TESTING THE EFFICIENCY AND EFFECTIVENESS OF SOLDIER PERFORMANCE UNDER INCREASING TASK DEMAND
|
|
|
- Darlene Lynette Banks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PROCEEDINGS of the HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 49th ANNUAL MEETING TESTING THE EFFICIENCY AND EFFECTIVENESS OF SOLDIER PERFORMANCE UNDER INCREASING TASK DEMAND K.A. Burke, J. Szalma, T. Oron-Gilad, A. Duley, and P.A. Hancock University of Central Florida Orlando, FL Combat is inherently a demanding situation which may increase stress, heighten arousal, and increase anxiety. The Processing Efficiency Theory (PET) was specifically developed to account for how anxiety influences performance. Therefore, the PET provides a potential theory to explain the positive and negative changes in performance in a combat environment. This study is the first attempt to examine PET in the military domain. Using the Small Arms Simulator Testbed (SAST), we investigated the relationship between processing efficiency and performance, considering mental workload, stress, and anxiety effects. Shooting performance effectiveness measures were target acquisition and friend/foe discrimination. Changes in processing efficiency were manipulated by varying degrees of working memory demand and sustained information transfer. The results indicated that shooting performance and processing efficiency, as well as mental workload demands, decreased as the global demand of both tasks increased. Further analyses for anxiety and stress and future directions are discussed. INTRODUCTION Combat is inherently a demanding situation which may increase stress, heighten arousal, and increase anxiety especially when the outcome is important and uncertain (Jones & Swain, 1995). Additionally, in a combat environment, maintaining a high level of performance, both of cognitive skills (i.e., decision making tasks) and motor skills (i.e., shooting accurately) is critical and may mean the difference between life and death. Although the relationship between anxiety and performance has been investigated extensively (Eysenck & Calvo, 1992; Yerkes & Dodson, 1908), the mechanisms underlying the facilitative or debilitative effects of anxiety on performance are not yet clearly understood. The Processing Efficiency Theory (PET; Eysenck & Calvo, 1992) was specifically developed to account for how anxiety influences performance. Traditionally, anxiety has been considered detrimental to performance, however a significant body of literature suggests that anxiety has both facilitative and debilitative functions (e.g., Jones, Hanton, & Swain, 1994; Jones & Swain, 1992; Jones, Swain, & Hardy, 1993). The PET (Eysenck & Calvo) seeks to explain how individual differences in trait anxiety interact with variations in state anxiety and attentional mechanisms to affect performance. The PET has primarily been applied to the examination of test anxiety (Eysenck, 1996), but the theory is broad enough to have wide application in other domains. In spite of its potentially broad applicability, the theory has not been empirically validated in other domains (Woodman & Hardy, 2001) with the exception of one study in the sport psychology domain (Murray & Janelle, 2003). As far as we know, our study is the first to investigate the PET in the military domain and in a high fidelity environment. The SAST II (Small Arms Simulator Testbed II) is a high fidelity simulation allowing for superior assessment of shooting performance in simulation. In this study the SAST II was utilized to test hypotheses based on PET. In many instances performance on a primary task may be maintained in the face of anxiety or stress only at the cost of increased effort. That is, performance may remain effective but less efficient. Primary task performance may therefore mask detrimental effects of anxiety and stress. The aim of the current study was to identify changes in processing efficiency under varying degrees of working memory demand and sustained information transfer and to examine the interaction between taskrelated stress. METHOD Participants Thirty-eight participants (mean age = 20.4, SD = 4.6, range = 18-43) were recruited on a voluntary basis from undergraduate psychology classes at the University
2 PROCEEDINGS of the HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 49th ANNUAL MEETING of Central Florida and were paid $22.50 for their participation (based on an hourly rate of $7.50). Materials Questionnaires. Participants completed several subjective questionnaires to measure individual differences including workload, stress, and anxiety. All subjective measures were administered via Inquisit, psychological data collection software, on a Dell Inspiron Experimental Tasks Primary Task. Target acquisition task and a Friend/foe discrimination task: two different types of stimuli/targets appeared on the screen (Figure 1): the non-target was an M-16 (friend), the target was an AK- 47 (foe); both stimuli/targets were superimposed over the silhouette stimulus; the discrimination was based upon the weapon. The spatial location of each stimulus (targets/non-targets) was randomly generated to prevent the predictability of the appearance of a target. pressed in response to the presentation of a valid cue word and true association word, the second trigger was pressed in response to the presentation of a valid cue word and false association word, and the third trigger was pressed in response to an invalid cue word. Apparatus Small Arms Simulator Testbed II (SAST II). (Naval Air Warfare Center Training Systems Division, 2000) is a single user research testbed for the evaluation and study of both current and new weapon concepts. The SAST controlled the presentation of targets (target type, location, time of onset, and exposure time), and recorded weapon aim-point data and shot results from an M16 rifle equipped with an infrared emitting diode and collimator lens. Weapon recoil was simulated with an electromechanical recoil system and weapon sounds were simulated via digital audio surroundsound (as shown in Figure 2). AK47 M16 Figure 1. Screenshot from the SAST II displaying the two types of targets superimposed on the silhouette stimuli. Secondary Task. Memory recall task: consisted of the auditory presentation of cue words and association words which simulated unit battalion numbers (e.g., 21, 23, 27) and locations (north, south, east, west), respectively, and were designed to provide varying demands on working memory. There were three secondary task conditions which varied according to working memory task demand, these being zero (control condition), and two or four items to be retained in memory. During execution of the primary task the participant was presented with the secondary task. The participants responded to the secondary task stimuli via three triggers mounted to the weapon. One trigger was Figure 2. The SAST II facility including the weapon and the visual display. LabVIEW 7.0. (National Instruments, 2004). LabVIEW is a graphical development environment for creating flexible and scalable test, measurement, and control applications rapidly and at minimal cost. For the current study, LabVIEW was used to integrate the SAST II system, and the presentation of the secondary task. Design Overview The dependent measures of interest were: 1) response time for the primary task (mean response time participants required to pull the trigger on the weapon after the appearance of the targets); 2) response time for the secondary task (mean response time participants required to press a trigger in response to the secondary
3 PROCEEDINGS of the HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 49th ANNUAL MEETING task stimuli); 3) shooting accuracy; 4) accuracy on the secondary task; and 5) subjective measures. The experiment included the following withinparticipant factors: 1) presentation of secondary task (present, not present); 2) increasing levels of working memory demand tasks (recognition/recall; three levels); and 3) friend/foe discrimination task (half of the trials included a target (foe), half of the trials did not include a target. Procedure Each participant was randomly assigned to one of the three working memory presentation orders, with the constraint that an equal number of participants were tested in each order. For each participant, the sand bags enabling a seated, supported firing position were adjusted for differences in height, the weapon was calibrated for accurate tracking and aiming vectors, and the triggers attached to the weapon (to allow the participant to respond to the secondary task stimuli) were adjusted for handedness and finger position. The participants received training and practice so that they would become familiar with firing the weapon, identifying the targets, and the secondary task. Each session (approximately three hours) consisted of administration of the subjective measures, training and practice on both the primary and secondary tasks, and of the presentation of the three conditions of the secondary task. Each participant completed shooting scenarios for each condition of the secondary task (each working memory demand condition) which consisted of four blocks of 16 trials totaling 64 trials per working memory condition. Each trial consisted of the simultaneous presentation of one of two types of target stimuli (target, or non-target) and in half of the trials, the presentation of the secondary task. The trials were organized such that each participant was presented with an equal number of trials which included: the secondary task with an enemy target, secondary task without an enemy target, no secondary task with an enemy target, and no secondary task without an enemy target. The presentation of trials within each working memory demand condition was randomized so that each condition was presented to each participant an equal number of times. Additionally, the order of presentation of each working memory demand condition (0, 2, and 4) was counterbalanced. Following each block, participants completed the RSME and between conditions, participant received a five-minute break. RESULTS Primary Task Performance. A two-way 2(secondary task present or not ) X 3(working memory (0,2, and 4)) within-participants repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted on performance in the friend/foe discrimination primary shooting task. The independent variables consisted of presentation of the secondary task in which the battalion number and location combinations were presented to the participant and varying levels of working memory demand. The dependent variable was the percent correct (number of times the participant correctly identified and hit the target) at each level of working memory demand. The main effect of presence of the secondary task and working memory demand on shooting performance was not statistically significant, Wilk s Λ =.98, F (1, 36) =.38, p =.69, partial η 2 =.11, and Wilk s Λ =.99, F(1, 36) =.03, p =.87, partial η 2 =.001, respectively. However, as depicted in Figure 3, in working memory conditions 0 and 2, participants were more accurate in the shooting task when there was no secondary task than when the secondary task was present. This was not the case in working memory condition 4; possibly due to the combination of practice and fatigue effects. Percent Corre Secondary Task No task Figure 3. Relationship between presence of the secondary task and working memory demand. Secondary Task Performance. A two-way 2(primary task target present or not) X 2(working memory demand (2, 4)) within-participants repeated measures ANOVA was conducted on secondary task performance (percent correct-- number of times the participant correctly recognized and responded to the presentation of the battalion number and azimuth location). There was a significant main effect of presence of a target and working memory demand, Wilk s Λ =.61, F (1, 18) = 11.47, p =.003, partial η 2 =.39, and Wilk s Λ =.76, F(1, 18) = 5.61, p =.03, partial η 2 =.61, respectively. These results show that participants were significantly more accurate on the recognition task when there was not a
4 PROCEEDINGS of the HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 49th ANNUAL MEETING target present than when a target was present and when the working memory demand level was two (see Figure 4). Percent Corre Target No target Figure 4. Relationship between the presence of a target and working memory demand. Perceived Workload. A 3(working memory demand) X 4(block) within-participants repeated measures ANOVA was conducted on the subjective ratings of mental workload (RSME). There was a significant main effect of working memory demand and block, Wilk s Λ =.35, F (2, 31) = 29.32, p =.001, partial η 2 =.65, and Wilk s Λ =.55, F(3, 31) = 8.08, p =.001, partial η 2 =.45, respectively. Specifically, participants reported that a higher level of mental effort was required as a function of working memory demand; as the working memory demand increased, the ratings of mental effort increased (see Figure 5). Additionally, and consistent with our hypotheses, participants reported that a lower level of mental effort was required as a function of time in each working memory demand condition. Correct Block 1 Block 2 Block 3 Block 4 Figure 5. Relationship between subjective mental effort and working memory demand. DISCUSSION This study is the first to investigate processing efficiency in a military context and in a high fidelity simulator. The use of a high fidelity simulator is important in this case because the target aiming and target acquisition task are performed using a real weapon which adds to the physical and the hand-eye coordination demands of the task. As can be seen from the results there are changes in performance for both the primary and the secondary task as the global demands change, clearly indicating that it is not the case of one task dominating the other. However, contrary to our hypothesis, when the task was most demanding (both primary and secondary tasks were present in the highest working memory demand condition), participants were more accurate on the shooting task when the secondary was present than when there was no secondary task. One possible explanation for these results is that there were combined practice and fatigue effects. Hence, the variability among participants increased, and possibly the analysis of the anxiety data could contribute to the understanding of these changes. Additionally, because participants were significantly less accurate on the recognition task in the same high demand condition, it is possible that participants stopped attending to the secondary task and focused all of their attention on the primary, more salient shooting task. This would be consistent with the Hancock and Warm (1989) model indicating that participants were no longer in their comfort zone and were unable to maintain an optimal level of performance on both tasks. Furthermore, such pattern could also be explained using Hockey s (1997) compensatory control model. Specifically, it may be that as attentional demand increased participants regulated their effort downward on the secondary task to free resources required to successfully engage the primary task. Furthermore, the mental workload measures correlate with this global demand, indicating a performance-workload association (Hancock, 1996; Yeh & Wickens, 1988). Further investigations of this relationship are necessary. Current efforts are underway to examine the hypothesized effects of trait anxiety on performance and perceived workload. In addition, the other form of workload assessment, physiological measurement, will be examined to test whether there is physiological evidence that participants reduced their effort in the face of high working memory demand. These analyses will provide a more coherent understanding of the results. Future studies will be able to refine these findings and better explain the tradeoff in performance as task demand increases.
5 PROCEEDINGS of the HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 49th ANNUAL MEETING ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The views expressed in this work are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect official Army policy. This work was supported by the DoD Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative (MURI) program administered by the Army Research Office under grant DAAD , Peter A. Hancock, Principal Investigator. REFERENCES Baddeley, A.D. (1986). Working memory. Oxford, UK: Clarendon Press. Eysenck, M.W. (1996). Anxiety, processing efficiency theory and performance. In W. Battmann & S. Duke (Eds.), Processes of the molar regulation of behavior (pp ). Scottsdale, AZ: Pabst Science Publishing. Eysenck, M.W., & Calvo, M.G. (1992). Anxiety and performance: The processing efficiency theory. Cognition and Emotion, 6, Hockey, R.G. (1997). Compensatory control in the regulation of human performance under stress and high workload: A cognitive-energetical framework. Biological Psychology, 45(1-3), Hancock, P.A., & Warm, J.S. (1989). A dynamic model of stress and sustained attention. Human Factors, 31(5), Jones, G., & Swain, A.B.J. (1992). Intensity and direction dimensions of competitive state anxiety and relationships with competitiveness. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 74, Jones, G., Swain, A.B.J., & Hardy, L. (1993). Intensity and direction dimensions of competitive state anxiety and self-confidence. Journal of Sports Sciences, 11, Woodman, T. & Hardy, L. (2001). A case study of organizational stress in elite sport. Journal of Applied Sport Psychology, 13(2), Yeh, Y., & Wickens, C.D. (1988). Dissociation of performance and subjective measures of workload. Human Factors, 30(1), Yerkes, R.M., & Dodson, J.D. (1908). The relation of strength of stimulus to rapidity of habit formation. Journal of Comparative Neurology & Psychology, 18, Zijlstra, F.R.H. (1993). Efficiency in work behavior. A design approach for modern tools. PhD thesis, Delft University of Technology. Delft, The Netherlands: Delft University Press. Zijlstra, F.R.H. & Van Doorn, L. (1985). The construction of a scale to measure perceived effort. Delft, The Netherlands: Department of Philosophy and Social Sciences, Delft University of Technology.
PERFORMANCE OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS FOR SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL DISCRIMINATIONS: COMMON OR SEPARATE CAPACITIES?
 PROCEEDINGS of the HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 8th ANNUAL MEETING 88 PERFORMANCE OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS FOR SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL DISCRIMINATIONS: COMMON OR SEPARATE CAPACITIES? J. E. Thropp,
PROCEEDINGS of the HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 8th ANNUAL MEETING 88 PERFORMANCE OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS FOR SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL DISCRIMINATIONS: COMMON OR SEPARATE CAPACITIES? J. E. Thropp,
APPLICATION OF FUZZY SIGNAL DETECTION THEORY TO VIGILANCE: THE EFFECT OF CRITERION SHIFTS
 i.-, 1678 APPLICATION OF FUZZY SIGNAL DETECTION THEORY TO VIGILANCE: THE EFFECT OF CRITERION SHIFTS Shawn C. Stafford, James L. Szalma, 2 Peter A. Hancock,,* & Mustapha Mouloua I Department of Psychology
i.-, 1678 APPLICATION OF FUZZY SIGNAL DETECTION THEORY TO VIGILANCE: THE EFFECT OF CRITERION SHIFTS Shawn C. Stafford, James L. Szalma, 2 Peter A. Hancock,,* & Mustapha Mouloua I Department of Psychology
Shoot or don t shoot? Why police officers are more inclined to shoot when they are anxious
 5 Shoot or don t shoot? Why police officers are more inclined to shoot when they are anxious Published as: Nieuwenhuys, A., Savelsbergh, G. J. P., & Oudejans, R. R. D. (2012). Shoot or don t shoot: Why
5 Shoot or don t shoot? Why police officers are more inclined to shoot when they are anxious Published as: Nieuwenhuys, A., Savelsbergh, G. J. P., & Oudejans, R. R. D. (2012). Shoot or don t shoot: Why
PERFORMANCE, WORKLOAD, AND STRESS IN VIGILANCE: THE POWER OF CHOICE
 PROCEEDINGS of the HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 50th ANNUAL MEETING 2006 1609 PERFORMANCE, WORKLOAD, AND STRESS IN VIGILANCE: THE POWER OF CHOICE J.L. Szalma and P.A. Hancock University of Central
PROCEEDINGS of the HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 50th ANNUAL MEETING 2006 1609 PERFORMANCE, WORKLOAD, AND STRESS IN VIGILANCE: THE POWER OF CHOICE J.L. Szalma and P.A. Hancock University of Central
A Process Tracing Approach to the Investigation of Situated Cognition
 PROCEEDINGS of the HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 48th ANNUAL MEETING 2004 658 A Process Tracing Approach to the Investigation of Situated Cognition Lawrence G. Shattuck United States Military Academy
PROCEEDINGS of the HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 48th ANNUAL MEETING 2004 658 A Process Tracing Approach to the Investigation of Situated Cognition Lawrence G. Shattuck United States Military Academy
The Effects of Feedback on Student Performance While Performing Multiple Tasks Simultaneously
 EFFECTS OF FEEDBACK 57 The Effects of Feedback on Student Performance While Performing Multiple Tasks Simultaneously Authors: Faculty Advisor: Department: Amber Reis, Danyel Janssen Dr. Deborah Spear Psychology
EFFECTS OF FEEDBACK 57 The Effects of Feedback on Student Performance While Performing Multiple Tasks Simultaneously Authors: Faculty Advisor: Department: Amber Reis, Danyel Janssen Dr. Deborah Spear Psychology
Interference with spatial working memory: An eye movement is more than a shift of attention
 Psychonomic Bulletin & Review 2004, 11 (3), 488-494 Interference with spatial working memory: An eye movement is more than a shift of attention BONNIE M. LAWRENCE Washington University School of Medicine,
Psychonomic Bulletin & Review 2004, 11 (3), 488-494 Interference with spatial working memory: An eye movement is more than a shift of attention BONNIE M. LAWRENCE Washington University School of Medicine,
Research Review: Multiple Resource Theory. out in multi-task environments. Specifically, multiple display layout and control design
 Research Review: Multiple Resource Theory Relevance to HCI Multiple resource theory is a framework for predicting effects on performance when multiple tasks are concurrently executed. These predictions
Research Review: Multiple Resource Theory Relevance to HCI Multiple resource theory is a framework for predicting effects on performance when multiple tasks are concurrently executed. These predictions
Friend/foe Identification Accuracy And Shooting Performance: Effects Of Prior Task Loading And Time Pressure
 University of Central Florida Electronic Theses and Dissertations Doctoral Dissertation (Open Access) Friend/foe Identification Accuracy And Shooting Performance: Effects Of Prior Task Loading And Time
University of Central Florida Electronic Theses and Dissertations Doctoral Dissertation (Open Access) Friend/foe Identification Accuracy And Shooting Performance: Effects Of Prior Task Loading And Time
CIA] Institute Report No. 365
![CIA] Institute Report No. 365 CIA] Institute Report No. 365](/thumbs/94/120602392.jpg) 4"9 CIA] Institute Report No. 365 Marksmanship Trainer Performance Using an Auditory Signal Warning of Simulated Laser Exposure G.R. Mastroianni J.O. Reed H. Zwick B.E. Stuck DIVISION OF OCULAR HAZARDS
4"9 CIA] Institute Report No. 365 Marksmanship Trainer Performance Using an Auditory Signal Warning of Simulated Laser Exposure G.R. Mastroianni J.O. Reed H. Zwick B.E. Stuck DIVISION OF OCULAR HAZARDS
Correlating Trust with Signal Detection Theory Measures in a Hybrid Inspection System
 Correlating Trust with Signal Detection Theory Measures in a Hybrid Inspection System Xiaochun Jiang Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering North Carolina A&T State University 1601 E Market St
Correlating Trust with Signal Detection Theory Measures in a Hybrid Inspection System Xiaochun Jiang Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering North Carolina A&T State University 1601 E Market St
Changing Driver Behavior Through Unconscious Stereotype Activation
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Driving Assessment Conference 2009 Driving Assessment Conference Jun 23rd, 12:00 AM Changing Driver Behavior Through Unconscious Stereotype Activation Rob Gray Arizona
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Driving Assessment Conference 2009 Driving Assessment Conference Jun 23rd, 12:00 AM Changing Driver Behavior Through Unconscious Stereotype Activation Rob Gray Arizona
Identity Theory: Reconstruction and Application
 P a g e 1 Identity Theory: Reconstruction and Application Curtis M. Kularski University of North Carolina at Charlotte 12 December 2014 SOCY 6651 P a g e 2 Identity Theory: Reconstruction and Application
P a g e 1 Identity Theory: Reconstruction and Application Curtis M. Kularski University of North Carolina at Charlotte 12 December 2014 SOCY 6651 P a g e 2 Identity Theory: Reconstruction and Application
THE EFFECT OF COGNITIVE TASKS ON PREDICTING EVENTS IN TRAFFIC
 THE EFFECT OF COGNITIVE TASKS ON PREDICTING EVENTS IN TRAFFIC Martin R.K. Baumann (DLR / BASt, Germany), Tibor Petzoldt (Chemnitz University of Technology, Germany), Chantal Groenewoud (Utrecht University,
THE EFFECT OF COGNITIVE TASKS ON PREDICTING EVENTS IN TRAFFIC Martin R.K. Baumann (DLR / BASt, Germany), Tibor Petzoldt (Chemnitz University of Technology, Germany), Chantal Groenewoud (Utrecht University,
Verbal-Spatial Cue Conflict: Implications for the Design of Collision-Avoidance Warning Systems
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Driving Assessment Conference 2009 Driving Assessment Conference Jun 24th, 12:00 AM Verbal-Spatial Cue Conflict: Implications for the Design of Collision-Avoidance
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Driving Assessment Conference 2009 Driving Assessment Conference Jun 24th, 12:00 AM Verbal-Spatial Cue Conflict: Implications for the Design of Collision-Avoidance
Encoding of Information in Auditory Displays: Initial Research on Flexibility and Processing Codes in Dual-task Scenarios
 PROCEEDINGS of the HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 52nd ANNUAL MEETING 2008 1820 Encoding of Information in Auditory Displays: Initial Research on Flexibility and Processing Codes in Dual-task Scenarios
PROCEEDINGS of the HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 52nd ANNUAL MEETING 2008 1820 Encoding of Information in Auditory Displays: Initial Research on Flexibility and Processing Codes in Dual-task Scenarios
Efficacy of Transfer in Simulation-Based Training: Implications for Stress Exposure Training
 Efficacy of Transfer in Simulation-Based Training: Implications for Stress Exposure Training Jennifer M. Ross, James L. Szalma, & Peter A. Hancock Psychology Department And Institute of Simulation and
Efficacy of Transfer in Simulation-Based Training: Implications for Stress Exposure Training Jennifer M. Ross, James L. Szalma, & Peter A. Hancock Psychology Department And Institute of Simulation and
Vibrotactile Signals -using tactile stimuli to present information
 Vibrotactile Signals -using tactile stimuli to present information William Hagman, Gustaf Hanson, Sanna Heurlén, Emma Nordlöf, Kristin Raukola, Linnea Wahlberg Linköping University 2010 Tactile stimulation
Vibrotactile Signals -using tactile stimuli to present information William Hagman, Gustaf Hanson, Sanna Heurlén, Emma Nordlöf, Kristin Raukola, Linnea Wahlberg Linköping University 2010 Tactile stimulation
Individual Differences in the Stress and Workload of Sustained Attention. James L. Szalma University of Central Florida Orlando, FL.
 1002 Individual Differences in the Stress and Workload of Sustained Attention James L. Szalma University of Central Florida Orlando, FL. The effects of individual differences in dispositional pessimism
1002 Individual Differences in the Stress and Workload of Sustained Attention James L. Szalma University of Central Florida Orlando, FL. The effects of individual differences in dispositional pessimism
Satiation in name and face recognition
 Memory & Cognition 2000, 28 (5), 783-788 Satiation in name and face recognition MICHAEL B. LEWIS and HADYN D. ELLIS Cardiff University, Cardiff, Wales Massive repetition of a word can lead to a loss of
Memory & Cognition 2000, 28 (5), 783-788 Satiation in name and face recognition MICHAEL B. LEWIS and HADYN D. ELLIS Cardiff University, Cardiff, Wales Massive repetition of a word can lead to a loss of
Tasks of Executive Control TEC. Interpretive Report. Developed by Peter K. Isquith, PhD, Robert M. Roth, PhD, Gerard A. Gioia, PhD, and PAR Staff
 Tasks of Executive Control TEC Interpretive Report Developed by Peter K. Isquith, PhD, Robert M. Roth, PhD, Gerard A. Gioia, PhD, and PAR Staff Client Information Client Name: Sample Client Client ID:
Tasks of Executive Control TEC Interpretive Report Developed by Peter K. Isquith, PhD, Robert M. Roth, PhD, Gerard A. Gioia, PhD, and PAR Staff Client Information Client Name: Sample Client Client ID:
The role of cognitive effort in subjective reward devaluation and risky decision-making
 The role of cognitive effort in subjective reward devaluation and risky decision-making Matthew A J Apps 1,2, Laura Grima 2, Sanjay Manohar 2, Masud Husain 1,2 1 Nuffield Department of Clinical Neuroscience,
The role of cognitive effort in subjective reward devaluation and risky decision-making Matthew A J Apps 1,2, Laura Grima 2, Sanjay Manohar 2, Masud Husain 1,2 1 Nuffield Department of Clinical Neuroscience,
psychological trauma is an experience of a threat to life, body, or sanity so severe as to overwhelm the ordinary process of emotional integration.
 Virtual Reality in the Treatment of Combat-Related PTSD with Warfighters Sarah D. Miyahira, Ph.D. Director of Intramural Research Co-Director, VR Behavioral Health Program & Laboratory Department of Veterans
Virtual Reality in the Treatment of Combat-Related PTSD with Warfighters Sarah D. Miyahira, Ph.D. Director of Intramural Research Co-Director, VR Behavioral Health Program & Laboratory Department of Veterans
The Effect of Training Context on Fixations Made During Visual Discriminations
 The Effect of Training Context on Fixations Made During Visual Discriminations Randy J. Brou (Rbrou@Inst.Msstate.Edu) 1 Teena M. Garrison (Teenag@Cavs.Msstate.Edu) 2 Stephanie M. Doane (Sdoane@Doane.Inst.Msstate.Edu)
The Effect of Training Context on Fixations Made During Visual Discriminations Randy J. Brou (Rbrou@Inst.Msstate.Edu) 1 Teena M. Garrison (Teenag@Cavs.Msstate.Edu) 2 Stephanie M. Doane (Sdoane@Doane.Inst.Msstate.Edu)
TOPICS TO BE EVALUATED BEFORE THE FORMAL OBSERVATION. Outcome: Make Ethical Decisions. Outcome: Provide Support to Athletes in Training
 Archery Canada - Practice Evaluation Tool NCCP Competition Development Name: Evaluator: CC#: Date: Evaluator signature: Scoring for : The evaluator should assign a Y (yes) or N (no) for each evidence found.
Archery Canada - Practice Evaluation Tool NCCP Competition Development Name: Evaluator: CC#: Date: Evaluator signature: Scoring for : The evaluator should assign a Y (yes) or N (no) for each evidence found.
Effect of spectral content and learning on auditory distance perception
 Effect of spectral content and learning on auditory distance perception Norbert Kopčo 1,2, Dávid Čeljuska 1, Miroslav Puszta 1, Michal Raček 1 a Martin Sarnovský 1 1 Department of Cybernetics and AI, Technical
Effect of spectral content and learning on auditory distance perception Norbert Kopčo 1,2, Dávid Čeljuska 1, Miroslav Puszta 1, Michal Raček 1 a Martin Sarnovský 1 1 Department of Cybernetics and AI, Technical
Auditory Dominance: Overshadowing or Response Competition?
 Auditory Dominance: Overshadowing or Response Competition? Christopher W. Robinson (robinson.777@osu.edu) Center for Cognitive Science The Ohio State University 208F Ohio Stadium East, 1961 Tuttle Park
Auditory Dominance: Overshadowing or Response Competition? Christopher W. Robinson (robinson.777@osu.edu) Center for Cognitive Science The Ohio State University 208F Ohio Stadium East, 1961 Tuttle Park
The role of recurrent CBT for increasing aviation security screeners visual knowledge and abilities needed in x-ray screening
 The role of recurrent CBT for increasing aviation security screeners visual knowledge and abilities needed in x-ray screening Diana Hardmeier University of Zurich, Department of Psychology, Visual Cognition
The role of recurrent CBT for increasing aviation security screeners visual knowledge and abilities needed in x-ray screening Diana Hardmeier University of Zurich, Department of Psychology, Visual Cognition
Training for vigilance: The effect of knowledge of results format and dispositional optimism and pessimism on performance and stress
 115 British Journal of Psychology (2006), 97, 115 135 The British Psychological Society www.bpsjournals.co.uk Training for vigilance: The effect of knowledge of results format and dispositional optimism
115 British Journal of Psychology (2006), 97, 115 135 The British Psychological Society www.bpsjournals.co.uk Training for vigilance: The effect of knowledge of results format and dispositional optimism
Is Facilitating Anxiety All in Your Head?
 Sophia Junior College Faculty Journal Vol.28, 2008, 1-7 Is Facilitating Anxiety All in Your Head? Kenneth E. Williams This paper examines research concerning facilitating anxiety that is often cited in
Sophia Junior College Faculty Journal Vol.28, 2008, 1-7 Is Facilitating Anxiety All in Your Head? Kenneth E. Williams This paper examines research concerning facilitating anxiety that is often cited in
The Relationship Between Task Cohesion and Competitive State Anxiety
 Wilfrid Laurier University Scholars Commons @ Laurier Kinesiology and Physical Education Faculty Publications Kinesiology and Physical Education 2003 The Relationship Between Task Cohesion and Competitive
Wilfrid Laurier University Scholars Commons @ Laurier Kinesiology and Physical Education Faculty Publications Kinesiology and Physical Education 2003 The Relationship Between Task Cohesion and Competitive
Conscious control of movements: increase of temporal precision in voluntarily delayed actions
 Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2001, 61: 175-179 Conscious control of movements: increase of temporal precision in voluntarily delayed actions El bieta Szel¹g 1, Krystyna Rymarczyk 1 and Ernst Pöppel 2 1 Department
Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2001, 61: 175-179 Conscious control of movements: increase of temporal precision in voluntarily delayed actions El bieta Szel¹g 1, Krystyna Rymarczyk 1 and Ernst Pöppel 2 1 Department
THE SPATIAL EXTENT OF ATTENTION DURING DRIVING
 THE SPATIAL EXTENT OF ATTENTION DURING DRIVING George J. Andersen, Rui Ni Department of Psychology University of California Riverside Riverside, California, USA E-mail: Andersen@ucr.edu E-mail: ruini@ucr.edu
THE SPATIAL EXTENT OF ATTENTION DURING DRIVING George J. Andersen, Rui Ni Department of Psychology University of California Riverside Riverside, California, USA E-mail: Andersen@ucr.edu E-mail: ruini@ucr.edu
Pupil Dilation as an Index of Learning
 PROCEEDINGS of the HUMAN FACTORS and ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 55th ANNUAL MEETING - 2011 237 Pupil Dilation as an Index of Learning Ciara Sibley 1, Joseph Coyne 1, Carryl Baldwin 2 1 Naval Research Laboratory,
PROCEEDINGS of the HUMAN FACTORS and ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 55th ANNUAL MEETING - 2011 237 Pupil Dilation as an Index of Learning Ciara Sibley 1, Joseph Coyne 1, Carryl Baldwin 2 1 Naval Research Laboratory,
The Simon Effect as a Function of Temporal Overlap between Relevant and Irrelevant
 University of North Florida UNF Digital Commons All Volumes (2001-2008) The Osprey Journal of Ideas and Inquiry 2008 The Simon Effect as a Function of Temporal Overlap between Relevant and Irrelevant Leslie
University of North Florida UNF Digital Commons All Volumes (2001-2008) The Osprey Journal of Ideas and Inquiry 2008 The Simon Effect as a Function of Temporal Overlap between Relevant and Irrelevant Leslie
The Effects of Stress on Marksmanship
 MOUNTAIN TACTICAL INSTITUTE, JACKSON, WY MTI The Effects of Stress on Marksmanship MOUNTAIN MILITARY LAW ENFORCEMENT FIRE/RESCUE HUMAN PERFORMANCE Copyright 2015 Mountain Tactical Institute - MTI Research
MOUNTAIN TACTICAL INSTITUTE, JACKSON, WY MTI The Effects of Stress on Marksmanship MOUNTAIN MILITARY LAW ENFORCEMENT FIRE/RESCUE HUMAN PERFORMANCE Copyright 2015 Mountain Tactical Institute - MTI Research
Factors Affecting Speed and Accuracy of Response Selection in Operational Environments
 Factors Affecting Speed and Accuracy of Response Selection in Operational Environments Robert W. Proctor & Motonori Yamaguchi Purdue University, W. Lafayette, Indiana MURI Grant W9112NF-05-1-0153 from
Factors Affecting Speed and Accuracy of Response Selection in Operational Environments Robert W. Proctor & Motonori Yamaguchi Purdue University, W. Lafayette, Indiana MURI Grant W9112NF-05-1-0153 from
Controlling Stable and Unstable Dynamic Decision Making Environments
 Controlling Stable and Unstable Dynamic Decision Making Environments Magda Osman (m.osman@qmul.ac.uk) Centre for Experimental and Biological Psychology, Queen Mary University of London, London, E1 4NS
Controlling Stable and Unstable Dynamic Decision Making Environments Magda Osman (m.osman@qmul.ac.uk) Centre for Experimental and Biological Psychology, Queen Mary University of London, London, E1 4NS
Limitations of Object-Based Feature Encoding in Visual Short-Term Memory
 Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 2002, Vol. 28, No. 2, 458 468 Copyright 2002 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 0096-1523/02/$5.00 DOI: 10.1037//0096-1523.28.2.458
Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 2002, Vol. 28, No. 2, 458 468 Copyright 2002 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 0096-1523/02/$5.00 DOI: 10.1037//0096-1523.28.2.458
TEMPORAL CHANGE IN RESPONSE BIAS OBSERVED IN EXPERT ANTICIPATION OF VOLLEYBALL SPIKES
 TEMPORAL CHANGE IN RESPONSE BIAS OBSERVED IN ANTICIPATION OF VOLLEYBALL SPIKES Tomoko Takeyama, Nobuyuki Hirose 2, and Shuji Mori 2 Department of Informatics, Graduate School of Information Science and
TEMPORAL CHANGE IN RESPONSE BIAS OBSERVED IN ANTICIPATION OF VOLLEYBALL SPIKES Tomoko Takeyama, Nobuyuki Hirose 2, and Shuji Mori 2 Department of Informatics, Graduate School of Information Science and
Optical Illusions 4/5. Optical Illusions 2/5. Optical Illusions 5/5 Optical Illusions 1/5. Reading. Reading. Fang Chen Spring 2004
 Optical Illusions 2/5 Optical Illusions 4/5 the Ponzo illusion the Muller Lyer illusion Optical Illusions 5/5 Optical Illusions 1/5 Mauritz Cornelis Escher Dutch 1898 1972 Graphical designer World s first
Optical Illusions 2/5 Optical Illusions 4/5 the Ponzo illusion the Muller Lyer illusion Optical Illusions 5/5 Optical Illusions 1/5 Mauritz Cornelis Escher Dutch 1898 1972 Graphical designer World s first
USER GUIDE FOR MATLAB BASED HEARING TEST SIMULATOR GUI FOR CLINICAL TESTING
 1 USER GUIDE FOR MATLAB BASED HEARING TEST SIMULATOR GUI FOR CLINICAL TESTING Serkan Tokgoz, Issa Panahi STATISTICAL SIGNAL PROCESSING LABORATORY (SSPRL) UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT DALLAS APRIL 2018 This work
1 USER GUIDE FOR MATLAB BASED HEARING TEST SIMULATOR GUI FOR CLINICAL TESTING Serkan Tokgoz, Issa Panahi STATISTICAL SIGNAL PROCESSING LABORATORY (SSPRL) UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT DALLAS APRIL 2018 This work
Measuring Vigilance Abilities to Enhance Combat Identification Performance
 Measuring Vigilance Abilities to Enhance Combat Identification Performance Clark Shingledecker, PhD; David E. Weldon, PhD; Kyle Behymer; Benjamin Simpkins; & Elizabeth Lerner JXT Applications, Inc. Joel
Measuring Vigilance Abilities to Enhance Combat Identification Performance Clark Shingledecker, PhD; David E. Weldon, PhD; Kyle Behymer; Benjamin Simpkins; & Elizabeth Lerner JXT Applications, Inc. Joel
Augmented Cognition to enhance human sensory awareness, cognitive functioning and psychic functioning: a research proposal in two phases
 Augmented Cognition to enhance human sensory awareness, cognitive functioning and psychic functioning: a research proposal in two phases James Lake MD (egret4@sbcglobal.net) Overview and objectives Augmented
Augmented Cognition to enhance human sensory awareness, cognitive functioning and psychic functioning: a research proposal in two phases James Lake MD (egret4@sbcglobal.net) Overview and objectives Augmented
Effect of Body Mass Index and Gender on Visual and Auditory Reaction Times in Young Adults
 Journal of US-China Medical Science 12 (2015) 64-69 doi: 10.17265/1548-6648/2015.02.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Effect of Body Mass Index and Gender on Visual and Auditory Reaction Times in Young Adults Aiesha
Journal of US-China Medical Science 12 (2015) 64-69 doi: 10.17265/1548-6648/2015.02.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Effect of Body Mass Index and Gender on Visual and Auditory Reaction Times in Young Adults Aiesha
Content Area: Physical Education Grade Level Expectations: Fifth Grade Standard: 1. Movement Competence & Understanding in Physical Education
 Colorado Academic Standards Physical Education - Fifth Grade Content Area: Physical Education Grade Level Expectations: Fifth Grade Standard: 1. Movement Competence & Understanding in Physical Education
Colorado Academic Standards Physical Education - Fifth Grade Content Area: Physical Education Grade Level Expectations: Fifth Grade Standard: 1. Movement Competence & Understanding in Physical Education
AC : USABILITY EVALUATION OF A PROBLEM SOLVING ENVIRONMENT FOR AUTOMATED SYSTEM INTEGRATION EDUCA- TION USING EYE-TRACKING
 AC 2012-4422: USABILITY EVALUATION OF A PROBLEM SOLVING ENVIRONMENT FOR AUTOMATED SYSTEM INTEGRATION EDUCA- TION USING EYE-TRACKING Punit Deotale, Texas A&M University Dr. Sheng-Jen Tony Hsieh, Texas A&M
AC 2012-4422: USABILITY EVALUATION OF A PROBLEM SOLVING ENVIRONMENT FOR AUTOMATED SYSTEM INTEGRATION EDUCA- TION USING EYE-TRACKING Punit Deotale, Texas A&M University Dr. Sheng-Jen Tony Hsieh, Texas A&M
COMBAT RELATED POST TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER: A MULTIPLE-CASE REPORT USING VIRTUAL REALITY GRADED EXPOSURE THERAPY WITH PHYSIOLOGICAL MONITORING
 COMBAT RELATED POST TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER: A MULTIPLE-CASE REPORT USING VIRTUAL REALITY GRADED EXPOSURE THERAPY WITH PHYSIOLOGICAL MONITORING CYBERTHERAPY 12 CONFERENCE ALEXANDIRA, VIRGINIA Dennis
COMBAT RELATED POST TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER: A MULTIPLE-CASE REPORT USING VIRTUAL REALITY GRADED EXPOSURE THERAPY WITH PHYSIOLOGICAL MONITORING CYBERTHERAPY 12 CONFERENCE ALEXANDIRA, VIRGINIA Dennis
Personality Type and Cued Vigil Performance
 107 Journal of the Indian Academy of Applied Psychology, January 2009, Vol. 35, No.1, 107-111. Personality Type and Cued Vigil Performance Upagya Rai and Indramani L. Singh Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi
107 Journal of the Indian Academy of Applied Psychology, January 2009, Vol. 35, No.1, 107-111. Personality Type and Cued Vigil Performance Upagya Rai and Indramani L. Singh Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi
Anxiety, Movement Kinematics, and Visual Attention in Elite-Level Performers. Joe Causer. Liverpool John Moores University
 Anxiety & Performance 1 Running head: ANXIETY & VISUAL ATTENTION IN SHOOTING Anxiety, Movement Kinematics, and Visual Attention in Elite-Level Performers Joe Causer Liverpool John Moores University Paul
Anxiety & Performance 1 Running head: ANXIETY & VISUAL ATTENTION IN SHOOTING Anxiety, Movement Kinematics, and Visual Attention in Elite-Level Performers Joe Causer Liverpool John Moores University Paul
RAW Mental Toughness. Mental Skills for Combat Effectiveness. Rangers Lead The Way
 RAW Mental Toughness Mental Skills for Combat Effectiveness RAW Pillars Functional Fitness Strength Endurance Movement skill Performance Nutrition Nutrient needs Ideal body composition Supplements Sports
RAW Mental Toughness Mental Skills for Combat Effectiveness RAW Pillars Functional Fitness Strength Endurance Movement skill Performance Nutrition Nutrient needs Ideal body composition Supplements Sports
APPLICATION OF SIMULATION TO STUDY DECISION MAKING IN HANDBALL
 APPLICATION OF SIMULATION TO STUDY DECISION MAKING IN HANDBALL Abdedaim Adda Boumesjed Abdelkader Sebbane Mohammed Laboratory Research Applied Sciences in Human Movement (LABSAMH) Institute of Physical
APPLICATION OF SIMULATION TO STUDY DECISION MAKING IN HANDBALL Abdedaim Adda Boumesjed Abdelkader Sebbane Mohammed Laboratory Research Applied Sciences in Human Movement (LABSAMH) Institute of Physical
SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
 SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Jayakumar.R Analysis of psychological characteristics of male and female sportspersons of selected sports discipline Thesis. Department of Physical Education, University
SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Jayakumar.R Analysis of psychological characteristics of male and female sportspersons of selected sports discipline Thesis. Department of Physical Education, University
Young table tennis players involvement in the practice: a test of Eysenck and Calvo processing efficiency theory
 Young table tennis players involvement in the practice: a test of Eysenck and Calvo processing efficiency theory Chia-Jung Lin 1, Yuh-Yuh Li 2, Chia-Yi Lin 3, Chiu-Ju Lu 4 1 Tainan University of Technology,
Young table tennis players involvement in the practice: a test of Eysenck and Calvo processing efficiency theory Chia-Jung Lin 1, Yuh-Yuh Li 2, Chia-Yi Lin 3, Chiu-Ju Lu 4 1 Tainan University of Technology,
I. PHILOSOPHY AND GOALS
 I. PHILOSOPHY AND GOALS PHILOSOPHY Physical Education Philosophy The Belén Jesuit Physical Education Department's philosophy is concerned with developing the students' total physical and mental well being
I. PHILOSOPHY AND GOALS PHILOSOPHY Physical Education Philosophy The Belén Jesuit Physical Education Department's philosophy is concerned with developing the students' total physical and mental well being
Object Substitution Masking: When does Mask Preview work?
 Object Substitution Masking: When does Mask Preview work? Stephen W. H. Lim (psylwhs@nus.edu.sg) Department of Psychology, National University of Singapore, Block AS6, 11 Law Link, Singapore 117570 Chua
Object Substitution Masking: When does Mask Preview work? Stephen W. H. Lim (psylwhs@nus.edu.sg) Department of Psychology, National University of Singapore, Block AS6, 11 Law Link, Singapore 117570 Chua
Mood and Anxiety Scores Predict Winning and Losing Performances in Tennis
 Mood and Anxiety Scores Predict Winning and Losing Performances in Tennis Peter C. Terry (terryp@usq.edu.au) Department of Psychology University of Southern Queensland, Toowoomba QLD 43 Australia Angus
Mood and Anxiety Scores Predict Winning and Losing Performances in Tennis Peter C. Terry (terryp@usq.edu.au) Department of Psychology University of Southern Queensland, Toowoomba QLD 43 Australia Angus
Detection of Task-Relevant Cues in Field Hockey
 JOURNAL OF SPORT PSYCHOLOGY, 1987, 9.74-78 Detection of Task-Relevant Cues in Field Hockey Susann G. Doody, Sharon Huddleston, Cherith Beavers University of Northern Iowa Marchelle Austin St. Francis Hospital
JOURNAL OF SPORT PSYCHOLOGY, 1987, 9.74-78 Detection of Task-Relevant Cues in Field Hockey Susann G. Doody, Sharon Huddleston, Cherith Beavers University of Northern Iowa Marchelle Austin St. Francis Hospital
MENTAL WORKLOAD AS A FUNCTION OF TRAFFIC DENSITY: COMPARISON OF PHYSIOLOGICAL, BEHAVIORAL, AND SUBJECTIVE INDICES
 MENTAL WORKLOAD AS A FUNCTION OF TRAFFIC DENSITY: COMPARISON OF PHYSIOLOGICAL, BEHAVIORAL, AND SUBJECTIVE INDICES Carryl L. Baldwin and Joseph T. Coyne Department of Psychology Old Dominion University
MENTAL WORKLOAD AS A FUNCTION OF TRAFFIC DENSITY: COMPARISON OF PHYSIOLOGICAL, BEHAVIORAL, AND SUBJECTIVE INDICES Carryl L. Baldwin and Joseph T. Coyne Department of Psychology Old Dominion University
This self-archived version is provided for scholarly purposes only. The correct reference for this article is as follows:
 SOCIAL AFFILIATION CUES PRIME HELP-SEEKING INTENTIONS 1 This self-archived version is provided for scholarly purposes only. The correct reference for this article is as follows: Rubin, M. (2011). Social
SOCIAL AFFILIATION CUES PRIME HELP-SEEKING INTENTIONS 1 This self-archived version is provided for scholarly purposes only. The correct reference for this article is as follows: Rubin, M. (2011). Social
Bridging the Gap: Predictors of Willingness to Engage in an Intercultural Interaction
 Bridging the Gap: Predictors of Willingness to Engage in an Intercultural Interaction Heather Dudley What influences people s willingness to interact with someone of a different cultural background from
Bridging the Gap: Predictors of Willingness to Engage in an Intercultural Interaction Heather Dudley What influences people s willingness to interact with someone of a different cultural background from
Computers in Human Behavior
 Computers in Human Behavior 24 (2008) 2965 2971 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Computers in Human Behavior journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/comphumbeh Social facilitation and human
Computers in Human Behavior 24 (2008) 2965 2971 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Computers in Human Behavior journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/comphumbeh Social facilitation and human
Chapter-III METHODOLOGY
 118 Chapter-III METHODOLOGY 3.0.0 INTRODUCTION In the preceding chapters, the researcher has presented introduction and the review of literature and review of related literature which is supporting and
118 Chapter-III METHODOLOGY 3.0.0 INTRODUCTION In the preceding chapters, the researcher has presented introduction and the review of literature and review of related literature which is supporting and
AN EPIC COMPUTATIONAL MODEL OF VERBAL WORKING MEMORY D. E. Kieras, D. E. Meyer, S. T. Mueller, T. L. Seymour University of Michigan Sponsored by the
 AN EPIC COMPUTATIONAL MODEL OF VERBAL WORKING MEMORY D. E. Kieras, D. E. Meyer, S. T. Mueller, T. L. Seymour University of Michigan Sponsored by the U.S. Office of Naval Research 1 Introduction During
AN EPIC COMPUTATIONAL MODEL OF VERBAL WORKING MEMORY D. E. Kieras, D. E. Meyer, S. T. Mueller, T. L. Seymour University of Michigan Sponsored by the U.S. Office of Naval Research 1 Introduction During
SPATIAL AUDIO VS. VERBAL DIRECTIONAL CUES: AN EXAMINATION OF SALIENCE AND DISRUPTIVENESS WITHIN A SIMULATED DRIVING CONTEXT
 SPATIAL AUDIO VS. VERBAL DIRECTIONAL CUES: AN EXAMINATION OF SALIENCE AND DISRUPTIVENESS WITHIN A SIMULATED DRIVING CONTEXT Jane H. Barrow and Carryl L. Baldwin George Mason University Psychology Dept.,
SPATIAL AUDIO VS. VERBAL DIRECTIONAL CUES: AN EXAMINATION OF SALIENCE AND DISRUPTIVENESS WITHIN A SIMULATED DRIVING CONTEXT Jane H. Barrow and Carryl L. Baldwin George Mason University Psychology Dept.,
Introductory Motor Learning and Development Lab
 Introductory Motor Learning and Development Lab Laboratory Equipment & Test Procedures. Motor learning and control historically has built its discipline through laboratory research. This has led to the
Introductory Motor Learning and Development Lab Laboratory Equipment & Test Procedures. Motor learning and control historically has built its discipline through laboratory research. This has led to the
Framework for Comparative Research on Relational Information Displays
 Framework for Comparative Research on Relational Information Displays Sung Park and Richard Catrambone 2 School of Psychology & Graphics, Visualization, and Usability Center (GVU) Georgia Institute of
Framework for Comparative Research on Relational Information Displays Sung Park and Richard Catrambone 2 School of Psychology & Graphics, Visualization, and Usability Center (GVU) Georgia Institute of
A FRÖHLICH EFFECT IN MEMORY FOR AUDITORY PITCH: EFFECTS OF CUEING AND OF REPRESENTATIONAL GRAVITY. Timothy L. Hubbard 1 & Susan E.
 In D. Algom, D. Zakay, E. Chajut, S. Shaki, Y. Mama, & V. Shakuf (Eds.). (2011). Fechner Day 2011: Proceedings of the 27 th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Psychophysics (pp. 89-94). Raanana,
In D. Algom, D. Zakay, E. Chajut, S. Shaki, Y. Mama, & V. Shakuf (Eds.). (2011). Fechner Day 2011: Proceedings of the 27 th Annual Meeting of the International Society for Psychophysics (pp. 89-94). Raanana,
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH Volume 3, Number 1 Submitted: August 10, 2007 Revisions: August 20, 2007 Accepted: August 27, 2007 Publication Date: September 10, 2007 The Effect of Cell Phone
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PSYCHOLOGICAL RESEARCH Volume 3, Number 1 Submitted: August 10, 2007 Revisions: August 20, 2007 Accepted: August 27, 2007 Publication Date: September 10, 2007 The Effect of Cell Phone
Topics. Experiment Terminology (Part 1)
 Topics The what, why, and how of empirical research Group participation in a real experiment Observations and measurements Research questions Experiment terminology Experiment design Hypothesis testing
Topics The what, why, and how of empirical research Group participation in a real experiment Observations and measurements Research questions Experiment terminology Experiment design Hypothesis testing
Chapter IV. Information Transfer Rate
 The goal of the experiments on information transfer rate was to assess the dynamic information transmission capabilities with the TACTUATOR. The IT rate is defined as the product of information transfer
The goal of the experiments on information transfer rate was to assess the dynamic information transmission capabilities with the TACTUATOR. The IT rate is defined as the product of information transfer
Automatic detection, consistent mapping, and training * Originally appeared in
 Automatic detection - 1 Automatic detection, consistent mapping, and training * Originally appeared in Bulletin of the Psychonomic Society, 1986, 24 (6), 431-434 SIU L. CHOW The University of Wollongong,
Automatic detection - 1 Automatic detection, consistent mapping, and training * Originally appeared in Bulletin of the Psychonomic Society, 1986, 24 (6), 431-434 SIU L. CHOW The University of Wollongong,
Use of Structure Mapping Theory for Complex Systems
 Gentner, D., & Schumacher, R. M. (1986). Use of structure-mapping theory for complex systems. Presented at the Panel on Mental Models and Complex Systems, IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man
Gentner, D., & Schumacher, R. M. (1986). Use of structure-mapping theory for complex systems. Presented at the Panel on Mental Models and Complex Systems, IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man
PROCEEDINGS of the HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 48th ANNUAL MEETING
 PROCEEDINGS of the HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 48th ANNUAL MEETING 2004 1464 EFFECT OF HANDLE DESIGN AND TARGET LOCATION ON WRIST POSTURE DURING AIMING WITH A LAPAROSCOPIC TOOL Judkins, T.N. 1,
PROCEEDINGS of the HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 48th ANNUAL MEETING 2004 1464 EFFECT OF HANDLE DESIGN AND TARGET LOCATION ON WRIST POSTURE DURING AIMING WITH A LAPAROSCOPIC TOOL Judkins, T.N. 1,
Effect of Positive and Negative Instances on Rule Discovery: Investigation Using Eye Tracking
 Effect of Positive and Negative Instances on Rule Discovery: Investigation Using Eye Tracking Miki Matsumuro (muro@cog.human.nagoya-u.ac.jp) Kazuhisa Miwa (miwa@is.nagoya-u.ac.jp) Graduate School of Information
Effect of Positive and Negative Instances on Rule Discovery: Investigation Using Eye Tracking Miki Matsumuro (muro@cog.human.nagoya-u.ac.jp) Kazuhisa Miwa (miwa@is.nagoya-u.ac.jp) Graduate School of Information
Pupil Dilation as an Indicator of Cognitive Workload in Human-Computer Interaction
 Pupil Dilation as an Indicator of Cognitive Workload in Human-Computer Interaction Marc Pomplun and Sindhura Sunkara Department of Computer Science, University of Massachusetts at Boston 100 Morrissey
Pupil Dilation as an Indicator of Cognitive Workload in Human-Computer Interaction Marc Pomplun and Sindhura Sunkara Department of Computer Science, University of Massachusetts at Boston 100 Morrissey
A Signal Improvement to Signal Detection Analysis: Fuzzy SDT on the ROCs
 Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 2013, Vol. 39, No. 6, 1741 1762 2013 American Psychological Association 0096-1523/13/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/a0032103 A Signal Improvement
Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance 2013, Vol. 39, No. 6, 1741 1762 2013 American Psychological Association 0096-1523/13/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/a0032103 A Signal Improvement
Upon starting the executable, a map with four exits at its corners is loaded.
 Pedestrian Simulation Software Version 0.0, Model and Documentation Peter Stephenson August 2007 Simulation Instructions Upon starting the executable, a map with four exits at its corners is loaded. People
Pedestrian Simulation Software Version 0.0, Model and Documentation Peter Stephenson August 2007 Simulation Instructions Upon starting the executable, a map with four exits at its corners is loaded. People
Types of Attentional Focus Key Several types of attentional focus are appropriate for specific sport skills & activities.
 Chapter 16: Concentration What Is Concentration? Types of Attentional Focus Shifting Attentional Focus Attentional Problems Choking as an Attentional Problem Self-Talk Assessing Attentional Skills Tips
Chapter 16: Concentration What Is Concentration? Types of Attentional Focus Shifting Attentional Focus Attentional Problems Choking as an Attentional Problem Self-Talk Assessing Attentional Skills Tips
The Influence of Induced Anxiety on the P3 Event Related Brain Potentials of Athletes and Novices in a Go/NoGo Task
 The Influence of Induced Anxiety on the P3 Event Related Brain Potentials of Athletes and Novices in a Go/NoGo Task Conley Waters and Keri Weed University of South Carolina Aiken An elite athlete employs
The Influence of Induced Anxiety on the P3 Event Related Brain Potentials of Athletes and Novices in a Go/NoGo Task Conley Waters and Keri Weed University of South Carolina Aiken An elite athlete employs
Pupil dilation accuracy in the prediction of random events. The name, affiliation, and address for the lead experimenter(s) for the study:
 KPU Registry ID Number: 1001 Date Initially Submitted: 26NOV2012 11/25/2012 The title or name of the experiment: Pupil dilation accuracy in the prediction of random events The name, affiliation, and email
KPU Registry ID Number: 1001 Date Initially Submitted: 26NOV2012 11/25/2012 The title or name of the experiment: Pupil dilation accuracy in the prediction of random events The name, affiliation, and email
Observation is the capacity of the individual to know the environment by the use of his senses. There are two steps in the process of observation:
 Definition Observation is the capacity of the individual to know the environment by the use of his senses. There are two steps in the process of observation: 1) Attention: is the preparatory step, the
Definition Observation is the capacity of the individual to know the environment by the use of his senses. There are two steps in the process of observation: 1) Attention: is the preparatory step, the
PSYCHOLOGICAL SCIENCE. Research Article
 Research Article VISUAL SEARCH REMAINS EFFICIENT WHEN VISUAL WORKING MEMORY IS FULL Geoffrey F. Woodman, Edward K. Vogel, and Steven J. Luck University of Iowa Abstract Many theories of attention have
Research Article VISUAL SEARCH REMAINS EFFICIENT WHEN VISUAL WORKING MEMORY IS FULL Geoffrey F. Woodman, Edward K. Vogel, and Steven J. Luck University of Iowa Abstract Many theories of attention have
CANTAB Test descriptions by function
 CANTAB Test descriptions by function The 22 tests in the CANTAB battery may be divided into the following main types of task: screening tests visual memory tests executive function, working memory and
CANTAB Test descriptions by function The 22 tests in the CANTAB battery may be divided into the following main types of task: screening tests visual memory tests executive function, working memory and
The Role of Feedback in Categorisation
 The Role of in Categorisation Mark Suret (m.suret@psychol.cam.ac.uk) Department of Experimental Psychology; Downing Street Cambridge, CB2 3EB UK I.P.L. McLaren (iplm2@cus.cam.ac.uk) Department of Experimental
The Role of in Categorisation Mark Suret (m.suret@psychol.cam.ac.uk) Department of Experimental Psychology; Downing Street Cambridge, CB2 3EB UK I.P.L. McLaren (iplm2@cus.cam.ac.uk) Department of Experimental
Running head: PERCEPTUAL GROUPING AND SPATIAL SELECTION 1. The attentional window configures to object boundaries. University of Iowa
 Running head: PERCEPTUAL GROUPING AND SPATIAL SELECTION 1 The attentional window configures to object boundaries University of Iowa Running head: PERCEPTUAL GROUPING AND SPATIAL SELECTION 2 ABSTRACT When
Running head: PERCEPTUAL GROUPING AND SPATIAL SELECTION 1 The attentional window configures to object boundaries University of Iowa Running head: PERCEPTUAL GROUPING AND SPATIAL SELECTION 2 ABSTRACT When
Exercise Science and Nutrition (MS) Student Learning Outcomes:
 Exercise Science and Nutrition (MS) Student Learning Outcomes: 1) Exhibit mastery of foundational and supporting areas of science and nutrition, resulting in safe and effective programming. 2) Demonstrate
Exercise Science and Nutrition (MS) Student Learning Outcomes: 1) Exhibit mastery of foundational and supporting areas of science and nutrition, resulting in safe and effective programming. 2) Demonstrate
Running head: CPPS REVIEW 1
 Running head: CPPS REVIEW 1 Please use the following citation when referencing this work: McGill, R. J. (2013). Test review: Children s Psychological Processing Scale (CPPS). Journal of Psychoeducational
Running head: CPPS REVIEW 1 Please use the following citation when referencing this work: McGill, R. J. (2013). Test review: Children s Psychological Processing Scale (CPPS). Journal of Psychoeducational
ΔTHC level. ΔTHC-COOH level
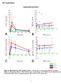 Supplemental information 12 2 11 18 1 16 THC (ng/dl) A 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 5 1 15 2 Minutes 25 ΔTHC level B 14 12 1 8 6 4 2-2 -4 y = 11.92x + 42.11 R² =.1375 y =.196x + 29.63 R² =.2977 y =.1513x +.8471 R²
Supplemental information 12 2 11 18 1 16 THC (ng/dl) A 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 5 1 15 2 Minutes 25 ΔTHC level B 14 12 1 8 6 4 2-2 -4 y = 11.92x + 42.11 R² =.1375 y =.196x + 29.63 R² =.2977 y =.1513x +.8471 R²
Neurocognitive and Psychophysiological Analysis of Human Performance within Virtual Reality Environments
 Medicine Meets Virtual Reality 17 J.D. Westwood et al. (Eds.) IOS Press, 2009 2009 The authors. All rights reserved. doi:10.3233/978-1-58603-964-6-247 247 Neurocognitive and Psychophysiological Analysis
Medicine Meets Virtual Reality 17 J.D. Westwood et al. (Eds.) IOS Press, 2009 2009 The authors. All rights reserved. doi:10.3233/978-1-58603-964-6-247 247 Neurocognitive and Psychophysiological Analysis
Sperling conducted experiments on An experiment was conducted by Sperling in the field of visual sensory memory.
 Levels of category Basic Level Category: Subordinate Category: Superordinate Category: Stages of development of Piaget 1. Sensorimotor stage 0-2 2. Preoperational stage 2-7 3. Concrete operational stage
Levels of category Basic Level Category: Subordinate Category: Superordinate Category: Stages of development of Piaget 1. Sensorimotor stage 0-2 2. Preoperational stage 2-7 3. Concrete operational stage
Application of ecological interface design to driver support systems
 Application of ecological interface design to driver support systems J.D. Lee, J.D. Hoffman, H.A. Stoner, B.D. Seppelt, and M.D. Brown Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, University of
Application of ecological interface design to driver support systems J.D. Lee, J.D. Hoffman, H.A. Stoner, B.D. Seppelt, and M.D. Brown Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, University of
Source memory and the picture superiority effect
 Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Master's Theses Graduate School 2007 Source memory and the picture superiority effect Noelle L. Brown Louisiana State University and Agricultural and
Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Master's Theses Graduate School 2007 Source memory and the picture superiority effect Noelle L. Brown Louisiana State University and Agricultural and
Coordination of Continuous and Discrete Components of Action
 Cleveland State University EngagedScholarship@CSU ETD Archive 2014 Coordination of Continuous and Discrete Components of Action Stephanie L. Kilian Cleveland State University How does access to this work
Cleveland State University EngagedScholarship@CSU ETD Archive 2014 Coordination of Continuous and Discrete Components of Action Stephanie L. Kilian Cleveland State University How does access to this work
Evaluating Reliance on Combat Identification Systems: The Role of Reliability Feedback
 Evaluating Reliance on Combat Identification Systems: The Role of Reliability Feedback Greg A. Jamieson, Heather F. Neyedli, Lu Wang University of Toronto; Justin G. Hollands - Defence Research and Development
Evaluating Reliance on Combat Identification Systems: The Role of Reliability Feedback Greg A. Jamieson, Heather F. Neyedli, Lu Wang University of Toronto; Justin G. Hollands - Defence Research and Development
TICK-MARKS, AXES, AND LABELS: THE EFFECTS OF ADDING CONTEXT TO AUDITORY GRAPHS
 TICK-MARKS, AXES, AND LABELS: THE EFFECTS OF ADDING CONTEXT TO AUDITORY GRAPHS Daniel R. Smith Sonification Lab, School of Psychology Georgia Institute of Technology, 274 5th Street Atlanta, GA 30332-0170
TICK-MARKS, AXES, AND LABELS: THE EFFECTS OF ADDING CONTEXT TO AUDITORY GRAPHS Daniel R. Smith Sonification Lab, School of Psychology Georgia Institute of Technology, 274 5th Street Atlanta, GA 30332-0170
PERFORMANCE PLANNING: YEARLY TRAINING PLAN
 PERFORMANCE PLANNING: YEARLY TRAINING PLAN Performance Planning Training Performance Planning training has three distinct parts: Long-Term Athlete Development Plans and Performance Planning Sport Profile
PERFORMANCE PLANNING: YEARLY TRAINING PLAN Performance Planning Training Performance Planning training has three distinct parts: Long-Term Athlete Development Plans and Performance Planning Sport Profile
BRIEF REPORTS. Signal probability effects on high-workload vigilance tasks
 Psychonomic Bulletin & Review 1996, 3 (3), 339-343 BRIEF REPORTS Signal probability effects on high-workload vigilance tasks GERALD MATTHEWS University ofdundee, Dundee, Scotland Signal probabilityis an
Psychonomic Bulletin & Review 1996, 3 (3), 339-343 BRIEF REPORTS Signal probability effects on high-workload vigilance tasks GERALD MATTHEWS University ofdundee, Dundee, Scotland Signal probabilityis an
Potential Benefits of a Concurrent Verbal Task when Feeling Fatigued Due to Monotonous Driving Conditions
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Driving Assessment Conference 2011 Driving Assessment Conference Jun 28th, 12:00 AM Potential Benefits of a Concurrent Verbal Task when Feeling Fatigued Due to Monotonous
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Driving Assessment Conference 2011 Driving Assessment Conference Jun 28th, 12:00 AM Potential Benefits of a Concurrent Verbal Task when Feeling Fatigued Due to Monotonous
An Affective Engineering Study of Vibrational Cues and Affect When Touching Car Interiors
 An Affective Engineering Study of Vibrational Cues and Affect When Touching Car Interiors Louise Manfredi, Brian Henson, Cathy Barnes, Tom Childs Affective Engineering Laboratory School of Mechanical Engineering
An Affective Engineering Study of Vibrational Cues and Affect When Touching Car Interiors Louise Manfredi, Brian Henson, Cathy Barnes, Tom Childs Affective Engineering Laboratory School of Mechanical Engineering
