Unit 6. Moving and Handling. Theory. Page 1 of 11
|
|
|
- Warren Payne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Moving and Handling Unit 6 Theory Page 1 of 11
2 Unit 6 Moving and Handling Theory INTRODUCTION All handling of objects, people and animals carries a risk of injury for the handler and others. More than a quarter of the accidents reported to the enforcing agencies are associated with manual handling the transporting or supporting of loads by hand or by bodily force. Lifting implies that you are taking most or all of the full weight of the object. This results in severe stress on the soft tissues of the spine, ligaments and discs, so it can lead to injury. Injury can result in staff being absent from work. Recurrent problems will affect the individual s ability to continue working, their social and home life. Severe injury may lead to the individual not being able to continue in their chosen profession and leave. Research (HSE, RoSPA) has shown that the repeated use of incorrect lifting techniques to move loads, and working in stressful postures increases the likelihood of injury to the spine. In light of this research and evidence gathered from injury statistics, legislation is now in place, outlining measures and responsibilities for both employer and employee to be taken to manage the problems associated with manual handling. Legislation There are 5 main pieces of legislation relating to Lifting and Handling Health and Safety at Work Act Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 (as amended). Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations Workplace (Health, Safety and Welfare) Regulations LOLER (Lifting operations and Lifting Equipment Regulations 1998): - These set out both Employer and Employee responsibilities. Employer Responsibilities Under the Health and Safety at Work Act, employers are responsible for the health, welfare and safety of their employees, and must provide instruction, supervision and training for them. Under the Manual Handling Operations Regulations, emphasis is placed on the avoidance of hazardous manual handling operations, and the provision of a safe system of work. Under the Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations, emphasis is placed on Risk Assessments and the provision of equipment appropriate for the task. Under the Workplace Regulations, emphasis is placed on maintenance of the workplace, equipment and to ensure all are in good state of repair. Page 2 of 11
3 Employee Responsibilities Under the Health and Safety at Work Act, the employee is responsible for his/her own health, safety and welfare and should co-operate with the employer to carry out his/her duties. Under the Manual Handling Operations Regulations, the employee is required to make use of any safe system of work provided by the employer. Under the Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations, the employee is required to use any equipment/ machinery/ aids in accordance with the training and instructions of the employer. Employees are required to alert management to new risks in the workplace. Please see Trust policy This document has been produced to set out guidelines concerning the safe movement of loads objects or people You are required to: Work within the framework set out by the above document. AVOID hazardous manual handling operations as far as is reasonably practicable. ASSESS your course of action. REDUCE your risk of injury, by acting on the information you have obtained. All staff are to be made aware of this information and it is to be documented, read, acted upon and changed as necessary. Definitions Load - is a discrete moveable object (thing, person or animal) Lifting the transporting and/or supporting of a load by hand or bodily force THEORY Anatomy The spine is one of the main components of the skeleton. It is made up of 33 vertebrae 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, the rest forming the sacrum and coccyx. Its functions are to provide central support for the body, attachments for muscles and ligaments, allow movement and provide protection for the spinal cord. Between the vertebrae are the discs, these act as spacers between the bones of the spine, as shock absorbers in the spine, aid smooth movement, and try to maintain the weight bearing pressures through the spine as evenly as possible. The most vulnerable areas of the spine are the lumbar (lower back), and the cervical (neck) regions. They are the most mobile, and susceptible to injury. The lower back is also the main weight bearing part of the spine. The spine is supported by muscles and ligaments. The trunk muscles are postural muscles and are not as strong as the muscles found in the arms and legs. There are many causes of pain and discomfort, but can be broadly divided into 2 groups problems with the bony structures of the spine, and problems with the soft tissues the muscles, ligaments and the discs. Page 3 of 11
4 Apart from some specific medical conditions, the majority of musculo-skeletal problems come about as a result of mechanical loading of the spine the 2 most common culprits are lifting of loads and poor working postures. Posture Correct posture is essential for everyone, it brings with it many advantages, particularly to the spine because it: There are 33 vertebrae in the human spine Re-aligns the spine, keeps the weight bearing stresses through the bodies of the vertebrae and the intervertebral discs as even as possible. Causes less weight bearing stresses on the soft tissues of the spine, the muscles and ligaments, which are not designed to be over-stretched. Maintains a good head position, particularly important if the person works in a sitting position, as there is less stress on the neck and upper limbs. Good posture encourages a healthy spine, and goes some way to reducing the risk of injury to the spine. Poor posture, standing or sitting in a slumped position, results in: Mechanical damage to the soft tissues of the spine the discs, muscles and ligaments. Increasing fatigue in these soft tissues. Herniation of the discs a slipped disc. Increasing neck and low back pain. In recent years research has shown that there is a link between poor working postures and cumulative back problems. Good posture can be attained by: Making the effort to sit and stand correctly. Regularly changing position standing, walking and stretching the spine. Working at the correct height for the particular task to be carried out. Adjusting seating, if available, for the individual. Wearing appropriate footwear. Lifting As the majority of injuries related to the moving of objects affects the spine, changes to the way we lift things is essential to reduce injuries. This entails Risk Assessments to be carried out, to identify problems and promote safe working. Assessing each situation as it arises. Using appropriate equipment that is available to help you. Altering how you manually lift anything instead of the smaller, weaker muscles in the back, use the longer and stronger muscles in the legs and arms. At all times, good posture and handling techniques will help to protect the spine from musculo-skeletal injury. Page 4 of 11
5 Moving Loads A load is a discrete moveable object a thing (inanimate), a person (animate), or an animal (animate). It takes too long. It is perceived as being more difficult, to bend the knees rather than bend the back. We have become lazy and have developed bad lifting habits. We do not perceive the risks in lifting lighter and smaller objects compared to larger, heavier objects i.e. boxes of files compared to tables and furniture. As many, if not more, back problems result from cumulative stress, so repeated lifting of lighter, smaller objects incorrectly is as bad for you as moving a single heavier or larger object. Principles of Safer Handling Wear appropriate clothing and footwear. Never manually handle, unless you have no other option. Always ask do I need to lift this? Assess the object to be moved prior to commencing a manoeuvre. Always select the appropriate manoeuvre and equipment for the task in hand. Make the load smaller/lighter if possible. Identify a team leader, to give instructions and explanations to everyone. If it is a person to be moved, explain the procedure to them. Prepare the area, clear away objects and try to create space. Apply the brakes on any equipment if necessary. Make a stable base with your legs and feet, feet apart for balance, knees bent so you can make use of the power in your leg muscles. Keep the object or person as close to you as possible. Make sure of a good hand grip. Avoid static stooping i.e. legs straight, spine bent forwards, arms stretched, as much as possible. Know your own limit or capacity, if you cannot move something, ask for help. Give clear, precise instructions. Raise the head on movement, this keeps the spine in good alignment and gives you good visibility. Do not twist your spine, this generates increased weight bearing forces within the discs and soft tissues of your lower spine. All of these principles reinforce the need to assess the situation, keep your balance and make use of the power in the stronger leg muscles rather than the weaker back muscles. Good posture is encouraged, as this also reduces the strain on the soft tissues in the back. Page 5 of 11
6 ASSESSMENT Assessment prior to moving any object has four components: Task what are you trying to do, is there any other way of making the task (job) simpler, is there any equipment to help you? Individual Capability can you do the task? Do not exceed your own capabilities, do you know how to use the appropriate equipment, if not - ask. Load what are you trying to move, is there any other way of lightening the load, can you divide it into smaller parts. If it is a patient, can they help you? Environment where are you and where do you want to be. Can you create space around you, is the area clear of obstacles, can you see where you are going? It is important to plan what you are going to do, communicate this to others if they are going to help you, use equipment to help you, and act on this information. Moving People Patient Assessment Why have a Safer Patient Handling Procedure? To eliminate hazardous manual handling operations in all but exceptional or life threatening circumstances. Nursing and other care related professions, are high risk professions for developing musculo-skeletal disorders particularly back problems, by persisting in manually moving patients. It is acceptable to give a patient some support, but not to take most or all of their weight. The Manual Handling Operations Regulations establish a hierarchy of measures: Avoid hazardous manual handling operations so far as is reasonably practicable. For those operations that cannot be avoided, the situation must be assessed. Reduce the risk of injury from those operations as far as is reasonably practicable. When dealing with patients: Avoid lifting/manually moving them, encourage them to do what they can for themselves. Assess what they can and cannot do for themselves, and then use the most appropriate technique or piece of equipment to move them. The number of staff needed to move the patient safely can vary so clinical staff should also work closely with carers/relatives or outside agencies to reduce the risk of injury to both staff and patient. It is essential to assess the patient s level of mobility. Page 6 of 11
7 All patients must be assessed for their moving and handling needs, as with all other protocols documented, changed as necessary and acted upon. The patients and their carers/relatives must be made aware of the Trust Safer Handling Policy and why we use safer handling techniques. What needs to be documented: What the patient can or cannot do for themselves. What equipment and numbers of staff are required to move them. If the patient uses any mobility aids sticks, walking frame. If the patient s condition changes, they need to be re-assessed. All staff must know and act on this information Acceptable and Unacceptable Techniques Staff must only use acceptable Moving and Handling Techniques approved by the Trust, these are described below. After assessing the patient Are they being nursed on the most suitable bed and mattress. Then, each time you attend the patient to move them: Encourage them to do what they can for themselves, and give them time to do so. Within the hospital all adult patients are nursed on electric profiling beds, these are designed to be of help to the staff, as well as to provide more comfort for the patient. To perform the following moves:- Rolling side to side the minimum of two people are required (more depending on the size and condition of the patient) to roll the patient, if they require to be positioned on either side or moved across the bed use sliding sheets, to reduce the effort required by the staff. Lying to sitting use the bed to raise the patient into sitting. Ensure the patients hips are positioned over the break in the bed, if the patient has slid further down the bed, lower the back rest, slide the patient up the bed to place their hips in the right position, then use the bed to sit them up. This also applies to trolleys. DO NOT DRAG THE PATIENT UP THE BED BY PULLING ON THEIR ARMS. Move up the bed slide recumbent patients up the bed using sliding sheets, and the minimum of two people (more may be required depending on assessment). Another alternative, if there are insufficient numbers of staff, is to use the hoist. Lying to sitting over the edge of the bed if the patient is lying flat, roll them onto their side, then ease them up into sitting. If semi-recumbent or sat up in bed, use the bed to sit them as upright as possible. Have the members of staff positioned one behind the patient to support the patient s trunk, and the other in front to support the patient s legs. Sitting to standing the patient must be able to bear their own weight, if not use the HOIST. Staff are to position themselves on either side of the patient, one arm supporting the patient s trunk, the other supporting the patient s upper arm, block the feet if necessary and rock the patient onto their feet. DO NOT DRAG THE PATIENT UPRIGHT BY PULLING ON THEIR ARMS. Page 7 of 11
8 Transfer to a chair once on their feet, allow the patient time to stand as upright as possible, get their balance, before asking them to step round to sit down in a controlled fashion, Turning them quickly, results in the patient losing their balance and not being able to help you. If you cannot get the patient onto their feet with two members of staff, either from the bed or from the chair back to bed, asking for more staff is not the most appropriate thing to do. To be surrounded by staff and manhandled into a bed or a chair, is not SAFE, DIGNIFIED OR NOT OFFERING THE BEST QUALITY OF CARE TO THE PATIENT, NEITHER IS IT SAFE FOR THE STAFF. If you cannot get the patient onto their feet use the appropriate hoist. Support whilst walking you are there to provide support and guidance, not hold the patient upright. If they use a walking aid use this, and you stand to the side. They can see you, but you are not in the way. Emergencies/life-threatening situations- if out of bed (including sitting on a chair, commode or wheelchair) lower the patient to the floor. Try to protect their head, but imperatively you do not put yourself at risk. Once on the floor deal with resuscitation there. Fallen/falling patient contact emergency services while keeping the patient as comfortable as possible until help arrives Unacceptable Techniques Refer to the Guide to the Handling of People 5th edition These moves were identified in 1980 as being dangerous to staff and patient, they were condemned by the RCN in 1984 as a means of moving patients, and MUST NOT be employed. Lying to sitting by pulling the patients arms, it is painful and damaging to the patient and can cause harm to the staff s neck, shoulder and back muscles. Move up the bed by pulling the patient s arms, it causes damage to the shoulders and can lead to the development of pressure areas. It also strains the staff s neck, shoulder and back muscles. Sitting to standing by pulling the patient s arms, this will cause the same problems as above. The patient is in danger of falling as the staff do not have full control of the situation. Manually lifting a patient out of a bed or chair the staff are carrying the whole weight of the patient, and may drop the patient. Manually lifting a patient off the floor unless in exceptional circumstances, because of the potential harm to patient and staff alike. Always assess the situation first, then use the most appropriate and safe technique to move the patient. Use equipment to help you it may take more time, but both you and the patient will be safe. Page 8 of 11
9 Unit 6 assessment: Moving & Handling 1. Is a person considered to be a load in legal terms? (a) Yes (b) No 2. Roughly what percentage of accidents reported to enforcing agencies are associated with manual handling? (a) Less that 25% (b) More than 25% (c) 50% (d) 70% 3. Apart from medical conditions, what causes most musculo-skeletal problems in the workplace? (a) Lifting of loads (b) Poor working postures (c) Both of these 4. How many vertebrae are there in the human spine? (a) 29 (b) 33 (c) Are leg muscles more powerful than trunk muscles? (a) Yes (b) No 6. Which of the four main pieces of legislation places emphasis on the employer to conduct risk assessments and provide equipment appropriate for tasks? (a) Health & Safety at Work Act 1974 (b) Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 (c) Management of Health & Safety at Work Regulations 1999 (d) Workplace (Health, Safety and Welfare) Regulations Which of the four main pieces of legislation says employees are responsible for their own health, safety and welfare and should co-operate with their employer to carry out duties? (a) Health & Safety at Work Act 1974 (b) Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 (c) Management of Health& Safety at Work Regulations 1999 (d) Workplace (Health, Safety and Welfare) Regulations What are the four components of any assessment of manual handling risk? (a) Task, load, location, individual fitness (b) Task, load, location, individual capability (c) Task, load, environment, individual capability Page 9 of 11
10 9. You re a nurse who needs to move a bed patient from side to side. Can you do this on your own, or should you ask for help? (a) You can do it on your own (b) There must be at least two people (c) Can vary with patients own capabilities 10. What is probably the best way of moving a recumbent patient up the bed? (a) Use sliding sheets with two people (b) Use sliding sheets with a minimum of four people (c) Manual handling with two people (d) Manual handling with a minimum of four people Page 10 of 11
11 Unit 6: Moving & Handling Completion Statement PLEASE only sign and return when you are satisfied that your staff member has completed all of the relevant mandatory units and correctly answered questions. A PHOTOCOPY of this completion statement ONLY, MUST be sent to Learning and Development. This is for input on to the Trusts Central Training Data Base (OLM) as evidence that your staff member has completed the Mandatory Training Assessment Pack. A further copy should be placed in your staff members personal development file. This is to confirm the Mandatory Training Assessment has been completed by: Surname: (Block Capitals)... Forename: (Block Capitals)... Job Title:... Department/Ward:... Division/Directorate:... Date Completed: (This must be within 12 weeks of receipt)... Staff Signature:... Manager: (Printname)... Manager:( Signature)... Return a copy to OLM, Blackpool Teaching Hospitals, ESR Department, Aster Offices, Blackpool Victoria Hospital, FY3 8NR An electronic copy can be ed to: olm@bfwhospitals.nhs.uk Date Sent: VERSION 4 - OCTOBER 2014 Page 11 of 11
Back Safety Healthcare #09-066
 Back Safety Healthcare Version #09-066 I. Introduction A. Scope of training This training program applies to healthcare employees whose job requires them to lift patients or other heavy objects. Lifting
Back Safety Healthcare Version #09-066 I. Introduction A. Scope of training This training program applies to healthcare employees whose job requires them to lift patients or other heavy objects. Lifting
the back book Your Guide to a Healthy Back
 the back book Your Guide to a Healthy Back anatomy Your spine s job is to: Support your upper body and neck Increase flexibility of your spine Protect your spinal cord There are 6 primary components of
the back book Your Guide to a Healthy Back anatomy Your spine s job is to: Support your upper body and neck Increase flexibility of your spine Protect your spinal cord There are 6 primary components of
Moving and Positioning Handout
 Moving and Positioning Handout Manual Handling is the transporting or supporting of a load by hand or by bodily force. This involves: Lifting, Carrying, Pushing, Pulling, Rolling, Moving and Supporting.
Moving and Positioning Handout Manual Handling is the transporting or supporting of a load by hand or by bodily force. This involves: Lifting, Carrying, Pushing, Pulling, Rolling, Moving and Supporting.
BODY MECHANICS CMHA-CEI
 BODY MECHANICS CMHA-CEI Basics about backs Facts about Back Disorders Maintaining a Healthy Back Common activities Lifting Techniques Stretching Techniques Topics Your back Spine & Vertebrae Discs Nerves
BODY MECHANICS CMHA-CEI Basics about backs Facts about Back Disorders Maintaining a Healthy Back Common activities Lifting Techniques Stretching Techniques Topics Your back Spine & Vertebrae Discs Nerves
Back Safety. Version 1.0
 This document is intended to provide basic safety guidelines for the Physical Plant Department at Community College of Allegheny County. The information provided in this guide may vary by site. Version
This document is intended to provide basic safety guidelines for the Physical Plant Department at Community College of Allegheny County. The information provided in this guide may vary by site. Version
Body Mechanics Training For Shelter Staff 2014
 Body Mechanics Training For Shelter Staff 2014 Valerie Risher, RN, BSN FDOH Region 5 Special Needs Consultant Terry B. Freeman, RN Disaster Health Services Advisor, Florida American Red Cross Robert Kosiba,
Body Mechanics Training For Shelter Staff 2014 Valerie Risher, RN, BSN FDOH Region 5 Special Needs Consultant Terry B. Freeman, RN Disaster Health Services Advisor, Florida American Red Cross Robert Kosiba,
Commonwealth Health Corporation NEXT
 Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Moving and Handling Guidance
 NIPEC/19/03 (replacing NIPEC/14/21) NORTHERN IRELAND PRACTICE AND EDUCATION COUNCIL FOR NURSING AND MIDWIFERY Moving and Handling Guidance February 2019 Review date: April 2021 Centre House 79 Chichester
NIPEC/19/03 (replacing NIPEC/14/21) NORTHERN IRELAND PRACTICE AND EDUCATION COUNCIL FOR NURSING AND MIDWIFERY Moving and Handling Guidance February 2019 Review date: April 2021 Centre House 79 Chichester
BACK SAFETY. How to prevent a lifetime of back problems! Source: https://www.summitholdings.com
 BACK SAFETY How to prevent a lifetime of back problems! Source: https://www.summitholdings.com Volunteer Annual Review 2017 BACK INJURIES More than 1 million workers suffer back injuries each year, accounting
BACK SAFETY How to prevent a lifetime of back problems! Source: https://www.summitholdings.com Volunteer Annual Review 2017 BACK INJURIES More than 1 million workers suffer back injuries each year, accounting
Body Mechanics and Safe Patient Handling
 Body Mechanics and Safe Patient Handling Body Mechanics means using the body in an efficient and careful way involves good posture, balance, and using your strongest and largest muscles for work good body
Body Mechanics and Safe Patient Handling Body Mechanics means using the body in an efficient and careful way involves good posture, balance, and using your strongest and largest muscles for work good body
Patient information leaflet. Royal Surrey County Hospital. NHS Foundation Trust. Lower back pain. Physiotherapy Department
 Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Lower back pain Physiotherapy Department Lower back pain This leaflet is intended for people who have been diagnosed with generalised
Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Lower back pain Physiotherapy Department Lower back pain This leaflet is intended for people who have been diagnosed with generalised
An overview of posture
 An overview of posture What is posture? Posture is the description of an overall body position. This can be intentional or unintentional how we are hold our bodies, but it is the way each individual will
An overview of posture What is posture? Posture is the description of an overall body position. This can be intentional or unintentional how we are hold our bodies, but it is the way each individual will
Original Date of Issue: 01/2009
 POLICIES AND PROCEDURES DEPARTMENT: Environmental Health and Safety SUBJECT: Safe Lift Program Original Date of Issue: 01/2009 Reviewed 01/09 04/09 12/2011 Revised 01/09 12/2011 POLICY: SUNY New Paltz
POLICIES AND PROCEDURES DEPARTMENT: Environmental Health and Safety SUBJECT: Safe Lift Program Original Date of Issue: 01/2009 Reviewed 01/09 04/09 12/2011 Revised 01/09 12/2011 POLICY: SUNY New Paltz
Guidance Tool: Manual Handling
 Guidance Tool: Manual Handling Please tick the relevant boxes to ensure you follow the correct procedures. Manual Handling Risk Assessments completed for Hazardous Activities Employee made aware of the
Guidance Tool: Manual Handling Please tick the relevant boxes to ensure you follow the correct procedures. Manual Handling Risk Assessments completed for Hazardous Activities Employee made aware of the
This training material presents very important information.
 Safe Lifting Disclaimer This training material presents very important information. Your organization must do an evaluation of all exposures, applicable codes and regulations, and establish proper controls,
Safe Lifting Disclaimer This training material presents very important information. Your organization must do an evaluation of all exposures, applicable codes and regulations, and establish proper controls,
Norfolk Public Schools: Back Safety in the Workplace. By: Arianne Conley RN, BSN
 Norfolk Public Schools: Back Safety in the Workplace By: Arianne Conley RN, BSN arianneconley@yahoo.com Back Safety & Lifting Training Objectives: Risk Factors - Occupational Back Injury Prevention Principles
Norfolk Public Schools: Back Safety in the Workplace By: Arianne Conley RN, BSN arianneconley@yahoo.com Back Safety & Lifting Training Objectives: Risk Factors - Occupational Back Injury Prevention Principles
Taking Care of Your Back
 Taking Care of Your Back Most people will feel back pain at some point in their lives, but not all back pain is the same for everyone. The good news is, most low back pain improves without any treatment
Taking Care of Your Back Most people will feel back pain at some point in their lives, but not all back pain is the same for everyone. The good news is, most low back pain improves without any treatment
SECTION 6: MOVING & HANDLING
 SECTION 6: MOVING & HANDLING Moving & Handling in Low Resourced Settings Definition of manual handling: Any transporting or supporting of a load (including the lifting, putting down, pushing, pulling,
SECTION 6: MOVING & HANDLING Moving & Handling in Low Resourced Settings Definition of manual handling: Any transporting or supporting of a load (including the lifting, putting down, pushing, pulling,
LOW BACK PAIN. what you can do
 LOW BACK PAIN what you can do Back pain Nearly 80 percent of adults will experience back pain at some point in their life. The good news is that back pain will normally go away within four to six weeks
LOW BACK PAIN what you can do Back pain Nearly 80 percent of adults will experience back pain at some point in their life. The good news is that back pain will normally go away within four to six weeks
Efficient Moving & Handling Course Handout
 Efficient Moving & Handling Course Handout Course Handout - Efficient Moving & Handling - 1 Contents Introduction and Employer Duties... 2 Employee Duties/Risk Assessment... 3 TILE... 4 Causes of Musculoskeletal
Efficient Moving & Handling Course Handout Course Handout - Efficient Moving & Handling - 1 Contents Introduction and Employer Duties... 2 Employee Duties/Risk Assessment... 3 TILE... 4 Causes of Musculoskeletal
Body Mechanics When caring for a client
 Body Mechanics When caring for a client If assistance is needed, find out the client's strengths and weaknesses. Often one side of the body is stronger. The stronger side should be transferred first. When
Body Mechanics When caring for a client If assistance is needed, find out the client's strengths and weaknesses. Often one side of the body is stronger. The stronger side should be transferred first. When
BACK SAFETY IN-SERVICE
 INTRODUCTION Many times back pain can be directly traced to the ergonomic hazards of your job as a home healthcare worker. These hazards may include frequent bending, twisting, lifting, pushing, pulling
INTRODUCTION Many times back pain can be directly traced to the ergonomic hazards of your job as a home healthcare worker. These hazards may include frequent bending, twisting, lifting, pushing, pulling
Osteoporosis Exercise:
 Osteoporosis Exercise: Posture, Body Mechanics, Alignment and Moving Safely Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction Using correct posture, proper body mechanics
Osteoporosis Exercise: Posture, Body Mechanics, Alignment and Moving Safely Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction Using correct posture, proper body mechanics
The best way to deal with back pain
 The best way to deal with back pain The best way to deal with back pain Back pain is common and can be very painful but, serious or permanent damage is rare. The Facts Most back pain is not due to any
The best way to deal with back pain The best way to deal with back pain Back pain is common and can be very painful but, serious or permanent damage is rare. The Facts Most back pain is not due to any
Hampstead Hill School Health and Safety Policy: Display Screen Equipment
 All Hampstead Hill School Policies are always to be read and considered in conjunction with Equal Opportunities, Race Equality and Inclusion Policies. This Policy of Hampstead Hill School applies to all
All Hampstead Hill School Policies are always to be read and considered in conjunction with Equal Opportunities, Race Equality and Inclusion Policies. This Policy of Hampstead Hill School applies to all
Posture. In this article
 Posture Posture is the way we hold our bodies against gravity and maintaining a good posture involves training yourself to become aware of how you hold yourself in all activities as your posture is constantly
Posture Posture is the way we hold our bodies against gravity and maintaining a good posture involves training yourself to become aware of how you hold yourself in all activities as your posture is constantly
Chronic Low Back Pain
 Chronic Low Back Pain This leaflet has been produced by Senior Physiotherapists working at the Queen Victoria Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. It has been designed to give you accurate up-to-date knowledge
Chronic Low Back Pain This leaflet has been produced by Senior Physiotherapists working at the Queen Victoria Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. It has been designed to give you accurate up-to-date knowledge
Staff Information Leaflet
 Posture Staff Information Leaflet This leaflet is designed to give you an understanding of posture and some advice on what you can do to help yourself. If your symptoms persist you should seek advice from
Posture Staff Information Leaflet This leaflet is designed to give you an understanding of posture and some advice on what you can do to help yourself. If your symptoms persist you should seek advice from
"BACK SAFETY IN OFFICE ENVIRONMENTS"
 PRESENTER'S GUIDE "BACK SAFETY IN OFFICE ENVIRONMENTS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM
PRESENTER'S GUIDE "BACK SAFETY IN OFFICE ENVIRONMENTS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM
Starting position: Lying flat (or if your legs go into spasm - lying with knees bent up and feet flat on floor/bed)
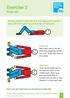 Exercise 2 Knee roll Starting position: Lying flat (or if your legs go into spasm - lying with knees bent up and feet flat on floor/bed) Roll knees over to the left, stretching diagonally across the trunk.
Exercise 2 Knee roll Starting position: Lying flat (or if your legs go into spasm - lying with knees bent up and feet flat on floor/bed) Roll knees over to the left, stretching diagonally across the trunk.
Posture. recreational activities.
 Posture Why maintain correct posture? When maintaining correct posture, the joints, ligaments and muscles of the neck and back are positioned optimally so they are under minimal stress. Maintaining this
Posture Why maintain correct posture? When maintaining correct posture, the joints, ligaments and muscles of the neck and back are positioned optimally so they are under minimal stress. Maintaining this
Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises. Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises
 Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction Weight-bearing and resistance exercises have
Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction Weight-bearing and resistance exercises have
Low Back and Leg Pain
 Low Back and Leg Pain d4105 Who gets low back pain? Almost everyone will experience low back pain at some point in their lives. Research suggests that 4 out of 5 adults are likely to develop low back pain
Low Back and Leg Pain d4105 Who gets low back pain? Almost everyone will experience low back pain at some point in their lives. Research suggests that 4 out of 5 adults are likely to develop low back pain
DRAFT. The best way to deal with back pain
 Services provided by Essex Parntership University NHS Foundation Trust and West Essex NHS Clinical Commissioning Group niversity The best way to deal with back pain The best way to deal with back pain
Services provided by Essex Parntership University NHS Foundation Trust and West Essex NHS Clinical Commissioning Group niversity The best way to deal with back pain The best way to deal with back pain
Strengthening Exercises for Back Pain
 Strengthening Exercises for Back Pain d4105 Who gets low back pain? Almost everyone will experience low back pain at some point in their lives. Research suggests that 4 out of 5 adults are likely to develop
Strengthening Exercises for Back Pain d4105 Who gets low back pain? Almost everyone will experience low back pain at some point in their lives. Research suggests that 4 out of 5 adults are likely to develop
Body Mechanics--Posture, Alignment & Core
 Body Mechanics--Posture, Alignment & Core Proper Alignment Proper body alignment allows you to safely perform different tasks throughout the day, and to do so in a way that does not require you to exert
Body Mechanics--Posture, Alignment & Core Proper Alignment Proper body alignment allows you to safely perform different tasks throughout the day, and to do so in a way that does not require you to exert
Back Care. When caring for a person with spinal cord injury. SPINAL OUTREACH TEAM SPINAL OUTREACH TEAM. PO Box 6053 Buranda QLD 4102
 SPINAL OUTREACH TEAM Back Care When caring for a person with spinal cord injury. SPINAL OUTREACH TEAM PO Box 6053 Buranda QLD 4102 Phone: (07) 3406 2300 Fax:(07) 3406 2399 Freecall: 1 800 624 832 (for
SPINAL OUTREACH TEAM Back Care When caring for a person with spinal cord injury. SPINAL OUTREACH TEAM PO Box 6053 Buranda QLD 4102 Phone: (07) 3406 2300 Fax:(07) 3406 2399 Freecall: 1 800 624 832 (for
Powerlift Lifting Techniques For A Healthy Back. Leader s Guide and Quiz
 ! Powerlift Lifting Techniques For A Healthy Back Leader s Guide and Quiz 4894 POWERLIFT: Lifting Techniques For A Healthy Back PROGRAM SYNOPSIS: Most workers have been instructed to lift objects safely
! Powerlift Lifting Techniques For A Healthy Back Leader s Guide and Quiz 4894 POWERLIFT: Lifting Techniques For A Healthy Back PROGRAM SYNOPSIS: Most workers have been instructed to lift objects safely
Quiz ACUTE STROKE UNIT ORIENTATION MODULE 7: MOBILITY, POSITIONING, AND TRANSFERS
 ACUTE STROKE UNIT ORIENTATION 2014 MODULE 7: MOBILITY, POSITIONING, AND TRANSFERS Name: Date: 1. Fill in the blanks (2 points) The goal of assisting the stroke survivor is to functional recovery and independence
ACUTE STROKE UNIT ORIENTATION 2014 MODULE 7: MOBILITY, POSITIONING, AND TRANSFERS Name: Date: 1. Fill in the blanks (2 points) The goal of assisting the stroke survivor is to functional recovery and independence
The best way to deal with back pain
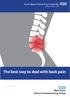 The best way to deal with back pain The best way to deal with back pain Back pain is common and can be very painful but, serious or permanent damage is rare. The Facts Most back pain is not due to any
The best way to deal with back pain The best way to deal with back pain Back pain is common and can be very painful but, serious or permanent damage is rare. The Facts Most back pain is not due to any
Ergonomics. Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques (EOHSS)
 Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
Falls Prevention Strength & Balance Programme Exercise Booklet
 Falls Prevention Strength & Balance Programme Exercise Booklet Working together to prevent falls This booklet describes the exercises which form the strength and balance component of the Trust falls prevention
Falls Prevention Strength & Balance Programme Exercise Booklet Working together to prevent falls This booklet describes the exercises which form the strength and balance component of the Trust falls prevention
HOW TO CHOOSE THE RIGHT CHAIR
 HOW TO CHOOSE THE RIGHT CHAIR ADJ SEAT HEIGHT & BACK: A GOOD SIZED SEAT: GOOD SEAT PADDING: Easy to adjust seat height. Provide a good range of approximately 40-53cm from the floor to the height of the
HOW TO CHOOSE THE RIGHT CHAIR ADJ SEAT HEIGHT & BACK: A GOOD SIZED SEAT: GOOD SEAT PADDING: Easy to adjust seat height. Provide a good range of approximately 40-53cm from the floor to the height of the
Lumbar Spine - Discectomy/ Decompression (page 1 of 5)
 i If you need your information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact Customer Care on 0800 374 208 or send an email to: customercare@ salisbury.nhs.uk You are entitled
i If you need your information in another language or medium (audio, large print, etc) please contact Customer Care on 0800 374 208 or send an email to: customercare@ salisbury.nhs.uk You are entitled
CHAPTER 8 BACK CARE 8 BACK CARE. Posture
 CHAPTER 8 BACK CARE 8 BACK CARE Nearly 25% of the lost-time injuries in construction are related to the back. More than half of these injuries result from lifting excessive weight or lifting incorrectly.
CHAPTER 8 BACK CARE 8 BACK CARE Nearly 25% of the lost-time injuries in construction are related to the back. More than half of these injuries result from lifting excessive weight or lifting incorrectly.
Low Res SAMPLE SPINAL CURVES THE SPINE
 THE SPINE The normal healthy spine has a naturally curved shape. Like a coiled spring, these curves help to absorb some of the forces that are placed on your spine while standing erect. When looking at
THE SPINE The normal healthy spine has a naturally curved shape. Like a coiled spring, these curves help to absorb some of the forces that are placed on your spine while standing erect. When looking at
Ergonomics. For additional assistance, contact the Occupational Safety office to schedule an evaluation.
 Ergonomics 1. Purpose: Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Safety and Risk and Risk Management (SRM) developed this program to improve the health and happiness of it s employees by assisting
Ergonomics 1. Purpose: Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Safety and Risk and Risk Management (SRM) developed this program to improve the health and happiness of it s employees by assisting
Advanced Life Support (ALS) Paramedic. Physical Capacity Testing Protocols Pre-Employment Candidate Pack
 Advanced Life Support (ALS) Paramedic Physical Capacity Testing Protocols Pre-Employment Candidate Pack Developed by: Mark Jansz (Health & Fitness Advisor) AV Physical Capacity Testing Protocols Version
Advanced Life Support (ALS) Paramedic Physical Capacity Testing Protocols Pre-Employment Candidate Pack Developed by: Mark Jansz (Health & Fitness Advisor) AV Physical Capacity Testing Protocols Version
Osteoporosis Exercise:
 Osteoporosis Exercise: Balance, Posture and Functional Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction You can help improve and maintain your balance, posture
Osteoporosis Exercise: Balance, Posture and Functional Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction You can help improve and maintain your balance, posture
Looking After Your Shoulders
 A patient s guide to Looking After Your Shoulders Shoulder protection following a Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) This information, for patients with paraplegia, is a guide only and not prescriptive. Your therapist
A patient s guide to Looking After Your Shoulders Shoulder protection following a Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) This information, for patients with paraplegia, is a guide only and not prescriptive. Your therapist
Acute Lower Back Pain. Physiotherapy department
 Acute Lower Back Pain Physiotherapy department Back pain is a common condition and in the UK it affects 7 out of 10 people at some point in their lives. Back pain can be very uncomfortable but it is not
Acute Lower Back Pain Physiotherapy department Back pain is a common condition and in the UK it affects 7 out of 10 people at some point in their lives. Back pain can be very uncomfortable but it is not
Back Protection. Training Guide
 Back Protection Training Guide Use a Back Support Belt to Prevent Back Injuries Because of the incidious progression of back problems, it is always difficult to determine how a back problem began. If you
Back Protection Training Guide Use a Back Support Belt to Prevent Back Injuries Because of the incidious progression of back problems, it is always difficult to determine how a back problem began. If you
Agenda and Objectives
 Agenda and Objectives Session 2 Handout: Activity Session One 1. Welcome & outline review today s agenda 2. Benefits of and barriers to regular exercise 3. Review of exercise homework and planning ahead
Agenda and Objectives Session 2 Handout: Activity Session One 1. Welcome & outline review today s agenda 2. Benefits of and barriers to regular exercise 3. Review of exercise homework and planning ahead
8. Counter Work essential tips
 8. Counter Work essential tips Find an effective posture to perform your work Optimize your keying & screen viewing postures Minimize grasping & lifting motions Use efficient body motions to reach Operate
8. Counter Work essential tips Find an effective posture to perform your work Optimize your keying & screen viewing postures Minimize grasping & lifting motions Use efficient body motions to reach Operate
Advice and exercises for managing knee and hip osteoarthritis October 2018 V1.2 April 2018 April 2021
 Advice and exercises for managing knee and hip osteoarthritis 0496 October 2018 V1.2 April 2018 April 2021 This advice and exercise booklet has been produced by senior physiotherapists working for DynamicHealth.
Advice and exercises for managing knee and hip osteoarthritis 0496 October 2018 V1.2 April 2018 April 2021 This advice and exercise booklet has been produced by senior physiotherapists working for DynamicHealth.
Seated Exercises Information for Patients
 Seated Exercises Information for Patients 1 Seated Exercise These exercises are designed to allow you to exercise and keep your joints moving and strong whilst you maybe using a wheelchair. They can all
Seated Exercises Information for Patients 1 Seated Exercise These exercises are designed to allow you to exercise and keep your joints moving and strong whilst you maybe using a wheelchair. They can all
Miami J Collar. General Guidelines. How to Put On Your. Miami J Collar. Safe Exercises to Do While in The Collar.
 Miami J Collar General Guidelines How to Put On Your Miami J Collar Safe Exercises to Do While in The Collar www.neurosurgery.med.miami.edu General Guidelines Wear the Miami J Collar at all times. Do not
Miami J Collar General Guidelines How to Put On Your Miami J Collar Safe Exercises to Do While in The Collar www.neurosurgery.med.miami.edu General Guidelines Wear the Miami J Collar at all times. Do not
Pregnancy-related low back pain and pelvic girdle pain (PGP) Information for patients Therapy Services - MSK
 Pregnancy-related low back pain and pelvic girdle pain (PGP) Information for patients Therapy Services - MSK We have written this booklet to answer some of the common questions that women ask about Pregnancy-Related
Pregnancy-related low back pain and pelvic girdle pain (PGP) Information for patients Therapy Services - MSK We have written this booklet to answer some of the common questions that women ask about Pregnancy-Related
Back Safety in Industrial Environments. Leaders Guide and Quiz
 ! Back Safety in Industrial Environments Leaders Guide and Quiz 4925 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in this program is presented in a definite order so that employees
! Back Safety in Industrial Environments Leaders Guide and Quiz 4925 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in this program is presented in a definite order so that employees
Driving (for work or fun) Can Contribute to the Development of Repetitive Strain Injuries:
 Driving (for work or fun) Can Contribute to the Development of Repetitive Strain Injuries: Driving in a vehicle for long distances can contribute to lower and upper back and neck pain, poor circulation
Driving (for work or fun) Can Contribute to the Development of Repetitive Strain Injuries: Driving in a vehicle for long distances can contribute to lower and upper back and neck pain, poor circulation
"INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS"
 PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
BACK PAIN. Spare 5 minutes to find out how to cope with back pain
 BACK PAIN Spare 5 minutes to find out how to cope with back pain You always managed your responsibilities as a wife, mother, sister, daughter, daughter in law, friend, boss, and colleague indeed managed
BACK PAIN Spare 5 minutes to find out how to cope with back pain You always managed your responsibilities as a wife, mother, sister, daughter, daughter in law, friend, boss, and colleague indeed managed
LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2955 LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics Leader s Guide Marcom Group Ltd. 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2955 LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics Leader s Guide Marcom Group Ltd. 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in
Do the same as above, but turn your head TOWARDS the side that you re holding on to the chair.
 Stretch 4-6 times per day and hold each stretch for a minimum of 30 seconds. Perform the stretch gently without bouncing. Discuss any problems with your Chiropractor. Sit upright with your head and shoulder
Stretch 4-6 times per day and hold each stretch for a minimum of 30 seconds. Perform the stretch gently without bouncing. Discuss any problems with your Chiropractor. Sit upright with your head and shoulder
MANUAL HANDLING TRAINING
 MANUAL HANDLING TRAINING HOUSEKEEPING Location of Fire Exits Location of Fire Assembly Point Location of Welfare Facilities (toilets, canteen etc.) All mobile phones must be turned off for the duration
MANUAL HANDLING TRAINING HOUSEKEEPING Location of Fire Exits Location of Fire Assembly Point Location of Welfare Facilities (toilets, canteen etc.) All mobile phones must be turned off for the duration
White Sands Guide for a Healthy Back
 White Sands Guide for a Healthy Back 7157 Curtiss Ave. Sarasota, FL 34231 Phone: (941) 924-9525 www.aquaticsphysicaltherapy.com Home of the Spinal Solutions Program 1 What Causes Back Pain? Since the lower
White Sands Guide for a Healthy Back 7157 Curtiss Ave. Sarasota, FL 34231 Phone: (941) 924-9525 www.aquaticsphysicaltherapy.com Home of the Spinal Solutions Program 1 What Causes Back Pain? Since the lower
Physical and Occupational Therapy after Spine Surgery. Preparation for your surgery
 Physical and Occupational Therapy after Spine Surgery Preparation for your surgery Agenda Pre-Operative Exercises What to Expect Post-Operative Plan Spinal Precautions Post-Discharge Plan S A I N T LU
Physical and Occupational Therapy after Spine Surgery Preparation for your surgery Agenda Pre-Operative Exercises What to Expect Post-Operative Plan Spinal Precautions Post-Discharge Plan S A I N T LU
Module 1 Slabbing, Rendering, Floating and Skimming UNIT: 2 Manual Handling
 TRADE OF PLASTERING PHASE 2 Module 1 Slabbing, Rendering, Floating and Skimming UNIT: 2 Produced by In cooperation with subject matter expert: Terry Egan Some images & text courtesy of Gypsum Industries
TRADE OF PLASTERING PHASE 2 Module 1 Slabbing, Rendering, Floating and Skimming UNIT: 2 Produced by In cooperation with subject matter expert: Terry Egan Some images & text courtesy of Gypsum Industries
UNIT 2. THE IMPORTANCE OF CORRECT POSTURE
 UNIT 2. THE IMPORTANCE OF CORRECT POSTURE 1. WHY IS POSTURE IMPORTANT? The term posture is used to describe how your body is positioned when you're sitting, standing and lying down. Proper posture is important
UNIT 2. THE IMPORTANCE OF CORRECT POSTURE 1. WHY IS POSTURE IMPORTANT? The term posture is used to describe how your body is positioned when you're sitting, standing and lying down. Proper posture is important
Chapter 13. Body Mechanics. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 13 Body Mechanics Body Mechanics Body mechanics means using the body in an efficient and careful way. It involves good posture, balance, and using your strongest and largest muscles for work. 2
Chapter 13 Body Mechanics Body Mechanics Body mechanics means using the body in an efficient and careful way. It involves good posture, balance, and using your strongest and largest muscles for work. 2
Manual Materials Handling
 Introduction to the Ergonomics of Manual Materials Handling OR-OSHA 206 9512 SC 206 Ergonomics of Manual Materials Handling 7/96 1 OR-OSHA Services Oregon OSHA offers a wide variety of safety and health
Introduction to the Ergonomics of Manual Materials Handling OR-OSHA 206 9512 SC 206 Ergonomics of Manual Materials Handling 7/96 1 OR-OSHA Services Oregon OSHA offers a wide variety of safety and health
November 09 Monthly Safety Spotlight
 November 09 Monthly Safety Spotlight November 09 Safety Discussion Topics, vertical format Get to Know Your Back Lifting Safety Checklist Maintaining a Healthy Back Easy as 1-2-3 Simple Stretches for a
November 09 Monthly Safety Spotlight November 09 Safety Discussion Topics, vertical format Get to Know Your Back Lifting Safety Checklist Maintaining a Healthy Back Easy as 1-2-3 Simple Stretches for a
Back Health and Safety
 Back Health and Safety Your back is at work every minute of every day, whether you are awake or asleep, active or quiet. Over time the effects of poor posture, bad body mechanics, physical deconditioning
Back Health and Safety Your back is at work every minute of every day, whether you are awake or asleep, active or quiet. Over time the effects of poor posture, bad body mechanics, physical deconditioning
Non Specific Low Back Pain
 Non Specific Low Back Pain d4105 Who gets low back pain? Almost everyone will experience low back pain at some point in their lives. Research suggests that 4 out of 5 adults are likely to develop low back
Non Specific Low Back Pain d4105 Who gets low back pain? Almost everyone will experience low back pain at some point in their lives. Research suggests that 4 out of 5 adults are likely to develop low back
Exercises to Strengthen Your Back
 Exercises to Strengthen Your Back Your 15 Minute Workout By doing your 15 minute workout 3-5 times per week, you can condition the muscles and joints that support your back and keep it in healthy balance
Exercises to Strengthen Your Back Your 15 Minute Workout By doing your 15 minute workout 3-5 times per week, you can condition the muscles and joints that support your back and keep it in healthy balance
Stretching - At the Workstation Why is stretching important?
 Stretching - At the Workstation Why is stretching important? No matter how well a workstation is designed, problems may arise if attention is not paid to the way the work is done. Working at a computer
Stretching - At the Workstation Why is stretching important? No matter how well a workstation is designed, problems may arise if attention is not paid to the way the work is done. Working at a computer
Post Lung Transplant Exercises
 Post Lung Transplant Exercises Post Lung Transplant Physical activity improves our strength and stamina, maintains optimal functioning of our major organs and increases our vitality, energy and overall
Post Lung Transplant Exercises Post Lung Transplant Physical activity improves our strength and stamina, maintains optimal functioning of our major organs and increases our vitality, energy and overall
TRAINING PACKAGE DISPLAY SCREEN EQUIPMENT (DSE) Any alphanumeric or graphic display screen, regardless of the display process involved
 TRAINING PACKAGE DISPLAY SCREEN EQUIPMENT (DSE) Any alphanumeric or graphic display screen, regardless of the display process involved Why? To Avoid ACHES AND PAINS - NECK, ARMS, WRISTS, LEGS & BACK (there
TRAINING PACKAGE DISPLAY SCREEN EQUIPMENT (DSE) Any alphanumeric or graphic display screen, regardless of the display process involved Why? To Avoid ACHES AND PAINS - NECK, ARMS, WRISTS, LEGS & BACK (there
Your Home Exercise Plan
 A Home Exercise Plan is designed for people who are unable to attend Pulmonary Rehabilitation classes in a community setting. This may be for a number of reasons such as travelling difficulties, personal
A Home Exercise Plan is designed for people who are unable to attend Pulmonary Rehabilitation classes in a community setting. This may be for a number of reasons such as travelling difficulties, personal
AMG Transfer Training and Ergonomics
 AMG Transfer Training and Ergonomics Musculoskeletal Disorders Healthcare workers often experience musculoskeletal disorders at a rate exceeding that of workers in construction, mining, and manufacturing.
AMG Transfer Training and Ergonomics Musculoskeletal Disorders Healthcare workers often experience musculoskeletal disorders at a rate exceeding that of workers in construction, mining, and manufacturing.
THE SECRETS TO GOOD POSTURE
 THE SECRETS TO GOOD POSTURE Postural Tips To Improve Movement Efficiency and Functional Independence BY DR. AARON LEBAUER, PT, DPT 2 P a g e Disclaimer The information in this book is not a replacement
THE SECRETS TO GOOD POSTURE Postural Tips To Improve Movement Efficiency and Functional Independence BY DR. AARON LEBAUER, PT, DPT 2 P a g e Disclaimer The information in this book is not a replacement
Strains and Sprains. Signs and Symptoms of MSI
 Strains and Sprains Strains and sprains (known as musculoskeletal injuries) are the most common type of workrelated injury. Musculoskeletal injury (MSI) is a term used to describe an injury of the muscles,
Strains and Sprains Strains and sprains (known as musculoskeletal injuries) are the most common type of workrelated injury. Musculoskeletal injury (MSI) is a term used to describe an injury of the muscles,
Exercise Program WARNING: DO NOT USE THIS OR ANY OTHER EXERCISE PROGRAM WITHOUT FIRST BEING CLEARED BY YOUR DOCTOR.
 Exercise Program WARNING: DO NOT USE THIS OR ANY OTHER EXERCISE PROGRAM WITHOUT FIRST BEING CLEARED BY YOUR DOCTOR. Things you MUST know before you begin Posture It is absolutely critical to maintain proper
Exercise Program WARNING: DO NOT USE THIS OR ANY OTHER EXERCISE PROGRAM WITHOUT FIRST BEING CLEARED BY YOUR DOCTOR. Things you MUST know before you begin Posture It is absolutely critical to maintain proper
Do s and Don ts with Low Back Pain
 Do s and Don ts with Low Back Pain Sitting Sit as little as possible and then only for short periods. Place a supportive towel roll at the belt line of the back especially when sitting in a car. When getting
Do s and Don ts with Low Back Pain Sitting Sit as little as possible and then only for short periods. Place a supportive towel roll at the belt line of the back especially when sitting in a car. When getting
Trinitas Regional Medical Center. Employee Safety Program
 Trinitas Regional Medical Center Employee Safety Program Revised: BW/September 2010 Needle Stick Prevention ALWAYS activate safety features per product instructions NEVER recap needles Avoid overstuffing
Trinitas Regional Medical Center Employee Safety Program Revised: BW/September 2010 Needle Stick Prevention ALWAYS activate safety features per product instructions NEVER recap needles Avoid overstuffing
MoveSafe For Industrial Athletes
 MoveSafe For Industrial Athletes Upper Island Safety Conference May 25, 2015 With every movement and posture You can make yourself stronger or get closer to an injury. It matters how we move every day.
MoveSafe For Industrial Athletes Upper Island Safety Conference May 25, 2015 With every movement and posture You can make yourself stronger or get closer to an injury. It matters how we move every day.
Central Office Ergonomics. Marie Robinson SBC Communications
 Central Office Ergonomics Marie Robinson SBC Communications Wire Stripping Use neutral wrist posture while stripping wire Use minimal force on your hands while wire stripping Keep right hand neutral while
Central Office Ergonomics Marie Robinson SBC Communications Wire Stripping Use neutral wrist posture while stripping wire Use minimal force on your hands while wire stripping Keep right hand neutral while
Choosing the right Office Chair
 Choosing the right Office Chair Choosing the Right Ergonomic Office Chair Working in an office typically involves spending a great deal of time sitting in an office chair a position that adds stress to
Choosing the right Office Chair Choosing the Right Ergonomic Office Chair Working in an office typically involves spending a great deal of time sitting in an office chair a position that adds stress to
Range of motion and positioning
 Range of motion and positioning Learning guide Why is motion important? Most people take free, comfortable movement for granted. Motion is meant to be smooth and painless. The ligaments, tendons, muscles,
Range of motion and positioning Learning guide Why is motion important? Most people take free, comfortable movement for granted. Motion is meant to be smooth and painless. The ligaments, tendons, muscles,
OH&S. Musculoskeletal Injury Prevention (MSIP)
 OH&S Musculoskeletal Injury Prevention (MSIP) Trainer s Guide to MSIP Supplies Needed: Slider sheet Pill crusher 2 volunteers Time required for session: 30 minutes Lifts Belts Flip chart paper Hand outs
OH&S Musculoskeletal Injury Prevention (MSIP) Trainer s Guide to MSIP Supplies Needed: Slider sheet Pill crusher 2 volunteers Time required for session: 30 minutes Lifts Belts Flip chart paper Hand outs
"LABORATORY ERGONOMICS"
 MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "LABORATORY ERGONOMICS" Part of the "LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES" Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow Outline of Major Points Covered in the "Laboratory Ergonomics"
MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "LABORATORY ERGONOMICS" Part of the "LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES" Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow Outline of Major Points Covered in the "Laboratory Ergonomics"
Back Injury Prevention and Safety
 Back Injury Prevention and Safety Jana L Kray MSPT, CEES Iowa Health Des Moines In a 3month period about oneforth of the US adults experience back pain. It is one of our society s most common medical problems
Back Injury Prevention and Safety Jana L Kray MSPT, CEES Iowa Health Des Moines In a 3month period about oneforth of the US adults experience back pain. It is one of our society s most common medical problems
To safely and effectively teach and supervise a Service User undertaking prescribed functional exercise
 BED MOBILITY Aim To safely and effectively teach and supervise a Service User undertaking prescribed functional exercise To enable Service User to practice moving in bed and sitting up in bed Turning in
BED MOBILITY Aim To safely and effectively teach and supervise a Service User undertaking prescribed functional exercise To enable Service User to practice moving in bed and sitting up in bed Turning in
What is the Musculoskeletal (MSK) System?
 Today s Agenda - What is the musculoskeletal (MSK) system? - MSK health - Posture perfect - Stretches to improve your posture, flexibility and strength What is the Musculoskeletal (MSK) System? The MSK
Today s Agenda - What is the musculoskeletal (MSK) system? - MSK health - Posture perfect - Stretches to improve your posture, flexibility and strength What is the Musculoskeletal (MSK) System? The MSK
Exercises for Older Adults
 Main Menu Future Residents Exercises for Older Adults Staying fit and healthy is essential at any age. But as we get older, it s especially important to continue exercising. Not only does regular exercise
Main Menu Future Residents Exercises for Older Adults Staying fit and healthy is essential at any age. But as we get older, it s especially important to continue exercising. Not only does regular exercise
CIRCULATORY MASSAGER OPERA TING INSTRUCTION HM01-08QI
 BLOOD CIRCULATORY MASSAGER OPERA TING INSTRUCTION HM01-08QI 1 Blood Circulatory Massager Thanks for you purchase our machine of Blood Circulatory Massager. Please read this manual carefully before using
BLOOD CIRCULATORY MASSAGER OPERA TING INSTRUCTION HM01-08QI 1 Blood Circulatory Massager Thanks for you purchase our machine of Blood Circulatory Massager. Please read this manual carefully before using
SAFE LIFTING TIPS. "Think Before You Lift"
 SAFE LIFTING TIPS Many jobs require frequent lifting, carrying, pushing, pulling, lowering and raising materials by hand. These jobs tasks are often referred to as manual material handling. The human body
SAFE LIFTING TIPS Many jobs require frequent lifting, carrying, pushing, pulling, lowering and raising materials by hand. These jobs tasks are often referred to as manual material handling. The human body
VON SMART. (Seniors Maintaining Active Role Together) In-Home Program. Exercise Instructions
 VON SMART (Seniors Maintaining Active Role Together) In-Home Program Exercise Instructions This VON SMART Exercise Instruction Packet is designed to guide you through the 15 VON SMART In- Home Exercises.
VON SMART (Seniors Maintaining Active Role Together) In-Home Program Exercise Instructions This VON SMART Exercise Instruction Packet is designed to guide you through the 15 VON SMART In- Home Exercises.
cysticfibrosis.org.uk Fighting for a Life Unlimited Patient name number Physiotherapy recommendations This leaflet was issued on:
 cysticfibrosis.org.uk How to improve your posture: A guide for adults with cystic fibrosis This guide explains the common postural problems that people with cystic fibrosis (CF) can have and shows you
cysticfibrosis.org.uk How to improve your posture: A guide for adults with cystic fibrosis This guide explains the common postural problems that people with cystic fibrosis (CF) can have and shows you
