREATMENT Table of Contents Introduction...3 Causes...4 Who s at Risk?...5
UNDERSTANDING FRACTURE CARE CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, AND TREATMENT PremierOrtho.com UNDERSTANDING FRACTURE CARE CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, AND TREATMENT Table of Contents Introduction...3 Causes...4 Who s at Risk?...5
Musculoskeletal Injuries
 Musculoskeletal Injuries KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the four main structures of the musculoskeletal system. 2. List five common signs or symptoms of musculoskeletal injuries. 3. List seven signs
Musculoskeletal Injuries KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the four main structures of the musculoskeletal system. 2. List five common signs or symptoms of musculoskeletal injuries. 3. List seven signs
Functions of Skeletal System
 Skeletal System Skeletal System Adult Human has 206 Bones This slideshow will offer fun ways to remember the names of some of the bones, and you can come up with your own tricks! Functions of Skeletal
Skeletal System Skeletal System Adult Human has 206 Bones This slideshow will offer fun ways to remember the names of some of the bones, and you can come up with your own tricks! Functions of Skeletal
Car a e e o f o th f e th e Pati Pa e ti n e t n wi w th i th a Mus u c s u c l u o l s o k s e k l e e l t e al a l Dis i o s r o de d r
 Care of the Patient with a Musculoskeletal Disorder 1 Slide 1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Function of the bones Support Protection Movement Mineral storage Hemopoiesis Slide 2 Functions of the muscles
Care of the Patient with a Musculoskeletal Disorder 1 Slide 1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Function of the bones Support Protection Movement Mineral storage Hemopoiesis Slide 2 Functions of the muscles
What Are Shoulder Problems?
 What Are the Parts of the Shoulder? The shoulder joint is made up of bones held in place by muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Tendons are tough cords of tissue that hold the shoulder muscles to bones. They
What Are the Parts of the Shoulder? The shoulder joint is made up of bones held in place by muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Tendons are tough cords of tissue that hold the shoulder muscles to bones. They
Everything. You Should Know. About Your Ankles
 Everything You Should Know About Your Ankles How Your Ankle Works The ankle joint is a hinge type joint that participates in movement and is involved in lower limb stability. There are 2 types of motions
Everything You Should Know About Your Ankles How Your Ankle Works The ankle joint is a hinge type joint that participates in movement and is involved in lower limb stability. There are 2 types of motions
Understanding Back Pain
 Understanding Back Pain Back pain affects the vast majority of Americans Back pain is second only to the common cold for the medical complaint doctors hear most often and for causing people to miss the
Understanding Back Pain Back pain affects the vast majority of Americans Back pain is second only to the common cold for the medical complaint doctors hear most often and for causing people to miss the
AMBULATION. Ambulation. Process of moving about. Walking Transferring to and from bed, chair, toilet, car
 AMBULATION AMBULATION Ambulation Process of moving about Walking Transferring to and from bed, chair, toilet, car AMBULATION Levels of ambulation training Independent Setup Supervised Limited Extensive
AMBULATION AMBULATION Ambulation Process of moving about Walking Transferring to and from bed, chair, toilet, car AMBULATION Levels of ambulation training Independent Setup Supervised Limited Extensive
Knee Replacement PROGRAM. Nightingale. Home Healthcare
 Knee Replacement PROGRAM TM Nightingale Home Healthcare With the help of Nightingale s experienced and professional rehabilitation team, you will be guided through a more complete and successful recovery
Knee Replacement PROGRAM TM Nightingale Home Healthcare With the help of Nightingale s experienced and professional rehabilitation team, you will be guided through a more complete and successful recovery
Musculoskeletal Trauma. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Recognize and manage patients with musculoskeletal trauma
 Musculoskeletal Trauma Lesson Goal Recognize and manage patients with musculoskeletal trauma Lesson Objectives Describe function of muscular system Describe composition of muscular system Describe, compare,
Musculoskeletal Trauma Lesson Goal Recognize and manage patients with musculoskeletal trauma Lesson Objectives Describe function of muscular system Describe composition of muscular system Describe, compare,
Musculoskeletal System
 Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system gives the body strength, structure, and capability of movement. Bones are the framework. Ligaments and tendons are the nails Muscles are the way we move
Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system gives the body strength, structure, and capability of movement. Bones are the framework. Ligaments and tendons are the nails Muscles are the way we move
March 2015 Stiff Back: Not a Good Way to Start the Day Morning back stiffness can stem from
 Stiff Back: Not a Good Way to Start the Day Morning back stiffness can stem from a large number of conditions, from the mundane to the exotic. In an otherwise healthy individual, it can simply be the result
Stiff Back: Not a Good Way to Start the Day Morning back stiffness can stem from a large number of conditions, from the mundane to the exotic. In an otherwise healthy individual, it can simply be the result
Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions
 Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions 1. What is caused by overexerting or tearing of a muscle? p. 375 A.) Dislocation B.) Sprain C.) Fracture *D.)
Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions 1. What is caused by overexerting or tearing of a muscle? p. 375 A.) Dislocation B.) Sprain C.) Fracture *D.)
Lesson 9: Bone & Joint Injuries. Emergency Reference Guide p
 Lesson 9: Bone & Joint Injuries Emergency Reference Guide p. 33-43 Objectives Define strain, sprain, fracture and dislocation List Signs & Symptoms of strain, sprain, fracture & dislocation Demonstrate
Lesson 9: Bone & Joint Injuries Emergency Reference Guide p. 33-43 Objectives Define strain, sprain, fracture and dislocation List Signs & Symptoms of strain, sprain, fracture & dislocation Demonstrate
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE
 DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
DIAGNOSIS CODING ESSENTIALS FOR LONG-TERM CARE: CHAPTER 13, M CODES MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Preferred Clinical Services for Leading Age Florida August 26-27, 2015 MUSCULOSKELETAL FUNCTIONS
Musculoskeletal System
 Musculoskeletal System CPT CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the
Musculoskeletal System CPT CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
How Are Shoulder Problems Diagnosed? How Are Shoulder Problems Treated? What Are the Most Common Shoulder Problems? What Are Shoulder Problems?
 How Are Shoulder Problems Diagnosed? Doctors diagnose shoulder problems by using: Medical history. Physical examination. Tests such as x rays, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) How Are Shoulder
How Are Shoulder Problems Diagnosed? Doctors diagnose shoulder problems by using: Medical history. Physical examination. Tests such as x rays, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) How Are Shoulder
Unit 6 Orthopedic Physiotherapy
 Unit 6 Orthopedic Physiotherapy Task 1 Human Body Look at the diagram and study the main muscles of the body. Define which muscles have the following functions: Pectoral muscle lowers the arm. Intercostals
Unit 6 Orthopedic Physiotherapy Task 1 Human Body Look at the diagram and study the main muscles of the body. Define which muscles have the following functions: Pectoral muscle lowers the arm. Intercostals
MENISCUS TEAR. Description
 MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
Range of motion and positioning
 Range of motion and positioning Learning guide Why is motion important? Most people take free, comfortable movement for granted. Motion is meant to be smooth and painless. The ligaments, tendons, muscles,
Range of motion and positioning Learning guide Why is motion important? Most people take free, comfortable movement for granted. Motion is meant to be smooth and painless. The ligaments, tendons, muscles,
What is arthroscopy? Normal knee anatomy
 What is arthroscopy? Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for examining and repairing the inside of your knee. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which uses an Arthroscope and other specialized
What is arthroscopy? Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for examining and repairing the inside of your knee. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which uses an Arthroscope and other specialized
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings. ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders. Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis?
 Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
JOINT HEALTH. Joints are areas in the body where two or more bones meet. They have the following components:
 JOINT HEALTH Joints are areas in the body where two or more bones meet. They have the following components: Articular Cartilage: tissue covering the surface of a bone at a joint. Cartilage helps reduce
JOINT HEALTH Joints are areas in the body where two or more bones meet. They have the following components: Articular Cartilage: tissue covering the surface of a bone at a joint. Cartilage helps reduce
ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE. Description
 Description ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE An acute ankle sprain involves the stretching and tearing of one or more ligaments in the ankle. A two-ligament sprain causes more disability than a single-ligament sprain.
Description ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE An acute ankle sprain involves the stretching and tearing of one or more ligaments in the ankle. A two-ligament sprain causes more disability than a single-ligament sprain.
Vancouver. CoastalHealth. Promoting wellness. Ensuring care. Mary Pack Arthritis Program Occupational Therapy
 Vancouver CoastalHealth Promoting wellness. Ensuring care. Mary Pack Arthritis Program Occupational Therapy O.T. IVA-9 01 12005 PATIENT EDUCATION: JOINT PROTECTION AND ENERGY CONSERVATION The goals of
Vancouver CoastalHealth Promoting wellness. Ensuring care. Mary Pack Arthritis Program Occupational Therapy O.T. IVA-9 01 12005 PATIENT EDUCATION: JOINT PROTECTION AND ENERGY CONSERVATION The goals of
Commonwealth Health Corporation NEXT
 Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE. The Exam
 Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE The Exam This examination is taken in "open book" format. That means you are free to answer the questions after research or discussion with your fellow workers. We feel this
Post test for O&P 2 Hrs CE The Exam This examination is taken in "open book" format. That means you are free to answer the questions after research or discussion with your fellow workers. We feel this
Module Eight. Application of Health Assessment NUR 225. Physical examination of Musculoskeletal System. King Saud University. Collage of Nursing
 King Saud University Collage of Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing depart Application of Health Assessment NUR 225 Module Eight Physical examination of Musculoskeletal System Obtaining a health history Ask
King Saud University Collage of Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing depart Application of Health Assessment NUR 225 Module Eight Physical examination of Musculoskeletal System Obtaining a health history Ask
Knee Replacement Recovery Guide
 Knee Replacement Recovery Guide Table of Contents Congratulations!... 2 Recuperating At home... 2 Range of Motion... 2 Wound Care... 3 Important Signs & Symptoms... 3 Bathing and Showering... 3 Bruising...
Knee Replacement Recovery Guide Table of Contents Congratulations!... 2 Recuperating At home... 2 Range of Motion... 2 Wound Care... 3 Important Signs & Symptoms... 3 Bathing and Showering... 3 Bruising...
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Page 1 of 8 Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures A fracture of the calcaneus, or heel bone, can be a painful and disabling injury. This type of fracture commonly occurs during a high-energy event such as a
Page 1 of 8 Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures A fracture of the calcaneus, or heel bone, can be a painful and disabling injury. This type of fracture commonly occurs during a high-energy event such as a
Hths 2231 Laboratory 13 Alterations in Musculoskeletal
 Watch Movie: Osteoporosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-4. Activity #1: Click on the website link in activity 1 to review the structure and function of bone. Activity
Watch Movie: Osteoporosis Answer the movie questions on the worksheet. Complete activities 1-4. Activity #1: Click on the website link in activity 1 to review the structure and function of bone. Activity
WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS?
 WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS? If you're finding when you climb out of bed each morning that your first couple steps cause your foot and heel to hurt, this might be a sign of plantar fasciitis. A common condition
WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS? If you're finding when you climb out of bed each morning that your first couple steps cause your foot and heel to hurt, this might be a sign of plantar fasciitis. A common condition
Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions
Injuries to the Extremities
 Injuries to the Extremities KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. List seven signs and symptoms that suggest a serious extremity injury. 2. Describe how to care for injuries to the shoulder, upper arm, and elbow. 3.
Injuries to the Extremities KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. List seven signs and symptoms that suggest a serious extremity injury. 2. Describe how to care for injuries to the shoulder, upper arm, and elbow. 3.
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Biology v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems. Skeletomuscular system cards
 Biology 90166 v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems Skeletomuscular system cards Test yourself / test me cards Cover answer bottom 1/3; Read question / notes / diagram
Biology 90166 v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems Skeletomuscular system cards Test yourself / test me cards Cover answer bottom 1/3; Read question / notes / diagram
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME
 ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
ESHE 250 Fall 2010 Table of Contents
 ESHE 250 Fall 2010 Table of Contents Two Person Adult CPR Beginning Together 2 Two Person Adult CPR Switching 3 Two Person Child CPR Beginning Together 4 Two Person Child CPR Switching 5 AED Bicycle Instruction
ESHE 250 Fall 2010 Table of Contents Two Person Adult CPR Beginning Together 2 Two Person Adult CPR Switching 3 Two Person Child CPR Beginning Together 4 Two Person Child CPR Switching 5 AED Bicycle Instruction
TIBIAL PLATEAU FRACTURE
 TIBIAL PLATEAU FRACTURE Description Preventive Measures A tibial plateau fracture is a complete or incomplete break Appropriately warm up and stretch before practice or in the larger of the two leg bones
TIBIAL PLATEAU FRACTURE Description Preventive Measures A tibial plateau fracture is a complete or incomplete break Appropriately warm up and stretch before practice or in the larger of the two leg bones
DISCOID MENISCUS. Description
 Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
ARTHRITIS. What Is Arthritis?
 There are many types of arthritic processes that can cause joint changes, pain and loss of motion and strength in the hands. Many excellent and detailed resources are available and will be listed under
There are many types of arthritic processes that can cause joint changes, pain and loss of motion and strength in the hands. Many excellent and detailed resources are available and will be listed under
Joint Disorders. Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10. Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System
 Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System Susie Turner, MD 1/9/13 Joint Disorders Arthritis Inflammation of Joint
Musculoskeletal Disorders (Part B-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Disorders of the Muscular System Disorders of the Skeletal System Susie Turner, MD 1/9/13 Joint Disorders Arthritis Inflammation of Joint
UNDERSTANDING ARTHROSCOPY
 UNDERSTANDING ARTHROSCOPY Diagnosing and Treating Your Joint Problem Looking into a Problem Joint Whether you re taking a step or raising your hand, your joints help you move freely. A worn, torn, or injured
UNDERSTANDING ARTHROSCOPY Diagnosing and Treating Your Joint Problem Looking into a Problem Joint Whether you re taking a step or raising your hand, your joints help you move freely. A worn, torn, or injured
Musculoskeletal System
 CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries
 CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
Shoulder Instability
 Shoulder Instability The shoulder is your body s most flexible joint. It is designed to let the arm move in almost any direction. But this flexibility has a price, making the joint prone to injury. The
Shoulder Instability The shoulder is your body s most flexible joint. It is designed to let the arm move in almost any direction. But this flexibility has a price, making the joint prone to injury. The
Y: Orthopedic Specialty
 Y: Orthopedic Specialty Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 253 Major Competency Area: Y Priority: One Competency: Y-1 HPA Authorization and Standards Date: September 1, 2005 Y-1-1 Demonstrate
Y: Orthopedic Specialty Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 253 Major Competency Area: Y Priority: One Competency: Y-1 HPA Authorization and Standards Date: September 1, 2005 Y-1-1 Demonstrate
Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis
 Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis Arthritis of the patellofemoral joint refers to degeneration (wearing out) of the cartilage on the underside of the patella (kneecap) and the trochlea (groove) of the femur.
Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis Arthritis of the patellofemoral joint refers to degeneration (wearing out) of the cartilage on the underside of the patella (kneecap) and the trochlea (groove) of the femur.
Anterior Total Hip Replacement
 Anterior Total Hip Replacement Home Care Instructions Full recovery from your total hip replacement surgery is going to take months. This information will help you understand your recovery and care at
Anterior Total Hip Replacement Home Care Instructions Full recovery from your total hip replacement surgery is going to take months. This information will help you understand your recovery and care at
Physiotherapist's Guide to Elbow Fracture
 Physiotherapist's Guide to Elbow Fracture An elbow fracture is a bone break that occurs in the middle of the arm, in the area of the elbow joint. Its main cause is trauma, such as falling on the elbow,
Physiotherapist's Guide to Elbow Fracture An elbow fracture is a bone break that occurs in the middle of the arm, in the area of the elbow joint. Its main cause is trauma, such as falling on the elbow,
Non weight bearing advice (post operative)
 Non weight bearing advice (post operative) Physiotherapy Department Patient information leaflet Who is this booklet for? This booklet is for post-operative patients who have been told that they will have
Non weight bearing advice (post operative) Physiotherapy Department Patient information leaflet Who is this booklet for? This booklet is for post-operative patients who have been told that they will have
How to Protect Your Joints
 Form: D-5855 How to Protect Your Joints For people with arthritis Arthritis can be painful and make every day activities difficult. This booklet will show you how to protect your joints. This can help
Form: D-5855 How to Protect Your Joints For people with arthritis Arthritis can be painful and make every day activities difficult. This booklet will show you how to protect your joints. This can help
1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles. Striated Skeletal. Smooth
 1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth 3 Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System 4 Skeletal System 5 Skeletal System Functions
1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth 3 Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System 4 Skeletal System 5 Skeletal System Functions
The Shoulder Complex. Anatomy. Articulations 12/11/2017. Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas. Clavicle Collar Bone Scapula Shoulder Blade Humerus
 The Shoulder Complex Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Anatomy Clavicle Collar Bone Scapula Shoulder Blade Humerus Articulations Sternoclavicular SC joint. Sternum and Clavicle. Acromioclavicular AC
The Shoulder Complex Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Anatomy Clavicle Collar Bone Scapula Shoulder Blade Humerus Articulations Sternoclavicular SC joint. Sternum and Clavicle. Acromioclavicular AC
the back book Your Guide to a Healthy Back
 the back book Your Guide to a Healthy Back anatomy Your spine s job is to: Support your upper body and neck Increase flexibility of your spine Protect your spinal cord There are 6 primary components of
the back book Your Guide to a Healthy Back anatomy Your spine s job is to: Support your upper body and neck Increase flexibility of your spine Protect your spinal cord There are 6 primary components of
( 1 ) Ball and socket. Shoulder capsule. Rotator cuff.
 Shoulder Arthroscopy Page ( 1 ) Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word arthroscopy comes from two Greek words, arthro
Shoulder Arthroscopy Page ( 1 ) Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word arthroscopy comes from two Greek words, arthro
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN
 CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN Description Cervical strain/sprain is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or forward. The structures involved are the muscles, ligaments,
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN Description Cervical strain/sprain is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or forward. The structures involved are the muscles, ligaments,
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash)
 CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash) Description time and using proper technique decrease the frequency of Whiplash is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash) Description time and using proper technique decrease the frequency of Whiplash is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or
Chapter 09: Musculoskeletal Disorders Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions 5th Edition VanMeter https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-goulds-pathophysiology-health-professions-
Instant download and all chapters Test Bank Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions 5th Edition VanMeter https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-goulds-pathophysiology-health-professions-
Contact us! Vanderbilt Orthopaedic Institute Medical Center East, South Tower, Suite 4200 Nashville, TN
 Contact us! Vanderbilt Orthopaedic Institute Medical Center East, South Tower, Suite 4200 Nashville, TN 37232-8774 615-343-9430 This information is intended for education of the reader about medical conditions
Contact us! Vanderbilt Orthopaedic Institute Medical Center East, South Tower, Suite 4200 Nashville, TN 37232-8774 615-343-9430 This information is intended for education of the reader about medical conditions
Session 3 or 6: Being Active: A Way of Life.
 Session 3 or 6: Being Active: A Way of Life. You can find the time to be active. Set aside one block of time every day to be active. When can you set aside 20 to 30 minutes to do an activity you like?
Session 3 or 6: Being Active: A Way of Life. You can find the time to be active. Set aside one block of time every day to be active. When can you set aside 20 to 30 minutes to do an activity you like?
GETTING READY FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT
 GETTING READY FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Pre-Op Exercises for a Better Recovery Your Recovery Begins Now Even if your hip replacement surgery is weeks or months away, start getting ready now. People who
GETTING READY FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Pre-Op Exercises for a Better Recovery Your Recovery Begins Now Even if your hip replacement surgery is weeks or months away, start getting ready now. People who
Posterior Total Hip Replacement
 Posterior Total Hip Replacement Home Care Instructions Full recovery from your total hip replacement surgery is going to take months. This information will help you understand your recovery and care at
Posterior Total Hip Replacement Home Care Instructions Full recovery from your total hip replacement surgery is going to take months. This information will help you understand your recovery and care at
Mr. Siva Chandrasekaran Orthopaedic Surgeon MBBS MSpMed MPhil (surg) FRACS
 Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word arthroscopy comes from two Greek words, "arthro" (joint)
Shoulder Arthroscopy Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word arthroscopy comes from two Greek words, "arthro" (joint)
DISCOID MENISCUS. Description
 DISCOID MENISCUS Description For participation in jumping (basketball, volleyball) or The meniscus is a cartilage structure in the knee that sits on contact sports, protect the knee joint with supportive
DISCOID MENISCUS Description For participation in jumping (basketball, volleyball) or The meniscus is a cartilage structure in the knee that sits on contact sports, protect the knee joint with supportive
OV United Soccer Club
 Preventing disease transmission Place an effective barrier between you and the victim s blood when you give first aid. Examples of such barriers are: the victim s hand, a piece of plastic, clean folded
Preventing disease transmission Place an effective barrier between you and the victim s blood when you give first aid. Examples of such barriers are: the victim s hand, a piece of plastic, clean folded
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation
 A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 2 Introduction When the joint surfaces of an elbow are forced apart, the elbow is dislocated. The elbow is the second most commonly dislocated joint in adults (after
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 2 Introduction When the joint surfaces of an elbow are forced apart, the elbow is dislocated. The elbow is the second most commonly dislocated joint in adults (after
Chapter 9: Exercise Instructions
 RESOURCES RESEARCHERS / MEDICAL HOW TO HELP SPONSORS GEHRIG CONNECTION MEDIA TELETHON MDA.ORG search our site Go MDA/ALS Newsmagazine Current Issue Home> Publications >Everyday Life With ALS: A Practical
RESOURCES RESEARCHERS / MEDICAL HOW TO HELP SPONSORS GEHRIG CONNECTION MEDIA TELETHON MDA.ORG search our site Go MDA/ALS Newsmagazine Current Issue Home> Publications >Everyday Life With ALS: A Practical
Physical & Occupational Therapy
 In this section you will find our recommendations for exercises and everyday activities around your home. We hope that by following our guidelines your healing process will go faster and there will be
In this section you will find our recommendations for exercises and everyday activities around your home. We hope that by following our guidelines your healing process will go faster and there will be
PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION
 PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION Description For jumping (basketball, volleyball) or contact sports, Patellar dislocation and subluxation are injuries to the protect the patella with supportive devices,
PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION Description For jumping (basketball, volleyball) or contact sports, Patellar dislocation and subluxation are injuries to the protect the patella with supportive devices,
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT GUIDE
 TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT GUIDE This manual was made by physical therapists and Patient, Family and Community Education at City of Hope. Your physical therapist is: who can be reached at 626-256-HOPE (4673),
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT GUIDE This manual was made by physical therapists and Patient, Family and Community Education at City of Hope. Your physical therapist is: who can be reached at 626-256-HOPE (4673),
Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction
 Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Name:... Surgery Date:... Graft:... Orthopaedic Outpatient Appointment Date: Time: Location: Contact Number: Contacting
Physiotherapy Information following Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Name:... Surgery Date:... Graft:... Orthopaedic Outpatient Appointment Date: Time: Location: Contact Number: Contacting
Chiropractic Glossary
 Chiropractic Glossary Anatomy Articulation: A joint formed where two or more bones in the body meet. Your foot bone, for example, forms an articulation with your leg bone. You call that articulation an
Chiropractic Glossary Anatomy Articulation: A joint formed where two or more bones in the body meet. Your foot bone, for example, forms an articulation with your leg bone. You call that articulation an
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN. Expected Outcome. Causes
 Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers
 CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers Joint replacement surgery removes a damaged joint and replaces it with a prosthesis or artificial joint. The purpose of
CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers Joint replacement surgery removes a damaged joint and replaces it with a prosthesis or artificial joint. The purpose of
What Are Sports Injuries?
 What Should I Do if I Get Injured? Never try to "work through" the pain of a sports injury. Stop playing or exercising when you feel pain. Playing or exercising more only causes more harm. Some injuries
What Should I Do if I Get Injured? Never try to "work through" the pain of a sports injury. Stop playing or exercising when you feel pain. Playing or exercising more only causes more harm. Some injuries
