Sleep disturbance and psychological distress are associated with functional dyspepsia based on Rome III criteria
|
|
|
- Oswald Barker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Li et al. BMC Psychiatry (2018) 18:133 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Sleep disturbance and psychological distress are associated with functional dyspepsia based on Rome III criteria Yong Li 1, Yaoyao Gong 2, Yinghui Li 4, Danjun He 1, Yuqin Wu 1, Haofei Wang 1, Xiaoyin Cong 1, Muxin Wei 3* and Lin Lin 2* Abstract Background: Functional dyspepsia (FD) is considered a bio-psychosocial disorder. The role of psychosocial factors in FD pathogenesis remains unclear. Methods: This study evaluated sleep quality and mood symptoms in patients with FD, assessing the associations of FD severity, disordered sleep, and psychological symptoms. One-hundred-and-fifteen adult patients with typical FD symptoms were enrolled alongside 61 healthy volunteers. Rome III criteria were used to evaluate FD symptoms; sleep disorder was assessed with the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), and Symptom Checklist-90-Revised (SCL-90R) was utilized to determine the status of depression, anxiety and other psychological symptoms. Results: PSQI scores and nine symptomatic dimensions of SCL-90R were significantly higher in FD patients than in controls. Multiple logistic regression indicated that lower BMI, lower level of education, and sleep disturbance were independently associated with FD and FD subgroups. Hostility and phobic anxiety were independent risk factors for FD. Further analysis showed that hostility was an independent risk factor for both FD subgroups, and somatization and additional psychiatric symptoms for epigastric pain syndrome. Conclusions: We found that FD was associated with sleep disorder and psychopathological factors. These findings suggest that implementing sleeping and/or psychological therapies may help reduce FD symptoms. Keywords: Functional dyspepsia, Sleep disturbance, Psychological factors, Rome III criteria Background Functional dyspepsia (FD), one of the most common functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs), is defined as pain and/or discomfort centered in the upper abdomen in the absence of obvious organic abnormalities [1]. The Rome III Consensus divided FD into two subgroups: epigastric pain syndrome (EPS, characterized by epigastric pain and burning) and postprandial distress syndrome (PDS, characterized by postprandial fullness and early satiety). FD is currently considered a bio-psychosocial disorder as a result of impaired motor function, Helicobacter * Correspondence: weimuxin@njmu.edu.cn; lin9100@aliyun.com Yong Li and Yaoyao Gong contributed equally to this work. 3 Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing , China 2 Department of Gastroenterology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing , China Full list of author information is available at the end of the article pylori infection, heightened visceral sensitivity, central nervous system disturbance, and unhealthy lifestyle [2]. Due to the differences in dietary habits, lifestyle, and Helicobacter pylori infection prevalence, the symptoms, epidemiology, pathogenetic factors, and management differ between Asian and Western FD patients [3]. Mounting evidence suggests that psychological distress is associated with FD; however, very few studies have assessed psychological factors that contribute to FD development. A Swedish 10-year-follow-up study of FD patients applying the Rome III definition showed an association of anxiety but not depression with FD [4]; meanwhile, a retrospective study based on the Rome III definition revealed that postprandial distress syndrome but not epigastric pain syndrome is associated with somatization, depression, and phobia [5]. The Author(s) Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Li et al. BMC Psychiatry (2018) 18:133 Page 2 of 7 Besides psychological factors, sleep disorder is a common phenomenon in FD patients and may influence the severity of dyspepsia symptoms [6]. In addition, sleep disturbance, anxiety, and depression are usually closely related; previous studies also found that sleep disturbance in FD patients appears to be associated with higher levels of anxiety [6]. However, whether sleep disorder or various psychological factors are independently associated with the development and severity of FD remains unclear. In the present study, we used an integrated questionnaire consisting of the major dyspepsia symptom scale, Symptom Checklist-90-Revised (SCL-90R), and Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) to assess FD severity, psychological health and sleeping condition in patients meeting Rome III criteria for FD. The study aimed to explore the associations of psychological distress or sleep disturbance with FD and FD subgroups based on Rome III criteria. Methods Participants and setting Adult outpatients from the digestive and psychological departments of First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University meeting ROME III criteria for FD between July 2015 and May 2016 were recruited for this study. The included patients have undergone an upper endoscopic test to exclude organic digestive diseases that might have explained the observed symptoms. Local adult volunteers without known gastrointestinal or psychological disorders, who underwent gastric endoscopy as regular medical examination, were recruited as healthy controls. All patients and controls underwent detailed history taking. All subjects with the following conditions were excluded: (a) a history of upper gastrointestinal tract surgery, (b) a history of ulcerative disease or malignancy, (c) current treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), (d) use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, (e) pregnancy for women, (f) pancreatitis or hepatobiliary disorders, and (g) physical or psychological impairments that prevented from completing the questionnaires. Patients with concomitant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms but not meeting the ROME III criteria for IBS were not excluded. FD symptoms definition and Rome III diagnostic questionnare FD was defined as the presence of postprandial fullness/ early satiation or pain/burning more than once per week, in the last 3 months according to the Rome III criteria. To diagnose FD and evaluate the severity of dyspepsia related symptoms, the original Rome III functional dyspepsia module [1] was translated into Chinese, confirmed by two digestive disease experts, and scrutinized by two native Chinese speakers without medical background to ensure that the text was easily understandable. The severity of major dyspeptic symptoms (postprandial abdominal fullness or discomfort, early satiety, epigastric pain, and epigastric burning) was rated on a 7-point Likert scale (0, absent; 1, hardly any; 2, mild; 3, moderate; 4, moderately severe;5,severe;6,verysevere). Sleep quality assessment (PSQI) A Chinese version of the PSQI questionnaire was used to assess the patient s recent history of sleep quality. The PSQI questionnaire consisted of 19 self-rating items that can be categorized into seven components, including subjective sleep quality, sleep latency, sleep duration, habitual sleep efficiency, sleep disturbance, use of sleep medication, and daytime dysfunction. The score of each component score was rated from 0 to 3. The sum of these seven component scores provided a global PSQI score, which ranged from 0 to 21. Higher scores indicate poorer sleep. The Chinese Version of PSQI was translated and validated by Liu et al. [7]. In that study, the internal consistency Cronbach s α was 0.84, the split-half reliability was 0.87, and the 2-week test-retest reliability was Evaluation of psychiatric distress and lifestyle factors Psychiatric distress was estimated using the Chinese version of SCL-90R [8]. The SCL-90R is a self-reporting, clinical symptom rating scale consisting of 90 items. Responses indicate symptoms associated with 9 symptom dimensions, which included somatization (distress arising from perceptions of bodily dysfunction), obsessive-compulsive (thoughts, impulses and actions that are experienced as irresistible and unremitting), interpersonal sensitivity (feelings of inferiority or inadequacy), depression, anxiety, hostility (thoughts, feelings and actions that are characteristic of the negative affect state of anger), phobic anxiety (irrational fear of specific situations or persons), paranoid ideation (paranoid behavior as fundamentally a disordered mode of thinking), and psychoticism [9]. Additionally, a global symptom score is calculated. The Chinese-version SCL-90R questionnaire [8] with established reliability and validity is widely used in measuring psychological distress in Chinese clinical practice and research. In a recent study carried out in patients with alopecia areata, the internal consistency Cronbach s α was 0.98 and split-half coefficient was 0.95 [10]. Demographic data and lifestyle factors (including age, gender, marital status, body mass index (BMI), education level, smoking, and consumption of alcohol were recorded in all patients and controls). Tobacco and alcohol use was divided into never/rare and regular use (more than once a week). Each questionnaire was completed individually and independently by the participant.
3 Li et al. BMC Psychiatry (2018) 18:133 Page 3 of 7 Data analysis Data were assessed with Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) for Windows, version Measurement data are mean ± standard deviation (SD). Student t test and one way analysis of variance (ANOVA) were used to statistically assess demographic variables such as weight, height, and BMI. Various sleep disorder parameters and psychological factors between FD patients and healthy controls were also assessed by Student t test. The association of total PSQI score and FD symptom severity score was assessed by Spearman correlation analysis. Risk factors for dyspepsia were initially explored by univariate analysis. Those with P < 0.05 were then entered into a multivariate analysis. Independent risk factors for dyspepsia were subsequently determined by backward elimination logistic regression. Data were expressed as odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (95% CI). P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results Response rate and demographics Of the 263 subjects eligible for inclusion, a total of 224 (85.1%) individuals agreed to participate in the study. However, 109 individuals did not complete the questionnaires because of low education level or desire to withdraw. Therefore, a total of 115 FD outpatients completed questionnaires, yielding a response rate of 43.7%. Meanwhile, 61 healthy controls were enrolled. The mean age of the control population was ± years; 80.3% of control individuals were female. Table 1 describes the basic demography of the study population. The mean age of interviewees was ± years, ranging from 17 to 61 years. A total of 143 (81.3%) adults were female. There were no significant differences between the two groups in terms of age, gender, marital status, regular tobacco use, and regular alcohol intake. FD patients had lower BMI and level of education compared with the control group. FD symptoms Mean duration of FD symptoms was 52 ± 50 months, and the patients reported that FD symptoms were present 4.1 ± 2.3 days per week. Among the 115 FD participants, 87 (75.7%) had symptoms consistent with EPS (including 61 individuals with pure EPS symptoms) and 54 (47.0%) conformed to PDS (including 28 with pure PDS symptoms); 26 patients (22.6%) reported dyspeptic symptoms compatible with both EPS and PDS. Sleep symptoms Average sleep durations in FD patients and healthy controls were 6.24 ± 1.37 and 6.87 ± 1.05 h, respectively (P <0.05). Occasional sleep problems were common in both FD and control groups; indeed, 67.2 and 58.6% of FD patients and control participants, respectively, reported having sleep abnormality 1 to 3 days a month. Significantly higher PSQI scores were found in FD patients compared with controls (10.49 ± 3.38 vs 6.77 ± 2.77, respectively; P < 0.01). In addition, as shown in Table 2, six parameters, including subjective sleep quality, sleep latency, sleep duration, sleep disturbance, use of sleeping medication, and daytime dysfunction showed remarkably higher scores in FD patients compared with controls. Association of Sleep Disturbance with FD symptoms To further investigate the association between overall sleep score and FD symptom score, we applied a Spearman regression analysis within patients with FD. There was a significant correlation between total PSQI sleep score and overall FD symptom score (r p =0.63, P < 0.01). A total of 61 FD patients had a score above 11, with 5 having values > 15, which reflects severe sleep disturbance in all domains. Table 1 Basic demographics of the study population Characteristic FD (n = 115) Controls (n = 61) P value Age (year) ± ± BMI ± ± * Gender Female (%) 94 (81.7) 49 (80.3) 0.82 Marital status Single/widower/divorced (%) 21 (18.5) 6 (10.0) 0.14 Married (%) 94 (81.7) 54 (90.0) 0.15 Years of education (year) ± ± * Regular tobacco use (%) 42 (36.5) 22 (36.7) 0.98 Regular alcohol intake (%) 44 (38.3) 25 (41.7) 0.66 Duration of symptoms (mo) 52 ± 50 Days per week with symptoms 4.1 ± 2.3 BMI body mass index calculated as weight (kg)/height (m 2 )
4 Li et al. BMC Psychiatry (2018) 18:133 Page 4 of 7 Table 2 PSQI scores in FD patients and healthy controls (mean ± SD) Groups Subjective sleep quality Sleep latency Sleep duration Habitual sleep efficiency Sleep disturbance Use of sleeping medications Daytime dysfunction Total score FD 1.94 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± 3.38 HC 1.61 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± 2.77 t P 0.009* 0.000* 0.001* * 0.000* 0.000* 0.000* Moreover, there was a consistent, stepwise increase of FD symptom scores with increasing sleep scores (Fig. 1). Psychological symptoms To assess the associations of various psychological factors with FD development, we first compared ten symptomatic dimensions as well as total SCL-90R scores between FD patients and healthy controls. Interestingly, somatization, obsessive-compulsive, interpersonal sensitivity, depression, anxiety, hostility, phobic anxiety, psychoticism, additional items, and total score showed markedly higher levels in the FD group than in controls (Table 3). To further identify which psychological factors were independent risk factors for FD, a multivariate logistic regression model was employed (Table 4). Hostility (OR = 4.29, 95%CI , P < 0.05) and phobic anxiety (OR = 6.41, 95%CI = , P < 0.05) were independent risk factors for dyspepsia. However, no significant associations of symptomatic dimension scores withthefdsymptomscorewerefound. Independent risk factors for FD Besides hostility and phobic anxiety, lower BMI (OR = 0.75; 95%CI ; P < 0.05), lower education levels (OR = 0.77; 95%CI ; P < 0.001), and higher PSQI Fig. 1 Univariate association of PSQI score with FD symptom score. The FD symptom score increased stepwise with sleep score. The higher the sleep score, the more severe the sleep disturbance was score (OR = 1.55; 95%CI ; P < 0.001) were also independent risk factors for FD (Table 4). Independent risk factors for FD subgroups To assess the associations of each FD subgroup with psychiatric distress and sleep disorder, subgroup analysis was performed. EPS was independently associated with somatization, hostility and additional symptoms, while PDS was independently associated with hostility. Both subgroups were independently associated with lower BMI, lower education level, and higher PSQI score (Table 5). Discussion Previous studies suggested that psychological distress is common in patients with FD [4, 5, 11, 12]. However, the psychological factors associated with FD remain undefined. In this study, both PSQI and SCL-90R were applied to assess the sleeping and psychological conditions of patients with FD, analyzing the associations of sleep disturbance, somatization, obsessive-compulsive, interpersonal sensitivity, depression, anxiety, hostility, phobic anxiety, paranoid ideation and psychoticism with FD, respectively. We found that FD was associated with sleep disorder and several psychopathological factors (somatization, obsessivecompulsive, interpersonal sensitivity, depression, anxiety, hostility, phobic anxiety, psychoticism). In addition, we found that lower BMI, lower level of education, sleep disorder, hostility and phobic anxiety were independent risk factors for FD. The associations of poor sleep with functional gastrointestinal disorders have been evaluated in previous physiological and epidemiological studies [6, 13 17]. However, whether sleep disturbance is independently associated with FD remains controversial. A previous study assessing 505 patients with functional gastrointestinal disorders and 247 healthy controls found that 68 and 50.2% of individuals with FD and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), respectively, have sleep disturbance [15]. A study based on Rome III criteria for FD showed that FD symptoms are significantly correlated with sleep disturbance [6]. A community-based cohort study reported that sleep dysfunction and somatization are independent risk factors for dyspepsia [14]. A population-based research indicated that IBS is significantly more common in people with
5 Li et al. BMC Psychiatry (2018) 18:133 Page 5 of 7 Table 3 SCL-90R scores in FD patients and healthy controls (mean ± SD) Groups Somatization Obsessivecompulsive Interpersonal sensitivity Depression Anxiety Hostility Phobic anxiety Paranoid ideation Psychoticism Additional items FD 1.75 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± HC 1.40 ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± t P < 0.000* 0.014* 0.003* 0.002* 0.002* 0.003* 0.002* * * Total score sleep disturbance, while its association with FD was not statistically significant [13]. In the present study, sleep disturbance was an independent risk factor for FD and both FD subgroups. In addition, PSQI scores were higher in FD patients with more severe symptoms, suggesting that impaired sleep may be an important factor affecting the severity of FD symptoms. The mechanisms underlying mutual interactions between sleep disturbance and FD symptom expression may be quite complex. We hypothesized that on one hand, severe epigastric pain or burning may lead to disorders that initiate and maintain sleep; on the other hand, disrupted sleep could lead to increased symptom expression in patients with FD. In support of this hypothesis, a previous study demonstrated that both rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and slow wave sleep (SWS) interruption could decrease mechanical pain thresholds in healthy volunteers [18]. The role of adverse psychological factors in the development of functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs) attracts increasing attention [19]. In a recent retrospective study, data of 4966 patients diagnosed with a FGID and 1002 randomly selected individuals indicated that twice as much patients are diagnosed with a mood disorder before an FGID; mood disorder was on average diagnosed more than 3 years before FGID [20]. As mentioned above, studies assessing the psychological factors that contribute to FD development are limited. In this study, SCL-90R was applied to assess mood condition, and the scores of 9 symptomatic dimensions, including somatization, obsessivecompulsive, interpersonal sensitivity, depression, anxiety, hostility, phobic anxiety, psychoticism and additional items, were markedly higher in patients with FD than in healthy controls. These findings demonstrated that negative emotions are common in patients with FD. Given the chronicity of symptoms in the current patient cohort, this is unsurprising because chronic disease status may cause increased prevalence of mood disorders. Further analysis of independent risk factors for FD indicated that hostility and phobic anxiety were independently associated with FD; subgroup analysis showed that hostility Table 4 Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis of risk factors for FD Variables Univariate analysis Multivariate analysis OR 95%CI P OR 95%CI P Age Gender BMI < * Years of education < < 0.001* PSQI score < < 0.001* SCL-90R score Somatization Obsessive-compulsive Interpersonal sensitivity Depression Anxiety Hostility * Phobic anxiety * Paranoid ideation Psychoticism Additional items
6 Li et al. BMC Psychiatry (2018) 18:133 Page 6 of 7 Table 5 Multivariate logistic regression analysis of risk factors for FD subgroups Variables EPS PDS OR 95%CI P OR 95%CI P BMI * < 0.001* Years of education * * PSQI score < 0.001* < 0.001* SCL-90R score Somatization * Obsessive-compulsive Interpersonal sensitivity Depression , Anxiety Hostility * * Phobic anxiety Paranoid ideation Psychoticism Additional items * was an independent risk factor for both FD subgroups, while somatization and additional psychiatric symptoms predicted EPS. With respect to clinical application, whether treating FD patients with sleep or psychotherapeutic medications improves dyspeptic symptoms remains unclear. Related data are limited, as only few randomized controlled trials have been conducted for FD psychotherapy [21, 22]. A systematic review assessing the effects of psychotherapy on dyspepsia symptoms was withdrawn because only four trials were eligible [5]. Nevertheless, all four trials suggested that psychological interventions benefit dyspepsia symptoms [21]. A 6-month-follow-up randomized controlled trial reported that adding psychotherapy to standard medical therapy improves short- and long-term curative effects [22]. In a recent randomized, placebo-controlled trial, treating FD patients with mirtazapine was shown to significantly improve early satiation, the quality of life, gastrointestinal-specific anxiety, nutrient tolerance, and weight loss [23]. This is a cross-disciplinary research spanning gastroenterology and psychology. We focused on evaluating sleep quality and mood symptoms in Chinese patients with FD, with a view to compare with other racial population in future. It is helpful for clinicians to pay more attention to the sleep disturbance and psychological factors of FD patients and to provide more effective treatments for them. The present study had several limitations. For example, no physiological measurements were used in this study, although the diagnosis of sleep disturbance is still largely dependent on patient s subjective feelings and symptoms. Conclusions In conclusion, this study demonstrated that sleep disturbance and negative emotions were common in patients with FD. Impaired sleep was an independent risk factor for FD and both FD subgroups, and may play a role in symptom expression. Hostility and phobic anxiety were independently associated with FD development. We further demonstrated that hostility was an independent risk factor for both FD subgroups, while somatization and additional psychiatric symptoms predicted EPS. Further exploration of the mechanisms linking sleep disturbance and negative emotions with FD may yield new approaches to interventions that reduce FD symptoms. Abbreviations BMI: Body mass index; EPS: Epigastric pain syndrome; FD: Functional dyspepsia; FGIDs: Functional gastrointestinal disorders; IBS: Irritable bowel syndrome; PDS: Postprandial distress syndrome; PSQI: Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index; REM: Rapid eye movement; SCL-90R: Symptom Checklist-90-Revised; SWS: Slow wave sleep Funding This study was supported by Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of Jiangsu Province, China (Grant No.YB ) and the Research Foundation of Jiangsu provincial commission of health and family planning (Grant No.Y ). The funders had no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript. Availability of data and materials The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Authors contributions YL, with help of MW, planned the present study s content and analysis, interpreted the data and wrote the paper. LL helped in the conception of the study s aim and content, together with YG were responsible for the diagnosis of FD. YL, YG, DH, YHL, YW, HW, XC initiated and performed the
7 Li et al. BMC Psychiatry (2018) 18:133 Page 7 of 7 whole survey, analysed the data and helped to interpret the findings and to write the paper. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript. Ethics approval and consent to participate This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, and conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consents were obtained from all participants. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Publisher s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Author details 1 Department of Psychiatry, the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing , China. 2 Department of Gastroenterology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing , China. 3 Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing , China. 4 Department of Psychiatry, Zhongda Hospital, Southeast University, Nanjing , China. Received: 7 February 2018 Accepted: 3 May Schurman JV, Friesen CA, Dai H, Danda CE, Hyman PE, Cocjin JT. Sleep problems and functional disability in children with functional gastrointestinal disorders: an examination of the potential mediating effects of physical and emotional symptoms. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012;12: Onen SH, Alloui A, Gross A, Eschallier A, Dubray C. The effects of total sleep deprivation, selective sleep interruption and sleep recovery on pain tolerance thresholds in healthy subjects. J Sleep Res. 2001;10(1): Locke GR 3rd, Weaver AL, Melton LJ 3rd, Talley NJ. Psychosocial factors are linked to functional gastrointestinal disorders: a population based nested case-control study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99(2): Jones MP, Tack J, Van Oudenhove L, Walker MM, Holtmann G, Koloski NA, Talley NJ. Mood and anxiety disorders precede development of functional gastrointestinal disorders in patients but not in the population. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15(7): e Soo S, Moayyedi P, Deeks JJ, Delaney B, Lewis M, Forman D. WITHDRAWN: psychological interventions for non-ulcer dyspepsia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;2:CD Orive M, Barrio I, Orive VM, Matellanes B, Padierna JA, Cabriada J, Orive A, Escobar A, Quintana JM. A randomized controlled trial of a 10week group psychotherapeutic treatment added to standard medical treatment in patients with functional dyspepsia. J Psychosom Res. 2015;78(6): Tack J, Ly HG, Carbone F, Vanheel H, Vanuytsel T, Holvoet L, Boeckxstaens G, Caenepeel P, Arts J, Van Oudenhove L. Efficacy of mirtazapine in patients with functional dyspepsia and weight loss. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016; 14(3): e384 References 1. Drossman DA. The functional gastrointestinal disorders and the Rome III process. Gastroenterol. 2006;130(5): Fang YJ, Liou JM, Chen CC, Lee JY, Hsu YC, Chen MJ, Tseng PH, Chang CY, Yang TH, Chang WH, et al. Distinct aetiopathogenesis in subgroups of functional dyspepsia according to the Rome III criteria. Gut. 2015;64(10): Miwa H, Ghoshal UC, Gonlachanvit S, Gwee KA, Ang TL, Chang FY, Fock KM, Hongo M, Hou X, Kachintorn U, et al. Asian consensus report on functional dyspepsia. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012;18(2): Aro P, Talley NJ, Johansson SE, Agreus L, Ronkainen J. Anxiety is linked to new-onset dyspepsia in the Swedish population - a 10 year follow-up Study. Gastroenterology. 2015;148(5): Hsu YC, Liou JM, Liao SC, Yang TH, Wu HT, Hsu WL, Lin HJ, Wang HP, Wu MS. Psychopathology and personality trait in subgroups of functional dyspepsia based on Rome III criteria. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104(10): Lacy BE, Everhart K, Crowell MD. Functional dyspepsia is associated with sleep disorders. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;9(5): Liu X, Tang M, Hu L, Wang A. Reliability and validity of the Pittsburgh sleep quality index (Chinese) chin. J Psychiatry. 1996;29(2): Tang Q, Cheng Z, Yuan A, Deng Y. The use and reanalysis of SCL-90 in China (Chinese). Chinese J Clin Psychol. 1999;7: Derogatis LR. Symptom Checklist-90-revised. In: Handbook of psychiatric measures. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; Tan H, Lan XM, Yu NL, Yang XC. Reliability and validity assessment of the revised symptom checklist 90 for alopecia areata patients in China. J Dermatol. 2015;42(10): Mahadeva S, Yadav H, Rampal S, Goh KL. Risk factors associated with dyspepsia in a rural Asian population and its impact on quality of life. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105(4): Jones MP, Maganti K. Symptoms, gastric function, and psychosocial factors in functional dyspepsia. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2004;38(10): Vege SS, Locke GR 3rd, Weaver AL, Farmer SA, Melton LJ 3rd, Talley NJ. Functional gastrointestinal disorders among people with sleep disturbances: a population-based study. Mayo Clin Proc. 2004;79(12): Gathaiya N, Locke GR 3rd, Camilleri M, Schleck CD, Zinsmeister AR, Talley NJ. Novel associations with dyspepsia: a community-based study of familial aggregation, sleep dysfunction and somatization. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2009;21(9):922 e Fass R, Fullerton S, Tung S, Mayer EA. Sleep disturbances in clinic patients with functional bowel disorders. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95(5): Cremonini F, Camilleri M, Zinsmeister AR, Herrick LM, Beebe T, Talley NJ. Sleep disturbances are linked to both upper and lower gastrointestinal symptoms in the general population. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2009;21(2):
The Risk Factors and Quality of Life in Patients with Overlapping Functional Dyspepsia or Peptic Ulcer Disease with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 8, No. 2, March 2014, pp. 160-164 ORiginal Article The Risk Factors and Quality of Life in Patients with Overlapping Functional Dyspepsia or Peptic Ulcer Disease with Gastroesophageal
Gut and Liver, Vol. 8, No. 2, March 2014, pp. 160-164 ORiginal Article The Risk Factors and Quality of Life in Patients with Overlapping Functional Dyspepsia or Peptic Ulcer Disease with Gastroesophageal
Classification of pediatric functional gastrointestinal disorders related to abdominal pain using Rome III vs. Rome IV criterions
 Edwards et al. BMC Gastroenterology (2018) 18:41 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-018-0769-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Classification of pediatric functional gastrointestinal disorders related to abdominal
Edwards et al. BMC Gastroenterology (2018) 18:41 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12876-018-0769-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Classification of pediatric functional gastrointestinal disorders related to abdominal
Sleep disorders are common in the United States; nearly 50% Functional Dyspepsia Is Associated With Sleep Disorders. Methods Survey Generation
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2011;9:410 414 Functional Dyspepsia Is Associated With Sleep Disorders BRIAN E. LACY,* KELLY EVERHART,* and MICHAEL D. CROWELL *Section of Gastroenterology and
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2011;9:410 414 Functional Dyspepsia Is Associated With Sleep Disorders BRIAN E. LACY,* KELLY EVERHART,* and MICHAEL D. CROWELL *Section of Gastroenterology and
Distinct aetiopathogenesis in subgroups of functional dyspepsia according to the Rome III criteria
 Additional material is published online only. To view please visit the journal online (http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/ gutjnl-2014-308114). For numbered affiliations see end of article. Correspondence to Professor
Additional material is published online only. To view please visit the journal online (http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/ gutjnl-2014-308114). For numbered affiliations see end of article. Correspondence to Professor
Number of studies. Endoscopic finding. Number of subjects. Pooled prevalence 95% CI
 Clinical Approach to the Patient t with Dyspepsia William D. Chey, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine University of Michigan Prevalence of Endoscopic Findings in Individuals with Dyspepsia Systematic Review
Clinical Approach to the Patient t with Dyspepsia William D. Chey, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine University of Michigan Prevalence of Endoscopic Findings in Individuals with Dyspepsia Systematic Review
J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 17 No. 3 July, 2011 DOI: /jnm Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility
 ㅋ JNM J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 17 No. 3 July, 2011 DOI: 10.5056/jnm.2011.17.3.279 Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility Original Article Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Diagnosed
ㅋ JNM J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 17 No. 3 July, 2011 DOI: 10.5056/jnm.2011.17.3.279 Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility Original Article Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Diagnosed
Non-Ulcer Dyspepsia: what is it? What can we do with these patients? Overview. Dyspepsia Definition. Functional Dyspepsia. Dyspepsia the Basics
 Non-Ulcer : what is it? What can we do with these patients? Temporal Changes and Geographic Variations in Developing Peptic Ulcer Disease Gastric Cancer 1900 Eamonn M M Quigley MD FACG Alimentary Pharmabiotic
Non-Ulcer : what is it? What can we do with these patients? Temporal Changes and Geographic Variations in Developing Peptic Ulcer Disease Gastric Cancer 1900 Eamonn M M Quigley MD FACG Alimentary Pharmabiotic
Cigarette Smoking and its Association with Overlapping Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Functional Dyspepsia, or Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cigarette Smoking and its Association with Overlapping Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Functional Dyspepsia, or Irritable Bowel Syndrome Yasuhiro Fujiwara, Makiko Kubo, Yukie Kohata,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cigarette Smoking and its Association with Overlapping Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Functional Dyspepsia, or Irritable Bowel Syndrome Yasuhiro Fujiwara, Makiko Kubo, Yukie Kohata,
History and Design of the SCL-90-R
 History and Design of the SCL-90-R Leonard R. Derogatis, PhD Brief History of the SCL-90-R / BSI Personal Data Sheet (1918) Cornell Medical Index (1948) Hopkins Symptom Checklist (1968) SCL-90-R (1975)
History and Design of the SCL-90-R Leonard R. Derogatis, PhD Brief History of the SCL-90-R / BSI Personal Data Sheet (1918) Cornell Medical Index (1948) Hopkins Symptom Checklist (1968) SCL-90-R (1975)
... SELECTED ABSTRACTS...
 ... SELECTED ABSTRACTS... The following abstracts, from medical journals containing literature on irritable bowel syndrome, were selected for their relevance to this supplement. A Technical Review for
... SELECTED ABSTRACTS... The following abstracts, from medical journals containing literature on irritable bowel syndrome, were selected for their relevance to this supplement. A Technical Review for
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University
 CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
Factors Influencing Satisfaction with Life in Female Nursing College Students with Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Vol.132 (Healthcare and Nursing 2016), pp.198-203 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016. Factors Influencing Satisfaction with Life in Female Nursing College Students with Irritable Bowel Syndrome Sung
Vol.132 (Healthcare and Nursing 2016), pp.198-203 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016. Factors Influencing Satisfaction with Life in Female Nursing College Students with Irritable Bowel Syndrome Sung
Peer Support in Improving Self-Efficacy of Rural Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and the Application of Drugs to Reduce the Pain from Diabetes
 Open Journal of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, 2016, 6, 135-140 Published Online April 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojemd http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojemd.2016.64018 Peer Support in Improving
Open Journal of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, 2016, 6, 135-140 Published Online April 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojemd http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojemd.2016.64018 Peer Support in Improving
Medication Risk-Taking Behavior in Functional Dyspepsia Patients
 Citation: (2015) 6, e69; doi:10.1038/ctg.2014.18 & 2015 the American College of Gastroenterology All rights reserved 2155-384X/15 www.nature.com/ctg Medication Risk-Taking Behavior in Functional Dyspepsia
Citation: (2015) 6, e69; doi:10.1038/ctg.2014.18 & 2015 the American College of Gastroenterology All rights reserved 2155-384X/15 www.nature.com/ctg Medication Risk-Taking Behavior in Functional Dyspepsia
Functional Dyspepsia
 Functional Dyspepsia American College of Gastroenterology Boston Massachusetts, June 2015 Brian E. Lacy, PhD, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Chief, Section of Gastroenterology
Functional Dyspepsia American College of Gastroenterology Boston Massachusetts, June 2015 Brian E. Lacy, PhD, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Chief, Section of Gastroenterology
Outline. Definition (s) Epidemiology Pathophysiology Management With an emphasis on recent developments
 Chronic Dyspepsia Eamonn M M Quigley MD FRCP FACP MACG FRCPI Lynda K and David M Underwood Center for Digestive Disorders Houston Methodist Hospital Houston, Texas Outline Definition (s) Epidemiology Pathophysiology
Chronic Dyspepsia Eamonn M M Quigley MD FRCP FACP MACG FRCPI Lynda K and David M Underwood Center for Digestive Disorders Houston Methodist Hospital Houston, Texas Outline Definition (s) Epidemiology Pathophysiology
Management of Functional Dyspepsia (FD)
 Management of Functional Dyspepsia (FD) Amy S. Oxentenko, MD, FACG Program Director and Associate Chair, IM Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic, Rochester Outline Define functional dyspepsia (FD)
Management of Functional Dyspepsia (FD) Amy S. Oxentenko, MD, FACG Program Director and Associate Chair, IM Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic, Rochester Outline Define functional dyspepsia (FD)
Functional Heartburn and Dyspepsia
 Functional Heartburn and Dyspepsia Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina Objectives Understand the means of diagnosing functional heartburn
Functional Heartburn and Dyspepsia Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina Objectives Understand the means of diagnosing functional heartburn
Real World Efficacy and Tolerability of Acotiamide in Relieving Multiple and Overlapping Symptoms in Patients of Functional Dyspepsia
 Archives of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Volume 1, Issue 1, 2018, PP: 1-6 Real World Efficacy and Tolerability of Acotiamide in Relieving Multiple and Overlapping Symptoms in Varsha Narayanan 1 *, Shailesh
Archives of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Volume 1, Issue 1, 2018, PP: 1-6 Real World Efficacy and Tolerability of Acotiamide in Relieving Multiple and Overlapping Symptoms in Varsha Narayanan 1 *, Shailesh
Alternating bowel pattern: what do people mean?
 Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Alternating bowel pattern: what do people mean? R. S. CHOUNG*, G. R. LOCKE III*, A. R. ZINSMEISTER, L.J.MELTONIIIà &N.J.TALLEY* *Dyspepsia Center and Division of
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Alternating bowel pattern: what do people mean? R. S. CHOUNG*, G. R. LOCKE III*, A. R. ZINSMEISTER, L.J.MELTONIIIà &N.J.TALLEY* *Dyspepsia Center and Division of
pissn: eissn: Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility
 JNM J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 18 No. 3 July, 2012 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 http://dx.doi.org/10.5056/jnm.2012.18.3.284 Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility Original Article The
JNM J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 18 No. 3 July, 2012 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 http://dx.doi.org/10.5056/jnm.2012.18.3.284 Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility Original Article The
Mehr über EFT - und wie Sie die Methode erfolgreich anwenden lernen können:
 The Effects of EFT on Long-Term Psychological Symptoms Jack E. Rowe Texas A&M University - Kingsville Abstract Previous research (Salas, 2000; Wells, et al., 2003), theoretical writings (Arenson, 2001,
The Effects of EFT on Long-Term Psychological Symptoms Jack E. Rowe Texas A&M University - Kingsville Abstract Previous research (Salas, 2000; Wells, et al., 2003), theoretical writings (Arenson, 2001,
pissn: eissn: Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility
 JNM J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 24 No. 2 April, 218 pissn: 293-879 eissn: 293-887 https://doi.org/.556/jnm1798 Original Article Self-reported Sleep Impairment in Functional Dyspepsia and Irritable
JNM J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 24 No. 2 April, 218 pissn: 293-879 eissn: 293-887 https://doi.org/.556/jnm1798 Original Article Self-reported Sleep Impairment in Functional Dyspepsia and Irritable
Setting The setting was primary care. The economic study was conducted in Canada.
 Treating Helicobacter pylori infection in primary care patients with uninvestigated dyspepsia: the Canadian adult dyspepsia empiric treatment - Helicobacter pylori positive (CADET-Hp) randomised controlled
Treating Helicobacter pylori infection in primary care patients with uninvestigated dyspepsia: the Canadian adult dyspepsia empiric treatment - Helicobacter pylori positive (CADET-Hp) randomised controlled
Prevalence of Temporomandibular Disorder Diagnoses and Psychologic Status in Croatian patients
 Prevalence of Temporomandibular Disorder Diagnoses and Psychologic Status in Croatian patients Robert ΔeliÊ 1 Samuel Dworkin 2 Vjekoslav Jerolimov 1 Mirela Maver -BiπÊanin 3 Milica Julia Bago 4 1 Department
Prevalence of Temporomandibular Disorder Diagnoses and Psychologic Status in Croatian patients Robert ΔeliÊ 1 Samuel Dworkin 2 Vjekoslav Jerolimov 1 Mirela Maver -BiπÊanin 3 Milica Julia Bago 4 1 Department
Study of psychological health of healthy volunteers by symptom checklist 90 (SCL-90) and eysenck personality questionnaire (EPQ).
 Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (5): 901-905 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Study of psychological health of healthy volunteers by symptom checklist 90 (SCL-90) and eysenck personality questionnaire (EPQ).
Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (5): 901-905 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Study of psychological health of healthy volunteers by symptom checklist 90 (SCL-90) and eysenck personality questionnaire (EPQ).
The speed of eating and functional dyspepsia
 Original Article * CABM, FRCP, FACP MD JFac Med Baghdad 2016; Vol.58, No.4 Receive June. 2016 Accepted Nov..2016 Introduction: Abstract: Background: dyspepsia is a common complaint, affecting about 26-41%
Original Article * CABM, FRCP, FACP MD JFac Med Baghdad 2016; Vol.58, No.4 Receive June. 2016 Accepted Nov..2016 Introduction: Abstract: Background: dyspepsia is a common complaint, affecting about 26-41%
PSYCHOPATHOLOGY IN MOTHERS OF CHILDREN WITH GLOBAL DEVELOPMENTAL DELAY DUE TO SPASTIC DIPLEGIA
 Asian Journal of Medical Science, Volume-5(2014) PSYCHOPATHOLOGY IN MOTHERS OF CHILDREN WITH GLOBAL DEVELOPMENTAL DELAY DUE TO SPASTIC DIPLEGIA ORIGINAL ARTICLE,Vol-5 No.2 http://nepjol.info/index.php/ajms
Asian Journal of Medical Science, Volume-5(2014) PSYCHOPATHOLOGY IN MOTHERS OF CHILDREN WITH GLOBAL DEVELOPMENTAL DELAY DUE TO SPASTIC DIPLEGIA ORIGINAL ARTICLE,Vol-5 No.2 http://nepjol.info/index.php/ajms
Quality of life in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease in an Iranian population
 Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench. 2013 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases ORIGINAL ARTICLE Quality of life in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench. 2013 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases ORIGINAL ARTICLE Quality of life in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease
Internet Addiction and Psychological Well-being among Youth of Kashmir
 The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 3, Issue 3, No.3, DIP: 18.01.040/20160303 ISBN: 978-1-365-03419-0 http://www.ijip.in April - June, 2016 Internet
The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 3, Issue 3, No.3, DIP: 18.01.040/20160303 ISBN: 978-1-365-03419-0 http://www.ijip.in April - June, 2016 Internet
FUNCTIONAL GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS: RELATIONS BETWEEN PSYCHOSOCIAL FACTORS, SYMPTOMS AND SENSORIMOTOR DISTURBANCE
 FUNCTIONAL GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS: RELATIONS BETWEEN PSYCHOSOCIAL FACTORS, SYMPTOMS AND SENSORIMOTOR DISTURBANCE ETHELLE JEANETTE BENNETT BA (HONS) A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements
FUNCTIONAL GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS: RELATIONS BETWEEN PSYCHOSOCIAL FACTORS, SYMPTOMS AND SENSORIMOTOR DISTURBANCE ETHELLE JEANETTE BENNETT BA (HONS) A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements
Journal of Science and today's world 2013, volume 2, issue 5, pages: Mental Health Levels in IBS, IBD and Healthy People: a Comparative Study
 Scholar Journal Available online: www.journalsci.com Journal of Science and today's world ISSN 2322-326X Research Article Mental Health Levels in IBS, IBD and Healthy People: a Comparative Study Majid
Scholar Journal Available online: www.journalsci.com Journal of Science and today's world ISSN 2322-326X Research Article Mental Health Levels in IBS, IBD and Healthy People: a Comparative Study Majid
JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility
 JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 21 No. 2 April, 2015 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 http://dx.doi.org/10.5056/jnm14116 Original Article The Effect
JNM Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 21 No. 2 April, 2015 pissn: 2093-0879 eissn: 2093-0887 http://dx.doi.org/10.5056/jnm14116 Original Article The Effect
Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome according to different diagnostic criteria in a non-selected adult population
 https://helda.helsinki.fi Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome according to different diagnostic criteria in a non-selected adult population Hillilä, M. T. 2004-08-01 Hillilä, M T & Färkkilä, MA 2004,
https://helda.helsinki.fi Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome according to different diagnostic criteria in a non-selected adult population Hillilä, M. T. 2004-08-01 Hillilä, M T & Färkkilä, MA 2004,
Current status of functional dyspepsia in Korea
 REVIEW Korean J Intern Med 2014;29:156-165 Current status of functional dyspepsia in Korea Hyuk Lee 1, Hye-Kyung Jung 2, Kyu Chan Huh 3, and Functional Dyspepsia Study Group in the Korean Society of Neurogastroenterology
REVIEW Korean J Intern Med 2014;29:156-165 Current status of functional dyspepsia in Korea Hyuk Lee 1, Hye-Kyung Jung 2, Kyu Chan Huh 3, and Functional Dyspepsia Study Group in the Korean Society of Neurogastroenterology
A Community-Based, Controlled Study of the Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Dyspepsia
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2004;2:985 996 A Community-Based, Controlled Study of the Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Dyspepsia EMMA JANET CASTILLO,* MICHAEL CAMILLERI,* G. RICHARD LOCKE
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2004;2:985 996 A Community-Based, Controlled Study of the Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Dyspepsia EMMA JANET CASTILLO,* MICHAEL CAMILLERI,* G. RICHARD LOCKE
Reliability and Validity of the Chinese Translation of Insomnia Severity Index and Comparison with Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index
 ORIGINAL PAPER Reliability and Validity of the Chinese Translation of Insomnia Severity Index and Comparison with Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index Shapour BA 1, Gang CK 2 1 Complementary Medicine Research
ORIGINAL PAPER Reliability and Validity of the Chinese Translation of Insomnia Severity Index and Comparison with Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index Shapour BA 1, Gang CK 2 1 Complementary Medicine Research
The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011
 DOI 10.1186/s40880-015-0042-6 REVIEW Open Access The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011 Wanqing Chen *, Rongshou Zheng, Hongmei Zeng and Siwei Zhang Abstract Introduction:
DOI 10.1186/s40880-015-0042-6 REVIEW Open Access The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011 Wanqing Chen *, Rongshou Zheng, Hongmei Zeng and Siwei Zhang Abstract Introduction:
Agomelatine Efficacy in Treating First-Episode Senile Depression
 JPBS Article Agomelatine Efficacy in Treating First-Episode Senile Depression Juan Niu 1 *, Xiaoqin Chen 2, Tiantian Zhou 2, Yang Yu 3 1 Psychological Clinic of the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University,
JPBS Article Agomelatine Efficacy in Treating First-Episode Senile Depression Juan Niu 1 *, Xiaoqin Chen 2, Tiantian Zhou 2, Yang Yu 3 1 Psychological Clinic of the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University,
Original Article Anxiety and depression are associated with increased counts and degranulation of duodenal mast cells in functional dyspepsia
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(5):8010-8014 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0006959 Original Article Anxiety and depression are associated with increased counts and degranulation of duodenal mast cells in
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(5):8010-8014 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0006959 Original Article Anxiety and depression are associated with increased counts and degranulation of duodenal mast cells in
Impact of functional gastrointestinal disorders on health-related quality of life: a population-based case control study
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2004; 19: 233 242. doi: 10.1111/j.0269-2813.2004.01807.x Impact of functional gastrointestinal disorders on health-related quality of life: a population-based case control study
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2004; 19: 233 242. doi: 10.1111/j.0269-2813.2004.01807.x Impact of functional gastrointestinal disorders on health-related quality of life: a population-based case control study
Impact of Shiftwork on Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Functional Dyspepsia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastroenterology & Hepatology http://dx.doi.org/./jkms... J Korean Med Sci ; : -7 Impact of Shiftwork on Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Functional Dyspepsia Hye In Kim, Sung-Ae Jung, Ju
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastroenterology & Hepatology http://dx.doi.org/./jkms... J Korean Med Sci ; : -7 Impact of Shiftwork on Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Functional Dyspepsia Hye In Kim, Sung-Ae Jung, Ju
The PPI Doesn t Work, Now What? PPI Non-responsive Dyspepsia. Disclosures
 The PPI Doesn t Work, Now What? PPI Non-responsive Dyspepsia Lana Bistritz MD FRCPC Royal Alexandra Hospital GI Update 2016 Disclosures I have no relevant financial disclosures I will be discussing off
The PPI Doesn t Work, Now What? PPI Non-responsive Dyspepsia Lana Bistritz MD FRCPC Royal Alexandra Hospital GI Update 2016 Disclosures I have no relevant financial disclosures I will be discussing off
The Association of Psychological Comorbidity with the Number of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders
 The Association of Psychological Comorbidity with the Number of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Hamidreza Roohafza 1, Ali Molaee 2, Hamid Afshar 3, Mina Mazaheri 4, Awat Feizi 5, Ammar Hassanzadeh-Keshteli
The Association of Psychological Comorbidity with the Number of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Hamidreza Roohafza 1, Ali Molaee 2, Hamid Afshar 3, Mina Mazaheri 4, Awat Feizi 5, Ammar Hassanzadeh-Keshteli
Relationship between Psychological Factors and Quality of Life in Subtypes of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 3, No. 4, December 2009, pp. 259-265 original article Relationship between Psychological Factors and Quality of Life in Subtypes of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Jung-Hwan Oh*, Tae-Suk
Gut and Liver, Vol. 3, No. 4, December 2009, pp. 259-265 original article Relationship between Psychological Factors and Quality of Life in Subtypes of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Jung-Hwan Oh*, Tae-Suk
ANXIETY AND IBS REVISITED: TEN YEARS LATER
 DOI: 10.15386/cjmed-495 Review ANXIETY AND IBS REVISITED: TEN YEARS LATER STEFAN-LUCIAN POPA, DAN LUCIAN DUMITRASCU 2nd Medical Department, Iuliu Hatieganu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Cluj-Napoca,
DOI: 10.15386/cjmed-495 Review ANXIETY AND IBS REVISITED: TEN YEARS LATER STEFAN-LUCIAN POPA, DAN LUCIAN DUMITRASCU 2nd Medical Department, Iuliu Hatieganu University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Cluj-Napoca,
The Clinical Efficacy, Evaluation and Central Mechanism Study on Acupuncture for Treating Functional Dyspepsia
 Section 2 08 Physical Methods The Clinical Efficacy, Evaluation and Central Mechanism Study on Acupuncture for Treating Functional Dyspepsia China Fanrong Liang, Ying Li, Fang Zeng, Tingting Ma, Lei Lan,
Section 2 08 Physical Methods The Clinical Efficacy, Evaluation and Central Mechanism Study on Acupuncture for Treating Functional Dyspepsia China Fanrong Liang, Ying Li, Fang Zeng, Tingting Ma, Lei Lan,
Gastrointestinal symptoms are still common in a general Western population
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastrointestinal are still common in a general Western population L.A.S. van Kerkhoven *, T. Eikendal, R.J.F. Laheij, M.G.H. van Oijen, J.B.M.J. Jansen Department of Gastroenterology &
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastrointestinal are still common in a general Western population L.A.S. van Kerkhoven *, T. Eikendal, R.J.F. Laheij, M.G.H. van Oijen, J.B.M.J. Jansen Department of Gastroenterology &
Daofang Zhu, Xianming Dou, Liang Tang, Dongdong Tang, Guiyi Liao, Weihua Fang, and Xiansheng Zhang
 Hindawi BioMed Research International Volume 2017, Article ID 3473796, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3473796 Clinical Study Prevalence of Prostatitis-Like Symptoms and Outcomes of NIH-CPSI in Outpatients
Hindawi BioMed Research International Volume 2017, Article ID 3473796, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3473796 Clinical Study Prevalence of Prostatitis-Like Symptoms and Outcomes of NIH-CPSI in Outpatients
Validated questionnaire on diagnosis and symptom severity for functional constipation in the Chinese population
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005; 22: 483 488. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02621.x Validated questionnaire on diagnosis and symptom severity for functional constipation in the Chinese population A. O. O.
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005; 22: 483 488. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02621.x Validated questionnaire on diagnosis and symptom severity for functional constipation in the Chinese population A. O. O.
The Importance of Hypochondriasis in Dyspeptic Patients
 American Journal of Psychology and Behavioral Sciences 2018; 5(1): 1-9 http://www.openscienceonline.com/journal/ajpbs ISSN: 2381-5957 (Print); ISSN: 2381-5965 (Online) The Importance of Hypochondriasis
American Journal of Psychology and Behavioral Sciences 2018; 5(1): 1-9 http://www.openscienceonline.com/journal/ajpbs ISSN: 2381-5957 (Print); ISSN: 2381-5965 (Online) The Importance of Hypochondriasis
Correlates of Internalizing and Externalizing Behavior Problems: Perceived Competence, Causal Attributions, and Parental Symptoms
 Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, Vol. 19, No. 2, 1991 Correlates of Internalizing and Externalizing Behavior Problems: Perceived Competence, Causal Attributions, and Parental Symptoms Bruce E. Compas,
Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, Vol. 19, No. 2, 1991 Correlates of Internalizing and Externalizing Behavior Problems: Perceived Competence, Causal Attributions, and Parental Symptoms Bruce E. Compas,
Subgroups of Dyspepsia
 Chapter 2 Subgroups of Dyspepsia Bojan Tepeš Keywords: Dyspepsia, Organic dyspepsia, Functional dyspepsia, Diagnostic criteria, Postprandial distress syndrome, Epigastric pain syndrome Introduction Dyspepsia
Chapter 2 Subgroups of Dyspepsia Bojan Tepeš Keywords: Dyspepsia, Organic dyspepsia, Functional dyspepsia, Diagnostic criteria, Postprandial distress syndrome, Epigastric pain syndrome Introduction Dyspepsia
STUDY ON THE CORRELATION BETWEEN SELF-ESTEEM, COPING AND CLINICAL SYMPTOMS IN A GROUP OF YOUNG ADULTS: A BRIEF REPORT
 STUDY ON THE CORRELATION BETWEEN SELF-ESTEEM, COPING AND CLINICAL SYMPTOMS IN A GROUP OF YOUNG ADULTS: A BRIEF REPORT Giulia Savarese, PhD Luna Carpinelli, MA Oreste Fasano, PhD Monica Mollo, PhD Nadia
STUDY ON THE CORRELATION BETWEEN SELF-ESTEEM, COPING AND CLINICAL SYMPTOMS IN A GROUP OF YOUNG ADULTS: A BRIEF REPORT Giulia Savarese, PhD Luna Carpinelli, MA Oreste Fasano, PhD Monica Mollo, PhD Nadia
Clinical Trial Synopsis TL , NCT#
 Clinical Trial Synopsis, NCT#00492011 Title of Study: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Group Study to Evaluate the Ability of Ramelteon 1 mg, 4 mg, and 8 mg to Alleviate the Insomnia
Clinical Trial Synopsis, NCT#00492011 Title of Study: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Group Study to Evaluate the Ability of Ramelteon 1 mg, 4 mg, and 8 mg to Alleviate the Insomnia
Predictors of Cigarette Smoking Behavior Among Military University Students in Taiwan. Wang, Kwua-Yun; Yang, Chia-Chen
 The Henderson Repository is a free resource of the Honor Society of Nursing, Sigma Theta Tau International. It is dedicated to the dissemination of nursing research, researchrelated, and evidence-based
The Henderson Repository is a free resource of the Honor Society of Nursing, Sigma Theta Tau International. It is dedicated to the dissemination of nursing research, researchrelated, and evidence-based
Functional Dyspepsia, Delayed Gastric Emptying and Impaired Quality of Life
 Gut Online First, published on December 1, 2005 as 10.1136/gut.2005.078634 Functional Dyspepsia, Delayed Gastric Emptying and Impaired Quality of Life NJ Talley 1, GR Locke III 1, BD Lahr 2, AR Zinsmeister
Gut Online First, published on December 1, 2005 as 10.1136/gut.2005.078634 Functional Dyspepsia, Delayed Gastric Emptying and Impaired Quality of Life NJ Talley 1, GR Locke III 1, BD Lahr 2, AR Zinsmeister
High Prevalence of Nausea in Children With Pain-Associated Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: Are Rome Criteria Applicable?
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE: GASTROENTEROLOGY High Prevalence of Nausea in Children With Pain-Associated Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: Are Rome Criteria Applicable? Katja Kovacic, Sara Williams, B U.K. Li,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE: GASTROENTEROLOGY High Prevalence of Nausea in Children With Pain-Associated Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: Are Rome Criteria Applicable? Katja Kovacic, Sara Williams, B U.K. Li,
Original article: International Journal of Human and Health Sciences Vol. 02 No. 02 April 18
 Original article: Dyspepsia among Endoscopy Patients in Two Major Hospitals in Jordan: Correlation Psychological and Lifestyle Disorders Sumaia A. N. Shiban 1 Abstract Background: Dyspepsia is a common
Original article: Dyspepsia among Endoscopy Patients in Two Major Hospitals in Jordan: Correlation Psychological and Lifestyle Disorders Sumaia A. N. Shiban 1 Abstract Background: Dyspepsia is a common
College Smartphone Dependency: Relationships Between Social- Emotional Well-Being and Personality
 College Smartphone Dependency: Relationships Between Social- Emotional Well-Being and Personality Adam M. Volungis, Ph.D., Maria Kalpidou, Ph.D., Colleen Popores, B.S., & Mark Joyce, B.A. Presented at
College Smartphone Dependency: Relationships Between Social- Emotional Well-Being and Personality Adam M. Volungis, Ph.D., Maria Kalpidou, Ph.D., Colleen Popores, B.S., & Mark Joyce, B.A. Presented at
J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 17 No. 3 July, 2011 DOI: /jnm Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility
 ㅋ JNM J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 17 No. 3 July, 2011 DOI: 10.5056/jnm.2011.17.3.235 Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility Review Epidemiology of Uninvestigated and Functional Dyspepsia in
ㅋ JNM J Neurogastroenterol Motil, Vol. 17 No. 3 July, 2011 DOI: 10.5056/jnm.2011.17.3.235 Journal of Neurogastroenterology and Motility Review Epidemiology of Uninvestigated and Functional Dyspepsia in
June By: Reza Gholami
 ACG/CAG guideline on Management of Dyspepsia June 2017 By: Reza Gholami DEFINITION OF DYSPEPSIA AND SCOPE OF THE GUIDELINE Dyspepsia was originally defined as any symptoms referable to the upper gastrointestinal
ACG/CAG guideline on Management of Dyspepsia June 2017 By: Reza Gholami DEFINITION OF DYSPEPSIA AND SCOPE OF THE GUIDELINE Dyspepsia was originally defined as any symptoms referable to the upper gastrointestinal
FUNCTIONAL DISORDERS TREATMENT ADVANCES. Dr. Adriana Lazarescu MD FRCPC Director GI Motility Lab, Edmonton Associate Professor University of Alberta
 FUNCTIONAL DISORDERS TREATMENT ADVANCES Dr. Adriana Lazarescu MD FRCPC Director GI Motility Lab, Edmonton Associate Professor University of Alberta Name: Dr. Adriana Lazarescu Conflict of Interest Disclosure
FUNCTIONAL DISORDERS TREATMENT ADVANCES Dr. Adriana Lazarescu MD FRCPC Director GI Motility Lab, Edmonton Associate Professor University of Alberta Name: Dr. Adriana Lazarescu Conflict of Interest Disclosure
HELICOBACTER PYLORI; PATIENTS WITH FUNCTIONAL DYSPEPSIA
 The Professional Medical Journal www.theprofesional.com ORIGINAL PROF-2404 1. Associate Professor and Health Sciences, (LUMHS) 2. MD, Consultant Physician,, Medical-III, Ward 06 Liaquat University Hospital,
The Professional Medical Journal www.theprofesional.com ORIGINAL PROF-2404 1. Associate Professor and Health Sciences, (LUMHS) 2. MD, Consultant Physician,, Medical-III, Ward 06 Liaquat University Hospital,
Men report good mental health 20 to 23 years after in vitro fertilisation treatment
 Sydsjö et al. BMC Public Health (2015) 15:1175 DOI 10.1186/s12889-015-2398-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Men report good mental health 20 to 23 years after in vitro fertilisation treatment Gunilla Sydsjö
Sydsjö et al. BMC Public Health (2015) 15:1175 DOI 10.1186/s12889-015-2398-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Men report good mental health 20 to 23 years after in vitro fertilisation treatment Gunilla Sydsjö
Functionele Maagdarmklachten als Stoornissen van Gut-Brain Interacties Leiden alle wegen naar Rome IV?
 Functionele Maagdarmklachten als Stoornissen van Gut-Brain Interacties Leiden alle wegen naar Rome IV? Lukas Van Oudenhove, MD, PhD Assistant Professor (KU Leuven Special Research Fund) Laboratory for
Functionele Maagdarmklachten als Stoornissen van Gut-Brain Interacties Leiden alle wegen naar Rome IV? Lukas Van Oudenhove, MD, PhD Assistant Professor (KU Leuven Special Research Fund) Laboratory for
Prevalence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome among Medical Students and Interns in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
 Prevalence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome among Medical Students and Interns in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia Mohammed Y Hasosah 1*, Samer A Alamri 2, Faisal A Al-Husayni 2, Rakan M. Aljedaani 2, Mohammad A Zwawy
Prevalence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome among Medical Students and Interns in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia Mohammed Y Hasosah 1*, Samer A Alamri 2, Faisal A Al-Husayni 2, Rakan M. Aljedaani 2, Mohammad A Zwawy
Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome in Japan: Internet survey using Rome III criteria
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome in Japan: Internet survey using Rome III criteria Hiroto Miwa Division of Upper Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hyogo College
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome in Japan: Internet survey using Rome III criteria Hiroto Miwa Division of Upper Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Hyogo College
DANCE MOVEMENT THERAPY IMPROVES EMOTIONAL RESPONSES AND MODULATES NEUROHORMONES IN ADOLESCENTS WITH MILD DEPRESSION
 Intern. J. Neuroscience, 115:1711 1720, 2005 Copyright 2005 Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 0020-7454 / 1543-5245 online DOI: 10.1080/00207450590958574 DANCE MOVEMENT THERAPY IMPROVES EMOTIONAL RESPONSES AND
Intern. J. Neuroscience, 115:1711 1720, 2005 Copyright 2005 Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 0020-7454 / 1543-5245 online DOI: 10.1080/00207450590958574 DANCE MOVEMENT THERAPY IMPROVES EMOTIONAL RESPONSES AND
The improved cure fraction for esophageal cancer in Linzhou city
 Liu et al. BMC Cancer (2018) 18:949 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4867-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The improved cure fraction for esophageal cancer in Linzhou city Shuzheng Liu 1, Lanwei Guo 1,
Liu et al. BMC Cancer (2018) 18:949 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4867-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The improved cure fraction for esophageal cancer in Linzhou city Shuzheng Liu 1, Lanwei Guo 1,
The Impact of Gender on the Symptom Presentation and Life Quality of Patients with Erosive Esophagitis and Non-Erosive Reflux Disease
 ARC Journal of Hepatology and Gastroenterology Volume 1, Issue 1, 2016, PP 3-8 www.arcjournals.org The Impact of Gender on the Symptom Presentation and Life Quality of Patients with Erosive Esophagitis
ARC Journal of Hepatology and Gastroenterology Volume 1, Issue 1, 2016, PP 3-8 www.arcjournals.org The Impact of Gender on the Symptom Presentation and Life Quality of Patients with Erosive Esophagitis
F unctional gastrointestinal disorders (FGID) are clinical
 1445 IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME Symptom patterns in functional dyspepsia and irritable bowel syndrome: relationship to disturbances in gastric emptying and response to a nutrient challenge in consulters
1445 IRRITABLE BOWEL SYNDROME Symptom patterns in functional dyspepsia and irritable bowel syndrome: relationship to disturbances in gastric emptying and response to a nutrient challenge in consulters
Dyspepsia is a problem commonly seen by primary
 Concise Review for Clinicians Nonulcer Dyspepsia: What It Is and What It Is Not G. RICHARD LOCKE III, MD Nonulcer dyspepsiais a description of persistent or recurrent upper abdominal pain or discomfort
Concise Review for Clinicians Nonulcer Dyspepsia: What It Is and What It Is Not G. RICHARD LOCKE III, MD Nonulcer dyspepsiais a description of persistent or recurrent upper abdominal pain or discomfort
The impact of Irritable Bowel Syndrome on health-related quality of life: a Singapore perspective
 Wang et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2012, 12:104 RESEARCH ARTICLE The impact of Irritable Bowel Syndrome on health-related quality of life: a Singapore perspective Yu Tien Wang 1*, Hwee Yong Lim 2, David
Wang et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2012, 12:104 RESEARCH ARTICLE The impact of Irritable Bowel Syndrome on health-related quality of life: a Singapore perspective Yu Tien Wang 1*, Hwee Yong Lim 2, David
A Study on the Efficacy of Proton Pump Inhibitors in Helicobacter pylori- Negative Primary Care Patients with Dyspepsia in Japan
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 7, No. 1, January 2013, pp. 16-22 ORiginal Article A Study on the Efficacy of Proton Pump Inhibitors in Helicobacter pylori- Negative Primary Care Patients with Dyspepsia in Japan Tomoari
Gut and Liver, Vol. 7, No. 1, January 2013, pp. 16-22 ORiginal Article A Study on the Efficacy of Proton Pump Inhibitors in Helicobacter pylori- Negative Primary Care Patients with Dyspepsia in Japan Tomoari
The Cost Of Functional Dyspepsia Results From A Large US Employer Database
 European ISPOR Meeting Copenhagen, Denmark October 30, 2006 The Cost Of Functional Dyspepsia Results From A Large US Employer Database Researchers: Stephen George, MS, RPh 1, Nathan Kleinman, PhD 2, Richard
European ISPOR Meeting Copenhagen, Denmark October 30, 2006 The Cost Of Functional Dyspepsia Results From A Large US Employer Database Researchers: Stephen George, MS, RPh 1, Nathan Kleinman, PhD 2, Richard
Our evidence. Your expertise. SmartPill : The data you need to evaluate motility disorders.
 Our evidence. Your expertise. SmartPill : The data you need to evaluate motility disorders. SmartPill benefits your practice: Convenient performed right in your office Test standardization Provides direct
Our evidence. Your expertise. SmartPill : The data you need to evaluate motility disorders. SmartPill benefits your practice: Convenient performed right in your office Test standardization Provides direct
The effectiveness of telephone reminders and SMS messages on compliance with colorectal cancer screening: an open-label, randomized controlled trial
 Page1 of 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 The effectiveness of telephone reminders and SMS messages on compliance with colorectal cancer screening: an
Page1 of 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 The effectiveness of telephone reminders and SMS messages on compliance with colorectal cancer screening: an
Grigoris Leontiadis, MD PhD. McMaster University Upper Gastrointestinal and Pancreatic Diseases Cochrane Group
 Grigoris Leontiadis, MD PhD McMaster University Upper Gastrointestinal and Pancreatic Diseases Cochrane Group No relevant financial relationships with any commercial interests CDDW/CASL Meeting Session:
Grigoris Leontiadis, MD PhD McMaster University Upper Gastrointestinal and Pancreatic Diseases Cochrane Group No relevant financial relationships with any commercial interests CDDW/CASL Meeting Session:
Antidepressant Medication use is Associated with Abdominal Symptoms in People without a Functional Gastrointestinal Diagnosis
 Antidepressant Medication use is Associated with Abdominal Symptoms in People without a Functional Gastrointestinal Diagnosis Heenan PE, Keenan JI, Roy NC, Gearry RB Introduction Functional Gastrointestinal
Antidepressant Medication use is Associated with Abdominal Symptoms in People without a Functional Gastrointestinal Diagnosis Heenan PE, Keenan JI, Roy NC, Gearry RB Introduction Functional Gastrointestinal
BRL /RSD-101C0D/1/CPMS-704. Report Synopsis
 Report Synopsis Study Title: A Randomized, Multicenter, 10-Week, Double-Blind, Placebo- Controlled, Flexible-Dose Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Paroxetine in Children and Adolescents with
Report Synopsis Study Title: A Randomized, Multicenter, 10-Week, Double-Blind, Placebo- Controlled, Flexible-Dose Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Paroxetine in Children and Adolescents with
British outpatient norms for the Brief Symptom Inventory
 183 Psychology and Psychotherapy: Theory, Research and Practice (2007), 80, 183 191 q 2007 The British Psychological Society The British Psychological Society www.bpsjournals.co.uk British outpatient norms
183 Psychology and Psychotherapy: Theory, Research and Practice (2007), 80, 183 191 q 2007 The British Psychological Society The British Psychological Society www.bpsjournals.co.uk British outpatient norms
Disclosures. GI Motility Disorders. Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome None Disclosures Jasmine Zia, MD Acting Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology, University of Washington 6 th Asian Health Symposium
Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome None Disclosures Jasmine Zia, MD Acting Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology, University of Washington 6 th Asian Health Symposium
6/25/ % 20% 50% 19% Functional Dyspepsia Peptic Ulcer GERD Cancer Other
 Peptic Ulcer Disease and Dyspepsia John M. Inadomi, MD Professor of Medicine UCSF Chief, Clinical Gastroenterology San Francisco General Hospital Case History 49 y/o woman complains of several months of
Peptic Ulcer Disease and Dyspepsia John M. Inadomi, MD Professor of Medicine UCSF Chief, Clinical Gastroenterology San Francisco General Hospital Case History 49 y/o woman complains of several months of
Validation of the Social Phobia Inventory (SPIN) in Nigeria
 Journal of Psychiatry and Psychiatric Disorders doi: 10.26502/jppd.2572-519X0040 Research Article Volume 2, Issue 2 Validation of the Social Phobia Inventory (SPIN) in Nigeria Chukwujekwu DC 1* and Olose
Journal of Psychiatry and Psychiatric Disorders doi: 10.26502/jppd.2572-519X0040 Research Article Volume 2, Issue 2 Validation of the Social Phobia Inventory (SPIN) in Nigeria Chukwujekwu DC 1* and Olose
Psychosocial conditions after occupational injury
 Psychosocial conditions after occupational injury Leon Guo, Judith Shiao, Weishan Chin National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, NHRI, Taiwan EOM, National Taiwan University and NTU Hospital
Psychosocial conditions after occupational injury Leon Guo, Judith Shiao, Weishan Chin National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, NHRI, Taiwan EOM, National Taiwan University and NTU Hospital
instrument. When 13C-UBT positive value is greater than or equal to / - 0.4, the the subject can be 1. Data and methods details are as follows:
 Application of 13 C-urea breath test in screening helicobacter pylori infection during health examination in Chengdu, Sichuan YANG Yan-hua. LIU Yu-ping. CHENG You-fu, SHUAI Ping. LU Qiao. ZHENG Xiao-xia,
Application of 13 C-urea breath test in screening helicobacter pylori infection during health examination in Chengdu, Sichuan YANG Yan-hua. LIU Yu-ping. CHENG You-fu, SHUAI Ping. LU Qiao. ZHENG Xiao-xia,
Sleep Quality and Restless Legs Syndrome among Health-care Workers: Shift Workers and Non-shift Workers
 Original Research Sleep Quality and Restless Legs Syndrome among Health-care Workers: Shift Workers and Non-shift Workers Zahra Banafsheh Alemohammad 1*, Seyed Mohammad Esmaeil Taghavi 1, Akbar Sharifian
Original Research Sleep Quality and Restless Legs Syndrome among Health-care Workers: Shift Workers and Non-shift Workers Zahra Banafsheh Alemohammad 1*, Seyed Mohammad Esmaeil Taghavi 1, Akbar Sharifian
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for the management of irritable bowel syndrome: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
 Clinical research Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for the management of irritable bowel syndrome: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials Roja Rahimi 1, Shekoufeh Nikfar 2, Mohammad Abdollahi
Clinical research Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for the management of irritable bowel syndrome: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials Roja Rahimi 1, Shekoufeh Nikfar 2, Mohammad Abdollahi
Validation of a specific quality of life questionnaire for functional digestive disorders
 Gut 1999;44:527 533 527 Service de Médecine, Hôpital Lariboisière, 75010 Paris, France O Chassany J F Bergmann C Caulin MAPI Values, 27 rue de la Villette, 69003 Lyon, France P Marquis Institut de Recherche
Gut 1999;44:527 533 527 Service de Médecine, Hôpital Lariboisière, 75010 Paris, France O Chassany J F Bergmann C Caulin MAPI Values, 27 rue de la Villette, 69003 Lyon, France P Marquis Institut de Recherche
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only.
 The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
Safety and health training model It is expected that better recognition of hazards can reduce risks to workers. Course depth and suitable teaching met
 Y.J. Hong, Y.H. Lin, H.H. Pai, et al DEVELOPING A SAFETY AND HEALTH TRAINING MODEL FOR PETROCHEMICAL WORKERS Yu-Jue Hong, Ya-Hsuan Lin, Hsiu-Hua Pai, 1 Yung-Chang Lai, 2 and I-Nong Lee 3 Institute of Public
Y.J. Hong, Y.H. Lin, H.H. Pai, et al DEVELOPING A SAFETY AND HEALTH TRAINING MODEL FOR PETROCHEMICAL WORKERS Yu-Jue Hong, Ya-Hsuan Lin, Hsiu-Hua Pai, 1 Yung-Chang Lai, 2 and I-Nong Lee 3 Institute of Public
Cognitive Function and Congenital Heart Disease Anxiety and Depression in Adults with Congenital Heart Disease
 Joint Annual Meeting of the Swiss Society of Cardiology and the Swiss Society for Cardio and Thoracic Vascular Surgery Palazzo dei Congressi Lugano: 14 June 2013 Cognitive Function and Congenital Heart
Joint Annual Meeting of the Swiss Society of Cardiology and the Swiss Society for Cardio and Thoracic Vascular Surgery Palazzo dei Congressi Lugano: 14 June 2013 Cognitive Function and Congenital Heart
Association between multiple comorbidities and self-rated health status in middle-aged and elderly Chinese: the China Kadoorie Biobank study
 Song et al. BMC Public Health (2018) 18:744 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-5632-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Association between multiple comorbidities and self-rated health status in middle-aged and elderly
Song et al. BMC Public Health (2018) 18:744 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-5632-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Association between multiple comorbidities and self-rated health status in middle-aged and elderly
Prevalence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Migraine and Co-existing IBSmigraine in Medical Students
 Prevalence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Migraine and Co-existing IBSmigraine in Medical Students Dr Rukhsana Parvin Associate Professor Department of Medicine Enam Medical College & Hospital 1. Irin
Prevalence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Migraine and Co-existing IBSmigraine in Medical Students Dr Rukhsana Parvin Associate Professor Department of Medicine Enam Medical College & Hospital 1. Irin
Does the Injection of Botulinum Toxin Improve Symptoms in Patients With Gastroparesis?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2014 Does the Injection of Botulinum Toxin
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2014 Does the Injection of Botulinum Toxin
Effects of Ramadan Fasting on Dyspepsia Symptoms
 Govaresh/ Vol. 22, No.3, Autumn 2017; 188-194. Effects of Ramadan Fasting on Dyspepsia Symptoms Hojjatolah Rahimi 1,*, Emad Fayyazi 2, Mohammad Hasan Emami 1, Alireza Fahim 1, Najmeh Tavakol 2, Sadegh
Govaresh/ Vol. 22, No.3, Autumn 2017; 188-194. Effects of Ramadan Fasting on Dyspepsia Symptoms Hojjatolah Rahimi 1,*, Emad Fayyazi 2, Mohammad Hasan Emami 1, Alireza Fahim 1, Najmeh Tavakol 2, Sadegh
Elements for a Public Summary
 VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Generalised anxiety disorder Generalised anxiety disorder (GAD) is an umbrella term that covers a wide range of anxiety disorders
VI.2 Elements for a Public Summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Generalised anxiety disorder Generalised anxiety disorder (GAD) is an umbrella term that covers a wide range of anxiety disorders
Clinical Observations on 46 Cases of Globus Hystericus Treated with Modified Banxia Houpu Decoction
 Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, June 2010, Vol. 30, No. 2 103 Clinical Observations on 46 Cases of Globus Hystericus Treated with Modified Banxia Houpu Decoction BO Ping 1, CHEN Qi-ming 2, ZHU
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, June 2010, Vol. 30, No. 2 103 Clinical Observations on 46 Cases of Globus Hystericus Treated with Modified Banxia Houpu Decoction BO Ping 1, CHEN Qi-ming 2, ZHU
Sleep Quality, Stress, and Eating Disorders: A Correlational Study
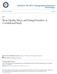 Intuition: The BYU Undergraduate Journal in Psychology Volume 11 Issue 2 Article 3 2015 Sleep Quality, Stress, and Eating Disorders: A Correlational Study Follow this and additional works at: https://scholarsarchive.byu.edu/intuition
Intuition: The BYU Undergraduate Journal in Psychology Volume 11 Issue 2 Article 3 2015 Sleep Quality, Stress, and Eating Disorders: A Correlational Study Follow this and additional works at: https://scholarsarchive.byu.edu/intuition
