Shock Wave Therapy. Shockwave - The Essentials
|
|
|
- Annabelle Bradford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Shockwave - The Essentials Shock Wave Therapy Professor Tim Watson School of Health & Social Work University of Hertfordshire E Mail : t.watson@herts.ac.uk Web Pages : A SHOCKWAVE is essentially a PRESSURE DISTURBANCE that propagates rapidly through a MEDIUM. It can be defined thus : A large-amplitude compression wave, as that produced by an explosion or by supersonic motion of a body in a medium which just a formal version of the first sentence. Although the adjacent image is from a plane flying at supersonic speed, it clearly illustrates the principle. Obvious examples of shock waves are the sonic boom from an aircraft, thunder or the sound following an explosion. A shockwave is, put simply, an acoustic wave, as is a means of transmitting energy. GENERAL PROFILE OF A SHOCKWAVE (GYMNA UNIPHY) Shockwave - A Brief History A clinically useful shockwave is effectively a controlled explosion (Ogden et al 2001), and when it enters the tissues, it will be reflected, refracted, transmitted and dissipated like any other energy form. The energy content of the wave will vary and the propagation of the wave will vary with tissue type. Just like an ultrasound wave, the shock wave consists of a high pressure phase followed by a low pressure (or relaxation) phase. When a shock wave reaches a 'boundary', some of the energy will be reflected and some transmitted. Shock waves were initially employed as a non invasive treatment for kidney stones (from the early 1970's, with treatment proper starting in the 1980's), and it has become a first line intervention for such conditions. In the process of the animal model experimentation associated with this work, it was identified that shockwaves could have an effect (an adverse one initially) on bone. This led to a series of experimental investigations looking at the effect of shockwaves on bone, cartilage and associated soft tissues (tendon, ligament, fascia) resulting in what is now becoming an intervention of increasing popularity, most especially for the recalcitrant lesions of these tissues, though the clinical uses are expanding and now include wound management, treatment of fractures and numerous additional applications. The use of shock waves to treat bone problems was researched through the early 1980's. with the earliest clinical work (that I can easily identify) being Shockwave Therapy Tim Watson (2014) Page 1
2 around the middle of that decade on delayed and non unions. By the early 1990's, reports start to appear in the journals and conference papers where shockwave is being employed to deal with soft tissue problems, most commonly calcific tendinitis in the first instance, and then on to a variety of other long term problems in tendon, ligament and similar tissues. Although becoming much more popular (especially in Europe and to some extent, in the UK), it is still a relatively new technology for musculoskeletal intervention, and although the publication volume is steadily increasing, some of the published trials are of doubtful methodological quality and need to be considered with some caution. The treatment goes by several names, the most popular being SHOCK WAVE THERAPY or EXTRACORPORAL SHOCKWAVE THERAPY, though, as ever, there are several variations, often linked to the names of particular machines. Some have recently suggested that the therapy version of shockwave therapy might be usefully called RADIAL SHOCKWAVE THERAPY to distinguish the nature of the wave from the focused versions employed elsewhere in medical practice. A very readable but succinct history of the development of shock waves for medical applications can be found in Thiel (2001). Shockwave - Principles of Production There are basically four different way to produce the 'shock wave', which, without getting technical about it are : spark discharge; piezoelectric; electromagnetic and pneumatic (or electrohydrualic). The wave that is generated will vary in its energy content and also will have different penetration characteristics in human tissue. In therapy the most commonly employed generation method is based on the pneumatic system, and the key reason for this is that a radial (dispersive) wave results. The focussed waves are essential for 'surgical' interventions, but given their destructive nature, they are less appropriate for therapeutic uses. Focussed waves are sometimes also referred to as 'hard' shockwaves, the radial or dispersive wave sometimes called a 'soft' shockwave (another twist in the terminology). ESSENTIAL SHOCKWAVE PRODUCTION METHODS (AFTER SPECTRUM TECHNOLOGY). Shockwave Therapy Tim Watson (2014) Page 2
3 Shockwave - Characteristics The characteristics of a shock wave are (typically) : Peak pressure - typically 50-80MPa (according to Ogden et al, 2001) and MPa (according to Speed, 2004) Fast pressure rise (usually less than 10 ns (nanoseconds) Short duration (usually about 10 microseconds) Narrow effective beam (2-8mm diameter) (more detailed descriptions can be found in Ogden et al 2001, Speed, 2004) SHOCKWAVE CHARACTERISTICS AFTER CHUNG AND WILEY, 2002 Shockwaves are divided in terms of their energy content and although there is some controversy, it is generally accepted that the following groups would be reasonable (after Rompe et al, 1998): LOW (up to 0.08mJ/mm 2 ) MEDIUM (up to 0.28mJ/mm 2 - though some authorities elect for a higher value) HIGH (over 0.6mJ/mm 2 ) Though almost all authors, manufacturers and others divide the range into these energy bands, there is (as yet) no universal agreement with regards the boundary values. PRINCIPAL ENERGY DIVISIONS FOR SHOCKWAVE USE IN MEDICAL PRACTICE Shockwave Therapy Tim Watson (2014) Page 3
4 Shockwave - Physiological Effects and Mechanisms of Action The pressure wave causes direct effects (as one would expect) and also 'indirect' effects associated with the subsequent low pressure part of the cycle (often referred too as the tensile phase), and during this phase, cavitation will occur (as with therapeutic ultrasound). The collapse of these cavitations (bubbles) is in part at least, responsible for the efficacy of the therapy. The waves are focused in order to achieve the effects in a volume limited zone of tissue, though the focus does not actually come to a 'point' in therapy devices - more like a zone or small volume typically several mm across (2-8mm), and thus the destructive effects are eliminated. There is no evidence of tissue destructive effects at therapy level doses. As the shock wave travels through a medium and comes to an interface, part of the wave will be reflected and part transmitted. There are equations around for calculating this proportional relationship, but effectively, the dissipation of the energy at the interface is almost certainly responsible for the generation of the physical, physiological and thus the therapeutic effects. The full details of physiological and therapeutic mechanisms are yet to be identified, though a range of effects have been confirmed and several others postulated. Some of the effects relate to an increase in local blood flow which has been clearly evidenced, even in relatively avascular tissues. It is suggested that the beneficial effects are partly also due to a stimulation of an inflammatory response therefore enhancing tissue repair responses, which is especially relevant when dealing with recalcitrant tissues, such as some chronic tendinopathies and delayed and non unions in bone. One of the strongest arguments for the use of shockwave in therapy is that it effectively takes a Tissue from a more chronic to a more acute state, and in doing so, provides a stimulus (trigger) to a 'stalled' repair sequence. This is actually consistent with other approaches employed in therapy - such as some manual therapies (e.g. transverse frictions), some exercise based approaches (e.g. eccentric loading) and some electrotherapy interventions (e.g. provocative ultrasound or laser treatments). The following are the most strongly established treatment effects at therapy shockwave levels. Mechanical stimulation Increased local blood flow Increase in cellular activity release of substance P, prostaglandin E2, NO, TGF β, VEGF, and almost certainly other inflammatory cytokines Transient analgesic effect on afferent nerves Break down calcific deposits (primarily, but not exclusively in tendon) Shockwave Therapy Tim Watson (2014) Page 4
5 PROPOSED MECHANISMS HIERARCHY (AFTER GYMNA UNIPHY, 2010) Energy Levels for Detrimental Effects High energy shockwave (considered to be over 0.6 mj/mm2) have been shown to have detrimental effects in soft tissues, though it is proposed that this is not a dose that would normally be employed in therapy, and is likely to require at least some form of local analgesia to be able to tolerate the treatment! There is some evidence that energy densities greater than 0.4 mj/mm2 may have detrimental effects, though this has yet to be confirmed. In tendon *(using an animal model), shockwave at 0.6 mj/mm2 was demonstrated to have a damaging effect on local blood vessels (Rompe et al 1998). Adverse Effects Provided that the applied energy levels are in the therapy range (LOW and?possibly MEDIUM), there have been no significant adverse effects reported. Some reports of pain or discomfort during, and sometimes after the treatment, but this usually subsides within a relatively short period (1-2 days). It is worth advising the patient of this possibility when discussing the treatment, prior to application. There can be minor skin irritation, and sometimes numbness or paraesthesia, but all are temporary. The potential for and the incidence of adverse effects is included in the Wang et al (2012) review. Shockwave - Clinical Applications [a range of clinical application trials and literature is included in the reference list at the end of this material] Treatment Dose Issues In addition to the applied energy (mj/mm 2 ) in therapy we are using the LOW (up to 0.08mJ/mm 2 ) and possibly the MEDIUM (up to 0.28 mj/mm 2 ) energy levels, the other significant factors are a) number of shocks and b) number of treatment session repetitions Shock Number Shock number usually between 1000 and 1500, though some authorities suggest up to 2000 Some research has tried as few as 100 and also more effective than have been used in the clinical trials with the best (most significant) outcomes Anecdotally, shocks per session appears to be the most commonly applied range Shockwave Therapy Tim Watson (2014) Page 5
6 Number of Treatment Sessions Some evidence for a single session BUT only for High level treatment using local anaesthesia not physiotherapy Most clinical research has used between 3 5 sessions at low energy levels (typical therapy application), suggested up to 7 may be needed in the more recalcitrant lesions There have been no RCT trials yet to determine the maximally effective therapy session number (or interval) Typically 3-5 session appears to be effective for the majority of patients, spaced such as to let the tissue 'reaction' at least partly subside from the first session before the next treatment is delivered. Optimal treatment spacing has yet to be identified in the published research evidence. In terms of specific lesions that have been supported by the research evidence, the tendinopathies are certainly the most frequently reported in the literature, though open wounds and bone union (delayed and non union) problems are also found. Of the chronic and especially recalcitrant tendon lesions, those with strongest research and anecdotal support include : Plantar fasciitis Achilles tendinopathy Patellar tendonipathy Tennis and Golfers elbow (medial and lateral epicondylalgia) Biceps tendinopathy Supraspinatus tendinopathy Other include trochanteric bursitis, though it is appreciated that this is clearly not a tendinopathy type lesion. Interestingly, this 'problem' list closely mirrors the clinical presentations identified by Poltawski, Watson and Byrne (2008) as those identified by therapists as being 'highly problematic'. Shockwave - Research Evidence The attached reference list identifies a range of research and review papers which have been published. Not all are strongly conclusive, and some of the reviews are less enthusiastic than others - but that largely depends on when the review was carried out, which literature was included, and conversely, which papers were excluded from the review. The weight of the evidence is more supportive of the intervention than not, with the anecdotal evidence being even stronger. If one were to deliver an evidence based approach to the clinical management of a chronic tendinopathy, it would be difficult to justify the exclusion of shockwave as a therapy. It is not suggested that it is best used instead of other (effective) interventions, but as an adjunct to overall management (see for example the papers by Rompe et al with regards Achilles problems, shockwave and eccentric loading). Additional references are added as they appear to the web pages which is a non commercial, non partisan, free/open access internet resource. Shockwave - Contraindications, Dangers and Precautions Whilst not intended to constitute a definitive list, there are several areas/pathologies where concern has been expressed with regards the use of shockwave, and until further clarification has been obtained, some of the Shockwave Therapy Tim Watson (2014) Page 6
7 key issues are identified below. This list is compiled from the best (currently) available evidence and expert advice/opinion. It may be that this is an over conservative approach, but as with many 'new' or 'emerging' therapies, it is normal to err on the side of caution in the initial stages of clinical application. Lung tissue appears to be damaged unequivocally and should be avoided The epiphysis has been considered and whilst some experiments demonstrate a detrimental outcome, others do not. Whilst clarification is being obtained, it would make sense to avoid epiphyseal regions Patients who are haemophiliac or who are on anticoagulant therapy are best not treated with shockwave given that some visible tissue damage (skin petechiae and disruption of the microvasculature) has been noted in several studies. Malignancy remains on the contraindication list, though, as with other modalities, some experimental work is ongoing whereby shockwave therapies are being employed to try and minimise the growth and spread of malignant tissue. Given the unknowns at the moment, it is considered best to avoid such areas. Metal implants appear to be OK with regards bone based treatments, but implanted cardiac stents and implanted heart valves have not been fully evaluated. If however, one is avoiding the lungs, then they should not be exposed anyway. Infection in the local area should be treated with strong caution given the as yet unknown effect of the therapy in this field. Joint replacements - interestingly - come up with a mixed result. Some have used the therapy experimentally as a means to help with the removal of prostheses, making extraction easier. Given this, it would seem wise to avoid cemented implants. On the other hand, it is suggested that several researchers have actually used shockwave as a means to stimulate bone growth around an already lose prosthesis (osseous ingrowth). It would seem prudent to avoid the area given the possible loosening effect which, unless desired, would certainly constitute a detrimental outcome. Shockwave Therapy Tim Watson (2014) Page 7
8 References (2005). "Extracorporeal shock wave treatment for chronic plantar fasciitis." Technol Eval Cent Asses Program Exec Summ 19(18): 1-4. Albert, J. D. et al. (2007). "High-energy extracorporeal shock-wave therapy for calcifying tendinitis of the rotator cuff: A RANDOMISED TRIAL." J Bone Joint Surg Br 89(3): Alper, B. S. (2007). "Evidence-based medicine. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy appears ineffective for lateral elbow pain." Clinical Advisor 10(3): 181. Aqil, A. et al. (2013). "Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Is Effective In Treating Chronic Plantar Fasciitis: A Meta-analysis of RCTs." Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 471(11): Bisset, L. et al. (2005). "A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials on physical interventions for lateral epicondylalgia." Br J Sports Med 39(7): ; discussion Borchers, J. R. and T. M. Best (2006). "Corticosteroid injection compared with extracorporeal shock wave therapy for plantar fasciopathy." Clin J Sport Med 16(5): Buchbinder, R. et al. (2005). "Shock-wave therapy for plantar fasciitis." J Bone Joint Surg Am 87(3): 680-1; author reply Buchbinder, R. et al. (2005). "Shock wave therapy for lateral elbow pain." Cochrane Database Syst Rev(4): CD Buchbinder, R. et al. (2006). "Systematic review of the efficacy and safety of shock wave therapy for lateral elbow pain." J Rheumatol 33(7): Buchbinder, R. et al. (2006). "Shock wave therapy for lateral elbow pain." The Cochrane Library 4. Burton, A. M. and T. J. Overend (2005). "Low-energy extracorporeal shock wave therapy: a critical analysis of the evidence for effectiveness in the treatment of plantar fasciitis." Phys-Ther-Rev. 10(3): Buselli, P. et al (2010). "Shock waves in the treatment of post-traumatic myositis ossificans." Ultrasound Med Biol 36(3): Cacchio, A. et al. (2006). "Effectiveness of radial shock-wave therapy for calcific tendinitis of the shoulder: single-blind, randomized clinical study." Phys-Ther. 86(5): Cacchio, A. et al (2011). "Shockwave Therapy for the Treatment of Chronic Proximal Hamstring Tendinopathy in Professional Athletes." Am J Sports Med 39(1): Chow, I. H. W. and G. L. Y. Cheing (2007). "Comparison of different energy densities of extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) for the management of chronic heel pain." Clinical Rehabilitation 21(2): Chung, B. et al. (2005). "Long-term effectiveness of extracorporeal shockwave therapy in the treatment of previously untreated lateral epicondylitis." Clin J Sport Med 15(5): Cook, J. (2007). "Eccentric exercise and shock-wave therapy benefit patients with chronic Achilles tendinopathy." Aust J Physiother 53(2): 131. Costa, M. L. et al. (2005). "Shock wave therapy for chronic Achilles tendon pain: a randomized placebo-controlled trial." Clin Orthop Relat Res 440: Shockwave Therapy Tim Watson (2014) Page 8
9 Crawford, F. and C. Thomson (2006). "Interventions for treating plantar heel pain." The Cochrane Library 4. Csaszar, N. B. and C. Schmitz (2013). "Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders." J Orthop Surg Res 8(1): 22. Dizon, J. N. et al. (2013). "Effectiveness of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in chronic plantar fasciitis: a meta-analysis." Am J Phys Med Rehabil 92(7): Dorotka, R. et al. (2006). "Location modalities for focused extracorporeal shock wave application in the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis." Foot Ankle Int 27(11): Foldager, C et al (2012). "Clinical Application of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in Orthopedics: Focused versus Unfocused Shock Waves." Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology 38(10): Fridman, R. et al (2008). "Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for the treatment of Achilles tendinopathies: a prospective study." J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 98(6): Furia, J. F. (2005). "The safety and efficacy of high energy extracorporeal shock wave therapy in active, moderately active, and sedentary patients with chronic plantar fasciitis." Orthopedics 28(7): Furia, J. P. (2005). "Safety and efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for chronic lateral epicondylitis." Am J Orthop 34(1): 13-9; discussion 19. Furia, J. P. (2005). "The safety and efficacy of high energy extracorporeal shock wave therapy in active, moderately active, and sedentary patients with chronic plantar fasciitis." Orthopedics 28(7): Furia, J. P. et al. (2013). "A single application of low-energy radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy is effective for the management of chronic patellar tendinopathy." Knee Surgery Sports Traumatology Arthroscopy 21(2): Greve, J. M. et al (2009). "Comparison of radial shockwaves and conventional physiotherapy for treating plantar fasciitis." Clinics (Sao Paulo) 64(2): Griffin, X et al (2012). "Ultrasound and shockwave therapy for acute fractures in adults." Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2: CD Gur, A. et al. (2013). "Comparison of the Efficacy of Ultrasound and Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapies in Patients with Myofascial Pain Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Study." Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain 21(3): Haake, M. and L. Gerdesmeyer (2005). "Fasciitis plantaris. Frequency, symptoms, pathogenesis and therapy." Internistische-Praxis. 45(1): Ho, C. (2007). "Extracorporeal shock wave treatment for chronic lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow)." Issues Emerg Health Technol(96 (part 2)): 1-4. Ho, C. (2007). "Extracorporeal shock wave treatment for chronic plantar fasciitis (heel pain)." Issues Emerg Health Technol(96 (part 1)): 1-4. Ho, C. (2007). "Extracorporeal shock wave treatment for chronic rotator cuff tendonitis (shoulder pain)." Issues Emerg Health Technol(96 (part 3)): 1-4. Hsu, C. J. et al. (2007). "Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for calcifying tendinitis of the shoulder." J Shoulder Elbow Surg. Ioppolo, F. et al. (2013). "Clinical Improvement and Resorption of Calcifications in Calcific Tendinitis of the Shoulder After Shock Wave Therapy at 6 Months' Follow-Up: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis." Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 94(9): Shockwave Therapy Tim Watson (2014) Page 9
10 Iserentant, C. and J. M. Crielaard (2006). "[Extracorporeal shock wave therapy value in calcific soft tissue pathologies]." Rev Med Liege 61(5-6): Kersh, K. D. et al. (2006). "The evaluation of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on collagenase induced superficial digital flexor tendonitis." Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol 19(2): Khan, K. (2005). "Best of the literature. Can shock-wave therapy help relieve 'tennis elbow' pain?" Physician and Sportsmedicine 33(7): 8. Khan, K. (2005). "Can Shock-Wave Therapy Help Relieve 'Tennis Elbow' Pain?" Physician-Sports-Med. 33(7): 8. Krasny, C. et al. (2005). "Ultrasound-guided needling combined with shock-wave therapy for the treatment of calcifying tendonitis of the shoulder." Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 7(36 ref). Kudo, P. et al. (2006). "Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial evaluating the treatment of plantar fasciitis with an extracoporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) device: A North American confirmatory study." J Orthop Res 24(2): Lebrun, C. M. (2005). "Low-dose extracorporeal shock wave therapy for previously untreated lateral epicondylitis." Clin J Sport Med 15(5): Lebrun, C. M. (2005). "Shock-wave treatment for chronic lateral epicondylitis in recreational tennis players." Clin J Sport Med 15(3): Lebrun, C. M. (2006). "Needling combined with shock-wave therapy for calcifying tendonitis of the shoulder." Clin J Sport Med 16(4): Lee, J.-H. and E.-Y. Han (2013). "A Comparison of the Effects of PNF, ESWT, and TPI on Pain and Function of Patients with Myofascial Pain Syndrome." Journal of Physical Therapy Science 25(3): Lee, S. et al. (2014). "Effects of extracorporeal shockwave therapy on patients with chronic low back pain and their dynamic balance ability." J Phys Ther Sci 26(1): Liang, H. W. et al. (2007). "Thinner Plantar Fascia Predicts Decreased Pain After Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy." Clin Orthop Relat Res. Liu, S. et al (2012). "Radial Extracorporeal Pressure Pulse Therapy for the Primary Long Bicipital Tenosynovitis a Prospective Randomized Controlled Study." Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology 38(5): Martinez. M. E. and A. A. Pena (2005). "Treatment of tendinitis and calcified subacromiodeltoid bursitis with shock waves." Rehabilitacion. 39(1): 2-7. Marwan, Y. et al. (2014). "Extracorporeal shock wave therapy relieved pain in patients with coccydynia: a report of two cases." Spine Journal 14(1): e1-e4. Moretti, B. et al. (2005). "Medium-energy shock wave therapy in the treatment of rotator cuff calcifying tendinitis." Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 13(5): Moretti, B. et al. (2006). "Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in runners with a symptomatic heel spur." Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 14(10): Moretti, B. et al (2009). "Shock waves in the treatment of stress fractures." Ultrasound Med Biol 35(6): Moretti, B. et al (2009). "A volleyball player with bilateral knee osteochondritis dissecans treated with extracorporeal shock wave therapy." Chir Organi Mov 93(1): Shockwave Therapy Tim Watson (2014) Page 10
11 Mouzopoulos, G. et al. (2007). "Extracorporeal shock wave treatment for shoulder calcific tendonitis: a systematic review." Skeletal Radiol. NICE (2009). Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory Achilles tendinopathy. Interventional Procedure Guidance. London, NICE. Interventional procedure guidance 312. NICE (2009). Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory plantar fasciitis. Interventional Procedure Guidance. London, NICE. Interventional procedure guidance 311. NICE (2009). Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory tennis elbow. Interventional Procedure Guidance. London, NICE. Interventional procedure guidance 313. Norris, D. M. et al. (2005). "Effectiveness of extracorporeal shockwave treatment in 353 patients with chronic plantar fasciitis." J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 95(6): Notarnicola, A. et al (2010). "Shockwave therapy in the management of complex regional pain syndrome in medial femoral condyle of the knee." Ultrasound Med Biol 36(6): Pettrone, F. A. and B. R. McCall (2005). "Extracorporeal shock wave therapy without local anesthesia for chronic lateral epicondylitis." Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 304(19 ref). Qin, L. et al (2010). "Osteogenesis induced by extracorporeal shockwave in treatment of delayed osteotendinous junction healing." J Orthop Res 28(1): Radwan, Y. A. et al. (2007). "Resistant tennis elbow: shock-wave therapy versus percutaneous tenotomy." Int Orthop. Rasmussen, S.et al (2008). "Shockwave therapy for chronic Achilles tendinopathy: a double-blind, randomized clinical trial of efficacy." Acta Orthop 79(2): Reznik, J. E. et al. (2013). "Extracorporeal shock wave therapy as a treatment for heterotopic ossification." Physical Therapy Reviews 18(4): Roehrig, G. J. et al. (2005). "The role of extracorporeal shock wave on plantar fasciitis." Foot Ankle Clin 10(4): , ix. Romeo, P. et al (2011). "Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in pillar pain after carpal tunnel release: a preliminary study." Ultrasound Med Biol 37(10): Romeo, P. et al. (2014). "Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in Musculoskeletal Disorders: A Review." Medical Principles and Practice 23(1): Rompe, J. D. et al. (2005). "Repetitive low-energy shock wave application without local anesthesia is more efficient than repetitive low-energy shock wave application with local anesthesia in the treatment of chronic plantar fasciitis." J Orthop Res 23(4): Rompe, J. D. (2005). "Shock-wave therapy for plantar fasciitis." J Bone Joint Surg Am 87(3): 681-2; author reply Rompe, J. D. (2005). "Effectiveness of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the management of tennis elbow." Am J Sports Med 33(3): 461-2; author reply Rompe, J. D. (2006). "Shock wave therapy for chronic Achilles tendon pain: a randomized placebo-controlled trial." Clin Orthop Relat Res 445: 276-7; author reply 277. Rompe, J. D. (2007). "Repetitive low-energy shock wave treatment is effective for chronic symptomatic plantar fasciitis." Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 15(1): 107; author reply 108. Shockwave Therapy Tim Watson (2014) Page 11
12 Rompe, J. D. et al. (2007). "Shock wave therapy for chronic plantar fasciopathy." Br Med Bull. Rompe, J. D. et al. (2007). "Eccentric loading, shock-wave treatment, or a wait-and-see policy for tendinopathy of the main body of tendo Achillis: a randomized controlled trial." Am J Sports Med 35(3): Rompe, J. D.et al (2008). "Eccentric loading compared with shock wave treatment for chronic insertional achilles tendinopathy. A randomized, controlled trial." J Bone Joint Surg Am 90(1): Rompe, J. D. et al (2009). "Eccentric loading versus eccentric loading plus shock-wave treatment for midportion achilles tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial." Am J Sports Med 37(3): Rompe, J. D. et al (2009). "Home training, local corticosteroid injection, or radial shock wave therapy for greater trochanter pain syndrome." Am J Sports Med 37(10): Rompe, J. D.et al (2010). "Low-energy extracorporeal shock wave therapy as a treatment for medial tibial stress syndrome." Am J Sports Med 38(1): Sabeti, M. et al. (2007). "A comparison of two different treatments with navigated extracorporeal shock-wave therapy for calcifying tendinitis - a randomized controlled trial." Wien Klin Wochenschr 119(3-4): Sabeti-Aschraf, M. et al. (2005). "Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the treatment of calcific tendinitis of the rotator cuff." Am J Sports Med 33(9): Sarkar, B. et al. (2013). "Efficacy of low-energy extracorporeal shockwave therapy and a supervised clinical exercise protocol for the treatment of chronic lateral epicondylitis: A randomised controlled study." Hong Kong Physiotherapy Journal 31(1): Saw, A. (2005). "Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for musculoskeletal pathology--a literature review." Med J Malaysia 60 Suppl C: Schmitz, C. and R. Depace (2009). "Pain relief by extracorporeal shockwave therapy: an update on the current understanding." Urological Research 37(4): Schmitz, C. et al. (2013). "Treatment of chronic plantar fasciopathy with extracorporeal shock waves (review)." J Orthop Surg Res 8(1): 31. Seco, J. et al (2011). "The efficacy, safety, effectiveness, and cost-effectiveness of ultrasound and shock wave therapies for low back pain: a systematic review." Spine J 11(10): Seil, R. et al. (2006). "Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for tendinopathies." Expert Rev Med Devices 3(4): Sems, A. et al. (2006). "Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the treatment of chronic tendinopathies." J Am Acad Orthop Surg 14(4): Seok, H. and S. H. Kim (2013). "The effectiveness of extracorporeal shock wave therapy vs. local steroid injection for management of carpal tunnel syndrome: a randomized controlled trial." Am J Phys Med Rehabil 92(4): Spacca, G. et al. (2005). "Radial shock wave therapy for lateral epicondylitis: a prospective randomised controlled singleblind study." Eura Medicophys 41(1): Stasinopoulous, D. and M. I. Johnson (2005). "Effectiveness of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis)." British Journal of Sports Medicine 39(3): Taki, M. et al. (2007). "Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for resistant stress fracture in athletes: a report of 5 cases." Am J Sports Med 35(7): Shockwave Therapy Tim Watson (2014) Page 12
13 Thomson, C. E. et al. (2005). "The effectiveness of extra corporeal shock wave therapy for plantar heel pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis." BMC Musculoskelet Disord 6: 19. Trebinjac, S. et al. (2005). "Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in orthopaedic diseases." Bosn J Basic Med Sci 5(2): van der Worp, H. et al. (2013). "ESWT for tendinopathy: technology and clinical implications." Knee Surgery Sports Traumatology Arthroscopy 21(6): van Leeuwen, M. T., J. Zwerver and I. van den Akker-Scheek (2009). "Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for patellar tendinopathy: a review of the literature." Br J Sports Med 43(3): Vetrano, M. et al. (2013). "Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Focused Shock Waves in the Treatment of Jumper's Knee in Athletes." Am J Sports Med 41(4): Vulpiani, M. C. et al (2009). "Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) in Achilles tendinopathy. A long-term follow-up observational study." J Sports Med Phys Fitness 49(2): Wang, C. et al. (2006). "Long-term results of extracorporeal shockwave treatment for plantar fasciitis." American Journal of Sports Medicine 34(4): Wang, C. J. et al. (2007). "Extracorporeal shockwave for chronic patellar tendinopathy." Am J Sports Med 35(6): Wang, C. J. et al. (2007). "The effects of extracorporeal shockwave on acute high-energy long bone fractures of the lower extremity." Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 127(2): Wang, C. J. et al. (2007). "Treatment of osteonecrosis of the hip: comparison of extracorporeal shockwave with shockwave and alendronate." Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. Wang, C. J. et al. (2005). "The effect of shock wave treatment at the tendon-bone interface-an histomorphological and biomechanical study in rabbits." J Orthop Res 23(2): Wang, C. J. (2009). "The effects of shockwave on bone healing and systemic concentrations of nitric oxide (NO), TGFbeta1, VEGF and BMP-2 in long bone non-unions." Nitric Oxide 20(4): Wang, C.-J. (2012). "Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders." Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 7(1): 11. Wang, L. et al. (2008). "Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in treatment of delayed bone-tendon healing." Am J Sports Med 36(2): Wood, W. et al. (2006). "Lateral epicondylalgia: an overview." Physical Therapy Reviews 11(3): Yalcin, E. et al. (2012). "Effects of extracorporal shock wave therapy on symptomatic heel spurs: a correlation between clinical outcome and radiologic changes." Rheumatol Int 32(2): Zhu, F. et al. (2005). "Chronic plantar fasciitis: acute changes in the heel after extracorporeal high-energy shock wave therapy--observations at MR imaging." Radiology 234(1): Zwerver, J. et al (2011). "No effect of extracorporeal shockwave therapy on patellar tendinopathy in jumping athletes during the competitive season: a randomized clinical trial." Am J Sports Med 39(6): Shockwave Therapy Tim Watson (2014) Page 13
Shockwave Therapies for Musculoskeletal Problems Useful Literature
 Shockwave Therapies for Musculoskeletal Problems Useful Literature I have some 1600 references related to shockwave therapy. Those listed below are the main musculoskeletal related papers from 2005-07
Shockwave Therapies for Musculoskeletal Problems Useful Literature I have some 1600 references related to shockwave therapy. Those listed below are the main musculoskeletal related papers from 2005-07
E-Shock Wave in Physical Therapy. Mohammed TA Omar PhD PT Rehabilitation Health Science
 E-Shock Wave in Physical Therapy Mohammed TA Omar PhD PT Rehabilitation Health Science Objectives Following completion of this lecture the student will be able to: Describe the mechanical characteristics
E-Shock Wave in Physical Therapy Mohammed TA Omar PhD PT Rehabilitation Health Science Objectives Following completion of this lecture the student will be able to: Describe the mechanical characteristics
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy. Outcomes in Shoulder Tendinopathy and Plantar Fasciitis. American University of Beirut Medical Center
 Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy. Outcomes in Shoulder Tendinopathy and Plantar Fasciitis Nagham HADDAD, PT Nagham HADDAD, PT American University of Beirut Medical Center Introduction: Tendinosis is the
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy. Outcomes in Shoulder Tendinopathy and Plantar Fasciitis Nagham HADDAD, PT Nagham HADDAD, PT American University of Beirut Medical Center Introduction: Tendinosis is the
3.3.1 Introduction. Nikolaus B.M. Császár and Christoph Schmitz
 3.3 Shock Wave Therapy 55 Nikolaus B.M. Császár and Christoph Schmitz 3.3 Shock Wave Therapy Effectiveness and safety of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for disorders of the tendons: A systematic review
3.3 Shock Wave Therapy 55 Nikolaus B.M. Császár and Christoph Schmitz 3.3 Shock Wave Therapy Effectiveness and safety of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for disorders of the tendons: A systematic review
Radial Shockwave Therapy
 Radial Shockwave Therapy New Uses for Old Technology Nick Savva FRCS(Tr&Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Radial Shockwave Therapy What is a shockwave? Radial Shockwave Therapy What is a shockwave?
Radial Shockwave Therapy New Uses for Old Technology Nick Savva FRCS(Tr&Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Radial Shockwave Therapy What is a shockwave? Radial Shockwave Therapy What is a shockwave?
Coverage Guidelines. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for Musculoskeletal/Orthopedic Indications
 Coverage Guidelines Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for Musculoskeletal/Orthopedic Indications Disclaimer: Please note that Baptist Health Plan Coverage Guidelines may be updated throughout the
Coverage Guidelines Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for Musculoskeletal/Orthopedic Indications Disclaimer: Please note that Baptist Health Plan Coverage Guidelines may be updated throughout the
Plantar Fasciitis. Medical Coverage Policy Extracorporeal Shock Wave Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis and Other Musculoskeletal Conditions
 Medical Coverage Policy Extracorporeal Shock Wave Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis and Other Musculoskeletal Conditions EFFECTIVE DATE: 10 01 2015 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 10 16 2018 OVERVIEW Extracorporeal
Medical Coverage Policy Extracorporeal Shock Wave Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis and Other Musculoskeletal Conditions EFFECTIVE DATE: 10 01 2015 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 10 16 2018 OVERVIEW Extracorporeal
MEDICAL POLICY. Proprietary Information of Excellus Health Plan, Inc. A nonprofit independent licensee of the BlueCross BlueShield Association
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE PAGE: 1 OF: 8 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE PAGE: 1 OF: 8 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical
EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) FOR CHRONIC TENDINITIS AND RELATED DISORDERS
 BACKGROUND EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) FOR CHRONIC TENDINITIS AND RELATED DISORDERS REVIEW OF THE MEDICAL LITERATURE FOR EFFICACY, SAFETY, AND COST-EFFECTIVENESS Low energy ESWT is a byproduct
BACKGROUND EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) FOR CHRONIC TENDINITIS AND RELATED DISORDERS REVIEW OF THE MEDICAL LITERATURE FOR EFFICACY, SAFETY, AND COST-EFFECTIVENESS Low energy ESWT is a byproduct
Kevin Jones Medical Services Director
 Kevin Jones Medical Services Director MSK 2016 Extra Corporeal Shockwave Therapy Shock! Some Examples Of A Shockwave Atomic Bomb John Non Neumann 1945 Mathematician. Invented the WWII 1945 Atomic Bomb
Kevin Jones Medical Services Director MSK 2016 Extra Corporeal Shockwave Therapy Shock! Some Examples Of A Shockwave Atomic Bomb John Non Neumann 1945 Mathematician. Invented the WWII 1945 Atomic Bomb
MEDICAL POLICY. Proprietary Information of YourCare Health Plan
 MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 8 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 8 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) FOR MUSCULOSKELETAL CONDITIONS AND SOFT TISSUE WOUNDS
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE PAGE: 1 OF: 9 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE PAGE: 1 OF: 9 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
Shockwave Therapy. Also referred to as Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy
 Shockwave Therapy Also referred to as Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy TensCare Shockwave Therapy Unit Introduction ESWT Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy is a non-invasive therapy that uses acoustic waves
Shockwave Therapy Also referred to as Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy TensCare Shockwave Therapy Unit Introduction ESWT Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy is a non-invasive therapy that uses acoustic waves
Protocol. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis and Other Musculoskeletal Conditions
 Extracorporeal Shock Wave Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis and (20140) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/13 Next Review Date: 07/15 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 02/07, 11/07, 11/08, 03/09, 01/10,
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis and (20140) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/13 Next Review Date: 07/15 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 02/07, 11/07, 11/08, 03/09, 01/10,
EMERGING TECHNOLOGY IN THE TREATMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS AND LATERAL EPICONDYLITIS By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D.
 1 of 5 7/8/2005 1:47 PM EMERGING TECHNOLOGY IN THE TREATMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS AND LATERAL EPICONDYLITIS By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Abstract: Chronic proximal plantar fasciitis is an extremely common
1 of 5 7/8/2005 1:47 PM EMERGING TECHNOLOGY IN THE TREATMENT OF PLANTAR FASCIITIS AND LATERAL EPICONDYLITIS By: George E. Quill, Jr., M.D. Abstract: Chronic proximal plantar fasciitis is an extremely common
HI THERE FOURLEG FOLKS
 January February 2015 Volume 4, Issue 1A HI THERE FOURLEG FOLKS I am so very excited to bring you this newsletter. It was a monumental task to put together! Searching for the articles, sorting through
January February 2015 Volume 4, Issue 1A HI THERE FOURLEG FOLKS I am so very excited to bring you this newsletter. It was a monumental task to put together! Searching for the articles, sorting through
What I Will Cover. Shock Wave Therapy. What are shock waves? What are shock waves? What are shock waves? What are shock waves?
 Shock Wave Therapy Sarah Matyjaszek Large Animal Surgery University of Florida April 25 th, 2009 What I Will Cover How they work Applications Research Case example Potential complications The future A
Shock Wave Therapy Sarah Matyjaszek Large Animal Surgery University of Florida April 25 th, 2009 What I Will Cover How they work Applications Research Case example Potential complications The future A
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) Jeff Blea, DVM Von Bluecher, Blea, Hunkin, Inc. Equine Medicine and Surgery Sierra Madre, CA
 Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) Jeff Blea, DVM Von Bluecher, Blea, Hunkin, Inc. Equine Medicine and Surgery Sierra Madre, CA History Shock waves used in human medicine as early as 1980s: Break
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) Jeff Blea, DVM Von Bluecher, Blea, Hunkin, Inc. Equine Medicine and Surgery Sierra Madre, CA History Shock waves used in human medicine as early as 1980s: Break
Orthospec. ESWT - Extracorporeal Shock WaveTherapy
 Orthospec ESWT - Extracorporeal Shock WaveTherapy TM There are many things in life that seemed impossible to us. For example walking on the moon; or getting from London to Paris in just an hour; or talking
Orthospec ESWT - Extracorporeal Shock WaveTherapy TM There are many things in life that seemed impossible to us. For example walking on the moon; or getting from London to Paris in just an hour; or talking
orthopace Noninvasive Regenerative Medicine for Musculoskeletal Conditions
 orthopace Noninvasive Regenerative Medicine for Musculoskeletal Conditions SANUWAVE Health, Inc. is a regenerative medicine company focused on the development and commercialization of noninvasive, biological
orthopace Noninvasive Regenerative Medicine for Musculoskeletal Conditions SANUWAVE Health, Inc. is a regenerative medicine company focused on the development and commercialization of noninvasive, biological
EMS Swiss Dolorclast System (ESWT)
 EMS Swiss Dolorclast System (ESWT) What is Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy? (ESWT) Extracorporeal Radial shockwaves are high-energy acoustic waves. They are transmitted through the surface of the skin
EMS Swiss Dolorclast System (ESWT) What is Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy? (ESWT) Extracorporeal Radial shockwaves are high-energy acoustic waves. They are transmitted through the surface of the skin
What is Shockwave therapy?
 Shockwave Therapy ShockMaster : the proven solution What is Shockwave therapy? Shockwave therapy is a modern and highly effective treatment method. The term shockwave refers to mechanical pressure pulses
Shockwave Therapy ShockMaster : the proven solution What is Shockwave therapy? Shockwave therapy is a modern and highly effective treatment method. The term shockwave refers to mechanical pressure pulses
SWISS DOLORCLAST METHOD CLINICAL TRIALS PUBLISHED IN THE INTERNATIONAL PEER-REVIEWED LITERATURE
 SWISS DOLORCLAST METHOD CLINICAL TRIALS PUBLISHED IN THE INTERNATIONAL PEER-REVIEWED LITERATURE Clinical trials published in the international peer-reviewed literature 1 demonstrating efficacy and safety
SWISS DOLORCLAST METHOD CLINICAL TRIALS PUBLISHED IN THE INTERNATIONAL PEER-REVIEWED LITERATURE Clinical trials published in the international peer-reviewed literature 1 demonstrating efficacy and safety
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for Musculoskeletal Conditions and Soft Tissue Wounds
 Medical Coverage Policy Effective Date... 1/15/2018 Next Review Date... 1/15/2019 Coverage Policy Number... 0004 Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for Musculoskeletal Conditions and Soft Tissue
Medical Coverage Policy Effective Date... 1/15/2018 Next Review Date... 1/15/2019 Coverage Policy Number... 0004 Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for Musculoskeletal Conditions and Soft Tissue
Plantar fasciitis: p. 1/6
 Clinical trials published in the international peer-reviewed literature 1 demonstrating efficacy and safety of treatment with the EMS Swiss Dolorclast according to Evidence Based Medicine criteria 2 :
Clinical trials published in the international peer-reviewed literature 1 demonstrating efficacy and safety of treatment with the EMS Swiss Dolorclast according to Evidence Based Medicine criteria 2 :
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders Abstract Keywords:
 J Orthop Surg Res. 2012; 7: 11. Published online 2012 Mar 20. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders Ching-Jen Wang1 Author information Article notes Copyright and License information
J Orthop Surg Res. 2012; 7: 11. Published online 2012 Mar 20. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders Ching-Jen Wang1 Author information Article notes Copyright and License information
Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy Inflamed Achilles tendon
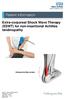 Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy Inflamed Achilles tendon Source: Trauma & Orthopaedics Reference No: 6459-1 Issue date: 1/2/19 Review date: 1/2/22 Page
Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy Inflamed Achilles tendon Source: Trauma & Orthopaedics Reference No: 6459-1 Issue date: 1/2/19 Review date: 1/2/22 Page
Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for plantar fasciitis / heel pain
 Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for plantar fasciitis / heel pain Source: Trauma & Orthopaedics Reference No: 6460-1 Issue date: 1/2/19 Review date: 1/2/22 Page 1 of 6 Plantar fasciitis / heel
Extra-corporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) for plantar fasciitis / heel pain Source: Trauma & Orthopaedics Reference No: 6460-1 Issue date: 1/2/19 Review date: 1/2/22 Page 1 of 6 Plantar fasciitis / heel
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Plantar Fasciitis and Other Musculoskeletal Conditions
 Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Plantar Fasciitis and Other Musculoskeletal Conditions Policy Number: 2.01.40 Last Review: 9/2017 Origination: 5/2001 Next Review: 9/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Plantar Fasciitis and Other Musculoskeletal Conditions Policy Number: 2.01.40 Last Review: 9/2017 Origination: 5/2001 Next Review: 9/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue
Extracorporeal shock wave treatment for chronic calcific rotator cuff tendonitis.
 Extracorporeal shock wave treatment for chronic calcific rotator cuff tendonitis. From the Brisbane Hand & Upper Limb Clinic, Arnold Janssen Centre, Brisbane Private Hospital, 259 Wickham Terrace, Brisbane,
Extracorporeal shock wave treatment for chronic calcific rotator cuff tendonitis. From the Brisbane Hand & Upper Limb Clinic, Arnold Janssen Centre, Brisbane Private Hospital, 259 Wickham Terrace, Brisbane,
SPORTS MEDICINE OVERUSE MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES FOR
 SPORTS MEDICINE OVERUSE INJURIES: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES FOR THE FAMILY PHYSICIAN DR NG CHUNG SIEN MBBS (SPORE) MSPMED (AUSTRALIA) DFD CAW SENIOR REGISTRAR CHANGI SPORTS MEDICINE CENTRE CHANGI
SPORTS MEDICINE OVERUSE INJURIES: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES FOR THE FAMILY PHYSICIAN DR NG CHUNG SIEN MBBS (SPORE) MSPMED (AUSTRALIA) DFD CAW SENIOR REGISTRAR CHANGI SPORTS MEDICINE CENTRE CHANGI
Lööklaineravi kasutus tendinopaatiate ravis. Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for Tendinopaties
 LÖÖKLAINETERAAPIA Lööklaineravi kasutus tendinopaatiate ravis Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for Tendinopaties Tõnis Mandel taastusarst SA Tartu Ülikooli Kliinikum Spordimeditsiini ja taastusravi kliinik
LÖÖKLAINETERAAPIA Lööklaineravi kasutus tendinopaatiate ravis Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy for Tendinopaties Tõnis Mandel taastusarst SA Tartu Ülikooli Kliinikum Spordimeditsiini ja taastusravi kliinik
Shockwave Therapy. Leading Rehabilitation Technology
 Excellence in Shockwave Therapy Leading Rehabilitation Technology Since its foundation in 2003, REMED has tried to care for the patients suffering from different types of physical pains all over the world
Excellence in Shockwave Therapy Leading Rehabilitation Technology Since its foundation in 2003, REMED has tried to care for the patients suffering from different types of physical pains all over the world
A patient s guide to. Radial Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT)
 A patient s guide to Radial Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) The Foot & Ankle Unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital is made up of a multi-disciplinary team. The team consists of four specialist
A patient s guide to Radial Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) The Foot & Ankle Unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital is made up of a multi-disciplinary team. The team consists of four specialist
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis and Other Musculoskeletal Conditions. Original Policy Date
 MP 2.01.28 Extracorporeal Shock Wave Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis and Other Musculoskeletal Conditions Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date
MP 2.01.28 Extracorporeal Shock Wave Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis and Other Musculoskeletal Conditions Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date
The Next Piezo Shockwave Generation
 The Next Piezo Shockwave Generation The PiezoWave2 The piezoelectric principle / focused Piezo-ceramic elements are geometrically arranged in a compact therapy source design and a precise and on a concave
The Next Piezo Shockwave Generation The PiezoWave2 The piezoelectric principle / focused Piezo-ceramic elements are geometrically arranged in a compact therapy source design and a precise and on a concave
ORTHOPEDICS BONE Recalcitrant nonunions In total hip replacement total knee surgery increased callus volume
 ORTHOPEDICS Orthopedics has to do with a variety of tissue: bone, cartilage, tendon, ligament, muscle. In this regard orthopedic and sports medicine share the same tissue targets. Orthopedics is mostly
ORTHOPEDICS Orthopedics has to do with a variety of tissue: bone, cartilage, tendon, ligament, muscle. In this regard orthopedic and sports medicine share the same tissue targets. Orthopedics is mostly
Cellular and molecular basis for shock wave application to the musculo-skeletal system
 Cellular and molecular basis for shock wave application to the musculo-skeletal system Dr. Christoph Schmitz, MD Dept. Psychiat. Neuropsychol., Div. Cell. Neurosci. Maastricht University Maastricht The
Cellular and molecular basis for shock wave application to the musculo-skeletal system Dr. Christoph Schmitz, MD Dept. Psychiat. Neuropsychol., Div. Cell. Neurosci. Maastricht University Maastricht The
EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT)
 UnitedHealthcare Commercial Medical Policy EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) Policy Number: 2017T0269T Effective Date: June 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE... 1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...
UnitedHealthcare Commercial Medical Policy EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) Policy Number: 2017T0269T Effective Date: June 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE... 1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...
LASER THERAPY FOR PHYSIOTHERAPISTS
 BioFlex Laser Therapy presents LASER THERAPY FOR PHYSIOTHERAPISTS Expand your knowledge. Build your practice. Did you know? Laser Therapy is one of the strongest evidence-based therapies according to Clinical
BioFlex Laser Therapy presents LASER THERAPY FOR PHYSIOTHERAPISTS Expand your knowledge. Build your practice. Did you know? Laser Therapy is one of the strongest evidence-based therapies according to Clinical
PLATELET-RICH PLASMA FOR TREATING CHRONIC TENDINOPATHY
 PLATELET-RICH PLASMA FOR TREATING CHRONIC TENDINOPATHY Written by Jean-François Kaux, Belgium Tendinopathy is a major problem in medicine and sports traumatology 1. It is due, inter alia, to mechanical
PLATELET-RICH PLASMA FOR TREATING CHRONIC TENDINOPATHY Written by Jean-François Kaux, Belgium Tendinopathy is a major problem in medicine and sports traumatology 1. It is due, inter alia, to mechanical
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory Achilles tendinopathy
 Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory Achilles Issued: August 2009 www.nice.org.uk/ipg312 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory Achilles Issued: August 2009 www.nice.org.uk/ipg312 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce
Osteonecrosis of the knee Treatment with ESWT. Dr Shrenik Shah Shrey hospital Ahmedabad
 Osteonecrosis of the knee Treatment with ESWT Dr Shrenik Shah Shrey hospital Ahmedabad Osteonecrosis(ON) of the knee SPONK- Spontaneous ON of the knee Secondary ON of the knee Postarthrosopic ON of the
Osteonecrosis of the knee Treatment with ESWT Dr Shrenik Shah Shrey hospital Ahmedabad Osteonecrosis(ON) of the knee SPONK- Spontaneous ON of the knee Secondary ON of the knee Postarthrosopic ON of the
COURSE OUTLINE-IB 128: SPORTS MEDICINE INTRODUCTION
 COURSE OUTLINE-IB 128: SPORTS MEDICINE INTRODUCTION Definition of sports medicine Pre-participation physical exam Epidemiology of sports injuries injury rates for various sports sports risks relative to
COURSE OUTLINE-IB 128: SPORTS MEDICINE INTRODUCTION Definition of sports medicine Pre-participation physical exam Epidemiology of sports injuries injury rates for various sports sports risks relative to
Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request
 Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) Individual Funding Requests Policy Date Adopted: 6 th February 2017 Version: 1617.1 Individual Funding Request Team
Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) Individual Funding Requests Policy Date Adopted: 6 th February 2017 Version: 1617.1 Individual Funding Request Team
INTERQUAL CARE PLANNING CRITERIA BIBLIOGRAPHY: Procedures- Podiatry 2017
 INTERQUAL CARE PLANNING CRITERIA BIBLIOGRAPHY: Procedures- Podiatry 2017 BIB-1 BIB-2 McKesson Clinical Evidence Classification References cited in the clinical content are classified according to the type
INTERQUAL CARE PLANNING CRITERIA BIBLIOGRAPHY: Procedures- Podiatry 2017 BIB-1 BIB-2 McKesson Clinical Evidence Classification References cited in the clinical content are classified according to the type
Treatment of Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions
 APPENDIX G Treatment of Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions The purpose of this document is to provide information for physiotherapists of common medical and surgical interventions
APPENDIX G Treatment of Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy: Medical and Surgical Interventions The purpose of this document is to provide information for physiotherapists of common medical and surgical interventions
PLATELET- RICH PLASMA (PRP) INJECTIONS
 PLATELET- RICH PLASMA (PRP) INJECTIONS Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections have become an extremely popular treatment option for patients with chronic tendon injuries. Although PRP injections have received
PLATELET- RICH PLASMA (PRP) INJECTIONS Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections have become an extremely popular treatment option for patients with chronic tendon injuries. Although PRP injections have received
JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 01 Page January 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Management of Chronic Plantar Fasciitis using Hyperosmolar Dextrose Injection Authors Ansarul Haq Lone 1, Omar Khursheed 2, Shakir Rashid
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Management of Chronic Plantar Fasciitis using Hyperosmolar Dextrose Injection Authors Ansarul Haq Lone 1, Omar Khursheed 2, Shakir Rashid
Page 1 of 6. Appendix 1
 Page 1 Appendix 1 Rotation Objectives and Schedule 1. Introductory Month 4 weeks 2. Total Joints 4 weeks a. Diagnosis and management of hip and knee arthritis b. Indications for surgery c. Implant selection;
Page 1 Appendix 1 Rotation Objectives and Schedule 1. Introductory Month 4 weeks 2. Total Joints 4 weeks a. Diagnosis and management of hip and knee arthritis b. Indications for surgery c. Implant selection;
Intelect Focus Shockwave
 Intelect Focus Shockwave A non-invasive treatment, proven effective for plantar fasciitis Intelect Focus Shockwave - the Technology Greater Power & Depth for Better Treatment In Extracorporeal Shock Wave
Intelect Focus Shockwave A non-invasive treatment, proven effective for plantar fasciitis Intelect Focus Shockwave - the Technology Greater Power & Depth for Better Treatment In Extracorporeal Shock Wave
Treating Chronic Tendon Pain at the Source
 Treating Chronic Tendon Pain at the Source Causes of Tendon Pain Tendons are strong, flexible bands of connective tissue that connect muscle to bone, and transmit the energy needed to allow muscles and
Treating Chronic Tendon Pain at the Source Causes of Tendon Pain Tendons are strong, flexible bands of connective tissue that connect muscle to bone, and transmit the energy needed to allow muscles and
Specific Question: In adults with chronic trochanteric bursitis is physiotherapy more effective in reducing pain than usual care? Clinical bottom line
 Short Question: Specific Question: In adults with chronic trochanteric bursitis is physiotherapy more effective in reducing pain than usual care? Clinical bottom line Corticosteroid Injection therapy for
Short Question: Specific Question: In adults with chronic trochanteric bursitis is physiotherapy more effective in reducing pain than usual care? Clinical bottom line Corticosteroid Injection therapy for
EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT)
 UnitedHealthcare Commercial Medical Policy EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) Policy Number: 2018T0269V Effective Date: July 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE... 1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...
UnitedHealthcare Commercial Medical Policy EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) Policy Number: 2018T0269V Effective Date: July 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE... 1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...
STUDY OF PLATELET RICH PLASMA INJECTIONS IN PATIENTS OF TENDINOPATHY IN SOUTH GUJARAT POPULATION
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE STUDY OF PLATELET RICH PLASMA INJECTIONS IN PATIENTS OF TENDINOPATHY IN SOUTH GUJARAT POPULATION Manish Patel 1, Chintan Sheth 2, Jignesh Patel 1, PrabhavTijoriwala 1 Author s Affiliations:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE STUDY OF PLATELET RICH PLASMA INJECTIONS IN PATIENTS OF TENDINOPATHY IN SOUTH GUJARAT POPULATION Manish Patel 1, Chintan Sheth 2, Jignesh Patel 1, PrabhavTijoriwala 1 Author s Affiliations:
EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT)
 MEDICAL POLICY EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) Policy Number: 2014T0269P Effective Date: July 1, 2014 Table of Contents BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS COVERAGE RATIONALE APPLICABLE CODES.. DESCRIPTION
MEDICAL POLICY EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) Policy Number: 2014T0269P Effective Date: July 1, 2014 Table of Contents BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS COVERAGE RATIONALE APPLICABLE CODES.. DESCRIPTION
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM. What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders
 MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT)
 UnitedHealthcare Commercial Medical Policy EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) Policy Number: SUR036 Effective Date: January 1, 2019 Table of Contents Page COVERAGE RATIONALE... 1 APPLICABLE CODES...
UnitedHealthcare Commercial Medical Policy EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCK WAVE THERAPY (ESWT) Policy Number: SUR036 Effective Date: January 1, 2019 Table of Contents Page COVERAGE RATIONALE... 1 APPLICABLE CODES...
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT)
 Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Gladys L.Y. Cheing, PhD 1 Hua Chang, MSc 2 Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) is an emerging treatment modality for managing pain caused by various musculoskeletal
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Gladys L.Y. Cheing, PhD 1 Hua Chang, MSc 2 Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) is an emerging treatment modality for managing pain caused by various musculoskeletal
Overuse Injuries & special skeletal injuries Dr M.Taghavi Director of sport medicine center of olympic academy
 Overuse Injuries & special skeletal injuries Dr M.Taghavi Director of sport medicine center of olympic academy Prevalence of Overuse Injuries 30 to 50% of all sport injuries are from overuse In some sports
Overuse Injuries & special skeletal injuries Dr M.Taghavi Director of sport medicine center of olympic academy Prevalence of Overuse Injuries 30 to 50% of all sport injuries are from overuse In some sports
Populations Interventions Comparators Outcomes Individuals: With plantar fasciitis
 Extracorporeal Shock Wave Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis and (20140) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/13 Next Review Date: 07/18 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 02/07, 11/07, 11/08, 03/09, 01/10,
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis and (20140) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 01/01/13 Next Review Date: 07/18 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 02/07, 11/07, 11/08, 03/09, 01/10,
72a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction!
 72a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! 72a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active
72a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! 72a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active
Post-op / Pre-op Page (ALREADY DONE)
 Post-op / Pre-op Page (ALREADY DONE) We offer individualized treatment plans based on your physician's recommendations, our evaluations, and your feedback. Most post-operative and preoperative rehabilitation
Post-op / Pre-op Page (ALREADY DONE) We offer individualized treatment plans based on your physician's recommendations, our evaluations, and your feedback. Most post-operative and preoperative rehabilitation
New Generation Of Shockwave Devices with The Controls in the Handpiece
 New Generation Of Shockwave Devices with The Controls in the Handpiece Contents The Ultimate Shockwave Device 1 The Ultimate Shockwave Device The Tissue Regenerator is the world s most effective Shockwave
New Generation Of Shockwave Devices with The Controls in the Handpiece Contents The Ultimate Shockwave Device 1 The Ultimate Shockwave Device The Tissue Regenerator is the world s most effective Shockwave
(c) Tim Watson
 Professor Tim Watson School of Health & Social Work University of Hertfordshire www.electrotherapy.org Areas to consider Basic phasing model of injury and repair Electro Physical Agents : Key concepts
Professor Tim Watson School of Health & Social Work University of Hertfordshire www.electrotherapy.org Areas to consider Basic phasing model of injury and repair Electro Physical Agents : Key concepts
What is the clinical effectiveness of extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy or barbotage in the management of rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy?
 Specific Question: What is the clinical effectiveness of extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy or barbotage in the management of rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy? Clinical bottom line There is moderate evidence
Specific Question: What is the clinical effectiveness of extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy or barbotage in the management of rotator cuff calcific tendinopathy? Clinical bottom line There is moderate evidence
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory tennis elbow Tennis elbow
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory tennis elbow Tennis elbow
Adjunctive Treatments for Tendinopathy. Brendan O Neill Sports Physician Anglesea Sports Medicine Unisports Sports Medicine
 Adjunctive Treatments for Tendinopathy Brendan O Neill Sports Physician Anglesea Sports Medicine Unisports Sports Medicine About Me Sports Physician Unisports Sports Medicine Anglesea Sports Medicine BikeNZ
Adjunctive Treatments for Tendinopathy Brendan O Neill Sports Physician Anglesea Sports Medicine Unisports Sports Medicine About Me Sports Physician Unisports Sports Medicine Anglesea Sports Medicine BikeNZ
Tendon & Ligament Application of PRP
 Tendon & Ligament Application of PRP Sang Chul Lee, M.D, PhD. Department of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, Myongji hospital, Kwandong University College of Medicine Tendon and Ligament Low metabolic
Tendon & Ligament Application of PRP Sang Chul Lee, M.D, PhD. Department of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, Myongji hospital, Kwandong University College of Medicine Tendon and Ligament Low metabolic
Principles of Treatment. Case Studies. Principles of Treatment. Clinical Perspectives for the GP
 Principles of Treatment Clinical Perspectives for the GP Case Studies 1. Jumping athlete with an acute exacerbation of chronic patellar tendinopathy major competition in 9 days time 2 week tournament 2.
Principles of Treatment Clinical Perspectives for the GP Case Studies 1. Jumping athlete with an acute exacerbation of chronic patellar tendinopathy major competition in 9 days time 2 week tournament 2.
RPW Shockwave Therapy. Scientific Studies Overview
 RPW Shockwave Therapy Scientific Studies Overview 0 Evidence based indications Myofascial Trigger Points Rotator Cuff & Calcific Tendinitis Spasticity Epicondylitis Hip/Trochanter Pain Cellulitis Hamstring
RPW Shockwave Therapy Scientific Studies Overview 0 Evidence based indications Myofascial Trigger Points Rotator Cuff & Calcific Tendinitis Spasticity Epicondylitis Hip/Trochanter Pain Cellulitis Hamstring
Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain
 PATIENT INFORMATION Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain What is plantar fasciitis? Heel pain and plantar fasciitis Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed
PATIENT INFORMATION Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain What is plantar fasciitis? Heel pain and plantar fasciitis Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed
Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines
 Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines Introduction These guidelines have been developed to provide an integrated musculoskeletal service. They are based on reasonable clinical practice and will initially
Musculoskeletal Referral Guidelines Introduction These guidelines have been developed to provide an integrated musculoskeletal service. They are based on reasonable clinical practice and will initially
Priorities Forum Statement
 Priorities Forum Statement Number 75 Subject Autologous Blood and Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection in Tendinopathy Date of decision February 2017 Date refreshed February 2017 Date of review February 2020
Priorities Forum Statement Number 75 Subject Autologous Blood and Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection in Tendinopathy Date of decision February 2017 Date refreshed February 2017 Date of review February 2020
Specific Question: In an adult population is a corticosteroid injection a safe and effective treatment for tennis elbow compared to usual care.
 Short Question: Specific Question: In an adult population is a corticosteroid a safe and effective treatment for tennis elbow compared to usual care. Clinical bottom line There is evidence to suggest that
Short Question: Specific Question: In an adult population is a corticosteroid a safe and effective treatment for tennis elbow compared to usual care. Clinical bottom line There is evidence to suggest that
SAKRA CENTER FOR SPORTS MEDICINE & REHABILITATION
 SAKRA CENTER FOR SPORTS MEDICINE & REHABILITATION www. s a k rawo r l d h o s p i t a l.co m Exclusive Services of Sports Medicine Rehabilitation Comprehensive Fitness Screening Package Basic / Advanced
SAKRA CENTER FOR SPORTS MEDICINE & REHABILITATION www. s a k rawo r l d h o s p i t a l.co m Exclusive Services of Sports Medicine Rehabilitation Comprehensive Fitness Screening Package Basic / Advanced
Gymna ShockMaster. More than just Shockwave Therapy. And that Gymna ShockMaster supports you in this? Did you know that with Shockwave Therapy
 Gymna ShockMaster More than just Shockwave Therapy Did you know that with Shockwave Therapy you are able to treat more than just chronic tendinopathy? you can remedy back and neck conditions? you can provide
Gymna ShockMaster More than just Shockwave Therapy Did you know that with Shockwave Therapy you are able to treat more than just chronic tendinopathy? you can remedy back and neck conditions? you can provide
ESWT Mechanisms of Action in Veterinary Applications
 ESWT Mechanisms of Action in Veterinary Applications Extracorporeal Shock Wave Technology (ESWT) is a high energy acoustic pressure wave technology that has been demonstrated to treat a variety of musculoskeletal
ESWT Mechanisms of Action in Veterinary Applications Extracorporeal Shock Wave Technology (ESWT) is a high energy acoustic pressure wave technology that has been demonstrated to treat a variety of musculoskeletal
Salisbury Foundation Trust Radiology Department Referral Guidelines for Primary Care: Musculoskeletal Imaging
 Salisbury Foundation Trust Radiology Department Referral Guidelines for Primary Care: Musculoskeletal Imaging These guidelines have been issued in conjunction with the Royal College of Radiology referral
Salisbury Foundation Trust Radiology Department Referral Guidelines for Primary Care: Musculoskeletal Imaging These guidelines have been issued in conjunction with the Royal College of Radiology referral
A Patient s Guide to Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatment of Musculoskeletal Problems
 A Patient s Guide to Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatment of Musculoskeletal Problems Iain is a specialist in musculoskeletal imaging and the diagnosis of musculoskeletal pain. This information is provided with
A Patient s Guide to Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatment of Musculoskeletal Problems Iain is a specialist in musculoskeletal imaging and the diagnosis of musculoskeletal pain. This information is provided with
Plantar Fasciitis. What is Plantar Fasciitis: Anatomy of the Plantar Fascia: Problems with the Plantar Fascia:
 Plantar Fasciitis What is Plantar Fasciitis: Plantar Fasciitis is one of the most common causes of heel pain in Los Angeles and globally. The Foot and Ankle Institute is a world leader in the research
Plantar Fasciitis What is Plantar Fasciitis: Plantar Fasciitis is one of the most common causes of heel pain in Los Angeles and globally. The Foot and Ankle Institute is a world leader in the research
MASTERPULS»elite edition«application BROCHURE ESWT
 MASTERPULS»elite edition«application BROCHURE ESWT Non-invasive therapy for people Our objective Better therapies through new technologies. Established in 1987, STORZ MEDICAL AG is a Swiss member company
MASTERPULS»elite edition«application BROCHURE ESWT Non-invasive therapy for people Our objective Better therapies through new technologies. Established in 1987, STORZ MEDICAL AG is a Swiss member company
Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow.
 Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow. Prepared for The Canadian Orthopaedic Association Contents Executive
Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow. Prepared for The Canadian Orthopaedic Association Contents Executive
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACJ. See Acromioclavicular joint (ACJ) Acromioclavicular joint (ACJ) procedures of, 557 559 Ankle and foot procedures of, 649 671 (See also
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ACJ. See Acromioclavicular joint (ACJ) Acromioclavicular joint (ACJ) procedures of, 557 559 Ankle and foot procedures of, 649 671 (See also
TOPAZ TM What you should know
 TOPAZ TM What you should know Not for distribution in the United States. Need to know 2 Tendon: is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone and is capable of withstanding
TOPAZ TM What you should know Not for distribution in the United States. Need to know 2 Tendon: is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone and is capable of withstanding
emoryhealthcare.org/ortho
 COMMON SOCCER INJURIES Oluseun A. Olufade, MD Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopedics and PM&R 1/7/18 GOALS Discuss top soccer injuries and treatment strategies Simplify hip and groin injuries in
COMMON SOCCER INJURIES Oluseun A. Olufade, MD Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopedics and PM&R 1/7/18 GOALS Discuss top soccer injuries and treatment strategies Simplify hip and groin injuries in
A Patient s Guide to Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatment of Musculoskeletal Compliments of: The Central Orthopedic Group
 A Patient s Guide to Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatment of Musculoskeletal Problems The Central Orthopedic Group 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com
A Patient s Guide to Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatment of Musculoskeletal Problems The Central Orthopedic Group 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME
 ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY
 The Athlete s Guide to REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY THE ATHLETE S GUIDE TO REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY Table of Contents Introduction...3 Common Sports
The Athlete s Guide to REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY THE ATHLETE S GUIDE TO REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY Table of Contents Introduction...3 Common Sports
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) and Radial Pulse Therapy (RPT) August 2016
 Commissioning Policy Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) and Radial Pulse Therapy (RPT) August 2016 This policy applies to patients for whom the following Clinical Commissioning Groups are responsible:
Commissioning Policy Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) and Radial Pulse Therapy (RPT) August 2016 This policy applies to patients for whom the following Clinical Commissioning Groups are responsible:
TITLE: Shockwave Therapy for Pain Associated with Lower Extremity Orthopedic Disorders: A Review of the Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness
 TITLE: Shockwave Therapy for Pain Associated with Lower Extremity Orthopedic Disorders: A Review of the Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness DATE: 16 September 2016 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES Orthopedic disorders
TITLE: Shockwave Therapy for Pain Associated with Lower Extremity Orthopedic Disorders: A Review of the Clinical and Cost-Effectiveness DATE: 16 September 2016 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES Orthopedic disorders
April 17, :53 Gymna 2010
 Design Product design Gymna curve Screen design Graphic design Product design Design Product design Gymna display Screen design Graphic design Product design Design Product design 2 intensity regulators
Design Product design Gymna curve Screen design Graphic design Product design Design Product design Gymna display Screen design Graphic design Product design Design Product design 2 intensity regulators
Key words: Laser, sprain, strain, lameness, tendon
 MLS Master Class - Veterinary Imaging Presented by CelticSMR Ltd Free Phone (UK): 0800 279 9050 International: +44 (0) 1646 603150 AUTHOR DETAILS Carl Gorman BVSc MRCVS PUBLISHER DETAILS Mike Howe B Vet
MLS Master Class - Veterinary Imaging Presented by CelticSMR Ltd Free Phone (UK): 0800 279 9050 International: +44 (0) 1646 603150 AUTHOR DETAILS Carl Gorman BVSc MRCVS PUBLISHER DETAILS Mike Howe B Vet
Dr abedi yekta. Assistant Professor of Sports and Exercise Medicine Faculty of Medicine shahid beheshti University of Medical Sciences
 Dr abedi yekta Assistant Professor of Sports and Exercise Medicine Faculty of Medicine shahid beheshti University of Medical Sciences Pain in midportion of Achilles tendon. Morning stiffness Tendinitis
Dr abedi yekta Assistant Professor of Sports and Exercise Medicine Faculty of Medicine shahid beheshti University of Medical Sciences Pain in midportion of Achilles tendon. Morning stiffness Tendinitis
0RTHOPEDIC MASSAGE. Orthopedic Massage Benefits. Orthopedic Massage Applications
 0RTHOPEDIC MASSAGE Orthopedic Massage involves therapeutic assessment, manipulation, and movement of locomotor soft tissues to eliminate pain and dysfunction throughout the body. It is more than a technique.
0RTHOPEDIC MASSAGE Orthopedic Massage involves therapeutic assessment, manipulation, and movement of locomotor soft tissues to eliminate pain and dysfunction throughout the body. It is more than a technique.
100% Effective Natural Hormone Treatment Menopause, Andropause And Other Hormone Imbalances Impair Healthy Healing In People Over The Age Of 30!
 This Free E Book is brought to you by Natural Aging.com. 100% Effective Natural Hormone Treatment Menopause, Andropause And Other Hormone Imbalances Impair Healthy Healing In People Over The Age Of 30!
This Free E Book is brought to you by Natural Aging.com. 100% Effective Natural Hormone Treatment Menopause, Andropause And Other Hormone Imbalances Impair Healthy Healing In People Over The Age Of 30!
EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCKWAVE THERAPY (ESWT) INDIVIDUAL FUNDING REQUESTS POLICY
 EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCKWAVE THERAPY (ESWT) INDIVIDUAL FUNDING REQUESTS POLICY Version: 1718.v1 Recommendation by: Date Ratified: 01 November 2017 Name of Originator/Author: Approved by Responsible Committee/Individual:
EXTRACORPOREAL SHOCKWAVE THERAPY (ESWT) INDIVIDUAL FUNDING REQUESTS POLICY Version: 1718.v1 Recommendation by: Date Ratified: 01 November 2017 Name of Originator/Author: Approved by Responsible Committee/Individual:
No difference in effectiveness between focused and radial shockwave therapy for treating patellar tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial
 DOI 10.1007/s00167-013-2522-z KNEE No difference in effectiveness between focused and radial shockwave therapy for treating patellar tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial H. van der Worp J. Zwerver
DOI 10.1007/s00167-013-2522-z KNEE No difference in effectiveness between focused and radial shockwave therapy for treating patellar tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial H. van der Worp J. Zwerver
