Supplementary material 3 (S3) Studies included in the data analysis
|
|
|
- Albert Perkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary material 3 (S3) Studies included in the data analysis The majority of data cases compiled, and used in the analysis, were for LF baleen whales and MF toothed cetaceans, exposed to three categories of human-generated sounds (hereon referred to as noise): continuous (shipping including ice-breaking, and construction), mid-frequency active sonar (MFAS), and seismic/explosions (n = 195, see Table 6 and Figure 3 in the manuscript). Data cases came from the following 80 studies (note that one study can be represented by one or multiple data cases depending on the level of detailed information reported, see raw data in S2): 1. Aguilar Soto, N., Johnson, M., Madsen, P., Tyack, P., Bocconcelli, A., and Borsani, F Does Intense Ship Noise Disrupt Foraging in Deep-Diving Cuvier s Beaked Whales (Ziphius cavirostris)? Mar. Mamm. Sci. 22 (3): Alves, A., Antunes, R., Bird, A. Tyack, P. Miller, P. Lam, F., and Kvadsheim, P Vocal Matching of Naval Sonar Signals by Long-Finned Pilot Whales (Globicephala melas). Mar. Mamm. Sci. 30 (3): doi: /mms Antunes, R., Kvadsheim, P., Lam, F., Tyack, P., Thomas, L., Wensveen, P., and Miller, P High thresholds for avoidance of sonar by free-ranging longfinned pilot whales (Globicephala melas). Mar. Poll. Bull. 83 (1): Baird, R., Martin, S., Webster, D., and Southall, B Assessment of modeled received sound pressure levels and movements of satellite-tagged odontocetes Page 1
2 exposed to mid-frequency active sonar at the Pacific Missile Range Facility: February 2011 through February Retrieved from 5. Baker, C., Herman, L., Bays, B., and Stifel, W The impact of vessel traffic on the behavior of humpback whales in southeast Alaska. Seattle, WA. 6. Bernasconi, M., Patel, R., and Nøttestad, L Behavioral observations of baleen whales in proximity of a modern fishing vessel. In the effects of noise on aquatic life. Edited by A. Popper and A. Hawkins, New York, NY: Springer. pp Biassoni, N., Miller, P., and Tyack, P Preliminary results of the effects of SURTASS-LFA Sonar on singing humpback whales. WHOI Technical Report. Retrieved from Miller, Tyack_2000_Unknown_Preliminary results of the effects of SURTASS-LFA Sonar on singing humpback whales 8. Blackwell, S., Nations, C., McDonald, T., Greene, C., Thode, A., Guerra, M., and Macrander, A Effects of airgun sounds on bowhead whale calling rates in the Alaskan Beaufort Sea. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 29 (4): Buckstaff, K. C Effects of watercraft noise on the acoustic behaviour of bottlenose dolphins in Sarasota Bay, Florida. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 20 (4): Castellote, M., Clark, C., and Lammers, M Acoustic and behavioural changes by fin whales (Balaenoptera physalus) in response to shipping and airgun noise. Biol. Conserv. 147 (1): Page 2
3 11. Cerchio, S, Strindberg, S., Collins, T., Bennett, C., and Rosenbaum, H Seismic surveys negatively affect humpback whale singing activity off Northern Angola. PLoS ONE 9 (3): e doi: /journal.pone Croll, D., Clark, C., Calambokidis, J., Ellison, W., and Tershy, B Effect of anthropogenic low-frequency noise on the foraging ecology of Balaenoptera whales. Anim. Conserv. 4 (01): doi: S. L., Boyd, I. L., 13. Claridge, D. E., Clark, C. W., Gagnon, C., Southall, B. L., and Tyack, P. L Delphinid whistle production and call matching during playback of simulated military sonar. Mar. Mamm. Sci., 29 (2): E46-E59. DOI: /j x 14. DeRuiter, S., Southall, B., Calambokidis, J., Zimmer, W., Sadykova, D., Falcone, Friedlaender, A. Joseph, J., Moretti, D., Schorr, G., Thomas, L., Tyack P First direct measurements of behavioural responses by Cuvier s beaked whales to mid-frequency active sonar. Biol. Lett. 9 (4): Di lorio, L., and Clark, C Exposure to seismic survey alters blue whale acoustic communication. Biol. Lett. 6 (1): Doyle, L., McCowan, B., Hanser, S., Chyba, C. Bucci, T., and Blue, J Applicability of information theory to the quantification of responses to anthropogenic noise by Southeast Alaskan humpback whales. Entropy 10 (2): Ellison, W., Southall, B., Clark, C., and Frankel, A A New context-based approach to assess marine mammal behavioral responses to anthropogenic Page 3
4 sounds. Conserv. Biol. 26 (1): Frankel, A., and Clark, C Results of low-frequency playback of M- sequence noise to humpback whales, Megaptera novaeangliae, in Hawai. Can. J. Zool. 76: Frankel, A., and Clark, C Behavioral responses of humpback whales (Megaptera novaeangliae) to full-scale ATOC signals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 108 (4), Fristrup, K., Hatch, L., and Clark, C Variation in humpback whale (Megaptera novaeangliae) song length in relation to low-frequency sound broadcasts. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 113 (6): Gailey, G., Würsig, B., and McDonald, T Abundance, behavior, and movement patterns of western gray whales in relation to a 3-D seismic survey, Northeast Sakhalin Island, Russia. Environ. Model. Assess. 134 (1-3), Goldbogen, J., Southall, B., DeRuiter, S., Calambokidis, J., Friedlaender, A., Hazen, E., Falcone, E., Schorr, G., Douglas, A., Moretti, D., Kyburg, C., McKenna, M., and Tyack, P Blue whales respond to simulated midfrequency military sonar. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 280 (1765): doi: Goold, J Acoustic assessment of populations of common dolphin Delphinus delphis in conjunction with seismic surveying J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 76 (3), Page 4
5 24. Goold, J., and Fish, P Broadband spectra of seismic survey air-gun emissions, with reference to dolphin auditory thresholds. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 103 (4), Gordon, J., Leaper, R., Hartley, F, and Chappell, O Effects of whale watching vessels on the surface and underwater acoustic behaviour of sperm whales off Kaikoura, New Zealand. Science and research series. Department of Conservation, Wellington, New Zealand. 35 pp. 26. Henderson, E., Smith, M., Gassmann, S., Wiggins, M., Douglas, A., and Hildebrand, J Delphinid behavioral responses to incidental mid-frequency active sonar. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 136 (4), Holt, M. M., Noren, D. P., Veirs, V., Emmons, C. K., and Veirs, S. (2009). Speaking up: Killer whales (Orcinus orca) increase their call amplitude in response to vessel noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 125 (1), EL27 L Holt, M., Noren, D., and Emmons, C Effects of noise levels and call types on the source levels of killer whale calls. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 130 (5), Jochens, A., Biggs, D., Benoit-Bird, K., Engelhaupt, J., Gordon, C., Hu, N., Jaquet, M., Johnson, L., Mate, B., Miller, P., Ortega-Ortiz, J., Thode, A., Tyack, P., and B. Wu rsig Sperm whale seismic study - Synthesis report. Department of Oceanography, Texas A&M University. 341pp. 30. Jochens, A. E., & Biggs, D. (2003). Sperm Whale Seismic Study in the Gulf of Mexico. Annual Report: Year 1. New Orleans, LA. U.S. Dept. of the Interior, Page 5
6 Minerals Management Service, Gulf of Mexico OCS Region, OCS Study MMS pp. 31. Johnson, S., Richardson, W., Yazvenko, S., Blokhin, S., Gailey, G., Jenkerson, M., Meier, S., Melton, H., Newcomer, M., Perlov, A., Rutenko, S., Wursig, B., Martin, C., Egging, D A western gray whale mitigation and monitoring program for a 3-D seismic survey, Sakhalin Island, Russia. Environ. Model. Assess. 134 (1-3), Koski, W., Funk, D., Ireland, D., Lyons, C., Christie, K., Macrander, A., and Blackwell, S An update on feeding by bowhead whales near an offshore seismic survey in the central Beaufort Sea. Retrieved from bowhead whales near Offshore Seismic in Beaufort Sea.pdf 33. Ljungblad, D. K., Wursig, B., Swartz, S. L., & Keene, J. M Observations on the behavioral responses of bowhead whales (Balaena mysticetus) to active geophysical vessels in the Alaskan Beaufort Sea. Arctic 41 (3), Madsen, P., and Møhl, B Sperm whales (Physeter catodon L. 1758) do not react to sounds from detonators. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 107 (1), Madsen, P., Møhl, B., Nielsen, B., and Wahlberg, M Male sperm whale behaviour during exposures to distant seismic survey pulses. Aquat. Mamm. 28(3), Madsen, P., Johnson, M., Miller, P., Aguilar Soto, N., Lynch, L., and Tyack, P Quantitative measures of air-gun pulses recorded on sperm whales (Physeter macrocephalus) using acoustic tags during controlled exposure Page 6
7 experiments. J. Acoust. Soc. Am.120 (4): Malme, C., Miles, P., Clark, C., Tyack, P., and Bird, J Investigations of the potential effects of underwater noise from petroleum industry activities on migrating Gray whale behaviour. Phase II. BBN Report 5586, Bolt Beranek & Newman Inc., Cambridge, MA, for U.S. Minerals Management Service, Anchorage, AK. NTIS PB pp. Available from [accessed January ] 38. Malme, C., Miles, P., Tyack, Clark, C., and Bird, J Investigation of the potential effects of underwater noise from petroleum industry activities on feeding humpback whale behaviour. BBN Report 5586, Bolt Beranek & Newman Inc., Cambridge, MA, for U.S. Minerals Management Service, Anchorage, AK. Report to U-S. Department of the Interior. Anchorage, AK. Available from Newsroom/Library/Publications/1985/85_0019.aspx. [accessed January ] 39. Malme, C., Würsig, B., Bird, J., and Tyack, P Behavioral responses of gray whales to industrial noise: feeding observations and predictive modeling. Outer Continental Shelf Environmental Assessment Program, Final Report of Principal Investigators. 207 pp. Available from [accessed January ] 40. Malme, C., Miles, P., Clark, C., Tyack, P., and Bird, J Investigations of the potential effects of underwater noise from petroleum industry activities on Page 7
8 migrating gray whale behaviour. BBN Report 5366, Bolt Beranek & Newman Inc., Cambridge, MA, for U.S. Minerals Management Service, Anchorage, AK. NTIS PB Available from Newsroom/Library/Publications/1983/rpt5366.aspx. [accessed January ] 41. McCarthy, E., Moretti, D., Thomas, L., DiMarzio, N., Morrissey, R., Jarvis, S., Ward, J., Izzi, A., and Dilley, A Changes in spatial and temporal distribution and vocal behavior of Blainville s beaked whales (Mesoplodon densirostris) during multiship exercises with mid-frequency sonar. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 27 (3): E McCauley, R., Cato, D., and Jeffery, A A study of the impacts of vessel noise on humpback whales in Hervey Bay. Queensland, Australia. 43. McCauley, R., Fewtrell, D., Duncan, A., Jenner, C., Jenner, M., Penrose, J., Prince, R., Adhitya, A., Murdoch, J., and McCabe, K Marine seismic surveys - a study of environmental implications. APPEA J., 40: McCauley, R., Jenner, M., Jenner, C., and Murdoch, J. (1998). The response of humpback whales (Megaptera novaeangliae) to offshore seismic survey noise: Preliminary results of observations about a working seismic vessel and experimental exposures. Petroleum Production and Exploration Association Journal, 38, McDonald, M., Hildebrand, J., and Webb, S Blue and fin whales observed on a seafloor array in the Northeast Pacific. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 98 (2 Pt 1): Page 8
9 46. Melcón, M., Cummins, A., Kerosky, S., Roche, L., Wiggins, S., and Hildebrand, J Blue whales respond to anthropogenic noise. PLoS ONE 7 (2): e Miller, G., Moulton, V., Davis, R., Holst, M., Millman, P., MacGillivray, A., and Hannay, D Monitoring seismic effects on marine mammals southeastern Beaufort Sea, In Offshore oil and gas environmental effects monitoring/approaches and technologies. Edited by S. L. Armsworthy, P. J. Cranford, and K. Lee. Battelle Press, Columbus, OH. pp Miller, P., Antunes, R., Alves, C., Wensveen, P., Kvadsheim, P., Kleivane, L., Nordlund, N., Lam, F., van Ijsselmuide, S., Visser, F., and Tyack, P The 3S experiments: studying the behavioural effects of naval sonar on killer whales (Orcinus orca), sperm whales (Physeter macrocephalus) and long-finned pilot whales (Globicephala melas) in Norwegian water. SOI technical report, Scotland. 290 pp. 49. Miller, P., Biassoni, N., Samuels, A., and Tyack, P Whale songs lengthen in response to sonar. Nature 405 (6789): Miller, P., Antunes, R., Wensveen, P., Samarra, F., Alves, A., Tyack, P., Kvadsheim, P., Kleivane, L., Lam, P., Ainslie, M., and Thomas, L Doseresponse relationships for the onset of avoidance of sonar by free-ranging killer whales. J. Acoust. Soc. Am.135 (2): Miller, P., Johnson, P., Madsen, P., Biassoni, N., Quero, N., and Tyack, P Using at-sea experiments to study the effects of airguns on the foraging behavior of sperm whales in the Gulf of Mexico. Deep. Sea. Res. Part 1 Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 56 (7): Page 9
10 52. Miller, P., Kvadsheim, P., Lam, F., Wensveen, P., Antunes, R., Alves, C., Visser, F., Kleivane, L., Tyack, P., and Sivle, L The severity of behavioral changes observed during experimental exposures of killer (Orcinus orca), longfinned pilot (Globicephala melas), and sperm (Physeter macrocephalus) whales to naval sonar. Aquatic Mammals 38 (4): Morisaka, T., Shinohara, M., Nakahara, F., and Akamatsu, T Effects of ambient noise on the whistles of Indo-pacific bottlenose dolphin populations. J. Mammal. 86 (3): Nowacek, D., Johnson, M., and Tyack, P North Atlantic right whales (Eubalaena glacialis) ignore ships but respond to alerting stimuli. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 271(1536), DOI /rspb Palka, D., and Hammond, P Accounting for responsive movement in line transect estimates of abundance. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 58, DOI: /cjfas Papale, E., Gamba, M., Perez-Gil, M., Martin, V., and Giacoma, C Dolphins adjust species-specific frequency parameters to compensate for increasing background noise. PloS One, 10(4), e Parks, S., Johnson, E., Nowacek, D., and Tyack, P Individual right whales call louder in increased environmental noise. Biol. Lett. 7 (1): Parks, S., Johnson, M., Nowacek, D., and Tyack, P Changes in Vocal Behavior of North Atlantic Right Whales in Increased Noise. In The Effects of Page 10
11 Noise on Aquatic Life. Edited by A. Popper and A. Hawkins, Springer, New York. pp Pirotta, E., Milor, R., Quick, N., Moretti, D., Di Marzio, N., Tyack, P., Boyd, I., Hastie, G Vessel noise affects beaked whale behavior: Results of a dedicated acoustic response study. PLoS ONE, 7(8): e Richardson, W., Fraker, J., Würsig, B., and Wells, R Behaviour of Bowhead whales Balaena mysticetus summering in the Beaufort Sea: Reactions to industrial activities. Biol. Conserv. 32 (3): Richardson, W., Greene, C., Hanna, J., Koski, W., Miller, M., Patenaude, M., and Smultea, M Acoustic effects of oil production activities on Bowhead and white whales visible during spring migration New Pt. Barrow, Alaska and 1994 phases: sound propagation and whale responses to playbacks of icebreaker noise. King City, Ontario. Available from [accessed on January ] 62. Richardson, W., Greene, C., Koski, W., Smultea, M., Cameron, G., Holdsworth, C., and Al., E Acoustic effects of oil production activities on bowhead and white whales visible during spring migration near Pt. Barrow, Alaska 1990 phase. Herndon, VA. 63. Richardson, W., Würsig, B., and Greene, B Reactions of Bowhead whales, Balaena mysticetus, to seismic exploration in the Canadian Beaufort Sea. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 80 (4): Page 11
12 64. Richardson, W., Miller, G., and Greene, C Displacement of migrating bowhead whales by sounds from seismic surveys in shallow waters of the Beaufort Sea. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 106(4): Richardson, W., Würsig, J., and Greene, C Reactions of bowhead whales, Balaena mysticetus, to drilling and dredging noise in the Canadian Beaufort Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 29 (2): doi: / (90)90032-j. 66. Risch, D., Corkeron, P., Ellison, W., and van Parijs, S Changes in humpback whale song occurrence in response to an acoustic source 200 Km away. PLoS ONE 7 (1): e Robertson, F Effects of seismic operations on bowhead whale behaviour: implications for distribution and abundance assessments. Univeristy of British Columbia. PhD thesis. 231 pp. Available from [accessed on January 2016] 68. Robertson, F., Koski, W., Thomas, T., Richardson, W., Würsig, B., and Trites, A Seismic operations have variable effects on dive-cycle behavior of bowhead whales in the Beaufort Sea. Endanger. Species Res. 21 (2): Rutenko, A., Borisov, S., Gritsenko, A., and Jenkerson, M Calibrating and monitoring the western gray whale mitigation zone and estimating acoustic transmission during a 3D seismic survey, Sakhalin Island, Russia. Environ. Model. Assess. 134(1-3): Sivle, L. D., P. H. Kvadsheim, A. Fahlman, F. P A Lam, P. L. Tyack, and P. J O Miller Changes in dive behavior during Naval sonar exposure in killer whales, long-finned pilot whales, and sperm whales. Front. Psychol. 3 (400): 1- Page 12
13 11. doi: /fphys Southall, B., Bowles, A., Ellison, W., Finneran, J., Gentry, R., Greene, C., Kastak, D., Ketten, D., Miller, J., Nachtigall, P., Richardson, J., Thomas, J., and Tyack, P Marine mammal Noise exposure criteria: initial scientific recommendations. Aquatic Mammals 33 (4): Southall, B., Moretti, D., Abraham, B., Calambokidis, J., DeRuiter, S., and Tyack, P Marine mammal behavioral response studies in Southern California: advances in technology and experimental methods. Mar. Technol. Soc. J. 46 (4): Stimpert, A., DeRuiter, S., Southall, B., Moretti, D., Falcone, E., Goldbogen, J., Friedlaender, A., Schorr, G., and Calambokidis J Acoustic and foraging behavior of a Baird s beaked whale, Berardius bairdii, exposed to simulated sonar. Sci. Rep. 4 (7031) 1 8. doi: /srep Todd, S., Stevick, P., Lien, J., Marques, F., and Ketten, D Behavioural effects of exposure to underwater explosions in humpback whales (Megaptera novaeangliae). Can. J. Zool. 74: Tyack, P., Zimmer, W., Moretti, D., Southall, B., Claridge, D., Durban, J., Clark, C., D'Amico, A., DiMario, N., Jarvis, S., McCarthy, E., Morrissely, R., Ward, J., and Boyd, I Beaked whales respond to simulated and actual Navy sonar. PLoS ONE 6 (3): e Wensveen, P The effects of sound propagation and avoidance behaviour on naval sonar levels received by cetaceans. PhD. University of St. Andrews, Scotland. 116pp. Page 13
14 77. Williams, R., Bain, D., Ford, J., and Trites, A Behavioural responses of male killer whales to a leapfrogging vessel. J. Cetac. Res. Manage. 4 (3): Williams, R., Erbe, C., Ashe, E., Beerman, A., and Smith, J Severity of killer whale behavioral responses to ship noise: A dose-response study. Mar. Poll. Bull. 79 (1-2): Yazvenko, S., McDonald, T., Blokhin, S., Johnson, S., Melton, H., Newcomer, M. Nielson, R. Wainwright, P. W Feeding of western gray whales during a seismic survey near Sakhalin Island, Russia. Environ. Model. Assess. 134 (1-3), Page 14
15 Section I. Data analysis The following analysis supports two key results presented in the manuscript: 1) Behavioural responses of cetaceans are best explained by the interaction between the type of sound sources (continuous, MFAS or seismic/explosion) and functional hearing group (as a proxy for the hearing capabilities of marine mammals); 2) The sound intensity received by the animals (received sound level or RL) did not explain behavioural reactions: more severe behavioural scores were not consistently related with higher RL, and vice versa. The purpose of this supplementary material is to demonstrate that conclusions drawn from the analysis are not affected by different measurements of RL (Analysis 1, Figure S1), or by using an alternative dichotomous behavioural response ranking approach (avoidance or no-avoidance; Analysis 2, Figures S2 and S3). For the dichotomous behavioural response ranking, using the narrative extracted from the studies reviewed, a score of 1 was assigned for each data case that reported avoidance and/or displacement of individuals or populations due to noise exposure. A score of 0 was assigned when the narrative described that individuals remained in the area and/or did not avoid the sound source. Analysis 1. Analysis to determine what variable(s) best explained marine mammal behavioural responses to noise; RL SPL measured as rms Analysis: Ordinal Logistic Regression. Response variable: Behavioural response severity scores (High, Moderate, Low). Behavioural response severity scores ~ RL + Functional hearing group + Sound source Page 15
16 + Functional hearing group * Sound source + Functional hearing group * RL + Sound source * RL Number of data cases: 173 Key finding: Behavioural response severity scores did not consistently escalate with increasing RL (Figure S1). The most parsimonious model to describe the behavioural response severity scores included the interaction between sound source and functional hearing group, but did not include RL (Table S1). The analysis of relative variable importance showed that the sound source (w+( sound source )=0.99) and functional hearing groups (w+( hearing group )=0.89) were important variables for describing the severity of behavioural response of wild cetaceans, while RL was irrelevant (w+( RL )=0.49). Page 16
17 Probability Density Function Density function Kernel density function Probability Density Function Kernel density function S3: Analysis and data exploration - Behavioural Responses of Wild Marine Mammals to Noise High Moderate Low MF toothed cetaceans and LF baleen whales exposed to continuous, MFAS and seismic/explosion Mid-frequency N = 173 odontocetes/low-frequency sonar (N = 46) Behavioural severity score High Moderate Low a MF toothed cetaceans exposed to continuous N = 48 b Data used in analysis 0.05 MF toothed cetaceans exposed to MFAS N = c MF odontocetes/lf sonar N = 46 LF baleen whales exposed to seismic/explosion N = 32 d RL SPL RMS Received Sound Level Received Sound Levels (db re 1 µ Pa) Received Sound Level Figure S1. Probability density function (via Kernel density estimation) of the behavioural response severity scores (low, moderate, high) of cetaceans low-frequency hearing (LF baleen whales) and cetaceans with mid-frequency hearing (MF toothed cetaceans) in relation to RL SPL rms of continuous, MFAS, and seismic/explosion sound sources. Page 17
18 Table S1. Model selection statistics ΔAICc: delta Akaike information criterion; Ei: evidence ratio; k: number of estimated parameters (Burnham and Anderson 2002, Anderson 2008). Model k ΔAICc Ei Functional hearing group + Sound source + Functional hearing group * Sound source Functional hearing group + Sound source + RL + Functional hearing group * Sound source Functional hearing group + Sound source Functional hearing group + Sound source + RL Sound source Functional hearing group + Sound source + RL + Sound source * RL Analysis 2. Replacing the behavioural response severity score with Avoidance Analysis: Logistic regression. Response variable: Avoidance (1), no-avoidance (0). Avoidance ~ RL + Functional hearing group + Sound source + Functional hearing group * Sound source + Functional hearing group * RL + Sound source * RL 2.1 RL SPL measured as rms, peak, or peak-to-peak Number of data cases: 196 (73 avoidance and 123 no-avoidance) Key finding: Avoidance was not related with higher RL compared with situations where no-avoidance was reported (Figure S2). The most parsimonious model to describe avoidance responses included the interaction between sound source and functional hearing group, but did not include RL (Table S2). The inclusion of RL into the model did not improve the fit (difference in log likelihoods: 0.10). This indicates that the small Page 18
19 Probability Density Function Density function Probability Density Function Kernel density function S3: Analysis and data exploration - Behavioural Responses of Wild Marine Mammals to Noise difference in the value of the delta Akaike between the first- and second-best models (ΔAICc = 1.94) is due to the bias correction term not being sufficiently large, thus the variable RL conforms to the definition of pretending variable (Anderson 2008). The analysis of relative variable importance showed that the sound source (w+( sound source)=0.99) and functional hearing groups (w+( hearing group )=0.99) were important variables for describing the severity of behavioural response of wild cetaceans, while RL was irrelevant (w+( RL )=0.27). High Moderate Low Mid-frequency odontocetes/low-frequency sonar (N = 46) MF toothed cetaceans and LF baleen whales exposed to continuous, MFAS and seismic/explosion N = 196 a High Moderate Low Avoidance No-avoidance MF toothed cetaceans exposed to continuous N = 50 b Data used in analysis MF toothed cetaceans exposed to MFAS N = 80 c MF odontocetes/lf sonar N = 46 LF baleen whales exposed to seismic/explosion N = 42 d RL SPL RMS and peak measures Received Received Sound Level Sound Levels (db re 1 µ Pa) Received Sound Level Figure S2. Probability density function (via Kernel density estimation) of the behavioural responses, avoidance or no-avoidance, for cetaceans with low-frequency hearing (LF Page 19
20 baleen whales) and cetaceans with mid-frequency hearing (MF toothed cetaceans) in relation to RL SPL of continuous, MFAS, and seismic/explosion sound sources. Table S2. Model selection statistics ΔAICc: delta Akaike information criterion; Ei: evidence ratio; k: number of estimated parameters (Burnham and Anderson 2002, Anderson 2008). Model k ΔAICc Ei Functional hearing group + Sound source + Functional hearing group * Sound source Functional hearing group + Sound source + RL + Functional hearing group * Sound source Functional hearing group + Sound source RL SPL measured as rms Data cases: 172 (62 avoidance and 110 no-avoidance). Key finding: Avoidance was not consistently related with higher RL (Figure S3). The most parsimonious model to describe avoidance responses included the interaction between sound source and functional hearing group, but did not include RL (Table S3). The inclusion of RL into the model did not improve the fit (difference in log likelihoods: 0.01). This indicates that the small difference in the value of the delta Akaike between the first- and second-best models (ΔAICc = 2.14) is due to the bias correction term not being sufficiently large, thus the variable RL conforms to the definition of pretending variable (Anderson 2008). The analysis of relative variable importance showed that the Page 20
21 Density function Probability Density Function Probability Density Function Kernel density function S3: Analysis and data exploration - Behavioural Responses of Wild Marine Mammals to Noise sound source (w+( sound source )=0.99) and functional hearing groups (w+( hearing group )=0.97) were important variables for describing the severity of behavioural response of wild cetaceans, while RL was irrelevant (w+( RL )=0.25). High Moderate Low 0.06 a Mid-frequency odontocetes/low-frequency sonar (N = 46) 0.03 MF toothed cetaceans and LF baleen whales exposed to continuous, MFAS and seismic/explosion N = 172 High Moderate Low Avoidance No-avoidance MF toothed cetaceans exposed to continuous N = 48 b Data used in analysis MF toothed cetaceans exposed to MFAS N = 75 c MF odontocetes/lf sonar N = 46 LF baleen whales exposed to seismic/explosion N = 32 d RL SPL RMS Received Sound Levels (db re 1 µ Pa) Received Sound Level Received Sound Level Figure S3. Probability density function (via Kernel density estimation) of the behavioural responses, avoidance or no-avoidance, for cetaceans with low-frequency hearing (LF baleen whales) and cetaceans with mid-frequency hearing (MF toothed cetaceans) in relation to RL SPL (measured as rms) of continuous, MFAS, and seismic/explosion sound sources. Page 21
22 Table S3. Model selection statistics ΔAICc: delta Akaike information criterion; Ei: evidence ratio; k: number of estimated parameters (Burnham and Anderson 2002, Anderson 2008). Model k ΔAICc Ei Functional hearing group + Sound source + Functional hearing group * Sound source Functional hearing group + Sound source + Functional hearing group * Sound source + RL Sound source Section II. Pseudo-replication In the process of gathering data from the systematic literature review we made an effort to avoid counting replicates of the same individual/group (pseudo-replication) by considering the following strategies: 1) Instances in which two or more publications analyzed the same data set (as defined in the methods section) and the findings were reported in two or more different publications (e.g., Miller et al. 2000, Biassoni et al. 2000) these were all combined and recorded as one data case. 2) Instances in which it was possible to identify groups or individuals within a study (tag ID or group number was reported), each individual was reported as a different data case (e.g., Williams et al. 2014). 3) When two independent studies analyzed the same data set but disagreed on the final interpretation of the results (e.g., Di lorio and Clark 2010 but see Pinet et al. Page 22
23 2010), this was considered as one data case. For consistency, the highest behavioural response severity score was reported. The examples above comprised 131 data cases used in the analysis (highest behavioural response severity score was used, as reported in the manuscript). The remaining 65 data cases were reported by a study as different data points although those were replicates of the same individuals (Table S4, same individuals [same tag ID] were reported in multiple data cases with different RL values and behavioural response severity scores, as in Appendix A in Miller et al. 2012). Note that when removing the data cases that included replicates of the same individual (Figure S4) the patterns of this study remained the same: more severe behavioural response severity scores were not consistently related with higher RL, and vice versa. Table S4. Number of data cases included in the analysis that reported replicates of the same individual. One data case reported a very high behavioural response severity score; thus was not included in the analysis. Publications Species group Number of data cases of the same individual DeRuiter et al. 2013a Beaked whale 2 Miller et al 2011, 2012, 2014 Killer whale 20 Miller et al 2012, 2011, Antunes et al. 2014, Alves et al Miller et al 2012, 2011, Wensveen 2012, Sivle et al Black fish 18 Sperm whale 25 Total 65 Page 23
24 Density function Probability Density Function Probability Density Function Kernel density function S3: Analysis and data exploration - Behavioural Responses of Wild Marine Mammals to Noise 0.05 MF toothed cetaceans and LF baleen whales exposed to continuous, MFAS and seismic/explosion N = 131 a MF toothed cetaceans exposed to continuous N = 49 b High Moderate Low 0.05 MF toothed cetaceans exposed to MFAS N = 17 Mid-frequency odontocetes/low-frequency sonar (N = 46) Behavioural severity score High Moderate Low c LF baleen whales exposed to seismic/explosion N = 41 d Data used in analysis Received Sound Levels (db re 1 µ Pa) Received Sound Level Received Sound Level RL SPL RMS and peak measures Not including pseudo-replicates MF odontocetes/lf sonar N = 46 Figure S4. Probability density function (via Kernel density estimation) of the behavioural response severity score (low, moderate, high) of cetaceans in relation to RL SPL (rms and peak measures) of sound sources without including data cases provided in Table S4. Page 24
25 Section III. Real operating sound sources: real context of sound exposure As discussed in the manuscript, behavioural responses of marine mammals to noise during playback experiments differed from those responses observed when exposed to real operating sources (e.g., Richardson et al. 1986). Early behavioural response studies used in some cases very low powered transducers for the playback, and consequently, the acoustic information (relative movement, multipath structure and spectrum) from these playbacks did not replicate the same level of sound at considerably greater distance from a full scale sound source (Ellison et al. 2012). Some of those early studies were used to inform the generic RL thresholds for behavioural disturbance in current use in North America (e.g., Richardson et al. 1990) and were included in our analysis. Behavioural response studies conducted during real operations in terms of time and sound source exposure will provide the most realistic context of exposure. Nine data cases of scaled playbacks of recorded airgun and drilling/construction sounds were removed from the analysis (Richardson et al. 1985a,b, 1990a,b, 1991, 1995, Malme et al. 1983, 1984, 1985, 1986) which corresponded to studies 37 40, 60 62, and 65, in the list provided at the beginning of this supplementary material. Note that when removing data cases that included playbacks from airguns and construction sounds, the main patterns of this study remained the same: more severe behavioural Page 25
26 Probability Density Function Density function Kernel density function Probability Density Function Kernel density function S3: Analysis and data exploration - Behavioural Responses of Wild Marine Mammals to Noise response severity scores were not consistently related with higher RL, and vice versa (Figure S5). High Moderate Low 0.05 MF toothed cetaceans and LF baleen whales Mid-frequency exposed to continuous, odontocetes/low-frequency sonar (N = 46) Behavioural severity score MFAS and High seismic/explosion N = 168 Moderate Low a MF toothed cetaceans exposed to continuous N = 47 b Data used in analysis 0.0 MF odontocetes/lf sonar N = MF toothed cetaceans exposed to MFAS N = 76 c LF baleen whales exposed to seismic/explosion N = 30 d RL SPL RMS Received Sound Level Not including air gun or drilling/construction playbacks Received Sound Levels (db re 1 µ Pa) Received Sound Level Figure S5. Probability density function (via Kernel density estimation) of the behavioural response severity scores (low, moderate, high) of cetaceans with low-frequency hearing (LF baleen whales) and cetaceans with mid-frequency hearing (MF toothed cetaceans) in relation to RL SPL rms of continuous, MFAS, and seismic/explosion sound sources. N = 168 (only including RL SPL measured as rms). Page 26
27 Section IV. Other variables The following results show some patterns of the data that were not included in the logistic regressions due to small sample sizes. The first section (data exploration 1) highlights the importance of including acoustic behavioural changes in every study that evaluates responses of marine mammals to noise. The second section (data exploration 2) shows the patterns of the data cases that reported behaviour prior to sound exposure in relation to RL. Data exploration 1: Considering acoustic behavioural change, in addition to avoidance behavioural reaction, is vital Using the narrative of behavioural reactions of individuals or population to noise, a scoring of 1 was applied when the study reported a change in the vocalizations of marine mammals and a score of 0 when an acoustic change did not occur (Figure S6). When including all data cases (with and without RL reported) for studies that measured and reported acoustic behavioural change (see Table 8 in the manuscript), about 90% data cases documented a change in the acoustic behaviour (Figure S7). This supports one of the recommendations of the manuscript that acoustic behavioural change must be considered in studies that aim at evaluating behavioural responses of marine mammals to noise. For comparison, when including all data cases that belong to studies that measured physical behavioural change (avoidance), approximately half reported avoidance (46%) and the other half of data cases did not report avoidance (Figure S8). Page 27
28 Received Sound Levels (db re 1 µ Pa) S3: Analysis and data exploration - Behavioural Responses of Wild Marine Mammals to Noise No Yes Acoustic behavioural change Figure S6. Box plot showing data cases of studies that recorded potential acoustic behavioural responses of marine mammals to noise at different RL. The majority of data cases reported changes in the acoustic behaviour (N = 54) and only few data cases (N = 7) did not report acoustic behavioural responses. Page 28
29 All data cases Data cases that reported RL No change Acoustic change Species group Sound source Figure S7. Number of data cases per marine mammal species group and sound source that reported acoustic behavioural responses to noise. N = 89 data cases; 81 data cases reported acoustic behavioural change while 8 data cases reported no acoustic behavioural change (N = 61 data cases reported RL). Page 29
30 All data cases Data cases that reported RL No-avoidance Avoidance Sound source Figure S8. Number of data cases that reported avoidance behavioural responses of marine mammals to noise. N = 357 data cases; 166 data cases reported avoidance while 191 data cases reported not avoidance (N = 255 data cases reported RL). Page 30
31 Data exploration 2: Data cases that included information on the behaviour of marine mammals (foraging and traveling) prior to sound exposure The number of data cases that included behaviour prior to sound exposure in addition to RL, functional hearing group, and sound source, was very limited (Table S5) and thus this variable was not included in the logistic regressions presented in section I. Table S5. Number of data cases that included behaviour prior to sound exposure in addition to sound source, functional hearing group, RL SPL rms (N = 173). Sound source LF baleen whales MF toothed cetaceans Continuous Foraging 4 4 Traveling 3 39 (blank) 3 5 MFAS Foraging 3 22 Socializing 1 Traveling 37 (blank) 1 15 Seismic/Explosion Foraging 6 1 Resting 1 Traveling 6 (blank) 19 2 When exploring these data in relation to RL, there was no difference in the frequency of data cases for individuals/populations foraging and traveling prior to sound exposure (Figure S9a-c) with the exception of baleen whales exposed to seismic. In the latter, data cases that reported individuals/populations foraging prior to sound exposure were more related with higher RL compared with traveling (Fid S9d; note that sample sizes are very small). Page 31
32 Density function Probability Density Function Probability Density Function S3: Analysis and data exploration - Behavioural Responses of Wild Marine Mammals to Noise Behaviour prior to sound exposure Foraging Traveling a MF toothed cetaceans exposed to continuous N = 43 b MF toothed cetaceans and LF baleen whales exposed to continuous, sonar and seismic/explosion N = MF toothed cetaceans exposed to MF sonar N = 59 c LF baleen whales exposed to seismic/explosion N = 19 d RL SPL RMS and peak measures Received Sound Level Received Sound Levels (db re 1 µ Pa) Received Sound Level Figure S9. Probability density function of data cases that reported behaviour prior to sound exposure, foraging or traveling, in relation to RL SPL (rms and peak measures) of sound sources. Page 32
Cetaceans and Naval Sonar: Behavioral Response as a Function of Sonar Frequency
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Cetaceans and Naval Sonar: Behavioral Response as a Function of Sonar Frequency Patrick Miller Sea Mammal Research Unit
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Cetaceans and Naval Sonar: Behavioral Response as a Function of Sonar Frequency Patrick Miller Sea Mammal Research Unit
3S2 Behavioral Response Studies of Cetaceans to Naval Signals in Norwegian Waters
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. 3S2 Behavioral Response Studies of Cetaceans to Naval Signals in Norwegian Waters Peter L. Tyack Woods Hole Oceanographic
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. 3S2 Behavioral Response Studies of Cetaceans to Naval Signals in Norwegian Waters Peter L. Tyack Woods Hole Oceanographic
Cetaceans and Naval Sonar: Behavioral Response as a Function of Sonar Frequency
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Cetaceans and Naval Sonar: Behavioral Response as a Function of Sonar Frequency Patrick Miller Sea Mammal Research Unit,
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Cetaceans and Naval Sonar: Behavioral Response as a Function of Sonar Frequency Patrick Miller Sea Mammal Research Unit,
Behavioral and Physiological Response of Baleen Whales to Ships and Ship Noise
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Behavioral and Physiological Response of Baleen Whales to Ships and Ship Noise John Calambokidis Cascadia Research Collective
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Behavioral and Physiological Response of Baleen Whales to Ships and Ship Noise John Calambokidis Cascadia Research Collective
3S 2 : Behavioral Response Studies of Cetaceans to Navy Sonar Signals in Norwegian Waters
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. 3S 2 : Behavioral Response Studies of Cetaceans to Navy Sonar Signals in Norwegian Waters Patrick Miller Sea Mammal Research
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. 3S 2 : Behavioral Response Studies of Cetaceans to Navy Sonar Signals in Norwegian Waters Patrick Miller Sea Mammal Research
Ceteacean Social Behavioral Response to Sonar
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Ceteacean Social Behavioral Response to Sonar Fleur Visser Kelp Marine Research Loniusstraat 9, 1624 CJ Hoorn, the Netherlands
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Ceteacean Social Behavioral Response to Sonar Fleur Visser Kelp Marine Research Loniusstraat 9, 1624 CJ Hoorn, the Netherlands
Overview of the 3S-project in Norwegian waters
 Overview of the 3S-project in Norwegian waters Petter Kvadsheim Research manager - Marine Environment 3S chief scientist Sea Mammals and Sonar Safety project International research project with the aim
Overview of the 3S-project in Norwegian waters Petter Kvadsheim Research manager - Marine Environment 3S chief scientist Sea Mammals and Sonar Safety project International research project with the aim
Dose response severity functions for acoustic disturbance in cetaceans using recurrent event survival analysis
 Dose response severity functions for acoustic disturbance in cetaceans using recurrent event survival analysis C. M. HARRIS, 1, D. SADYKOVA, 1 S. L. DERUITER, 1 P. L. TYACK, 2 P. J. O. MILLER, 2 P. H.
Dose response severity functions for acoustic disturbance in cetaceans using recurrent event survival analysis C. M. HARRIS, 1, D. SADYKOVA, 1 S. L. DERUITER, 1 P. L. TYACK, 2 P. J. O. MILLER, 2 P. H.
A Brief Review of Known Effects of Noise on Marine Mammals
 International Journal of Comparative Psychology, 2007, 20, 159-168. Copyright 2007 by the International Society for Comparative Psychology A Brief Review of Known Effects of Noise on Marine Mammals Linda
International Journal of Comparative Psychology, 2007, 20, 159-168. Copyright 2007 by the International Society for Comparative Psychology A Brief Review of Known Effects of Noise on Marine Mammals Linda
California Cooperative Fisheries Investigation Marine Mammal Surveys for
 California Cooperative Fisheries Investigation Marine Mammal Surveys for 2016-2017 John A. Hildebrand, Amanda J. Debich, and Bruce Thayre Marine Physical Laboratory Scripps Institution of Oceanography
California Cooperative Fisheries Investigation Marine Mammal Surveys for 2016-2017 John A. Hildebrand, Amanda J. Debich, and Bruce Thayre Marine Physical Laboratory Scripps Institution of Oceanography
The reaction of Southern resident orca to sensitive frequencies produced by nearby vessels
 The reaction of Southern resident orca to sensitive frequencies produced by nearby vessels Literature Review Luritta E. Whiting Beam Reach Marine Science and Sustainability School Friday Harbor Labs, University
The reaction of Southern resident orca to sensitive frequencies produced by nearby vessels Literature Review Luritta E. Whiting Beam Reach Marine Science and Sustainability School Friday Harbor Labs, University
Marine Mammal Monitoring on Navy Ranges (M3R)- Southern California Offshore Anti-submarine Warfare Range (SOAR) FY12 Test Summary
 Marine Mammal Monitoring on Navy Ranges (M3R)- Southern California Offshore Anti-submarine Warfare Range (SOAR) FY12 Test Summary POC: David J. Moretti Naval Undersea Warfare Center Division Newport: Marine
Marine Mammal Monitoring on Navy Ranges (M3R)- Southern California Offshore Anti-submarine Warfare Range (SOAR) FY12 Test Summary POC: David J. Moretti Naval Undersea Warfare Center Division Newport: Marine
3S 2 : Behavioral Response Studies of Cetaceans to Navy Sonar Signals in Norwegian Waters
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. 3S 2 : Behavioral Response Studies of Cetaceans to Navy Sonar Signals in Norwegian Waters Patrick Miller Sea Mammal Research
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. 3S 2 : Behavioral Response Studies of Cetaceans to Navy Sonar Signals in Norwegian Waters Patrick Miller Sea Mammal Research
Seismic testing and the impacts of high intensity sound on whales. Lindy Weilgart Department of Biology Dalhousie University Halifax, Nova Scotia
 Seismic testing and the impacts of high intensity sound on whales Lindy Weilgart Department of Biology Dalhousie University Halifax, Nova Scotia Marine Seismic Surveys Main technique for finding and monitoring
Seismic testing and the impacts of high intensity sound on whales Lindy Weilgart Department of Biology Dalhousie University Halifax, Nova Scotia Marine Seismic Surveys Main technique for finding and monitoring
INTERPRETING RESEARCH RESULTS: GOVERNMENT REGULATION OF ANTHROPOGENIC NOISE SOURCES
 INTERPRETING RESEARCH RESULTS: GOVERNMENT REGULATION OF ANTHROPOGENIC NOISE SOURCES By Naomi A. Rose, Ph.D. Marine Mammal Scientist The Humane Society of the United States INTRODUCTION The Precautionary
INTERPRETING RESEARCH RESULTS: GOVERNMENT REGULATION OF ANTHROPOGENIC NOISE SOURCES By Naomi A. Rose, Ph.D. Marine Mammal Scientist The Humane Society of the United States INTRODUCTION The Precautionary
Behavioural response studies of marine mammals in relation to noise
 Behavioural response studies of marine mammals in relation to noise CREEM (MOCHA project): Catriona Harris, Len Thomas, Lindesay Scott Hayward, Louise Burt, Tiago Marques, Monique MacKenzie, Roland Langrock,
Behavioural response studies of marine mammals in relation to noise CREEM (MOCHA project): Catriona Harris, Len Thomas, Lindesay Scott Hayward, Louise Burt, Tiago Marques, Monique MacKenzie, Roland Langrock,
Cetaceans and Naval Sonar: Behavioral Response as a Function of Sonar Frequency
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Cetaceans and Naval Sonar: Behavioral Response as a Function of Sonar Frequency Patrick Miller Sea Mammal Research Unit,
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Cetaceans and Naval Sonar: Behavioral Response as a Function of Sonar Frequency Patrick Miller Sea Mammal Research Unit,
Short Note. An Acoustic Scene Perspective on Spatial, Temporal, and Spectral Aspects of Marine Mammal Behavioral Responses to Noise
 Aquatic Mammals 2018, 44(3), 239-243, DOI 10.1578/AM.44.3.2018.239 Short Note An Acoustic Scene Perspective on Spatial, Temporal, and Spectral Aspects of Marine Mammal Behavioral Responses to Noise William
Aquatic Mammals 2018, 44(3), 239-243, DOI 10.1578/AM.44.3.2018.239 Short Note An Acoustic Scene Perspective on Spatial, Temporal, and Spectral Aspects of Marine Mammal Behavioral Responses to Noise William
Protecting Cuvier s Beaked Whales from Underwater Noise. Lindy Weilgart, Ph.D. Dept. of Biology
 Protecting Cuvier s Beaked Whales from Underwater Noise Lindy Weilgart, Ph.D. Dept. of Biology Cetaceans (Whales, Dolphins) Highly Acoustic Very vocal, hearing is primary sense Speed of sound 5x that in
Protecting Cuvier s Beaked Whales from Underwater Noise Lindy Weilgart, Ph.D. Dept. of Biology Cetaceans (Whales, Dolphins) Highly Acoustic Very vocal, hearing is primary sense Speed of sound 5x that in
CALIFORNIA COOPERATIVE OCEANIC FISHERIES INVESTIGATION (CALCOFI) CRUISES:
 CALIFORNIA COOPERATIVE OCEANIC FISHERIES INVESTIGATION (CALCOFI) CRUISES: 2009-2010 Greg Campbell, Karlina Merkens and John Hildebrand Marine Physical Laboratory, Scripps Institution of Oceanography University
CALIFORNIA COOPERATIVE OCEANIC FISHERIES INVESTIGATION (CALCOFI) CRUISES: 2009-2010 Greg Campbell, Karlina Merkens and John Hildebrand Marine Physical Laboratory, Scripps Institution of Oceanography University
FY14 Summary. Contact: David J. Moretti Robin W. Baird Naval Undersea Warfare Center Cascadia Research Collective
 Marine Mammal Monitoring on Navy Ranges (M3R) An Opportunistic Study of the Effect of Sonar on Marine Mammals on the Pacific Missile Range Facility PMRF FY14 Summary Contact: David J. Moretti Robin W.
Marine Mammal Monitoring on Navy Ranges (M3R) An Opportunistic Study of the Effect of Sonar on Marine Mammals on the Pacific Missile Range Facility PMRF FY14 Summary Contact: David J. Moretti Robin W.
Fine-scale Focal Dtag Behavioral Study of Diel Trends in Activity Budgets and Sound Production of Endangered Baleen Whales in the Gulf of Maine
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Fine-scale Focal Dtag Behavioral Study of Diel Trends in Activity Budgets and Sound Production of Endangered Baleen Whales
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Fine-scale Focal Dtag Behavioral Study of Diel Trends in Activity Budgets and Sound Production of Endangered Baleen Whales
Baleen Whale Responses to a High-Frequency Active Pinger: Implications for Upper Frequency Hearing Limits
 TECHNICAL REPORT 3037 September 2016 Baleen Whale Responses to a High-Frequency Active Pinger: Implications for Upper Frequency Hearing Limits Elizabeth Henderson Approved for public release. SSC Pacific
TECHNICAL REPORT 3037 September 2016 Baleen Whale Responses to a High-Frequency Active Pinger: Implications for Upper Frequency Hearing Limits Elizabeth Henderson Approved for public release. SSC Pacific
Tagging and Playback Studies to Toothed Whales
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Tagging and Playback Studies to Toothed Whales Peter Tyack Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution MS#50 266 Woods Hole Road
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Tagging and Playback Studies to Toothed Whales Peter Tyack Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution MS#50 266 Woods Hole Road
Deafening Silence: The Impact of Naval Sonar Activity on Cetaceans
 Deafening Silence: The Impact of Naval Sonar Activity on Cetaceans Andrew Mooney Senior Sophister Zoology The ban on commercial whaling by most countries in the 1970 s paved the way for the co-existence
Deafening Silence: The Impact of Naval Sonar Activity on Cetaceans Andrew Mooney Senior Sophister Zoology The ban on commercial whaling by most countries in the 1970 s paved the way for the co-existence
High Frequency Acoustic Recording Package Annual Data Summary Report March 14, 2009 March 26, 2010 SOCAL Site N
 High Frequency Acoustic Recording Package Annual Data Summary Report March 14, 2009 March 26, 2010 SOCAL Site N John Hildebrand, Hannah Bassett, Simone Baumann, Greg Campbell, Amanda Cummins, Sara Kerosky,
High Frequency Acoustic Recording Package Annual Data Summary Report March 14, 2009 March 26, 2010 SOCAL Site N John Hildebrand, Hannah Bassett, Simone Baumann, Greg Campbell, Amanda Cummins, Sara Kerosky,
Assessing Beaked Whale Reproduction and Stress Response Relative to Sonar Activity at the Atlantic Undersea Test and Evaluation Center (AUTEC)
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Assessing Beaked Whale Reproduction and Stress Response Relative to Sonar Activity at the Atlantic Undersea Test and Evaluation
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Assessing Beaked Whale Reproduction and Stress Response Relative to Sonar Activity at the Atlantic Undersea Test and Evaluation
Cetaceans and Naval Sonar: Behavioral Response as a Function of Sonar Frequency
 Cetaceans and Naval Sonar: Behavioral Response as a Function of Sonar Frequency Patrick Miller Sea Mammal Research Unit, Gatty Marine Laboratory School of Biology, University of Saint Andrews St. Andrews
Cetaceans and Naval Sonar: Behavioral Response as a Function of Sonar Frequency Patrick Miller Sea Mammal Research Unit, Gatty Marine Laboratory School of Biology, University of Saint Andrews St. Andrews
Baseline Behavior of Pilot Whales and their Responses to Playback of Anthropogenic and Natural Sounds
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Baseline Behavior of Pilot Whales and their Responses to Playback of Anthropogenic and Natural Sounds Peter Tyack Senior
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Baseline Behavior of Pilot Whales and their Responses to Playback of Anthropogenic and Natural Sounds Peter Tyack Senior
The effects of seismic operations in UK waters: analysis of Marine Mammal Observer data
 J. CETACEAN RES. MANAGE. 16: 71 85, 2017 71 The effects of seismic operations in UK waters: analysis of Marine Mammal Observer data CAROLYN J. STONE, KAREN HALL, SÓNIA MENDES AND MARK L. TASKER Joint Nature
J. CETACEAN RES. MANAGE. 16: 71 85, 2017 71 The effects of seismic operations in UK waters: analysis of Marine Mammal Observer data CAROLYN J. STONE, KAREN HALL, SÓNIA MENDES AND MARK L. TASKER Joint Nature
Marine Mammals and Sound
 Marine Mammals and Sound Acoustics Why sound? Light attenuates rapidly Sound travels farther & faster (higher density of fluid) Over large spatial scales in water, visual communication is not practical
Marine Mammals and Sound Acoustics Why sound? Light attenuates rapidly Sound travels farther & faster (higher density of fluid) Over large spatial scales in water, visual communication is not practical
Population Consequences of Acoustic Disturbance of Blainville s Beaked Whales at AUTEC
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Population Consequences of Acoustic Disturbance of Blainville s Beaked Whales at AUTEC Diane Elaine Claridge & Charlotte
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Population Consequences of Acoustic Disturbance of Blainville s Beaked Whales at AUTEC Diane Elaine Claridge & Charlotte
Progress Report on the CODA Project
 15 th ASCOBANS Advisory Committee Meeting Document AC15/Doc.39 (S) UN Campus, Bonn, Germany, 31 March-3 April 2008 Dist. 27 March 2008 Agenda Item 14.4.2 Implementation of the ASCOBANS Triennial Work Plan
15 th ASCOBANS Advisory Committee Meeting Document AC15/Doc.39 (S) UN Campus, Bonn, Germany, 31 March-3 April 2008 Dist. 27 March 2008 Agenda Item 14.4.2 Implementation of the ASCOBANS Triennial Work Plan
Answer to DG Environment request on scientific information concerning impact of sonar activities on cetacean populations
 International Council for the Exploration of the Sea Conseil International pour l Exploration de la Mer JUNE 2001 FEBRUARY 2005 Answer to DG Environment request on scientific information concerning impact
International Council for the Exploration of the Sea Conseil International pour l Exploration de la Mer JUNE 2001 FEBRUARY 2005 Answer to DG Environment request on scientific information concerning impact
Quantifying Vocal Response
 Quantifying Vocal Response in experimental playbacks to Risso s dolphins Aimee Boucher Dr. Andrew Read, Advisor Dr. Doug Nowacek, Advisor May 2014 Master s project submitted in partial fulfillment of the
Quantifying Vocal Response in experimental playbacks to Risso s dolphins Aimee Boucher Dr. Andrew Read, Advisor Dr. Doug Nowacek, Advisor May 2014 Master s project submitted in partial fulfillment of the
Delphinid behavioral responses to incidental mid-frequency active sonar
 Delphinid behavioral responses to incidental mid-frequency active sonar E. Elizabeth Henderson a) Scripps Institution of Oceanography, University of California San Diego, 9500 Gilman Drive, La Jolla, California
Delphinid behavioral responses to incidental mid-frequency active sonar E. Elizabeth Henderson a) Scripps Institution of Oceanography, University of California San Diego, 9500 Gilman Drive, La Jolla, California
Sonar induced temporary hearing loss in dolphins
 Sonar induced temporary hearing loss in dolphins T. Aran Mooney 1*+, Paul E. Nachtigall 1 and Stephanie Vlachos 1 1 Department of Zoology and HIMB, University of Hawaii, Kaneohe, HI, 96734, USA *Author
Sonar induced temporary hearing loss in dolphins T. Aran Mooney 1*+, Paul E. Nachtigall 1 and Stephanie Vlachos 1 1 Department of Zoology and HIMB, University of Hawaii, Kaneohe, HI, 96734, USA *Author
Conserving cetaceans and manatees in the western African region
 CMS Technical Series No. 26 Conserving cetaceans and manatees in the western African region Bonn, 2012 (WATCH) Compilation of articles based on the Scientific Symposium of the Western African Talks on
CMS Technical Series No. 26 Conserving cetaceans and manatees in the western African region Bonn, 2012 (WATCH) Compilation of articles based on the Scientific Symposium of the Western African Talks on
Behavioural Response Study 2008
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Behavioural Response Study 2008 I. L. Boyd Sea Mammal Research Unit, Scottish Oceans Institute University of St. Andrews,
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Behavioural Response Study 2008 I. L. Boyd Sea Mammal Research Unit, Scottish Oceans Institute University of St. Andrews,
ACOUSTIC VOCALIZATIONS OF DOLPHINS AND EFFECTS OF ANTHROPOGENIC NOISE
 ACOUSTIC VOCALIZATIONS OF DOLPHINS AND EFFECTS OF ANTHROPOGENIC NOISE Undergraduate Research Scholars Thesis by JOCLYN DESTINY BOSQUEZ Submitted to Honors and Undergraduate Research Texas A&M University
ACOUSTIC VOCALIZATIONS OF DOLPHINS AND EFFECTS OF ANTHROPOGENIC NOISE Undergraduate Research Scholars Thesis by JOCLYN DESTINY BOSQUEZ Submitted to Honors and Undergraduate Research Texas A&M University
MSFD and MEDCIS contribution
 MSFD and MEDCIS contribution Continuous underwater noise in the Mediterranean Sea with emphasis on modelling of shipping noise Noise Workshop, 23 Feb 2018, Athens, Greece Aristides Prospathopoulos, HCMR
MSFD and MEDCIS contribution Continuous underwater noise in the Mediterranean Sea with emphasis on modelling of shipping noise Noise Workshop, 23 Feb 2018, Athens, Greece Aristides Prospathopoulos, HCMR
Beaked whales. 1) Zoophysiology, Dept. of Bioscience, Aarhus University, Denmark. 2) BIOECOMAC, La Laguna University, Tenerife, Spain
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Beaked whales Madsen P.T. 1*, Aguilar de Soto N. 2, Tyack P.L. 3, and Johnson M. 3 10 11 12 13 14 15 1) Zoophysiology, Dept. of Bioscience, Aarhus University, Denmark 2) BIOECOMAC, La
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Beaked whales Madsen P.T. 1*, Aguilar de Soto N. 2, Tyack P.L. 3, and Johnson M. 3 10 11 12 13 14 15 1) Zoophysiology, Dept. of Bioscience, Aarhus University, Denmark 2) BIOECOMAC, La
Underwater environmental impact assessments on marine mammals and fish by high power anthropogenic radiated sound
 Paper Number 27, Proceedings of ACOUSTICS 2011 2-4 November 2011, Gold Coast, Australia Underwater environmental impact assessments on marine mammals and fish by high power anthropogenic radiated sound
Paper Number 27, Proceedings of ACOUSTICS 2011 2-4 November 2011, Gold Coast, Australia Underwater environmental impact assessments on marine mammals and fish by high power anthropogenic radiated sound
Marine Protected Species Permi:ng: In-water construc8on and noise impact assessment
 July 20, 2016 Florida Permi,ng Summer School Marine Protected Species Permi:ng: In-water construc8on and noise impact assessment Florida Marine Mammals and Turtles Shelf 2 whale species (North Atlan8c
July 20, 2016 Florida Permi,ng Summer School Marine Protected Species Permi:ng: In-water construc8on and noise impact assessment Florida Marine Mammals and Turtles Shelf 2 whale species (North Atlan8c
POINTLESS PERIL. [Deadlines and Death Counts]
![POINTLESS PERIL. [Deadlines and Death Counts] POINTLESS PERIL. [Deadlines and Death Counts]](/thumbs/81/84504231.jpg) POINTLESS PERIL [Deadlines and Death Counts] Marine mammals, such as whales and dolphins, are some of the most beloved creatures in the ocean. Each year thousands of marine mammals are unnecessarily killed
POINTLESS PERIL [Deadlines and Death Counts] Marine mammals, such as whales and dolphins, are some of the most beloved creatures in the ocean. Each year thousands of marine mammals are unnecessarily killed
Male sperm whale behaviour during exposures to distant seismic survey pulses
 Aquatic Mammals 2002, 28.3, 231 240 Male sperm whale behaviour during exposures to distant seismic survey pulses P. T. Madsen, B. Møhl, B. K. Nielsen and M. Wahlberg Department of Zoophysiology, Institute
Aquatic Mammals 2002, 28.3, 231 240 Male sperm whale behaviour during exposures to distant seismic survey pulses P. T. Madsen, B. Møhl, B. K. Nielsen and M. Wahlberg Department of Zoophysiology, Institute
LMR Program Launches New Project Initiatives
 LMR Program Launches New Project Initiatives Efforts Continue to Expand the Navy s Knowledge of Marine Mammals THE LATEST ROUND of Living Marine Resources (LMR) program projects continue to support the
LMR Program Launches New Project Initiatives Efforts Continue to Expand the Navy s Knowledge of Marine Mammals THE LATEST ROUND of Living Marine Resources (LMR) program projects continue to support the
Fine-scale Focal DTAG Behavioral Study in the Gulf of Maine
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Fine-scale Focal DTAG Behavioral Study in the Gulf of Maine Alessandro Bocconcelli Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Fine-scale Focal DTAG Behavioral Study in the Gulf of Maine Alessandro Bocconcelli Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
Final Report. Passive Acoustic Monitoring of Cetaceans in the Hawaii Range Complex Using Ecological Acoustic Recorders (EARs) July 2015
 Final Report Prepared for: Commander, U.S. Pacific Fleet Submitted to: Naval Facilities Engineering Command, Pacific under Contract No. N62470-10-D-3011, Task Orders KB14 and KB22, issued to HDR, Inc.
Final Report Prepared for: Commander, U.S. Pacific Fleet Submitted to: Naval Facilities Engineering Command, Pacific under Contract No. N62470-10-D-3011, Task Orders KB14 and KB22, issued to HDR, Inc.
Final Report. Development of Statistical Methods for Examining Relationships Between Odontocete Vocal Behavior and Navy Sonar Signals
 Final Report Submitted to: Naval Facilities Engineering Command Atlantic under Contract No. N62470-10-D-3011, CTO 39, issued to HDR, Inc. Development of Statistical Methods for Examining Relationships
Final Report Submitted to: Naval Facilities Engineering Command Atlantic under Contract No. N62470-10-D-3011, CTO 39, issued to HDR, Inc. Development of Statistical Methods for Examining Relationships
Distribution and demographics of Cuvier s beaked whales in the Southern California Bight. Final Report Contract N C-0145 Option 6, CLIN 15 &16
 Distribution and demographics of Cuvier s beaked whales in the Southern California Bight Final Report Contract N66604-14-C-0145 Option 6, CLIN 15 &16 Final report of on-water surveys in conjunction with
Distribution and demographics of Cuvier s beaked whales in the Southern California Bight Final Report Contract N66604-14-C-0145 Option 6, CLIN 15 &16 Final report of on-water surveys in conjunction with
Marine Mammal Conservation Corridor for Northern South America (MaMa CoCo Sea) Follow-Up Workshop March Paramaribo, Suriname
 Marine Mammal Conservation Corridor for Northern South America (MaMa CoCo Sea) Follow-Up Workshop 18-20 March 2013 - Paramaribo, Suriname 1. New data on marine mammal populations in French Guiana and regional
Marine Mammal Conservation Corridor for Northern South America (MaMa CoCo Sea) Follow-Up Workshop 18-20 March 2013 - Paramaribo, Suriname 1. New data on marine mammal populations in French Guiana and regional
Estimating Sound Pressure Levels that correspond to maximum legal disturbance of seals and turtles
 Estimating Sound Pressure Levels that correspond to maximum legal disturbance of seals and turtles Marshall V. Hall Moya Crescent, Kingsgrove, NSW 2208, Australia ABSTRACT Loud underwater sounds can disturb
Estimating Sound Pressure Levels that correspond to maximum legal disturbance of seals and turtles Marshall V. Hall Moya Crescent, Kingsgrove, NSW 2208, Australia ABSTRACT Loud underwater sounds can disturb
Does ramp-up reduce risks to marine mammals? Assessing the effectiveness of a mitigation method Paul Wensveen & Sander von Benda-Beckmann
 Does ramp-up reduce risks to marine mammals? Assessing the effectiveness of a mitigation method Paul Wensveen & Sander von Benda-Beckmann Sea Mammals and Sonar Symposium 27 October 2015, St Andrews, Scotland,
Does ramp-up reduce risks to marine mammals? Assessing the effectiveness of a mitigation method Paul Wensveen & Sander von Benda-Beckmann Sea Mammals and Sonar Symposium 27 October 2015, St Andrews, Scotland,
A Review of the Effects of Seismic Surveys on Marine Mammals
 PAPER A Review of the Effects of Seismic Surveys on Marine Mammals AUTHORS Jonathan Gordon Sea Mammal Research Unit, Gatty Marine Laboratory, University of St Andrews Douglas Gillespie Song of the Whale
PAPER A Review of the Effects of Seismic Surveys on Marine Mammals AUTHORS Jonathan Gordon Sea Mammal Research Unit, Gatty Marine Laboratory, University of St Andrews Douglas Gillespie Song of the Whale
Gulf of Mexico Acoustic Exposure Model Variable Analysis
 Gulf of Mexico Acoustic Exposure Model Variable Analysis Submitted to: Robert Gisiner Director, Marine Environmental Science/Biology International Association of Geophysical Contractors and Andy Radford
Gulf of Mexico Acoustic Exposure Model Variable Analysis Submitted to: Robert Gisiner Director, Marine Environmental Science/Biology International Association of Geophysical Contractors and Andy Radford
Population parameters of Blainville s and Cuvier s beaked whales
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Population parameters of Blainville s and Cuvier s beaked whales Natacha Aguilar de Soto University of La Laguna (ULL)
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Population parameters of Blainville s and Cuvier s beaked whales Natacha Aguilar de Soto University of La Laguna (ULL)
Results of Nature Foundation Marine Mammal Monitoring Project Jan-May 2011
 NATURE FOUNDATION Results of Nature Foundation Marine Mammal Monitoring Project Jan-May 2011 Mailing address P. O. Box 863 Philipsburg St. Maarten Netherlands Antilles Physical address Wellsberg Street
NATURE FOUNDATION Results of Nature Foundation Marine Mammal Monitoring Project Jan-May 2011 Mailing address P. O. Box 863 Philipsburg St. Maarten Netherlands Antilles Physical address Wellsberg Street
Term Paper. Midterm Exam
 Term Paper Outline due on Thursday (paper copy) See website for details and example 1 outline paragraph, title, 2 references Goals Read and cite scientific papers Learn about a specific topic of marine
Term Paper Outline due on Thursday (paper copy) See website for details and example 1 outline paragraph, title, 2 references Goals Read and cite scientific papers Learn about a specific topic of marine
Cetacean Distribution & Relative Abundance Survey
 R.V. Celtic Explorer Rockall Trough Oceanographic Survey Cetacean Distribution & Relative Abundance Survey 24 January 2 February 2007 Surveyor: Dave Wall Ship Surveys Unit Irish Whale and Dolphin Group
R.V. Celtic Explorer Rockall Trough Oceanographic Survey Cetacean Distribution & Relative Abundance Survey 24 January 2 February 2007 Surveyor: Dave Wall Ship Surveys Unit Irish Whale and Dolphin Group
Criteria and Thresholds for U.S. Navy Acoustic and Explosive Effects Analysis
 April 2012 Criteria and Thresholds for U.S. Navy Acoustic and Explosive Effects Analysis J. J. Finneran and A. K. Jenkins SSC Pacific Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. SSC Pacific
April 2012 Criteria and Thresholds for U.S. Navy Acoustic and Explosive Effects Analysis J. J. Finneran and A. K. Jenkins SSC Pacific Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. SSC Pacific
Technical Support Information to the CMS Family Guidelines on Environmental Impact Assessments for Marine Noise-generating Activities
 Technical Support Information to the CMS Family Guidelines on Environmental Impact Assessments for Marine Noise-generating Activities Module B.6. Polar Bears The full CMS Family Guidelines on Environmental
Technical Support Information to the CMS Family Guidelines on Environmental Impact Assessments for Marine Noise-generating Activities Module B.6. Polar Bears The full CMS Family Guidelines on Environmental
Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals Secretariat provided by the United Nations Environment Programme
 Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals Secretariat provided by the United Nations Environment Programme 14 th MEETING OF THE CMS SCIENTIFIC COUNCIL Bonn, Germany, 14-17 March
Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals Secretariat provided by the United Nations Environment Programme 14 th MEETING OF THE CMS SCIENTIFIC COUNCIL Bonn, Germany, 14-17 March
APPENDIX INTERIM PROGRESS REPORT: ANALYSIS OF LONG-TERM ACOUSTIC DATASETS FROM MIRC
 APPENDIX INTERIM PROGRESS REPORT: ANALYSIS OF LONG-TERM ACOUSTIC DATASETS FROM MIRC This Page Intentionally Left Blank REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden
APPENDIX INTERIM PROGRESS REPORT: ANALYSIS OF LONG-TERM ACOUSTIC DATASETS FROM MIRC This Page Intentionally Left Blank REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE Form Approved OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden
MARINE MAMMAL MONITORING ON CALIFORNIA COOPERATIVE OCEANIC FISHERIES INVESTIGATION (CALCOFI) CRUISES:
 MARINE MAMMAL MONITORING ON CALIFORNIA COOPERATIVE OCEANIC FISHERIES INVESTIGATION (CALCOFI) CRUISES: 2012-2013 Greg Campbell, Lauren Roche, Katherine Whitaker, Elizabeth Vu and John Hildebrand Marine
MARINE MAMMAL MONITORING ON CALIFORNIA COOPERATIVE OCEANIC FISHERIES INVESTIGATION (CALCOFI) CRUISES: 2012-2013 Greg Campbell, Lauren Roche, Katherine Whitaker, Elizabeth Vu and John Hildebrand Marine
Zones of impact around icebreakers affecting beluga whales in the Beaufort Sea
 Zones of impact around icebreakers affecting beluga whales in the Beaufort Sea Christine Erbe a) and David M. Farmer Institute of Ocean Sciences, 9860 West Saanich Road, Sidney, British Columbia V8L 4B2,
Zones of impact around icebreakers affecting beluga whales in the Beaufort Sea Christine Erbe a) and David M. Farmer Institute of Ocean Sciences, 9860 West Saanich Road, Sidney, British Columbia V8L 4B2,
GRAY WHALE. Text source: The Marine Mammal Center
 GRAY WHALE Gray whales are found only in the Pacific Ocean, and they have one of the longest migrations of any mammal. During the summer, they live in the Arctic. In the fall, they travel to Baja California,
GRAY WHALE Gray whales are found only in the Pacific Ocean, and they have one of the longest migrations of any mammal. During the summer, they live in the Arctic. In the fall, they travel to Baja California,
DolphinWatch: Dolphins in the Chesapeake Bay. Amber Fandel Faculty Research Assistant
 DolphinWatch: Dolphins in the Chesapeake Bay Amber Fandel Faculty Research Assistant 1 Lots of dolphins! Philip Yunger Kevin McDonald Carolyn Wilson Chris Moe Chris Bache Dennis DePriest Tania Richardson
DolphinWatch: Dolphins in the Chesapeake Bay Amber Fandel Faculty Research Assistant 1 Lots of dolphins! Philip Yunger Kevin McDonald Carolyn Wilson Chris Moe Chris Bache Dennis DePriest Tania Richardson
Movements and Habitat Use of Dwarf and Pygmy Sperm Whales using Remotely-deployed LIMPET Satellite Tags
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Movements and Habitat Use of Dwarf and Pygmy Sperm Whales using Remotely-deployed LIMPET Satellite Tags Robin W. Baird
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Movements and Habitat Use of Dwarf and Pygmy Sperm Whales using Remotely-deployed LIMPET Satellite Tags Robin W. Baird
Marine mammal demographics off the outer Washington coast and near Hawaii. Monterey, California. Naval Postgraduate School; Department of Oceanography
 Author(s) Oleson, Erin; Hildebrand, John Title Marine mammal demographics off the outer Washington coast and near Hawaii Publisher Monterey, California. Naval Postgraduate School; Department of Oceanography
Author(s) Oleson, Erin; Hildebrand, John Title Marine mammal demographics off the outer Washington coast and near Hawaii Publisher Monterey, California. Naval Postgraduate School; Department of Oceanography
Effects of Disturbance on Populations of Marine Mammals
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Effects of Disturbance on Populations of Marine Mammals Erica Fleishman, Ph.D., Principal Investigator John Muir Institute
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Effects of Disturbance on Populations of Marine Mammals Erica Fleishman, Ph.D., Principal Investigator John Muir Institute
May 16, Dear Ms. Harrison:
 Clean Ocean Action The Ocean Foundation Center for Biological Diversity Hands Across the Sand Save Barnegat Bay Clean Water Action CWA Local 1075 Paddleout.org May 16, 2014 Via electronic mail sent to
Clean Ocean Action The Ocean Foundation Center for Biological Diversity Hands Across the Sand Save Barnegat Bay Clean Water Action CWA Local 1075 Paddleout.org May 16, 2014 Via electronic mail sent to
Ecological Constraints on Sound Production in Marine Animals: the Importance of Listening
 Ecological Constraints on Sound Production in Marine Animals: the Importance of Listening Lance Barrett-Lennard Vancouver Aquarium University of British Columbia Overview. passive vs active use of sound
Ecological Constraints on Sound Production in Marine Animals: the Importance of Listening Lance Barrett-Lennard Vancouver Aquarium University of British Columbia Overview. passive vs active use of sound
Auditory Weighting Functions and Frequency-Dependent Effects of Sound in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops Truncatus)
 Auditory Weighting Functions and Frequency-Dependent Effects of Sound in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops Truncatus) James J. Finneran Space and Naval Warfare Systems Center Pacific, Biosciences Division,
Auditory Weighting Functions and Frequency-Dependent Effects of Sound in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops Truncatus) James J. Finneran Space and Naval Warfare Systems Center Pacific, Biosciences Division,
Distribution Ecology attempts to explain the restricted and generally patchy distribution of species
 Marine Mammal Ecology Ecology : An attempt to describe and explain the patterns of distribution and abundance of organisms. These patterns reflect the history of complex interactions with other organisms
Marine Mammal Ecology Ecology : An attempt to describe and explain the patterns of distribution and abundance of organisms. These patterns reflect the history of complex interactions with other organisms
Provide a Vessel to Conduct Observations and Deploy Sound Source for a Behavioral Response Study of Cetaceans off Southern California in 2011
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Provide a Vessel to Conduct Observations and Deploy Sound Source for a Behavioral Response Study of Cetaceans off Southern
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Provide a Vessel to Conduct Observations and Deploy Sound Source for a Behavioral Response Study of Cetaceans off Southern
Research Article High-Speed Vessel Noises in West Hong Kong Waters and Their Contributions Relative to Indo-Pacific Humpback Dolphins (Sousachinensis)
 Journal of Marine Biology Volume 2012, Article ID 169103, 11 pages doi:10.1155/2012/169103 Research Article High-Speed Vessel Noises in West Hong Kong Waters and Their Contributions Relative to Indo-Pacific
Journal of Marine Biology Volume 2012, Article ID 169103, 11 pages doi:10.1155/2012/169103 Research Article High-Speed Vessel Noises in West Hong Kong Waters and Their Contributions Relative to Indo-Pacific
Psychophysical Studies of Auditory Masking in Marine Mammals: Key Concepts and New Directions
 Psychophysical Studies of Auditory Masking in Marine Mammals: Key Concepts and New Directions Colleen Reichmuth 1 Introduction In recent years, growing awareness of the potentially harmful effects of human-generated
Psychophysical Studies of Auditory Masking in Marine Mammals: Key Concepts and New Directions Colleen Reichmuth 1 Introduction In recent years, growing awareness of the potentially harmful effects of human-generated
NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL
 NPS-OC-09-00 NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL MONTEREY, CALIFORNIA Acoustic and visual monitoring for cetaceans along the outer Washington coast by Erin M. Oleson, John Calambokidis, Erin Falcone, Greg Schorr,
NPS-OC-09-00 NAVAL POSTGRADUATE SCHOOL MONTEREY, CALIFORNIA Acoustic and visual monitoring for cetaceans along the outer Washington coast by Erin M. Oleson, John Calambokidis, Erin Falcone, Greg Schorr,
Sightings! Secac Secac. Secac horas miles. sightings. Sailing ( km) hours Watching
 Sightings! There s evidence of 30 species of cetaceans belonging to 7 families in the Canary Archipel, which is a 34.5 % of the 87 species described in the whole planet; this makes The Canary Islands one
Sightings! There s evidence of 30 species of cetaceans belonging to 7 families in the Canary Archipel, which is a 34.5 % of the 87 species described in the whole planet; this makes The Canary Islands one
Assessing Stress Responses in Beaked and Sperm Whales in the Bahamas
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Assessing Stress Responses in Beaked and Sperm Whales in the Bahamas Rosalind M. Rolland, D.V.M., Kathleen E. Hunt, Ph.D.,
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Assessing Stress Responses in Beaked and Sperm Whales in the Bahamas Rosalind M. Rolland, D.V.M., Kathleen E. Hunt, Ph.D.,
I nterspecific interactions across multiple scales (species, population, individual) remain a central question in
 SUBJECT AREAS: BEHAVIOURAL ECOLOGY ZOOLOGY ANIMAL BEHAVIOUR ECOLOGY Received 14 December 2012 Accepted 28 February 2013 Published 2 April 2013 Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed
SUBJECT AREAS: BEHAVIOURAL ECOLOGY ZOOLOGY ANIMAL BEHAVIOUR ECOLOGY Received 14 December 2012 Accepted 28 February 2013 Published 2 April 2013 Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed
Coastal Commission Comments on the Effects of Anthropogenic Sound on Marine Mammals. Statement for
 Statement [ ] submitted by Sara Wan, California Coastal Commision Coastal Commission Comments on the Effects of Anthropogenic Sound on Marine Mammals Statement for The Report of the Advisory Committee
Statement [ ] submitted by Sara Wan, California Coastal Commision Coastal Commission Comments on the Effects of Anthropogenic Sound on Marine Mammals Statement for The Report of the Advisory Committee
RESEARCH ACTIVITIES OF CETACEAN IN INDONESIA. Dharmadi Research Centre for Fisheries Management and Conservation
 RESEARCH ACTIVITIES OF CETACEAN IN INDONESIA Dharmadi Research Centre for Fisheries Management and Conservation CETACEAN MANAGEMENT WORKS BY SOME INDONESIAN INSTITUTIONS. WWF (World Wide Foundation) 2.
RESEARCH ACTIVITIES OF CETACEAN IN INDONESIA Dharmadi Research Centre for Fisheries Management and Conservation CETACEAN MANAGEMENT WORKS BY SOME INDONESIAN INSTITUTIONS. WWF (World Wide Foundation) 2.
Auditory studies on harbour porpoises in relation to offshore wind turbines
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Auditory studies on harbour porpoises in relation to offshore wind turbines This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Auditory studies on harbour porpoises in relation to offshore wind turbines This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository
Sperm whales reduce foraging effort during exposure to 1 2 khz sonar and killer whale sounds
 Ecological Applications, 26(1), 2016, pp. 77 93 2016 by the Ecological Society of America Sperm whales reduce foraging effort during exposure to 1 2 khz sonar and killer whale sounds S AANA I SOJUNNO 1,5
Ecological Applications, 26(1), 2016, pp. 77 93 2016 by the Ecological Society of America Sperm whales reduce foraging effort during exposure to 1 2 khz sonar and killer whale sounds S AANA I SOJUNNO 1,5
Effects of Disturbance on Populations of Marine Mammals
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Effects of Disturbance on Populations of Marine Mammals Erica Fleishman John Muir Institute of the Environment The Barn
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Effects of Disturbance on Populations of Marine Mammals Erica Fleishman John Muir Institute of the Environment The Barn
Auditory Weighting Functions and Frequency-Dependent Effects of Sound in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus)
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Auditory Weighting Functions and Frequency-Dependent Effects of Sound in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) James
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Auditory Weighting Functions and Frequency-Dependent Effects of Sound in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) James
Effect of seismic operations on cetaceans sightings off-shore Akwa Ibom State, south-south, Nigeria
 Available online at http://ajol.info/index.php/ijbcs Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 8(4): 1570-1580, August 2014 ISSN 1997-342X (Online), ISSN 1991-8631 (Print) Original Paper http://indexmedicus.afro.who.int
Available online at http://ajol.info/index.php/ijbcs Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 8(4): 1570-1580, August 2014 ISSN 1997-342X (Online), ISSN 1991-8631 (Print) Original Paper http://indexmedicus.afro.who.int
Playbacks of predator signals and what might they tell us about responses to sonar
 Playbacks of predator signals and what might they tell us about responses to sonar Doug Nowacek Duke University Nicholas School of the Environment & Pratt School of Engineering SMM BRS Workshop, 12 December
Playbacks of predator signals and what might they tell us about responses to sonar Doug Nowacek Duke University Nicholas School of the Environment & Pratt School of Engineering SMM BRS Workshop, 12 December
Underwater hearing in California sea lions (Zalophus californianus): Expansion and interpretation of existing data
 MARINE MAMMAL SCIENCE, **(*): *** *** (*** 2011) C 2011 by the Society for Marine Mammalogy DOI: 10.1111/j.1748-7692.2011.00473.x Underwater hearing in California sea lions (Zalophus californianus): Expansion
MARINE MAMMAL SCIENCE, **(*): *** *** (*** 2011) C 2011 by the Society for Marine Mammalogy DOI: 10.1111/j.1748-7692.2011.00473.x Underwater hearing in California sea lions (Zalophus californianus): Expansion
Small-Vessel Surveys for Protected Marine Species in Navy OPAREAs off the. U.S. Atlantic Coast: 2017 Annual Progress Report
 Small-Vessel Surveys for Protected Marine Species in Navy OPAREAs off the Submitted to: Naval Facilities Engineering Command Atlantic under Contract No. N62470-10-D-8006, Task Order 34 issued to HDR, Inc.
Small-Vessel Surveys for Protected Marine Species in Navy OPAREAs off the Submitted to: Naval Facilities Engineering Command Atlantic under Contract No. N62470-10-D-8006, Task Order 34 issued to HDR, Inc.
Moving in concert: Social and migratory behaviour of dolphins and whales in the North Atlantic Ocean Visser, F.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Moving in concert: Social and migratory behaviour of dolphins and whales in the North Atlantic Ocean Visser, F. Link to publication Citation for published version
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Moving in concert: Social and migratory behaviour of dolphins and whales in the North Atlantic Ocean Visser, F. Link to publication Citation for published version
Naval sonar disrupts foraging in humpback whales
 1 2 3 Naval sonar disrupts foraging in humpback whales 4 5 6 7 Sivle, Lise Doksæter 1* ; Wensveen, Paul J. 2 ; Kvadsheim, Petter H. 3 ; Lam, Frans-Peter A. 4 ; Visser, Fleur 5,6 ; Curé, Charlotte 7 ; Harris,
1 2 3 Naval sonar disrupts foraging in humpback whales 4 5 6 7 Sivle, Lise Doksæter 1* ; Wensveen, Paul J. 2 ; Kvadsheim, Petter H. 3 ; Lam, Frans-Peter A. 4 ; Visser, Fleur 5,6 ; Curé, Charlotte 7 ; Harris,
Let us know how access to this document benefits you. Follow this and additional works at:
 Portland State University PDXScholar University Honors Theses University Honors College 5-25-2018 Anthropogenic Noise and Cetacean Interactions in the 21st Century: A Contemporary Review of the Impacts
Portland State University PDXScholar University Honors Theses University Honors College 5-25-2018 Anthropogenic Noise and Cetacean Interactions in the 21st Century: A Contemporary Review of the Impacts
Population parameters of Blainville s and Cuvier s beaked whales
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Population parameters of Blainville s and Cuvier s beaked whales Natacha Aguilar de Soto University of La Laguna (ULL)
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Population parameters of Blainville s and Cuvier s beaked whales Natacha Aguilar de Soto University of La Laguna (ULL)
ONR Marine Mammal & Biology Program Review
 ONR Marine Mammal & Biology Program Review 20-24 March 2017 Abstract Book AGENDA Day 1: Monday 20 March 2017 Program Time Thrust Last Name Performer Award Number Project Title 830 Weise ONR ONR MMB Program
ONR Marine Mammal & Biology Program Review 20-24 March 2017 Abstract Book AGENDA Day 1: Monday 20 March 2017 Program Time Thrust Last Name Performer Award Number Project Title 830 Weise ONR ONR MMB Program
Archimer
 Please note that this is an author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication following peer review. The definitive publisher-authenticated version is available on the publisher Web site Marine
Please note that this is an author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication following peer review. The definitive publisher-authenticated version is available on the publisher Web site Marine
M-weighting. high-frequency cetaceans, M. hf mid-frequency cetaceans, M mf. low-frequency cetaceans, M lf. Frequency (Hz) M-weighting
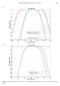 Marine Mammal Noise Exposure Criteria 435 (A) M-weighting Weighting (db) high-frequency cetaceans, M hf mid-frequency cetaceans, M mf low-frequency cetaceans, M lf Frequency (Hz) (B) M-weighting Weighting
Marine Mammal Noise Exposure Criteria 435 (A) M-weighting Weighting (db) high-frequency cetaceans, M hf mid-frequency cetaceans, M mf low-frequency cetaceans, M lf Frequency (Hz) (B) M-weighting Weighting
Outline. North Pacific Cetaceans - Biogeographic Distributions - Migrations and Breeding Cycle
 Hawaiian Cetaceans Outline North Pacific Cetaceans - Biogeographic Distributions - Migrations and Breeding Cycle Hawaiian Cetaceans - Seasonal Visitors: Humpback Whale - Year-around Residents: Melon-headed
Hawaiian Cetaceans Outline North Pacific Cetaceans - Biogeographic Distributions - Migrations and Breeding Cycle Hawaiian Cetaceans - Seasonal Visitors: Humpback Whale - Year-around Residents: Melon-headed
