In understanding the relationship between brain and mind,
|
|
|
- Muriel Spencer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE PHILOSOPHY OF CONSCIOUSNESS Pritam Majumdar 1 Abstract: In understanding the relationship between brain and mind, many spiritual, religious and metaphysical theories were evolved. Some became influential and others were discarded. Today, Neurophysiology and Cognitive science bundled together many disciplines and try to grapple with the complex phenomenon of mind or consciousness and its relationship with brain. Pritam Majumdar, a budding neuroscientist examines these conflicting theories and tires to arrive at some clear notions on consciousness. Key Words: externalism, perception, occasionalism, behaviorism, functionalism, reductionism. What and where is the mind located? If the mind is a physical phenomenon of some kind, it has to be located somewhere. According to some, there are two possible options: either the mind is internal to the body (internalism) or the mind is external to it (externalism). More generally, either the mind depends only on events and properties taking place inside the subject s body or it depends also on factors external to it.externalism differentiates into several versions. The main ones are semantic externalism, 1 Pritam Manjumdar is an aspiring scientist who researches on the brain-mind relationship and an associate at the North-spring Neurosciences-A Center for Excellence in Bangalore.
2 212 Happiness and Consciousness cognitive externalism, and phenomenal externalism. Each of these versions of externalism can further be divided whether they refer only to the content or to the vehicles of mind. Cognitive externalism is a very broad collection of views that suggests the role of the environment, of tools, of development, and of the body in fleshing out cognition. Embodied cognition, the extended mind, and en-activism are good examples. Mind is more psychological notion in cognitive or Neuroscientific meaning; it refers to processes of thinking, processes which are running in brain and so on; Consciousness is more phenomenological notion; it supposes specific mental reality which presumably differs from physical reality. A related problem is how someone s propositional attitudes (e.g. beliefs and desires) cause that individual s neurons to fire and his muscles to contract. These comprise some of the puzzles that have confronted epistemologists and philosophers of mind from at least the time of René Descartes. Philosophy of perception- is concerned with the nature of perceptual experience and the status of perceptual objects, in particular how perceptual experience relates to appearances and beliefs about the world. The main contemporary views within philosophy of perception include naive realism, enactivism and representational views. Within the field of neurobiology, there are many sub-disciplines that are concerned with the relations between mental and physical states and processes: Sensory neurophysiology investigates the relation between the processes of perception and stimulation. Cognitive neuroscience studies the correlations between mental processes and neural processes. Neuropsychology describes the dependence of mental faculties on specific anatomical regions of the brain. A simple example is multiplication. But it is clear that computers do not use a mind to multiply. Could they, someday, come to have what we call a mind? This question has been propelled into the forefront of much philosophical debate because of investigations in the field of artificial intelligence (AI). In taking the identity theory (in its various forms) as a species of physicalism, I should say that this is an ontological, not a translational physicalism. It would be absurd to try to translate sentences containing the word brain or the word sensation into sentences about electrons, protons and so on.
3 Happiness and Consciousness 213 Generally speaking there two possible answers to these questions: 1. On the one hand, we can assert that the mind it something material; therefore Mind is just a part of body. 2. On the other hand, it s possible to state that Mind is not a material or physical one; therefore, it s somehow connected with a body, but not reduced to it. It s pretty obvious and evident that Mind is related to the brain and physical processes in the brain. For instance, some brain traumas might cause changes in mental states. Moreover, when we effect on the brain (particular parts of brain) some specific mental states can be caused as hallucinations or uncommon sensual states. In these cases, a brain can be considered as a material part of a material body. Consequently the mind is a material entity. It s impossible to observe our thought as a physical phenomenon and, that there is not an access to our mental life, which is constituted of private non-observed experience. For example, when we conceive a yellow lemon or a pink elephant it doesn t mean that someone can find them in my brain. The lemon and the elephant as my mental images are nonphysical objects. Therefore mind is not a material entity. Causal Interactionism-Descartes thought that causal interaction between the mind and the body occurred in the pineal gland. He speculated that animal spirits - fluids made up of extremely fine particles flowing around the pineal gland cause it to move in various ways, and these motions of the gland in turn are because of the conscious states of the mind Pre-established Harmony» Between Mind and Body- Leibnitz, like many of his contemporaries, thought that no coherent sense could be made of Descartes, idea that an immaterial mind, which is not even in physical space, could causally interact with a material body like the pineal gland, managing to move this not-so-insignificant lump of tissue hither and thither. Occasionalism- According to Malebranche, another great continental rationalist, whenever a mental event appears to cause a physical event or a physical event appears to cause a mental event, it is only an illusion.
4 214 Happiness and Consciousness In Western Philosophy, the earliest discussions of dualist ideas are in the writings of Plato who maintained that humans intelligence (a faculty of the mind or soul) could not be identified with, or explained in terms of, their physical body 1. There substances of two fundamentally different kinds in the world, mind and bodies. The essential nature of a body is to be extended in space; the essence of a mind is to think and engage in other mental activities. 2. A human person is a composite being ( union, as Descartes called it) of a mind and a body; 3. Minds are diverse from bodies; 4. Minds and bodies causally influence each other. Some mental phenomena are causes of physical phenomena and vice versa. The most frequently used argument in favor of dualism appeals to the commonsense intuition that conscious experience is distinct from inanimate matter. If asked what the mind is, the average person would usually respond by identifying it with their self, their personality, their soul, or some other such entity. Another important argument in favor of dualism is that the mental and the physical seem to have quite different, and perhaps irreconcilable, properties. Mental events have a subjective quality, whereas physical events do not. So, for example, one can reasonably ask what a burnt finger feels like, or what a blue sky looks like, or what nice music sounds like to a person. If consciousness (the mind) can exist independently of physical reality (the brain), one must explain how physical memories are created concerning consciousness.each mind is such that there is a unique subject who has direct and privileged access to contents; No material body has a specially privileged knower-knowledge of material things is in principle public and inter-subjective;therefore, minds are not identical with material bodies. David Chalmers recently developed a thought experiment inspired by the movie The Matrix in which substance dualism could be true: Consider a computer simulation in which the bodies of the creatures are controlled by their minds and the minds remain strictly
5 Happiness and Consciousness 215 external to the simulation. The creatures can do all the science they want in the world, but they will never be able to figure out where their minds are, for they do not exist in their observable universe. This is a case of substance dualism with respect to computer simulation. This naturally differs from a computer simulation in which the minds are part of the simulation. In such a case, substance monism would be true. Behaviorism- arose early in the twentieth century as a doctrine on the nature and methodology of psychology, in reaction to what some psychologists took to be the subjective and unscientific character of intro-spectionist psychology. W.James: Psychology is the Science of Mental Life of its phenomena and of their conditions. The phenomena are such things as we call feelings, desires, cognitions, reasoning, decisions, and the like.j. Watson: Psychology is a purely objective experimental branch of nature science. It s the goal is the prediction and control of behavior. Four possible types of Behavior: 1) Physiological reactions and responses: for example, perspiration, salivation, increase in the pulse rate, and increase in blood pressure. 2) Bodily movements: for example, raising and waving a hand, opening a door, throwing a baseball, a cat scratching at the door, a rat turning left in a T-maze. 3) Actions involving bodily motions: for example, typing an invitation, greeting a friend, checking a book out of the library, going shopping, writing a check, and signing a contract. 4) Actions not involving overt bodily motions: for example, reasoning, guessing, calculating, judging, and deciding. Our knowledge is not based on evidence or inference; somehow we directly know. In contrast we have no such privileged access to our brain states. Mental states are directly accessible, brain states are not. So how can mental states be brain states? We have two types of identities:contingent Identity one term is rigid designator (name) and another is non-rigid designator
6 216 Happiness and Consciousness (description).necessary Identity both of terms are rigid designators names or natural terms. Pain is C-fibers stimulation consists on rigid designators (they are natural terms). Therefore this identity must be necessary, which means that it is impossible to conceive one without other pain without brain reactions. But we can easily conceive pain without brain stimulation and vice versa.so mind-body identity is false.how we can be sure that all pain-capable organisms have C-fibres. Functionalism- What makes something a tea-kettle or a vending machine is its ability to perform a certain function, not any specific physicochemical structure or mechanism. Many concepts seem to be functional concepts (for example, catalyst, gene, heart) appear to have an essentially functional component. Mentality can arise only in complex biological systems, like the human brain. It seems that the same neurobiological causal processes will go on matter what the neural states involved represent about the world or whether they represent anything at all. Neural processes seem no more responsive no meaning and representational content than are computational processes. Local physical biological conditions in the brain, not the distal states of affairs represented by them, are what drive neural processes. 1. Bridge-Law reduction (E. Nagel) the reduction of a higherlevel theory to a more fundamental theory. For example, the reduction of optics to electromagnetic theory or genetics to molecular biology. 2. Identity Reduction; 3. Functional Reduction. Mind is not Consciousness: There is something more (over and above) physical events in the brain; It could be very plausible that human mind has natural limitations to succeed in mind-body problem (R. Penrose, C. McGinn, S. Pinker, N. Chomsky). Some philosophers have closely associated subjectivity of Consciousness with the notion of a first person point
7 Happiness and Consciousness 217 of view, or perspective.there is no impersonal what is like to be ; it is always what is like for a given subject (for you, for me, for humans, for bats strictly speaking only for me) to see yellow, to taste pineapple, to eat a chocolate bar in flight.we have problems and mysteries. Mindbody problem is not a problem, it s a mystery. The operations of the human mind that can be carried out, are incapable in principle of taking us to a proper appreciation of what consciousness is and how it works. Mind-body problem doesn t have any appropriate solution for human beings. What do we need to be conscious? The anatomy and physiology of the brain: Coupled with some kind of basic set of processes through which we gather and generate information and use the gathered information in dealing with whatever is the next thing that comes along. Covering neurons, synapses, neurotransmitters; Localizations of function; neural assemblies and neural systems.the reigning question seems to be: Does consciousness stand alone, separate in some way with respect to the brain, or is it an intrinsic aspect of the brain s functioning? If consciousness is intrinsic then the question is, whether there are some sort of place within the brain that we can isolate as being the seat of consciousness? Or do we have to look more for an arrangement distributed over a larger scale? In looking at the connectivity in the visual system Dennett dispenses with the idea of the homunculus or a little man inside the brain which does the consciousness work. As Dennett says, it is an empirical fact that there is not a homunculus in the brain, and even if there were we would still have to go through the same investigation of the homunculus consciousness, and so on ad infinitum. It seems pretty unlikely that there would be a particular organ of the brain which takes the incoming, by-now-integrated (necessarily so, if this model were to work), data flow from one s body and the world and converts it (puts it up on the screen of the minds eye) into the qualia laden subjective world that report. They interweave their connectivity throughout the brain, supplying divergent and convergent information pathways wherever necessary.
8 218 Happiness and Consciousness Rodolfo Llinas: The brain is not a sausage...it is more like a well-tuned musical instrument. consciousness has emerged as an inevitable consequence of one particular evolutionary strategy which has so far proved remarkably successful, that of the development of increasingly flexible and modifiable behavioral performance, achieved by increasing the size of the brain and the complexity of the possible interactions of its components (my italics). [Rose, 1973] As I have said consciousness is a dynamic system and requires a theory of dynamic activity, in interaction with its environment. We cannot be a closed system without at least losing our humanity.one might suppose if an infant were to be abandoned at birth to complete isolation then (apart from the problem of its nutritional survival) it would possibly have nothing which we would recognize as consciousness. In a very complex system with a multitude of feedback loops relating to different neural pathways, operating with a variety of delays inherent such that the whole system will be in all kinds of states of inhibition of some signals and excitation of others, will inevitably have some pathways which are oscillating and reverberating such that the whole system may be said to be live. I contend that as an infant develops any impact on the body, limbs or muscles stimulates the afferent nerves. This stimulation initiates myelination of the nerve axon, and also asserts in the brain the existence of the fiber and its mapping into whichever cortical area it is involved with. Adjacent fibers carrying stimuli (signals) from adjacent areas on the sensing surface are similarly myelinated and mapped into the cortex. At the same time efferent nerves are carrying signals which initiate movements, the nerves are myelinated by their use and the muscles are stimulated to develop in their ability to respond. In the brain nerve processes from the sensory areas feed data to other areas of the brain including direct and higher level motor control areas.the first thing we notice when we talk about consciousness is that we, as humans, come in two conditions, either awake or not (viz. asleep, knocked out, in a coma, or dead), either conscious or unconscious.
9 Happiness and Consciousness 219 From this Descartes produced the famous Cogito ergo sum. I think therefore I am. Having established that there was a thinking thing which he knew as himself, he then had to discover where this thing lay! One thing Descartes did usefully establish was the recognition that-...faithful copies of the objects. Nothing can come from external objects to our mind by the medium of the senses, he said, except certain corporeal movements; but neither these movements themselves nor the figures arising from them, are conceived by us such as they are in the organs of sense. [Descartes: Dioptrics in Riese, W p133] The immediate condition of a state of consciousness is an activity of some sort in the cerebral hemispheres... One has only to consider how quickly consciousness may be abolished by a blow on the head... by a full dose of alcohol...to see how at the mercy of bodily happenings our spirit is... Destruction of certain definite portions of the cerebral hemispheres involves losses of memory and of acquired motor faculty of quite determinate sort... References: 1) José Luis Bermudez, Anthony Marcel & Naomi Eilan, eds., The Body and the Self, ) David Chalmers, The Conscious Mind, ) Paul Churchland, Neurophilosophy, ) Andy Clark, Supersizing the Mind, ) Jaegwon Kim, Philosophy of Mind 6) R. Penrose, C. McGinn, S. Pinker, N. Chomsky, Mind-Body problem. 7) Rose, 1973, complexity of the possible interactions of its components (my italics). 8) Descartes: Dioptrics in Riese, W p133
Materialism and the Mind and Body Problem:
 Materialism and the Mind and Body Problem: A Critical Analysis SeanAgius The philosophy of mind has become dominated by the mind and body problem: the relation between the physical (the body) and the mental
Materialism and the Mind and Body Problem: A Critical Analysis SeanAgius The philosophy of mind has become dominated by the mind and body problem: the relation between the physical (the body) and the mental
REVIEW. P.M. Churchland, Matter Bnd Consciousness. Revised Edition, Cambridge, Mass.: MIT Press, 1988.
 REVIEW P.M. Churchland, Matter Bnd Consciousness. Revised Edition, Cambridge, Mass.: MIT Press, 1988. Philosophy of mind is a lively issue these days. The abandonment of behaviorism, together with the
REVIEW P.M. Churchland, Matter Bnd Consciousness. Revised Edition, Cambridge, Mass.: MIT Press, 1988. Philosophy of mind is a lively issue these days. The abandonment of behaviorism, together with the
The Conscious Mind. - What is Mind? -No matter. -What is Matter? -Never mind. -Homer Simpson. Misha Sokolov B.A., M.Cog.Sci.
 The Conscious Mind - What is Mind? -No matter. -What is Matter? -Never mind -Homer Simpson Misha Sokolov B.A., M.Cog.Sci., PhD Candidate Overview Philosophical Framework Defining Consciousness The easy
The Conscious Mind - What is Mind? -No matter. -What is Matter? -Never mind -Homer Simpson Misha Sokolov B.A., M.Cog.Sci., PhD Candidate Overview Philosophical Framework Defining Consciousness The easy
CHAPTER TWO. The Philosophical Approach: Enduring Questions
 CHAPTER TWO The Philosophical Approach: Enduring Questions The Philosophy Perspective Philosophy is the search for knowledge. The branch of metaphysics examines the nature of reality. The branch of epistemology
CHAPTER TWO The Philosophical Approach: Enduring Questions The Philosophy Perspective Philosophy is the search for knowledge. The branch of metaphysics examines the nature of reality. The branch of epistemology
AI and Philosophy. Gilbert Harman. Thursday, October 9, What is the difference between people and other animals?
 AI and Philosophy Gilbert Harman Thursday, October 9, 2008 A Philosophical Question about Personal Identity What is it to be a person? What is the difference between people and other animals? Classical
AI and Philosophy Gilbert Harman Thursday, October 9, 2008 A Philosophical Question about Personal Identity What is it to be a person? What is the difference between people and other animals? Classical
AI and Philosophy. Gilbert Harman. Tuesday, December 4, Early Work in Computational Linguistics (including MT Lab at MIT)
 AI and Philosophy Gilbert Harman Tuesday, December 4, 2007 My Background Web site http://www.princeton.edu/~harman Philosophy Early Work in Computational Linguistics (including MT Lab at MIT) Cognitive
AI and Philosophy Gilbert Harman Tuesday, December 4, 2007 My Background Web site http://www.princeton.edu/~harman Philosophy Early Work in Computational Linguistics (including MT Lab at MIT) Cognitive
Identity theory and eliminative materialism. a) First trend: U. T. Place and Herbert Feigl- mental processes or events such as
 Lecture 2 Identity theory and eliminative materialism 1. The identity theory Two main trends: a) First trend: U. T. Place and Herbert Feigl- mental processes or events such as sensations = physical phenomena.
Lecture 2 Identity theory and eliminative materialism 1. The identity theory Two main trends: a) First trend: U. T. Place and Herbert Feigl- mental processes or events such as sensations = physical phenomena.
Eliminative materialism
 Michael Lacewing Eliminative materialism Eliminative materialism (also known as eliminativism) argues that future scientific developments will show that the way we think and talk about the mind is fundamentally
Michael Lacewing Eliminative materialism Eliminative materialism (also known as eliminativism) argues that future scientific developments will show that the way we think and talk about the mind is fundamentally
Explaining an Explanatory Gap Gilbert Harman Princeton University
 Explaining an Explanatory Gap Gilbert Harman Princeton University Discussions of the mind-body problem often refer to an explanatory gap (Levine 1983) between some aspect of our conscious mental life and
Explaining an Explanatory Gap Gilbert Harman Princeton University Discussions of the mind-body problem often refer to an explanatory gap (Levine 1983) between some aspect of our conscious mental life and
What is the relationship between the mind and the brain?
 What is the relationship between the mind and the brain? Ben White 05.02.2019 Mental Consciousness Belief Desire Thought Memory Sensation Perception Emotion Imagination Rationality What distinguishes the
What is the relationship between the mind and the brain? Ben White 05.02.2019 Mental Consciousness Belief Desire Thought Memory Sensation Perception Emotion Imagination Rationality What distinguishes the
Intro to Perception. Dr. Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Spring 2017, Princeton University
 Intro to Perception Dr. Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Spring 2017, Princeton University Time: Tues / Thurs 10-10:50am. Location: PNI A32. Sensation and Perception Fall 2017
Intro to Perception Dr. Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Spring 2017, Princeton University Time: Tues / Thurs 10-10:50am. Location: PNI A32. Sensation and Perception Fall 2017
PSYCHOLOGICAL CONSCIOUSNESS AND PHENOMENAL CONSCIOUSNESS. Overview
 Lecture 28-29 PSYCHOLOGICAL CONSCIOUSNESS AND PHENOMENAL CONSCIOUSNESS Overview David J. Chalmers in his famous book The Conscious Mind 1 tries to establish that the problem of consciousness as the hard
Lecture 28-29 PSYCHOLOGICAL CONSCIOUSNESS AND PHENOMENAL CONSCIOUSNESS Overview David J. Chalmers in his famous book The Conscious Mind 1 tries to establish that the problem of consciousness as the hard
Representational Content and Phenomenal Character
 By David Hilbert, Unversity of Illinois at Chicago, Forthcoming in Sage Encyclopedia of Perception QUALIA Perception and thought are often, although not exclusively, concerned with information about the
By David Hilbert, Unversity of Illinois at Chicago, Forthcoming in Sage Encyclopedia of Perception QUALIA Perception and thought are often, although not exclusively, concerned with information about the
CONSCIOUSNESS. Phil/Psych 256. Chris Eliasmith
 CONSCIOUSNESS Phil/Psych 256 Chris Eliasmith The C Word One main difficulty with consciousness is defining what we are talking about: Do we mean awareness (e.g., awake vs. asleep)? Qualia (what-it-is-like)?
CONSCIOUSNESS Phil/Psych 256 Chris Eliasmith The C Word One main difficulty with consciousness is defining what we are talking about: Do we mean awareness (e.g., awake vs. asleep)? Qualia (what-it-is-like)?
PHENOMENAL CONSCIUOSNESS: QUALIA & QUINNING QUALIA. Prof. Rajakishore Nath, Department of Humanities & Social Science, IIT Bombay
 PHENOMENAL CONSCIUOSNESS: QUALIA & QUINNING QUALIA Phenomenal Consciousness Phenomenal Concept of Mind Psychological Concept of Mind The phenomenal concept of mind is the concept of mind as conscious experience,
PHENOMENAL CONSCIUOSNESS: QUALIA & QUINNING QUALIA Phenomenal Consciousness Phenomenal Concept of Mind Psychological Concept of Mind The phenomenal concept of mind is the concept of mind as conscious experience,
Computation and Consciousness
 Computation and Consciousness Instructor: Viola Schiaffonati April,21 st 2016 Consciousness and the human biological system 2 Biological naturalism Consciousness as high level feature of the whole biological
Computation and Consciousness Instructor: Viola Schiaffonati April,21 st 2016 Consciousness and the human biological system 2 Biological naturalism Consciousness as high level feature of the whole biological
What Is Behavior? Statement of Logical Behaviorism (aka, philosophical/analytical behaviorism)
 What Is Behavior? 1. Physiological reactions and responses: for example, perspiration, salivation, increase in the pulse rate, increase in blood pressure. 2. Bodily movements: for example, raising and
What Is Behavior? 1. Physiological reactions and responses: for example, perspiration, salivation, increase in the pulse rate, increase in blood pressure. 2. Bodily movements: for example, raising and
David Chalmers, The hard problem of consciousness
 24.09x Minds and Machines David Chalmers, The hard problem of consciousness Excerpts from David Chalmers, The hard problem of consciousness, in The Norton Introduction to Philosophy, edited by Gideon Rosen,
24.09x Minds and Machines David Chalmers, The hard problem of consciousness Excerpts from David Chalmers, The hard problem of consciousness, in The Norton Introduction to Philosophy, edited by Gideon Rosen,
A Direct Object of Perception
 E-LOGOS Electronic Journal for Philosophy 2015, Vol. 22(1) 28 36 ISSN 1211-0442 (DOI 10.18267/j.e-logos.411),Peer-reviewed article Journal homepage: e-logos.vse.cz A Direct Object of Perception Mika Suojanen
E-LOGOS Electronic Journal for Philosophy 2015, Vol. 22(1) 28 36 ISSN 1211-0442 (DOI 10.18267/j.e-logos.411),Peer-reviewed article Journal homepage: e-logos.vse.cz A Direct Object of Perception Mika Suojanen
Phil 490: Consciousness and the Self Handout [16] Jesse Prinz: Mental Pointing Phenomenal Knowledge Without Concepts
![Phil 490: Consciousness and the Self Handout [16] Jesse Prinz: Mental Pointing Phenomenal Knowledge Without Concepts Phil 490: Consciousness and the Self Handout [16] Jesse Prinz: Mental Pointing Phenomenal Knowledge Without Concepts](/thumbs/88/117469450.jpg) Phil 490: Consciousness and the Self Handout [16] Jesse Prinz: Mental Pointing Phenomenal Knowledge Without Concepts Main Goals of this Paper: Professor JeeLoo Liu 1. To present an account of phenomenal
Phil 490: Consciousness and the Self Handout [16] Jesse Prinz: Mental Pointing Phenomenal Knowledge Without Concepts Main Goals of this Paper: Professor JeeLoo Liu 1. To present an account of phenomenal
24.500/Phil253 topics in philosophy of mind/perceptual experience
 24.500/Phil253 topics in philosophy of mind/perceptual experience session 10 24.500/Phil253 S07 1 plan tea @ 2.30 Block on consciousness, accessibility, FFA VWFA 24.500/Phil253 S07 2 phenomenal consciousness
24.500/Phil253 topics in philosophy of mind/perceptual experience session 10 24.500/Phil253 S07 1 plan tea @ 2.30 Block on consciousness, accessibility, FFA VWFA 24.500/Phil253 S07 2 phenomenal consciousness
U. T. Place, Is consciousness a brain process?
 24.09x Minds and Machines U. T. Place, Is consciousness a brain process? Excerpts from U.T. Place, Is consciousness a brain process?, British Journal of Psychology 47: 44-50, 1956. Place begins by noting
24.09x Minds and Machines U. T. Place, Is consciousness a brain process? Excerpts from U.T. Place, Is consciousness a brain process?, British Journal of Psychology 47: 44-50, 1956. Place begins by noting
Introduction. Chapter The Perceptual Process
 Chapter 1 Introduction Most of us take for granted our ability to perceive the external world. However, this is no simple deed at all. Imagine being given a task of designing a machine that can perceive,
Chapter 1 Introduction Most of us take for granted our ability to perceive the external world. However, this is no simple deed at all. Imagine being given a task of designing a machine that can perceive,
MIND BODY Problem. distinction: body soul. Mind-Body Problem 1. Psychology of Religous. Beliefs
 MIND BODY Problem distinction: body soul Mind-Body Problem 1 SOUL already Aristotle (384 322 BC) distinguishes: 1 soul as principle of life (animate, animer, beseelen): transforms dead matter into living
MIND BODY Problem distinction: body soul Mind-Body Problem 1 SOUL already Aristotle (384 322 BC) distinguishes: 1 soul as principle of life (animate, animer, beseelen): transforms dead matter into living
Introducing Psychology $
 Introducing Psychology $ INFLUENTIAL FIGURES IN THE HISTORY OF PSYCHOLOGY The formal study of Psychology dates from the late 1880s. The first proper Psychologists were Wilhelm Wundt, William James and
Introducing Psychology $ INFLUENTIAL FIGURES IN THE HISTORY OF PSYCHOLOGY The formal study of Psychology dates from the late 1880s. The first proper Psychologists were Wilhelm Wundt, William James and
Computers, Brains and Minds:
 Computers, Brains and Minds: Where are the ghosts within the machines? Anja Stemme a,, Gustavo Deco b, Stefan Büttner-von Stülpnagel c a Institute for Biophysics, University of Regensburg, Germany b ICREA
Computers, Brains and Minds: Where are the ghosts within the machines? Anja Stemme a,, Gustavo Deco b, Stefan Büttner-von Stülpnagel c a Institute for Biophysics, University of Regensburg, Germany b ICREA
Consciousness II. Mechanical Consciousness. Carlotta Pavese
 Consciousness II Mechanical Consciousness Carlotta Pavese 11.19.13 Outline 1 The Consciousness Debate 2 Outline 1 The Consciousness Debate 2 What is Consciousness? Some Things are Not So Baffling or Hard
Consciousness II Mechanical Consciousness Carlotta Pavese 11.19.13 Outline 1 The Consciousness Debate 2 Outline 1 The Consciousness Debate 2 What is Consciousness? Some Things are Not So Baffling or Hard
The hard problem of consciousness
 The hard problem of consciousness The hard problem of consciousness is to explain how qualia arise from physical processes in the brain. (èdavid Chalmers) Some thought experiments underscoring the hard
The hard problem of consciousness The hard problem of consciousness is to explain how qualia arise from physical processes in the brain. (èdavid Chalmers) Some thought experiments underscoring the hard
Complementarity and the Relation Between Psychological and Neurophysiological Phenomena
 the Relation Between Psychological and Neurophysiological Phenomena Douglas M. Snyder Berkeley, California ABSTRACT In their recent article, Kirsch and Hyland questioned the relation between psychological
the Relation Between Psychological and Neurophysiological Phenomena Douglas M. Snyder Berkeley, California ABSTRACT In their recent article, Kirsch and Hyland questioned the relation between psychological
How to reach Functionalism in 4 choices (and 639 words)
 How to reach Functionalism in 4 choices (and 639 words) Pack your baggage mine includes Physics aka Natural Philosophy Atheism (maybe Humanism) I don t t do God Information Technology (& OO Programming)
How to reach Functionalism in 4 choices (and 639 words) Pack your baggage mine includes Physics aka Natural Philosophy Atheism (maybe Humanism) I don t t do God Information Technology (& OO Programming)
Consciousness (Response to the Hard Problem)
 Indiana Undergraduate Journal of Cognitive Science 3 (2008) 21-27 Copyright 2008 IUJCS. All rights reserved Consciousness (Response to the Hard Problem) Artem Tsvetkov Cognitive Science and Biological
Indiana Undergraduate Journal of Cognitive Science 3 (2008) 21-27 Copyright 2008 IUJCS. All rights reserved Consciousness (Response to the Hard Problem) Artem Tsvetkov Cognitive Science and Biological
Comments on David Rosenthal s Consciousness, Content, and Metacognitive Judgments
 Consciousness and Cognition 9, 215 219 (2000) doi:10.1006/ccog.2000.0438, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Comments on David Rosenthal s Consciousness, Content, and Metacognitive Judgments
Consciousness and Cognition 9, 215 219 (2000) doi:10.1006/ccog.2000.0438, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Comments on David Rosenthal s Consciousness, Content, and Metacognitive Judgments
Psychology, Neuroscience, and the Consciousness Dilemma. Katalin Balog
 Psychology, Neuroscience, and the Consciousness Dilemma Katalin Balog In this paper, I present a dilemma for theorizing about the connection between phenomenality (the what it s like character of mental
Psychology, Neuroscience, and the Consciousness Dilemma Katalin Balog In this paper, I present a dilemma for theorizing about the connection between phenomenality (the what it s like character of mental
Functionalism. (1) Machine Functionalism
 Functionalism As Levine indicates, from a functionalist viewpoint, the status of a mental state is not given by its internal constitution but by its function. For instance, a thought or a pain depends
Functionalism As Levine indicates, from a functionalist viewpoint, the status of a mental state is not given by its internal constitution but by its function. For instance, a thought or a pain depends
Behaviorism: Laws of the Observable
 Behaviorism: Laws of the Observable Figure out what behaviors they find rewarding, and then reward them with those behaviors Behaviorism versus Behavioral Research According to Wilfred Sellars: a person
Behaviorism: Laws of the Observable Figure out what behaviors they find rewarding, and then reward them with those behaviors Behaviorism versus Behavioral Research According to Wilfred Sellars: a person
Ch 16. The Problem of Consciousness
 Ch 16. The Problem of Consciousness Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by S.-H. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
Ch 16. The Problem of Consciousness Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by S.-H. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
Metaphysics and consciousness. Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Metaphysics and consciousness Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Why neurophilosophy? Nature of the mind Classically part of philosophy Thought about without insight from neuroscience.
Metaphysics and consciousness Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Why neurophilosophy? Nature of the mind Classically part of philosophy Thought about without insight from neuroscience.
MIND, CONSCIOUSNESS AND CHOICEFULNESS
 MIND, CONSCIOUSNESS AND CHOICEFULNESS MIND "Originating from the mind" versus originating from the body. Thoughts Dreams Emotions Hunches and Intuitions Experience of sensations (I heard... I saw... )
MIND, CONSCIOUSNESS AND CHOICEFULNESS MIND "Originating from the mind" versus originating from the body. Thoughts Dreams Emotions Hunches and Intuitions Experience of sensations (I heard... I saw... )
On A Distinction Between Access and Phenomenal Consciousness
 On A Distinction Between Access and Phenomenal Consciousness By BRENT SILBY Department of Philosophy University of Canterbury New Zealand Copyright (c) Brent Silby 1998 www.def-logic.com/articles In his
On A Distinction Between Access and Phenomenal Consciousness By BRENT SILBY Department of Philosophy University of Canterbury New Zealand Copyright (c) Brent Silby 1998 www.def-logic.com/articles In his
Foundation for Mind-Being research. The Relationships and Evidence: Consciousness, Science, Spirituality, and Nature of the Universe
 Foundation for Mind-Being research The Relationships and Evidence: Consciousness, Science, Spirituality, and Nature of the Universe Search for a Scientific Theory of Consciousness Slides from FMBR Lecture
Foundation for Mind-Being research The Relationships and Evidence: Consciousness, Science, Spirituality, and Nature of the Universe Search for a Scientific Theory of Consciousness Slides from FMBR Lecture
Computational Perception and Cognition
 Computational Perception and Cognition ELL788 [Slides by Santanu Chaudhury, Hiranmay Ghosh, and Sumeet Agarwal] [Material sourced from Friedenberg and Silverman, 2006] Introduction: Philosophical & Psychological
Computational Perception and Cognition ELL788 [Slides by Santanu Chaudhury, Hiranmay Ghosh, and Sumeet Agarwal] [Material sourced from Friedenberg and Silverman, 2006] Introduction: Philosophical & Psychological
Key words: Qualia, First Person Perspective, The Hard Problem of Consciousness, and Subjectivity
 Lecture 43-44 THE NONREDUCTIVE MIND Overview Mind cannot be described only through objective behavioural or neurophysical terms. The real meaning of consciousness lies in its subjective and qualitative
Lecture 43-44 THE NONREDUCTIVE MIND Overview Mind cannot be described only through objective behavioural or neurophysical terms. The real meaning of consciousness lies in its subjective and qualitative
Paradoxes of personal identity: teletransportation, split brains, and immaterial souls
 Paradoxes of personal identity: teletransportation, split brains, and immaterial souls What is a theory of personal identity? Suppose that you have a person, A, who exists at some time, and a person, B,
Paradoxes of personal identity: teletransportation, split brains, and immaterial souls What is a theory of personal identity? Suppose that you have a person, A, who exists at some time, and a person, B,
The Importance of the Mind for Understanding How Emotions Are
 11.3 The Importance of the Mind for Understanding How Emotions Are Embodied Naomi I. Eisenberger For centuries, philosophers and psychologists alike have struggled with the question of how emotions seem
11.3 The Importance of the Mind for Understanding How Emotions Are Embodied Naomi I. Eisenberger For centuries, philosophers and psychologists alike have struggled with the question of how emotions seem
Perception Lie Paradox: Mathematically Proved Uncertainty about Humans Perception Similarity
 Perception Lie Paradox: Mathematically Proved Uncertainty about Humans Perception Similarity Ahmed M. Mahran Computer and Systems Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering, Alexandria University,
Perception Lie Paradox: Mathematically Proved Uncertainty about Humans Perception Similarity Ahmed M. Mahran Computer and Systems Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering, Alexandria University,
Important dates. PSY 3360 / CGS 3325 Historical Perspectives on Psychology Minds and Machines since Vitalism vs. Mechanism
 PSY 3360 / CGS 3325 Historical Perspectives on Psychology Minds and Machines since 1600 Dr. Peter Assmann Spring 2019 Important dates Feb 20 *** TODAY *** Term paper draft due by midnight Upload paper
PSY 3360 / CGS 3325 Historical Perspectives on Psychology Minds and Machines since 1600 Dr. Peter Assmann Spring 2019 Important dates Feb 20 *** TODAY *** Term paper draft due by midnight Upload paper
NEUROPHILOSOPHICAL FOUNDATIONS 1
 Disciplines of the Mind and Brain NEUROPHILOSOPHICAL FOUNDATIONS 1 Once philosophy incorporated all the fields of inquiry other than the applied fields of medicine, law, and theology What came to be identified
Disciplines of the Mind and Brain NEUROPHILOSOPHICAL FOUNDATIONS 1 Once philosophy incorporated all the fields of inquiry other than the applied fields of medicine, law, and theology What came to be identified
SEARLE AND FUNCTIONALISM. Is the mind software?
 SEARLE AND FUNCTIONALISM Is the mind software? 1 Materialist Theories of the Mind The Identity Theory Each type of mental property is identical to a certain type of physical property. E.g. pain is just
SEARLE AND FUNCTIONALISM Is the mind software? 1 Materialist Theories of the Mind The Identity Theory Each type of mental property is identical to a certain type of physical property. E.g. pain is just
SEARLE AND FUNCTIONALISM. Is the mind software?
 SEARLE AND FUNCTIONALISM Is the mind software? 1 Materialist Theories of the Mind The Identity Theory Each type of mental property is identical to a certain type of physical property. (E.g. pain is just
SEARLE AND FUNCTIONALISM Is the mind software? 1 Materialist Theories of the Mind The Identity Theory Each type of mental property is identical to a certain type of physical property. (E.g. pain is just
A conversation with Professor David Chalmers, May 20, 2016 Participants
 A conversation with Professor David Chalmers, May 20, 2016 Participants Professor David Chalmers Professor of Philosophy, New York University (NYU) Luke Muehlhauser Research Analyst, Open Philanthropy
A conversation with Professor David Chalmers, May 20, 2016 Participants Professor David Chalmers Professor of Philosophy, New York University (NYU) Luke Muehlhauser Research Analyst, Open Philanthropy
Functionalist theories of content
 Functionalist theories of content PHIL 93507 April 22, 2012 Let s assume that there is a certain stable dependence relation between the physical internal states of subjects and the phenomenal characters
Functionalist theories of content PHIL 93507 April 22, 2012 Let s assume that there is a certain stable dependence relation between the physical internal states of subjects and the phenomenal characters
Artificial intelligence (and Searle s objection) COS 116: 4/29/2008 Sanjeev Arora
 Artificial intelligence (and Searle s objection) COS 116: 4/29/2008 Sanjeev Arora Artificial Intelligence Definition of AI (Merriam-Webster): The capability of a machine to imitate intelligent human behavior
Artificial intelligence (and Searle s objection) COS 116: 4/29/2008 Sanjeev Arora Artificial Intelligence Definition of AI (Merriam-Webster): The capability of a machine to imitate intelligent human behavior
Conclusion. Course Evaluation Forms. Please pick up a set of forms before taking your seat. You may use either pen or pencil
 Conclusion Fall 2005 1 In which the mysteries of consciousness are explained or further mystified. 2 Course Evaluation Forms Please pick up a set of forms before taking your seat One for lectures One for
Conclusion Fall 2005 1 In which the mysteries of consciousness are explained or further mystified. 2 Course Evaluation Forms Please pick up a set of forms before taking your seat One for lectures One for
NEUROPHILOSOPHICAL FOUNDATIONS 1
 NEUROPHILOSOPHICAL FOUNDATIONS 1 Disciplines of the Mind and Brain Once upon a time philosophy incorporated all the fields of inquiry other than the applied fields of medicine, law, and theology What came
NEUROPHILOSOPHICAL FOUNDATIONS 1 Disciplines of the Mind and Brain Once upon a time philosophy incorporated all the fields of inquiry other than the applied fields of medicine, law, and theology What came
A High Resolution Picture of the Observer Questions and Answers
 A High Resolution Picture of the Observer Questions and Answers After further contemplation, our most recent revelations regarding the observer have been further modified. The precise locations of conscious
A High Resolution Picture of the Observer Questions and Answers After further contemplation, our most recent revelations regarding the observer have been further modified. The precise locations of conscious
Consciousness The final frontier!
 Consciousness The final frontier! How to Define it??? awareness perception - automatic and controlled memory - implicit and explicit ability to tell us about experiencing it attention. And the bottleneck
Consciousness The final frontier! How to Define it??? awareness perception - automatic and controlled memory - implicit and explicit ability to tell us about experiencing it attention. And the bottleneck
Neuroscience and Generalized Empirical Method Go Three Rounds
 Bruce Anderson, Neuroscience and Generalized Empirical Method Go Three Rounds: Review of Robert Henman s Global Collaboration: Neuroscience as Paradigmatic Journal of Macrodynamic Analysis 9 (2016): 74-78.
Bruce Anderson, Neuroscience and Generalized Empirical Method Go Three Rounds: Review of Robert Henman s Global Collaboration: Neuroscience as Paradigmatic Journal of Macrodynamic Analysis 9 (2016): 74-78.
Slide 1. Psychology 386b Fundamentals of Cognitive Science. Slide 2 Cognitive Science?
 Slide 1 Psychology 386b Fundamentals of Cognitive Science Instructor: Kevin D. Johnston Office: Rm. 6254 SSC E-Mail: kjohnsto@uwo.ca Slide 2 Cognitive Science? This course deals with the field of Cognitive
Slide 1 Psychology 386b Fundamentals of Cognitive Science Instructor: Kevin D. Johnston Office: Rm. 6254 SSC E-Mail: kjohnsto@uwo.ca Slide 2 Cognitive Science? This course deals with the field of Cognitive
Minds or Machines. John Beloff (1988) Intro to Philosophy Professor Douglas Olena
 Minds or Machines John Beloff (1988) Intro to Philosophy Professor Douglas Olena The Computational Metaphor 415 The Strong Claim is the claim put forward by some proponents of artificial intelligence that
Minds or Machines John Beloff (1988) Intro to Philosophy Professor Douglas Olena The Computational Metaphor 415 The Strong Claim is the claim put forward by some proponents of artificial intelligence that
Our previous accounts of perceptual experience accepted the phenomenal principle:
 PHL340 Handout 3: Representationalism 1 Representationalism and the Phenomenal Principle An experience s representational content is the way the world must be if the experience is to be veridical. Representationalism
PHL340 Handout 3: Representationalism 1 Representationalism and the Phenomenal Principle An experience s representational content is the way the world must be if the experience is to be veridical. Representationalism
Brain Mechanisms Explain Emotion and Consciousness. Paul Thagard University of Waterloo
 Brain Mechanisms Explain Emotion and Consciousness Paul Thagard University of Waterloo 1 1. Why emotions matter 2. Theories 3. Semantic pointers 4. Emotions 5. Consciousness Outline 2 What is Emotion?
Brain Mechanisms Explain Emotion and Consciousness Paul Thagard University of Waterloo 1 1. Why emotions matter 2. Theories 3. Semantic pointers 4. Emotions 5. Consciousness Outline 2 What is Emotion?
WHAT CONSCIOUS STATES ARE LIKE
 WHAT CONSCIOUS STATES ARE LIKE Thomas Nagel: Consciousness is what makes the mind-body problem really intractable [F]undamentally an organism has conscious mental states if and only if there is something
WHAT CONSCIOUS STATES ARE LIKE Thomas Nagel: Consciousness is what makes the mind-body problem really intractable [F]undamentally an organism has conscious mental states if and only if there is something
Learning from the Unwell Brain
 Neurophilosophy and the Healthy Mind Learning from the Unwell Brain Georg Northoff University of Ottawa Institute of Mental Health Research 10 The Neuropsychotherapist issue 21 December 2015 Mind and Brain
Neurophilosophy and the Healthy Mind Learning from the Unwell Brain Georg Northoff University of Ottawa Institute of Mental Health Research 10 The Neuropsychotherapist issue 21 December 2015 Mind and Brain
5.8 Departure from cognitivism: dynamical systems
 154 consciousness, on the other, was completely severed (Thompson, 2007a, p. 5). Consequently as Thompson claims cognitivism works with inadequate notion of cognition. This statement is at odds with practical
154 consciousness, on the other, was completely severed (Thompson, 2007a, p. 5). Consequently as Thompson claims cognitivism works with inadequate notion of cognition. This statement is at odds with practical
The Developing Viewpoints
 Chapter 2 The Developing Viewpoints The Developing Viewpoints In the second chapter of the book From Skinner to Rogers; Contrasting Approaches to Education by Frank Milhollan and Bill E. Forisha, the authors
Chapter 2 The Developing Viewpoints The Developing Viewpoints In the second chapter of the book From Skinner to Rogers; Contrasting Approaches to Education by Frank Milhollan and Bill E. Forisha, the authors
The scope of perceptual content, II: properties
 The scope of perceptual content, II: properties Jeff Speaks November 16, 2009 1 What are the candidates?............................ 1 2 Arguments for inclusion............................. 2 2.1 From
The scope of perceptual content, II: properties Jeff Speaks November 16, 2009 1 What are the candidates?............................ 1 2 Arguments for inclusion............................. 2 2.1 From
Mind & Body Behaviourism
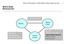 Blutner/Philosophy of Mind/Mind & Body/Behaviourism 1 Mind & Body Behaviourism Cartesian Dualism Duality Mental Cause Parallelism Occasionalism Epiphenomenalism Causal Closure Idealism Double-aspect theory
Blutner/Philosophy of Mind/Mind & Body/Behaviourism 1 Mind & Body Behaviourism Cartesian Dualism Duality Mental Cause Parallelism Occasionalism Epiphenomenalism Causal Closure Idealism Double-aspect theory
Psychology, Neuroscience, and the Consciousness Dilemma. Katalin Balog. Draft (comments welcome)
 Psychology, Neuroscience, and the Consciousness Dilemma Katalin Balog Draft (comments welcome) In this paper, I present a dilemma for theorizing about the connection between phenomenality (the what it
Psychology, Neuroscience, and the Consciousness Dilemma Katalin Balog Draft (comments welcome) In this paper, I present a dilemma for theorizing about the connection between phenomenality (the what it
NEUROPHILOSOPHICAL FOUNDATIONS
 NEUROPHILOSOPHICAL FOUNDATIONS Disciplines of the Mind and Brain Once upon a time philosophy incorporated all the fields of inquiry other than the applied fields of medicine, law, and theology What came
NEUROPHILOSOPHICAL FOUNDATIONS Disciplines of the Mind and Brain Once upon a time philosophy incorporated all the fields of inquiry other than the applied fields of medicine, law, and theology What came
Consciousness : An Integrative Systems Modelling Approach
 TSC 2014 East-West Forum Vision Talk Abstract Consciousness : An Integrative Systems Modelling Approach Prem Saran Satsangi Chairman, Advisory Committee on Education Dayalbagh Educational Institutions
TSC 2014 East-West Forum Vision Talk Abstract Consciousness : An Integrative Systems Modelling Approach Prem Saran Satsangi Chairman, Advisory Committee on Education Dayalbagh Educational Institutions
Subjective Consciousness: A Self-Representational Theory
 Book reviews Subjective Consciousness: A Self-Representational Theory, by Uriah Kriegel. Oxford University Press Inc., 2009, 335 pp. BIBLID [0873-626X (2012) 32; pp. 413-417] In the last decades interest
Book reviews Subjective Consciousness: A Self-Representational Theory, by Uriah Kriegel. Oxford University Press Inc., 2009, 335 pp. BIBLID [0873-626X (2012) 32; pp. 413-417] In the last decades interest
History and Approaches CHAPTER
 History and Approaches CHAPTER J :.-.. - n ;..., "".. =:1 KEY TERMS Wilhelm Wundt Psychoanalytic theory Biopsychology (or (1832-1920) John Watson neuroscience) Introspection (1878-1958) perspective Structuralism
History and Approaches CHAPTER J :.-.. - n ;..., "".. =:1 KEY TERMS Wilhelm Wundt Psychoanalytic theory Biopsychology (or (1832-1920) John Watson neuroscience) Introspection (1878-1958) perspective Structuralism
Chapter 1: Introduction MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Chapter 1: Introduction MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Historiography is: a. another term for psychology b. the study of the proper way to write history c. the use of photographs in presenting history d. another term
Chapter 1: Introduction MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Historiography is: a. another term for psychology b. the study of the proper way to write history c. the use of photographs in presenting history d. another term
Realism and Qualitative Research. Joseph A. Maxwell George Mason University
 Realism and Qualitative Research Joseph A. Maxwell George Mason University Philosophic realism in general is "the view that entities exist independently of being perceived, or independently of our theories
Realism and Qualitative Research Joseph A. Maxwell George Mason University Philosophic realism in general is "the view that entities exist independently of being perceived, or independently of our theories
History of Psychology: The Philosophical Roots
 Psychology 1000 Sept 14 th History of Psychology: The Philosophical Roots Early Greeks and other ancients Humans and Gods were quite separate from other living things. Humans and gods reasoned about the
Psychology 1000 Sept 14 th History of Psychology: The Philosophical Roots Early Greeks and other ancients Humans and Gods were quite separate from other living things. Humans and gods reasoned about the
Effective Intentions: The Power of Conscious Will
 Book Review Effective Intentions: The Power of Conscious Will Alfred R. Mele Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2009 Marco Fenici* fenici@unisi.it Mele s book is a concise analysis of much research in neurophysiology
Book Review Effective Intentions: The Power of Conscious Will Alfred R. Mele Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2009 Marco Fenici* fenici@unisi.it Mele s book is a concise analysis of much research in neurophysiology
Skepticism about perceptual content
 Skepticism about perceptual content phil 93515 Jeff Speaks March 29, 2007 1 Contents v. objects of perception The view that perceptual experiences have contents is the view that perceptual experiences
Skepticism about perceptual content phil 93515 Jeff Speaks March 29, 2007 1 Contents v. objects of perception The view that perceptual experiences have contents is the view that perceptual experiences
The issue (1) Some spikes. The issue (2) Am I spikes over time?
 Am I spikes over time? Leslie Smith Computing Science and Mathematics University of Stirling Stirling FK9 4LA, UK Email: l.s.smith@cs.stir.ac.uk URL: http://www.cs.stir.ac.uk/~lss The issue (1) What is
Am I spikes over time? Leslie Smith Computing Science and Mathematics University of Stirling Stirling FK9 4LA, UK Email: l.s.smith@cs.stir.ac.uk URL: http://www.cs.stir.ac.uk/~lss The issue (1) What is
Assessing the Foundations of Conscious Computing: A Bayesian Exercise
 Assessing the Foundations of Conscious Computing: A Bayesian Exercise Eric Horvitz June 2001 Questions have long been posed with about whether we might one day be able to create systems that experience
Assessing the Foundations of Conscious Computing: A Bayesian Exercise Eric Horvitz June 2001 Questions have long been posed with about whether we might one day be able to create systems that experience
Neither Brain nor Ghost: A Non-Dualist Alternative to the Mind-Brain Identity Theory. by Teed Rockwell Forthcoming on Bradford Books, MIT press
 Back to CQ Homepage Neither Brain nor Ghost: A Non-Dualist Alternative to the Mind-Brain Identity Theory. by Teed Rockwell Forthcoming on Bradford Books, MIT press Table of Contents with Summary Introduction:
Back to CQ Homepage Neither Brain nor Ghost: A Non-Dualist Alternative to the Mind-Brain Identity Theory. by Teed Rockwell Forthcoming on Bradford Books, MIT press Table of Contents with Summary Introduction:
Definition, History, Branches, Areas, Research Methods
 Definition, History, Branches, Areas, Research Methods Psychology is a word derived from ancient Greek roots: Psyche soul or mind, logos study Psychology is the study of the mind. The science of behavior
Definition, History, Branches, Areas, Research Methods Psychology is a word derived from ancient Greek roots: Psyche soul or mind, logos study Psychology is the study of the mind. The science of behavior
Brainy Brownson & the Body of Brown: The Reduction of Psychological Identity to
 1 Brainy Brownson & the Body of Brown: The Reduction of Psychological Identity to Bodily Identity Abstract: Psychological accounts of personal identity have typically taken the psychological aspects of
1 Brainy Brownson & the Body of Brown: The Reduction of Psychological Identity to Bodily Identity Abstract: Psychological accounts of personal identity have typically taken the psychological aspects of
An Escalation Model of Consciousness
 Bailey!1 Ben Bailey Current Issues in Cognitive Science Mark Feinstein 2015-12-18 An Escalation Model of Consciousness Introduction The idea of consciousness has plagued humanity since its inception. Humans
Bailey!1 Ben Bailey Current Issues in Cognitive Science Mark Feinstein 2015-12-18 An Escalation Model of Consciousness Introduction The idea of consciousness has plagued humanity since its inception. Humans
1.1 FEATURES OF THOUGHT
 SEC 1 Page 1 of 7 1.1 FEATURES OF THOUGHT Thought can refer to the ideas or arrangements of ideas that result from thinking, the act of producing thoughts, or the process of producing thoughts. Despite
SEC 1 Page 1 of 7 1.1 FEATURES OF THOUGHT Thought can refer to the ideas or arrangements of ideas that result from thinking, the act of producing thoughts, or the process of producing thoughts. Despite
PHILOSOPHY OF MIND AND COGNITIVE SCIENCE PHIL 30400, FALL 2018
 PHILOSOPHY OF MIND AND COGNITIVE SCIENCE PHIL 30400, FALL 2018 Dr. Devin Sanchez Curry dcurry@wooster.edu Class sessions: Scovel 205, M/W 2:00 3:20 Office hours: Scovel 002, T/W 9:30 10:50 The first unit
PHILOSOPHY OF MIND AND COGNITIVE SCIENCE PHIL 30400, FALL 2018 Dr. Devin Sanchez Curry dcurry@wooster.edu Class sessions: Scovel 205, M/W 2:00 3:20 Office hours: Scovel 002, T/W 9:30 10:50 The first unit
Is it ever possible, in being aware of an attribute of one s own body from the inside, to
 This is the author s version of an article that is forthcoming in Philosophical Studies. All citations should be to the published version, available online at http://www.springerlink.com/content/r63ht43687310366/.
This is the author s version of an article that is forthcoming in Philosophical Studies. All citations should be to the published version, available online at http://www.springerlink.com/content/r63ht43687310366/.
Over the years, philosophers, psychoanalysts, psychologists, psychiatrists,
 DEVELOPING A SELF: A GENERAL SEMANTICS WAY MILTON DAWES Over the years, philosophers, psychoanalysts, psychologists, psychiatrists, and others have asked: Is there such a thing as a self? Does the self
DEVELOPING A SELF: A GENERAL SEMANTICS WAY MILTON DAWES Over the years, philosophers, psychoanalysts, psychologists, psychiatrists, and others have asked: Is there such a thing as a self? Does the self
Towards a Scientific Account of Experience. Dennis Nicholson. 1. Introduction
 Towards a Scientific Account of Experience Dennis Nicholson 1. Introduction I defend the thesis that the physicalist two perspectives position on qualia described below merits further examination and debate
Towards a Scientific Account of Experience Dennis Nicholson 1. Introduction I defend the thesis that the physicalist two perspectives position on qualia described below merits further examination and debate
Three Themes in Understanding Psychology: Science, Philosophy, and History
 Three Themes in Understanding Psychology: Science, Philosophy, and History I. INTRODUCTION A. Issues and Goals Understanding psychology involves adopting three perspectives: Scientific Perspective: Understanding
Three Themes in Understanding Psychology: Science, Philosophy, and History I. INTRODUCTION A. Issues and Goals Understanding psychology involves adopting three perspectives: Scientific Perspective: Understanding
Competing Frameworks in Perception
 Competing Frameworks in Perception Lesson II: Perception module 08 Perception.08. 1 Views on perception Perception as a cascade of information processing stages From sensation to percept Template vs. feature
Competing Frameworks in Perception Lesson II: Perception module 08 Perception.08. 1 Views on perception Perception as a cascade of information processing stages From sensation to percept Template vs. feature
Competing Frameworks in Perception
 Competing Frameworks in Perception Lesson II: Perception module 08 Perception.08. 1 Views on perception Perception as a cascade of information processing stages From sensation to percept Template vs. feature
Competing Frameworks in Perception Lesson II: Perception module 08 Perception.08. 1 Views on perception Perception as a cascade of information processing stages From sensation to percept Template vs. feature
The Standard Theory of Conscious Perception
 The Standard Theory of Conscious Perception C. D. Jennings Department of Philosophy Boston University Pacific APA 2012 Outline 1 Introduction Motivation Background 2 Setting up the Problem Working Definitions
The Standard Theory of Conscious Perception C. D. Jennings Department of Philosophy Boston University Pacific APA 2012 Outline 1 Introduction Motivation Background 2 Setting up the Problem Working Definitions
Artificial Intelligence: Its Scope and Limits, by James Fetzer, Kluver Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Boston, London. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
 Artificial Intelligence: Its Scope and Limits, by James Fetzer, Kluver Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Boston, London. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the study of how to make machines behave intelligently,
Artificial Intelligence: Its Scope and Limits, by James Fetzer, Kluver Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Boston, London. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the study of how to make machines behave intelligently,
Lecture 14. Functionalism
 Lecture 14 Functionalism Overview Functionalism may be defined as a theory that explains mental phenomena in terms of the external input and the observable output. It explains the mind as a complicated
Lecture 14 Functionalism Overview Functionalism may be defined as a theory that explains mental phenomena in terms of the external input and the observable output. It explains the mind as a complicated
PSY 3360 / CGS 3325 Historical Perspectives on Psychology Minds and Machines since 1600
 PSY 3360 / CGS 3325 Historical Perspectives on Psychology Minds and Machines since 1600 Dr. Peter Assmann Spring 2019 Franz Gall (1758-1828) Gall postulated that the cerebral cortex serves the highest
PSY 3360 / CGS 3325 Historical Perspectives on Psychology Minds and Machines since 1600 Dr. Peter Assmann Spring 2019 Franz Gall (1758-1828) Gall postulated that the cerebral cortex serves the highest
THE POSSIBILITY OF EMPIRICAL TEST OF HYPOTHESES ABOUT CONSCIOUSNESS
 THE POSSIBILITY OF EMPIRICAL TEST OF HYPOTHESES ABOUT CONSCIOUSNESS Jean E. Burns, Ph.D. Consciousness Research 1525-153rd Avenue San Leandro, CA 94578 The possibility of empirical test is discussed with
THE POSSIBILITY OF EMPIRICAL TEST OF HYPOTHESES ABOUT CONSCIOUSNESS Jean E. Burns, Ph.D. Consciousness Research 1525-153rd Avenue San Leandro, CA 94578 The possibility of empirical test is discussed with
ID + MD = OD Towards a Fundamental Algorithm for Consciousness. by Thomas McGrath. June 30, Abstract
 ID + MD = OD Towards a Fundamental Algorithm for Consciousness by Thomas McGrath June 30, 2018 Abstract The Algorithm described in this short paper is a simplified formal representation of consciousness
ID + MD = OD Towards a Fundamental Algorithm for Consciousness by Thomas McGrath June 30, 2018 Abstract The Algorithm described in this short paper is a simplified formal representation of consciousness
Can Conscious Experience Affect Brain Activity?
 Benjamin Libet Can Conscious Experience Affect Brain Activity? The chief goal of Velmans article (2002) is to find a way to solve the problem of how conscious experience could have bodily effects. I shall
Benjamin Libet Can Conscious Experience Affect Brain Activity? The chief goal of Velmans article (2002) is to find a way to solve the problem of how conscious experience could have bodily effects. I shall
Experimental Psychology PSY 433. Appendix A Experimental Psychology: A Historical Sketch
 Experimental Psychology PSY 433 Appendix A Experimental Psychology: A Historical Sketch Origins in Philosophy Mind-body problem are the mind and body the same or different? If they are different substances,
Experimental Psychology PSY 433 Appendix A Experimental Psychology: A Historical Sketch Origins in Philosophy Mind-body problem are the mind and body the same or different? If they are different substances,
Is it possible to gain new knowledge by deduction?
 Is it possible to gain new knowledge by deduction? Abstract In this paper I will try to defend the hypothesis that it is possible to gain new knowledge through deduction. In order to achieve that goal,
Is it possible to gain new knowledge by deduction? Abstract In this paper I will try to defend the hypothesis that it is possible to gain new knowledge through deduction. In order to achieve that goal,
