Administrative Representative: Susan Livvix Medical Director if applicable: na
|
|
|
- Jewel Lawrence
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Policy Title: Rapid Response Team/ Code Blue Department/Scope: All Departments Page 1 of 9 Replaces Policy Dates: See all electronic dates Original Issue Date:11/19/2007 Reviewed/Revised ALL Dates: See all electronic Attachments: Y* dates captured Administrative Representative: Susan Livvix Medical Director if applicable: na RN,MSN, CNO Approved by: Susan Livvix RN, MSN, CNO Date:8/14/2014 Secondary Approver if applicable: na Date: na PURPOSE: To outline Rapid Response Team s (RRT) duties, and to define the role of each team member. To list criteria to be utilized by the RRT team and other members as defined by the Code Blue or Rapid Response Team (RRT) called To improve patient outcomes by early identification of progressively deteriorating and/or clinically unstable by providing a dedicated multidisciplinary team that rapidly assesses and intervenes for each patient. POLICY: The Rapid Response Team (RRT) of critically trained staff will assist with and evaluate any patient in the hospital who has clinically compromised values. The RRT may be summoned at any time by anyone in the hospital if there is a question or concern regarding the patient s condition. This team development is based on the Institute of Healthcare Improvement (IHI) campaign and NPSG s of TJC to save lives. The purpose of the team is to improve the clinical outcome of the patient who is clinically compromised or in a potentially critical situation, to use a proactive nursing assessment approach to clinical data, to communicate this data to the physician, and together determine the best ongoing treatment for the patient. There is a designed RRT for every shift that will respond to any Code Blue or RRT (patient in critical condition) The staff may announce overhead on the PA by dialing 88, or pressing code blue button in any area that has one, family may activate the RRT by dialing RRT (778) For Code Blue events the hospital staff will begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation until the RRT arrives to manage the patient with Advanced Cardiopulmonary Life Support (ACLS/PALS) protocol or Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS). If the physician has written an order for Do Not Resuscitate, then a Code Blue will not be initiated but if needed staff may deploy the RRT for the patient, the patient/ family may also deploy the RRT by dialing the RRT= 778 For RRT the Situation, Background, Assessment and Recommendation (SBAR) either for Pediatric or Adult patients tool will be utilized (Addendum attached). The staff may be trained in initial orientation on the use of SBAR and in an ongoing basis as per manager s discretion. For Code Blue please utilize the code recording sheet (Addendum) as attached. Upon admission the patient or caregiver should be told by the staff, If your medical condition changes you will need to use the call light, and call for your nurse immediately. If the response is not timely, you can dial 778 (RRT) and tell the hospital staff you need help. This information will also be communicated in patient areas in the hospital, in the welcome packet and upon admission to the hospital (Addendum attached). *The RRT team may consist of: (those highlighted must attend) 1. Respiratory Care Practitioner (RCP) *if available 2. Hospital Supervisor *if available 3. Hospitalist/ ER physician from the ER (MD) 4. Lab technician *if available
2 5. Pharmacy department *if available 6. Anesthesia CRNA *if available 7. Department manager or designee *if available 8. Emergency Room experienced Registered Nurse (RN) 9. Direct Care Nurse caring for patient at the time of the incident if inpatient 10. This team will evaluate all patients under the RRT/ Code Blue/Pink situation. 11. The team may contact the patient s physician 12. The team may assist staff with the care of the patient until the critical situation and/or patient is stabilized. 13. * RCP, Pharmacy department, departmental managers and designees, anesthesia, and house supervisor are not scheduled 24/7 at PCH, if they are present when a code is called they may be required or asked to assist. PROCEDURE: I. Rapid Response Team members and duties: 1. Duties to be performed a. Crash Cart- ER RN, ED Manager(designee) a. Pediatric code/rrt bring the Broselow bag b. Will bring a crash cart to the Code/RRT if called in an area that does not provide a crash cart (see list of where carts are located to bring) b. Team Lead duty- Hospitalist/ ER physician, House Supervisor, ED manager (designee) c. Monitor duty- ED manager (designee), ED RN, House Supervisor, any manager d. Medication duty- ED RN, Primary Nurse, unit manager, e. Airway management- Hospitalist/ ER physician f. Documenter/Recorder of event: ED RN, Primary RN, House Supervisor, any manager, see attachments RRT pediatric sheet (addendum E) RRT adult sheet (addendum F) g. BLS/ACLS/PALS/PALS initiation- team lead, ED RN, ED Manager (designee) 2. Team Members role as defined by but not limited to: a. The unit manager may respond to assist and may assist with debriefing of the RRT and ensure all proper paperwork and documentation is completed. b. A Respiratory Care Practitioner who will respond to every Condition code when available (as they are not scheduled 24/7) will assist with providing respiratory interventions and securing patient s airway as defined by their job description. c. The Hospital Supervisor, who will respond to every Condition code when available (as they are not scheduled 24/7), will guide the team to work swiftly, will ensure documentation of the RRT code sheet is completed and may perform an RRT debriefing post RRT. d. The Hospital Supervisor will collaborate with the ER Nurse RN and team for data collection and may assist in the assessment and implementation of any interventions necessary as ordered by the physician. e. An ER experienced RN who will respond to every Condition code, will assess the patient and help with the implementation of the interventions as ordered by Hospitalist/ ER physician, may assist in calling the physician and receiving any orders, and may assist with transfer of the patient, if necessary, to a more acute hospital setting based on condition of patient and physician orders. 1. ER RN may act as the team lead role in the absence of the Hospitalist/ ER physician 2. In the event of a Pediatric RRT, the ER RN/ Manager / or House supervisor staff who is PALS certified may respond 3. The ER RN will bring the pediatric Broselow bag 4. May need to enact in the duty of administering medications as needed or required during code/rrt call.
3 f. The Emergency Department/ Hospitalist/ ER physician (ED) will respond to any Code Blue or RRT 1. If unable to respond due to an emergency situation in The ED, an ED nurse will notify the unit. 2. The role of the physician is airway management, if needed by the condition of the patient/individual. 3. The physician will direct the team in the care of the patient, based upon the SBAR. g. Anesthesia (CRNA) may need to respond while in-house (on duty) to RRT and Code Blue h. The RRT will work in collaboration with the Primary RN and staff to ensure that the patient is taken care of holistically. 1. Ensure documentation is adequate via paper, electronic i. Role of the Primary Nursing Staff in RRT: 1. Use of the SBAR Tool (See Addendums attached) 2. Utilize the criteria established to call the RRT 3. Primary Nurse will be available during RRT Code 4. Work collaboratively with RRT and give a detailed quick report of patient 5. Provide patient information and have patient chart and history available 6. Use of Medication Administration Record 7. Assessment of the RRT in the medical record 8. Notify the family and physician 9. The Primary nurse may need to remain close to help facilitate notification of physician and act as liaison with family. Initiation of RRT adult or child in response to an actual cardiac or respiratory arrest A. Identify that the person is breathless and/or pulseless. B. Summon help from the nearest source. One or more persons will immediately begin Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) until the RRT arrives. C. One person should go to the nearest telephone and dial RRT 778 to access the hospital staff person or the person should push the code button located in areas where there is a code blue button. D. After calling 778, inform the PCH/FMC staff person there is a RRT and give the exact location of the patient E. The PCH/FMC staff may announce Code Blue via overhead page by dialing 88. F. The RRT may become the Code team with roles as defined G. The RRT may initiate the ACLS/PALS protocol if needed. H. The Primary nurse may need to remain close to help facilitate notification of physician and act as liaison with family. Reasons a team may be activated include but not limited to the following: Caregiver or family member is concerned about the patients clinical status Acute changes in VS from previously recorded or baseline parameters For any Stroke like symptoms For any suspicious chest pain Respiratory distress/ decrease in oxygen saturation Mental status change, changes the LOC, seizure activity Sudden onset or acute increase in pain Failure to respond to treatment
4 Documentation Process: 1. The team is to utilize the approved RRT order set guide (the house supervisor/ or manager will provide a copy of the order set to be utilized during the RRT event) 2. RRT will be documented in computer with details surrounding the event and outcome by the primary nurse 3. After the RRT the team may need to participate in a debriefing 4. If a RRT is called in areas in the hospital or adjacent to the hospital that do not house Emergency carts, a certified ACLS/PALS employee will take an Emergency Cart from the Emergency Department. Use of the med/surg, OR, and ER crash cart are options to utilize for the ER RN: list non inclusive to 1. Downstairs departments, Cafeteria, Purchasing, CSS etc. 2. Wound center, Infusion Center, VSC, ER waiting, Front desk, Lab, Radiology, FMC, Cardiac stress unit 3. Med/Surg crash cart is closest to PT department, Outpatient waiting area, MRI, and OR waiting are Data Collection: There is an RRT order set sheet that has necessary information that must be completed: Date Location Unit/Room if applicable Time called Time the RRT team arrived Reason for the RRT Who called the team, staff, patient or family Time the RRT ended Outcome of patient post RRT Did they stay on the unit Transfer to another unit Change in code status Other A copy of the RRT order set is copied and sent to the staff development office Staff Development/Education department role: Review information Audit information regarding code Ensure timeliness of team arrival Monitor outcome of patient immediately and post discharge--for readmission/or another RRT/ Code Blue call RRT for a patient clinically compromised or in a potentially critical situation: A. Criteria for initiation RRT for an adult patient (age 13 years and older) may include, but are not limited to the following: 1. Staff worried about patient 2. Change in heart rate less than 40 beats per minute (bpm) or greater than 130 bpm 3. Change in systolic blood pressure less than 90 millimeters (mm) Mercury (Hg) 4. Change in respiratory rate less than eight or greater than 28 breaths per minute 5. Change in oxygen saturation less than 90% despite oxygen usage 6. Change in level of consciousness 7. Change in urine output of less than 50 milliliters in four hours 8. Unknown seizure activity 9. Failure to respond to any treatment 10. Acute bleeding 11. Change in neurological status 12. Symptomatic hypovolemia
5 13. Symptomatic hypoglycemia blood glucose level <60 in adult patients especially with changes in metal status, confusion, slow to respond) B. Criteria for initiation of RRT for a Pediatric patient (age 12 years and under) may include, but are not limited to the following: 1. Staff worried about patient 2. Change in heart or respiratory rates. 3. Change in oxygen saturation less than 90% despite oxygen usage 4. Change in level of consciousness 5. Change in output 6. Unknown seizure activity 7. Failure to respond to any treatment 8. Acute bleeding 9. Symptomatic hypoglycemia <40 in pediatric patients If any patient s condition deteriorates in the presence of the RRT, then a Code Blue may be initiated by the RRT following ACLS/PALS protocol Components of the RRT: a) Immediate Response b) Nonjudgmental c) Accessible and onsite d) Critical care skills e) ACLS/PALS certified staff available f) Quick assessment and evaluation of patient completed and documented RRT Audit: *RRT Team Record sheet is on The Pulse under Forms* *The purpose of Audit: is to collect data on effectiveness of response to change or deterioration in a patient s condition, measures may include length of stay, response time for responding, changes in VS, arrest, code status etc.* 1. Utilize the RRT Team Record Sheet 2. All copies go to the professional Development coordinator 3. This sheet is NOT part of the patients record, all information regarding the RRT call, must documented in the patients electronic record, or on downtime patient documentation records. 4. *The RRT Record sheet include written criteria for describing early warning signs or deterioration in patient medical condition and when staff or family should seek immediate attention. (the criteria are outlined as above and are NOT limited to just those warning signs, if as a staff person you need to assistance with a patient because of medical condition change, call the RRT immediately) 5. The RRT Team Record Sheet must include all the following and completed before turning in to the staff development office: a. Date b. Room c. Unit d. Time called e. Time team arrived f. Time RRT ended g. Primary Reason for call h. VS on arrival i. Situation (free text what lead up to the event, describe in detail) j. Background (any historical data including what is on the sheet be detailed) k. Assessment (findings on the assessment, and ongoing assessment of the patient with times if necessary) l. Recommendation/Interventions: what did the team decide to implement at the time (THESE are not orders, anything that requires an order must be written as an order, this is for documentation of the events and interventions utilized based on physician intervention). m. If Medications were ordered please document the time, dose, route, dose and drug, these are to be documented electronically as they are to be given on any patient in that area. n. Outcome- immediate disposition of the patient must be documented 1. Additional outcomes are monitored for RRT s the patient will be monitored for 24 hour outcomes and discharge outcomes by staff development office. o. Attending Physician name/ notification and any other physicians that joined the RRT. p. Document the RRT team members including the primary care nurses present. q. You may document any additional information or notes r. Document your name, title and date.
6 6. RRT Debriefing/ opportunities if any identified/ recognized a. Immediately post RRT call assessments and interventions are completed and outcome of patient is determined, the house supervisor or unit manager may lead the team into a quick discussion of the case to determine that all pertinent information was documented and completed during the RRT and to see if there is an opportunity to ensure that flow of the event was successful b. Documentation of any opportunities will be forwarded to staff development specialist for the RRT audit and/or identification of any educational needs 7. See attachments for SBAR documentation and communication for adult and pediatric conditions/ the code blue documentation sheet *the RRT order set can be accessed from the house supervisor, manager, and forms folder on The Pulse.
7 Addendum PCH/FMC: Adult SBAR Form PCH/FMC-SBAR report to physician about an Adult-critical situation Situation I am calling about <patient name and location>. The patient s code status is <code status>. The problem I am calling about is I am afraid the patient is going to arrest. S B Assessment A R I have just assessed the patient personally: Vital signs are: Blood pressure _/_, Pulse_, Respiration and Temperature I am concerned about the potential VS readings of and of any symptomatic: Blood pressure because it is over 200 or less than 90 or 30 mmhg below usual. Heart rate because it is over 130 or less than 40. Respiration because it is less than 8 or over 28. Temperature Background b it i l th The patient s mental status is: Alert and oriented to person, place and time. Confused and cooperative or non-cooperative. Agitated or combative. Lethargic but conversant and able to swallow. Stuporous and not talking clearly and possibly not able to swallow. Comatose. Eyes closed. Not responding to stimulation. The skin is: Warm and dry Pale Mottled Diaphoretic Extremities are cold Extremities are warm The patient is not or is on oxygen. The patient has been on (l/min) or (%) oxygen for minutes (hours). The oximeter is reading _% The oximeter does not detect a good pulse and is giving erratic readings. This is what I think the problem is: <say what you think is the problem> The problem seems to be: cardiac, hypoglycemic, sepsis, neurological, respiratory am not sure what the problem is but the patient is deteriorating. The patient seems to be unstable and may get worse, we need to do something. Recommendation I suggest or request that you: <say what you would like to see done>. Transfer the patient to critical care. Come to see the patient at this time. Talk to the patient or family about code status. Ask for a consultant to see the patient now. Are any tests needed: Do you need any tests like: CXR, ABG, EKG, CBC, or BMP? Others? If a change in treatment is ordered then ask: How often do you want vital signs? Is there anything else you would like to be done at this time? I will call you back in (amount of time).. I
8 Addendum PCH/FMC Pediatric SBAR form PCH/FMC-Pediatric SBAR report to physician about a Pediatric critical situation S B Assessment A R Situation I am calling about <patient name and location> status is <code status>. I am afraid the patient is going to arrest. I have just assessed the patient personally:. The patient s code _. The problem I am calling about is Vital signs are: Blood pressure _/_, Pulse_, Respiration and Temperature I am concerned about the: Background The patient s mental status is: Alert and oriented to person, place and time. Confused and cooperative or non-cooperative. Agitated or combative. Lethargic but conversant and able to swallow. Stuporous and not talking clearly and possibly not able to swallow. Comatose. Eyes closed. Not responding to stimulation. Pediatric Assessment: Normal vital signs guidelines for the following age groups: I. Age: infant up to six months Heart rate (HR) 80 to160 beats per minute (bpm) Respiratory rate (RR) 25 to 45 breaths per minute Systolic blood pressure (B/P) not applicable Diastolic B/P not applicable Oxygen saturation (O2sat): room air greater than 96% Rectal temperature 98 to 99.5º Fahrenheit (F) II. Age: six months to three years HR 70 to 120 bpm RR 20 to 40 breaths per minute Systolic B/P 72 to 110 millimeters (mm) of Mercury (Hg) Diastolic B/P 36 to 70 mm Hg O2sat room air greater than 96% Rectal temperature 98.6 to 99º III. Age: Preschool HR 60 to 90 bpm RR 25 to 30 breaths per minute Systolic B/P 72 to 113 mm Hg Diastolic B/P 39 to 74 mm Hg O2sat room air greater than 96% Oral temperature 96.5 to 99º IV. Age: School age to 12 years HR 50 to 90 bpm RR 15 to 20 breaths per minute Systolic B/P 72 to 126 mm Hg Diastolic B/P 40 to 78 mm Hg This is what I think the problem is: <say what you think is the problem>. The problem seems to be: cardiac, infection, neurological, respiratory _. I am not sure what the problem is but the patient is deteriorating. The patient seems to be unstable and may get worse; we need to do something. Recommendation I suggest or request that you: <say what you would like to see done>. Transfer the patient to critical care. Come to see the patient at this time. Talk to the patient or family about code status. Ask for a consultant to see the patient now. Are any tests needed: Do you need any tests like: CXR, ABG, EKG, CBC, or BMP? Others? If a change in treatment is ordered then ask: -Howoftendoyouwantvitalsigns? Howlongdoyouexpectthisproblem to last: If the patient does not get better when would you want us to call again? Addendum to Code Blue/Pink Policy: PCH/FMC-Cardiopulmonary Arrest Flow Sheet
9 Date: Time: Facility Code Location: Witnessed Arrest: YES / NO Initial Assessment: Event Time Event Time Responsive: Yes No Respiration: Absent Present Pulse: Absent Present Initial Rhythm: IV Access Present: Yes No IV Obtained Time: Code Alarm Initiated: CPR Initiated: Doctor Arrived: Intubation: Intubated by: ETT Size: mm / Taped at: cm End Tidal Co2 Checked: Yes No External Pacer Time: Rate/MA Pacer Applied by: Time IV Solution Drip Rate Vital Signs every 5 minutes Time HR RR BP SP02 Time HR RR BP SP02 Time HR RR BP SP02 Time Rhythm Defib/Cardio Joules Amiodarone Bolus Medication Dosage Atropine Epinephrine Other Sodium Bicarb Vasopressin Amiodarone IV Infusion ( ml / hour) Dopamine Dobutamine Epinephrine Other Comments: ie IV placement, Chest Tube, Foley Cath, Response to Interventions ***** Medications are given IV, if other document in comments Outcome Resuscitation Ended Successful Expired Signature of Code Physician: Disposition Time Gift of Hope Time Family Notified Time Attending MD Notified Time Signature of Recording RN/LPN: Signature of Lead Code RN: Gift of Hope Referral Number Coroner Notified Time PCH Code Blue: updated: 04/2014
10 Continued: PCH/FMC Code Blue Nurses Notes: EKG Rhythm Key A = Asystole D5W AF = Atrial Fibrillation NS AFl = Atrial Flutter P = PEA 1:1000 SB = Sinus Bradycardia SR = Sinus Rhythm ST = Sinus Tachycardia SVT = Supraventricular Tachycardia VF = Ventricular Fibrillation VT = Ventricular Tachycardia IV Infusion Dosage Key/ Guide Amiodarone Drip 225mg/125cc Dobutamine Drip 250mg/250cc Dopamine Drip 400 mg/250cc NS Epinephrine Code Attended By: Names of all staff involved: legible please. 10
ACLS Prep. Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep.
 November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION. 1. Safe scene, standard precautions. 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness. 3. Quick look (monitor)
 LUCAS COUNTY EMS SUMMARY PAGES VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness 3. Quick look (monitor) 4. Identify rhythm 5. Provide 2 minutes CPR if unwitnessed by EMS
LUCAS COUNTY EMS SUMMARY PAGES VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION 2. Establish unresponsiveness, apnea, and pulselessness 3. Quick look (monitor) 4. Identify rhythm 5. Provide 2 minutes CPR if unwitnessed by EMS
MICHIGAN. State Protocols. Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
STANDARDIZED PROCEDURE CARDIAC STRESS TESTING-DOBUTAMINE INFUSION (Adult)
 I. Definition: This test is performed to evaluate for cardiac ischemia, arrhythmias, and/or response to exercise. II. Background Information A. Setting: The setting (inpatient vs outpatient) and population
I. Definition: This test is performed to evaluate for cardiac ischemia, arrhythmias, and/or response to exercise. II. Background Information A. Setting: The setting (inpatient vs outpatient) and population
MASTER SYLLABUS
 A. Academic Division: Health Sciences B. Discipline: Respiratory Care MASTER SYLLABUS 2018-2019 C. Course Number and Title: RESP 2330 Advanced Life Support Procedures D. Course Coordinator: Tricia Winters,
A. Academic Division: Health Sciences B. Discipline: Respiratory Care MASTER SYLLABUS 2018-2019 C. Course Number and Title: RESP 2330 Advanced Life Support Procedures D. Course Coordinator: Tricia Winters,
SUMMARY OF MAJOR CHANGES 2010 AHA GUIDELINES FOR CPR & ECC
 SUMMARY OF MAJOR CHANGES 2010 AHA GUIDELINES FOR CPR & ECC The following is a summary of the key issues and changes in the AHA 2010 Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Emergency Cardiac
SUMMARY OF MAJOR CHANGES 2010 AHA GUIDELINES FOR CPR & ECC The following is a summary of the key issues and changes in the AHA 2010 Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Emergency Cardiac
West Penn Allegheny Health System Forbes Regional Hospital
 Policy Name: Treatment of Anaphylactic Reaction In the Cath Lab Original Date: West Penn Allegheny Health System Forbes Regional Hospital Policy No. 16553 Page 1 of 6 Reviewed by : Mark Taylor, MD, Michael
Policy Name: Treatment of Anaphylactic Reaction In the Cath Lab Original Date: West Penn Allegheny Health System Forbes Regional Hospital Policy No. 16553 Page 1 of 6 Reviewed by : Mark Taylor, MD, Michael
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015 What s New in ACLS for 2015? Adult CPR CPR remains (Compressions, Airway, Breathing Chest compressions has priority over all other
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) Science Update 2015 What s New in ACLS for 2015? Adult CPR CPR remains (Compressions, Airway, Breathing Chest compressions has priority over all other
PEDIATRIC CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES. -Jason Haag, CCEMT-P
 PEDIATRIC CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES -Jason Haag, CCEMT-P General: CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES - More often the result and not the cause of acute cardiovascular emergencies - Typically the end result
PEDIATRIC CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES -Jason Haag, CCEMT-P General: CARDIAC RHYTHM DISTURBANCES - More often the result and not the cause of acute cardiovascular emergencies - Typically the end result
Pediatric Medical Emergencies
 Audience: Purpose: Policy: Pediatric Medical Emergencies All personnel in the. Explicit criteria for defining cardiac, respiratory, neurologic, and psychiatric emergencies and other life-threatening events,
Audience: Purpose: Policy: Pediatric Medical Emergencies All personnel in the. Explicit criteria for defining cardiac, respiratory, neurologic, and psychiatric emergencies and other life-threatening events,
STANDARDIZED PROCEDURE CARDIAC STRESS TESTING-EXERCISE TESTING (Adult, Peds)
 I. Definition: During the exercise test, the patient exercises on a bike or treadmill while being monitored with a 12 lead ECG, blood pressure device, pulse oximetry and, if requested, oxygen consumption,
I. Definition: During the exercise test, the patient exercises on a bike or treadmill while being monitored with a 12 lead ECG, blood pressure device, pulse oximetry and, if requested, oxygen consumption,
ACLS Review. Pulse Oximetry to be between 94 99% to avoid hyperoxia (high oxygen tension can lead to tissue death
 ACLS Review BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. After establishing unresponsiveness and calling for a code, check for a pulse less than 10 seconds then begin
ACLS Review BLS CPR BLS CPR changed in 2010. The primary change is from the ABC format to CAB. After establishing unresponsiveness and calling for a code, check for a pulse less than 10 seconds then begin
Resuscitation Patient Management Tool May 2015 MET Event
 OPTIONAL: Local Event ID: Date/Time MET was activated: Time Not Documented MET 2.1 Pre-Event Pre-Event Tab Was patient discharged from an Intensive Care Unit (ICU) at any point during this admission and
OPTIONAL: Local Event ID: Date/Time MET was activated: Time Not Documented MET 2.1 Pre-Event Pre-Event Tab Was patient discharged from an Intensive Care Unit (ICU) at any point during this admission and
Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult
 Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult All levels of provider will complete an initial & focused assessment on every patient, and as standing order, use necessary and appropriate skills and procedures
Routine Patient Care Guidelines - Adult All levels of provider will complete an initial & focused assessment on every patient, and as standing order, use necessary and appropriate skills and procedures
table of contents pediatric treatment guidelines
 table of contents pediatric treatment guidelines P1 PEDIATRIC PATIENT CARE...70 P2 APPARENT LIFE-THREATENING EVENT (ALTE)...71 P3 CARDIAC ARREST INITIAL CARE AND CPR...72 73 P4 NEONATAL CARE AND RESUSCITATION...74
table of contents pediatric treatment guidelines P1 PEDIATRIC PATIENT CARE...70 P2 APPARENT LIFE-THREATENING EVENT (ALTE)...71 P3 CARDIAC ARREST INITIAL CARE AND CPR...72 73 P4 NEONATAL CARE AND RESUSCITATION...74
DYSRHYTHMIAS. D. Assess whether or not it is the arrhythmia that is making the patient unstable or symptomatic
 DYSRHYTHMIAS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS A. The 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines were referred to for this protocol development. Evidence-based science was implemented in those areas where the AHA
DYSRHYTHMIAS GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS A. The 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines were referred to for this protocol development. Evidence-based science was implemented in those areas where the AHA
Preparing for your upcoming PALS course
 IU Health PALS Study Guide Preparing for your upcoming PALS course UPDATED November 2016 Course Curriculum: 2015 American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) AHA
IU Health PALS Study Guide Preparing for your upcoming PALS course UPDATED November 2016 Course Curriculum: 2015 American Heart Association (AHA) Guidelines for Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) AHA
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes
 Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes Name: Score: Date: 1. You are on the scene of a 4 year old in cardiac arrest. CPR is initiated and an E.T. tube has been placed, an I.V. has been established. What is the correct
Shifts 28, 29, 30 Quizzes Name: Score: Date: 1. You are on the scene of a 4 year old in cardiac arrest. CPR is initiated and an E.T. tube has been placed, an I.V. has been established. What is the correct
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Pediatric Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Pediatric Revised: 11/2013 (10 questions from this outline in the blue section) Emergency Medical
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Pediatric Revised: 11/2013 (10 questions from this outline in the blue section) Emergency Medical
Objectives: This presentation will help you to:
 emergency Drugs Objectives: This presentation will help you to: Five rights for medication administration Recognize different cardiac arrhythmias and determine the common drugs used for each one List the
emergency Drugs Objectives: This presentation will help you to: Five rights for medication administration Recognize different cardiac arrhythmias and determine the common drugs used for each one List the
Pediatric CPR. Mustafa SERİNKEN MD Professor of Emergency Medicine, Pamukkale University, TURKEY
 Pediatric CPR Mustafa SERİNKEN MD Professor of Emergency Medicine, Pamukkale University, TURKEY What are the differences? Normal limits ADULT CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST CAUSES INFANTS AND CHILDREN İschemic
Pediatric CPR Mustafa SERİNKEN MD Professor of Emergency Medicine, Pamukkale University, TURKEY What are the differences? Normal limits ADULT CARDIOPULMONARY ARREST CAUSES INFANTS AND CHILDREN İschemic
Chapter 9. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Cardiac Arrhythmias. Define electrical therapy
 Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Frank Sebat, MD - June 29, 2006
 Types of Shock Hypovolemic Shock Low blood volume decreasing cardiac output. AN INTEGRATED SYSTEM OF CARE FOR PATIENTS AT RISK SHOCK TEAM and RAPID RESPONSE TEAM Septic or Distributive Shock Decrease in
Types of Shock Hypovolemic Shock Low blood volume decreasing cardiac output. AN INTEGRATED SYSTEM OF CARE FOR PATIENTS AT RISK SHOCK TEAM and RAPID RESPONSE TEAM Septic or Distributive Shock Decrease in
Simulation 15: 51 Year-Old Woman Undergoing Resuscitation
 Simulation 15: 51 Year-Old Woman Undergoing Resuscitation Flow Chart Flow Chart Opening Scenario Section 1 Type: DM Arrive after 5-6 min in-progress resuscitation 51 YO female; no pulse or BP, just received
Simulation 15: 51 Year-Old Woman Undergoing Resuscitation Flow Chart Flow Chart Opening Scenario Section 1 Type: DM Arrive after 5-6 min in-progress resuscitation 51 YO female; no pulse or BP, just received
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING DEPARTMENT POLICY
 PS1070 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING DEPARTMENT POLICY TITLE: ADMISSION/DISCHARGE CRITERIA: CARDIOVASCULAR INTENSIVE Job Title of Reviewer: Director, CVICU EFFECTIVE DATE: REVIEWED/REVISED DATE: POLICY
PS1070 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING DEPARTMENT POLICY TITLE: ADMISSION/DISCHARGE CRITERIA: CARDIOVASCULAR INTENSIVE Job Title of Reviewer: Director, CVICU EFFECTIVE DATE: REVIEWED/REVISED DATE: POLICY
EFFECTIVE DATE: 01/2007 REVISED: 07/2008, 6/11, 3/12, 8/12, 1/15. Purpose:
 1 TITLE/DESCRIPTION: DEPARTMENT: PERSONNEL: Rapid Response Team (RRT) Patient Care Services RN s and RT s EFFECTIVE DATE: 01/2007 REVISED: 07/2008, 6/11, 3/12, 8/12, 1/15 Purpose: A group of select health
1 TITLE/DESCRIPTION: DEPARTMENT: PERSONNEL: Rapid Response Team (RRT) Patient Care Services RN s and RT s EFFECTIVE DATE: 01/2007 REVISED: 07/2008, 6/11, 3/12, 8/12, 1/15 Purpose: A group of select health
INSTITUTE FOR MEDICAL SIMULATION & EDUCATION ACLS PRACTICAL SCENARIOS
 Practical Teaching for Respiratory Arrest with a Pulse (Case 1) You are a medical officer doing a pre-operative round when 60-year old patient started coughing violently and becomes unconscious. Fortunately
Practical Teaching for Respiratory Arrest with a Pulse (Case 1) You are a medical officer doing a pre-operative round when 60-year old patient started coughing violently and becomes unconscious. Fortunately
Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies)
 SLO County Emergency Medical Services Agency Bulletin 2012-09 PLEASE POST Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies) July
SLO County Emergency Medical Services Agency Bulletin 2012-09 PLEASE POST Updated Policies and Procedures # s 606, 607, 610, 611, 612, 613, 625, 628, 630, 631, and 633 (ACLS Protocols and Policies) July
Resident At Risk. The National Early Warning Score (NEWS) and Monitoring Vital Signs
 Resident At Risk The National Early Warning Score (NEWS) and Monitoring Vital Signs Schein et al 64 consecutive ward patients requiring CPR 84% clinical deterioration 8 hours before arrest Pathophysiology
Resident At Risk The National Early Warning Score (NEWS) and Monitoring Vital Signs Schein et al 64 consecutive ward patients requiring CPR 84% clinical deterioration 8 hours before arrest Pathophysiology
PALS PRETEST. PALS Pretest
 PALS PRETEST 1. A child with a fever, immune system compromise, poor perfusion and hypotension is most likely to be experiencing which type of shock A. cardiogenic B. Neurogenic C. Septic D. Hypovolemic
PALS PRETEST 1. A child with a fever, immune system compromise, poor perfusion and hypotension is most likely to be experiencing which type of shock A. cardiogenic B. Neurogenic C. Septic D. Hypovolemic
Cardiac arrest simulation teaching (CASTeach) session
 Cardiac arrest simulation teaching (CASTeach) session Instructor guidance Key learning outcomes Overall aim: Scenarios should be facilitated by the Instructor in such a way that they are performed correctly.
Cardiac arrest simulation teaching (CASTeach) session Instructor guidance Key learning outcomes Overall aim: Scenarios should be facilitated by the Instructor in such a way that they are performed correctly.
Student Guide Module 4: Pediatric Trauma
 Student Guide Module 4: Pediatric Trauma Problem based learning exercise objectives Understand how to manage traumatic injuries in mass casualty events. Discuss the features and the approach to pediatric
Student Guide Module 4: Pediatric Trauma Problem based learning exercise objectives Understand how to manage traumatic injuries in mass casualty events. Discuss the features and the approach to pediatric
2. General Cardiac Arrest Protocol Medical Newborn/Neonatal. Protocol 8-3 Resuscitation 4. Medical Supraventricular
 PEDIATRIC CARDIAC SECTION: Pediatric Cardiovascular Emergencies REVISED: 06/2017 Section 8 1. Cardiac Arrest Unknown Rhythm (i.e. Protocol 8-1 BLS) 2. General Cardiac Arrest Protocol 8-2 3. Medical Newborn/Neonatal
PEDIATRIC CARDIAC SECTION: Pediatric Cardiovascular Emergencies REVISED: 06/2017 Section 8 1. Cardiac Arrest Unknown Rhythm (i.e. Protocol 8-1 BLS) 2. General Cardiac Arrest Protocol 8-2 3. Medical Newborn/Neonatal
PALS Case Scenario Testing Checklist Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction
 Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction Directs administration of 100% oxygen or supplementary oxygen as needed to support oxygenation Identifies signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction
Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction Directs administration of 100% oxygen or supplementary oxygen as needed to support oxygenation Identifies signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction
Verde Valley Medical Center Orientation Manual and Treatment Guidelines Changes
 Verde Valley Medical Center Orientation Manual and Treatment Guidelines 2017 Changes Description Page Change Why Orientation Manual changes Verde Valley Provider agencies Application for Medical Direction
Verde Valley Medical Center Orientation Manual and Treatment Guidelines 2017 Changes Description Page Change Why Orientation Manual changes Verde Valley Provider agencies Application for Medical Direction
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency
 Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
Yolo County Health & Human Services Agency Kristin Weivoda EMS Administrator John S. Rose, MD, FACEP Medical Director DATE: December 28, 2017 TO: Yolo County Providers and Agencies FROM: Yolo County EMS
WESTMEAD Cardiac QUESTIONS PRACTICE SAQ
 QUESTION 1 A 65-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a history of palpitations. His vital signs are: BP 105/60 mmhg HR 156 beats/min RR 26 /min Temperature 36.2 o C His ECG is on the
QUESTION 1 A 65-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a history of palpitations. His vital signs are: BP 105/60 mmhg HR 156 beats/min RR 26 /min Temperature 36.2 o C His ECG is on the
Scene Safety First always first, your safety is above everything else, hands only CPR (use pocket
 BLS BASICS: Scene Safety First always first, your safety is above everything else, hands only CPR (use pocket facemask or AMBU bag) Adults call it in, start CPR, get AED Child CPR First, Phone call second
BLS BASICS: Scene Safety First always first, your safety is above everything else, hands only CPR (use pocket facemask or AMBU bag) Adults call it in, start CPR, get AED Child CPR First, Phone call second
Adult Drug Reference. Dopamine Drip Chart. Pediatric Drug Reference. Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES
 Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
Adult Drug Reference Dopamine Drip Chart Pediatric Drug Reference Pediatric Drug Dosage Charts DRUG REFERENCES ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments ADENOSINE Paroxysmal
Requirements to successfully complete PALS:
 The American Heart Association released new resuscitation science and treatment guidelines on October 19, 2010. The new AHA Handbook of Emergency Cardiac Care (ECC) contains these 2010 Guidelines.The 2010
The American Heart Association released new resuscitation science and treatment guidelines on October 19, 2010. The new AHA Handbook of Emergency Cardiac Care (ECC) contains these 2010 Guidelines.The 2010
CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL
 CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL Item Changed Airway Management Procedure Oral Intubation Procedure Tube Confirmation and Monitoring Procedure C10 Chest Pain/ACS M2 Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis
CHANGES FOR DECEMBER 2008 PREHOSPITAL CARE MANUAL Item Changed Airway Management Procedure Oral Intubation Procedure Tube Confirmation and Monitoring Procedure C10 Chest Pain/ACS M2 Allergic Reaction/Anaphylaxis
Johnson County Emergency Medical Services Page 23
 Non-resuscitation Situations: Resuscitation should not be initiated in the following situations: Prolonged arrest as evidenced by lividity in dependent parts, rigor mortis, tissue decomposition, or generalized
Non-resuscitation Situations: Resuscitation should not be initiated in the following situations: Prolonged arrest as evidenced by lividity in dependent parts, rigor mortis, tissue decomposition, or generalized
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case. VF/Asystole
 Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
Update of CPR AHA Guidelines
 Update of CPR AHA Guidelines Donald Hal Shaffner Course objective is to have an updated understanding of the American Heart Association s treatment algorithms for the management of cardiac decompensation
Update of CPR AHA Guidelines Donald Hal Shaffner Course objective is to have an updated understanding of the American Heart Association s treatment algorithms for the management of cardiac decompensation
PALS Study Guide 2016
 Mandatory Precourse Self-Assessment at least 70% pass. Bring proof of completion to class. The PALS Provider exam is 50 multiple-choice questions. Passing score is 84%. Student may miss 8 questions. All
Mandatory Precourse Self-Assessment at least 70% pass. Bring proof of completion to class. The PALS Provider exam is 50 multiple-choice questions. Passing score is 84%. Student may miss 8 questions. All
ADVANCED CARDIAC LIFE SUPPORT (ACLS) RECERTIFICATION EXAMINATION
 ADVANCED CARDIAC LIFE SUPPORT (ACLS) RECERTIFICATION EXAMINATION 1. Ten minutes after an 85 year old woman collapses, paramedics arrive and start CPR for the first time. The monitor shows fine (low amplitude)
ADVANCED CARDIAC LIFE SUPPORT (ACLS) RECERTIFICATION EXAMINATION 1. Ten minutes after an 85 year old woman collapses, paramedics arrive and start CPR for the first time. The monitor shows fine (low amplitude)
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: PALS Revised: 11/2013
 NUMBERS Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: PALS Revised: 11/2013 Weight in kg = 8 + (age in yrs X 2) Neonate (less than 1 month)
NUMBERS Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: PALS Revised: 11/2013 Weight in kg = 8 + (age in yrs X 2) Neonate (less than 1 month)
Stayin Alive: Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) Updated Guidelines
 Stayin Alive: Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) Updated Guidelines Margaret Oates, PharmD, BCPPS Pediatric Critical Care Specialist GSHP Summer Meeting July 16, 2016 Disclosures I have nothing to
Stayin Alive: Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) Updated Guidelines Margaret Oates, PharmD, BCPPS Pediatric Critical Care Specialist GSHP Summer Meeting July 16, 2016 Disclosures I have nothing to
Blood/Blood Component Utilization and Administration Annual Compliance Education
 Blood/Blood Component Utilization and Administration Annual Compliance Education This course contains annual compliance education necessary to meet compliance and regulatory requirements. Instructions:
Blood/Blood Component Utilization and Administration Annual Compliance Education This course contains annual compliance education necessary to meet compliance and regulatory requirements. Instructions:
Indications The AED mode is to be used only on patients in cardiopulmonary arrest.
 14 October 2008 TO: Dr. Copass FR: Brian W. Chinn B3 A2 1018 RE: SFD LP12 Guidelines: I. AED / Advisory II. Manual A. Defibrillation B. Synchronize Cardioversion C. Noninvasive Pacing 1. Demand 2. Non-Demand
14 October 2008 TO: Dr. Copass FR: Brian W. Chinn B3 A2 1018 RE: SFD LP12 Guidelines: I. AED / Advisory II. Manual A. Defibrillation B. Synchronize Cardioversion C. Noninvasive Pacing 1. Demand 2. Non-Demand
OBSERVATION UNIT ASTHMA PATHWAY OUTLINE Westmoreland Hospital PAGE 1 OF 5
 PAGE 1 OF 5 Exclusion Criteria: (Reason to admit to hospital) A. New EKG changes except sinus tachycardia B. Respiratory Rate > 40 C. Signs/symptoms of Heart Failure D. Impending respiratory failure or
PAGE 1 OF 5 Exclusion Criteria: (Reason to admit to hospital) A. New EKG changes except sinus tachycardia B. Respiratory Rate > 40 C. Signs/symptoms of Heart Failure D. Impending respiratory failure or
Welcome to ACLS with Medical Education Angels!
 Welcome to ACLS with Medical Education Angels! For your greatest success, please be aware that the AHA assumes those taking ACLS have the ability to interpret and determine appropriate treatments for a
Welcome to ACLS with Medical Education Angels! For your greatest success, please be aware that the AHA assumes those taking ACLS have the ability to interpret and determine appropriate treatments for a
TEACHING BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (& ALS)
 TEACHING BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (& ALS) Anton Koželj, R.N., B. Sc., lecturer Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Maribor Žitna ulica 15, 2000 Maribor, Slovenia Fact s To know-how to perform basic life
TEACHING BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (& ALS) Anton Koželj, R.N., B. Sc., lecturer Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Maribor Žitna ulica 15, 2000 Maribor, Slovenia Fact s To know-how to perform basic life
A walk through a STEMI
 A walk through a STEMI M.M. s Story Kim Robison Ashley Corcoran Situation M.M. is an 82 year old male brought in by private vehicle on 10/22/17 to the Emergency Department Pt. c/o left arm numbness, pain
A walk through a STEMI M.M. s Story Kim Robison Ashley Corcoran Situation M.M. is an 82 year old male brought in by private vehicle on 10/22/17 to the Emergency Department Pt. c/o left arm numbness, pain
Stroke Transfer Checklist
 Stroke Transfer Checklist When preparing to transfer an acute stroke patient to the UF Health Shands Comprehensive Stroke Center, please make every attempt to include the following information: Results
Stroke Transfer Checklist When preparing to transfer an acute stroke patient to the UF Health Shands Comprehensive Stroke Center, please make every attempt to include the following information: Results
Advanced Resuscitation - Child
 C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
The ARREST Trial: Amiodarone for Resuscitation After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Due to Ventricular Fibrillation
 The ARREST Trial: Amiodarone for Resuscitation After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Due to Ventricular Fibrillation Introduction The ARREST (Amiodarone in out-of-hospital Resuscitation of REfractory Sustained
The ARREST Trial: Amiodarone for Resuscitation After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Due to Ventricular Fibrillation Introduction The ARREST (Amiodarone in out-of-hospital Resuscitation of REfractory Sustained
ADULT TREATMENT GUIDELINES
 A1 Adult Patient Care A2 Chest Pain / Suspected ACS A3 Cardiac Arrest Initial Care and CPR A4 Ventricular Fibrillation / Ventricular Tachycardia A5 PEA / Asystole A6 Symptomatic Bradycardia A7 Ventricular
A1 Adult Patient Care A2 Chest Pain / Suspected ACS A3 Cardiac Arrest Initial Care and CPR A4 Ventricular Fibrillation / Ventricular Tachycardia A5 PEA / Asystole A6 Symptomatic Bradycardia A7 Ventricular
MARSHALLTOWN MEDICAL & SURGICAL CENTER Marshalltown, Iowa
 MARSHALLTOWN MEDICAL & SURGICAL CENTER Marshalltown, Iowa INTENSIVE CARE POLICY & PROCEDURES Policy Number: R-25 Subject: Policy: Purpose: Cardioversion - Synchronized An RN may perform a synchronized
MARSHALLTOWN MEDICAL & SURGICAL CENTER Marshalltown, Iowa INTENSIVE CARE POLICY & PROCEDURES Policy Number: R-25 Subject: Policy: Purpose: Cardioversion - Synchronized An RN may perform a synchronized
Advanced Resuscitation - Adult
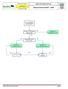 C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
Infection. Risk factor for infection ACoRN alerting sign with * Clinical deterioration. Problem List. Respiratory. Cardiovascular
 The ACoRN Process Baby at risk Unwell Risk factors Post-resuscitation requiring stabilization Resuscitation Ineffective breathing Heart rate < 100 bpm Central cyanosis Support Infection Risk factor for
The ACoRN Process Baby at risk Unwell Risk factors Post-resuscitation requiring stabilization Resuscitation Ineffective breathing Heart rate < 100 bpm Central cyanosis Support Infection Risk factor for
ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Basic Pre-Test
 ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Basic Pre-Test 1. You arrive at the scene of a motor vehicle collision and are directed to evaluate a child who was in one of the vehicles. The patient appears to be a child
ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Basic Pre-Test 1. You arrive at the scene of a motor vehicle collision and are directed to evaluate a child who was in one of the vehicles. The patient appears to be a child
ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments
 ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL. NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 716. Effective Date: March 3, 2007
 COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 716 Effective Date: March 3, 2007 SUBJECT: MONITOR/DEFIBRILLATOR 1. PURPOSE: This policy and procedure
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION Emergency Procedures POLICY NUMBER: 716 Effective Date: March 3, 2007 SUBJECT: MONITOR/DEFIBRILLATOR 1. PURPOSE: This policy and procedure
CalvertHealth Medical Center s Moderate Sedation Competency Examination
 Medical Staff Office Use Only: Congratulations! You passed the Moderate Sedation Competency Examination. Enclosed is the test for your follow-up review. Test Results: % ( of 35 correct) Your test result
Medical Staff Office Use Only: Congratulations! You passed the Moderate Sedation Competency Examination. Enclosed is the test for your follow-up review. Test Results: % ( of 35 correct) Your test result
Supplemental Digital Content 1. Simulation scenarios and critical action checklist for debriefing
 Supplemental Digital Content 1. Simulation scenarios and critical action checklist for debriefing Simulation Scenario #1 I. Title (ACS)-VF-Asystole-ROSC II. Target learner 6-7 medical students per team
Supplemental Digital Content 1. Simulation scenarios and critical action checklist for debriefing Simulation Scenario #1 I. Title (ACS)-VF-Asystole-ROSC II. Target learner 6-7 medical students per team
1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update What s New for 2010? 3 CPR. 4 4 Steps of BLS Survey 5 CPR 6 CPR.
 1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update 2010 2 What s New for 2010? 3 CPR Take no longer than seconds for pulse check Rate at least on per minute (instead of around 100 per minute ) Depth change:
1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update 2010 2 What s New for 2010? 3 CPR Take no longer than seconds for pulse check Rate at least on per minute (instead of around 100 per minute ) Depth change:
Northwest Community EMS System November 2018 CE: Cardiac Treatment Credit Questions
 Northwest Community EMS System November 2018 CE: Cardiac Treatment Credit Questions Name: EMS Agency/hospital: EMSC/Educator reviewer: Date submitted: Credit awarded (date): Returned for revisions: Revisions
Northwest Community EMS System November 2018 CE: Cardiac Treatment Credit Questions Name: EMS Agency/hospital: EMSC/Educator reviewer: Date submitted: Credit awarded (date): Returned for revisions: Revisions
Manual Defibrillation. CPR AGE: 18 years LOA: Altered HR: N/A RR: N/A SBP: N/A Other: N/A
 ROC AMIODARONE, LIDOCAINE OR PLACEBO FOR OUT OF HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST DUE TO VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR TACHYCARDIA (ALPS) STUDY: MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST MEDICAL DIRECTIVE An Advanced Care Paramedic
ROC AMIODARONE, LIDOCAINE OR PLACEBO FOR OUT OF HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST DUE TO VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR TACHYCARDIA (ALPS) STUDY: MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST MEDICAL DIRECTIVE An Advanced Care Paramedic
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY
 COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8024.31 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Cardiac Dysrhythmias Last Approval Date: 11/01/16 Effective Date: 11/01/18 Next Review
COUNTY OF SACRAMENTO EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY Document # 8024.31 PROGRAM DOCUMENT: Initial Date: 10/26/94 Cardiac Dysrhythmias Last Approval Date: 11/01/16 Effective Date: 11/01/18 Next Review
Capnography: The Most Vital Sign
 Capnography: The Most Vital Sign Mike McEvoy, PhD, NRP, RN, CCRN Cardiac Surgical ICU RN & Chair Resuscitation Committee Albany Medical Center EMS Coordinator Saratoga County, NY www.mikemcevoy.com CO
Capnography: The Most Vital Sign Mike McEvoy, PhD, NRP, RN, CCRN Cardiac Surgical ICU RN & Chair Resuscitation Committee Albany Medical Center EMS Coordinator Saratoga County, NY www.mikemcevoy.com CO
1. Normal sinus rhythm 2. SINUS BRADYCARDIA
 1. Normal sinus rhythm 2. SINUS BRADYCARDIA No signs and symptoms observe There are severe signs or symptoms o What are the signs and symptom Hypotension
1. Normal sinus rhythm 2. SINUS BRADYCARDIA No signs and symptoms observe There are severe signs or symptoms o What are the signs and symptom Hypotension
Albany Medical Center:
 Time to Get With The Guidelines for Resuscitation? Mike McEvoy, PhD, RN, CCRN, NRP Chair Resuscitation Committee Albany Medical Center, NY Sr. Staff RN CTICU Albany Medical Center EMS Coordinator Saratoga
Time to Get With The Guidelines for Resuscitation? Mike McEvoy, PhD, RN, CCRN, NRP Chair Resuscitation Committee Albany Medical Center, NY Sr. Staff RN CTICU Albany Medical Center EMS Coordinator Saratoga
CSI Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment
 CSI 202 - Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment Origins of the ACLS Approach: CSI 202 - Skills Lab 5 Notes ACLS training originated in Nebraska in the early 1970 s. Its purpose was to
CSI 202 - Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment Origins of the ACLS Approach: CSI 202 - Skills Lab 5 Notes ACLS training originated in Nebraska in the early 1970 s. Its purpose was to
Ventricular Assist Devices and Emergency Services
 Ventricular Assist Devices and Emergency Services Margaret Murray, DNP, FAHA Clinical Nurse Specialist- Cardiac Surgery, Cardiac Transplant and Ventricular Assist Devices ma.murray@hosp.wisc.edu Janean
Ventricular Assist Devices and Emergency Services Margaret Murray, DNP, FAHA Clinical Nurse Specialist- Cardiac Surgery, Cardiac Transplant and Ventricular Assist Devices ma.murray@hosp.wisc.edu Janean
national CPR committee Saudi Heart Association (SHA). International Liason Commission Of Resuscitation (ILCOR)
 2 It is our pleasure to present to you this work as a result of team work of the national CPR committee at the Saudi Heart Association (SHA). We adapted the 2010 guidelines as per International Liason
2 It is our pleasure to present to you this work as a result of team work of the national CPR committee at the Saudi Heart Association (SHA). We adapted the 2010 guidelines as per International Liason
Administrative Policies and Procedures. Originating Venue: Provision of Care, Treatment and Services Policy No.: PC 2916
 Administrative Policies and Procedures Originating Venue: Provision of Care, Treatment and Services Policy No.: PC 2916 Title: Sedation Cross Reference: Date Issued: 05/09 Date Reviewed: 04/11 Date: Revised:
Administrative Policies and Procedures Originating Venue: Provision of Care, Treatment and Services Policy No.: PC 2916 Title: Sedation Cross Reference: Date Issued: 05/09 Date Reviewed: 04/11 Date: Revised:
Management of Cardiac Arrest Based on : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines
 Management of Cardiac Arrest Based on : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines www.circ.ahajournals.org Elham Pishbin. M.D Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine MUMS C H E S Advanced Life Support
Management of Cardiac Arrest Based on : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines www.circ.ahajournals.org Elham Pishbin. M.D Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine MUMS C H E S Advanced Life Support
ACLS. Advanced Cardiac Life Support Practice Test Questions. 1. The following is included in the ACLS Survey?
 1. The following is included in the ACLS Survey? a. Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Differential Diagnosis b. Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Defibrillation c. Assessment, Breathing, Circulation, Defibrillation
1. The following is included in the ACLS Survey? a. Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Differential Diagnosis b. Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Defibrillation c. Assessment, Breathing, Circulation, Defibrillation
Vital Signs. Vital Signs. Vital Signs
 Vital Signs Vital Signs Why do vital signs? Determine relative status of vital organs Establish baseline Monitor response to Rx, meds Observe trends Determine need for further evaluation, Rx, intervention
Vital Signs Vital Signs Why do vital signs? Determine relative status of vital organs Establish baseline Monitor response to Rx, meds Observe trends Determine need for further evaluation, Rx, intervention
Naloxone Intranasal EMT OPTIONAL SKILL. Cell Phones and Pagers. Course Outline 09/2017
 EMT OPTIONAL SKILL Naloxone Intranasal Cell Phones and Pagers Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off. Course Outline Introduction and Overview
EMT OPTIONAL SKILL Naloxone Intranasal Cell Phones and Pagers Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off. Course Outline Introduction and Overview
But unfortunately, the first sign of cardiovascular disease is often the last. Chest-Compression-Only Resuscitation Gordon A.
 THE UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA Sarver Heart Center 1 THE UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA Sarver Heart Center 2 But unfortunately, the first sign of cardiovascular disease is often the last 3 4 1 5 6 7 8 2 Risk of Cardiac
THE UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA Sarver Heart Center 1 THE UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA Sarver Heart Center 2 But unfortunately, the first sign of cardiovascular disease is often the last 3 4 1 5 6 7 8 2 Risk of Cardiac
URN: Family name: Given name(s): Address: Initial Signature Print Name Role
 Do Not Write in this binding margin v5.00-02/2012 Mat. No.: 10206019 SW030b The State of Queensland (Queensland Health) 2012 Contact CIM@health.qld.gov.au ÌSW030bIÎ Facility: s Never Replace Clinical Judgement
Do Not Write in this binding margin v5.00-02/2012 Mat. No.: 10206019 SW030b The State of Queensland (Queensland Health) 2012 Contact CIM@health.qld.gov.au ÌSW030bIÎ Facility: s Never Replace Clinical Judgement
PBCFR ALS/BLS Protocols 2009 ALS Pretest
 1. In the patient with a blood glucose of 300mg/dL or higher without signs or symptoms of dehydration should receive how much normal saline? Pg 61 a. 250cc b. 500cc c. 20cc/kg d. None 2. The adult dose
1. In the patient with a blood glucose of 300mg/dL or higher without signs or symptoms of dehydration should receive how much normal saline? Pg 61 a. 250cc b. 500cc c. 20cc/kg d. None 2. The adult dose
Pediatric Resuscitation
 Pediatric Resuscitation Section 24 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Protocol The successful resuscitation of a child in cardiac arrest is dependent of a systematic approach of initiating life-saving CPR, recognition
Pediatric Resuscitation Section 24 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Protocol The successful resuscitation of a child in cardiac arrest is dependent of a systematic approach of initiating life-saving CPR, recognition
Admission of patient CVICU and hemodynamic monitoring
 Admission of patient CVICU and hemodynamic monitoring Prepared by: Rami AL-Khatib King Fahad Medical City Pi Prince Salman Heart tcentre CVICU-RN Admission patient to CVICU Introduction All the patients
Admission of patient CVICU and hemodynamic monitoring Prepared by: Rami AL-Khatib King Fahad Medical City Pi Prince Salman Heart tcentre CVICU-RN Admission patient to CVICU Introduction All the patients
ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Advanced Pre-Test
 ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Advanced Pre-Test 1. You arrive at the scene of a motor vehicle crash and are directed to evaluate a child who was in one of the vehicles. The patient appears to be a child
ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Advanced Pre-Test 1. You arrive at the scene of a motor vehicle crash and are directed to evaluate a child who was in one of the vehicles. The patient appears to be a child
HealthCare Training Service
 HealthCare Training Service Advanced Life Support Exam Time: Perusal Time: 20 minutes 5 minutes Total Marks: 25 Instructions: Read each question carefully. Using a pencil, record your response to each
HealthCare Training Service Advanced Life Support Exam Time: Perusal Time: 20 minutes 5 minutes Total Marks: 25 Instructions: Read each question carefully. Using a pencil, record your response to each
Mercy San Juan Medical Center. Preeclampsia and Other Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy
 SUBJECT: Preeclampsia and Other Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy DEPARTMENTS: FBC, Emergency Department PURPOSE: To outline the nursing management of inpatients who have preeclampsia or other hypertensive
SUBJECT: Preeclampsia and Other Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy DEPARTMENTS: FBC, Emergency Department PURPOSE: To outline the nursing management of inpatients who have preeclampsia or other hypertensive
PALS PROVIDER Course Study Guide/Pre-Test
 PALS PROVIDER Course Study Guide/Pre-Test *PLEASE COMPLETE AND BRING THIS DOCUMENT WITH YOU TO CLASS* Heartland CPR, llc 8101 NW 10 th St, Suite #C3 Oklahoma City, OK 73127 405-603-6666 contact@heartlandcpr.com
PALS PROVIDER Course Study Guide/Pre-Test *PLEASE COMPLETE AND BRING THIS DOCUMENT WITH YOU TO CLASS* Heartland CPR, llc 8101 NW 10 th St, Suite #C3 Oklahoma City, OK 73127 405-603-6666 contact@heartlandcpr.com
Don t let your patients turn blue! Isn t it about time you used etco 2?
 Don t let your patients turn blue! Isn t it about time you used etco 2? American Association of Critical Care Nurses National Teaching Institute Expo Ed 2013 Susan Thibeault MS, CRNA, APRN, CCRN, EMT-P
Don t let your patients turn blue! Isn t it about time you used etco 2? American Association of Critical Care Nurses National Teaching Institute Expo Ed 2013 Susan Thibeault MS, CRNA, APRN, CCRN, EMT-P
Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off.
 1 2 EMT OPTIONAL SKILL Naloxone Intranasal Cell Phones and Pagers Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off. 3 4 5 6 Course Outline Introduction
1 2 EMT OPTIONAL SKILL Naloxone Intranasal Cell Phones and Pagers Be courteous to your classmates! Please set your cell phones and/or pagers to silent or turn them off. 3 4 5 6 Course Outline Introduction
9/15/2017. Joyce Turner RN Director of Clinical Program Development
 Joyce Turner RN Director of Clinical Program Development A toxic response to an infection that spirals out of control attacking the body s own organs and tissues. The infection can be bacterial, viral
Joyce Turner RN Director of Clinical Program Development A toxic response to an infection that spirals out of control attacking the body s own organs and tissues. The infection can be bacterial, viral
ECG Changes in Patients Treated with Mild Hypothermia after Cardio-pulmonary Resuscitation for Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest
 ECG Changes in Patients Treated with Mild Hypothermia after Cardio-pulmonary Resuscitation for Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest R. Schneider, S. Zimmermann, W.G. Daniel, S. Achenbach Department of Internal
ECG Changes in Patients Treated with Mild Hypothermia after Cardio-pulmonary Resuscitation for Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest R. Schneider, S. Zimmermann, W.G. Daniel, S. Achenbach Department of Internal
Pediatric Advanced Life Support
 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Pediatric Chain of Survival Berg M D et al. Circulation 2010;122:S862-S875 Prevention Early cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) Prompt access to the emergency response system
Pediatric Advanced Life Support Pediatric Chain of Survival Berg M D et al. Circulation 2010;122:S862-S875 Prevention Early cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) Prompt access to the emergency response system
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 13 Resuscitation and Preparation for Anesthesia & Surgery Key Points 2 13.1 Management of Emergencies and Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation The emergency measures that
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 13 Resuscitation and Preparation for Anesthesia & Surgery Key Points 2 13.1 Management of Emergencies and Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation The emergency measures that
Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support. Emergency Procedures in PT
 Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Emergency Procedures in PT BLS Can be learned & practiced by the general public Includes: CPR First Aid (e.g. choking relief) Use of AED ACLS Used by healthcare
Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support Emergency Procedures in PT BLS Can be learned & practiced by the general public Includes: CPR First Aid (e.g. choking relief) Use of AED ACLS Used by healthcare
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on Tetracaine and Morgan Lens this may be optional in your region. *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your controlled substance license if required by
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Please check regional policy on Tetracaine and Morgan Lens this may be optional in your region. *Ketamine and Fentanyl must be added to your controlled substance license if required by
