Alvin Chao-Yu Chen *, Chih-Hao Chiu, Kuo-Yau Hsu and Yi-Sheng Chan
|
|
|
- Kerry Floyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chen et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:495 DOI /s RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Influence of age, gender, and radiographic features on the deltoid splitting approach for surgical osteosynthesis in displaced proximal humerus fractures: a comparison study Alvin Chao-Yu Chen *, Chih-Hao Chiu, Kuo-Yau Hsu and Yi-Sheng Chan Abstract Background: The deltoid splitting approach has recently been widely adopted to facilitate less invasive procedures for proximal humerus fractures. However, there are still concerns regarding its effectiveness in aging people and in cases involving complex fractures. This study was conducted to evaluate the efficacy of a proximal humeral locking plate using the anterolateral deltoid splitting approach and to specifically examine the effect of patient age, gender, and fracture pattern on surgical outcomes. Methods: Forty-two cases of proximal humeral fractures treated using the deltoid splitting approach and locking plate fixation were reviewed. Outcome differences were evaluated in terms of age, gender distribution, and radiographic analysis based on the Neer Classification. The influence of the surgical approach was further investigated by age-matched paired analysis after subdividing patients into two age groups (younger than 60 years vs. older than 60 years; N = 21, in each group). Results: In total, 41 patients (98%) demonstrated fracture union. The average Constant score was No significant differences were found between patients younger than 60 years, and the older patients. Higher mean scores were found in men than in women (p = 0.448) and in simple fractures than in complex fractures (p = 0.454), without any significant differences. Better postoperative functional outcomes were observed when the humeral head neck angle was greater than 105, with a significant difference (p = 0.000). Surgical complications were found in 16 patients (38%) without significant difference between two age groups (p = 0.268). The most common complication was screw penetration. Conclusions: Anterolateral deltoid splitting using locking plate fixation provided a feasible alternative for surgery of proximal humerus fractures in different age groups and yielded comparable outcomes when the neck-shaft angle was properly restored. Surgeons must be cautious regarding potential complications, especially with screw penetration when using the locking plate through a less invasive approach. Trial registration: ISRCTN Trial Date: 2017/01/31. Keywords: Proximal humerus fracture, Neer classification, Osteosynthesis, Deltoid splitting, Locking plate * Correspondence: alvinchen@cgmh.org.tw Bone and Joint Research Center, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital-Linkou and University College of Medicine, 333, 5th, Fu-Hsin St., Kweishan Dist., Taoyuan 333, Taiwan, Republic of China The Author(s) Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Chen et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:495 Page 2 of 6 Background Proximal humeral fractures are among the most frequent fractures associated with osteoporosis, and may represent a major cause of functional disability [1, 2]. Unfortunately, the treatment of these fractures remains controversial, and surgical complications are common [3, 4]. The introduction of locked plating offers a novel biomechanical approach in stabilizing these fractures [5, 6]. Surgical approach using anterolateral deltoid splitting is a less invasive technique [7 9] in which the axially nerve is carefully located and protected [10], while avoiding potential disadvantages of extensive dissection and muscle retraction inthetraditionaldeltopectoral approach [1, 11, 12]. However, some reports have expressed concerns regarding potential construct failures and inferior surgical outcomes in patients with more complex fractures and in an aging population [13, 14]. The present study aimed to evaluate the influence of the surgical approach for management of displaced proximal humerus fractures and to specifically examine the impact of patient age and fracture pattern on the outcomes. Table 1 Demographic data of patients Characteristics Age < 60-years-old Age > 60-years-old P value Mean age Gender Women 14 (67%) 15 (71%) Men 7 (33%) 6 (29%) Neer classification Two-part 9 (43%) 10 (48%) Three- & four-part 12 (57%) 11 (52%) Time to surgery (days) Methods We retrospectively evaluated cases of unilateral proximal humerus fractures that were treated surgically with the Locking Compression Plate (LCP), as per the Neer classification criteria at our institute between 2009 and Institutional review board approval (No B0) was obtained to perform a review of patients records and radiographs; informed consent was obtained from 132 patients with displaced proximal humerus fractures. All these cases of proximal humerus fractures either met the indications for operative treatment outlined by Neer [15] or were considered unstable when tested for passive motion with an image intensifier. Patients with pathological fractures, head split fractures, open fractures, fractures with primary neurovascular damage, multiple fractures, and cases lost to follow-up were excluded from the study. Forty-two patients, who underwent anterolateral deltoid splitting surgery, were selected for a retrospective matched pairs analysis according to their age (younger than 60 years vs. older than 60 years), gender, and fracture type (Table 1) with a minimum followup of 24 months. One single surgeon performed all the surgeries. Preoperative assessment showed 10 patients in younger group and 15 patients in older group had chronic diseases; most common was hypertension (3 and 10 in younger and older group respectively) and diabetes mellitus (3 and 6 in younger and old group respectively). All procedures were performed in the beach-chair position on a radiolucent Table. A skin incision was made from the anterolateral lip of the acromion and was extended approximately 3 to 4 cm distally. The subcutaneous tissue layer was then bluntly dissected to identify the avascular raphe separating the anterior and middle head of the deltoid. Deltoid muscle splitting was limited to within 3 cm of the acromial end. The axial nerve was palpated and protected, but not dissected. The greater tuberosity was reduced by pulling forward the stay sutures on the bony fragment. Provisional Kirschner wire fixation was used to temporarily secure fracture fragments. A PHILOS plate (Synthes, Switzerland) was applied using the technique of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) [16]. The plate was inserted along the anterolateral cortex of the humeral shaft while avoiding touching or hinging on the axial nerve branch. A second skin incision was made about 5 to 7 cm distal to the first incision to facilitate plate positioning along the proximal humerus shaft. Fracture reduction and plate location was then confirmed as adequate by using an image intensifier before definite fixation (Fig. 1). After placing the plate securely, four locking screws were inserted into the humeral head through the first incision and three screws for the shaft were applied through the second skin incision. For better visualization of screw holes and easier screw placement on the humeral head, the humerus was elevated to a 30-degree abduction position to relieve muscle tension and to avoid excessive retraction of the deltoid muscle. The Kirschner wires were then removed, and tension band fixation was applied to secure the rotator cuff using the premeditated Ethibond sutures. The surgical wound was closed with 3-O Vicryl sutures. Functional evaluation was done using Constant Scores [17], which were further graded as excellent ( points), good (80 89 points), fair (70 79 points), or poor (less than 70 points). In a secondary comparison, patients were divided into two age groups: a group of less than 60-year-old patients (n = 21) and a group of more than 60-year-old patients (n = 21). Constant scores at 1- year follow up were further compared between the two age groups in terms of distribution by gender, fracture patterns, and complication rates to determine the differences in outcome with index surgery. Statistical analysis Data analyses were performed with the SPSS 18 statistical software for Windows. For normally distributed
3 Chen et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:495 Page 3 of 6 Fig. 1 The fracture pattern is assessed by using a C-arm image intensifier (top left). Reduction is achieved by elevating the humeral head fragment (top right). Provisional wire fixation is applied, followed by insertion of a locking plate and proximal screws through a deltoid splitting approach (bottom left). Distal screws are applied through another skin incision (bottom right) data (patient age and time between fracture and fixation) an independent sample t-test was used. For data that were not normally distributed (the Constant shoulder score), the Mann Whitney rank sum test was used. For categorical data (gender and fracture pattern), a chisquare test was used. A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results Time to surgery averaged at 2.81 ± 1.89 days; it was 3 ± 2.26 days in the younger group (age younger than 60 years) and 2.62 ± 1.47 in the aged group (over 60 years old) respectively. The difference was not significant (p = 0.262). There were 11 men and 31 women; the average age was years (range, 36 to 77 years). The difference of gender distribution in the younger and older groups was not significant (p = 0.448; Table 2.). Nineteen cases were of two-part fractures (45%); among them, 4 fractures were long oblique fractures (10%) that extended to the metaphyseal and the proximal diaphyseal regions. Fourteen cases were of three-part fractures (33%) and 9 were of four-part fractures (21%). In total, 23 out of 42 cases involved complex (Neer 3- and 4- part) fractures with 12 and 11 such fractures seen in the younger and older groups, respectively; the difference was not significant (p = 0.374). Radiographic follow-up revealed complete osseous union within 6 months (Fig. 2) in 41 fractures (98%). The mean overall Constant score was 80.4 ± Table 2 Comparison of functional and radiographic outcomes Patients No. of cases Constant score P value All cases Age < 60-years-old > 60-years-old Gender Men Women Fracture pattern Simple Complex Neck shaft angle 0.000* > < Neer classification: simple, two-part fracture; three- four-part fracture *Statistically significant
4 Chen et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:495 Page 4 of 6 Fig. 2 Postoperative radiographs at three months post-surgery, showing osseous union. a Anteroposterior projection. b Lateral projection. c Axial projection Functional grading according to Constant score was good or excellent in 25 of 42 patients (60%). In analysis of age-matched pairs, the average Constant scores were ± 7.61 for patients younger than 60 years (n = 21) and ± for patients older than 60 years (n = 21); the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.054). Regarding gender differences, the average Constant score for female patients (n = 26) was ± 7.37 and for male patients (n = 13) was ± 11.74; the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.448). Based on Neer fracture classification, the average Constant score was ± for simple fractures (2-part; n = 19) and ± 7.37 for complex fractures (three- and four-part; n = 23). The difference was not significant (p = 0.454). One of the 4 patients had long, spiral two-part fractures, which remained ununited at the 2-year follow-up and showed a poor result; the other 3 showed good or excellent results. On reviewing postoperative radiographs (Fig. 3), patients with humeral head neck angles greater than 105 (n = 21, mean angle 119 ) tended to have better outcomes (mean Constant score = 86.24) than those with angles lesser than 105 (n = 21, mean angle 97.19, mean Constant score = 74.57). The difference was statistically significant (p =0.000). Immediate postoperative complications or neurovascular injuries were not found. No infections or wounds were observed. Complications observed within 2 years included screw penetration, avascular necrosis, and nonunion. Screw protrusion was observed in 12 patients (29%) with 5 and 7 in young and older groups respectively. Four patients (12%) developed subsequent necrosis of the humeral head; 2 were in each group. One patient had a second surgery with hemiarthroplasty 6 months after the osteosynthesis surgery. One patient (2%) with a two-part fracture had an accidental fall 6 weeks after surgery; radiographs revealed a secondary displacement of the humeral head. She underwent hemiarthroplasty; Fig. 3 A comparison of the postoperative neck-shaft angles. a Varus alignment with an angle of 96. b Neutral position with an angle of 135
5 Chen et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:495 Page 5 of 6 however, the patient had another accidental fall 1 month later, which caused a periprosthetic humeral fracture and a proximal ulnar fracture. The fracture remained unhealed at the 2-year follow-up. Both of the patients with hemiarthroplasty were in older group. In total, out of 16 patients (38%) who had surgical complications, 7 (33%) were in the younger group and the other 9 (43%) were in the older group. The incidence of complications was not statistically different between the two age groups (p = 0.268). Discussion In an aging society, osteoporosis-related fractures and their comorbidities have increasingly become major medical concerns among elderly people [18]. The ultimate aim in treating these fractures in a geriatric population is to achieve a rapid bony union and allow early mobilization, thus minimizing side effects such as joint stiffness and muscle wasting. While the anterolateral deltoid splitting approach using a locking plate is popularly adopted to enhance early osseous union and functional recovery in proximal humerus fractures, some studies reported inferior outcomes and potential construct failures in aging population and in complex fractures [19 22]. The impact of age on the outcome is generally of concern since surgical fixation is getting more popular in this fracture entity in an increasing aging population as well as in patients with severe fractures [23, 24]. In our series, we found no significant differences in functional outcomes and complication rates between the patients younger than and older than 60 years; both age groups had an almost equal number of patients with complex fracture patterns. Female gender was also considered as an independent risk factor for proximal humerus fractures owing to lower bone density and bone fragility [22]; however, there was no gender-specific difference in fracture healing and functional outcome in our series. On reviewing postoperative radiographic analysis, it was found that the optimal correction of proper neckshaft angles was critically important in maintaining realignment and avoiding varus collapse. This was a common complication in elderly patients and in patients with complex fractures [9]; it seemed to be a major contributor to satisfactory outcomes [22, 25]. A cut-off value of 105 o was associated with a significant difference in the functional scores and it could be considered as radiographic criteria for fracture reduction. Nevertheless, common criticism about the deltoid splitting approach regarding potential axial nerve and deltoid muscle damage exists [10]. Based on anatomical studies, a safe area for lateral deltoid splitting was calculated from the acromial end as <5.2 cm by distance or as <0.19 in ratio to arm length [26, 27]. In our surgeries, we constantly limited the deltoid split to approximately 3 cm in length from the acromial end, and this resulted in no cases of iatrogenic axial nerve injury. Complication rate was comparable to other reports with the deltoid splitting approach for either plating or nailing humerus fractures [8, 9, 11, 28]. During fracture reduction and implant application, the deltoid split was used as a moving window by gently rotating the proximal humerus to expose the fracture site. The tension of the deltoid muscle around this moving window could be further released with arm abduction, thereby avoiding forceful retraction. It has been recommended that using a stepwise surgical procedure and a longer plate may avoid nerve damage and achieve reliable outcomes [8]. While the deltoid function was not quantified by any electrophysiological studies, none of the patients complained of sensation change or weakness around the deltoid muscle. Surgical complications were experienced by as many as 38% of our patients, which was another important concern. A relatively high incidence of screw protrusion was found in both age groups. A previous study reported a radiographic complication rate of 36% in their patients, with a 43% rate of cutout in patients over 60 years [29]. In a review of 12 studies with locking plate fixation, the overall rate of complications was 49%, including screw perforation, malunion, and nonunion [30]. This study found that an overall complication rate of 18.2% was presumed to be due to the use of an indirect reduction maneuver and a minimally invasive technique. Since a limited surgical field and dissection may certainly jeopardize the proper placement of implants, it is crucially important to have meticulous intraoperative examination of reduction quality and an awareness of shortened screw length while maintaining secure fixation. The main limitations of this study include the small cohort number and the heterogeneity of fracture patterns. Furthermore, deltoid muscle function was not quantified and compared using different surgical options. In addition, the lack of a randomized control may be critical. Finally, a follow-up study of osseous necrosis, preferably after a long interval, should be conducted. Conclusions The deltoid splitting approach for proximal humeral fractures provided good functional results and early osseous union in both age groups. Better functional scores were obtained in male patients. A tendency to achieve a superior outcome was observed when the neck-shaft angles were well corrected. Implant-related complications, most frequently screw penetration, continue to be a common concern using locking plate fixation in the region. Abbreviations LCP: Locking Compression Plate; MIPO: Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis
6 Chen et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:495 Page 6 of 6 Acknowledgements Not applicable. Funding Funding sources from Chang Gung Memorial Foundation: CMRPG3F311. Availability of data and materials The authors are unable to share raw data because ethical approval was not obtained for data sharing. In addition, informed consent for data sharing was not obtained from the individuals. Please find all summarized datasets reported in the results section and the tables. Authors contributions ACC formulated the outline, searched and retrieved the articles, and drafted the manuscript. CCC assisted in data collection and calculation. KYH and YSC assisted in the outline and drafting/revision of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Ethics approval and consent to participate The study was approved by the Ethical Review Boards of Chang Gung Memorial Hospital and was performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki of Written consent to participate in the study was obtained from all the patients. All the images or clinical details of participants did not compromise anonymity. Consent for publication We have obtained consent to publish from the participants. Not applicable. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Publisher s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Received: 3 August 2017 Accepted: 14 November 2017 References 1. Helmy N, Hintermann B. New trends in the treatment of proximal humerus fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;442: Calvo E, Morcillo D, Foruria AM, Redondo-Santamaria E, Osorio-Picorne F, Caeiro JR. Nondisplaced proximal humeral fractures: high incidence among outpatient-treated osteoporotic fractures and severe impact on upper extremity function and patient subjective health perception. J Shoulder Elb Surg. 2011;20: Hertel R, Hempfing A, Stiehler M, Leunig M. Predictors of humeral head ischemia after intracapsular fracture of the proximal humerus. J Shoulder Elb Surg. 2004;13: Meier RA, Messmer P, Regazzoni P, Rothfischer W, Gross T. Unexpected high complication rate following internal fixation of unstable proximal humerus fractures with an angled blade plate. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20: Edwards SL, Wilson NA, Zhang LQ, Flores S, Merk BR. Two-part surgical neck fractures of the proximal part of the humerus: a biomechanical evaluation of two fixation techniques. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88: Südkamp N, Bayer J, Hepp P, Voigt C, Oestern H, Kääb M, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation of proximal humeral fractures with use of the locking proximal humerus plate. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91: Gardner MJ, Griffith MH, Dines JS, Briggs SM, Weiland AJ, Lorich DG. The extended anterolateral acromial approach allows minimally invasive access to the proximal humerus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;434: Ruchholtz S, Hauk C, Lewan U, Franz D, Ku hne C, Zettl R. Minimally invasive polyaxial locking plate fixation of proximal humeral fractures: a prospective study. J Trauma. 2011;71: Lin T, Xiao B, Ma X, Fu D, Yang S. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with a locking compression plate is superior to open reduction and internal fixation in the management of the proximal humerus fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15: Gradl G, Knobe M, Pape H-C, Neuhaus PV, Ring D, Guitton T. Decision making in displaced fractures of the proximal humerus: fracture or surgeon based? Int Orthop. 2015;39: Hepp H, Theopold J, Voigt C, Engel T, Josten C, Lill H. The surgical approach for locking plate osteosynthesis of displaced proximal humeral fractures influences the functional outcome. J Shoulder Elb Surg. 2008;17: Szyszkowitz R, Seggl W, Schleifer P, Cundy PJ. Proximal humeral fractures. Management techniques and expected results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; 292: Hata Y, Saitoh S, Murakami N, Kobayashi H, Takaoka K. Atrophy of the deltoid muscle following rotator cuff surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86: Owsley KC, Gorczyca JT. Displacement/screw cutout after open reduction and locked plate fixation of humeral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90: Neer CS. Displaced proximal humeral fractures I. Classification and evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg. 1970;52: Lau TW, Leung F, Chan CF, Chow SP. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in the treatment of proximal humeral fracture. Int Orthop. 2007;31: Constant CR, Murley AHGA. Clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder. Clin Orthop. 1987;214: Sattui SE, Saag KG. Fracture mortality: associations with epidemiology and osteoporosis treatment. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2014;10: Koljonen PA, Fang C, Lau TW, Leung F, Cheung NWK. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for proximal humeral fractures. J Orthop Surg. 2015;23: Bogner R, Hübner C, Matis N, Auffarth A, Lederer S, Resch H. Minimallyinvasive treatment of three- and four-part fractures of the proximal humerus in elderly patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2008;90: Brunner F, Sommer C, Bahrs C, Heuwinkel R, Hafner C, Rillmann P, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation of proximal humerus fractures using a proximal humeral locked plate: a prospective multicenter analysis. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23: Olsson C, Nordqvist A, Petersson CJ. Increased fragility in patients with fracture of the proximal humerus: a case control study. Bone. 2004;34(6): Björkenheim JM, Pajarinen J, Savolainen V. Internal fixation of proximal humeral fractures with a locking compression plate: a retrospective evaluation of 72 patients followed for a minimum of 1 year. Acta Orthop Scand. 2004;75: Moonot P, Ashwood N, Hamlet M. Early results for treatment of three- and four-part fractures of the proximal humerus using the PHILOS plate system. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89: Jung SW. Indirect reduction maneuver and minimally invasive approach for displaced proximal Humerus fractures in elderly patients. Clinics. Orthop Surg. 2013;5: Apaydin N, Uz A, Bozkurt M, Elhan A. The anatomic relationships of the axillary nerve and surgical landmarks for its localization from the anterior aspect of the shoulder. Clin Anat. 2006;20: Cetik O, Uslu M, Acar HI, Comert A, Tekdemir I, Cift HI. There a safe area for the axillary nerve in the deltoid muscle? A cadaveric study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88: Gallo RA, Zeiders GJ, Altman GT. Two-incision technique for treatment of complex proximal humerus fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19: Park MC, Murthi AM, Roth NS, Blaine TA, Levine WN, Bigliani LU. Two-part and three-part fractures of the proximal humerus treated with suture fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2003;17: Sproul RC, Iyengar JJ, Devcic Z, Feeley BT. A systematic review of locking plate fixation of proximal humerus fractures. Injury. 2011;42:
Malaysian Orthopaedic Journal 2018 Vol 12 No 2
 Malaysian Orthopaedic Journal 2018 Vol 12 No 2 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1807.004 Complex Proximal Humeral Fracture Fixation with PHILOS Plate using Minimal Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis
Malaysian Orthopaedic Journal 2018 Vol 12 No 2 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1807.004 Complex Proximal Humeral Fracture Fixation with PHILOS Plate using Minimal Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis
Risk of Axillary Nerve Injury in Standard Anterolateral Approach of Shoulder: Cadaveric Study
 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1811.001 Risk of Axillary Nerve Injury in Standard Anterolateral Approach of Shoulder: Cadaveric Study Kongcharoensombat W, MD, Wattananon P, MD Department of Orthopaedics,
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1811.001 Risk of Axillary Nerve Injury in Standard Anterolateral Approach of Shoulder: Cadaveric Study Kongcharoensombat W, MD, Wattananon P, MD Department of Orthopaedics,
MANAGEMENT OF PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE WITH LOCKING COMPRESSION PLATE Shivananda S 1, Radhakrishna A. M 2, Kumar M 3
 MANAGEMENT OF PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE WITH LOCKING COMPRESSION PLATE Shivananda S 1, Radhakrishna A. M 2, Kumar M 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Shivananda S, Radhakrishna A. M, Kumar M. Management of Proximal
MANAGEMENT OF PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE WITH LOCKING COMPRESSION PLATE Shivananda S 1, Radhakrishna A. M 2, Kumar M 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Shivananda S, Radhakrishna A. M, Kumar M. Management of Proximal
Open reduction; plate fixation 1 Principles
 Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
Proximal fractures of the humerus in patients older than 75 years of age: should we consider operative treatment?
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2014) 15:111 115 DOI 10.1007/s10195-013-0273-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Proximal fractures of the humerus in patients older than 75 years of age: should we consider operative treatment?
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2014) 15:111 115 DOI 10.1007/s10195-013-0273-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Proximal fractures of the humerus in patients older than 75 years of age: should we consider operative treatment?
Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humeral Fractures with Use of the Locking Proximal Humerus Plate
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 643-650, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humeral Fractures with Use of the Locking Proximal Humerus
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 643-650, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humeral Fractures with Use of the Locking Proximal Humerus
The study of distal ¼ diaphyseal extra articular fractures of humerus treated with antegrade intramedullary interlocking nailing
 2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
Index. B Backslap technique depth assessment, 82, 83 diaphysis distal trocar, 82 83
 Index A Acromial impingement, 75, 76 Aequalis intramedullary locking avascular necrosis, 95 central humeral head, 78, 80 clinical and functional outcomes, 95, 96 design, 77, 79 perioperative complications,
Index A Acromial impingement, 75, 76 Aequalis intramedullary locking avascular necrosis, 95 central humeral head, 78, 80 clinical and functional outcomes, 95, 96 design, 77, 79 perioperative complications,
EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE VOICE
 EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE VOICE Orthofix approach to Evidence Based Medicine: For years, clinical decision-making was based primarily on physician knowledge and expert opinion. Now, the medical community
EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE VOICE Orthofix approach to Evidence Based Medicine: For years, clinical decision-making was based primarily on physician knowledge and expert opinion. Now, the medical community
Proximal Humerus Fractures: contemporary perspectives
 Proximal Humerus Fractures: contemporary perspectives Diego L Fernandez M.D Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Lindenhof Hospital, Berne, Switzerland www.diegofernandez.ch
Proximal Humerus Fractures: contemporary perspectives Diego L Fernandez M.D Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Lindenhof Hospital, Berne, Switzerland www.diegofernandez.ch
Proximal humerus fractures operated with PHILOS plate: 4 year prospective study
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kulkarni S et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Mar;3(2):304-309 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20170790
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kulkarni S et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Mar;3(2):304-309 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20170790
Technique Guide. PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus.
 Technique Guide PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus. Table of Contents Introduction PHILOS and PHILOS Long 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical Technique
Technique Guide PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus. Table of Contents Introduction PHILOS and PHILOS Long 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical Technique
Proximal Humerus Fractures
 Proximal Humerus Fractures Trafford General Hospital, June 2010 Nehmat Singh, Jawad Sultan Anatomy of the Proximal Humerus Consists of four parts: humeral head, surgical neck and greater and lesser tubercles
Proximal Humerus Fractures Trafford General Hospital, June 2010 Nehmat Singh, Jawad Sultan Anatomy of the Proximal Humerus Consists of four parts: humeral head, surgical neck and greater and lesser tubercles
Orthopedics in Motion Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016
 Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
P.R.C.T II FIXATION PLATE FOR ARTICULAR FRACTURE OF THE PROXIMAL HUMERUS SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 P.R.C.T II FIXATION PLATE FOR ARTICULAR FRACTURE OF THE PROXIMAL HUMERUS SURGICAL TECHNIQUE INDICATIONS - Surgical technique...page 0 - Mini invasive approach...page 04 - Diaphyseal plates...page 05 -
P.R.C.T II FIXATION PLATE FOR ARTICULAR FRACTURE OF THE PROXIMAL HUMERUS SURGICAL TECHNIQUE INDICATIONS - Surgical technique...page 0 - Mini invasive approach...page 04 - Diaphyseal plates...page 05 -
To Detect the Outcome of Proximal Humerus Fractures Treated With a Locking Proximal Humerus Plate
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE To Detect the Outcome of Proximal Humerus Fractures Treated With a Locking Proximal Humerus Plate NASIR AHMED 1, TARIQUE ALI KHAN 2, MUHAMMAD ABSAR ANWAR 3, AHMED ALI 4 ABSTRACT Aim: To
ORIGINAL ARTICLE To Detect the Outcome of Proximal Humerus Fractures Treated With a Locking Proximal Humerus Plate NASIR AHMED 1, TARIQUE ALI KHAN 2, MUHAMMAD ABSAR ANWAR 3, AHMED ALI 4 ABSTRACT Aim: To
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Humerus Plate 2 AO Principles
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Humerus Plate 2 AO Principles
Clinico-radiological outcome of closed reduction and percutaneous fixation of proximal humerus fractures
 2018; 4(1): 614-618 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 614-618 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 10-11-2017 Accepted: 11-12-2017 Dr. Dharmendra Kumar Assistant Professor, KGMU, Lucknow, Dr. Neerav Anand
2018; 4(1): 614-618 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 614-618 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 10-11-2017 Accepted: 11-12-2017 Dr. Dharmendra Kumar Assistant Professor, KGMU, Lucknow, Dr. Neerav Anand
LCP Percutaneous Aiming System 3.5 for PHILOS. For less invasive surgery at the proximal humerus.
 LCP Percutaneous Aiming System 3.5 for PHILOS. For less invasive surgery at the proximal humerus. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants
LCP Percutaneous Aiming System 3.5 for PHILOS. For less invasive surgery at the proximal humerus. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants
Humerus Block. Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) Surgical Technique. This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA.
 Humerus Block Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Contents
Humerus Block Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Contents
Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures. OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD
 Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD OBJECTIVES TREATMENT OPTIONS SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONTROVERSIES IN MANAGEMENT Humerus Fractures Treatment Goals: Functional
Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD OBJECTIVES TREATMENT OPTIONS SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONTROVERSIES IN MANAGEMENT Humerus Fractures Treatment Goals: Functional
NCB Proximal Humerus Plating System
 NCB Proximal Humerus Plating System Surgical Technique The right locking option for tough fractures Disclaimer This document is intended exclusively for experts in the field, i.e. physicians in particular,
NCB Proximal Humerus Plating System Surgical Technique The right locking option for tough fractures Disclaimer This document is intended exclusively for experts in the field, i.e. physicians in particular,
Review Article Meta-analysis comparing deltoid-splitting approach with deltopectoral approach for treatment of proximal humeral fractures
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2019;12(1):58-66 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0073587 Review Article Meta-analysis comparing deltoid-splitting approach with deltopectoral approach for treatment of proximal humeral
Int J Clin Exp Med 2019;12(1):58-66 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0073587 Review Article Meta-analysis comparing deltoid-splitting approach with deltopectoral approach for treatment of proximal humeral
Outcome of proximal humerus fractures treated by PHILOS plate internal fixation Experience of a District General Hospital
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 602-608 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of proximal humerus fractures treated by PHILOS plate internal fixation Experience of a District General Hospital Rizwan SHAHID, Abid MUSHTAQ,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 602-608 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of proximal humerus fractures treated by PHILOS plate internal fixation Experience of a District General Hospital Rizwan SHAHID, Abid MUSHTAQ,
Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique
 Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique Percutaneous Pinning Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Closed reduction followed by percutaneous fixation reduces risk from soft tissue dissection
Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique Percutaneous Pinning Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Closed reduction followed by percutaneous fixation reduces risk from soft tissue dissection
A new nail with a locking blade for complex proximal humeral fractures
 Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol (2016) 26:831 836 DOI 10.1007/s00590-016-1817-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SHOULDER - FRACTURES A new nail with a locking blade for complex proximal humeral fractures F. R. Hashmi 1 Edgar
Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol (2016) 26:831 836 DOI 10.1007/s00590-016-1817-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SHOULDER - FRACTURES A new nail with a locking blade for complex proximal humeral fractures F. R. Hashmi 1 Edgar
3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 8. DISTAL GUIDED LOCKING FOR PROXIMAL NAIL PROXIMAL LOCKING FOR LONG NAIL 13
 Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL NAIL INSERTION 6-7 7. PROXIMAL LOCKING
Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL NAIL INSERTION 6-7 7. PROXIMAL LOCKING
Locked Plating of 3- and 4-Part Proximal Humerus Fractures in Older Patients: The Effect of Initial Fracture Pattern on Outcome
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Locked Plating of 3- and 4-Part Proximal Humerus Fractures in Older Patients: The Effect of Initial Fracture Pattern on Outcome Brian D. Solberg, MD,* Charles N. Moon, MD, Dennis P. Franco,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Locked Plating of 3- and 4-Part Proximal Humerus Fractures in Older Patients: The Effect of Initial Fracture Pattern on Outcome Brian D. Solberg, MD,* Charles N. Moon, MD, Dennis P. Franco,
Shoulder hemiarthroplasty in the management of humeral head fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 214-218 ORIGINAL STUDY Shoulder hemiarthroplasty in the management of humeral head fractures Joseph J. CHRISTOFORAKIS, George M. KONTAKIS, Pavlos G. KATONIS, Konstantinos
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 214-218 ORIGINAL STUDY Shoulder hemiarthroplasty in the management of humeral head fractures Joseph J. CHRISTOFORAKIS, George M. KONTAKIS, Pavlos G. KATONIS, Konstantinos
Does medial support decrease major complications of unstable proximal humerus fractures treated with locking plate?
 Jung et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:102 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Does medial support decrease major complications of unstable proximal humerus fractures treated with locking plate? Woo-Bin
Jung et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:102 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Does medial support decrease major complications of unstable proximal humerus fractures treated with locking plate? Woo-Bin
AcUMEDr. Locking Proximal Humeral Plate. PoLARUSr PHPt
 AcUMEDr Locking Proximal Humeral Plate PoLARUSr PHPt PoLARUSr PHPt LOCKING PROXIMAL HUMERAL PLATE Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons,
AcUMEDr Locking Proximal Humeral Plate PoLARUSr PHPt PoLARUSr PHPt LOCKING PROXIMAL HUMERAL PLATE Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons,
Locking Plate for Proximal Humeral Fracture in the Elderly Population: Serial Change of Neck Shaft Angle
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:209-215 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.3.209 Locking Plate for Proximal Humeral Fracture in the Elderly Population: Serial Change of Neck Shaft
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:209-215 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.3.209 Locking Plate for Proximal Humeral Fracture in the Elderly Population: Serial Change of Neck Shaft
Proximal Humerus System 3.5
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Proximal Humerus System 3.5 APTUS Shoulder Contents 4 Proximal Humerus System 3.5 5 Proximal Humerus Fracture Fixation with Plate and Spiral Blade 14 Proximal Humerus Fracture Fixation
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Proximal Humerus System 3.5 APTUS Shoulder Contents 4 Proximal Humerus System 3.5 5 Proximal Humerus Fracture Fixation with Plate and Spiral Blade 14 Proximal Humerus Fracture Fixation
THE HUMERUS 20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW
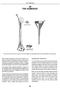 20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW The marrow canal of the humerus is funnel-shaped. Its successful pinning is influenced by many factors. With a few exceptions, the entire humerus
20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW The marrow canal of the humerus is funnel-shaped. Its successful pinning is influenced by many factors. With a few exceptions, the entire humerus
System. Humeral Nail. Surgical Technique
 System Humeral Nail Surgical Technique Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL
System Humeral Nail Surgical Technique Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL
Technique Guide. DHS Blade. For osteoporotic bone.
 Technique Guide DHS Blade. For osteoporotic bone. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits 2 Indications and Contraindications 4 Clinical Cases 5 Surgical Technique Implantation 6 Implant
Technique Guide DHS Blade. For osteoporotic bone. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits 2 Indications and Contraindications 4 Clinical Cases 5 Surgical Technique Implantation 6 Implant
Locked Plating: Clinical Indications
 Techniques in Orthopaedics 22(3):181 185 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Locked Plating: Clinical Indications Kyle F. Dickson, M.D., M.B.A., John Munz, M.D. Summary: As shown in the previous article,
Techniques in Orthopaedics 22(3):181 185 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Locked Plating: Clinical Indications Kyle F. Dickson, M.D., M.B.A., John Munz, M.D. Summary: As shown in the previous article,
Olecranon fracture. Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital
 Olecranon fracture Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital 20% of forearm fracture 12 per 100.000 persons per year Low-energy fall Increased risk >50 years 90% AO 21.B1.1
Olecranon fracture Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital 20% of forearm fracture 12 per 100.000 persons per year Low-energy fall Increased risk >50 years 90% AO 21.B1.1
Tao Lin, Baojun Xiao, Xiucai Ma, Dehao Fu * and Shuhua Yang
 Lin et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:206 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with a locking compression plate is superior to open reduction and internal fixation
Lin et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:206 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with a locking compression plate is superior to open reduction and internal fixation
TORNIER AEQUALIS FX. Shoulder System SYSTEM OVERVIEW
 TORNIER AEQUALIS FX Shoulder System SYSTEM OVERVIEW Simple in design, but used for the most complex fractures Each year, approximately 4 million people in the United States seek medical care for shoulder
TORNIER AEQUALIS FX Shoulder System SYSTEM OVERVIEW Simple in design, but used for the most complex fractures Each year, approximately 4 million people in the United States seek medical care for shoulder
LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) system.
 LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) system. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) system. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
TABLE OF CONTENTS. 2 (8144 Rev 2)
 1 (8144 Rev 2) TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction Conventus CAGE TM - Proximal Humerus...3 Indications and Contraindications...4 Surgical Summary...5 Patient Positioning & Approach...6 Surgical Technique Plate
1 (8144 Rev 2) TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction Conventus CAGE TM - Proximal Humerus...3 Indications and Contraindications...4 Surgical Summary...5 Patient Positioning & Approach...6 Surgical Technique Plate
PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE TSHT 2017
 PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE TSHT 2017 ANIL DUTTA, M.D. ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR Displacement > 1 cm Angulation > 45 degree SHOULDER AND ELBOW SURGERY UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS HEALTH SCIENCE CENTER SAN ANTONIO DISCLOSURE
PROXIMAL HUMERUS FRACTURE TSHT 2017 ANIL DUTTA, M.D. ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR Displacement > 1 cm Angulation > 45 degree SHOULDER AND ELBOW SURGERY UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS HEALTH SCIENCE CENTER SAN ANTONIO DISCLOSURE
Comparison Study of Different Approach (Deltoid Splitting Approach and Delto-pectoral Interval Approach) for Proximal Humeral Fractures
 Original Article Comparison Study of Different Approach (Deltoid Splitting Approach and Delto-pectoral Interval Approach) for Proximal Humeral Fractures Seung-Hee Kim, M.D., Jinmyoung Dan, M.D., Byoung-Kook
Original Article Comparison Study of Different Approach (Deltoid Splitting Approach and Delto-pectoral Interval Approach) for Proximal Humeral Fractures Seung-Hee Kim, M.D., Jinmyoung Dan, M.D., Byoung-Kook
Proximal humeral fractures: current controversies
 J Shoulder Elbow Surg (2011) 20, 827-832 www.elsevier.com/locate/ymse REVIEW ARTICLES At the International Congress of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery (ICSES) in Edinburgh, Scotland, in September 2010, Dr Herbert
J Shoulder Elbow Surg (2011) 20, 827-832 www.elsevier.com/locate/ymse REVIEW ARTICLES At the International Congress of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery (ICSES) in Edinburgh, Scotland, in September 2010, Dr Herbert
Proximal Humerus System 3.5
 PRODUCT INFORMATION Proximal Humerus System 3.5 APTUS Shoulder 2 Proximal Humerus System 3.5 Contents 3 New Treatment Concept for Proximal Humerus Fractures 4 Proximal Humerus System 3.5 6 Portfolio 7
PRODUCT INFORMATION Proximal Humerus System 3.5 APTUS Shoulder 2 Proximal Humerus System 3.5 Contents 3 New Treatment Concept for Proximal Humerus Fractures 4 Proximal Humerus System 3.5 6 Portfolio 7
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation.
 LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
Results of 131 consecutive operated patients with a displaced proximal humerus fracture: an analysis with more than two years follow-up
 Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol (2011) 21:7 12 DOI 10.1007/s00590-010-0655-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Results of 131 consecutive operated patients with a displaced proximal humerus fracture: an analysis with more
Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol (2011) 21:7 12 DOI 10.1007/s00590-010-0655-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Results of 131 consecutive operated patients with a displaced proximal humerus fracture: an analysis with more
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques
 Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct
 Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct Tak-Wing Lau Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Singapore Trauma 2015 Trauma Through the
Distal Femur Fractures in The Elderly The Ideal Construct Tak-Wing Lau Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Singapore Trauma 2015 Trauma Through the
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi
 Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Surgical Technique. Intramedullary locked Nailing With Screws for Humerus Fractures Solid/Cannulated. Humeral Interlocking Nail.
 Screws for Humerus Fractures Surgical Technique Humeral Interlocking Nail Approved by Humerus Nail Kit Code 08050001 Contents Introduction Implant design Indications Pre-operative planning Patient positioning
Screws for Humerus Fractures Surgical Technique Humeral Interlocking Nail Approved by Humerus Nail Kit Code 08050001 Contents Introduction Implant design Indications Pre-operative planning Patient positioning
Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini
 Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Technique Guide. 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology.
 Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP
Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP
PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus.
 PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the
PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the
Fixation of the greater tuberosity in proximal humeral fractures : FiberWire or wire cerclage?
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 9-16 ORIGINAL STUDY Fixation of the greater tuberosity in proximal humeral fractures : FiberWire or wire cerclage? Benjamin Bockmann, Benjamin Buecking, Daphne Asimenia Eschbach,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 9-16 ORIGINAL STUDY Fixation of the greater tuberosity in proximal humeral fractures : FiberWire or wire cerclage? Benjamin Bockmann, Benjamin Buecking, Daphne Asimenia Eschbach,
Surgical Technique. Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90
 Surgical Technique Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Table of contents Indications/Contraindications 2 Implants 3 Surgical technique 5 Implant
Surgical Technique Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Table of contents Indications/Contraindications 2 Implants 3 Surgical technique 5 Implant
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Tibia Plate. Part of the Synthes Small Fragment LCP System.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Tibia Plate. Part of the Synthes Small Fragment LCP System. Table of Contents AO ASIF Principles of Internal Fixation 4 Indications/Contraindications 5 Surgical Technique
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Tibia Plate. Part of the Synthes Small Fragment LCP System. Table of Contents AO ASIF Principles of Internal Fixation 4 Indications/Contraindications 5 Surgical Technique
LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate 3.5. The anatomic fixation system with anterolateral shaft placement.
 LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate 3.5. The anatomic fixation system with anterolateral shaft placement. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate 3.5. The anatomic fixation system with anterolateral shaft placement. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
Technique Guide. 2.7 mm/3.5 mm LCP Distal Fibula Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide 2.7 mm/3.5 mm LCP Distal Fibula Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 2.7 mm/3.5 mm LCP Distal Fibula Plates 2 AO Principles
Technique Guide 2.7 mm/3.5 mm LCP Distal Fibula Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 2.7 mm/3.5 mm LCP Distal Fibula Plates 2 AO Principles
AcUMEDr. LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM
 AcUMEDr LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients.
AcUMEDr LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients.
Techique. Results. Discussion. Materials & Methods. Vol. 2 - Year 1 - December 2005
 to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR. Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR. Introduction
 Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR Xavier A. Duralde, MD Peachtree Orthopaedic Clinic Atlanta, GA Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR Consultant: Smith+Nephew Board of Directors: CORR Introduction Incidence
Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR Xavier A. Duralde, MD Peachtree Orthopaedic Clinic Atlanta, GA Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR Consultant: Smith+Nephew Board of Directors: CORR Introduction Incidence
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability.
 LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
Technique Guide. LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System.
 Technique Guide LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits 2 AO ASIF Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
Technique Guide LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits 2 AO ASIF Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do?
 HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do? TRAUMA 101 2018 FRACTURE CARE FOR THE COMMUNITY ORTHOPEDIST William W. Cross III, MD Assistant Professor Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Chair, Division
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do? TRAUMA 101 2018 FRACTURE CARE FOR THE COMMUNITY ORTHOPEDIST William W. Cross III, MD Assistant Professor Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Chair, Division
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability.
 LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
Orthopedics - Dr. Ahmad - Lecture 2 - Injuries of the Upper Limb
 The shoulder and the upper arm Fractures of the clavicle 1. Fall on the shoulder. 2. Fall on outstretched hand. In mid shaft fractures, the outer fragment is pulled down by the weight of the arm and the
The shoulder and the upper arm Fractures of the clavicle 1. Fall on the shoulder. 2. Fall on outstretched hand. In mid shaft fractures, the outer fragment is pulled down by the weight of the arm and the
The Treatment of the Proximal Humeral Fracture with the Use of the PHN Nailing System: the Importance of Reduction
 250/, p. 250 255 The Treatment of the Proximal Humeral Fracture with the Use of the PHN Nailing System: the Importance of Reduction Léčení zlomenin proximálního humeru pomocí PHN hřebovacího systému S.
250/, p. 250 255 The Treatment of the Proximal Humeral Fracture with the Use of the PHN Nailing System: the Importance of Reduction Léčení zlomenin proximálního humeru pomocí PHN hřebovacího systému S.
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
Treatment Approach To Cases Of Nonunion Intercondylar Fracture Humerus
 The Journal of Maharashtra Orthopaedic Association June - 2006 Treatment Approach To Cases Of Nonunion Intercondylar Fracture Humerus Dr. Vikas Agashe Dr. Vivek Shetty Dr. Anurag Awasthy P. D. Hinduja
The Journal of Maharashtra Orthopaedic Association June - 2006 Treatment Approach To Cases Of Nonunion Intercondylar Fracture Humerus Dr. Vikas Agashe Dr. Vivek Shetty Dr. Anurag Awasthy P. D. Hinduja
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures:
 Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Comparison between Intramedullary Nailing and Percutaneous K-Wire Fixation for Fractures in the Distal Third of the Metacarpal Bone
 Comparison between Nailing and K-Wire Fixation for Fractures in the Distal Third of the Metacarpal Bone Original Article Sung Jun Moon 1, Jae-Won Yang 2, Si Young Roh 1, Dong Chul Lee 1, Jin Soo Kim 1
Comparison between Nailing and K-Wire Fixation for Fractures in the Distal Third of the Metacarpal Bone Original Article Sung Jun Moon 1, Jae-Won Yang 2, Si Young Roh 1, Dong Chul Lee 1, Jin Soo Kim 1
Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing and Dynamic Hip Screw in Intertrochanteric Fracture of Femur *
 Open Journal of Orthopedics, 2013, 3, 291-295 Published Online November 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojo) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojo.2013.37053 291 Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing
Open Journal of Orthopedics, 2013, 3, 291-295 Published Online November 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojo) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojo.2013.37053 291 Comparitive Study between Proximal Femoral Nailing
CiSE. PHILOS Plate Osteosynthesis in Metaphyseal Fractures of the Distal Humerus through an Anterolateral Approach. Introduction ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow Vol. 18, No. 3, September, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5397/cise.2015.18.3.128 CiSE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow PHILOS Plate Osteosynthesis in Metaphyseal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow Vol. 18, No. 3, September, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5397/cise.2015.18.3.128 CiSE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow PHILOS Plate Osteosynthesis in Metaphyseal
TREATMENT OF DISPLACED PROXIMAL HUMERAL FRACTURES IN ELDERLY PATIENTS
 TREATMENT OF DISPLACED PROXIMAL HUMERAL FRACTURES IN ELDERLY PATIENTS KAROL ZYTO, LEIF AHRENGART, ANDERS SPERBER, HANS TÖRNKVIST From Söder Hospital and the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden We randomised
TREATMENT OF DISPLACED PROXIMAL HUMERAL FRACTURES IN ELDERLY PATIENTS KAROL ZYTO, LEIF AHRENGART, ANDERS SPERBER, HANS TÖRNKVIST From Söder Hospital and the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden We randomised
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates
Technical Note Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:
 Technical Note Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:327-333 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.4.327 Biologic Fixation through Bridge Plating for Comminuted Shaft Fracture of the Clavicle: Technical
Technical Note Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:327-333 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.4.327 Biologic Fixation through Bridge Plating for Comminuted Shaft Fracture of the Clavicle: Technical
Surgical Technique Guide PANTERA. Proximal Humerus Fracture Fixation Plate System
 Surgical Technique Guide PANTERA Proximal Humerus Fracture Fixation Plate System Installing the PANTERA is a 4-Step Process: The following technique is designed to optimize the surgical exercise. Step
Surgical Technique Guide PANTERA Proximal Humerus Fracture Fixation Plate System Installing the PANTERA is a 4-Step Process: The following technique is designed to optimize the surgical exercise. Step
Clinical Study Clinical Effects of the Probing Method with Depth Gauge for Determining the Screw Depth of Locking Proximal Humeral Plate
 BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 5898161, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5898161 Clinical Study Clinical Effects of the Probing Method with Depth Gauge for Determining the
BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 5898161, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5898161 Clinical Study Clinical Effects of the Probing Method with Depth Gauge for Determining the
A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report
 CASE REPORT 41 OPEN ACCESS A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report Aysha Rajeev, John Harrison ABSTRACT Introduction: The phalangeal
CASE REPORT 41 OPEN ACCESS A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report Aysha Rajeev, John Harrison ABSTRACT Introduction: The phalangeal
3.5 MM VA-LCP PROXIMAL TIBIA PLATE SYSTEM
 3.5 MM VA-LCP PROXIMAL TIBIA PLATE SYSTEM Part of the DePuy Synthes Variable Angle Periarticular Plating System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3.5 mm VA-LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 2 AO
3.5 MM VA-LCP PROXIMAL TIBIA PLATE SYSTEM Part of the DePuy Synthes Variable Angle Periarticular Plating System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3.5 mm VA-LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 2 AO
Zimmer Periarticular Proximal Humeral Locking Plate
 Zimmer Periarticular Proximal Humeral Locking Plate Surgical Technique The Science of the Landscape Zimmer Periarticular Proximal Humeral Locking Plate 1 Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction
Zimmer Periarticular Proximal Humeral Locking Plate Surgical Technique The Science of the Landscape Zimmer Periarticular Proximal Humeral Locking Plate 1 Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction
Distal Femur Fractures: Tips and Tricks for Plating and Nailing? Conflict of Interest 9/24/2015
 Distal Femur Fractures: Tips and Tricks for Plating and Nailing? Cory Collinge, MD Professor of Orthopedic Surgery Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN Conflict of Interest Consultant: Smith
Distal Femur Fractures: Tips and Tricks for Plating and Nailing? Cory Collinge, MD Professor of Orthopedic Surgery Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN Conflict of Interest Consultant: Smith
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus. H. Sithebe 2012
 Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Acu-Sinch Repair System. Technical Monograph
 Acu-Sinch Repair System Technical Monograph Acumed is a global leader of innovative orthopaedic and medical solutions. We are dedicated to developing products, service methods, and approaches that improve
Acu-Sinch Repair System Technical Monograph Acumed is a global leader of innovative orthopaedic and medical solutions. We are dedicated to developing products, service methods, and approaches that improve
LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates 3.5 mm. Anatomic plates with low profile head for intra- and extraarticular fractures.
 LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates 3.5 mm. Anatomic plates with low profile head for intra- and extraarticular fractures. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the
LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates 3.5 mm. Anatomic plates with low profile head for intra- and extraarticular fractures. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the
LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia.
 LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia. LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia.
LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia. LISS DF and LISS PLT. Less Invasive Stabilization Systems for Distal Femur and Proximal Lateral Tibia.
Philos Plate: Its Complications and Functional Outcome
 Original Research Article Philos Plate: Its Complications and Functional Outcome Jairam Jagiasi 1, Amit Joshi 2*, Ashish Gupta 3 1Professor And Head, 2* Senior Registrar, 3 Registrar, Department of Orthopaedics,
Original Research Article Philos Plate: Its Complications and Functional Outcome Jairam Jagiasi 1, Amit Joshi 2*, Ashish Gupta 3 1Professor And Head, 2* Senior Registrar, 3 Registrar, Department of Orthopaedics,
LCP Proximal Radius Plates 2.4. Plates for radial head rim and for radial head neck address individual fracture patterns of the proximal radius.
 Technique Guide LCP Proximal Radius Plates 2.4. Plates for radial head rim and for radial head neck address individual fracture patterns of the proximal radius. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Proximal
Technique Guide LCP Proximal Radius Plates 2.4. Plates for radial head rim and for radial head neck address individual fracture patterns of the proximal radius. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Proximal
What s New in the Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures?
 NHMI Winter Meeting Stowe, VT January 2015 What s New in the Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures? John Bell, M.D., M.S. Associate Professor Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center
NHMI Winter Meeting Stowe, VT January 2015 What s New in the Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures? John Bell, M.D., M.S. Associate Professor Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center
Provision of Rotational Stability: Prevention of Collapse: Closed Fracture Reduction: Minimally Invasive Surgery with no Exposure of the Fracture:
 INTRODUCTION Percutaneous Compression Plating was developed by considering each of the stages in the surgical procedure for pertrochanteric fractures and the ways in which these might be improved. Primary
INTRODUCTION Percutaneous Compression Plating was developed by considering each of the stages in the surgical procedure for pertrochanteric fractures and the ways in which these might be improved. Primary
The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 425, pp. 82 86 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 425, pp. 82 86 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture.
 Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture. stud. med. David Andreas Lunde Hatfield stud. med. Mohammed Sherif
Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture. stud. med. David Andreas Lunde Hatfield stud. med. Mohammed Sherif
3.5 mm LCP Clavicle Hook Plates
 Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Clavicle Hook Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Clavicle Hook Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
Part of the Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Clavicle Hook Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Clavicle Hook Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery. Zimmer NCB Plating System
 A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery Zimmer NCB Plating System The Power of Choice The power of having true intraoperative options is at your fingertips. Using standard
A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery Zimmer NCB Plating System The Power of Choice The power of having true intraoperative options is at your fingertips. Using standard
Fracture complexe ESH Que choisir? Hémi ou Inversée Ph Valenti Paris
 Fracture complexe ESH Que choisir? Hémi ou Inversée Ph Valenti Paris Proximal Complex fracture of the humerus Surgeon is not always happy!!!! Reduction is not anatomical!!!! Great tuberosity is not reduced!!!
Fracture complexe ESH Que choisir? Hémi ou Inversée Ph Valenti Paris Proximal Complex fracture of the humerus Surgeon is not always happy!!!! Reduction is not anatomical!!!! Great tuberosity is not reduced!!!
The Mechanical Properties Of Fixing Greater Trochanter Or Lesser Trochanter In Complex Four Part Intertrochanteric Fractures
 The Mechanical Properties Of Fixing Greater Trochanter Or Lesser Trochanter In Complex Four Part Intertrochanteric Fractures Chih-Hui Chen 1, Kui-Chou Huang 2, Cheng-Kung Cheng, PhD 3, Hung-Chan Kao 4.
The Mechanical Properties Of Fixing Greater Trochanter Or Lesser Trochanter In Complex Four Part Intertrochanteric Fractures Chih-Hui Chen 1, Kui-Chou Huang 2, Cheng-Kung Cheng, PhD 3, Hung-Chan Kao 4.
The Surgical And Functional Outcome In Two Part And Three Part Fracture Of The Proximal Humerus Using Proximal Humerus Locking Plate (Philos Plate).
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 10 Ver. 2 (October. 2018), PP 01-06 www.iosrjournals.org The Surgical And Functional Outcome
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 10 Ver. 2 (October. 2018), PP 01-06 www.iosrjournals.org The Surgical And Functional Outcome
