Ergonomic Design of Trowel Handle
|
|
|
- Erin Gregory
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ergonomic Design of Trowel Handle Amit Bhatia 1, Parveen Kalra 2, Jagjit Singh 3 1Student, Production and Industrial Engineering, PEC University of technology, Chandigarh, U.T. 2Professor, Production and Industrial Engineering, PEC University of technology, Chandigarh, India 3Assistant Professor, Production and Industrial Engineering, PEC University of technology, Chandigarh, India *** Abstract -Plastering is an occupation requiring the use Using ergonomic standards to enhance mason s comfort of hand and wrist movements. A variety of trowels has will improve productivity and make the job more been developed and used for plastering and pointing work. appealing to young inhabitants choosing a career. Most Trowels differ from region to region which may or may not manufacturers claim that they have always given be manufactured on the basis of hand anthropometry. emphasis to user comfort in their tool designs, but the However, some masons experience discomfort or injury when plastering and using trowel. So in order to improve minorities actually advertise ergonomic advantages in the quality of the trowels, it is necessary to rationalize its their manufactured goods literature. Some users say the dimensions that should be used in its manufacture. A handle should also minimize sweating, which can cause standard-design trowel was considered as reference to masons to grasp their trowels using more force. Tools find out the optimal diameter of the trowel handle. Hand with handles that extend beyond the base of the palm Anthropometric data of 40 participants, right hand should be selected. Short or undersized tools press into dominant, was collected. The comfort ratings of all these the palm and squeeze nerves in the hand. Avoid tools participants were collected. This comfort rating was related to the Normalized Handle Size (NHS). The with slim handles, which needs a tighter grip. A habitual regression equation was found out using Minitab matter was the commercial strains on workers which Software. The resulting regression equation was force them to work as rapidly as possible and therefore used to find out the dimensions of the optimal handle of they risk compromising wellbeing or safety. the trowel. Optimal diameter handles were fabricated for a subset of the participants. Contact area on the trowel handle was evaluated for both standard-design trowel and ergonomically designed trowel.. EMG (Electromyography) activity of muscles used in grasping both the handles was also assessed for muscle fatigue. Key Words: NHS, MSD, Subjective Comfort Rating, Anthropometry, Muscle fatigue 1. INTRODUCTION Construction is a high risk trade for musculoskeletal disorders. Trowels have been playing a critical role in plastering occupation. The uses of trowels vary from non-professional use at domestic level to professional use at industrial level. The Masonry trowels had been used in brickwork or stonework for levelling, spreading and shaping mortar or concrete. They come in different shapes and sizes depending on the task.most of the tasks carried out within construction trades involve the use of hand tools; require the use of several body regions, continuous movement in awkward positions.there are various methods of gripping the hand tools, but the most common type of grip is the Power Grip. Use "ergonomically" designed hand tools, which maintain the wrist in the "neutral" pose. Hand tool ergonomics is an interdisciplinary technical discipline which concerns with understanding interactions among individuals and other elements of a system. In this context, the user has a vital role in product development process. Product ergonomics applies principles,theory, data and methods to optimize human well-being and overall system performance. Ergonomics is described as fitting the work or task to the worker in order to minimize the menace of musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs). These injuries extend slowly over time and arise in the soft tissues of user s body like the tendons, muscles, nerves, ligaments, and joints. Examples of musculoskeletal disorders are carpal tunnel syndrome, low back strain and tendonitis. The unnecessary twisting of the wrist, elbow, arm and shoulder is prevented by the use of ergonomic tools. Therefore, excessive force is needed to grip the trowel in between the fingers which results in hand muscle fatigue. Kong and Lowe proposed that the finger s maximal voluntary contraction (MVC) force is dependent upon diameter of the handle. So, the variability in sizes of the handle should be in accordance with finger and hand sizes [1]. 2016, IRJET Impact Factor value: 4.45 ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal Page 819
2 The authors also explained that while gripping, the ring finger's contribution, for smaller handles, is higher than that of the index finger whereas for the larger handles, the order of contributions is overturned. There is increase in the role of the middle finger when the diameter of the handle is increased up to diameter of 40mm. Some examiners also used electromyography and force sensors, considering muscle activity and finger forces to identify the optimal diameters of cylindrical handle [2]. In some cases, where the trowels are not designed ergonomically, it may lead to various Musculoskeletal disorders (MSD). Ergonomically designed handle of trowel ensures a relaxed grip with the reduction of point pressures on palm s muscle enhancing grip of the trowel. In real world, it is very difficult to examine the grasping of any object and depends on the user s comfort ratings[3]. The author has examined a strong correlation between user performance and perceived subjective comfort and suggested to incorporate this aspect during the design phase [4]. GregorHarih and BojanDolšak proposed that development of the digital human hand model using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and following 3D printing of optimal diameter tool handle considering the anthropometric data will provide an anatomical profile to the tool handle [5]. This would enhance the perceived level of comfort. The focus of the present work is to work out the optimal handle dimensions of the trowel handle that would outcome in increased contact area, increased user comfort rating and reduced muscle fatigue. The objective is to build up an approach that would, in conclusion, give optimal size for a range of various hand sizes based on the design for human variability. The paper is arranged along the following lines: Section 2 describes the processes used in present investigation; Results and discussion are specified in section 3 whereas conclusions are given in section METHODOLOGY A. Subjects Hand Anthropometric data of forty participants, right hand dominant, was collected. There was no grievance of hand muscle fatigue in their entire life. Consent to take part in the study was taken from the participants prior to the research. The averages of their ring finger length (from hand crease) and hand width were 171.5±20.5mm, 1780±42.0mm and 81.5±13.5mm respectively. B. Equipment Vernier caliper.vernier caliper (least count of 1/20 mm = 0.05mm) was utilized to measure the hand anthropometric data of all the participants for the design purpose. Hand length was measured from the hand crease to the finger tip considered in design. Electromyographic measuring system. The electromyographic activity was acquired, for the Extensor Digitorum (ED) muscle, at a sampling frequency of 1000 HZ. EMG is utilized in the experimentation to identify the muscle fatigue while grasping the trowel. Surface electrodes, used to detect the EMG activity of muscle, were placed over the Extensor Digitorum (ED) muscle corresponding to the longitudinal axis of the muscle fibers [6]. C. Experimental Design The handle shape of a standard design trowel which is commonly available in market and used by most of the masons was considered as the reference due to its simple design. Procedure for experimentation is shown in Fig.2.Before the Fbeginning of the experiment, all participants were asked about complaints or injuries of their upper extremities which could affect the result. Brief purposes and processes of the experimentation were discussed with the participants. Experiment has been conducted in two phases as given below: i. Phase 1 (Experimentation phase). Four different circumferences (27, 29, 31 and 33 mm) of handle at location of ring finger were fabricated and used in experimentation. Each subject was asked to rate all trowels with variable circumferences on the scale of 1 to 7 ( 1 - Very uncomfortable, 2 - Moderately Uncomfortable, 3 - Somewhat Uncomfortable, 4 - Neutral, 5 - Somewhat Comfortable, 6 - Moderately Comfortable and 7 - Very Comfortable). As the ratings for various trowels were taken in random order, therefore, it was a balanced design. Hand Anthropometric measurements of the volunteers were assessed. All volunteers were asked to grip the trowels of various circumferences in their right hand and subjective comfort ratings were collected. For smaller handle, the ring finger has higher contribution than the index finger while gripping and vice-versa (Kong and Lowe, 2005). They also proposed that the contribution of the middle finger increases as the handle diameter 2016, IRJET Impact Factor value: 4.45 ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal Page 820
3 increased up to 40 mm. Therefore middle finger and ring finger was considered during the experiment. The regression analysis was performed which showed the p- value significant (p < 0.05) for ring finger and insignificant (p > 0.05) for middle finger. This means that contribution the ring finger is more than that of middle finger when gripping. Then the regression analysis was done for single variable i.e. the ring finger. The resulting regression equation was used to find out the optimal handle dimensions. ii.phase 2 (Validation phase). Four trowels handles were fabricated using the optimal handle dimensions. The volunteers were provided with the trowel of optimized handle design and were asked to grip in their hand. The EMG muscle activity was recorded and analyzed to check the muscle fatigue. In surface EMG, for the assessment of muscle fatigue, Mean Frequency (MNF) and Median Frequency (MDF) are most useful frequency domain features. The MNF and MDF features, extracted from EMG signal are used to identify the muscle fatigue. Extensor Digitorum muscle was chosen to find out the Median Frequency (MDF) of the EMG activity. These muscles stabilize the wrist during gripping motions. The stronger the grip, the stronger the muscle (extensor digitorum) gets activated. The contact area signifies the comfort level of any object. For handles, more the contact area more will be the comfort in gripping the handle. Paint was used on the handles during the experimentation and the volunteers were asked to grip the handle and trace it on the A4 size blank paper. The contact area was compared for the commercially available handle and the ergonomically designed handle and the results were assessed. 3. RESULTS Experimentation Phase 1 NHS is stated as a function of key hand anthropometric dimensions related to the grasping and the handle size. NHS is considered as the proportion of Handle Circumference (HC) at position of ring/ middle finger to hand length (HL) at ring/middle finger. NHS (Normalized Handle Size) was termed in an approach similar to that specified by Kong, 2001and is computed as: handle circumference(mm) of handle j,nhs j is the Normalized Handle Size based on hand length measured at middle finger, NHS i is the Normalized Handle Size based on hand length measured at ring finger. These parameters are shown in Fig.1 and Fig. 2. F Fig -1. Hand length measurements for ring and middle finger Fig -2. Handle diameter and circumference of the trowel Subjective comfort rating for the grasping task was evaluated and relation between subjective comfort rating and NHS was evaluated using Minitab Software. The regression model was exercised for the relationship between the subjective comfort ratings and NHS. It was further employed to obtain the NHS maximizing the subjective comfort ratings for trowel handle. The effect of both fingers (middle and ring finger) in grasping the trowel handle was worked out using Minitab A variety of Regression analysis i.e. Linear Regression, Quadratic Regression and Cubic Regression were done. Regression data is given in Table 1. Table-1: Outcomes of linear, quadratic and cubic regression analysis NHS ij,k = HC j HL i 100 (1) where HL is the Hand Length(mm) of volunteer i, i is the subject, j is the handle, k is the subject number, HC is the Regression R- Square (%) Ring Finger p-value Middle Finger Significant factor 2016, IRJET Impact Factor value: 4.45 ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal Page 821
4 Linear Quadratic Ring Finger Cubic For Cubic Regression, the p values for both the fingers were and respectively, which were insignificant. Despite of the significant values of R-sq 74.72%, this regression was not undergone as the p- values were insignificant. For quadratic regression, the result was significant for Quadratic Regression with R 2 value 72.59%. Moreover the NHS based on the ring finger shows the p value (p=0.004) less than 0.05 which is significant than that of the middle finger for this regression model. This shows that while gripping the trowel, the ring finger contributes more as compared to middle finger. Therefore the NHS based on ring finger was considered for the design purpose. For Linear Regression undergone during experimentation, the p- values were significant but the R-sq value was 5.80%, which is very low and hence was not considered for design purpose. Quadratic Regression analysis for ring finger As from the outputs of quadratic regression model, it is clear that ring finger contributes more than the middle finger as the p-value for the ring finger came out to be significant. Therefore, ring finger was taken into consideration for the design purpose. The relationship between the subjective comfort ratings and NHS was assessed. The Quadratic Regression analysis for ring finger came out to be significant with R 2 value 72.2%. Furthermore, the NHS based on the ring finger shows the significant p-value (p<0.05) for this regression model. The relationship between subjective comfort rating and NHS that maximizes subjective comfort rating of handle comfort is shown in Figure 3. Fig -3: Relationship between subjective comfort rating and NHS During quadratic regression for ring finger, R-sq value (R-Sq = 72.2%) came out to be significant along with a significant p-value. The following regression model (Eq. (2)), representing the relationship between subjective comfort rating and NHS, was used to derive the NHS that maximizes subjective rating of handle comfort. The relation between NHS and comfort rating works out to be in form of the regression equation as: Subjective comfort rating= *(NHS) *(NHS) (2) The optimal value NHS obtained by first derivative of the Eq. (2) works out to be 53.66%, [NHS% = 0.410/ (2* )]. The Optimal NHS was used to find out the dimension of handle based upon user s hand length. The optimal NHS can be used to obtain recommended handle diameters according to the user s hand length [i.e. HandleDiameter Optimal = User s hand length*nhs Optimal /π] The various hand sizes of masons was divided into three equal ranges (i.e. small, medium and large hand) according to which the optimal handle diameters for trowel handle was assessed. Recommended handle diameters for the specified range for maximizing subjective comfort are shown in the Table-2. Table-2: Recommended handle diameters for maximizing subjective comfort Hand size Ring finger length(mm) Handle diameter (mm) Small Medium Large Handle sections for 4 volunteers were evaluated. Four participants ring finger length was noted. Handles of optimal diameter based on their ring finger lengths were fabricated (see Table-3). The trowel was fixed with the handle of optimal diameter based upon the user s hand length. 2016, IRJET Impact Factor value: 4.45 ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal Page 822
5 Table-3: Optimal handle diameters for 4 volunteers Volunteers Hand Length (mm) Handle Width (mm) Handle Depth (mm) Experimentation Phase 2 Contact area The contact area of both the trowel handles was assessed. These handles were painted and the volunteers were asked to grasp both the trowels one by one. After gripping, hand impressions on blank paper for both handles were obtained. Areas were calculated by Meshing/Triangulation technique. The results of contact area were compared for the hand impressions for both handles. It was seen that the contact area for the designed handle was more as compared to the standarddesign trowel handle. The contact areas obtained on the blank sheets for both the handles are shown in Figure 4. LEFT SIDE Impression- Using standard-design trowel RIGHT SIDE Impression- Using ergonomically designed trowel Muscle fatigue The EMG Activity during grasping of standard design handle as well as the ergonomically designed trowel handle was extracted. The muscle activity was recorded using EMG and analyzed to check the muscle fatigue.the graph between their Median Frequencies is plotted for all the 4 volunteers are in Figure 5. Figure 5(a). (Volunteer 1) Fig -4(a) Fig -4(b) Figure 5(b). (Volunteer 2) Fig -4(c) Fig -4(d) Figure 4. Experimentation for contact area The contact area for the four trowel handles of the considered four volunteers is given in Table 4. Table I: Contacts areas of both the handle Volunteers Areas (cm 2 ) Standarddesign trowel Optimally designed trowel , IRJET Impact Factor value: 4.45 ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal Page 823
6 Figure 5(d). (Volunteer 4) Figure 5(c). (Volunteer 3) Figure 5: The Graph showing the Median Frequencies on both the handles for 4 volunteers It was observed that the fatigue occurred earlier for the standard design handle the as compared to the ergonomically designed handle for all volunteers. 4. CONCLUSION From the above study carried out, the following conclusions have been made: 1. The muscle fatigue was less in case of ergonomically designed trowel handles as compared to the standard design trowels. Experimentation shows that plastering with the ergonomically designed trowel handle result in increase of perceived comfort and reduction of muscle fatigue. This means that work time for user is increased as his muscle will get fatigue later than that for the standard design trowel. This will increase the user s efficiency. 2. In the ergonomically designed trowel the contact area is more than that of the standard trowel. This shows that there is no specific point of pressure on the palm, which means that the pressure is uniformly distributed all over the palm. Therefore, the risk of injuries will be minimized. 3. As the ergonomically designed trowel handle is fabricated based upon the hand anthropometric data, the force required by muscles to grip thetrowel handle will be minimum. This also minimizes the risk of muscle fatigue. range used while plastering. Symptoms of musculoskeletal disorders may affect individuals differently so preference, comfort, and ease of use are just a few of the factors that need to be considered in order to fit the person with the right size of trowel handle. A variety of trowels should be tried out by clients prior to recommendation of a tool. A trowel handle should therefore be designed on the basis of suitable hand anthropometric parameters. This would include the hand length measured at ring finger. In future, effort would be made to consider different sections and designs of trowel handle and inclusion of additional anthropometric parameters for evaluation of dependent design parameters. Shape and surface properties (such as texture, surface roughness etc.) of trowel handle can be incorporated in the ergonomic design of trowel. REFERENCES [1] Kong, Y., Lowe, B., 2005.Optimal cylindrical handle diameter for grip force tasks. Int. J. Ind. Ergonom. 35, [2] Grant, K.A., Habes, D.J.,Steward,L.L., 1992.An analysis of handle designs for reducing manual efforts: the influence of grip diameter.. Int. J. Ind. Ergonom. 10, [3] De Looze, M., Kuijt-Evers, L., Van Dieën, J., Sitting comfort and discomfort and the relationship with objective measures. TERG Ergonomics 46, [4] Kuijt-Evers, L.F.M., Vink, P., de Looze, M.P., Comfort predictores for different kinds of hand tools :Differences and similarities. Int. J. Ind. Ergonom. 37, [5] GregorHarih, BojanDolšak, Tool-handle design based on a digital human hand model, International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, Volume 43, Issue 4 July 2013, Pages [6] Zipp, P., Recommendations for the standardization of lead positions in surface electromyography, European Journal of Applied Physiology 50, Therefore, occupational therapists should be careful when recommending a trowel that is labeled ergonomic. Not all tools that are ergonomic actually provide ergonomic benefits. Trowels need to be found for masons with physical problems that will help keep the wrist in a neutral position and decrease the amount of 2016, IRJET Impact Factor value: 4.45 ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal Page 824
Evaluation of Handle Diameter in Maximum Horizontal and Vertical Torque Tasks. Yong-Ku Kong and Brian D. Lowe
 Evaluation of Handle Diameter in Maximum Horizontal and Vertical Torque Tasks Yong-Ku Kong and Brian D. Lowe National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health Cincinnati, OH 6, USA Abstract The effects
Evaluation of Handle Diameter in Maximum Horizontal and Vertical Torque Tasks Yong-Ku Kong and Brian D. Lowe National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health Cincinnati, OH 6, USA Abstract The effects
Evaluation of handle diameters and orientations in a maximum torque task
 International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics 35 (2005) 1073 1084 www.elsevier.com/locate/ergon Evaluation of handle diameters and orientations in a maximum torque task Yong-Ku Kong, Brian D. Lowe Robert
International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics 35 (2005) 1073 1084 www.elsevier.com/locate/ergon Evaluation of handle diameters and orientations in a maximum torque task Yong-Ku Kong, Brian D. Lowe Robert
Ergonomics Glossary. Force The amount of physical effort a person uses to do a task.
 Ergonomics Glossary Administrative controls Procedures used to reduce the duration, frequency, or severity of exposure to a hazard. They may include training, job rotation, and gradual introduction to
Ergonomics Glossary Administrative controls Procedures used to reduce the duration, frequency, or severity of exposure to a hazard. They may include training, job rotation, and gradual introduction to
COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH
 COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH Purpose: To reduce fatigue of the elbow, forearm, wrist and fingers. Workers who perform forceful or repetitive grasping may benefit by performing this stretch every 2 hours.
COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH Purpose: To reduce fatigue of the elbow, forearm, wrist and fingers. Workers who perform forceful or repetitive grasping may benefit by performing this stretch every 2 hours.
Ergonomics in Sonography
 Ergonomics in Sonography Marissa Pentico, MS, OT/L Duke Ergonomics Division Occupational and Environmental Safety Office Janet Ellis, RT(R), RDMS, RVT Duke Radiology Ultrasound What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics
Ergonomics in Sonography Marissa Pentico, MS, OT/L Duke Ergonomics Division Occupational and Environmental Safety Office Janet Ellis, RT(R), RDMS, RVT Duke Radiology Ultrasound What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics
Ergonomics. Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques (EOHSS)
 Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
The Evolution of Human s? Objectives. Agenda. Defining Ergonomics. History of Ergonomics. Office Ergonomics Train the Trainer.
 Office Ergonomics Train the Trainer The Evolution of Human s? Presented By: Steve Grimmett Ergonomic Consultant Agenda Introduction to Ergonomics Form and Function of the Human Body Ergonomic Issues in
Office Ergonomics Train the Trainer The Evolution of Human s? Presented By: Steve Grimmett Ergonomic Consultant Agenda Introduction to Ergonomics Form and Function of the Human Body Ergonomic Issues in
Risk Factors and Control Measures for Musculoskeletal Injuries. Presented by: Gina Vahlas, Ergonomist Chloe Eaton, Ergonomist
 Risk Factors and Control Measures for Musculoskeletal Injuries Presented by: Gina Vahlas, Ergonomist Chloe Eaton, Ergonomist Agenda Musculoskeletal Injuries Risk factors Risk controls Tools and resources
Risk Factors and Control Measures for Musculoskeletal Injuries Presented by: Gina Vahlas, Ergonomist Chloe Eaton, Ergonomist Agenda Musculoskeletal Injuries Risk factors Risk controls Tools and resources
International Journal of Advancements in Technology ISSN
 Ergonomic evaluation of effects of handle shape and task orientation on human performance in screw driving task. Asmar Husain 1, Abid Ali Khan and Faisal Hasan Ergonomics Research Division, Department
Ergonomic evaluation of effects of handle shape and task orientation on human performance in screw driving task. Asmar Husain 1, Abid Ali Khan and Faisal Hasan Ergonomics Research Division, Department
ACGIH TLV for Hand Activity Level (HAL)
 ACGIH TLV for Hand Activity Level (HAL) 1(6) ACGIH TLV for Hand Activity Level (HAL) General description and development of the method The ACGIH HAL TLV uses HAL (Hand activity level) and peak hand forces
ACGIH TLV for Hand Activity Level (HAL) 1(6) ACGIH TLV for Hand Activity Level (HAL) General description and development of the method The ACGIH HAL TLV uses HAL (Hand activity level) and peak hand forces
Ergonomic Test of Two Hand-Contoured Mice Wanda Smith, Bob Edmiston, and Dan Cronin Global Ergonomic Technologies, Inc., Palo Alto, CA ABSTRACT
 Complete Study Available Upon Request Condensed Version Ergonomic Test of Two Hand-Contoured Mice Wanda Smith, Bob Edmiston, and Dan Cronin Global Ergonomic Technologies, Inc., Palo Alto, CA ABSTRACT A
Complete Study Available Upon Request Condensed Version Ergonomic Test of Two Hand-Contoured Mice Wanda Smith, Bob Edmiston, and Dan Cronin Global Ergonomic Technologies, Inc., Palo Alto, CA ABSTRACT A
Evaluation of handles in a maximum screwdriving torque task
 Evaluation of handles in a maximum screwdriving torque task Y. K. Kong a, B. D. Lowe b, S. J. Lee c a Department of Systems Management Engineering, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, 440-746, Korea b National
Evaluation of handles in a maximum screwdriving torque task Y. K. Kong a, B. D. Lowe b, S. J. Lee c a Department of Systems Management Engineering, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, 440-746, Korea b National
Prepared by the Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety. 5th Edition
 Prepared by the Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety 5th Edition Summary Ergonomics deals with the compatibility between workers and their work. Work is made up of the work environment, workstations,
Prepared by the Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety 5th Edition Summary Ergonomics deals with the compatibility between workers and their work. Work is made up of the work environment, workstations,
Ergonomic Risk Factors Resolved in Microelectronics Shop at Naval Air Station Jacksonville
 Ergonomic Risk Factors Resolved in Microelectronics Shop at Naval Air Station Jacksonville Ergonomics is the science of fitting the work task to the worker, instead of requiring the worker to adapt to
Ergonomic Risk Factors Resolved in Microelectronics Shop at Naval Air Station Jacksonville Ergonomics is the science of fitting the work task to the worker, instead of requiring the worker to adapt to
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings. ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders. Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
An Investigation of Hand Force Distribution, Hand Posture and Surface Orientation
 An Investigation of Hand Force Distribution, Hand Posture and Surface Orientation R. FIGUEROA and T. ARMSTRONG Department of Industrial and Operations Engineering, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI
An Investigation of Hand Force Distribution, Hand Posture and Surface Orientation R. FIGUEROA and T. ARMSTRONG Department of Industrial and Operations Engineering, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI
Department of Defense Ergonomics Working Group
 Welcome to the module. The purpose of the module is to explain the importance of ergonomics and the risks that can result when ergonomics principles are not applied to work activities. Upon completion
Welcome to the module. The purpose of the module is to explain the importance of ergonomics and the risks that can result when ergonomics principles are not applied to work activities. Upon completion
Table of Contents. 2. What are work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders?
 Table of Contents 1. Introduction O 2. What are work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders? P 3. Common types of work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders Q 4. Risk factors associated with
Table of Contents 1. Introduction O 2. What are work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders? P 3. Common types of work-related upper limb musculoskeletal disorders Q 4. Risk factors associated with
Ergonomics and Back Safety PPT-SM-BACKSFTY V.A.0.0
 Ergonomics and Back Safety 1 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomics Scientific study of equipment design for the purpose of improving efficiency, comfort and safety 2 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomic
Ergonomics and Back Safety 1 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomics Scientific study of equipment design for the purpose of improving efficiency, comfort and safety 2 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomic
ERGONOMICS in Office.
 ERGONOMICS in Office ก ก. ก What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics ก ก ก ก. ก ergonomic ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก Static vs Dynamic muscular effort ก ก vs. ก ก Dynamic Effort Static Effort What are the risks of ignoring
ERGONOMICS in Office ก ก. ก What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics ก ก ก ก. ก ergonomic ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก Static vs Dynamic muscular effort ก ก vs. ก ก Dynamic Effort Static Effort What are the risks of ignoring
Ergonomics Keeping the Worker on the Job
 Ergonomics Keeping the Worker on the Job Job Site Analysis WorkRisk Analysis WorkTask Analysis WorkStation Analysis David Raptosh, MA, OTR/L Regional Director of WorkStrategies Job Site Analysis - Identify
Ergonomics Keeping the Worker on the Job Job Site Analysis WorkRisk Analysis WorkTask Analysis WorkStation Analysis David Raptosh, MA, OTR/L Regional Director of WorkStrategies Job Site Analysis - Identify
Commonwealth Health Corporation NEXT
 Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
ERGONOMICS, BIOMECHANICS & MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDER- A REVIEW
 ERGONOMICS, BIOMECHANICS & MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDER- A REVIEW Md Shakibul Haque 1, Manoj Kumar ² 1,2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Invertis University, Bareilly, U.P., (India) ABSTRACT Through
ERGONOMICS, BIOMECHANICS & MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDER- A REVIEW Md Shakibul Haque 1, Manoj Kumar ² 1,2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Invertis University, Bareilly, U.P., (India) ABSTRACT Through
Version February 2016
 Version 3.1 29 February 2016 Health and Safety Unit 1 Table of Contents 1. Setting up your computer workstation... 3 Step 1: Adjusting yourself to the correct height... 3 Step 2 Adjusting your Chair...
Version 3.1 29 February 2016 Health and Safety Unit 1 Table of Contents 1. Setting up your computer workstation... 3 Step 1: Adjusting yourself to the correct height... 3 Step 2 Adjusting your Chair...
The Ergonomic Alternative
 The Economics Of Ergonomics What Is Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the field of study concerned with finding ways to keep people safe, comfortable, and productive while they perform tasks at work. We Refer
The Economics Of Ergonomics What Is Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the field of study concerned with finding ways to keep people safe, comfortable, and productive while they perform tasks at work. We Refer
About Humanscale Consulting Service Philosophy Engage Evaluate Plan Implement Measure Support
 About Humanscale Consulting Humanscale Consulting assists organizations with the development and implementation of cost effective ergonomics programs. Our research based training and assessment programs
About Humanscale Consulting Humanscale Consulting assists organizations with the development and implementation of cost effective ergonomics programs. Our research based training and assessment programs
Musculoskeletal Disorders of Gardening Labour Due To Hand Tools
 ISSN (e): 2250 3005 Volume, 07 Issue, 07 July 2017 International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER) Musculoskeletal Disorders of Gardening Labour Due To Hand Tools * Srivastava Supriya
ISSN (e): 2250 3005 Volume, 07 Issue, 07 July 2017 International Journal of Computational Engineering Research (IJCER) Musculoskeletal Disorders of Gardening Labour Due To Hand Tools * Srivastava Supriya
"INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS"
 PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
Muscular Skeletal Disorders
 Alabama Department of REHABILITATION SERVICES "for Alabama's children and adults with disabilities" Muscular Skeletal Disorders Michael Papp, MSE Muscular Skeletal Disorders What are MSDs? Muscles Nerves
Alabama Department of REHABILITATION SERVICES "for Alabama's children and adults with disabilities" Muscular Skeletal Disorders Michael Papp, MSE Muscular Skeletal Disorders What are MSDs? Muscles Nerves
Feel Better. Stanford University ADJUSTING YOUR WORKSTATION PROPER ERGONOMIC POSTURE. USEFUL ERGONOMIC TIPS Work Better.
 Feel Better. PROPER ERGONOMIC POSTURE ADJUSTING YOUR WORKSTATION USEFUL ERGONOMIC TIPS Work Better. Stanford University Your workspace should respond to your changing needs, helping you eliminate uncomfortable
Feel Better. PROPER ERGONOMIC POSTURE ADJUSTING YOUR WORKSTATION USEFUL ERGONOMIC TIPS Work Better. Stanford University Your workspace should respond to your changing needs, helping you eliminate uncomfortable
ERGONOMICS. Risk Management
 ERGONOMICS Risk Management ERGONOMICS-What is it? Derived from two Greek words: Nomoi meaning natural laws Ergon meaning work Hence, ergonomists study human capabilities in relationship to work demands
ERGONOMICS Risk Management ERGONOMICS-What is it? Derived from two Greek words: Nomoi meaning natural laws Ergon meaning work Hence, ergonomists study human capabilities in relationship to work demands
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every
 According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every year. For some, the problem becomes so severe that they
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every year. For some, the problem becomes so severe that they
Muscle Function Analysis
 Muscle Function Analysis LabQuest 15 Muscle tissues maintain electrical imbalances, or potentials, across cell membranes by concentrating positive or negative charges on opposite sides of those membranes.
Muscle Function Analysis LabQuest 15 Muscle tissues maintain electrical imbalances, or potentials, across cell membranes by concentrating positive or negative charges on opposite sides of those membranes.
Ergonomic Evaluation of the. PadsONMouse Product Concept
 UNITED STATES ERGONOMICS Ergonomic Evaluation of the PadsONMouse Product Concept June 19, 2009 Prepared for: Emil Jacob Jacobs Innovations LLC Prepared by: Kevin J. Costello Certified Professional Ergonomist
UNITED STATES ERGONOMICS Ergonomic Evaluation of the PadsONMouse Product Concept June 19, 2009 Prepared for: Emil Jacob Jacobs Innovations LLC Prepared by: Kevin J. Costello Certified Professional Ergonomist
International Journal on Emerging Technologies 5(2): 61-65(2014) ISSN No. (Print) : ISSN No. (Online) :
 e t International Journal on Emerging Technologies 5(2): 61-65(2014) ISSN No. (Print) : 0975-8364 ISSN No. (Online) : 2249-3255 REBA Technique on Small Scale Casting Industry Er. Girish Joshi* and Harvinder
e t International Journal on Emerging Technologies 5(2): 61-65(2014) ISSN No. (Print) : 0975-8364 ISSN No. (Online) : 2249-3255 REBA Technique on Small Scale Casting Industry Er. Girish Joshi* and Harvinder
Advanced Ergonomic Benefits of Pneumatic Scissors
 Advanced Ergonomic Benefits of Pneumatic Scissors Abstract While a certain of automation within the poultry industry has been reached, there will always be an interaction between the product, individual,
Advanced Ergonomic Benefits of Pneumatic Scissors Abstract While a certain of automation within the poultry industry has been reached, there will always be an interaction between the product, individual,
Analysis of EMG Signal to Evaluate Muscle Strength and Classification
 Analysis of EMG Signal to Evaluate Muscle Strength and Classification Kiran K. 1, Uma Rani K. 2 1MTech Student, Biomedical Signal Processing and Instrumentation, Dept. of IT, SJCE, Mysuru, Karnataka, India
Analysis of EMG Signal to Evaluate Muscle Strength and Classification Kiran K. 1, Uma Rani K. 2 1MTech Student, Biomedical Signal Processing and Instrumentation, Dept. of IT, SJCE, Mysuru, Karnataka, India
Evaluation copy. EMG and Muscle Fatigue. Computer
 EMG and Muscle Fatigue Computer 18 Voluntary muscle contraction is the result of communication between the brain and individual muscle fibers of the musculoskeletal system. A thought is transformed into
EMG and Muscle Fatigue Computer 18 Voluntary muscle contraction is the result of communication between the brain and individual muscle fibers of the musculoskeletal system. A thought is transformed into
Evaluation of Interactive Systems. Anthropometry & Anatomy
 Evaluation of Interactive Systems Anthropometry & Anatomy Caroline Appert - 2018/2019 References and Inspirations [1] Halla Olafsdottir s slides and discussions [2] http://researchguides.library.tufts.edu/
Evaluation of Interactive Systems Anthropometry & Anatomy Caroline Appert - 2018/2019 References and Inspirations [1] Halla Olafsdottir s slides and discussions [2] http://researchguides.library.tufts.edu/
IAIABC 2003 Upper Extremity Impairment Guides Part 3 of the Supplemental Impairment Rating Guides
 IAIABC 2003 Upper Extremity Impairment Guides Part 3 of the Supplemental Impairment Rating Guides Draft 11-03 IAIABC Executive Office 5610 Medical Circle, Suite 14 Madison, WI 53719 Phone: (608) 663-6355
IAIABC 2003 Upper Extremity Impairment Guides Part 3 of the Supplemental Impairment Rating Guides Draft 11-03 IAIABC Executive Office 5610 Medical Circle, Suite 14 Madison, WI 53719 Phone: (608) 663-6355
OH&S. Musculoskeletal Injury Prevention (MSIP)
 OH&S Musculoskeletal Injury Prevention (MSIP) Trainer s Guide to MSIP Supplies Needed: Slider sheet Pill crusher 2 volunteers Time required for session: 30 minutes Lifts Belts Flip chart paper Hand outs
OH&S Musculoskeletal Injury Prevention (MSIP) Trainer s Guide to MSIP Supplies Needed: Slider sheet Pill crusher 2 volunteers Time required for session: 30 minutes Lifts Belts Flip chart paper Hand outs
Repetitive Upper Limb Tasks. Introductions. ' Crown Copyright Health & Safety Laboratory. 1. Dr Lanre Okunribido: HSL Ergonomist.
 Repetitive Upper Limb s Dr Lanre Okunribido: HSL Ergonomist Introductions Sessions 1. Why repetitive upper limb tasks? 2. Common Upper Limb Disorders (ULD) and injuries? 3. 4. Introduction to the ART tool
Repetitive Upper Limb s Dr Lanre Okunribido: HSL Ergonomist Introductions Sessions 1. Why repetitive upper limb tasks? 2. Common Upper Limb Disorders (ULD) and injuries? 3. 4. Introduction to the ART tool
Resources: Ergonomic/Musculoskeletal Hazards in Patient Handling. Sustained and/or Awkward Postures. Contact Stresses or Pressures
 Resources: Ergonomic/Musculoskeletal Hazards in Patient Handling Forceful Exertions Sustained and/or Awkward Postures Repetition Gripping Contact Stresses or Pressures High Risk Patient Handling Tasks
Resources: Ergonomic/Musculoskeletal Hazards in Patient Handling Forceful Exertions Sustained and/or Awkward Postures Repetition Gripping Contact Stresses or Pressures High Risk Patient Handling Tasks
The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES (SOP) FOR COMPUTER WORK, DESK TOP General Guidelines-Best Practices: The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES (SOP) FOR COMPUTER WORK, DESK TOP General Guidelines-Best Practices: The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity
 Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity D. Mowry 1 Mowry, D. 1995. Current Development in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion
Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity D. Mowry 1 Mowry, D. 1995. Current Development in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion
Session Objectives. Business & Legal Reports, Inc. 0903
 Ofis Ergonomisi Session Objectives Define ergonomics and MSDs Identify ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up your workstation to minimize stress and strain Perform tasks safely and avoid
Ofis Ergonomisi Session Objectives Define ergonomics and MSDs Identify ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up your workstation to minimize stress and strain Perform tasks safely and avoid
13/02/2011. Ergonomics
 13/02/2011 Ergonomics Workplace Safety Electrical Safety Medical & First Aid Lockout/Tag-out Confined Space Asbestos Control Fire Prevention Personal Protective Equipment Hazard Communication Chemical
13/02/2011 Ergonomics Workplace Safety Electrical Safety Medical & First Aid Lockout/Tag-out Confined Space Asbestos Control Fire Prevention Personal Protective Equipment Hazard Communication Chemical
Introduction to Ergonomics Ergonomics (er'gõ nom'iks):
 March 10 th 2009 Construction Ergonomics Introduction to ergonomics Risk factors of MSDs Solutions to minimize risk factors Q & A Resources Yutonah Bowes, Oregon OSHA Mark Noll, SAIF Corp. Kim Rhodes,
March 10 th 2009 Construction Ergonomics Introduction to ergonomics Risk factors of MSDs Solutions to minimize risk factors Q & A Resources Yutonah Bowes, Oregon OSHA Mark Noll, SAIF Corp. Kim Rhodes,
Development and application of a hand force measurement system
 Development and application of a hand force measurement system B.D. Lowe a, Y. Kong b, and J. Han c a National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Cincinnati, OH, USA b Systems Management Engineering,
Development and application of a hand force measurement system B.D. Lowe a, Y. Kong b, and J. Han c a National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, Cincinnati, OH, USA b Systems Management Engineering,
Corporate Safety Manual. Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics
 Corporate Safety Manual Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics Last updated: April 2015 Office Ergonomics Chapter 8: Office Ergonomics Index Page Introduction to Ergonomics...8-3 Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders
Corporate Safety Manual Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics Last updated: April 2015 Office Ergonomics Chapter 8: Office Ergonomics Index Page Introduction to Ergonomics...8-3 Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders
2/28/2017. EMC Insurance Companies Risk Improvement Department. Ergonomics for School Districts. Objectives. What is Ergonomics?
 Ergonomics for School Districts February 28, 2017 Dave Young, CSP EMC Insurance Companies Objectives Define ergonomics and its effect on the workplace Discuss ergonomic risk factors Review the preferred
Ergonomics for School Districts February 28, 2017 Dave Young, CSP EMC Insurance Companies Objectives Define ergonomics and its effect on the workplace Discuss ergonomic risk factors Review the preferred
"LABORATORY ERGONOMICS"
 MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "LABORATORY ERGONOMICS" Part of the "LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES" Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow Outline of Major Points Covered in the "Laboratory Ergonomics"
MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "LABORATORY ERGONOMICS" Part of the "LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES" Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow Outline of Major Points Covered in the "Laboratory Ergonomics"
Office Ergonomics. Presented by: Samar Khalil, Environmental & Chemical Safety Officer
 Office Ergonomics Presented by: Samar Khalil, Environmental & Chemical Safety Officer Objectives Define Ergonomics & MSDs Identify Ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up workstations to minimize
Office Ergonomics Presented by: Samar Khalil, Environmental & Chemical Safety Officer Objectives Define Ergonomics & MSDs Identify Ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up workstations to minimize
Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis
 Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis Ergonomics is the study of the relationship between people and their environment. In the workplace, ergonomics is the science of designing or redesigning the
Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis Ergonomics is the study of the relationship between people and their environment. In the workplace, ergonomics is the science of designing or redesigning the
Ergonomics in General Industry
 Ergonomics in General Industry Any job requires physical movement Some tasks may be repetitious and may require you to stand or sit for extended periods Jobs in the industrial environment can be physically
Ergonomics in General Industry Any job requires physical movement Some tasks may be repetitious and may require you to stand or sit for extended periods Jobs in the industrial environment can be physically
Reducing Computer Workstation Hazards Through Proper Set-up and Design
 PPT Presentation page 1 Reducing Computer Workstation Hazards Through Proper Set-up and Design Presented by the NYS Public Employees Federation Paige Engelhardt PEF Health & Safety Trainer www.pef.org
PPT Presentation page 1 Reducing Computer Workstation Hazards Through Proper Set-up and Design Presented by the NYS Public Employees Federation Paige Engelhardt PEF Health & Safety Trainer www.pef.org
Operator tooling for the Touch-up Procedure
 Operator tooling for the Touch-up Procedure Current State Current Process: After the printing process is complete part of the gold ink is not connected and the operator is required to touch-up this portion
Operator tooling for the Touch-up Procedure Current State Current Process: After the printing process is complete part of the gold ink is not connected and the operator is required to touch-up this portion
GENERAL EXERCISES THUMB, WRIST, HAND BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017
 GENERAL EXERCISES THUMB, WRIST, HAND BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017 Disclosure: The exercises, stretches, and mobilizations provided in this presentation are for educational purposes only
GENERAL EXERCISES THUMB, WRIST, HAND BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017 Disclosure: The exercises, stretches, and mobilizations provided in this presentation are for educational purposes only
Preventing Work-related Injuries Among Sonographers
 Preventing Work-related Injuries Among Sonographers Carolyn T. Coffin, MPH, RDMS, RVT, RDCS, FSDMS Joan P. Baker, MSR, RDMS, RDCS, FSDMS Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WRMSD) have been reported
Preventing Work-related Injuries Among Sonographers Carolyn T. Coffin, MPH, RDMS, RVT, RDCS, FSDMS Joan P. Baker, MSR, RDMS, RDCS, FSDMS Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WRMSD) have been reported
260- OFFICE ERGONOMICS
 260.1 PURPOSE A. To provide some universally applicable suggestions and procedures that may be helpful when setting up an ergonomically correct work station in an office setting. 260.2 SCOPE A. This procedure
260.1 PURPOSE A. To provide some universally applicable suggestions and procedures that may be helpful when setting up an ergonomically correct work station in an office setting. 260.2 SCOPE A. This procedure
Beginning of Process: Development of the Office Ergonomics program.
 CNM WAY PROCESS CNM Process Name Office Ergonomics Program (05/15/2018 Revision) Overview of Office Ergonomics Program Purpose: To provide applicable suggestions and procedures that may be help reduce
CNM WAY PROCESS CNM Process Name Office Ergonomics Program (05/15/2018 Revision) Overview of Office Ergonomics Program Purpose: To provide applicable suggestions and procedures that may be help reduce
ERGONOMIC STUDY ON THE VARIER MOVE CHAIR
 ERGONOMIC STUDY ON THE VARIER MOVE CHAIR TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION AND OBJECTIVE... 3 INTRODUCTION AND OBJECTIVE... 3 METHODOLOGY... 5 METHODOLOGY... 5 1A) INFORMATION FOR USERS...5 1A) INFORMATION
ERGONOMIC STUDY ON THE VARIER MOVE CHAIR TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION AND OBJECTIVE... 3 INTRODUCTION AND OBJECTIVE... 3 METHODOLOGY... 5 METHODOLOGY... 5 1A) INFORMATION FOR USERS...5 1A) INFORMATION
College of Public Health and Human Sciences Occupational Safety and Ergonomics
 College of Public Health and Human Sciences Occupational Safety and Ergonomics Laurel Kincl, PhD, Assistant Professor Brittany Heller, MPH student Environmental and Occupational Health Outline of seminar
College of Public Health and Human Sciences Occupational Safety and Ergonomics Laurel Kincl, PhD, Assistant Professor Brittany Heller, MPH student Environmental and Occupational Health Outline of seminar
CS, IT Occupational Hazard
 CS, IT Occupational Hazard Ergonomics 1 485 patients average age of 38.5 years. 63% females. 70% computer users, 28% musicians, 2% were others engaged in repetitive work. A majority sought care within
CS, IT Occupational Hazard Ergonomics 1 485 patients average age of 38.5 years. 63% females. 70% computer users, 28% musicians, 2% were others engaged in repetitive work. A majority sought care within
The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person
 OFFICE ERGONOMICS The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person What is Ergonomics? By the end of this chapter, You will be able to: Demonstrate a general knowledge of office ergonomics Identify
OFFICE ERGONOMICS The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person What is Ergonomics? By the end of this chapter, You will be able to: Demonstrate a general knowledge of office ergonomics Identify
Ergonomics. MSD Injury Prevention
 Ergonomics MSD Injury Prevention Ergonomics Definition The International Ergonomics Association offers a very comprehensive definition: The scientific discipline concerned with the understanding of interactions
Ergonomics MSD Injury Prevention Ergonomics Definition The International Ergonomics Association offers a very comprehensive definition: The scientific discipline concerned with the understanding of interactions
CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
 WHAT IS CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME? SYMPTOMS Cubital tunnel syndrome is the second most commonly occurring nerve compression in the upper body It is caused by compression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow The
WHAT IS CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME? SYMPTOMS Cubital tunnel syndrome is the second most commonly occurring nerve compression in the upper body It is caused by compression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow The
Ergonomics. For additional assistance, contact the Occupational Safety office to schedule an evaluation.
 Ergonomics 1. Purpose: Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Safety and Risk and Risk Management (SRM) developed this program to improve the health and happiness of it s employees by assisting
Ergonomics 1. Purpose: Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Safety and Risk and Risk Management (SRM) developed this program to improve the health and happiness of it s employees by assisting
Carpal tunnel syndrome
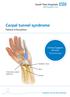 Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Reference Material Searched and Brought to you
 Reference Material Searched and Brought to you by While requesting for additional reference material, always mention Title and Reference of the document. Please ensure you provide your name, company email
Reference Material Searched and Brought to you by While requesting for additional reference material, always mention Title and Reference of the document. Please ensure you provide your name, company email
Deborah Ruediger, ASAR, DipHlthSc, MHlthSc Manager Non-Invasive Cardiology Lab Heart Centre King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre
 Deborah Ruediger, ASAR, DipHlthSc, MHlthSc Manager Non-Invasive Cardiology Lab Heart Centre King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre 1 No Disclosures 2 Musculoskeletal Injury (MSI) refers to damage
Deborah Ruediger, ASAR, DipHlthSc, MHlthSc Manager Non-Invasive Cardiology Lab Heart Centre King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre 1 No Disclosures 2 Musculoskeletal Injury (MSI) refers to damage
Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03
 Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03 Working from home is becoming more of an option for employees today. The type of work usually entails working from the home computer work station.
Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03 Working from home is becoming more of an option for employees today. The type of work usually entails working from the home computer work station.
Save Your Wrists 2002 Lawrence Gold, certified Hanna somatic educator
 Save Your Wrists 2002 Lawrence Gold, certified Hanna somatic educator Is wrist pain starting to interfere with your work? Wonder why? Here s an answer: You get better at what you practice. Every time you
Save Your Wrists 2002 Lawrence Gold, certified Hanna somatic educator Is wrist pain starting to interfere with your work? Wonder why? Here s an answer: You get better at what you practice. Every time you
Dimensional Requirements. Minimum space requirements for passageways and hallways.
 Dimensional Requirements Minimum space requirements for passageways and hallways. Dimensional Requirements Minimum access openings from MIL-HDBK 759. Dimensional Requirements Minimum access openings to
Dimensional Requirements Minimum space requirements for passageways and hallways. Dimensional Requirements Minimum access openings from MIL-HDBK 759. Dimensional Requirements Minimum access openings to
ELECTROMYOGRAM ANALYSIS OF MUSCLE FUNCTION INTRODUCTION
 ELECTROMYOGRAM ANALYSIS OF MUSCLE FUNCTION STANDARDS: 3.3.10.B - Explain cell functions and processes in terms of chemical reactions and energy changes. 3.3.12.B - Evaluate relationships between structure
ELECTROMYOGRAM ANALYSIS OF MUSCLE FUNCTION STANDARDS: 3.3.10.B - Explain cell functions and processes in terms of chemical reactions and energy changes. 3.3.12.B - Evaluate relationships between structure
Hand discomfort in production assembly workers
 Agronomy Research 11 (2), 407 412, 2013 Hand discomfort in production assembly workers K. Jansen¹,*, M. Luik², M. Reinvee², V. Viljasoo², J. Ereline¹, H. Gapeyeva¹ and M. Pääsuke¹ ¹Institute of Exercise
Agronomy Research 11 (2), 407 412, 2013 Hand discomfort in production assembly workers K. Jansen¹,*, M. Luik², M. Reinvee², V. Viljasoo², J. Ereline¹, H. Gapeyeva¹ and M. Pääsuke¹ ¹Institute of Exercise
LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2955 LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics Leader s Guide Marcom Group Ltd. 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2955 LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics Leader s Guide Marcom Group Ltd. 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in
NHS Buckinghamshire Musculoskeletal Integrated Care Service (MusIC) Carpal tunnel syndrome
 NHS Buckinghamshire Musculoskeletal Integrated Care Service (MusIC) Carpal tunnel syndrome What is carpal tunnel? The carpal tunnel refers to an area at the base of the wrist which contains bones, nerves,
NHS Buckinghamshire Musculoskeletal Integrated Care Service (MusIC) Carpal tunnel syndrome What is carpal tunnel? The carpal tunnel refers to an area at the base of the wrist which contains bones, nerves,
What We Do To Reduce Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders and Injuries at Occupational Ergonomics and Biomechanics (OEB) Laboratory
 What We Do To Reduce Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders and Injuries at Occupational Ergonomics and Biomechanics (OEB) Laboratory Jay Kim, PhD, MS Assistant Professor Environmental & Occupational Health
What We Do To Reduce Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders and Injuries at Occupational Ergonomics and Biomechanics (OEB) Laboratory Jay Kim, PhD, MS Assistant Professor Environmental & Occupational Health
PLEASE SCROLL DOWN FOR ARTICLE
 This article was downloaded by:[2007 Sung Kyun Kwan University Science Lib] On: 4 October 2007 Access Details: [subscription number 769136873] Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England
This article was downloaded by:[2007 Sung Kyun Kwan University Science Lib] On: 4 October 2007 Access Details: [subscription number 769136873] Publisher: Taylor & Francis Informa Ltd Registered in England
OPNAVINST G 30 Dec 05
 Appendix 23-B Computer Workstation Checklist The computer workstation checklist is one method available for performing computer workstation assessments. The checklist is designed to be printed as two double-sided
Appendix 23-B Computer Workstation Checklist The computer workstation checklist is one method available for performing computer workstation assessments. The checklist is designed to be printed as two double-sided
Strength and conditioning specialists are continually
 THE INFLUENCE OF BAR DIAMETER ON NEUROMUSCULAR STRENGTH AND ACTIVATION: INFERENCES FROM AN ISOMETRIC UNILATERAL BENCH PRESS DOUGLAS FIORANELLI AND C. MATTHEW LEE Exercise Physiology Laboratory, Department
THE INFLUENCE OF BAR DIAMETER ON NEUROMUSCULAR STRENGTH AND ACTIVATION: INFERENCES FROM AN ISOMETRIC UNILATERAL BENCH PRESS DOUGLAS FIORANELLI AND C. MATTHEW LEE Exercise Physiology Laboratory, Department
Enhancing Safety Through Ergonomics
 Enhancing Safety Through Ergonomics Targeting Risk Factors Definition of Risk Factors: Actions or conditions found to contribute to worker discomfort or development of Musculoskeletal Disorders MAIN RISK
Enhancing Safety Through Ergonomics Targeting Risk Factors Definition of Risk Factors: Actions or conditions found to contribute to worker discomfort or development of Musculoskeletal Disorders MAIN RISK
CMTM10 INVESTIGATION ON UPPER LIMB AND LOWER BACK MUSCLES ACTIVITIES DURING SEDENTARY WORK.
 CMTM10 INVESTIGATION ON UPPER LIMB AND LOWER BACK MUSCLES ACTIVITIES DURING SEDENTARY WORK. Nurhayati Mohd Nur 1, Siti Zawiah Md Dawal 2 1 University of Kuala Lumpur-MIAT, Jenderam Hulu, 43800 Dengkil,
CMTM10 INVESTIGATION ON UPPER LIMB AND LOWER BACK MUSCLES ACTIVITIES DURING SEDENTARY WORK. Nurhayati Mohd Nur 1, Siti Zawiah Md Dawal 2 1 University of Kuala Lumpur-MIAT, Jenderam Hulu, 43800 Dengkil,
Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue
 Anatomy & Physiology Foothill High School Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of individual muscle fibers (see Figure 1) and has unique properties which allow it to
Anatomy & Physiology Foothill High School Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of individual muscle fibers (see Figure 1) and has unique properties which allow it to
Ergonomics and Risk Factor Awareness
 Ergonomics and Risk Factor Awareness PART 1 Objectives To gain an understanding of: What is ergonomics How cumulative trauma disorders develop Ergonomic risk factors Controlling risk factors To gain an
Ergonomics and Risk Factor Awareness PART 1 Objectives To gain an understanding of: What is ergonomics How cumulative trauma disorders develop Ergonomic risk factors Controlling risk factors To gain an
Contents INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND 1. SECTION 1 Data collection methodology 2
 Contents Page No INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND 1 SECTION 1 Data collection methodology 2 SECTION 2 5 DATASHEETS. 1. Push and pull strength 5 2. Push with the thumb or 2 or more fingers 11 3. Push with the
Contents Page No INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND 1 SECTION 1 Data collection methodology 2 SECTION 2 5 DATASHEETS. 1. Push and pull strength 5 2. Push with the thumb or 2 or more fingers 11 3. Push with the
Fleet Readiness Center (FRC) East Uses Lazy Susan Design to Prevent Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders
 Fleet Readiness Center (FRC) East Uses Lazy Susan Design to Prevent Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Fleet Readiness Center (FRC) East in Cherry Point, NC is one of six fleet readiness centers operated
Fleet Readiness Center (FRC) East Uses Lazy Susan Design to Prevent Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Fleet Readiness Center (FRC) East in Cherry Point, NC is one of six fleet readiness centers operated
Ergonomics: Why do workers get injured? Presented by: Steve Bilan Ergonomic Specialist
 Ergonomics: Why do workers get injured? Presented by: Steve Bilan Ergonomic Specialist What do you know about Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the study of designing equipment and devices that fit the human body,
Ergonomics: Why do workers get injured? Presented by: Steve Bilan Ergonomic Specialist What do you know about Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the study of designing equipment and devices that fit the human body,
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Q: What is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)? A: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the name for a group of problems that includes swelling, pain, tingling, and loss of strength in your
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Q: What is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)? A: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the name for a group of problems that includes swelling, pain, tingling, and loss of strength in your
Ergonomics and the Farm. Keri A. Gill-Smith, Physical Therapist
 Ergonomics and the Farm Keri A. Gill-Smith, Physical Therapist Farm Injury Rates Farming involves hard physical work Every day about 167 agricultural workers suffer a lost-work-time injury From 2008-2010,
Ergonomics and the Farm Keri A. Gill-Smith, Physical Therapist Farm Injury Rates Farming involves hard physical work Every day about 167 agricultural workers suffer a lost-work-time injury From 2008-2010,
BIO 360: Vertebrate Physiology Lab 8b: Electrical activity of muscular contractions
 Lab report DUE 3/19 Muscle tissues maintain electrical imbalances, or potentials, across cell membranes by concentrating positive or negative charges on opposite sides of those membranes. These potentials
Lab report DUE 3/19 Muscle tissues maintain electrical imbalances, or potentials, across cell membranes by concentrating positive or negative charges on opposite sides of those membranes. These potentials
Ergonomics Application to Work Design on Seafood Processing Line
 Ergonomics Application to Work Design on Seafood Processing Line Chung Van Nguyen Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering International University-Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh City,
Ergonomics Application to Work Design on Seafood Processing Line Chung Van Nguyen Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering International University-Vietnam National University, Ho Chi Minh City,
Hand-Arm Vibration. Table 1 Stages of Vibration White Finger (Taylor-Pelmear System)
 Physical Agent Data Sheet (PADS) Description Hand-Arm Vibration Hand-arm vibration is caused by the use of vibrating hand-held tools, such as pneumatic jack hammers, drills, gas powered chain saws, and
Physical Agent Data Sheet (PADS) Description Hand-Arm Vibration Hand-arm vibration is caused by the use of vibrating hand-held tools, such as pneumatic jack hammers, drills, gas powered chain saws, and
Technical Report. New Ergonomic Design Criteria for Handles of Laparoscopic Dissection Forceps ABSTRACT
 JOURNAL OF LAPAROENDOSCOPIC & ADVANCED SURGICAL TECHNIQUES Volume 11, Number 1, 2001 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Technical Report New Ergonomic Design Criteria for Handles of Laparoscopic Dissection Forceps
JOURNAL OF LAPAROENDOSCOPIC & ADVANCED SURGICAL TECHNIQUES Volume 11, Number 1, 2001 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Technical Report New Ergonomic Design Criteria for Handles of Laparoscopic Dissection Forceps
PURPOSE To provide the tools to set up and maintain a healthy office workspace & environment
 Office Ergonomics PURPOSE To provide the tools to set up and maintain a healthy office workspace & environment WHAT IS A GOOD POSTURE? OFFICE SETUP CHAIR WORK SURFACE INPUT DEVICES MONITOR ACCESSORIES
Office Ergonomics PURPOSE To provide the tools to set up and maintain a healthy office workspace & environment WHAT IS A GOOD POSTURE? OFFICE SETUP CHAIR WORK SURFACE INPUT DEVICES MONITOR ACCESSORIES
Workstation Design in Medical Device Manufacturing
 Workstation Design in Medical Device Manufacturing Rachel Michael, CPE, CHSP Senior Consultant Ergonomics Thought Leadership Aon Risk Solutions Global Risk Consulting Casualty Risk Consulting m: +1.385.230.5838
Workstation Design in Medical Device Manufacturing Rachel Michael, CPE, CHSP Senior Consultant Ergonomics Thought Leadership Aon Risk Solutions Global Risk Consulting Casualty Risk Consulting m: +1.385.230.5838
EVALUATION AND MEASUREMENTS. I. Devreux
 EVALUATION AND MEASUREMENTS I. Devreux To determine the extent and degree of muscular weakness resulting from disease, injury or disuse. The records obtained from these tests provide a base for planning
EVALUATION AND MEASUREMENTS I. Devreux To determine the extent and degree of muscular weakness resulting from disease, injury or disuse. The records obtained from these tests provide a base for planning
Uneo Collection. Design by Martin Ballendat
 Uneo Collection Design by Martin Ballendat The perfect dynamic chair for weighty work. Uneo is a self-adjusting, high-performance task chair that dynamically responds to your body weight. Its durable frame
Uneo Collection Design by Martin Ballendat The perfect dynamic chair for weighty work. Uneo is a self-adjusting, high-performance task chair that dynamically responds to your body weight. Its durable frame
