Standard Rotation: Neonatal Intensive Care at UHB or KCHC Junior Resident. Residents: PL-1 pediatrics, EM-1 or EM-2 emergency medicine residents
|
|
|
- Cordelia Bishop
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Standard Rotation: Neonatal Intensive Care at UHB or KCHC Junior Resident Residents: PL-1 pediatrics, EM-1 or EM-2 emergency medicine residents Prerequisites: Successful completion of NRP course with certification Primary Goals for this Rotation GOAL: Perinatal Prevention. Understand the pediatrician's role in and be an active advocate for programs to reduce morbidity and mortality from high-risk pregnancies. 1 : Identify and describe strategies to reduce fetal and neonatal mortality, including use of group B strep prophylaxis and perinatal steroids. 2 : Understand and know how to access: 1 :Basic vital statistics that apply to newborns (neonatal and perinatal mortality, etc) 2 :Prenatal services available in one's region 3 :Tests commonly used by obstetricians to measure fetal well-being 3 : Recognize potential adverse outcomes for the fetus and neonate of common prenatal and perinatal conditions, and demonstrate the pediatrician's role in assessment and management strategies to minimize the risk to the fetus and/or newborn in the following situations: 1. Maternal infections/exposure to infection during pregnancy including HIV, tuberculosis, varicella, rubella, hepatitis, and others 2. Fetal exposure to harmful substances (alcohol, tobacco, environmental toxins, medications, street drugs) 3. Maternal insulin-dependent diabetes and pregnancy-induced glucose intolerance 4. Multiple gestation 5. Placental abnormalities (placenta previa, abruption, etc) 6. Pre-eclampsia, eclampsia 7. Chorioamnionitis 8. Polyhydramnios 9. Oligohydramnios 10. Premature labor, premature and/or prolonged ruptured membranes 11. Complications of anesthesia and common delivery practices (e.g., Caesarian, vacuum, forceps assisted, epidural, induction of labor) 12. Fetal distress during delivery 13. Postpartum maternal fever or infection 14. Blood group incompatibilities 15. Other common maternal conditions having implications for the infant s - 1 -
2 health such as lupus, HELLP syndrome, maternal thrombocytopenia GOAL: Resuscitation and Stabilization. With supervision, assess, resuscitate and stabilize critically ill neonates. 1 : Explain and perform steps in resuscitation and stabilization, particularly airway management, vascular access, volume resuscitation, indications for and techniques of chest compressions, resuscitative pharmacology and management of meconium deliveries. 2 : Describe the common causes of acute deterioration in previously stable NICU patients. 3 : Function appropriately in neonatal resuscitations as part of the NICU team by: 1. Participating in resuscitations 2. Completing Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) 3. Using neonatal resuscitation skills and drugs appropriately GOAL: Common Signs and Symptoms. Evaluate and manage, under the supervision of a neonatologist, common signs and symptoms of disease in premature and ill newborns. 1 : Under supervision, evaluate and manage patients with the signs and symptoms that present commonly in the NICU. 1 :General: feeding problems, history of maternal infection or exposure, hyperthermia, hypothermia, intrauterine growth failure, irritability, jitteriness, large for gestational age, lethargy, poor post-natal weight gain, prematurity 2 :Cardiorespiratory: apnea, bradycardia, cyanosis, dehydration, heart murmur, hypertension, hypotension, hypovolemia, poor pulses, respiratory distress (flaring, grunting, tachypnea), shock 3 :Dermatologic: birthmarks, common skin rashes/conditions, discharge and/or inflammation of the umbilicus, hyper- and hypopigmented lesions, proper skin care for extreme prematures 4 :GI/surgical: abdominal mass, bloody stools, diarrhea, distended abdomen, failure to pass stool, gastric retention or reflux, hepatosplenomegaly, vomiting 5 :Genetic/metabolic: apparent congenital defect or dysmorphic syndrome, metabolic derangements (glucose, calcium, acid-base, urea, amino acids, etc.) 6 :Hematologic: abnormal bleeding, anemia, jaundice in a premature or seriously ill neonate, neutropenia, petechiae, polycythemia, - 2 -
3 thrombocytopenia 7 :Musculoskeletal: birth defects and deformities, birth trauma and related fractures and soft tissue injuries, dislocations 8 :Neurologic: birth trauma related nerve damage, early signs of neurologic impairment, hypotonia, macrocephaly, microcephaly, seizures, spina bifida 9 :Parental stress and dysfunction: anxiety disorders, poor attachment, postpartum depression, substance abuse, teen parents 10 :Renal/urologic: abnormal genitalia, edema, hematuria, oliguria, proteinuria, renal mass, urinary retention GOAL: Common Conditions. Recognize and manage, under the supervision of a neonatologist, the common conditions in patients encountered in the NICU. 1 : Under appropriate supervision, evaluate and manage patients with conditions that present commonly in the NICU: 1. General: congenital malformations 2. Cardiovascular: cardiomyopathy, congenital heart disease (cyanotic and acyanotic), congestive heart failure, dysrhythmias (e.g. supraventricular tachyarhythmia, complete heart block), pericarditis 3. Genetic, endocrine disorders: abnormalities discovered from neonatal screening programs as they affect the premature infant, common chromosomal anomalies (Trisomy 13, 18, 21, Turner's), inborn errors of metabolism, infant of a diabetic mother, infant of a mother with thyroid disease, uncommon conditions such as congenital adrenal hyperplasia, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism 4. GI/nutrition: biliary atresia, breast feeding support for mothers and infants with special needs (high risk premature, maternal illness, multiple birth, etc.), complications of umbilical catheterization, gastroesophageal reflux, growth retardation, hepatitis, hyperbilirubinemia, meconium plug, necrotizing enterocolitis, nutritional management of high risk neonates or those with special needs 5. Hematologic conditions: coagulopathy of the newborn, erythroblastosis fetalis, hemophilia, hydrops fetalis, hyperbilirubinemia, splenomegaly 6. Infectious disease: central line infections, Group B Streptococcal infections, hepatitis, herpes simplex, immunization of the premature neonate, infant of mother with HIV, intrauterine viral infections, neonatal sepsis and meningitis, nosocomial infections in the NICU, syphilis, varicella exposure 7. Neurologic disorders: central apnea, CNS malformations, drug withdrawal, hearing loss in high risk newborns (prevention and screening), hydrocephalus, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, intraventricular hemorrhage, retinopathy of prematurity, seizures, - 3 -
4 spina bifida 8. Pulmonary disorders: atelectasis, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, meconium aspiration, persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn, pneumonia, pneumothorax, respiratory distress syndrome, transient tachypnea of the newborn 9. Renal: acute and chronic renal failure, hematuria, hydronephrosis, oliguria, proteinuria 10. Surgery (pre- and post-operative care), diaphragmatic hernia, esophageal or gut atresia, gastroschisis, omphalocele, intestinal obstruction, necrotizing enterocolitis, perforated viscus, volvulus GOAL: Diagnostic Testing. Under the supervision of a neonatologist, order and understand the indications for, limitations of, and interpretation of laboratory and imaging studies unique to the NICU. 1 : Demonstrate understanding of common diagnostic tests and imaging studies used in the NICU by being able to: 1 :Explain the indications for and limitations of each study. 2 :Know or be able to locate readily gestational age-appropriate normal ranges. 3 :Interpret the results in the context of the specific patient. 4 :Discuss therapeutic options for correction of abnormalities. 2 : Use appropriately the following evaluations that may have specific application to neonatal care: 1. Serologic and other studies for transplacental infection 2. Direct and indirect Coomb's tests 3. Neonatal drug screening 4. Cranial ultrasound for intraventricular hemorrhage 5. Abdominal X-rays for placement of umbilical catheter 6. Chest X-rays for endotracheal tube placement, air leak, heart size, and vascularity 3 : Use appropriately the following laboratory tests when indicated for patients in the neonatal intensive care setting: 1. CBC with differential, platelet count, RBC indices 2. Blood chemistries: electrolytes, glucose, calcium, magnesium, phosphate 3. Renal function tests 4. Tests of hepatic function (PT, albumin) and damage (liver enzymes, - 4 -
5 bilirubin) 5. Serologic tests for infection (e.g., hepatitis, HIV) 6. CRP, ESR 7. Therapeutic drug concentrations 8. Coagulation studies: platelets, PT/PTT, fibrinogen, fibrin split products, D-dimers, DIC screen 9. Arterial, capillary, venous and cord blood gases 10. Detection of bacterial, viral, and fungal pathogens 11. Urinalysis 12. CSF analysis 13. Gram stain 14. Stool studies 15. Toxicologic screens/drug levels 16. Other fluid studies (e.g., pleural fluid, joint fluid) 17. Newborn screening tests 4 : Appropriately use the following imaging or radiographic or other studies when indicated for patients in the NICU setting: 1. Chest X-ray 2. Abdominal series 3. Skeletal survey 4. CT scans 5. MRI 6. Nuclear medicine scans 7. Electrocardiogram and echocardiogram 8. Cranial ultrasonography GOAL: Monitoring and Therapeutic Modalities. Understand how to use the physiologic monitoring, special technology and therapeutic modalities used commonly in the care of the fetus and newborn. 1 : Demonstrate understanding of the monitoring techniques and special treatments commonly used in the NICU by being able to: 1. Discuss the indications, contraindications and complications. 2. Describe the general technique for use in infants. 3. Interpret the results of monitoring. 2 : Use appropriately the following monitoring and therapeutic techniques in NICU. 1. Physiologic monitoring of temperature, pulse, respiration, blood pressure - 5 -
6 2. Pulse oximetry 3. Neonatal pain and drug withdrawal scales 3 : Use appropriately the following treatments and techniques in the neonatal intensive care unit under supervision by the attending neonatologist, monitoring effects and anticipating potential complications specific to each procedure. 1. CPAP or assisted ventilation 2. Endotracheal intubation 3. Administration of surfactant 4. Positive pressure ventilation and basic ventilator management 5. Nitric oxide therapy 6. Phototherapy 7. Umbilical arterial and venous catheterization 8. Central hyperalimentation and parenteral nutrition 9. Enteral nutrition 10. Analgesic, sedatives and paralytics 11. Blood and blood product transfusions, including exchange transfusion 12. Vasoactive drugs (pressors and inotropes) 13. Judicious use of antibiotics 14. Administration of medications specific to the needs of the newborn (e.g., Vitamin K) 15. Arterial puncture 16. Venous access by peripheral vein 17. Umbilical artery and vein catheterization 4 : Use appropriate resources to facilitate the transition to home of the technology-dependent neonate. GOAL: Pediatric Competencies in Brief: Demonstrate high standards of professional competence while working with patients in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Competency 1: Patient Care. Provide family-centered patient care that is development- and age-appropriate, compassionate, and effective for the treatment of health problems and the promotion of health
7 1 :Use a logical and appropriate approach to the assessment and daily management of seriously ill neonates and their families, under the guidance of a neonatologist, using evidence-based decision-making and problemsolving skills. 2 :Learn to prioritize patients problems. 3 :Gather essential and accurate information via interviewing parents and performing a complete physical exam on the neonate. 4 :Monitor and follow up on patients appropriately. 5 :Provide emotional, social, and culturally sensitive support to families of NICU infants, including those at home. 6 :Work with other members of the health care team to provide family centered care. Competency 2: Medical Knowledge. Understand the scope of established and evolving biomedical, clinical, epidemiological and socialbehavioral knowledge needed by a pediatrician; demonstrate the ability to acquire, critically interpret and apply this knowledge in patient care. 1 :Demonstrate a commitment to acquiring the knowledge base expected of general pediatricians caring for seriously ill neonates under the guidance of a neonatologist. 2 :Know and/or access medical information efficiently, evaluate it critically, and apply it appropriately to the care of ill newborns Competency 3: Interpersonal Skills and Communication. Demonstrate interpersonal and communication skills that result in information exchange and partnering with patients, their families and professional associates. 1 :Provide effective and sensitive communication with families of infants in the NICU setting. 2 :Function effectively as part of an interdisciplinary team member in the NICU to create and sustain information exchange and teamwork for patient care. 3 :Maintain accurate, timely, organized and legally appropriate medical records in the critical care setting of the NICU. Competency 4: Practice-based Learning and Improvement. Demonstrate knowledge, skills and attitudes needed for continuous self-assessment, using scientific methods and evidence to investigate, evaluate, and improve one's patient care practice
8 1 :Use scientific methods and evidence to investigate, evaluate, and improve one's patient care practice in NICU setting. 2 :Identify personal learning needs, systematically organize relevant information resources for future reference, and plan for continuing acquisition of knowledge and skills. 3 :Learn to identify limitations and ask for help when needed. 4 :Learn to accept feedback and develop plans for self-improvement. Competency 5: Professionalism. Demonstrate a commitment to carrying out professional responsibilities, adherence to ethical principles and sensitivity to diversity. 1 :Demonstrate a commitment to carrying out professional responsibilities while providing care in the NICU setting. 2 :Adhere to ethical and legal principles, and be sensitive to diversity in caring for critically ill newborns. 3 :Establish trusting relationships with parents and staff. 4 :Acknowledge errors and work to minimize them in the future. Competency 6: Systems-Based Practice. Understand how to practice high-quality health care and advocate for patients within the context of the health care system. 1 :Identify key aspects of health care systems, cost control and mechanisms for payment in the NICU setting. 2 :Learn to function as a patient advocate. 3 :Recognize the limits of one's knowledge and expertise and take steps to avoid medical errors. Procedures GOAL: Technical and therapeutic procedures. Describe the following procedures, including how they work and when they should be used; competently perform those commonly used by the pediatrician in the NICU. Arterial puncture Endotracheal intubation Direct laryngoscopy Exchange transfusion: newborn Gastric tube placement (OG/NG) Lumbar puncture Medication delivery: endotracheal - 8 -
9 Pulse oximeter: placement Suctioning: nares, oral pharynx, trachea (newborn) Umbilical artery and vein catheter placement Ventilation: bag-valve-mask Ventilation support: initiation GOAL: Diagnostic and screening procedures. Describe the following tests or procedures, including how they work and when they should be used; competently perform those commonly used by the pediatrician in practice. Monitoring interpretation: cardiac Monitoring interpretation: pulse oximetry Monitoring interpretation: respiratory Monitoring interpretation: Capnometry/end-tidal CO2 Source Adapted from Kittredge, D., Baldwin, C. D., Bar-on, M. E., Beach, P. S., Trimm, R. F. (Eds.). (2004). APA Educational Guidelines for Pediatric Residency. Ambulatory Pediatric Association Website
NEONATAL-PERINATAL MEDICINE ROTATION Competency Based Goals and Objectives
 NEONATAL-PERINATAL MEDICINE ROTATION Competency Based Goals and Objectives Competency 1. Patient Care: Provide family centered patient care that is developmentally and age appropriate, compassionate, and
NEONATAL-PERINATAL MEDICINE ROTATION Competency Based Goals and Objectives Competency 1. Patient Care: Provide family centered patient care that is developmentally and age appropriate, compassionate, and
Pediatric Learning Solutions A clinical education program exclusively for pediatric professionals
 Pediatric Learning Solutions A clinical education program exclusively for pediatric professionals The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the Neonatal CCRN Exam Content
Pediatric Learning Solutions A clinical education program exclusively for pediatric professionals The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the Neonatal CCRN Exam Content
Pediatric Critical Care
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Pediatric Critical Care 1. GOAL: Recognize the critically ill patient and initiate appropriate stabilization and/or resuscitative
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Pediatric Critical Care 1. GOAL: Recognize the critically ill patient and initiate appropriate stabilization and/or resuscitative
Pediatric Learning Solutions course alignment with the Neonatal/Pediatric Specialty Examination Detailed Content Outline.
 Pediatric Learning Solutions course alignment with the Neonatal/Pediatric Specialty Examination Detailed Content Outline. The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the
Pediatric Learning Solutions course alignment with the Neonatal/Pediatric Specialty Examination Detailed Content Outline. The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the
Lectures 4 Early fetal assessment, screening, ultrasound and treatment modalities during pregnancy. II. Asphyxia and Resuscitation (3 lectures)...
 Outline of a 2 year Neonatology educational course (80 lectures) PLUS 2 graduate level courses (GENETICS and BIOSTATISTICS & EPIDEMIOLOGY Approximate Percent in Examination I. Maternal-Fetal Medicine (6
Outline of a 2 year Neonatology educational course (80 lectures) PLUS 2 graduate level courses (GENETICS and BIOSTATISTICS & EPIDEMIOLOGY Approximate Percent in Examination I. Maternal-Fetal Medicine (6
Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia
 Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia Faculty: John Heaton, M.D. GOAL: Maintenance of Airway Patency and Oxygenation. Recognize and manage upper airway obstruction and desaturation. Recognize and manage upper
Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia Faculty: John Heaton, M.D. GOAL: Maintenance of Airway Patency and Oxygenation. Recognize and manage upper airway obstruction and desaturation. Recognize and manage upper
Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems
 Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems Respiratory Distress Occurs in about 7% of infants Clinical presentation includes: Apnea Cyanosis Grunting Inspiratory stridor Nasal flaring Poor feeding Tachypnea
Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems Respiratory Distress Occurs in about 7% of infants Clinical presentation includes: Apnea Cyanosis Grunting Inspiratory stridor Nasal flaring Poor feeding Tachypnea
Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in Please DO NOT mail or fax this form to the CPQCC Data Center. This form is for internal use ONLY.
 Selection Criteria Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in 2016 To be eligible, you MUST answer YES to at least one of the possible criteria (A-C) A. 401 1500 grams o Yes B. GA range 22 0/7 31 6/7
Selection Criteria Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in 2016 To be eligible, you MUST answer YES to at least one of the possible criteria (A-C) A. 401 1500 grams o Yes B. GA range 22 0/7 31 6/7
The high risk neonate
 The high risk neonate Infant classification by gestational (postmenstrual) age Preterm. Less than 37 completed weeks (259 days). Term. Thirty-seven to 416/7 weeks (260-294 days). Post-term. Forty-two weeks
The high risk neonate Infant classification by gestational (postmenstrual) age Preterm. Less than 37 completed weeks (259 days). Term. Thirty-seven to 416/7 weeks (260-294 days). Post-term. Forty-two weeks
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Genetics
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Genetics 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing genetic disease, and in counseling and screening
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Genetics 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing genetic disease, and in counseling and screening
: Provide cardiovascular preventive counseling to parents and patients with specific cardiac diseases about:
 Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland Cardiology Primary Goals for this Rotation 5.13 GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Cardiovascular). Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing
Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland Cardiology Primary Goals for this Rotation 5.13 GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Cardiovascular). Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Skills Checklist
 _ XXX-XX- Print Name Last 4 of SS # Date Completed Directions Please circle a value for each question to provide us and the interested facilities with an assessment of your clinical experience. These values
_ XXX-XX- Print Name Last 4 of SS # Date Completed Directions Please circle a value for each question to provide us and the interested facilities with an assessment of your clinical experience. These values
COMPETENCY BASED CURRICULUM FOR PEDIATRIC RESIDENCY EDUCATION TERM NEWBORN NURSERY AT KCHC OR UHB JUNIOR RESIDENT
 Standard Rotation: Term Newborn Nursery at KCHC or UHB Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1 level, Family Medicine residents at the PGY 1 or 2 level. Prerequisites: none Patient Care: Residents must
Standard Rotation: Term Newborn Nursery at KCHC or UHB Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1 level, Family Medicine residents at the PGY 1 or 2 level. Prerequisites: none Patient Care: Residents must
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Pulmonary
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Pulmonary 1. GOAL: Diagnose and manage patients with asthma. 2. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Pulmonary 1. GOAL: Diagnose and manage patients with asthma. 2. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing
Experience. Initials Medical Staffing Network Rev. 06/15 F01201 NNICU 2 of 5
 Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Self Assessment Directions Please circle a value for each question to provide us and the interested facilities with an assessment of your clinical experience. These values
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Self Assessment Directions Please circle a value for each question to provide us and the interested facilities with an assessment of your clinical experience. These values
TABLE I-1: RESIDENT INFANT DEATHS PER 1,000 LIVE BIRTHS, BY RACE AND ETHNICITY, FLORIDA AND UNITED STATES, CENSUS YEARS AND
 TABLE I-1: RESIDENT INFANT DEATHS PER 1,000 LIVE BIRTHS, BY RACE AND ETHNICITY, FLORIDA AND UNITED STATES, CENSUS YEARS 1970-2000 AND 2004-2014 FLORIDA 1 UNITED STATES 1 YEAR WHITE2 BLACK2 HISPANIC3 WHITE2
TABLE I-1: RESIDENT INFANT DEATHS PER 1,000 LIVE BIRTHS, BY RACE AND ETHNICITY, FLORIDA AND UNITED STATES, CENSUS YEARS 1970-2000 AND 2004-2014 FLORIDA 1 UNITED STATES 1 YEAR WHITE2 BLACK2 HISPANIC3 WHITE2
NEONATOLOGY Healthy newborn. Neonatal sequelaes
 NEONATOLOGY Healthy newborn. Neonatal sequelaes Ágnes Harmath M.D. Ph.D. senior lecturer 11. November 2016. Tasks of the neonatologist Prenatal diagnosed condition Inform parents, preparation of necessary
NEONATOLOGY Healthy newborn. Neonatal sequelaes Ágnes Harmath M.D. Ph.D. senior lecturer 11. November 2016. Tasks of the neonatologist Prenatal diagnosed condition Inform parents, preparation of necessary
Product Catalog. Pediatric Learning Solutions. Listing of all current products (as of May, 2013) offered by Children's Hospital Association.
 Product Catalog Pediatric Learning Solutions Listing of all current products (as of May, 2013) offered by Children's Hospital Association. Acquired Heart Disease in Children WBT Acute Respiratory Distress
Product Catalog Pediatric Learning Solutions Listing of all current products (as of May, 2013) offered by Children's Hospital Association. Acquired Heart Disease in Children WBT Acute Respiratory Distress
Emergency Department Suite
 Emergency Department Suite This suite of Pediatric Learning Solutions (PLS) online courseware and curriculums provides 24/7 access to the foundational knowledge and just-in-time job aids clinicians working
Emergency Department Suite This suite of Pediatric Learning Solutions (PLS) online courseware and curriculums provides 24/7 access to the foundational knowledge and just-in-time job aids clinicians working
Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level
 Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level Prerequisites: Any prior pediatric rotations and experience Primary Goals for this
Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level Prerequisites: Any prior pediatric rotations and experience Primary Goals for this
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdomen ultrasound of, 521 522 Abdominal diseases ultrasound in evaluation of, 529 540 gastrointestinal tract disease, 529 536 urinary tract
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdomen ultrasound of, 521 522 Abdominal diseases ultrasound in evaluation of, 529 540 gastrointestinal tract disease, 529 536 urinary tract
Infection. Risk factor for infection ACoRN alerting sign with * Clinical deterioration. Problem List. Respiratory. Cardiovascular
 The ACoRN Process Baby at risk Unwell Risk factors Post-resuscitation requiring stabilization Resuscitation Ineffective breathing Heart rate < 100 bpm Central cyanosis Support Infection Risk factor for
The ACoRN Process Baby at risk Unwell Risk factors Post-resuscitation requiring stabilization Resuscitation Ineffective breathing Heart rate < 100 bpm Central cyanosis Support Infection Risk factor for
Hypoglycaemia of the neonate. Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics
 Hypoglycaemia of the neonate Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics Why is glucose important? It provides 60-70% of energy needs Utilization obligatory by red blood cells, brain and kidney as major source of
Hypoglycaemia of the neonate Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics Why is glucose important? It provides 60-70% of energy needs Utilization obligatory by red blood cells, brain and kidney as major source of
MODULE VII. Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care
 MODULE VII Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care NEONATAL ASPHYXIA About one million deaths per year In Latin America 12% of newborns suffer some degree of asphyxia Main cause of perinatal and neonatal
MODULE VII Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care NEONATAL ASPHYXIA About one million deaths per year In Latin America 12% of newborns suffer some degree of asphyxia Main cause of perinatal and neonatal
Cedars Sinai Medical Center Pediatric Electives
 PE 235.03 MEDICAL GENETICS COURSE CHAIR: John M. Graham, M.D., ScD.. By arrangement - Please contact the Student Coordinator 1. Counseling techniques and the approach to the patient and family with hereditary
PE 235.03 MEDICAL GENETICS COURSE CHAIR: John M. Graham, M.D., ScD.. By arrangement - Please contact the Student Coordinator 1. Counseling techniques and the approach to the patient and family with hereditary
The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine
 The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine Prompt and Personalized Care for Women with Complex Pregnancies A Team of Experts additional training in maternal and fetal complications
The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine Prompt and Personalized Care for Women with Complex Pregnancies A Team of Experts additional training in maternal and fetal complications
MODULE VII. Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care
 MODULE VII Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care NEONATAL ASPHYXIA About one million deaths per year In Latin America 12% of newborns suffer some degree of asphyxia A major cause of perinatal and neonatal
MODULE VII Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care NEONATAL ASPHYXIA About one million deaths per year In Latin America 12% of newborns suffer some degree of asphyxia A major cause of perinatal and neonatal
Pediatric Learning Solutions course alignment with Pediatric CRRN Exam Content Outline. (Note: PLS Courses are in italics under topic area)
 The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the Pediatric CRRN Exam Content Outline. These courses equip candidates with the foundational knowledge necessary to approach
The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the Pediatric CRRN Exam Content Outline. These courses equip candidates with the foundational knowledge necessary to approach
Neonatal Life Support Provider (NLSP) Certification Preparatory Materials
 Neonatal Life Support Provider (NLSP) Certification Preparatory Materials NEONATAL LIFE SUPPORT PROVIDER (NRP) CERTIFICATION TABLE OF CONTENTS NEONATAL FLOW ALGORITHM.2 INTRODUCTION 3 ANTICIPATION OF RESUSCITATION
Neonatal Life Support Provider (NLSP) Certification Preparatory Materials NEONATAL LIFE SUPPORT PROVIDER (NRP) CERTIFICATION TABLE OF CONTENTS NEONATAL FLOW ALGORITHM.2 INTRODUCTION 3 ANTICIPATION OF RESUSCITATION
How to Recognize a Suspected Cardiac Defect in the Neonate
 Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: How to Recognize a Suspected Cardiac Defect in the Neonate https://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcareprofessionals/education/continuing-medical-nursing-education/neonatalnursing-education-briefs/
Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: How to Recognize a Suspected Cardiac Defect in the Neonate https://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcareprofessionals/education/continuing-medical-nursing-education/neonatalnursing-education-briefs/
Subspecialty Inpatient Rotation: Pediatric Oncology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Senior Resident
 Subspecialty Inpatient Rotation: Pediatric Oncology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Senior Resident Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL3 level Prerequisites: Successful completion or waiver
Subspecialty Inpatient Rotation: Pediatric Oncology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Senior Resident Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL3 level Prerequisites: Successful completion or waiver
Interpret clinical and laboratory tests to identify conditions that require surgical intervention, including:
 Pediatric Surgery Note: The goals and objectives described in detail below are not meant to be completed in a single one month block rotation but are meant to be cumulative, culminating in a thorough and
Pediatric Surgery Note: The goals and objectives described in detail below are not meant to be completed in a single one month block rotation but are meant to be cumulative, culminating in a thorough and
Neonatology ICD-10 documentation
 Neonatology documentation Seven key impacts to documentation 1. Disease or disorder site 2. Acuity and/or encounter status of treatment 3. Etiology, causative agent, or disease type and injury/ poisoning
Neonatology documentation Seven key impacts to documentation 1. Disease or disorder site 2. Acuity and/or encounter status of treatment 3. Etiology, causative agent, or disease type and injury/ poisoning
Neonatal ICU Skills Checklist. Applicant Full Legal Name (please print):
 Applicant Full Legal Name (please print): The following checklist is a profile used to assess your clinical efficiency and assist in matching your skills with available assignments. Your employment is
Applicant Full Legal Name (please print): The following checklist is a profile used to assess your clinical efficiency and assist in matching your skills with available assignments. Your employment is
ADMISSION/DISCHARGE FORM FOR INFANTS BORN IN 2019 DO NOT mail or fax this form to the CPQCC Data Center. This form is for internal use ONLY.
 1 Any eligible inborn infant who dies in the delivery room or at any other location in your hospital within 12 hours after birth and prior to admission to the NICU is defined as a "Delivery Room Death."
1 Any eligible inborn infant who dies in the delivery room or at any other location in your hospital within 12 hours after birth and prior to admission to the NICU is defined as a "Delivery Room Death."
Clinical evaluation Jaundice skin and mucous membranes
 JAUNDICE Framework The definition of Neonatal Jaundice Billirubin Metabolism Special characteristic in neonates Dangerous of the Hyperbillirubinemia The diseases in relation with Neonatal Jaundice Objectives:
JAUNDICE Framework The definition of Neonatal Jaundice Billirubin Metabolism Special characteristic in neonates Dangerous of the Hyperbillirubinemia The diseases in relation with Neonatal Jaundice Objectives:
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Endocrinology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Endocrinology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing endocrine dysfunction, and in counseling and
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Endocrinology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing endocrine dysfunction, and in counseling and
BASIC TRAINING Knowledge Guide Neonatal and Perinatal Medicine
 COMMON PRESENTATIONS AND CONDITIONS Basic Trainees will require a sufficient depth of knowledge of these presentations and conditions. Antenatal conditions such as cerebral ventricular dilatation, choroid
COMMON PRESENTATIONS AND CONDITIONS Basic Trainees will require a sufficient depth of knowledge of these presentations and conditions. Antenatal conditions such as cerebral ventricular dilatation, choroid
List of Chapters. 5. Care of the sick child Evidence-based pediatrics (page 77 to 80)
 Illustrated Textbook of Paediatrics, 4th Edition Tom Lissauer, and Graham Clayden, 2012 List of Chapters 1. The child in society 2. History and examination 3. Normal child development, hearing and vision
Illustrated Textbook of Paediatrics, 4th Edition Tom Lissauer, and Graham Clayden, 2012 List of Chapters 1. The child in society 2. History and examination 3. Normal child development, hearing and vision
M3 Pediatric Clerkship
 M3 Pediatric Clerkship The overall goals for the third year Pediatric Clerkship are to educate future physicians to provide competent, effective and compassionate care of patients by developing clinical
M3 Pediatric Clerkship The overall goals for the third year Pediatric Clerkship are to educate future physicians to provide competent, effective and compassionate care of patients by developing clinical
Neonatal sepsis INCIDENCE RISK FACTORS RISK FACTORS 5/18/2015
 Angelica Floren MD.FAAP. Caring for Little Miracles 6 Th Annual Care Of the Sick Newborn Conference Neonatal sepsis Neonatal sepsis is a disease that may start with minimal or nonspecific symptoms and
Angelica Floren MD.FAAP. Caring for Little Miracles 6 Th Annual Care Of the Sick Newborn Conference Neonatal sepsis Neonatal sepsis is a disease that may start with minimal or nonspecific symptoms and
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Neurology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Neurology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing neurological diseases, and in counseling and screening
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Neurology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing neurological diseases, and in counseling and screening
OB Well Baby Nursery Admission (Term) [ ] For specialty focused order sets for your patient, refer to: General
![OB Well Baby Nursery Admission (Term) [ ] For specialty focused order sets for your patient, refer to: General OB Well Baby Nursery Admission (Term) [ ] For specialty focused order sets for your patient, refer to: General](/thumbs/85/91909911.jpg) OB Well Baby Nursery Admission (Term) [3040000234] For specialty focused order sets for your patient, refer to: 3040000424 Neonatal Circumcision Order Set 3040000522 Neonatal Herpes Viral Order Set 3040000524
OB Well Baby Nursery Admission (Term) [3040000234] For specialty focused order sets for your patient, refer to: 3040000424 Neonatal Circumcision Order Set 3040000522 Neonatal Herpes Viral Order Set 3040000524
Guslihan Dasa Tjipta Division of Perinatology Department of Child Health Medical School University of Sumatera Utara
 Guslihan Dasa Tjipta Division of Perinatology Department of Child Health Medical School University of Sumatera Utara 1 Definition Perinatal asphyxia is a fetus/newborn, due to: is an insult to the Lack
Guslihan Dasa Tjipta Division of Perinatology Department of Child Health Medical School University of Sumatera Utara 1 Definition Perinatal asphyxia is a fetus/newborn, due to: is an insult to the Lack
Hypothermia in Neonates with HIE TARA JENDZIO, DNP(C), RN, RNC-NIC
 Hypothermia in Neonates with HIE TARA JENDZIO, DNP(C), RN, RNC-NIC Objectives 1. Define Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) 2. Identify the criteria used to determine if an infant qualifies for therapeutic
Hypothermia in Neonates with HIE TARA JENDZIO, DNP(C), RN, RNC-NIC Objectives 1. Define Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) 2. Identify the criteria used to determine if an infant qualifies for therapeutic
Addendum to the NRP Provider Textbook 6 th Edition Recommendations for specific modifications in the Canadian context
 Addendum to the NRP Provider Textbook 6 th Edition Recommendations for specific modifications in the Canadian context A subcommittee of the Canadian Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) Steering Committee
Addendum to the NRP Provider Textbook 6 th Edition Recommendations for specific modifications in the Canadian context A subcommittee of the Canadian Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) Steering Committee
Ashley Robson Canyon Creek Dr. Mckinney, TX 75070
 1 Ashley Robson 2212 Canyon Creek Dr. Mckinney, TX 75070 September 2 nd 2014 Debra Brandon PhD, RN, CCNS, FAAN Duke University School of Nursing Durham, NC Dear Mrs. Brandon- I would like the opportunity
1 Ashley Robson 2212 Canyon Creek Dr. Mckinney, TX 75070 September 2 nd 2014 Debra Brandon PhD, RN, CCNS, FAAN Duke University School of Nursing Durham, NC Dear Mrs. Brandon- I would like the opportunity
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Gastroenterology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Gastroenterology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the general pediatrician in the assessment and management of patients with
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Gastroenterology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the general pediatrician in the assessment and management of patients with
Credential Maintenance Program
 First Quarter of the Calendar 5 I. COMPETENCIES SHARED BETWEEN CRITICAL AND GENERAL CARE 3 7 0 A. Assess Patient Information 0 2 2. Patient history, for example, immunizations environmental pre-existing
First Quarter of the Calendar 5 I. COMPETENCIES SHARED BETWEEN CRITICAL AND GENERAL CARE 3 7 0 A. Assess Patient Information 0 2 2. Patient history, for example, immunizations environmental pre-existing
Stabilization of the Newborn for Transport. Relevant Disclosure. Learning Objectives
 Stabilization of the Newborn for Transport Arlen Foulks, DO FAAP FACOP Medical Director, CCMH Level II NICU Medical Director, NeoFlight Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Neonatal Perinatal Medicine Section,
Stabilization of the Newborn for Transport Arlen Foulks, DO FAAP FACOP Medical Director, CCMH Level II NICU Medical Director, NeoFlight Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Neonatal Perinatal Medicine Section,
Table 1: The major changes in AHA / AAP neonatal resuscitation guidelines2010 compared to previous recommendations in 2005
 Table 1: The major changes in AHA / AAP neonatal guidelines2010 compared to previous recommendations in 2005 Resuscitation step Recommendations (2005) Recommendations (2010) Comments/LOE 1) Assessment
Table 1: The major changes in AHA / AAP neonatal guidelines2010 compared to previous recommendations in 2005 Resuscitation step Recommendations (2005) Recommendations (2010) Comments/LOE 1) Assessment
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease
 Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Otolaryngology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Otolaryngology 1. GOAL: Hearing Loss. Understand the morbidity of hearing loss, intervention strategies, and the pediatrician's
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Otolaryngology 1. GOAL: Hearing Loss. Understand the morbidity of hearing loss, intervention strategies, and the pediatrician's
Neonatal Hypoglycemia. Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010
 Neonatal Hypoglycemia Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010 Definition The S.T.A.B.L.E. Program defines hypoglycemia as: Glucose delivery or availability is inadequate to meet glucose demand (Karlsen,
Neonatal Hypoglycemia Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010 Definition The S.T.A.B.L.E. Program defines hypoglycemia as: Glucose delivery or availability is inadequate to meet glucose demand (Karlsen,
Preface. The ACoRN Neonatal Society. ACoRN xiii
 Preface For most health professionals, few events are more challenging or stressful than caring for a sick or preterm baby. It is therefore not surprising that the management and stabilization of these
Preface For most health professionals, few events are more challenging or stressful than caring for a sick or preterm baby. It is therefore not surprising that the management and stabilization of these
PROFESSOR DR. NUMAN NAFIE HAMEED الاستاذ الدكتور نعمان نافع الحمداني
 Lecture 6 PROFESSOR DR. NUMAN NAFIE HAMEED الاستاذ الدكتور نعمان نافع الحمداني Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) 2010 MCQ? In neonatal resuscitation program, the preterm neonates need special preparations
Lecture 6 PROFESSOR DR. NUMAN NAFIE HAMEED الاستاذ الدكتور نعمان نافع الحمداني Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) 2010 MCQ? In neonatal resuscitation program, the preterm neonates need special preparations
Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Pulmonary / Critical Care Medicine
 Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Pulmonary / Critical Care Medicine American Osteopathic Association and American College of Osteopathic Internists BOT Rev. 2/2011 These
Specific Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Pulmonary / Critical Care Medicine American Osteopathic Association and American College of Osteopathic Internists BOT Rev. 2/2011 These
Emergency Medicine Scope of Practice
 Emergency Medicine Scope of Practice All Physician Assistants working in Emergency Medicine will encounter a wide variety of non acute, urgent and emergent patient complaints and conditions. Given the
Emergency Medicine Scope of Practice All Physician Assistants working in Emergency Medicine will encounter a wide variety of non acute, urgent and emergent patient complaints and conditions. Given the
Cardiology Competency Based Goals and Objectives
 Cardiology Competency Based Goals and Objectives COMPETENCY 1. Patient Care. Provide family centered patient care that is developmentally and age appropriate, compassionate, and effective for the treatment
Cardiology Competency Based Goals and Objectives COMPETENCY 1. Patient Care. Provide family centered patient care that is developmentally and age appropriate, compassionate, and effective for the treatment
Neonatal/Pediatric Specialty Examination Detailed Content Outline
 I. COMPETENCIES SHARED BETWEEN CRITICAL AND GENERAL CARE 10 32 17 59 A. Assess Patient Information 1 5 7 13 1. Patient history, for example, immunizations environmental pre-existing conditions 2. Physical
I. COMPETENCIES SHARED BETWEEN CRITICAL AND GENERAL CARE 10 32 17 59 A. Assess Patient Information 1 5 7 13 1. Patient history, for example, immunizations environmental pre-existing conditions 2. Physical
5 Million neonatal deaths each year worldwide. 20% caused by neonatal asphyxia. Improvement of the outcome of 1 million newborns every year
 1 5 Million neonatal deaths each year worldwide 20% caused by neonatal asphyxia Improvement of the outcome of 1 million newborns every year International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR) American
1 5 Million neonatal deaths each year worldwide 20% caused by neonatal asphyxia Improvement of the outcome of 1 million newborns every year International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR) American
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Spontaneous intestinal perforation or necrotizing enterocolitis?
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Spontaneous intestinal perforation or necrotizing enterocolitis? June 2004 2 Stocker M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Children s Hospital of Lucerne,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Spontaneous intestinal perforation or necrotizing enterocolitis? June 2004 2 Stocker M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Children s Hospital of Lucerne,
Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat
 Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 18\7\2010 Transient Tachpnea of the Definition:- newborn (TTN) TTN is a benign disease of near term or term infant who display respiratory distress shortly after delivery.
Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 18\7\2010 Transient Tachpnea of the Definition:- newborn (TTN) TTN is a benign disease of near term or term infant who display respiratory distress shortly after delivery.
Hyaline membrane disease. By : Dr. Ch Sarishma Peadiatric Pg
 Hyaline membrane disease By : Dr. Ch Sarishma Peadiatric Pg Also called Respiratory distress syndrome. It occurs primarily in premature infants; its incidence is inversely related to gestational age and
Hyaline membrane disease By : Dr. Ch Sarishma Peadiatric Pg Also called Respiratory distress syndrome. It occurs primarily in premature infants; its incidence is inversely related to gestational age and
Premature: is live born infants delivered before 37 wk from the 1 st day of the last menstrual period.
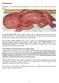 Prematurity Premature: is live born infants delivered before 37 wk from the 1 st day of the last menstrual period. Low birth weight (LBW): (birth weight
Prematurity Premature: is live born infants delivered before 37 wk from the 1 st day of the last menstrual period. Low birth weight (LBW): (birth weight
Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland. Endocrinology
 Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland Endocrinology 5.22 GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Endocrine). Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing endocrine PC, MK, dysfunction,
Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland Endocrinology 5.22 GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Endocrine). Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing endocrine PC, MK, dysfunction,
WHAT IT MEANS or WHY YOU DO IT
 WHAT IT MEANS or WHY YOU DO IT Dr. Patrick Sauer Billings Clinic Pediatrics Objective Increase understanding of prenatal tests Increase understanding of routine newborn procedures Increase knowledge to
WHAT IT MEANS or WHY YOU DO IT Dr. Patrick Sauer Billings Clinic Pediatrics Objective Increase understanding of prenatal tests Increase understanding of routine newborn procedures Increase knowledge to
Hematology/Oncology/BMT
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Hematology/Oncology/BMT 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing hematologic or oncologic conditions,
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Hematology/Oncology/BMT 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing hematologic or oncologic conditions,
Neonatal Seizure. Dr.Nawar Yahya. Presented by: Sarah Khalil Zeina Shamil Zainab Waleed Zainab Qahtan. Supervised by:
 Neonatal Seizure Supervised by: Dr.Nawar Yahya Presented by: Sarah Khalil Zeina Shamil Zainab Waleed Zainab Qahtan Objectives: What is neonatal seizure Etiology Clinical presentation Differential diagnosis
Neonatal Seizure Supervised by: Dr.Nawar Yahya Presented by: Sarah Khalil Zeina Shamil Zainab Waleed Zainab Qahtan Objectives: What is neonatal seizure Etiology Clinical presentation Differential diagnosis
RECOMMENDED COURSE ORDER
 Although you have the flexibility to view the videos in any order, we strongly recommend that you watch the videos in the order in which your dashboard presents them regardless of how many videos you view
Although you have the flexibility to view the videos in any order, we strongly recommend that you watch the videos in the order in which your dashboard presents them regardless of how many videos you view
Neonatal Resuscitation. Dustin Coyle, M.D. Anesthesiology
 Neonatal Resuscitation Dustin Coyle, M.D. Anesthesiology Recognize complications Maternal-fetal factors Maternal DM PIH Chronic HTN Previous stillbirth Rh sensitization Infection Substance abuse/certain
Neonatal Resuscitation Dustin Coyle, M.D. Anesthesiology Recognize complications Maternal-fetal factors Maternal DM PIH Chronic HTN Previous stillbirth Rh sensitization Infection Substance abuse/certain
 NEONATAL LIFE SUPPORT PROVIDER (NLSP) CERTIFICATION EXAMINATION 1. To determine if an infant requires resuscitation, you must rapidly assess gestation period, presence of meconium in amniotic fluid, breaths
NEONATAL LIFE SUPPORT PROVIDER (NLSP) CERTIFICATION EXAMINATION 1. To determine if an infant requires resuscitation, you must rapidly assess gestation period, presence of meconium in amniotic fluid, breaths
CONTENTS 1. PUBLIC HEALTH ISSUES 2. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS 3. DIAGNOSTIC TESTS 4. CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES 5. RESPIRATORY DISEASES
 CONTENTS 1. PUBLIC HEALTH ISSUES 2. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS 3. DIAGNOSTIC TESTS 4. CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES 5. RESPIRATORY DISEASES 6. GASTROINTESTINAL DISEASES 7. UROGENITAL DISEASES 8. SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED
CONTENTS 1. PUBLIC HEALTH ISSUES 2. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS 3. DIAGNOSTIC TESTS 4. CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES 5. RESPIRATORY DISEASES 6. GASTROINTESTINAL DISEASES 7. UROGENITAL DISEASES 8. SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED
Children s of Alabama. Birmingham, Alabama
 Preoperative Evaluation of Pediatric Patients Heather Rankin, CRNA, MSN Children s of Alabama Birmingham, Alabama Objectives Define NPO guidelines Review history assessment Review system assessment Review
Preoperative Evaluation of Pediatric Patients Heather Rankin, CRNA, MSN Children s of Alabama Birmingham, Alabama Objectives Define NPO guidelines Review history assessment Review system assessment Review
USMLE STEP 2 CK REVIEW STUDY GUIDE
 USMLE STEP 2 CK REVIEW STUDY GUIDE 2014 edition Brian Jenkins, MD Although you have the flexibility to view the videos in any order, we strongly recommend that you watch the videos in the order in which
USMLE STEP 2 CK REVIEW STUDY GUIDE 2014 edition Brian Jenkins, MD Although you have the flexibility to view the videos in any order, we strongly recommend that you watch the videos in the order in which
Neonatal infections and neonatal seizures. Mohamed Waheed Elsharief Dept. of paediatrics Faculty of medicine Jazan University KSA
 Neonatal infections and neonatal seizures Mohamed Waheed Elsharief Dept. of paediatrics Faculty of medicine Jazan University KSA objectives By the end of this lecture the student should Define neonatal
Neonatal infections and neonatal seizures Mohamed Waheed Elsharief Dept. of paediatrics Faculty of medicine Jazan University KSA objectives By the end of this lecture the student should Define neonatal
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Nephrology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Nephrology 1. GOAL: Understand the general pediatrician's role in diagnosis and management of hypertension in children.
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Nephrology 1. GOAL: Understand the general pediatrician's role in diagnosis and management of hypertension in children.
Appropriate Use Criteria for Initial Transthoracic Echocardiography in Outpatient Pediatric Cardiology (scores listed by Appropriate Use rating)
 Appropriate Use Criteria for Initial Transthoracic Echocardiography in Outpatient Pediatric Cardiology (scores listed by Appropriate Use rating) Table 1: Appropriate indications (median score 7-9) Indication
Appropriate Use Criteria for Initial Transthoracic Echocardiography in Outpatient Pediatric Cardiology (scores listed by Appropriate Use rating) Table 1: Appropriate indications (median score 7-9) Indication
Fever in the Newborn Period
 Fever in the Newborn Period 1. Definitions 1 2. Overview 1 3. History and Physical Examination 2 4. Fever in Infants Less than 3 Months Old 2 a. Table 1: Rochester criteria for low risk infants 3 5. Fever
Fever in the Newborn Period 1. Definitions 1 2. Overview 1 3. History and Physical Examination 2 4. Fever in Infants Less than 3 Months Old 2 a. Table 1: Rochester criteria for low risk infants 3 5. Fever
General Principles: 5% 7%
 General Principles: 5% 7% International Foundations of Medicine Clinical Science Exam Blueprint Infancy and Childhood (normal growth and development) Adolescence (sexuality, separation from parents/autonomy,
General Principles: 5% 7% International Foundations of Medicine Clinical Science Exam Blueprint Infancy and Childhood (normal growth and development) Adolescence (sexuality, separation from parents/autonomy,
Pulmonary Problems of the Neonate. Jon Palmer, VMD, DACVIM Chief, Neonatal Intensive Care Service New Bolton Center, University of Pennsylvania, USA
 Pulmonary Problems of the Neonate Jon Palmer, VMD, DACVIM Chief, Neonatal Intensive Care Service New Bolton Center, University of Pennsylvania, USA Lower Respiratory Diseases Ventilation/Perfusion Abnormalities
Pulmonary Problems of the Neonate Jon Palmer, VMD, DACVIM Chief, Neonatal Intensive Care Service New Bolton Center, University of Pennsylvania, USA Lower Respiratory Diseases Ventilation/Perfusion Abnormalities
NICU SKILLS CHECKLIST
 NICU SKILLS CHECKLIST 1111 North 3rd Street Instructions: Please complete this checklist to enable us to match your skills and interests with available assignments. Place an "X" in the appropriate column
NICU SKILLS CHECKLIST 1111 North 3rd Street Instructions: Please complete this checklist to enable us to match your skills and interests with available assignments. Place an "X" in the appropriate column
Supplemental Digital Content: Definitions Based on the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification
 Supplemental Digital Content: Definitions Based on the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) Diagnose and Procedures Codes 1. ICD-9-CM definition of
Supplemental Digital Content: Definitions Based on the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) Diagnose and Procedures Codes 1. ICD-9-CM definition of
UCLA General Surgery Residency Program Rotation Educational Policy Goals and Objectives ROTATION: SURGICAL CRITICAL CARE AND TRANSPLANTATION SURGERY
 UPDATED: August 2009 UCLA General Surgery Residency Program ROTATION: SURGICAL CRITICAL CARE AND TRANSPLANTATION SURGERY ROTATION DIRECTOR: Gerald Lipshutz, M.D. SITE: UCLA Medical Center LEVEL OF TRAINEE:
UPDATED: August 2009 UCLA General Surgery Residency Program ROTATION: SURGICAL CRITICAL CARE AND TRANSPLANTATION SURGERY ROTATION DIRECTOR: Gerald Lipshutz, M.D. SITE: UCLA Medical Center LEVEL OF TRAINEE:
Babies First and CaCoon Risk Factors (A Codes and B Codes)
 Babies First and Risk Factors (A Codes and B Codes) (Birth through 4 years of age) Medical Risk Factors A1. Drug exposed infant (See A29) A2. Infant HIV positive A3. Maternal PKU or HIV positive A4. Intracranial
Babies First and Risk Factors (A Codes and B Codes) (Birth through 4 years of age) Medical Risk Factors A1. Drug exposed infant (See A29) A2. Infant HIV positive A3. Maternal PKU or HIV positive A4. Intracranial
NurseAchieve. CHAPTERS INCLUDED IN THE NURSEACHIEVE COMPREHENSIVE NCLEX REVIEW NURSING SKILLS AND FUNDAMENTALS:
 NurseAchieve www.nurseachieve.com CHAPTERS INCLUDED IN THE NURSEACHIEVE COMPREHENSIVE NCLEX REVIEW NCLEX TEST STRATEGIES: NCLEX EXAM OVERVIEW TEST TAKING STRATEGIES NURSING SKILLS AND FUNDAMENTALS: ADMINISTRATION
NurseAchieve www.nurseachieve.com CHAPTERS INCLUDED IN THE NURSEACHIEVE COMPREHENSIVE NCLEX REVIEW NCLEX TEST STRATEGIES: NCLEX EXAM OVERVIEW TEST TAKING STRATEGIES NURSING SKILLS AND FUNDAMENTALS: ADMINISTRATION
Uses 1,2,3 : Labeled: Prevention of respiratory distress syndrome in premature infants
 Brand Name: Surfaxin Generic Name: lucinactant Manufacturer 1 : Discovery Laboratories, Inc. Drug Class 2,3 : Synthetic lung surfactant Uses 1,2,3 : Labeled: Prevention of respiratory distress syndrome
Brand Name: Surfaxin Generic Name: lucinactant Manufacturer 1 : Discovery Laboratories, Inc. Drug Class 2,3 : Synthetic lung surfactant Uses 1,2,3 : Labeled: Prevention of respiratory distress syndrome
The Case Begins. The case continued. Necrotizing Enterocolitis
 Bugs, Drugs and Things that go Bump in the Night From ghoulies to ghosties and long leggety beasties & things that go bump in the night, good lord deliver us Old Cornish Prayer Caring for premature infant
Bugs, Drugs and Things that go Bump in the Night From ghoulies to ghosties and long leggety beasties & things that go bump in the night, good lord deliver us Old Cornish Prayer Caring for premature infant
Medical Complications of Pregnancy
 Medical Complications of Pregnancy Systems Cardiovascular Pulmonary Endocrine Gastrointestinal Urologic Neurologic Cardiovascular System Physiologic anemia 3:1 increase of plasma volume:rbc mass Treat
Medical Complications of Pregnancy Systems Cardiovascular Pulmonary Endocrine Gastrointestinal Urologic Neurologic Cardiovascular System Physiologic anemia 3:1 increase of plasma volume:rbc mass Treat
TRAINING NEONATOLOGY SILVANA PARIS
 TRAINING ON NEONATOLOGY SILVANA PARIS RESUSCITATION IN DELIVERY ROOM INTRODUCTION THE GLOBAL RESUSCITATION BURDEN IN NEWBORN 136 MILL NEWBORN BABIES EACH YEAR (WHO WORLD REPORT) 5-8 MILL NEWBORN INFANTS
TRAINING ON NEONATOLOGY SILVANA PARIS RESUSCITATION IN DELIVERY ROOM INTRODUCTION THE GLOBAL RESUSCITATION BURDEN IN NEWBORN 136 MILL NEWBORN BABIES EACH YEAR (WHO WORLD REPORT) 5-8 MILL NEWBORN INFANTS
3/25/2012. numerous micro-organismsorganisms
 Congenital & Neonatal TB A Case of Tuberculosis Congenital or Acquired? Felicia Dworkin, MD NYC DOHMH Bureau TB Control World TB Day March 23, 2012 Congenital TB: acquired by the fetus during pregnancy
Congenital & Neonatal TB A Case of Tuberculosis Congenital or Acquired? Felicia Dworkin, MD NYC DOHMH Bureau TB Control World TB Day March 23, 2012 Congenital TB: acquired by the fetus during pregnancy
Standard of Newborn Care in the Age of Birth Plans. Stephanie Deal, MD Tiffany McKee-Garrett, MD
 Standard of Newborn Care in the Age of Birth Plans Stephanie Deal, MD Tiffany McKee-Garrett, MD Disclosure We have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers(s) of any commercial products(s)
Standard of Newborn Care in the Age of Birth Plans Stephanie Deal, MD Tiffany McKee-Garrett, MD Disclosure We have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers(s) of any commercial products(s)
The Blue Baby. Network Stabilisation of the Term Infant Study Day 15 th March 2017 Joanna Behrsin
 The Blue Baby Network Stabilisation of the Term Infant Study Day 15 th March 2017 Joanna Behrsin Session Structure Definitions and assessment of cyanosis Causes of blue baby Structured approach to assessing
The Blue Baby Network Stabilisation of the Term Infant Study Day 15 th March 2017 Joanna Behrsin Session Structure Definitions and assessment of cyanosis Causes of blue baby Structured approach to assessing
Effectively communicate with the mother's obstetrician during the hospital stay and her primary care provider prior to the infant's discharge.
 Newborn Nursery Description: Residents are expected to see all patients on the Marshall Pediatrics service. They will round on patients with the assigned attending physician. Any problems or concerns should
Newborn Nursery Description: Residents are expected to see all patients on the Marshall Pediatrics service. They will round on patients with the assigned attending physician. Any problems or concerns should
Milestone Guide. CBD Anesthesia
 Table of Contents Department of Anesthesiology Foundations 1 Airway 1 Pharmacology 1 Physiology 1 Common Uncomplicated Anesthetics Practice 2 Obstetrics 2 Pain 2 Core 3 Perioperative Medicine 3 Complex
Table of Contents Department of Anesthesiology Foundations 1 Airway 1 Pharmacology 1 Physiology 1 Common Uncomplicated Anesthetics Practice 2 Obstetrics 2 Pain 2 Core 3 Perioperative Medicine 3 Complex
Provide specific counseling to parents and patients with neurological disorders, addressing:
 Neurology Description: The Pediatric Neurology elective will give the resident the opportunity to learn how to obtain an appropriate history and perform a complete neurologic exam. Four to five half days
Neurology Description: The Pediatric Neurology elective will give the resident the opportunity to learn how to obtain an appropriate history and perform a complete neurologic exam. Four to five half days
APPENDIX A. Comparability Ratios for the Major Causes of Death in North Carolina Vital Statistics, Volume 2
 APPENDIX A Comparability Ratios for the Major Causes of Death in North Carolina Vital Statistics, Volume 2 The comparability ratio is an adjustment factor that is applied to the number of deaths coded
APPENDIX A Comparability Ratios for the Major Causes of Death in North Carolina Vital Statistics, Volume 2 The comparability ratio is an adjustment factor that is applied to the number of deaths coded
Pediatric emergencies (SHOCK & COMA) Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University
 Pediatric emergencies (SHOCK & COMA) Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University SHOCK Definition: Shock is a syndrome = inability to provide sufficient oxygenated blood to tissues. Oxygen
Pediatric emergencies (SHOCK & COMA) Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University SHOCK Definition: Shock is a syndrome = inability to provide sufficient oxygenated blood to tissues. Oxygen
McMaster Neonatal Skills Workshop Procedure Pearls
 McMaster Neonatal Skills Workshop Procedure Pearls November 2, 2016 Image from: www.prweb.com Procedures www.laerdal.com www.gaumard.com www.rch.org.au www.laerdal.com ekja.org NRP Epinephrine: 0.1ml/kg
McMaster Neonatal Skills Workshop Procedure Pearls November 2, 2016 Image from: www.prweb.com Procedures www.laerdal.com www.gaumard.com www.rch.org.au www.laerdal.com ekja.org NRP Epinephrine: 0.1ml/kg
Radiology Rotation Educational Goals & Objectives for Internal Medicine
 Radiology Rotation Educational Goals & Objectives for Internal Medicine Internists provide continuing care for patients with a myriad of medical and psychosocial problems. During many patient encounters,
Radiology Rotation Educational Goals & Objectives for Internal Medicine Internists provide continuing care for patients with a myriad of medical and psychosocial problems. During many patient encounters,
