Review for Midterm II. Study tips and insights to help you understand the material
|
|
|
- Adelia Richards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review for Midterm II Study tips and insights to help you understand the material
2 Exam scope: All of the readings and lectures for weeks 4, 5 and 6. Except: Dr. Boyle s Neural Network lecture
3 Topic 1: Social skills and development Lecture: Dr. Deák (1/29) How do we become socially skilled? Readings: How Babies Think
4 What is kin recognition? - An organism's ability to distinguish between close genetic kin and non-kin. - Also called kin detection - Very important! - Different sensory modalities - E.g. Mother Penguin and ewes use olfactory information to distinguish their kids from others; long-tailed tits (Aegithalos caudatus) are capable of discriminating kin and non-kin based on contact calls.
5 How should we study infant minds? - Verbal response? - Response time? Instead - Infants tend to pay more attention to something new, or more favorable. - Indirect measure: the relative amounts of time they pay attention to different events,
6 Can infants do face discrimination? (Layton & Rochat, 2007) - 4 months: no clear evidence of differential response - 8 months: distinguish mom s face from stranger s (still or moving) - Even within a few months we improve at face processing
7 What about Biological Motion?(Bertenthal et al, 1987). Stimulus In both conditions, 3-month-olds look at the scrambled walker longer. It indicates they think it s novel, which means that they CAN understand biological motion! Canonical Scrambled
8 Why do we have longer childhoods? - Precocial species: Mature early and show independent activities at birth. - Altricial species: Mature late. Require help from parents. Rely on learning.
9 What can a baby do? Babies are scientists!
10 What can a baby do? Cont. - They use statistics! - Babies and young children have an extraordinary ability to learn from statistical patterns. - They use statistics to learn sound patterns of language (Saffran et.al 1966). - Babies can even understand the relation between a statistical sample and a population (Xu, 2008). - They understand physics! - Elizabeth Spelke (Harvard) found that infants understand fundamental physical phenomena such as movement trajectories, gravity and containment. Ex: They look longer at a toy car appearing to pass through a solid wall than at events that violate basic principles of everyday physics.
11 What can a baby do? Cont. - They can be more creative than us! - They outperform us at tasks involving unusual possibilities, because they are more open-minded than adults. - e.g. Blicket detector task - Instructions make young children less creative! - Young children who think they are being instructed modify their statistical analysis and may become less creative as a result.
12 Topic 2: Social cognition and Mirror neurons Lectures: - Dr. Boyle (1/31) Introduction to Social Cognition - Dr. Singh (2/9) Mirror Neurons and Schizophrenia Readings: - First direct recording made of mirror neurons in human brain
13 What is embodied cognition? Classical View (or Cognitivism): Treats the brain as an input-output device that uses the internal manipulation of symbols to perform cognitive processes. Word meanings ultimately grounded on abstract symbols Embodied Cognition: Cognition is influenced and biased by states of the body, the environment, and the complex interaction between the two Word meanings are grounded on states of the body Ex: action words
14 What is embodied cognition? Embodied Cognition: Cognition is influenced and biased by states of the body, the environment, and the complex interaction between the two Word meanings are grounded on states of the body Ex: action words
15 What are mirror neurons? Mirror neurons are activated during the... Execution of an action Observation of an action Mirror neurons are multimodal! They become active both when either seeing or hearing an action being performed
16 What are mirror neurons really? Mirror neurons code for an action with a certain intention: Active in both full and occluded conditions Respond to either robotic or human hands Differentiate between different intentions
17 How can we measure mirror neurons? When? Where? EEG MEG TMS fmri
18 How can we measure mirror neurons? When? Where? EEG MEG TMS fmri
19 What is the relationship between mu suppression and mirror neurons? Mu = 8-12 Hz (Alpha-range) wave over M1 and S1 Changed by movement, attention, sleep, and visual tasks In typically developing subjects Suppressed while performing motor actions, observing motor actions, and imagining motor actions Suppression is increased for actions embedded in social context
20 What are mirror neurons for?
21 How does mu suppression differ across populations? Autism: Reduced mu suppression and social abilities in high functioning autistic children compared to typical children. Schizophrenia: Reduced mu suppression and social abilities compared to neurotypical controls. Perhaps, there is a relationship between these two variables. Mu suppression can be altered administration of oxytocin or by using neurofeedback
22 What is social cognition? Theory of Mind (ToM) Those with ToM are mindsighted The ability to attribute others mental states Commonly assessed using false-belief or Sally-Anne tasks Mindblindness The inability to attribute mental states to others Describes many on the autism spectrum
23 Topic 3: Social Cognition and Interaction Lecture: Dr. Rossano (2/14) Interacting like a human being. Reading: The Ultra-Social Animal
24 What is diversity? Diversity is: An assumption A tool Occurs across time (evolutionary or developmental) Occurs across individuals (individual differences are not noise!)
25 Who are the WEIRD? WEIRD people are Western, Educated, Industrialized, Rich, Democratic *96% of subjects in psychology experiments are WEIRD - WEIRD people make up 12% of the world population, and 80% of subjects are undergraduates.
26 What does social cognition involve? Intelligibility: how do we see what others see? (social attention) Accountability: taking into consideration how others will perceive, understand, and judge our actions when we act/plan to act Answerability/Responsibility: social norms, fairness and justice, social planning, trust, morality
27 How do humans and other species differ with regards to social interaction and social cognition? Requesting food Stealing food
28 How do humans and other species differ with regards to social interaction and social cognition? Voice Following Voice Following (Domestication vs. Socialization)
29 How do humans and other species differ with regards to social interaction and social cognition? Eye Direction Frontal eyes are good for depth perception and 3D vision, while lateral eyes are useful for peripheral vision. Eye Sclera Humans are the only primate with a white sclera. Why?
30 Topic 4: Animal cognition Lecture: Dr. Johnson (2/7) Animal Intelligence and Alien Minds. Reading: Cetaceans Have Complex Brains
31 How can we know the minds of non-humans? 1. We must appreciate each species sensorimotor constraints a. What a animal can/cannot do
32 What are some examples of sensorimotor constraints? -- Where are they on this spectrum? Vision?
33 What are some examples of sensorimotor constraints? Vision -- Where are they on this spectrum? Infrared Ultraviolet Human Visible Lights No color perception BUT good sensitivity to Motion & Contrast!
34 What are some examples of sensorimotor constraints? -- What do these structures enable? Vision Specialized body parts Primates forward facing eyes: Depth perception For hunting and arboreal activities Opposable thumbs: Grasping and tool manipulation
35 What are some examples of sensorimotor constraints? -- Yet why don t rodents use tools? Vision Specialized body parts Also have opposable thumbs
36 What are some examples of sensorimotor constraints? -- Different animals have different coordinations Vision Specialized body parts Body - eye coordination Primates: Hand-eye coordination Crows: Eye-beak-foot coordination Elephants: Trunk-eye coordination
37 What are some examples of universal principles? Classical example: Pavlov s dog Temporal contiguity: Animals will use Event 1 to predict Event 2 when the events overlap in time BUT EXCEPTION: Taste Aversion Learning: Event Correlations Only learns association between food and illness if the poisonous effect appears with >1 hour delay! Because?
38 What are some examples of universal principles? Win stay /Lose shift If Win (get reward) then Stay (continue same response) If Lose (don t get reward) then Shift (try another strategy) BUT EXCEPTION: What if the animal gets reward from a non-reusable resource, in the natural habitat? Win shift
39 How can we know the minds of non-humans? - Ecological Validity: The degree to which a research setup resembles an animal s real experience. - Is this research taking place in something that approximates an animal s natural environment?
40 What does ecological validity look like?
41 How can we know the minds of non-humans? Keep these principles in mind: -- sensorimotor constraints -- learning principles -- environmental validity
42 Making dolphins do Match to Sample using Color or Contrast as cues bad good good bad Training Pigeons or Hummingbirds using Win stay / lose shift strategy really good Running rats in mazes? Considering: sensorimotor constraints learning principles environmental validity
43 More experiments Know the results!
44 What about a dolphin s brain allows it to be so smart? Large mass Large relative mass with respect to body Regional parcellation with expanded insula and cingulate cortices Large number of layer V spindle neurons High ratio of white matter to gray matter High ratio of glial cells to neurons
45 What are glial cells? Oligodendrocytes: Astrocytes: provide myelination in the Central Nervous System Reason of white matter Predominate in the gray matter Maintain extracellular ion (electrical) balance Nurture nervous tissues and repair traumatic injuries Microglia: Immune cells in the Central Nervous System
46 Dolphins have smart brains, but are they smart? (from Cetacean reading) Declarative knowledge: understand symbolic representations and events Can learn imposed language, including the languages semantics and syntax Procedural knowledge: understand how things work or how to manipulate them Can use simple tools and otherwise interact with the world Social knowledge: understand activities, identities, behaviors of others Understand and provide attention guidance via pointing and head gaze Self knowledge: understand own image, behavior, and body parts Recognize themselves in the mirror So Many of these, Go to your reading!
47 Why are dolphins and humans cognitively similar? (from Cetacean reading) Convergent Evolution!
48 Topic 5: Distributed cognition Lecture: Dr. Scott (2/12) Introduction to Distributed Cognition Reading: Cognition, Distributed
49 How have researchers thought about cognition before? 1. Behaviorism: Concerned with observable behaviors rather than internal mental processes. a. e.g. Pavlov s classical conditioning
50 2. Cognitivism: Concerned less with visible behavior and more with the internal processes of the mind. Treats the brain as an input-output device that uses the internal manipulation of symbols to perform cognitive processes. e.g. The Information Processing Theory is a metaphor that equates the work of the human brain to that of the computer.
51 3. Post-cognitivism! (Combination of embodied, distributed, and other approaches to cognition)
52 What insights about cognition come from the distributed cognition approach? - Brain is important but not enough! - Brain should be seen as the controller for body-world interaction. - Action can reveal underlying cognitive processes - Bidirectional interactions of the brain & body with the material and social world is a form of cognition too. - Entails a broader unit of analysis.
53 What insights about cognition come from the distributed cognition approach? Social requirements/information bottlenecks result in information transfer systems Information needs to transfer across low-traffic boundaries, and symbol systems arise to deal with transferring information across these bottlenecks
54 Where did d-cog come from and how do we apply it? - Cognition in the Wild describes observing human cognition in its natural habitat. - The book describes Cognitive Ethnography which entails: - The scientific description of the customs of individual peoples and cultures. - Accurate records of specific instances of real world human behavior. - Analyze of the cognitive aspects of those instances. Edwin Hutchins
55 What is the BIG problem with cognitive ethnography? Seeing but not seeing problem: Neglecting details but remembering the gist Filling the gaps in visual scenes Neglecting background info e.g. Invisible gorilla Not hearing disfluencies and unimportant words Shared cultural models We need guidelines: Cognito-scope: Slow down and be honest, pay attention to how representations are transformed across time, people, and the environment. Look at the process of the manipulation of cognitive representations with a martian perspective.
56 That s it! Thank you to the other TA/IA s for helping with the slides! Happy to answer your questions!
Mirror Neurons in Primates, Humans, and Implications for Neuropsychiatric Disorders
 Mirror Neurons in Primates, Humans, and Implications for Neuropsychiatric Disorders Fiza Singh, M.D. H.S. Assistant Clinical Professor of Psychiatry UCSD School of Medicine VA San Diego Healthcare System
Mirror Neurons in Primates, Humans, and Implications for Neuropsychiatric Disorders Fiza Singh, M.D. H.S. Assistant Clinical Professor of Psychiatry UCSD School of Medicine VA San Diego Healthcare System
Reminders. What s a Neuron? Animals at Birth. How are Neurons formed? Prenatal Neural Development. Week 28. Week 3 Week 4. Week 10.
 Reminders What s a Neuron? Exam 1 Thursday Multiple Choice and Short Answer Bring Scantron form and #2 pencil Includes Chapter 1- Chapter 3 BUT NOT 3.1 (We will cover this on the next test) You may use
Reminders What s a Neuron? Exam 1 Thursday Multiple Choice and Short Answer Bring Scantron form and #2 pencil Includes Chapter 1- Chapter 3 BUT NOT 3.1 (We will cover this on the next test) You may use
Animal Cognition. Introduction to Cognitive Science
 Animal Cognition Introduction to Cognitive Science Intelligent Animals? Parrot Intelligence Crow Intelligence I Crow Intelligence II Cow Intelligence Orca Intelligence Dolphin Play Funny Animal Intelligence
Animal Cognition Introduction to Cognitive Science Intelligent Animals? Parrot Intelligence Crow Intelligence I Crow Intelligence II Cow Intelligence Orca Intelligence Dolphin Play Funny Animal Intelligence
INTRODUCTION TO MIRROR NEURONS MARY ET BOYLE, PH.D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE UCSD
 INTRODUCTION TO MIRROR NEURONS MARY ET BOYLE, PH.D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE UCSD Announcements Midterm 1 Review Friday during Lecture Midterm 1 Exam February 5 Monday! During lecture come prepared
INTRODUCTION TO MIRROR NEURONS MARY ET BOYLE, PH.D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE UCSD Announcements Midterm 1 Review Friday during Lecture Midterm 1 Exam February 5 Monday! During lecture come prepared
Learning. Learning: Problems. Chapter 6: Learning
 Chapter 6: Learning 1 Learning 1. In perception we studied that we are responsive to stimuli in the external world. Although some of these stimulus-response associations are innate many are learnt. 2.
Chapter 6: Learning 1 Learning 1. In perception we studied that we are responsive to stimuli in the external world. Although some of these stimulus-response associations are innate many are learnt. 2.
COGS 1: FALL Section E
 COGS 1: FALL 2018 Section E Professor Boyle mboyle@ucsd.edu Monday, 2-3:50pm CSB 130 Zoe tzcheng@ucsd.edu Monday, 12-12:50pm CSB 223 Lauren lcurley@ucsd.edu Monday, 2:-250pm CSB 225 Subathra suraj@ucsd.edu
COGS 1: FALL 2018 Section E Professor Boyle mboyle@ucsd.edu Monday, 2-3:50pm CSB 130 Zoe tzcheng@ucsd.edu Monday, 12-12:50pm CSB 223 Lauren lcurley@ucsd.edu Monday, 2:-250pm CSB 225 Subathra suraj@ucsd.edu
Autism & intellectual disabilities. How to deal with confusing concepts
 Autism & intellectual disabilities How to deal with confusing concepts dr. Gerard J. Nijhof Orthopedagogue / GZ-psychologist PhD, Free University Amsterdam Private practice contact@gerardnijhof.nl +31
Autism & intellectual disabilities How to deal with confusing concepts dr. Gerard J. Nijhof Orthopedagogue / GZ-psychologist PhD, Free University Amsterdam Private practice contact@gerardnijhof.nl +31
0-3 DEVELOPMENT. By Drina Madden. Pediatric Neuropsychology 1
 0-3 DEVELOPMENT By Drina Madden DrinaMadden@hotmail.com www.ndcbrain.com 1 PHYSICAL Body Growth Changes in height and weight are rapid in the first two years of life. Development moves from head to tail
0-3 DEVELOPMENT By Drina Madden DrinaMadden@hotmail.com www.ndcbrain.com 1 PHYSICAL Body Growth Changes in height and weight are rapid in the first two years of life. Development moves from head to tail
Mirror neurons in the infant brain are formed by the interactions between self and other. M. Iacoboni SELF AND OTHER. J. A. Pineda COGS171 UCSD
 Mirror neurons in the infant brain are formed by the interactions between self and other. M. Iacoboni SELF AND OTHER J. A. Pineda COGS171 UCSD What is the SELF? There are multiple attributes of SELF including
Mirror neurons in the infant brain are formed by the interactions between self and other. M. Iacoboni SELF AND OTHER J. A. Pineda COGS171 UCSD What is the SELF? There are multiple attributes of SELF including
Psychology Perception
 Psychology 343 - Perception James R. Sawusch, 360 Park Hall jsawusch@buffalo.edu 645-0238 TA is Timothy Pruitt, 312 Park tapruitt@buffalo.edu Text is Sensation & Perception by Goldstein (8th edition) PSY
Psychology 343 - Perception James R. Sawusch, 360 Park Hall jsawusch@buffalo.edu 645-0238 TA is Timothy Pruitt, 312 Park tapruitt@buffalo.edu Text is Sensation & Perception by Goldstein (8th edition) PSY
Social Cognition and the Mirror Neuron System of the Brain
 Motivating Questions Social Cognition and the Mirror Neuron System of the Brain Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Cognitive Neuroscience Laboratory COGS1 class How do our brains perceive the mental states of others
Motivating Questions Social Cognition and the Mirror Neuron System of the Brain Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Cognitive Neuroscience Laboratory COGS1 class How do our brains perceive the mental states of others
GRADE LEVEL AND SUBJECT: ADVANCED PLACEMENT PSYCHOLOGY (11 TH AND 12 TH )
 GRADE LEVEL AND SUBJECT: ADVANCED PLACEMENT PSYCHOLOGY (11 TH AND 12 TH ) DOMAIN CONTENT STANDARDS PERFORMANCE STANDARDS ASSESSMENT AUGUST METHODS Careers and Subfields Define psychology Weekly Quizzes
GRADE LEVEL AND SUBJECT: ADVANCED PLACEMENT PSYCHOLOGY (11 TH AND 12 TH ) DOMAIN CONTENT STANDARDS PERFORMANCE STANDARDS ASSESSMENT AUGUST METHODS Careers and Subfields Define psychology Weekly Quizzes
Changing Community Perceptions About Autism
 Changing Community Perceptions About Autism Be Aware, Accept, Include In a world filled with change and diversity I feel it s time to change the views and perceptions of Autism I believe it is something
Changing Community Perceptions About Autism Be Aware, Accept, Include In a world filled with change and diversity I feel it s time to change the views and perceptions of Autism I believe it is something
The Perceptual Experience
 Dikran J. Martin Introduction to Psychology Name: Date: Lecture Series: Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception Pages: 35 TEXT: Lefton, Lester A. and Brannon, Linda (2003). PSYCHOLOGY. (Eighth Edition.) Needham
Dikran J. Martin Introduction to Psychology Name: Date: Lecture Series: Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception Pages: 35 TEXT: Lefton, Lester A. and Brannon, Linda (2003). PSYCHOLOGY. (Eighth Edition.) Needham
5.8 Departure from cognitivism: dynamical systems
 154 consciousness, on the other, was completely severed (Thompson, 2007a, p. 5). Consequently as Thompson claims cognitivism works with inadequate notion of cognition. This statement is at odds with practical
154 consciousness, on the other, was completely severed (Thompson, 2007a, p. 5). Consequently as Thompson claims cognitivism works with inadequate notion of cognition. This statement is at odds with practical
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT: HELPING ALL CHILDREN DO AND BE THEIR BEST. February 9, :30 8:00 p.m. (Delicious Dinner First!)
 BRAIN DEVELOPMENT: HELPING ALL CHILDREN DO AND BE THEIR BEST February 9, 2012 5:30 8:00 p.m. (Delicious Dinner First!) Most annoying thing about learning about the brainmom was right! Everything we talk
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT: HELPING ALL CHILDREN DO AND BE THEIR BEST February 9, 2012 5:30 8:00 p.m. (Delicious Dinner First!) Most annoying thing about learning about the brainmom was right! Everything we talk
COGS 1: FALL Section D
 COGS 1: FALL 2018 Section D Professor Boyle mboyle@ucsd.edu Monday, 2-3:50pm CSB 130 Zoe tzcheng@ucsd.edu Monday, 12-12:50pm CSB 223 Lauren lcurley@ucsd.edu Monday, 2:-250pm CSB 225 Subathra suraj@ucsd.edu
COGS 1: FALL 2018 Section D Professor Boyle mboyle@ucsd.edu Monday, 2-3:50pm CSB 130 Zoe tzcheng@ucsd.edu Monday, 12-12:50pm CSB 223 Lauren lcurley@ucsd.edu Monday, 2:-250pm CSB 225 Subathra suraj@ucsd.edu
Human Cognitive Developmental Neuroscience. Jan 27
 Human Cognitive Developmental Neuroscience Jan 27 Wiki Definition Developmental cognitive neuroscience is an interdisciplinary scientific field that is situated at the boundaries of Neuroscience Psychology
Human Cognitive Developmental Neuroscience Jan 27 Wiki Definition Developmental cognitive neuroscience is an interdisciplinary scientific field that is situated at the boundaries of Neuroscience Psychology
MSc Psychological Research Methods/ MPsych Advanced Psychology Module Catalogue / 2018
 MSc Psychological Research Methods/ MPsych Advanced Psychology Module Catalogue - 2017 / 2018 PSY555: Communication of Research for Psychology (Semester 2) 10 credits core PRM, option MPsych This module
MSc Psychological Research Methods/ MPsych Advanced Psychology Module Catalogue - 2017 / 2018 PSY555: Communication of Research for Psychology (Semester 2) 10 credits core PRM, option MPsych This module
Learning & Language Development
 Learning & Language Development Classical Conditioning An involuntary response when a stimulus that normally causes a particular response is paired with a new, neutral stimulus. After enough pairings,
Learning & Language Development Classical Conditioning An involuntary response when a stimulus that normally causes a particular response is paired with a new, neutral stimulus. After enough pairings,
Lesson 5 Sensation, Perception, Memory, and The Conscious Mind
 Lesson 5 Sensation, Perception, Memory, and The Conscious Mind Introduction: Connecting Your Learning The beginning of Bloom's lecture concludes his discussion of language development in humans and non-humans
Lesson 5 Sensation, Perception, Memory, and The Conscious Mind Introduction: Connecting Your Learning The beginning of Bloom's lecture concludes his discussion of language development in humans and non-humans
The Central Nervous System
 The Central Nervous System Cellular Basis. Neural Communication. Major Structures. Principles & Methods. Principles of Neural Organization Big Question #1: Representation. How is the external world coded
The Central Nervous System Cellular Basis. Neural Communication. Major Structures. Principles & Methods. Principles of Neural Organization Big Question #1: Representation. How is the external world coded
Grounded Cognition. Lawrence W. Barsalou
 Grounded Cognition Lawrence W. Barsalou Department of Psychology Emory University July 2008 Grounded Cognition 1 Definition of grounded cognition the core representations in cognition are not: amodal symbols
Grounded Cognition Lawrence W. Barsalou Department of Psychology Emory University July 2008 Grounded Cognition 1 Definition of grounded cognition the core representations in cognition are not: amodal symbols
Expert Strategies for Working with Anxiety
 Expert Strategies for Working with Anxiety Bonus 1 - Transcript - pg. 1 Expert Strategies for Working with Anxiety An EMDR Approach for Healing Generalized Anxiety Disorder with Laurel Parnell, PhD; Rick
Expert Strategies for Working with Anxiety Bonus 1 - Transcript - pg. 1 Expert Strategies for Working with Anxiety An EMDR Approach for Healing Generalized Anxiety Disorder with Laurel Parnell, PhD; Rick
Psychology Formative Assessment #2 Answer Key
 Psychology Formative Assessment #2 Answer Key 1) C 2) B 3) B 4) C 5) D AP Objective: Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters 6) E AP Objective: Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters
Psychology Formative Assessment #2 Answer Key 1) C 2) B 3) B 4) C 5) D AP Objective: Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters 6) E AP Objective: Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters
Psychology: Exploring Behavior. Table of Contents. Chapter: Psychology: Its Nature and Nurture 1. Chapter: Methods and Data 37
 i Table of Contents Chapter: Psychology: Its Nature and Nurture 1 What Is Psychology? 1 Psychology: Its Nature and Nurture 3 Definition of psychology 4 The History of Psychology 6 Psychology in the 1800s
i Table of Contents Chapter: Psychology: Its Nature and Nurture 1 What Is Psychology? 1 Psychology: Its Nature and Nurture 3 Definition of psychology 4 The History of Psychology 6 Psychology in the 1800s
Vision and Action. 10/3/12 Percep,on Ac,on 1
 Vision and Action Our ability to move thru our environment is closely tied to visual perception. Simple examples include standing one one foot. It is easier to maintain balance with the eyes open than
Vision and Action Our ability to move thru our environment is closely tied to visual perception. Simple examples include standing one one foot. It is easier to maintain balance with the eyes open than
EHDI 2015 Louisville, KY Patricia E. Spencer Marilyn Sass-Lehrer Gallaudet University, Washington, DC
 It s Only Natural: Nurturing Development of Deaf and Hard-of-Hearing Babies in the First 6 Months EHDI 2015 Louisville, KY Patricia E. Spencer Marilyn Sass-Lehrer Gallaudet University, Washington, DC Overview
It s Only Natural: Nurturing Development of Deaf and Hard-of-Hearing Babies in the First 6 Months EHDI 2015 Louisville, KY Patricia E. Spencer Marilyn Sass-Lehrer Gallaudet University, Washington, DC Overview
Why is He Doing That?
 Bruno & Pontello All Rights Reserved Why is He Doing That? The Functions and Management of Behavior By: John Bruno, Ph.D. and Jennifer Pontello, M.Ed. Agenda Introductions Differences that contribute to
Bruno & Pontello All Rights Reserved Why is He Doing That? The Functions and Management of Behavior By: John Bruno, Ph.D. and Jennifer Pontello, M.Ed. Agenda Introductions Differences that contribute to
What can we do to improve the outcomes for all adolescents? Changes to the brain and adolescence-- Structural and functional changes in the brain
 The Adolescent Brain-- Implications for the SLP Melissa McGrath, M.A., CCC-SLP Ball State University Indiana Speech Language and Hearing Association- Spring Convention April 15, 2016 State of adolescents
The Adolescent Brain-- Implications for the SLP Melissa McGrath, M.A., CCC-SLP Ball State University Indiana Speech Language and Hearing Association- Spring Convention April 15, 2016 State of adolescents
The Relation Between Perception and Action: What Should Neuroscience Learn From Psychology?
 ECOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY, 13(2), 117 122 Copyright 2001, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. The Relation Between Perception and Action: What Should Neuroscience Learn From Psychology? Patrick R. Green Department
ECOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY, 13(2), 117 122 Copyright 2001, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc. The Relation Between Perception and Action: What Should Neuroscience Learn From Psychology? Patrick R. Green Department
Chapter 1: Thinking Critically With Psychological Science
 The Need for Psychological Science Did we Know it All Along? Hindsight Bias Overconfidence Perceiving Order in Random Events The Scientific Attitude: Curious, Skeptical, and Humble Critical Thinking 1-1
The Need for Psychological Science Did we Know it All Along? Hindsight Bias Overconfidence Perceiving Order in Random Events The Scientific Attitude: Curious, Skeptical, and Humble Critical Thinking 1-1
Computational Explorations in Cognitive Neuroscience Chapter 7: Large-Scale Brain Area Functional Organization
 Computational Explorations in Cognitive Neuroscience Chapter 7: Large-Scale Brain Area Functional Organization 1 7.1 Overview This chapter aims to provide a framework for modeling cognitive phenomena based
Computational Explorations in Cognitive Neuroscience Chapter 7: Large-Scale Brain Area Functional Organization 1 7.1 Overview This chapter aims to provide a framework for modeling cognitive phenomena based
Developmental Social Cognition Cognitive Development
 Developmental Social Cognition Cognitive Development People Concepts Do we think about people in the same way that we think about inanimate objects? What if your brother was... a zombie? Walk slowly About
Developmental Social Cognition Cognitive Development People Concepts Do we think about people in the same way that we think about inanimate objects? What if your brother was... a zombie? Walk slowly About
Cognitive Science (COG SCI)
 University of California, Berkeley 1 Cognitive Science (COG SCI) Courses Expand all course descriptions [+]Collapse all course descriptions [-] COG SCI 1 Introduction to Cognitive Science 4 Terms offered:
University of California, Berkeley 1 Cognitive Science (COG SCI) Courses Expand all course descriptions [+]Collapse all course descriptions [-] COG SCI 1 Introduction to Cognitive Science 4 Terms offered:
ANAT2010. Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018
 ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
Epilepsy and Neuropsychology
 Epilepsy and Neuropsychology Dr. Sare Akdag, RPsych Neuropsychology Service, BC Children s Hospital Clinical Assistant Professor, Dept of Paediatrics, UBC November 24, 2008 BC Epilepsy Society Lecture
Epilepsy and Neuropsychology Dr. Sare Akdag, RPsych Neuropsychology Service, BC Children s Hospital Clinical Assistant Professor, Dept of Paediatrics, UBC November 24, 2008 BC Epilepsy Society Lecture
DYNAMICISM & ROBOTICS
 DYNAMICISM & ROBOTICS Phil/Psych 256 Chris Eliasmith Dynamicism and Robotics A different way of being inspired by biology by behavior Recapitulate evolution (sort of) A challenge to both connectionism
DYNAMICISM & ROBOTICS Phil/Psych 256 Chris Eliasmith Dynamicism and Robotics A different way of being inspired by biology by behavior Recapitulate evolution (sort of) A challenge to both connectionism
Audio: In this lecture we are going to address psychology as a science. Slide #2
 Psychology 312: Lecture 2 Psychology as a Science Slide #1 Psychology As A Science In this lecture we are going to address psychology as a science. Slide #2 Outline Psychology is an empirical science.
Psychology 312: Lecture 2 Psychology as a Science Slide #1 Psychology As A Science In this lecture we are going to address psychology as a science. Slide #2 Outline Psychology is an empirical science.
COURSE DESCRIPTIONS 科目簡介
 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS 科目簡介 COURSES FOR 4-YEAR UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAMMES PSY2101 Introduction to Psychology (3 credits) The purpose of this course is to introduce fundamental concepts and theories in psychology
COURSE DESCRIPTIONS 科目簡介 COURSES FOR 4-YEAR UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAMMES PSY2101 Introduction to Psychology (3 credits) The purpose of this course is to introduce fundamental concepts and theories in psychology
Brain & Behavior Syllabus V Instructor Mike Hawken Spring 2006
 Brain & Behavior Syllabus V55.0306 Instructor Mike Hawken Spring 2006 Week 1 INTRODUCTION 1/17 Lecture 1 Introduction and History of Neuroscience early influences Reading: Chapter 1, pp 2 23 1/19 Lecture
Brain & Behavior Syllabus V55.0306 Instructor Mike Hawken Spring 2006 Week 1 INTRODUCTION 1/17 Lecture 1 Introduction and History of Neuroscience early influences Reading: Chapter 1, pp 2 23 1/19 Lecture
Cetacean Brains Cogs 143 * UCSD
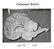 Cetacean Brains Cogs 143 * UCSD EQ -- Encephalization Quotient EQ = Actual brain mass / Expected brain mass Where expected = 0.12 x (Body mass) 2/3 EQ -- Encephalization Quotient Chimp Human Dolphin Globular
Cetacean Brains Cogs 143 * UCSD EQ -- Encephalization Quotient EQ = Actual brain mass / Expected brain mass Where expected = 0.12 x (Body mass) 2/3 EQ -- Encephalization Quotient Chimp Human Dolphin Globular
The Benefits of Aquatic Therapy for Children Diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder(s)
 The Benefits of Aquatic Therapy for Children Diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder(s) Understand Autism Autism Terminology Myths & Facts around Autism Perceptions of Autism Symptoms and Characteristics
The Benefits of Aquatic Therapy for Children Diagnosed with Autism Spectrum Disorder(s) Understand Autism Autism Terminology Myths & Facts around Autism Perceptions of Autism Symptoms and Characteristics
4/3/2017. Myles, THE NEUROLOGY OF ASD. Anna. Brenda Smith Myles, Ph.D. NOT ALL SLIDES ARE IN YOUR HANDOUTS.
 THE NEUROLOGY OF ASD Brenda Smith Myles, Ph.D. www.texasautism.org NOT ALL SLIDES ARE IN YOUR HANDOUTS Anna Facebook, 2016 Myles, 2016 1 Austin wrote: I wish that they knew that I am autistic. I wish that
THE NEUROLOGY OF ASD Brenda Smith Myles, Ph.D. www.texasautism.org NOT ALL SLIDES ARE IN YOUR HANDOUTS Anna Facebook, 2016 Myles, 2016 1 Austin wrote: I wish that they knew that I am autistic. I wish that
Piaget. Updates/Announcements. Overview. Cognitive Development. Jean Piaget. Try this
 Updates/Announcements Piaget Exams end of class Papers end of class Assignment #4 dispersed today February 20, 2007 Bryan T. Karazsia, M.A. Overview Cognitive Development What is cognition? Jean Piaget
Updates/Announcements Piaget Exams end of class Papers end of class Assignment #4 dispersed today February 20, 2007 Bryan T. Karazsia, M.A. Overview Cognitive Development What is cognition? Jean Piaget
shows syntax in his language. has a large neocortex, which explains his language abilities. shows remarkable cognitive abilities. all of the above.
 Section: Chapter 14: Multiple Choice 1. Alex the parrot: pp.529-530 shows syntax in his language. has a large neocortex, which explains his language abilities. shows remarkable cognitive abilities. all
Section: Chapter 14: Multiple Choice 1. Alex the parrot: pp.529-530 shows syntax in his language. has a large neocortex, which explains his language abilities. shows remarkable cognitive abilities. all
Livingston American School Quarterly Lesson Plan
 Livingston American School Quarterly Lesson Plan Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Concept / Topic To Teach: VISION & HEARING OTHER IMPORTANT SENSES & PERCEPTUAL ORGANIZATION Standards Addressed: PERCEPTUAL
Livingston American School Quarterly Lesson Plan Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Concept / Topic To Teach: VISION & HEARING OTHER IMPORTANT SENSES & PERCEPTUAL ORGANIZATION Standards Addressed: PERCEPTUAL
CS/NEUR125 Brains, Minds, and Machines. Due: Friday, April 14
 CS/NEUR125 Brains, Minds, and Machines Assignment 5: Neural mechanisms of object-based attention Due: Friday, April 14 This Assignment is a guided reading of the 2014 paper, Neural Mechanisms of Object-Based
CS/NEUR125 Brains, Minds, and Machines Assignment 5: Neural mechanisms of object-based attention Due: Friday, April 14 This Assignment is a guided reading of the 2014 paper, Neural Mechanisms of Object-Based
Views of autistic adults on assessment in the early years
 Views of autistic adults on what should be assessed and how assessment should be conducted on children with autism in the early years Summary of autistic adults views on assessment 1. Avoid drawing negative
Views of autistic adults on what should be assessed and how assessment should be conducted on children with autism in the early years Summary of autistic adults views on assessment 1. Avoid drawing negative
A Three Agent Model of Consciousness Explains Spirituality and Multiple Nondual Enlightened States Frank Heile, Ph.D.
 A Three Agent Model of Consciousness Explains Spirituality and Multiple Nondual Enlightened States Frank Heile, Ph.D. Author and Physicist (Degrees from Stanford and MIT) frank@spiritualityexplained.com
A Three Agent Model of Consciousness Explains Spirituality and Multiple Nondual Enlightened States Frank Heile, Ph.D. Author and Physicist (Degrees from Stanford and MIT) frank@spiritualityexplained.com
This Lecture: Psychology of Memory and Brain Areas Involved
 Lecture 18 (Nov 24 th ): LEARNING & MEMORY #1 Lecture Outline This Lecture: Psychology of Memory and Brain Areas Involved Next lecture: Neural Mechanisms for Memory 1) Psychology of Memory: Short Term
Lecture 18 (Nov 24 th ): LEARNING & MEMORY #1 Lecture Outline This Lecture: Psychology of Memory and Brain Areas Involved Next lecture: Neural Mechanisms for Memory 1) Psychology of Memory: Short Term
Understanding Early Childhood Brain Development
 Understanding Early Childhood Brain Development 201 Understanding Early Childhood Brain Development Why should caregivers know about brain development? The brain is the part of the body that allows us
Understanding Early Childhood Brain Development 201 Understanding Early Childhood Brain Development Why should caregivers know about brain development? The brain is the part of the body that allows us
Time Experiencing by Robotic Agents
 Time Experiencing by Robotic Agents Michail Maniadakis 1 and Marc Wittmann 2 and Panos Trahanias 1 1- Foundation for Research and Technology - Hellas, ICS, Greece 2- Institute for Frontier Areas of Psychology
Time Experiencing by Robotic Agents Michail Maniadakis 1 and Marc Wittmann 2 and Panos Trahanias 1 1- Foundation for Research and Technology - Hellas, ICS, Greece 2- Institute for Frontier Areas of Psychology
CLASSROOM & PLAYGROUND
 The information contained in this booklet was most generously provided to Autism South Africa by the UK National Autistic Society The production and printing of this and 12 other brochures was made possible
The information contained in this booklet was most generously provided to Autism South Africa by the UK National Autistic Society The production and printing of this and 12 other brochures was made possible
the human 1 of 3 Lecture 6 chapter 1 Remember to start on your paper prototyping
 Lecture 6 chapter 1 the human 1 of 3 Remember to start on your paper prototyping Use the Tutorials Bring coloured pencil, felts etc Scissor, cello tape, glue Imagination Lecture 6 the human 1 1 Lecture
Lecture 6 chapter 1 the human 1 of 3 Remember to start on your paper prototyping Use the Tutorials Bring coloured pencil, felts etc Scissor, cello tape, glue Imagination Lecture 6 the human 1 1 Lecture
Joint Attention. Joint Attention. Joint Attention. Joint Attention and ASD: Enhancing Language and Social Competence
 The and ASD: Enhancing Language and Social Competence Joanne Gerenser, Ph.D., CCC-SLP The ability to coordinate attention between people and objects Loveland & Landry (1986) An attentionalstate during
The and ASD: Enhancing Language and Social Competence Joanne Gerenser, Ph.D., CCC-SLP The ability to coordinate attention between people and objects Loveland & Landry (1986) An attentionalstate during
using deep learning models to understand visual cortex
 using deep learning models to understand visual cortex 11-785 Introduction to Deep Learning Fall 2017 Michael Tarr Department of Psychology Center for the Neural Basis of Cognition this lecture A bit out
using deep learning models to understand visual cortex 11-785 Introduction to Deep Learning Fall 2017 Michael Tarr Department of Psychology Center for the Neural Basis of Cognition this lecture A bit out
2 Psychological Processes : An Introduction
 2 Psychological Processes : An Introduction 2.1 Introduction In our everyday life we try to achieve various goals through different activities, receive information from our environment, learn about many
2 Psychological Processes : An Introduction 2.1 Introduction In our everyday life we try to achieve various goals through different activities, receive information from our environment, learn about many
BOROUGH OF MANHATTAN COMMUNITY COLLEGE City University of New York Department of Social Sciences
 BOROUGH OF MANHATTAN COMMUNITY COLLEGE City University of New York Department of Social Sciences Developmental Psychology: PSY 240-1704 and 1403 Prof. Zorn, Adjunct Lecturer-Spring 2016 Extra Credit Voluntary
BOROUGH OF MANHATTAN COMMUNITY COLLEGE City University of New York Department of Social Sciences Developmental Psychology: PSY 240-1704 and 1403 Prof. Zorn, Adjunct Lecturer-Spring 2016 Extra Credit Voluntary
Supporting Children with an Autism Spectrum Disorder. An Introduction for Health and Social Care Practitioners
 Supporting Children with an Autism Spectrum Disorder An Introduction for Health and Social Care Practitioners Overview This learning tool has been developed to support professionals working with children
Supporting Children with an Autism Spectrum Disorder An Introduction for Health and Social Care Practitioners Overview This learning tool has been developed to support professionals working with children
Change Blindness. The greater the lie, the greater the chance that it will be believed.
 Change Blindness The greater the lie, the greater the chance that it will be believed. (kurt@kloover.com) Department of Computer Science Rochester Institute of Technology 1 Definitions Seeing: the use
Change Blindness The greater the lie, the greater the chance that it will be believed. (kurt@kloover.com) Department of Computer Science Rochester Institute of Technology 1 Definitions Seeing: the use
2017 Texas Symposium on DeafBlindness The Impact of Stress on Brain Architecture and Resilience Friday, Keynote March 3-4, 2017
 Texas School for the Blind and Visually Impaired Outreach Programs www.tsbvi.edu 512-454-8631 1100 W. 45 th St. Austin, TX 78756 2017 Texas Symposium on DeafBlindness The Impact of Stress on Brain Architecture
Texas School for the Blind and Visually Impaired Outreach Programs www.tsbvi.edu 512-454-8631 1100 W. 45 th St. Austin, TX 78756 2017 Texas Symposium on DeafBlindness The Impact of Stress on Brain Architecture
COGS 121 HCI Programming Studio. Week 03
 COGS 121 HCI Programming Studio Week 03 Direct Manipulation Principles of Direct Manipulation 1. Continuous representations of the objects and actions of interest with meaningful visual metaphors. 2. Physical
COGS 121 HCI Programming Studio Week 03 Direct Manipulation Principles of Direct Manipulation 1. Continuous representations of the objects and actions of interest with meaningful visual metaphors. 2. Physical
The origins of localization
 Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions Michael E. Goldberg, M.D. The origins of localization The concept that different parts of the brain did different
Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions Michael E. Goldberg, M.D. The origins of localization The concept that different parts of the brain did different
Prof. Greg Francis 7/7/08
 Perceptual development IIE 366: Developmental Psychology Chapter 5: Perceptual and Motor Development Module 5.1 Basic Sensory and Perceptual Processes Greg Francis Lecture 11 Children and Their Development,
Perceptual development IIE 366: Developmental Psychology Chapter 5: Perceptual and Motor Development Module 5.1 Basic Sensory and Perceptual Processes Greg Francis Lecture 11 Children and Their Development,
NCERT Solutions Class 11 Psychology. Chapter - The Bases of Human Behaviour
 NCERT Solutions Class 11 Psychology Chapter - The Bases of Human Behaviour Question 1. How does the evolutionary perspective explain the biological basis of behaviour? Answer: Evolution refers to gradual
NCERT Solutions Class 11 Psychology Chapter - The Bases of Human Behaviour Question 1. How does the evolutionary perspective explain the biological basis of behaviour? Answer: Evolution refers to gradual
2017 Texas Symposium on DeafBlindness The Impact of Stress on Brain Architecture and Resilience Friday, Keynote March 3-4, 2017
 Texas School for the Blind and Visually Impaired Outreach Programs www.tsbvi.edu 512-454-8631 1100 W. 45 th St. Austin, TX 78756 2017 Texas Symposium on DeafBlindness The Impact of Stress on Brain Architecture
Texas School for the Blind and Visually Impaired Outreach Programs www.tsbvi.edu 512-454-8631 1100 W. 45 th St. Austin, TX 78756 2017 Texas Symposium on DeafBlindness The Impact of Stress on Brain Architecture
Bell work: What are some advances in mental representation with children who are in the preoperational stage? What are some limitations of thought?
 Bell work: What are some advances in mental representation with children who are in the preoperational stage? What are some limitations of thought? Preoperational Stage: - Thoughts aren t logical yet.
Bell work: What are some advances in mental representation with children who are in the preoperational stage? What are some limitations of thought? Preoperational Stage: - Thoughts aren t logical yet.
Sensation. I. Basic Concepts II. Characteristics of Sensory Systems III. The Visual System
 Sensation I. Basic Concepts II. Characteristics of Sensory Systems III. The Visual System Sensation The process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies
Sensation I. Basic Concepts II. Characteristics of Sensory Systems III. The Visual System Sensation The process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies
Is Cognitive Science Special? In what way is it special? Cognitive science is a delicate mixture of the obvious and the incredible
 Sept 3, 2013 Is Cognitive Science Special? In what way is it special? Zenon Pylyshyn, Rutgers Center for Cognitive Science Cognitive science is a delicate mixture of the obvious and the incredible What
Sept 3, 2013 Is Cognitive Science Special? In what way is it special? Zenon Pylyshyn, Rutgers Center for Cognitive Science Cognitive science is a delicate mixture of the obvious and the incredible What
A Scientific Model of Consciousness that Explains Spirituality and Enlightened States
 A Scientific Model of Consciousness that Explains Spirituality and Enlightened States Frank Heile, Ph.D. Physics degrees from Stanford and MIT consciousness@frankheile.com April 2016 Outline Part 1: Agents
A Scientific Model of Consciousness that Explains Spirituality and Enlightened States Frank Heile, Ph.D. Physics degrees from Stanford and MIT consciousness@frankheile.com April 2016 Outline Part 1: Agents
Chapter 6: Attribution Processes
 Chapter 6: Attribution Processes 1. Which of the following is an example of an attributional process in social cognition? a. The act of planning the actions to take given a social situation b. The act
Chapter 6: Attribution Processes 1. Which of the following is an example of an attributional process in social cognition? a. The act of planning the actions to take given a social situation b. The act
Dr Lisa Bunting (Lecturer in Social Work, QUB) Mairead Lavery (title, SEHSCT) Nov 2017
 Dr Lisa Bunting (Lecturer in Social Work, QUB) Mairead Lavery (title, SEHSCT) Nov 2017 STRUCTURE Defining Trauma and Adversity The Prevalence and Impact of Multiple Adversities How adversity causes poor
Dr Lisa Bunting (Lecturer in Social Work, QUB) Mairead Lavery (title, SEHSCT) Nov 2017 STRUCTURE Defining Trauma and Adversity The Prevalence and Impact of Multiple Adversities How adversity causes poor
The Helping Relationship
 The Helping Relationship A Certificate Program in Psychosocial Rehabilitation Instructor s Manual 2002 Copyright 2002 by California Association of Social Rehabilitation Agencies (). All rights reserved.
The Helping Relationship A Certificate Program in Psychosocial Rehabilitation Instructor s Manual 2002 Copyright 2002 by California Association of Social Rehabilitation Agencies (). All rights reserved.
Halgin, Richard P. Taking Sides: Clashing Views on Controversial Issues in Abnormal Psychology, 3 rd ed. Dubuque, Iowa: McGraw- Hill, 2005
 Advanced Placement Psychology, 2016-2017 Textbook: Myers Psychology for AP, 2 st ed. New York: Worth, 2014 Supplemental Reading: Hock, Roger R. Forty Studies that Changed Psychology: Explorations into
Advanced Placement Psychology, 2016-2017 Textbook: Myers Psychology for AP, 2 st ed. New York: Worth, 2014 Supplemental Reading: Hock, Roger R. Forty Studies that Changed Psychology: Explorations into
Multiple Intelligences: Let em show you how they re smart! Diana Beasley April 17, 2007 East Carolina University
 Multiple Intelligences: Let em show you how they re smart! Diana Beasley April 17, 2007 East Carolina University Some facts about me: Name 3 things you like to do in nature. Write the name of a favorite
Multiple Intelligences: Let em show you how they re smart! Diana Beasley April 17, 2007 East Carolina University Some facts about me: Name 3 things you like to do in nature. Write the name of a favorite
Sperling conducted experiments on An experiment was conducted by Sperling in the field of visual sensory memory.
 Levels of category Basic Level Category: Subordinate Category: Superordinate Category: Stages of development of Piaget 1. Sensorimotor stage 0-2 2. Preoperational stage 2-7 3. Concrete operational stage
Levels of category Basic Level Category: Subordinate Category: Superordinate Category: Stages of development of Piaget 1. Sensorimotor stage 0-2 2. Preoperational stage 2-7 3. Concrete operational stage
Autism Spectrum Disorders
 Autism Spectrum Disorders The gap between research and interventions Sara Schroer & Michael Goldstein The plan 1. What is autism? 2. How does it emerge across development? 3. What are the core impairments?
Autism Spectrum Disorders The gap between research and interventions Sara Schroer & Michael Goldstein The plan 1. What is autism? 2. How does it emerge across development? 3. What are the core impairments?
NEURO-BRAIN BOOTCAMP Expanding Leadership and Creativity through the Miracle of Modern (Neuro)Science
 NEURO-BRAIN BOOTCAMP Expanding Leadership and Creativity through the Miracle of Modern (Neuro)Science Gina Paigen, PCC, CPCC, CNTC Chief Impact Officer Two Roles Role #1: Be fully immersed in your experience
NEURO-BRAIN BOOTCAMP Expanding Leadership and Creativity through the Miracle of Modern (Neuro)Science Gina Paigen, PCC, CPCC, CNTC Chief Impact Officer Two Roles Role #1: Be fully immersed in your experience
Rules of apparent motion: The shortest-path constraint: objects will take the shortest path between flashed positions.
 Rules of apparent motion: The shortest-path constraint: objects will take the shortest path between flashed positions. The box interrupts the apparent motion. The box interrupts the apparent motion.
Rules of apparent motion: The shortest-path constraint: objects will take the shortest path between flashed positions. The box interrupts the apparent motion. The box interrupts the apparent motion.
ESF Strategic Report and its Conclusions
 ESF Strategic Report and its Conclusions The Human Brain From Cells to Society Towards Better Mental Health in Europe Presenter: Professor, Ph.D., Daniel David ESF Steering Committee for the Strategic
ESF Strategic Report and its Conclusions The Human Brain From Cells to Society Towards Better Mental Health in Europe Presenter: Professor, Ph.D., Daniel David ESF Steering Committee for the Strategic
Competing Frameworks in Perception
 Competing Frameworks in Perception Lesson II: Perception module 08 Perception.08. 1 Views on perception Perception as a cascade of information processing stages From sensation to percept Template vs. feature
Competing Frameworks in Perception Lesson II: Perception module 08 Perception.08. 1 Views on perception Perception as a cascade of information processing stages From sensation to percept Template vs. feature
Competing Frameworks in Perception
 Competing Frameworks in Perception Lesson II: Perception module 08 Perception.08. 1 Views on perception Perception as a cascade of information processing stages From sensation to percept Template vs. feature
Competing Frameworks in Perception Lesson II: Perception module 08 Perception.08. 1 Views on perception Perception as a cascade of information processing stages From sensation to percept Template vs. feature
Chapter 6. Attention. Attention
 Chapter 6 Attention Attention William James, in 1890, wrote Everyone knows what attention is. Attention is the taking possession of the mind, in clear and vivid form, of one out of what seem several simultaneously
Chapter 6 Attention Attention William James, in 1890, wrote Everyone knows what attention is. Attention is the taking possession of the mind, in clear and vivid form, of one out of what seem several simultaneously
Demonstratives in Vision
 Situating Vision in the World Zenon W. Pylyshyn (2000) Demonstratives in Vision Abstract Classical theories lack a connection between visual representations and the real world. They need a direct pre-conceptual
Situating Vision in the World Zenon W. Pylyshyn (2000) Demonstratives in Vision Abstract Classical theories lack a connection between visual representations and the real world. They need a direct pre-conceptual
Psychology UNIT 1: PSYCHOLOGY AS A SCIENCE. Core
 Core provides a solid overview of the field's major domains: methods, biopsychology, cognitive and developmental psychology, and variations in individual and group behavior. By focusing on significant
Core provides a solid overview of the field's major domains: methods, biopsychology, cognitive and developmental psychology, and variations in individual and group behavior. By focusing on significant
Chapter 3. Perception and Memory. Factors That Affect Teacher s Guidance
 Chapter 3 A Key to Guiding children Effectively All rights reserved. Part 1 Perception and Memory 3-2 Factors That Affect Teacher s Guidance Perception-process of organizing information obtained through
Chapter 3 A Key to Guiding children Effectively All rights reserved. Part 1 Perception and Memory 3-2 Factors That Affect Teacher s Guidance Perception-process of organizing information obtained through
Floortime - Affectively rich play to match child s individual differences and stimulate developmental growth
 What is DIR /Floortime? Developmental - children progress through stages toward ability to think and communicate flexibly in the world Individual Difference - each child has an unique set of biologically
What is DIR /Floortime? Developmental - children progress through stages toward ability to think and communicate flexibly in the world Individual Difference - each child has an unique set of biologically
Psychology Chapter 4. Sensation and Perception. Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed!
 Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
The Methods of Cognitive Neuroscience. Sensory Systems and Perception: Auditory, Mechanical, and Chemical Senses 93
 Contents in Brief CHAPTER 1 Cognitive Neuroscience: Definitions, Themes, and Approaches 1 CHAPTER 2 The Methods of Cognitive Neuroscience CHAPTER 3 Sensory Systems and Perception: Vision 55 CHAPTER 4 CHAPTER
Contents in Brief CHAPTER 1 Cognitive Neuroscience: Definitions, Themes, and Approaches 1 CHAPTER 2 The Methods of Cognitive Neuroscience CHAPTER 3 Sensory Systems and Perception: Vision 55 CHAPTER 4 CHAPTER
Visual Context Dan O Shea Prof. Fei Fei Li, COS 598B
 Visual Context Dan O Shea Prof. Fei Fei Li, COS 598B Cortical Analysis of Visual Context Moshe Bar, Elissa Aminoff. 2003. Neuron, Volume 38, Issue 2, Pages 347 358. Visual objects in context Moshe Bar.
Visual Context Dan O Shea Prof. Fei Fei Li, COS 598B Cortical Analysis of Visual Context Moshe Bar, Elissa Aminoff. 2003. Neuron, Volume 38, Issue 2, Pages 347 358. Visual objects in context Moshe Bar.
Multimodal Interaction for Users with Autism in a 3D Educational Environment
 Multimodal Interaction for Users with Autism in a 3D Educational Environment Ing. Alessandro Trivilini Prof. Licia Sbattella Ing. Roberto Tedesco 1 Screenshots 2 Screenshots 3 Introduction Existing Projects
Multimodal Interaction for Users with Autism in a 3D Educational Environment Ing. Alessandro Trivilini Prof. Licia Sbattella Ing. Roberto Tedesco 1 Screenshots 2 Screenshots 3 Introduction Existing Projects
Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg
 Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg The concept that different parts of the brain did different things started with Spurzheim and Gall, whose phrenology became quite
Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg The concept that different parts of the brain did different things started with Spurzheim and Gall, whose phrenology became quite
Modules 7. Consciousness and Attention. sleep/hypnosis 1
 Modules 7 Consciousness and Attention sleep/hypnosis 1 Consciousness Our awareness of ourselves and our environments. sleep/hypnosis 2 Dual Processing Our perceptual neural pathways have two routes. The
Modules 7 Consciousness and Attention sleep/hypnosis 1 Consciousness Our awareness of ourselves and our environments. sleep/hypnosis 2 Dual Processing Our perceptual neural pathways have two routes. The
Action and Emotion Understanding
 Action and Emotion Understanding How do we grasp what other people are doing and feeling? Why does it seem so intuitive? Why do you have a visceral reaction when you see a wound or someone in a physically
Action and Emotion Understanding How do we grasp what other people are doing and feeling? Why does it seem so intuitive? Why do you have a visceral reaction when you see a wound or someone in a physically
Note:- Receptors are the person who receives any images from outer environment.
 Concept According to Oxford Advanced Learner s Dictionary, Perception means the way you notice things especially with the senses. Perception is the process of organizing and attempting to understand the
Concept According to Oxford Advanced Learner s Dictionary, Perception means the way you notice things especially with the senses. Perception is the process of organizing and attempting to understand the
Autism Spectrum Disorders: Interventions and supports to promote independence
 Autism Spectrum Disorders: Interventions and supports to promote independence Presented by: Greg Valcante, Ph.D. University of Florida www.card.ufl.edu How to Get a Copy of These Handouts www.card.ufl.edu/training/asd-powerpoint
Autism Spectrum Disorders: Interventions and supports to promote independence Presented by: Greg Valcante, Ph.D. University of Florida www.card.ufl.edu How to Get a Copy of These Handouts www.card.ufl.edu/training/asd-powerpoint
Social and Pragmatic Language in Autistic Children
 Parkland College A with Honors Projects Honors Program 2015 Social and Pragmatic Language in Autistic Children Hannah Li Parkland College Recommended Citation Li, Hannah, "Social and Pragmatic Language
Parkland College A with Honors Projects Honors Program 2015 Social and Pragmatic Language in Autistic Children Hannah Li Parkland College Recommended Citation Li, Hannah, "Social and Pragmatic Language
Improving Communication in Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) Eniola Lahanmi Speech & Language Therapist
 Improving Communication in Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) Eniola Lahanmi Speech & Language Therapist Communication in ASD We will cover Typical language development Language presentation in ASD Language
Improving Communication in Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD) Eniola Lahanmi Speech & Language Therapist Communication in ASD We will cover Typical language development Language presentation in ASD Language
