International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
|
|
|
- Rudolph Johns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN: Original Research Article Effect of Neuromuscular Taping Along with Reactive Postural Adjustment and Anticipatory Postural Adjustment in Improving Sitting Balance in Children with Spastic Diplegic Cerebral Palsy Jaya Dixit, Sujoy Roy Occupational Therapist, Sir Sunderlal Hospital, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, UP, India Corresponding Author: Jaya Dixit ABSTRACT Background: The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of neuromuscular taping over trunk muscles along with providing activities which gives internal and external perturbations on the static, dynamic trunk balancing abilities of children with cerebral palsy and generate some postural response in the trunk of these children with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy. Objective: To find out the effect of neuromuscular taping along with activities providing Reactive Postural Adjustments & Anticipatory Postural Adjustments, in improving sitting balance, in children with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy. Study Design: Pretest and Posttest experimental study design. Method: Spastic diplegic cerebral palsy children who were fulfilling the inclusion criteria were selected by convenient sampling from Occupational Therapy unit of Sir Sunderlal Hospital, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, India with sample size of 60. A written informed consent was obtained from the guardians. Ethical permission was taken from the institute. Pediatric Balance Scale & Pediatric Reach Test was used as instruments for measuring improvement in sitting balance. A frame for reaching and a platform for external perturbation were designed for the study. Therapy for both groups was given for 1 hour per session. Children in experimental group were exposed to 30 minutes each of Reactive Postural Adjustment & Anticipatory Postural Adjustment along with application of neuromuscular taping over the muscle belly of erector spinae. While control group, was exposed to Reactive Postural Adjustment & Anticipatory Postural Adjustment without neuromuscular taping over the trunk muscles. Results: Results of Wilcoxon signed rank test of Pediatric Reach Test were significant for experimental group and control group (P=0.004; 95% CI: 5.34 to and P=0.014; 95% CI: 4.16 to 7.89 respectively). There was also significance of results of Wilcoxon signed rank test of Pediatric Balance Scale in experimental and control group (P=0.025; 95% CI: 8.98 to for experimental group and P=0.005; 95% CI: 8.09 to 9.54 for control group) with the level of significance set atp This shows that results were significant for experimental group as well as control group. Also the results of Mann Whitney U test show that Z= for Pediatric Balance Scale is more making it more sensitive to capture changes in balances in children than Pediatric Reach Test with Z= with P=0.002; 95% CI: 4.14 to 9.00 and P=0.001; 95% CI: 7.56 to 9.70 with the level of significance set atp Conclusion: It can be concluded that application of neuromuscular taping along with activities providing Reactive Postural Adjustment &Anticipatory Postural Adjustment can be used to enhance & improve sitting balance among children with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy; so that they can have the functional balance in sitting, to safely meet the demands of everyday life. Key Words: Balance, Functional Activities, Perturbations, kinesiotape. International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 116
2 INTRODUCTION Disabled children are of great concern to a family as well as to the society. When disability is discussed, particularly in children, about a quarter of chronic childhood problems are neurological in origin. Cerebral palsy (CP) is the leading cause of chronic disability in children (Shoals MG 2007) making them physically and mentally handicapped and socially aloof. The worldwide incidence of CP is approximately 2 to 2.5 cases per 1000 live births (Health Grades Inc; c2011).in India, it is estimated at around 3 cases per 1000 live births; however, being a developing country the actual figure may be much higher than probable figures. There are about 25 lakhs CP children in India as per the last statistical information (MedIndia Inc; c ). It is a symptom complex or syndrome condition rather than a single disease. It is an umbrella term encompassing a group of non-progressive, non-contagious condition that causes motor impairment syndrome characterized by abnormalities in movement, posture, and tone (cdc.gov 2012). In short, it is a group of symptoms occurring due to the involvement of musculature, sense organs (i.e. vision, hearing, speech, etc.), and the mind, including intelligence at variable extents. It can be caused by any of pre-natal, natal, and post-natal factors and the primary eventual pathology is any type of injury to the developing brain. Due to the nonprogressive nature of the lesion, historically it is considered as static encephalopathy and excludes all the progressive neurological disorders (Parthasarathy A 2009).No effective treatment for the underlying brain damage has been formulated to date. All the sophisticated technologies and highly expensive and complicated therapies in the medical research field have failed to find a definite cure for this disease. As far as management or preventive aspect is concerned, no satisfactory criteria have been developed to date. Spastic quadriplegia constituted the predominant group (61 per cent), followed by spastic diplegia (22 per cent). Dyskinetic CP was present in 7.8 per cent of the cases. Acquired CP, particularly secondary to nervous system infections, constituted a significant proportion of cases. The clinical spectrum of CP is different in developing countries compared with developed countries. Associated problems were present in a majority (75 per cent) of cases, of which mental retardation was the commonest (72.5 per cent). Comprehensive assessment and early management of these problems are emphasized, which can minimize the extent of disabilities (Singhi PD et al 2002).One of the most common clinical types of cerebral palsy is spastic diplegia in which there is sensory motor impairment in the lower extremities more than in the upper ones as well as significant weakness in their trunk musculature (Tong- Wai R et al 2006). Most children with spastic diplegia have fine motor impairment in their upper extremities milder than lower ones. The primary functional problems include difficulty with reaching and grasping objects (Rosenbaum P 2008). Sitting is an important step for child to achieve the upright posture against gravity and also an essential activity to provide the postural background tone required for the functional movement of upper extremity (Milner M 1992). The control mechanism for reacting to unexpected external postural perturbation is called as Reactive Postural Adjustment (RPA) (Westcott Sarah L 2004) and that for anticipating internal postural perturbation related to production of voluntary movements in upper extremity is Anticipatory Postural adjustment (APA) (Westcott Sarah L 2004). The children with cerebral palsy failed to demonstrate, anticipatory activation of postural muscles as found not be activated first in these children when they reach in any directions, which shows that anticipatory postural adjustment in spastic diplegic cerebral palsy children is severely impaired (Gayle A et al 2006). Reactive Postural Adjustment is impaired among the children with spastic diplegic type of cerebral palsy (A Shumway International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 117
3 cook et al 2003). Results of sitting perturbation studies suggest that the children with cerebral palsy have disordered muscle activations during perturbations. Kinesio Taping (KT) or neuromuscular taping method which was first described by Dr. Kenzo Kasein 1996 (Kase Ket 1996)as it can be used to increase sensory stimulation, strengthen the weak muscles, inhibit spastic muscles, increase joint stability, increase functional motor skills, help with postural control and improve functional independence in pediatric rehabilitation clinics in addition to other therapeutic techniques (Kase K, Martin P, Yasukawa A 2006).KT, according to its inventor (Kase Ket 1996), is said to inhibit muscle tone if it is applied distally to proximally, whereas application in the opposite direction is used to facilitate a weak muscle. Results of different research works concluded that improvement in motor control can be achieved through enhancement of postural alignment, facilitation of sensor motor system and modulation of muscle tone. One of the most important problems in cerebral palsied children is the disturbance of normal postural control mechanisms, which seriously affect both functional activities of upper extremity and activities of daily living of the children (Carlberg EB 2005). Children with CP often rely upon inappropriate control strategies and faulty feedback mechanisms when learning to perform upper extremity functions and fine motor functions, which inevitably leads to functional dependency.the fundamental thought behind the therapeutic approaches applied in CP relies on achieving normal postural control and regaining motor functions and maximum possible independency in the activities of daily living. Neuromuscular taping is also used in pediatric clinical settings commonly, though, without proper evidence of its effectiveness in pediatric applications. Thus, this study may be considered as one of the fundamental works investigating the effectiveness of neuromuscular taping on sitting postural control related to independency in activities of daily living in cerebral palsied children. Effect of neuromuscular taping over the trunk muscles have been studied & followed however; there is a paucity of studies showing its effect along with Reactive Postural Adjustment & Anticipatory Postural Adjustment on improving sitting balance in children with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy. METHOD The study was conducted between November 2014 and July 2015 at Occupational Therapy unit of Sir Sunderlal Hospital, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, India. 60 children who were diagnosed as spastic diplegic cerebral palsy and referred to Occupational therapy unit by Department of pediatrics were included for the study. All cases were selected by convenient sampling. This study was a pretest& posttest experimental study. Inclusion Criteria 1. Children with Spastic diplegic cerebral palsy were included. 2. Both male & female children were included in the study. 3. Children between age group of 3 to 8 years were included. 4. Children in level 3 & 4 of Chailey floor sitting assessment were recruited. 5. Children having grade 1 criteria of Modified Ashworth scale were included. Exclusion Criteria 1. Children having other types of cerebral palsy were excluded. 2. Those children who were having cognitive problems making it difficult to follow the instructions were discarded from the study. 3. Children having associated neurological problems were excluded from the study. 4. Children having severe to moderate mental retardation were not taken for the study. 5. Children who were medically unstable as determined by history, or medical records, if International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 118
4 they had epilepsy, visual or auditory problems. 6. Children who had structural scoliosis. 7. Children who had participated in any previous application for therapeutic taping to the trunk muscles. 8. If children demonstrated allergic reactions to the adhesive neuromuscular taping. 9. All the children were free from any structural deformities; however, children demonstrated variable degrees of tightness Variables of Study Application of neuromuscular taping and Activities providing Reactive Postural Adjustments & Anticipatory Postural Adjustments were provided to the children as independent variables & sitting balance was considered as dependent variable. Instruments Used 1) Pediatric Balance Scale (PBS) (MR Franjoine et al 2003) & Pediatric Reach Test (PRT) (Bartlett D 2003) were used as instruments, to measure the changes in sitting balance in these children. 2) A frame was made with plastic to encourage horizontal & cross midline functional reach. This frame has 2 vertical plastic tubes placed over the wooden base & small platform made of ether flex secured in three positions. The width of wooden base was 45cm and height of two vertical plastic pipes was 46 cm. Three platforms were position on the frame each consecutive platform was 10cm above previous platform located on the far right & the far left of the frame. Two vertical plastic pipe along with small platforms were connected to the wooden base, which allowed the frame to slide forward & away from the child to accommodate each child s arm length.reach was consider successful when child touched the sticker which were placed over the platforms in the frame. Children were verbally encouraged to touch the sticker with one hand & then the other. We consider reach to be successful when the child touched (i.e. not grasped) the sticker. To assure consistency the motivators chosen were according to child s preferences.(gayle A 2006) 3) A platform for providing external perturbation was made with wood of 48x37 cm with 10cm height from the floor. It had four small wheels in the inferior surface, which made it move in forward & backward directions. Speed of movement was 60 mm at mm/s. (A Shumway cook 2003) 4) Kinesio tape is thin, cotton, porous fabric with acrylic adhesive that is non mediated and latexfree (Kinesio Tex 2005). Kinesio tape can be comfortably worn for 3 4 consecutive days, (including in the shower), without compromising the adhesive quality (Kase et al. 2003; Kinesio Tex 2005). Furthermore, due to the latex-free quality of Kinesio tape, moisture and air can flow through this porous fabric, limiting skin irritation (Kase et al. 2003; Kinesio Tex 2005). Kinesio tape can be stretched up to 130% 140% of its original length and can contract back to the normal resting position (Kase et al.2003; Kinesio Tex 2005). The elastic properties of Kinesio tape makes it unique, however, the efficacy of kinesio tape compared with other types of elastic tapes has yet to be investigated, and, therefore, substitution at this juncture cannot be recommended. Procedures The parents of the selected children were explained about the application of neuromuscular taping and activities providing Reactive Postural Adjustments & Anticipatory Postural Adjustments to their children and were told about the outcome of study. Written ethical consent was taken from the guardians of children with cerebral palsy who were taking part in the study. Ethical permission was also obtained from the institute for conducting the study. This study adhered to the tenets of Declaration of Helsinki. The children who were fulfilling the inclusion criteria were randomly distributed into two equal groups, International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 119
5 experimental group & control group. Then, the children were engaged in a three-day skin check to rule out rare toxic responses to adhesive neuromuscular taping before full inclusion in this study. A baseline assessment score of PBS and PRT was collected for children present in both the groups. Therapy for both the groups consisted of 1 hour of session (1) Control group who received activities providing RPA and APA. (2) Study group who received neuromuscular taping in addition to the same activities providing RPA and APA. Post test scores of Pediatric Balance Scale& Pediatric Reach Test were recorded after 9 months of study. Protocol Neuromuscular tape was applied on the erector spinae muscles from spinal level S1 to spinal level of C7 in the way Dr. Kase recommended (from insertion to origin) (Kase K 1966). KT of 5 cm width was used in the form of "fan technique" bilaterally applied to provide a predominantly sensory inhibition on the erector spinae muscles. The bands were applied for three days and then removed leaving the skin free for 24 hours, and then neuromuscular taping was applied again. In experimental group, Anticipatory Postural Adjustment activity was provided to the children by placing them in a comfortable & secured sitting over the mat. They were encouraged to touch cartoon stickers over the platform in the frame placed in front of them. For providing activity of Reactive Postural Adjustment children were placed comfortably & securely over the movable platform & were given forward / backward perturbations, which caused body to sway, forward &backward. Two mats were placed on either sides of platform to avoid injury to the children. All the activities given were demonstrated initially. RESULTS Data analysis: The test parameters were compared before & after therapy. Statistical calculations were performed with SPSS version 16.0 package. Statistical test were carried with the level of significance set atp 0.05.The raw score of Pediatric Balance Scale & Pediatric Reach Test pre intervention &post intervention were added & summed up into final scores. It was 2- tailed non parametric study because of ordinal data and small sample size. The changes in the Pediatric Balance Scale and Pediatric Reach Test within experimental and control groups were analyzed using Wilcoxon signed rank test. Mann Whitney U test was performed for knowing the significance outside the group. Descriptive characteristics: Number of subjects in experimental & control group were 30 in each within the age range of 3 to 7years in experimental group & 3 to 8 in control group. Mean age was 5.20±1.31 in experimental group and 6.00 ±1.63 in control group. There were 15 male and 15 female in experimental group were as there were 13 male and 17 female in control group. Wilcoxon signed rank test for Pediatric Reach Test: Significant results of experimental group and control group were obtained with (P=0.004; 95% CI: 5.34 to and P=0.014; 95% CI: 4.16 to 7.89 respectively) and Z= &Z=2.449 respectively with the level of significance set at P Wilcoxon signed rank test for Pediatric Balance Scale: The results (P=0.025; 95% CI: 8.98 to for experimental group and P=0.005; 95% CI: 8.09 to 9.54 for control group) shows that findings were more significant for experimental group as compared to control group with Z= & Z= respectively with level of significance set at P Results of Mann Whitney U test: Z= for Pediatric Balance Scale making it more sensitive to capture changes in balances in children as compared to Pediatric Reach Test with Z = and P=0.002; 95% CI:4.14 to 9.00 and P=0.001; 95% CI: 7.56 to 9.70 respectively with level of significance set at P International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 120
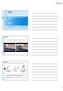
6 Figure 1: Showing a Child, Performing an Activity Providing Anticipatory Postural Adjustment on frame Figure 3: Showing the fanning technique of kinesiotaping over the trunk of a child Table 1: Descriptive Characteristics Characteristics Control Experimental Number of Subjects Age Range (Years) Mean Age(± Standard Deviation) 6.00± ±1.31 Gender (Male/Female) 13/17 15/15 Figure 2: Showing a Child, Performing an Activity Providing Reactive Postural Adjustment over the platform Table 2:Results of Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test (Pediatric Reach Test) Groups Z(2 tailed) P (2 tailed) 95% Confidence Interval Value Lower Limit Upper Limit Experimental Control *For both the groups P value is significant Table 3:Results of Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test (Pediatric Balance Scale) Groups Z (2 tailed) P (2 tailed) 95% Confidence Interval Value Lower Limit Upper Limit Experimental Control *For both the groups P value is significant Table 4: Results of Mann Whitney U tests (Pediatric Balance Scale & Pediatric Reach Test) Outcome Measures Z P 95% Confidence Interval Value Lower Limit Upper Limit PRT PBS *For both the groups P value is significant *PRT: Pediatric Reach Test; PBS: Pediatric Balance Scale DISCUSSION Sitting balance is commonly affected in children with cerebral palsy leading to difficulty in functional performance of upper extremity, as these children frequently use upper extremity for maintaining balance in sitting. Hence sitting is an important area for intervention to be considered while treating children with spastic diplegia cerebral palsy. The pre treatment results of the two groups indicated that children with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy often shows the difficulty to achieve well-balanced sitting posture and display poor trunk control. This agrees with Shumway-Cook A et al 2000 who revealed that children with CP often rely upon inappropriate control strategies and faulty feedback mechanisms when learning to maintain both static and dynamic sitting postures, which predictably leads to postural dyscontrol and functional dependency. International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 121
7 The purpose of this study was to determine that, if children with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy, who were given kinesiotape over the trunk muscles along with activities providing Reactive Postural Adjustment & Anticipatory Postural Adjustment, would exhibit greater improvement in sitting balance, than those who merely received the RPA and APA. Improvement in experimental group In respect to the study group who received kinesio taping which applied over the paraspinal region in addition to the designed RPA and APA therapeutic activity program, there was significant improvement in the sitting posture and trunk control in young children with spastic diplegic CP. This comes in consistent with Hsu et al., who reported that neuromuscular taping as an adjunct to the therapeutic procedures can improve strength, functional activities, proprioception, control and positioning. The postural control system in children with cerebral palsy cannot effectively control the body's position and motion in space because it lacks the ability to generate appropriate muscular force and to coordinate and integrate the sensory information received from various receptors throughout the body (Hsu Y.H et al 2009). KT increases blood circulation in the taped area (Ogura1998; Oliveria 1999; Vorhies 1999; Wallis 1999; Kase 1994; Kase and Hashimoto 2005; Murray 2005), and this physiological change may affect the muscle and myofascia functions after the application of neuromuscular taping helping the children to generated the necessary force required for the function. An additional theory is that neuromuscular taping stimulates sensory receptors and cutaneous mechanoreceptors at the taped area. Cutaneous mechanoreceptors activate nerve impulses when mechanical loads create deformation. The activation of cutaneous mechanoreceptors by an adequate stimulus causes local depolarizations that trigger nerve impulses along the afferent fiber traveling toward the central nervous system (Garcia 2001; Goo 2001; Halseth et al. 2004; Maruko 1999; Mori 2001; Murray and Husk 2001; Ogura1998; Vorhies 1999; Wallis 1999; Kase et al. 2003). The application of KT may apply pressure to the skin or stretch the skin, and this external load may stimulate cutaneous mechanoreceptors causing physiological changes in the taped area. Studies previously conducted to determine the effects of neuromuscular taping on cutaneous mechanoreceptors (Garcia 2001; Goo 2001; Halseth et al. 2004; Maruko 1999; Mori 2001; Murray and Husk 2001;Ogura 1998; Vorhies 1999; Wallis 1999) have reported that neuromuscular taping on select muscles and joints may improved muscle excitability. There is no study in the literature investigating the use of neuromuscular taping application with RPA and APA which is used in CP children with spastic diplegia. The current work is the first study conducted to investigate the effect of neuromuscular taping application on trunk posture along with RPA and APA in CP children with spastic diplegia. Improvement in control group The results of this study indicate that, there was improvement in control group. Perturbations were given to children with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy, by providing activities which challenge their Reactive Postural Adjustment & Anticipatory Postural Adjustment in neck, trunk & lower extremity, which helped them to improve sitting balance. These results can be supported by the results of A Shumway cook 2003 he found that typically developing children showed improvement in sitting balance in response to the massed practice on a moveable platform providing external perturbations. Also the results can be supported by the results of TR Kaminski 2001 which suggest that, during the performance of a functional task, dynamic changes that occur in the trunk and lower extremities prior to initiation of arm movement serve to stabilize the body and are used to initiate and assist whole body reaching.to maintain a good and stable posture is a challenge, because stability International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 122
8 requires complex interactions between nervous system, motor system, and the sensory system. In children with CP, these interactions are known to be affected, which may be a reason of postural control impairment and the inability to maintain stability. The sensory system cues the individual that there has been a perturbation which is provided by tactile, verbal and visual system Motor system organizes& cues appropriate activation of the muscle. While musculoskeletal system provides frame work on which we move and create the force to produce the postural activity (Westcott Sarah L 2004). The state of any of these system affects the overall postural activity in the individual.other system can also have an effect on the postural activity, like the directions given to the individuals, or the behavioral state and alertness of the individual (Nashner LM 1982).These components of balance were also taken care of while providing the activities. The improvement in balance as measured by Pediatric Balance Scale and Pediatric Reach Test can be attributed to an improvement in the coordination and recruitment of trunk and limb musculature that occurs as a result of practicing Anticipatory Postural Adjustment & Reactive Postural Adjustment through different type of activities.repetition of task is a prerequisite to skill acquisition, including balance in sitting, repetition in this study is provided by giving same activities throughout the study duration in each session (Dean CM 1997). Activities providing Anticipatory Postural Adjustment and Reactive Postural Adjustment which are used in his study need both cognition and motor process for performance. Limitations 1. Duration of study was small 2. Small sample size 3. Overhead reaching activities were not taken for activities providing Anticipatory postural Adjustment 4. No follow up study done. Recommendations 1. Study could be made by providing functional activities which provide balance perturbations along with kinesiotaping over the trunk musculatures for improving sitting balance in children with cerebral palsy. 2. Additional study can be conducted of long term benefits on children with cerebral palsy and other functional disabilities. 3. Future efforts also need to examine the effectiveness of balance perturbations along with kinesiotaping over the trunk musculature with a large sample. 4. Future studied in which improvement in sitting balance after application of kinesiotaping is captured by different measure which should include some functional measures. CONCLUSION It can be concluded that application of neuromuscular taping along with activities providing Reactive Postural Adjustment & Anticipatory Postural Adjustment can enhance & improve sitting balance among children with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy, so that they can have the functional balance in sitting, to safely meet demands of everyday life. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT I thank my patients and their parents for trusting me, and their cooperation during the course of study. Above all I thank God Almighty for providing me all that I wanted and much more to carry out my study. REFERENCES Shoals MG. Cerebral palsy: Diagnosis, Risk factors, Early intervention and Management of the spastic child. In: Datta AK, Sachdeva A, editors. Advances in Pediatrics. 1st ed. New Delhi: Jaypee Publishers; p Health Grades Inc; c2011. [Updated 2009 Apr 15; Accessed on 2013 Jan 22]. Rightdiagnosis.com [homepage on the Internet] Available from: http// y/stats-country.htm. MedIndia Inc; c [Updated on 2010 Oct 04; Accessed on 2013 Jan 22]. Medindia.net [homepage on the Internet]. Kathy Jones. Incidence of Cerebral Palsy International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 123
9 Remains Constant in India on Indian Health News. Available from: Cerebral-Palsy-Remains-Constant-in-India htm. cdc.gov [homepage on the Internet] Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. [last updated 2012 Sep 7; accessed on 2013 Jan 22]. Available from: Parthasarathy A. e book. 4th ed. Vol. 2. Jaypee Digital; IAP Textbook of Pediatrics; p Singhi PD et al 2002.Clinical spectrum of cerebral palsy in north India - an analysis of 1000 cases.j Trop Pediatr.june 48(3): Shumway-Cook A and Woollacott M.H (2000). Motor Control: Theory and Practical Applications. 2nd Edition, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. Hsu Y.H., Chen W.Y., Lin H.C., Wang W.T. And Shih Y.F (2009). The Effects of Taping On Scapular Kinematics and Muscle Performance in Baseball Players with Shoulder Impingement Syndrome. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol; Furderer S et al (1999) Influence of dual tasks on sitting postural sway in children and adolescents with myelomeningocele. Gait Posture; 30: Furderer S, Eysel P, Hopf C, Heine J (1999). Sagittal static imbalance in myelomeningocele patients: Improvement in sitting ability by partial and total gibbus resection. Eur Spine J; 8: Sarah L Westcott, Robert J, Palisano et al (2004). Muscle force and range of motion as predictors of standing balance in children with cerebral palsy. Journal of Physical and Occupational Therapy in Pediatrics; 24, 1-2: Keshner EA, Woollacott MH, Debu (1988).Neck, trunk & limb muscle response during postural perturbations in humans. Exp. Brain Res; 71, 3: Gayle A, Wiens PT, Kenneth P, Pitetti (2006). A Method for measure reaching capacity of children with neuromuscular disorders. Pediatric Physical Therapy; 18: A Shumway cook, S Hutchinson, D Kartin (2003).Effect of balance training on recovery of stability in children with cerebral palsy. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology; 45: TR Kaminski, S.Simpkins (2001).The effect of stance confirmation and target distance on reaching. Exp Brain Res; January, 136: Bernstein N (1967). Coordination and regulation of movement.2 nd edition. Dergranmon Publications. Oxford University press. Nashner LM, Cordo PJ (1982).Properties of postural adjustments associated with rapid arm movement s.j Neurophysiol; Feb, 47, 2: Dean CM, Sheperd RB (1997) Task related training improves performance of seated reaching tasks after stroke. A randomized controlled trail. Stroke; April, 28, 4: MR Franjoine et al (2003).Pediatric balance scale. A modified version of the berg balance scale for the school age child with mild to moderate motor impairment. Pediat Phys Ther; 2: Bartlett D, Birmingham T (2003).Validity and reliability of pediatric reach test. Pediat. PhysTher; 15: Dean, Shephared (1997). Task related training improves performance of seated reaching task following stroke. A randomized control trail. Stroke; 28: Frossberg H, Hirschfed H (1994). Postural adjustment in sitting humans following external perturbations. Muscle activity and kinematics. Exp Brain Res; 97,3: Rosenbaum P.L., Palisano R.J., Bartlett D.J., Galuppi B.E. And Russell D.J (2008). Development of the Gross Motor Function Classification System for Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol; 50: Yasukawa A, Patel P, Sisung C (2006). Pilot study: Investigation the effects of Kinesio Taping in an acute pediatric rehabilitation setting. Am J OccupTher; 60: Kase K, Tatsuyuk H and Tomoki O (1996). Development of KinesioTM tape. Kinesio TM Taping Perfect Manual. Kinesio Taping Association, 6-10: Kase K, Martin P, Yasukawa A (2006). Kinesiotaping in pediatrics. Fundamentals and whole body taping. Kinesio Taping Association; Albuquerque, New Mexico, USA; Tong-Wai R, Webster R and Shevel M (2006). A clinical and etiologic profile of spastic diplegia. Pediatric Neurology; 34(3): Bax M., Goldstein M., Rosenbaum P., Gold- Stein M., Rosenbaum P., Leviton A., Paneth N., Dan B., Jacobsson B. And Damiano D (2005).Exec-Utive Committee For The Definition Of Cerebral Palsy: Proposed International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 124
10 Definition And Classification Of Cerebral Palsy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol; Aug, 47 (8): Jones M.W., Morgan E., Shelton J.E. And Thorogood C (2007). Cerebral Palsy: Introduction and Diagnosis (Part I). J. Pediatr. Health Care; May-Jun, 21 (3): Miller C.M., Greenwood S., Michael Gleeson M., Nardone F. And Faigle K (2010).Kiensio Taping and Hypotonia. The International Organisation of Physical Therapists in Paediatrics; Vol. 5, Pp. 10. Ogura R (1998) Overuse syndrome for longdistance runners and taping [in Japanese]. 14th Annual Kinesio Taping International Symposium Review Oliveria R (1999) Soft tissue injuries in sports people The contribution of kinesiotaping [in Japanese]. 15th Annual Kinesio Taping International Symposium Review Vorhies, D (1999).Testimonial of a kinesiotape convert [in Japanese]. 15th Annual Kinesio Taping International Symposium Review Wallis J (1999) Effects of kinesio taping on pain perception of athletes with patellofe pain syndrome A pilot study [in Japanese]. 15th Annual Kinesio Taping International Symposium Review Kase K (1994) Illustrated Kinesio-Taping. 2nd ed. Tokyo, Japan: Ken i-kai Information. 6 9, 73. Kase K (2001) Until today from birth of Kinesio taping method [in Japanese]. Albuquerque,NM: KMS, LLC Kase K, Hashimoto T (13 March 2005) Changes in the volume of peripheral blood flow by using kinesio tape. Available at asp?custcomkey =13776&CategoryKey=13777&pn=Page&Do mname= kinesiotaping.com Kase K, Hashimoto T, Okane T (1996) Kinesio taping perfect manual: Amazing taping therapy to eliminate pain and muscle disorders. Albuquerque, NM: KMS, LLC. Kase K, Wallis J, Kase T (2003) Clinical Therapeutic Applications of the Kinesio Taping Method. Tokyo, Japan: Ken i-kai Information. Murray H (25 February 2005) Effects of kinesio taping on muscle strength after ACLrepair. Available at mkey = 13776&CategoryKey= 13785&pn= Page&DomName=kinesiotaping.com Murray H, Husk L (2001) Effect of kinesio taping on proprioception in the ankle. Journal of Orthopedic Sports Physical Therapy 31: A- 37. Garcia D (2001) Kinesio taping for the sense of balance on knee [in Japanese]. 16 th Annual Kinesio Taping International Symposium Review; Goo J (2001) A new step for treatment of ankle sprain [in Japanese]. 16th Annual Kinesio Taping International Symposium Review: Halseth T, McChesney JW, DeBeliso M, Vaughn R, Lien, J (2004) The effects of kinesio taping on proprioception at the ankle. Journal of Sports Science and Medicine 3:1-7. Maruko K (1999) Aqua therapy using kinesio taping of central cooperation disabled pediatrics [in Japanese]. 15th Annual Kinesio Taping International Symposium Review , Mori S (2001) How Kinesio taping method can induce effectiveness for treatment of scapular arch [in Japanese]. 16th Annual Kinesio Taping International Symposium Review Murray H (25 February 2005) Effects of kinesio taping on muscle strength after ACLrepair. Available at mkey = 13776&CategoryKey= 13785&pn= Page&DomName=kinesiotaping.com Murray H, Husk L (2001) Effect of kinesio taping on proprioception in the ankle. Journal of Orthopedic Sports Physical Therapy; 31: A- 37. How to cite this article: Dixit J, Roy S. Effect of neuromuscular taping along with reactive postural adjustment and anticipatory postural adjustment in improving sitting balance in children with spastic diplegic cerebral palsy. Int J Health Sci Res. 2018; 8(11): ****** International Journal of Health Sciences & Research ( 125
JMSCR Vol 07 Issue 01 Page January 2019
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.95 The Effect of Neuromuscular Taping in Improving Upper Extremity Functions in Children with
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.95 The Effect of Neuromuscular Taping in Improving Upper Extremity Functions in Children with
The Effect of Kinesio Taping on Lower Trunk Range of Motions
 Research in Sports Medicine ISSN: 1543-8627 (Print) 1543-8635 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/gspm20 The Effect of Kinesio Taping on Lower Trunk Range of Motions Ayako Yoshida
Research in Sports Medicine ISSN: 1543-8627 (Print) 1543-8635 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/gspm20 The Effect of Kinesio Taping on Lower Trunk Range of Motions Ayako Yoshida
Int J Physiother.Vol1 (2), 40-45, June (2014) ISSN:
 Int J Physiother.Vol1 (2), 40-45, June (2014) ISSN: 2348-8336 Sandesh Rayamajhi 1 Dipika Khanal 2 Mallikarjunaiah H S 3 ABSTRACT Background: Stroke has been considered to be the most common cause of neurological
Int J Physiother.Vol1 (2), 40-45, June (2014) ISSN: 2348-8336 Sandesh Rayamajhi 1 Dipika Khanal 2 Mallikarjunaiah H S 3 ABSTRACT Background: Stroke has been considered to be the most common cause of neurological
Cross Syndrome. Advisor: Rodger Tepe PhD. Submitted By: Ian Ahearn Seth Bird Matthew Gordon
 1 Cross Syndrome Advisor: Rodger Tepe PhD Submitted By: Ian Ahearn Seth Bird Matthew Gordon A research project done in partial completion for the degree of Doctorate of Chiropractic for Logan College of
1 Cross Syndrome Advisor: Rodger Tepe PhD Submitted By: Ian Ahearn Seth Bird Matthew Gordon A research project done in partial completion for the degree of Doctorate of Chiropractic for Logan College of
KT & Hypotonia. Introduction: Study completed by:
 KT & Hypotonia Study completed by: Carol Motyka-Miller, MAPT, CKTP Susan Greenwood, PT, DPT Michael Gleeson, PT, DPT Florence Nardone, PT, DPT Kristen Faigle, SPT (University of Medicine and Dentistry,
KT & Hypotonia Study completed by: Carol Motyka-Miller, MAPT, CKTP Susan Greenwood, PT, DPT Michael Gleeson, PT, DPT Florence Nardone, PT, DPT Kristen Faigle, SPT (University of Medicine and Dentistry,
TheraSuit Orthosis I. The History and Development of TheraSuit :
 -- www.genius4kids.com -- TheraSuit Orthosis I. The History and Development of TheraSuit : TheraSuit, a soft, dynamic, proprioceptive orthotic, is a full-featured dynamic correction clothing. The invention
-- www.genius4kids.com -- TheraSuit Orthosis I. The History and Development of TheraSuit : TheraSuit, a soft, dynamic, proprioceptive orthotic, is a full-featured dynamic correction clothing. The invention
The Effect of Kinesio Taping on Seated Postural Control in Spastic Diplegic Cerebral Palsy Children
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, December: 37-44, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net The Effect of Kinesio Taping on Seated Postural Control in Spastic Diplegic Cerebral Palsy Children WANEES
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, December: 37-44, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net The Effect of Kinesio Taping on Seated Postural Control in Spastic Diplegic Cerebral Palsy Children WANEES
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Short Term Effects of Kinesiology Taping on Mechanical Neck Pain Joshi Rasika S 1, Srivastava
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Short Term Effects of Kinesiology Taping on Mechanical Neck Pain Joshi Rasika S 1, Srivastava
Objectives_ Series II
 Interaction Between the Development of Posture Control and Executive Function of Attention (Reilly et. al 2008) Journal of Motor Behavior, Vol. 40, No. 2, 90 102 Objectives_ Series II Gain an understanding
Interaction Between the Development of Posture Control and Executive Function of Attention (Reilly et. al 2008) Journal of Motor Behavior, Vol. 40, No. 2, 90 102 Objectives_ Series II Gain an understanding
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Intro to Physical Therapy for Neuromuscular Conditions. PT Evaluation. PT Evaluation
 Slide 1 Intro to Physical Therapy for Neuromuscular Conditions PTA 103 Introduction to Clinical Practice 2 Slide 2 Mental status: consciousness, attention, orientation, cognition Communication: speech
Slide 1 Intro to Physical Therapy for Neuromuscular Conditions PTA 103 Introduction to Clinical Practice 2 Slide 2 Mental status: consciousness, attention, orientation, cognition Communication: speech
Integrating Sensorimotor Control Into Rehabilitation
 Integrating Sensorimotor Control Into Rehabilitation BRADY L. TRIPP, PhD, LAT, ATC Florida International University Key Points As evidence accumulates, so does our appreciation of the integral roles that
Integrating Sensorimotor Control Into Rehabilitation BRADY L. TRIPP, PhD, LAT, ATC Florida International University Key Points As evidence accumulates, so does our appreciation of the integral roles that
Standing in children with bilateral spastic cerebral palsy: Aspects of muscle strength, vision and motor function
 Standing in children with bilateral spastic cerebral palsy: Aspects of muscle strength, vision and motor function Cecilia Lidbeck, PT, PhD Department of Women s and Children s Health Karolinska Institutet
Standing in children with bilateral spastic cerebral palsy: Aspects of muscle strength, vision and motor function Cecilia Lidbeck, PT, PhD Department of Women s and Children s Health Karolinska Institutet
Normal development & reflex
 Normal development & reflex Definition of Development : acquisition & refinement of skills 1 대근육운동발달 2 소근육운동발달 3 대인관계및사회성발달 4 적응능력혹은비언어성발달 5 의사소통및언어발달 6 학습, 청각, 시각의발달 Department of Rehabilitation Medicine,
Normal development & reflex Definition of Development : acquisition & refinement of skills 1 대근육운동발달 2 소근육운동발달 3 대인관계및사회성발달 4 적응능력혹은비언어성발달 5 의사소통및언어발달 6 학습, 청각, 시각의발달 Department of Rehabilitation Medicine,
Effect of backward walking training on dynamic balance in children with spastic. hemiplegic cerebral palsy.
 Effect of backward walking training on dynamic balance in children with spastic hemiplegic cerebral palsy Yu-Jin Kim 1, Hyun-Ik Jang 2, Kum-Hee Ko 3, Woo-Nam Chang 4, Sun-Kyu Lim 5 1,2,3,4,5 Department
Effect of backward walking training on dynamic balance in children with spastic hemiplegic cerebral palsy Yu-Jin Kim 1, Hyun-Ik Jang 2, Kum-Hee Ko 3, Woo-Nam Chang 4, Sun-Kyu Lim 5 1,2,3,4,5 Department
ii. Reduction of tone in upper limb Lycra arm splints improve movement fluency in children with cerebral palsy.
 Guidelines for the Provision of Dynamic Compression for people diagnosed with Multiple Sclerosis The use of Lycra garments in patients with the diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis has been initiated with very
Guidelines for the Provision of Dynamic Compression for people diagnosed with Multiple Sclerosis The use of Lycra garments in patients with the diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis has been initiated with very
The Effect of Intrinsic Foot Muscle on Type of Feedback According to Ability of Ankle Instability and Balance
 Vol.132 (Healthcare and Nursing 2016), pp.155-160 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016. The Effect of Intrinsic Foot Muscle on Type of Feedback According to Ability of Ankle Instability and Balance Eunsang
Vol.132 (Healthcare and Nursing 2016), pp.155-160 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016. The Effect of Intrinsic Foot Muscle on Type of Feedback According to Ability of Ankle Instability and Balance Eunsang
CHAPTER 8 BACK CARE 8 BACK CARE. Posture
 CHAPTER 8 BACK CARE 8 BACK CARE Nearly 25% of the lost-time injuries in construction are related to the back. More than half of these injuries result from lifting excessive weight or lifting incorrectly.
CHAPTER 8 BACK CARE 8 BACK CARE Nearly 25% of the lost-time injuries in construction are related to the back. More than half of these injuries result from lifting excessive weight or lifting incorrectly.
Pilates for Chronic Low Back Pain
 Pilates for Chronic Low Back Pain Julianne Bettencourt March 23, 2015 Course Year: 2014 Integrated Fitness, Visalia, CA Abstract Low back pain is an injury that affects thousands of people every day and
Pilates for Chronic Low Back Pain Julianne Bettencourt March 23, 2015 Course Year: 2014 Integrated Fitness, Visalia, CA Abstract Low back pain is an injury that affects thousands of people every day and
Forskning inden for truncus postural kontrol. CPOP DAG 22. maj What difference does trunk postural control make to function?
 Forskning inden for truncus postural kontrol CPOP DAG 22. maj 2014 Derek Curtis PT MSc Phd stud. Hvidovre Hospital Københavns Universitet What difference does trunk postural control make to function? Clinical
Forskning inden for truncus postural kontrol CPOP DAG 22. maj 2014 Derek Curtis PT MSc Phd stud. Hvidovre Hospital Københavns Universitet What difference does trunk postural control make to function? Clinical
The SUPPORT Trial: SUbacromial impingement syndrome and Pain: a randomised controlled trial Of exercise and injection
 The SUPPORT Trial: SUbacromial impingement syndrome and Pain: a randomised controlled trial Of exercise and injection SUPPORT Physiotherapy Intervention Training Manual Authors: Sue Jackson (SJ) Julie
The SUPPORT Trial: SUbacromial impingement syndrome and Pain: a randomised controlled trial Of exercise and injection SUPPORT Physiotherapy Intervention Training Manual Authors: Sue Jackson (SJ) Julie
Posture. Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 10 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Posture Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 10 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Posture = body alignment = the relative arrangement of parts of the body Changes with the positions and movements of the body throughout the day
Posture Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 10 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Posture = body alignment = the relative arrangement of parts of the body Changes with the positions and movements of the body throughout the day
Physical Therapist Assistant Principles of Neuromuscular Rehabilitation
 Western Technical College 10524144 Physical Therapist Assistant Principles of Neuromuscular Rehabilitation Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total
Western Technical College 10524144 Physical Therapist Assistant Principles of Neuromuscular Rehabilitation Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total
Orthopedic Issues in Children with Special Healthcare Needs
 Orthopedic Issues in Children with Special Healthcare Needs Kathryn A Keeler, MD Assistant Professor University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Department
Orthopedic Issues in Children with Special Healthcare Needs Kathryn A Keeler, MD Assistant Professor University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Medicine, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery and Department
Brunel balance assessment (BBA)
 Brunel balance assessment (BBA) Tyson, S Title Authors Type URL Brunel balance assessment (BBA) Tyson, S Published Date 2004 Monograph This version is available at: http://usir.salford.ac.uk/4886/ USIR
Brunel balance assessment (BBA) Tyson, S Title Authors Type URL Brunel balance assessment (BBA) Tyson, S Published Date 2004 Monograph This version is available at: http://usir.salford.ac.uk/4886/ USIR
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Effects of Neurodevelopmental Therapy on Gross Motor Function in Children with Cerebral Palsy. Introduction. Abstract Objective
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of Neurodevelopmental Therapy on Gross Motor Function in Children with Cerebral Palsy How to Cite This Article: labaf S, Shamsoddini A, Hollisaz MT, Sobhani V, Shakibaee A. Effects
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of Neurodevelopmental Therapy on Gross Motor Function in Children with Cerebral Palsy How to Cite This Article: labaf S, Shamsoddini A, Hollisaz MT, Sobhani V, Shakibaee A. Effects
Functional Ability Screening Tools for the Clinic
 Functional Ability Screening Tools for the Clinic Shelley Hockensmith,, P.T., NCS Objectives Review screening tools for physical or functional ability including Five Times Sit to Stand, Walking Speed,
Functional Ability Screening Tools for the Clinic Shelley Hockensmith,, P.T., NCS Objectives Review screening tools for physical or functional ability including Five Times Sit to Stand, Walking Speed,
ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals TRUNK
 ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals TRUNK Posture and Balance Posture refers to the biomechanical alignment of the individual body parts and the orientation of the body to the
ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals TRUNK Posture and Balance Posture refers to the biomechanical alignment of the individual body parts and the orientation of the body to the
By: Griffin Smith & Eric Foch
 By: Griffin Smith & Eric Foch What is Cerebral Palsy? Non progressive neurodevelopmentalcondition Signs: Spasticity Ataxia Muscle rigidity idit Athetosis Tremor Distribution Among Limbs Why study cerebral
By: Griffin Smith & Eric Foch What is Cerebral Palsy? Non progressive neurodevelopmentalcondition Signs: Spasticity Ataxia Muscle rigidity idit Athetosis Tremor Distribution Among Limbs Why study cerebral
University of Manitoba - MPT: Neurological Clinical Skills Checklist
 Name: Site: Assessment Skills Observed Performed Becoming A. Gross motor function i. Describe movement strategies (quality, devices, timeliness, independence): supine sidelying sit stand supine long sitting
Name: Site: Assessment Skills Observed Performed Becoming A. Gross motor function i. Describe movement strategies (quality, devices, timeliness, independence): supine sidelying sit stand supine long sitting
Core exercises. Abdominal Ball Passing
 Abdominal Ball Passing Start with ball in hands, tighten abdominal muscle to stabilize spine and lift legs up to grasp ball. Pass ball to feet. Lower legs down while keeping your abdominal muscles tight
Abdominal Ball Passing Start with ball in hands, tighten abdominal muscle to stabilize spine and lift legs up to grasp ball. Pass ball to feet. Lower legs down while keeping your abdominal muscles tight
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Yasukawa, A., Patel, P., & Sisung, C. (2006). Pilot study: Investigating the effects of Kinesio Taping in an acute pediatric rehabilitation setting. American Journal of
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Yasukawa, A., Patel, P., & Sisung, C. (2006). Pilot study: Investigating the effects of Kinesio Taping in an acute pediatric rehabilitation setting. American Journal of
Presented by Lori P. Michiel
 Presented by Lori P. Michiel NASM Certified Personal Trainer Fifty Plus FitnessTM www.fiftyplusfitness.biz Learn how to build a functionally fit, strong and stable body for active, healthy aging: 1. Evaluate
Presented by Lori P. Michiel NASM Certified Personal Trainer Fifty Plus FitnessTM www.fiftyplusfitness.biz Learn how to build a functionally fit, strong and stable body for active, healthy aging: 1. Evaluate
Benefits of Weight bearing increased awareness of the involved side decreased fear improved symmetry regulation of muscle tone
 From the information we have gathered during our Evaluation, the Clinical Reasoning we used to identify key problem areas and the Goals Established with functional outcomes we now have enough information
From the information we have gathered during our Evaluation, the Clinical Reasoning we used to identify key problem areas and the Goals Established with functional outcomes we now have enough information
Re-establishing establishing Neuromuscular
 Re-establishing establishing Neuromuscular Control Why is NMC Critical? What is NMC? Physiology of Mechanoreceptors Elements of NMC Lower-Extremity Techniques Upper-Extremity Techniques Readings Chapter
Re-establishing establishing Neuromuscular Control Why is NMC Critical? What is NMC? Physiology of Mechanoreceptors Elements of NMC Lower-Extremity Techniques Upper-Extremity Techniques Readings Chapter
American Council on Exercise
 American Council on Exercise February 23, 2015 Fitnovatives Blog Exercise Progressions for Clients Who Are Overweight or Are Affected by Obesity While there is no single right way to train clients who
American Council on Exercise February 23, 2015 Fitnovatives Blog Exercise Progressions for Clients Who Are Overweight or Are Affected by Obesity While there is no single right way to train clients who
Physical activity effects on postural adjustments: a review
 Proceeding 10th INSHS International Christmas Sport Scientific Conference, 4-5 December 2015. International Network of Sport and Health Science. Szombathely, Hungary Physical activity effects on postural
Proceeding 10th INSHS International Christmas Sport Scientific Conference, 4-5 December 2015. International Network of Sport and Health Science. Szombathely, Hungary Physical activity effects on postural
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Effect of Scapular Position on Neck Pain in Swimmers Dr Jyoti Dahiya 1, Dr Tarundeep Kaur 2
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Effect of Scapular Position on Neck Pain in Swimmers Dr Jyoti Dahiya 1, Dr Tarundeep Kaur 2
LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS. Please check with the LCC bookstore for the required texts for this class.
 LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS SPECIAL NOTE: This brief syllabus is not intended to be a legal contract. A full syllabus will be distributed to students at the first class session. TEXT AND SUPPLEMENTARY
LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS SPECIAL NOTE: This brief syllabus is not intended to be a legal contract. A full syllabus will be distributed to students at the first class session. TEXT AND SUPPLEMENTARY
Home Exercise Program Progression and Components of the LTP Intervention. HEP Activities at Every Session Vital signs monitoring
 Home Exercise Program Progression and Components of the LTP Intervention HEP Activities at Every Session Vital signs monitoring Blood pressure, heart rate, Borg Rate of Perceived Exertion (RPE) and oxygen
Home Exercise Program Progression and Components of the LTP Intervention HEP Activities at Every Session Vital signs monitoring Blood pressure, heart rate, Borg Rate of Perceived Exertion (RPE) and oxygen
GLOSSARY. Active assisted movement: movement where the actions are assisted by an outside force.
 GLOSSARY The technical words used in this guide are listed here in alphabetic order. The first time one of these words is used in the guide, it is written in italics. Sometimes there is reference to a
GLOSSARY The technical words used in this guide are listed here in alphabetic order. The first time one of these words is used in the guide, it is written in italics. Sometimes there is reference to a
DEEP SQUAT. Upper torso is parallel with tibia or toward vertical Femur below horizontal Knees are aligned over feet Dowel aligned over feet
 APPENDIX 9 SCORING CRITERIA DEEP SQUAT Upper torso is parallel with tibia or toward vertical Femur below horizontal Knees are aligned over feet Dowel aligned over feet Upper torso is parallel with tibia
APPENDIX 9 SCORING CRITERIA DEEP SQUAT Upper torso is parallel with tibia or toward vertical Femur below horizontal Knees are aligned over feet Dowel aligned over feet Upper torso is parallel with tibia
Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment
 Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott, Williams
Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott, Williams
تأثير شريط الكينسيو فى التحكم بالركبة الطرقاء عند أطفال متالزمة داون
 EFFICACY OF KINESIO TAPING IN CONTROLLING GENU RECURVATUM IN DOWN SYNDROME CHILDREN تأثير شريط الكينسيو فى التحكم بالركبة الطرقاء عند أطفال متالزمة داون SUPERVISORS PROF. DR. FATEN HASSAN ABDELAZEM Chairman
EFFICACY OF KINESIO TAPING IN CONTROLLING GENU RECURVATUM IN DOWN SYNDROME CHILDREN تأثير شريط الكينسيو فى التحكم بالركبة الطرقاء عند أطفال متالزمة داون SUPERVISORS PROF. DR. FATEN HASSAN ABDELAZEM Chairman
Posture and balance. Center of gravity. Dynamic nature of center of gravity. John Milton BIO-39 November 7, 2017
 Posture and balance John Milton BIO-39 November 7, 2017 Center of gravity The center of gravity (COG) of the human body lies approximately at the level of the second sacral vertebrae (S2), anterior to
Posture and balance John Milton BIO-39 November 7, 2017 Center of gravity The center of gravity (COG) of the human body lies approximately at the level of the second sacral vertebrae (S2), anterior to
A Collection of Brief, Reliable and Valid Instruments to Obtain a Holistic Picture of Children with Cerebral Palsy: Products of the Move & PLAY Study
 A Collection of Brief, Reliable and Valid Instruments to Obtain a Holistic Picture of Children with Cerebral Palsy: Products of the Move & PLAY Study Move & PLAY Study Team Lehmann Day May 2013 Movement
A Collection of Brief, Reliable and Valid Instruments to Obtain a Holistic Picture of Children with Cerebral Palsy: Products of the Move & PLAY Study Move & PLAY Study Team Lehmann Day May 2013 Movement
114 Franjoine et al Pediatric Physical Therapy /03/ Pediatric Physical Therapy Copyright 2003 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc.
 RESEARCH REPORT Pediatric Balance Scale: A Modified Version of the Berg Balance Scale for the School-Age Child with Mild to Moderate Motor Impairment Mary Rose Franjoine, MS, PT, PCS, Joan S. Gunther,
RESEARCH REPORT Pediatric Balance Scale: A Modified Version of the Berg Balance Scale for the School-Age Child with Mild to Moderate Motor Impairment Mary Rose Franjoine, MS, PT, PCS, Joan S. Gunther,
Sensory. Physical. Cognitive. Language 4/12/2016 LEARNING OBJECTIVES AT ASSESSMENT: SKILLS EVALUATION OVERVIEW
 ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT: SEATING AND POSITIONING FOR ACCESS Anne Cronin 2016 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the principles related to assessment and intervention in assistive technology (AT) service
ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY ASSESSMENT: SEATING AND POSITIONING FOR ACCESS Anne Cronin 2016 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the principles related to assessment and intervention in assistive technology (AT) service
Somatic Adaptation in Cerebral Palsy LINKING ASSESSMENT WITH TREATMENT: AN NDT PERSPECTIVE. By W. Michael Magrun, M.S., OTR/L
 Somatic Adaptation in Cerebral Palsy LINKING ASSESSMENT WITH TREATMENT: AN NDT PERSPECTIVE By W. Michael Magrun, M.S., OTR/L INTRODUCTION Somatic adaptation is one of the primary functions of the central
Somatic Adaptation in Cerebral Palsy LINKING ASSESSMENT WITH TREATMENT: AN NDT PERSPECTIVE By W. Michael Magrun, M.S., OTR/L INTRODUCTION Somatic adaptation is one of the primary functions of the central
CORE MEASURE: CORE MEASURE: BERG BALANCE SCALE (BBS)
 OVERVIEW NUMBER OF TEST ITEMS SCORING EQUIPMENT TIME (NEW CLINICIAN) TIME (EXPERIENCED CLINICIAN) COST o The BBS is a widely-used, clinician-rated scale used to assess sitting and standing, static and
OVERVIEW NUMBER OF TEST ITEMS SCORING EQUIPMENT TIME (NEW CLINICIAN) TIME (EXPERIENCED CLINICIAN) COST o The BBS is a widely-used, clinician-rated scale used to assess sitting and standing, static and
Curriculum Vitae. Anat Lubetzky-Vilnai. RESEARCH INTERESTS: Motor Control and Learning, Biomechanics, Postural Control, Balance Training
 Curriculum Vitae Anat Lubetzky-Vilnai RESEARCH INTERESTS: Motor Control and Learning, Biomechanics, Postural Control, Balance Training APPOINTMENTS: Sep 2014 Present Visiting Assistant Professor, New York
Curriculum Vitae Anat Lubetzky-Vilnai RESEARCH INTERESTS: Motor Control and Learning, Biomechanics, Postural Control, Balance Training APPOINTMENTS: Sep 2014 Present Visiting Assistant Professor, New York
IJPHY COMPARISON OF MULTISENSORY VERSUS STRENGTHENING EXERCISES ON FUNCTIONAL MOBILITY AND BALANCE IN ELDERS ABSTRACT
 Int J Physiother. Vol (5), 557-561, October (2016) ISSN: 248-86 ORIGINAL ARTICLE IJPHY ABSTRACT COMPARISON OF MULTISENSORY VERSUS STRENGTHENING EXERCISES ON FUNCTIONAL MOBILITY AND BALANCE IN ELDERS ¹Y.
Int J Physiother. Vol (5), 557-561, October (2016) ISSN: 248-86 ORIGINAL ARTICLE IJPHY ABSTRACT COMPARISON OF MULTISENSORY VERSUS STRENGTHENING EXERCISES ON FUNCTIONAL MOBILITY AND BALANCE IN ELDERS ¹Y.
Effects of Kinesio Tape vs Rigid Tape on Shoulder Muscle Strength in Healthy Tennis Players
 2322-3537 Vol.5 No.1 Received: October, 2015 Accepted: February, 2016 Available online: March, 2016 Effects of Kinesio Tape vs Rigid Tape on Shoulder Muscle Strength in Healthy Tennis Players Parisa Tanoori
2322-3537 Vol.5 No.1 Received: October, 2015 Accepted: February, 2016 Available online: March, 2016 Effects of Kinesio Tape vs Rigid Tape on Shoulder Muscle Strength in Healthy Tennis Players Parisa Tanoori
Realtà virtuale: l esperienza dell IRCCS Medea
 Emilia Biffi Realtà virtuale: l esperienza dell IRCCS Medea Emilia Biffi, C. Maghini, E. Beretta, E. Diella, D. Panzeri, F. Brunati, M. Delle Fave, S. Strazzer, A.C. Turconi, G. Reni Scientific Institute
Emilia Biffi Realtà virtuale: l esperienza dell IRCCS Medea Emilia Biffi, C. Maghini, E. Beretta, E. Diella, D. Panzeri, F. Brunati, M. Delle Fave, S. Strazzer, A.C. Turconi, G. Reni Scientific Institute
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Kwon, J. Y., Chang, H. J., Yi, S. H., Lee, J. Y., Shin, H. Y., & Kim, Y. H. (2015). Effect of hippotherapy on gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy: A randomized
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Kwon, J. Y., Chang, H. J., Yi, S. H., Lee, J. Y., Shin, H. Y., & Kim, Y. H. (2015). Effect of hippotherapy on gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy: A randomized
Effect of proprioceptive training along with breathing and imagery on performance of gymnasts at various levels
 2018; 5(3): 14-19 P-ISSN: 2394-1685 E-ISSN: 2394-1693 Impact Factor (ISRA): 5.38 IJPESH 2018; 5(3): 14-19 2018 IJPESH www.kheljournal.com Received: 05-03-2018 Accepted: 06-04-2018 Dr. Harish Padinjarethil
2018; 5(3): 14-19 P-ISSN: 2394-1685 E-ISSN: 2394-1693 Impact Factor (ISRA): 5.38 IJPESH 2018; 5(3): 14-19 2018 IJPESH www.kheljournal.com Received: 05-03-2018 Accepted: 06-04-2018 Dr. Harish Padinjarethil
Original Article. The acute effect of kinesio taping on hamstring extensibility in university students
 Journal of Physical Education and Sport -, 11(2), Art #18, pp.133-137, 2011 E- ISSN 2066-2483 P-ISSN 1582-8131 Original Article The acute effect of kinesio taping on hamstring extensibility in university
Journal of Physical Education and Sport -, 11(2), Art #18, pp.133-137, 2011 E- ISSN 2066-2483 P-ISSN 1582-8131 Original Article The acute effect of kinesio taping on hamstring extensibility in university
MOON SHOULDER GROUP NONOPERATIVE TREATMENT OF ROTATOR CUFF TENDONOPATHY PHYSICAL THERAPY GUIDELINES
 MOON SHOULDER GROUP NONOPERATIVE TREATMENT OF ROTATOR CUFF TENDONOPATHY PHYSICAL THERAPY GUIDELINES From: Kuhn JE. Exercise in the treatment of rotator cuff impingement. A systematic review and synthesized
MOON SHOULDER GROUP NONOPERATIVE TREATMENT OF ROTATOR CUFF TENDONOPATHY PHYSICAL THERAPY GUIDELINES From: Kuhn JE. Exercise in the treatment of rotator cuff impingement. A systematic review and synthesized
Outline 3D Core Training with Rubber Resistance
 Outline 3D Core Training with Rubber Resistance Mike Bracko, Ed.D. CSCS, FACSM Fitness Educator / Sports Physiologist drbrackofitness@aol.com Introduction Rubber resistance was originally used to train
Outline 3D Core Training with Rubber Resistance Mike Bracko, Ed.D. CSCS, FACSM Fitness Educator / Sports Physiologist drbrackofitness@aol.com Introduction Rubber resistance was originally used to train
Low Back Pain Home Exercises
 Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
Overview The BBS is a widely-used, clinician-rated scale used to assess sitting and standing, static and dynamic balance.
 Core Measure: Berg Balance Scale (BBS) Overview The BBS is a widely-used, clinician-rated scale used to assess sitting and standing, static and dynamic balance. Number of Test Items The BBS consists of
Core Measure: Berg Balance Scale (BBS) Overview The BBS is a widely-used, clinician-rated scale used to assess sitting and standing, static and dynamic balance. Number of Test Items The BBS consists of
LEARNING OBJECTIVES PILLAR PREPARATION. Understand how the concept of the Core has evolved. Identify the components of the pillar and their function
 PILLAR PREPARATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand how the concept of the Core has evolved Identify the components of the pillar and their function Explain the concept of kinetic linking and explain its
PILLAR PREPARATION LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand how the concept of the Core has evolved Identify the components of the pillar and their function Explain the concept of kinetic linking and explain its
FOUR FOUNDATIONS OF FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT FOUR FOUNDATIONS OF FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT FOUR FOUNDATIONS OF FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT
 FOUR FOUNDATIONS OF FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT #1. Dynamic Stability Static Stability: is the ability to maintain proper alignment and muscle activation in a given joint or structure through a defined range of
FOUR FOUNDATIONS OF FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT #1. Dynamic Stability Static Stability: is the ability to maintain proper alignment and muscle activation in a given joint or structure through a defined range of
 Introduction 1/1 To build better athletes, start with the basics. The exercises here may seem familiar, but they represent the foundation on which you will build strength, mobility, speed, and power. And
Introduction 1/1 To build better athletes, start with the basics. The exercises here may seem familiar, but they represent the foundation on which you will build strength, mobility, speed, and power. And
CORE STABILIZATION EXERCISE. Vincent J. Hudson, PhD, DPT, MBA, ATC Chief Operating Officer OAA Orthopaedic Specialists Allentown, PA
 CORE STABILIZATION EXERCISE Vincent J. Hudson, PhD, DPT, MBA, ATC Chief Operating Officer OAA Orthopaedic Specialists Allentown, PA Stepping Back What are the goals? What is the value? Is it Sport Specific
CORE STABILIZATION EXERCISE Vincent J. Hudson, PhD, DPT, MBA, ATC Chief Operating Officer OAA Orthopaedic Specialists Allentown, PA Stepping Back What are the goals? What is the value? Is it Sport Specific
NZQA Expiring unit standard 7026 version 4 Page 1 of 7. Apply knowledge of functional anatomy and biomechanics
 Page 1 of 7 Title Apply knowledge of functional anatomy and biomechanics Level 5 Credits 5 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to: apply knowledge of human anatomy relevant to exercise
Page 1 of 7 Title Apply knowledge of functional anatomy and biomechanics Level 5 Credits 5 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to: apply knowledge of human anatomy relevant to exercise
Reliability of time to stabilization in single leg standing
 Northern Michigan University The Commons Conference Papers in Published Proceedings 2009 Reliability of time to stabilization in single leg standing Randall L. Jensen Northern Michigan University Follow
Northern Michigan University The Commons Conference Papers in Published Proceedings 2009 Reliability of time to stabilization in single leg standing Randall L. Jensen Northern Michigan University Follow
3 Moves To Improve Your Lifts
 1 Each lift has three exercises outlined to help you perform at your best. Muscle strength, endurance and stability are taken into account and serves as a guide to help coordinate all of your systems.
1 Each lift has three exercises outlined to help you perform at your best. Muscle strength, endurance and stability are taken into account and serves as a guide to help coordinate all of your systems.
Journal of Sport and Kinetic Movement Vol. I, No. 27/2016 THE THERAPY WITH KINETIC TAPE APPLICATION IN PEDIATRIC RECOVERY
 THE THERAPY WITH KINETIC TAPE APPLICATION IN PEDIATRIC RECOVERY Andrei DUMITRU Faculty of Sciences Department of Kinethic Therapy and Medical Assistance University of Pitesti Correspondence address: padrefortete@yahoo.com
THE THERAPY WITH KINETIC TAPE APPLICATION IN PEDIATRIC RECOVERY Andrei DUMITRU Faculty of Sciences Department of Kinethic Therapy and Medical Assistance University of Pitesti Correspondence address: padrefortete@yahoo.com
Scapular Protraction in Sitting
 9 Pause and Practice: Scapular Protraction in Sitting This practice lab is an example of putting muscles on length in order to achieve proper alignment of shoulder structures in preparation for facilitating
9 Pause and Practice: Scapular Protraction in Sitting This practice lab is an example of putting muscles on length in order to achieve proper alignment of shoulder structures in preparation for facilitating
NDTA BASIC ADULT COURSE KEY TO COURSE CONTENT
 Topic: Atypical Patterns of Movement Learning outcome(s) that pertain to occupational therapists 1. Identify the influence of atypical patterns of movement on: Postural alignment Transitional movements
Topic: Atypical Patterns of Movement Learning outcome(s) that pertain to occupational therapists 1. Identify the influence of atypical patterns of movement on: Postural alignment Transitional movements
Importance of Developmental Kinesiology for Manual Medicine
 Importance of Developmental Kinesiology for Manual Medicine Pavel Kolá!, 1996 Dpt. of Rehabilitation, University Hospital Motol, Prague, Czech Republic (Czech Journal of Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy)
Importance of Developmental Kinesiology for Manual Medicine Pavel Kolá!, 1996 Dpt. of Rehabilitation, University Hospital Motol, Prague, Czech Republic (Czech Journal of Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy)
VIPR and Power plate EXERCISE - 1 EXERCISE Fitness Professionals Ltd 2011 Job No. 2968
 FIT FOR DAILY LIFE To be fit for daily life includes many movement abilities. Dynamic stability, co-ordination, balance, motor control, mobility and efficiency are all vital (including basic strength and
FIT FOR DAILY LIFE To be fit for daily life includes many movement abilities. Dynamic stability, co-ordination, balance, motor control, mobility and efficiency are all vital (including basic strength and
Older Adult Advanced
 Older Adult Advanced Older Adult - Advanced Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women above the age of 55, who have experience in exercise and are relatively fit. The workout includes
Older Adult Advanced Older Adult - Advanced Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women above the age of 55, who have experience in exercise and are relatively fit. The workout includes
Core (machines) Medicine Ball Back Extension
 Medicine Ball Back Extension Medicine Ball Back Extension 1. Position body face down on apparatus placing hips and ankles on respective pads. 2. Place hips (and not stomach) on pad. Place lower leg or
Medicine Ball Back Extension Medicine Ball Back Extension 1. Position body face down on apparatus placing hips and ankles on respective pads. 2. Place hips (and not stomach) on pad. Place lower leg or
Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001)
 Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001) TEST 1 DEEP SQUAT Purpose - The Deep Squat is used to assess bilateral, symmetrical, mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. The dowel held overhead assesses bilateral,
Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001) TEST 1 DEEP SQUAT Purpose - The Deep Squat is used to assess bilateral, symmetrical, mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. The dowel held overhead assesses bilateral,
Advances in Environmental Biology
 AENSI Journals Advances in Environmental Biology Journal home page: http://www.aensiweb.com/aeb.html Effect and Sustainability of 8-weeks Rebound Therapy Exercise on Dynamic and Static Balance of High
AENSI Journals Advances in Environmental Biology Journal home page: http://www.aensiweb.com/aeb.html Effect and Sustainability of 8-weeks Rebound Therapy Exercise on Dynamic and Static Balance of High
Flexibility. STRETCH: Kneeling gastrocnemius. STRETCH: Standing gastrocnemius. STRETCH: Standing soleus. Adopt a press up position
 STRETCH: Kneeling gastrocnemius Adopt a press up position Rest one knee on mat with the opposite leg straight Maintain a neutral spine position Push through arms to lever ankle into increased dorsiflexion
STRETCH: Kneeling gastrocnemius Adopt a press up position Rest one knee on mat with the opposite leg straight Maintain a neutral spine position Push through arms to lever ankle into increased dorsiflexion
05/16/2016 CURRICULUM VITAE. NAME: Hyun-jeong Jang. PT, Ph.D. PRESENT POSITION EDUCATION. BOARD CERTIFICATION and LICENSURE INFORMATION
 CURRICULUM VITAE 05/16/2016 NAME: Hyun-jeong Jang. PT, Ph.D. PRESENT POSITION EDUCATION Post-Doctoral Fellow University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston Physical Therapy Department 301 University Blvd.
CURRICULUM VITAE 05/16/2016 NAME: Hyun-jeong Jang. PT, Ph.D. PRESENT POSITION EDUCATION Post-Doctoral Fellow University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston Physical Therapy Department 301 University Blvd.
 1 of 8 9/21/2006 1:02 PM Smith College Dept. of Athletics Program for The Average Division III Female Athlete Trainer : Timothy Bacon Introduction Core, functional and complementary exercises. Warm Up
1 of 8 9/21/2006 1:02 PM Smith College Dept. of Athletics Program for The Average Division III Female Athlete Trainer : Timothy Bacon Introduction Core, functional and complementary exercises. Warm Up
EFFECIVENESS OF THE WILLIAMS EXCERCISE IN MECHANICAL LOW BACK PAIN
 EFFECIVENESS OF THE WILLIAMS EXCERCISE IN MECHANICAL LOW BACK PAIN Dr.U.Ganapathy Sankar, Ph.D Dean I/C, SRM College of Occupational Therapy, SRMUniversity, Kattankulathur, KancheepuramDistrict, Tamil
EFFECIVENESS OF THE WILLIAMS EXCERCISE IN MECHANICAL LOW BACK PAIN Dr.U.Ganapathy Sankar, Ph.D Dean I/C, SRM College of Occupational Therapy, SRMUniversity, Kattankulathur, KancheepuramDistrict, Tamil
Inspiring Athleticism in Children and Youth. By Peter Twist. IDEA World 2011
 Inspiring Athleticism in Children and Youth By Peter Twist IDEA World 2011 Critical Factors to Consider When Training Young Athletes o Children are not little adults they have very specialized needs o
Inspiring Athleticism in Children and Youth By Peter Twist IDEA World 2011 Critical Factors to Consider When Training Young Athletes o Children are not little adults they have very specialized needs o
FUNCTIONAL TESTING GUIDELINES FOR ACL RECONSTRUCTION TESTING INSTRUCTIONS FOR CLINICIANS
 FUNCTIONAL TESTING GUIDELINES FOR ACL RECONSTRUCTION TESTING INSTRUCTIONS FOR CLINICIANS A number of criteria should be met before advanced functional testing of ACL reconstruction or ACL deficient knees
FUNCTIONAL TESTING GUIDELINES FOR ACL RECONSTRUCTION TESTING INSTRUCTIONS FOR CLINICIANS A number of criteria should be met before advanced functional testing of ACL reconstruction or ACL deficient knees
Hands on Sports Therapy KNOWLEDGE REVIEW QUESTIONS 2004 Thomson Learning. Q1:From the following list of acronyms, write down the full title of each
 CHAPTER 09 Knowledge Review Q1:From the following list of acronyms, write down the full title of each treatment technique: NMT; PRT; SCS; FT; MET; PNF; PIR; RI; CRAC; INIT; ICT; ICCT. A1: NMT: Neuromuscular
CHAPTER 09 Knowledge Review Q1:From the following list of acronyms, write down the full title of each treatment technique: NMT; PRT; SCS; FT; MET; PNF; PIR; RI; CRAC; INIT; ICT; ICCT. A1: NMT: Neuromuscular
At-Home Dryland Training Program
 At-Home Dryland Training Program Name of Player Team Name Program start date Player's Information Session 1 (Weeks 1-5) Age Exercises Reps Wts (Lb) Weeks Sets Rest Gender Squats 15 5 2 0 Height (Feet)
At-Home Dryland Training Program Name of Player Team Name Program start date Player's Information Session 1 (Weeks 1-5) Age Exercises Reps Wts (Lb) Weeks Sets Rest Gender Squats 15 5 2 0 Height (Feet)
EFFECTIVENESS OF NEUROMUSCULAR TRAINING IN YOUNG ATHLETES AT RISK OF LOWER EXTREMITY MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES
 EFFECTIVENESS OF NEUROMUSCULAR TRAINING IN YOUNG ATHLETES AT RISK OF LOWER EXTREMITY MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES Original Research Article ABSTRACT ISSN CODE: 2456-1045 (Online) (ICV-MDS/Impact Value): 3.08
EFFECTIVENESS OF NEUROMUSCULAR TRAINING IN YOUNG ATHLETES AT RISK OF LOWER EXTREMITY MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES Original Research Article ABSTRACT ISSN CODE: 2456-1045 (Online) (ICV-MDS/Impact Value): 3.08
Handling Skills Used in the Management of Adult Hemiplegia: A Lab Manual
 Handling Skills Used in the Management of Adult Hemiplegia: A Lab Manual 2nd Edition Isabelle M. Bohman, M.S., P.T., NDT Coordinator Instructor TM Published by Clinician s View Albuquerque, NM 505-880-0058
Handling Skills Used in the Management of Adult Hemiplegia: A Lab Manual 2nd Edition Isabelle M. Bohman, M.S., P.T., NDT Coordinator Instructor TM Published by Clinician s View Albuquerque, NM 505-880-0058
GOLFERS TEN PROGRAM 1. SELF STRETCHING OF THE SHOULDER CAPSULE
 GOLFERS TEN PROGRAM 1. SELF STRETCHING OF THE SHOULDER CAPSULE POSTERIOR CAPSULAR STRETCH Bring your arm across your chest toward the opposite shoulder. With the opposite arm grasp your arm at your elbow.
GOLFERS TEN PROGRAM 1. SELF STRETCHING OF THE SHOULDER CAPSULE POSTERIOR CAPSULAR STRETCH Bring your arm across your chest toward the opposite shoulder. With the opposite arm grasp your arm at your elbow.
Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University, Seongnam, Korea
 Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2015;39(4):624-629 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2015.39.4.624 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Gross Motor Function Outcome After Intensive
Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2015;39(4):624-629 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2015.39.4.624 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Gross Motor Function Outcome After Intensive
PROGRESSION OF EXERCISE
 PROGRESSION OF EXERCISE PLANNING YOUR TREATMENT Evaluation guides your treatment How? IRRITABILITY Pain level Linger Sleep How quickly does the pain come on? Consistency or behavior STAGE Acute Chemical
PROGRESSION OF EXERCISE PLANNING YOUR TREATMENT Evaluation guides your treatment How? IRRITABILITY Pain level Linger Sleep How quickly does the pain come on? Consistency or behavior STAGE Acute Chemical
The Golfers Ten Program. 1. Self Stretching of the Shoulder Capsule
 The Golfers Ten Program 1. Self Stretching of the Shoulder Capsule A. Posterior capsular stretch Bring your arm across your chest toward the opposite shoulder. With the opposite arm grasp your arm at your
The Golfers Ten Program 1. Self Stretching of the Shoulder Capsule A. Posterior capsular stretch Bring your arm across your chest toward the opposite shoulder. With the opposite arm grasp your arm at your
Balance & Coordination
 Balance & Coordination What is balance and coordination? Balance is the ability to maintain a controlled body position during task performance, whether it is sitting at a table, walking the balance beam
Balance & Coordination What is balance and coordination? Balance is the ability to maintain a controlled body position during task performance, whether it is sitting at a table, walking the balance beam
DON T JUST PROVIDE A BAND-AID ELIZABETH COLE, MSPT, ATP U.S. Rehab / VGM
 DON T JUST PROVIDE A BAND-AID ELIZABETH COLE, MSPT, ATP U.S. Rehab / VGM Selecting the most appropriate product solutions for specific postural problems should be a thoughtful exercise in analyzing the
DON T JUST PROVIDE A BAND-AID ELIZABETH COLE, MSPT, ATP U.S. Rehab / VGM Selecting the most appropriate product solutions for specific postural problems should be a thoughtful exercise in analyzing the
THE COMPLETE GUIDE TO PILATES EXERCISES
 THE COMPLETE GUIDE TO PILATES EXERCISES By Beenax Healthy living. Healthy you. INTRODUCTION Pilates (or the Pilates method) is a series of about 500 exercises inspired by calisthenics, yoga and ballet.
THE COMPLETE GUIDE TO PILATES EXERCISES By Beenax Healthy living. Healthy you. INTRODUCTION Pilates (or the Pilates method) is a series of about 500 exercises inspired by calisthenics, yoga and ballet.
Why Train Your Calf Muscles
 Why Train Your Calf Muscles 1 Why Train Your Calf Muscles The muscles of the calf are often considered genetic muscles among fitness enthusiasts, suggesting that one is born with sizable and well developed
Why Train Your Calf Muscles 1 Why Train Your Calf Muscles The muscles of the calf are often considered genetic muscles among fitness enthusiasts, suggesting that one is born with sizable and well developed
RIDING FOR THE DISABLED ASSOCIATION OF QLD INC. Megan Wray June 2014
 RIDING FOR THE DISABLED ASSOCIATION OF QLD INC Megan Wray June 2014 Our Organisation Provides horse base activities for people with disabilities We are: Not for profit, Volunteer based Registered Charity
RIDING FOR THE DISABLED ASSOCIATION OF QLD INC Megan Wray June 2014 Our Organisation Provides horse base activities for people with disabilities We are: Not for profit, Volunteer based Registered Charity
Most Dangerous Man! FACTS ON STREGNTH. Session #627 Functionally Fit Seniors
 FACTS ON STREGNTH We lose strength as we age. Over a 5 year study, Men experienced a 16.1% loss of muscle torque (isometric strength) and women saw a 13.4% loss. (1) Session #627 Functionally Fit Seniors
FACTS ON STREGNTH We lose strength as we age. Over a 5 year study, Men experienced a 16.1% loss of muscle torque (isometric strength) and women saw a 13.4% loss. (1) Session #627 Functionally Fit Seniors
Fulfill your potential
 Fulfill your potential Clinical Concept and Advanced Technologies MediTouch creates innovative physical rehabilitation solutions for hospital, community clinic and home care use. The unique patented products
Fulfill your potential Clinical Concept and Advanced Technologies MediTouch creates innovative physical rehabilitation solutions for hospital, community clinic and home care use. The unique patented products
Functional electrical stimulation. FES applications
 Functional electrical stimulation FES applications For all therapeutic areas The functional electrical stimulation (FES) is highly important for the therapy and rehabilitation of paralytic illnesses. If
Functional electrical stimulation FES applications For all therapeutic areas The functional electrical stimulation (FES) is highly important for the therapy and rehabilitation of paralytic illnesses. If
EFFECT OF POSTURAL SWAY SCALE AS A PROGNOSTIC TOOL IN LOW BACK PAIN MANAGEMENT.
 Original Research Article Allied Science International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 EFFECT OF POSTURAL SWAY SCALE AS A PROGNOSTIC TOOL IN LOW BACK PAIN MANAGEMENT. 1 MANJULADEVI.NB.P.T,
Original Research Article Allied Science International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 EFFECT OF POSTURAL SWAY SCALE AS A PROGNOSTIC TOOL IN LOW BACK PAIN MANAGEMENT. 1 MANJULADEVI.NB.P.T,
BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER. Planes of Lumbar Pelvic Femoral (Back, Pelvic, Hip) Muscle Function
 BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER Functional performance of the soccer player reflects functional capability of certain specific muscle and muscle groups of the back, pelvis and hip to work
BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER Functional performance of the soccer player reflects functional capability of certain specific muscle and muscle groups of the back, pelvis and hip to work
