Contrast-Bath Therapy and Sensation Over the Anterior Talofibular Ligament
|
|
|
- Geoffrey Johnston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Contrast-Bath Therapy and Sensation Over the Anterior Talofibular Ligament Billy E. Cotts, Kenneth L. Knight, J. William Myrer, and Shane S. Schulthies Context: It has been suggested that contrast-bath therapy alters sensation and enables patients to return to exercise more quickly. Objective: To determine whether contrast-bath therapy alters sensation of pressure in the ankle. Design: A factorial design with repeated measures on 2 factors. Independent variables included gender, time (preapplication and 1, 6, and 11 min postapplication), and treatment (control, cold bath, hot bath, and contrast bath). Setting: Laboratory. Participants: 12 men and 12 women, college track athletes actively engaged in preseason workouts 5 6 days/wk. Interventions: Sensation of pressure was tested preapplication and 1, 6, and 11 min postapplication. Each treatment lasted 20 min. Main Outcome Measure: Sensation of pressure at baseline and 1, 6, and 11 min postapplication over the anterior talofibular ligament of the right ankle. Results: There was no difference between genders. Sensation of pressure was greater for the heat condition than the other 3 conditions at 1 and 6 min postapplication. During the heating condition, sensation of pressure was greater at 1 and 6 min postapplication than during preapplication. During the contrast condition, sensation of pressure was less at 6 min postapplication than during preapplication. Conclusion: Contrast- and coldbath therapy (at 13 C) do not affect numbness. Key Words: sensation of pressure, hot bath, cold bath, numbness, therapeutic modalities Cotts BE, Knight KL, Myrer JW, Schulthies SS. Contrast-bath therapy and sensation over the anterior talofibular ligament. J Sport Rehabil. 2004;13: Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Contrast-bath therapy is the immersion of an injured limb in hot- and coldwater baths in cycles of 1 10 minutes. 1-5 Typically, contrast baths are applied to postacute injuries to reduce edema. The traditional hypothesis for contrast-bath therapy is that the alternating of hot and cold applications causes temperature fluctuations in the target tissue, which causes alternating vasodilation and vasoconstriction, thus creating a pumping action within the vessels. 1,3-5 This hypothesis has been challenged, however. 1,3-6 Cotts is with the Athletic Dept, Weber State University, Ogden, UT Knight, Myrer, and Schulthies are with the Therapeutic Modality Research Laboratory, Brigham Young University, Provo, UT
2 Contrast-Bath Therapy 115 Contrast therapy cannot reduce swelling via vascular events 1 because cellular debris is removed via the lymphatic system, 3,5,6 and even if it were removed by the vascular system, intramuscular temperature (1 cm below skinfold) changes during contrast therapy are minimal 4,7 and so would not induce significant vascular changes. Another hypothesis for the use of contrast-bath therapy is that it might decrease sensation (including pain) and therefore facilitate active exercise. 3 Thus, rehabilitation can begin sooner. Decreased pain has been seen with both heat and cold applications, 3,5,6,8-10 but no one has studied the effects of contrast bath on sensation nor suggested a mechanism for how contrast baths might reduce sensation. One way to measure decreased sensation is by measuring sensation of pressure Sensation of pressure is commonly used to measure sensory changes during hand rehabilitation, 11,15,16 when treating diabetic feet, and, recently, during ice massage. 20 Although no one has demonstrated a direct correlation between pain and sensation of pressure, there is evidence that these sensations are related. 21 Ankle sprains are a common injury 6,22-24 and one of the most common injuries treated with contrast baths. 3,9,25 Thus, we have chosen to investigate sensation-of-pressure changes in the ankle after contrast-bath therapy. Methods This study followed a factorial design with repeated measures on 2 factors. Independent variables included gender (male and female), time (preapplication and 1, 6, and 11 minutes postapplication), and treatment (control, cold bath, heat bath, and contrast bath). Sensation of pressure and actual time of measurement were dependent variables. Each subject participated in all 4 treatment conditions. The 6- and 11-minute postapplication measurements began 4.5 minutes after the previous measurement concluded and lasted approximately 30 seconds. Thus, the final measurements were at approximately 6 and 11 minutes. Subjects for this study included 24 Division I college track athletes, 12 men and 12 women (age 22.9 ± 2.5 years, height ± 8.4 cm, weight 67.8 ± 13.3 kg, activity 5.7 ± 0.6 days). All subjects gave informed consent and completed a health questionnaire, as approved by the university institutional review board, before participating in this study. Four treatment orders were established using a balanced Latin square. Subjects were randomly assigned to 1 of the 4 treatment orders. All hydrotherapy treatments were performed in 2 metal lowboy 3- by 3- ft whirlpools (Whitehall Manufacturing, City of Industry, Calif, Model #S- 90-M) in the athletic training room of Brigham Young University. A temperature of 41 C 1,2,4-6,9,10,25 was maintained by adding hot water, as needed,
3 116 Cotts et al for the hot bath. A temperature of 13 C 1,2,6,+,9,10,14,25 was maintained by adding ice, as needed, for the cold bath. Semmes Weinstein nylon monofilaments (Connecticut Bioinstruments, Danbury, Conn) were used to measure sensation of pressure. Handheld stopwatches (Ambassador Accusplit, Magnum XL 620X, San Jose, Calif) were used to monitor treatment and testing times. All conditions (control, contrast, hot bath, and cold bath) lasted 20 minutes, during which time subjects sat on a whirlpool bench with the right leg immersed to midcalf. During the control treatment condition, the right foot rested on a bucket for support. Contrast-bath conditions consisted of a hot bath for 3 minutes followed by a 1-minute cold bath, repeating the cycle 5 times. Hot-bath conditions had subjects in hot whirlpool only. Coldbath conditions had subjects in cold whirlpool only. Whirlpool jets were not turned on for any treatment conditions. Subjects were asked to wear shorts and remove both their socks and shoes. They were in a supine position on treatment tables with their feet hanging off the tables. They were required to close their eyes, disallowing visual input. One of us (BC) palpated and marked the skin over the anterior talofibular ligament for a reference point. A brief explanation of how testing would be conducted was given by the tester. Palpation and explanation were done before baseline measurements only. Sensation of pressure was measured with Semmes Weinstein nylon monofilaments following the technique outlined by Bell-Krotoski. 11 The monofilament was held about 1 in above the mark on the right anterior talofibular ligament. Within approximately 1.5 seconds, the monofilament was brought into contact with the skin within 1 cm of the center reference point. Contact was sustained for approximately 1.5 seconds. Subjects were told to respond by saying yes if they detected a sensation. Failure to respond when a monofilament was touching the skin was interpreted as a failure to detect the pressure of that monofilament. Two or 3 attempts with each filament were made; if the first 2 attempts elicited the same response, the third attempt was unnecessary. If 2 touches resulted in positive responses from the subjects, the next-lower filament was used. This technique was continued until the subject could no longer detect a sensory stimulus, at which time the last filament felt was accepted as the measurement. If two touches resulted in negative responses, the nexthigher filament was used. This continued until the subject could detect a sensory stimulus, at which time the filament became the baseline, or reference, monofilament. Each attempt was made within 1 cm of the reference mark. No touches were made in the same spot with the same filament. The same examiner performed all tests on the subjects. Posttreatment tests began at approximately 10 seconds, 5.5 minutes, and 10.5 minutes from the time a subject s legs exited the water and were completed by 1, 6, and 11 minutes. Actual time of measurement was monitored using a stopwatch. Testing began with the last monofilament detected by
4 Contrast-Bath Therapy 117 the subject during their previous testing session. Adjustments made in monofilament size were based on given responses. Statistical Analysis Means and standard deviations were calculated for both dependent variables by gender, time, and treatment. A 3-way ANOVA with repeated measures (on time and treatment) was used to determine overall differences among gender, time, and treatments. There was a significant 3-way interaction (F 9,48 = 269.7, P =.0001), necessitating simple main-effects testing, which was accomplished with 1-way ANOVAs. Significant ANOVAs were followed by Tukey Kramer multiple-range tests (TK). All tests were evaluated with an alpha of.05 Results There was no difference between genders treatment-time combination (F 1,22 < 4.65, P >.042), so men s and women s data were combined for subsequent analysis. Sensation of pressure was greater for the heat condition than for the cold, contrast, or control conditions at 1 minute (F 3,69 = 9.59, P =.01, TK <.05) and 6 minutes postapplication (Table 1; F 3,69 = 7.68, P =.01, TK <.05). During the heating condition, sensation of pressure was greater at 1 minute and 6 minutes postapplication than during preapplication (F 3,69 = 8.48, P =.0001, TK <.05). During the contrast condition, sensation of pressure was less at 6 minutes postapplication than during preapplication (F 3,69 = 2.93, P =.04, TK <.05). The time to obtain sensation-of-pressure measurements was the same between conditions (Table 2; F 3,3 = 1.44, P =.39). There were some minor Table 1 Sensation of Pressure for All Subjects (g, mean ± SD, N = 24) Pre- 1 min post- 6 min post- 11 min post- Treatment application application* application* application Control 1.28 ± ± ± ± 1.19 Cold 1.45 ± ± ± ± 0.74 Heat 1.38 ± ± ± ± 1.35 Contrast 1.25 ± ± ± ± 1.11 *Heat > control, contrast, cold; P <.05 1 minute postapplication > preapplication and 11 minutes postapplication; 6 minutes postapplication > preapplication; P <.05. Preapplication > 6 minutes postapplication; P <.05.
5 118 Cotts et al Table 2 Time Required to Obtain Sensation-of-Pressure Measurements (seconds, mean ± SD) 1 min 6 min 11 min postapplication postapplication postapplication Men control ± ± ± 2.3 cold* ± ± ± 3.3 heat ± ± ± 2.3 contrast ± ± ± 2.4 Women control ± ± ± 2.7 cold* ± ± ± 2.0 heat ± ± ± 2.8 contrast ± ± ± 2.4 *Women > men; P < minute postapplication > 11 minutes postapplication; P < minute postapplication > 6 minutes postapplication, 11 minutes postapplication; P <.05. differences in time to measure sensation of pressure between genders and between testing times (see Table 2), but they were less than 5 seconds and therefore are probably not clinically significant. Discussion The theory that contrast-bath therapy affects sensation of pressure is not supported by this study. A similar study with colder water (we used 13 C), however, might yield different results. In other research, 7 minutes of ice massage, 8,20 20-minute immersion in 1 C water, 8 20-minute application of ice packs, 8 and 5 minutes of forced chilled air 8 caused a reduction in sensation (increase in sensation of pressure). Because all these studies and ours involved the same body part, it seems that the major difference between them is the temperature. Current pilot work from our laboratory indicates that 15-minute cold applications of 1 C water increase numbness, whereas applications of 10 C do not. Numbness after contrast therapy with a colder water temperature should be investigated. It is possible that contrast baths have no effect on sensation. If so, we question whether there are any therapeutic benefits to them. Contrast-bath therapy does not alter intramuscular temperature significantly, 2,4,7 even though 20- to 31-minute applications of heat or cold do alter intramuscular temperature. 2,4,7,26,27 It is logical to think that the brief cold applications (1 5 minutes) and interspersed heat applications counter each other and prevent net intramuscular temperature changes.
6 Contrast-Bath Therapy 119 Rogers et al 20 reported that cold applications affected sensation of pressure. They applied ice massage for 7 minutes, which reduced surface temperature to 13 C. We did not monitor skin temperature but doubt that it got this cold, because our water-bath temperature was only 13 C. The effect of the massage part of ice massage also appears to be a factor in decreasing sensation. 20 Lehmann, Warren, and Scham 28 suggested that tissue temperatures must reach 40 C to produce significant physiologic responses. We wonder about that. We used hot baths of 41 C, which probably were not hot enough to increase tissue temperature to 40 C, yet sensation of pressure was affected. Future investigations should involve monitoring tissue and surface temperature so as to evaluate Lehman et al s 28 suggested temperature. Is there a place for contrast-bath therapy in rehabilitation? Perhaps not. The traditional theory that contrast-bath therapy causes a pumping action to reduce swelling 1,3-5 has been challenged. 1,3-6 The alternative explanation that it might decrease sensation (including pain) and therefore facilitate active exercise 3 is now in question, at least when used with 13 C cold-water baths. If future research indicates that contrast baths at lower temperatures are effective in altering sensation, their use will be justified. We recommend, however, that proven treatments such as cryokinetics 3,8 be used to treat acute joint injuries. Conclusion The use of 13 C water-bath immersions for contrast- and cold-bath therapy does not affect sensation of pressure. Contrast-bath therapy with 1 C water might alter sensation, but this has yet to be studied. Of the modalities we used, only hot baths (41 C) resulted in numbness, which lasted through the 6-minute measurement. Sensation of pressure was not different between genders, even though women s sensation of pressure was consistently slightly lower than that of the men. Time to obtain sensation-of-pressure measurements after cold baths was slightly greater (<5 seconds) for women, but we do not think that this affected the results of the sensation of pressure. References 1. Cote DJ, Prentice WE, Hooker DN, Shields EW. Comparison of 3 treatment procedures for minimizing ankle sprain swelling. Phys Ther. 1988;68: Higgins D, Kaminski TW. Contrast therapy does not cause fluctuations in human gastrocnemius intramuscular temperature. J Athletic Train. 1998;33: Knight KL. Cryotherapy in Sport Injury Management. Champaign, Ill: Human Kinetics; 1995.
7 120 Cotts et al 4. Myrer JW, Draper DO, Durrant E. Contrast therapy and intramuscular temperature in the human leg. J Athletic Train. 1994;29: Prentice WE. Therapeutic Modalities in Sports Medicine. 3rd ed. St Louis, Mo: Mosby-Year Book Inc; Arnheim DD, Prentice WE. Principles of Athletic Training. 9th ed. St Louis, Mo: Mosby-Year Book Inc; Myrer JW, Measom G, Durrant E, Fellingham GW. Cold- and hot-pack contrast therapy: subcutaneous and intramuscular temperature change. J Athletic Train. 1997;32: Knight KL, Han KM, Rubley MA, Brucker JB. Comparison of tissue cooling and numbness during application of cryo5 air cooling, crushed ice packs, ice massage, and ice water immersion. J Athletic Train. 2002;36:S Michlovitz, SL. Thermal Agents in Rehabilitation. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, Pa: FA Davis Co; Starkey C. Therapeutic Modalities for Athletic Trainers. Philadelphia, Pa: FA Davis Co; Bell-Krotoski J, Weinstein S, Weinstein C. Testing sensibility, including touchpressure, two-point discrimination, point localization, and vibration. J Hand Ther. 1993;6: Dellon AL, Mackinnon SE, Brandt KE. The markings of the Semmes Weinstein nylon monofilaments. J Hand Ther. 1993;18(A): Ingersoll CD, Knight KL, Merrick MA. Sensory perception of the foot and ankle following therapeutic applications of heat and cold. J Athletic Train. 1992;27: McGill M, Molyneaux L, Yue DK. Use of the Semmes Weinstein 5.07/10 gram monofilament: the long and the short of it. Diabet Med. 1998;15: Fess E. The need for reliability and validity in hand assessment instruments. J Hand Ther. 1986;11: Greenspan JD, La Motte RH. Cutaneous mechanoreceptors of the hand: experimental studies and their implications for clinical testing of tactile sensation. J Hand Ther. 1993;6: de Sonnaville JJ, Colly LP, Wijkel D, Heine RJ. The prevalence and determinants of foot ulceration in type II diabetic patients in a primary health care setting. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1997;35: Mueller MJ. Identifying patients with diabetes mellitus who are at risk for lowerextremity complications: use of Semmes Weinstein monofilaments. Phys Ther. 1996;76: Simoneau GG, Derr JA, Ulbrecht JS, Becker MB, Cavanagh PR. Diabetic sensory neuropathy effect on ankle joint movement perception. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1996;77: Rogers JW, Knight KL, Draper DO, Schulthies SS. Increasing ice massage application pressure results in increased calf skin numbness [abstract]. J Athletic Train. 2001;36:S Gardner EP, Kandel ER. Touch. In: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, eds. Principles of Neural Science. 4th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2000:
8 Contrast-Bath Therapy Hutson MA. Sports Injuries. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; Safran MR, Benedetti RS, Bartolozzi AR, Mandelbaum BF. Lateral ankle sprains: a comprehensive review. Part 1: etiology, pathoanatomy, histopathogenesis, and diagnosis. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1999;31:S Rundle E. Foot and ankle. In: Zuluaga M, Briggs C, Carlisle J, et al, eds. Sports Physiotherapy Applied Science and Practice. New York, NY: Churchill Livingstone; 1995: Quillen WS, Underwood FB. Laboratory Manual to Accompany Therapeutic Modalities in Sports Medicine. 3rd ed. St Louis, Mo: Mosby-Year Book Inc; Johnson DJ, Moore S, Moore J, Oliver RA. Effect of cold submersion on intramuscular temperature of the gastrocnemius muscle. Phys Ther. 1979;59: Wolf SL, Basmajian JV. Intramuscular temperature changes deep to localize cutaneous cold stimulation. Phys Ther. 1973;53: Lehmann JF, Warren CG, Scham SM. Therapeutic heat and cold. Clin Orthop. 1974;99:
Temperature Changes in the Human Leg During and After Two Methods of
 Journal ofathletic Training 1998;33: 25-29 C by the National Athletic Trainers' Association, Inc Temperature Changes in the Human Leg During and After Two Methods of Cryotherapy J. William Myrer, PhD*;
Journal ofathletic Training 1998;33: 25-29 C by the National Athletic Trainers' Association, Inc Temperature Changes in the Human Leg During and After Two Methods of Cryotherapy J. William Myrer, PhD*;
Examining Rewarming Trends Following Cryokinetics Using Different Cooling Modalities on Ankle Skin Surface Temperature
 University of Montana ScholarWorks at University of Montana Undergraduate Theses and Professional Papers 2015 Examining Rewarming Trends Following Cryokinetics Using Different Cooling Modalities on Ankle
University of Montana ScholarWorks at University of Montana Undergraduate Theses and Professional Papers 2015 Examining Rewarming Trends Following Cryokinetics Using Different Cooling Modalities on Ankle
Ice Bag Application Induced Numbness in Uninjured Ankles with Less Discomfort than Cold Water Immersion
 Ice Bag Application Induced Numbness in Uninjured Ankles with Less Discomfort than Cold Water Immersion An Honors Thesis (HONRS 499) by Krista Lewis Kevin Miller Thesis Advisor Lisa Jutte PhD, ATe, LAT
Ice Bag Application Induced Numbness in Uninjured Ankles with Less Discomfort than Cold Water Immersion An Honors Thesis (HONRS 499) by Krista Lewis Kevin Miller Thesis Advisor Lisa Jutte PhD, ATe, LAT
Journal of Rehabilitation Sciences and Research
 JRSR 3 (2016) 62-66 Journal of Rehabilitation Sciences and Research Journal Home Page: jrsr.sums.ac.ir Original Article The Comparison of the Effects of Contrast Bath on Circulation of Contralateral Lower
JRSR 3 (2016) 62-66 Journal of Rehabilitation Sciences and Research Journal Home Page: jrsr.sums.ac.ir Original Article The Comparison of the Effects of Contrast Bath on Circulation of Contralateral Lower
The Effects of Three Different Ice Bath Immersion Times on Numbness (Sensation of Pressure), Surface Temperature, and Perceived Pain
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2004-08-12 The Effects of Three Different Ice Bath Immersion Times on Numbness (Sensation of Pressure), Surface Temperature, and
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2004-08-12 The Effects of Three Different Ice Bath Immersion Times on Numbness (Sensation of Pressure), Surface Temperature, and
Introduction to Cryotherapy The What and Why of Cryotherapy Why the Confusion? What Is Cryotherapy? Cryotherapeutic Techniques What Happens When Cold
 Introduction to Cryotherapy The What and Why of Cryotherapy Why the Confusion? What Is Cryotherapy? Cryotherapeutic Techniques What Happens When Cold Is Applied? Heat vs. Cold: When and Why Historical
Introduction to Cryotherapy The What and Why of Cryotherapy Why the Confusion? What Is Cryotherapy? Cryotherapeutic Techniques What Happens When Cold Is Applied? Heat vs. Cold: When and Why Historical
Cryotherapy Effects, Part 1: Comparison of Skin Temperatures and Patient-Reported Sensations for Different Modes of Administration
 Therapeutic Modalities Cryotherapy Effects, Part 1: Comparison of Skin Temperatures and Patient-Reported Sensations for Different Modes of Administration Hailey N. Love, MEd, ATC William Campbell Combined
Therapeutic Modalities Cryotherapy Effects, Part 1: Comparison of Skin Temperatures and Patient-Reported Sensations for Different Modes of Administration Hailey N. Love, MEd, ATC William Campbell Combined
Local Ice-Bag Application and Triceps Surae Muscle Temperature During Treadmill Walking
 Journal of Athletic Training 2005;40(4):271 275 by the National Athletic Trainers Association, Inc www.journalofathletictraining.org Local Ice-Bag Application and Triceps Surae Muscle Temperature During
Journal of Athletic Training 2005;40(4):271 275 by the National Athletic Trainers Association, Inc www.journalofathletictraining.org Local Ice-Bag Application and Triceps Surae Muscle Temperature During
Jane Kennet, BSc; Natalie Hardaker, BSc (Hons); Sarah Hobbs, PhD; James Selfe, PhD
 Journal of Athletic Training 2007;42(3):343 348 by the National Athletic Trainers Association, Inc www.journalofathletictraining.org Cooling Efficiency of 4 Common Cryotherapeutic Agents Jane Kennet, BSc;
Journal of Athletic Training 2007;42(3):343 348 by the National Athletic Trainers Association, Inc www.journalofathletictraining.org Cooling Efficiency of 4 Common Cryotherapeutic Agents Jane Kennet, BSc;
International Journal of Medical and Exercise Science
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE International Journal of Medical and Exercise Science (Multidisciplinary, Peer Reviewed and Indexed Journal) COMPARATIVE EFFECT OF CRUSHED ICE AND ELASTOGEL COLD WRAP ON ANKLE SPRAIN Search
ORIGINAL ARTICLE International Journal of Medical and Exercise Science (Multidisciplinary, Peer Reviewed and Indexed Journal) COMPARATIVE EFFECT OF CRUSHED ICE AND ELASTOGEL COLD WRAP ON ANKLE SPRAIN Search
Effectiveness of Clinical Ultrasound Parameters on Changing Intramuscular Temperature
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2008, 17, 1-10 2008 Human Kinetics, Inc. Effectiveness of Clinical Ultrasound Parameters on Changing Intramuscular Temperature Timothy J. Demchak and Marcus B. Stone Context:
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 2008, 17, 1-10 2008 Human Kinetics, Inc. Effectiveness of Clinical Ultrasound Parameters on Changing Intramuscular Temperature Timothy J. Demchak and Marcus B. Stone Context:
Open and Closed Chained Activity Effect on Shoulder External Rotation Range of Motion using Whole Body Vibration Therapy
 Open and Closed Chained Activity Effect on Shoulder External Rotation Range of Motion using Whole Body Vibration Therapy Timothy L. Cooley, MS, ATC University of Utah Craig L. Switzler, MS, ATC University
Open and Closed Chained Activity Effect on Shoulder External Rotation Range of Motion using Whole Body Vibration Therapy Timothy L. Cooley, MS, ATC University of Utah Craig L. Switzler, MS, ATC University
Brochure. The Professional s Choice
 Brochure The CET CryoSpa s were the right choice & a huge success, allowing us to provide the best possible support to Team GB in London. Dave Reddin Director of Performance Services Team GB 2012 The Professional
Brochure The CET CryoSpa s were the right choice & a huge success, allowing us to provide the best possible support to Team GB in London. Dave Reddin Director of Performance Services Team GB 2012 The Professional
Unit 9 MODALITIES AND REHABILITATION Lecture Guide
 Unit 9 MODALITIES AND REHABILITATION Lecture Guide Therapeutic Modalities What are they? Therapeutic= Modality= Many different modalities to choose from- selection is dependant on: Smaller, slower nerve
Unit 9 MODALITIES AND REHABILITATION Lecture Guide Therapeutic Modalities What are they? Therapeutic= Modality= Many different modalities to choose from- selection is dependant on: Smaller, slower nerve
UNDERSTANDING WHAT YOUR BODY IS SAYING PAIN VS INJURY KURT MENAPACE, MD ATC TOBY BLOSSER, MS ATC OTC
 UNDERSTANDING WHAT YOUR BODY IS SAYING PAIN VS INJURY KURT MENAPACE, MD ATC TOBY BLOSSER, MS ATC OTC OBJECTIVES Define Pain vs. Injury What you might be feeling now vs. later How to Treat Pain / Injury
UNDERSTANDING WHAT YOUR BODY IS SAYING PAIN VS INJURY KURT MENAPACE, MD ATC TOBY BLOSSER, MS ATC OTC OBJECTIVES Define Pain vs. Injury What you might be feeling now vs. later How to Treat Pain / Injury
Shortwave Diathermy. Objectives. What is Shortwave Diathermy? What is Shortwave Diathermy? Physiological Responses
 Shortwave Diathermy http://www.rehaboutlet.com/images/me300.jpg Michael Banes Deep Bhavsar Ryan Machuca ATPE 414 11/6/05 http://www.btlnet.com/imgen/shortwave.jpg Objectives To learn what shortwave diathermy
Shortwave Diathermy http://www.rehaboutlet.com/images/me300.jpg Michael Banes Deep Bhavsar Ryan Machuca ATPE 414 11/6/05 http://www.btlnet.com/imgen/shortwave.jpg Objectives To learn what shortwave diathermy
Effect of cold treatment on the concentric and eccentric torque-velocity relationship of the quadriceps femoris
 Effect of cold treatment on the concentric and eccentric torque-velocity relationship of the quadriceps femoris By: Kerriann Catlaw *, Brent L. Arnold, and David H. Perrin Catlaw, K., Arnold, B.L., & Perrin,
Effect of cold treatment on the concentric and eccentric torque-velocity relationship of the quadriceps femoris By: Kerriann Catlaw *, Brent L. Arnold, and David H. Perrin Catlaw, K., Arnold, B.L., & Perrin,
The Effect of Therapeutic Modalities on Blood Flow in the Human Calf1
 The Effect of Therapeutic Modalities on Blood Flow in the Human Calf1 ROBERT J. BAKER, MS, ATC? GERALD W. BELL, EdD, PT, ATC? Local blood flow to the calf of human subjects during the application of therapeutic
The Effect of Therapeutic Modalities on Blood Flow in the Human Calf1 ROBERT J. BAKER, MS, ATC? GERALD W. BELL, EdD, PT, ATC? Local blood flow to the calf of human subjects during the application of therapeutic
Chapter 23 Unit 28. Therapeutic Modalities
 Chapter 23 Unit 28 Therapeutic Modalities Chapter Objectives Discuss the purpose of therapeutic modalities Explain the legal implications associated with the use of therapeutic modalities List the different
Chapter 23 Unit 28 Therapeutic Modalities Chapter Objectives Discuss the purpose of therapeutic modalities Explain the legal implications associated with the use of therapeutic modalities List the different
Course Syllabus PTH 123A Physical Agents Theory 2 credit hours/ 2 contact hours Fall 2016
 Course Syllabus PTH 123A Physical Agents Theory 2 credit hours/ 2 contact hours Fall 2016 INSTRUCTOR: Timothy Davis, MS ATC/PTA tdavis@siu.edu Office: ASA 118A (618) 453-8820 OFFICE HOURS: Monday 2:00
Course Syllabus PTH 123A Physical Agents Theory 2 credit hours/ 2 contact hours Fall 2016 INSTRUCTOR: Timothy Davis, MS ATC/PTA tdavis@siu.edu Office: ASA 118A (618) 453-8820 OFFICE HOURS: Monday 2:00
Therapeutic Heat: Effects of Superficial and Deep Heating Modalities on Hamstring Flexibility
 University of North Florida UNF Digital Commons All Volumes (2001-2008) The Osprey Journal of Ideas and Inquiry 2008 Therapeutic Heat: Effects of Superficial and Deep Heating Modalities on Hamstring Flexibility
University of North Florida UNF Digital Commons All Volumes (2001-2008) The Osprey Journal of Ideas and Inquiry 2008 Therapeutic Heat: Effects of Superficial and Deep Heating Modalities on Hamstring Flexibility
THE POWER to ACCELERATE RECOVERY
 THE POWER to ACCELERATE RECOVERY THE NEW STANDARD OF CARE IN INJURY AND POST-OP RECOVERY COMPRESSION AND COLD WORKING TOGETHER LIKE NEVER BEFORE Forget about passive cold and compression applications.
THE POWER to ACCELERATE RECOVERY THE NEW STANDARD OF CARE IN INJURY AND POST-OP RECOVERY COMPRESSION AND COLD WORKING TOGETHER LIKE NEVER BEFORE Forget about passive cold and compression applications.
Unit 9 MODALITIES AND REHABILITATION Mobility Worksheet
 Unit 9 MODALITIES AND REHABILITATION Mobility Worksheet Name Period The selection of specific treatments is based on a variety of factors list four: What is the protocol for RICE? What are the purposes
Unit 9 MODALITIES AND REHABILITATION Mobility Worksheet Name Period The selection of specific treatments is based on a variety of factors list four: What is the protocol for RICE? What are the purposes
HEAT & COLD. Heat and cold applications applied to skin surface help treat certain conditions
 HEAT AND COLD HEAT & COLD Heat and cold applications applied to skin surface help treat certain conditions Heat and cold applications require a doctor s order when being used on a patient The body can
HEAT AND COLD HEAT & COLD Heat and cold applications applied to skin surface help treat certain conditions Heat and cold applications require a doctor s order when being used on a patient The body can
The Effects of Voodoo Floss on Closed Chain Gastrocnemius Extensibility. Todd Gilmore Kati Major Denise Massie ATC, PT, DPT Shatora Lane MS, ATC
 The Effects of Voodoo Floss on Closed Chain Gastrocnemius Extensibility Todd Gilmore Kati Major Denise Massie ATC, PT, DPT Shatora Lane MS, ATC Introduction Restricted range of motion is an issue that
The Effects of Voodoo Floss on Closed Chain Gastrocnemius Extensibility Todd Gilmore Kati Major Denise Massie ATC, PT, DPT Shatora Lane MS, ATC Introduction Restricted range of motion is an issue that
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN. Expected Outcome. Causes
 Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
August 12, Sports Med Critical Question 4.notebook. Critical Question 4. How is injury rehabilitation managed?
 Critical Question 4 How is injury rehabilitation managed? 1 2 Syllabus 3 Big Heading: Critical Questions 4: How is injury rehabilitation managed Heading: Rehabilitation Procedures Rehabilitation after
Critical Question 4 How is injury rehabilitation managed? 1 2 Syllabus 3 Big Heading: Critical Questions 4: How is injury rehabilitation managed Heading: Rehabilitation Procedures Rehabilitation after
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the
The Clinical Effects of Cold Application on the Production of Electrically Induced Involuntary Muscle Contractions
 The Clinical Effects of Cold Application on the Production of Electrically Induced Involuntary Muscle Contractions Bonnie L. Van Lunen, Clayton Carroll, Kristen Gratias, and Doug Straley Context: Rehabilitation.
The Clinical Effects of Cold Application on the Production of Electrically Induced Involuntary Muscle Contractions Bonnie L. Van Lunen, Clayton Carroll, Kristen Gratias, and Doug Straley Context: Rehabilitation.
lntertester and lntratester Reliability of a Dynamic Balance Protocol Using the Biodex Stability System
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1998, 7, 95-101 0 1998 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. lntertester and lntratester Reliability of a Dynamic Balance Protocol Using the Biodex Stability System Randy Schmitz
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1998, 7, 95-101 0 1998 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. lntertester and lntratester Reliability of a Dynamic Balance Protocol Using the Biodex Stability System Randy Schmitz
Beginning Athletic Medicine. Non-Penetrating Therapy
 Beginning Athletic Medicine Non-Penetrating Therapy Therapeutic Modalities What are they? Therapeutic= something that promotes healing and injury repair Modality= the method of application of any therapeutic
Beginning Athletic Medicine Non-Penetrating Therapy Therapeutic Modalities What are they? Therapeutic= something that promotes healing and injury repair Modality= the method of application of any therapeutic
Bunion (hallux valgus deformity) surgery
 Bunion (hallux valgus deformity) surgery Bunion surgery is generally reserved for bunions that are severe and impacting on function. There most frequent surgical procedure used involves a medial incision
Bunion (hallux valgus deformity) surgery Bunion surgery is generally reserved for bunions that are severe and impacting on function. There most frequent surgical procedure used involves a medial incision
Musculoskeletal Therapy Sports Injury Management 2. Bachelor of Health Science (Musculoskeletal Therapy) Core 2 credit points
 Outline Name: Code: Award(s): Core/Elective: Pre/corequisites: Student Workload: Delivery Mode: Coordinator: Musculoskeletal Therapy Sports Injury Management 2 MSTS322 Bachelor of Health Science (Musculoskeletal
Outline Name: Code: Award(s): Core/Elective: Pre/corequisites: Student Workload: Delivery Mode: Coordinator: Musculoskeletal Therapy Sports Injury Management 2 MSTS322 Bachelor of Health Science (Musculoskeletal
METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures)
 METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures) Description Possible Complications Metatarsal fracture is a broken bone (fracture) in the middle Nonunion (fracture does not heal, particularly
METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures) Description Possible Complications Metatarsal fracture is a broken bone (fracture) in the middle Nonunion (fracture does not heal, particularly
What Are Sports Injuries?
 What Should I Do if I Get Injured? Never try to "work through" the pain of a sports injury. Stop playing or exercising when you feel pain. Playing or exercising more only causes more harm. Some injuries
What Should I Do if I Get Injured? Never try to "work through" the pain of a sports injury. Stop playing or exercising when you feel pain. Playing or exercising more only causes more harm. Some injuries
LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS. Please check with the LCC bookstore for the required texts for this class.
 LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS SPECIAL NOTE: This brief syllabus is not intended to be a legal contract. A full syllabus will be distributed to students at the first class session. TEXT AND SUPPLEMENTARY
LABETTE COMMUNITY COLLEGE BRIEF SYLLABUS SPECIAL NOTE: This brief syllabus is not intended to be a legal contract. A full syllabus will be distributed to students at the first class session. TEXT AND SUPPLEMENTARY
Ankle Sprain. Information for patients. This booklet provides information for patients with ankle sprain. Physiotherapy
 Ankle Sprain Information for patients This booklet provides information for patients with ankle sprain. Physiotherapy Website http://www.mtw.nhs.uk/physiotherapy/ Telephone 01892 632902 / 01622 224308
Ankle Sprain Information for patients This booklet provides information for patients with ankle sprain. Physiotherapy Website http://www.mtw.nhs.uk/physiotherapy/ Telephone 01892 632902 / 01622 224308
How can DIABETES affect my FEET? Emma Howard Specialist Podiatrist and Team Leader, Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust
 How can DIABETES affect my FEET? By: Emma Howard Specialist Podiatrist and Team Leader, Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust HOW CAN DIABETES AFFECT MY FEET? What is neuropathy? This leaflet explains how
How can DIABETES affect my FEET? By: Emma Howard Specialist Podiatrist and Team Leader, Oxford Health NHS Foundation Trust HOW CAN DIABETES AFFECT MY FEET? What is neuropathy? This leaflet explains how
ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT
 ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT Description Possible Complications Pinching of bone or soft tissue, including scar tissue, at the Frequent recurrence of symptoms, resulting in chronically front of the ankle
ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT Description Possible Complications Pinching of bone or soft tissue, including scar tissue, at the Frequent recurrence of symptoms, resulting in chronically front of the ankle
HEATING HAS LONG BEEN used clinically to increase. The Effect of Heat on Tissue Extensibility: A Comparison of Deep and Superficial Heating
 819 The Effect of Heat on Tissue Extensibility: A Comparison of Deep and Superficial Heating Val J. Robertson, PhD, Alex R. Ward, PhD, Peter Jung, BPhysio ABSTRACT. Robertson VJ, Ward AR, Jung P. The effect
819 The Effect of Heat on Tissue Extensibility: A Comparison of Deep and Superficial Heating Val J. Robertson, PhD, Alex R. Ward, PhD, Peter Jung, BPhysio ABSTRACT. Robertson VJ, Ward AR, Jung P. The effect
When a muscle has. Shortwave Diathermy and Prolonged Stretching Increase Hamstring Flexibility More Than Prolonged Stretching Alone
 Shortwave Diathermy and Prolonged Stretching Increase Hamstring Flexibility More Than Prolonged Stretching Alone David O. Draper, EdD, ATC 1 Jennifer L. Castro, MS, ATC 2 Brent Feland, PT, PhD 3 Shane
Shortwave Diathermy and Prolonged Stretching Increase Hamstring Flexibility More Than Prolonged Stretching Alone David O. Draper, EdD, ATC 1 Jennifer L. Castro, MS, ATC 2 Brent Feland, PT, PhD 3 Shane
WELLNESS UPDATE 2001, #1 THE PROPER TREATMENT OF ATHLETIC INJURIES
 WELLNESS UPDATE 2001, #1 THE PROPER TREATMENT OF ATHLETIC INJURIES There are three common errors coaches make in treating athletic injuries: 1) not referring the athlete to a physician or other health
WELLNESS UPDATE 2001, #1 THE PROPER TREATMENT OF ATHLETIC INJURIES There are three common errors coaches make in treating athletic injuries: 1) not referring the athlete to a physician or other health
The Star Excursion Balance Test (SEBT) is a unilateral, UNILATERAL BALANCE PERFORMANCE IN FEMALE COLLEGIATE SOCCER ATHLETES
 UNILATERAL BALANCE PERFORMANCE IN FEMALE COLLEGIATE SOCCER ATHLETES JENNIFER L. THORPE AND KYLE T. EBERSOLE University of Illinois, Department of Kinesiology and Community Health, Urbana, Illinois ABSTRACT
UNILATERAL BALANCE PERFORMANCE IN FEMALE COLLEGIATE SOCCER ATHLETES JENNIFER L. THORPE AND KYLE T. EBERSOLE University of Illinois, Department of Kinesiology and Community Health, Urbana, Illinois ABSTRACT
ATHLETIC INJURIES **********
 ATHLETIC INJURIES We publish here below an article by Mr. Larry CARTER Athletics Trainer at the University of Los Angeles ********** ATHLETIC INJURIES The most prevalent injuries from long distance running
ATHLETIC INJURIES We publish here below an article by Mr. Larry CARTER Athletics Trainer at the University of Los Angeles ********** ATHLETIC INJURIES The most prevalent injuries from long distance running
Modalities and Rehab in the Athletic Training Room. Thomas Hunkele MPT, ATC, NASM-PES,CES Coordinator of Rehabilitation
 Modalities and Rehab in the Athletic Training Room Thomas Hunkele MPT, ATC, NASM-PES,CES Coordinator of Rehabilitation Disclosures The Great Debate To Be or Not To Be (Included) Active vs Passive rehabilitation
Modalities and Rehab in the Athletic Training Room Thomas Hunkele MPT, ATC, NASM-PES,CES Coordinator of Rehabilitation Disclosures The Great Debate To Be or Not To Be (Included) Active vs Passive rehabilitation
Cryotherapy A call for further research
 Authors: Jeremy R. Hawkins 1, PhD, ATC Michael Reeder 2, DO Kristin J. Heumann 3, PhD, CSCS, c-ep Affiliations: 1 Colorado Mesa University E-mail: jrhawkins@coloradomesa.edu 2 Colorado Mesa University
Authors: Jeremy R. Hawkins 1, PhD, ATC Michael Reeder 2, DO Kristin J. Heumann 3, PhD, CSCS, c-ep Affiliations: 1 Colorado Mesa University E-mail: jrhawkins@coloradomesa.edu 2 Colorado Mesa University
THE ADVANTAGES OF INTERMITTENT PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION AND CRYOTHERAPY TREATMENT FOR POST-OPERATIVE PATIENT CARE
 THE ADVANTAGES OF INTERMITTENT PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION AND CRYOTHERAPY TREATMENT FOR POST-OPERATIVE PATIENT CARE WWW.GAMEREADY.COM 1.888.426.3732 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION SURGERIES THAT BENEFIT FROM INTERMITTENT
THE ADVANTAGES OF INTERMITTENT PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION AND CRYOTHERAPY TREATMENT FOR POST-OPERATIVE PATIENT CARE WWW.GAMEREADY.COM 1.888.426.3732 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION SURGERIES THAT BENEFIT FROM INTERMITTENT
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg)
 MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS SYNDROME (Shin Splints)
 MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS SYNDROME (Shin Splints) Description Expected Outcome Shin splints is a term broadly used to describe pain in the lower extremity brought on by exercise or athletic activity. Most commonly
MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS SYNDROME (Shin Splints) Description Expected Outcome Shin splints is a term broadly used to describe pain in the lower extremity brought on by exercise or athletic activity. Most commonly
Journal of Undergraduate Kinesiology Research
 Chronic PNF Stretching Program 21 Journal of Undergraduate Kinesiology Research Official Research Journal of the Department of Kinesiology University of Wisconsin Eau Claire Volume 2 Number 1 December
Chronic PNF Stretching Program 21 Journal of Undergraduate Kinesiology Research Official Research Journal of the Department of Kinesiology University of Wisconsin Eau Claire Volume 2 Number 1 December
Intertester Reliability of Assessing Postural Sway Using the Chattecx Balance System
 Intertester Reliability of Assessing Postural Sway Using the Chattecx Balance System By: Carl G. Mattacola, MEd, ATC; Denise A. Lebsack, PhD, ATC; David H. Perrin, PhD, ATC * Mattacola, C.G., Lebsack,
Intertester Reliability of Assessing Postural Sway Using the Chattecx Balance System By: Carl G. Mattacola, MEd, ATC; Denise A. Lebsack, PhD, ATC; David H. Perrin, PhD, ATC * Mattacola, C.G., Lebsack,
Comparison of Weight-Bearing and Non-Weight-Bearing Conditions on Knee Joint Reposition Sense
 Comparison of Weight-Bearing and Non-Weight-Bearing Conditions on Knee Joint Reposition Sense By: Michael J. Higgins and David H. Perrin Higgins, M.J., Perrin, D.H. (1997). Comparison of weight bearing
Comparison of Weight-Bearing and Non-Weight-Bearing Conditions on Knee Joint Reposition Sense By: Michael J. Higgins and David H. Perrin Higgins, M.J., Perrin, D.H. (1997). Comparison of weight bearing
ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE. Description
 Description ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE An acute ankle sprain involves the stretching and tearing of one or more ligaments in the ankle. A two-ligament sprain causes more disability than a single-ligament sprain.
Description ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE An acute ankle sprain involves the stretching and tearing of one or more ligaments in the ankle. A two-ligament sprain causes more disability than a single-ligament sprain.
PAIN. Headache. enstrual Pain. Low Back Pain. Osteoarthritis. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Sprains and Strains. Taking Care of. Pain of
 Low Back Pain Sprains and Strains Taking Care of PAIN TIPS FOR UNDERSTANDING, AVOIDING, AND CARING FOR COMMON TYPES OF PAIN Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain of Osteoarthritis enstrual Pain Headache BROUGHT
Low Back Pain Sprains and Strains Taking Care of PAIN TIPS FOR UNDERSTANDING, AVOIDING, AND CARING FOR COMMON TYPES OF PAIN Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain of Osteoarthritis enstrual Pain Headache BROUGHT
Deep heating using microwave diathermy decreases muscle hardness: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial
 J Rehabil Health Sci 2016; 14:9-13 C 2016 Osaka Prefecture University Journal of Rehabilitation and Health Sciences 9 Online ISSN 2185-8004 Original Article Deep heating using microwave diathermy decreases
J Rehabil Health Sci 2016; 14:9-13 C 2016 Osaka Prefecture University Journal of Rehabilitation and Health Sciences 9 Online ISSN 2185-8004 Original Article Deep heating using microwave diathermy decreases
Cubed-ice vs Wetted-ice as a Cryotherapeutic Agent in the Malaysian Climate
 Cubed-ice vs Wetted-ice as a Cryotherapeutic Agent in the Malaysian Climate Norlizah Abdul Hamid, Mohd Firdaus Nawawi, Nagoor Meera Abdullah, Rozita Abd Latif Faculty of Sports Science and Recreation,
Cubed-ice vs Wetted-ice as a Cryotherapeutic Agent in the Malaysian Climate Norlizah Abdul Hamid, Mohd Firdaus Nawawi, Nagoor Meera Abdullah, Rozita Abd Latif Faculty of Sports Science and Recreation,
Unit 9 MODALITIES AND REHABILITATION Lecture Notes
 Unit 9 MODALITIES AND REHABILITATION Lecture Notes THERAPEUTIC MODALITIES Objective 1: Explore Therapeutic Modalities I. Introduction A. Create an optimum environment for injury healing by reducing pain,
Unit 9 MODALITIES AND REHABILITATION Lecture Notes THERAPEUTIC MODALITIES Objective 1: Explore Therapeutic Modalities I. Introduction A. Create an optimum environment for injury healing by reducing pain,
Injury Prevention and Treatment in Sport and Exercise
 Unit 26: Injury Prevention and Treatment in Sport and Exercise Unit code: F/601/1870 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit examines the causes of common injuries in sport and exercise and how they
Unit 26: Injury Prevention and Treatment in Sport and Exercise Unit code: F/601/1870 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit examines the causes of common injuries in sport and exercise and how they
Peripheral Neuropathy
 Peripheral Neuropathy Neuropathy affects 30-50% of patient population with diabetes and this prevalence tends to increase proportionally with duration of diabetes and dependant on control. Often presents
Peripheral Neuropathy Neuropathy affects 30-50% of patient population with diabetes and this prevalence tends to increase proportionally with duration of diabetes and dependant on control. Often presents
Nearly 80% of all RESEARCH REPORT
 Paraspinal Musculature and Skin Temperature Changes: Comparing the ThermaCare HeatWrap, the Johnson & Johnson Back Plaster, and the ABC Warme-Pflaster RESEARCH REPORT Cynthia A. Trowbridge, PhD, ATC, CSCS
Paraspinal Musculature and Skin Temperature Changes: Comparing the ThermaCare HeatWrap, the Johnson & Johnson Back Plaster, and the ABC Warme-Pflaster RESEARCH REPORT Cynthia A. Trowbridge, PhD, ATC, CSCS
Foot and ankle fractures
 Foot and ankle fractures Some fractures can be managed without surgery, but others require surgery to achieve the best possible outcome. Fractures and injuries to joints have a high risk of developing
Foot and ankle fractures Some fractures can be managed without surgery, but others require surgery to achieve the best possible outcome. Fractures and injuries to joints have a high risk of developing
EVect of stretching duration on active and passive range of motion in the lower extremity
 Br J Sports Med 1999;33:259 263 259 School of Health Sciences, University of Sunderland J M Roberts K Wilson Correspondence to: J M Roberts, School of Health Sciences, University of Sunderland, Chester
Br J Sports Med 1999;33:259 263 259 School of Health Sciences, University of Sunderland J M Roberts K Wilson Correspondence to: J M Roberts, School of Health Sciences, University of Sunderland, Chester
Urgent care. Ankle sprain advice
 Ankle sprain advice What is an ankle sprain? An ankle sprain is an injury to the ligaments of the ankle joint. These are elastic-band-like structures which hold the bones of the ankle joint together and
Ankle sprain advice What is an ankle sprain? An ankle sprain is an injury to the ligaments of the ankle joint. These are elastic-band-like structures which hold the bones of the ankle joint together and
Comparing the Effects of Ultrasound and Stretching on Hip Flexor Flexibility and Postural Control
 Skyline - The Big Sky Undergraduate Journal Volume 3 Issue 1 Article 1 2015 Comparing the Effects of Ultrasound and Stretching on Hip Flexor Flexibility and Postural Control Cali A. VanValkenburg University
Skyline - The Big Sky Undergraduate Journal Volume 3 Issue 1 Article 1 2015 Comparing the Effects of Ultrasound and Stretching on Hip Flexor Flexibility and Postural Control Cali A. VanValkenburg University
p The Y Balance Test
 The Y Balance Test Star Excursion Balance Test First described by Gary Gray 1995 Requires measurement in 8 directions (each leg) 6 practice trials in each direction 3 measurements 144 reaches to test one
The Y Balance Test Star Excursion Balance Test First described by Gary Gray 1995 Requires measurement in 8 directions (each leg) 6 practice trials in each direction 3 measurements 144 reaches to test one
ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Research Received on:15/05/12 Revised on:20/05/12 Accepted on:25/05/12
 SCREENING OF SUBCLINICAL SENSORY IMPAIRMENT IN HAND AMONG DIABETIC BLINDS ijcrr Vol 04 issue 1 Category: Research Received on:15/05/1 Revised on:/05/1 Accepted on:5/05/1 Janakiraman Balamurugan 1, Ravichandran
SCREENING OF SUBCLINICAL SENSORY IMPAIRMENT IN HAND AMONG DIABETIC BLINDS ijcrr Vol 04 issue 1 Category: Research Received on:15/05/1 Revised on:/05/1 Accepted on:5/05/1 Janakiraman Balamurugan 1, Ravichandran
MENISCUS TEAR. Description
 MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
Our Vision NADA BoD Strategic Planning Session -
 Who we are NADA is a not-for-profit members-led organization established in 1995 as a result of the rising rates of diabetes among First Nations, Inuit and Métis Peoples in Canada Our Vision - 2016 NADA
Who we are NADA is a not-for-profit members-led organization established in 1995 as a result of the rising rates of diabetes among First Nations, Inuit and Métis Peoples in Canada Our Vision - 2016 NADA
CRYOTHERAPY IS a widely used technique in the immediate. Skin Temperature Response to Cryotherapy
 543 Skin Temperature Response to Cryotherapy Linda S. Chesterton, BSc, MCSP, SRP, Nadine E. Foster, MCSP, DPhil, Lesley Ross, Grad Dip Phys, MCSP, SRP ABSTRACT. Chesterton LS, Foster NE, Ross L. Skin temperature
543 Skin Temperature Response to Cryotherapy Linda S. Chesterton, BSc, MCSP, SRP, Nadine E. Foster, MCSP, DPhil, Lesley Ross, Grad Dip Phys, MCSP, SRP ABSTRACT. Chesterton LS, Foster NE, Ross L. Skin temperature
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
U01 Doherty-Restrepo, Jennifer UPPER PET 3353C U01 Phys Ex Spt Sci Lec Principles of Human Physiology Stanfield & Germann PET 4148
 COLLEGE DEPARTMENT PREFIX NUMBER SECTION PROFESSOR'S NAME COURSE_LEVEL COURSE CLASS DESCRIPTION REQUIRED BOOK 1 TITLE ISBN # AUTHOR(S) HSC 4406 U01 Riddle, Kari and Casanova, Gabe UPPER HSC 4406 U01 Mgmt
COLLEGE DEPARTMENT PREFIX NUMBER SECTION PROFESSOR'S NAME COURSE_LEVEL COURSE CLASS DESCRIPTION REQUIRED BOOK 1 TITLE ISBN # AUTHOR(S) HSC 4406 U01 Riddle, Kari and Casanova, Gabe UPPER HSC 4406 U01 Mgmt
OBSERVATIONS ON THE REACTION TIME TO CUTANEOUS
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1955, 18, 120. OBSERVATIONS ON THE REACTION TIME TO CUTANEOUS THERMAL STIMULI BY P. P. LELE* and D. C. SINCLAIR From the Department of Anatomy, University of Oxford The
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1955, 18, 120. OBSERVATIONS ON THE REACTION TIME TO CUTANEOUS THERMAL STIMULI BY P. P. LELE* and D. C. SINCLAIR From the Department of Anatomy, University of Oxford The
Importance of Topic 5/17/2013. Rethinking Proprioception Training & Ankle Instability. Dr Emily Splichal, DPM, MS, CES
 Rethinking Proprioception Training & Ankle Instability Dr Emily Splichal, DPM, MS, CES Evidence Based Fitness Academy Applying Research Achieving Results Importance of Topic JBJS 2010 study found average
Rethinking Proprioception Training & Ankle Instability Dr Emily Splichal, DPM, MS, CES Evidence Based Fitness Academy Applying Research Achieving Results Importance of Topic JBJS 2010 study found average
Dr Emily Splichal, DPM, MS, CES Evidence Based Fitness Academy Applying Research Achieving Results
 Rethinking Proprioception Training & Ankle Instability Dr Emily Splichal, DPM, MS, CES Evidence Based Fitness Academy Applying Research Achieving Results Importance of Topic JBJS 2010 study found average
Rethinking Proprioception Training & Ankle Instability Dr Emily Splichal, DPM, MS, CES Evidence Based Fitness Academy Applying Research Achieving Results Importance of Topic JBJS 2010 study found average
Localized collection of pus in a cavity
 Localized collection of pus in a cavity Loss of feeling or sensation induced to permit surgery Common example: Injection given to numb up the toe prior to performing an ingrown toenail procedure Mechanical
Localized collection of pus in a cavity Loss of feeling or sensation induced to permit surgery Common example: Injection given to numb up the toe prior to performing an ingrown toenail procedure Mechanical
DIAGNOSIS OF DIABETIC NEUROPATHY
 DIAGNOSIS OF DIABETIC NEUROPATHY Dept of PM&R, College of Medicine, Korea University Dong Hwee Kim Electrodiagnosis ANS Clinical Measures QST DIAGRAM OF CASUAL PATHWAYS TO FOOT ULCERATION Rathur & Boulton.
DIAGNOSIS OF DIABETIC NEUROPATHY Dept of PM&R, College of Medicine, Korea University Dong Hwee Kim Electrodiagnosis ANS Clinical Measures QST DIAGRAM OF CASUAL PATHWAYS TO FOOT ULCERATION Rathur & Boulton.
motion (ROM). Participants were grouped according to injured and non-injured knees within
 The effect of gender on range of motion (ROM) for knee joint Dr.Fatehiya F.Hasan Ph.D Medical Physics Abstract Elham Khalid Ibrahim Master Medical Physics This study was distinguished there is a difference
The effect of gender on range of motion (ROM) for knee joint Dr.Fatehiya F.Hasan Ph.D Medical Physics Abstract Elham Khalid Ibrahim Master Medical Physics This study was distinguished there is a difference
Ischial Bursitis and Piriformis Syndrome. Author: Anthony J Ross ATC, CSCS, M.Ed.
 Author: Anthony J Ross ATC, CSCS, M.Ed. Contents About the Author Background/History Common Signs and Symptoms Treatment Options Sample Program Conclusion Reference Material 3 4 5 6 7 8 2 About the Author
Author: Anthony J Ross ATC, CSCS, M.Ed. Contents About the Author Background/History Common Signs and Symptoms Treatment Options Sample Program Conclusion Reference Material 3 4 5 6 7 8 2 About the Author
First Aid Policy. One member of every coaching staff (competitive) is "required" to be first aid certified.
 First Aid Policy When you accept the role of coach with LSSC, regardless of what level, you accept a major responsibility for the care and safety of your players. Although the athletes share in the responsibility
First Aid Policy When you accept the role of coach with LSSC, regardless of what level, you accept a major responsibility for the care and safety of your players. Although the athletes share in the responsibility
Physical Therapy for the Lower Extremity: What You and Your Patient Should Expect from Rehab
 1 Physical Therapy for the Lower Extremity: What You and Your Patient Should Expect from Rehab Thomas Clennell, PT, DPT, SCS Physical Therapist UCSF Benioff Children s Hospital Oakland Sports Medicine
1 Physical Therapy for the Lower Extremity: What You and Your Patient Should Expect from Rehab Thomas Clennell, PT, DPT, SCS Physical Therapist UCSF Benioff Children s Hospital Oakland Sports Medicine
Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome
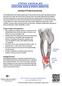 Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon passes
Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon passes
The Reliability of Four Different Methods. of Calculating Quadriceps Peak Torque Angle- Specific Torques at 30, 60, and 75
 The Reliability of Four Different Methods. of Calculating Quadriceps Peak Torque Angle- Specific Torques at 30, 60, and 75 By: Brent L. Arnold and David H. Perrin * Arnold, B.A., & Perrin, D.H. (1993).
The Reliability of Four Different Methods. of Calculating Quadriceps Peak Torque Angle- Specific Torques at 30, 60, and 75 By: Brent L. Arnold and David H. Perrin * Arnold, B.A., & Perrin, D.H. (1993).
Impact of Achilles Tendon Lengthening on Functional Limitations and Perceived Disability in People With a Neuropathic Plantar Ulcer
 Clinical Care/Education/Nutrition O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Impact of Achilles Tendon Lengthening on Functional Limitations and Perceived Disability in People With a Neuropathic Plantar Ulcer MICHAEL
Clinical Care/Education/Nutrition O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Impact of Achilles Tendon Lengthening on Functional Limitations and Perceived Disability in People With a Neuropathic Plantar Ulcer MICHAEL
A COMPARISION OF CRYOPRESS AND CRYO/CUFF EFFECTS ON ANKLE EDEMA AND PAIN. A thesis presented to. the faculty of. In partial fulfillment
 A COMPARISION OF CRYOPRESS AND CRYO/CUFF EFFECTS ON ANKLE EDEMA AND PAIN A thesis presented to the faculty of the College of Health and Human Services of Ohio University In partial fulfillment of the requirements
A COMPARISION OF CRYOPRESS AND CRYO/CUFF EFFECTS ON ANKLE EDEMA AND PAIN A thesis presented to the faculty of the College of Health and Human Services of Ohio University In partial fulfillment of the requirements
Week minutes weekly (moderate) 300 minutes weekly (moderate)
 Healthy Living Advanced Tips We recommend a warm-up and cool-down activity each time you exercise. We suggest using a comfortable walking pace for 5-10 before and after each activity. If at any point you
Healthy Living Advanced Tips We recommend a warm-up and cool-down activity each time you exercise. We suggest using a comfortable walking pace for 5-10 before and after each activity. If at any point you
William G. Carson, Jr., M.D.
 1 William G. Carson, Jr., M.D. Publications: 1. Carson, W.G., Lowell, W.W. and Whitesides, T.E.: Congenital Elevation of Scapula: Surgical Correction by the Woodward Procedure. Journal of Bone and Joint
1 William G. Carson, Jr., M.D. Publications: 1. Carson, W.G., Lowell, W.W. and Whitesides, T.E.: Congenital Elevation of Scapula: Surgical Correction by the Woodward Procedure. Journal of Bone and Joint
Examination of some physiotherapy methods for treatment of Knee joint injury
 Fatehiya F. Hasan MSc, PhD *, Elham Khald Ibraham MSc** Abstract: Objective: This study investigates different range of motion of Knee joint, the effect of age, sex, regular, irregular patients treated
Fatehiya F. Hasan MSc, PhD *, Elham Khald Ibraham MSc** Abstract: Objective: This study investigates different range of motion of Knee joint, the effect of age, sex, regular, irregular patients treated
Beginner Fitness Program
 Beginner We recommend a warm-up and cool-down activity each time you exercise. WE SUGGEST Slow, easy walking pace for a few before and after activity. -7 Slow, easy walking pace for 5 before and after
Beginner We recommend a warm-up and cool-down activity each time you exercise. WE SUGGEST Slow, easy walking pace for a few before and after activity. -7 Slow, easy walking pace for 5 before and after
CHAPTER 4: Injury prevention and the rehabilitation of injury
 SECTION TOPIC 2 3 CHAPTER 46 CHAPTER 4: Injury prevention and the rehabilitation of injury Practice questions - text book pages 67-68 1) Elevation of an injured body part helps reduce injury by: a. helping
SECTION TOPIC 2 3 CHAPTER 46 CHAPTER 4: Injury prevention and the rehabilitation of injury Practice questions - text book pages 67-68 1) Elevation of an injured body part helps reduce injury by: a. helping
Sports Med Critical Question 3.notebook May 05, Critical Question 3
 Critical Question 3 What role do preventative actions play in enhancing the wellbeing of the athlete? Syllabus Apr 21 5:37 PM Big Heading: Critical Questions 2: What role do preventative actions play in
Critical Question 3 What role do preventative actions play in enhancing the wellbeing of the athlete? Syllabus Apr 21 5:37 PM Big Heading: Critical Questions 2: What role do preventative actions play in
MODALITY MANAGEMENT OF AN ACUTE ANKLE SPRAIN IN A PROFESSIONAL BASEBALL PLAYER: CASE REPORT
 ANKLE SPRAIN MODALITY MANAGEMENT OF AN ACUTE ANKLE SPRAIN IN A PROFESSIONAL BASEBALL PLAYER: CASE REPORT Authors: Steve Scher, MSPT, ATC, CSCS, PES, Henry Ford Health System, Center for Athletic Medicine;
ANKLE SPRAIN MODALITY MANAGEMENT OF AN ACUTE ANKLE SPRAIN IN A PROFESSIONAL BASEBALL PLAYER: CASE REPORT Authors: Steve Scher, MSPT, ATC, CSCS, PES, Henry Ford Health System, Center for Athletic Medicine;
Knee Pain. Pain in the pressure on. the kneecap. well as being supported (retinaculum) quadricep. Abnormal. to the knee. or dislocate.
 Knee Pain in Children and Adolescents Description Pain in the knee can occur from various causess but is usually from increased pressure on the kneecap (patella) or abnormal motion. Softening of the cartilage
Knee Pain in Children and Adolescents Description Pain in the knee can occur from various causess but is usually from increased pressure on the kneecap (patella) or abnormal motion. Softening of the cartilage
Understanding. Ankle Sprains
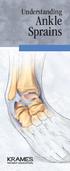 Understanding Ankle Sprains What Causes Ankle Sprains? The ankle is one of the most common places in the body for a sprain. Every day thousands of people sprain their ankles. Landing wrong on your foot
Understanding Ankle Sprains What Causes Ankle Sprains? The ankle is one of the most common places in the body for a sprain. Every day thousands of people sprain their ankles. Landing wrong on your foot
Effect of superficial pre-cooling on a hamstring stretching protocol
 The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Effect of superficial pre-cooling on a hamstring stretching protocol Kristin Orwig Medical University
The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Effect of superficial pre-cooling on a hamstring stretching protocol Kristin Orwig Medical University
Spondylolysis DESCRIPTION EXPECTED OUTCOME POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS COMMON SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS GENERAL TREATMENT CONSIDERATIONS CAUSES
 DESCRIPTION is a stress or fatigue fracture of the bones of the spine (vertebrae) that does not involve the main weight-bearing part of those bones, the body of the vertebra. Instead, it involves an area
DESCRIPTION is a stress or fatigue fracture of the bones of the spine (vertebrae) that does not involve the main weight-bearing part of those bones, the body of the vertebra. Instead, it involves an area
Hip Strains. Anyone can experience a hip strain just doing everyday tasks, but strains most often occur during sports activities.
 Hip Strains A hip strain occurs when one of the muscles supporting the hip joint is stretched beyond its limit or torn. Strains may be mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the extent of the injury.
Hip Strains A hip strain occurs when one of the muscles supporting the hip joint is stretched beyond its limit or torn. Strains may be mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the extent of the injury.
COMPARING THE EFFECTS OF DIATHERMY AND DYNAMIC STRETCHING ON HIP FLEXOR FLEXIBILITY AND POSTURAL CONTROL
 University of Montana ScholarWorks at University of Montana Undergraduate Theses and Professional Papers 2015 COMPARING THE EFFECTS OF DIATHERMY AND DYNAMIC STRETCHING ON HIP FLEXOR FLEXIBILITY AND POSTURAL
University of Montana ScholarWorks at University of Montana Undergraduate Theses and Professional Papers 2015 COMPARING THE EFFECTS OF DIATHERMY AND DYNAMIC STRETCHING ON HIP FLEXOR FLEXIBILITY AND POSTURAL
CARROLL UNIVERSITY College of Natural and Health Sciences Athletic Training Education Program. Athletic Training Seminar I or instructor s approval
 CARROLL UNIVERSITY College of Natural and Health Sciences Athletic Training Education Program Course Number: Athletic Training 102 Course Title: Prerequisites: Credit Hours: Contact Hours: Athletic Training
CARROLL UNIVERSITY College of Natural and Health Sciences Athletic Training Education Program Course Number: Athletic Training 102 Course Title: Prerequisites: Credit Hours: Contact Hours: Athletic Training
When to Use Cold or Heat Therapy
 www.amazon.com/shops/reliablemedicalsupply When to Use Cold or Heat Therapy Instructions for Cold Therapy, also known as Cryotherapy For Acute Injuries, when you have sharp, stabbing or shooting pain,
www.amazon.com/shops/reliablemedicalsupply When to Use Cold or Heat Therapy Instructions for Cold Therapy, also known as Cryotherapy For Acute Injuries, when you have sharp, stabbing or shooting pain,
Inflammation: Friend or Foe?
 Inflammation: Friend or Foe? Benjamin Reich, DPT Marshfield Clinic Outline 1. Why this topic? 2. Muscle regeneration 3. Inflammatory Process 4. Impact of NSAIDs 5. Impact of Ice, heat, ultrasound 2 Why?
Inflammation: Friend or Foe? Benjamin Reich, DPT Marshfield Clinic Outline 1. Why this topic? 2. Muscle regeneration 3. Inflammatory Process 4. Impact of NSAIDs 5. Impact of Ice, heat, ultrasound 2 Why?
