FAILURE TO THRIVE F A IL U RE T O T H RI V E. Case Definition. Screening. Principles of Management. Prevention
|
|
|
- Eustacia Gardner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AILUR HRI Screening By regular growth monitoring. 0-2 year olds are particularly affected by long term effects of growth failure and should be specifically targeted through child health programs. Growth monitoring must include: measuring weight / height / length / head circumference. length is measured in children < 2 yo, and height in children > 2 yo. No shoes or caps, heels against wall. plotting measurements on standard growth charts. AND taking action if growth is not normal. requency of screening (how often?): Growth monitoring is recommended at following times: 0-6 months: At 2 and 6 weeks of age, then monthly months: 2 monthly. 1-2 years: 3 monthly. 2-5 years: 6 monthly years: Height and weight annually with routine Child Health Check; measure HC only if developmental or growth concerns identified. More frequent monitoring is recommended for children at risk of growth problems, including low birth weight or premature infants and those with birth defects such as fetal alcohol syndrome discuss with GP and / or Paediatrician. Recommended growth charts are the World Health rganisation (WH) International Child Growth Standards charts: Case Definition is the failure to achieve the growth potential expected for a child. Usually diagnosed if growth crosses two or more lines downwards on a standard growth chart (see last page of this protocol for sample growth charts). Changes happen to weight first, then length, then head circumference. If weight has been increasing normally but falls during an acute illness such as gastro, this is not failure to thrive unless the child s growth fails to recover fully and continue along the previous centile. Always monitor closely to be sure that growth recovers fully after such an episode. ailure to thrive includes: Underweight weight for age is below the 3rd centile (z score < -2). his may be due to wasting, or stunting, or both. Wasted weight for length (or height) below the 3rd centile (z score < -2). he child looks thin, as their weight is low compared to their height. Wasting is due to malnutrition over a shorter time, and may be reversible with appropriate care. Stunted length (or height) for age is below the 3rd centile (z score < -2). he child is short for their age, but if their weight and height match, they may not look thin. Stunting is more often due to chronic malnutrition and may not be reversible. Prevention Prevention of is the most important goal, and is achievable. nsuring pregnant women and mothers of young children have access to good food and health care. Promote breastfeeding. Access for infants to safe and nutritious solids, with early education about introduction of solids (see HALHY KIDS protocol). Safe living conditions including access to safe and reliable water and sanitation, and lack of overcrowding. Nutritional support programs hose targeting mothers and children at risk have been shown to be effective in prevention of growth failure. Recommended by the World Health rganisation for communities where affects more than 5% of children. Aim to: (a) provide nutritious food without cost for pregnant women and for infants at risk, at least until 2 years of age; (b) be community based and driven; and (c) change behaviour / feeding practices rather than simply providing information. See also HALHY KIDS and ANAMIA IN CHILDRN protocols for more information on prevention. Principles of Management 1. Deal with the immediate risks from acute illness, including infection and dehydration. 2. Address both energy (kilojoule / calorie) and micronutrient (e.g. iron) deficiencies. 3. Minimise the long term impact of growth failure. xtensive investigations are rarely needed as rganic disease is found in less than 5% of cases of and is usually suspected from history and examination. Recognition by health professionals of the cultural values and belief systems of the child s family and community is critical. Where resources are limited priority must be given to follow up of children under 2 years of age improving nutrition in this age group may reverse the adverse effects of growth failure. Community-based management of is as effective, and much less disruptive, for child and carer. Routine hospitalisation is not recommended but may be necessary in particular circumstances, e.g. treatment of acute on chronic malnutrition or dehydration, failure of community-based therapy. U R C - Last Modified: November 3, :59 AM Kimberley Aboriginal Medical Services Council (KAMSC) and WA Country Health Service (WACHS) Kimberley 23/10/09
2 AILUR HRI Baseline Assessment Any acutely unwell child should be discussed early with the GP. his includes any child with signs of acute infection (e.g. fever, respiratory distress, vomiting, lethargic) and / or dehydration (See ASSSSING H SICK CHILD protocol). If child is not acutely unwell, do a full history and examination including dietary history. wo important questions to answer are: 1. Is the child at immediate risk and where are they best managed right now? See management section on page What are the likely causes of poor growth in this child? In the Kimberley, is commonly due to a combination of: (a) actors relating to child low birth weight. lack of breastfeeding or stopping breastfeeds early. not enough, poor quality and / or late introduction of solids. recurrent infections, particularly gut infections. maternal malnutrition during pregnancy +/- while breastfeeding. (b) Social and environmental factors poverty, difficulty accessing food supplies. lack of knowledge about child care practices. inadequate environmental health, including overcrowding, lack of safe water supply, and inadequate sanitation. 3. Is mucosal damage a likely factor? Damage to the lining of the gut ( mucosa ) from recurrent gastroenteritis causes lactose intolerance as well as impaired digestion. Lactose intolerance is more common in Aboriginal children and is more likely to be found in children with. It is not usually the main cause of, but finding and treating lactose intolerance will improve outcomes (see Box 1). INSIGAINS: While lots of tests are not usually necessary, the following tests are useful and are recommended for all children with : 1. Urinalysis dipstick analysis; send to laboratory for MC&S (see KIDNY DISAS IN CHILDRN protocol for advice on specimen collection). 2. B and iron studies. If not feasible, Haemocue test for finger-prick Hb may be adequate (see ANAMIA IN CHILDRN protocol). 3. Stool samples (note: both collection and processing can take time proceed with management section of this protocol rather than delaying treatment while waiting). i) or infection, such as Giardia, other parasites, bacterial infection. Ask for MC&S and CP (Microscopy, Culture and Sensitivities, and Cysts, ocytes and Parasites). ii) If the stools are loose / watery, check also for lactose intolerance using Clinitest tablets. BX 1 esting for lactose intolerance: his is best done on-site in the clinic, or in the lab if the sample can get to the lab quickly. Collect a sample of loose / liquid stools. A paediatric urine collection bag can be useful for this. Do not scrape sample from nappy this will give a falsely low result. est the sample immediately after collection. Mix a small amount of stool (1ml of liquid stool, or a tiny dollop if it s not liquid) with 2mL water, take 15 drops from that mixture, place in plain glass blood collection tube, add 1 Clinitest tablet, wait until tablet stops reacting, shake and compare with the colour chart on the Clinitest box. Principles of Management See flow chart on page 4. All children less than 6 months old with should be discussed immediately with a regional Paedicatrician. Discuss immediately with a GP any child with who: Has just been diagnosed, or where is suspected but you are uncertain. Develops an acute illness; and / or; Is failing to respond to a management plan developed by the health team. When to admit to hospital: If dehydrated and / or has an acute infection, a child with is likely to need hospital inpatient care. Remember that children with are more likely to develop bacterial infections so maintain a high level of suspicion in the child with and fever (See ASSSSING H SICK CHILD protocol). When a trial of therapy in the community has failed (see below). In this situation, hospital is not a long term solution but will: Allow supervised re-feeding for a child with severe wasting. Provide an opportunity to assess dietary intake, feeding techniques, and parent child interactions. Community-based therapy he most appropriate place for managing a child with is usually in the community. Success of community-based treatment will depend on: Gaining the carer(s) trust, through an approach which is mutually respectful and recognises the central role of the carer(s) in the child s development and well-being. Providing an environment in which the carer(s) feel comfortable to talk about their own concerns, and discuss issues which they feel may be affecting the child s growth and well-being. U R C - Last Modified: November 3, :59 AM
3 AILUR HRI Principles of Management (cntd) Sharing information in a manner which is understandable and meaningful for carer(s), increasing knowledge and understanding of their child s condition. In many instances, this will best be provided by an Aboriginal Health Worker and / or formal interpreter services. Community based therapy includes: 1. Development of a Care Plan involving as a minimum carer(s), GP, AHW, nurse. he carer(s) may wish to have other community members involved. 2. Actively encourage continued breastfeeding. 3. Provide specific education for carer(s) and family about appropriate types and amounts of food the child needs (see HALHY CHILDRN protocol). stablishing a normal, healthy diet may be enough to re-establish growth. 4. Children with severe and / or those not responding to the steps above will need extra energy. Provide advice on fortified solids, or energy booster foods (see Box 2) - discuss with the dietician for assistance if needed. 5. Assume parasites may be present and give a single course of albendazole (200mg if < 10kg and 400mg if > 10kg) once a day for three days in all children over 6 months of age. his provides effective treatment for giardia and hookworm; if strongyloides is found in stool samples, further treatment may be needed (see Parasites protocol). 6. Review the child weekly. If child s growth is moving downward across centile lines at any follow up visit, call / discuss immediately with the GP. 7. Review progress with the GP at the 4 week mark. If catchup growth (moving upwards across centile lines) is not occurring, a nutritional supplement should be added as follows: 0-12 months: discuss with Paediatrician, nutritional supplementation in children of this age is complex. > 12 months: Pediasure 235ml cans 1-2 per day. N: Nutritional supplements can be seen as a form of treatment, similar to using iron medicine for treatment of iron deficiency anaemia the cost of both treatments should be met by the health system. BX 2 nergy Boosters ( fortified solids ) Concentrated sources of energy (energy boosters) should be added to the healthy foods the child usually eats to increase the energy density. nergy boosters include: Cheese / cream cheese - Add grated cheese to soups, pasta, stews, mashed vegetables, scrambled egg, tinned spaghetti or baked beans. Use cream cheese in sandwiches. Peanut butter /avocado - spread on toast and sandwiches. Milk powder - for children over the age of 1 year, add 2 teaspoons of milk powder to each glass of milk. Use this milk as a drink, on cereal and in cooked foods (i.e. scrambled eggs, white sauce, soups). Margarine (recommend monounsaturated such as olive or canola-based margarines) - melt one to two teaspoons over vegetables, rice and pasta. Spread thickly on bread and toast. il (recommend monounsaturated oil such as olive, canola or peanut) - fry meats, vegetables and rice. Specific treatment for conditions identified with baseline investigations: In all cases, discuss first with GP. Any of the conditions below will not be tolerated as well in children with compared to children whose nutrition and growth is K. Anaemia / iron deficiency: see Anaemia in Children protocol. Parasite infection: see Parasites protocol. Abnormal urinalysis, see Kidney Disease in Children protocol. reatment of lactose intolerance Discuss first with GP. Paediatric advice may also be needed. he diagnosis of lactose intolerance should always be confirmed (see previous section Investigations ) before commencing treatment. Unless symptoms are severe, breastfeeding should continue. or children already on formula feeds, and for breastfed infants with more severe lactose intolerance, replace the child s usual milk with a lactose-free milk formula. A low osmolarity formula is preferred, such as De-Lact. If the child is over 12 months and requires nutritional supplementation use Pediasure, which is lactose free. rial reintroduction of normal milk after 6 weeks or most children, treatment with lactose-free formula will only be needed in the short-term - for example, lactose intolerance after a gut infection will usually resolve within 6 weeks. How to re-introduce normal milk: 1. Infants not yet on solids: Swap one De-Lact feed with usual milk source (preferably breastmilk), increasing the number of normal feeds by one a day until the child is off De-Lact. 2. or children who are already on solids, re-introduction of their usual milk source can occur more rapidly over 1-3 days. If diarrhea starts while normal milk is being re-introduced, replace all milk feeds again with lactose-free formula and discuss with Paediatrician. U R C - Last Modified: November 3, :59 AM
4 AILUR HRI ollow-up Refer / Discuss AHW / RN review weekly until growth is improving. At each visit: Check weight, plot on growth curve and interpret progress. Check with carer(s) re child s progress since last visit. Ask in detail about feeds amount, type and frequency, specific symptoms (e.g. diarrhoea) and behaviour. ollow-up any specific abnormalities found on baseline. nce growth is improving, review according to Care Plan monthly will usually be enough, but individual children may need closer monitoring. Provide regular screening and follow-up for siblings and other children in the same household as the child with, who are at increased risk of themselves. Provide access for the mother to additional care and support during future pregnancies. Discuss all children with with a GP, and arrange for review in the clinic with the GP at the earliest opportunity. Regional Paediatrician: All children < 6 months. All children being considered for hospital admission. If a trial of community-based therapy is failing. If underlying organic disease (kidney disease, metabolic disorder, etc) is diagnosed or suspected. At any time if uncertain. Dietician: Discuss / refer as needed for input into development of individual care plans. All children requiring nutritional supplementation. All children on admission to hospital with. Department of Child Protection (DCP) may be able to provide practical supports for families of children who are failing to thrive, including financial counselling and parenting education / support. DCP should be notified where there are concerns about the welfare of the child, including emotional neglect, physical neglect and / or abuse. U R C - Last Modified: November 3, :59 AM
5 AILUR HRI MANAGMN LW CHAR YS Always discuss new diagnosis with GP. Is the child acutely unwell (infection, dehydration) and / or severely wasted? N U R Arrange hospital admission with GP. Notify dietician early during admission. Discuss / refer to Paediatrician all children with severe, or those not responding quickly to hospital treatment. Perform detailed history, examination. Investigations: urinalysis, B and iron studies (or Haemaccue of not feasible). Stool samples for MC&S and parasites. Clinitest if history of recurrent / chronic diarrhea. Arrange appropriate explanation and education for parents/ carers; may include family meeting(s), home visits, intensive AHW follow-up, etc. Arrange comprehensive Care Plan. Community-based trial of therapy Develop individualized feeding plan for child discuss with dietician if needed. Give all children over 6 months one course of albendazole. Review weekly check progress including feeding history, weight. At review visit, child s growth moving along or upwards across lines (centiles) on growth curve? N YS Continue to review weekly. Arrange review by GP at 4 weeks. < 12 m Age > 12 m Is catch-up growth occurring at GP review (moving upwards on growth curve)? YS Discuss with Paediatrician re appropriate nutritional supplementation N Start nutritional supplementation with Paediasure Review weekly is catch-up growth occurring? YS Continue to review monthly until growth has followed appropriate curve for at least 3 months, then continue to review at least 3 monthly for the next 2 years. C - Last Modified: November 3, :59 AM
6 AILUR HRI Sample Growth Charts his graph plots the child s weight against her age. he child s birth weight was just below the 15th centile at 2200g so although the baby was born full term, she was of low birth weight. In the first few weeks after birth, she grew well, reaching the 50th centile by the time she was 6 weeks old. She then continued to grow steadily along this line until she was 7 months old. hen she lost weight suddenly the notes in her clinic file explain she had a bout of gastro and was unwell on and off for a few weeks around that time. Although her weight returned to what it had been before the illness, she had missed out on some growth time and her weight never returned to the 50th centile again. In fact, after that time, her growth curve started to flatten out and from 10 months onwards, her growth is seen crossing downwards across the growth centile lines on the chart. By the time she is seen today, now almost 17 months old, she is back below the 15th centile. Although the child has had her weight measured regularly, there has been no action when the growth curve started showing warning signs the red arrow shows the point where health staff should start following the steps outlined in this protocol. his graph is from the same child s chart. he one below shows her length plotted against her age. You can see she is quite long ( tall ) for her age, perhaps reflecting the fact that both her parents are tall. Although her weight began to show problems around 7 months of age, her length continued to increase along the same centile until just recently. With malnutrition, it is common for problems to occur with weight first, then later with length / height if nutrition is not improved. his graph shows her weight compared to her length. We already know her weight is dropping off at 1 year and 5 months, her weight is only 8.2kg, below the 15th centile. However, because she is a tall child, we would expect her weight to be even greater for her age to match her tallness. his graph shows that, compared to her length, her weight is indeed very low well below the 3rd centile. his is stunting weight for length which is now below the 3rd centile U R C - Last Modified: November 3, :59 AM
WHOLE: Wellbeing and Healthy Choices for Older Adults and their Carers
 WHOLE: Wellbeing and Healthy Choices for Older Adults and their Carers Malnutrition in Older Age This dietary information fact sheet is intended for informational purposes only. It is not a substitute
WHOLE: Wellbeing and Healthy Choices for Older Adults and their Carers Malnutrition in Older Age This dietary information fact sheet is intended for informational purposes only. It is not a substitute
Objectives. Types of HIV Tests. Age Appropriateness of Tests. Breastfeeding and HIV Testing. Why are there different tests for different ages?
 Objectives At the end of the lesson participants will be able to: Identify the types of HIV tests available in Botswana State who should be tested Identify which tests are used for infants and children
Objectives At the end of the lesson participants will be able to: Identify the types of HIV tests available in Botswana State who should be tested Identify which tests are used for infants and children
Annex 2: Assessment and treatment of diarrhoea 53
 Annex 2: Assessment and treatment of diarrhoea 53 A-2.1 Assessment of diarrhoeal patients for dehydration Table 1: Assessment of diarrhoea patients for dehydration A B C 1. Look at: Condition a Eyes b
Annex 2: Assessment and treatment of diarrhoea 53 A-2.1 Assessment of diarrhoeal patients for dehydration Table 1: Assessment of diarrhoea patients for dehydration A B C 1. Look at: Condition a Eyes b
Answer Key for Introduction to Food Packages
 Practice Activity-A Answer Key for Introduction to Food Packages Observe how food package assignment is conducted in your clinic. Answer the following questions for each certification that you observe.
Practice Activity-A Answer Key for Introduction to Food Packages Observe how food package assignment is conducted in your clinic. Answer the following questions for each certification that you observe.
Advice on taking enzyme replacement capsules
 Advice on taking enzyme replacement capsules Hepatobiliary Services Information for Patients i University Hospitals of Leicester NHS Trust Introduction What is the pancreas? The pancreas is part of your
Advice on taking enzyme replacement capsules Hepatobiliary Services Information for Patients i University Hospitals of Leicester NHS Trust Introduction What is the pancreas? The pancreas is part of your
Early Years Foundation Stage
 Early Years Foundation Stage Food and Nutrition Policy Introduction all settings Food and nutrition is an integral part of the ethos of all GEMS settings. We believe that it is important for children to
Early Years Foundation Stage Food and Nutrition Policy Introduction all settings Food and nutrition is an integral part of the ethos of all GEMS settings. We believe that it is important for children to
Advice on taking enzyme replacement capsules
 Advice on taking enzyme replacement capsules Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services Hepatobiliary Services i Information for patients Introduction What is the pancreas? The pancreas is part of
Advice on taking enzyme replacement capsules Leicestershire Nutrition and Dietetic Services Hepatobiliary Services i Information for patients Introduction What is the pancreas? The pancreas is part of
How to improve your food and drink intake if you have a poor appetite
 5800 - How to increase your food and drink intake Leaflet June 2018.qxp_Layout 1 07/06/2018 11:07 Page 2 How to improve your food and drink intake if you have a poor appetite BREAD - RICE - POTATOES -
5800 - How to increase your food and drink intake Leaflet June 2018.qxp_Layout 1 07/06/2018 11:07 Page 2 How to improve your food and drink intake if you have a poor appetite BREAD - RICE - POTATOES -
Nutritional Assessment & Monitoring of Hospitalized Children
 Nutritional Assessment & Monitoring of Hospitalized Children Kehkashan Zehra, Clinical Dietitian Sindh Institute of Urology & Transplantation, Karachi In Pakistan 42% of children aged < 5 years are stunted
Nutritional Assessment & Monitoring of Hospitalized Children Kehkashan Zehra, Clinical Dietitian Sindh Institute of Urology & Transplantation, Karachi In Pakistan 42% of children aged < 5 years are stunted
Infant and Young Child Feeding
 Infant and Young Child Feeding At six months (180 days), start giving your child complementary foods. Continue to breastfeed Wash your hands before feeding your child Continue to breastfeed Give your child
Infant and Young Child Feeding At six months (180 days), start giving your child complementary foods. Continue to breastfeed Wash your hands before feeding your child Continue to breastfeed Give your child
Are you eating & drinking enough?
 Are you eating & drinking enough? A guide to the MUST & GULP screening tools GULP Dehydration Risk Screening Tool To complete GULP, tick the boxes which represent your findings. Add up the total tick scores
Are you eating & drinking enough? A guide to the MUST & GULP screening tools GULP Dehydration Risk Screening Tool To complete GULP, tick the boxes which represent your findings. Add up the total tick scores
Nutrition and Dietetics Patient Information Leaflet
 Dietary advice for people with diabetes Underweight/weight loss Nutrition and Dietetics Patient Information Leaflet How can I make the most of my food? If you want to gain weight, prevent weight loss or
Dietary advice for people with diabetes Underweight/weight loss Nutrition and Dietetics Patient Information Leaflet How can I make the most of my food? If you want to gain weight, prevent weight loss or
CHILD HEALTH. There is a list of references at the end where you can find more information. FACT SHEETS
 SOME 18,000 CHILDREN STILL DIE EVERY DAY FROM DISEASES THAT ARE MOSTLY PREVENTABLE. This fact sheet outlines some of the basic information related to the health and wellbeing of children under five years
SOME 18,000 CHILDREN STILL DIE EVERY DAY FROM DISEASES THAT ARE MOSTLY PREVENTABLE. This fact sheet outlines some of the basic information related to the health and wellbeing of children under five years
Eating Well After Gastro-intestinal Surgery
 Lady Sobell Gastrointestinal Unit Wexham Park Hospital Introduction Eating Well After Gastro-intestinal Surgery This leaflet contains general information to help you with eating after surgery. If you need
Lady Sobell Gastrointestinal Unit Wexham Park Hospital Introduction Eating Well After Gastro-intestinal Surgery This leaflet contains general information to help you with eating after surgery. If you need
Eating after a Gastrectomy
 Eating after a Gastrectomy Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm There
Eating after a Gastrectomy Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm There
Dietary advice for people with colostomies
 Dietary advice for people with colostomies Introduction During your surgery, you have had a colostomy formed. Colostomies are formed due to problems in the colon (large bowel). This leaflet is designed
Dietary advice for people with colostomies Introduction During your surgery, you have had a colostomy formed. Colostomies are formed due to problems in the colon (large bowel). This leaflet is designed
14 Superfoods for your baby and how to serve them
 Your baby needs a variety of macro and micronutrients to grow and thrive. Here are some of the important ones: Protein: Protein suppliers our bodies structural blocks and it is extremely important for
Your baby needs a variety of macro and micronutrients to grow and thrive. Here are some of the important ones: Protein: Protein suppliers our bodies structural blocks and it is extremely important for
Detection and Treatment of Malnutrition in Care Homes. Fiona McKenna, Community Dietitian Sutton and Merton Community Services
 Detection and Treatment of Malnutrition in Care Homes Fiona McKenna, Community Dietitian Sutton and Merton Community Services Topics to be covered The importance of nutrition Malnutrition: causes and consequences
Detection and Treatment of Malnutrition in Care Homes Fiona McKenna, Community Dietitian Sutton and Merton Community Services Topics to be covered The importance of nutrition Malnutrition: causes and consequences
choosing food to keep you and your baby healthy Healthy eating
 choosing food to keep you and your baby healthy Healthy eating Contents What should I be eating? 1 Is there any food I should avoid? 2 Should I avoid peanuts? 2 Do I need any vitamin supplements? 3 Do
choosing food to keep you and your baby healthy Healthy eating Contents What should I be eating? 1 Is there any food I should avoid? 2 Should I avoid peanuts? 2 Do I need any vitamin supplements? 3 Do
Diet advice for patients with a stoma
 Diet advice for patients with a stoma There are two different types of stoma; a colostomy or an ileostomy. A colostomy is a stoma that is formed from a part of the large bowel (colon). When undigested
Diet advice for patients with a stoma There are two different types of stoma; a colostomy or an ileostomy. A colostomy is a stoma that is formed from a part of the large bowel (colon). When undigested
ALGORITHM FOR MANAGING MALNUTRITION IN ADULTS
 ALGORITHM FOR MANAGING MALNUTRITION IN ADULTS HISTORY ASSESS LOOK AND FEEL CRITERIA CLASSIFICATION TREATMENT/CARE Ask the client or refer to records: 1. Has the client lost weight in the past month/since
ALGORITHM FOR MANAGING MALNUTRITION IN ADULTS HISTORY ASSESS LOOK AND FEEL CRITERIA CLASSIFICATION TREATMENT/CARE Ask the client or refer to records: 1. Has the client lost weight in the past month/since
Definition. Failure to Thrive. No clear consensus Growth below the 3 rd or 5 th percentile Decreased growth crossing 2 major growth percentiles
 Failure to Thrive Karen Swarts, MD 6/4/2004 Definition No clear consensus Growth below the 3 rd or 5 th percentile Decreased growth crossing 2 major growth percentiles 1 Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics,
Failure to Thrive Karen Swarts, MD 6/4/2004 Definition No clear consensus Growth below the 3 rd or 5 th percentile Decreased growth crossing 2 major growth percentiles 1 Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics,
Positive health, dignity and prevention for women and their babies
 FLIPCHART Positive health, dignity and prevention for women and their babies A treatment literacy guide for pregnant women and mothers living with HIV Module 1: Human rights in healthcare settings 1 Knowing
FLIPCHART Positive health, dignity and prevention for women and their babies A treatment literacy guide for pregnant women and mothers living with HIV Module 1: Human rights in healthcare settings 1 Knowing
Rotavirus. Children s Ward Macclesfield District General Hospital.
 Rotavirus Children s Ward 01625 661080 Macclesfield District General Hospital www.eastcheshire.nhs.uk Leaflet Ref: 10941 Published: 07/15 Review: 07/18 Page 1 Rotavirus is a viral infection that can cause
Rotavirus Children s Ward 01625 661080 Macclesfield District General Hospital www.eastcheshire.nhs.uk Leaflet Ref: 10941 Published: 07/15 Review: 07/18 Page 1 Rotavirus is a viral infection that can cause
Eating Well for Wound Healing
 Eating Well for Wound Healing 2 Introduction The aim of this leaflet is to help you to have the correct diet to enable your wound to heal. What you eat plays an important role in: Looking after your skin
Eating Well for Wound Healing 2 Introduction The aim of this leaflet is to help you to have the correct diet to enable your wound to heal. What you eat plays an important role in: Looking after your skin
Training Course on Child Growth Assessment. WHO Child Growth Standards. Answer Sheets. Department of Nutrition for Health and Development
 Training Course on Child Growth Assessment WHO Child Growth Standards F Answer Sheets Department of Nutrition for Health and Development Answers for Module B: Measuring a Child s Growth 1 B: Measuring
Training Course on Child Growth Assessment WHO Child Growth Standards F Answer Sheets Department of Nutrition for Health and Development Answers for Module B: Measuring a Child s Growth 1 B: Measuring
ABLE TO READ THE LABEL?
 ARE ABLE TO READ THE LABEL? A Consumer s Guide to Navigating Food Labels Food and Drug Safety Program Consumer and Environmental Health Services Phone: 609-826-4935 Fax: 609-826-4990 http://nj.gov/health/eoh/foodweb/
ARE ABLE TO READ THE LABEL? A Consumer s Guide to Navigating Food Labels Food and Drug Safety Program Consumer and Environmental Health Services Phone: 609-826-4935 Fax: 609-826-4990 http://nj.gov/health/eoh/foodweb/
Information for health professionals
 Introduction of a new screening test for newborn babies in Wales Newborn bloodspot screening for Medium chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency (MCADD) Newborn bloodspot screening for MCADD is being introduced
Introduction of a new screening test for newborn babies in Wales Newborn bloodspot screening for Medium chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency (MCADD) Newborn bloodspot screening for MCADD is being introduced
Care of the HIV-Exposed Infant
 Care of the HIV-Exposed Infant Use of Flipchart To promote quality and consistency of counseling Why use the counseling flipchart? To improve HIV-exposed infant outcomes through high quality counseling.
Care of the HIV-Exposed Infant Use of Flipchart To promote quality and consistency of counseling Why use the counseling flipchart? To improve HIV-exposed infant outcomes through high quality counseling.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) stages 3b to 5 Overview
 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) stages 3b to 5 Overview This infokid topic is for parents and carers about children s kidney conditions. This leaflet has the overview only. Go to www.infokid.org.uk to find
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) stages 3b to 5 Overview This infokid topic is for parents and carers about children s kidney conditions. This leaflet has the overview only. Go to www.infokid.org.uk to find
Temporary lactose intolerance. Patient information leaflet
 Temporary lactose intolerance Patient information leaflet This advice leaflet has been produced to support families of children who are thought to be suffering from temporary lactose intolerance resulting
Temporary lactose intolerance Patient information leaflet This advice leaflet has been produced to support families of children who are thought to be suffering from temporary lactose intolerance resulting
St Christopher s School
 Healthy Eating Policy Infant and Junior Document Reference Version/Revision Effective Date 18 March 2015 Review Date March 2017 Author(s) Reviewer(s) Approved by LMT LMT Ed Goodwin, Principal Version/Revision
Healthy Eating Policy Infant and Junior Document Reference Version/Revision Effective Date 18 March 2015 Review Date March 2017 Author(s) Reviewer(s) Approved by LMT LMT Ed Goodwin, Principal Version/Revision
Child and Adult Nutrition
 Children in Egypt 2015 A STATISTICAL DIGEST Chapter 5 Child and Adult Nutrition Children in Egypt 2015 Children in Egypt 2015 is a statistical digest produced by UNICEF Egypt to present updated and quality
Children in Egypt 2015 A STATISTICAL DIGEST Chapter 5 Child and Adult Nutrition Children in Egypt 2015 Children in Egypt 2015 is a statistical digest produced by UNICEF Egypt to present updated and quality
Endoscopy Unit MOVIPREP. Afternoon Appointment - GASTROSCOPY AND COLONOSCOPY. Information for patients
 Endoscopy Unit MOVIPREP Afternoon Appointment - GASTROSCOPY AND COLONOSCOPY Information for patients This leaflet contains important information about MOVIPREP. You have been given MOVIPREP to cleanse
Endoscopy Unit MOVIPREP Afternoon Appointment - GASTROSCOPY AND COLONOSCOPY Information for patients This leaflet contains important information about MOVIPREP. You have been given MOVIPREP to cleanse
How to Prepare for your. Colonoscopy using. Bowel Preparation. Type 2 Oral Medication. Diabetes Management YOUR QUESTIONS ANSWERED
 How to Prepare for your Colonoscopy using Bowel Preparation Type 2 Oral Medication Diabetes Management YOUR QUESTIONS ANSWERED Page 1 of 12 Page 2 of 12 Contents Introduction Page 4 What is the bowel preparation?
How to Prepare for your Colonoscopy using Bowel Preparation Type 2 Oral Medication Diabetes Management YOUR QUESTIONS ANSWERED Page 1 of 12 Page 2 of 12 Contents Introduction Page 4 What is the bowel preparation?
WHO Child Growth Standards. Training Course on Child Growth Assessment. Answer Sheets
 WHO Child Growth Standards Training Course on Child Growth Assessment BB F Answer Sheets WHO Child Growth Standards Training Course on Child Growth Assessment F Answer Sheets Version 1 November 006 Department
WHO Child Growth Standards Training Course on Child Growth Assessment BB F Answer Sheets WHO Child Growth Standards Training Course on Child Growth Assessment F Answer Sheets Version 1 November 006 Department
SOME ASPECTS OF INFANT FEEDING. Quak Seng Hock
 SOME ASPECTS OF INFANT FEEDING Quak Seng Hock Contents Introduction Importance of proper nutrition in the infant Breastfeeding Nutritional requirements of infants Introducing solid food Vitamin requirements
SOME ASPECTS OF INFANT FEEDING Quak Seng Hock Contents Introduction Importance of proper nutrition in the infant Breastfeeding Nutritional requirements of infants Introducing solid food Vitamin requirements
What and when to feed your child (6 to 24 months)
 Page 1 of 8 0:00:20.2 All parents want their children to grow up to be fit and healthy adults. In the first two years of a child s life their brains and bodies grow and develop more than at any other time.
Page 1 of 8 0:00:20.2 All parents want their children to grow up to be fit and healthy adults. In the first two years of a child s life their brains and bodies grow and develop more than at any other time.
Part I: Summary of New Regulations on Nutrition for Group Child Care Services
 NEW YORK CITY DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND MENTAL HYGIENE Part I: Summary of New Regulations on Nutrition for Group Child Care Services Effective Date: January 1, 2007 Effective January 1, 2007, Article 47
NEW YORK CITY DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND MENTAL HYGIENE Part I: Summary of New Regulations on Nutrition for Group Child Care Services Effective Date: January 1, 2007 Effective January 1, 2007, Article 47
To help make sense of some of the different dietary approaches out there, the Ministry has reviewed eight popular diets.
 Popular diets review The Ministry of Health recommends a nutritionally balanced eating pattern consistent with the Eating and Activity Guidelines for New Zealand Adults for good health. For people wanting
Popular diets review The Ministry of Health recommends a nutritionally balanced eating pattern consistent with the Eating and Activity Guidelines for New Zealand Adults for good health. For people wanting
Guidelines for the prescribing of specialist infant formula in primary care: Luton and Bedfordshire
 Guidelines for the prescribing of specialist infant formula in primary care: Luton and Bedfordshire September 2017 This document is a revised edition written and agreed by paediatricians, paediatric dietitians,
Guidelines for the prescribing of specialist infant formula in primary care: Luton and Bedfordshire September 2017 This document is a revised edition written and agreed by paediatricians, paediatric dietitians,
Nutrition. A Guide. A guide to the nutrition of babies and children with liver disease
 A Guide A guide to the nutrition of babies and children with liver disease Why is nutrition so important?... 4 What is a nutritional assessment?... 5 Why do some children with liver disease have poor nutrition?...
A Guide A guide to the nutrition of babies and children with liver disease Why is nutrition so important?... 4 What is a nutritional assessment?... 5 Why do some children with liver disease have poor nutrition?...
Algorithms & Information Sheets
 Minor Ailment Scheme Algorithms & Information Sheets Acute Diarrhoea Diarrhoea is an increased frequency, fluidity or volume of the bowel movements with the passage of soft and watery stools as compared
Minor Ailment Scheme Algorithms & Information Sheets Acute Diarrhoea Diarrhoea is an increased frequency, fluidity or volume of the bowel movements with the passage of soft and watery stools as compared
Staff Quiz. 1. Serial measurements are necessary for identification of growth trends in children. TRUE / FALSE
 Staff Quiz 1. Serial measurements are necessary for identification of growth trends in children. TRUE / FALSE 2. The WHO Child Growth Standards illustrate how healthy children should grow, whereas the
Staff Quiz 1. Serial measurements are necessary for identification of growth trends in children. TRUE / FALSE 2. The WHO Child Growth Standards illustrate how healthy children should grow, whereas the
Introduction to Global Child Health Elective for Pediatric Residents and Fellows Children s National Medical Center, Washington, DC.
 Introduction to Global Child Health Elective for Pediatric Residents and Fellows Children s National Medical Center, Washington, DC October 11-15, 2010 Pre-Course Test 1. You are preparing for an elective
Introduction to Global Child Health Elective for Pediatric Residents and Fellows Children s National Medical Center, Washington, DC October 11-15, 2010 Pre-Course Test 1. You are preparing for an elective
Diet, Nutrition and Inflammatory
 Diet, Nutrition and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Sumner Brooks, MPH, RDN, LD March 11, 2017 Objectives Identify factors that may alter nutritional status in IBD Understand the role of diet and nutrition
Diet, Nutrition and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Sumner Brooks, MPH, RDN, LD March 11, 2017 Objectives Identify factors that may alter nutritional status in IBD Understand the role of diet and nutrition
3. How would you balance this Breakfast?
 Healthy Eating and You A few questions before we start: 1. Eggs belong to which food group? A. Vegetables and fruit B. Grains C. Milk and Alternatives D. Meats and Alternatives Questions Continued 2. Which
Healthy Eating and You A few questions before we start: 1. Eggs belong to which food group? A. Vegetables and fruit B. Grains C. Milk and Alternatives D. Meats and Alternatives Questions Continued 2. Which
Afternoon Appointment - GASTROSCOPY AND COLONOSCOPY
 Endoscopy Unit MOVIPREP Afternoon Appointment - GASTROSCOPY AND COLONOSCOPY Information for patients Please follow these instructions and NOT the instructions in the box of bowel prep medication that you
Endoscopy Unit MOVIPREP Afternoon Appointment - GASTROSCOPY AND COLONOSCOPY Information for patients Please follow these instructions and NOT the instructions in the box of bowel prep medication that you
Bangladesh Breastfeeding Foundation
 Dealing with Child Undernutrition Using Local Foods: Experience from Bangladesh WBC 2012 New Delhi Dr. S. K. Roy MBBS, MSc. Nutri., Dip-in-Biotech, PhD, FRCP, Chairperson, Bangladesh Breastfeeding Foundation
Dealing with Child Undernutrition Using Local Foods: Experience from Bangladesh WBC 2012 New Delhi Dr. S. K. Roy MBBS, MSc. Nutri., Dip-in-Biotech, PhD, FRCP, Chairperson, Bangladesh Breastfeeding Foundation
Iron in your diet IMPORTANT PATIENT INFORMATION
 Iron in your diet IMPORTANT PATIENT INFORMATION Iron in your diet Why is iron important? Iron is very important because it helps your body to make haemoglobin. Haemoglobin, or Hb, is the protein found
Iron in your diet IMPORTANT PATIENT INFORMATION Iron in your diet Why is iron important? Iron is very important because it helps your body to make haemoglobin. Haemoglobin, or Hb, is the protein found
Understanding gestational diabetes
 Understanding gestational diabetes Gestational diabetes is a form of diabetes that occurs in women during pregnancy. About 12 14% of pregnant women will develop gestational diabetes, usually around the
Understanding gestational diabetes Gestational diabetes is a form of diabetes that occurs in women during pregnancy. About 12 14% of pregnant women will develop gestational diabetes, usually around the
Frequently Asked Questions on Zinc and Suggested Responses
 Last edited: September 27, 2012 Zinc Treatment of Childhood Diarrhea Frequently Asked Questions Diarrhoea still remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in developing countries. Every year more
Last edited: September 27, 2012 Zinc Treatment of Childhood Diarrhea Frequently Asked Questions Diarrhoea still remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in developing countries. Every year more
Medical Provider Guide to the Louisiana WIC Special Supplemental Nutrition Program
 Medical Provider Guide to the Louisiana WIC Special Supplemental Nutrition Program Rev 1/16 Provided by the Louisiana WIC Program Department of Health and Hospitals Office of Public Health Nutrition Services
Medical Provider Guide to the Louisiana WIC Special Supplemental Nutrition Program Rev 1/16 Provided by the Louisiana WIC Program Department of Health and Hospitals Office of Public Health Nutrition Services
5 DAY FOOD DIARY (1 YEAR)
 Please Fill in the Following Details: Child s Name:. Surname:..... Mother s Name:.. Surname:.... Child s Date of Birth:.. (DD/MM/YYYY) Please Select ( ) the Group Your Child is in: EARLY Introduction STANDARD
Please Fill in the Following Details: Child s Name:. Surname:..... Mother s Name:.. Surname:.... Child s Date of Birth:.. (DD/MM/YYYY) Please Select ( ) the Group Your Child is in: EARLY Introduction STANDARD
Hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar) & ketotic hypoglycaemia
 Information for parents and carers Hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar) & ketotic hypoglycaemia What is hypoglycaemia? Hypoglycemia is having a blood glucose (also known as blood sugar) level that is too low
Information for parents and carers Hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar) & ketotic hypoglycaemia What is hypoglycaemia? Hypoglycemia is having a blood glucose (also known as blood sugar) level that is too low
Nutritional Protocol for Blood and Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT)
 Nutritional Protocol for Blood and Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT) Scope This protocol details pre, during and post BMT nutritional assessment and management for all forms of BMT undertaken by OxBMT,
Nutritional Protocol for Blood and Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT) Scope This protocol details pre, during and post BMT nutritional assessment and management for all forms of BMT undertaken by OxBMT,
Eating After Your Gastric Bypass Surgery or Whipple Procedure
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Eating After Your Gastric Bypass Surgery or Whipple Procedure This information describes the dietary (eating and drinking) g uidelines you will need to follow after your g
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Eating After Your Gastric Bypass Surgery or Whipple Procedure This information describes the dietary (eating and drinking) g uidelines you will need to follow after your g
Contemporary Maternal-Newborn Nursing: 8 Edition Test Bank Ladewig
 Contemporary Maternal-Newborn Nursing: 8 Edition Test Bank Ladewig Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-contemporarymaternal-newborn-nursing-care-8th-edition/ Chapter 12 Question
Contemporary Maternal-Newborn Nursing: 8 Edition Test Bank Ladewig Link full download: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-contemporarymaternal-newborn-nursing-care-8th-edition/ Chapter 12 Question
Global Update. Reducing Mortality From Major Childhood Killer Diseases. infant feeding, including exclusive breastfeeding.
 INDIAN PEDIATRICS VOLUME 35-FEBRUARY 1998 Global Update Reducing Mortality From Major Childhood Killer Diseases Seven out of 10 childhood deaths in developing countries can be attributed to just five main
INDIAN PEDIATRICS VOLUME 35-FEBRUARY 1998 Global Update Reducing Mortality From Major Childhood Killer Diseases Seven out of 10 childhood deaths in developing countries can be attributed to just five main
Small. c h a n g e s big. benefits
 Small c h a n g e s big benefits Did you know that 3 in 5 adults in Northern Ireland weigh too much? Being overweight increases the risk of health problems, including heart disease, some cancers, diabetes
Small c h a n g e s big benefits Did you know that 3 in 5 adults in Northern Ireland weigh too much? Being overweight increases the risk of health problems, including heart disease, some cancers, diabetes
NUTRITION FOR A YOUNG BASKETBALL PLAYER
 NUTRITION FOR A YOUNG BASKETBALL PLAYER Nutrients Are substances in food that are necessary for a person s growth, development, reproduction and ability to do strenuous work. We can divide them into 6
NUTRITION FOR A YOUNG BASKETBALL PLAYER Nutrients Are substances in food that are necessary for a person s growth, development, reproduction and ability to do strenuous work. We can divide them into 6
NUTRITION MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN AND ADULTS WITH EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA. Colleen Vicente, RD, LDN, CNSC July 23 rd, 2018
 NUTRITION MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN AND ADULTS WITH EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA Colleen Vicente, RD, LDN, CNSC July 23 rd, 2018 1 MY BACKGROUND Pediatric Oncology, Burns,GI Home Infusion Ketogenic Diet, General
NUTRITION MANAGEMENT OF CHILDREN AND ADULTS WITH EPIDERMOLYSIS BULLOSA Colleen Vicente, RD, LDN, CNSC July 23 rd, 2018 1 MY BACKGROUND Pediatric Oncology, Burns,GI Home Infusion Ketogenic Diet, General
World Health Organization Growth Standards. First Nations and Inuit Health Alberta Region: Training Module May 2011
 World Health Organization Growth Standards First Nations and Inuit Health Alberta Region: Training Module May 2011 Acknowledgements First Nation and Inuit Health Alberta Region would like to thank the
World Health Organization Growth Standards First Nations and Inuit Health Alberta Region: Training Module May 2011 Acknowledgements First Nation and Inuit Health Alberta Region would like to thank the
LIFIB. Your Local Infant Feeding Information Board. LIFIB Briefing Paper: Lactose Intolerance in Infants
 LIFIB Your Local Infant Feeding Information Board Briefing Paper 2 January 2015 LIFIB Briefing Paper: in Infants The purpose of this Briefing Paper is to equip Midwives, Health Visitors and partners (including
LIFIB Your Local Infant Feeding Information Board Briefing Paper 2 January 2015 LIFIB Briefing Paper: in Infants The purpose of this Briefing Paper is to equip Midwives, Health Visitors and partners (including
A guide to the treatment and management of Childhood Nephrotic Syndrome
 A guide to the treatment and management of Childhood Nephrotic Syndrome CONTENTS Introduction What is Nephrotic Syndrome? What is the cause of Nephrotic Syndrome? What is the treatment? Side-effects of
A guide to the treatment and management of Childhood Nephrotic Syndrome CONTENTS Introduction What is Nephrotic Syndrome? What is the cause of Nephrotic Syndrome? What is the treatment? Side-effects of
How does my weight affect my fertility? Maternity Services
 How does my weight affect my fertility? Maternity Services Why is it important that i lose weight? You may be aware that being overweight or obese can lead you to develop a number of diseases such as diabetes,
How does my weight affect my fertility? Maternity Services Why is it important that i lose weight? You may be aware that being overweight or obese can lead you to develop a number of diseases such as diabetes,
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Common questions about treating diarrhoea with zinc and oral rehydration salts (ORS) SPACE FOR LOGO INTRODUCTION To treat childhood diarrhoea, the World Health Organization recommends
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS Common questions about treating diarrhoea with zinc and oral rehydration salts (ORS) SPACE FOR LOGO INTRODUCTION To treat childhood diarrhoea, the World Health Organization recommends
Nutrition Inspection Notebook (Updated April, 2011)
 Nutrition Inspection Notebook (Updated April, 2011) Publication code: HCR-0412-049 Name of Care Service: Address: Date of Inspection: Care Homes for Older People This Notebook is a tool to assist the Professional
Nutrition Inspection Notebook (Updated April, 2011) Publication code: HCR-0412-049 Name of Care Service: Address: Date of Inspection: Care Homes for Older People This Notebook is a tool to assist the Professional
Healthy Eating During Pregnancy
 Healthy Eating During Pregnancy Eating Well with Canada s Food Guide Food group Food Guide Serving Food Guide Servings per day Builds a healthy Women age 14 to 18 Women age 19 to 50 baby Vegetables and
Healthy Eating During Pregnancy Eating Well with Canada s Food Guide Food group Food Guide Serving Food Guide Servings per day Builds a healthy Women age 14 to 18 Women age 19 to 50 baby Vegetables and
It is important that you eat at regular times and divide the food intake well throughout the day.
 Dietary Advice Dietary treatment after surgery is divided into three periods. During the first two weeks after surgery, you should follow a liquid diet, then you should eat puree for two weeks, and thereafter
Dietary Advice Dietary treatment after surgery is divided into three periods. During the first two weeks after surgery, you should follow a liquid diet, then you should eat puree for two weeks, and thereafter
Emma Jordan Specialist Paediatric Dietitian
 Emma Jordan Specialist Paediatric Dietitian - Referred by school nurse age 11 years and 6 months - Presenting complaint: Low dietary intake, mainly vegetarian, low fat intake, getting increasing fussy
Emma Jordan Specialist Paediatric Dietitian - Referred by school nurse age 11 years and 6 months - Presenting complaint: Low dietary intake, mainly vegetarian, low fat intake, getting increasing fussy
Organic Acid Disorders
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Organic Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
EATING WELL AND CANCER
 EATING WELL AND CANCER 2 Why is it important for people with cancer to eat well? If the person you care for has cancer, it is more important than ever that they eat well. Unfortunately, it is often at
EATING WELL AND CANCER 2 Why is it important for people with cancer to eat well? If the person you care for has cancer, it is more important than ever that they eat well. Unfortunately, it is often at
Nutrition for sport and exercise. Our Bupa nurses have put together these simple tips to help you eat well for sport and exercise.
 Nutrition for sport and exercise Our Bupa nurses have put together these simple tips to help you eat well for sport and exercise. Whether you re doing a casual workout or training for a major sporting
Nutrition for sport and exercise Our Bupa nurses have put together these simple tips to help you eat well for sport and exercise. Whether you re doing a casual workout or training for a major sporting
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
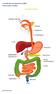 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) consists of a number of symptoms. The most
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) consists of a number of symptoms. The most
A Fact Sheet for Parents and Carers Healthy Eating for Diabetes
 A Fact Sheet for Parents and Carers Healthy Eating for Diabetes Healthy eating is important for children of all ages, including those living with diabetes. Children and teenagers with diabetes have the
A Fact Sheet for Parents and Carers Healthy Eating for Diabetes Healthy eating is important for children of all ages, including those living with diabetes. Children and teenagers with diabetes have the
15 Ileostomy. Eating and drinking with an ileostomy
 5 Ileostomy Eating and drinking with an ileostomy The function of the large bowel (colon) is to absorb water and salts from our food during the process of digestion. If you have an ileostomy either temporarily
5 Ileostomy Eating and drinking with an ileostomy The function of the large bowel (colon) is to absorb water and salts from our food during the process of digestion. If you have an ileostomy either temporarily
Nutrition for the heart. Geoffrey Axiak Nutritionist
 Nutrition for the heart Geoffrey Axiak Nutritionist The Food Pyramid Dairy 2-3 servings Vegetables 3-5 servings Breads/Grains 6-11 servings Fats & Oils Use Sparingly Proteins 2-3 servings Fruits 2-4 servings
Nutrition for the heart Geoffrey Axiak Nutritionist The Food Pyramid Dairy 2-3 servings Vegetables 3-5 servings Breads/Grains 6-11 servings Fats & Oils Use Sparingly Proteins 2-3 servings Fruits 2-4 servings
Don t delay Immunise for. Whooping Cough. Immunisation is FREE. weeks months. months
 Don t delay Immunise for Whooping Cough Immunisation is FREE 6 3 weeks months 5 months What is whooping cough? Whooping cough (Pertussis) is a highly contagious bacterial infection that is spread by coughing
Don t delay Immunise for Whooping Cough Immunisation is FREE 6 3 weeks months 5 months What is whooping cough? Whooping cough (Pertussis) is a highly contagious bacterial infection that is spread by coughing
Dietary information for people with polycystic kidney disease. Information for patients Sheffield Dietetics
 Dietary information for people with polycystic kidney disease Information for patients Sheffield Dietetics Introduction What is Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD)? PKD is a genetic disorder where your body
Dietary information for people with polycystic kidney disease Information for patients Sheffield Dietetics Introduction What is Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD)? PKD is a genetic disorder where your body
Nutrition & Dietetics Service
 Nutrition & Dietetics Service Dietitian: 0151 430 1201 This information has been produced by Registered Dietitians for the majority of the population taking into account ethnicity and religious beliefs.
Nutrition & Dietetics Service Dietitian: 0151 430 1201 This information has been produced by Registered Dietitians for the majority of the population taking into account ethnicity and religious beliefs.
Why is my Blood Sugar Too High?
 What is Gestational Diabetes? Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes which can occur during pregnancy and usually goes away after the baby is delivered. Gestational means in pregnancy and Diabetes
What is Gestational Diabetes? Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes which can occur during pregnancy and usually goes away after the baby is delivered. Gestational means in pregnancy and Diabetes
Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust. Love Your Bones. Diet and Osteoporosis. Richenda Rook Community Dietitian June 2016
 Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust Love Your Bones Diet and Osteoporosis Richenda Rook Community Dietitian June 2016 Page 2 Measures to Reduce the Risk of Osteoporosis Nutrition: - Calcium - Vitamin D - Nutrients
Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust Love Your Bones Diet and Osteoporosis Richenda Rook Community Dietitian June 2016 Page 2 Measures to Reduce the Risk of Osteoporosis Nutrition: - Calcium - Vitamin D - Nutrients
Returning. Diet P K U
 Returning to Diet P K U RETURNING TO A LOW PHENYLALANINE DIET PHENYLKETONURIA What is it? Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a condition inherited from both parents. It was diagnosed when you were about a week old
Returning to Diet P K U RETURNING TO A LOW PHENYLALANINE DIET PHENYLKETONURIA What is it? Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a condition inherited from both parents. It was diagnosed when you were about a week old
Case Study. The 4-year journey of feeding intolerance of an enterally-fed child from 9 months of age. Synopsis. Introduction/Overview
 Case Study The 4-year journey of feeding intolerance of an enterally-fed child from 9 months of age Library image Emma Liesl Silbernagl, Clinical lead HEN Dietitian, Home Enteral Nutrition Team, Lewisham
Case Study The 4-year journey of feeding intolerance of an enterally-fed child from 9 months of age Library image Emma Liesl Silbernagl, Clinical lead HEN Dietitian, Home Enteral Nutrition Team, Lewisham
MOVIPREP. Morning Appointment. Information for patients. Endoscopy Unit
 Endoscopy Unit MOVIPREP Morning Appointment Information for patients Please follow these instructions and NOT the instructions in the box of bowel prep medication that you have been sent This leaflet contains
Endoscopy Unit MOVIPREP Morning Appointment Information for patients Please follow these instructions and NOT the instructions in the box of bowel prep medication that you have been sent This leaflet contains
CHAPTER 4 Nutrition 51
 AP TE R CH 4 Nutrition 51 Learning About Nutrition Nutrition Nutrition is how the body uses food to stay healthy. Good nutrition means that the body gets enough of the foods it needs to stay healthy. Poor
AP TE R CH 4 Nutrition 51 Learning About Nutrition Nutrition Nutrition is how the body uses food to stay healthy. Good nutrition means that the body gets enough of the foods it needs to stay healthy. Poor
Healthy Eating. Eating healthily is about eating the right amount of food for your energy needs. Based on the eatwell plate, you should try to eat:
 Healthy Eating The eatwell plate shows the different types of food we need to eat and in what proportions to have a wellbalanced and healthy diet. It's a good idea to try to get this balance right every
Healthy Eating The eatwell plate shows the different types of food we need to eat and in what proportions to have a wellbalanced and healthy diet. It's a good idea to try to get this balance right every
Protecting your baby against rotavirus
 Protecting your baby against rotavirus Answers to your questions on the vaccine that protects babies against rotavirus infection the safest way to protect your baby From 1 July 2013, the routine childhood
Protecting your baby against rotavirus Answers to your questions on the vaccine that protects babies against rotavirus infection the safest way to protect your baby From 1 July 2013, the routine childhood
Appropriate prescribing of specialist infant formula feeds
 Appropriate Prescribing of Specialist Infant Formula Feeds Purpose of the guidance These guidelines aim to assist GPs and Health Visitors with information on the appropriate use of infant formula that
Appropriate Prescribing of Specialist Infant Formula Feeds Purpose of the guidance These guidelines aim to assist GPs and Health Visitors with information on the appropriate use of infant formula that
Lactation Diet. Purpose:
 Lactation Diet Purpose: During both pregnancy and lactation recommended dietary allowances should have a substantial increase in the intake of dietary energy, protein, and other nutrients. The National
Lactation Diet Purpose: During both pregnancy and lactation recommended dietary allowances should have a substantial increase in the intake of dietary energy, protein, and other nutrients. The National
Nutrition and Safe Food Handling Policy
 Nutrition and Safe Food Handling Policy Published November 2017 Review Date May 2019 Sources Education and Care Services National Regulations, October 2017 Guide to the Education and Care Services National
Nutrition and Safe Food Handling Policy Published November 2017 Review Date May 2019 Sources Education and Care Services National Regulations, October 2017 Guide to the Education and Care Services National
Chapter 3: Macronutrients. Section 3.1 Pages 52-55
 Chapter 3: Macronutrients Section 3.1 Pages 52-55 Diet Terms Nutrients The substances in food that gives us structural materials and energy. Macronutrients Nutrients that are required in large amounts.
Chapter 3: Macronutrients Section 3.1 Pages 52-55 Diet Terms Nutrients The substances in food that gives us structural materials and energy. Macronutrients Nutrients that are required in large amounts.
Nutrition and Safe Food Handling Policy
 Nutrition and Safe Food Handling Policy Published May 2016 Review Date November 2018 Sources Education and Care Services National Regulations, October 2017 Guide to the Education and Care Services National
Nutrition and Safe Food Handling Policy Published May 2016 Review Date November 2018 Sources Education and Care Services National Regulations, October 2017 Guide to the Education and Care Services National
Healthy Living. Making healthy meals and snacks is a good way to get healthy.
 40 Healthy Living Making healthy meals and snacks is a good way to get healthy. Healthy Food Gives us the fuel to nourish our bodies. Gives us energy. Helps us to cope with stress and keeps us healthy.
40 Healthy Living Making healthy meals and snacks is a good way to get healthy. Healthy Food Gives us the fuel to nourish our bodies. Gives us energy. Helps us to cope with stress and keeps us healthy.
Amino Acid Disorders. Disorder name: Tyrosinemia, type 1. What is tyrosinemia 1? Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Amino Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Amino Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Nutrition and Dietetics Patient Information Leaflet
 Dietary advice for patients following fundoplication surgery Nutrition and Dietetics Patient Information Leaflet Introduction The operation you have undergone has made the food pipe (oesophagus) less flexible
Dietary advice for patients following fundoplication surgery Nutrition and Dietetics Patient Information Leaflet Introduction The operation you have undergone has made the food pipe (oesophagus) less flexible
American University Of Beirut Medical Center Dietary Department DIET FOR LACTATION
 American University Of Beirut Medical Center Dietary Department Breast Feeding, your best choice WHY? DIET FOR LACTATION Breast milk Is nutritious: it provides your baby with a nutritionally complete feed
American University Of Beirut Medical Center Dietary Department Breast Feeding, your best choice WHY? DIET FOR LACTATION Breast milk Is nutritious: it provides your baby with a nutritionally complete feed
Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station
 Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station 1 Vitamin A deficiency 1 Instructions Please read through this Vitamin A information package and discuss amongst your group. You have 15 minutes to review this
Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station 1 Vitamin A deficiency 1 Instructions Please read through this Vitamin A information package and discuss amongst your group. You have 15 minutes to review this
Preparing for a Flexible Sigmoidoscopy
 The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Information for patients Preparing for a Flexible Sigmoidoscopy (an Examination of the Left Lower Part of Your Colon) Endoscopy Unit Tel: 01473 702352 DPS ref: 01086-18(RP)
The Ipswich Hospital NHS Trust Information for patients Preparing for a Flexible Sigmoidoscopy (an Examination of the Left Lower Part of Your Colon) Endoscopy Unit Tel: 01473 702352 DPS ref: 01086-18(RP)
