Achilles tendinopathy: new insights in cause of pain, diagnosis and management van Sterkenburg, M.N.
|
|
|
- Norma Robertson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Achilles tendinopathy: new insights in cause of pain, diagnosis and management van Sterkenburg, M.N. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Sterkenburg, M. N. (2012). Achilles tendinopathy: new insights in cause of pain, diagnosis and management General rights It is not permitted to download or to forward/distribute the text or part of it without the consent of the author(s) and/or copyright holder(s), other than for strictly personal, individual use, unless the work is under an open content license (like Creative Commons). Disclaimer/Complaints regulations If you believe that digital publication of certain material infringes any of your rights or (privacy) interests, please let the Library know, stating your reasons. In case of a legitimate complaint, the Library will make the material inaccessible and/or remove it from the website. Please Ask the Library: or a letter to: Library of the University of Amsterdam, Secretariat, Singel 425, 1012 WP Amsterdam, The Netherlands. You will be contacted as soon as possible. UvA-DARE is a service provided by the library of the University of Amsterdam ( Download date: 03 Nov 2018
2 Chapter 10 Endoscopic calcaneoplasty MN van Sterkenburg PAJ de Leeuw CN van Dijk Accepted in Minimally Invasive Foot & Ankle Surgery, editor Maffulli, 2010
3
4 Introduction In 1928, the Swedish orthopedic surgeon Patrick Haglund described a patient with a painful hindfoot caused by a prominent posterosuperior aspect of the calcaneus in conjunction with a sharp rigid heel counter 8. The term Haglund s disease, deformity and syndrome have been used interchangeably, but have also been described as different entities by others. Nowadays, the term Haglund s deformity is used to describe tenderness and pain on the posterolateral aspect of the calcaneus. On physical examination, a bony prominence can be palpated at this location. This entity is described by a variety of different names such as pump-bump 5, cucumber heel 6, high-prow heels 31 and winter heel 6. There is more uncertainty on the definition of Haglund s disease. It is described to be a synonym for deformity or syndrome, but has also been referred to as an osteochondrosis of the accessory navicular bone 1,30,35. For this reason, it will not be considered in this chapter. In Haglund s syndrome, the retrocalcaneal bursa is inflamed with concomitant swelling. The swelling is present on both sides of the Achilles tendon at the level of the posterosuperior calcaneal prominence, sometimes in combination with insertional tendinopathy of the Achilles tendon. The syndrome is caused by repetitive impingement of the retrocalcaneal bursa between the anterior aspect of the Achilles tendon and the enlarged posterosuperior aspect of the calcaneus. It occurs most often at the end of the 2 nd or the 3 rd decade, mainly in females, and is often bilateral. However, it may occur in both sexes and at any age. In this chapter, the diagnosis and endoscopic treatment for patients with complaints of a chronic retrocalcaneal bursitis is described, which can be part of Haglund s deformity and Haglund s syndrome. Chapter 10 Endoscopic calcaneoplasty 161 Diagnosis Patients typically describe the onset of pain when starting to walk after a period of rest. The distinction between Haglund s deformity, Haglund s syndrome, and other pathologic conditions of the posterior aspect of the heel, most importantly Achilles tendinopathy, should be made. Insertional tendinopathy is defined as a tendinopathy of the tendon at its insertion. The pain is most frequently located in the midline at the insertion into the calcaneus. Co-existence with retrocalcaneal bursitis is known. In Haglund s deformity, a bony prominence can be seen at the posterosuperolateral aspect of the heel, which is painful on palpation. The superficial bursa may be swollen, and the overlying skin can be thickened and dyschromic. A retrocalcaneal bursitis occasionally develops as a result of this deformity. In Haglund s syndrome, on physical examination swelling can be seen on both sides of the tendon at the level of the posterosuperior calcaneal prominence, and pain can be reproduced
5 by palpation of the lateral and medial side of the Achilles tendon at this level. With dorsiflexion of the ankle, the anterior part of the tendon impinges against the posterosuperior rim of the calcaneus, leading to retrocalcaneal bursitis. A hindfoot varus and a pes cavus are both predisposing factors for heel pain. In the cavus foot, the calcaneus is not only in varus malalignment, but it is also more vertical, which results in a more prominent projection posteriorly 7. Management 162 Multiple options have been described to manage chronic retrocalcaneal bursitis, including avoidance of tight shoe heel counters, cast immobilization, NSAIDs, activity modification, padding, shock wave treatment, physical therapy and a single injection of corticosteroids into the retrocalcaneal space. If conservative management fails, there are essentially two distinct operative methods, and one endoscopic surgical technique. The open operative alternatives include resection of the posterosuperior part of the calcaneus or a calcaneal wedge osteotomy. Complications include skin breakdown, tenderness in the region of the operative scar, esthetically non-appealing operative scars and altered sensation around the heel 2,9,15,19,25. More serious complications include Achilles tendon avulsions and calcaneal (stress) fractures 14,15,19. Recurrent persistent pain secondary to an inadequate amount of bone resected, and stiffness of the Achilles tendon resulting in decreased dorsiflexion have also been reported 22. Wound healing problems have been described in 30% of patients treated with open procedures 29. Endoscopic treatment Endoscopic treatment offers advantages that are related to any minimal invasive surgical procedure, such as a low morbidity, excellent scar healing, functional aftertreatment, Figure 1. (A) A patient with Haglund s syndrome in the right hindfoot. (B) The typical swelling (S) on both sides of the Achilles tendon (AT) at the level of the posterosuperior calcaneal prominence is indicated
6 short recovery time and a shorter time to sport resumption as compared to open surgical approaches. Here we describe the technique of endoscopic calcaneoplasty, and compare the results of this minimal invasive technique 34 with those reported for the open surgical techniques. Indication Patient complaints include pain at rest, when standing, walking (uphill), running and walking on hard surfaces. Conventional lateral radiographs show hypertrophy of the posterosuperior Chapter 10 Endoscopic calcaneoplasty 163 A B C D Figure 2. (A) Schematic lateral view of a hindfoot showing Kager s triangle (black). (B) Plain conventional lateral standing radiograph of an ankle with a normal aspect of the bony and soft tissues in the hindfoot. Kager s triangle is indicated (dotted line). The arrow points at the retrocalcaneal recess. (C) Kager s triangle is schematically drawn (black). Indicated in red is the fluid-filled retrocalcaneal bursa. (D) Lateral standing radiograph of a patient s right ankle showing hypertrophy of the posterosuperior aspect of the calcaneus with infiltration of the retrocalcaneal recess of Kager s triangle by the fluid-filled retrocalcaneal bursa
7 164 Figure 3. The patient is placed in prone position (A). The affected right leg is placed on a bolster and right over the end of the table (B). The other foot is positioned in a way that the surgeon has sufficient working area (C) Figure 4. (A) Schematic drawing of lateral view of the foot. The ankle is placed in plantigrade position. A line is drawn through the tip of the fibula parallel to the sole of the foot. The incision for the lateral portal in conventional posterior arthroscopy is placed directly above this line; the center of the incision in patients undergoing endoscopic calcaneoplasty is placed cm below this line (red). (B) Preoperatively this can be verified by drawing these same lines on a lateral standing radiograph of the foot. (C) Location of lateral and medial (D) portal as indicated by the probe (red line)
8 aspect of the calcaneus and deep retrocalcaneal bursitis, identified by diminished radiolucency of the retrocalcaneal recess and the lower portion of Kager s triangle (Figure 2). If conservative treatment fails, we undertake endoscopic surgery. Surgical technique Surgery is performed with the patient in prone position under general or regional anesthesia. The involved leg is marked with an arrow by the patient, to avoid wrong side surgery. The feet are positioned just over the edge of the operation table. The involved leg is slightly elevated by placing a bolster under the lower leg (Figure 3). The position of the foot is in plantarflexion through gravity. Prior to surgery important anatomical structures are marked. These include the medial and lateral border of the Achilles tendon and the calcaneus (Figure 4). The lateral portal is made first, just lateral of the Achilles tendon at the level of the superior aspect of the calcaneus. This portal is produced as a small vertical incision through the skin only. The retrocalcaneal space is penetrated with a blunt trocar. A 4.5 mm arthroscopic shaft with an inclination angle of 30 o is introduced (Figure 5). Chapter 10 Endoscopic calcaneoplasty 165 Irrigation is performed by gravity flow. A 70 o arthroscope can also be used but is seldom necessary. Under direct vision, a spinal needle is introduced just medial to the Achilles tendon, again at the level of the superior aspect of the calcaneus, to locate the medial portal (Figure 6). After having prepared the medial portal by a vertical stab incision, a 5.5 mm bonecutter shaver (Dyonics Bonecutter, Smith & Nephew, Andover, USA) is introduced and visualized by the arthroscope. The inflamed retrocalcaneal bursa is removed first (Figure 7) to provide a better view. Now the superior surface of the calcaneus is visualized and its fibrous layer Figure 5. (A) incision for lateral portal in a left ankle. (B) Penetration of retrocalcaneal space with blunt trocar followed by blunt dissection. (C) Introduction of arthroscope with 30 o inclination angle
9 166 Figure 6. (A) Introduction of spinal needle (left ankle) under direct vision (B) for placement of medial portal Figure 7. Endoscopic calcaneoplasty of the right hindfoot of a 38-year-old female patient with Haglund s syndrome. (A) The retrocalcaneal recess. AT= Achilles tendon; INF= inflamed retrocalcaneal bursa; CA= calcaneus. (B) Retrocalcaneal bursa is removed with bonecutter shaver. BS= bonecutter shaver Figure 8. (A) Removal of bone at the posteromedial border of the calcaneus with arthroscope in the lateral portal. (B) Removal of bone at the lateral border of the calcaneus after change of portals. AT= Achilles tendon; BS= bonecutter shaver; PM= posteromedial border of calcaneus; LB= posterolateral border of calcaneus; CA= calcaneus
10 and periosteum are stripped off. During resection of the bursa and the fibrous layer and periosteum of the superior aspect of the calcaneus, the full radius resector is facing the bone to avoid damage to the Achilles tendon. When the foot is brought into full dorsiflexion, impingement between the posterosuperior calcaneal edge and the Achilles tendon can be perceived. The foot is subsequently brought into plantarflexion and now the posterosuperior calcaneal rim is removed. This bone is quite soft and can be removed by the aggressive synovial full radius resector or bone cutter. A burr is not needed at this point. The portals are used interchangeably for both the arthroscope and the resector, so as to remove the entire bony prominence. It is important to remove a sufficient amount of bone at the posteromedial and lateral corner (Figure 8). These edges have to be rounded off by moving the synovial resector beyond the posterior edge onto the lateral respectively medial wall of the calcaneus. The Achilles tendon is protected throughout the entire procedure by keeping the closed end of the resector against the tendon. With the foot in full plantarflexion, the insertion of the Achilles tendon can be visualized. Chapter 10 Endoscopic calcaneoplasty 167 The bonecutter is placed on the insertion against the calcaneus to smoothen this part of the calcaneus. Finally, the resector is introduced to clean up loose debris and to smooth possible rough edges. In the first several patients, fluoroscopic control can be used to ascertain whether sufficient bone has been resected. With some experience, this will no longer be necessary. Figure 9 shows an endoscopic view of the end result. To prevent sinus formation, at the end of the procedure the skin incisions are closed with 3.0 Ethilon sutures. The incisions and surrounding skin are injected with 10 ml of a 0.5% bupivacain/morphine solution. A sterile compressive dressing is applied. Post-operative management Postoperatively, the patient is allowed weight -bearing as tolerated and is instructed to elevate the foot when not walking. The dressing is removed 3 days postoperatively, after which the patient is allowed to shower. Patients are encouraged to perform active range of motion exercises for at least 3 times a day for 10 minutes each. The patient is allowed to return to wearing regular shoes as soon as tolerated. The sutures are removed after two weeks. A conventional lateral radiograph is made to ensure that sufficient bone has been excised (Figure 10). With satisfaction of the surgeon and patient, no further outpatient department contact is necessary. Patients with limited range of motion are directed to a physiotherapist. Patient outcome Between 1995 and 2000 in the Academic Medical Center in Amsterdam we performed 39 procedures in 36 patients 28. The average age was 35 years (range 16-50). Patients had a
11 168 Figure 9. Result at the end of procedure. CA= calcaneus, BS= bonecutter shaver, AT= Achilles tendon Figure 10. (A) Preoperative X-ray, with retrocalcaneal bursitis and prominence of the posterosuperior part of the calcaneus (arrow). (B) postoperative X-ray. The posterosuperior part of the calcaneus is sufficiently excised (arrow)
12 painful swelling of the soft tissue of the posterior heel, medial and lateral of the Achilles tendon on physical examination, without pain on palpation of the tendon itself. Conservative management for at least 6 months did not relieve symptoms. The conventional lateral radiograph showed a superior calcaneal angle (subtended by lines drawn from the bursal projection to the posterior calcaneal tuberosity and from the medial calcaneal tuberosity to the anterior calcaneal tuberosity) of more than 75. An angle larger than 75 has been deemed pathologic 6,31. The mean follow up after endoscopic calcaneoplasty was 4.5 years (range 2-7.5). There were no surgical complications except from one 1 patient who experienced an area of hypoesthesia over the heel pad. Postoperatively there were no infections, tender or esthetically non-appealing scars and all patients were content with their small incisions. Except for two patients, all patients improved. The Ogilvie-Harris score 23 was rated fair by 4 patients, 6 rated good and 24 had excellent results. Work and sport resumption took place at an average of 5 weeks (range 10 days-6 months) and 11 weeks (range 6 weeks-6 months) respectively 28,34. Discussion Chapter 10 Endoscopic calcaneoplasty 169 Conservative management for retrocalcaneal bursitis includes a single cortisone injection in the retrocalcaneal bursa 21,22,32. Repeated injections are not advised since these can weaken the tendon with the potential danger of rupture. The aim of surgery for retrocalcaneal bursitis, after failure of the conservative treatment, is preventing impingement between the Achilles tendon and the calcaneus. This can be accomplished by means of removing the inflamed retrocalcaneal bursa followed by either resection of the posterosuperior calcaneal rim or by a closing wedge osteotomy. Posterosuperior calcaneal resection can be performed through a posterolateral or posteromedial incision or via a combination of both 2,13,25. A widely used technique, especially in North America, is the midline-posterior skin incision combined with a central tendon splitting approach for debridement, retrocalcaneal bursectomy, and removal of the calcaneal bursal projection as necessary 18. Another approach is the Cincinnati-type incision, a transverse skin incision at the level of the insertion of the Achilles tendon. With this technique, a wide exposure of the insertion of the Achilles tendon is possible, to debride the peritendinous and tendon tissue and if necessary bursectomy. The transverse skin incision at the level of the Achilles insertion also allows osteotomy of the posterosuperior corner of the calcaneus 4, and, being in the direction of the skin creases, it has a lesser potential for healing problems than the longitudinal approaches. Endoscopic calcaneoplasty offers a good, minimally invasive alternative to open surgery. Surgeons familiar with the endoscopic approach tend to favor this procedure, because of its better visualization as compared to the open procedure. Due to inappropriate visualization of the Achilles tendon during the open procedure, weakening or even rupture of this tendon
13 170 has been reported 14,19. Full recovery time after the open resection can take as long as 2 years. Our patient series shows a high percentage of good to excellent results based on the Ogilvie- Harris score. Our results are comparable with other recently published reports on endoscopic treatment. Jerosh and co-workers published a prospective study in which they described the results of endoscopic calcaneoplasty in 81 patients with an average follow-up of 35.3 months (range 12 to 72). Using the Ogilvie-Harris score, 41 patients presented excellent results, 34 presented good results, 3 had fair, and 3 patients showed poor results. These 3 patients showed an ossified area of the Achilles tendon insertion, and were revised in an open procedure. Only one patient experienced a superficial inflammation of the skin was found 10,11. Ortmann and co-workers operated on 30 patients (32 heels) with retrocalcaneal bursitis with the endoscopic technique. The means follow-up was 35 months, and the AOFAS score averaged 62 preoperatively and 97 postoperatively. There were 26 excellent results, three good results and one poor result. One patient ruptured an Achilles tendon, one had residual pain and swelling that required reoperation through an open procedure. There were no other complications. Patients returned to work after on average of 8 weeks, and all athletes resumed their sporting activities in an average of 12 weeks 24. Morag and co-workers treated 4 patients with endoscopic calcaneoplasty, and after an average follow-up of 2 years (range 1 to 3.5 years), no complications, pain, disability, or range of motion deficits were reported 20. The advantages of the endoscopic over the open procedure are the small incisions, avoiding complications such a wound dehiscence, painful and/or ugly scars and nerve entrapment within the scar, as described for the open procedure 9. He found a considerable amount of residual complaints in 32 clinically and radiographically examined patients treated by surgical resection of the posterosuperior calcaneal prominence for Haglund s syndrome at a mean follow-up of 18.6 years (range 2-41). 14 of these 32 patients had soft tissue problems including excessive scar formation and persistent swelling. In 8 patients not enough bone was excised and 2 had new bone formation, both resulting in persistent painful swelling. The function of the Achilles tendon was disturbed in 8 patients 9. There is no consensus regarding the ideal open surgical approach: medial, lateral, or both 2,12,25. Jones and James performed 10 partial calcaneal osteotomies for retrocalcaneal bursitis, followed by a short leg walking cast for 8 weeks, progressively increasing weightbearing. Rehabilitation consisted of wearing an elevated heel of 1 inch until the foot came easily to the neutral position. All patients were back to their desired level of activity within 6 months 12. Angermann operated on 40 heels for the same indication using the posterolateral approach in 32 patients. Postoperatively 29 patients were allowed immediate weightbearing. Complications consisted of one superficial heel infection, one haematoma and two patients with delayed skin healing. At an average follow-up of 6 years (range 1-12) 50%
14 of the patients were cured, 20% improved, 20% remained unchanged and in 10% the pre-operative symptoms worsened 2. The rate of poor results in this study corresponds to the results of Taylor, who reported 36% poor results after the same type of surgery 33. Pauker and co-workers operated on 28 heels in 22 patients with Haglund s syndrome. 18 heels were approached laterally, and 10 medially, depending on the direction of the prominent bone. All patients received a short leg walking cast for 4 weeks followed by mobilization exercises for aftertreatment. At a mean follow up of 13 years in 19 patients (range 3-20), 15 had good results, 2 fair and 2 poor. No difference in outcome between the two approaches was reported. The authors advocate using one incision, as many patients have complaints of tenderness over the operative scar up to one year postoperatively which might be exaggerated by a more extensive approach 25. Schepsis and co-workers used the medial approach in 24 patients with retrocalcaneal bursitis: 6 (25%) had a fair result requiring re-operation. In 49 heels (36 patients) operated through a lateral approach with a mean follow-up of 4.7 years (range 1 to 11 years), early complications were reported in 4 cases (3 haematomas and a superficial infection), and late complications in 3 cases resulting in revision surgery. 7 patients noted some improvement, 1 patient described no change and 7 patients reported worsening of their symptoms after surgery 27. Brunner and co-workers performed calcaneal osteotomies on 39 heels (36 patients), and reported at an average follow-up of 51 months, an average improvement of the AOFAS score of 32 points as compared to the mean pre-operative score. Recovery time ranged from 6 months up to 2 years. 6 of the 36 patients reported persisting posterior heel pain after surgery 3. There are two comparative studies in which both endoscopic and open procedures were performed. Leitze and co-workers compared the endoscopic approach (n=30, 22 months follow-up) with the open surgical technique (n=17, 42 months follow-up). The endoscopic approach revealed 19 excellent, 5 good, 3 fair and 3 poor results, which was numerically but not significantly better than the open surgical procedure. Recovery time was identical, but operation time, the amount of complications and scar tissue formation favoured the endoscopic approach 16. In a recent study by Lohrer and co-workers, a comparison was made between the endoscopic and open resection for Haglund s syndrome. In this anatomic study, 9 cadaver feet were operated by means of open surgery and 6 were operated through endoscopic calcaneoplasty. After the procedure the ankles were dissected to determine the amount of damage following the surgery. Comparable amounts of damage were found for the sural nerve, the plantaris tendon and the medial column of the Achilles tendon 17. Since this was an anatomic study, no data could be gathered regarding recovery time and scar healing, which seem to be the advantageous points of the endoscopic procedure. Also, cadaveric ankles could have been stiffer as compared to patients, which made the endoscopic approach more difficult to perform. Chapter 10 Endoscopic calcaneoplasty 171
15 Overall, looking at the available results of open surgery, studies reported 61-83% good results and 17-36% complications or poor results requiring re-operation 3,12,16,25,26,33. Endoscopic surgery leads up to an estimated rate of 83-93% good results, and 0.6-5% complications or poor results requiring re-operation 9,11,24,28. Conclusion 172 In summary, whether the operation is performed by endoscopic or open surgery, enough bone has to be removed to prevent impingement between the calcaneus and Achilles tendon. The endoscopic calcaneoplasty has demonstrated to show several advantages including low morbidity, functional aftertreatment, outpatient treatment, excellent scar healing, a short recovery time and quick sport resumption as compared to the results for the open technique.
16 Reference List 1. Alm A, Lamke LO, Liljedahl SO. Surgical treatment of dislocation of the peroneal tendons. Injury 1975; 7(1): Angermann P. Chronic retrocalcaneal bursitis treated by resection of the calcaneus. Foot Ankle 1990; 10(5): Brunner J, Anderson J, O Malley M, Bohne W, Deland J, Kennedy J. Physician and patient based outcomes following surgical resection of Haglund s deformity. Acta Orthop Belg 2005; 71(6): Carmont MR, Maffulli N. Management of insertional Achilles tendinopathy through a Cincinnati incision. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2007; 8: Dickinson PH, Coutts MB, Woodward EP, Handler D. Tendo Achillis bursitis. Report of twenty-one cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1966; 48(1): Fowler A. Abnormalities of the calcaneus as a cause of painful heel: its diagnosis and operative treatment. Br J Surg 1945; 32: Fuglsang F, Torup D. Bursitis retrocalcanearis. Acta Orthop Scand 1961; 30: Haglund P. Beitrag zur Klinik der Achillessehne. Zeitschr Orthop Chir 1928; 49: Huber HM, Waldis M. [The Haglund exostosis--a surgical indication and a minor intervention?]. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 1989; 127(3): Jerosch J, Nasef NM. Endoscopic calcaneoplasty--rationale, surgical technique, and early results: a preliminary report. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2003; 11(3): Jerosch J, Schunck J, Sokkar SH. Endoscopic calcaneoplasty (ECP) as a surgical treatment of Haglund s syndrome. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2007; 15(7): Jones DC, James SL. Partial calcaneal ostectomy for retrocalcaneal bursitis. Am J Sports Med 1984; 12(1): Kolodziej P, Glisson RR, Nunley JA. Risk of avulsion of the Achilles tendon after partial excision for treatment of insertional tendonitis and Haglund s deformity: a biomechanical study. Foot Ankle Int 1999; 20(7): Le TA, Joseph PM. Common exostectomies of the rearfoot. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 1991; 8(3): Leach RE, DiIorio E, Harney RA. Pathologic hindfoot conditions in the athlete. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1983; (177): Leitze Z, Sella EJ, Aversa JM. Endoscopic decompression of the retrocalcaneal space. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2003; 85-A(8): Lohrer H, Nauck T, Dorn NV, Konerding MA. Comparison of endoscopic and open resection for Haglund tuberosity in a cadaver study. Foot Ankle Int 2006; 27(6): McGarvey WC, Palumbo RC, Baxter DE, Leibman BD. Insertional Achilles tendinosis: surgical treatment through a central tendon splitting approach. Foot Ankle Int 2002; 23(1): Miller AE, Vogel TA. Haglund s deformity and the Keck and Kelly osteotomy: a retrospective analysis. J Foot Surg 1989; 28(1): Morag G, Maman E, Arbel R. Endoscopic treatment of hindfoot pathology. Arthroscopy 2003; 19(2): E Myerson MS, McGarvey W. Disorders of the Achilles tendon insertion and Achilles tendinitis. Instr Course Lect 1999; 48: Nesse E, Finsen V. Poor results after resection for Haglund s heel. Analysis of 35 heels in 23 patients after 3 years. Acta Orthop Scand 1994; 65(1): Ogilvie-Harris DJ, Mahomed N, Demaziere A. Anterior impingement of the ankle treated by arthroscopic removal of bony spurs. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1993; 75(3): Chapter 10 Endoscopic calcaneoplasty 173
17 Ortmann FW, McBryde AM. Endoscopic bony and soft-tissue decompression of the retrocalcaneal space for the treatment of Haglund deformity and retrocalcaneal bursitis. Foot Ankle Int 2007; 28(2): Pauker M, Katz K, Yosipovitch Z. Calcaneal ostectomy for Haglund disease. J Foot Surg 1992; 31(6): Schepsis AA, Wagner C, Leach RE. Surgical management of Achilles tendon overuse injuries. A long-term follow-up study. Am J Sports Med 1994; 22(5): Schneider W, Niehus W, Knahr K. Haglund s syndrome: disappointing results following surgery -- a clinical and radiographic analysis. Foot Ankle Int 2000; 21(1): Scholten PE, van Dijk CN. Endoscopic calcaneoplasty. Foot Ankle Clin 2006; 11(2): Segesser B, Goesele A, Renggli P. [The Achilles tendon in sports]. Orthopade 1995; 24(3): Sella EJ, Caminear DS, McLarney EA. Haglund s Syndrome. J Foot Ankle Surg 1997; 37(2): Stephens MM. Haglund s deformity and retrocalcaneal bursitis. Orthop Clin North Am 1994; 25(1): Subotnick SI, Block AJ. Retrocalcaneal problems. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 1990; 7(2): Taylor GJ. Prominence of the calcaneus: is operation justified? J Bone Joint Surg Br 1986; 68(3): van Dijk CN, van Dyk GE, Scholten PE, Kort NP. Endoscopic calcaneoplasty. Am J Sports Med 2001; 29(2): Vega MR, Cavolo DJ, Green RM, Cohen RS. Haglund s deformity. J Am Podiatry Assoc 1984; 74(3):
Achilles tendinopathy: new insights in cause of pain, diagnosis and management van Sterkenburg, M.N.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Achilles tendinopathy: new insights in cause of pain, diagnosis and management van Sterkenburg, M.N. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Achilles tendinopathy: new insights in cause of pain, diagnosis and management van Sterkenburg, M.N. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van
Modified Bunnell suture expands the surgical indication of the treatment of Haglund's syndrome heel pain with endoscope
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 15: 4817-4821, 2018 Modified Bunnell suture expands the surgical indication of the treatment of Haglund's syndrome heel pain with endoscope JI HUA XU, SHI-LI DING,
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 15: 4817-4821, 2018 Modified Bunnell suture expands the surgical indication of the treatment of Haglund's syndrome heel pain with endoscope JI HUA XU, SHI-LI DING,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
mechanical stresses on the tendon with repetitive loading
 Tendinopathy.. How does it happen? mechanical stresses on the tendon with repetitive loading Impingement of the tendon between adjacent structures (bones, ligaments) and impaired blood supply Presentation
Tendinopathy.. How does it happen? mechanical stresses on the tendon with repetitive loading Impingement of the tendon between adjacent structures (bones, ligaments) and impaired blood supply Presentation
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Osteochondral talar lesions and ankle biomechanics Zengerink, M. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Osteochondral talar lesions and ankle biomechanics Zengerink, M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Zengerink, M. (2017). Osteochondral talar
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Osteochondral talar lesions and ankle biomechanics Zengerink, M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Zengerink, M. (2017). Osteochondral talar
Achilles tendinopathy: new insights in cause of pain, diagnosis and management van Sterkenburg, M.N.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Achilles tendinopathy: new insights in cause of pain, diagnosis and management van Sterkenburg, M.N. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Achilles tendinopathy: new insights in cause of pain, diagnosis and management van Sterkenburg, M.N. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van
Achilles Tendon Anatomy. Achilles Tendon Anatomy. Acute Achilles Rupture. Acute Achilles Rupture 8/19/14. Primary plantarflexor
 Disclosure Conditions of the Achilles Tendon Brian Clowers, M.D. I have no financial relationships that would influence the content of this presentation Oklahoma Sports and Orthopedic Institute September
Disclosure Conditions of the Achilles Tendon Brian Clowers, M.D. I have no financial relationships that would influence the content of this presentation Oklahoma Sports and Orthopedic Institute September
EndoBlade Soft Tissue Release System
 Surgical Technique Endoscopic Gastroc Recession Endoscopic Plantar Fascia Release EndoBlade Soft Tissue Release System Endoscopic Gastroc Recession Arthrex has developed a comprehensive, completely disposable
Surgical Technique Endoscopic Gastroc Recession Endoscopic Plantar Fascia Release EndoBlade Soft Tissue Release System Endoscopic Gastroc Recession Arthrex has developed a comprehensive, completely disposable
Index. Clin Sports Med 23 (2004) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Clin Sports Med 23 (2004) 169 173 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achilles enthesopathy, calcaneal spur with, 133 clinical presentation of, 135 136 definition of, 131
Clin Sports Med 23 (2004) 169 173 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achilles enthesopathy, calcaneal spur with, 133 clinical presentation of, 135 136 definition of, 131
Foot and ankle update
 Foot and ankle update Mr Ian Garnham Consultant Foot and Ankle Surgeon Whipps Cross University Hospital Hallux Rigidus Symptoms first ray and 1st MTP pain and swelling worse with push off or forced dorsiflexion
Foot and ankle update Mr Ian Garnham Consultant Foot and Ankle Surgeon Whipps Cross University Hospital Hallux Rigidus Symptoms first ray and 1st MTP pain and swelling worse with push off or forced dorsiflexion
Surgery for Haglund s deformity
 Patient information Surgery for Haglund s deformity Introduction This leaflet outlines the surgical treatments available for the heel condition known as Haglund s deformity. What is Haglund s deformity?
Patient information Surgery for Haglund s deformity Introduction This leaflet outlines the surgical treatments available for the heel condition known as Haglund s deformity. What is Haglund s deformity?
Disorders of the Achilles tendon The ageing athlete
 Disorders of the Achilles tendon The ageing athlete John P. Negrine F.R.A.C.S. Foot and Ankle Surgeon Orthosports Sydney The Bad news Maximum heart rate decreases VO2 Max decreases Runners when compared
Disorders of the Achilles tendon The ageing athlete John P. Negrine F.R.A.C.S. Foot and Ankle Surgeon Orthosports Sydney The Bad news Maximum heart rate decreases VO2 Max decreases Runners when compared
Mr. Siva Chandrasekaran Orthopaedic Surgeon MBBS MSpMed MPhil (surg) FRACS
 Bunion Surgery Most people with bunions find pain relief with simple treatments to reduce pressure on the big toe, such as wearing wider shoes or using pads in their shoes. However, if these measures do
Bunion Surgery Most people with bunions find pain relief with simple treatments to reduce pressure on the big toe, such as wearing wider shoes or using pads in their shoes. However, if these measures do
Outcomes of Surgical Treatment for Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy Using a Central Tendon Splitting Approach
 Outcomes of Surgical Treatment for Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy Using a Central Tendon Splitting Approach Elizabeth Martin, MD; Ruth Chimenti, DPT; Josh Tome, MS; Andrew Hollenbeck, BS; John Ketz,
Outcomes of Surgical Treatment for Insertional Achilles Tendinopathy Using a Central Tendon Splitting Approach Elizabeth Martin, MD; Ruth Chimenti, DPT; Josh Tome, MS; Andrew Hollenbeck, BS; John Ketz,
Bony Tendo-Achilles Presenting as a Chronic Heel Ulcer: A Case Report
 American-Eurasian Journal of Scientific Research 2 (1): 63-67, 2007 ISSN 1818-6785 IDOSI Publications, 2007 Bony Tendo-Achilles Presenting as a Chronic Heel Ulcer: A Case Report S.B. Agaja Department of
American-Eurasian Journal of Scientific Research 2 (1): 63-67, 2007 ISSN 1818-6785 IDOSI Publications, 2007 Bony Tendo-Achilles Presenting as a Chronic Heel Ulcer: A Case Report S.B. Agaja Department of
FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY
 FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY Information for Patients WHAT IS FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY? The foot and the ankle are crucial for human movement. The balanced action of many bones, joints, muscles and tendons
FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY Information for Patients WHAT IS FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY? The foot and the ankle are crucial for human movement. The balanced action of many bones, joints, muscles and tendons
Clinics in diagnostic imaging (170)
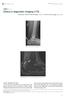 Singapore Med J 2016; 57(9): 517-522 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2016155 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (170) Mohammad Taufik Bin Mohamed Shah 1, MBBS, FRCR, Bak Siew Steven Wong 1, MBChB, MMed Fig.
Singapore Med J 2016; 57(9): 517-522 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2016155 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (170) Mohammad Taufik Bin Mohamed Shah 1, MBBS, FRCR, Bak Siew Steven Wong 1, MBChB, MMed Fig.
Arthroscopic Treatment of Osteochondral Talar Defects
 Arthroscopic Treatment of Osteochondral Talar Defects Christiaan J.A. van Bergen, MD, Ruben Zwiers, MSc, and C. Niek van Dijk, MD, PhD Based on an original article: J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013 Mar 20;95(6):519-25.
Arthroscopic Treatment of Osteochondral Talar Defects Christiaan J.A. van Bergen, MD, Ruben Zwiers, MSc, and C. Niek van Dijk, MD, PhD Based on an original article: J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013 Mar 20;95(6):519-25.
Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101
 Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101 Servers Disease Causes a disturbance to the growing area at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) where the strong Achilles tendon attaches to it. It is most
Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101 Servers Disease Causes a disturbance to the growing area at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) where the strong Achilles tendon attaches to it. It is most
Ankle Arthroscopy.
 Ankle Arthroscopy Key words: Ankle pain, ankle arthroscopy, ankle sprain, ankle stiffness, day case surgery, articular cartilage, chondral injury, chondral defect, anti-inflammatory medication Our understanding
Ankle Arthroscopy Key words: Ankle pain, ankle arthroscopy, ankle sprain, ankle stiffness, day case surgery, articular cartilage, chondral injury, chondral defect, anti-inflammatory medication Our understanding
Fascial Turn-Down Flap Repair of Chronic Achilles Tendon Rupture
 19 Fascial Turn-Down Flap Repair of Chronic Achilles Tendon Rupture S. Ghosh, P. Laing, and Nicola Maffulli Introduction Fascial turn-down flaps can be used for an anatomic repair of chronic Achilles tendon
19 Fascial Turn-Down Flap Repair of Chronic Achilles Tendon Rupture S. Ghosh, P. Laing, and Nicola Maffulli Introduction Fascial turn-down flaps can be used for an anatomic repair of chronic Achilles tendon
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Copyright 2004, Yoshiyuki Shiratori. All right reserved.
 Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
BUCKS MSK: FOOT AND ANKLE PATHWAY GP MANAGEMENT. Hallux Valgus. Assessment: Early Management. (must be attempted prior to any referral to imsk):
 Hallux Valgus Common condition: affecting around 28% of the adult population. Prevalence increases with age and in females. Observation: Lateral deviation of the great toe. May cause secondary irritation
Hallux Valgus Common condition: affecting around 28% of the adult population. Prevalence increases with age and in females. Observation: Lateral deviation of the great toe. May cause secondary irritation
CIC Edizioni Internazionali. Treating Haglund's Deformity with percutaneous Achilles tendon decompression: a case series.
 Fabrizio Sergio 1 Ottorino Catani 2 Federico Fusini 3 Francesco Langella 4 Giovanni Cautiero 5 Ida Ponzo 5 Fabio Zanchini 5 1 Department of Orthopaedic and Traumatology, Casa di Cura S. Maria della Salute,
Fabrizio Sergio 1 Ottorino Catani 2 Federico Fusini 3 Francesco Langella 4 Giovanni Cautiero 5 Ida Ponzo 5 Fabio Zanchini 5 1 Department of Orthopaedic and Traumatology, Casa di Cura S. Maria della Salute,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The Achilles heel of adults and children Wiegerinck, J.I. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The Achilles heel of adults and children Wiegerinck, J.I. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Wiegerinck, J. I. (2014). The Achilles heel of
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The Achilles heel of adults and children Wiegerinck, J.I. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Wiegerinck, J. I. (2014). The Achilles heel of
Case Report Combined Posterior and Anterior Ankle Arthroscopy
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2012, Article ID 693124, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/693124 Case Report Combined Posterior and Anterior Ankle Arthroscopy Peter E. Scholten 1, 2 andc.niekvandijk 2 1 Department
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2012, Article ID 693124, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/693124 Case Report Combined Posterior and Anterior Ankle Arthroscopy Peter E. Scholten 1, 2 andc.niekvandijk 2 1 Department
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE THE TENDON ANCHOR SYSTEM
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE THE TENDON ANCHOR SYSTEM TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction PAGE 1 Features and Benefits PAGE 1-2 Applications PAGE 3 Ordering Information PAGE 4 Indications & Contra-indications PAGE 5
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE THE TENDON ANCHOR SYSTEM TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction PAGE 1 Features and Benefits PAGE 1-2 Applications PAGE 3 Ordering Information PAGE 4 Indications & Contra-indications PAGE 5
PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION. At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral)
 PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral) They are contained within the tendons of Flexor Hallucis Brevis
PAINFUL SESAMOID OF THE GREAT TOE Dr Vasu Pai ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION At the big toe MTP joint: Tibial sesamoid (medial) & fibular (lateral) They are contained within the tendons of Flexor Hallucis Brevis
FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test]
![FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test] FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test]](/thumbs/83/88335212.jpg) FOOT IN CEREBRAL PALSY GAIT IN CEREBRAL PALSY I True Equinus II Jump gait III Apparent Equinus IV Crouch gait Group I True Equinus Extended hip and knee Equinus at ankle II Jump Gait [commonest] Equinus
FOOT IN CEREBRAL PALSY GAIT IN CEREBRAL PALSY I True Equinus II Jump gait III Apparent Equinus IV Crouch gait Group I True Equinus Extended hip and knee Equinus at ankle II Jump Gait [commonest] Equinus
8 Rearfoot Surgery. Lawrence A. DiDomenico, D.P.M.; and Danielle Butto, D.P.M.
 8 Rearfoot Surgery Lawrence A. DiDomenico, D.P.M.; and Danielle Butto, D.P.M. The authors certify that they have no commercial associations (e.g., consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patient/licensing
8 Rearfoot Surgery Lawrence A. DiDomenico, D.P.M.; and Danielle Butto, D.P.M. The authors certify that they have no commercial associations (e.g., consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patient/licensing
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
A Patient s Guide to Haglund s Deformity of the Foot. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Haglund s Deformity of the Foot Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly
A Patient s Guide to Haglund s Deformity of the Foot Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly
Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): ten Berg,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): ten Berg,
Scar Engorged veins. Size of the foot [In clubfoot, small foot]
![Scar Engorged veins. Size of the foot [In clubfoot, small foot] Scar Engorged veins. Size of the foot [In clubfoot, small foot]](/thumbs/78/77722241.jpg) 6. FOOT HISTORY Pain: Walking, Running Foot wear problem Swelling; tingly feeling Deformity Stiffness Disability: At work; recreation; night; walk; ADL, Sports Previous Rx Comorbidities Smoke, Sugar, Steroid
6. FOOT HISTORY Pain: Walking, Running Foot wear problem Swelling; tingly feeling Deformity Stiffness Disability: At work; recreation; night; walk; ADL, Sports Previous Rx Comorbidities Smoke, Sugar, Steroid
Welcome to the: Orthopaedic Opinion Online Website The website for the answer to all your Orthopaedic Questions
 Welcome to the: Orthopaedic Opinion Online Website The website for the answer to all your Orthopaedic Questions Orthopaedic Opinion Online is a website designed to provide information to patients who have
Welcome to the: Orthopaedic Opinion Online Website The website for the answer to all your Orthopaedic Questions Orthopaedic Opinion Online is a website designed to provide information to patients who have
Anatomy Your shoulder is made up of three bones: your upper arm bone (humerus), your shoulder blade (scapula), and your collarbone (clavicle).
 Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great
Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great
NORTHEAST OHIO NEIGHBORHOOD HEALTH SERVICES, INC. PODIATRY CLINICAL GUIDELINES TABLE OF CONTENTS. Diabetes Mellitus and Podiatric Care 2
 NORTHEAST OHIO NEIGHBORHOOD HEALTH SERVICES, INC. PODIATRY 2012-2013 CLINICAL GUIDELINES TABLE OF CONTENTS CONDITION PAGE(S) Diabetes Mellitus and Podiatric Care 2 Fractures 3-4 Heel Pain (Posterior) Retrocalcaneal
NORTHEAST OHIO NEIGHBORHOOD HEALTH SERVICES, INC. PODIATRY 2012-2013 CLINICAL GUIDELINES TABLE OF CONTENTS CONDITION PAGE(S) Diabetes Mellitus and Podiatric Care 2 Fractures 3-4 Heel Pain (Posterior) Retrocalcaneal
Posterior Ankle Impingement: Don t Get Pinched
 Posterior Ankle Impingement: Don t Get Pinched 11 th Annual Sports Medicine Continuing Education Conference Gregory P Witkowski, MD Orthopaedic Trauma and Foot/Ankle Surgery Disclosures I have nothing
Posterior Ankle Impingement: Don t Get Pinched 11 th Annual Sports Medicine Continuing Education Conference Gregory P Witkowski, MD Orthopaedic Trauma and Foot/Ankle Surgery Disclosures I have nothing
Chronic insertional Achilles tendinopathy: surgical outcomes
 Original article Chronic insertional Achilles tendinopathy: surgical outcomes Yael Oshri 1, Ezequiel Palmanovich 2, Yaron Shagra Brin 2, Ronen Karpf 2, Sabri Massarwe 2, Benny Kish 2, Meir Nyska 2 1 Meir
Original article Chronic insertional Achilles tendinopathy: surgical outcomes Yael Oshri 1, Ezequiel Palmanovich 2, Yaron Shagra Brin 2, Ronen Karpf 2, Sabri Massarwe 2, Benny Kish 2, Meir Nyska 2 1 Meir
Disorders of the Achilles Tendon. Jamal Ahmad, M.D. Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Surgery March 2018
 Disorders of the Achilles Tendon Jamal Ahmad, M.D. Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Surgery March 2018 Disclosure Statement American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) Committee member American Orthopaedic
Disorders of the Achilles Tendon Jamal Ahmad, M.D. Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Surgery March 2018 Disclosure Statement American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) Committee member American Orthopaedic
Fractures of the Calcaneus
 Fractures of the Calcaneus Anthony T. Sorkin, M.D. Rockford Orthopedic Trauma Service Rajeev Garapati, MD Illinois Bone and Joint Institute Assistant Clinical Professor University of Illinois at Chicago
Fractures of the Calcaneus Anthony T. Sorkin, M.D. Rockford Orthopedic Trauma Service Rajeev Garapati, MD Illinois Bone and Joint Institute Assistant Clinical Professor University of Illinois at Chicago
4 ACHILLES TENDONITIS
 4 ACHILLES TENDONITIS What is it? The Achilles tendon is a band of connective tissue that attaches your calf muscle (gastrocnemius and soleus) onto the back of your heel (calcaneus) and is the bodies largest
4 ACHILLES TENDONITIS What is it? The Achilles tendon is a band of connective tissue that attaches your calf muscle (gastrocnemius and soleus) onto the back of your heel (calcaneus) and is the bodies largest
Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle. Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle
 Objectives Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle Learn the basics of diagnosis and treatment of ankle sprains Overview of other common causes
Objectives Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle Learn the basics of diagnosis and treatment of ankle sprains Overview of other common causes
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Improving aspects of palliative care for children Jagt, C.T. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Improving aspects of palliative care for children Jagt, C.T. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Jagt, C. T. (2017). Improving aspects of palliative
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Improving aspects of palliative care for children Jagt, C.T. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Jagt, C. T. (2017). Improving aspects of palliative
Posterior Tibialis Tendon Dysfunction & Repair
 1 Posterior Tibialis Tendon Dysfunction & Repair Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: The posterior tibialis muscle arises from the interosseous membrane and the adjacent
1 Posterior Tibialis Tendon Dysfunction & Repair Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: The posterior tibialis muscle arises from the interosseous membrane and the adjacent
.org. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction. Anatomy. Cause. Symptoms
 Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Page ( 1 ) Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed
Haglund s Deformity of the Foot
 A Patient s Guide to Haglund s Deformity of the Foot 20295 NE 29th Place, Ste 300 Aventura, FL 33180 Phone: (786) 629-0910 Fax: (786) 629-0920 admin@instituteofsports.com DISCLAIMER: The information in
A Patient s Guide to Haglund s Deformity of the Foot 20295 NE 29th Place, Ste 300 Aventura, FL 33180 Phone: (786) 629-0910 Fax: (786) 629-0920 admin@instituteofsports.com DISCLAIMER: The information in
7:53 am Central Tendon Splitting Approach William C. McGarvey, MD
 7:53 am Central Tendon Splitting Approach William C. McGarvey, MD a Arthrex, Inc; Biomet; DePuy, A Johnson & Johnson Company; Smith & Nephew; Stryker; b DePuy, A Johnson & Johnson Company; e Arthrex, Inc
7:53 am Central Tendon Splitting Approach William C. McGarvey, MD a Arthrex, Inc; Biomet; DePuy, A Johnson & Johnson Company; Smith & Nephew; Stryker; b DePuy, A Johnson & Johnson Company; e Arthrex, Inc
Hindfoot endoscopy for posterior ankle impingement. Surgical technique van Dijk, C.N.; de Leeuw, P.A.J.; Scholten, P.E.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Hindfoot endoscopy for posterior ankle impingement. Surgical technique van Dijk, C.N.; de Leeuw, P.A.J.; Scholten, P.E. Published in: The journal of bone and joint
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Hindfoot endoscopy for posterior ankle impingement. Surgical technique van Dijk, C.N.; de Leeuw, P.A.J.; Scholten, P.E. Published in: The journal of bone and joint
REPAIR VERSUS OPEN REPAIR FOR ACUTE
 RETROSPECTIVE ANALYSIS OF MINI-OPEN REPAIR VERSUS OPEN REPAIR FOR ACUTE ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURES Erin E. Klein, DPM, MS Lowell Weil, Jr., DPM, MBA Jeffrey R. Baker, DPM Lowell Scott Weil, Sr., DPM Jessica
RETROSPECTIVE ANALYSIS OF MINI-OPEN REPAIR VERSUS OPEN REPAIR FOR ACUTE ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURES Erin E. Klein, DPM, MS Lowell Weil, Jr., DPM, MBA Jeffrey R. Baker, DPM Lowell Scott Weil, Sr., DPM Jessica
Surgical treatment of non-melanoma skin cancer of the head and neck: expanding reconstructive options van der Eerden, P.A.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Surgical treatment of non-melanoma skin cancer of the head and neck: expanding reconstructive options van der Eerden, P.A. Link to publication Citation for published
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Surgical treatment of non-melanoma skin cancer of the head and neck: expanding reconstructive options van der Eerden, P.A. Link to publication Citation for published
Ankle Arthritis PATIENT INFORMATION. The ankle joint. What is ankle arthritis?
 PATIENT INFORMATION Ankle Arthritis The ankle joint The ankle is a very complex joint. It is actually made up of two joints: the true ankle joint and the subtalar ankle joint. The ankle joint consists
PATIENT INFORMATION Ankle Arthritis The ankle joint The ankle is a very complex joint. It is actually made up of two joints: the true ankle joint and the subtalar ankle joint. The ankle joint consists
WHAT IS THIS CONDITION? COMMON CAUSES:
 Mr Laurence James BSc MBBS MRCS(Eng) FRCS(Tr&Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Foot, Ankle and Sports Injuries WHAT IS THIS CONDITION? The posterior tibial tendon is an important structure that is normally
Mr Laurence James BSc MBBS MRCS(Eng) FRCS(Tr&Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Foot, Ankle and Sports Injuries WHAT IS THIS CONDITION? The posterior tibial tendon is an important structure that is normally
The utility of hip arthroscopy has certainly increased
 Hip Arthroscopy and the Anterolateral Portal: Avoiding Labral Penetration and Femoral Articular Injuries Stephen Kenji Aoki, M.D., James Thomas Beckmann, M.D., and James Derek Wylie, M.D. Abstract: Establishing
Hip Arthroscopy and the Anterolateral Portal: Avoiding Labral Penetration and Femoral Articular Injuries Stephen Kenji Aoki, M.D., James Thomas Beckmann, M.D., and James Derek Wylie, M.D. Abstract: Establishing
ACHILLES TENDON REPAIRS. Priya Parthasarathy, DPM
 ACHILLES TENDON REPAIRS Priya Parthasarathy, DPM DISCLOSURES NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST ANATOMY 10-12 cm long 0.5-1.0 cm diameter Avascular zone 2-6 cm proximal to insertion Fibers rotate 90 degrees at insertion
ACHILLES TENDON REPAIRS Priya Parthasarathy, DPM DISCLOSURES NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST ANATOMY 10-12 cm long 0.5-1.0 cm diameter Avascular zone 2-6 cm proximal to insertion Fibers rotate 90 degrees at insertion
5 minutes: Attendance and Breath of Arrival. 50 minutes: Problem Solving Ankles and Feet
 5 minutes: Attendance and Breath of Arrival 50 minutes: Problem Solving Ankles and Feet Punctuality- everybody's time is precious: o o Be ready to learn by the start of class, we'll have you out of here
5 minutes: Attendance and Breath of Arrival 50 minutes: Problem Solving Ankles and Feet Punctuality- everybody's time is precious: o o Be ready to learn by the start of class, we'll have you out of here
Long-Term Results After Functional Nonoperative Treatment of Achilles Tendon Rupture
 FOOT &ANKLE INTERNATIONAL Copyright 2006 by the American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society, Inc. Long-Term Results After Functional Nonoperative Treatment of Achilles Tendon Rupture Tobias M. Hufner, M.D.
FOOT &ANKLE INTERNATIONAL Copyright 2006 by the American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society, Inc. Long-Term Results After Functional Nonoperative Treatment of Achilles Tendon Rupture Tobias M. Hufner, M.D.
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Sports Injuries of the Ankle and Ankle Arthritis. Mr Amit Amin Consultant Foot and Ankle Surgeon Parkside Hospital
 Sports Injuries of the Ankle and Ankle Arthritis Mr Amit Amin Consultant Foot and Ankle Surgeon Parkside Hospital Impingement Painful mechanical limitation of full ankle movement secondary to osseous
Sports Injuries of the Ankle and Ankle Arthritis Mr Amit Amin Consultant Foot and Ankle Surgeon Parkside Hospital Impingement Painful mechanical limitation of full ankle movement secondary to osseous
A Patient s Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing
 A Patient s Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing Surgical Outcomes System (SOS ) www.orthoillustrated.com OrthoIllustrated is a leading Internet-based resource for patient education. Please visit this website
A Patient s Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing Surgical Outcomes System (SOS ) www.orthoillustrated.com OrthoIllustrated is a leading Internet-based resource for patient education. Please visit this website
emoryhealthcare.org/ortho
 COMMON SOCCER INJURIES Oluseun A. Olufade, MD Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopedics and PM&R 1/7/18 GOALS Discuss top soccer injuries and treatment strategies Simplify hip and groin injuries in
COMMON SOCCER INJURIES Oluseun A. Olufade, MD Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopedics and PM&R 1/7/18 GOALS Discuss top soccer injuries and treatment strategies Simplify hip and groin injuries in
Mr Keith Winters MBChB, FRACS (Orth) Specialist Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Mr Keith Winters MBChB, FRACS (Orth) Specialist Orthopaedic Surgeon Ph: (03) 9598 0691 Post op Instructions: Achilles Tendon Repair Recommended appliances for after your surgery: Crutches, walking frame
Mr Keith Winters MBChB, FRACS (Orth) Specialist Orthopaedic Surgeon Ph: (03) 9598 0691 Post op Instructions: Achilles Tendon Repair Recommended appliances for after your surgery: Crutches, walking frame
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT
 C H A P T E R 1 7 SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT William D. Fishco, DPM, MS INTRODUCTION Arthroereisis is a surgical procedure designed to limit the motion of a joint. Subtalar joint arthroereisis
C H A P T E R 1 7 SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT William D. Fishco, DPM, MS INTRODUCTION Arthroereisis is a surgical procedure designed to limit the motion of a joint. Subtalar joint arthroereisis
Meniscus Problems - Torn Meniscus Repair
 Meniscus Problems - Torn Meniscus Repair The two crescent-shaped menisci in each knee absorb shock, disperse weight, and reduce friction when the knee moves. Activities such as walking or jumping transfer
Meniscus Problems - Torn Meniscus Repair The two crescent-shaped menisci in each knee absorb shock, disperse weight, and reduce friction when the knee moves. Activities such as walking or jumping transfer
Bunion Surgery. This article provides information on surgery for bunions. For more general information: Bunions (topic.cfm? topic=a00155).
 Bunion Surgery This article provides information on surgery for bunions. For more general information: Bunions (topic.cfm? topic=a00155). Most people with bunions find pain relief with simple treatments
Bunion Surgery This article provides information on surgery for bunions. For more general information: Bunions (topic.cfm? topic=a00155). Most people with bunions find pain relief with simple treatments
Achilles Tendon Rupture
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353 Website: philip-bayliss.com Achilles Tendon Rupture Summary Achilles tendon ruptures commonly occur in athletic individuals in their
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353 Website: philip-bayliss.com Achilles Tendon Rupture Summary Achilles tendon ruptures commonly occur in athletic individuals in their
ACHILLES SENAN. - Nya synpunkter - Jon Karlsson. Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg Sweden
 ACHILLES SENAN - Nya synpunkter - Jon Karlsson Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg Sweden ACHILLES SENAN Operation vs icke-operation Tidigare studier; Nistor, MöllerM Aktuell studie; Nilsson-Helander
ACHILLES SENAN - Nya synpunkter - Jon Karlsson Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg Sweden ACHILLES SENAN Operation vs icke-operation Tidigare studier; Nistor, MöllerM Aktuell studie; Nilsson-Helander
ARTHROSCOPIC GIANT NEEDLE ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR AS A ROUTINE PROCEDURE SINCE 1990
 ARTHROSCOPIC GIANT NEEDLE ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR AS A ROUTINE PROCEDURE SINCE 1990 A 10 minutes transhumeral footprint repair using only sutures AIG Medical GmbH Bonn (Aeratec) Essential for this surgery
ARTHROSCOPIC GIANT NEEDLE ROTATOR CUFF REPAIR AS A ROUTINE PROCEDURE SINCE 1990 A 10 minutes transhumeral footprint repair using only sutures AIG Medical GmbH Bonn (Aeratec) Essential for this surgery
Acute Ankle Injuries, Part 1: Office Evaluation and Management
 t June 08, 2009 Obesity [1] Each acute ankle injury commonly seen in the office has associated with it a mechanism by which it can be injured, trademark symptoms that the patient experiences during the
t June 08, 2009 Obesity [1] Each acute ankle injury commonly seen in the office has associated with it a mechanism by which it can be injured, trademark symptoms that the patient experiences during the
DIABETES AND YOUR FEET
 FOOTNOTES DIABETES AND YOUR FEET Diabetes is chronic disease that occurs when your body s ability to process sugars, starches, and other foods into energy is impaired. Some of the long-term effects of
FOOTNOTES DIABETES AND YOUR FEET Diabetes is chronic disease that occurs when your body s ability to process sugars, starches, and other foods into energy is impaired. Some of the long-term effects of
5 COMMON CONDITIONS IN THE FOOT & ANKLE
 5 COMMON CONDITIONS IN THE FOOT & ANKLE MICHAEL P. CLARE, MD FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE TAMPA, FL USA IN A NUTSHELL ~ ALL ANATOMY & BIOMECHANICS >90% OF CONDITIONS IN FOOT & ANKLE DIAGNISED FROM GOOD
5 COMMON CONDITIONS IN THE FOOT & ANKLE MICHAEL P. CLARE, MD FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE TAMPA, FL USA IN A NUTSHELL ~ ALL ANATOMY & BIOMECHANICS >90% OF CONDITIONS IN FOOT & ANKLE DIAGNISED FROM GOOD
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 Introduction Compartment Syndromes of the Leg Related to Athletic Activity Mark M. Casillas, M.D. Consequences of a misdiagnosis persistence of a performance limitation loss of function/compartment loss
Introduction Compartment Syndromes of the Leg Related to Athletic Activity Mark M. Casillas, M.D. Consequences of a misdiagnosis persistence of a performance limitation loss of function/compartment loss
Arthroscopy Of the Ankle.
 Arthroscopy Of the Ankle www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Ankle Arthroscopy Anatomy Patient setup Portal placement Procedures Complications Anatomy Portals Anterior Anteromedial Anterolateral Anterocentral Posterior
Arthroscopy Of the Ankle www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Ankle Arthroscopy Anatomy Patient setup Portal placement Procedures Complications Anatomy Portals Anterior Anteromedial Anterolateral Anterocentral Posterior
Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents
 Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents Cook Children s SPORTS Symposium July 2, 2014 Running Injuries Overuse injuries Acute injuries Anatomic conditions 1 Overuse Injuries Pain that cannot be tied
Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents Cook Children s SPORTS Symposium July 2, 2014 Running Injuries Overuse injuries Acute injuries Anatomic conditions 1 Overuse Injuries Pain that cannot be tied
AOFAS Resident Review Course September 28, Andrew J. Elliott, MD Assistant Attending Surgeon Hospital for Special Surgery Foot and Ankle Service
 Course September 28, 2013 Andrew J. Elliott, MD Assistant Attending Surgeon Hospital for Special Surgery Foot and Ankle Service Disclosure I have a financial relationship with Bacterin. Its products are
Course September 28, 2013 Andrew J. Elliott, MD Assistant Attending Surgeon Hospital for Special Surgery Foot and Ankle Service Disclosure I have a financial relationship with Bacterin. Its products are
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle
 Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. It can cause pain and stiffness in any joint in the body, and is common in the small joints of the foot and ankle.
Arthritis of the Foot and Ankle Arthritis is inflammation of one or more of your joints. It can cause pain and stiffness in any joint in the body, and is common in the small joints of the foot and ankle.
Calcaneus Fractures: My Small Incision Tricks
 Calcaneus Fractures: My Small Incision Tricks Steven Steinlauf, MD The Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Institute of South Florida CSFA Tampa, February 2018 Disclosures Smith & Nephew Design surgeon, Royalties
Calcaneus Fractures: My Small Incision Tricks Steven Steinlauf, MD The Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Institute of South Florida CSFA Tampa, February 2018 Disclosures Smith & Nephew Design surgeon, Royalties
Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan. Schedule Of Anaesthetic Rates Applicable To Podiatry. Procedure List. As Of. 01 April Government of Alberta
 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Procedure List As Of 01 April 2017 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Page i Generated 2017/03/14 TABLE OF CONTENTS As of 2017/04/01 II. OPERATIONS ON THE NERVOUS SYSTEM.......................
Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Procedure List As Of 01 April 2017 Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan Page i Generated 2017/03/14 TABLE OF CONTENTS As of 2017/04/01 II. OPERATIONS ON THE NERVOUS SYSTEM.......................
Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): ten Berg,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): ten Berg,
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
 CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME Carpal tunnel syndrome results from the pinching or entrapping of the median nerve in the underside of the wrist. The actual pathology in most cases is due to either a decrease in
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME Carpal tunnel syndrome results from the pinching or entrapping of the median nerve in the underside of the wrist. The actual pathology in most cases is due to either a decrease in
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
Index. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 22 (2005) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type.
 Clin Podiatr Med Surg 22 (2005) 137 141 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Achilles tendinopathy, 19 43. See also Achilles classification of, 20 differential diagnosis
Clin Podiatr Med Surg 22 (2005) 137 141 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Achilles tendinopathy, 19 43. See also Achilles classification of, 20 differential diagnosis
Midfoot exostectomy for dorsal midfoot exostosis. Information for patients Department of Podiatric Surgery
 Midfoot exostectomy for dorsal midfoot exostosis Information for patients Department of Podiatric Surgery What is dorsal midfoot exostosis? A dorsal midfoot exostosis is a bony prominence on the top of
Midfoot exostectomy for dorsal midfoot exostosis Information for patients Department of Podiatric Surgery What is dorsal midfoot exostosis? A dorsal midfoot exostosis is a bony prominence on the top of
WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS?
 WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS? If you're finding when you climb out of bed each morning that your first couple steps cause your foot and heel to hurt, this might be a sign of plantar fasciitis. A common condition
WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS? If you're finding when you climb out of bed each morning that your first couple steps cause your foot and heel to hurt, this might be a sign of plantar fasciitis. A common condition
A Patient information guide to. Ankle Arthroscopy. Foot and Ankle Unit. Mr Amit Amin Mr Ali Abbasian ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY JAN
 A Patient information guide to Ankle Arthroscopy Foot and Ankle Unit Mr Amit Amin Mr Ali Abbasian 1 What does surgery involve? An ankle arthroscopy is a keyhole operation to gain access to the inside of
A Patient information guide to Ankle Arthroscopy Foot and Ankle Unit Mr Amit Amin Mr Ali Abbasian 1 What does surgery involve? An ankle arthroscopy is a keyhole operation to gain access to the inside of
Toe walking gives rise to parental concern. Therefore, toe-walkers are often referred at the 3 years of age.
 IDIOPATHIC TOE WALKING Toe walking is a common feature in immature gait and is considered normal up to 3 years of age. As walking ability improves, initial contact is made with the heel. Toe walking gives
IDIOPATHIC TOE WALKING Toe walking is a common feature in immature gait and is considered normal up to 3 years of age. As walking ability improves, initial contact is made with the heel. Toe walking gives
Physical Examination of the Foot & Ankle
 Inspection Standing, feet straight forward facing toward examiner Swelling Deformity Flatfoot (pes planus and hindfoot valgus) High arch (pes cavus and hindfoot varus) Peek-a-boo heel Varus Too many toes
Inspection Standing, feet straight forward facing toward examiner Swelling Deformity Flatfoot (pes planus and hindfoot valgus) High arch (pes cavus and hindfoot varus) Peek-a-boo heel Varus Too many toes
Injuries to the Foot. NOCROP Sports Medicine and Therapy
 Injuries to the Foot Arches of the Foot Plantar Fascia - a flat band of connective tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. It supports the arch of your foot. Muscle of the Foot and Lower Leg
Injuries to the Foot Arches of the Foot Plantar Fascia - a flat band of connective tissue that connects your heel bone to your toes. It supports the arch of your foot. Muscle of the Foot and Lower Leg
Patellofemoral Instability
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Patellofemoral Instability. All decisions about the management of Patellofemoral Instability must be made in conjunction
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Patellofemoral Instability. All decisions about the management of Patellofemoral Instability must be made in conjunction
Foot Injuries. Dr R B Kalia
 Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
POSTOP FOLLOW-UP & REHABILITATION FOLLOWING FOOT & ANKLE SURGERY
 1 POSTOP FOLLOW-UP & REHABILITATION FOLLOWING FOOT & ANKLE SURGERY The following instructions are general guidelines, but surgeon post-op instructions will dictate the individual patient's post-op management
1 POSTOP FOLLOW-UP & REHABILITATION FOLLOWING FOOT & ANKLE SURGERY The following instructions are general guidelines, but surgeon post-op instructions will dictate the individual patient's post-op management
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The artificial pancreas Kropff, J. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The artificial pancreas Kropff, J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Kropff, J. (2017). The artificial pancreas: From logic to life General
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The artificial pancreas Kropff, J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Kropff, J. (2017). The artificial pancreas: From logic to life General
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg)
 MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
