Clinical outcomes of single versus double row, transosseous equivalent arthroscopic rotator cuff repair
|
|
|
- Sarah Marshall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2016; 2(1): ISSN: IJOS 2016; 2(1): IJOS Received: Accepted: Singapore General Hospital. Outram Road, Singapore Singapore. Clinical outcomes of single versus double row, transosseous equivalent arthroscopic rotator cuff repair Abstract Rotator cuff tears are common and are expected to present with increasing frequency as the population ages. Various techniques in surgical repair have been described to improve clinical outcomes. A arthroscopic transosseous-equivalent double row repair is believed to be superior, with improved tendon to bone contact area and reduced gap formation. In our series of 143 patients, with 76 undergoing single row repair, and 67 double row repairs by a single surgeon, we describe the observed clinical improvements and complication rates. Though surgical times were not significantly different, no significant advantage from double row repairs were observed with regards to clinical outcome measures. Keywords: arthroscopic transosseous, clinical outcomes, musculoskeletal structure Correspondence Singapore General Hospital. Outram Road, Singapore Singapore. Introduction The shoulder is a complex musculoskeletal structure [1]. Despite the exceptional range of motion, only a few millimeters of humeral head translation occurs during movement in the glenohumeral joint [2]. A functional rotator cuff contributes to the stability of this joint [1, 3, 4]. The incidence of shoulder complaints is high, with approximately 13.7 million doctor visits in 2003 alone [3]. Some injuries are a result of excessive, repetitive overhead motion such as swimming, tennis, pitching and weightlifting [3]. However, many occur with daily activities - household chores such as cleaning the windows and hanging curtains have been associated with shoulder injuries, especially so in the elderly [3]. Even in normal cadavers, rotator cuff tears were found in 30% to 50% of specimens, suggesting that they may be part of the normal aging process [4, 5]. With an aging population, the number of patient visits for degenerative rotator cuff pathologies is expected to rise [6]. Regardless of the etiology, proper management of the rotator cuff disease is crucial for both physical function and wellbeing of the patient. In the patient group that undergoes surgical repair, we question the superiority of a dual-row repair technique, if it translates to better clinical outcomes and reduced re-tear rates. With a three-space digitizer, Dugas et al. examined 20 normal cadaveric shoulders. He reported the mean minimum transverse diameter across the cuff insertion to be 14.7mm and the total area of supraspinatus attachment on the greater tuberosity was approximately 350mm [7]. Oguma et al. showed that the potential for woven bone formation to anchor collagen fibers at the bone-tendon interface increases as the available contact area for the fibrovascular tissue interface increases [15]. Thus, creating a similar area during surgical repair is essential as this insertion point undergoes large stresses [10, 11]. The belief is that a dual-row repair technique achieves this, hence better healing and reduced gap formation [14]. This has been supported by in vitro studies [7, 8]. Waltripet al [21] reported that double row repair was superior to single row with regards to initial fixation strength in a cadaver study. Meier and Meier [22] in their cadaveric study, reports that double row repair restores the supraspinatus footprint closer to its original level than does the single row repair. Brady et al [23] in a clinical study demonstrated increased coverage in double row compared to single row. This was quantified by measuring coverage before and after tying of the lateral row, whereby single row repair was achieved prior to lateral anchorage. It was found that single row repair left on average, 52.7% of the original rotator cuff footprint uncovered, while double row technique achieved complete coverage [43]. ~ 117 ~
2 This significant advantage has not been observed in clinical studies. We recognize that functional improvement after surgical repair is not as predictable as pain relief, and depends on many other factors [7, 8, 12, 13]. Design and Methods We studied a total of 143 patients, recruited from 2004 to All were diagnosed with isolated supraspinatus tendon tears of up to 4cm. The pre-operative diagnoses were made via ultrasound or MRI, and were correlated with intra-operative findings. All had surgical repair performed arthroscopically by a single surgeon. The first 76 patients had repair performed via the single row technique while 67 patients after had double row repair performed. Patients with previous surgery to the ipsilateral shoulder and multiple rotator cuff pathologies were excluded from the study. This was not a double-blinded study and patients were not randomized nor selected based on tear size, pathology or characteristics. Surgical method Patients were positioned in a beach chair with back of bed flexed about 70. Shoulders were examined under anaesthesia for range of motion (ROM). A posterior portal was established for the initial assessment of the joint. An anterior portal through the rotator interval was established as the working portal for intra-articular debridement. Up to four portals were required for rotator cuff repair: posterior and posterolateral portals were used mainly for the standard 30 angled 4-mm arthroscope (the viewing portals), while anterosuperior and lateral portals were used for the instruments (the working portals). All patients had subacromial decompression with acromioplasty performed. After adequate visualization, preparation, and release of the tendon, tear edges were fashioned and opposed to simulate repair and for assessment of eventual outcome. In single row repairs (see diagram 1) tear edges were opposed and anchored with up to 2Healix suture anchors. Double row repairs (see diagram 2) in essence have two anchoring points, after initial repair with the medial row anchor(s), the sutures were then tightened and anchored laterally with Versalok. Depending on the size of tear, a 1:1 configuration (1 Healix and 1 Versalok ) or a 2:2 configuration was performed. The arm was immobilized in a sling following routine portal closure. Diagram 1: Single Row Diagram 2: Double Row Immediate post-operatively, patients were allowed to perform passive ROM exercises, including pendulum exercises, passive forward flexion, and external rotation. No active motion was allowed until 6 weeks post-operatively. Active-assisted motion was initiated at six weeks postoperatively. They were then advised on muscle strengthening exercises and routine follow up assessments in the outpatient clinic. Clinical evaluation The patients were evaluated pre-operatively, 3 months, 6 months, and 24 months post-operatively. Clinical scoring systems used include Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and University of California, Los Angeles Score (UCLA). Assessments and records of complications were also sought, such as infection, anchor pullout, re-tear of cuff, and need for revision surgery. Scoring system The UCLA score is a combination of subjective scoring and physical examination, and the variables are evaluated and weighted as follows: pain (28.6%), motion (14.3%), strength (14.3%), function (28.6%), and satisfaction (14.3%). The Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) measures pain based on a ~ 118 ~ continuum of values, as it cannot easily be directly measured. A horizontal line, 100 mm in length, anchored by word descriptors at each end is offered to the patient and advised to mark on the line the point that they feel represents their perception of their current state. Demographics Patient demographics between the two arms are clinically comparable and are summarized in table 1. The average age for single row (SR) arm is / years while that for double row (DR) is /- 9.6 years. A total of 45 males to 31 females in single row arm versus 34 males and 33 females in double row arm were studied. Duration of surgery between both arms was also comparable / minutes for single row, while double row took / minutes on average. The mean tear size for single row was / cm and /- 0.85cm for double row group. Pre-operative UCLA scores and VAS scores were also comparable between both arms. See Table 2. UCLA scores preoperatively for single row was / while double row was / VAS scores preoperatively for single row was / while double row was /
3 Table 1: Patient demographics and peri-operative data Results Patients were assessed at 3 months, 6 months, and 24 months postoperatively. See graph 1 and 2. Both arms showed significant improvement (p <0.01) in UCLA and VAS scores post-operatively. However, no significant improvements in scores were observed in double row repairs compared to single row repairs at both early post-operative period and 24 months post operatively. UCLA scores in single row arm improved from / to / at 24 months post operatively. Double row scores improved from / to / (p<0.05). There was no statistical difference in UCLA scores for both arms at 24 months (p>0.65).(graph 1.) VAS scores in single row arm improved from / to / (p<0.05) at 24 months. Double row scores improved from / to / (p<0.05) at 24 months. However, no significant differences were noted between both arms at the end of evaluation. (Graph 2.). Graph 1: UCLA scores Graph 2: VAS scores No reported cases of post-operative wound infection was noted in both arms by 24 months of follow up. Each arm had a single case of anchor pullout (Single row 1.3%, Double row 1.4%). Both cases were diagnosed within 12 weeks post-operatively, presenting with progressive pain and weakness. 6 re-tears were noted in single row arm (7.89%) while double row had 4 re-tears (5.97%). After 24 months, a total of 4 cases required revision surgery, with 2 cases in each arm (single row 2.6%, double row 2.9%). Table 2. ~ 119 ~
4 Table 2: Complication rates Discussion Recurrent tears after rotator cuff repair is a common and has been reported in up to 40% of patients undergoing surgical repair [7-12]. Of interest, these were diagnosed via second-look arthroscopy after the initial repair surgery. With post-surgical ultrasonography, Galatz et al [13] reported astonishingly high recurrence rates, with 17 (94%) out of 18 cases having a retear, though it did not correlate with the clinical improvements observed. Sugaya et al [20] using magnetic resonance imaging reported that 43.6% of the rotator cuff repairs had sufficient thickness, 30.8% had insufficient thickness, and 25.6% had a re-tear in the single-row group, compared with 73.2%, 17.1%, and 9.8%, respectively, in the double-row group. Along with findings by Franschesci et al and Charousset et al. [16, 19], it is suggestive that clinical outcomes do not correlate with radiological findings of a re-tear post-operatively. In this study, significant improvements in functional and pain scores were observed in both arms (SR and DR). We were not surprised, as previous studies have reported similar outcomes. Unfortunately, despite the reduction of a variable i.e. surgical expertise, we did not find significant improvements in patient outcome when comparing double row to single row repairs. This validates the findings of several authors. With the exception of Sugaya et al. [20] and Park et al. [23], who, after subdividing their patients by tear size, found improved outcomes and lower re-tear rates when large tears were repaired with double row technique, the majority of studies failed to show significant clinical advantage of double row repairs over single row. Increased surgical time required for double row repair was a major initial deterrent. Franceschi et al. [16] reported on operative times required for the different procedures. Average time was 42 +/ minutes for the single row and 65 +/ minutes for the double row procedures. In his study, the time Difference was significant. However, in our series and several others, no significant difference in operative time was noted. Hence, we feel that surgical duration should not serve to discourage employment of either technique. Several potential bias were identified in these studies. They include type-ii error in analysis secondary to insufficient power, to selection bias in studies that were not randomized or prospective. The studies by Charousset et al. [19] and Grasso et al. [17] each involved multiple surgeons, which introduced the variable of skill level. In our study, a single surgeon performed all the surgeries. This reduces the variability of skill level. However, we recognize that this introduces yet another variable that of surgeon experience. The potential benefit of double row repair was thus confounded by improved surgeon s experience after performing a series of single row repairs. We can expect predictable healing with either repair techniques, especially for small and medium sized tears. The potential benefit of double row repair may lie in improved outcomes with large and massive tears. Clinical studies, however, have not yet demonstrated a substantial improvement ~ 120 ~ over single row repairs with regards to either the degree of structural healing or functional outcomes in ASES, UCLA and Constant scores. Although double row repair may provide an improved mechanical environment for the healing tendon, several confounding variables have complicated attempts to establish a definitive relationship with improved rates of healing. Larger prospective randomized studies that include clinical assessments and that take tear size into account are necessary to determine the true efficacy of double row repair. We have to recognize that despite the apparent superiority of structural outcomes in association with the double-row repair method, there are some potential drawbacks to employing this technique in all cases. First, in the studies reviewed, the required number of anchors ranged from one to two for singlerow fixation, compared with two to four for double-row fixation, increasing the cost of the procedure [16-20]. Furthermore, the double-row fixation procedure is technically more difficult. It was also suggested that multiple strands necessitated by the double-row repair could potentially interfere with the neovascularization process and thus inhibit healing, although none of the studies reported addressed this issue. Despite the various biomechanical studies that demonstrate mechanical advantage of double row repairs, this has not been translated into superior clinical outcomes in our patient cohort. This finding is also supported by several other studies that have not shown improved clinical outcomes with double row repairs. As no significant difference in clinical outcomes has been demonstrated between the two repair techniques except for, perhaps, large-to-massive rotator cuff repairs, a risk-reward analysis of patient age, functional demands, and other qualityof-life issues should be considered before deciding which surgical method to employ. References 1. Canale Beaty. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics, 11th ed 2. Clark JM, Harryman DT. 2 nd Tendons, ligaments, and capsule of the rotator cuff. Gross and microscopic anatomy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992; 74(5): Chen AL, Mears SC, Hawkins RJ. Orthopaedic care of the aging athlete. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2005; 13: De Palma AF. The classic. Surgical anatomy of the rotator cuff and the natural history of degenerative per arthritis. Surg Clin North Am 1963; 43: Sher JS, Uribe JW, Posada A, Murphy BJ, Zlatkin MB. Abnormal findings on magnetic resonance images of asymptomatic shoulders. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995; 77(1): Tempelhof S, Rupp S, Seil R. Age-related prevalence of rotator cuff tears in asymptomatic shoulders. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1999; 8(4): Dugas JR, Campbell DA, Warren RF, Robie BH, Millet PJ. Anatomy and dimensions of rotator cuff insertions. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2002; 11(5):
5 8. Gazielly DF, Gleyze P, Montagnon C. Functional and anatomical results after rotator cuff repair, Clin Orthop Relat Res 1994; 304: Wolf EM, Bayliss RW. Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: clinical and arthroscopic second-look assessment. In: Gazi-elly DF, Gleyze P, Thomas T, eds, The cuff. Paris: Elsevier; 1996, Bostrom MPG, Boskey A, Kauffman JK, Einhorn TA. Form and function of bone. In: Buckwalter JA, Einhorn TA, Simon SR, editors. Orthopaedic basic science. Rosemont, IL: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 2000, Woo SL, An K, Frank CB, Livesay GA, Ma CB, Zeminski JA et al. Anatomy, biology, and biomechanics of tendon and liga- ment. In: Orthopaedic basic science. Rosemont, IL: AAOS, 2000, Boileau P, Brassart N, Watkinson DJ, Carles M, Hatzidakis AM, Krishnan SG. Arthroscopic repair of fullthickness tears of the supraspinatus: does the tendon really heal? J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87(6): Galatz LM, Ball CM, Teefey SA, Middleton WD, Yamaguchi K. The outcome and repair integrity of completely arthros- copically repaired large and massive rotator cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86(2): Gerber C, Wirth SH, Farshad M. Treatment options for massive rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2011; 20(2):S Oguma H, Murakami G, Takahashi-Iwanaga H, Aoki M, Ishii S. Early anchoring collagen fibers at the bone-tendon interface are conducted by woven bone formation: light microscope and scanning electron microscope observation using a canine model. J Orthop Res. 2001; 19(5): Franceschi F, Ruzzini L, Longo UG. Equivalent results of arthroscopic single-row and double-row suture anchor repair for rotator cuff tears: A randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. 2007; 35: Grasso A, Milano G, Salvatore M, Falcone G, Deriu L, Fabbriciani C. Single row versus double row arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: A prospective randomized clinical study Arthroscopy 2009; 25: Charousset C, Grimberg J, Duranthon LD, Bellaiche L, Petrover D. Can a double row anchorage technique improve tendon healing in arthroscopic cuff repair? A prospective, nonrandomized, comparative study of double row and single row anchorage techniques with computed tomographic arthrography tendon healing assessment, Am J Sports Med. 2007; 35: Sugaya H, Maeda K, Matsuki K, Moriishi J. Functional and structural outcome after arthroscopic full-thickness rotator cuff repair: Single row versus dual row fixation. Arthroscopy 2005; 21: Sugaya H, Maeda K, Matsuki K, Moriishi J. Repair integrity and functional outcome after arthroscopic full thickness rotator cuff repair: A prospective outcome study, J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89: Waltrip RL, Zheng N, Dugas JR, Andrews JR. Rotator cuff repair. A biome- chanical comparison of three techniques, Am J Sports Med. 2003; 31: Meier SW, Meier JD. The effect of double-row fixation on initial repair strength in rotator cuff repair: a biomechanical study Arthroscopy 2006; 22: Brady PC, Arrigoni P, Burkhart SS. Evaluation of residual rotator cuff defects after in vivo single- versus double-row rotator cuff repairs Arthroscopy 2006; 22: ~ 121 ~
11/13/2017. Disclosures: The Irreparable Rotator Cuff. I am a consultant for Arhtrex, Inc and Endo Pharmaceuticals.
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis THE CASE FOR SUPERIOR CAPSULAR RECONSTRUCTION MICHAEL GARCIA, MD NOVEMBER 4, 2017 FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE Disclosures: I am a consultant for Arhtrex,
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis THE CASE FOR SUPERIOR CAPSULAR RECONSTRUCTION MICHAEL GARCIA, MD NOVEMBER 4, 2017 FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE Disclosures: I am a consultant for Arhtrex,
Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Techniques What should we really be doing?
 COA 2014 Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Techniques What should we really be doing? C. Benjamin Ma, MD Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery University of California, San Francisco Department of
COA 2014 Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Techniques What should we really be doing? C. Benjamin Ma, MD Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery University of California, San Francisco Department of
Dual Row Rotator Cuff Repair. Jeffrey Halbrecht,, MD
 Dual Row Rotator Cuff Repair Jeffrey Halbrecht,, MD Why Dual Row? Poor structural integrity on f/u studies of single row repair Restore anatomy ( footprint) Stronger Repair? Faster rehab? Better results?
Dual Row Rotator Cuff Repair Jeffrey Halbrecht,, MD Why Dual Row? Poor structural integrity on f/u studies of single row repair Restore anatomy ( footprint) Stronger Repair? Faster rehab? Better results?
Rotator Cuff Repair in Patients over 75 Years of Age: Clinical Outcome and Repair Integrity
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:420-427 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.420 Rotator Cuff Repair in Patients over 75 Years of Age: Clinical Outcome and Repair Integrity Jung
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:420-427 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.420 Rotator Cuff Repair in Patients over 75 Years of Age: Clinical Outcome and Repair Integrity Jung
Rotator Cuff Repair TRENDS OF REPAIRS. Evolution of Arthroscopic Repair. Shoulder Girdle. Rotator Cuff Repair 8/29/2013
 Rotator Cuff Repair Indications, Patient Selection, Outcomes James C. Vailas, M.D. New Hampshire Orthopaedic Center September 14, 2013 New Hampshire Musculoskeletal Institute 20 th Annual Symposium Evolution
Rotator Cuff Repair Indications, Patient Selection, Outcomes James C. Vailas, M.D. New Hampshire Orthopaedic Center September 14, 2013 New Hampshire Musculoskeletal Institute 20 th Annual Symposium Evolution
Kevin Kaplan, M.D., Neal S. ElAttrache, M.D., Oscar Vazquez, M.D., Yu-Jen Chen, M.D., and Thay Lee, Ph.D.
 Knotless Rotator Cuff Repair in an External Rotation Model: The Importance of Medial-Row Horizontal Mattress Sutures Kevin Kaplan, M.D., Neal S. ElAttrache, M.D., Oscar Vazquez, M.D., Yu-Jen Chen, M.D.,
Knotless Rotator Cuff Repair in an External Rotation Model: The Importance of Medial-Row Horizontal Mattress Sutures Kevin Kaplan, M.D., Neal S. ElAttrache, M.D., Oscar Vazquez, M.D., Yu-Jen Chen, M.D.,
High-Tension Double-Row Footprint Repair Compared with Reduced-Tension Single-Row Repair for Massive Rotator Cuff Tears
 35 COPYRIGHT 2008 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED High-Tension Double-Row Footprint Repair Compared with Reduced-Tension Single-Row Repair for Massive Rotator Cuff Tears By Benjamin
35 COPYRIGHT 2008 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED High-Tension Double-Row Footprint Repair Compared with Reduced-Tension Single-Row Repair for Massive Rotator Cuff Tears By Benjamin
Anatomy Your shoulder is made up of three bones: your upper arm bone (humerus), your shoulder blade (scapula), and your collarbone (clavicle).
 Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great
Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
The Factors Affecting the Clinical Outcome and Integrity of Arthroscopically Repaired Rotator Cuff Tears of the Shoulder
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2009;1:96-104 doi:10.4055/cios.2009.1.2.96 The Factors Affecting the Clinical Outcome and Integrity of Arthroscopically Repaired Rotator Cuff Tears of the
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2009;1:96-104 doi:10.4055/cios.2009.1.2.96 The Factors Affecting the Clinical Outcome and Integrity of Arthroscopically Repaired Rotator Cuff Tears of the
ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT
 ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH
ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH
Management of Massive/Revision Rotator Cuff Tears
 Management of Massive/Revision Rotator Cuff Tears Nikhil N. Verma MD, Director Sports Medicine, Rush University Medical Center, Midwest Orthopedics at Rush, Chicago, IL nverma@rushortho.com I. Anatomy
Management of Massive/Revision Rotator Cuff Tears Nikhil N. Verma MD, Director Sports Medicine, Rush University Medical Center, Midwest Orthopedics at Rush, Chicago, IL nverma@rushortho.com I. Anatomy
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears. Rafael M. Williams, MD
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Rafael M. Williams, MD Rotator Cuff MRI MRI Small / Partial Thickness Medium Tear Arthroscopic View Massive Tear Fatty Atrophy Arthroscopic View MassiveTears Tear is > 5cm
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Rafael M. Williams, MD Rotator Cuff MRI MRI Small / Partial Thickness Medium Tear Arthroscopic View Massive Tear Fatty Atrophy Arthroscopic View MassiveTears Tear is > 5cm
DK7215-Levine-ch12_R2_211106
 12 Arthroscopic Rotator Interval Closure Andreas H. Gomoll Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A. Brian J. Cole Departments
12 Arthroscopic Rotator Interval Closure Andreas H. Gomoll Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A. Brian J. Cole Departments
Asymptomatic acromioclavicular joint arthritis in arthroscopic rotator cuff tendon repair: a prospective randomized comparison study
 Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (2011) 131:363 369 DOI 10.1007/s00402-010-1216-y ARTHROSCOPY AND SPORTS MEDICINE Asymptomatic acromioclavicular joint arthritis in arthroscopic rotator cuff tendon repair: a prospective
Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (2011) 131:363 369 DOI 10.1007/s00402-010-1216-y ARTHROSCOPY AND SPORTS MEDICINE Asymptomatic acromioclavicular joint arthritis in arthroscopic rotator cuff tendon repair: a prospective
Rotator Cuff Tears: Surgical Treatment Options
 Rotator Cuff Tears: Surgical Treatment Options The following article provides in depth information about surgical treatment for rotator cuff injuries, and is a continuation of the article "Rotator Cuff
Rotator Cuff Tears: Surgical Treatment Options The following article provides in depth information about surgical treatment for rotator cuff injuries, and is a continuation of the article "Rotator Cuff
A comparative clinical evaluation of arthroscopic single-row versus double-row supraspinatus tendon repair
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 588-594 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparative clinical evaluation of arthroscopic single-row versus double-row supraspinatus tendon repair Eduard BUESS, Bernhard WAIBL, Roger VOGEL,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 588-594 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparative clinical evaluation of arthroscopic single-row versus double-row supraspinatus tendon repair Eduard BUESS, Bernhard WAIBL, Roger VOGEL,
Rotator Cuff Repair Outcomes. Patrick Birmingham, MD
 Rotator Cuff Repair Outcomes Patrick Birmingham, MD Outline Arthroscopic Vs. Mini-open Subjective Outcomes Objective Outcomes Timing Arthroscopic Vs. Mini-open Sauerbrey Arthroscopy 2005 Twenty-six patients
Rotator Cuff Repair Outcomes Patrick Birmingham, MD Outline Arthroscopic Vs. Mini-open Subjective Outcomes Objective Outcomes Timing Arthroscopic Vs. Mini-open Sauerbrey Arthroscopy 2005 Twenty-six patients
Adress correspondence and reprint requests to Hyun Seok Song, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St.Paul s Hospital, The Catholic University of
 Adress correspondence and reprint requests to Hyun Seok Song, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St.Paul s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea 620-56 Jeonnong-dong, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul, Korea
Adress correspondence and reprint requests to Hyun Seok Song, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St.Paul s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea 620-56 Jeonnong-dong, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul, Korea
Clinical and Radiological Evaluation after Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Using Suture Bridge Technique
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:306-313 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.4.306 Clinical and Radiological Evaluation after Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Using Suture Bridge
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:306-313 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.4.306 Clinical and Radiological Evaluation after Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Using Suture Bridge
The Current State of Rotator Cuff Repairs
 Conflict of Interest Slide The Current State of Rotator Cuff Repairs Gerald R. Williams, Jr, MD John M. Fenlin, Jr, MD Professor of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Royalties Depuy: shoulder arthroplasty DJO:
Conflict of Interest Slide The Current State of Rotator Cuff Repairs Gerald R. Williams, Jr, MD John M. Fenlin, Jr, MD Professor of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Royalties Depuy: shoulder arthroplasty DJO:
Point/Counterpoint: Single vs Double Row RCR. Disclosures. The Problem 09/24/2015. Todd M. Tupis M.D. None
 Point/Counterpoint: Single vs Double Row RCR Todd M. Tupis M.D. Disclosures None The Problem Numerous studies show good to excellent functional results of arthroscopic RCR Healing rates range from 91%-10%
Point/Counterpoint: Single vs Double Row RCR Todd M. Tupis M.D. Disclosures None The Problem Numerous studies show good to excellent functional results of arthroscopic RCR Healing rates range from 91%-10%
Single-Row Suture Anchor Repair of the Rotator Cuff is Biomechanically Equivalent to Double-Row Repair in a Bovine Model
 Single-Row Suture Anchor Repair of the Rotator Cuff is Biomechanically Equivalent to Double-Row Repair in a Bovine Model Andrew Mahar, M.S., Jeffrey Tamborlane, M.D., Richard Oka, M.S., James Esch, M.D.,
Single-Row Suture Anchor Repair of the Rotator Cuff is Biomechanically Equivalent to Double-Row Repair in a Bovine Model Andrew Mahar, M.S., Jeffrey Tamborlane, M.D., Richard Oka, M.S., James Esch, M.D.,
Repair Integrity and Functional Outcome After Arthroscopic Double-Row Rotator Cuff Repair
 953 COPYRIGHT 2007 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Repair Integrity and Functional Outcome After Arthroscopic Double-Row Rotator Cuff Repair A Prospective Outcome Study By Hiroyuki
953 COPYRIGHT 2007 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Repair Integrity and Functional Outcome After Arthroscopic Double-Row Rotator Cuff Repair A Prospective Outcome Study By Hiroyuki
Early Structural and Functional Outcomes for Arthroscopic Double-Row Transosseous-Equivalent Rotator Cuff Repair
 Early Structural and Functional Outcomes for Arthroscopic Double-Row Transosseous-Equivalent Rotator Cuff Repair Bruno Toussaint,* MD, Erik Schnaser, y MD, Jacob Bosley, y MD, Yves Lefebvre,* MD, and Reuben
Early Structural and Functional Outcomes for Arthroscopic Double-Row Transosseous-Equivalent Rotator Cuff Repair Bruno Toussaint,* MD, Erik Schnaser, y MD, Jacob Bosley, y MD, Yves Lefebvre,* MD, and Reuben
Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair
 Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair CHRISTOPHER S. AHMAD, MD; WILLIAM N. LEVINE, MD; LOUIS U. BIGLIANI, MD Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair offers less pain, quicker recovery, and less stiffness compared
Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair CHRISTOPHER S. AHMAD, MD; WILLIAM N. LEVINE, MD; LOUIS U. BIGLIANI, MD Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair offers less pain, quicker recovery, and less stiffness compared
Nuri Aydin and Bedri Karaismailoglu *
 Aydin and Karaismailoglu Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:118 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0619-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access High-grade bursal-side partial rotator cuff tears: comparison
Aydin and Karaismailoglu Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:118 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0619-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access High-grade bursal-side partial rotator cuff tears: comparison
Rehabilitation Following Rotator Cuff Repair: When Should We Start and What Should We Do? Martin J. Kelley, PT, DPT, OCS. Dangerous Territory 3/9/2018
 Rehabilitation Following Rotator Cuff Repair: When Should We Start and What Should We Do? Martin J. Kelley, PT, DPT, OCS Dangerous Territory Rotator Cuff/capsuloligamentous Complex 1 The Rotator Cuff Tear
Rehabilitation Following Rotator Cuff Repair: When Should We Start and What Should We Do? Martin J. Kelley, PT, DPT, OCS Dangerous Territory Rotator Cuff/capsuloligamentous Complex 1 The Rotator Cuff Tear
Rotator cuff repair: The effect of double-row fixation on three-dimensional repair site
 Rotator cuff repair: The effect of double-row fixation on three-dimensional repair site Steven W. Meier, MD, a,b and Jeffrey D. Meier, DO, a Summit and Newark, NJ There is a high rate of recurrent and
Rotator cuff repair: The effect of double-row fixation on three-dimensional repair site Steven W. Meier, MD, a,b and Jeffrey D. Meier, DO, a Summit and Newark, NJ There is a high rate of recurrent and
The modified massive cuff stitch: functional and structural outcome in massive cuff tears
 Gotoh et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2013, 8:26 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The modified massive cuff stitch: functional and structural outcome in massive cuff tears Masafumi Gotoh
Gotoh et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2013, 8:26 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The modified massive cuff stitch: functional and structural outcome in massive cuff tears Masafumi Gotoh
Introduction & Question 1
 Page 1 of 7 www.medscape.com To Print: Click your browser's PRINT button. NOTE: To view the article with Web enhancements, go to: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/424981 Case Q & A Shoulder Pain, Part
Page 1 of 7 www.medscape.com To Print: Click your browser's PRINT button. NOTE: To view the article with Web enhancements, go to: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/424981 Case Q & A Shoulder Pain, Part
Arthroscopic Versus Mini-Open Rotator Cuff Repair: A Comparison of Clinical Outcome
 Arthroscopic Versus Mini-Open Rotator Cuff Repair: A Comparison of Clinical Outcome Andreas M. Sauerbrey, M.D., Charles L. Getz, M.D., Marco Piancastelli, M.D., Joseph P. Iannotti, M.D., Ph.D., Matthew
Arthroscopic Versus Mini-Open Rotator Cuff Repair: A Comparison of Clinical Outcome Andreas M. Sauerbrey, M.D., Charles L. Getz, M.D., Marco Piancastelli, M.D., Joseph P. Iannotti, M.D., Ph.D., Matthew
Technique For SLAP Repair in 2016
 Technique For SLAP Repair in 2016 Eric J. Strauss MD Division of Sports Medicine NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases Hospital for Joint Diseases Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Disclosures Joint Restoration
Technique For SLAP Repair in 2016 Eric J. Strauss MD Division of Sports Medicine NYU Hospital for Joint Diseases Hospital for Joint Diseases Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Disclosures Joint Restoration
Arthroscopic Primary Rotator Cuff Repairs in Patients Aged Younger Than 45 Years
 Arthroscopic Primary Rotator Cuff Repairs in Patients Aged Younger Than 45 Years Emery C. Lin, B.A., Nathan A. Mall, M.D., Aman Dhawan, M.D., Seth L. Sherman, M.D., Kevin C. McGill, M.D., M.P.H., Matthew
Arthroscopic Primary Rotator Cuff Repairs in Patients Aged Younger Than 45 Years Emery C. Lin, B.A., Nathan A. Mall, M.D., Aman Dhawan, M.D., Seth L. Sherman, M.D., Kevin C. McGill, M.D., M.P.H., Matthew
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME
 ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
Partial Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears: All-Inside Repair of PASTA Lesions in Athletes
 Partial Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears: All-Inside Repair of PASTA Lesions in Athletes Thomas M. DeBerardino, MD Associate Professor, UConn Health Center Team Physician, Orthopaedic Consultant UConn Huskie
Partial Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears: All-Inside Repair of PASTA Lesions in Athletes Thomas M. DeBerardino, MD Associate Professor, UConn Health Center Team Physician, Orthopaedic Consultant UConn Huskie
Temporal Evolution of MRI Findings After Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Crim et al. MRI of Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Julia Crim 1,2 Robert Burks 2 Betty J. Manaster 1 Christopher Hanrahan
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Crim et al. MRI of Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Julia Crim 1,2 Robert Burks 2 Betty J. Manaster 1 Christopher Hanrahan
Arthroscopic repair for subacromial incarceration of a torn rotator cuff
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Asia-Pacific Journal of Sports Medicine, Arthroscopy, Rehabilitation and Technology 2 (2015) 90e94 www.ap-smart.com Original article Arthroscopic
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Asia-Pacific Journal of Sports Medicine, Arthroscopy, Rehabilitation and Technology 2 (2015) 90e94 www.ap-smart.com Original article Arthroscopic
Does the Literature Confirm Superior Clinical Results in Radiographically Healed Rotator Cuffs After Rotator Cuff Repair?
 Systematic Review Does the Literature Confirm Superior Clinical Results in Radiographically Healed Rotator Cuffs After Rotator Cuff Repair? Mark A. Slabaugh, M.D., Shane J. Nho, M.D., M.S., Robert C. Grumet,
Systematic Review Does the Literature Confirm Superior Clinical Results in Radiographically Healed Rotator Cuffs After Rotator Cuff Repair? Mark A. Slabaugh, M.D., Shane J. Nho, M.D., M.S., Robert C. Grumet,
Technical Note. The Accessory Posteromedial Portal Revisited: Utility for Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair
 Technical Note The Accessory Posteromedial Portal Revisited: Utility for Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair R. Edward Glenn, Jr., M.D., L. Pearce McCarty, M.D., and Brian J. Cole, M.D., M.B.A. Abstract:
Technical Note The Accessory Posteromedial Portal Revisited: Utility for Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair R. Edward Glenn, Jr., M.D., L. Pearce McCarty, M.D., and Brian J. Cole, M.D., M.B.A. Abstract:
Rotator cuff strength following open subscapularis tendon repair
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 173179 ORIGAL STUDY Rotator cuff strength following open subscapularis tendon repair Roger P. VAN RIET, Sean T. O LEARY, Alexander HOOP, Simon N. BELL From the Melbourne Shoulder
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 173179 ORIGAL STUDY Rotator cuff strength following open subscapularis tendon repair Roger P. VAN RIET, Sean T. O LEARY, Alexander HOOP, Simon N. BELL From the Melbourne Shoulder
06/Μαρ/2013 FUNCTION OF THE ROTATOR CUFF. ARTHROSCOPIC ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR Primarily to stabilize and centralize the humeral head GENERAL GUIDE LINES
 FUNCTION OF THE ROTATOR CUFF ARTHROSCOPIC ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR Primarily to stabilize and centralize the humeral head GENERAL GUIDE LINES Achieved by balancing the force couples in coronal and transverse
FUNCTION OF THE ROTATOR CUFF ARTHROSCOPIC ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR Primarily to stabilize and centralize the humeral head GENERAL GUIDE LINES Achieved by balancing the force couples in coronal and transverse
Arthroscopic Tenodesis Through Positioning Portals to Treat Proximal Lesions of the Biceps Tendon
 Cell Biochem Biophys (2014) 70:1499 1506 DOI 10.1007/s12013-014-0071-9 ORIGINAL PAPER Arthroscopic Tenodesis Through Positioning Portals to Treat Proximal Lesions of the Biceps Tendon Ji Shen Qing-feng
Cell Biochem Biophys (2014) 70:1499 1506 DOI 10.1007/s12013-014-0071-9 ORIGINAL PAPER Arthroscopic Tenodesis Through Positioning Portals to Treat Proximal Lesions of the Biceps Tendon Ji Shen Qing-feng
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Large Rotator Cuff Repair
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Large Rotator Cuff Repair The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Large Rotator Cuff Repair The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the
D Degenerative joint disease, rotator cuff deficiency with, 149 Deltopectoral approach component removal with, 128
 Index A Abduction exercise, outpatient with, 193, 194 Acromioclavicular arthritis, with, 80 Acromiohumeral articulation, with, 149 Acromio-humeral interval (AHI), physical examination with, 9, 10 Active
Index A Abduction exercise, outpatient with, 193, 194 Acromioclavicular arthritis, with, 80 Acromiohumeral articulation, with, 149 Acromio-humeral interval (AHI), physical examination with, 9, 10 Active
Patient Presentation. Prevalence of Rotator Cu Tears. By Derek S. Shia, M.D.
 Rotator Cu Tears By Derek S. Shia, M.D. Rotator cu tears are one of the most common orthopedic problems and e ect more than 17 million persons annually in the United States. The rotator cu is an essential
Rotator Cu Tears By Derek S. Shia, M.D. Rotator cu tears are one of the most common orthopedic problems and e ect more than 17 million persons annually in the United States. The rotator cu is an essential
Chronic Shoulder Instability
 Chronic Shoulder Instability The shoulder is the most moveable joint in your body. It helps you to lift your arm, to rotate it, and to reach up over your head. It is able to turn in many directions. This
Chronic Shoulder Instability The shoulder is the most moveable joint in your body. It helps you to lift your arm, to rotate it, and to reach up over your head. It is able to turn in many directions. This
Assessment of functional outcome of mini-open rotator cuff repair: a hospital based prospective study
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180681 Assessment of functional outcome of
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180681 Assessment of functional outcome of
Short term results of arthroscopic repair of subscapularis tendon tear
 Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 23, No. 3, November, 2009. pp. 117-121 Short term results of arthroscopic repair of subscapularis tendon tear Hamid Reza Aslani, MD.
Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 23, No. 3, November, 2009. pp. 117-121 Short term results of arthroscopic repair of subscapularis tendon tear Hamid Reza Aslani, MD.
Biomechanical Comparison Of A Novel Suture Configuration As An Alternative Single-Row Repair Technique For Rotator Cuff Repair
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 19 Number 3 Biomechanical Comparison Of A Novel Suture Configuration As An Alternative Single-Row Repair D Lieu, S Tan, D Bell, B Walsh, A Rubin
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 19 Number 3 Biomechanical Comparison Of A Novel Suture Configuration As An Alternative Single-Row Repair D Lieu, S Tan, D Bell, B Walsh, A Rubin
Shoulder Injuries: Treatments that Work, Do Not Work, and When ENOUGH is Enough? Mark Ganjianpour, M.D. Beverly Hills, CA April 20, 2012
 Shoulder Injuries: Treatments that Work, Do Not Work, and When ENOUGH is Enough? Mark Ganjianpour, M.D. Beverly Hills, CA April 20, 2012 Multiaxial ball and socket Little Inherent Instability Glenohumeral
Shoulder Injuries: Treatments that Work, Do Not Work, and When ENOUGH is Enough? Mark Ganjianpour, M.D. Beverly Hills, CA April 20, 2012 Multiaxial ball and socket Little Inherent Instability Glenohumeral
Review Article Tissue Engineering for Rotator Cuff Repair: An Evidence-Based Systematic Review
 Stem Cells International Volume 2012, Article ID 418086, 11 pages doi:10.1155/2012/418086 Review Article Tissue Engineering for Rotator Cuff Repair: An Evidence-Based Systematic Review Nicola Maffulli,
Stem Cells International Volume 2012, Article ID 418086, 11 pages doi:10.1155/2012/418086 Review Article Tissue Engineering for Rotator Cuff Repair: An Evidence-Based Systematic Review Nicola Maffulli,
Arthroscopic fixation of isolated type II SLAP lesions using a two-portal technique
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 160-166 ORIGINAL STUDY Arthroscopic fixation of isolated type II SLAP lesions using a two-portal technique Aristotelis KAisiDis, Panagiotis PAntOs, Horst HEGER, Dimitrios
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 160-166 ORIGINAL STUDY Arthroscopic fixation of isolated type II SLAP lesions using a two-portal technique Aristotelis KAisiDis, Panagiotis PAntOs, Horst HEGER, Dimitrios
How repaired rotator cuff function influences Constant scoring
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2010) 96, 500 505 ORIGINAL ARTICLE How repaired rotator cuff function influences Constant scoring D. Goutallier a,, J.-M. Postel a, C. Radier b, J. Bernageau
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2010) 96, 500 505 ORIGINAL ARTICLE How repaired rotator cuff function influences Constant scoring D. Goutallier a,, J.-M. Postel a, C. Radier b, J. Bernageau
Dual Row Rotator Cuff Repair using the CHIA PERCPASSER
 Dual Row Rotator Cuff Repair using the CHIA PERCPASSER THOMAS P. KNAPP, M.D. Santa Monica Orthopaedic & Sports Medicine Group TM CHIA PERCPASSER Surgical Technique Dual Row Rotator Cuff Repair using the
Dual Row Rotator Cuff Repair using the CHIA PERCPASSER THOMAS P. KNAPP, M.D. Santa Monica Orthopaedic & Sports Medicine Group TM CHIA PERCPASSER Surgical Technique Dual Row Rotator Cuff Repair using the
STATE OF CONNECTICUT ETHICS BOARD NONE ARTHREX INC ARTHREX INC
 Rationale, Biomechanics,Early Results after Superior Capsular Reconstruction Augustus D Mazzocca MS, MD Director of the New England Musculoskeletal Institute Chairman Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
Rationale, Biomechanics,Early Results after Superior Capsular Reconstruction Augustus D Mazzocca MS, MD Director of the New England Musculoskeletal Institute Chairman Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
Shoulder Arthroscopy. Dr. J.J.A.M. van Raaij. NOV Jaarvergadering Den Bosch 25 jan 2018
 Shoulder Arthroscopy Dr. J.J.A.M. van Raaij NOV Jaarvergadering Den Bosch 25 jan 2018 No disclosures Disclosure Shoulder Instability Traumatic anterior Traumatic posterior Acquired atraumatic Multidirectional
Shoulder Arthroscopy Dr. J.J.A.M. van Raaij NOV Jaarvergadering Den Bosch 25 jan 2018 No disclosures Disclosure Shoulder Instability Traumatic anterior Traumatic posterior Acquired atraumatic Multidirectional
3/9/2018. Algorithm for Massive RCT s. Massive Rotator Cuff Tears: When is Reverse TSA the only option?
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears: When is Reverse TSA the only option? Anthony A. Romeo, MD Professor, Department of Orthopedics Head, Section of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Team Physician, Chicago White Sox
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears: When is Reverse TSA the only option? Anthony A. Romeo, MD Professor, Department of Orthopedics Head, Section of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Team Physician, Chicago White Sox
Rehabilitation Considerations for Post-Operative Rotator Cuff Repair. Adam Shutts, MSPT
 Rehabilitation Considerations for Post-Operative Rotator Cuff Repair Adam Shutts, MSPT Post-Operative Rotator Cuff Repair Delayed vs. early mobilization Differing rehabilitation strategies for different
Rehabilitation Considerations for Post-Operative Rotator Cuff Repair Adam Shutts, MSPT Post-Operative Rotator Cuff Repair Delayed vs. early mobilization Differing rehabilitation strategies for different
What Influence Does Progression of a Nonhealing Rotator Cuff Tear Have on Shoulder Pain and Function?
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2017) 475:1596 1604 DOI 10.1007/s11999-017-5251-7 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH What Influence
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2017) 475:1596 1604 DOI 10.1007/s11999-017-5251-7 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH What Influence
Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair: Mastering the Essentials
 Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair: Mastering the Essentials Dr. Robert Hunter Director, Orthopedic Sports Medicine Center Heart of the Rockies Regional Medical Center Salida, Colorado U of Colorado Sports
Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair: Mastering the Essentials Dr. Robert Hunter Director, Orthopedic Sports Medicine Center Heart of the Rockies Regional Medical Center Salida, Colorado U of Colorado Sports
ROTATOR CUFF TEAR, SURGERY FOR
 ROTATOR CUFF TEAR, SURGERY FOR Indications (Who Needs Surgery, When, electricity is used to cauterize small capillaries. Electricity or Why, and Goals) a motorized shaver is used to remove the bursa and
ROTATOR CUFF TEAR, SURGERY FOR Indications (Who Needs Surgery, When, electricity is used to cauterize small capillaries. Electricity or Why, and Goals) a motorized shaver is used to remove the bursa and
Conflict of Interest. New Strategies in Rotator Cuff Repair. Objectives. Learner Outcome
 Conflict of Interest New Strategies in Rotator Cuff Repair Sheri Lankford, BSN, CNOR I hereby certify that, to the best of my knowledge, no aspect of my current personal or professional situation might
Conflict of Interest New Strategies in Rotator Cuff Repair Sheri Lankford, BSN, CNOR I hereby certify that, to the best of my knowledge, no aspect of my current personal or professional situation might
Curative effects of under-arthroscopic anchor implantation fixation to martial arts player s shoulder joint injury.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (19): 8295-8299 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Curative effects of under-arthroscopic anchor implantation fixation to martial arts player s shoulder joint injury. Zonghao
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (19): 8295-8299 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Curative effects of under-arthroscopic anchor implantation fixation to martial arts player s shoulder joint injury. Zonghao
Arthroscopic Preparation of the Posterior and Posteroinferior Glenoid Labrum
 Arthroscopic Preparation of the Posterior and Posteroinferior Glenoid Labrum By Matthew T. Provencher, MD, LCDR, MC, USNR; Anthony A. Romeo, MD; Daniel J. Solomon, MD, CDR, MC, USN; Bernard R. Bach, Jr.,
Arthroscopic Preparation of the Posterior and Posteroinferior Glenoid Labrum By Matthew T. Provencher, MD, LCDR, MC, USNR; Anthony A. Romeo, MD; Daniel J. Solomon, MD, CDR, MC, USN; Bernard R. Bach, Jr.,
BIOKNOTLESSRC ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR SUTURE ANCHOR SURGICAL TECHNIQUE. Surgical Technique for Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair. Raymond Thal, M.D.
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR BIOKNOTLESSRC SUTURE ANCHOR Surgical Technique for Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Raymond Thal, M.D. Town Center Orthopaedic Associates Reston, Virginia Surgical
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR BIOKNOTLESSRC SUTURE ANCHOR Surgical Technique for Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Raymond Thal, M.D. Town Center Orthopaedic Associates Reston, Virginia Surgical
Clinical outcomes and structural integrity of C-shaped rotator cuff tears after arthroscopic repair: comparison with crescent-shaped tears
 Lee et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:154 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0863-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Clinical outcomes and structural integrity of C-shaped rotator
Lee et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:154 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0863-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Clinical outcomes and structural integrity of C-shaped rotator
Case Report Rotator Interval Lesion and Damaged Subscapularis Tendon Repair in a High School Baseball Player
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 890721, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/890721 Case Report Rotator Interval Lesion and Damaged Subscapularis Tendon Repair in a High School Baseball
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 890721, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/890721 Case Report Rotator Interval Lesion and Damaged Subscapularis Tendon Repair in a High School Baseball
Rotator Cuff Tear FAQs
 What is the rotator cuff? The rotator cuff is the joined-up of tendon of four of the muscles which move the shoulder, namely the subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus and teres minor. While most
What is the rotator cuff? The rotator cuff is the joined-up of tendon of four of the muscles which move the shoulder, namely the subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus and teres minor. While most
Labral Tears. Fig 1: Intact labrum and biceps tendon
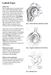 Labral Tears What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone that is
Labral Tears What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone that is
Arthroscopic repair of rotator cuff tears. using absorbable anchors with a single-row technique
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2010;18(3):332-7 Arthroscopic repair of rotator cuff tears using absorbable anchors with a single-row technique Raffele Russo, 1 Fabio Cautiero, 1 Gerardo Giudice, 1 Michele
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2010;18(3):332-7 Arthroscopic repair of rotator cuff tears using absorbable anchors with a single-row technique Raffele Russo, 1 Fabio Cautiero, 1 Gerardo Giudice, 1 Michele
Most rotator cuff tears occur in individuals older
 A Load-Sharing Rip-Stop Fixation Construct for Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Patrick J. Denard, M.D., and Stephen S. Burkhart, M.D. Abstract: Despite advancements in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair
A Load-Sharing Rip-Stop Fixation Construct for Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Patrick J. Denard, M.D., and Stephen S. Burkhart, M.D. Abstract: Despite advancements in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair
Considerations 3/9/2018. Asheesh Bedi, MD. I have no disclosures or conflicts of interest related to the content of this presentation.
 Radiological Assessment of the Rotator Cuff What predicts outcomes? Asheesh Bedi, MD Harold and Helen W. Gehring Professor Chief, Sports Medicine & Shoulder Surgery MedSport, Department of Orthopedic Surgery
Radiological Assessment of the Rotator Cuff What predicts outcomes? Asheesh Bedi, MD Harold and Helen W. Gehring Professor Chief, Sports Medicine & Shoulder Surgery MedSport, Department of Orthopedic Surgery
The ball-and-socket articulation at the glenohumeral joint is between the convex
 SLAP Lesion Repair Emily Cotey, Emily Hurysz, and Patrick Schroeder Abstract SLAP lesion, which stands for Superior Labrum Anterior and Posterior, is a detachment tear of the superior labrum that originates
SLAP Lesion Repair Emily Cotey, Emily Hurysz, and Patrick Schroeder Abstract SLAP lesion, which stands for Superior Labrum Anterior and Posterior, is a detachment tear of the superior labrum that originates
( 1 ) Ball and socket. Shoulder capsule. Rotator cuff.
 Shoulder Arthroscopy Page ( 1 ) Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word arthroscopy comes from two Greek words, arthro
Shoulder Arthroscopy Page ( 1 ) Arthroscopy is a procedure that orthopaedic surgeons use to inspect, diagnose, and repair problems inside a joint. The word arthroscopy comes from two Greek words, arthro
Dr. Denard s Rehabilitation Protocols Arthroscopic Shoulder Surgery
 2780 E. Barnett Rd Medford, OR 97530 541-779-6250 Dr. Denard s Rehabilitation Protocols Arthroscopic Shoulder Surgery These rehabilitation protocols are based on current studies detailing healing time
2780 E. Barnett Rd Medford, OR 97530 541-779-6250 Dr. Denard s Rehabilitation Protocols Arthroscopic Shoulder Surgery These rehabilitation protocols are based on current studies detailing healing time
Passive mobilization after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair is not detrimental in the early postoperative period
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 485-492 ORIGINAL STUDY Passive mobilization after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair is not detrimental in the early postoperative period Pieter-Jan De Roo, Stijn Muermans,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 485-492 ORIGINAL STUDY Passive mobilization after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair is not detrimental in the early postoperative period Pieter-Jan De Roo, Stijn Muermans,
Management of Humeral Bone Loss in Anterior Shoulder Instability. Scott D. Mair, MD University of Kentucky Sports Medicine
 Management of Humeral Bone Loss in Anterior Shoulder Instability Scott D. Mair, MD University of Kentucky Sports Medicine Disclosure Smith and Nephew Endoscopy fellowship support Importance Bone loss (glenoid
Management of Humeral Bone Loss in Anterior Shoulder Instability Scott D. Mair, MD University of Kentucky Sports Medicine Disclosure Smith and Nephew Endoscopy fellowship support Importance Bone loss (glenoid
Shoulder Instability. Fig 1: Intact labrum and biceps tendon
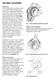 Shoulder Instability What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone
Shoulder Instability What is it? The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, with the humeral head (upper arm bone) as the ball and the glenoid as the socket. The glenoid (socket) is a shallow bone
The goal of rotator cuff repair is to decrease pain, Double-Row Rotator Cuff Repairs: Biomechanical Rationale and Surgical Techniques
 Techniques in Shoulder & Elbow Surgery 9(1):1 9, 2008 Ó 2008 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia T E C H N I Q U E Double-Row Rotator Cuff Repairs: Biomechanical Rationale and Surgical Techniques
Techniques in Shoulder & Elbow Surgery 9(1):1 9, 2008 Ó 2008 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia T E C H N I Q U E Double-Row Rotator Cuff Repairs: Biomechanical Rationale and Surgical Techniques
SLAP Lesions Assessment & Treatment
 SLAP Lesions Assessment & Treatment Kevin E. Wilk,, PT, DPT Glenoid Labral Lesions Introduction Common injury - difficult to diagnose May occur in isolation or in combination SLAP lesions: Snyder: Arthroscopy
SLAP Lesions Assessment & Treatment Kevin E. Wilk,, PT, DPT Glenoid Labral Lesions Introduction Common injury - difficult to diagnose May occur in isolation or in combination SLAP lesions: Snyder: Arthroscopy
ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR: TIPS FOR THE DIFFICULT TEAR
 ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR: TIPS FOR THE DIFFICULT TEAR Felix H. Savoie III, M.D. Lee C. Schlesinger Professor Shoulder, Elbow & Sports Surgery Tulane University, New Orleans, LA USA COI J&J Mitek: consultant
ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR: TIPS FOR THE DIFFICULT TEAR Felix H. Savoie III, M.D. Lee C. Schlesinger Professor Shoulder, Elbow & Sports Surgery Tulane University, New Orleans, LA USA COI J&J Mitek: consultant
Prevention and Management of Stiffness After Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair: Systematic Review and Implications for Rotator Cuff Healing
 Systematic Review With Video Illustrations Prevention and Management of Stiffness After Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair: Systematic Review and Implications for Rotator Cuff Healing Patrick J. Denard,
Systematic Review With Video Illustrations Prevention and Management of Stiffness After Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair: Systematic Review and Implications for Rotator Cuff Healing Patrick J. Denard,
How they begin 8/18/15. Arthroscopic Management of Complex RCT. Disclosures in AAOS Database
 Arthroscopic Management of Complex RCT Brian J. Cole, MD, MBA Professor and Vice-Chairman, Department of Orthopedics Chairman, Department of Surgery, Rush OPH Team Physician, Chicago Whites Sox and Bulls
Arthroscopic Management of Complex RCT Brian J. Cole, MD, MBA Professor and Vice-Chairman, Department of Orthopedics Chairman, Department of Surgery, Rush OPH Team Physician, Chicago Whites Sox and Bulls
POSTERIOR INSTABILITY OF THE SHOULDER Vasu Pai
 POSTERIOR INSTABILITY OF THE SHOULDER Vasu Pai Posterior instability is less common among cases of shoulder instability, accounting for 2% to 10% of all cases of instability. More common in sporting groups:
POSTERIOR INSTABILITY OF THE SHOULDER Vasu Pai Posterior instability is less common among cases of shoulder instability, accounting for 2% to 10% of all cases of instability. More common in sporting groups:
DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS
 DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS Lyndon B. Gross M.D. Ph.D. The Orthopedic Center of St. Louis SHOULDER PAIN Third most common musculoskeletal
DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS Lyndon B. Gross M.D. Ph.D. The Orthopedic Center of St. Louis SHOULDER PAIN Third most common musculoskeletal
SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT
 SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT DR.SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant-KNEE & SHOULDER Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital,Delhi Peculiarities of Shoulder Elegant piece of machinery It has the
SHOULDER PROBLEMS & ARTHROSCOPIC MANAGEMENT DR.SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant-KNEE & SHOULDER Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital,Delhi Peculiarities of Shoulder Elegant piece of machinery It has the
Acromioplasty. Surgical Indications and Considerations
 1 Acromioplasty Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: Any abnormality that disrupts the intricate relationship within the subacromial space may lead to impingement. Both intrinsic
1 Acromioplasty Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: Any abnormality that disrupts the intricate relationship within the subacromial space may lead to impingement. Both intrinsic
Rotator cuff injuries are commonly attributed to repetitive
 [ Orthopaedics ] Massive Rotator Cuff Tear in an Adolescent Athlete: A Case Report Kimberly A. Turman, MD,* Mark W. Anderson, MD, and Mark D. Miller, MD Full-thickness rotator cuff tears in the young athlete
[ Orthopaedics ] Massive Rotator Cuff Tear in an Adolescent Athlete: A Case Report Kimberly A. Turman, MD,* Mark W. Anderson, MD, and Mark D. Miller, MD Full-thickness rotator cuff tears in the young athlete
Management of Anterior Shoulder Instability
 Management of Anterior Shoulder Instability Angelo J. Colosimo, MD Head Orthopaedic Surgeon University of Cincinnati Athletics Director of Sports Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center Associate
Management of Anterior Shoulder Instability Angelo J. Colosimo, MD Head Orthopaedic Surgeon University of Cincinnati Athletics Director of Sports Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center Associate
Arthroscopic Treatment of Anterosuperior Rotator Cuff Tears
 Arthroscopic Treatment of Anterosuperior Rotator Cuff Tears Erik Schnaser, MD; Bruno Toussaint, MD; Robert Gillespie, MD; Yves Lefebvre, MD; Reuben Gobezie, MD abstract Full article available online at
Arthroscopic Treatment of Anterosuperior Rotator Cuff Tears Erik Schnaser, MD; Bruno Toussaint, MD; Robert Gillespie, MD; Yves Lefebvre, MD; Reuben Gobezie, MD abstract Full article available online at
Recurrent and Chronic Elbow Instability
 Recurrent and Chronic Elbow Instability Elbow instability is a looseness in the elbow joint that may cause the joint to catch, pop, or slide out of place during certain arm movements. It most often occurs
Recurrent and Chronic Elbow Instability Elbow instability is a looseness in the elbow joint that may cause the joint to catch, pop, or slide out of place during certain arm movements. It most often occurs
SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder
 Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic and Related Surgery 6(4):21&279 Published by Raven Press, Ltd. Q 1990 Arthroscopy Association of North America SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder Stephen J. Snyder, M.D.,
Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic and Related Surgery 6(4):21&279 Published by Raven Press, Ltd. Q 1990 Arthroscopy Association of North America SLAP Lesions of the Shoulder Stephen J. Snyder, M.D.,
Shoulder Arthroscopy Lab Manual
 Shoulder Arthroscopy Lab Manual Dalhousie University Orthopaedic Program May 5, 2017 Skills Centre OBJECTIVES 1. Demonstrate a competent understanding of the arthroscopic anatomy and biomechanics of the
Shoulder Arthroscopy Lab Manual Dalhousie University Orthopaedic Program May 5, 2017 Skills Centre OBJECTIVES 1. Demonstrate a competent understanding of the arthroscopic anatomy and biomechanics of the
Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations
 MRI of Internal Impingement of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Eddie L. Giaroli 1 Nancy M. Major Laurence D. Higgins Giaroli EL, Major NM, Higgins LD DOI:10.2214/AJR.04.0971
MRI of Internal Impingement of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Eddie L. Giaroli 1 Nancy M. Major Laurence D. Higgins Giaroli EL, Major NM, Higgins LD DOI:10.2214/AJR.04.0971
Impingement syndrome. Clinical features. Management. Rotator cuff tear diagnosed. Go to rotator cuff tear
 Impingement syndrome Clinical features Management Poor response Good response Refer to orthopaedic surgery R Review as appropriate Investigations Rotator cuff tear diagnosed Go to rotator cuff tear Consider
Impingement syndrome Clinical features Management Poor response Good response Refer to orthopaedic surgery R Review as appropriate Investigations Rotator cuff tear diagnosed Go to rotator cuff tear Consider
Common Surgical Shoulder Injury Repairs
 Common Surgical Shoulder Injury Repairs Mr Ilia Elkinson BHB, MBChB, FRACS (Ortho), FNZOA Orthopaedic and Upper Limb Surgeon Bowen Hospital Wellington Hospital Objectives Review pertinent anatomy of the
Common Surgical Shoulder Injury Repairs Mr Ilia Elkinson BHB, MBChB, FRACS (Ortho), FNZOA Orthopaedic and Upper Limb Surgeon Bowen Hospital Wellington Hospital Objectives Review pertinent anatomy of the
ARTHROSCOPIC DEBRIDEMENT VERSUS OPEN REPAIR FOR ROTATOR CUFF TEARS. From the University of Toronto and the Toronto Hospital, Canada
 ARTHROSCOPIC DEBRIDEMENT VERSUS OPEN REPAIR FOR ROTATOR CUFF TEARS A PROSPECTIVE COHORT STUDY D. J. OGILVIE-HARRIS, ALAIN DEMAZIERE From the University of Toronto and the Toronto Hospital, Canada We compared
ARTHROSCOPIC DEBRIDEMENT VERSUS OPEN REPAIR FOR ROTATOR CUFF TEARS A PROSPECTIVE COHORT STUDY D. J. OGILVIE-HARRIS, ALAIN DEMAZIERE From the University of Toronto and the Toronto Hospital, Canada We compared
Double bucket handle tears of the superior labrum
 Case Report http://dx.doi.org/10.14517/aosm13013 pissn 2289-005X eissn 2289-0068 Double bucket handle tears of the superior labrum Dong-Soo Kim, Kyoung-Jin Park, Yong-Min Kim, Eui-Sung Choi, Hyun-Chul
Case Report http://dx.doi.org/10.14517/aosm13013 pissn 2289-005X eissn 2289-0068 Double bucket handle tears of the superior labrum Dong-Soo Kim, Kyoung-Jin Park, Yong-Min Kim, Eui-Sung Choi, Hyun-Chul
