Junming Cao, Yongsheng Lin, Xiangbei Qi, Zhihong Wang, Yipeng Yang, Hehuan Xia, Bin Xu
|
|
|
- Imogen McDaniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2): /ISSN: /IJCEM Original Article Effect of intramedullary signal intensity on T2-weighted magnetic resonance images on prognosis in patients with thoracic spinal stenosis Junming Cao, Yongsheng Lin, Xiangbei Qi, Zhihong Wang, Yipeng Yang, Hehuan Xia, Bin Xu Department of Orthopedics, The Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei Province, P. R. China Received October 16, 2017; Accepted November 21, 2017; Epub February 15, 2018; Published February 28, 2018 Abstract: Objective: To investigate the effect of intramedullary magnetic resonance (MR) changes on T2-weighted MR images (T2WI) on the postoperative prognosis in patients with thoracic spinal stenosis. Methods: Between January 2014 and December 2016, a total of 40 patients undergoing surgeries for thoracic spinal stenosis who had been diagnosed as having thoracic spinal stenosis in the Department of Orthopedics in our hospital were enrolled as subjects in this study. The enrolled patients were assigned to the high-intense signal group or the non-highintense signal group in terms of the results of intramedullary signal intensity on T2WI of the thoracic canal. The preoperative JOA score, the rate of postoperative recovery and the severity of thoracic spinal stenosis were compared between the two groups. The patients in the high-intense signal group were stratified into some with increased signal intensity for single segment and the others with increased signal intensity for multiple segments according to the range of lesions, and the differences in the preoperative JOA score and the rate of postoperative recovery were compared between the two subgroups. Results: Compared to the non-high-intense signal group, the preoperative JOA score was markedly lower (4.5±1.5 vs 6.5±1.7; P<0.0001) but the proportion of patients with severe thoracic spinal stenosis was larger in the high-intense signal group (P<0.001). The rate of postoperative recovery was strikingly different between the two groups (38.5±14.6% vs. 48.9±17.8%; P<0.001). The preoperative JOA score and the rate of postoperative recovery were remarkably lower among the patients with increased signal intensity for multiple segments than those with increased signal intensity for single segment (Both P<0.001). Conclusion: The high signal intensity on T2WI of the patients with thoracic spinal stenosis demonstrates that more severe spinal cord injury indicates worse prognosis. The high signal intensity on T2WI can be used as one of the predictors for assessment of surgical prognosis of the patients with thoracic spinal stenosis. Keywords: Thoracic spinal stenosis, magnetic resonance imaging, intramedullary high signal intensity Introduction Thoracic spinal stenosis is a set of clinical syndrome of spinal cord dysfunction caused by thoracic cord compression as a result of reduction in the thoracic transverse area which is impacted by various factors including developmental factors, ligament thickening and intervertebral disc degeneration [1, 2]. Once thoracic spinal stenosis is confirmed, surgery is the only applicable way to treat it [3, 4]. If it is not treated in time, irreversible damage would occur to the thoracic spinal cord. However, there are such neurological complications as paralysis in approximately 18-50% patients after a surgery for thoracic spinal stenosis [5]. The factors influencing surgical outcomes have been shown to be age, course of disease, the Japanese Orthopedic Association (JOA) scale score, operation technique, the degree, duration and rang of spinal cord compression [6]. Nevertheless, with only these preoperative data, it is difficult to evaluate and predict the prognosis of the surgery [7]. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is one of the major radiological imaging examination tools for thoracic spinal stenosis. It has high sensitivity to the spinal cord lesion and clearly reflects the spinal cord compression and the intramedullary signal alternations [8, 9]. On T2-weighted MR images (T2WI) or T1-weighted MR images
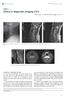
2 Table 1. Comparison of general data of patients Variable High-intense signal Non-highintense signal Case (n) Male/Female (n) 14/6 15/ Age (year) 50.2± ± Course of disease (mon) 11.2± ± Pathological segment (n) Upper thoracic level 7 6 Mid-thoracic level 3 5 Lower thoracic level 10 9 Clinical symptoms (n) Chest and abdominal girdle sensation 7 9 Intermittent claudication 8 7 Fecal and urinary dysfunction 5 4 Figure 1. T2WI of patients with thoracic spinal stenosis. A: Intramedullary non-high SI; B: Intramedullary high SI. t/χ 2 From January 2014 to December 2016, a total of 40 patients undergoing the surgery for confirmed thoracic spinal stenosis in the Department of Orthopedics in our hospital were recruited as subjects. Patients older than 18 years old were eligible for enrollment if they were diagnosed as having thoracic spinal stenosis on thoracic CT or MRI, were consent to perform decompression in the spinal canal and intervertebral fusion with internal fixation, but no contraindications. Patients were excluded if they had complications of cervical spondylosis, intraspinal space-occupying lesion, lumbar spinal stenosis or osteoporosis, severe thoracic instability or deformity, or organ dysfunction in the heart, the brain, the lung, the kidney or other organs. This study obtained approval from the Hospital Ethics Committee and written informed consent was given by each patient or their families. MRI examination P surgical prognosis of thoracic spinal stenosis. Materials and methods Participants (T1WI), the area of the normal spinal cord shows moderate intensity signals. Some lesions of the spinal cord show high signal intensity (SI) on the T2WI images due to prolonged compression leading to ischemia, edema, degeneration, or necrosis. Multiple studies have demonstrated that the intramedullary high SI on T2WI in patients with cervical spondylosis is correlated with prognosis after surgery, but the relation between the prognosis after surgery for thoracic spinal stenosis and the high SI on T2WI is unclear [10, 11]. Therefore, in this study, 40 patients hospitalizing for thoracic spinal stenosis and undergoing the relevant surgery from January 2014 to December 2016 were followed up and the effect of preoperative high SI on T2WI on clinical prognosis were examined, aiding in support for assessing the All the eligible patients underwent preoperative MRI examination on the thoracic vertebrae using 1.5T MRI (Siemens, German). The patients were placed in a supine position, and T1- and T2-weighted MR imaging of the transverse and sagittal planes was performed routinely of the thoracic spinal canal. The parameters regarding T2-weighted MR imaging of the transverse and sagittal planes were as follows: rapidly self-selected Huibo series, TR4000ms, TE 90ms, matrix 256 * 160, 4 mm of layer thickness, 0.5 mm of layer spacing, and 4 NEX. Two independent radiologists in spinal imaging evaluated the MRI of thoracic vertebrae, to determine if there was high SI in the spinal cord. The thoracic narrowest level with the most severe stenosis was selected from sagittal 742 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):
3 a scale of 11 points including 2 for physical sensory dysfunction, 4 for motor dysfunction in the lower extremity, 2 for sensory dysfunction in the lower extremity, 3 for sphincter dysfunction [12]. The JOA grading was performed in all the patients at 1 month preoperatively and postoperatively. The postoperative recovery rates were calculated according to the following equation: Postoperative recovery rate = [(Postoperative JOA score - Preoperative JOA score)/[(11- Preoperative JOA score)] * 100%. Figure 2. Comparison of preoperative JOA scores between the two groups. Compared with the non-highintense signal group, * P< Statistical analyses All the data analyses were performed with the SPSS19.0 software. Measurement data were represented as mean ± standard deviation; a paired t-test was applied for intragroup comparison between preoperative and postoperative variables and the two independent-samples t-test was utilized for intergroup comparisons at the same time interval. Enumeration data were represented as percentage, and a chi-square test was used for intergroup comparisons. The P value less than 0.05 was deemed to be statistically significant. Results General data of patients Figure 3. Comparison of the severity of preoperative thoracic spinal stenosis between the two groups. Compared with the non-high-intense signal group, * P<0.05. images. The most serious compressed transverse area of the spinal cord and the transverse area of the spinal canal were examined using the Advantage Workstation AW 4.6 software, and the ratio of the two measured values is the residual rate of spinal canal area. The residual rate of the spinal canal area larger than 2/3 is considered mild stenosis; the rate is larger than 1/3 but less than 2/3 is considered moderate stenosis, and the rate less than 1/3 severe stenosis. Thoracic spinal function score The JOA scoring scale was utilized to assess the injury status in the thoracic spinal cord (on The eligible patients were assigned to the high signal intensity group (high-intense group, n= 20) and the normal signal intensity group (nonhigh-intense signal group, n=20) in terms of the SI of the thoracic spinal cord on T2WI. The patients in the two groups differed insignificantly in sex, age, course of disease, lesion segment and clinical symptoms (P>0.05), so they were comparable (Table 1 and Figure 1). Preoperative JOA score The mean preoperative JOA score in the highintense signal group (4.5±1.5) was substantially lower than that (6.5±1.7) in the non-highintense signal group (P<0.001; Figure 2). Preoperative thoracic spinal stenosis In the high-intense signal group, mild thoracic spinal stenosis (the ratio of canal residual area is greater than 2/3) occurred in 3 patients (15%); moderate thoracic spinal stenosis (the ratio of canal residual area ranges from 1/3 to 2/3) occurred in 7 patients (35%) and severe thoracic spinal stenosis (the ratio of canal 743 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):
4 Table 2. Comparison of the rate of postoperative recovery between the two groups Variable Case (n) Postoperative JOA score Postoperative recovery rate (%) High-intense signal ± ±14.6 Non-high-intense signal ± ±17.8 t P increased signal intensity for single segment and others with increased signal intensity for multiple segments. Among them, increased signal intensity for single segment was present in 12 patients with preoperative JOA score of 4.8±1.6; increased signal intensity for multiple segments was present in 8 patients with preoperative JOA score of 4.1±1.4. There was a significant disparity in the preoperative JOA score between the two subgroups (t=9.014, P=0.018, Figure 4). Figure 4. Comparison of preoperative JOA scores between the patients with increased signal intensity for single segment and those for multi segments. Compared with the patients with increased signal intensity for single segment, * P< residual area is less than 1/3) in 10 patients (50%). In the non-high-intense signal group, 11 patients had mild thoracic canal stenosis (55%), 5 had moderate stenosis (25%) and 4 had severe stenosis (20%). The severity of thoracic spinal stenosis of patients was notably different between the two groups (P=0.024, Figure 3). Rate of postoperative recovery The mean postoperative JOA score was 7.0±1.6 in the high-intensive signal group and 8.7±1.9 in the non-high-intensive signal group, and there was a significant discrepancy in the JOA score between the two groups (P=0.004). Additionally, the rate of postoperative recovery was also markedly different, with (38.5±14.6)% in the high-intensive signal group and (48.9± 17.8)% in the non-high-intensive signal group (P=0.013, Table 2). Impact of increased signal intensity on clinical outcomes in the high-intense signal group On the basis of the increased signal intensity on T2WI, the patients in the high-intense signal group were further stratified into some with Apart from that, the postoperative JOA score was strikingly different, with 7.3±1.7 among the patients with increased signal intensity for single segment versus 6.6±1.5 among those with increased signal intensity for multiple segment (P=0.022). The rate of postoperative recovery was also strikingly different, with (44.3±15.7)% of the patients with increased signal intensity for single segment and (29.8±13.4)% of those with increased signal intensity for multiple segments (P=0.017, Table 3). Discussion Currently, MRI examination is a tool commonly used for the diagnosis of thoracic spinal stenosis. Compared to CT and other examination tools, MRI has more advantages [13]. On T2WI, intervertebral disc herniation and ossification of the ligament were present as low intense signals, the size, shape, range of the compressed components were seen clearly on the sagittal view and prognosis of the patients could be assessed according to the intramedullary signal changes [14]. According to a study, high signal intensity appeared on T2WI in approximately 41%-79% of thoracic spinal stenosis patients with ossification of the ligamentum flavum [15]. An analysis on the data from 16 patients with severe thoracic spinal stenosis revealed that up to 68.8% of the patients had changes in the intramedullary high signal intensity [16]. Although many patients with thoracic spinal stenosis had intramedullary high signal intensity on T2WI, scholars knowledge of the high signal intensity on T2WI of the thoracic spinal cord is poor and the impact of high signal intensity on T2WI on the postoperative outcomes is controversial. Recently, few studies have been implicated in the high signal intensity on T2WI of the thoracic spinal cord and surgical prognosis of patients 744 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):
5 Table 3. Comparison of the postoperative recovery rates between the patients with increased signal intensity for single segment and those for multiple segments Variable Case Postoperative JOA score Postoperative recovery rate (%) Single segment ± ±15.7 Multiple segment 8 6.6± ±13.4 t/χ P with thoracic spinal cord, but the opinions are inconsistent. Previous studies have indicated that the intramedullary high signal intensity on T2WI is not correlated with the surgical effect, prognosis and the severity of spinal cord lesions; some patients with high signal intensity on T2WI have a favorable recovery after surgical treatment; the spinal cord lesion is a reversible change [17]. An assessment of the surgical outcomes of 24 patients with thoracic spinal stenosis revealed that intramedullary high signal intensity on T2WI could not be taken as a predictor of surgical outcomes [18]. Nevertheless, according to Eck et al. and He et al., among the patients with thoracic spinal stenosis, a poor postoperative recovery was observed in those with intramedullary high signal intensity on T2WI [7, 19]. In the current study, MRI was performed on 40 patients with thoracic spinal stenosis, and 50% of them had high signal intensity on T2WI. Compared to the patients in the non-highintense signal group, those in the high-intense signal group had a notably lower preoperative JOA score and a lower rate of postoperative recovery of the spinal cord, indicating that the high signal intensity on T2WI in the thoracic spinal cord had certain impact on the surgical prognosis of the patients with thoracic spinal stenosis. Moreover, the studies on the impact of intramedullary high signal intensity on the surgical outcomes have demonstrated that the preoperative JOA score and the postoperative recovery of the spinal cord are significantly higher among the patients who have increased signal intensity for single segment than those who have increased signal intensity for multiple segment, suggesting that the severity of spinal cord injury is correlated with the high signal intensity on T2WI, with greater extent of signal intensity on T2WI indicating more severe spinal cord injury. The current study suggests that the high signal intensity on T2WI of the thoracic spinal cord may be explained by long-term compression of the spinal cord, which gives rise to disturbance of intramedullary blood circulation, obstruction and congestion in the venous vessels and increased permeability in the vascular walls, leading to irreversible pathological changes, such as edema, degeneration and necrosis of the spinal cord. As the cord function is impaired seriously, the recovery of the spinal cord would be still worse even after timely surgical decompression. It is indicated that T2WI is used as a tool of imaging examination to examine the pathological changes in the spinal cord, and the intramedullary high signal intensity is partly correlated with the impairment of neurological function of the spinal cord. There are a variety of methods for measuring thoracic spinal stenosis in MRI, including the ratio of the stenotic sagittal diameter of the spinal canal to the sagittal diameter of the vertebral body and the ratio of the sagittal diameter to the transverse diameter of the spinal cord. In the current study, we adopted the ratio of the most obvious compressed transverse area of the spinal cord to the transverse area of the spinal canal. In one study, a reduced rate of preoperative thoracic spinal stenosis had an obvious impact on postoperative recovery and tended to cause deterioration of preoperative function of the spinal cord, and the status and recovery of preoperative function of the spinal cord was closely related to the severity of stenosis of the thoracic canal [20]. The results of the current study demonstrated that compared to the non-high-intensive signal group, thoracic spinal stenosis was markedly deteriorated among the patients in the high-intensive signal group, indicating that the patients with high signal intensity on T2WI had more severe spinal stenosis, worse preoperative function and poorer postoperative recovery of the spinal cord. All this suggests poor prognosis of the patients. In conclusion, high signal intensity on T2WI can be used as a predictor for assessment of postoperative prognosis of patients suffering from thoracic spinal stenosis. High signal intensity is correlated with the extent of spinal cord injury, with greater extent of high signal intensity indicating more severe spinal cord injury. Besides, high signal intensity also has an effect on the surgical prognosis of patients. However, there are some limits in the current study, such as the small sample size and short-term follow-up. 745 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):
6 Additional multicenter randomized controlled studies with large sample size and mid-term and long-term follow-up studies are needed to make further validation. Disclosure of conflict of interest None. Address correspondence to: Junming Cao, Department of Orthopedics, The Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University, No.139, Ziqiang Road, Shijiazhuang , Hebei Province, P. R. China. Tel: ; Fax: ; References [1] Hitchon PW, Abode-Iyamah K, Dahdaleh NS, Grossbach AJ, El Tecle NE, Noeller J and He W. Risk factors and outcomes in thoracic stenosis with myelopathy: a single center experience. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2016; 147: [2] Sun J, Zhang C, Ning G, Li Y, Li Y, Wang P and Feng S. Surgical strategies for ossified ligamentum flavum associated with dural ossification in thoracic spinal stenosis. J Clin Neurosci 2014; 21: [3] Onishi E, Yasuda T, Yamamoto H, Iwaki K and Ota S. Outcomes of surgical treatment for thoracic myelopathy: a single-institutional study of 73 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2016; 41: E1356-E1363. [4] Melancia JL, Francisco AF and Antunes JL. Spinal stenosis. Handb Clin Neurol 2014; 119: [5] Xu N, Yu M, Liu X, Sun C, Chen Z and Liu Z. A systematic review of complications in thoracic spine surgery for ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament. Eur Spine J 2017; 26: [6] Miyakoshi N, Shimada Y, Suzuki T, Hongo M, Kasukawa Y, Okada K and Itoi E. Factors related to long-term outcome after decompressive surgery for ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine. J Neurosurg 2003; 99: [7] He S, Hussain N, Li S and Hou T. Clinical and prognostic analysis of ossified ligamentum flavum in a Chinese population. J Neurosurg Spine 2005; 3: [8] Shin HK, Jeong HJ, Kim E, Park JH, Park SJ and Cho Y. Should we check the routine postoperative MRI for hematoma in spinal decompression surgery? Clin Orthop Surg 2017; 9: [9] Cheung JP, Samartzis D, Shigematsu H and Cheung KM. Defining clinically relevant values for developmental spinal stenosis: a largescale magnetic resonance imaging study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2014; 39: [10] Karpova A, Arun R, Kalsi-Ryan S, Massicotte EM, Kopjar B and Fehlings MG. Do quantitative magnetic resonance imaging parameters correlate with the clinical presentation and functional outcomes after surgery in cervical spondylotic myelopathy? A prospective multicenter study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2014; 39: [11] Kim TH, Ha Y, Shin JJ, Cho YE, Lee JH and Cho WH. Signal intensity ratio on magnetic resonance imaging as a prognostic factor in patients with cervical compressive myelopathy. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016; 95: e4649. [12] Liu FJ, Chai Y, Shen Y, Xu JX, Du W and Zhang P. Posterior decompression with transforaminal interbody fusion for thoracic myelopathy due to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and the ligamentum flavum at the same level. J Clin Neurosci 2013; 20: [13] Xiong L, Zeng QY and Jinkins JR. CT and MRI characteristics of ossification of the ligamenta flava in the thoracic spine. Eur Radiol 2001; 11: [14] Li Z, Ren D, Zhao Y, Hou S, Li L, Yu S and Hou T. Clinical characteristics and surgical outcome of thoracic myelopathy caused by ossification of the ligamentum flavum: a retrospective analysis of 85 cases. Spinal Cord 2016; 54: [15] Inamasu J and Guiot BH. A review of factors predictive of surgical outcome for ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine. J Neurosurg Spine 2006; 5: [16] Wang LF, Liu FJ, Zhang YZ, Shen Y, Ding WY and Xu JX. Clinical results and intramedullary signal changes of posterior decompression with transforaminal interbody fusion for thoracic myelopathy caused by combined ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament and ligamentum flavum. Chin Med J (Engl) 2013; 126: [17] Yone K, Sakou T, Yanase M and Ijiri K. Preoperative and postoperative magnetic resonance image evaluations of the spinal cord in cervical myelopathy. Spine 1992; 17: [18] Liao CC, Chen TY, Jung SM and Chen LR. Surgical experience with symptomatic thoracic ossification of the ligamentum flavum. J Neurosurg Spine 2005; 2: [19] Eck JC, Drew J and Currier BL. Effects of magnetic resonance imaging signal change in myelopathic patients: a meta-analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010; 35: E [20] Kalb S, Martirosyan NL, Perez-Orribo L, Kalani MY and Theodore N. Analysis of demographics, risk factors, clinical presentation, and surgical treatment modalities for the ossified posterior longitudinal ligament. Neurosurg Focus 2011; 30: E Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):
Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation Medicine Fuculty of Medical Sciences University of Fukui
 Quantitative analysis and prognostic value of changes in spinal cord signal intensity on magnetic resonance imaging in patients with cervical compressive myelopathy Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation Medicine
Quantitative analysis and prognostic value of changes in spinal cord signal intensity on magnetic resonance imaging in patients with cervical compressive myelopathy Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation Medicine
Disclosures: T. Yoshii: None. T. Yamada: None. T. Taniyama: None. S. Sotome: None. T. Kato: None. S. Kawabata: None. A. Okawa: None.
 Dynamic Changes in Spinal Cord Compression by Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Evaluated by Kinematic Computed Tomography Myelogram Toshitaka Yoshii, Tsuyoshi Yamada, Takashi
Dynamic Changes in Spinal Cord Compression by Cervical Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament Evaluated by Kinematic Computed Tomography Myelogram Toshitaka Yoshii, Tsuyoshi Yamada, Takashi
Contributing factors affecting the prognosis surgical outcome for thoracic OLF
 Eur Spine J (2006) 15: 485 491 DOI 10.1007/s00586-005-0903-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sung Uk Kuh Young Soo Kim Yong Eun Cho Byung Ho Jin Keun Su Kim Young Sul Yoon Dong Kyu Chin Contributing factors affecting
Eur Spine J (2006) 15: 485 491 DOI 10.1007/s00586-005-0903-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sung Uk Kuh Young Soo Kim Yong Eun Cho Byung Ho Jin Keun Su Kim Young Sul Yoon Dong Kyu Chin Contributing factors affecting
decompression combined with interbody fusion and internal fixation for thoracic spinal stenosis
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):818-823 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0066999 Original Article Posterolateral decompression combined with interbody fusion and internal fixation for thoracic spinal stenosis
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):818-823 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0066999 Original Article Posterolateral decompression combined with interbody fusion and internal fixation for thoracic spinal stenosis
Radiological pathogenesis of cervical myelopathy in 60 consecutive patients with cervical ossi cation of the posterior longitudinal ligament
 Spinal Cord (1999) 37, 853 ± 857 ã 1999 International Medical Society of Paraplegia All rights reserved 1362 ± 4393/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/sc Radiological pathogenesis of cervical myelopathy
Spinal Cord (1999) 37, 853 ± 857 ã 1999 International Medical Society of Paraplegia All rights reserved 1362 ± 4393/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/sc Radiological pathogenesis of cervical myelopathy
Effect of Swallowing Function After ROI-C Anterior Cervical Interbody Fusion
 Journal of Surgery 2016; 4(6): 141-145 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/js doi: 10.11648/j.js.20160406.14 ISSN: 2330-0914 (Print); ISSN: 2330-0930 (Online) Effect of Swallowing Function After ROI-C
Journal of Surgery 2016; 4(6): 141-145 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/js doi: 10.11648/j.js.20160406.14 ISSN: 2330-0914 (Print); ISSN: 2330-0930 (Online) Effect of Swallowing Function After ROI-C
Risk factors for development of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: results of a systematic review
 Systematic review Risk factors for development of cervical spondylotic myelopathy 35 35 42 Risk factors for development of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: results of a systematic review Authors Anoushka
Systematic review Risk factors for development of cervical spondylotic myelopathy 35 35 42 Risk factors for development of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: results of a systematic review Authors Anoushka
Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3-6 Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3-6 Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Sakaura H, Miwa T, Kuroda Y, Ohwada T Dept. of Orthop. Surg., Kansai
Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3-6 Laminoplasty in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Sakaura H, Miwa T, Kuroda Y, Ohwada T Dept. of Orthop. Surg., Kansai
Spinal canal stenosis Degenerative diseases F 06
 What is spinal canal stenosis? The condition known as spinal canal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that in most cases develops due to the degenerative (wear-induced) deformation
What is spinal canal stenosis? The condition known as spinal canal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that in most cases develops due to the degenerative (wear-induced) deformation
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2): /ISSN: /IJCEM Yi Yang, Hao Liu, Yueming Song, Tao Li
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):1278-1284 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0063093 Case Report Dislocation and screws pull-out after application of an Isobar TTL dynamic stabilisation system at L2/3 in
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):1278-1284 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0063093 Case Report Dislocation and screws pull-out after application of an Isobar TTL dynamic stabilisation system at L2/3 in
Factors related to long-term outcome after decompressive surgery for ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine
 J Neurosurg (Spine 3) 99:251 256, 2003 Factors related to long-term outcome after decompressive surgery for ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine NAOHISA MIYAKOSHI, M.D., YOICHI SHIMADA,
J Neurosurg (Spine 3) 99:251 256, 2003 Factors related to long-term outcome after decompressive surgery for ossification of the ligamentum flavum of the thoracic spine NAOHISA MIYAKOSHI, M.D., YOICHI SHIMADA,
ASJ. Analysis of the Prevalence and Distribution of Cervical and Thoracic Compressive Lesions of the Spinal Cord in Lumbar Degenerative Disease
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Cervical and thoracic Asian compressive Spine J 2014;8(1):19-26 lesions in http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.1.19 lumbar degenerative disease 19
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Cervical and thoracic Asian compressive Spine J 2014;8(1):19-26 lesions in http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.1.19 lumbar degenerative disease 19
Spinal Cord (2005) 43, & 2005 International Spinal Cord Society All rights reserved /05 $
 (2005) 43, 503 507 & 2005 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/05 $30.00 www.nature.com/sc Case Report Postmortem study of the spinal cord showing snake-eyes appearance due to damage by
(2005) 43, 503 507 & 2005 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/05 $30.00 www.nature.com/sc Case Report Postmortem study of the spinal cord showing snake-eyes appearance due to damage by
Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment of multi-segmental cervical spondylotic myelopathy
 92 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2016; 22(6): 92-96 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.jhmuweb.net/ Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment
92 Journal of Hainan Medical University 2016; 22(6): 92-96 Journal of Hainan Medical University http://www.jhmuweb.net/ Comparative study on the effect of anterior and posterior decompression in the treatment
S.S.K.MUNASINGHE ARACHCHIGE NATIONAL HOSPITAL OF SRI LANKA
 AN INSIGHT TO THE DILEMMA- CO-EXISTENCE OF OSSIFICAION OF POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT AND CERVICAL DISC PROLAPSE A SRI LANKAN EXPERIENCE S.S.K.MUNASINGHE ARACHCHIGE NATIONAL HOSPITAL OF SRI LANKA BACKGROUND
AN INSIGHT TO THE DILEMMA- CO-EXISTENCE OF OSSIFICAION OF POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT AND CERVICAL DISC PROLAPSE A SRI LANKAN EXPERIENCE S.S.K.MUNASINGHE ARACHCHIGE NATIONAL HOSPITAL OF SRI LANKA BACKGROUND
Impact of Preoperative Spinal Cord Signal Intensity and Symptom Duration on Surgical Outcome of the Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 American Journal of Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery Vol. 1, No. 2, 2015, pp. 102-106 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/ajcnn Impact of Preoperative Spinal Cord Signal Intensity and Symptom Duration
American Journal of Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery Vol. 1, No. 2, 2015, pp. 102-106 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/ajcnn Impact of Preoperative Spinal Cord Signal Intensity and Symptom Duration
Case SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra
 Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
Abstract Study Design Systematic review. Weerasak Singhatanadgige 1 Worawat Limthongkul 1 Frank Valone III 2 Wicharn Yingsakmongkol 1 K.
 702 Review Article GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL THIEME Outcomes following or Fusion in Patients with Myelopathy Caused by Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament: A Systematic Review Weerasak Singhatanadgige
702 Review Article GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL THIEME Outcomes following or Fusion in Patients with Myelopathy Caused by Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament: A Systematic Review Weerasak Singhatanadgige
Hehuan Xia, Yongsheng Lin, Zhihong Wang, Yipeng Yang, Bin Xu, Junming Cao
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(5):5039-5044 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0075161 Original Article Efficacy of posterior decompression and vertebral fusion for treatment of patients with unstable cervical
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(5):5039-5044 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0075161 Original Article Efficacy of posterior decompression and vertebral fusion for treatment of patients with unstable cervical
Original Article Prognosis of Cervical Degenerative Myelopathy after Multilevel Anterior Cervical Discectomies and Fusion
 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. / January - March 4 57-6 Original Article Prognosis of Cervical Degenerative Myelopathy after Multilevel Anterior Cervical Discectomies and Fusion Ahmed
Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. / January - March 4 57-6 Original Article Prognosis of Cervical Degenerative Myelopathy after Multilevel Anterior Cervical Discectomies and Fusion Ahmed
Surgical outcomes for lumbar spinal canal stenosis with coexisting cervical stenosis (tandem spinal stenosis): a retrospective analysis of 565 cases
 Yamada et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:60 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0765-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Surgical outcomes for lumbar spinal canal stenosis with coexisting
Yamada et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:60 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0765-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Surgical outcomes for lumbar spinal canal stenosis with coexisting
Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression and Fusion
 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. 4 / October - December 014 51-56 Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression
Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. 4 / October - December 014 51-56 Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression
Clinical Analysis of Minimally Invasive Single-segment Reduction and Internal Fixation in Patients with Thoracolumbar Fractures
 Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research 2018, 2(1): 23-27 Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research Clinical Analysis of Minimally Invasive Single-segment Reduction and Internal Fixation in Patients with
Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research 2018, 2(1): 23-27 Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research Clinical Analysis of Minimally Invasive Single-segment Reduction and Internal Fixation in Patients with
Static and dynamic cervical MRI: two useful exams in cervical myelopathy
 Original Study Static and dynamic cervical MRI: two useful exams in cervical myelopathy Lorenzo Nigro 1, Pasquale Donnarumma 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Marika Rullo 2, Antonio Santoro 1, Roberto Delfini 1
Original Study Static and dynamic cervical MRI: two useful exams in cervical myelopathy Lorenzo Nigro 1, Pasquale Donnarumma 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Marika Rullo 2, Antonio Santoro 1, Roberto Delfini 1
ORIGINAL PAPER. Department of Orthopedic Surgery,Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine,Nagoya,Japan 2
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 80. 583 589, 2018 doi:10.18999/nagjms.80.4.583 ORIGINAL PAPER Evaluation of sagittal alignment and range of motion of the cervical spine using multi-detector- row computed tomography
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 80. 583 589, 2018 doi:10.18999/nagjms.80.4.583 ORIGINAL PAPER Evaluation of sagittal alignment and range of motion of the cervical spine using multi-detector- row computed tomography
Case Report Delayed myelopathy secondary to stab wound with a retained blade tip within the laminae: case report
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(9):16787-16792 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0012160 Case Report Delayed myelopathy secondary to stab wound with a retained blade tip within the laminae: case report Hui
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(9):16787-16792 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0012160 Case Report Delayed myelopathy secondary to stab wound with a retained blade tip within the laminae: case report Hui
Is OPLL-induced canal stenosis a risk factor of cord injury in cervical trauma?
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 567-574 ORIGINAL STUDY Is OPLL-induced canal stenosis a risk factor of cord injury in cervical trauma? Kyung-Jin Song, Chan-Il Park, Do-Yeon Kim, Young-Ran Jung, Kwang-Bok
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 567-574 ORIGINAL STUDY Is OPLL-induced canal stenosis a risk factor of cord injury in cervical trauma? Kyung-Jin Song, Chan-Il Park, Do-Yeon Kim, Young-Ran Jung, Kwang-Bok
Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 456940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/456940 Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion Koshi Ninomiya, Koichi Iwatsuki,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 456940, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/456940 Case Report Adjacent Lumbar Disc Herniation after Lumbar Short Spinal Fusion Koshi Ninomiya, Koichi Iwatsuki,
Clinical Results and Complications of Surgical Treatment for Thoracic Myelopathy Caused by Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
 Clinical Results and Complications of Surgical Treatment for Thoracic Myelopathy Caused by Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament - A Multicenter Retrospective Study - Mitsumasa Hayashida,
Clinical Results and Complications of Surgical Treatment for Thoracic Myelopathy Caused by Ossification of the Posterior Longitudinal Ligament - A Multicenter Retrospective Study - Mitsumasa Hayashida,
Mitsuhiro Hashimto 1), Masashi Yamazaki 2), Macondo Mochizuki 3), Masatsune Yamagata 1), Yoshikazu Ikeda 1), Fumitake Nakajima 1)
 Long-term results of anterior cervical corpectomy and arthrodesis for cervical degenerative diseases with more than ten years of follow-up Mitsuhiro Hashimto 1), Masashi Yamazaki 2), Macondo Mochizuki
Long-term results of anterior cervical corpectomy and arthrodesis for cervical degenerative diseases with more than ten years of follow-up Mitsuhiro Hashimto 1), Masashi Yamazaki 2), Macondo Mochizuki
Ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament
 J Neurosurg Spine 13:319 323, 2010 Using the T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging signal intensity ratio and clinical manifestations to assess the prognosis of patients with cervical ossification of
J Neurosurg Spine 13:319 323, 2010 Using the T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging signal intensity ratio and clinical manifestations to assess the prognosis of patients with cervical ossification of
흉추척수증을유발한황색인대골화증의골절 - 증례보고 -
 대한척추외과학회지제 14 권제 1 호 Journal of Korean Spine Surg. Vol. 14, No. 1, pp 52~56, 2007 흉추척수증을유발한황색인대골화증의골절 - 증례보고 - 하기용 김영훈 # 지원희 $ 가톨릭대학교의과대학강남성모병원정형외과, 성모자애병원정형외과 #, 강남성모병원영상의학과 $ Fracture of Ossification
대한척추외과학회지제 14 권제 1 호 Journal of Korean Spine Surg. Vol. 14, No. 1, pp 52~56, 2007 흉추척수증을유발한황색인대골화증의골절 - 증례보고 - 하기용 김영훈 # 지원희 $ 가톨릭대학교의과대학강남성모병원정형외과, 성모자애병원정형외과 #, 강남성모병원영상의학과 $ Fracture of Ossification
Cervical corpectomy for sub-axial retro-vertebral body lesions
 Eshra Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery (2019) 33:2 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41984-018-0004-9 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery RESEARCH Open Access Cervical corpectomy for sub-axial retro-vertebral body
Eshra Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery (2019) 33:2 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41984-018-0004-9 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery RESEARCH Open Access Cervical corpectomy for sub-axial retro-vertebral body
Cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) is a
 WScJ 4: 1-5, 2013 Functional Evaluation Using the Modified Japanese Orthopedic Association Score (mjoa) for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy by Age, Gender, and Type of Disease Parisa Azimi 1*, Sohrab Shahzadi
WScJ 4: 1-5, 2013 Functional Evaluation Using the Modified Japanese Orthopedic Association Score (mjoa) for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy by Age, Gender, and Type of Disease Parisa Azimi 1*, Sohrab Shahzadi
Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome
 Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome Hez Progect Israel 2016 Ran Harel, MD Spine Surgery Unit, Department of Neurosurgery, Sheba Medical Center, Ramat-Gan, Israel Sackler Medical School, Tel-Aviv
Cervical Spine Surgery: Approach related outcome Hez Progect Israel 2016 Ran Harel, MD Spine Surgery Unit, Department of Neurosurgery, Sheba Medical Center, Ramat-Gan, Israel Sackler Medical School, Tel-Aviv
Evaluation of conservative treatment and timing of surgical intervention for mild forms of cervical spondylotic myelopathy
 852 Evaluation of conservative treatment and timing of surgical intervention for mild forms of cervical spondylotic myelopathy LING-DE KONG *, LING-CHEN MENG *, LIN-FENG WANG, YONG SHEN, PAN WANG and ZI-KUN
852 Evaluation of conservative treatment and timing of surgical intervention for mild forms of cervical spondylotic myelopathy LING-DE KONG *, LING-CHEN MENG *, LIN-FENG WANG, YONG SHEN, PAN WANG and ZI-KUN
ORIGINAL PAPER. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Chubu Rosai Hospital, Nagoya, Japan ABSTRACT
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 77. 221 ~ 228, 2015 ORIGINAL PAPER RANGE OF MOTION DETERMINED BY MULTIDETECTOR-ROW COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL OSSIFICATION OF THE POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 77. 221 ~ 228, 2015 ORIGINAL PAPER RANGE OF MOTION DETERMINED BY MULTIDETECTOR-ROW COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL OSSIFICATION OF THE POSTERIOR LONGITUDINAL LIGAMENT
CSM is the most common cause of spinal cord dysfunction
 Published December 22, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2756 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Sato T. Horikoshi A. Watanabe M. Uchida K. Ishigame T. Araki H. Kinouchi Evaluation of Cervical Myelopathy Using Apparent Diffusion
Published December 22, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2756 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Sato T. Horikoshi A. Watanabe M. Uchida K. Ishigame T. Araki H. Kinouchi Evaluation of Cervical Myelopathy Using Apparent Diffusion
Rick C. Sasso MD Professor Chief of Spine Surgery Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery Indiana University School of Medicine
 Cervical Myelopathy: Anterior Surgery is Best Rick C. Sasso MD Professor Chief of Surgery Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University School of Medicine Disclosure: Research support-medtronic, Stryker, AO,
Cervical Myelopathy: Anterior Surgery is Best Rick C. Sasso MD Professor Chief of Surgery Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery University School of Medicine Disclosure: Research support-medtronic, Stryker, AO,
Morphological changes of the cervical spinal canal and cord due to aging on MR imaging
 Morphological changes of the cervical spinal canal and cord due to aging on MR imaging Shigeru Kobayashi, MD,PhD 1, Katsuhiko Hayakawa, MD, PhD 2, Takashi Nakane, MD, PhD 2, Riya Kosaka MD,PhD 3. 1 Department
Morphological changes of the cervical spinal canal and cord due to aging on MR imaging Shigeru Kobayashi, MD,PhD 1, Katsuhiko Hayakawa, MD, PhD 2, Takashi Nakane, MD, PhD 2, Riya Kosaka MD,PhD 3. 1 Department
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(4): /ISSN: /IJCEM
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(4):3289-3295 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0065310 Original Article Effect of surgical treatment on mild cervical spondylotic myelopathy with remarkable intramedullary magnetic
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(4):3289-3295 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0065310 Original Article Effect of surgical treatment on mild cervical spondylotic myelopathy with remarkable intramedullary magnetic
Radiologic Finding of Failed Percutaneous Vertebroplasty
 Radiologic Finding of Failed Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Liu, Wei Chiang 1, M.D., Sang-Ho Lee 2, M.D., Won Gyu Choi 2, M.D., Dong-Yeob Lee 2, M.D., Sung Suk Paeng 3, M.D., Amy Kwon 4, Ph.D. Department
Radiologic Finding of Failed Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Liu, Wei Chiang 1, M.D., Sang-Ho Lee 2, M.D., Won Gyu Choi 2, M.D., Dong-Yeob Lee 2, M.D., Sung Suk Paeng 3, M.D., Amy Kwon 4, Ph.D. Department
) ACDF. (Japanese Orthopaedic Association,JOA) ACCF (175.4±12.1ml VS 201.3±80.4ml) ACDF JOA VAS (P=0.000),ACCF :A : X(2015)
 2015 25 5 Chinese Journal of Spine and Spinal Cord,2015,Vol.25,No.5 433 1, 2, 2, 3, 3 (1 ;2 466000 ;3 466000 ) : (anterior cervical discectomy and fusion,acdf) (anterior cervical corpectomy and fusion,accf)
2015 25 5 Chinese Journal of Spine and Spinal Cord,2015,Vol.25,No.5 433 1, 2, 2, 3, 3 (1 ;2 466000 ;3 466000 ) : (anterior cervical discectomy and fusion,acdf) (anterior cervical corpectomy and fusion,accf)
Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic resonance imaging study evidence
 See the Editorial and the Response in this issue, p 1. J Neurosurg (Spine 1) 100:2 6, 2004 Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic
See the Editorial and the Response in this issue, p 1. J Neurosurg (Spine 1) 100:2 6, 2004 Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic
Same Segment Early Recurrence in Surgery of Lumbar Canal Stenosis- Role of Dissectomy
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. II (August. 2016), PP 34-40 www.iosrjournals.org Same Segment Early Recurrence in Surgery
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. II (August. 2016), PP 34-40 www.iosrjournals.org Same Segment Early Recurrence in Surgery
Outcome of Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion with Autograft and Plating in management of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Spine Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Outcome of Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion with Autograft and Plating in management of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy V Kumar,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Spine Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Outcome of Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion with Autograft and Plating in management of Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy V Kumar,
ProDisc-C versus fusion with Cervios chronos prosthesis in cervical degenerative disc disease: Is there a difference at 12 months?
 Original research ProDisc-C versus fusion with Cervios chronos prosthesis in cervical degenerative disc ( ) 51 51 56 ProDisc-C versus fusion with Cervios chronos prosthesis in cervical degenerative disc
Original research ProDisc-C versus fusion with Cervios chronos prosthesis in cervical degenerative disc ( ) 51 51 56 ProDisc-C versus fusion with Cervios chronos prosthesis in cervical degenerative disc
CMEARTICLE * * * Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed
 Singapore Med J 2015; 56(7): 373-378 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015107 CMEARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (161) Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed 2a 2b Fig. 1 Lateral radiograph of
Singapore Med J 2015; 56(7): 373-378 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015107 CMEARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (161) Wen Qi Tan 1, BEng, Bak Siew Steven Wong 2, MBChB, MMed 2a 2b Fig. 1 Lateral radiograph of
Jing Tao Zhang 1, Lin Feng Wang 1, Yue Ju Liu 2, Jun Ming Cao 1, Jie Li 1, Shuai Wang 1 and Yong Shen 1*
 Zhang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2015) 16:267 DOI 10.1186/s12891-015-0728-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Relationship between developmental canal stenosis and surgical results of anterior decompression
Zhang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2015) 16:267 DOI 10.1186/s12891-015-0728-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Relationship between developmental canal stenosis and surgical results of anterior decompression
Dynamic Mri of the Cervical Spine An Important Tool in Planning Surgical Treatment of Cervical Compressive Myelopathy
 International Journal of Neurosurgery 2018; 2(1): 17-22 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijn doi: 10.11648/j.ijn.20180201.14 Dynamic Mri of the Cervical Spine An Important Tool in Planning Surgical
International Journal of Neurosurgery 2018; 2(1): 17-22 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijn doi: 10.11648/j.ijn.20180201.14 Dynamic Mri of the Cervical Spine An Important Tool in Planning Surgical
Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...)
 Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...) 59 59 66 Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine:
Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...) 59 59 66 Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine:
Medical Policy. MP Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Medical Policy MP 6.01.48 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 6.01.48 Last Review: 09/19/2018 Effective Date: 09/19/2018 Section: Radiology Related Policies 6.01.46 Dynamic Spinal Visualization and Vertebral Motion Analysis
Medical Policy MP 6.01.48 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 6.01.48 Last Review: 09/19/2018 Effective Date: 09/19/2018 Section: Radiology Related Policies 6.01.46 Dynamic Spinal Visualization and Vertebral Motion Analysis
Original Article Local vs. general anesthesia for decompression for thoracic spinal stenosis
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(7):7208-7215 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0069528 Original Article Local vs. general anesthesia for decompression for thoracic spinal stenosis Ye Zhao 1, Juan Xu 2 Departments
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(7):7208-7215 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0069528 Original Article Local vs. general anesthesia for decompression for thoracic spinal stenosis Ye Zhao 1, Juan Xu 2 Departments
Interlaminar Bony Fusion after C3-6 Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: Its Predictors and Characteristics
 Interlaminar Bony Fusion after C3-6 Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: Its Predictors and Characteristics Yoshiro Nanjo, Hideki Nagashima, Shinji Tanishima,Tokumitsu Mihara,
Interlaminar Bony Fusion after C3-6 Double-Door Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy: Its Predictors and Characteristics Yoshiro Nanjo, Hideki Nagashima, Shinji Tanishima,Tokumitsu Mihara,
The reliability of MRI diagnosis of anterior and posterior longitudinal ligament of lower cervical spine.
 Biomedical Research 2017; Special Issue: S271-S278 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info The reliability of MRI diagnosis of anterior and posterior longitudinal ligament of lower cervical spine. Huang Kun
Biomedical Research 2017; Special Issue: S271-S278 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info The reliability of MRI diagnosis of anterior and posterior longitudinal ligament of lower cervical spine. Huang Kun
Case Report Two-year follow-up results of C2/3 Prestige-LP cervical disc replacement: first report
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(4):7349-7353 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0018962 Case Report Two-year follow-up results of C2/3 Prestige-LP cervical disc replacement: first report Yi Yang 1, Mengying
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(4):7349-7353 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0018962 Case Report Two-year follow-up results of C2/3 Prestige-LP cervical disc replacement: first report Yi Yang 1, Mengying
102 Results RESULTS. Age Mean=S.D Range 42= years -84 years Number % <30 years years >50 years
 102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Description
 Subject: Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: June 2015 Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Description Positional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows imaging
Subject: Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: June 2015 Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Description Positional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows imaging
Clinical Correlation of a New Practical MRI Method for Assessing Cervical Spinal Canal Compression
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE
 CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE Cervical spondylosis l Cervical osteophytosis l Most common progressive disease in the aging cervical spine l Seen in 95% of the people by 65 years Pathophysiology
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE Cervical spondylosis l Cervical osteophytosis l Most common progressive disease in the aging cervical spine l Seen in 95% of the people by 65 years Pathophysiology
Daniel J. Blizzard, MD, MS
 Daniel J. Blizzard, MD, MS None Common degenerative (usually) condition caused by compression on the spinal cord that is characterized by clumsiness and difficulty with fine motor tasks in the hands and
Daniel J. Blizzard, MD, MS None Common degenerative (usually) condition caused by compression on the spinal cord that is characterized by clumsiness and difficulty with fine motor tasks in the hands and
Lumbar spinal canal stenosis Degenerative diseases F 08
 What is lumbar spinal canal stenosis? This condition involves the narrowing of the spinal canal, and of the lateral recesses (recesssus laterales) and exit openings (foramina intervertebralia) for the
What is lumbar spinal canal stenosis? This condition involves the narrowing of the spinal canal, and of the lateral recesses (recesssus laterales) and exit openings (foramina intervertebralia) for the
Cervical spondylarthrotic myelopathy with early onset in Down's syndrome: five cases and a review of the literature
 283 Journal of Intellectual Disability Research VOLUME 43 PART 4 pp 283±288 AUGUST 1999 Cervical spondylarthrotic myelopathy with early onset in Down's syndrome: five cases and a review of the literature
283 Journal of Intellectual Disability Research VOLUME 43 PART 4 pp 283±288 AUGUST 1999 Cervical spondylarthrotic myelopathy with early onset in Down's syndrome: five cases and a review of the literature
The Evaluation of Bladder Symptoms in Patients With Lumbar Compression Disorders Who Have Undergone Decompressive Surgery
 The Evaluation of Bladder Symptoms in Patients With Lumbar Compression Disorders Who Have Undergone Decompressive Surgery SPINE Volume 35, Number 17, pp E849 E854 2010, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Chun-Hao
The Evaluation of Bladder Symptoms in Patients With Lumbar Compression Disorders Who Have Undergone Decompressive Surgery SPINE Volume 35, Number 17, pp E849 E854 2010, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Chun-Hao
Is unilateral pedicle screw fixation superior than bilateral pedicle screw fixation for lumbar degenerative diseases: a meta-analysis
 Lu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:296 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-1004-x SYSTEMATIC REVIEW Open Access Is unilateral pedicle screw fixation superior than bilateral
Lu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:296 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-1004-x SYSTEMATIC REVIEW Open Access Is unilateral pedicle screw fixation superior than bilateral
Asymmetrical degenerative marrow (Modic) changes in cervical spine: prevalence, correlative factors, and surgical outcomes
 Gao et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:85 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0807-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Asymmetrical degenerative marrow (Modic) changes in cervical spine:
Gao et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:85 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0807-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Asymmetrical degenerative marrow (Modic) changes in cervical spine:
Comparative Analysis of outcome in patients of Lumbar Canal Stenosis undergoing decompression with and without Instrumentation
 Document heading doi: 10.21276/apjhs.2017.4.1.18 Research Article Comparative Analysis of outcome in patients of Lumbar Canal Stenosis undergoing decompression with without Instrumentation ABSTRACT Sanjay
Document heading doi: 10.21276/apjhs.2017.4.1.18 Research Article Comparative Analysis of outcome in patients of Lumbar Canal Stenosis undergoing decompression with without Instrumentation ABSTRACT Sanjay
Surgery in cervical disc herniation: anterior cervical discectomy without fusion or with fusion
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 1 2017 January - March Article Surgery in cervical disc herniation: anterior cervical discectomy without fusion or with fusion Andrei Stefan Iencean ROMANIA DOI:
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 1 2017 January - March Article Surgery in cervical disc herniation: anterior cervical discectomy without fusion or with fusion Andrei Stefan Iencean ROMANIA DOI:
Magnetic resonance image (MRI) is a useful tool for
 SPINE Volume 40, Number 6, pp 392-398 2015, Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved. DIAGNOSTICS Abnormal Findings on Magnetic Resonance Images of the Cervical Spines in 1211 Asymptomatic Subjects
SPINE Volume 40, Number 6, pp 392-398 2015, Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved. DIAGNOSTICS Abnormal Findings on Magnetic Resonance Images of the Cervical Spines in 1211 Asymptomatic Subjects
Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3 C6 Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 THIEME GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL Original Article 53 Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3 C6 Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Hironobu Sakaura 1 Toshitada Miwa
THIEME GLOBAL SPINE JOURNAL Original Article 53 Incidence and Risk Factors for Late Neurologic Deterioration after C3 C6 Laminoplasty for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Hironobu Sakaura 1 Toshitada Miwa
Radiographic Dimensional Analysis of Open Door Laminoplasty with Plate in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 Radiographic Dimensional Analysis of Open Door Laminoplasty with Plate in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Woo-Kie Min,MD,PhD Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kyungpook National University College of Medicine,
Radiographic Dimensional Analysis of Open Door Laminoplasty with Plate in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Woo-Kie Min,MD,PhD Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kyungpook National University College of Medicine,
Radiculopathy Caused by Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures in the Lumbar Spine
 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 51, 484 489, 2011 Radiculopathy Caused by Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures in the Lumbar Spine Manabu SASAKI, 1 Masanori AOKI, 2 Kazuya NISHIOKA, 3 and Toshiki YOSHIMINE 4 1 Department
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 51, 484 489, 2011 Radiculopathy Caused by Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures in the Lumbar Spine Manabu SASAKI, 1 Masanori AOKI, 2 Kazuya NISHIOKA, 3 and Toshiki YOSHIMINE 4 1 Department
Gillian Wooldridge, DO Houston Methodist Willowbrook Hospital Primary Care Sports Medicine Fellowship May 3, 2018
 Gillian Wooldridge, DO Houston Methodist Willowbrook Hospital Primary Care Sports Medicine Fellowship May 3, 2018 Disclosures Neither I nor any family members have financial disclosures Special thanks
Gillian Wooldridge, DO Houston Methodist Willowbrook Hospital Primary Care Sports Medicine Fellowship May 3, 2018 Disclosures Neither I nor any family members have financial disclosures Special thanks
Spinal injury is very common in Ireland: 19 per 100,000 (1). It poses a significant disease burden.
 MRI in traumatic spinal cord injury: a single national spinal centre experience and study of imaging features with clinical correlation with ASIA score and outcome Poster No.: C-1235 Congress: ECR 2011
MRI in traumatic spinal cord injury: a single national spinal centre experience and study of imaging features with clinical correlation with ASIA score and outcome Poster No.: C-1235 Congress: ECR 2011
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29800 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Moojen, Wouter Anton Title: Introducing new implants and imaging techniques for
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29800 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Moojen, Wouter Anton Title: Introducing new implants and imaging techniques for
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(5): /ISSN: /IJCEM Ye Zhao 1, Juan Xu 2, Shukui Li 1, Cai Cheng 1, Hongjiang Sun 1
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(5):8685-8691 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0020477 Original Article Comparative study on clinical efficacy of posterior laminectomy and a modified transfacet joints approach
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(5):8685-8691 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0020477 Original Article Comparative study on clinical efficacy of posterior laminectomy and a modified transfacet joints approach
Comparison of outcomes between patients using SSEP/TcMEP monitoring during PVCR procedure and no monitoring in a single center:
 Comparison of outcomes between patients using SSEP/TcMEP monitoring during PVCR procedure and no monitoring in a single center: --Dose monitoring truly detect all spinal cord abnormalities and improve
Comparison of outcomes between patients using SSEP/TcMEP monitoring during PVCR procedure and no monitoring in a single center: --Dose monitoring truly detect all spinal cord abnormalities and improve
Adjacent Segment Degeneration Following Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Versus the Bryan Cervical Disc Arthroplasty
 e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.905178 Received: 2017.05.05 Accepted: 2017.05.22 Published: 2017.06.02 Adjacent Segment Degeneration Following Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Versus the Bryan
e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.905178 Received: 2017.05.05 Accepted: 2017.05.22 Published: 2017.06.02 Adjacent Segment Degeneration Following Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Versus the Bryan
Reduced invasiveness of myoarchitectonic laminectomy compared with open-door laminoplasty in patients with cervical myelopathy
 Reduced invasiveness of myoarchitectonic laminectomy compared with open-door laminoplasty in patients with cervical myelopathy Department of Spinal Surgery 1), Brain Attack Center Ota Memorial Hospital,
Reduced invasiveness of myoarchitectonic laminectomy compared with open-door laminoplasty in patients with cervical myelopathy Department of Spinal Surgery 1), Brain Attack Center Ota Memorial Hospital,
Segmental stability following minimally invasive decompressive surgery with tubular retractor for lumbar spinal stenosis
 Segmental stability following minimally invasive decompressive surgery with tubular retractor for lumbar spinal stenosis Department of Spinal surgery, Research Institute for Brain and Blood Vessels-Akita
Segmental stability following minimally invasive decompressive surgery with tubular retractor for lumbar spinal stenosis Department of Spinal surgery, Research Institute for Brain and Blood Vessels-Akita
ASJ. Radiologic and Clinical Courses of Degenerative Lumbar Scoliosis (10 25 ) after a Short-Segment Fusion. Asian Spine Journal.
 Asian Spine Journal 570 Kyu Yeol Clinical Lee et al. Study Asian Spine J 2017;11(4):570-579 https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2017.11.4.570 Asian Spine J 2017;11(4):570-579 Radiologic and Clinical Courses of
Asian Spine Journal 570 Kyu Yeol Clinical Lee et al. Study Asian Spine J 2017;11(4):570-579 https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2017.11.4.570 Asian Spine J 2017;11(4):570-579 Radiologic and Clinical Courses of
PREOPERATIVE RETROLISTHESIS IS A RISK FACTOR OF LUMBAR DISC HERNIATION AFTER FENESTRATION WITHOUT DISCECTOMY
 PREOPERATIVE RETROLISTHESIS IS A RISK FACTOR OF LUMBAR DISC HERNIATION AFTER FENESTRATION WITHOUT DISCECTOMY Shota Takenaka*, Noboru Hosono, Yoshihiro Mukai, Kosuke Tateishi, Takeshi Fuji Osaka Kosei-nenkin
PREOPERATIVE RETROLISTHESIS IS A RISK FACTOR OF LUMBAR DISC HERNIATION AFTER FENESTRATION WITHOUT DISCECTOMY Shota Takenaka*, Noboru Hosono, Yoshihiro Mukai, Kosuke Tateishi, Takeshi Fuji Osaka Kosei-nenkin
Pott s kyphosis. University Affiliated Sixth People s Hospital, 600 Yishan Road, Shanghai , P.
 QJM Advance Access published November 17, 2014 Pott s kyphosis Author Names: Yi Zhang, Yong-Sheng Yu, Zheng-Hao Tang and Guo-Qing Zang Author Affiliations: Department of Infectious Diseases, Shanghai Jiao
QJM Advance Access published November 17, 2014 Pott s kyphosis Author Names: Yi Zhang, Yong-Sheng Yu, Zheng-Hao Tang and Guo-Qing Zang Author Affiliations: Department of Infectious Diseases, Shanghai Jiao
Life expectancy after cervical laminoplasty Causes of the fatal prognosis at the early stage (within 5 years)
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Life expectancy after cervical laminoplasty Causes of the fatal prognosis at the early stage (within 5 years) Yoshiharu Kawaguchi 1), Masato Nakano 1),
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Life expectancy after cervical laminoplasty Causes of the fatal prognosis at the early stage (within 5 years) Yoshiharu Kawaguchi 1), Masato Nakano 1),
Adjacent segment disease after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion
 Adjacent segment disease after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion, Besar, Akar and Abdelkader MD. 43 Adjacent segment disease after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion *Mohamed Abdulrahman Besar.MD;
Adjacent segment disease after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion, Besar, Akar and Abdelkader MD. 43 Adjacent segment disease after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion *Mohamed Abdulrahman Besar.MD;
Changes in Spinal Canal Diameter and Vertebral Body Height with Age
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/1.3349/ymj.213.54.6.1498 pissn: 513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 54(6):1498-154, 213 Changes in Spinal Canal Diameter and Vertebral Body Height with Age Kyung
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/1.3349/ymj.213.54.6.1498 pissn: 513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 54(6):1498-154, 213 Changes in Spinal Canal Diameter and Vertebral Body Height with Age Kyung
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Minamide A*, Yoshida M*, Yamada H*, Hashizume H*, NakagawaY*, Iwasaki H*, Tsutsui S*, Hiroyuki Oka H**.
 Efficacy of Posterior Segmental Decompression Surgery for Pincer Mechanism in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy -A retrospective case control study using propensity score matching Minamide A*, Yoshida M*,
Efficacy of Posterior Segmental Decompression Surgery for Pincer Mechanism in Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy -A retrospective case control study using propensity score matching Minamide A*, Yoshida M*,
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS AND CERVICAL SPONDYLOTIC MYELOPATHY
 CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS AND CERVICAL SPONDYLOTIC MYELOPATHY A NEUROSURGEON S VIEW A Preventable Journey to a wheelchair bound-life Dr H. BOODHOO F.C.S (Neurosurgery) Cervical Spondylosis Spinal Osteoarthritis
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS AND CERVICAL SPONDYLOTIC MYELOPATHY A NEUROSURGEON S VIEW A Preventable Journey to a wheelchair bound-life Dr H. BOODHOO F.C.S (Neurosurgery) Cervical Spondylosis Spinal Osteoarthritis
Range of motion of thoracic spine in sagittal plane
 DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-3088-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Range of motion of thoracic spine in sagittal plane Daigo Morita Yasutsugu Yukawa Hiroaki Nakashima Keigo Ito Go Yoshida Masaaki Machino Syunsuke Kanbara
DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-3088-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Range of motion of thoracic spine in sagittal plane Daigo Morita Yasutsugu Yukawa Hiroaki Nakashima Keigo Ito Go Yoshida Masaaki Machino Syunsuke Kanbara
Age-related and degenerative changes in the osseous anatomy, alignment, and range of motion
 Age-related and degenerative changes in the osseous anatomy, alignment, and range of motion of the cervical spine: a comparative study of radiographic data from 1016 patients with cervical spondylotic
Age-related and degenerative changes in the osseous anatomy, alignment, and range of motion of the cervical spine: a comparative study of radiographic data from 1016 patients with cervical spondylotic
Morphological Patterns of the Anterior Median Fissure in the Cervical Spinal Cord Evaluated by Computed Tomography After Myelography
 Neurospine 2018;15(4):388-393. https://doi.org/10.14245/ns.1836112.056 Neurospine pissn 2586-6583 eissn 2586-6591 Original Article Corresponding Author Yuki Oichi https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0225-8158
Neurospine 2018;15(4):388-393. https://doi.org/10.14245/ns.1836112.056 Neurospine pissn 2586-6583 eissn 2586-6591 Original Article Corresponding Author Yuki Oichi https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0225-8158
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients
 Original Article J Nepal Health Res Counc 2015 Sep - Dec;13(31):196-200 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients Karki DB, 1 Gurung G,
Original Article J Nepal Health Res Counc 2015 Sep - Dec;13(31):196-200 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients Karki DB, 1 Gurung G,
The Relationship amongst Intervertebral Disc Vertical Diameter, Lateral Foramen Diameter and Nerve Root Impingement in Lumbar Vertebra
 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1803.004 The Relationship amongst Intervertebral Disc Vertical Diameter, Lateral Foramen Diameter and Nerve Root Impingement in Lumbar Vertebra Yusof MI, MMed Orth, Hassan
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1803.004 The Relationship amongst Intervertebral Disc Vertical Diameter, Lateral Foramen Diameter and Nerve Root Impingement in Lumbar Vertebra Yusof MI, MMed Orth, Hassan
Ten Second Step Test" as a New Quantifiable Parameter of Cervical Myelopathy. Spine January 1, 2009; Volume 34; Issue 1; pp 82-86
 Ten Second Step Test" as a New Quantifiable Parameter of Cervical Myelopathy 1 Spine January 1, 2009; Volume 34; Issue 1; pp 82-86 Yukawa, Yasutsugu; Kato, Fumihiko; Ito, Keigo; Horie, Yumiko; Nakashima,
Ten Second Step Test" as a New Quantifiable Parameter of Cervical Myelopathy 1 Spine January 1, 2009; Volume 34; Issue 1; pp 82-86 Yukawa, Yasutsugu; Kato, Fumihiko; Ito, Keigo; Horie, Yumiko; Nakashima,
Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life
 Original Study Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life Lorenzo Nigro 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Pasquale
Original Study Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life Lorenzo Nigro 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Pasquale
Lumbar Laminotomy DEFINING APPROPRIATE COVERAGE POSITIONS NASS COVERAGE POLICY RECOMMENDATIONS TASKFORCE
 NASS COVERAGE POLICY RECOMMENDATIONS Lumbar Laminotomy DEFINING APPROPRIATE COVERAGE POSITIONS North American Spine Society 7075 Veterans Blvd. Burr Ridge, IL 60527 TASKFORCE Introduction North American
NASS COVERAGE POLICY RECOMMENDATIONS Lumbar Laminotomy DEFINING APPROPRIATE COVERAGE POSITIONS North American Spine Society 7075 Veterans Blvd. Burr Ridge, IL 60527 TASKFORCE Introduction North American
Treatment of Two Level Artificial Disc Replacement for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
 Journal of Minimally Invasive Spine JMISST Surgery and Technique 3(1):34-38, 2018 Case Report eissn 2508-2043 https://doi.org/10.21182/jmisst.2017.00269 www.jmisst.org for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
Journal of Minimally Invasive Spine JMISST Surgery and Technique 3(1):34-38, 2018 Case Report eissn 2508-2043 https://doi.org/10.21182/jmisst.2017.00269 www.jmisst.org for Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy
Lumbar Disc Herniation Presented with Contralateral Symptoms
 Clinical Article J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (2) : 220-224, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.1010.015 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 Lumbar Disc Herniation Presented with Contralateral Symptoms Pius
Clinical Article J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (2) : 220-224, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.1010.015 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 Lumbar Disc Herniation Presented with Contralateral Symptoms Pius
Cervical canal stenosis and adjacent segment degeneration after anterior cervical arthrodesis
 Eur Spine J (215) 24:159 1596 DOI 1.17/s586-15-3975-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cervical canal stenosis and adjacent segment degeneration after anterior cervical arthrodesis Jing Tao Zhang 1 Jun Ming Cao 1 Fan
Eur Spine J (215) 24:159 1596 DOI 1.17/s586-15-3975-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cervical canal stenosis and adjacent segment degeneration after anterior cervical arthrodesis Jing Tao Zhang 1 Jun Ming Cao 1 Fan
