Identification, Causes And Prevention Of Cumulative Trauma Disorders (CTDS) In The Construction Industry In Nigeria
|
|
|
- Victor Davidson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Identification, Causes And Prevention Of Cumulative Trauma Disorders (CTDS) In The Construction Industry In Nigeria By C. A. JOHN (Ph.D) Department Of The Technology Education, Federal University of Technology, P. M. B.2076 Yola, Adamawa State, Nigeria. N. A. NWANKWOR Department Of The Technology Education, Federal University of Technology, P. M. B.2076, Yola, Adamawa State, Nigeria. T. J. TIKA Department Of The Technology Education, Federal University Of Technology, P. M. B Yola, Adamawa State, Nigeria Abstract Construction workers stand high risk of occupational hazards such as accident, diseases and disorders. Report from occupational safety Organizations such as Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), National Safety Council (NSC); International Labour Organization (ILO) among others indicate that a good percentage of victims of occupational hazards are in the construction Industry. The Cumulative Trauma Disorders (CTDs) which rank high among the occupational hazards are doing great havoc among the construction workers in Nigeria. This paper identified the CTDs that are commonly found in the Nigeria construction Industry. They include: Tendonitis, Thoracic outlet Syndrome, Tennis Elbow, Golfer s Elbow and Reynaud s Syndrome among others. Furthermore, the paper enumerated the possible preventive measure that would go a long way, in reducing or even preventing the effects of these disorders. Recommendations such as the need for proper education of workers on site, training of engineers, trade foremen on preventive measures and acquisition of improved equipment, among others were advanced. 1
2 The Coconut Introduction The construction industry, the world over, is a place of high level of specialized activities involving constant repetitive motions, compression of body tissue against hard and sharper corners, body frequent vibration, e.t.c. according to Charles and James (1999), these activities seem normal in the life of the construction worker, the supervisor and the engineer. The effects are not noticed. The fact of the matter is that the continuous subjection of the body to these activities would eventually lead to conditions that are detrimental to the body system, thereby resulting to the development of occupational ailment or disease. The Occupation Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) advised that construction workers stand high risk of occupational diseases, if proper care is not taken in implementing rules and safety work procedure on site. For instance, on sites where asphalt is handled, there is high risk of damage to skin, eye, chronic lung diseases and cancer. Similarly, where welding, soldering, cutting and brazing operations are carried out, construction workers stand the risk of being infected with occupational diseases such as skin dermatitis, sensitizer and nervous system infections, thereby affecting the lungs, kidney and the blood system. (OSHA,1997). The International Labour Organization ILO (2004) estimated that about 160 million workers are infected with work-related illness annually across the globe. A good percentage of this figure is in the construction industry, due largely to poor welfare system, and lack adherence to rules and safe work procedures on the construction site. One set of the common occupational diseases which occur on site, yet under reported within the construction industry, is the cumulative Trauma Disorders (CTDs). Putz-Anderson (1988) in a study found that these diseases are caused by repeated and accumulated exposure to risk factors such as repetitive movement of the body and body segment, unnatural or awkward body position and high levels of force among others. With the ever increasing sophistication in construction methods, improved tools and equipment and the growth taking place in the construction industry in Nigeria, it has become imperative to focus on the CTDs which are silently affecting thousands of construction workers in the country. This paper therefore seeks to indentify the common CTDs, their causes and the possible preventive strategies that would be employed with the hope that the skilled workforce in our construction industry, who are cumulatively put out of work as result of CTDs are well sensitized on the need to be conscious and adhere to laid own rules and safe work procedure on the construction sites. Identification of the Cumulative Trauma Disorders (CTDs) The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) reported that 6.8 million non-fatal occupational injuries and illnesses occur each year in the United States of America. Cumulative Trauma Disorders (CTDs) form one of this class of illnesses (OSHA, 1997). These disorders are caused by repeated and accumulated 2
3 Identification, Causes and Prevention of Cumulative Trauma Disorders (CTDS) in the Construction Industry in Nigeria. C. A. John (Ph.D); N. A. Nwankwor & T. J. Tika exposure to risky conditions which leads to tiring breaks and tears called the micro trauma. Sufficient recovery time is needed for workers to get better, however if the time required is not attained the Micro trauma can result in serious damage to the musculoskelotal system. In performing their professional responsibility on site, construction workers are required frequently to utilize their hands, arms and shoulder. The National Safety Council (NSC) reported that most of CTDs suffered by construction workers are of the upper extremities. It is necessary to identify the CTDs so that proactive steps can be taken to reduce their effects to the bearest minimum in construction sites in Nigeria. Charles and James (1999) identified the most common CTDs which affect construction workers on site. They include tendonitis, thoracic outlet syndrome, tennis elbow or carpenter s elbow, rotator cuff tendonitis, Raynaud s syndrome and golfer s elbow. Others are trigger finger, ganglion cyst and carpel tunnel syndrome. A critical analsyis of each of the CTDs shall be made. Tendonitis This is the inflammation of the tendons which attach muscle to the bones and allow movement of the bones. This condition occurs with continued use of the constant tensioning of the muscles which pull the tendons. Tendonitis usually occur in the writst, elbow and shoulders. It can also occur in the kneens and ankles. Putz-Anderson (1988) gave the example of construction works that can result in tendonitis which include working with hands above the shoulder such as ceiling works, electrical fitting, blocklaying etc. Force extension, repeated throwing of heavy loads and pulling works among others. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome This occurs when the muscular and connective tissue structures of the shoulder and upper arm entrap and compress the blood vessels from the heart and nerves from the spine arm which serve the arm. The effect can be felt as numbness in the fingers and a weakened wrist pulse, this causes the arm to feel like it is falling asleep the risk for this syndrome is increased by a number of activities such an working above one s shoulder head, carrying heavy items such as concrete blocks, pulling the shoulders outward/back and up and up and carrying loads while using shoulder straps. Some of the common tradesmen on site affected by this syndrome are the painters, sheet metal workers, welders and truck drivers, (Putz Anderson, 1988 and National Safety Council, 1993). Tennis Elbow Cumulative Trauma Disorder, otherwise known as Lateral Epicondylitis is a painful inflammation of the fore arm tendons that attach to the outer side of the elbow. It is caused by a Jerky throwing motion, strong wrist finger extension, pulling the wrist and fingers away from a curled position. It is often in combination with the 3
4 The Coconut forearm/wrist twisting. Construction workers involved in repetitive throwing of heavy loads are in high risk of the CTD (OSHA, 1997). Rotator Cuff Tendonitis This CTD is the most common shoulder tendon disorder and is usually caused by repeated elevation of the arm above the shoulder. According to Charles and James (1999) the condition may result to what is called Frozen Shoulder which is very painful loss of shoulder function. Workers on construction site performing sheet metal work, painting plumbing and drywall installation may have a higher risk of this cumulative trauma disorder. Reynaud s Syndrome This disorder is often called Vibration write finger or Hand arm vibration syndrome. It is caused by the forceful gripping and/or prolonged use of vibrating tools driven by electrical or pneumatic sources. Blosser (1992) found out that this disorder is extreme among workers handling vibrating tools in cold weather condition. Workers who handle construction equipment such jigs, poker vibrators, vibrating tamping tool, terrazzo tools etc. have very high risk of being victim of this CTD. Golfter s Elbow of Carpenter s Elbow This CTD is medically called medial Epicondylitis. This is the painful inflammation of the inside of the elbow. OSHA (1997) stated that Golfter s Elbow is caused by the repeated rotating of the forearm and bending of the wrist and fingers at the same time. Higher rates or incidence have been found among individuals doing electrical wiring operation. It is also common among other workers who perform repetitive and awkward task and use poorly designed tools. Trigger Finger This CTD affect the synovial sheath. With over use, the synovial sheath can become so swollen that the tendons become temporarily locked inside. When a worker attempt to move the finger it will often snap or move in a jerking manner. This type of CTD is often caused by using tools with hard edges or ridged handle and/or repeated bending of the finger while maintaining a forceful grip (OSHA, 1997). Ganglion Cyst This CTD another possible response of the body of the overuse of the synovial sheath. In this case the sheath become irritated and filled with fluid (Synovial Fluid) to the point that the sheath swells and becomes a bump under the skin. This often occurs at the wrist. It is caused by blunt force injury or repetitive and forceful gripping or opening of the hand. Construction workers who often pound objects with their hand or who accidentally strike hard objects with their hands fall victims of this disorder. 4
5 Identification, Causes and Prevention of Cumulative Trauma Disorders (CTDS) in the Construction Industry in Nigeria. C. A. John (Ph.D); N. A. Nwankwor & T. J. Tika Carpal Tunnel Syndrome This disorder derived its name from carpal tunnel which accommodate major nerve called the median nerve and nine tendons in their sheath. The tunnel which is located between the wrist bone and the strong ligaments stabilize the underside of the wrist. The disorder starts if the tendons in their sheaths become irritated through overuse and awkward postures which become swollen and cause narrowing of the carpal tunnel. The indications of the CTD are pain, swelling, numbness, tingling or burning sensations in the thumb and the three fingers. This, in turn results in loss of finger sensation and grip strength and may cause permanent disability of the fingers. Construction works mostly affected by this syndrome include electrical, caulking windows, brickwork and carpentry trades. All these tasks require bending, twisting and straining of the wrist, hand and fingers. Causes of CTDs Accidents and illness in the work place don t just happen, they are always caused. In the same vein, Cumulative Trauma Disorders (CTDs) are caused as result of risk factor encountered on site during construction processes. Although the cause of each of the CTDs was mentioned it is proper to have an overview of the causes. Charles and James (1999), our lined them a follows:- 1. Constantly repeated motions during the process of carrying of construction processes. 2. Use of high level of force during task implementation. For example the use of burnt chisel in concrete work. 3. Unnatural or awkward position as a result of use of tools that can not allow natural body posture. 4. Body position that are held for long periods of time for example electrical wiring of ceilings, and blocklaying at above the shoulder. 5. Compressing of body tissue against hard and sharp corners, like in the case of poorly design tools handles and tight operation space. 6. Whole body vibration, as well as hand and arm vibration such as in the use of jigs and power trowels. 7. Mental stress due to time pressure, low control of job processes, and problems with social support on the job. 8. Fatigue due to inadequate recovery times, having frequent breaks are not the normal mode of operation on construction sites. Prevention of Cumulative Trauma Disorders The enforcement of the occupational safety and health rules and safe work procedures can go a long way in preventing occupational diseases and disorders. In Nigeria the laws of the Federation Factories Act (CAP 126) has adequate provision to protect workers in workplaces. Part V sections of the document presented clear requirements for employers to prevent occupational disease, disorder and accidents. 5
6 Though The Coconut the resultant effects of Cumulative Trauma Disorder can be devastating on the victims some fairly simply measures can go a long way to decrease of prevent CTDs. These include: i. Use of tools with smooth handles, rounded edges, long handles and the proper diameter. ii. Provide adequate insulation to handles of vibrating equipment to reduce the degree of vibration. iii. Set up the work area to minimize excessive stretching, bending or other awkward posture. iv. Rotate between tasks so that different muscles and body parts are being used. v. Decrease repetition rates, reduce force requirement, and reduce awkward posture whenever possible. vi. Take regular mini-breaks at least five minutes to allow for some recovery time. vii. Take longer breaks shifts to allow for natural healing periods viii. Workers should get up, move and stretch whenever stress, or pain is felt (micro-breaks of thirty seconds or one minute) ix. The use of gloves which can reduce chilling of the hands. (Charles and James, 1999.p565). The listed preventive measures as simple as they may appear if not properly considered may result in more workers getting out of job as a result of ill health caused by the Cumulative Trauma Disorder. Therefore, foremen of various trades, supervisors and engineers should pay keen interest in making sure that causes of CTDs are reduced to the bearest minimum or even eliminated on our construction sites. Conclusion and Recommendations A common safety reminder in the construction industry is that a smart worker is a safe worker. This statement implies that a worker need to engage all his senses when carrying out trade task to ensure his safety, irrespective of non-chalant attitude of the employer because if he is out of job as a result of accident or occupational diseases the employer can only settle him and that is all. This paper identified some common Cumulative Trauma Disorders which affect the efficiency of workers on site, the causes of the CTDs and the possible prevention. Strategies are provided with hope that this silent killer would occupy the centre stage in the mind of stake-holders in the construction industry so that more effort could be put to prevent CTDs from affecting more skilled workforce on construction sites in Nigeria. In order to reduce this traumatic experience the following recommendations are made: 1. Management of construction firm should from time to time organize enlightenment campaign on accident in workplaces and exceptional diseases with emphasis on CTDs as they are hardly noted and reported. The enlightenment campaign can be achieved through workshops, seminars, posters etc. 6
7 Identification, Causes and Prevention of Cumulative Trauma Disorders (CTDS) in the Construction Industry in Nigeria. C. A. John (Ph.D); N. A. Nwankwor & T. J. Tika 2. Site supervisors, engineers and foremen of various trades on site should be adequately trained to enable them easily identify risk factors that cause, Cumulative Trauma Disorders (CTDs) on site. 3. The health units of construction firms should be well equipped and the staff be given adequate training on prevention and treatment of CTDs on sites. 4. Construction firms should acquire latest tools and care of equipment that have taken ergonomic risk in their design and production to reduce the incidences of CTDs on sites. 5. The Federal Government of Nigeria should empower the authorities concern with enforcement of all safety provisions in factories Act (CAP 126) in all workplaces to reduce causes of workplace diseases Cumulative Trauma Disorder in particular. 6. The National Board for Technical Education (NBTE), the National Universities Commission (NUC) and National Commission for Colleague of Education (NCE). Should introduce occupational safety and Senior Secondary School and Post-Secondary Education with emphasis on Technical and Engineering fields. References Blosser, F. (1992). Primer on occupational safety and health. Washington D.C. The Bureau of National Affairs Inc. Charles, R.D. & James E.V. (1999) Hand book of OSHA construction safety and health. London: Lew is publisher. Federal Republic Oil Nigeria (1990). The Laws of the federation. Factories Act (CAP126) Abuja International Labour Organization (2005). World day for safety and health at work in Focus on safe work. retrieved on 15 th February, National Safety Council (1993). Ergonomics: Practical guide (2 nd Ed.) Etasca Ilonois OSHA (1997). Training courses in OSHA for institution industry OSHA Training institute Deplaines, USA. Puts-Anderson, V. (1988). Cumulative trauma disorder: Manual for Muscu skeletal Diseases of Upper Lumbs. Texas: Taylor and Francis Inc. 7
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM. What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders
 MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
Ergonomics Glossary. Force The amount of physical effort a person uses to do a task.
 Ergonomics Glossary Administrative controls Procedures used to reduce the duration, frequency, or severity of exposure to a hazard. They may include training, job rotation, and gradual introduction to
Ergonomics Glossary Administrative controls Procedures used to reduce the duration, frequency, or severity of exposure to a hazard. They may include training, job rotation, and gradual introduction to
Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders
 Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Upper Extremity Disorders Carpel tunnel syndrome Cubital tunnel syndrome Thoracic outlet syndrome Raynaud s syndrome (white finger) Rotator cuff syndrome DeQuervain
Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Upper Extremity Disorders Carpel tunnel syndrome Cubital tunnel syndrome Thoracic outlet syndrome Raynaud s syndrome (white finger) Rotator cuff syndrome DeQuervain
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings. ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders. Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
13/02/2011. Ergonomics
 13/02/2011 Ergonomics Workplace Safety Electrical Safety Medical & First Aid Lockout/Tag-out Confined Space Asbestos Control Fire Prevention Personal Protective Equipment Hazard Communication Chemical
13/02/2011 Ergonomics Workplace Safety Electrical Safety Medical & First Aid Lockout/Tag-out Confined Space Asbestos Control Fire Prevention Personal Protective Equipment Hazard Communication Chemical
The Ergonomic Alternative
 The Economics Of Ergonomics What Is Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the field of study concerned with finding ways to keep people safe, comfortable, and productive while they perform tasks at work. We Refer
The Economics Of Ergonomics What Is Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the field of study concerned with finding ways to keep people safe, comfortable, and productive while they perform tasks at work. We Refer
Introduction to Ergonomics Ergonomics (er'gõ nom'iks):
 March 10 th 2009 Construction Ergonomics Introduction to ergonomics Risk factors of MSDs Solutions to minimize risk factors Q & A Resources Yutonah Bowes, Oregon OSHA Mark Noll, SAIF Corp. Kim Rhodes,
March 10 th 2009 Construction Ergonomics Introduction to ergonomics Risk factors of MSDs Solutions to minimize risk factors Q & A Resources Yutonah Bowes, Oregon OSHA Mark Noll, SAIF Corp. Kim Rhodes,
2/28/2017. EMC Insurance Companies Risk Improvement Department. Ergonomics for School Districts. Objectives. What is Ergonomics?
 Ergonomics for School Districts February 28, 2017 Dave Young, CSP EMC Insurance Companies Objectives Define ergonomics and its effect on the workplace Discuss ergonomic risk factors Review the preferred
Ergonomics for School Districts February 28, 2017 Dave Young, CSP EMC Insurance Companies Objectives Define ergonomics and its effect on the workplace Discuss ergonomic risk factors Review the preferred
KEEPING IRONWORKERS HEALTHY: ERGONOMICS AND WMSDs
 KEEPING IRONWORKERS HEALTHY: ERGONOMICS AND WMSDs Funded by: With assistance from: WMSDs are preventable! 1 This training is dedicated to the memory of 2 GOALS OF THIS CLASS You will understand: What WMSDs
KEEPING IRONWORKERS HEALTHY: ERGONOMICS AND WMSDs Funded by: With assistance from: WMSDs are preventable! 1 This training is dedicated to the memory of 2 GOALS OF THIS CLASS You will understand: What WMSDs
How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck
 OR How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck COURSE INTRODUCTION Computers are found in almost every workplace. Unfortunately, many employees suffer work related injuries from prolonged use of a computer. This CE
OR How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck COURSE INTRODUCTION Computers are found in almost every workplace. Unfortunately, many employees suffer work related injuries from prolonged use of a computer. This CE
"INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS"
 PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
Commonwealth Health Corporation NEXT
 Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Repetitive Upper Limb Tasks. Introductions. ' Crown Copyright Health & Safety Laboratory. 1. Dr Lanre Okunribido: HSL Ergonomist.
 Repetitive Upper Limb s Dr Lanre Okunribido: HSL Ergonomist Introductions Sessions 1. Why repetitive upper limb tasks? 2. Common Upper Limb Disorders (ULD) and injuries? 3. 4. Introduction to the ART tool
Repetitive Upper Limb s Dr Lanre Okunribido: HSL Ergonomist Introductions Sessions 1. Why repetitive upper limb tasks? 2. Common Upper Limb Disorders (ULD) and injuries? 3. 4. Introduction to the ART tool
Muscular Skeletal Disorders
 Alabama Department of REHABILITATION SERVICES "for Alabama's children and adults with disabilities" Muscular Skeletal Disorders Michael Papp, MSE Muscular Skeletal Disorders What are MSDs? Muscles Nerves
Alabama Department of REHABILITATION SERVICES "for Alabama's children and adults with disabilities" Muscular Skeletal Disorders Michael Papp, MSE Muscular Skeletal Disorders What are MSDs? Muscles Nerves
Risk Management Department. Office Ergonomics
 Risk Management Department Office 1 Introduction In order to prevent injuries, reduce stress and improve work productivity, APS has developed this training to provide you the knowledge to help yourself
Risk Management Department Office 1 Introduction In order to prevent injuries, reduce stress and improve work productivity, APS has developed this training to provide you the knowledge to help yourself
Introduction. Safety Tip For more data on ergonomic injuries, go to the BLS website at
 Introduction Ergonomics in Construction Welcome Given current OSHA and industry information regarding construction worksite incidents and disabling injuries, the student should be able to recognize the
Introduction Ergonomics in Construction Welcome Given current OSHA and industry information regarding construction worksite incidents and disabling injuries, the student should be able to recognize the
Ergonomics. Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques (EOHSS)
 Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every
 According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every year. For some, the problem becomes so severe that they
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every year. For some, the problem becomes so severe that they
Ergonomics in General Industry
 Ergonomics in General Industry Any job requires physical movement Some tasks may be repetitious and may require you to stand or sit for extended periods Jobs in the industrial environment can be physically
Ergonomics in General Industry Any job requires physical movement Some tasks may be repetitious and may require you to stand or sit for extended periods Jobs in the industrial environment can be physically
Department of Defense Ergonomics Working Group
 Welcome to the module. The purpose of the module is to explain the importance of ergonomics and the risks that can result when ergonomics principles are not applied to work activities. Upon completion
Welcome to the module. The purpose of the module is to explain the importance of ergonomics and the risks that can result when ergonomics principles are not applied to work activities. Upon completion
CITY OF TURLOCK ERGONOMICS POLICY
 CITY OF TURLOCK ERGONOMICS POLICY POLICY An ergonomics program is a systematic process that communicates information so that adequate and feasible solutions to ergonomic risks can be implemented to improve
CITY OF TURLOCK ERGONOMICS POLICY POLICY An ergonomics program is a systematic process that communicates information so that adequate and feasible solutions to ergonomic risks can be implemented to improve
Risk Factors and Control Measures for Musculoskeletal Injuries. Presented by: Gina Vahlas, Ergonomist Chloe Eaton, Ergonomist
 Risk Factors and Control Measures for Musculoskeletal Injuries Presented by: Gina Vahlas, Ergonomist Chloe Eaton, Ergonomist Agenda Musculoskeletal Injuries Risk factors Risk controls Tools and resources
Risk Factors and Control Measures for Musculoskeletal Injuries Presented by: Gina Vahlas, Ergonomist Chloe Eaton, Ergonomist Agenda Musculoskeletal Injuries Risk factors Risk controls Tools and resources
Ergonomics Keeping the Worker on the Job
 Ergonomics Keeping the Worker on the Job Job Site Analysis WorkRisk Analysis WorkTask Analysis WorkStation Analysis David Raptosh, MA, OTR/L Regional Director of WorkStrategies Job Site Analysis - Identify
Ergonomics Keeping the Worker on the Job Job Site Analysis WorkRisk Analysis WorkTask Analysis WorkStation Analysis David Raptosh, MA, OTR/L Regional Director of WorkStrategies Job Site Analysis - Identify
Ergonomics in Sonography
 Ergonomics in Sonography Marissa Pentico, MS, OT/L Duke Ergonomics Division Occupational and Environmental Safety Office Janet Ellis, RT(R), RDMS, RVT Duke Radiology Ultrasound What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics
Ergonomics in Sonography Marissa Pentico, MS, OT/L Duke Ergonomics Division Occupational and Environmental Safety Office Janet Ellis, RT(R), RDMS, RVT Duke Radiology Ultrasound What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics
ERGONOMICS. Risk Management
 ERGONOMICS Risk Management ERGONOMICS-What is it? Derived from two Greek words: Nomoi meaning natural laws Ergon meaning work Hence, ergonomists study human capabilities in relationship to work demands
ERGONOMICS Risk Management ERGONOMICS-What is it? Derived from two Greek words: Nomoi meaning natural laws Ergon meaning work Hence, ergonomists study human capabilities in relationship to work demands
Ergonomics and Risk Factor Awareness
 Ergonomics and Risk Factor Awareness PART 1 Objectives To gain an understanding of: What is ergonomics How cumulative trauma disorders develop Ergonomic risk factors Controlling risk factors To gain an
Ergonomics and Risk Factor Awareness PART 1 Objectives To gain an understanding of: What is ergonomics How cumulative trauma disorders develop Ergonomic risk factors Controlling risk factors To gain an
ERGONOMICS in Office.
 ERGONOMICS in Office ก ก. ก What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics ก ก ก ก. ก ergonomic ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก Static vs Dynamic muscular effort ก ก vs. ก ก Dynamic Effort Static Effort What are the risks of ignoring
ERGONOMICS in Office ก ก. ก What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics ก ก ก ก. ก ergonomic ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก Static vs Dynamic muscular effort ก ก vs. ก ก Dynamic Effort Static Effort What are the risks of ignoring
Deborah Ruediger, ASAR, DipHlthSc, MHlthSc Manager Non-Invasive Cardiology Lab Heart Centre King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre
 Deborah Ruediger, ASAR, DipHlthSc, MHlthSc Manager Non-Invasive Cardiology Lab Heart Centre King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre 1 No Disclosures 2 Musculoskeletal Injury (MSI) refers to damage
Deborah Ruediger, ASAR, DipHlthSc, MHlthSc Manager Non-Invasive Cardiology Lab Heart Centre King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre 1 No Disclosures 2 Musculoskeletal Injury (MSI) refers to damage
Ergonomics Wanda Daley Drive Ames, Iowa (515) Copyright
 2408 Wanda Daley Drive Ames, Iowa 50011-3602 (515) 294-5359 www.ehs.iastate.edu Copyright Reviewed 2016 2 Ergonomics Directory of Service and Emergency Providers Services Environmental Health and Safety
2408 Wanda Daley Drive Ames, Iowa 50011-3602 (515) 294-5359 www.ehs.iastate.edu Copyright Reviewed 2016 2 Ergonomics Directory of Service and Emergency Providers Services Environmental Health and Safety
Ergonomic Education For Computer Workstations
 Ergonomic Education For Computer Workstations The University of Maryland Baltimore County s (UMBC) on-line ergonomic workstation tutorial is intended to provide you with the knowledge, skills, and educational
Ergonomic Education For Computer Workstations The University of Maryland Baltimore County s (UMBC) on-line ergonomic workstation tutorial is intended to provide you with the knowledge, skills, and educational
BOHS-Series. Series. Ergonomics Training Module
 BOHS-Series Series Ergonomics Training Module IAOH - 2013 2 INTRODUCTION IAOH - 2013 3 What is Ergonomics? Ergo = nomics = work laws or rules Ergonomics = the laws of work OSHA defines ergonomics as: the
BOHS-Series Series Ergonomics Training Module IAOH - 2013 2 INTRODUCTION IAOH - 2013 3 What is Ergonomics? Ergo = nomics = work laws or rules Ergonomics = the laws of work OSHA defines ergonomics as: the
Strains and Sprains. Signs and Symptoms of MSI
 Strains and Sprains Strains and sprains (known as musculoskeletal injuries) are the most common type of workrelated injury. Musculoskeletal injury (MSI) is a term used to describe an injury of the muscles,
Strains and Sprains Strains and sprains (known as musculoskeletal injuries) are the most common type of workrelated injury. Musculoskeletal injury (MSI) is a term used to describe an injury of the muscles,
BOHS-Series. Ergonomics Training Module
 BOHS-Series Ergonomics Training Module IAOH - 2013 2 INTRODUCTION IAOH - 2013 3 What is Ergonomics? Ergo = nomics = work laws or rules Ergonomics = the laws of work OSHA defines ergonomics as: the science
BOHS-Series Ergonomics Training Module IAOH - 2013 2 INTRODUCTION IAOH - 2013 3 What is Ergonomics? Ergo = nomics = work laws or rules Ergonomics = the laws of work OSHA defines ergonomics as: the science
Ergonomics. For additional assistance, contact the Occupational Safety office to schedule an evaluation.
 Ergonomics 1. Purpose: Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Safety and Risk and Risk Management (SRM) developed this program to improve the health and happiness of it s employees by assisting
Ergonomics 1. Purpose: Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Safety and Risk and Risk Management (SRM) developed this program to improve the health and happiness of it s employees by assisting
A Patient s Guide to Tendonitis. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Tendonitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
A Patient s Guide to Tendonitis Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written and professionally
LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2955 LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics Leader s Guide Marcom Group Ltd. 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2955 LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics Leader s Guide Marcom Group Ltd. 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in
Maine. Video Display Terminal Law. Training Program SAFE345
 Maine Video Display Terminal Law Training Program By the end of this presentation you will be able to: Identify the elements of the law Identify the training requirements Define ergonomics and its benefits
Maine Video Display Terminal Law Training Program By the end of this presentation you will be able to: Identify the elements of the law Identify the training requirements Define ergonomics and its benefits
Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity
 Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity D. Mowry 1 Mowry, D. 1995. Current Development in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion
Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity D. Mowry 1 Mowry, D. 1995. Current Development in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion
BACK SPRAINS AND STRAINS FIRST AID FOR MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES
 BACK SPRAINS AND STRAINS FIRST AID FOR MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES This information sheet is designed to increase your awareness of factors that can contribute to the formation of Musculoskeletal Injuries
BACK SPRAINS AND STRAINS FIRST AID FOR MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES This information sheet is designed to increase your awareness of factors that can contribute to the formation of Musculoskeletal Injuries
Ergonomics: Why do workers get injured? Presented by: Steve Bilan Ergonomic Specialist
 Ergonomics: Why do workers get injured? Presented by: Steve Bilan Ergonomic Specialist What do you know about Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the study of designing equipment and devices that fit the human body,
Ergonomics: Why do workers get injured? Presented by: Steve Bilan Ergonomic Specialist What do you know about Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the study of designing equipment and devices that fit the human body,
Office Ergonomics. Presented by: Samar Khalil, Environmental & Chemical Safety Officer
 Office Ergonomics Presented by: Samar Khalil, Environmental & Chemical Safety Officer Objectives Define Ergonomics & MSDs Identify Ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up workstations to minimize
Office Ergonomics Presented by: Samar Khalil, Environmental & Chemical Safety Officer Objectives Define Ergonomics & MSDs Identify Ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up workstations to minimize
Ergonomics 101: CREATING A PLAYBOOK FOR WORKSTATION ANALYSIS
 Ergonomics 101: CREATING A PLAYBOOK FOR WORKSTATION ANALYSIS Andy Litchfield Loss Prevention Consultant Gibson Presentation Objectives What Is Ergonomics? What Does OSHA Say? Identifying Problems Hierarchy
Ergonomics 101: CREATING A PLAYBOOK FOR WORKSTATION ANALYSIS Andy Litchfield Loss Prevention Consultant Gibson Presentation Objectives What Is Ergonomics? What Does OSHA Say? Identifying Problems Hierarchy
Prepared by the Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety. 5th Edition
 Prepared by the Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety 5th Edition Summary Ergonomics deals with the compatibility between workers and their work. Work is made up of the work environment, workstations,
Prepared by the Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety 5th Edition Summary Ergonomics deals with the compatibility between workers and their work. Work is made up of the work environment, workstations,
This training material presents very important information.
 Safe Lifting Disclaimer This training material presents very important information. Your organization must do an evaluation of all exposures, applicable codes and regulations, and establish proper controls,
Safe Lifting Disclaimer This training material presents very important information. Your organization must do an evaluation of all exposures, applicable codes and regulations, and establish proper controls,
"LABORATORY ERGONOMICS"
 MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "LABORATORY ERGONOMICS" Part of the "LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES" Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow Outline of Major Points Covered in the "Laboratory Ergonomics"
MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "LABORATORY ERGONOMICS" Part of the "LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES" Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow Outline of Major Points Covered in the "Laboratory Ergonomics"
OFFICE ERGONOMICS TODAY FACILITATOR S GUIDE
 OFFICE ERGONOMICS TODAY FACILITATOR S GUIDE What s Inside 1 Facilitator s Guidelines 1-a Overview 1-b Getting Started 1-c Presentation Guidelines 1-d Lesson Plan 1-e Frequently Asked Questions 2 Why these
OFFICE ERGONOMICS TODAY FACILITATOR S GUIDE What s Inside 1 Facilitator s Guidelines 1-a Overview 1-b Getting Started 1-c Presentation Guidelines 1-d Lesson Plan 1-e Frequently Asked Questions 2 Why these
WRIST SPRAIN. Description
 WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
Session Objectives. Business & Legal Reports, Inc. 0903
 Ofis Ergonomisi Session Objectives Define ergonomics and MSDs Identify ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up your workstation to minimize stress and strain Perform tasks safely and avoid
Ofis Ergonomisi Session Objectives Define ergonomics and MSDs Identify ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up your workstation to minimize stress and strain Perform tasks safely and avoid
Physiology of Injuries
 Presented By: Du-All Safety, 2019 Physiology of Injuries Strains: the muscles and tendons that support the spine are twisted, pulled or torn. Ex. Overstretching when carrying extra weight. Over flexion:
Presented By: Du-All Safety, 2019 Physiology of Injuries Strains: the muscles and tendons that support the spine are twisted, pulled or torn. Ex. Overstretching when carrying extra weight. Over flexion:
Incidence, Prevalence and Consequences of work-related musculoskeletal disorders: Current Canadian Evidence
 Incidence, Prevalence and Consequences of work-related musculoskeletal disorders: Current Canadian Evidence Cam Mustard, ScD President, Institute for Work & Health JASP Conference Montreal, October 2006
Incidence, Prevalence and Consequences of work-related musculoskeletal disorders: Current Canadian Evidence Cam Mustard, ScD President, Institute for Work & Health JASP Conference Montreal, October 2006
Ergonomics and the Farm. Keri A. Gill-Smith, Physical Therapist
 Ergonomics and the Farm Keri A. Gill-Smith, Physical Therapist Farm Injury Rates Farming involves hard physical work Every day about 167 agricultural workers suffer a lost-work-time injury From 2008-2010,
Ergonomics and the Farm Keri A. Gill-Smith, Physical Therapist Farm Injury Rates Farming involves hard physical work Every day about 167 agricultural workers suffer a lost-work-time injury From 2008-2010,
POLICY NUMBER: POL 91
 Summary of Proposed Amendments Amendments to the policy, Repetitive Strain Injuries (POL 91), are proposed to set out the criteria for acceptance of repetitive strain injuries and provide clarification
Summary of Proposed Amendments Amendments to the policy, Repetitive Strain Injuries (POL 91), are proposed to set out the criteria for acceptance of repetitive strain injuries and provide clarification
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Q: What is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)? A: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the name for a group of problems that includes swelling, pain, tingling, and loss of strength in your
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Q: What is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)? A: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the name for a group of problems that includes swelling, pain, tingling, and loss of strength in your
The Reasons We Experience Pain
 Pain signals can originate in the skin, bone, muscles or nerves. We have all experienced aches and pains from daily activities, work activities, sports activities or accidents and trauma. Our bodies have
Pain signals can originate in the skin, bone, muscles or nerves. We have all experienced aches and pains from daily activities, work activities, sports activities or accidents and trauma. Our bodies have
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a relatively common complaint in individuals
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a relatively common complaint in individuals
Beginning of Process: Development of the Office Ergonomics program.
 CNM WAY PROCESS CNM Process Name Office Ergonomics Program (05/15/2018 Revision) Overview of Office Ergonomics Program Purpose: To provide applicable suggestions and procedures that may be help reduce
CNM WAY PROCESS CNM Process Name Office Ergonomics Program (05/15/2018 Revision) Overview of Office Ergonomics Program Purpose: To provide applicable suggestions and procedures that may be help reduce
OFFICE ERGONOMICS. Department of Environmental Health and Safety University of Pittsburgh
 OFFICE ERGONOMICS Department of Environmental Health and Safety University of Pittsburgh Ergonomics What is it? Why should I be interested? What do I need to know to help myself? Where can I get help?
OFFICE ERGONOMICS Department of Environmental Health and Safety University of Pittsburgh Ergonomics What is it? Why should I be interested? What do I need to know to help myself? Where can I get help?
The 3E Approach to Eliminating Musculoskeletal Injuries: Utility Spotlight
 The 3E Approach to Eliminating Musculoskeletal Injuries: Utility Spotlight Fall Occupational Safety & Health Committee Conference September 2017 Portland, OR Jon Kabance, RKT BIOKINETIX Jon graduated from
The 3E Approach to Eliminating Musculoskeletal Injuries: Utility Spotlight Fall Occupational Safety & Health Committee Conference September 2017 Portland, OR Jon Kabance, RKT BIOKINETIX Jon graduated from
TOP RYDE CHIROPRACTIC
 1. Ankle Pain Conditions Helped by Chiropractic The ankle joint is made up of ligaments, tendons, nerves, and a disc to cushion motion. Distortions of motion of the ankle can strain the ligaments and muscles
1. Ankle Pain Conditions Helped by Chiropractic The ankle joint is made up of ligaments, tendons, nerves, and a disc to cushion motion. Distortions of motion of the ankle can strain the ligaments and muscles
Corporate Safety Manual. Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics
 Corporate Safety Manual Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics Last updated: April 2015 Office Ergonomics Chapter 8: Office Ergonomics Index Page Introduction to Ergonomics...8-3 Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders
Corporate Safety Manual Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics Last updated: April 2015 Office Ergonomics Chapter 8: Office Ergonomics Index Page Introduction to Ergonomics...8-3 Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders
whoah billy, that s no way to lift a heavy weight Stay healthy and happy at work with advice from the Chartered Society of Physiotherapy
 whoah billy, that s no way to lift a heavy weight yee-ow!! Stay healthy and happy at work with advice from the Chartered Society of Physiotherapy This leaflet has been compiled with the help of chartered
whoah billy, that s no way to lift a heavy weight yee-ow!! Stay healthy and happy at work with advice from the Chartered Society of Physiotherapy This leaflet has been compiled with the help of chartered
260- OFFICE ERGONOMICS
 260.1 PURPOSE A. To provide some universally applicable suggestions and procedures that may be helpful when setting up an ergonomically correct work station in an office setting. 260.2 SCOPE A. This procedure
260.1 PURPOSE A. To provide some universally applicable suggestions and procedures that may be helpful when setting up an ergonomically correct work station in an office setting. 260.2 SCOPE A. This procedure
Ergonomic Risk Factors Resolved in Microelectronics Shop at Naval Air Station Jacksonville
 Ergonomic Risk Factors Resolved in Microelectronics Shop at Naval Air Station Jacksonville Ergonomics is the science of fitting the work task to the worker, instead of requiring the worker to adapt to
Ergonomic Risk Factors Resolved in Microelectronics Shop at Naval Air Station Jacksonville Ergonomics is the science of fitting the work task to the worker, instead of requiring the worker to adapt to
ERGONOMIC CHECKLIST. Area: Date of Survey: Assessors Name: BODY PART RISK FACTORS NECK/SHOULDER ELBOW HAND/WRIST Carpel tunnel
 ERGONOMIC CHECKLIST Area: Date of Survey: Assessors Name: Job Description Job Risk priority as per Risk Assessment ( X applicable column) H H-M M M-L L ERGONOMIC FACTORS Repetition BODY PART RISK FACTORS
ERGONOMIC CHECKLIST Area: Date of Survey: Assessors Name: Job Description Job Risk priority as per Risk Assessment ( X applicable column) H H-M M M-L L ERGONOMIC FACTORS Repetition BODY PART RISK FACTORS
Enhancing Safety Through Ergonomics
 Enhancing Safety Through Ergonomics Targeting Risk Factors Definition of Risk Factors: Actions or conditions found to contribute to worker discomfort or development of Musculoskeletal Disorders MAIN RISK
Enhancing Safety Through Ergonomics Targeting Risk Factors Definition of Risk Factors: Actions or conditions found to contribute to worker discomfort or development of Musculoskeletal Disorders MAIN RISK
This tool box talk will address the potential risks of working with vibrating tools, and what you can do to minimise those risks
 This tool box talk will address the potential risks of working with vibrating tools, and what you can do to minimise those risks You are at risk of hand arm vibration syndrome, HAVs, if you regularly use
This tool box talk will address the potential risks of working with vibrating tools, and what you can do to minimise those risks You are at risk of hand arm vibration syndrome, HAVs, if you regularly use
Office and Laboratory Ergonomics. WSU-TFREC Safety Training
 Office and Laboratory Ergonomics WSU-TFREC Safety Training What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the scientific study of human work Ergonomic principals adapt work to a specific person by designing tasks &
Office and Laboratory Ergonomics WSU-TFREC Safety Training What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the scientific study of human work Ergonomic principals adapt work to a specific person by designing tasks &
Original Date of Issue: 01/2009
 POLICIES AND PROCEDURES DEPARTMENT: Environmental Health and Safety SUBJECT: Safe Lift Program Original Date of Issue: 01/2009 Reviewed 01/09 04/09 12/2011 Revised 01/09 12/2011 POLICY: SUNY New Paltz
POLICIES AND PROCEDURES DEPARTMENT: Environmental Health and Safety SUBJECT: Safe Lift Program Original Date of Issue: 01/2009 Reviewed 01/09 04/09 12/2011 Revised 01/09 12/2011 POLICY: SUNY New Paltz
Electrician s Job Demands Literature Review Manual & Power Tools
 Electrician s Job Demands Literature Review Manual & Power Tools An electrician s job is physical in nature, and the physical demands of the job are affected by the use of handheld manual and power tools
Electrician s Job Demands Literature Review Manual & Power Tools An electrician s job is physical in nature, and the physical demands of the job are affected by the use of handheld manual and power tools
This was good at the time - see ergoanalyst.com for the latest in manual tasks risk management
 Burgess-Limerick & Associates Ergonomics and Research Consultants ABN 84976421949 This was good at the time - see ergoanalyst.com for the latest in manual tasks risk management Procedure for Managing Injury
Burgess-Limerick & Associates Ergonomics and Research Consultants ABN 84976421949 This was good at the time - see ergoanalyst.com for the latest in manual tasks risk management Procedure for Managing Injury
Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis
 Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis Ergonomics is the study of the relationship between people and their environment. In the workplace, ergonomics is the science of designing or redesigning the
Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis Ergonomics is the study of the relationship between people and their environment. In the workplace, ergonomics is the science of designing or redesigning the
Section 3: Ergonomics and Materials Handling
 Section 3: Ergonomics and Materials Handling OVERVIEW This section provides information about designing your work area and completing tasks in a way that makes you more comfortable while performing your
Section 3: Ergonomics and Materials Handling OVERVIEW This section provides information about designing your work area and completing tasks in a way that makes you more comfortable while performing your
Computer Ergonomics. Static Efforts
 Welcome to Essential WorkWellness online continuing education activities. Please be aware that this activity does not include a post test or certificate of completion. Simply read the article below to
Welcome to Essential WorkWellness online continuing education activities. Please be aware that this activity does not include a post test or certificate of completion. Simply read the article below to
Ergonomics and Back Safety PPT-SM-BACKSFTY V.A.0.0
 Ergonomics and Back Safety 1 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomics Scientific study of equipment design for the purpose of improving efficiency, comfort and safety 2 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomic
Ergonomics and Back Safety 1 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomics Scientific study of equipment design for the purpose of improving efficiency, comfort and safety 2 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomic
Back Safety. Version 1.0
 This document is intended to provide basic safety guidelines for the Physical Plant Department at Community College of Allegheny County. The information provided in this guide may vary by site. Version
This document is intended to provide basic safety guidelines for the Physical Plant Department at Community College of Allegheny County. The information provided in this guide may vary by site. Version
Hand, Wrist and Finger Safety in Construction Environments. Leader s Guide and Quiz
 ! Hand, Wrist and Finger Safety in Construction Environments Leader s Guide and Quiz 3961 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in this program is presented in a definite order
! Hand, Wrist and Finger Safety in Construction Environments Leader s Guide and Quiz 3961 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in this program is presented in a definite order
Safety Meeting. Meeting Leader Instructions. Safety, Teamwork & Our Customer s 1 st Choice
 Meeting Leader Instructions These meetings are more than safety meetings. While they address safety as a top priority, these meetings are also an opportunity for you to interact with your team; a chance
Meeting Leader Instructions These meetings are more than safety meetings. While they address safety as a top priority, these meetings are also an opportunity for you to interact with your team; a chance
Version February 2016
 Version 3.1 29 February 2016 Health and Safety Unit 1 Table of Contents 1. Setting up your computer workstation... 3 Step 1: Adjusting yourself to the correct height... 3 Step 2 Adjusting your Chair...
Version 3.1 29 February 2016 Health and Safety Unit 1 Table of Contents 1. Setting up your computer workstation... 3 Step 1: Adjusting yourself to the correct height... 3 Step 2 Adjusting your Chair...
Vermeulen, Liebenberg, Dippenaar en Louw Fisioterapeute
 Vermeulen, Liebenberg, Dippenaar en Louw Fisioterapeute In the Office Relaxation? Relaxation at work? Why doesn t my pain go away? Acute pain = Short term pain (Sprained ankle) Persistent/ Chronic
Vermeulen, Liebenberg, Dippenaar en Louw Fisioterapeute In the Office Relaxation? Relaxation at work? Why doesn t my pain go away? Acute pain = Short term pain (Sprained ankle) Persistent/ Chronic
Spine Conditions and Treatments. Your Guide to Common
 Your Guide to Common Spine Conditions and Treatments The spine is made up of your neck and backbone. It allows your body to bend and move freely. As you get older, it is normal to have aches and pains.
Your Guide to Common Spine Conditions and Treatments The spine is made up of your neck and backbone. It allows your body to bend and move freely. As you get older, it is normal to have aches and pains.
EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow)
 EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow) Description Expected Outcome Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) is the most common painful condition of the elbow. Inflammation and pain occur on the outer side
EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow) Description Expected Outcome Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) is the most common painful condition of the elbow. Inflammation and pain occur on the outer side
ERGONOMICS, BIOMECHANICS & MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDER- A REVIEW
 ERGONOMICS, BIOMECHANICS & MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDER- A REVIEW Md Shakibul Haque 1, Manoj Kumar ² 1,2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Invertis University, Bareilly, U.P., (India) ABSTRACT Through
ERGONOMICS, BIOMECHANICS & MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDER- A REVIEW Md Shakibul Haque 1, Manoj Kumar ² 1,2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Invertis University, Bareilly, U.P., (India) ABSTRACT Through
Table of Contents. 2. What are work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders?
 Table of Contents 1. Introduction O 2. What are work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders? P 3. Common types of work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders Q 4. Risk factors associated with
Table of Contents 1. Introduction O 2. What are work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders? P 3. Common types of work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders Q 4. Risk factors associated with
OH&S. Musculoskeletal Injury Prevention (MSIP)
 OH&S Musculoskeletal Injury Prevention (MSIP) Trainer s Guide to MSIP Supplies Needed: Slider sheet Pill crusher 2 volunteers Time required for session: 30 minutes Lifts Belts Flip chart paper Hand outs
OH&S Musculoskeletal Injury Prevention (MSIP) Trainer s Guide to MSIP Supplies Needed: Slider sheet Pill crusher 2 volunteers Time required for session: 30 minutes Lifts Belts Flip chart paper Hand outs
Arm Injuries and Disorders
 Arm Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your arms are made up of muscles, joints, tendons and other connective tissue. There are many injuries and disorders that can affect the arm. Some arm injuries and
Arm Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your arms are made up of muscles, joints, tendons and other connective tissue. There are many injuries and disorders that can affect the arm. Some arm injuries and
Supervisors Safety Update Ideas and Strategies for Leaders
 Supervisors Safety Update Ideas and Strategies for Leaders SSU 2006-07 SUPERVISING REPTITIVE MOTION WORK TASKS By SeaBright Insurance Loss Control I n only a relatively short number of years, the word
Supervisors Safety Update Ideas and Strategies for Leaders SSU 2006-07 SUPERVISING REPTITIVE MOTION WORK TASKS By SeaBright Insurance Loss Control I n only a relatively short number of years, the word
PROPER ERGONOMICS HOW TO AVOID OVERUSE INJURIES GRETCHEN ROMAN, PT, DPT GREATER ROCHESTER PHYSICAL THERAPY
 PROPER ERGONOMICS HOW TO AVOID OVERUSE INJURIES GRETCHEN ROMAN, PT, DPT GREATER ROCHESTER PHYSICAL THERAPY Tobey Village Office Park 140 Office Park Way Pittsford, NY 14534 V: (585)370-7180 www.grpt.com
PROPER ERGONOMICS HOW TO AVOID OVERUSE INJURIES GRETCHEN ROMAN, PT, DPT GREATER ROCHESTER PHYSICAL THERAPY Tobey Village Office Park 140 Office Park Way Pittsford, NY 14534 V: (585)370-7180 www.grpt.com
Carpal tunnel syndrome
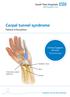 Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Ergonomics. MSD Injury Prevention
 Ergonomics MSD Injury Prevention Ergonomics Definition The International Ergonomics Association offers a very comprehensive definition: The scientific discipline concerned with the understanding of interactions
Ergonomics MSD Injury Prevention Ergonomics Definition The International Ergonomics Association offers a very comprehensive definition: The scientific discipline concerned with the understanding of interactions
Most construction workers have to undertake some lifting and moving, this toolbox talk is about identifying the hazards and eliminating them.
 Most construction workers have to undertake some lifting and moving, this toolbox talk is about identifying the hazards and eliminating them. As well as preventing musculoskeletal injury Musculoskeletal
Most construction workers have to undertake some lifting and moving, this toolbox talk is about identifying the hazards and eliminating them. As well as preventing musculoskeletal injury Musculoskeletal
disorders Self-care training programme for hand-intensive occupations
 Preventing workrelated upper limb disorders Self-care training programme for hand-intensive occupations Aims of the programme - To increase awareness of work-related upper limb disorders (WRULDs) associated
Preventing workrelated upper limb disorders Self-care training programme for hand-intensive occupations Aims of the programme - To increase awareness of work-related upper limb disorders (WRULDs) associated
Rotator Cuff Injuries
 Rotator Cuff Injuries Introduction Shoulder injuries are fairly common, especially for people who tend to exercise a lot. Some of the most common shoulder injuries are called rotator cuff injuries. This
Rotator Cuff Injuries Introduction Shoulder injuries are fairly common, especially for people who tend to exercise a lot. Some of the most common shoulder injuries are called rotator cuff injuries. This
Back Safety Healthcare #09-066
 Back Safety Healthcare Version #09-066 I. Introduction A. Scope of training This training program applies to healthcare employees whose job requires them to lift patients or other heavy objects. Lifting
Back Safety Healthcare Version #09-066 I. Introduction A. Scope of training This training program applies to healthcare employees whose job requires them to lift patients or other heavy objects. Lifting
Ergonomics questions will account for 13% or 26 questions of the ASP exam.
 1 Ergonomics questions will account for 13% or 26 questions of the ASP exam. This lesson will help in preparing you for those questions, to include several review and sample questions for practice. 2 Carpal
1 Ergonomics questions will account for 13% or 26 questions of the ASP exam. This lesson will help in preparing you for those questions, to include several review and sample questions for practice. 2 Carpal
Display Screen Equipment Risk Assessment Workshop
 Display Screen Equipment Risk Assessment Workshop Objectives Hazard Identification Use of HSE checklist Provision of information Drawing conclusions from assessments Risk reduction and control. What is
Display Screen Equipment Risk Assessment Workshop Objectives Hazard Identification Use of HSE checklist Provision of information Drawing conclusions from assessments Risk reduction and control. What is
Preventing Work-related Injuries Among Sonographers
 Preventing Work-related Injuries Among Sonographers Carolyn T. Coffin, MPH, RDMS, RVT, RDCS, FSDMS Joan P. Baker, MSR, RDMS, RDCS, FSDMS Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WRMSD) have been reported
Preventing Work-related Injuries Among Sonographers Carolyn T. Coffin, MPH, RDMS, RVT, RDCS, FSDMS Joan P. Baker, MSR, RDMS, RDCS, FSDMS Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WRMSD) have been reported
Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb
 Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb Introduction Trigger finger and trigger thumb are conditions affecting the movement of the tendons as they bend the
Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb Introduction Trigger finger and trigger thumb are conditions affecting the movement of the tendons as they bend the
Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03
 Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03 Working from home is becoming more of an option for employees today. The type of work usually entails working from the home computer work station.
Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03 Working from home is becoming more of an option for employees today. The type of work usually entails working from the home computer work station.
What you need to know about Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 What you need to know about Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Disorders of the Neck, Shoulder, Elbow, Wrist and Hands It is my mission to empower patients with knowledge and care so that they can enjoy
What you need to know about Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Other Disorders of the Neck, Shoulder, Elbow, Wrist and Hands It is my mission to empower patients with knowledge and care so that they can enjoy
Ergonomic Guidelines for Computer Users Frank Gonzales, CEES, CEAS
 Office Ergonomics Ergonomic Guidelines for Computer Users Frank Gonzales, CEES, CEAS Ergonomics Program Services What other services are provided? Training sessions Office, Industrial (can be specific
Office Ergonomics Ergonomic Guidelines for Computer Users Frank Gonzales, CEES, CEAS Ergonomics Program Services What other services are provided? Training sessions Office, Industrial (can be specific
