CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT OF INJURY. Rend CETTI, MD. Hospital of Orthopaedic Surgery, Sordi, Denmark ABSTRACT
|
|
|
- Esther Sullivan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
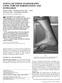
1 R.Cett Brit J. Sports Med. - Vol., No., March 9, pp. 7-5 CONSERVATIVE TREATMENT OF INJURY TO THE FIBULAR LIGAMENTS OF THE ANKLE Rend CETTI, MD Hospital of Orthopaedic Surgery, Sordi, Denmark ABSTRACT Fifty-one patients with fibular ligamentous injury of the ankle are presented. The treatment consisted of complete nonweight-bearing of the affected foot by use of elbow crutches for three weeks. All patients were seen at follow-up eighteen months after the accident. The results are discussed in the light of previous literature on conservative and operative treatment of lateral ligament injuries. Residual symptoms were present in 5.7 per cent, but none needed further treatment. It is emphasized that the treatment described in the present study diminishes the risk of subjective functional instability and gives a quick return to normal gait and sport. INTRODUCTION Among problems in traumatology only few have been subjected to such a great interest and such diverging opinions as the treatment of fibular ligamentous injuries of the ankle. Many authors employ conservative treatment, and only resort to operation in those cases were conservative treatment results in unacceptable ankle malfunction or where the trauma has resulted in severe damage to the ligaments (Adler, H., 97), (Anderson, K. J. and Lecocq, J. F., 95), (Duquennoy, A. et al, 975), (Dziob, J. H., 95). Problems in the treatment of ligamentous ankle injuries deal not only with the advantages and disadvantages of conservative versus operative treatment, but also with the length and kind of immobilisation. Freeman (95) stressed that early mobilisation after ligamentous injury to the ankle enhances muscular stimulation and proprioception and thereby adds to the stability of the ankle. Address for Correspondence: Dr. Rend Cetti, MD, Betty Nansens Alle, 5 Valby, Copenhagen, Denmark The aim of this study is to elucidate to what extent non-weight-bearing without plaster is a sufficient treatment of injured fibular ankle ligaments. PATIENTS AND METHODS During the period February, 97 to November, 979, 7 patients with acute ankle sprains were treated in the Hospital of Orthopaedic Surgery in SorO. Fifty-seven had rupture of the lateral ligaments. The diagnosis was based on the presence of tenderness, oedema and/or haematoma in front of and distal to the lateral malleolus, corresponding to the lateral ligaments. The anterior drawer test and talar tilt test were included in the clinical examination.* To exclude fractures standard radiograms of the ankle were taken. Verification of the ruptured fibular ankle ligaments was based on talar tilt seen on X-Ray. A difference of six degrees or more between the injured (I) and the uninjured (U) ankle was considered diagnostic of ligamentous rupture (Fig. ). All patients with ligament injuries were requested to return for clinical and radiological re-examination. Four could not be traced and two failed to attend. Fifty-one were thus fully re-examined eighteen months after the *See preceding paper by Kristiansen for definition of these tests 7 Br J Sports Med: first published as./bjsm...7 on March 9. Downloaded from on July by guest. Protected by copyright.
2 U== t bib a tlus t a talus (I- U) = -= > I= Fig. : Roentgenological talar tilt The difference between the injured (I) and uninjured (U) ankle is more than five degree& This is considered diagnostic of ligamentous rupture. injury. Twenty-five were men and twenty-six women, the mean age at the time of accident was twenty-two years (range -5). The left ankle was injured in twenty-nine patients, the right in twenty-two. The relations between age, sex and side of injury are shown in Table. TABLE I Age, sex and side of injury in fifty-one patients with injured fibular ankle ligaments Age group years Average age Males Right Left s Right Left no. no. no. no Most patients sustained their sprains while engaged in sport (%). The cause of injury is shown in Table II, and the sports involved in Table Ill. Treatment consisted of complete non-weight-bearing of the affected foot by the use of elbow crutches for three weeks. Active exercises were started immediately. Treatment was initiated within thirty-six hours from the time of accident. Forty-two patients (%) reached hospital within six hours. The mean time from accident to arrival at the emergency room was four hours (Table IV). TABLE Distribution of fifty-one patients with injured fibular ankle ligaments according to the circumstances of the accident Cause of injury Sport Work Home Traffic Others No. 9 5 TABLE III Sport situations in thirty-one patients with fibular ligamentous ankle injuries. Sport Soccer Running Handball Badminton Trampoline Gymnastics Competitive Sport No TABLE IV Exercising Sport No Time between accident and arrival at emergency room in fifty-one patients with ruptured fibular ankle ligaments and in 5 patients with ankle sprains but without ligamentous damage. Without liga- With ligamentous Injury mentous injury Males s s s Percent Hours No. No. No. No Br J Sports Med: first published as./bjsm...7 on March 9. Downloaded from on July by guest. Protected by copyright.
3 At clinical examination three weeks after injury weight-bearing of the injured foot was allowed, if the ankle movements were normal and without pain. Otherwise further non-weight-bearing was indicated followed by weekly clinical examination. Forty-two patients were treated for three weeks and nine for four weeks (mean twenty-two days). All patients were advised not to participate in sport for five weeks. RESULTS On arrival at hospital all patients were asked whether weight-bearing on the injured foot was still possible after the accident. The answers are seen in Table V, where the term "possible" means that the injured foot could be used as in normal gait, but with slight pain, "limited" means that limping is marked on account of pain. TABLE V Possibility of using the injured foot from the time of accident to arrival at hospital in fifty-one patients with injured fibular ankle ligaments, and in 5 patients with ankle sprains but without ligamentous damage. Injured Uninjured Use of foot Males s s s Possible I mpossible At the primary examination all patients had painful movements of the ankle, tenderness located around the lateral malleolus and swelling. Twelve patients (%) had haematomatous discolouration of the skin at the fibular side of the foot beneath the malleolus. Before X-Ray examination all patients had a provisional diagnosis of injury to the fibulat ligaments of the ankle made on clinical grounds. At the primary clinical examination a positive anterior drawer test was present in fourteen patients (Table VI). Clinical positive talar tilt test was present in two females who also had a positive anterior drawer test (Table VII). The results of the primary radiological talar tilt examination are shown in Table Vil. The mean talar tilt difference (I-U) was eight degrees (range -5). At follow-up eighteen months after the accident, all patients were questioned about residual symptoms, examined clinically, and X-Rays for anterior drawer sign and talar tilt were repeated (Table IX and X). The TABLE VI Clinical anterior drawer test at the time of accident in fifty-one patients with injured fibular ankle ligaments. Clinical anterior drawer sign Absent Doubtful Present 9 Males s s TABLE VII Clinical talar tilt test at the time of accident in fifty-one patients with injured fibular ankle ligaments. Clinical talar tilt Males s s Absent Doubtful Present TABLE Vill Primary radiological talar tilt in fifty-one patients with injured fibular ankle ligaments. I = talar tilt of the injured foot U = talar tilt of the uninjured foot (I - U) Males > 5 s 9 s 5 5. TABLE IX Radiological talar tilt at follow-up in fifty-one patients with previous injured fibular ankle ligaments. (I - U) Males s s > mean radiological talar tilt difference (I-U) was three degrees (range -7); one boy, sixteen years old, had primarily a talar tilt difference (I-U) of fifteen degrees, but at follow-up his talar tilt difference (I-U) was seven- Br J Sports Med: first published as./bjsm...7 on March 9. Downloaded from on July by guest. Protected by copyright.
4 5 TABLE X Radiological drawer test (millimetre) at follow-up in fifty-one patients with previous injured fibular ankle ligaments. Anterior drawer test mm Males s s > teen degrees, the drawer test five millimetres and the patient suffered from subjective instability in the ankle joint. Eight out of fifty-one patients (%) had residual symptoms (Table XI), the most serious being functional instability () of the ankle joint. was defined as a feeling of insecurity in the ankle joint and tendency for the foot to "give way". The relations between primary talar tilt, secondary talar tilt, anterior drawer test and residual symptoms are shown in Table Xi. The relations between arrival time at hospital, ability to use the injured foot before treatment and residual symptoms are seen in Table XIII. TABLE Xl Residual symptoms in fifty-one patients with previously injured fibular ankle ligaments at follow-up months after injury. Residual symptoms Males s None Recurrent pain and swelling in the ankle Functional instability s None of the patients with residual symptoms consulted a doctor about further treatment. All patients went back to work without having inconvenient ankle problems. Among the eight patients with residual symptoms, four (numbers,, 7 and in Table XII) sustained the ligamentous rupture during sport. Two of these were still active sportsmen at the same level as before the accident, while the remaining two gave up sport because of subjective. All of the patients without residual symptoms, who had the injury during sport, were still active. Two patients who had returned to competitive sport had a new sprain in the interval between treatment and follow-up. Both had no residual symptoms and were not correlating the new sprain with the TABLE XII Radiological primary talar tilt (I - U), secondary talar tilt (I - U) and anterior drawer test in eight patients with residual symptoms after injury to the fibular ankle ligaments. = subjective functional instability. PS = recurrent pain and swelling in the ankle. Patients Age Patients 5 7 Sex Male Male Male Time from accident to arrival at hospital hours Radiological talar Anterior tilt (I - U) drawer Residual Primary Secondary test mm. Symptoms 7 5 PS PS PS TABLE XIII Time of arrival at hospital and possibility of using the injured foot after the trauma but before treatment in eight patients with residual symptoms after injury to the fibular ankle ligaments. Possibility of using the injured foot after accident to arrival at hospital Impossible Possible Possible Impossible Impossible Residual Symptoms PS PS PS previous injured fibular ankle ligaments. Both needed no treatment after the new sprain. At follow-up all patients were asked whether they were satisfied with the treatment. Eighty-nine per cent stated that the treatment was excellent, eleven per cent that it was good, thus none was dissatisfied. DISCUSSION Brostrom (9) in a study of surgical versus conser vative treatment of rupture to the fibular ankle ligaments, stressed that although surgical treatment gave the best long-term results, it could not be recommended for routine treatment. Three reasons were behind this statement: () The risk of post-operative infection and osteoarthritis, () discomfort from the scar *such as altered sensibility and traumatic neuroma and () because secondary surgical repair, if necessary, can be Br J Sports Med: first published as./bjsm...7 on March 9. Downloaded from on July by guest. Protected by copyright.
5 performed with good results even several years after the injury. He also pointed out that residual symptoms after non-surgical treatment are usually mild and not disabling, and that the duration of sick leave after operation is considerably longer than after conservative treatment. Conservative treatment usually consists of immobilisation in plaster. Ruth (9) found that fifty-eight per cent of the patients treated with plaster immobilisation for six weeks had persistent minor or major complaints two years later. Wiles (959) stated that immobilised ankles remained stiff for long periods after exercises were started. Freeman (95) and Niethard (97) also found poor results after conservative treatment; as fortyfour and fifty-five per cent respectively of the patients treated with plaster immobilisation had residual symptoms. Freeman (95) concluded that early mobilisation could be recommended as the treatment of choice for most, perhaps all, ruptures of the fibular ligaments of the ankle. Freeman (95) in a study of physiotherapy versus immobilisation of injured lateral ligaments found that ligamentous injuries frequently produce a proprioceptive deficit affecting the muscles of the injured leg. He stressed that such a deficit could be responsible for the symptom of the foot "giving way". He also emphasised that the incidence of both the proprioceptive deficit and the symptom of "giving way" could be reduced sybstantially by early mobilisation and coordinating exercises. Hansen et al (979) in a follow-up of patients treated with plaster for six weeks found that twentyone per cent of the patients had residual symptoms. was present in eighteen per cent. Four patients reported major complaints having weekly episodes of "sprains", and one developed reflex dystrophy. Clark et al (95) found no difference between conservative and operative treatment, but concluded that, in young patients with severe damage of the fibular ankle ligaments (unilateral talar tilt exceeding fifteen degrees), surgery is to be preferred to plaster immobilisation. Termansen et al (979) emphasised that there was no correlation between roentgenological instability and residual symptoms. He found that nineteen per cent of the patients treated with plaster immobilisation had secondary radiological instability in the ankle joint. Residual symptoms, in patients with previous fibular ligamentous injury, were present in twenty-one per cent. Niedermann et al (9) in a prospective study on operative as compared with conservative treatment, emphasised that there was no difference between the two groups. Seventy-six per cent of the patients treated by plaster immobilisation for five weeks obtained good results. In the present study 5.7 per cent had residual symptoms. Five patients had subjective functional instability in the ankle joint. None needed further treatment and all went back to work without ankle problems. These results are better than those seen in previous publications on conservative treatment of injury to the fibular ankle ligaments (Adler, 97; Brostrom, 9; Delplace et al, 975; Freeman et al, 95; Gross and McIntosh, 97; Russe, 97; Staples, 97; Tonino, 97). It might be assumed that patients with less serious ankle sprains would wait longer before seeking medical care than those with severe damage. This point of view could not be verified in the present study. Consequently a severe ligamentous lesion is still a possibility in patients arriving "late" to the emergency room, and so lateness does not justify omission of adequate examination and treatment. One of the aspects in ankle sprains that might suggest a severe injury is the post traumatic dysfunction of the joint, which is reflected in the inability to use the injured foot fully after the accident. Seventy-seven per cent of the patients with ligamentous injury had marked difficulties in walking after the accident, while fifty-four per cent of the patients with ankle sprains but without ligamentous injury had the same difficulties. Among all the patients - with and without ligamentous injury - who had marked problems in using the injured foot after injury, the statistical probability of having a ligamentous rupture could be estimated at.. So the ability to use the injured foot after a sprain is a poor diagnostic criterion, which is not applicable in the diagnosis of ligamentous injury. The treatment described in this study was based on the presumption that a partial nerve de-afferentation is caused by the ligamentous injury. The consequent proprioceptive nerve deficit might be compensated by a central process, but only if movements are taking place in the talo-tibial joint. By these movements the proprioceptive deficit might be momentary, and accordingly the risk of subjective functional instability should diminish. The results support the suggestion that early mobilisation does have a positive influence on the risk of subjective functional instability in the ankle joint. Because is far the most serious residual symptom, there is in my opinion no doubt that early mobilisation following ligamentous ankle injury deserves a much higher priority than is usually observed. 5 Among sportsmen sustaining a ligamentous ankle Br J Sports Med: first published as./bjsm...7 on March 9. Downloaded from on July by guest. Protected by copyright.
6 5 injury, it is of the utmost importance to have treatment which leads to a quick return to sport at the same level as before the accident. Plaster immobilisation and especially operative treatment both make a very large REFERENCES break in the training programme. The treatment carried out in this series gives a very quick return to sport and furthermore diminishes the risk of subjective functional instability in the ankle joint. Adler, H., 97 "Therapie und Prognose der frischen Aussenknockelbandlasion". Unfallheilkunde 79: -. Anderson, K. J. and Lecocq, J. F., 95 "Operative treatment of injury to the fibular collateral ligament of the ankle". J.Bone Jt.Surg. (Am.) : 5-. Brostrom, L., 9 "Sprained ankles. Treatment and prognosis in recent ligament ruptures". Acta Chir.Scand. : Clark, B. L., Derby, A. C. and Power, G. R. J., 95 "Injuries of the lateral ligament of the ankle. Conservative vs. operative repair". Can.J.Surg. : 5-. Delplace, J., ocoud, D. and Castaing, J., 975 "Resultat a propos de cas observes la service des Urgances du CH R de tours". (suppl. ): -5. Duquennoy, A., Lisddle, D. and Torabi, D. J., 975 "Resultat du traitement chirurgical de la rupture du ligament lateral externe de la cheville". Rev.Chir.Orthop. : 59-. Dziob, J. H., 95 "Ligamentous injuries about the ankle joint". Am.J.Surg. 9: 9-9. Freeman, M. A. R., Dean, M. R. E. and Hanham, I. W. D., 95 "The etiology and prevention of functional instability of the foot". J.Bone Jt.Surg. 7 B: 7-5. Freeman, M. A. R., 95 "Treatment of ruptures of the lateral ligament of the ankle". J.Bone Jt.Surg.(Br.) 7 B: -. Gross, A. E. and McIntosh, D. L., 97 "Injury to the lateral ligament of the ankle: A clinical study". Can.J.Surg. : 5-7. Hansen, H., Damholt, V. and Termansen, N. B., 979 "Clinical and social status following injury to the lateral ligaments of the ankle". Acta Orthop.Scand. 5: Niedermann, B., Andersen, A., Bryde-Andersen, S., Funder, V., Jjrgensen, J. P., Lindholmer, E. and Vuust, M., 9 "Rupture of the lateral ligaments of the ankle: Operation or plaster cast?" Acta Orthop.Scand. 5: Niethard, F. V., 97 "Die stabilitat des sprunggelenkes nach ruptur des lateralen bandapparates". Arch orthop.unfall- Chir. : 5-. Russe, O., 97 "Subluxatio tali supinatoria". Z.Unfallheilk 9: -7. Ruth, C. J., 9 "The surgical treatment of injuries of the fibular collateral ligaments of the ankle". J.Bone Jt.Surg. (Am.) A: 9-. Staples,. S., 97 "Result study of ruptures of the lateral ligaments of the ankle". Clin.Orthop. 5: 5-5. Termansen, N. B., Hansen, H. and Damholt, V., 979 "Radiological and muscular status following injury to the lateral ligaments of the ankle". Acta Orthop.Scand. 5: Tonino, A. J., 97 "Treatment of partial ruptures of the lateral ligament of the ankle in acute ankle sprains". Arch. Chir.Neerl. 5: 9-9. Wiles, P., 959 "Essentials of orthopaedics". Third edition, J. and A. Churchill Ltd.,. Br J Sports Med: first published as./bjsm...7 on March 9. Downloaded from on July by guest. Protected by copyright.
65 patients in each and all were participating in the follow-up sixth months after the accident. There were no
 104 Brit. J. Sports Med. - Vol. 18, No. 2, June 1984, pp. 104-199 R. Cetti S. E. Christensen M. T. Corfitsen RUPTURED FIBULAR ANKLE LIGAMENT: PLASTER OR PLITON BRACE? R. CETTI, MD, S.-E. CHRISTENSEN, MD
104 Brit. J. Sports Med. - Vol. 18, No. 2, June 1984, pp. 104-199 R. Cetti S. E. Christensen M. T. Corfitsen RUPTURED FIBULAR ANKLE LIGAMENT: PLASTER OR PLITON BRACE? R. CETTI, MD, S.-E. CHRISTENSEN, MD
Rupture of the Lateral Ligaments of the Ankle: Operation or Plaster Cast?: A Prospective Study
 Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica ISSN: 0001-6470 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iort19 Rupture of the Lateral Ligaments of the Ankle: Operation or Plaster Cast?: A Prospective
Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica ISSN: 0001-6470 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iort19 Rupture of the Lateral Ligaments of the Ankle: Operation or Plaster Cast?: A Prospective
From the Middlesex Hospital, London
 INSTABILITY OF THE FOOT AFFER INJURIES TO THE LATERAL LIGAMENT OF THE ANKLE M. A. R. FREEMAN, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Middlesex Hospital, London The tendency for the foot to give way (a complaint here
INSTABILITY OF THE FOOT AFFER INJURIES TO THE LATERAL LIGAMENT OF THE ANKLE M. A. R. FREEMAN, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Middlesex Hospital, London The tendency for the foot to give way (a complaint here
Grade III injuries of the lateral ligaments of the ankle: the incidence and
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1986, 3, 247-251 Grade III injuries of the lateral ligaments of the ankle: the incidence and a simple stress test C. L. MUWANGA, MARGARET HELLIER, D. N. QUINTON, J. P. SLOAN
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1986, 3, 247-251 Grade III injuries of the lateral ligaments of the ankle: the incidence and a simple stress test C. L. MUWANGA, MARGARET HELLIER, D. N. QUINTON, J. P. SLOAN
Paris) and the surgical reconstructive approach, both of
 Brit. J. Sports Med. - Vol. 16, No. 4, December 1982, pp. 245-2492 INJURIES TO THE LATERAL LIGAMENT OF THE ANKLE. ASSESSMENT AND TREATMENT M. A. HUTSON and J. P. JACKSON, FRCS Sports Injury Clinic, General
Brit. J. Sports Med. - Vol. 16, No. 4, December 1982, pp. 245-2492 INJURIES TO THE LATERAL LIGAMENT OF THE ANKLE. ASSESSMENT AND TREATMENT M. A. HUTSON and J. P. JACKSON, FRCS Sports Injury Clinic, General
Sprain or fracture? An analysis of 2000
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1986, 3, 101-106 Sprain or fracture? An analysis of 2000 ankle injuries P. SUJITKUMAR, J. M. HADFIELD* AND D. W. YATES* Accident and Emergency Department, Hope Hospital,
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1986, 3, 101-106 Sprain or fracture? An analysis of 2000 ankle injuries P. SUJITKUMAR, J. M. HADFIELD* AND D. W. YATES* Accident and Emergency Department, Hope Hospital,
Imaging of the anterolateral instability of the ankle by ultrasound Summary Introduction Methods
 Imaging of the anterolateral instability of the ankle by ultrasound Hrazdira, L.Skotáková J. St. Anna s Faculty Hospital in Brno, Orthopedic Department Summary This article reviews ten year results of
Imaging of the anterolateral instability of the ankle by ultrasound Hrazdira, L.Skotáková J. St. Anna s Faculty Hospital in Brno, Orthopedic Department Summary This article reviews ten year results of
Ankle Ligament Injury: Don t Worry- It s Only a Sprain Wes Jackson MD Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle
 Ankle Ligament Injury: Don t Worry- It s Only a Sprain Wes Jackson MD Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Outline I. Epidemiology II. Classification and Types of Sprains III. Anatomy IV. Clinical Assessment and Imaging
Ankle Ligament Injury: Don t Worry- It s Only a Sprain Wes Jackson MD Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Outline I. Epidemiology II. Classification and Types of Sprains III. Anatomy IV. Clinical Assessment and Imaging
Investigation of the factors to affect the duration to return sports after the surgery of anterior talofibular ligament repair with arthroscopy
 Investigation of the factors to affect the duration to return sports after the surgery of anterior talofibular ligament repair with arthroscopy Hamamatsu University School of Medicine Mitsuru Hanada, Shoichi
Investigation of the factors to affect the duration to return sports after the surgery of anterior talofibular ligament repair with arthroscopy Hamamatsu University School of Medicine Mitsuru Hanada, Shoichi
The Lauge Hansen Classification of Malleolar Fractures
 Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica ISSN: 0001-6470 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iort19 The Lauge Hansen Classification of Malleolar Fractures Johannes Yde To cite this
Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica ISSN: 0001-6470 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iort19 The Lauge Hansen Classification of Malleolar Fractures Johannes Yde To cite this
We investigated a new method of stress
 SUBTALAR STRESS RADIOGRAPHY USING FORCED DORSIFLEXION AND SUPINATION TOMOO ISHII, SHUMPEI MIYAGAWA, TORU FUKUBAYASHI, KOICHIRO HAYASHI From the University of Tsukuba, Japan We investigated a new method
SUBTALAR STRESS RADIOGRAPHY USING FORCED DORSIFLEXION AND SUPINATION TOMOO ISHII, SHUMPEI MIYAGAWA, TORU FUKUBAYASHI, KOICHIRO HAYASHI From the University of Tsukuba, Japan We investigated a new method
THE ETIOLOGY AND PREVENTION OF FUNCTIONAL INSTABILITY OF THE FOOT
 THE ETOLOGY AND PREVENTON OF FUNCTONAL NSTABLTY OF THE FOOT M. A. R. FREEMAN, M. R. E. DEAN and. W. F. HANHAM, LONDON, ENGLAND From tile Westminster Hospital, London Functional instability of the foot
THE ETOLOGY AND PREVENTON OF FUNCTONAL NSTABLTY OF THE FOOT M. A. R. FREEMAN, M. R. E. DEAN and. W. F. HANHAM, LONDON, ENGLAND From tile Westminster Hospital, London Functional instability of the foot
But it s only an ankle sprain. Ankle injuries are the most common injury to the lower limb as a result of sports.
 But it s only an ankle sprain Ankle injuries are the most common injury to the lower limb as a result of sports. Fortunately, most of them are minor and require little specific treatment, however, some
But it s only an ankle sprain Ankle injuries are the most common injury to the lower limb as a result of sports. Fortunately, most of them are minor and require little specific treatment, however, some
BCCH Emergency Department LOWER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack
 1 BCCH Emergency Department LOWER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack Developed by: Rena Heathcote RN. 2 Knee Injuries The knee joint consists of a variety of structures including: 3 bones (excluding the patella)
1 BCCH Emergency Department LOWER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack Developed by: Rena Heathcote RN. 2 Knee Injuries The knee joint consists of a variety of structures including: 3 bones (excluding the patella)
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries. Anatomy. Anatomy. Tibia: the second longest bone in the body
 Prevention and Treatment of Injuries The Ankle and Lower Leg Westfield High School Houston, Texas Anatomy Tibia: the second longest bone in the body Serves as the principle weight-bearing bone of the leg.
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries The Ankle and Lower Leg Westfield High School Houston, Texas Anatomy Tibia: the second longest bone in the body Serves as the principle weight-bearing bone of the leg.
June 2013 Case Study. Author: T. Walker Robinson, MD, MPH, Nationwide Children s Hospital
 June 2013 Case Study Author: T. Walker Robinson, MD, MPH, Nationwide Children s Hospital Chief Complaint: Right ankle pain HPI: A 10 year old female dancer presents to the clinic with a five day history
June 2013 Case Study Author: T. Walker Robinson, MD, MPH, Nationwide Children s Hospital Chief Complaint: Right ankle pain HPI: A 10 year old female dancer presents to the clinic with a five day history
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2155/14
 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2155/14 BEFORE: S. Netten: Vice-Chair HEARING: November 17, 2014 at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: January 9, 2015 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2015
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2155/14 BEFORE: S. Netten: Vice-Chair HEARING: November 17, 2014 at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: January 9, 2015 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2015
Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle
 Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY I. I. Reidsma, P. A. Nolte, R. K. Marti, E. L. F. B. Raaymakers From Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY I. I. Reidsma, P. A. Nolte, R. K. Marti, E. L. F. B. Raaymakers From Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Knee Injuries. PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS. Medial Collateral Ligament Sprain
 Knee Injuries PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS Medial Collateral Ligament Sprain Result from either a direct blow from the lateral side in a medial direction or a severe outward twist Greater injury
Knee Injuries PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS Medial Collateral Ligament Sprain Result from either a direct blow from the lateral side in a medial direction or a severe outward twist Greater injury
Ankle Sprain. 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) Website: philip-bayliss.com
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353 Website: philip-bayliss.com Ankle Sprain An Ankle sprain is one of the most common musculoskeletal injuries. Patients typically describe
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353 Website: philip-bayliss.com Ankle Sprain An Ankle sprain is one of the most common musculoskeletal injuries. Patients typically describe
Ankle Fracture Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet. Under review. Page 1
 Ankle Fracture Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 Ankle Fracture Welcome to the Dudley Group NHS Foundation Trust. This leaflet will provide you with information regarding the diagnosis
Ankle Fracture Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 Ankle Fracture Welcome to the Dudley Group NHS Foundation Trust. This leaflet will provide you with information regarding the diagnosis
CASE ONE CASE ONE. RADIAL HEAD FRACTURE Mason Classification. RADIAL HEAD FRACTURE Mechanism of Injury. RADIAL HEAD FRACTURE Imaging
 CASE ONE An eighteen year old female falls during a basketball game, striking her elbow on the court. She presents to your office that day with a painful, swollen elbow that she is unable to flex or extend
CASE ONE An eighteen year old female falls during a basketball game, striking her elbow on the court. She presents to your office that day with a painful, swollen elbow that she is unable to flex or extend
Disclosures. Syndesmosis Injury. Syndesmosis Ligaments. Objectives. Mark M. Casillas, M.D.
 Disclosures Syndesmosis Injury No relevant disclosures Mark M. Casillas, M.D. 1 Objectives Syndesmosis Ligaments Understand the syndesmosis anatomy and function Classify syndesmosis injuries Describe treatment
Disclosures Syndesmosis Injury No relevant disclosures Mark M. Casillas, M.D. 1 Objectives Syndesmosis Ligaments Understand the syndesmosis anatomy and function Classify syndesmosis injuries Describe treatment
Surgery-Ortho. Fractures of the tibia and fibula. Management. Treatment of low energy fractures. Fifth stage. Lec-6 د.
 Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Ankle Pain After a Sprain.
 Ankle Pain After a Sprain www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Anterior Drawer Stress Test Talar Tilt Talar Tilt (CFL) Difficult to isolate from subtalar ROM Slight plantar flexion (dorsi = relative subtalar isolation)
Ankle Pain After a Sprain www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Anterior Drawer Stress Test Talar Tilt Talar Tilt (CFL) Difficult to isolate from subtalar ROM Slight plantar flexion (dorsi = relative subtalar isolation)
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2568/06
 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2568/06 BEFORE: R. McClellan : Vice-Chair HEARING: December 22, 2006 at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: January 3, 2007 NEUTRAL CITATION:
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 2568/06 BEFORE: R. McClellan : Vice-Chair HEARING: December 22, 2006 at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: January 3, 2007 NEUTRAL CITATION:
Outline. Ankle/Foot Anatomy Ankle Sprains Ottawa Ankle Rules DDx: The Sprain That Wasn t
 Ankle Injuries Outline Ankle/Foot Anatomy Ankle Sprains Ottawa Ankle Rules DDx: The Sprain That Wasn t Anatomy: Ankle Mortise Bony Anatomy Lateral Ligament Complex Medial Ligament Complex Ankle Sprains
Ankle Injuries Outline Ankle/Foot Anatomy Ankle Sprains Ottawa Ankle Rules DDx: The Sprain That Wasn t Anatomy: Ankle Mortise Bony Anatomy Lateral Ligament Complex Medial Ligament Complex Ankle Sprains
Modified Brostrom-Evans-Gould technique for recurrent lateral ankle ligament instability
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2007;15(3):306-10 Modified Brostrom-Evans-Gould technique for recurrent lateral ankle ligament instability ZD Ng, S Das De Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, National University
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2007;15(3):306-10 Modified Brostrom-Evans-Gould technique for recurrent lateral ankle ligament instability ZD Ng, S Das De Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, National University
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 12 Page December 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v4i12.78 A Study to Find out the Effectiveness of
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-45 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/1.18535/jmscr/v4i12.78 A Study to Find out the Effectiveness of
Common Athletic Injuries of the Ankle
 Common Athletic Injuries of the Ankle Common Injuries of the Ankle in Athletes Ankle Sprains Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability Peroneal Tendon Injuries Achilles Tendon Tears Ankle Sprains What s an Ankle
Common Athletic Injuries of the Ankle Common Injuries of the Ankle in Athletes Ankle Sprains Chronic Lateral Ankle Instability Peroneal Tendon Injuries Achilles Tendon Tears Ankle Sprains What s an Ankle
A Randomized, Prospective Study of Operative and Non-Operative Treatment of Injuries of the Fibular Collateral Ligaments of the Ankle*
 Copyright 998 by The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, Incorporated A Randomized, Prospective Study of Operative and n-operative Treatment of Injuries of the Fibular Collateral Ligaments of the Ankle*
Copyright 998 by The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, Incorporated A Randomized, Prospective Study of Operative and n-operative Treatment of Injuries of the Fibular Collateral Ligaments of the Ankle*
COMPREHENSIVE TREATMENT PROGRAM FOR UNCOMPLICATED LATERAL ANKLE SPRAINS
 1 COMPREHENSIVE TREATMENT PROGRAM FOR UNCOMPLICATED LATERAL ANKLE SPRAINS John G. Aronen, M.D. Consultant, Center for Sports Medicine Saint Francis Memorial Hospital San Francisco, CA James G. Garrick,
1 COMPREHENSIVE TREATMENT PROGRAM FOR UNCOMPLICATED LATERAL ANKLE SPRAINS John G. Aronen, M.D. Consultant, Center for Sports Medicine Saint Francis Memorial Hospital San Francisco, CA James G. Garrick,
Ankle Arthroscopy.
 Ankle Arthroscopy Key words: Ankle pain, ankle arthroscopy, ankle sprain, ankle stiffness, day case surgery, articular cartilage, chondral injury, chondral defect, anti-inflammatory medication Our understanding
Ankle Arthroscopy Key words: Ankle pain, ankle arthroscopy, ankle sprain, ankle stiffness, day case surgery, articular cartilage, chondral injury, chondral defect, anti-inflammatory medication Our understanding
Leg and Ankle Problems in Primary Care.
 Leg and Ankle Problems in Primary Care www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Leg and Ankle Presentations 4Trauma 4Pain Ankle Trauma 41. Twist and Fall--Fracture or Sprain 42. Patient hears/feels a pop--tendon or
Leg and Ankle Problems in Primary Care www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Leg and Ankle Presentations 4Trauma 4Pain Ankle Trauma 41. Twist and Fall--Fracture or Sprain 42. Patient hears/feels a pop--tendon or
Index. Clin Sports Med 23 (2004) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Clin Sports Med 23 (2004) 169 173 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achilles enthesopathy, calcaneal spur with, 133 clinical presentation of, 135 136 definition of, 131
Clin Sports Med 23 (2004) 169 173 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achilles enthesopathy, calcaneal spur with, 133 clinical presentation of, 135 136 definition of, 131
Mary Lloyd Ireland, M.D. Associate Professor University of Kentucky Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery and Sports Medicine Lexington, Kentucky
 Common Ankle Injuries: Diagnosis and Treatment Mary Lloyd Ireland, M.D. Associate Professor University of Kentucky Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery and Sports Medicine Lexington, Kentucky Disclaimer Slide
Common Ankle Injuries: Diagnosis and Treatment Mary Lloyd Ireland, M.D. Associate Professor University of Kentucky Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery and Sports Medicine Lexington, Kentucky Disclaimer Slide
ii ANKLE INJURIES SPECIFIC TRAINING AFTER INJURY TO THE FOOT OR ANKLE
 40 Ankle injuries are among the most common injuries in sport. Ankle sprain (which is a mechanism rather than a diagnosis) is the most common injury in virtually all epidemiological studies. Being the
40 Ankle injuries are among the most common injuries in sport. Ankle sprain (which is a mechanism rather than a diagnosis) is the most common injury in virtually all epidemiological studies. Being the
Deltoid and Syndesmosis Ligament Injury of the Ankle Without Fracture
 Deltoid and Syndesmosis Ligament Injury of the Ankle Without Fracture Chris D. Miller, MD, Walter R. Shelton,* MD, Gene R. Barrett, MD, F. H. Savoie, MD, and Andrea D. Dukes, MS From the Mississippi Sports
Deltoid and Syndesmosis Ligament Injury of the Ankle Without Fracture Chris D. Miller, MD, Walter R. Shelton,* MD, Gene R. Barrett, MD, F. H. Savoie, MD, and Andrea D. Dukes, MS From the Mississippi Sports
Pure Closed Posteromedial Dislocation of the Tibiotalar Joint without Fracture
 214 2013 Chinese Orthopaedic Association and Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd BRIEF REPORT Pure Closed Posteromedial Dislocation of the Tibiotalar Joint without Fracture Yun-tao Wang, MD, PhD, Xiao-tao Wu,
214 2013 Chinese Orthopaedic Association and Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd BRIEF REPORT Pure Closed Posteromedial Dislocation of the Tibiotalar Joint without Fracture Yun-tao Wang, MD, PhD, Xiao-tao Wu,
Anatomy and evaluation of the ankle.
 Anatomy and evaluation of the ankle www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Ankle Anatomical Structures Tibia Fibular Talus Tibia This is the strongest largest bone of the lower leg. It bears weight and the bone creates
Anatomy and evaluation of the ankle www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Ankle Anatomical Structures Tibia Fibular Talus Tibia This is the strongest largest bone of the lower leg. It bears weight and the bone creates
SOFT TISSUE KNEE INJURIES
 SOFT TISSUE KNEE INJURIES Soft tissue injuries of the knee commonly occur in all sports or in any activity that requires sudden changes in activity or movement. The knee is a complex joint and any injury
SOFT TISSUE KNEE INJURIES Soft tissue injuries of the knee commonly occur in all sports or in any activity that requires sudden changes in activity or movement. The knee is a complex joint and any injury
Ankle Injuries. Ankle Sprain. Range of Motion. The most likely diagnosis is lateral ligament sprain. Dorsiflexion Plantarflexion Inversion
 Ankle Injuries Dr Peter Brukner, OAM Sports Physician Associate Professor Centre for Sports Medicine Research & Education The University of Melbourne Adjunct Professor School of Human Movement Studies
Ankle Injuries Dr Peter Brukner, OAM Sports Physician Associate Professor Centre for Sports Medicine Research & Education The University of Melbourne Adjunct Professor School of Human Movement Studies
Acute Ankle Injuries, Part 1: Office Evaluation and Management
 t June 08, 2009 Obesity [1] Each acute ankle injury commonly seen in the office has associated with it a mechanism by which it can be injured, trademark symptoms that the patient experiences during the
t June 08, 2009 Obesity [1] Each acute ankle injury commonly seen in the office has associated with it a mechanism by which it can be injured, trademark symptoms that the patient experiences during the
Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Lower Limb
 Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Lower Limb JMAJ 48(1): 25 29, 2005 Motonobu NATSUYAMA Chief Surgeon, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kantoh
Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Lower Limb JMAJ 48(1): 25 29, 2005 Motonobu NATSUYAMA Chief Surgeon, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kantoh
Scar Engorged veins. Size of the foot [In clubfoot, small foot]
![Scar Engorged veins. Size of the foot [In clubfoot, small foot] Scar Engorged veins. Size of the foot [In clubfoot, small foot]](/thumbs/78/77722241.jpg) 6. FOOT HISTORY Pain: Walking, Running Foot wear problem Swelling; tingly feeling Deformity Stiffness Disability: At work; recreation; night; walk; ADL, Sports Previous Rx Comorbidities Smoke, Sugar, Steroid
6. FOOT HISTORY Pain: Walking, Running Foot wear problem Swelling; tingly feeling Deformity Stiffness Disability: At work; recreation; night; walk; ADL, Sports Previous Rx Comorbidities Smoke, Sugar, Steroid
.org. Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Anatomy
 Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Welcome to the: Orthopaedic Opinion Online Website The website for the answer to all your Orthopaedic Questions
 Welcome to the: Orthopaedic Opinion Online Website The website for the answer to all your Orthopaedic Questions Orthopaedic Opinion Online is a website designed to provide information to patients who have
Welcome to the: Orthopaedic Opinion Online Website The website for the answer to all your Orthopaedic Questions Orthopaedic Opinion Online is a website designed to provide information to patients who have
RESIDUAL ADDUCTION OF THE FOREFOOT IN TREATED CONGENITAL
 RESIDUAL ADDUCTION OF THE FOREFOOT IN TREATED CONGENITAL CLUB FOOT L. W. LOWE and M. A. HANNON, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Hospitalfor Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London Adduction of the forefoot
RESIDUAL ADDUCTION OF THE FOREFOOT IN TREATED CONGENITAL CLUB FOOT L. W. LOWE and M. A. HANNON, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Hospitalfor Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London Adduction of the forefoot
Ultrasonic assessment of injuries to the lateral complex of the ankle
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1990, 7, 90-94 Ultrasonic assessment of injuries to the lateral complex of the ankle A. K. SINGH, T. S. MALPASS & G. WALKER Department of Accident and Emergency, Wycombe
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1990, 7, 90-94 Ultrasonic assessment of injuries to the lateral complex of the ankle A. K. SINGH, T. S. MALPASS & G. WALKER Department of Accident and Emergency, Wycombe
Competence of the Deltoid Ligament in Bimalleolar Ankle Fractures After Medial Malleolar Fixation *
 Competence of the Deltoid Ligament in Bimalleolar Ankle Fractures After Medial Malleolar Fixation * BY PAUL TORNETTA, III, M.D. Investigation performed at Kings County Hospital, New York, N.Y. Abstract
Competence of the Deltoid Ligament in Bimalleolar Ankle Fractures After Medial Malleolar Fixation * BY PAUL TORNETTA, III, M.D. Investigation performed at Kings County Hospital, New York, N.Y. Abstract
Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101
 Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101 Servers Disease Causes a disturbance to the growing area at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) where the strong Achilles tendon attaches to it. It is most
Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101 Servers Disease Causes a disturbance to the growing area at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) where the strong Achilles tendon attaches to it. It is most
Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain
 What is lateral collateral ligament sprain? Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain A sprain is a joint injury that causes a stretch or tear in a ligament, a strong band of tissue connecting one bone to another.
What is lateral collateral ligament sprain? Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain A sprain is a joint injury that causes a stretch or tear in a ligament, a strong band of tissue connecting one bone to another.
Diabetes and malleolar fractures
 Diabetes and malleolar fractures Frank Linde Foot and ankle section Department of Orthopaedics University Hospital of Aarhus Diabetic complications and unstable malleolar fractures 40% risk of serious
Diabetes and malleolar fractures Frank Linde Foot and ankle section Department of Orthopaedics University Hospital of Aarhus Diabetic complications and unstable malleolar fractures 40% risk of serious
3/6/2012 STATE OF THE ART: FOOT AND ANKLE GENERAL KNOWLEDGE 1. TRASP REHABILITATION CONTENTS. General knowledge Trasp Prevention
 STATE OF THE ART: FOOT AND ANKLE ILITATION Fabienne Van De Steene. CONTENTS General knowledge Trasp Prevention Rehab Ankle sprain CAI Achilles tendon Plantar fasciitis Take home message 2 1. TRASP Ankle
STATE OF THE ART: FOOT AND ANKLE ILITATION Fabienne Van De Steene. CONTENTS General knowledge Trasp Prevention Rehab Ankle sprain CAI Achilles tendon Plantar fasciitis Take home message 2 1. TRASP Ankle
MEMORANDUM 171/91. DATE: June 26, 1991 TO: ALL WCAT STAFF SUBJECT: DECISION NO. 171/91. Continuity (of treatment) - Strains and sprains (ankle).
 MEMORANDUM 171/91 DATE: June 26, 1991 TYPE: A TO: ALL WCAT STAFF SUBJECT: DECISION NO. 171/91 Continuity (of treatment) - Strains and sprains (ankle). The worker sprained his ankle in a compensable accident
MEMORANDUM 171/91 DATE: June 26, 1991 TYPE: A TO: ALL WCAT STAFF SUBJECT: DECISION NO. 171/91 Continuity (of treatment) - Strains and sprains (ankle). The worker sprained his ankle in a compensable accident
AN INVESTIGATION INTO MINOR ORTHOPAEDIC DEFORMITIES
 AN INVESTIGATION INTO MINOR ORTHOPAEDIC DEFORMITIES IN FIRST YEAR SECONDARY SCHOOLCHILDREN J. Moncur, M.B., Ch.B., D.Phys.Med, Dip.P.E. Scottish School of Physical Education, Jordanhill College, Glasgow.
AN INVESTIGATION INTO MINOR ORTHOPAEDIC DEFORMITIES IN FIRST YEAR SECONDARY SCHOOLCHILDREN J. Moncur, M.B., Ch.B., D.Phys.Med, Dip.P.E. Scottish School of Physical Education, Jordanhill College, Glasgow.
Post-traumatic osteonecrosis of distal tibia
 Injury Extra (2007) 38, 262 266 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Post-traumatic osteonecrosis of distal tibia D. Chakravarty a, *, A. Khanna a,1, A. Kumar b,2 a Department of Orthopaedics, Peterborough
Injury Extra (2007) 38, 262 266 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Post-traumatic osteonecrosis of distal tibia D. Chakravarty a, *, A. Khanna a,1, A. Kumar b,2 a Department of Orthopaedics, Peterborough
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A case of long thoracic nerve palsy
 Article Chance-Larsen, Kenneth and Littlewood, Chris Available at http://clok.uclan.ac.uk/20413/ Chance Larsen, Kenneth and Littlewood, Chris (2010). International Journal of Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation,
Article Chance-Larsen, Kenneth and Littlewood, Chris Available at http://clok.uclan.ac.uk/20413/ Chance Larsen, Kenneth and Littlewood, Chris (2010). International Journal of Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation,
Duration of Follow-up (mo)
 Page 1 of 7 Fig. E-1 Fig. E-2 Fig. E-1 Medial ankle arthritis with medial translation of the talus and mortise widening. Note the shape of the medial malleolus (white arrow). Fig. E-2 Measurement of mortise
Page 1 of 7 Fig. E-1 Fig. E-2 Fig. E-1 Medial ankle arthritis with medial translation of the talus and mortise widening. Note the shape of the medial malleolus (white arrow). Fig. E-2 Measurement of mortise
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation
 A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 2 Introduction When the joint surfaces of an elbow are forced apart, the elbow is dislocated. The elbow is the second most commonly dislocated joint in adults (after
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 2 Introduction When the joint surfaces of an elbow are forced apart, the elbow is dislocated. The elbow is the second most commonly dislocated joint in adults (after
Title Management of Ankle and Lower Limb Injuries Protocol in MIUs and WICs
 Document Control Title Management of Ankle and Lower Limb Injuries Protocol in MIUs and WICs Author Author s job title Professional Lead, Minor Injuries Unit Directorate Emergency Services, Logistics and
Document Control Title Management of Ankle and Lower Limb Injuries Protocol in MIUs and WICs Author Author s job title Professional Lead, Minor Injuries Unit Directorate Emergency Services, Logistics and
Sequalae of Ankle Sprains: Peri Articular Fractures of the Ankle in Sports Medicine.
 Sequalae of Ankle Sprains: Peri Articular Fractures of the Ankle in Sports Medicine www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Chronic Ankle Pain The most common cause of chronic pain following an ankle sprain is a missed
Sequalae of Ankle Sprains: Peri Articular Fractures of the Ankle in Sports Medicine www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Chronic Ankle Pain The most common cause of chronic pain following an ankle sprain is a missed
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018
 Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018 I. Objectives A. By the end of the lecture attendees will
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018 I. Objectives A. By the end of the lecture attendees will
Rehabilitation of an ACL injury in a 29 year old male with closed kinetic chain exercises: A case study
 Abstract Objective: This paper will examine a rehabilitation program for a healthy 29 year old male who sustained an incomplete tear of the left ACL. Results: Following a 9 week treatment plan focusing
Abstract Objective: This paper will examine a rehabilitation program for a healthy 29 year old male who sustained an incomplete tear of the left ACL. Results: Following a 9 week treatment plan focusing
Can you help us? Are you over 50 and have broken a bone in your upper limb? Do you treat or care for someone who has? If so, we need your help.
 Can you help us? Are you over 50 and have broken a bone in your upper limb? Do you treat or care for someone who has? If so, we need your help. All medical treatment and advice that people receive should
Can you help us? Are you over 50 and have broken a bone in your upper limb? Do you treat or care for someone who has? If so, we need your help. All medical treatment and advice that people receive should
V E R I TAS MGH 1811 MGH 1811 V E R I TAS. *Gerber JP. Persistent disability with ankle sprains. Foot Ankle Int 19: , 1998.
 MGH 1811 Management of Ankle Instability Richard J. de Asla, M.D. V E R I TAS MGH 1811 I have no potential conflicts with this presentation. V E R I TAS It s just a sprain Lateral Ankle Sprains Most common
MGH 1811 Management of Ankle Instability Richard J. de Asla, M.D. V E R I TAS MGH 1811 I have no potential conflicts with this presentation. V E R I TAS It s just a sprain Lateral Ankle Sprains Most common
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 111/07
 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 111/07 BEFORE: S. Ryan: Vice-Chair HEARING: January 15, 2007 at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: January 17, 2007 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2007 ONWSIAT
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 111/07 BEFORE: S. Ryan: Vice-Chair HEARING: January 15, 2007 at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: January 17, 2007 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2007 ONWSIAT
Sprains. Initially the ankle is swollen, painful, and may turn eccyhmotic (bruised). The bruising, and the initial swelling, is due to ruptured
 Sprains Introduction An ankle sprain is a common injury and usually results when the ankle is twisted, or inverted. The term sprain signifies injury to the soft tissues, usually the ligaments, of the ankle.
Sprains Introduction An ankle sprain is a common injury and usually results when the ankle is twisted, or inverted. The term sprain signifies injury to the soft tissues, usually the ligaments, of the ankle.
Tendo Achilles rupture
 Tendo Achilles rupture Conservative and surgical management Therapy Department 01935 475 122 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk What is the Achilles tendon? The Achilles tendon is a large tendon at the back of the
Tendo Achilles rupture Conservative and surgical management Therapy Department 01935 475 122 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk What is the Achilles tendon? The Achilles tendon is a large tendon at the back of the
Growth Plate Injuries
 Growth Plate Injuries 1 What Is the Growth Plate? The growth plate, is the area of growing tissue near the end of the long bones in children and adolescents. Each long bone has at least two growth plates:
Growth Plate Injuries 1 What Is the Growth Plate? The growth plate, is the area of growing tissue near the end of the long bones in children and adolescents. Each long bone has at least two growth plates:
Satisfaction analysis of Figure 8 (open heel) short leg cast
 Chan Kang, MD, PhD Dong-Hun Kang, MD Jae-Hwang Song, MD Min-Gu Jang, MD Ki-Jun Ahn, MD Ki-Soo, Lee, MD Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chungnam National University School of Medicine. Daejeon, Republic
Chan Kang, MD, PhD Dong-Hun Kang, MD Jae-Hwang Song, MD Min-Gu Jang, MD Ki-Jun Ahn, MD Ki-Soo, Lee, MD Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chungnam National University School of Medicine. Daejeon, Republic
THE NATURAL HISTORY OF 271 PATIENTS WITH MITRAL STENOSIS UNDER MEDICAL TREATMENT
 THE NATURAL HISTORY OF 271 PATIENTS WITH MITRAL STENOSIS UNDER MEDICAL TREATMENT BY KNUD H. OLESEN Fi om the Medical Department B, Rigshospitalet, (Chief: Professor Erik Warburg) University of Copenhagen,
THE NATURAL HISTORY OF 271 PATIENTS WITH MITRAL STENOSIS UNDER MEDICAL TREATMENT BY KNUD H. OLESEN Fi om the Medical Department B, Rigshospitalet, (Chief: Professor Erik Warburg) University of Copenhagen,
Evidenced-Based Medicine: Where Does it Fit in Foot and Ankle Surgery?
 Jeffrey R. Baker, DPM, AACFAS Weil Foot & Ankle Institute Des Plaines, IL Evidenced-Based Medicine: Where Does it Fit in Foot and Ankle Surgery? MODULE: Bimalleolar Equivalent Ankle Fracture Evidence-Based
Jeffrey R. Baker, DPM, AACFAS Weil Foot & Ankle Institute Des Plaines, IL Evidenced-Based Medicine: Where Does it Fit in Foot and Ankle Surgery? MODULE: Bimalleolar Equivalent Ankle Fracture Evidence-Based
Fibular Malalignment in Subjects with Chronic Ankle Instability
 Fibular Malalignment in Subjects with Chronic Ankle Instability Takumi Kobayashi 1,2, Eiichi Suzuki 3, Naohito Yamazaki 3, Makoto Suzukawa 4, Atsushi Akaike 4, Kuniaki Shimizu 4, Kazuyoshi Gamada 1. 1
Fibular Malalignment in Subjects with Chronic Ankle Instability Takumi Kobayashi 1,2, Eiichi Suzuki 3, Naohito Yamazaki 3, Makoto Suzukawa 4, Atsushi Akaike 4, Kuniaki Shimizu 4, Kazuyoshi Gamada 1. 1
CASE REPORT RARE CASE OF DELTOID LIGAMENT AVULSION WITH MEDIAL MALLEOLUS FRACTURE OF ANKLE JOINT: CASE REPORT
 RARE CASE OF DELTOID LIGAMENT AVULSION WITH MEDIAL MALLEOLUS FRACTURE OF ANKLE JOINT: CASE REPORT Maruthi C.V 1, Roshan Pais 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Maruthi CV, Roshan Pais. Rare case of deltoid ligament
RARE CASE OF DELTOID LIGAMENT AVULSION WITH MEDIAL MALLEOLUS FRACTURE OF ANKLE JOINT: CASE REPORT Maruthi C.V 1, Roshan Pais 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Maruthi CV, Roshan Pais. Rare case of deltoid ligament
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 1417/12
 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 1417/12 BEFORE: S. Martel: Vice-Chair HEARING: July 9, 2012 at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: September 5, 2012 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2012 ONWSIAT
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 1417/12 BEFORE: S. Martel: Vice-Chair HEARING: July 9, 2012 at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: September 5, 2012 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2012 ONWSIAT
Clin Podiatr Med Surg 19 (2002) Index
 Clin Podiatr Med Surg 19 (2002) 335 344 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Accessory soleus muscle, magnetic resonance imaging of, 300 Achilles tendon injury of, magnetic
Clin Podiatr Med Surg 19 (2002) 335 344 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Accessory soleus muscle, magnetic resonance imaging of, 300 Achilles tendon injury of, magnetic
ruptures of the lateral ligaments of the
 The accuracy of three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of ruptures of the lateral ligaments of the ankle* EDDY F. C. VERHAVEN, MD, MARYAM SHAHABPOUR, MD, FRANK W. J. HANDELBERG,
The accuracy of three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of ruptures of the lateral ligaments of the ankle* EDDY F. C. VERHAVEN, MD, MARYAM SHAHABPOUR, MD, FRANK W. J. HANDELBERG,
Integra. Salto Talaris Total Ankle Prosthesis PATIENT INFORMATION
 Integra Salto Talaris Total Ankle Prosthesis PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal
Integra Salto Talaris Total Ankle Prosthesis PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal
Age of the patients-the average age of our patients
 TWO-LEVEL FRACTURES OF THE TIBIA Results in Thirty-six Cases Treated by Blind Nailing J. ZUCMAN and P. MAURER, PARIS, FRANCE From the Cliizique de Chirurgie Orthop#{232}dique et R#{233}paratrice, H#{243}pital
TWO-LEVEL FRACTURES OF THE TIBIA Results in Thirty-six Cases Treated by Blind Nailing J. ZUCMAN and P. MAURER, PARIS, FRANCE From the Cliizique de Chirurgie Orthop#{232}dique et R#{233}paratrice, H#{243}pital
Barriers Between Injury and Returnto-Work. Lower Extremity. Why the Extreme Variability
 Barriers Between Injury and Returnto-Work in the Lower Extremity Why the Extreme Variability Barriers to Diagnosis Failure or delay in reporting injury Employee expectations: Not really a serious injury
Barriers Between Injury and Returnto-Work in the Lower Extremity Why the Extreme Variability Barriers to Diagnosis Failure or delay in reporting injury Employee expectations: Not really a serious injury
HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS
 HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS A. B. NEVELOS, p. R. J. BURCH From Leeds/Bradford Orthopaedic Training Schetne Six boys were examined during the second year of life, each with symptoms
HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS A. B. NEVELOS, p. R. J. BURCH From Leeds/Bradford Orthopaedic Training Schetne Six boys were examined during the second year of life, each with symptoms
Servicemen were not included in this survey. 80% of
 40 Brit.J.Sports Med.: 980, 4, 40-44 REFERENCES Campbell's operative Orthopedics. 963, Vol.. The C. V. Mosby Company, Saint Louis, 339. Hendryson, J. E., 964 "Bursitis in the region of the fibular collateral
40 Brit.J.Sports Med.: 980, 4, 40-44 REFERENCES Campbell's operative Orthopedics. 963, Vol.. The C. V. Mosby Company, Saint Louis, 339. Hendryson, J. E., 964 "Bursitis in the region of the fibular collateral
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries
 Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries One of the most common knee injuries is an anterior cruciate ligament sprain or tear.athletes who participate in high demand sports like soccer, football, and basketball
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries One of the most common knee injuries is an anterior cruciate ligament sprain or tear.athletes who participate in high demand sports like soccer, football, and basketball
Clinical practice guidelines for physical therapy in patients with acute ankle sprain
 Clinical practice guidelines for physical therapy in patients with acute ankle sprain RA de Bie PT PhD, I HJM Hendriks PT PhD, II AF Lenssen PT MSc, III SR van Moorsel PT, IV KWF Opraus PT, V WFA Remkes
Clinical practice guidelines for physical therapy in patients with acute ankle sprain RA de Bie PT PhD, I HJM Hendriks PT PhD, II AF Lenssen PT MSc, III SR van Moorsel PT, IV KWF Opraus PT, V WFA Remkes
ACL Patient Assessment and Progress Sheet. Patient Sticker
 Patient Sticker Thank you for taking the time to answer these questions which should only take a few minutes. The answers you give are very useful as they will help us assess your progress following your
Patient Sticker Thank you for taking the time to answer these questions which should only take a few minutes. The answers you give are very useful as they will help us assess your progress following your
Tibialis Posterior Tendon Dysfunction. Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet
 Tibialis Posterior Tendon Dysfunction Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet What is Tibialis Posterior Tendon Dysfunction? The Tibialis Posterior Tendon (see diagram) is an important structure
Tibialis Posterior Tendon Dysfunction Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet What is Tibialis Posterior Tendon Dysfunction? The Tibialis Posterior Tendon (see diagram) is an important structure
An older systematic review looked at the evidence behind the best approach to evaluate acute knee pain in primary care (Ann Int Med.2003;139:575).
 There is so much we don't know in medicine that could make a difference, and often we focus on the big things, and the little things get forgotten. To highlight some smaller but important issues, we've
There is so much we don't know in medicine that could make a difference, and often we focus on the big things, and the little things get forgotten. To highlight some smaller but important issues, we've
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation
 A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 20295 NE 29th Place, Ste 300 Aventura, FL 33180 Phone: (786) 629-0910 Fax: (786) 629-0920 admin@instituteofsports.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 20295 NE 29th Place, Ste 300 Aventura, FL 33180 Phone: (786) 629-0910 Fax: (786) 629-0920 admin@instituteofsports.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
Foot Injuries. Dr R B Kalia
 Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
Badminton. 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) Website: philip-bayliss.com
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353 Website: philip-bayliss.com Badminton Badminton's origin may be traced as far back as fifth century China when players would volley a
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353 Website: philip-bayliss.com Badminton Badminton's origin may be traced as far back as fifth century China when players would volley a
Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus
 Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus Introduction The purpose of this document is to provide a recommended syllabus for medical students in Trauma & Orthopaedics (T&0). It should help students on
Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus Introduction The purpose of this document is to provide a recommended syllabus for medical students in Trauma & Orthopaedics (T&0). It should help students on
Diagnosis and Management of Knee Conditions. Jenny Love / Lynn Robertson AFLAR Oct 2009
 Diagnosis and Management of Knee Conditions Jenny Love / Lynn Robertson AFLAR Oct 2009 AIMS Review 4 common Knee Conditions: Anterior knee pain Meniscal Injuries Ligament injuries ACL Osteoarthritis Discuss
Diagnosis and Management of Knee Conditions Jenny Love / Lynn Robertson AFLAR Oct 2009 AIMS Review 4 common Knee Conditions: Anterior knee pain Meniscal Injuries Ligament injuries ACL Osteoarthritis Discuss
Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION
 Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal Fibular
Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal Fibular
Sky Ridge Medical Center, Aspen Building Ridgegate Pkwy., Suite 309 Lone Tree, Colorado Office: Fax:
 ANKLE SPRAIN What is the ATFL? The ankle joint is made up of the tibia, fibula (bones in the lower leg) and the talus (bone below the tibia and fibula). Ligaments in the ankle connect bone to bone and
ANKLE SPRAIN What is the ATFL? The ankle joint is made up of the tibia, fibula (bones in the lower leg) and the talus (bone below the tibia and fibula). Ligaments in the ankle connect bone to bone and
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY
 ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY WHAT IS THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT? The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four major ligaments that stabilizes the knee joint. A ligament is a tough band
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY WHAT IS THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT? The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four major ligaments that stabilizes the knee joint. A ligament is a tough band
Lateral ligament injuries of the knee
 Knee Surg, Sports Traumatol, Arthrosc (1998) 6:21 25 KNEE Springer-Verlag 1998 Y. Krukhaug A. Mølster A. Rodt T. Strand Lateral ligament injuries of the knee Received: 22 January 1997 Accepted: 20 June
Knee Surg, Sports Traumatol, Arthrosc (1998) 6:21 25 KNEE Springer-Verlag 1998 Y. Krukhaug A. Mølster A. Rodt T. Strand Lateral ligament injuries of the knee Received: 22 January 1997 Accepted: 20 June
Salisbury Foundation Trust Radiology Department Referral Guidelines for Primary Care: Musculoskeletal Imaging
 Salisbury Foundation Trust Radiology Department Referral Guidelines for Primary Care: Musculoskeletal Imaging These guidelines have been issued in conjunction with the Royal College of Radiology referral
Salisbury Foundation Trust Radiology Department Referral Guidelines for Primary Care: Musculoskeletal Imaging These guidelines have been issued in conjunction with the Royal College of Radiology referral
