Original Article mir-144 regulates transforming growth factor-β1 iduced hepatic stellate cell activation in human fibrotic liver
|
|
|
- Eustacia Lydia Hill
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(4): /ISSN: /IJCEP Original Article mir-144 regulates transforming growth factor-β1 iduced hepatic stellate cell activation in human fibrotic liver Zhiyong Liu, Jian Yi, Rong Ye, Jianping Liu, Qing Duan, Junqi Xiao, Fengen Liu Department of Vascular and Breast Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Gannan Medical University, 23 Qingnian Road, Ganzhou , China Received January 20, 2015; Accepted March 20, 2015; Epub April 1, 2015; Published April 15, 2015 Abstract: Objectives: Activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) into collagen producing myofibroblasts is critical for pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) is one of the main profibrogenic mediators for HSC transdifferentiation. Recent studies have shown effect of micrornas (mirnas) on regulating TGF-β1-induced HSC activation during liver fibrosis. Here, we aimed to explore the roles of mir-144 and mir-200c in human liver fibrosis. Methods: Expression of TGF-β1 was detected in 42 fibrotic and 18 normal human liver tissues by quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (qrt-pcr) and immunohistochemistry, and its correlation with α-smooth muscle actin (α-sma) was calculated. mir-144 and mir-200c expression level in fibrotic liver tissues were also detected by qrt-pcr. The correlation of TGF-β1 expression with mir-200c and mir-144 in the fibrotic liver was analyzed. Results: The results showed that TGF-β1 expression was much higher in fibrotic liver than that in normal liver tissues (P<0.05). TGF-β1 protein high expressing liver fibrosis showed α-sma positive cells in the liver parenchyma indicating activated HSCs. Expression of TGF-β1 in fibrotic liver was significantly correlated with α-sma expression (R=0.633, P<0.001). Furthermore, mir-144 was less expressed in liver fibrosis (P<0.05) and was significantly correlated with expression of TGF-β1 in fibrotic liver tissues (R=-0.442, P<0.01). However, mir-200c did not show significant difference between normal and fibrotic liver (P=0.48) and correlation with TGF-β1 expression (R=0.106, P=0.51). Conclusion: All the results indicate that mir-144 can be a novel regulator of TGF-β1-induced HSC activation during liver fibrosis. Keywords: Hepatic stellate cell, liver fibrosis, mir-200c, mir-144, TGF-β1 Introduction Liver fibrosis is a common outcome of virtually all chronic hepatic injuries including viral hepatitis, alcoholic or nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, autoimmune and chronic inflammatory conditions, and metabolic disorders, among others [1]. Liver fibrosis will finally lead to liver cirrhosis and liver failure. To investigate the mechanism of liver fibrosis is important to find new ways to prevent and treat it. Fibrosis is an excessive wound healing response that occurs in most forms of chronic liver disease and results in the deposition of scar tissue, such as excess extracellular matrix (ECM). Activation of collagen producing myofibroblast cells is critical for pathogenesis of liver fibrosis, which has been proved both in animal models of liver fibrosis and patients liver tissue [2]. Myofibroblast cells originate from distinct cellular sources. Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), portal fibroblasts and bone marrow-derived collagen producing cells are three cellular populations that mainly contribute to hepatic myofibroblast cells in response to chronic liver injury. Among these cellular sources, activated HSCs are the major source of myofibroblast cells in chronic toxic liver injury, such as hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [3]. Targeting hepatic stellate cell activation in chronic toxic liver injury may be an effective way preventing and treating liver fibrosis. Many cytokines, including transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), epidermal growth factor (EGF) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)
2 [4], stimulate quiescent HSCs activating into myofibroblast cells. Myofibroblast cells further secret cytokines in an autocrine and paracrine way leading to more sever fibrosis [5]. TGF-β1 is an important profibrogenic mediator, promoting HSC activation and proliferation. Absence of TGF-β1 inhibits hepatic collagen α1 mrna and α-smooth muscle actin (α-sma) protein expression and overexpression of TGF-β1 increases collagen α1 mrna and α-sma protein levels in vivo [6]. Targeting TGF-β1 could be a potential way to treat liver fibrosis. However, due to the essential roles of TGF-β1 in regulating many cellular pathways, anti-tgf-β1 therapies have to be carefully focused on specific cell types in case of producing multiple unpredictable adverse effects. Therefore, it is necessary to find some specific treatment targeting TGF-β1 in liver fibrosis. MicroRNAs (mirnas) are endogenous ~23nt RNAs that play important gene-regulatory roles in animals and plants by pairing to the mrnas of protein-coding genes to direct their posttranscriptional repression [7]. In the past few years, mirnas were found to be involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis [7]. mir- NAs also involve in promoting and suppressing HSC activation. mirnas that regulate TGFβ1 expression could be a way modulating TGFβ1- induced HSC activation in liver fibrosis. mir- 146a affects TGF-β1-induced HSC activation, overexpression of which suppresses TGFβ1- induced proliferation and increases HSC apoptosis [8]. Moreover, up-regulation of mir-200a negatively regulates TGF-β1-induced HSC activation and proliferation [9] while up-regulation of mir-200b accelerates proliferation and migration of HSC by activating PI3K/Akt signaling [10]. However, mir-200c belongs to mir-200 family and there has been no report about role of mir-200c in liver fibrosis. mir-144 is reported to be down-regulated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and one target of mir-144 is TGFβ1 according to mirtarbase [11]. Both mir-144 and mir-200c have been previously reported to be down-regulated in lung fibrosis [12, 13]. There have been no reports about whether mir- 144 and mir-200c target TGF-β1 or relate to liver fibrosis. Besides, there have been only few reports investigating role of mirnas in human liver tissues. In this study, we quantified the expression of TGF-β1 in human fibrotic liver and analyzed its correlation with HSC activation in liver fibrosis. Then we evaluated expression of mir-144 and mir-200c in human fibrotic liver and analyzed their correlation with TGF-β1. We proved mir- 144 may be involved in regulating TGF-β1- induced HSC activation in liver fibrosis. Materials and methods Patients and specimens Forty-two hepatocellular carcinoma and 18 liver metastasis patients, who underwent hepatectomy at the First Affiliated Hospital of Gannan Medical University from January 2008 to December 2013, were enrolled in this study. All non-tumor liver tissues from hepatocellular carcinoma exhibit liver fibrosis and non-tumor tissue from liver metastasis without fibrosis were taken as normal liver according to pathology report. Resected liver tissue specimens were stored at -80 C until RNA extraction. Total RNA was extracted using the TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen) in accordance with the manufacturer s instructions from non-tumor tissue of resected liver. This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Gannan Medical University. Informed consent was obtained from all patients. Real-time PCR Gene expression level was checked by quantitative reverse-transcription PCR (qrt-pcr), cd- NA for TGF-β1 and α-sma was prepared using a reverse transcription kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). cdna for mirna was reverse-transcribed by using the TaqMan MicroRNA Reverse Transcription Kit (Applied Biosystems). Primers for TGF-β1 (Hs _ m1), α-sma (Hs _g1), hsa-mir-200c (002300) and hsa-mir-144 (002676) were obtained from Applied Biosystems. GAPDH and RNU6B (Applied Biosystems) were used as endogenous controls. TaqMan gene expression assays were performed in duplicate in Taqman Array 96-well plates using the Applied Biosystems 7500 Real-Time PCR System, in accordance with the manufacturer s instructions. Immunohistochemical analysis Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections of the surgical specimens were used for TGF-β1 protein analysis. A rabbit polyclonal antibody for TGF-β1 (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO) was 3995 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(4):
3 Table 1. Clinical and Pathological Factors of All Patients Factors HCC (n=42) Meta (n=18) p value Age (median, range) 67, , Gender (male/female) 37/8 16/ Child-pugh (A/B) 44/1 21/ Liver cirrhosis NL 0 17 LF 1, LF 3, Virus Infection HBs Antigen (+/-) 36/6 1/17 HCV Antibody (+/-) 6/36 0/18 Alb (g/dl) 3.7± ± T-bil (mg/dl) 1.0± ± GOT (IU/L) 50.9± ±7.9 <0.01 GPT (IU/L) 41.7± ±7.6 <0.01 Abbreviations: HBs: hepatitis B surface; HCV: hepatitis C virus; Alb: albumin; T-bil: Total bilirubin; GPT: glutamic pyruvic transaminase; GOT: glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase; ICG: Indocyanine green; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma. used to evaluate TGF-β1 expression in liver tissues. Immunohistochemistry was performed following standard protocols, using a secondary horseradish peroxidase-tagged antibody labeled with anti-rabbit/mouse polymers (DA- KO A/S, Glostup, Denmark). Fractured bone tissue was taken as a positive control. Staining was independently evaluated by two trained pathologists. TGF-β1 expression was evaluated by positive cell number and staining intensity. Statistical analysis All statistical analyses were performed with statistical software SPSS version 21.0, (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). Experimental results are expressed as the means ± standard deviation. The Mann Whitney test or Chi-square test was used to compare values between the two groups. Correlations between TGF-β1 and α-sma, TGF-β1 and mirnas were calculated by Pearson correlation coefficients. For all statistical analyses, P<0.05 was considered significant. Results TGF-β1 is highly expressed in fibrotic liver and significantly correlates with HSC activation HSCs are activated in the fibrotic liver characterized by high expression of α-sma. Non-tumor tissues from 42 hepatocellular carcinoma patients and 18 liver metastasis patients (Table 1) were used to compare TGF-β1 and α-sma expression. Gene expression of TGF-β1 was significantly higher in the fibrotic liver tissues (P= 0.04), while expression of α-sma tended to be highly expressed (P=0.13, Figure 1A, 1B). Moreover, TGF-β1 expression in F3-F4 fibrotic liver was higher than that in F0-F2 (P<0.01, data not shown). We also compared protein expression of TGF-β1 and α-sma by immunohistochemistry. Figure 1C shows the representative staining of TGF-β1 and α-sma in two patients. α-sma is positive in the cells located at liver parenchyma in the TGF-β1 highly expressing liver tissue (Figure 1C upper). Then we compared the correlation of TGF-β1 with α-sma expression in the fibrotic liver tissues. It showed significant correlation between these two genes (R=0.633, P<0.001, Figure 1D). These results indicate TGF-β1 may induce liver fibrosis by activating HSCs. Expression of mir-200c and mir-144 in fibrotic liver tissues To investigate the possible mechanism of upregulated TGF-β1 expression in the liver fibrosis, we analyzed mir-144 and mir-200c expression in fibrotic liver tissues. We compared mir-200c and mir-144 expression nontumor tissues from HCC and liver metastasis. mir-144 showed decreased expression in fibrotic liver tissues compare to normal liver (P=0.04, Figure 2A). However, mir-200c did not show significant difference (P=0.48, Figure 2B). Correlation of mir-200c and mir-144 with TGF-β1 expression in liver fibrosis To investigate whether mir-200c or mir-144 regulates TGF-β1 expression, we calculated the correlation of mir-144 and mir-200c with TGFβ1 expression level. As shown in Figure 3A, mir-144 was significantly correlated with TGFβ1 expression (R=-0.442, P<0.01). And these correlation were even stronger in the F3-F4 fibrotic liver tissues (R=0.551, P<0.01, data not shown). However, mir-200c did not show any correlation with TGF-β1 (R=0.106, P=0.51, Figure 3B). These results demonstrate that mir-144 may regulate TGF-β1 expression in fibrotic liver Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(4):
4 Figure 1. TGF-β1 significantly correlates with hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation. mrna expression of TGF-β1 (A) and α-sma (B) in liver fibrosis and normal liver. (C) Representative immunohistochemical staining of TGF-β1 and α-sma in liver fibrosis. (D) Correlation of TGF-β1 and α-sma in liver fibrosis. Discussion Liver fibrosis, which is characterized by accumulation of ECM, is a common response to many kinds of liver injuries. During the progression of liver fibrosis, quiescent HSCs can be provoked by hepatitis B and C viruses and transdifferentiate into myofibroblast cells. Recent studies have been focused on the function of mirnas in liver fibrosis [8, 14, 15]. Our study investigated the role of mir-144 and mir-200c on TGF-β1-induced HSC activation in liver fibrosis. We confirmed TGF-β1 was up-regulated in human liver fibrosis and was correlated with HSC activation. mir-144 was down-regulated in fibrotic liver and its expression was significantly correlated with TGF-β1 expression. Quiescent HSCs reside in the space of Disse in normal liver, serving as a major storage of vitamin A. In response to hepatic injury, Kupffer cells and sinusoidal endothelial cells triggers apoptosis of hepatocytes, further inducing activation and recruitment of inflammatory cells into injured liver and differentiation of liver resident cells, such as HSC [16]. The earliest changes observed during HSCs activation result from paracrine stimulation by different cytokines, including TGF-β1, PDGF and EGF. TGF-β1 can be secreted by endothelial cells, platelets and Kupffer cells. TGF-β1 activates HSC th-rough TGF-β1/Smad signal pathway at initiating and early step during HSC activation [17]. Moreover, TGF-β1 stimulates HSCs generate fi-brosis not only by increased cell number, but also by increasing matrix production per cell [4] through a hydrogen peroxide- and C/ EBPβ-de-pendent mechanism [18]. In response to TGF-β1, HSCs undergo rapid functional and morphological changes and become collagen secreting and α-sma positive 3997 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(4):
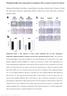
5 Figure 2. Expression of mir-200c and mir-144 in fibrotic liver tissues. A. mir-144, B. mir-200c. Figure 3. Correlation of mir-200c and mir-144 with TGF-β1 expression in fibrotic liver tissues. mir-144 was significantly correlated with TGF-β1 (A). mir-200c showed no correlation with TGF-β1 (B). myofibroblast cells. Changes in composition of ECM can further stimulated fibrogenesis and HSC activation, which strongly produce TGF-β1 to maintain its elevated level. In our study, gene expression of TGF-β1 was significantly higher in human fibrotic liver tissues. Expression of α- SMA tended to be high in fibrotic liver tissues. Immunohistochemistry showed that α-sma was positive in the liver parenchyma area in the TGF-β1 highly expressing liver tissues, indicating activation of HSCs. These results indicate that TGF-β1 expression was up-regulated during hepatitis liver injury and HSCs transdifferentiate into myofibroblast cells. The significant correlation of TGF-β1 with α-sma expression in fibrotic live indicates that TGF-β1 may induce HSC activation in liver fibrosis. Specific contribution of different mirnas in HSC has been described. mirnas play diverse roles during liver fibrosis. mir-181b could induce proliferation or migration of myofibroblastic-like HSC while others such as mir-150 and mir-146a inhibit HSC activation and proliferation by disturbing TGF-β signaling [8, 14, 19]. We investigated the role of mir-144 and mir-200c in human liver fibrosis. mir-144, one target of which is TGF-β1 according to mirtar- Base [11], was previously reported to be downregulated in lung fibrosis [12]. Previous study about mir-144 showed that mir 144 may act as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting AKT3, and mir 144 may be a potential therapeutic candidate for hepatocellular carcinoma [20]. Our results showed mir Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(4):
6 144 was down-regulated in fibrotic liver tissue compared to normal liver tissues. mir-144 expression was significantly correlated with TGF-β1 expression in liver fibrosis, indicating that it may be a regulator of TGF-β1-induced HSC activation. Besides, mir-200c belongs to mir-200 family. mir-200a and mir-200c were reduced in the lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and introduction of mir- 200c diminishes experimental pulmonary fibrosis in mice [13]. Previous study has shown that endogenous mir-200a expression was decreased in vitro in TGF-β1-induced HSC activation as well as in vivo in CCl 4 -induced rat liver fibrosis, while overexpression of mir-200a significantly inhibited α-sma activity and further affected the proliferation of TGF-β1-dependent activation of HSC, revealing the critical regulatory role of mir-200a in HSC activation [9]. In our study, mir-200c expression did not show significant difference between fibrotic and normal liver. Moreover, mir-200c did not show any correlation with TGF-β1 expression in the fibrotic liver. Our results demonstrate that mir-144, but not mir-200c, regulates TGF-β1-induced HSC activation in liver fibrosis. However, since only 42 liver fibrosis and 18 liver metastasis patients were involved in this study, our results require further validation in a prospective and large-scale clinical study. And the underlying mechanism and function of mir-144 in HSCs may be more complicated, further functional studies is required to investigate it in HSCs and rodent models. In conclusion, our results indicate that mir-144 can be a novel regulator of TGF-β1-induced HSC activation during liver fibrosis in hepatitis liver. Acknowledgements This project was supported by the 2010 Ganzhou Guiding Technology Project Grant ( ). Disclosure of conflict of interest None. Address correspondence to: Dr. Fengen Liu, Department of Vascular and Breast Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Gannan Medical University, 23 Qingnian Road, Ganzhou , China. Tel: ; Fax: ; liufengen9356@163.com References [1] Hernandez-Gea V and Friedman SL. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol 2011; 6: [2] Brenner DA, Kisseleva T, Scholten D, Paik YH, Iwaisako K, Inokuchi S, Schnabl B, Seki E, Minicis S De, Oesterreicher C, and Taura K. Origin of myofibroblasts in liver fibrosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2012; 5: S17. [3] Xu J, Liu X, Koyama Y, Wang P, Lan T, Kim IG, Kim IH, Ma HY and Kisseleva T. The types of hepatic myofibroblasts contributing to liver fibrosis of different etiologies. Front Pharmacol 2014; 5: 167. [4] Friedman SL. Hepatic stellate cells: protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol Rev 2008; 88: [5] Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology 2008; 134: [6] Hellerbrand C, Stefanovic B, Giordano F, Burchardt ER and Brenner DA. The role of TGFbeta1 in initiating hepatic stellate cell activation in vivo. J Hepatol 1999; 30: [7] Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009; 136: [8] He Y, Huang C, Sun X, Long XR, Lv XW and Li J. MicroRNA-146a modulates TGF-beta1-induced hepatic stellate cell proliferation by targeting SMAD4. Cell Signal 2012; 24: [9] Sun X, He Y, Ma TT, Huang C, Zhang L and Li J. Participation of mir-200a in TGF-beta1-mediated hepatic stellate cell activation. Mol Cell Biochem 2014; 388: [10] Xiao Y, Wang J, Chen Y, Zhou K, Wen J, Wang Y, Zhou Y, Pan W and Cai W. Up-regulation of mir- 200b in biliary atresia patients accelerates proliferation and migration of hepatic stallate cells by activating PI3K/Akt signaling. Cell Signal 2014; 26: [11] Hsu SD, Tseng YT, Shrestha S, Lin YL, Khaleel A, Chou CH, Chu CF, Huang HY, Lin CM, Ho SY, Jian TY, Lin FM, Chang TH, Weng SL, Liao KW, Liao IE, Liu CC and Huang HD. mirtarbase update 2014: an information resource for experimentally validated mirna-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 2014; 42: D [12] Xie T, Liang J, Guo R, Liu N, Noble PW and Jiang D. Comprehensive microrna analysis in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis identifies multiple sites of molecular regulation. Physiol Genomics 2011; 43: [13] Yang S, Banerjee S, de Freitas A, Sanders YY, Ding Q, Matalon S, Thannickal VJ, Abraham E and Liu G. Participation of mir-200 in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol 2012; 180: Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(4):
7 [14] Wang B, Li W, Guo K, Xiao Y, Wang Y and Fan J. mir-181b promotes hepatic stellate cells proliferation by targeting p27 and is elevated in the serum of cirrhosis patients. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2012; 421: 4-8. [15] Li ZJ, Ou-Yang PH and Han XP. Profibrotic effect of mir-33a with Akt activation in hepatic stellate cells. Cell Signal 2014; 26: [16] Malhi H, Guicciardi ME and Gores GJ. Hepatocyte death: a clear and present danger. Physiol Rev 2010; 90: [17] Dooley S, Delvoux B, Streckert M, Bonzel L, Stopa M, ten Dijke P and Gressner AM. Transforming growth factor beta signal transduction in hepatic stellate cells via Smad2/3 phosphorylation, a pathway that is abrogated during in vitro progression to myofibroblasts. TGFbeta signal transduction during transdifferentiation of hepatic stellate cells. FEBS Lett 2001; 502: [18] Garcia-Trevijano ER, Iraburu MJ, Fontana L, Dominguez-Rosales JA, Auster A, Covarrubias- Pinedo A and Rojkind M. Transforming growth factor beta1 induces the expression of alpha1(i) procollagen mrna by a hydrogen peroxide-c/ebpbeta-dependent mechanism in rat hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 1999; 29: [19] Zheng J, Lin Z, Dong P, Lu Z, Gao S, Chen X, Wu C and Yu F. Activation of hepatic stellate cells is suppressed by microrna-150. Int J Mol Med 2013; 32: [20] Cao T, Li H, Hu Y, Ma D and Cai X. mir-144 suppresses the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting E2F3. Tumour Biol 2014; 35: Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(4):
Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis in chronic liver disease
 Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis in chronic liver disease JPEMS 2014, Physiopathology Module Corentin Bessy (Nantes) _ Gabrielle Cepella (Amsterdam) _ Charly Gaisne (Angers) _ Gwladys Guilloineau (Angers)
Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis in chronic liver disease JPEMS 2014, Physiopathology Module Corentin Bessy (Nantes) _ Gabrielle Cepella (Amsterdam) _ Charly Gaisne (Angers) _ Gwladys Guilloineau (Angers)
Laura Smart 9/22/2011
 Laura Smart 9/22/2011 Fibrosis is a wound healing response in which damaged regions are encapsulated by an extracellular matrix or scar. Fibrosis develops in almost all patients with chronic liver injury
Laura Smart 9/22/2011 Fibrosis is a wound healing response in which damaged regions are encapsulated by an extracellular matrix or scar. Fibrosis develops in almost all patients with chronic liver injury
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Expression of lncrna TCONS_ in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5655-5660 Expression of lncrna TCONS_00027978 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival Q. CHEN 1, G.-D.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5655-5660 Expression of lncrna TCONS_00027978 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival Q. CHEN 1, G.-D.
MEK/ERK INHIBITORS: A PROOF-OF-CONCEPT STUDY IN LUNG FIBROSIS
 MEK/ERK INHIBITORS: A PROOF-OF-CONCEPT STUDY IN LUNG FIBROSIS Andrew Leask Departments of Dentistry and Physiology and Pharmacology University of Western Ontario Dental Sciences Building London ON Canada
MEK/ERK INHIBITORS: A PROOF-OF-CONCEPT STUDY IN LUNG FIBROSIS Andrew Leask Departments of Dentistry and Physiology and Pharmacology University of Western Ontario Dental Sciences Building London ON Canada
Understanding Root Cause: Pathogenesis of Hepatic Fibrosis
 10/1/12 Understanding Root Cause: Pathogenesis of Hepatic Fibrosis Hepatitis C Virus Mild inflammation Inflammation Fibrosis Cirrhosis 1 10/1/12 Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Steatosis Steatohepatitis
10/1/12 Understanding Root Cause: Pathogenesis of Hepatic Fibrosis Hepatitis C Virus Mild inflammation Inflammation Fibrosis Cirrhosis 1 10/1/12 Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Steatosis Steatohepatitis
Nottingham Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance
 Nottingham 2006 Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance Alastair D Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine University of Newcastle upon Tyne Collapse of reticulin
Nottingham 2006 Patterns of liver fibrosis and their clinical significance Alastair D Burt Professor of Pathology and Dean of Clinical Medicine University of Newcastle upon Tyne Collapse of reticulin
Xiao-Ling Chi, Mei-Jie Shi, Huan-Ming Xiao, Yu-Bao Xie, and Gao-Shu Cai. Correspondence should be addressed to Xiao-Ling Chi;
 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 3743427, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3743427 Research Article The Score Model Containing Chinese Medicine Syndrome
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 3743427, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3743427 Research Article The Score Model Containing Chinese Medicine Syndrome
Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis
 Any Questions??? Ask now or contact support support@sabiosciences.com 1-888-503-3187 International customers: SABio@Qiagen.com Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis Webinar related questions:
Any Questions??? Ask now or contact support support@sabiosciences.com 1-888-503-3187 International customers: SABio@Qiagen.com Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis Webinar related questions:
CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value
 Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(2):2049-2053 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0014841 Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(2):2049-2053 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0014841 Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
IL10 rs polymorphism is associated with liver cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis B
 IL10 rs1800896 polymorphism is associated with liver cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis B L.N. Cao 1, S.L. Cheng 2 and W. Liu 3 1 Kidney Disease Department of Internal Medicine, Xianyang Central Hospital,
IL10 rs1800896 polymorphism is associated with liver cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis B L.N. Cao 1, S.L. Cheng 2 and W. Liu 3 1 Kidney Disease Department of Internal Medicine, Xianyang Central Hospital,
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The manuscript by Wu et al describes critical role of RNA binding protein CUGBP1 in the development of TGF-beta-mediated liver fibrosis. The activation
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The manuscript by Wu et al describes critical role of RNA binding protein CUGBP1 in the development of TGF-beta-mediated liver fibrosis. The activation
Association between downexpression of mir-1301 and poor prognosis in patients with glioma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4298-4303 Association between downexpression of mir-1301 and poor prognosis in patients with glioma Q.-L. BAI, C.-W. HU, X.-R. WANG, G.-F.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4298-4303 Association between downexpression of mir-1301 and poor prognosis in patients with glioma Q.-L. BAI, C.-W. HU, X.-R. WANG, G.-F.
Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 5126-5131 Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients F.-M. TIAN 1, F.-Q. MENG 2, X.-B. WANG
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 5126-5131 Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients F.-M. TIAN 1, F.-Q. MENG 2, X.-B. WANG
Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal. regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation
 Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation microenvironment to promote wound repair Qing Sun 1, +, Fang Li 1, +, Hong Li 2,
Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation microenvironment to promote wound repair Qing Sun 1, +, Fang Li 1, +, Hong Li 2,
Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10276-10281 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0059849 Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10276-10281 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0059849 Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Original Article The programmed death-1 gene polymorphism (PD-1.5 C/T) is associated with non-small cell lung cancer risk in a Chinese Han population
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):5832-5836 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002117 Original Article The programmed death-1 gene polymorphism (PD-1.5 C/T) is associated with non-small cell lung cancer risk
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):5832-5836 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002117 Original Article The programmed death-1 gene polymorphism (PD-1.5 C/T) is associated with non-small cell lung cancer risk
Investigation on ERCC5 genetic polymorphisms and the development of gastric cancer in a Chinese population
 Investigation on ERCC5 genetic polymorphisms and the development of gastric cancer in a Chinese population L.Q. Yang 1, Y. Zhang 2 and H.F. Sun 3 1 Department of Gastroenterology, The Second Affiliated
Investigation on ERCC5 genetic polymorphisms and the development of gastric cancer in a Chinese population L.Q. Yang 1, Y. Zhang 2 and H.F. Sun 3 1 Department of Gastroenterology, The Second Affiliated
Association between polymorphisms in the promoter region of pri-mir-34b/c and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma
 Association between polymorphisms in the promoter region of pri-mir-34b/c and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma L.L. Chen 1,2, Y. Shen 3, J.B. Zhang 4, S. Wang 5, T. Jiang 6, M.Q. Zheng 6, Z.J. Zheng 7
Association between polymorphisms in the promoter region of pri-mir-34b/c and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma L.L. Chen 1,2, Y. Shen 3, J.B. Zhang 4, S. Wang 5, T. Jiang 6, M.Q. Zheng 6, Z.J. Zheng 7
RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
 Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Highly Effective Wound Healing Enabled by Discrete Alternative Electric Fields from A Wearable Nanogenerator
 Highly Effective Wound Healing Enabled by Discrete Alternative Electric Fields from A Wearable Nanogenerator Yin Long, 1,3 Hao Wei, 2,4 Jun Li, 1 Guang Yao, 1,3 Bo Yu, 2 Dalong Ni, 2 Angela LF Gibson,
Highly Effective Wound Healing Enabled by Discrete Alternative Electric Fields from A Wearable Nanogenerator Yin Long, 1,3 Hao Wei, 2,4 Jun Li, 1 Guang Yao, 1,3 Bo Yu, 2 Dalong Ni, 2 Angela LF Gibson,
Study of Zinc in Cirrhosis of Liver
 74 Clinical Study Study of Zinc in Cirrhosis of Liver Kaushik Kar, Assistant Professor, Gorachand Bhattyacharya, Professor Department of Biochemistry, Calcutta National Medical College, Kolkata. Jayanta
74 Clinical Study Study of Zinc in Cirrhosis of Liver Kaushik Kar, Assistant Professor, Gorachand Bhattyacharya, Professor Department of Biochemistry, Calcutta National Medical College, Kolkata. Jayanta
The lncrna MIR4435-2HG is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cancer cell proliferation by upregulating mirna-487a
 Kong et al. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2019) 24:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-019-0148-y Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters RESEARCH LETTER Open Access The lncrna MIR4435-2HG is upregulated
Kong et al. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2019) 24:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-019-0148-y Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters RESEARCH LETTER Open Access The lncrna MIR4435-2HG is upregulated
Exploring a Link Between Spy1 and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression
 University of Windsor Scholarship at UWindsor UWill Discover Undergraduate Conference UWill Discover 2016 Mar 29th, 4:00 PM - 5:00 PM Exploring a Link Between Spy1 and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression
University of Windsor Scholarship at UWindsor UWill Discover Undergraduate Conference UWill Discover 2016 Mar 29th, 4:00 PM - 5:00 PM Exploring a Link Between Spy1 and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression
Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA MEG3 serves as an unfavorable risk factor for survival of patients with breast cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 5143-5147 Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA MEG3 serves as an unfavorable risk factor for survival of patients with breast cancer
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 5143-5147 Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA MEG3 serves as an unfavorable risk factor for survival of patients with breast cancer
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Original Article Downregulation of microrna-26b functions as a potential prognostic marker for osteosarcoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(6):6506-6510 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0024531 Original Article Downregulation of microrna-26b functions as a potential prognostic marker for osteosarcoma Zhihong
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(6):6506-6510 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0024531 Original Article Downregulation of microrna-26b functions as a potential prognostic marker for osteosarcoma Zhihong
(A) [DOI] /j.issn
![(A) [DOI] /j.issn (A) [DOI] /j.issn](/thumbs/91/105634385.jpg) Med J Chin PLA, Vol. 41, No. 3, March 1, 2016 175 [ ] 30 SD 5 (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 0.206 0.514 1.028mg/(kg d) ELISA HE Masson (TGF- ) 9(MMP-9) C D E A B (P
Med J Chin PLA, Vol. 41, No. 3, March 1, 2016 175 [ ] 30 SD 5 (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 0.206 0.514 1.028mg/(kg d) ELISA HE Masson (TGF- ) 9(MMP-9) C D E A B (P
Original Article Up-regulation of mir-10a and down-regulation of mir-148b serve as potential prognostic biomarkers for osteosarcoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):186-190 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0018032 Original Article Up-regulation of mir-10a and down-regulation of mir-148b serve as potential prognostic biomarkers for
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):186-190 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0018032 Original Article Up-regulation of mir-10a and down-regulation of mir-148b serve as potential prognostic biomarkers for
LincRNA-p21 Inhibits the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells via Sponging MicroRNA-17-5p
 Original Paper 2017 The Author(s). 2017 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: April 07, 07, 2017 2017 Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 1970 Accepted: February 21, 2017 This article
Original Paper 2017 The Author(s). 2017 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: April 07, 07, 2017 2017 Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 1970 Accepted: February 21, 2017 This article
Abnormally differentiating keratinocytes in the epidermis of systemic sclerosis patients show enhanced secretion of CCN2 and S100A9
 Abnormally differentiating keratinocytes in the epidermis of systemic sclerosis patients show enhanced secretion of CCN2 and S1A9 Joanna Nikitorowicz-Buniak UCL Division of Medicine Systemic sclerosis
Abnormally differentiating keratinocytes in the epidermis of systemic sclerosis patients show enhanced secretion of CCN2 and S1A9 Joanna Nikitorowicz-Buniak UCL Division of Medicine Systemic sclerosis
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Expressions of MiR-132 in patients with chronic hepatitis B, posthepatitic cirrhosis and hepatitis. B virus (HBV)-related hepatocellular carcinoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8431-8437 Expressions of MiR-132 in patients with chronic hepatitis B, posthepatitic cirrhosis and hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8431-8437 Expressions of MiR-132 in patients with chronic hepatitis B, posthepatitic cirrhosis and hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular
CYLD Negatively Regulates Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling via Deubiquitinating Akt
 Supplementary Information CYLD Negatively Regulates Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling via Deubiquitinating Akt Jae Hyang Lim, Hirofumi Jono, Kensei Komatsu, Chang-Hoon Woo, Jiyun Lee, Masanori Miyata,
Supplementary Information CYLD Negatively Regulates Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling via Deubiquitinating Akt Jae Hyang Lim, Hirofumi Jono, Kensei Komatsu, Chang-Hoon Woo, Jiyun Lee, Masanori Miyata,
Downregulation of long non-coding RNA LINC01133 is predictive of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 2103-2107 Downregulation of long non-coding RNA LINC01133 is predictive of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients J.-H. ZHANG 1,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 2103-2107 Downregulation of long non-coding RNA LINC01133 is predictive of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients J.-H. ZHANG 1,
Aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index in children with cholestatic liver diseases to assess liver fibrosis
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2015; 57: 492-497 Original Aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index in children with cholestatic liver diseases to assess liver fibrosis Aysel Ünlüsoy-Aksu 1,
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2015; 57: 492-497 Original Aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index in children with cholestatic liver diseases to assess liver fibrosis Aysel Ünlüsoy-Aksu 1,
Lack of association between an insertion/ deletion polymorphism in IL1A and risk of colorectal cancer
 Lack of association between an insertion/ deletion polymorphism in IL1A and risk of colorectal cancer H. Yan 1 *, R. Sun 2 *, X. Pan 3, Z. Li 4, X. Guo 5 and L. Gao 6 1 Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery,
Lack of association between an insertion/ deletion polymorphism in IL1A and risk of colorectal cancer H. Yan 1 *, R. Sun 2 *, X. Pan 3, Z. Li 4, X. Guo 5 and L. Gao 6 1 Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery,
Clinical value of combined detection of mir 1202 and mir 195 in early diagnosis of cervical cancer
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 17: 3387-3391, 2019 Clinical value of combined detection of mir 1202 and mir 195 in early diagnosis of cervical cancer XIELAN YANG 1, ZHILING YAN 1, HONGYING YANG 1, HUIJING NI 1, LEI
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 17: 3387-3391, 2019 Clinical value of combined detection of mir 1202 and mir 195 in early diagnosis of cervical cancer XIELAN YANG 1, ZHILING YAN 1, HONGYING YANG 1, HUIJING NI 1, LEI
Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis
 Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis S.-W. Wen 1, Y.-F. Zhang 1, Y. Li 1, Z.-X. Liu 2, H.-L. Lv 1, Z.-H. Li 1, Y.-Z. Xu 1, Y.-G. Zhu 1 and Z.-Q. Tian 1 1 Department of
Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis S.-W. Wen 1, Y.-F. Zhang 1, Y. Li 1, Z.-X. Liu 2, H.-L. Lv 1, Z.-H. Li 1, Y.-Z. Xu 1, Y.-G. Zhu 1 and Z.-Q. Tian 1 1 Department of
Research Article Expression and Clinical Significance of the Novel Long Noncoding RNA ZNF674-AS1 in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 3608914, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3608914 Research Article Expression and Clinical Significance of the Novel Long Noncoding RNA ZNF674-AS1
BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 3608914, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3608914 Research Article Expression and Clinical Significance of the Novel Long Noncoding RNA ZNF674-AS1
Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 A B mir-141, human cell lines mir-2c, human cell lines mir-141, hepatocytes mir-2c, hepatocytes Relative RNA.1.8.6.4.2 Relative RNA.3.2.1 Relative RNA 1.5 1..5 Relative RNA 2. 1.5
Supplementary Figure 1 A B mir-141, human cell lines mir-2c, human cell lines mir-141, hepatocytes mir-2c, hepatocytes Relative RNA.1.8.6.4.2 Relative RNA.3.2.1 Relative RNA 1.5 1..5 Relative RNA 2. 1.5
MicroRNA-132 inhibits migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating TGFβ1/Smad2 in human non-small cell lung cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences MicroRNA-132 inhibits migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating TGFβ1/Smad2 in human non-small cell lung cancer J.-X.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences MicroRNA-132 inhibits migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating TGFβ1/Smad2 in human non-small cell lung cancer J.-X.
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
contributes to reversal of biliary fibrosis by Popov et al.
 Supplementary data to MS Macrophage-mediated phagocytosis of apoptotic cholangiocytes contributes to reversal of biliary fibrosis by Popov et al. Supplementary table 1. Primers and probes used in quantitative
Supplementary data to MS Macrophage-mediated phagocytosis of apoptotic cholangiocytes contributes to reversal of biliary fibrosis by Popov et al. Supplementary table 1. Primers and probes used in quantitative
Supplemental Data. TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim.
 Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Original Article TET3 mediates the activation of human hepatic stellate cells via modulating the expression of long non-coding RNA HIF1A-AS1
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(11):7744-7751 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0002339 Original Article TET3 mediates the activation of human hepatic stellate cells via modulating the expression of long
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(11):7744-7751 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0002339 Original Article TET3 mediates the activation of human hepatic stellate cells via modulating the expression of long
Analysis of circulating long non-coding RNA UCA1 as potential biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of osteosarcoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 498-503 Analysis of circulating long non-coding RNA UCA1 as potential biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of osteosarcoma J.-J. WEN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 498-503 Analysis of circulating long non-coding RNA UCA1 as potential biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of osteosarcoma J.-J. WEN
Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis
 Author's response to reviews Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis Authors: Mei-Yin Zhang (zhangmy@sysucc.org.cn) Shu-Hong
Author's response to reviews Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis Authors: Mei-Yin Zhang (zhangmy@sysucc.org.cn) Shu-Hong
Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients
 1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p.
 Title Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma Author(s) Ma, NF; Lau, SH; Hu, L; Dong, SS; Guan, XY Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p. 44-47
Title Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma Author(s) Ma, NF; Lau, SH; Hu, L; Dong, SS; Guan, XY Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p. 44-47
Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4688-4693 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0047128 Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer Jun Ma, Xiaokun
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4688-4693 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0047128 Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer Jun Ma, Xiaokun
The Enhancement of Toxin-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Fatty Liver Disease. Ekihiro Seki, M.D.,Ph.D. University of California San Diego
 The Enhancement of Toxin-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Fatty Liver Disease Ekihiro Seki, M.D.,Ph.D. University of California San Diego - A manufactured chemical. - Does not exist naturally. Carbon tetrachloride
The Enhancement of Toxin-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Fatty Liver Disease Ekihiro Seki, M.D.,Ph.D. University of California San Diego - A manufactured chemical. - Does not exist naturally. Carbon tetrachloride
Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with
 Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with DMN Immunohistochemistry for hepcidin and H&E staining (left). qrt-pcr assays for hepcidin in the liver (right).
Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with DMN Immunohistochemistry for hepcidin and H&E staining (left). qrt-pcr assays for hepcidin in the liver (right).
ratio in patients treated by sorafenib alone decreased after treatment (P<0.05), while CD 8
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):4625-4629 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0015836 Original Article Effect of sorafenib combined with CIK cell treatment on immunity and adverse events in patients with late-stage
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):4625-4629 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0015836 Original Article Effect of sorafenib combined with CIK cell treatment on immunity and adverse events in patients with late-stage
mir-125a-5p expression is associated with the age of breast cancer patients
 mir-125a-5p expression is associated with the age of breast cancer patients H. He 1 *, F. Xu 2 *, W. Huang 1, S.Y. Luo 1, Y.T. Lin 1, G.H. Zhang 1, Q. Du 1 and R.H. Duan 1 1 The State Key Laboratory of
mir-125a-5p expression is associated with the age of breast cancer patients H. He 1 *, F. Xu 2 *, W. Huang 1, S.Y. Luo 1, Y.T. Lin 1, G.H. Zhang 1, Q. Du 1 and R.H. Duan 1 1 The State Key Laboratory of
A meta-analysis of the effect of microrna-34a on the progression and prognosis of gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8281-8287 A meta-analysis of the effect of microrna-34a on the progression and prognosis of gastric cancer Z. LI 1, Z.-M. LIU 2, B.-H.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8281-8287 A meta-analysis of the effect of microrna-34a on the progression and prognosis of gastric cancer Z. LI 1, Z.-M. LIU 2, B.-H.
Original Article Association of serum microrna-125b and HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma in Chinese Han patients
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(4):3699-3703 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0072426 Original Article Association of serum microrna-125b and HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma in Chinese Han patients Lijuan
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(4):3699-3703 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0072426 Original Article Association of serum microrna-125b and HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma in Chinese Han patients Lijuan
Original Article Pre-miR-149 rs polymorphism is associated with increased cancer risk and AKT1/cyclinD1 signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(8):13628-13633 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0012040 Original Article Pre-miR-149 rs71428439 polymorphism is associated with increased cancer risk and AKT1/cyclinD1 signaling
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(8):13628-13633 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0012040 Original Article Pre-miR-149 rs71428439 polymorphism is associated with increased cancer risk and AKT1/cyclinD1 signaling
Immunological Lung Diseases
 Emphysema and Fibrosis Universitätsklinik für Pneumologie Prof. Thomas Geiser Head Div. of Pulmonary Medicine and Laboratory of Lung Research, MU50 thomas.geiser@insel.ch The healthy lung: The pathway
Emphysema and Fibrosis Universitätsklinik für Pneumologie Prof. Thomas Geiser Head Div. of Pulmonary Medicine and Laboratory of Lung Research, MU50 thomas.geiser@insel.ch The healthy lung: The pathway
Correlation between expression levels of PTEN and p53 genes and the clinical features of HBsAg-positive liver cancer
 JBUON 2017; 22(4): 942-946 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation between expression levels of PTEN and p53 genes and the
JBUON 2017; 22(4): 942-946 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation between expression levels of PTEN and p53 genes and the
95% CI: , P=0.037).
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9248-9252 Reduced expression level of mir-205 predicts poor prognosis in Qiang Yang 1*#, Peng Sun 2#, Haotian Feng 1, Xin Li 1, Jianmin Li 1 1 Department of Orthopedics,
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9248-9252 Reduced expression level of mir-205 predicts poor prognosis in Qiang Yang 1*#, Peng Sun 2#, Haotian Feng 1, Xin Li 1, Jianmin Li 1 1 Department of Orthopedics,
Original Article Application of AFP whole blood one-step rapid detection kit in screening for HCC in Qidong
 Am J Cancer Res 2017;7(6):1384-1388 www.ajcr.us /ISSN:2156-6976/ajcr0048028 Original Article Application of AFP whole blood one-step rapid detection kit in screening for HCC in Qidong Jie Jin 1*, Xiao-yan
Am J Cancer Res 2017;7(6):1384-1388 www.ajcr.us /ISSN:2156-6976/ajcr0048028 Original Article Application of AFP whole blood one-step rapid detection kit in screening for HCC in Qidong Jie Jin 1*, Xiao-yan
Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 82-86 Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma P.-Q. WANG, Y.-X.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 82-86 Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma P.-Q. WANG, Y.-X.
Original Article The expression of MMP19 and its clinical significance in glioma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(11):5407-5412 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0085570 Original Article The expression of MMP19 and its clinical significance in glioma Qisheng Luo 1,2*, Hongcheng Luo 3*,
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(11):5407-5412 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0085570 Original Article The expression of MMP19 and its clinical significance in glioma Qisheng Luo 1,2*, Hongcheng Luo 3*,
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy
 Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Loureirin B inhibits the proliferation of hepatic stellate cells and the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by regulating mir-148-3p
 Hu et al. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2018) 23:35 https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-018-0098-9 Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters RESEARCH Open Access Loureirin B inhibits the proliferation of
Hu et al. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2018) 23:35 https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-018-0098-9 Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters RESEARCH Open Access Loureirin B inhibits the proliferation of
Long-term Clinical Outcomes and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with HBsAg Seroclearance
 Long-term Clinical Outcomes and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with HBsAg Seroclearance Gi-Ae Kim, Han Chu Lee *, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim,
Long-term Clinical Outcomes and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients with HBsAg Seroclearance Gi-Ae Kim, Han Chu Lee *, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim,
Original Article Expression of HDAC4 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its correlation with prognosis
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(11):12171-12177 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0025970 Original Article Expression of HDAC4 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its correlation with prognosis Xiaoyan Zhang
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(11):12171-12177 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0025970 Original Article Expression of HDAC4 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its correlation with prognosis Xiaoyan Zhang
Portal Fibroblasts in Biliary Fibrosis
 Curr Pathobiol Rep (2014) 2:185 190 DOI 10.1007/s40139-014-0054-y MYOFIBROBLAST (TATIANA KISSELEVA, SECTION EDITOR) Portal Fibroblasts in Biliary Fibrosis Rebecca G. Wells Published online: 14 September
Curr Pathobiol Rep (2014) 2:185 190 DOI 10.1007/s40139-014-0054-y MYOFIBROBLAST (TATIANA KISSELEVA, SECTION EDITOR) Portal Fibroblasts in Biliary Fibrosis Rebecca G. Wells Published online: 14 September
Stimulating healthy tissue regeneration by targeting the 5-HT 2B receptor in chronic liver disease.
 Stimulating healthy tissue regeneration by targeting the 5-HT 2B receptor in chronic liver disease. Mohammad R Ebrahimkhani, Fiona Oakley, Lindsay B Murphy, Jelena Mann, Anna Moles, Maria J Perugorria,
Stimulating healthy tissue regeneration by targeting the 5-HT 2B receptor in chronic liver disease. Mohammad R Ebrahimkhani, Fiona Oakley, Lindsay B Murphy, Jelena Mann, Anna Moles, Maria J Perugorria,
Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by regulating EZH2 and repressing E-cadherin in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 JBUON 2018; 23(1): 157-162 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis
JBUON 2018; 23(1): 157-162 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis
Interface hepatitis in PBC: Prognostic marker and therapeutic target
 Interface hepatitis in PBC: Prognostic marker and therapeutic target Raoul Poupon Service d Hépatologie, Hôpital Saint-Antoine, Paris Faculté de Médecine Pierre & Marie Curie, Paris Key features of
Interface hepatitis in PBC: Prognostic marker and therapeutic target Raoul Poupon Service d Hépatologie, Hôpital Saint-Antoine, Paris Faculté de Médecine Pierre & Marie Curie, Paris Key features of
Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006
 Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006 Xiao-Pan Li 1, Guang-Wen Cao 2, Qiao
Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006 Xiao-Pan Li 1, Guang-Wen Cao 2, Qiao
Original Article Down-regulation of tissue microrna-126 was associated with poor prognosis in patients with cutaneous melanoma
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(3):4297-4301 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0004684 Original Article Down-regulation of tissue microrna-126 was associated with poor prognosis in patients with cutaneous Nengxing
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(3):4297-4301 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0004684 Original Article Down-regulation of tissue microrna-126 was associated with poor prognosis in patients with cutaneous Nengxing
Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients
 Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients S. Yang, B. Chen, J. Shi, F. Chen, J. Zhang and Z. Sun Department of Nephrology, Huaihe Hospital
Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients S. Yang, B. Chen, J. Shi, F. Chen, J. Zhang and Z. Sun Department of Nephrology, Huaihe Hospital
Liver Fibrosis: Which Mechanisms Matter?
 REVIEW Liver Fibrosis: Which Mechanisms Matter? Ralf Weiskirchen, Ph.D.,* and Frank Tacke, M.D., Ph.D. HEPATIC FIBROSIS Historically, fibrosis was defined by a World Health Organization expert group in
REVIEW Liver Fibrosis: Which Mechanisms Matter? Ralf Weiskirchen, Ph.D.,* and Frank Tacke, M.D., Ph.D. HEPATIC FIBROSIS Historically, fibrosis was defined by a World Health Organization expert group in
mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer
 mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer X.X. Wang 1, S.J. Ge 2, X.L. Wang 2, L.X. Jiang 1, M.F. Sheng 2 and J.J. Ma 2 1 Department of General Surgery,
mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer X.X. Wang 1, S.J. Ge 2, X.L. Wang 2, L.X. Jiang 1, M.F. Sheng 2 and J.J. Ma 2 1 Department of General Surgery,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Jun Zheng 1, Rong-chun Xing 1, Wei-hong Zheng 2, Wei Liu 1, Ru-cheng Yao 1, Xiao-song Li 1, Jian-ping Du 1, Lin Li 1.
 JBUON 2017; 22(3): 709-713 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE A comparative study on postoperative mortality prediction of SFLI scoring
JBUON 2017; 22(3): 709-713 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE A comparative study on postoperative mortality prediction of SFLI scoring
Effects of VEGF/VEGFR/K-ras signaling pathways on mirna21 levels in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues in rats
 Effects of VEGF/VEGFR/K-ras signaling pathways on mirna21 levels in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues in rats J.Z. Gao 1,2 *, Y.L. Wang 1 *, J. Li 2 and L.X. Wei 2 1 Medical College, Xinxiang Medical University,
Effects of VEGF/VEGFR/K-ras signaling pathways on mirna21 levels in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues in rats J.Z. Gao 1,2 *, Y.L. Wang 1 *, J. Li 2 and L.X. Wei 2 1 Medical College, Xinxiang Medical University,
Accepted Manuscript. Unexpected high incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C in the era of DAAs: too alarming?
 Accepted Manuscript Unexpected high incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C in the era of DAAs: too alarming? Qing-Lei Zeng, Zhi-Qin Li, Hong-Xia Liang, Guang-Hua Xu, Chun-Xia
Accepted Manuscript Unexpected high incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C in the era of DAAs: too alarming? Qing-Lei Zeng, Zhi-Qin Li, Hong-Xia Liang, Guang-Hua Xu, Chun-Xia
Clinical significance of serum mir-21 in breast cancer compared with CA153 and CEA
 Original Article Clinical significance of serum mir-21 in breast cancer compared with CA153 and CEA Jianjian Gao, Qingyun Zhang, Jianjun Xu, Lijuan Guo, Xuefeng Li Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and
Original Article Clinical significance of serum mir-21 in breast cancer compared with CA153 and CEA Jianjian Gao, Qingyun Zhang, Jianjun Xu, Lijuan Guo, Xuefeng Li Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and
Long non-coding RNA CCHE1 overexpression predicts a poor prognosis for cervical cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 20: 479-483 Long non-coding RNA CCHE1 overexpression predicts a poor prognosis for cervical cancer Y. CHEN, C.-X. WANG, X.-X. SUN, C. WANG,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 20: 479-483 Long non-coding RNA CCHE1 overexpression predicts a poor prognosis for cervical cancer Y. CHEN, C.-X. WANG, X.-X. SUN, C. WANG,
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
Original Article Increased LincRNA ROR is association with poor prognosis for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4654-4660 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0048142 Original Article Increased LincRNA ROR is association with poor prognosis for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4654-4660 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0048142 Original Article Increased LincRNA ROR is association with poor prognosis for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients
Cirrhosis is different from Fibrosis
 Riunione Monotematica AISF 2016 «The Future of Liver Disease: Beyond HCV is there a Role for Hepatologist» Milan 13 th -14 th 2016 Cirrhosis is different from Fibrosis I have not disclosures to declare
Riunione Monotematica AISF 2016 «The Future of Liver Disease: Beyond HCV is there a Role for Hepatologist» Milan 13 th -14 th 2016 Cirrhosis is different from Fibrosis I have not disclosures to declare
Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(4):4241-4246 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0012296 Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer Hong Jiang,
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(4):4241-4246 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0012296 Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer Hong Jiang,
Original Article Reduced expression of mir-506 in glioma is associated with advanced tumor progression and unfavorable prognosis
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):181-185 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0017823 Original Article Reduced expression of mir-506 in glioma is associated with advanced tumor progression and unfavorable
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):181-185 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0017823 Original Article Reduced expression of mir-506 in glioma is associated with advanced tumor progression and unfavorable
1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples. Major Principles:
 Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Carcinogenesis Major Principles: 1. Nonlethal genetic damage is central to
Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Carcinogenesis Major Principles: 1. Nonlethal genetic damage is central to
Chronic infections with hepatitis B and hepatitis C
 Original Article / Liver The impact of family history of hepatocellular carcinoma on its patients' survival Wing Chiu Dai, Sheung Tat Fan, Tan To Cheung, Kenneth SH Chok, Albert CY Chan, Simon HY Tsang,
Original Article / Liver The impact of family history of hepatocellular carcinoma on its patients' survival Wing Chiu Dai, Sheung Tat Fan, Tan To Cheung, Kenneth SH Chok, Albert CY Chan, Simon HY Tsang,
Influence of interleukin-18 gene polymorphisms on acute pancreatitis susceptibility in a Chinese population
 Influence of interleukin-18 gene polymorphisms on acute pancreatitis susceptibility in a Chinese population H.B. Gui 1, X.G. Du 2, Z.H. Fu 3 and X.M. Chen 1 1 Department of Emergency, The First Affiliated
Influence of interleukin-18 gene polymorphisms on acute pancreatitis susceptibility in a Chinese population H.B. Gui 1, X.G. Du 2, Z.H. Fu 3 and X.M. Chen 1 1 Department of Emergency, The First Affiliated
Plasma MicroRNA Panel to Diagnose Hepatitis B Virus Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 Published Ahead of Print on November 21, 211 as 1.12/JCO.211.38.2697 The latest version is at http://jco.ascopubs.org/cgi/doi/1.12/jco.211.38.2697 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R
Published Ahead of Print on November 21, 211 as 1.12/JCO.211.38.2697 The latest version is at http://jco.ascopubs.org/cgi/doi/1.12/jco.211.38.2697 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY O R I G I N A L R E P O R
