The first steps in the management of esophageal atresia
|
|
|
- Malcolm Brown
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 The first steps in the management of esophageal atresia AUTHORS Radhames E. Lizardo, MD a Stephanie M. Bedzis, MD b Marion C. Henry, MD, FACS a Romeo C. Ignacio, Jr., MD, FACS a a Department of Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego, CA b Department of Surgery, Naval Medical Center Portsmouth, Portsmouth, VA CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Radhames E. Lizardo, MD Department of Surgery Naval Medical Center San Diego 00 Bob Wilson Dr. San Diego, CA 1-- eliel.lizardo@gmail.com 01 by the American College of Surgeons. All rights reserved. CC01 Poster Competition The first steps in the management of esophageal atresia
2 1 Called to see an infant who could not swallow, Thomas Gibson in 1 saw the first described case of esophageal atresia (EA) with tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF), the most common of congenital defects of the foregut. Surgeons struggled with the condition from the first attempt by Charles Steele in 1. Their persistence, epitomized by Thomas Lanman s 10 review of cases of EA that all ended in death, reached a climax when Cameron Haight in 11 reported the first patient to survive primary anastomosis for EA. In the years that have followed advances in intraoperative care, neonatology, and surgical technique have produced survival rates that approach 0 percent among babies with EA uncomplicated by prematurity and associated conditions such as cardiac malformations. Discovery In 10 William Durston made the first English description of esophageal atresia (EA) in a pair of conjoined twins. One of the twins, who did not survive, had an esophagus [that] from the mouth of the right head descended no lower than a little above half an inch off the mid-riff, and there it ended. 1 In 1 Thomas Gibson made the first description of the most frequently encountered combination of tracheoesophageal anomalies, a proximal EA with a distal tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF). His careful description clearly describes the symptoms and anatomy. About November 1 I was sent for to an infant that would not swallow. The child seem d very desirous of food, and took what was offer d it in a spoon with greediness; but when it went to swallow it, it was like to be choked, and what should have gone down returned by the mouth and nose, and it fell into a struggling convulsive sort of fit upon it. It was fleshy and large, and was two days old when I came to it but the next day died. The parents being willing to have it opened, I took two physicians and a surgeon with me We blew a pipe down the gullet (esophagus), but found no passage for the wind into the stomach. Then we made a slit in the stomach, and put a pipe into its upper orifice, and blowing, we found the wind had a vent, but not by the top of the gullet. Then we carefully slit open the back side of the gullet from the stomach upwards, and when we were gone a little above half way towards the pharynx, we found it hollow no further. Then we began to slit it open from the pharynx downward, and it was hollow till within an inch of the other slit the imperforated part did not seem ever to have been hollow the parts were here smooth as the bottom of an acorn-cup. Then searching what way the wind had passed when we blow from the stomach upwards, we found an oval hole on the fore-side of the gullet opening into the aspera arteria [trachea]. In 10 Thomas Hill described a case in that was associated with rectal agenesis, the first observation of one of the spectrum of associated anomalies known familiarly by the acronym VACTERL (Vertebral, Atresia duodenal and anorectal Cardiac, Tracheoesphageal, Renal, Limb). Failure In the latter half of the 1th century anesthesia and aseptic surgery allowed bolder operations, including the repair of EA. Timothy Holmes proposed in 1 a primary anastomosis for EA. While never performing the operation, he described how he would set about finding the two ends of the esophagus. [The} object would be to cut down upon the point of a catheter passed down the pharynx, and then attempt to trace the obliterated oesphagus down the front of the spine until the lower dilated portion is found. Charles Steele made the first attempt in 1 in an infant with EA under chloroform anesthesia. Approaching the defect 01 by the American College of Surgeons. All rights reserved. CC01 Poster Competition The first steps in the management of esophageal atresia
3 1 through an upper midline abdominal incision he found the gap between the upper pouch and the distal esophagus was an inch-and-a-half, too wide for a primary repair. He abandoned the attempt, and his patient died within hours. The hazard of the communication between the distal esophageal segment and the trachea was demonstrated by Joseph Brennemann in 1. He attempted to feed one patient through a gastrostomy, and in a second a jejunostomy. The procedures did not address the communication between the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts and both died from pulmonary aspiration. Harry Richter directly addressed the TEF through a thoracic approach in two patients that he reported in 1. He entered the right sixth interspace, extended the posterior aspect of the incision superiorly, and divided three or four ribs. While an assistant s finger held exposure by depressing the ipsilateral lung, Richter tried to assure adequate inflation of the lung (and presumably the contralateral lung) by maintaining positive pressure within the trachea using a homemade pump. He still was confronted by the unusual anatomy. Lack of familiarity with the surgical anatomy of the parts will obviously be a source of embarrassment to most general surgeons. It was to the author. The smallness of the parts in a new-born infant and the peculiarly difficult site of the operation made the hazard apparently. He closed the fistula and performed an anastomosis between the ends of the esophagus. Without the benefit of intravenous infusion, positive pressure ventilation, and having only auscultation to verify complete inflation of the lung after operation, he was able to complete both procedures only to have both infants die after operation. His approach, without the superior extension and division of the ribs above the thoracotomy, would become standard 0 years later. Thomas Lanman s (Figure 1) 10 review of the experience of the Children s Hospital in Boston with EA is a landmark in its thorough and candid appraisal of the management of these desperately ill infants. All patients died, including 0 who had undergone a variety of operative procedures. Among the hard-won lessons learned involved care of the infant before surgery. Early diagnosis and treatment was a priority. Aspiration was an ever-present threat, and delays only assured that the baby would be malnourished, dehydrated, and subject to an increasing risk of pneumonia. The diagnosis could be made without giving the child oral barium, a tube defining the limit of the proximal EA and air in the gastrointestinal tract below the diaphragm confirming the presence of a TEF. Children died of pulmonary infection even after technically successful operations. Babies could not tolerate injudicious fluid administration, as one infant who had undergone a successful primary anastomosis appeared to die in pulmonary edema. The immediate surgical priority was to prevent aspiration by exteriorization of the proximal EA and division of the TEF. The former was a comparatively simple task compared with the latter. Brenneman had showed already that gastrostomy alone was not going to work. The Boston surgeons tried Gage and Ochsner s operation, dividing the cardia at the level of the esophagogastric junction. It proved to be a failure because still attached to the trachea was a long diverticulum that once filled would spill into the lungs. A thoracotomy would be necessary to divide the fistula. Surgeons in Boston had adopted a posterior approach to the mediastinum with the baby prone, using a longitudinal incision to the right of the erector spinae, resecting the fourth rib, and dividing the posterior aspects of the ribs above and below. In the pre-antibiotic era they recognized the hazard of an esophageal leak and sought to contain it in the posterior mediastinum. Thus they kept the dissection out of the free 1 01 by the American College of Surgeons. All rights reserved. CC01 Poster Competition The first steps in the management of esophageal atresia 1
4 1 pleural cavity, another principle followed by many surgeons today. They tried to exteriorize the distal esophagus through the incision, but learned a hard lesson about the segmental blood supply of the distal esophagus when it became ischemic and retracted into the chest. When the two ends of the esophagus appeared sufficiently close and the child s condition would permit, they attempted primary anastomosis. Between 1 and 1 they made the attempt in five patients. One patient died during the operation and two within hours after surgery. However, two survived nine days after repair, proving that survival after primary anastomosis was possible. Lanman said, [Every] reasonable risk should be taken to secure a primary anastomosis. Despite deaths he said, That this method will eventually be successful I have no doubt. Given a suitable case in which the patient is seen early, I feel that, with greater experience, improved technic and good luck, the successful outcome of a direct anastomosis can and will be reported in the near future. Success In 1 a report in the literature appeared of a child with EA without TEF who survived with a gastrostomy and cutaneous esophagostomy for 1 years. In 1 William Ladd in Boston and Logan Leven in Minneapolis had babies with EA and TEF born under their care on consecutive days. Both divided the TEF and performed an esophagostomy and gastrostomy. Once survival was assured, each surgeon began to painstakingly construct in stages skin tubes from bipedicle skin grafts from the anterior thorax. Situated on the surface of the chest, the tube received swallowed material from the esophagus above and drained by gravity into the stomach below. The children were the first long-term survivors of EA with TEF., 01 by the American College of Surgeons. All rights reserved. Finally, in 11, Cameron Haight of Ann Arbor (Figure ) fulfilled Lanman s prediction and had a baby survive a primary anastomosis of an EA. 1 Hiram Langston gives an entertaining account of the operation. The infant, a girl, was in remarkably good shape, surviving 1 days without significant pulmonary contamination, and avoiding dehydration by means of intravenous fluids administered by her pediatrician. She had also evaded the hazard from a barium swallow, despite aspirating some of the material. Under local anesthesia Haight entered the posterior mediastinum through a vertical incision in the left chest by resecting the posterior portions of the nd through th ribs, keeping the parietal pleura intact. The aorta and left subclavian artery were clearly in the field, the latter requiring retraction during the rest of the case. Haight s illustration shows the entire field but clearly exposure was a problem, as he notes that the operative field had to be shifted during the case. 1 He ligated and divided the TEF. The blind end of the upper esophageal segment was nearby. Its mobilization required a deeper plane of anesthesia so open drop ether was administered. Using a single layer of silk sutures, Haight sewed the proximal end to the open distal segment that he had just freed from the trachea. He closed the thoracotomy over a rubber drain that he left near the anastomosis. The child received rectal sulfathiazole by rectum in an effort to address the possibility of perioperative infection. Saliva appeared in the drain a few days after surgery, the leak at the anastomosis verified by giving the child radio-opaque lipiodol. One of Haight s associates placed a gastrostomy, through which feedings were cautiously begun. They tried to probe the anastomosis with a catheter placed through the baby s mouth. Imagine the alarm when the catheter emerged out of the thoracotomy incision! They reduced the volume of gastrostomy feedings in the hope of avoiding any of it refluxing into the esophagus and out the repair. On the 1st day after operation the baby happened to burp some evaporated milk from her mouth. Correctly taking it as a sign that the anastomosis was patent, they repeated the lipiodol study. The leak had sealed, the first example of a lesson well known to pediatric surgeons, that esophageal leaks often seal after EA repairs. The child eagerly accepted oral feedings, the only problem being a stricture that required dilation when the child was 1 months old. The baby was discharged to her family 1 months after her birth. Haight proudly showed a photo of his patient, aged 1, at his presidential address to the American Association for Thoracic Surgery in 1.. She was the last patient Haight saw before his death in 10. As of a review published in 00 she was still alive. Her survival was a signal achievement, being sole survivor and number of a series of patients in his series. The remaining all died within two weeks of their operation. 1 Epilogue Still, Haight proved that survival after EA repair was possible. Other reports of successful EA repairs appeared after Haight s signal achievement. Improvements in positive pressure ventilation in newborn infants, intraoperative care, antibiotic therapy, and neonatal intensive care produced a survival CC01 Poster Competition The first steps in the management of esophageal atresia
5 1 rate of nearly 0 percent among infants that were free from extreme prematurity, other malformations, and heart defects. Advances in surgical technique produced solutions to long-gap EA and obviated the unwieldy skin tubes of Leven and Ladd. Right, not left, thoractotomy exposures are used. No longer do surgeons resect ribs to expose the posterior mediastinum. They routinely enter the pleural cavity to perform thoracoscopic repairs, avoiding a thoracotomy altogether. The -year story of surgery for EA demonstrates why one writer described it as the epitome of modern surgery. References 1 Durston W. A narrative of a monstrous birth in Plymouth October,10; together with the anatomical observations taken thereupon by William Durston, Doctor of Physick, and communication to Dr Tim Clerk. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society V: 0, 10. Gibson T. The anatomy of humane bodies epitomized, th ed. London, Awnsham and Churchill, 1. Hill TP. Congenital malformation. Boston Med Surg J. 10;1:0. Holmes T. The surgical treatment of diseases of infancy and childhood, nd ed. Philadelphia, Lindsay and Blakiston, 1. Steele C. Case of deficient oesophagus. Lancet. 1;:. Brennemann J. Congenital atresia of the oesophagus, with report of three cases. Am J Dis Child. 1;:-0. Richter HM. Congenital atresia of the esophagus, an operation designed for its cure. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1;1:. Lanman TH. Congenital atresia of the esophagus: a study of thirty-two cases. Arch Surg. 10;1:0-. Myers NA. The history of oesophageal atresia and tracheo-oesophageal fistula Prog Pediatr Surg. 1;0:-. Ladd WE. The surgical treatment of esophageal atresia and tracheo-esophageal fistulas. N Engl J Med. 1; 0:-. Leven NL. Congenital atresia of the esophagus with tracheoesophageal fistula. Report of successful extrapleural ligation of fistulous communication and cervical esophagostomy. J Thorac Surg. 11;:-. 1 Haight C, Towsley HA. Congenital atresia of the esophagus with tracheoesophageal fistula. Extrapleural ligation of fistula and end-toend anastomosis of esophageal segments. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1;:-. Langston HT. The first successful total repair of congenital atresia of the esophagus with tracheoesopageal fistula. Ann Thor Surg. 1;(1):-. Haight CC. Some observations on esophageal atresias and tracheoesophageal fistulas of congenital origin. J Thorac Surg. 1;():1-1. Myers NA. Oesophageal atresia: the epitome of modern surgery. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1;():-. Legend 1 Thomas Lanman, standing fourth from left. The famous 1 portrait of the surgical staff, The Children s Hospital, Boston. William Ladd, chief, is to the right of Lanman, Robert Gross is standing at the far right, Orvar Swenson and seventh from the left, seated. Cameron Haight. Courtesy University of Michigan Millennium Project. 01 by the American College of Surgeons. All rights reserved. CC01 Poster Competition The first steps in the management of esophageal atresia
Physical Exam. Vitals stable on room air Abdomen soft, non-distented Normal external genitalia Patent anus No limb anomalies
 Case Presentation 1 day-old full-term baby girl noted to have drooling of saliva and increased secretions at birth Fetal US @32wks had shown polyhydramnios Birth weight 3515g Apgar 7@1min and 8@5min Unable
Case Presentation 1 day-old full-term baby girl noted to have drooling of saliva and increased secretions at birth Fetal US @32wks had shown polyhydramnios Birth weight 3515g Apgar 7@1min and 8@5min Unable
Long-gap Oesophageal Atresia
 Long-gap Atresia A guide for parents Nate (6 weeks old) Atresia Research Association Are there different types of OA? There are four main types of oesophageal atresia with or without TOF. These include
Long-gap Atresia A guide for parents Nate (6 weeks old) Atresia Research Association Are there different types of OA? There are four main types of oesophageal atresia with or without TOF. These include
Tracheoesophageal Fistula and Esophageal Atresia
 Patient and Family Education Tracheoesophageal Fistula and Esophageal Atresia What is tracheoesophageal fistula? The word fistula means abnormal connection. Tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) is a condition
Patient and Family Education Tracheoesophageal Fistula and Esophageal Atresia What is tracheoesophageal fistula? The word fistula means abnormal connection. Tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) is a condition
POSTOPERATIVE CONGENITAL ESOPHAGEAL ATRESIA COMPLICATIONS: A REVIEW
 CHILDREN S HOSPITAL II POSTOPERATIVE CONGENITAL ESOPHAGEAL ATRESIA COMPLICATIONS: A REVIEW Dr. Nguyen Thuy Hanh Ngan Neonatal Department CONTENTS 1. Background 2. Classification 3. Management 4. Complications
CHILDREN S HOSPITAL II POSTOPERATIVE CONGENITAL ESOPHAGEAL ATRESIA COMPLICATIONS: A REVIEW Dr. Nguyen Thuy Hanh Ngan Neonatal Department CONTENTS 1. Background 2. Classification 3. Management 4. Complications
An 8-year experience of esophageal atresia repair in Sarvar children hospital (Mashhad- IRAN)
 An 8-year experience of esophageal atresia repair in Sarvar children hospital (Mashhad- IRAN) Mehran Hiradfar* Ahmad Bazrafshan* Marjan Judi** Mohammad Gharavi*** - Reza Shojaeian**** * Associate professor
An 8-year experience of esophageal atresia repair in Sarvar children hospital (Mashhad- IRAN) Mehran Hiradfar* Ahmad Bazrafshan* Marjan Judi** Mohammad Gharavi*** - Reza Shojaeian**** * Associate professor
Mehmet Melek 1 and Ufuk Cobanoglu Introduction. 2. Material and Method
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2011, Article ID 527323, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/527323 Methodology Report A New Technique in Primary Repair of Congenital Esophageal Atresia Preventing Anastomotic
Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2011, Article ID 527323, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/527323 Methodology Report A New Technique in Primary Repair of Congenital Esophageal Atresia Preventing Anastomotic
Development of Respiratory System. Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra
 Development of Respiratory System Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture the students should be able to: Identify the development of the laryngeotracheal (respiratory)
Development of Respiratory System Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture the students should be able to: Identify the development of the laryngeotracheal (respiratory)
Esophageal Atresia and Tracheoesophageal Fistula
 Esophageal Atresia and Tracheoesophageal Fistula James V. Richardson, M.D., Sharon E. Heintz, P.A., Nicholas P. Rossi, M.D., Creighton B. Wright, M.D., Donald B. Doty, M.D., and Johann L. Ehrenhaft, M.D.
Esophageal Atresia and Tracheoesophageal Fistula James V. Richardson, M.D., Sharon E. Heintz, P.A., Nicholas P. Rossi, M.D., Creighton B. Wright, M.D., Donald B. Doty, M.D., and Johann L. Ehrenhaft, M.D.
THE TREATMENT OF OESOPHAGEAL ATRESIA*
 THE TREATMENT OF OESOPHAGEAL ATRESIA* Though both the anatomy and the symptomatology of the first cases of oesophageal atresia were described in detail more than 250 years ago, it was not until 1941 that
THE TREATMENT OF OESOPHAGEAL ATRESIA* Though both the anatomy and the symptomatology of the first cases of oesophageal atresia were described in detail more than 250 years ago, it was not until 1941 that
ISSN East Cent. Afr. J. surg
 ISSN 073-9990 East Cent. Afr. J. surg Management of Congenital Tracheosophageal Atrasia and Fistula: A preliminary Bi-Cenre Study in Nigeria. E. Aiwanlehi., C. Odion, O. Osasumwen3 Department of Surgery,
ISSN 073-9990 East Cent. Afr. J. surg Management of Congenital Tracheosophageal Atrasia and Fistula: A preliminary Bi-Cenre Study in Nigeria. E. Aiwanlehi., C. Odion, O. Osasumwen3 Department of Surgery,
SETTING Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center. RESPONSIBLE PARTY Haiquan Chen MD.
 OFFICIAL TITLE A Phase Ⅲ Study of Left Side Thoracotomy Approach (SweetProcedure) Versus Right Side Thoracotomy Plus Midline Laparotomy Approach (Ivor-Lewis Procedure) Esophagectomy in Middle or Lower
OFFICIAL TITLE A Phase Ⅲ Study of Left Side Thoracotomy Approach (SweetProcedure) Versus Right Side Thoracotomy Plus Midline Laparotomy Approach (Ivor-Lewis Procedure) Esophagectomy in Middle or Lower
Lecture 21Development of respiratory system Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of session students should able to Describe formation of lung buds Describe
 Lecture 21Development of respiratory system Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of session students should able to Describe formation of lung buds Describe development of larynx, trachea and bronchi. Describe the
Lecture 21Development of respiratory system Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of session students should able to Describe formation of lung buds Describe development of larynx, trachea and bronchi. Describe the
Esophageal Perforation
 Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Departement of Surgery Faculty of Medicine University Sumatera Utara
 SSS EESOPHAGEAL HPOSAGEAL DISORDERS IN SURGICAL PERSPECTIVE Departement of Surgery Faculty of Medicine University Sumatera Utara CONTENT 1. Esophageal Atresia 2. Achalasia 3. Esophageal Rupture 4. Tumor
SSS EESOPHAGEAL HPOSAGEAL DISORDERS IN SURGICAL PERSPECTIVE Departement of Surgery Faculty of Medicine University Sumatera Utara CONTENT 1. Esophageal Atresia 2. Achalasia 3. Esophageal Rupture 4. Tumor
Thoracoscopic repair of esophageal atresia with a distal fistula lessons from the first 10 operations
 Original paper Thoracoscopic repair of esophageal atresia with a distal fistula lessons from the first 10 operations Paweł Nachulewicz 1, Kamila Zaborowska 1, Błażej Rogowski 1, Anita Kalińska 1, Marzena
Original paper Thoracoscopic repair of esophageal atresia with a distal fistula lessons from the first 10 operations Paweł Nachulewicz 1, Kamila Zaborowska 1, Błażej Rogowski 1, Anita Kalińska 1, Marzena
CASE REPORTS. Giant Esophagus. An Unusual Case of Massive Idiopathic Hypertrophy
 CASE REPORTS An Unusual Case of Massive Idiopathic Hypertrophy and Dilatation of the Esophagus and Proximal Stomach Mark H. Wall, M.D., Epifanio E. Espinas, M.D., Arthur W. Silver, M.D., and Francis X.
CASE REPORTS An Unusual Case of Massive Idiopathic Hypertrophy and Dilatation of the Esophagus and Proximal Stomach Mark H. Wall, M.D., Epifanio E. Espinas, M.D., Arthur W. Silver, M.D., and Francis X.
Alyssa Brzenski MD May 2, 2012
 Alyssa Brzenski MD May 2, 2012 Overview Background Pre repair bronchoscopy Thorascopic repair To extubate or not? Esophageal atresia treatment of long gap esophageal atresia Complications following TEF/EA
Alyssa Brzenski MD May 2, 2012 Overview Background Pre repair bronchoscopy Thorascopic repair To extubate or not? Esophageal atresia treatment of long gap esophageal atresia Complications following TEF/EA
Anatomy of the Thorax
 Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Esophageal atresia B Lessons I have learned in a 40-year experience
 Journal of Pediatric Surgery (2006) 41, 1635 1640 www.elsevier.com/locate/jpedsurg Original articles Esophageal atresia B Lessons I have learned in a 40-year experience Lewis Spitz Emeritus Nuffield Professor
Journal of Pediatric Surgery (2006) 41, 1635 1640 www.elsevier.com/locate/jpedsurg Original articles Esophageal atresia B Lessons I have learned in a 40-year experience Lewis Spitz Emeritus Nuffield Professor
Development of the nasal cavity :
 Development of the nasal cavity : several processes contribute to the development of the nose, the nose consists of 2 cavities separated by a septum, and the nasal cavity is separated from the oral cavity
Development of the nasal cavity : several processes contribute to the development of the nose, the nose consists of 2 cavities separated by a septum, and the nasal cavity is separated from the oral cavity
Limited en bloc Resection of the Gastroesophageal Junction with Isoperistaltic Jejunal Interposition
 22 Limited en bloc Resection of the Gastroesophageal Junction with Isoperistaltic Jejunal Interposition J.R. Izbicki, W.T. Knoefel, D. C. Broering ] Indications Severe dysplasia in the distal esophagus
22 Limited en bloc Resection of the Gastroesophageal Junction with Isoperistaltic Jejunal Interposition J.R. Izbicki, W.T. Knoefel, D. C. Broering ] Indications Severe dysplasia in the distal esophagus
AORTIC COARCTATION. Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta
 AORTIC COARCTATION Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta Definition: Aortic coarctation is a congenital narrowing of the aorta, usually located after the left subclavian artery, near the ductus or the ligamentum
AORTIC COARCTATION Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta Definition: Aortic coarctation is a congenital narrowing of the aorta, usually located after the left subclavian artery, near the ductus or the ligamentum
IN 1943, using an extrapleural approach, Haight and
 Long-Term Analysis of Children With Esophageal Atresia and Tracheoesophageal Fistula D.C. Little, F.J. Rescorla, J.L. Grosfeld, K.W. West, L.R. Scherer, and S.A. Engum Indianapolis, Indiana Background/Purpose:
Long-Term Analysis of Children With Esophageal Atresia and Tracheoesophageal Fistula D.C. Little, F.J. Rescorla, J.L. Grosfeld, K.W. West, L.R. Scherer, and S.A. Engum Indianapolis, Indiana Background/Purpose:
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
PBLD Anesthetic Management of Tracheoesophageal Fistula in a Premature Newborn with VACTERL Association and Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
 PBLD Anesthetic Management of Tracheoesophageal Fistula in a Premature Newborn with VACTERL Association and Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome Moderators: Greg Latham, MD, Assistant Professor, Anesthesiology
PBLD Anesthetic Management of Tracheoesophageal Fistula in a Premature Newborn with VACTERL Association and Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome Moderators: Greg Latham, MD, Assistant Professor, Anesthesiology
THE BLOOD SUPPLY OF THE OESOPHAGUS IN RELATION TO OESOPHAGEAL ATRESIA*
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1964, 39, 131. THE BLOOD SUPPLY OF THE OESOPHAGUS IN RELATION TO OESOPHAGEAL ATRESIA* BY JAMES LISTERt From the Nuffield Department of Paediatric Surgery, Institute of Child Health,
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1964, 39, 131. THE BLOOD SUPPLY OF THE OESOPHAGUS IN RELATION TO OESOPHAGEAL ATRESIA* BY JAMES LISTERt From the Nuffield Department of Paediatric Surgery, Institute of Child Health,
Introduction in human anatomy
 Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY. Guidelines. Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta.
 BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY Guidelines Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta. Course 1 The number of hours 3 1. The
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY Guidelines Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta. Course 1 The number of hours 3 1. The
Free Esophageal Perforation Following Hybrid Visceral Debranching and Distal Endograft Extension to Repair a Ruptured Thoracoabdominal Aortic
 Free Esophageal Perforation Following Hybrid Visceral Debranching and Distal Endograft Extension to Repair a Ruptured Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm History A 56-year-old gentleman, who had been referred
Free Esophageal Perforation Following Hybrid Visceral Debranching and Distal Endograft Extension to Repair a Ruptured Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm History A 56-year-old gentleman, who had been referred
Small bowel atresia. Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families
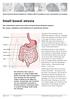 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Small bowel atresia This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital explains the causes, symptoms and treatment
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Small bowel atresia This information sheet from Great Ormond Street Hospital explains the causes, symptoms and treatment
Emergency Approach to the Subclavian and Innominate Vessels
 Emergency Approach to the Subclavian and Innominate Vessels Joseph J. Amato, M.D., Robert M. Vanecko, M.D., See Tao Yao, M.D., and Milton Weinberg, Jr., M.D. T he operative approach to an acutely injured
Emergency Approach to the Subclavian and Innominate Vessels Joseph J. Amato, M.D., Robert M. Vanecko, M.D., See Tao Yao, M.D., and Milton Weinberg, Jr., M.D. T he operative approach to an acutely injured
Dissection: The Fetal Pig
 Lab Exercise Dissection: The Fetal Pig Objectives - To learn some of anatomical structures of the fetal pig. - To be able to make contrasts and comparisons of structures between different animal phyla
Lab Exercise Dissection: The Fetal Pig Objectives - To learn some of anatomical structures of the fetal pig. - To be able to make contrasts and comparisons of structures between different animal phyla
Gastric transposition in infants and children
 DOI 10.1007/s00383-010-2736-9 REVIEW ARTICLE Gastric transposition in infants and children Robert A. Cowles Arnold G. Coran Accepted: 6 September 2010 Ó Springer-Verlag 2010 Abstract The loss of esophageal
DOI 10.1007/s00383-010-2736-9 REVIEW ARTICLE Gastric transposition in infants and children Robert A. Cowles Arnold G. Coran Accepted: 6 September 2010 Ó Springer-Verlag 2010 Abstract The loss of esophageal
Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body
 1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
1-1 Chapter 1 An Introduction to the Human Body Anatomy science of structure relationships revealed by dissection (cutting apart) Physiology science of body functions Levels of Organization Chemical Cellular
THE DESCENDING THORACIC AORTA
 Intercostal Arteries and Veins Each intercostal space contains a large single posterior intercostal artery and two small anterior intercostal arteries. The anterior intercostal arteries of the lower spaces
Intercostal Arteries and Veins Each intercostal space contains a large single posterior intercostal artery and two small anterior intercostal arteries. The anterior intercostal arteries of the lower spaces
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
Foker technique for long-gap oesophageal atresia
 Issue date: January 2006 Foker technique for long-gap oesophageal atresia Understanding NICE guidance information for parents and carers considering the procedure, and for the public Information about
Issue date: January 2006 Foker technique for long-gap oesophageal atresia Understanding NICE guidance information for parents and carers considering the procedure, and for the public Information about
Case report Esophageal lung: a rare case of communicating bronchopulmonary foregut malformation
 Case report Esophageal lung: a rare case of communicating bronchopulmonary foregut malformation 1 Dr.Varsha Rathi, 2 Dr. Saurabh Deshpande*, 3 Dr.Almas Nazim, 4 Dr.Shilpa Domkundwar 1 Professor, Department
Case report Esophageal lung: a rare case of communicating bronchopulmonary foregut malformation 1 Dr.Varsha Rathi, 2 Dr. Saurabh Deshpande*, 3 Dr.Almas Nazim, 4 Dr.Shilpa Domkundwar 1 Professor, Department
DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region.
 1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
T treat empyema, although modern day thoracic
 The Schede and Modern Thoracoplasty Benjamin J. Pomerantz, Joseph C. Cleveland, Jr, and Marvin Pomerantz THORACOPLASTY-GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS horacoplasty evolved as a procedure designed to T treat empyema,
The Schede and Modern Thoracoplasty Benjamin J. Pomerantz, Joseph C. Cleveland, Jr, and Marvin Pomerantz THORACOPLASTY-GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS horacoplasty evolved as a procedure designed to T treat empyema,
Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management
 Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management Mary Finn Gillian Lieberman, MD Primary Care Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School April 2014 Outline I. Definition and Epidemiology
Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management Mary Finn Gillian Lieberman, MD Primary Care Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School April 2014 Outline I. Definition and Epidemiology
Anatomy of the Lungs. Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy
 Anatomy of the Lungs Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy 1 Pulmonary Function Ventilation and Respiration Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Respiration is the process of gas
Anatomy of the Lungs Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy 1 Pulmonary Function Ventilation and Respiration Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Respiration is the process of gas
Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery
 A Doubtful Cause of Symptoms Thomas P. Comer, M.D., Malvin Weinberger, M.D., and Howard D. Sirak, M.D. ABSTRACT Ten patients with surgically treated aberrant right subclavian artery are reviewed. In half,
A Doubtful Cause of Symptoms Thomas P. Comer, M.D., Malvin Weinberger, M.D., and Howard D. Sirak, M.D. ABSTRACT Ten patients with surgically treated aberrant right subclavian artery are reviewed. In half,
Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings. M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid
 Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases The clinical signs of acquired
Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases Imaging approaches and findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Acquired pediatric esophageal diseases The clinical signs of acquired
Endoscopic Treatment of Luminal Perforations and Leaks
 Endoscopic Treatment of Luminal Perforations and Leaks Ali A. Siddiqui, MD Professor of Medicine Director of Interventional Endoscopy Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia, PA When Do You Suspect a Luminal
Endoscopic Treatment of Luminal Perforations and Leaks Ali A. Siddiqui, MD Professor of Medicine Director of Interventional Endoscopy Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia, PA When Do You Suspect a Luminal
Chest and cardiovascular
 Module 1 Chest and cardiovascular A. Doss and M. J. Bull 1. Regarding the imaging modalities of the chest: High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) uses a slice thickness of 4 6 mm to identify mass lesions
Module 1 Chest and cardiovascular A. Doss and M. J. Bull 1. Regarding the imaging modalities of the chest: High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) uses a slice thickness of 4 6 mm to identify mass lesions
Anatomy The study of the body's structure.
 Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N
 Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
The posterolateral thoracotomy is still probably the
 Posterolateral Thoracotomy Jean Deslauriers and Reza John Mehran The posterolateral thoracotomy is still probably the most commonly used incision in general thoracic surgery. It provides not only excellent
Posterolateral Thoracotomy Jean Deslauriers and Reza John Mehran The posterolateral thoracotomy is still probably the most commonly used incision in general thoracic surgery. It provides not only excellent
Procedure: Chest Tube Placement (Tube Thoracostomy)
 Procedure: Chest Tube Placement (Tube Thoracostomy) Basic Information: The insertion and placement of a chest tube into the pleural cavity for the purpose of removing air, blood, purulent drainage, or
Procedure: Chest Tube Placement (Tube Thoracostomy) Basic Information: The insertion and placement of a chest tube into the pleural cavity for the purpose of removing air, blood, purulent drainage, or
Clinical Case Presentation. Jared B. Smith, M.D. Surgical Grand Rounds, August 21, 2006
 Clinical Case Presentation Jared B. Smith, M.D. Surgical Grand Rounds, August 21, 2006 Clinical History CC: Can t swallow anything HPI: 50 y.o. male from western Colorado, greater than 2 years of emesis
Clinical Case Presentation Jared B. Smith, M.D. Surgical Grand Rounds, August 21, 2006 Clinical History CC: Can t swallow anything HPI: 50 y.o. male from western Colorado, greater than 2 years of emesis
Anal Atresia FACTS: There is no known cause for anal atresia. Children with anal atresia can lead very happy lives post surgery!
 Anal Atresia FACTS: Anal atresia affects 1 in 5,000 births and is slightly more common in boys. There is no known cause for this condition. With anal atresia, any of the following can occur: The anal passage
Anal Atresia FACTS: Anal atresia affects 1 in 5,000 births and is slightly more common in boys. There is no known cause for this condition. With anal atresia, any of the following can occur: The anal passage
90 th Annual Meeting The American Association for Thoracic Surgery May 1, 2010 Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Slide Tracheoplasty
 90 th Annual Meeting The American Association for Thoracic Surgery May 1, 2010 Toronto, Ontario, Canada Congenital Skills Course Slide Tracheoplasty Carl Lewis Backer, MD A.C. Buehler Professor of Surgery
90 th Annual Meeting The American Association for Thoracic Surgery May 1, 2010 Toronto, Ontario, Canada Congenital Skills Course Slide Tracheoplasty Carl Lewis Backer, MD A.C. Buehler Professor of Surgery
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
TRACHEOSTOMY. Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion
 TRACHEOSTOMY Definition Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion Indications for tracheostomy 1-upper airway obstruction with stridor, air hunger,
TRACHEOSTOMY Definition Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion Indications for tracheostomy 1-upper airway obstruction with stridor, air hunger,
Topics for discussion. Pediatric General Surgery. Physiology. Surgical Newborns. Neonatal Intestinal Obstruction
 Topics for discussion Pediatric General Surgery Professor General & Thoracic Surgery What makes Pediatric Surgery unique? Neonatal intestinal obstruction Abdominal wall defects Inguinal hernias Appendicitis
Topics for discussion Pediatric General Surgery Professor General & Thoracic Surgery What makes Pediatric Surgery unique? Neonatal intestinal obstruction Abdominal wall defects Inguinal hernias Appendicitis
B the mid-l940s, pulmonary resection and thoracoplasty
 - Thoracoplasty in the New Millennium Cleveland W. Lewis, Jr, MD, and Walter G. Wolfe, MD efore the development of antituberculosis drugs in B the mid-l940s, pulmonary resection and thoracoplasty stood
- Thoracoplasty in the New Millennium Cleveland W. Lewis, Jr, MD, and Walter G. Wolfe, MD efore the development of antituberculosis drugs in B the mid-l940s, pulmonary resection and thoracoplasty stood
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System
 Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX
 SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX 9 In the pig s digestive tract, food flows in only one direction from mouth to anus.this allows for greatly specialized sections that can act independently of each other.
SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX 9 In the pig s digestive tract, food flows in only one direction from mouth to anus.this allows for greatly specialized sections that can act independently of each other.
Tracheo-oesophageal fistula and oesophageal atresia:
 Thorax (197), 25, 46. Tracheo-oesophageal fistula and oesophageal atresia: results of 3 years' experience MICHAEL P. HOLDEN and GEOFFREY H. WOOLER Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, The General Infirmary
Thorax (197), 25, 46. Tracheo-oesophageal fistula and oesophageal atresia: results of 3 years' experience MICHAEL P. HOLDEN and GEOFFREY H. WOOLER Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, The General Infirmary
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content
 Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Ch16: Respiratory System
 Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy
 Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Tracheoesophageal fistula repair in a premature infant with VACTERL, infradiaphragmatic TAPVR, and pulmonary hypertension.
 PBLD Table # 26 Tracheoesophageal fistula repair in a premature infant with VACTERL, infradiaphragmatic TAPVR, and pulmonary hypertension. Moderators: Annette Schure, MD; Lauren Welsh, MD Objectives: 1.
PBLD Table # 26 Tracheoesophageal fistula repair in a premature infant with VACTERL, infradiaphragmatic TAPVR, and pulmonary hypertension. Moderators: Annette Schure, MD; Lauren Welsh, MD Objectives: 1.
STERNUM. Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts:
 STERNUM Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts: 1-Manubrium sterni 2-Body of the sternum 3- Xiphoid process The body of the sternum articulates above
STERNUM Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts: 1-Manubrium sterni 2-Body of the sternum 3- Xiphoid process The body of the sternum articulates above
Imaging features of VACTERL association
 Imaging features of VACTERL association Poster No.: C-2039 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit J. Y. Kim; Dae-jeon/KR Pediatric, Cardiovascular system, Gastrointestinal
Imaging features of VACTERL association Poster No.: C-2039 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit J. Y. Kim; Dae-jeon/KR Pediatric, Cardiovascular system, Gastrointestinal
Development of the Digestive System. W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong.
 Development of the Digestive System W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. Organization of the GI tract: Foregut (abdominal part) supplied by coeliac trunk; derivatives include
Development of the Digestive System W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. Organization of the GI tract: Foregut (abdominal part) supplied by coeliac trunk; derivatives include
A simple technique of oblique anastomosis can prevent stricture formation in primary repair of esophageal atresia
 Journal of Pediatric Surgery (2012) 47, 1767 1771 www.elsevier.com/locate/jpedsurg Operative Techniques A simple technique of oblique anastomosis can prevent stricture formation in primary repair of esophageal
Journal of Pediatric Surgery (2012) 47, 1767 1771 www.elsevier.com/locate/jpedsurg Operative Techniques A simple technique of oblique anastomosis can prevent stricture formation in primary repair of esophageal
Tracheal stenosis in infants and children is typically characterized
 Slide Tracheoplasty for Congenital Tracheal Stenosis Peter B. Manning, MD Tracheal stenosis in infants and children is typically characterized by the presence of complete cartilaginous tracheal rings and
Slide Tracheoplasty for Congenital Tracheal Stenosis Peter B. Manning, MD Tracheal stenosis in infants and children is typically characterized by the presence of complete cartilaginous tracheal rings and
Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology PHA322.10 D. Matesic, Spring, 2012 Class Notes Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology Levels of Structural Organization Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and
Human Anatomy & Physiology PHA322.10 D. Matesic, Spring, 2012 Class Notes Introduction to A & P Medical Terminology Levels of Structural Organization Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and
11.1 The Aortic Arch General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta
 456 11 Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta 11.1 The Aortic Arch 11.1.1 General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgery of the is one of the most challenging areas of cardiac and vascular surgery,
456 11 Surgical Anatomy of the Aorta 11.1 The Aortic Arch 11.1.1 General Anatomy of the Ascending Aorta and the Aortic Arch Surgery of the is one of the most challenging areas of cardiac and vascular surgery,
Abstract Introduction We present the experiences from two European centers performing the
 Original Article 3 The Foker Technique (FT) and Kimura Advancement (KA) for the Treatment of Children with Long-Gap Esophageal Atresia (LGEA): Lessons Learned at Two European Centers Mariusz Sroka 1 Robin
Original Article 3 The Foker Technique (FT) and Kimura Advancement (KA) for the Treatment of Children with Long-Gap Esophageal Atresia (LGEA): Lessons Learned at Two European Centers Mariusz Sroka 1 Robin
Anorectal Malformations
 CHAPTER Anorectal Malformations P. Stephen Almond Incidence The incidence of imperforate anus is one in every 5,000 live births, with cloaca malformations accounting for 10%. Males (58%) are more commonly
CHAPTER Anorectal Malformations P. Stephen Almond Incidence The incidence of imperforate anus is one in every 5,000 live births, with cloaca malformations accounting for 10%. Males (58%) are more commonly
The arterial switch operation has been the accepted procedure
 The Arterial Switch Procedure: Closed Coronary Artery Transfer Edward L. Bove, MD The arterial switch operation has been the accepted procedure for the repair of transposition of the great arteries (TGA)
The Arterial Switch Procedure: Closed Coronary Artery Transfer Edward L. Bove, MD The arterial switch operation has been the accepted procedure for the repair of transposition of the great arteries (TGA)
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Unusual cause of pneumoperitoneum in a spontaneously breathing 1-day-old term infant
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Unusual cause of pneumoperitoneum in a spontaneously breathing 1-day-old term infant March 2012 2 Berger TM, Winiker H, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (BTM), Pediatric
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Unusual cause of pneumoperitoneum in a spontaneously breathing 1-day-old term infant March 2012 2 Berger TM, Winiker H, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (BTM), Pediatric
Lung Function Abnormalities Following Repaired Esophageal Atresia and Tracheoesophageal Fistula
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No.4, December 2005 Lung Function Abnormalities Following Repaired Esophageal Atresia and Tracheoesophageal Fistula Hanaa Banjar, MD, FRCPC* Introduction: Esophageal
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No.4, December 2005 Lung Function Abnormalities Following Repaired Esophageal Atresia and Tracheoesophageal Fistula Hanaa Banjar, MD, FRCPC* Introduction: Esophageal
Pediatric Surgery MUHC MCH Siste. Objectives of Training
 Preamble A rotation in Pediatric Surgery must give residents the opportunity to become familiar with the unique needs of infants and children as surgical patients. Some of the surgical diseases encountered
Preamble A rotation in Pediatric Surgery must give residents the opportunity to become familiar with the unique needs of infants and children as surgical patients. Some of the surgical diseases encountered
Lines and tubes. 1 Nasogastric tubes Endotracheal tubes Central lines Permanent pacemakers Chest drains...
 Lines and tubes 1 Nasogastric tubes... 15 2 Endotracheal tubes.... 19 3 Central lines... 21 4 Permanent pacemakers.... 25 5 Chest drains... 30 This page intentionally left blank 1 Nasogastric tubes Background
Lines and tubes 1 Nasogastric tubes... 15 2 Endotracheal tubes.... 19 3 Central lines... 21 4 Permanent pacemakers.... 25 5 Chest drains... 30 This page intentionally left blank 1 Nasogastric tubes Background
Development of the Digestive System. W.S. O The University of Hong Kong
 Development of the Digestive System W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Plan for the GI system Then GI system in the abdomen first develops as a tube suspended by dorsal and ventral mesenteries. Blood
Development of the Digestive System W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Plan for the GI system Then GI system in the abdomen first develops as a tube suspended by dorsal and ventral mesenteries. Blood
Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes. Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center
 Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Neonatal and Pediatric Tracheostomy Tracheostomy
Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Neonatal and Pediatric Tracheostomy Tracheostomy
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II
 Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of this session, the student should be able to: Identify and discuss clinical anatomy of mediastinum such as its deflection,
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of this session, the student should be able to: Identify and discuss clinical anatomy of mediastinum such as its deflection,
Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body
 Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine
 Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine Word Parts: Roots Medical Terminology Language in the medical field is more extensive than the languages in many other fields. Rapid advances in science and
Medical Terminology: The Language of Medicine Word Parts: Roots Medical Terminology Language in the medical field is more extensive than the languages in many other fields. Rapid advances in science and
Controversies in management of squamous esophageal cancer
 2015.06.12 12.47.48 Page 4(1) IS-1 Controversies in management of squamous esophageal cancer C S Pramesh Thoracic Surgery, Department of Surgical Oncology, Tata Memorial Centre, India In Asia, squamous
2015.06.12 12.47.48 Page 4(1) IS-1 Controversies in management of squamous esophageal cancer C S Pramesh Thoracic Surgery, Department of Surgical Oncology, Tata Memorial Centre, India In Asia, squamous
ABERRANT RIGHT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY AND CALCIFIED ANEURYSM OF. Jose Rubio-Alvarez, Juan Sierra-Quiroga, Belen Adrio Nazar and Javier Garcia Carro.
 ABERRANT RIGHT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY AND CALCIFIED ANEURYSM OF KOMMERELL S DIVERTICULUM : AN ALTERNATIVE APPROACH. Jose Rubio-Alvarez, Juan Sierra-Quiroga, Belen Adrio Nazar and Javier Garcia Carro. Department
ABERRANT RIGHT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY AND CALCIFIED ANEURYSM OF KOMMERELL S DIVERTICULUM : AN ALTERNATIVE APPROACH. Jose Rubio-Alvarez, Juan Sierra-Quiroga, Belen Adrio Nazar and Javier Garcia Carro. Department
Combined Collis-Nissen Reconstruction. of the esophagogastric junction at. Mark B. Orringer, M.D., and Herbert Sloan, M.D.
 Combined Collis-Nissen Reconstruction of the Esophagogastric Junction Mark B. Orringer, M.D., and Herbert Sloan, M.D. ABSTRACT Recent reports have indicated that combined Collis-Belsey reconstruction of
Combined Collis-Nissen Reconstruction of the Esophagogastric Junction Mark B. Orringer, M.D., and Herbert Sloan, M.D. ABSTRACT Recent reports have indicated that combined Collis-Belsey reconstruction of
- Tamara Wahbeh. - Fareed Khdair. 0 P a g e
 -1 - Tamara Wahbeh - - Fareed Khdair 0 P a g e GI Embryology Note: I included everything in the records and slides; anything in the slide not included in this sheet was not mentioned by the doctor during
-1 - Tamara Wahbeh - - Fareed Khdair 0 P a g e GI Embryology Note: I included everything in the records and slides; anything in the slide not included in this sheet was not mentioned by the doctor during
AATS Focus on Thoracic Surgery: Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy: Are We Still Getting Better in 2017?
 AATS Focus on Thoracic Surgery: Mastering Surgical Innovation Las Vegas, NV October 28, 2017 Session VIII: Video Session Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy: Are We Still Getting Better in 2017? James D.
AATS Focus on Thoracic Surgery: Mastering Surgical Innovation Las Vegas, NV October 28, 2017 Session VIII: Video Session Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy: Are We Still Getting Better in 2017? James D.
T HERE is an unusual and interesting variety of craniosynostosis in
 SURGICAL TREATMENT OF CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF THE CORONAL AND METOPIC SUTURES TECHNICAL NOTE DONALD D. MATSON, M.D. Neurosurgical Service, The Children's Medical Center, and Deparlment of Surgery, Itarvard
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF THE CORONAL AND METOPIC SUTURES TECHNICAL NOTE DONALD D. MATSON, M.D. Neurosurgical Service, The Children's Medical Center, and Deparlment of Surgery, Itarvard
Chapter 3: Thorax. Thorax
 Chapter 3: Thorax Thorax Thoracic Cage I. Thoracic Cage Osteology A. Thoracic Vertebrae Basic structure: vertebral body, pedicles, laminae, spinous processes and transverse processes Natural kyphotic shape,
Chapter 3: Thorax Thorax Thoracic Cage I. Thoracic Cage Osteology A. Thoracic Vertebrae Basic structure: vertebral body, pedicles, laminae, spinous processes and transverse processes Natural kyphotic shape,
Fetal Pig Dissection Day 2 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 Name: Date: Period: Fetal Pig Dissection Day 2 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Dissection Roles (choose a different role from Day 1): Recorder reads directions out loud to group and records answers
Name: Date: Period: Fetal Pig Dissection Day 2 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Dissection Roles (choose a different role from Day 1): Recorder reads directions out loud to group and records answers
Manual on Preparation of Tissue for Neonatal Skills Course. Version 1.0_2018. Prepared by: Haitham Dagash. MBBS, FRCSEd (Paed)
 Manual on Preparation of Tissue for Neonatal Skills Course Version 1.0_2018 Prepared by: Haitham Dagash MBBS, FRCSEd (Paed) University of Leicester and Leicester Infirmary Hospital Prof.Kokila Lakhoo PhD,FRCS(ENG+EDIN),FCS(SA),FCS(SA:PAED),MRCPCH,MBCHB
Manual on Preparation of Tissue for Neonatal Skills Course Version 1.0_2018 Prepared by: Haitham Dagash MBBS, FRCSEd (Paed) University of Leicester and Leicester Infirmary Hospital Prof.Kokila Lakhoo PhD,FRCS(ENG+EDIN),FCS(SA),FCS(SA:PAED),MRCPCH,MBCHB
CARCINOMA IN A RECONSTRUCTED (ESOPHAGUS. By PERCY H. JAYES, M.B., F.R.C.S. From The Queen Victoria Hospital, East Grinstead
 CARCINOMA IN A RECONSTRUCTED (ESOPHAGUS By PERCY H. JAYES, M.B., F.R.C.S. From The Queen Victoria Hospital, East Grinstead THE purpose of this short paper is twofold: first, to report a condition which
CARCINOMA IN A RECONSTRUCTED (ESOPHAGUS By PERCY H. JAYES, M.B., F.R.C.S. From The Queen Victoria Hospital, East Grinstead THE purpose of this short paper is twofold: first, to report a condition which
Right lung. -fissures:
 -Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
-Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery Aneurysm
 Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery William S. Stoney, M.D., William C. Alford, Jr., M.D., George R. Burrus, M.D., and Clarence S. Thomas, Jr., M.D. ABSTRACT Ten patients with aneurysm of an aberrant right
Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery William S. Stoney, M.D., William C. Alford, Jr., M.D., George R. Burrus, M.D., and Clarence S. Thomas, Jr., M.D. ABSTRACT Ten patients with aneurysm of an aberrant right
THE SURGEON S LIBRARY
 THE SURGEON S LIBRARY THE HISTORY AND SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE VAGUS NERVE Lee J. Skandalakis, M.D., Chicago, Illinois, Stephen W. Gray, PH.D., and John E. Skandalakis, M.D., PH.D., F.A.C.S., Atlanta, Georgia
THE SURGEON S LIBRARY THE HISTORY AND SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE VAGUS NERVE Lee J. Skandalakis, M.D., Chicago, Illinois, Stephen W. Gray, PH.D., and John E. Skandalakis, M.D., PH.D., F.A.C.S., Atlanta, Georgia
Lung & Pleura. The Topics :
 Lung & Pleura The Topics : The Trachea. The Bronchi. The Brochopulmonary Segments. The Lungs. The Hilum. The Pleura. The Surface Anatomy Of The Lung & Pleura. The Root & Hilum. - first of all, the lung
Lung & Pleura The Topics : The Trachea. The Bronchi. The Brochopulmonary Segments. The Lungs. The Hilum. The Pleura. The Surface Anatomy Of The Lung & Pleura. The Root & Hilum. - first of all, the lung
Chapter One Study Guide Answers
 Chapter One Study Guide Answers I. Aids to Understanding Words Append to hang something Cardi heart Cran helmet pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain. Dors back Homeo same -logy
Chapter One Study Guide Answers I. Aids to Understanding Words Append to hang something Cardi heart Cran helmet pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain. Dors back Homeo same -logy
