FACT SHEET: Alzheimer s Disease
|
|
|
- Horatio Rodgers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Redwood Caregiver Resource Center 1140 Sonoma Ave., Ste. 1B Santa Rosa, CA (707) or (800) Fax (707) Serving: Del Norte, Humboldt, Mendocino, Lake, Sonoma, Napa & Solano Counties Definition Alzheimer s disease (AD) is an incurable neurological disease in which changes in the nerve cells of the brain result in the death of a large number of cells. This destruction of brain cells eventually leads to serious mental deterioration, dementia, and death. Facts According to the U.S. Congress Office of Technology Assessment, there are an estimated 4 million to 6.8 million persons nationwide with dementia. Up to 500,000 Alzheimer s patients may reside in California. Alzheimer s disease most commonly strikes individuals who are over 65; however, it can also afflict people much younger. An estimated 11 percent of all Americans over 65 and percent of those over 85 have the disease. Alzheimer s accounts for more than half of the number of persons described as having dementia; people with Alzheimer s fill more than half the beds in skilled nursing facilities. The mid-range medical and social service costs for one person with Alzheimer's are estimated to be more than $47,500 over the course of the disease. The average annual direct and indirect costs for all Americans with Alzheimer's have been estimated at $82.7 billion (1994 dollars). Symptoms During the first two to four years, people with Alzheimer s disease generally experience loss of memory for recent events, and disorientation. Later, the person will often have problems with progressive memory loss, judgment, FACT SHEET: Alzheimer s Disease concentration and speech. Loss of physical abilities, similar to that seen in Parkinson's disease, occurs in a small proportion of affected people. At this point, the person may forget to take a bath and will have problems with onceroutine chores. In time, the person's family and/or caregiver will probably have to provide full-time supervision because the confused person may tend to wander off, engage in meaningless and often socially unacceptable behavior, and lose the ability to perform basic self-care activities. People with Alzheimer s may also suffer sleeplessness, sundowning (confusion or agitation in the evening hours), and perseveration (repetition of the same ideas, words, movements, or thoughts). Final stage disease progression includes severe problems with eating, communication, and control of bodily functions. Diagnosis of Alzheimer s Disease The diagnosis of Alzheimer s disease can only be made after other diseases with similar symptoms such as brain tumors, strokes, and infections can be ruled out. It must also be differentiated from the occasional forgetfulness that occurs during normal aging and from depression and malnutrition, which can produce early Alzheimer s-like memory loss. Ideally, this diagnosis is made after a thorough medical evaluation followed by extensive neurological and neuropsychological assessments. This examination may be performed at designated Alzheimer s evaluation centers or by skilled medical specialists. A definitive diagnosis can be made only by an autopsy. 1
2 Over the past few years, many different methods have been developed and tested for diagnosing Alzheimer's disease in people with memory loss and dementia. These tests include an eye-drop test, genetic tests, spinal fluid tests, various types of neuropsychologic or cognitive tests, and brain imaging tests. While many of these tests are promising and may provide physicians with additional information useful in diagnosis, none has replaced the gold standard of a careful, thorough, clinical evaluation performed by an expert. In some cases, these tests have been studied in only a small number of individuals and often are compared to the standard of a clinical diagnosis. At this point, there is still no accurate diagnostic laboratory test for Alzheimer's disease. Imaging Research Research using brain imaging has led to more knowledge regarding Alzheimer s disease in three main areas: Brain structure and anatomy, diagnosis, and the physiology of the disease and its relationship to symptoms and behavior. Brain imaging has been used by clinicians and researchers for many years to look at differences in brain structure and anatomy in people with Alzheimer s disease. It has long been known that shrinking of the brain, or atrophy, accompanies Alzheimer s disease. This finding alone has not been helpful in diagnosing Alzheimer s disease because brain atrophy is also associated with normal aging. CT and MRI scans are helpful diagnostically, however, in that they are able to rule out other conditions such as brain tumors or major strokes, which might account for certain symptoms of dementia. More recent developments in brain imaging are scans which allow researchers to actually see how the living brain is functioning by looking at blood flow, oxygen and glucose metabolism and specific neuro-transmitter systems. Studies regarding brain blood flow and metabolism may help determine which parts of the brain are most affected at different stages of the illness and may help explain certain behaviors and symptoms which arise. In addition, high resolution MRI scans may show atrophy in the memory centers of the brain. These sorts of scans may at times be useful in helping to support the diagnosis of AD. Treatment After Diagnosis New drugs for the treatment of AD are now available. These drugs increase the brain levels of acetylcholine, a chemical involved in memory functions. The first of the drugs approved, Tacrine, requires frequent blood tests for monitoring. More recently, Donepezil (Aricept) was also approved by the FDA. A number of similar drugs are being tested. These drugs do not cure Alzheimer's or stop its progression, but may provide some symptomatic benefit. It is important to discuss this potential drug treatment with your physician and to have realistic expectations. Other compounds include Vitamin E, estrogen (a hormone), and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen, all of which are aimed at treating different possible causes of the disease. In addition, current experimental drug trials are looking at the treatment of agitated behaviors using both pharmacological and behavioral approaches. Many drug companies are involved in designing and testing drugs for the possible treatment of AD. None of these drugs has yet been shown to be effective, with the possible exception of Vitamin E. Alzheimer s disease is often called a family disease the chronic stress of watching a loved one slowly decline affects everyone. Comprehensive treatment must therefore address the needs of the entire family. This would include emotional support, counseling, and educational programs about Alzheimer s disease for individuals and family members as they strive to provide a safe and comfortable environment at home. Respite care, the use of a companion, homemaker, or aide at home or in a special Alzheimer s day care program, may be needed to allow the caregiver time away from his/her 24-hour responsibilities. 2
3 The person with Alzheimer s will need good medical follow-up throughout the course of the disease. If he/she experiences delusions or great psychological stress, careful use of drugs to treat these symptoms may be indicated. Comprehensive counseling should include suggesting that the patient and the family obtain early legal consultation concerning how they can responsibly provide for and make treatment plans for the affected family member who can no longer care for him/herself. The life span of someone with Alzheimer s can range from under five to more than twenty years. Families caring for a loved one with end-stage Alzheimer s should give thoughtful consideration to placement in a skilled nursing facility where adequate management and supervision can be provided. New Research Findings New developments in genetic research into Alzheimer s disease have recently come to light. For a number of years, investigators have known that there is a genetic connection in some cases of Alzheimer s disease, namely an abnormality on Chromosome 21 which results in Down s Syndrome. In such cases, children with Down s Syndrome who live into their 30 s and 40 s show Alzheimer changes in their brains. Chromosome 21 carries the gene for amyloid percursor protein (APP). This large protein is broken down into beta amyloid which is thought to be the source of senile plaques in the brains of people with Alzheimer's disease. It has been shown that mutations of the APP gene can lead to the development of Alzheimer's disease at a young age, typically in a person's fifties. This is a very rare genetic defect affecting a small number of families. Other genetic developments include the discovery on Chromosome 14 of the specific gene responsible for the cases of familial early onset AD. This gene encodes a protein called S182 and mutations of this protein can cause AD early in middle age, usually between the ages of 30 and 55. While this is not a very common cause of AD, it may account for the majority of familial early onset AD. Most recently, a gene located on Chromosome 1 was identified and linked to the type of AD found in people descended from Germans who lived in Russia near the Volga River. In some Volga German families, AD is inherited with an age of onset between 50 and 70. This gene and the protein it produces share a number of similarities with the Chromosome 14 gene. Again, this is a very rare mutation. A fourth gene, located on Chromosome 19, codes for a protein called APOE. This protein has three forms: Of the three forms of the protein, APOE4 has the strongest connection with the development of Alzheimer s disease, especially in those families with a high rate of disease in the family. Even in cases of Alzheimer s disease in which there is no clear familial tendency, APOE4 was present in more than half of the cases. APOE4 is important because it is the first discovery of a potential mechanism for the development of Alzheimer s disease. The APOE4 protein binds to amyloid, and if a drug could be developed which blocks this binding process, it might be a useful treatment. The presence of two copies of the APOE4 gene confers a high risk of developing the illness in families with genetically transmitted late-onset Alzheimer s disease and a higher risk of getting the disease for non-familial cases. How much it increases the risk cannot yet be established in individual cases, as the risk depends on family history, ethnicity, and other factors that interact with APOE4 but which are poorly understood at this time. The APOE4 gene is considered a susceptibility gene, not a disease gene, since not all persons who have the gene get the disease and some people may get the disease without having the gene. It is not a diagnostic test for Alzheimer's disease. It is a risk factor in somewhat the same way that high cholesterol is a risk for heart disease. With news of these discoveries, many families are asking whether or not they can be tested for 3
4 their risk of developing AD. A test to assess the APOE4 gene is available. It cannot be used to predict who will develop late-onset AD for anyone not yet showing symptoms of the disease. Apart from its technical aspects, which are not simple, the issue of genetic testing raises complex personal, social, legal and ethical issues. At this time, routine testing for Alzheimer s disease genes is not recommended. The APOE4 gene is only a risk factor and it is not possible to state the exact degree of risk it confers. Routine testing for these genes on Chromosomes 21, 14 and 1 is not available but even if it were, it would only account for a small number of people with AD. Having a negative test for these genes does not exclude the possibility of having AD. There are still only limited treatment options for this illness, so test results must be placed in the context of accurate information and careful communication and counseling. Recommended Readings The 36 Hour Day, Nancy Mace and Peter Rabins, 1999 edition, The Johns Hopkins University Press, 2715 N. Charles Street, Baltimore, MD, (800) The Complete Guide to Alzheimer's Proofing Your Home, 1998, Mark L. Warner, Purdue University Press, 1207 South Campus Courts-E, West Lafayette, IN , (800) The Best Friends Approach to Alzheimer's Care, Virginia Bell and David Troxel, 1997, Health Professions Press, P.O. Box 10624, Baltimore, MD, , (888) Alzheimer's: A Love Story, Ann Davidson, 1997, Carol Publishing, 120 Enterprise Avenue, Seacaucus, NJ, 07094, (201) Interventions for Alzheimer's Disease: A Caregiver's Complete Reference, Ruth Tappen, 1997, Health Professions Press, P.O. Box 10624, Baltimore, MD , (888) Alzheimer's Disease: Cause(s), Diagnosis, Treament and Care, Zaven S. Khachaturian and Teresa S. Redebaugh (eds.), 1996, CRC Press, LLC, 2000 Corporate Blvd. NW, Boca Raton, FL 33431, (561) Early Identification of Alzheimer's Diseases and Related Dementias: Quick Reference Guide for Clinicians, No. 19, Paul T. Costa, 1996, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Agency for Health Care Policy and Research (AHCPR Publication No ). Available from: AHCPR Publications Clearinghouse, P.O. Box 8547, Silver Spring, MD 20907, (800) Credits Alzheimer s Association, 1999, Alzheimer s Disease Statistics, Chicago, IL. Alzheimer's Third Most Costly Disease, American Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, March/April 1995:39. Ernst, R.L., and Hay, J.W., 1994, The U.S. Economic and Social Costs of Alzheimer's Disease Revisited, American Journal of Public Health 84(8): Evans, D.A., et al., 1990, Estimated Prevalence of Alzheimer's Disease in the United States, Milbank Quarterly, 68(2): Gunnarsson, L.G., and Lundberg, C., 1995, Cautiousness in Testing for Alzheimer's Disease, American Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, July/August: National Institute on Aging, Alzheimer s Disease : A Description of the Illness for the Family and Friends of Patients with this Disorder, reprinted by the Alzheimer s Association, Chicago, IL. Office of Technology Assessment, U.S. Congress, 1990, Confused Minds, Burdened Families, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC. 4
5 Resources Alzheimer s Disease Education and Referral Center (ADEAR)P.O. Box 8250 Silver Spring, MD (301) (800) Alzheimer s Association 919 North Michigan Ave., Ste Chicago, IL (312) (800) This office will provide information about regional chapter offices across the nation. Local chapters may give referrals for doctors, nursing homes, support groups and adult day care programs. Alz-heimer s Association chapters also send out newsletters and information about recent research Reviewed and updated by William Jagust, M.D., Director, Northern California Alzheimer s Disease Center and Associate Professor, Department of Neurology, University of California, Davis. Prepared by Family Caregiver Alliance in cooperation with California s Caregiver Resource Centers, a statewide system of Resource Centers serving families and caregivers of brain-impaired adults. Revised September Funded by the California Department of Mental Health. All rights reserved. 5
Alzheimer s Disease. Fact Sheet. Fact Sheet. Fact Sheet. What Causes AD?
 2 Alzheimer s Disease Dementia is a brain disorder that seriously affects a person s ability to carry out daily activities. The most common form of dementia among older people is Alzheimer s disease (AD),
2 Alzheimer s Disease Dementia is a brain disorder that seriously affects a person s ability to carry out daily activities. The most common form of dementia among older people is Alzheimer s disease (AD),
Alzheimer s disease is an
 Alzheimer s Disease FACT SHEET Alzheimer s disease is an irreversible, progressive brain disease that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills, and eventually even the ability to carry out the simplest
Alzheimer s Disease FACT SHEET Alzheimer s disease is an irreversible, progressive brain disease that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills, and eventually even the ability to carry out the simplest
Fact Sheet Alzheimer s disease
 What is Alzheimer s disease Fact Sheet Alzheimer s disease Alzheimer s disease, AD, is a progressive brain disorder that gradually destroys a person s memory and ability to learn, reason, make judgements,
What is Alzheimer s disease Fact Sheet Alzheimer s disease Alzheimer s disease, AD, is a progressive brain disorder that gradually destroys a person s memory and ability to learn, reason, make judgements,
Forgetfulness: Knowing When to Ask for Help
 National Institute on Aging AgePage Forgetfulness: Knowing When to Ask for Help Maria has been a teacher for 35 years. Teaching fills her life and gives her a sense of accomplishment, but recently she
National Institute on Aging AgePage Forgetfulness: Knowing When to Ask for Help Maria has been a teacher for 35 years. Teaching fills her life and gives her a sense of accomplishment, but recently she
Alzheimer s Disease: Getting the Facts
 Alzheimer s Disease: Getting the Facts What is Alzheimer s Disease? An Overview Alzheimer s disease damages the brain. With time this damage becomes worse. AD is the most common form of dementia. Dementia
Alzheimer s Disease: Getting the Facts What is Alzheimer s Disease? An Overview Alzheimer s disease damages the brain. With time this damage becomes worse. AD is the most common form of dementia. Dementia
Dementia is not normal aging!
 The Future of Alzheimer s Disease Treatment Adam L. Boxer, MD, PhD Director, Alzheimer s Disease Clinical Trials Program Memory and Aging Center Assistant Professor of Neurology University of California,
The Future of Alzheimer s Disease Treatment Adam L. Boxer, MD, PhD Director, Alzheimer s Disease Clinical Trials Program Memory and Aging Center Assistant Professor of Neurology University of California,
Alzheimer s Disease: Early Stage
 DEL MAR CAREGIVER RESOURCE CENTER A program of Health Projects Center Fact Sheet Alzheimer s Disease: Early Stage Overview A diagnosis of Alzheimer s disease for yourself or a loved one can be difficult
DEL MAR CAREGIVER RESOURCE CENTER A program of Health Projects Center Fact Sheet Alzheimer s Disease: Early Stage Overview A diagnosis of Alzheimer s disease for yourself or a loved one can be difficult
ALZHEIMER S DISEASE. Mary-Letitia Timiras M.D. Overlook Hospital Summit, New Jersey
 ALZHEIMER S DISEASE Mary-Letitia Timiras M.D. Overlook Hospital Summit, New Jersey Topics Covered Demography Clinical manifestations Pathophysiology Diagnosis Treatment Future trends Prevalence and Impact
ALZHEIMER S DISEASE Mary-Letitia Timiras M.D. Overlook Hospital Summit, New Jersey Topics Covered Demography Clinical manifestations Pathophysiology Diagnosis Treatment Future trends Prevalence and Impact
Dementia Basics. Welcome! What to expect and how to handle a dementia diagnosis. In partnership with Scripps Health.
 Dementia Basics What to expect and how to handle a dementia diagnosis March 18, 2017 In partnership with Scripps Health Welcome! 1 Welcome Kristin Gaspar San Diego County Supervisor District 3 2 Our Mission:
Dementia Basics What to expect and how to handle a dementia diagnosis March 18, 2017 In partnership with Scripps Health Welcome! 1 Welcome Kristin Gaspar San Diego County Supervisor District 3 2 Our Mission:
Research ALZHEIMER S DISEASE AND RISK FACTORS
 Research ALZHEIMER S DISEASE AND RISK FACTORS What is Alzheimer s disease? Alzheimer s disease is the most common of a large group of disorders known as dementias. It is an irreversible disease of the
Research ALZHEIMER S DISEASE AND RISK FACTORS What is Alzheimer s disease? Alzheimer s disease is the most common of a large group of disorders known as dementias. It is an irreversible disease of the
Old Age and Stress. Disorders of Aging and Cognition. Disorders of Aging and Cognition. Chapter 18
 Disorders of Aging and Cognition Chapter 18 Slides & Handouts by Karen Clay Rhines, Ph.D. Northampton Community College Comer, Abnormal Psychology, 8e Disorders of Aging and Cognition Dementia deterioration
Disorders of Aging and Cognition Chapter 18 Slides & Handouts by Karen Clay Rhines, Ph.D. Northampton Community College Comer, Abnormal Psychology, 8e Disorders of Aging and Cognition Dementia deterioration
Memory Loss, Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease: The Basics
 Memory Loss, Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease: The Basics What is memory loss? What is age-related memory loss? Typical changes Typical age-related changes involve: Making a bad decision once in a while
Memory Loss, Dementia and Alzheimer's Disease: The Basics What is memory loss? What is age-related memory loss? Typical changes Typical age-related changes involve: Making a bad decision once in a while
Evaluations. Alzheimer s Disease A Public Health Response. Viewer Call-In. July 19, Guest Speakers. Thanks to our Sponsors:
 Alzheimer s Disease A Public Health Response July 19, 2007 1 2 Guest Speakers Thanks to our Sponsors: Earl A. Zimmerman, M.D. Bender Endowed Chair of Neurology and Director of the Alzheimer s Center at
Alzheimer s Disease A Public Health Response July 19, 2007 1 2 Guest Speakers Thanks to our Sponsors: Earl A. Zimmerman, M.D. Bender Endowed Chair of Neurology and Director of the Alzheimer s Center at
Contents. Introduction. Introduction 03
 Genes and dementia Introduction This information is for anyone who wants to know more about the link between genes and dementia. This includes people living with dementia, their carers, friends and families.
Genes and dementia Introduction This information is for anyone who wants to know more about the link between genes and dementia. This includes people living with dementia, their carers, friends and families.
We Will Discuss. Dementia and Alzheimer s Disease Basics. Dementia. Developmental Disabilities and Dementia: A Behavior Management Guide
 10/18/2013 1 Dayna Thompson M.S., LMHC Alzheimer s Educator Developmental Disabilities and Dementia: A Behavior Management Guide Alzheimer s Resource Service IU Health Bloomington-Community Health 812-353-9299
10/18/2013 1 Dayna Thompson M.S., LMHC Alzheimer s Educator Developmental Disabilities and Dementia: A Behavior Management Guide Alzheimer s Resource Service IU Health Bloomington-Community Health 812-353-9299
Dementia. Assessing Brain Damage. Mental Status Examination
 Dementia Assessing Brain Damage Mental status examination Information about current behavior and thought including orientation to reality, memory, and ability to follow instructions Neuropsychological
Dementia Assessing Brain Damage Mental status examination Information about current behavior and thought including orientation to reality, memory, and ability to follow instructions Neuropsychological
Understanding Symptoms, Causes, and Risks for Alzheimer s Disease
 Understanding Symptoms, Causes, and Risks for Alzheimer s Disease Gene E. Alexander, Ph.D., Professor of Psychology, Neuroscience, and Physiological Sciences; Director, Brain Imaging, Behavior & Aging
Understanding Symptoms, Causes, and Risks for Alzheimer s Disease Gene E. Alexander, Ph.D., Professor of Psychology, Neuroscience, and Physiological Sciences; Director, Brain Imaging, Behavior & Aging
If you have dementia, you may have some or all of the following symptoms.
 About Dementia Dementia may be caused by a number of illnesses that affect the brain. Dementia typically leads to memory loss, inability to do everyday things, difficulty in communication, confusion, frustration,
About Dementia Dementia may be caused by a number of illnesses that affect the brain. Dementia typically leads to memory loss, inability to do everyday things, difficulty in communication, confusion, frustration,
Evaluations. Dementia Update: A New National Plan for Alzheimer s Disease Research, Care and Services. Disclosure Statements.
 Dementia Update: A New National Plan for Alzheimer s Disease Research, Care and Services June 21, 2012 Featured Speaker David Hoffman M.Ed. C.C.E, NYS DOH Office of Health Insurance Programs Clinical Associate
Dementia Update: A New National Plan for Alzheimer s Disease Research, Care and Services June 21, 2012 Featured Speaker David Hoffman M.Ed. C.C.E, NYS DOH Office of Health Insurance Programs Clinical Associate
10/17/2017. Causes of Dementia Alzheimer's Disease Vascular Dementia Diffuse Lewy Body Disease Alcoholic Dementia Fronto-Temporal Dementia Others
 1 Dementia Dementia comes from the Latin word demens, meaning out of mind. It is the permanent loss of multiple intellectual functions. It is progressive deterioration of mental powers accompanied by changes
1 Dementia Dementia comes from the Latin word demens, meaning out of mind. It is the permanent loss of multiple intellectual functions. It is progressive deterioration of mental powers accompanied by changes
What is Alzheimer s disease
 PBO 930022142 NPO 049-191 What is Alzheimer s disease Alzheimer s disease is the most common form of dementia. This information sheet outlines the symptoms and cause of Alzheimer s disease and describes
PBO 930022142 NPO 049-191 What is Alzheimer s disease Alzheimer s disease is the most common form of dementia. This information sheet outlines the symptoms and cause of Alzheimer s disease and describes
Dementia. Memory Evaluation Center Neurology
 Dementia Memory Evaluation Center Neurology Topics Overview of dementia Stages Medications Advanced planning What is Dementia? Dementia = significant global decline in cognitive function not due to medicine
Dementia Memory Evaluation Center Neurology Topics Overview of dementia Stages Medications Advanced planning What is Dementia? Dementia = significant global decline in cognitive function not due to medicine
Caring Sheet #11: Alzheimer s Disease:
 CARING SHEETS: Caring Sheet #11: Alzheimer s Disease: A Summary of Information and Intervention Suggestions with an Emphasis on Cognition By Shelly E. Weaverdyck, PhD Introduction This caring sheet focuses
CARING SHEETS: Caring Sheet #11: Alzheimer s Disease: A Summary of Information and Intervention Suggestions with an Emphasis on Cognition By Shelly E. Weaverdyck, PhD Introduction This caring sheet focuses
When the Diagnosis Is Dementia- What You Can Do? Howard Gruetzner, M.Ed., LPC Educational and Family Care Specialist North Central Texas Chapter
 When the Diagnosis Is Dementia- What You Can Do? Howard Gruetzner, M.Ed., LPC Educational and Family Care Specialist North Central Texas Chapter Visibility of Disease Only 19 percent of people with Alzheimer
When the Diagnosis Is Dementia- What You Can Do? Howard Gruetzner, M.Ed., LPC Educational and Family Care Specialist North Central Texas Chapter Visibility of Disease Only 19 percent of people with Alzheimer
National Plan to Address Alzheimer s Disease
 National Plan to Address Alzheimer s Disease On May 15, 2012, the Obama Administration released our country s first-ever National Alzheimer s Plan. What is this plan? Why is it needed? And how will it
National Plan to Address Alzheimer s Disease On May 15, 2012, the Obama Administration released our country s first-ever National Alzheimer s Plan. What is this plan? Why is it needed? And how will it
Research & Policy Brief
 USM Muskie School of Public Service Maine DHHS Office of Elder Services Research & Policy Brief Caring for People with Alzheimer s Disease or Dementia in Maine A Matter of Public Health Alzheimer s disease
USM Muskie School of Public Service Maine DHHS Office of Elder Services Research & Policy Brief Caring for People with Alzheimer s Disease or Dementia in Maine A Matter of Public Health Alzheimer s disease
Alzheimer s disease affects patients and their caregivers. experience employment complications,
 Alzheimer s Disease and Dementia A growing challenge The majority of the elderly population with Alzheimer s disease and related dementia are in fair to poor physical health, and experience limitations
Alzheimer s Disease and Dementia A growing challenge The majority of the elderly population with Alzheimer s disease and related dementia are in fair to poor physical health, and experience limitations
Alzheimer s Disease and Related Disorders: The Public Health Call to Action
 Levine Alzheimer s Disease and Related Disorders: The Public Health Call to Action Jed A. Levine, M.A. Executive Vice President Director of Programs and Services Alzheimer s Association, New York City
Levine Alzheimer s Disease and Related Disorders: The Public Health Call to Action Jed A. Levine, M.A. Executive Vice President Director of Programs and Services Alzheimer s Association, New York City
Alzheimer s disease. What is Alzheimer s disease?
 Alzheimer s disease What is Alzheimer s disease? What do we know about dementia and Alzheimer s disease? Alzheimer s disease is the most common form of dementia. Alzheimer s disease causes symptoms of
Alzheimer s disease What is Alzheimer s disease? What do we know about dementia and Alzheimer s disease? Alzheimer s disease is the most common form of dementia. Alzheimer s disease causes symptoms of
2016 Programs & Information
 Mayo Alzheimer s Disease Research Clinic Education Center 2016 Programs & Information BROCHURE TITLE FLUSH RIGHT for Persons & Families impacted by Mild Cognitive Impairment Alzheimer s Disease Dementia
Mayo Alzheimer s Disease Research Clinic Education Center 2016 Programs & Information BROCHURE TITLE FLUSH RIGHT for Persons & Families impacted by Mild Cognitive Impairment Alzheimer s Disease Dementia
Decline in Mental Capacity
 Decline in Mental Capacity Elder Law: Issues, Answers and Opportunities ALI-ABA, February 23-24, 2006 Robert B. Fleming 1 FLEMING & CURTI, P.L.C. 330 N. Granada Ave. Tucson, Arizona 85701 www.elder-law.com
Decline in Mental Capacity Elder Law: Issues, Answers and Opportunities ALI-ABA, February 23-24, 2006 Robert B. Fleming 1 FLEMING & CURTI, P.L.C. 330 N. Granada Ave. Tucson, Arizona 85701 www.elder-law.com
Understanding. Alzheimer s Disease. Lora, diagnosed in 2004, with her daughter, Jill.
 Understanding Alzheimer s Disease Lora, diagnosed in 2004, with her daughter, Jill. What Is Alzheimer s Disease? Alzheimer s disease is a neurologic disorder that affects the brain. It causes dementia.
Understanding Alzheimer s Disease Lora, diagnosed in 2004, with her daughter, Jill. What Is Alzheimer s Disease? Alzheimer s disease is a neurologic disorder that affects the brain. It causes dementia.
UNDERSTANDING ALZHEIMER S AND DEMENTIA
 UNDERSTANDING ALZHEIMER S AND DEMENTIA Geri T., living with Alzheimer's, and her husband and care partner, Jim T. THE IMPACT OF ALZHEIMER S AND DEMENTIA Currently, an estimated 50 million people worldwide
UNDERSTANDING ALZHEIMER S AND DEMENTIA Geri T., living with Alzheimer's, and her husband and care partner, Jim T. THE IMPACT OF ALZHEIMER S AND DEMENTIA Currently, an estimated 50 million people worldwide
Dementia is an overall term for a set of symptoms that is caused by disorders affecting the brain.
 Vascular Dementia Vascular Dementia Other Dementias This information sheet provides an overview of a type of dementia known as vascular dementia. In this information sheet you will find: An overview of
Vascular Dementia Vascular Dementia Other Dementias This information sheet provides an overview of a type of dementia known as vascular dementia. In this information sheet you will find: An overview of
Understanding Alzheimer s Disease What you need to know
 Understanding Alzheimer s Disease What you need to know From the National Institute on Aging For copies of this booklet, contact: Alzheimer s Disease Education and Referral Center P.O. Box 8250 Silver
Understanding Alzheimer s Disease What you need to know From the National Institute on Aging For copies of this booklet, contact: Alzheimer s Disease Education and Referral Center P.O. Box 8250 Silver
Diagnosis and assessment
 PBO 930022142 NPO 049-191 Diagnosis and assessment If you are close to someone who is feeling confused, agitated or forgetful, you may like to suggest that the person see their general practitioner (GP).
PBO 930022142 NPO 049-191 Diagnosis and assessment If you are close to someone who is feeling confused, agitated or forgetful, you may like to suggest that the person see their general practitioner (GP).
DEMENTIA? 45 Million. What is. WHAT IS DEMENTIA Dementia is a disturbance in a group of mental processes including: 70% Dementia is not a disease
 What is PRESENTS DEMENTIA? WHAT IS DEMENTIA Dementia is a disturbance in a group of mental processes including: Memory Reasoning Planning Learning Attention Language Perception Behavior AS OF 2013 There
What is PRESENTS DEMENTIA? WHAT IS DEMENTIA Dementia is a disturbance in a group of mental processes including: Memory Reasoning Planning Learning Attention Language Perception Behavior AS OF 2013 There
What is dementia? What is dementia?
 What is dementia? What is dementia? What is dementia? Dementia is an umbrella term for a range of progressive conditions that affect the brain. It has been identified that there are over 200 subtypes of
What is dementia? What is dementia? What is dementia? Dementia is an umbrella term for a range of progressive conditions that affect the brain. It has been identified that there are over 200 subtypes of
Facts About Alzheimer s
 Facts About Alzheimer s Frequently Asked Questions and More. with the compliments of Division of Health Services Diocese of Camden Alzheimer's disease affects about four million Americans today. In fact,
Facts About Alzheimer s Frequently Asked Questions and More. with the compliments of Division of Health Services Diocese of Camden Alzheimer's disease affects about four million Americans today. In fact,
Wisconsin Dementia Care Guiding Principles
 Page 1 of 8 Draft Dementia Care Guiding Principles There must be a widely shared understanding of appropriate and high quality care for people with dementia in order to have a dementia-capable system of
Page 1 of 8 Draft Dementia Care Guiding Principles There must be a widely shared understanding of appropriate and high quality care for people with dementia in order to have a dementia-capable system of
Our rapidly aging population means that more and more people will be diagnosed with Alzheimer s and other dementias in the next 20 years.
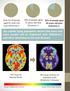 Only 1% of people aged 65 years old have Alzheimer s. 10% of people aged 75 years old have Alzheimer s. 20% of people aged 85 years old have Alzheimer s. Our rapidly aging population means that more and
Only 1% of people aged 65 years old have Alzheimer s. 10% of people aged 75 years old have Alzheimer s. 20% of people aged 85 years old have Alzheimer s. Our rapidly aging population means that more and
MetLife Foundation Alzheimer's Survey: What America Thinks
 MetLife Foundation Alzheimer's Survey: What America Thinks May 11, 2006 Conducted by: Harris Interactive 2005, Harris Interactive Inc. All rights reserved. Table of Contents Background and Objectives...
MetLife Foundation Alzheimer's Survey: What America Thinks May 11, 2006 Conducted by: Harris Interactive 2005, Harris Interactive Inc. All rights reserved. Table of Contents Background and Objectives...
a call to states: make alzheimer s a policy priority
 a call to states: make alzheimer s a policy priority the compassion to care, the leadership to conquer Alzheimer s is a public health crisis. One in eight Americans aged 65 and older have Alzheimer s disease
a call to states: make alzheimer s a policy priority the compassion to care, the leadership to conquer Alzheimer s is a public health crisis. One in eight Americans aged 65 and older have Alzheimer s disease
What is. frontotemporal. address? dementia?
 What is frontotemporal address? dementia? Contents 03 What is frontotemporal dementia? 04 Symptoms 05 Diagnosis 06 Treatments Information in this booklet is for anyone who wants to know more about frontotemporal
What is frontotemporal address? dementia? Contents 03 What is frontotemporal dementia? 04 Symptoms 05 Diagnosis 06 Treatments Information in this booklet is for anyone who wants to know more about frontotemporal
Learning Outcomes. To have a clear understanding of the term dementia, and current facts and statistics relating to dementia.
 Learning Outcomes To have a clear understanding of the term dementia, and current facts and statistics relating to dementia. To be familiar with some of the common types of dementia. To understand what
Learning Outcomes To have a clear understanding of the term dementia, and current facts and statistics relating to dementia. To be familiar with some of the common types of dementia. To understand what
6/20/2012. Early Stage. Part 1. Learning objectives: Early-Stage Program. Understanding dementia. Understanding Alzheimer s disease
 Learning objectives: Early-Stage Program Early Stage Objectives: Describe the symptoms of the early stage of Alzheimer s disease. Explain the legal, financial and resource planning that needs to be done
Learning objectives: Early-Stage Program Early Stage Objectives: Describe the symptoms of the early stage of Alzheimer s disease. Explain the legal, financial and resource planning that needs to be done
Biology 3201 Nervous System # 7: Nervous System Disorders
 Biology 3201 Nervous System # 7: Nervous System Disorders Alzheimer's Disease first identified by German physician, Alois Alzheimer, in 1906 most common neurodegenerative disease two thirds of cases of
Biology 3201 Nervous System # 7: Nervous System Disorders Alzheimer's Disease first identified by German physician, Alois Alzheimer, in 1906 most common neurodegenerative disease two thirds of cases of
MASSACHUSETTS ALZHEIMER S DISEASE RESEARCH CENTER
 MASSACHUSETTS ALZHEIMER S THE NEWSLETTER DISEASE RESEARCH OF THE CENTER Volume 1, Issue 4 Winter 2010 http://madrc.mgh.harvard.edu/ Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) A new look at early changes MASSACHUSETTS
MASSACHUSETTS ALZHEIMER S THE NEWSLETTER DISEASE RESEARCH OF THE CENTER Volume 1, Issue 4 Winter 2010 http://madrc.mgh.harvard.edu/ Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) A new look at early changes MASSACHUSETTS
What is dementia? alzheimers.org.uk
 alzheimers.org.uk What is dementia? If you, or a friend or relative, have been diagnosed with dementia, you may be feeling anxious or confused. You may not know what dementia is. This factsheet should
alzheimers.org.uk What is dementia? If you, or a friend or relative, have been diagnosed with dementia, you may be feeling anxious or confused. You may not know what dementia is. This factsheet should
Thank You to our Sponsors: Evaluations & CE Credits. Featured Speakers. Conflict of Interest & Disclosure Statements 11/15/2016
 Thank You to our Sponsors: University at Albany School of Public Health NYS Department of Health Conflict of Interest & Disclosure Statements The planners and presenters do not have any financial arrangements
Thank You to our Sponsors: University at Albany School of Public Health NYS Department of Health Conflict of Interest & Disclosure Statements The planners and presenters do not have any financial arrangements
Finding Quality of Life in End-Stage Dementia
 Finding Quality of Life in End-Stage Dementia Jennifer Malak, RN, BSN, Director-Access, Agrace HospiceCare Jennifer Flugaur, RN, BSN, CPHQ, Director-Quality & Compliance, Agrace HospiceCare Learn how to
Finding Quality of Life in End-Stage Dementia Jennifer Malak, RN, BSN, Director-Access, Agrace HospiceCare Jennifer Flugaur, RN, BSN, CPHQ, Director-Quality & Compliance, Agrace HospiceCare Learn how to
Mild Cognitive Impairment
 Mild Cognitive Impairment Victor W. Henderson, MD, MS Departments of Health Research & Policy (Epidemiology) and of Neurology & Neurological Sciences Stanford University Director, Stanford Alzheimer s
Mild Cognitive Impairment Victor W. Henderson, MD, MS Departments of Health Research & Policy (Epidemiology) and of Neurology & Neurological Sciences Stanford University Director, Stanford Alzheimer s
Memory Matters Service Dementia, Depression and Delerium Cancer Awareness Toolkit Evaluation Event
 Cumbria Partnership NHS Foundation Trust Memory Matters Service Dementia, Depression and Delerium Cancer Awareness Toolkit Evaluation Event Andrew Milburn Occupational Therapy Clinical Lead, Dementia Pathways
Cumbria Partnership NHS Foundation Trust Memory Matters Service Dementia, Depression and Delerium Cancer Awareness Toolkit Evaluation Event Andrew Milburn Occupational Therapy Clinical Lead, Dementia Pathways
alzheimers disease 1D BE7B EAE7AC73 Alzheimers Disease 1 / 6
 Alzheimers Disease 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Alzheimers Disease Alzheimer s disease is an irreversible, progressive brain disorder that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills, and eventually the ability to
Alzheimers Disease 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Alzheimers Disease Alzheimer s disease is an irreversible, progressive brain disorder that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills, and eventually the ability to
Dr. Adeniyi Mofoluwake and Stacy Kramer
 Dr. Adeniyi Mofoluwake and Stacy Kramer Definition of Alzheimer s Disease Alzheimer's disease is a neurological disorder in which insidious onset of the death of brain cells causes memory loss and cognitive
Dr. Adeniyi Mofoluwake and Stacy Kramer Definition of Alzheimer s Disease Alzheimer's disease is a neurological disorder in which insidious onset of the death of brain cells causes memory loss and cognitive
A Personal Guide to Organic Brain Disorders
 A Personal Guide to Organic Brain Disorders What is Dementia? Dementia is the decline of cognitive functions of sufficient severity to interfere with two or more of a person s daily living activities.
A Personal Guide to Organic Brain Disorders What is Dementia? Dementia is the decline of cognitive functions of sufficient severity to interfere with two or more of a person s daily living activities.
years Towards a world without dementia
 years 1 9 0 6-2 0 0 6 Towards a world without dementia A message from our patron A rewarding part of my public life has been my association with Alzheimer s Australia. During the National Consumer Summit
years 1 9 0 6-2 0 0 6 Towards a world without dementia A message from our patron A rewarding part of my public life has been my association with Alzheimer s Australia. During the National Consumer Summit
10 steps to planning for Alzheimer s disease & other dementias A guide for family caregivers
 10 steps to planning for Alzheimer s disease & other dementias A guide for family caregivers Caring for a person with memory loss or dementia can be challenging. The following ten steps can help caregivers
10 steps to planning for Alzheimer s disease & other dementias A guide for family caregivers Caring for a person with memory loss or dementia can be challenging. The following ten steps can help caregivers
Alzheimer s disease dementia: a neuropsychological approach
 Alzheimer s disease dementia: a neuropsychological approach Dr. Roberta Biundo, PhD Neuropsychology Coordinator at Parkinson s disease and movement disorders unit of San Camillo rehabilitation hospital
Alzheimer s disease dementia: a neuropsychological approach Dr. Roberta Biundo, PhD Neuropsychology Coordinator at Parkinson s disease and movement disorders unit of San Camillo rehabilitation hospital
Dementia. Information for service users and carers. RDaSH leading the way with care
 Dementia Information for service users and carers RDaSH leading the way with care What is Dementia is a term that is used to describe the symptoms that occur when the brain is affected by specific diseases
Dementia Information for service users and carers RDaSH leading the way with care What is Dementia is a term that is used to describe the symptoms that occur when the brain is affected by specific diseases
Alzheimer s Disease EARLY DETECTION AND TREATMENT ARE CRITICAL TO SLOWING ITS PROGRESS
 BEHAVIORAL HEALTH Alzheimer s Disease EARLY DETECTION AND TREATMENT ARE CRITICAL TO SLOWING ITS PROGRESS CONCETTA FORCHETTI, MD, PhD misperception that dementia is not as bad as Alzheimer s. Many of the
BEHAVIORAL HEALTH Alzheimer s Disease EARLY DETECTION AND TREATMENT ARE CRITICAL TO SLOWING ITS PROGRESS CONCETTA FORCHETTI, MD, PhD misperception that dementia is not as bad as Alzheimer s. Many of the
What is dementia? What is dementia?
 What is dementia? What is dementia? What is dementia? Dementia is an umbrella term for a range of progressive conditions that affect the brain. There are over 200 subtypes of dementia, but the five most
What is dementia? What is dementia? What is dementia? Dementia is an umbrella term for a range of progressive conditions that affect the brain. There are over 200 subtypes of dementia, but the five most
What is dementia? Symptoms of dementia. Memory problems
 What is dementia? What is dementia? What is dementia? Dementia is an umbrella term for a range of progressive conditions that affect the brain. The brain is made up of nerve cells (neurones) that communicate
What is dementia? What is dementia? What is dementia? Dementia is an umbrella term for a range of progressive conditions that affect the brain. The brain is made up of nerve cells (neurones) that communicate
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
 Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Other Dementias Introduction Alzheimer s disease is one type of a large group of disorders known as dementias. It is an irreversible disease of the brain in which the progressive
Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Other Dementias Introduction Alzheimer s disease is one type of a large group of disorders known as dementias. It is an irreversible disease of the brain in which the progressive
Cognitive Impairment - Parkinson's Disease Foundation (PDF)
 Page 1 of 8 Cognitive Impairment Another troublesome symptom of Parkinson s is mild cognitive impairment. Many people with Parkinson s are surprised to find that they feel distracted or disorganized, or
Page 1 of 8 Cognitive Impairment Another troublesome symptom of Parkinson s is mild cognitive impairment. Many people with Parkinson s are surprised to find that they feel distracted or disorganized, or
Toronto West Regional Stroke Prevention Clinic
 Toronto West Regional Stroke Prevention Clinic Information for patients with stroke or who are at risk for stroke, and their families/caregivers Read this pamphlet to learn: Who we are What we do How you
Toronto West Regional Stroke Prevention Clinic Information for patients with stroke or who are at risk for stroke, and their families/caregivers Read this pamphlet to learn: Who we are What we do How you
Michael A. Lobatz MD The Neurology Center Scripps Rehabilitation Center
 Michael A. Lobatz MD The Neurology Center Scripps Rehabilitation Center Dementia an acquired syndrome consisting of a decline in memory and other cognitive functions Alzheimer s Disease Fronto temporal
Michael A. Lobatz MD The Neurology Center Scripps Rehabilitation Center Dementia an acquired syndrome consisting of a decline in memory and other cognitive functions Alzheimer s Disease Fronto temporal
What is frontotemporal dementia?
 What is frontotemporal dementia? Introduction Information in this introductory booklet is for anyone who wants to know more about frontotemporal dementia (FTD). This includes people living with FTD, their
What is frontotemporal dementia? Introduction Information in this introductory booklet is for anyone who wants to know more about frontotemporal dementia (FTD). This includes people living with FTD, their
Teaching and Learning to Care:
 Teaching and Learning to Care: Training for Caregivers in Long Term Care Module Four When the Mind Falters: Cognitive Losses in Dementia by Joel Streim, MD Associate Professor of Psychiatry Director, Geriatric
Teaching and Learning to Care: Training for Caregivers in Long Term Care Module Four When the Mind Falters: Cognitive Losses in Dementia by Joel Streim, MD Associate Professor of Psychiatry Director, Geriatric
Alzheimer s It s a Family Affair Roles, Responsibilities and Family Dynamics
 ActivCare Town Hall Forum Montevalle Community Center Chula Vista, CA Wednesday, June 6, 2012 Alzheimer s It s a Family Affair Roles, Responsibilities and Family Dynamics Daniel D. Sewell, MD Clinical
ActivCare Town Hall Forum Montevalle Community Center Chula Vista, CA Wednesday, June 6, 2012 Alzheimer s It s a Family Affair Roles, Responsibilities and Family Dynamics Daniel D. Sewell, MD Clinical
Beyond memory loss. March 5, Alzheimer s Overview. In partnership with. Mary Ball President & CEO
 A new, Talking local and About independent the Hard organization Stuff: Beyond memory loss March 5, 2016 Alzheimer s Overview Mary Ball President & CEO In partnership with Welcome! Mary Ball, President/CEO
A new, Talking local and About independent the Hard organization Stuff: Beyond memory loss March 5, 2016 Alzheimer s Overview Mary Ball President & CEO In partnership with Welcome! Mary Ball, President/CEO
Current Issues and Initiatives in Alzheimer s Research and Services. Disclosure. I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose
 Current Issues and Initiatives in Alzheimer s Research and Services Carroll Rodriguez VP Public Policy and Communications Alzheimer s Association St. Louis Chapter 1 Disclosure I have no relevant financial
Current Issues and Initiatives in Alzheimer s Research and Services Carroll Rodriguez VP Public Policy and Communications Alzheimer s Association St. Louis Chapter 1 Disclosure I have no relevant financial
Dementia and cognitive decline
 Dementia and cognitive decline Expert Briefing Su Ray and Dr Susan Davidson Research Department Together, we can help everyone to love later life 01 Brain basics Normal ageing, cognitive impairment and
Dementia and cognitive decline Expert Briefing Su Ray and Dr Susan Davidson Research Department Together, we can help everyone to love later life 01 Brain basics Normal ageing, cognitive impairment and
What is dementia? Symptoms. alzheimers.org.uk
 alzheimers.org.uk What is dementia? This factsheet explains what dementia is, including the causes and symptoms, and how it is diagnosed and treated. It also looks at some of the different types of dementia.
alzheimers.org.uk What is dementia? This factsheet explains what dementia is, including the causes and symptoms, and how it is diagnosed and treated. It also looks at some of the different types of dementia.
annual report
 2010-11 annual report A year in motion Annual Report From the director The past year has been one of substantial achievement for the Virginia Commonwealth University Parkinson s Disease Center. As a result
2010-11 annual report A year in motion Annual Report From the director The past year has been one of substantial achievement for the Virginia Commonwealth University Parkinson s Disease Center. As a result
Alzheimer s Diagnostic Basics For Mental Health Professionals
 Alzheimer s Diagnostic Basics For Mental Health Professionals 1 CE Hour By: Kathryn Brohl, MA, LMFT Learning objectives List the possible causes of Alzheimer s disease. Describe diagnostic methods for
Alzheimer s Diagnostic Basics For Mental Health Professionals 1 CE Hour By: Kathryn Brohl, MA, LMFT Learning objectives List the possible causes of Alzheimer s disease. Describe diagnostic methods for
Understanding Dementia
 Dementia Handbook for Carers Essex Understanding Dementia What is dementia? 1 Summary of dementia symptoms 4 Medication and treatment 5 1 Dementia is the name for several conditions that lead to the progressive
Dementia Handbook for Carers Essex Understanding Dementia What is dementia? 1 Summary of dementia symptoms 4 Medication and treatment 5 1 Dementia is the name for several conditions that lead to the progressive
Assessing and Managing the Patient with Cognitive Decline
 Assessing and Managing the Patient with Cognitive Decline Center of Excellence For Alzheimer s Disease for State of NY Capital Region Alzheimer s Center of Albany Medical Center Earl A. Zimmerman, MD Professor
Assessing and Managing the Patient with Cognitive Decline Center of Excellence For Alzheimer s Disease for State of NY Capital Region Alzheimer s Center of Albany Medical Center Earl A. Zimmerman, MD Professor
2013 Purple Ribbon Task Force Surveys on Alzheimer s Disease and Related Dementias
 RICK SCOTT GOVERNOR CHARLES T. CORLEY SECRETARY 2013 Purple Ribbon Task Force Surveys on Alzheimer s Disease and Related Dementias elderaffairs.state.fl.us Bureau of Planning & Evaluation, May 2013 Table
RICK SCOTT GOVERNOR CHARLES T. CORLEY SECRETARY 2013 Purple Ribbon Task Force Surveys on Alzheimer s Disease and Related Dementias elderaffairs.state.fl.us Bureau of Planning & Evaluation, May 2013 Table
Raj C. Shah, MD Associate Professor in Family Medicine Rush Alzheimer s Disease Center Rush University Medical Center
 Raj C. Shah, MD Associate Professor in Family Medicine Rush Alzheimer s Disease Center Rush University Medical Center Raj_C_Shah@rush.edu From Legal Practice to What s Next: The Boomer-Lawyer s Guide to
Raj C. Shah, MD Associate Professor in Family Medicine Rush Alzheimer s Disease Center Rush University Medical Center Raj_C_Shah@rush.edu From Legal Practice to What s Next: The Boomer-Lawyer s Guide to
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD)
 Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) A topic in the Alzheimer s Association series on understanding dementia. Dementia is a condition in which a person has significant difficulty with daily functioning because
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) A topic in the Alzheimer s Association series on understanding dementia. Dementia is a condition in which a person has significant difficulty with daily functioning because
Resources: Types of dementia
 1/5 Dementia is an umbrella term for a number of progressive conditions affecting the functioning of the brain. Different types of dementia have different causes. There are a great number of rare forms.
1/5 Dementia is an umbrella term for a number of progressive conditions affecting the functioning of the brain. Different types of dementia have different causes. There are a great number of rare forms.
To help you prepare for your doctor's visit, the Alzheimer Society has developed the following list:
 The Alzheimer Society has a tool kit to help you prepare for a conversation with your doctor or health provider about your concerns and questions about a possible dementia diagnosis. Symptoms of dementia
The Alzheimer Society has a tool kit to help you prepare for a conversation with your doctor or health provider about your concerns and questions about a possible dementia diagnosis. Symptoms of dementia
Research and possible future brain health treatments
 Research and possible future brain health treatments Cheryl Brandi, DNSc, ARNP, NP-C Roskamp Institute Clinic July 21, 2016 brandi, roskamp institute 1 The Roskamp Institute Not for profit biomedical research
Research and possible future brain health treatments Cheryl Brandi, DNSc, ARNP, NP-C Roskamp Institute Clinic July 21, 2016 brandi, roskamp institute 1 The Roskamp Institute Not for profit biomedical research
BOOKS (alphabetical by title) Note: Books are NOT always available in bulk quantity. If interested in bulk quantity, please call for more information.
 1 BOOKS (alphabetical by title) Note: Books are NOT always available in bulk quantity. If interested in bulk quantity, please call for more information. Book Title Price (each) Quantity Total 1. Aging
1 BOOKS (alphabetical by title) Note: Books are NOT always available in bulk quantity. If interested in bulk quantity, please call for more information. Book Title Price (each) Quantity Total 1. Aging
Objectives. 1) Define Dementia and it s symptoms. 2) Review the diagnostic process
 Objectives 1) Define Dementia and it s symptoms 2) Review the diagnostic process 3) Learn about support services for persons with dementia and their families 2 The impact of Alzheimer s disease Ron Petersen,
Objectives 1) Define Dementia and it s symptoms 2) Review the diagnostic process 3) Learn about support services for persons with dementia and their families 2 The impact of Alzheimer s disease Ron Petersen,
In-Service Education. workbook 3. by Hartman Publishing, Inc. second edition
 In-Service Education workbook 3 second edition by Hartman Publishing, Inc. Alzheimer s Disease Dignity Diabetes Restraints and Restraint Alternatives Abuse and Neglect Death and Dying Managing Stress Perf
In-Service Education workbook 3 second edition by Hartman Publishing, Inc. Alzheimer s Disease Dignity Diabetes Restraints and Restraint Alternatives Abuse and Neglect Death and Dying Managing Stress Perf
The Person: Dementia Basics
 The Person: Dementia Basics Objectives 1. Discuss how expected age related changes in the brain might affect an individual's cognition and functioning 2. Discuss how changes in the brain due to Alzheimer
The Person: Dementia Basics Objectives 1. Discuss how expected age related changes in the brain might affect an individual's cognition and functioning 2. Discuss how changes in the brain due to Alzheimer
WHAT S NEW IN THE FIGHT AGAINST DEMENTIA
 WHAT S NEW IN THE FIGHT AGAINST DEMENTIA KAREN FOREN LAKE, PHD, RNC, NP MICHIGAN NURSES ASSOCIATION REVISED 7/2017 DEMENTIA This Independent Study is presented by Michigan Nurses Association. 1.0 contact
WHAT S NEW IN THE FIGHT AGAINST DEMENTIA KAREN FOREN LAKE, PHD, RNC, NP MICHIGAN NURSES ASSOCIATION REVISED 7/2017 DEMENTIA This Independent Study is presented by Michigan Nurses Association. 1.0 contact
ALZHEIMER S DISEASE FROM RESEARCH TO CARE: A COLLABORATIVE SEARCH FOR NEW DISCOVERIES
 ALZHEIMER S DISEASE FROM RESEARCH TO CARE: A COLLABORATIVE SEARCH FOR NEW DISCOVERIES T H E F I G H T AG A I N S T ALZHEIMER S DISEASE If you have experienced a loved one dealing with Alzheimer s, you
ALZHEIMER S DISEASE FROM RESEARCH TO CARE: A COLLABORATIVE SEARCH FOR NEW DISCOVERIES T H E F I G H T AG A I N S T ALZHEIMER S DISEASE If you have experienced a loved one dealing with Alzheimer s, you
T1: RESOURCES TO ADDRESS THE NEEDS OF PERSONS WITH DEMENTIA AND THEIR CAREGIVERS 2014 GOVERNOR S CONFERENCE ON AGING AND DISABILITY
 T1: RESOURCES TO ADDRESS THE NEEDS OF PERSONS WITH DEMENTIA AND THEIR CAREGIVERS 2014 GOVERNOR S CONFERENCE ON AGING AND DISABILITY Melanie Chavin, MNA, MS Alzheimer s Association, Greater Illinois Chapter
T1: RESOURCES TO ADDRESS THE NEEDS OF PERSONS WITH DEMENTIA AND THEIR CAREGIVERS 2014 GOVERNOR S CONFERENCE ON AGING AND DISABILITY Melanie Chavin, MNA, MS Alzheimer s Association, Greater Illinois Chapter
homeinstead.com Each Home Instead Senior Care franchise office is independently owned and operated Home Instead, Inc.
 Each Home Instead Senior Care franchise office is independently owned and operated. 2010 Home Instead, Inc. homeinstead.com Many of us may joke about having old timers disease, but when cognitive impairment
Each Home Instead Senior Care franchise office is independently owned and operated. 2010 Home Instead, Inc. homeinstead.com Many of us may joke about having old timers disease, but when cognitive impairment
PSYCHOTHERAPY. depression, loneliness, anxiety, adjustment issues, decision making, marital strife
 PSYCHOTHERAPY Athough life s challenges can become overwhelming at any age, mental health concerns compound the many changes that older adults face. Psychotherapy services are available at the UCCS Aging
PSYCHOTHERAPY Athough life s challenges can become overwhelming at any age, mental health concerns compound the many changes that older adults face. Psychotherapy services are available at the UCCS Aging
Fact Sheet Hypoxic-Anoxic Brain Injury
 Redwood Caregiver Resource Center 1140 Sonoma Ave., Ste. 1B Santa Rosa, CA 95405 (707) 542-0282 or (800) 834-1636 Fax (707) 542-0552 Email: rcrc@redwoodcrc.org Web: http://redwoodcrc.org Serving: Del Norte,
Redwood Caregiver Resource Center 1140 Sonoma Ave., Ste. 1B Santa Rosa, CA 95405 (707) 542-0282 or (800) 834-1636 Fax (707) 542-0552 Email: rcrc@redwoodcrc.org Web: http://redwoodcrc.org Serving: Del Norte,
Pocket Reference to Alzheimer s Disease Management
 Pocket Reference to Alzheimer s Disease Management Pocket Reference to Alzheimer s Disease Management Anna Burke, MD Geriatric Psychiatrist, Dementia Specialist Geri R Hall, PhD, ARNP, GCNS, FAAN Advanced
Pocket Reference to Alzheimer s Disease Management Pocket Reference to Alzheimer s Disease Management Anna Burke, MD Geriatric Psychiatrist, Dementia Specialist Geri R Hall, PhD, ARNP, GCNS, FAAN Advanced
Alzheimer's Association, Rhode Island Chapter ( )
 Alzheimer's Association, Rhode Island Chapter 1-800-272-3900 (401-421-0008) agarcia@alz.org TABLE OF CONTENTS I. Introduction.....3 A. About the Alzheimer s Association B. Facts and Figures National and
Alzheimer's Association, Rhode Island Chapter 1-800-272-3900 (401-421-0008) agarcia@alz.org TABLE OF CONTENTS I. Introduction.....3 A. About the Alzheimer s Association B. Facts and Figures National and
Clinical Research Studies at Johns Hopkins Bayview. Frequently Asked Questions
 Clinical Research Studies at Johns Hopkins Bayview Frequently Asked Questions Without clinical research, progress in improving health and treatment of disease would not be possible. To achieve success,
Clinical Research Studies at Johns Hopkins Bayview Frequently Asked Questions Without clinical research, progress in improving health and treatment of disease would not be possible. To achieve success,
Dementia in Independent Senior Housing: Concerns, Barriers and Solutions
 Dementia in Independent Senior Housing: Concerns, Barriers and Solutions LeadingAge NY April 13, 2016 Kelly Papa, MSN, RN Masonicare Corporate Director of Learning The Big Question How can we create systems
Dementia in Independent Senior Housing: Concerns, Barriers and Solutions LeadingAge NY April 13, 2016 Kelly Papa, MSN, RN Masonicare Corporate Director of Learning The Big Question How can we create systems
THE MULLER INSTITUTE FOR SENIOR HEALTH
 THE MULLER INSTITUTE FOR SENIOR HEALTH Rita Leinheiser, MA Social Gerontologist Elder Life Specialist OBJECTIVES 1. Discover the components of a comprehensive community wellness program for seniors and
THE MULLER INSTITUTE FOR SENIOR HEALTH Rita Leinheiser, MA Social Gerontologist Elder Life Specialist OBJECTIVES 1. Discover the components of a comprehensive community wellness program for seniors and
10 symptoms of caregiver stress
 10 symptoms of caregiver stress If you experience any of these signs of stress on a regular basis, make time to talk to your doctor. 1. Denial about the disease and its effect on the person who s been
10 symptoms of caregiver stress If you experience any of these signs of stress on a regular basis, make time to talk to your doctor. 1. Denial about the disease and its effect on the person who s been
