DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Dr. Alireza Safaeian MD Occupational Medicine Specialist
|
|
|
- Samantha Barton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DISORDERS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Dr. Alireza Safaeian MD Occupational Medicine Specialist
2 Neurologic Evaluation Bed side History Physical examination Paraclinics CT scan MRI EEG NCV EMG Neuropsychological testing
3 clinical manifestations Central Nervous System headache, cognitive and psychiatric disturbances, visual changes, seizures, Ataxia (vetigo/dizziness), tremors, rigidity, weakness (fatigue), sensory loss Peripheral Nervous System pain, weakness, paresthesias, and numbness autonomic disturbances.
4 Occupational injuries result in: Generalized poly neuropathy (Neurotoxines) Focal compressive mononeuropathies (Nerve trauma,nerve entrapment) Impaired neuromuscular transmission Myopathy
5 NEUROTOXICOLOGY
6 GENERAL PRINCIPLES A dose-toxicity relationship Nonfocal or symmetric neurologic syndrome Strong temporal relationship A limited capability to regenerate Multiple neurologic syndromes are possible from a single toxin Few toxins present with a pathognomonic neurologic syndrome
7 phenomenon of coasting the continuing deterioration sometimes seen for up to a few weeks after discontinuation of toxic exposure. 1. pyridoxine (vitamin B 6 ) abuse, 2. n-hexane toxicity, 3. vincristine chemotherapy. The delay reflects the time necessary for the pathophysiologic steps to evolve to neuronal injury and death.
8 APPROACH TO PATIENTS Sufficiently intense or prolonged exposure to the toxin Appropriate neurologic syndrome Evolution of symptoms and signs over a compatible temporal course Exclusion of other neurologic disorders that may account for a similar syndrome.
9 temporal course of the disease Symptoms may appear acutely (minutes or days) subacutely (weeks or months) chronically (years). Fluctuating symptoms may suggest recurrent exposures or unrelated superimposed factors. Recovery after discontinuation of exposure helps to implicate the exposure By contrast, a continuing progression of deficits beyond the "coasting" period argues against an etiologic role of the exposure.
10 Central Nervous System Encephalopathy (a common syndrome): diffuse dysfunction of cortical or subcortical structures. Acutely, the encephalopathy may be associated with alteration in the level of consciousness. Chronically, the primary symptoms may be cognitive and psychiatric
11 Central Nervous System Relatively selective injury: vestibular system or the cerebellum: resulting in dysequilibrium, vertigo, and gait or limb ataxia. Basal ganglia: lead to an extrapyramidal syndrome of bradykinesia, tremors, and rigidity. (same as idiopathic Parkinson disease)
12 Evaluation cognitive complaints : at least a mini-mental state examination. Patients with gait unsteadiness, dizziness, or vertigo : examined for cranial nerve or cerebellar deficits. (testing of gait, tandem walk, and Romberg sign) The examiner also should note extraocular movements and the presence or absence of nystagmus, hearing deficits, limb ataxia, and sensory deficits. Tremors : at rest, and with the hands performing Muscle tone should be tested for rigidity
13 Paraclinics often are needed to detect unrelated neurologic diseases that mimic neurotoxic disorders brain or spinal cord imaging studies (e.g., MRI), lumbar puncture, electroencephalogram (EEG), evoked potentials,
14 Peripheral Nervous System polyneuropathy : symmetric peripheral neuropathy. mononeuropathy : the result of local mechanical injury myopathy (alcoholism and medical use of the statins, toxic myopathy is uncommon)
15 polyneuropathies The hallmark: distal distribution of the clinical symptoms and signs. The most common syndrome: subacute onset of tingling or numbness experienced in a symmetric stocking-and-glove distribution. Neuropathic pain: burning, deep aching, lancinating,hyperpathia or allodynia.
16 polyneuropathies Motor nerve fibers involvement: muscle atrophy and weakness. (at first in the distal-most muscles i.e., the intrinsic foot and hand muscles). More severe cases : involve muscles of the lower legs and forearms, leading to bilateral foot drop or wrist drop Physical examination : muscle strength, sensation, and tendon reflexes of all four extremities.
17 Key points Hands or Feet The longest axons are the most vulnerable, SO neurologic deficits severity in feet > hands. If Prominent sensory impairment in the hands without signs of neuropathy in the feet:? carpal tunnel syndrome
18 Key points Most polyneuropathies are accompanied by diminished or absent stretch reflexes of the Achilles tendons and demonstrable sensory impairment in the toes. Testing of these functions is important.
19 DDx Common systemic diseases: alcoholism, uremia, diabetes mellitus, and vitamin B 12 deficiency. Hereditary and immunologic neuropathies (Charcot-Marie-Tooth ) Approximately one-half to two-thirds of all polyneuropathies remain undiagnosed despite thorough investigation
20 paraclinics evaluation NCV EMG Nerve biopsy Quantitative sensory testing (QST)
21 categorization of neuropathies Axonal neuropathy : primary degeneration of nerve axons Demyelinative neuropathy: significant myelin breakdown
22 Toxic polyneuropathies Mostly sensory or sensorimotor polyneuropathy (little or no weakness) Acrylamide Carbon disulfide Ethylene oxide Metals: arsenic, lead, mercury, thallium Methyl bromide Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) Thallium Predominantly motor polyneuropathy or sensorimotor polyneuropathy with significant weakness Hexacarbons: n-hexane, methyl n-butyl ketone Metals: lead, arsenic, mercury Organophosphates "Purely" sensory neuropathy (disabling sensory loss with no weakness) cis-platinum Pyridoxine abuse Cranial neuropathy Thallium Trichloroethylene (trigeminal neuropathy) Prominent autonomic dysfunction Acrylamide n-hexane (glue-sniffer) Thaliium Vacor(PNU) Possible, association with neuropathies (mostly anecdotal) Benzene Carbon monoxide Dioxin Methyl methacrylate Pyrethrins
23 NEUROLOGIC DISORDERS CAUSED BY SPECIFIC TOXINS
24 Acrylamide Workers who handle monomeric acrylamide in the production of polyacrylamides and those exposed to monomeric acrylamide used in grouting. Intoxication occurs by inhalation or skin absorption. Features of poisoning : local skin irritation, weight loss, lassitude, and neurologic symptoms of central and peripheral nervous system involvement.
25 Acrylamide (Acute exposure ) Typically causes a confusional state (disorientation, memory loss, and gait ataxia) Symptoms are largely reversible Very intense exposure : Irreversible dysfunction (rarely)
26 Acrylamide (Chronic lower-dose exposure ) Feature: dizziness, increased irritability, emotional changes, and sleep disturbances. The primary site of action: the peripheral nerve. Both sensory and motor nerves are affected (sensory loss, weakness, ataxia, and generalized loss of tendon reflexes) Autonomic involvement, such as hyperhidrosis and urinary retention, is common.
27 Arsenic arsenic compounds are used as wood preservatives, as gallium arsenide in the semiconductor industry, and as defoliant and desiccant in agriculture. Contamination of well water may result from leaching of arsenic byproducts in smelting or heavy agricultural use of arsenicals
28 Arsenic (acute exposure) Intense exposure: mental confusion, psychosis, anxiety, seizure, or coma, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Dermatologic lesions: hyperkeratosis, skin pigmentation, skin exfoliation, and Mees lines, occur in many patients 1-6 W after onset of disease. Peripheral neuropathy is the most common neurologic manifestation (acute or chronic exposure)
29 Arsenic (acute exposure) After a single massive dose: acute polyneuropathy (within 1-3 W) This neuropathy mimics Guillain-Barre syndrome (respiratory failure may occur rarely) Symmetric paresthesias, pain may occur (+/- distal weakness) With progression of neuropathy, sensory and motor deficits spread proximally. Shoulder and pelvic girdle weakness, as well as gait ataxia, are common in severe cases.
30 Arsenic (Chronic low-level exposure) subtle impairment of memory and concentration. EMG and NCV: nonspecific axonal neuropathy. Blood arsenic level returns to normal in about hours Urine arsenic clears within hours after exposure. Arsenic remains detectable in hair and nails for months after exposure. false-positive results! Pubic hair is preferable
31 Carbon Disulfide as a solvent in perfume production and varnishes, in soil fumigants and insecticides, and in industrial manufacturing
32 CS2 (acute exposure) brief inhalation exposure to a toxic level (300 ppm or above) : dizziness and headache, followed by delirium, mania, or mental dulling. Concentrations above 400 ppm have a narcotizing effect and may lead to convulsion, coma, and respiratory failure.
33 CS2 (chronic exposure) PNS: paresthesias and pain in the distal legs, loss of Achilles reflexes, and evidence of involvement of sensory and motor axons on NCV CNS: nonspecific syndrome of fatigue, headache, and sleep disturbances
34 Carbon Monoxide Inhaling low concentrations ( %) of carbon monoxide causes headache and mild confusion. A higher concentration of % may result in somnolence or stupor inhalation of 1% for more than 30 minutes can be fatal, Early symptoms: headache, dizziness, and disorientation. More prolonged or severe hypoxia : combination of tremor, chorea, spasticity, dystonia, rigidity, and bradykinesia.
35 CO (acute exposure) Recovery from the hypoxia : incomplete Residual dementia, spasticity, cortical blindness, and parkinsonian features are relatively common. Occasional patients recover completely after acute exposure only to worsen again 1-6 weeks later with acute disorientation, apathy, or psychosis
36 CO (acute exposure) Neurologic examination: 1) encephalopathy with prominent signs of frontal lobe and extrapyramidal dysfunction. (bradykinesia, retropulsion, frontal release signs, spasticity, and limb rigidity) 2) involvement of the basal ganglia, especially the globus pallidus and the thalamus. Partial recovery is possible (take one or more years) Some residual memory deficits and parkinsonism are common
37 CT or MRI: abnormalities in bilateral subcortical white matter, some patients have involvement of basal ganglia, especially globus pallidus and thalamus
38 CO (chronic exposure) Nonspecific symptoms: anorexia, headache, personality changes, and memory disturbances
39 Hexacarbons (n-hexane and Methyl n-butyl Ketone) Widely used volatile organic compounds (petroleum production and refining industries), as solvents and adhesives used in homes and industries (shoe and cabinet making) Toxic exposure : inhalation (especially in poorly ventilated spaces) or excessive skin contact.
40 Acute exposure Acute encephalopathy: euphoria, hallucination, and confusion. Glue-sniffer's neuropathy: The acute euphoric effect, distal symmetric sensorimotor polyneuropathy (paresthesias and sensory loss and weakness) Proximal musculatures involvement (in more severe cases) Ankle weakness (easy tripping) Optic neuropathy and facial numbness Autonomic symptoms (uncommon - in very severe cases) Nonspecific (CNS) symptoms : insomnia and irritability No Achilles stretch reflexes (early in the disease) Recovery: begins after a few months of abstinence -incomplete
41 Chronic exposure The clinical features are essentially similar, although the syndrome evolves more slowly and results in less severe deficits
42 Lead Industrial sources paint, batteries, pipes, solder, ammunition, cables. Nonindustrial sources pottery, bullet fragments, traditional folk remedies
43 Lead (Acute high-level exposure ) Accidental ingestion Inhalation Industrial exposure
44 Lead (Acute high-level exposure ) Syndrome of abdominal colic and intermittent vomiting, accompanied by neurologic symptoms such as headache, tremor, apathy, and lethargy. Massive intoxication : convulsions, cerebral edema, stupor, or coma and eventually to transtentorial herniation
45 Lead (in children) Children are more vulnerable than adults (immaturity of the blood-brain barrier) Behavioral disturbances and neuropsychologic impairment may be present at blood levels as low as 10 mg/dl Chronic low-level exposure to lead is responsible for impaired intellectual development in children.
46 Lead (Chronic low-level exposure) Peripheral neuropathy (well-recognized complication) Asymptomatic NCV abnormalities BLL>40 m/dl. Predominantly motor neuropathy (little or not sensory symptoms) Mimics motor neuron diseases (ALS) Bilateral wrist drop and foot drop. Generalized proximal and distal weakness and loss of the tendon reflexes. In some patients :distal limb paresthesias and no weakness.
47 Mercury Mercury poisoning by exposure to : 1) Elemental mercury: thermometers, barometers 2) Organic mercurial compounds: as preservative in latex paints, in various disinfectants, industrial catalysts 3) Inorganic mercurial salts: manufacture of chlorine, dental amalgams
48 Mercury Mercury is used in batteries, fungicides, electronics, and other industries. Mercury in sludge and waterways is methylated by microbes into methyl mercury that is readily absorbed by humans. Several large endemics :Minamata Bay (Japan), in Iraq and in the Amazon River basin
49 Mercury Dental Amalgam :there is no convincing evidence that the widely used mercury dental amalgam poses a significant health hazard There is no strong evidence to associate lowlevel exposure with significant neurologic disease
50 Mercury (acute exposure) Diffuse encephalopathy: (euphoria, irritability, anxiety, and emotional lability.) Confusion and an altered level of consciousness (More severe exposure) Tremor and Cerebellar ataxia, Hearing loss, visual field constriction, hyperreflexia, and Babinski sign
51 Mercury (acute exposure) Organic mercury poisoning : prominent CNS disturbances, with little or no peripheral nervous system involvement. Inorganic mercury poisoning: Neuropathy is prominent. acute syndrome resembles Guillain-Barre syndrome, subacute syndrome may mimic ALS.
52 Mercury (chronic exposure) Mercurialism Tremor Erethism Confusion Polyneuropathy (motor & sensory)
53 Organophosphafes Organophosphates (OPs) are used: commonly as pesticides and herbicides to a lesser extent, as petroleum additives, antioxidants, and flame retardants. They are highly lipid soluble and are absorbed through skin contact or through mucous membranes via inhalation and ingestion Inhibiting the enzyme acetylcholinesterase
54 acute neurologic effects Muscarinic and Nicotinic overactivity. Symptoms : (within hours of exposure) abdominal cramps, diarrhea, increased salivation, sweating, miosis, blurred vision, and muscle fasciculations. Severe intoxication: Convulsions, coma, muscle paralysis, and respiratory arrest Recovery : complete and within 1 week Acetylcholinesterase activity level: restored only partially.
55 intermediate syndrome occurs within hours of exposure result of excessive cholinergic stimulation of nicotinic receptors in skeletal muscles. (blockage of neuromuscular junction transmission) Weakness of proximal muscles, neck flexors, cranial muscles (extra ocular muscles), and even respiratory muscles Sensory function is spared
56 delayed syndrome Peripheral neuropathy occurs 1-4 W after acute exposure. OPs inhibit neuropathy target esterase (NTE), forming an OP-NTE complex. (irreversible OP-NTE complex -known as aging) Resulting in the delayed polyneuropathy. paresthesias and cramping pain in the legs Sensory loss is usually mild on physical examination. Weakness (distal to proximal muscles) Spasticity and other upper motor neuron signs Cranial neuropathy or autonomic dysfunction is unusual. Recovery is slow and incomplete
TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE
 TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE Objectives: For each of the following entities the student should be able to: 1. Describe the etiology/pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology, gross and microscopic morphology
TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE Objectives: For each of the following entities the student should be able to: 1. Describe the etiology/pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology, gross and microscopic morphology
Identification number: TÁMOP /1/A
 Manifestation of Novel Social Challenges of the European Union in the Teaching Material of Medical Biotechnology Master s Programmes at the University of Pécs and at the University of Debrecen Identification
Manifestation of Novel Social Challenges of the European Union in the Teaching Material of Medical Biotechnology Master s Programmes at the University of Pécs and at the University of Debrecen Identification
High Yield Neurological Examination
 High Yield Neurological Examination Vanja Douglas, MD Sara & Evan Williams Foundation Endowed Neurohospitalist Chair Director, Neurohospitalist Division Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology UCSF Department
High Yield Neurological Examination Vanja Douglas, MD Sara & Evan Williams Foundation Endowed Neurohospitalist Chair Director, Neurohospitalist Division Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology UCSF Department
A Practical Approach to Polyneuropathy SLOCUM DICKSON ANNUAL TEACHING DAY NOVEMBER 4, 2017
 A Practical Approach to Polyneuropathy SLOCUM DICKSON ANNUAL TEACHING DAY NOVEMBER 4, 2017 Disclosures Research support from Cytokinetics, Inc Catalyst, Inc Editorial fees from UptoDate. Objectives Describe
A Practical Approach to Polyneuropathy SLOCUM DICKSON ANNUAL TEACHING DAY NOVEMBER 4, 2017 Disclosures Research support from Cytokinetics, Inc Catalyst, Inc Editorial fees from UptoDate. Objectives Describe
Neurologic Examination
 John W. Engstrom, MD October 16, 2015 Neurologic Examination Overview The Neurologic Examination Neurologic Examination John W. Engstrom, M.D. Dept. of Neurology University of California, San Francisco
John W. Engstrom, MD October 16, 2015 Neurologic Examination Overview The Neurologic Examination Neurologic Examination John W. Engstrom, M.D. Dept. of Neurology University of California, San Francisco
Movement Disorders. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Background. Myasthenia Gravis. Many Types
 Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
3) Approach to Ataxia - Dr. Zana
 3) Approach to Ataxia - Dr. Zana Introduction Ataxia is derived from Greek word a -not, taxis -orderly, (not orderly/ not in order) Ataxia is the inability to make smooth, accurate and coordinated movements
3) Approach to Ataxia - Dr. Zana Introduction Ataxia is derived from Greek word a -not, taxis -orderly, (not orderly/ not in order) Ataxia is the inability to make smooth, accurate and coordinated movements
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists
 Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
P1: OTA/XYZ P2: ABC c01 BLBK231-Ginsberg December 23, :43 Printer Name: Yet to Come. Part 1. The Neurological Approach COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
 Part 1 The Neurological Approach COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 2 Chapter 1 Neurological history-taking The diagnosis and management of diseases of the nervous system have been revolutionized in recent years by
Part 1 The Neurological Approach COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 2 Chapter 1 Neurological history-taking The diagnosis and management of diseases of the nervous system have been revolutionized in recent years by
Approach to a Neurologic Diagnosis
 Approach to a Neurologic Diagnosis Neurologic Diagnosis History Physical & Neurological Examination Ancillary Procedures 3 Questions Asked Focal neurologic deficits Increased intracranial pressure Signs
Approach to a Neurologic Diagnosis Neurologic Diagnosis History Physical & Neurological Examination Ancillary Procedures 3 Questions Asked Focal neurologic deficits Increased intracranial pressure Signs
Brain and Central Nervous System Cancers
 Brain and Central Nervous System Cancers NICE guidance link: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta121 Clinical presentation of brain tumours History and Examination Consider immediate referral Management
Brain and Central Nervous System Cancers NICE guidance link: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta121 Clinical presentation of brain tumours History and Examination Consider immediate referral Management
A Hypothesis Driven Approach to the Neurological Exam
 A Hypothesis Driven Approach to the Neurological Exam Vanja Douglas, MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Department of Neurology Disclosures None 1 Purpose of Neuro Exam Screen asymptomatic patients Screen
A Hypothesis Driven Approach to the Neurological Exam Vanja Douglas, MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Department of Neurology Disclosures None 1 Purpose of Neuro Exam Screen asymptomatic patients Screen
Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives
 Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives Clinical skills Perform a neurological screening examination of the cranial nerves, motor system, reflexes, and sensory system under the observation and guidance
Neurology Clerkship Learning Objectives Clinical skills Perform a neurological screening examination of the cranial nerves, motor system, reflexes, and sensory system under the observation and guidance
Evolution of a concept: Apraxia/higher level gait disorder. ataxia v. apraxia gait = limb apraxia. low, middle, high gait disturbance levels
 Case #1 81-year-old woman Gait Imbalance: Two Unusual Cases in Older Patients February 2008: 3 years of gradually progressive gait imbalance no vertigo, dizziness or paresthesias etiology unclear on examination
Case #1 81-year-old woman Gait Imbalance: Two Unusual Cases in Older Patients February 2008: 3 years of gradually progressive gait imbalance no vertigo, dizziness or paresthesias etiology unclear on examination
Toxic and Metabolic Disease of Nervous System
 Toxic and Metabolic Disease of Nervous System Reid R. Heffner, MD Distinguished Teaching Professor Emeritus Department of Pathology and Anatomy January 14, 2019 1 I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST OR DISCLOSURES
Toxic and Metabolic Disease of Nervous System Reid R. Heffner, MD Distinguished Teaching Professor Emeritus Department of Pathology and Anatomy January 14, 2019 1 I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST OR DISCLOSURES
The Neurologic Examination. John W. Engstrom, M.D. University of California San Francisco School of Medicine
 The Neurologic Examination John W. Engstrom, M.D. University of California San Francisco School of Medicine Overview The Neurologic Examination Mental status demonstration/questions Cranial nerves demonstration/questions
The Neurologic Examination John W. Engstrom, M.D. University of California San Francisco School of Medicine Overview The Neurologic Examination Mental status demonstration/questions Cranial nerves demonstration/questions
IMPAIRMENT OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 IMPAIRMENT OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The following information provides criteria for the evaluation of permanent impairment resulting from dysfunction brain, spinal cord and cranial nerves and certain peripheral
IMPAIRMENT OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The following information provides criteria for the evaluation of permanent impairment resulting from dysfunction brain, spinal cord and cranial nerves and certain peripheral
A Neurologist s Approach to Altered Mental Status
 A Neurologist s Approach to Altered Mental Status S. Andrew Josephson, MD Department of Neurology University of California San Francisco October 23, 2008 The speaker has no disclosures Case 1 A 71 year-old
A Neurologist s Approach to Altered Mental Status S. Andrew Josephson, MD Department of Neurology University of California San Francisco October 23, 2008 The speaker has no disclosures Case 1 A 71 year-old
Heavy Metals. General concepts (EHL0036)
 Heavy Metals General concepts (EHL0036) Introduction Metals of concern; include Aluminium, antimony, arsenic, bismuth, cadmium, cerium, chromium, cobalt, copper, gallium, gold, iron, lead, manganese, mercury,
Heavy Metals General concepts (EHL0036) Introduction Metals of concern; include Aluminium, antimony, arsenic, bismuth, cadmium, cerium, chromium, cobalt, copper, gallium, gold, iron, lead, manganese, mercury,
NEUROLOGY CLERKSHIP CORE CURRICULUM GUIDELINES
 NEUROLOGY CLERKSHIP CORE CURRICULUM GUIDELINES Endorsed by the following organizations - October 2000: American Academy of Neurology Association of University Professors of Neurology American Neurological
NEUROLOGY CLERKSHIP CORE CURRICULUM GUIDELINES Endorsed by the following organizations - October 2000: American Academy of Neurology Association of University Professors of Neurology American Neurological
The Internist s Approach to Neuropathy
 The Internist s Approach to Neuropathy VOLKAN GRANIT, MD, MSC ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY NEUROMUSCU LAR DIVISION UNIVERSITY OF MIAMI, MILLER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE RELEVANT DECLARATIONS Financial disclosures:
The Internist s Approach to Neuropathy VOLKAN GRANIT, MD, MSC ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF NEUROLOGY NEUROMUSCU LAR DIVISION UNIVERSITY OF MIAMI, MILLER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE RELEVANT DECLARATIONS Financial disclosures:
Evaluation of Tingling and Numbness in the Upper Extremities
 Evaluation of Tingling and Numbness in the Upper Extremities DR. W. ANTHONY FRISELLA M.D. ADVANCED BONE & JOINT, ST CHARLES MO MONA 2018 Overview Polyneuropathy Compressive nerve lesions Carpal tunnel
Evaluation of Tingling and Numbness in the Upper Extremities DR. W. ANTHONY FRISELLA M.D. ADVANCED BONE & JOINT, ST CHARLES MO MONA 2018 Overview Polyneuropathy Compressive nerve lesions Carpal tunnel
Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy. Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy - Introduction
 Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy Chris Edwards, MD Ochsner Neurology, Main Campus Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy - Introduction A very common complaint in the clinic Presentation is variable Multiple
Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy Chris Edwards, MD Ochsner Neurology, Main Campus Evaluation of Peripheral Neuropathy - Introduction A very common complaint in the clinic Presentation is variable Multiple
Neurological Examination
 Neurological Examination Charles University in Prague 1st Medical Faculty and General University Hospital Neurological examination: Why important? clinical history taking and bedside examination: classical
Neurological Examination Charles University in Prague 1st Medical Faculty and General University Hospital Neurological examination: Why important? clinical history taking and bedside examination: classical
Elemental mercury. Inorganic mercury salts. Organic mercury compounds. Quick silver. Mercurous Mercuric
 MERCURY Elemental mercury Quick silver Inorganic mercury salts Mercurous Mercuric Organic mercury compounds Short chain mercury(methyl mercury) Long chain mercury compounds Dye makers, Elemental mercury
MERCURY Elemental mercury Quick silver Inorganic mercury salts Mercurous Mercuric Organic mercury compounds Short chain mercury(methyl mercury) Long chain mercury compounds Dye makers, Elemental mercury
By Dr. Magdy M. Awny. (nerve agent)
 By Dr. Magdy M. Awny (nerve agent) Pesticides Is any chemical substance or mixture of substances intended for preventing, destroying, repelling, or mitigating any pest are a group of insecticides or Organophosphorous
By Dr. Magdy M. Awny (nerve agent) Pesticides Is any chemical substance or mixture of substances intended for preventing, destroying, repelling, or mitigating any pest are a group of insecticides or Organophosphorous
Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases
 Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases Peripheral neuropathies according to which part affected Axonal Demyelinating with axonal sparing Many times: mixed features
Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases Peripheral neuropathies according to which part affected Axonal Demyelinating with axonal sparing Many times: mixed features
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T!
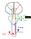 CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
Subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord following recreational nitrous oxide use
 Subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord following recreational nitrous oxide use Jae Park Hui Mei Cheng Royal Perth Hospital, Perth Western Australia Australia Background and aim Subacute combined
Subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord following recreational nitrous oxide use Jae Park Hui Mei Cheng Royal Perth Hospital, Perth Western Australia Australia Background and aim Subacute combined
Mini Research Paper: Traumatic Brain Injury. Allison M McGee. Salt Lake Community College
 Running Head: Mini Research Paper: Traumatic Brain Injury Mini Research Paper: Traumatic Brain Injury Allison M McGee Salt Lake Community College Abstract A Traumatic Brain Injury (also known as a TBI)
Running Head: Mini Research Paper: Traumatic Brain Injury Mini Research Paper: Traumatic Brain Injury Allison M McGee Salt Lake Community College Abstract A Traumatic Brain Injury (also known as a TBI)
VL VA BASAL GANGLIA. FUNCTIONAl COMPONENTS. Function Component Deficits Start/initiation Basal Ganglia Spontan movements
 BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
Functional Distinctions
 Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
UF NEUROLOGY HISTORY AND PHYSICAL GUIDELINES
 UF NEUROLOGY HISTORY AND PHYSICAL GUIDELINES HISTORY Chief Complaint A maximally succinct statement of the patient age, handedness, gender, main problem, and its duration (e.g. 56 year old right-handed
UF NEUROLOGY HISTORY AND PHYSICAL GUIDELINES HISTORY Chief Complaint A maximally succinct statement of the patient age, handedness, gender, main problem, and its duration (e.g. 56 year old right-handed
Solvents at Work. Exposure to solvents can have both short- and long-term health effects on workers.
 Solvents at Work Solvents are among the most commonly used chemicals in workplaces. Workers in different jobs regularly use solvents for degreasing, metal cleaning, adhesion and as paint thinners or lubricants.
Solvents at Work Solvents are among the most commonly used chemicals in workplaces. Workers in different jobs regularly use solvents for degreasing, metal cleaning, adhesion and as paint thinners or lubricants.
Peripheral Neuropathies
 Peripheral Neuropathies ELBA Y. GERENA MALDONADO, MD ACTING ASSISTANT PROFESSOR UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON MEDICAL CENTER Objectives Definition Neurophysiology Evaluation of polyneuropathies Cases Summary
Peripheral Neuropathies ELBA Y. GERENA MALDONADO, MD ACTING ASSISTANT PROFESSOR UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON MEDICAL CENTER Objectives Definition Neurophysiology Evaluation of polyneuropathies Cases Summary
American Board of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation. Part I Curriculum & Weights
 American Board of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Part I Curriculum & Weights Neurologic Disorders 30% Stroke Spinal Cord Injury Traumatic Brain Injury Neuropathies a) Mononeuropathies b) Polyneuropathies
American Board of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Part I Curriculum & Weights Neurologic Disorders 30% Stroke Spinal Cord Injury Traumatic Brain Injury Neuropathies a) Mononeuropathies b) Polyneuropathies
Introduction to Dementia: Diagnosis & Evaluation. Created in March 2005 Duration: about 15 minutes
 Introduction to Dementia: Diagnosis & Evaluation Created in March 2005 Duration: about 15 minutes Axel Juan, MD The Geriatrics Institute axel.juan@med.va.gov 305-575-3388 Credits Principal medical contributor:
Introduction to Dementia: Diagnosis & Evaluation Created in March 2005 Duration: about 15 minutes Axel Juan, MD The Geriatrics Institute axel.juan@med.va.gov 305-575-3388 Credits Principal medical contributor:
Central nervous system
 Central nervous system By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 7 th Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Symptoms, signs & tests. Specific diseases. Review of structure
Central nervous system By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 7 th Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Symptoms, signs & tests. Specific diseases. Review of structure
Peripheral Nerve Disorders - P a g e 1. Introduction
 Peripheral Nerve Disorders - P a g e 1 Introduction The peripheral nerves connect the central nervous system (the brain and the spinal cord) to the periphery (the sensory receptors and muscles). An illness
Peripheral Nerve Disorders - P a g e 1 Introduction The peripheral nerves connect the central nervous system (the brain and the spinal cord) to the periphery (the sensory receptors and muscles). An illness
From: Chronic Pain: Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy Prevention and Management. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida. H. Hooshmand, M.D. ELECTRICAL INJURIES
 From: Chronic Pain: Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy Prevention and Management CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida H. Hooshmand, M.D. ELECTRICAL INJURIES In our experience of over 100 patients suffering from electrical
From: Chronic Pain: Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy Prevention and Management CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida H. Hooshmand, M.D. ELECTRICAL INJURIES In our experience of over 100 patients suffering from electrical
Lyme Disease Specific Symptoms
 Did you have: Please indicate yes or no (Y / N) and/or date month/year tick bite spotted rash over large area circular or bull-eye rash linear red streaks Lyme test date(s) mm/year Results: (positive +,
Did you have: Please indicate yes or no (Y / N) and/or date month/year tick bite spotted rash over large area circular or bull-eye rash linear red streaks Lyme test date(s) mm/year Results: (positive +,
Organic Mental Disorders. Organic Mental Disorders. Axes. Damrongsak Bulyalert Department of Internal Medicine
 Organic Mental Disorders Damrongsak Bulyalert Department of Internal Medicine www.metadon.net 1 Organic Mental Disorders In DSM (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders), OMD includes Delirium,
Organic Mental Disorders Damrongsak Bulyalert Department of Internal Medicine www.metadon.net 1 Organic Mental Disorders In DSM (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders), OMD includes Delirium,
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Neurology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Neurology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing neurological diseases, and in counseling and screening
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Neurology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing neurological diseases, and in counseling and screening
May He Rest in Peace
 May He Rest in Peace Neurologic Complications of AIDS Medical Knowledge Fiesta 2012 Paul K. King MD pkingmd@yahoo.com Objectives definition of HIV/AIDS what are the neurologic complications of AIDS how
May He Rest in Peace Neurologic Complications of AIDS Medical Knowledge Fiesta 2012 Paul K. King MD pkingmd@yahoo.com Objectives definition of HIV/AIDS what are the neurologic complications of AIDS how
MUSCULOSKELETAL AND NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS
 MUSCULOSKELETAL AND NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS There are a wide variety of Neurologic and Musculoskeletal disorders which can impact driving safety. Impairment may be the result of altered muscular, skeletal,
MUSCULOSKELETAL AND NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS There are a wide variety of Neurologic and Musculoskeletal disorders which can impact driving safety. Impairment may be the result of altered muscular, skeletal,
sensory nerves, motor nerves, autonomic nerves
 damage or disease affecting nerves, which may impair sensation, movement, gland or organ function, or other aspects of health, depending on the type of nerve affected o chronic: long term, begins subtly
damage or disease affecting nerves, which may impair sensation, movement, gland or organ function, or other aspects of health, depending on the type of nerve affected o chronic: long term, begins subtly
Suspected neurological conditions: clinical questions
 Suspected neurological clinical questions For questions on signs and symptoms, the committee wanted to consider any studies that determine whether a certain sign or symptom accompanying a main presenting
Suspected neurological clinical questions For questions on signs and symptoms, the committee wanted to consider any studies that determine whether a certain sign or symptom accompanying a main presenting
A CASE OF GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY HEMANANTH T SECOND YEAR POST GRADUATE IN PAEDIATRICS INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL PAEDIATRICS GOVERNMENT STANLEY HOSPITAL
 A CASE OF GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY HEMANANTH T SECOND YEAR POST GRADUATE IN PAEDIATRICS INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL PAEDIATRICS GOVERNMENT STANLEY HOSPITAL CASE HISTORY Nine year old male child Second born Born
A CASE OF GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY HEMANANTH T SECOND YEAR POST GRADUATE IN PAEDIATRICS INSTITUTE OF SOCIAL PAEDIATRICS GOVERNMENT STANLEY HOSPITAL CASE HISTORY Nine year old male child Second born Born
PESTICIDE HEALTH EFFECTS ON HUMANS
 PESTICIDE HEALTH EFFECTS ON HUMANS Table Of Contents: Organophosphates Carbamates Organochlorines Nitrophenolic and Nitrocresolic Pesticides Chlorophenoxy Pesticides Paraquat and Diquat Thiocarbamates
PESTICIDE HEALTH EFFECTS ON HUMANS Table Of Contents: Organophosphates Carbamates Organochlorines Nitrophenolic and Nitrocresolic Pesticides Chlorophenoxy Pesticides Paraquat and Diquat Thiocarbamates
Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease. Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine
 Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine Normal Nerves 1. Anterior Horn Cell 2. Dorsal root ganglion cell 3.
Clinical Aspects of Peripheral Nerve and Muscle Disease Roy Weller Clinical Neurosciences University of Southampton School of Medicine Normal Nerves 1. Anterior Horn Cell 2. Dorsal root ganglion cell 3.
o They are usually used in Forensic or Medico-legal practice, Commonly used are Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) and Expired Air
 1 ETHANOL: UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL SEMINAR OVERVIEW OF ALCOHOL (ETHANOL & METHANOL)
1 ETHANOL: UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL SEMINAR OVERVIEW OF ALCOHOL (ETHANOL & METHANOL)
Karl McManus Foundation Representing the Australian Lyme Disease Community Symptoms Monitoring Chart
 Name Diagnosis Date Pathogens Present Date GENERAL Fever Chills Night sweats Fatigue Poor Stamina Weight Loss/Gain Gernalised Pain Migratory Pain Shooting Pain Daytime Napping Menstrual Irregularity Milk
Name Diagnosis Date Pathogens Present Date GENERAL Fever Chills Night sweats Fatigue Poor Stamina Weight Loss/Gain Gernalised Pain Migratory Pain Shooting Pain Daytime Napping Menstrual Irregularity Milk
Systematic Approach to Weakness Polat DURUKAN
 Systematic Approach to Weakness Polat DURUKAN Erciyes University Faculty of Medicine Department of EM, Kayseri, Turkey Subarachnoid hemorrhage? Hypoglycemia? Guillain-Barré syndrome? Sepsis? Dehydration
Systematic Approach to Weakness Polat DURUKAN Erciyes University Faculty of Medicine Department of EM, Kayseri, Turkey Subarachnoid hemorrhage? Hypoglycemia? Guillain-Barré syndrome? Sepsis? Dehydration
How to Think like a Neurologist Review of Exam Process and Assessment Findings
 Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist 2013 Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist Feb 20th, 5:10 PM - 5:40 PM How to Think like a Neurologist Review
Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist 2013 Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist Feb 20th, 5:10 PM - 5:40 PM How to Think like a Neurologist Review
Delirium & Dementia. Nicholas J. Silvestri, MD
 Delirium & Dementia Nicholas J. Silvestri, MD Outline Delirium vs. Dementia Neural pathways relating to consciousness Encephalopathy Stupor Coma Dementia Delirium vs. Dementia Delirium Abrupt onset Lasts
Delirium & Dementia Nicholas J. Silvestri, MD Outline Delirium vs. Dementia Neural pathways relating to consciousness Encephalopathy Stupor Coma Dementia Delirium vs. Dementia Delirium Abrupt onset Lasts
Chapter 20. Media Directory. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Alzheimer s Disease. Huntington s Chorea. Multiple Sclerosis
 Chapter 20 Drugs for Degenerative Diseases of the Nervous System Slide 18 Media Directory Levadopa Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Alzheimer s Disease Amyotrophic Lateral
Chapter 20 Drugs for Degenerative Diseases of the Nervous System Slide 18 Media Directory Levadopa Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Alzheimer s Disease Amyotrophic Lateral
United Council for Neurologic Subspecialties Geriatric Neurology Written Examination Content Outline
 United Council for Neurologic Subspecialties Geriatric Neurology Written Examination Content Outline REV 3/24/09 The UCNS Geriatric Neurology examination was established to determine the level of competence
United Council for Neurologic Subspecialties Geriatric Neurology Written Examination Content Outline REV 3/24/09 The UCNS Geriatric Neurology examination was established to determine the level of competence
AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer
 AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer ( )1. Choose one best answer for the following pathologic pictures. A. choroid cyst B. choroid papilloma C. pontine glioma D. ependymoma E. metastatic tumor
AII-type: Select the most appropriate answer ( )1. Choose one best answer for the following pathologic pictures. A. choroid cyst B. choroid papilloma C. pontine glioma D. ependymoma E. metastatic tumor
Delirium, Dementia, and Amnestic Disorders. Dr.Al-Azzam 1
 Delirium, Dementia, and Amnestic Disorders Dr.Al-Azzam 1 Introduction Disorders in which a clinically significant deficit in cognition or memory exists The number of people with these disorders is growing
Delirium, Dementia, and Amnestic Disorders Dr.Al-Azzam 1 Introduction Disorders in which a clinically significant deficit in cognition or memory exists The number of people with these disorders is growing
Provide specific counseling to parents and patients with neurological disorders, addressing:
 Neurology Description: The Pediatric Neurology elective will give the resident the opportunity to learn how to obtain an appropriate history and perform a complete neurologic exam. Four to five half days
Neurology Description: The Pediatric Neurology elective will give the resident the opportunity to learn how to obtain an appropriate history and perform a complete neurologic exam. Four to five half days
Obtaining an Exposure History from Records. CLCW SME training August, 2017
 Obtaining an Exposure History from Records CLCW SME training August, 2017 Purpose of an Exposure History Many hazardous exposures from environmental and occupational sources either manifest as common medical
Obtaining an Exposure History from Records CLCW SME training August, 2017 Purpose of an Exposure History Many hazardous exposures from environmental and occupational sources either manifest as common medical
Peripheral neuropathy (PN)
 Peripheral neuropathy (PN) damage or disease affecting nerves, which may impair sensation, movement, gland or organ function, or other aspects of health, depending on the type of nerve affected o chronic:
Peripheral neuropathy (PN) damage or disease affecting nerves, which may impair sensation, movement, gland or organ function, or other aspects of health, depending on the type of nerve affected o chronic:
Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care
 Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care Spencer Johnson, O.D., F.A.A.O. Northeastern State University Oklahoma College of Optometry johns137@nsuok.edu Course Objectives Review headache classification Understand
Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care Spencer Johnson, O.D., F.A.A.O. Northeastern State University Oklahoma College of Optometry johns137@nsuok.edu Course Objectives Review headache classification Understand
Multiple System Atrophy
 Multiple System Atrophy This document has been prepared to help you become more informed about Multiple System Atrophy. It is designed to answer questions about the condition and includes suggestions on
Multiple System Atrophy This document has been prepared to help you become more informed about Multiple System Atrophy. It is designed to answer questions about the condition and includes suggestions on
The Neurologic Examination: High-Yield Strategies
 The Neurologic Examination: High-Yield Strategies S. Andrew Josephson, MD Examination Approach Two types of neurologic examinations 1. Screening Examination 2. Testing Hypotheses Select high-yield tests
The Neurologic Examination: High-Yield Strategies S. Andrew Josephson, MD Examination Approach Two types of neurologic examinations 1. Screening Examination 2. Testing Hypotheses Select high-yield tests
DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM. Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine
 DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine THE MOTOR SYSTEM To understand disorders of the motor system, we need to review how a
DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine THE MOTOR SYSTEM To understand disorders of the motor system, we need to review how a
Neurological Conditions List by Practitioner Type MED-NEURODA~001
 Neurological Conditions List by Practitioner Type MED-NEURODA~001 Date: 26 May 2016 Foreword This guidance has been produced as part of a training programme for Healthcare Professionals approved by the
Neurological Conditions List by Practitioner Type MED-NEURODA~001 Date: 26 May 2016 Foreword This guidance has been produced as part of a training programme for Healthcare Professionals approved by the
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS PROFILE
 MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS PROFILE What is Multiple Sclerosis? Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic, inflammatory disease of unknown etiology that involves an immune-mediated attack on the central nervous system
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS PROFILE What is Multiple Sclerosis? Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic, inflammatory disease of unknown etiology that involves an immune-mediated attack on the central nervous system
Poisoning and Overdose Emergencies
 CHAPTER 21 Poisoning and Overdose Emergencies Key Term Poison Any substance that can harm the body Four Routes of Poisoning INHALATION INJECTION Drugs Sprays Cleaning Fluid INGESTION Lye Household Cleaners
CHAPTER 21 Poisoning and Overdose Emergencies Key Term Poison Any substance that can harm the body Four Routes of Poisoning INHALATION INJECTION Drugs Sprays Cleaning Fluid INGESTION Lye Household Cleaners
The signs and symptoms of diabetic neuropathy vary, depending on the type of neuropathy and which nerves are affected.
 DIABETIC NEUROPATHY Overview Diabetic neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that can occur if you have diabetes. High blood sugar (glucose) can injure nerve fibers throughout your body, but diabetic neuropathy
DIABETIC NEUROPATHY Overview Diabetic neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that can occur if you have diabetes. High blood sugar (glucose) can injure nerve fibers throughout your body, but diabetic neuropathy
Examination Approach. Examination Approach. Case 1: Mental Status. The Neurological Exam In the ICU: High Yield Techniques 5/8/2015
 The Neurological Exam In the ICU: High Yield Techniques Examination Approach Two types of neurologic examinations 1. Screening Examination 2. Testing Hypotheses Select high-yield tests and techniques S.
The Neurological Exam In the ICU: High Yield Techniques Examination Approach Two types of neurologic examinations 1. Screening Examination 2. Testing Hypotheses Select high-yield tests and techniques S.
The Neurology of HIV Infection. Carolyn Barley Britton, MD, MS Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology Columbia University
 The Neurology of HIV Infection Carolyn Barley Britton, MD, MS Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology Columbia University HIV/AIDS Epidemiology World-wide pandemic, 40 million affected U.S.- Disproportionate
The Neurology of HIV Infection Carolyn Barley Britton, MD, MS Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology Columbia University HIV/AIDS Epidemiology World-wide pandemic, 40 million affected U.S.- Disproportionate
Dizziness: Neurological Aspect
 Dizziness: Neurological Aspect..! E-mail: somtia@kku.ac.th http://epilepsy.kku.ac.th Features between peripheral and central vertigo 1. Peripheral Central 2.! " # $ " Imbalance Mild-moderate Severe 3.!
Dizziness: Neurological Aspect..! E-mail: somtia@kku.ac.th http://epilepsy.kku.ac.th Features between peripheral and central vertigo 1. Peripheral Central 2.! " # $ " Imbalance Mild-moderate Severe 3.!
Biology 3201 Nervous System # 7: Nervous System Disorders
 Biology 3201 Nervous System # 7: Nervous System Disorders Alzheimer's Disease first identified by German physician, Alois Alzheimer, in 1906 most common neurodegenerative disease two thirds of cases of
Biology 3201 Nervous System # 7: Nervous System Disorders Alzheimer's Disease first identified by German physician, Alois Alzheimer, in 1906 most common neurodegenerative disease two thirds of cases of
peripheral neuropathy peripheral neuropathy neuropathy peripheral neuropathy neuropathic foot heel Bilateral foot pain Bilateral heel pain bilateral
 Peripheral neuropathy (PN) is damage to or disease affecting nerves, which may impair sensation, movement, gland or organ function, or other aspects of health. The 2018 edition of ICD-10-CM G62.9. Auditory
Peripheral neuropathy (PN) is damage to or disease affecting nerves, which may impair sensation, movement, gland or organ function, or other aspects of health. The 2018 edition of ICD-10-CM G62.9. Auditory
Diabetic Neuropathy. Nicholas J. Silvestri, M.D.
 Diabetic Neuropathy Nicholas J. Silvestri, M.D. Types of Neuropathies Associated with Diabetes Mellitus p Chronic distal sensorimotor polyneuropathy p Focal compression neuropathies p Autonomic neuropathy
Diabetic Neuropathy Nicholas J. Silvestri, M.D. Types of Neuropathies Associated with Diabetes Mellitus p Chronic distal sensorimotor polyneuropathy p Focal compression neuropathies p Autonomic neuropathy
Parkinson Disease. Lorraine Kalia, MD, PhD, FRCPC. Presented by: Ontario s Geriatric Steering Committee
 Parkinson Disease Lorraine Kalia, MD, PhD, FRCPC Key Learnings Parkinson Disease (L. Kalia) Key Learnings Parkinson disease is the most common but not the only cause of parkinsonism Parkinson disease is
Parkinson Disease Lorraine Kalia, MD, PhD, FRCPC Key Learnings Parkinson Disease (L. Kalia) Key Learnings Parkinson disease is the most common but not the only cause of parkinsonism Parkinson disease is
Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level
 Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level Prerequisites: Any prior pediatric rotations and experience Primary Goals for this
Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level Prerequisites: Any prior pediatric rotations and experience Primary Goals for this
Dementia. Assessing Brain Damage. Mental Status Examination
 Dementia Assessing Brain Damage Mental status examination Information about current behavior and thought including orientation to reality, memory, and ability to follow instructions Neuropsychological
Dementia Assessing Brain Damage Mental status examination Information about current behavior and thought including orientation to reality, memory, and ability to follow instructions Neuropsychological
Common Pitfalls in Multiple Sclerosis and CNS Demyelinating Diseases
 Common Pitfalls in Multiple Sclerosis and CNS Demyelinating Diseases Case-Based Learning Common Pitfalls in Multiple Sclerosis and CNS Demyelinating Diseases Case-Based Learning Mayo Clinic College of
Common Pitfalls in Multiple Sclerosis and CNS Demyelinating Diseases Case-Based Learning Common Pitfalls in Multiple Sclerosis and CNS Demyelinating Diseases Case-Based Learning Mayo Clinic College of
Medications and the I/DD Population
 Medications and the I/DD Population A Supplemental Document to Session 4 in Webinar Series ADR Symptoms that Mimic Age Related/Associated Changes and Diseases Biological Changes Impaired senses Cardiovascular
Medications and the I/DD Population A Supplemental Document to Session 4 in Webinar Series ADR Symptoms that Mimic Age Related/Associated Changes and Diseases Biological Changes Impaired senses Cardiovascular
Stroke School for Internists Part 1
 Stroke School for Internists Part 1 November 4, 2017 Dr. Albert Jin Dr. Gurpreet Jaswal Disclosures I receive a stipend for my role as Medical Director of the Stroke Network of SEO I have no commercial
Stroke School for Internists Part 1 November 4, 2017 Dr. Albert Jin Dr. Gurpreet Jaswal Disclosures I receive a stipend for my role as Medical Director of the Stroke Network of SEO I have no commercial
MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE
 MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE Dr Arun Aggarwal Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, RPAH Department of Neurology, Concord Hospital. Motor Neurone Disease Umbrella term in UK and Australia (ALS in USA) Neurodegenerative
MOTOR NEURONE DISEASE Dr Arun Aggarwal Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, RPAH Department of Neurology, Concord Hospital. Motor Neurone Disease Umbrella term in UK and Australia (ALS in USA) Neurodegenerative
Lina AL-Lawama and Tasneem Montaj. Abdullah Nimer. Loai Zghoul
 2 Lina AL-Lawama and Tasneem Montaj Abdullah Nimer Loai Zghoul At the end of this sheet you should be able to understand the general characteristics of action potential and some of its clinical applications
2 Lina AL-Lawama and Tasneem Montaj Abdullah Nimer Loai Zghoul At the end of this sheet you should be able to understand the general characteristics of action potential and some of its clinical applications
e) None of the above e) None of the above
 Neurology 1) For the management of an acute delirium acquired in the hospital, which one of the following options would be least appropriate? a) Treating the underlying cause b) Promptly increasing antibiotic
Neurology 1) For the management of an acute delirium acquired in the hospital, which one of the following options would be least appropriate? a) Treating the underlying cause b) Promptly increasing antibiotic
CASE 48. What part of the cerebellum is responsible for planning and initiation of movement?
 CASE 48 A 34-year-old woman with a long-standing history of seizure disorder presents to her neurologist with difficulty walking and coordination. She has been on phenytoin for several days after having
CASE 48 A 34-year-old woman with a long-standing history of seizure disorder presents to her neurologist with difficulty walking and coordination. She has been on phenytoin for several days after having
New Patient History. Name: DOB: Sex: Date: If yes, give the name of the physician who did your evaluation or ordered your tests:
 New Patient History Name: DOB: Sex: Date: Chief Complaint: 1. Give a brief description of the problem you are seeking treatment for today: 2. Have you been evaluated for this problem or had any tests for
New Patient History Name: DOB: Sex: Date: Chief Complaint: 1. Give a brief description of the problem you are seeking treatment for today: 2. Have you been evaluated for this problem or had any tests for
extremities, bilateral icd 10
 Peripheral neuropathy, lower extremities, bilateral icd 10 The Borg System is 100 % Peripheral neuropathy, lower extremities, bilateral icd 10 Idiopathic peripheral autonomic neuropathy; Peripheral autonomic
Peripheral neuropathy, lower extremities, bilateral icd 10 The Borg System is 100 % Peripheral neuropathy, lower extremities, bilateral icd 10 Idiopathic peripheral autonomic neuropathy; Peripheral autonomic
HISTORY TAKING ON NERVOUS SYSTEM. Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal
 HISTORY TAKING ON NERVOUS SYSTEM Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal General points History of neurological symptoms should also be taken from patient and close relative or friend Memory loss, intoxication, aphasia Patient
HISTORY TAKING ON NERVOUS SYSTEM Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal General points History of neurological symptoms should also be taken from patient and close relative or friend Memory loss, intoxication, aphasia Patient
BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII
 463 Brain stem Case history BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII A 60 year old man with hypertension wakes one morning with trouble walking. He is feeling dizzy and is sick to his stomach. His wife
463 Brain stem Case history BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII A 60 year old man with hypertension wakes one morning with trouble walking. He is feeling dizzy and is sick to his stomach. His wife
Epilepsy DOJ Lecture Masud Seyal, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurology University of California, Davis
 Epilepsy DOJ Lecture - 2005 Masud Seyal, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurology University of California, Davis Epilepsy SEIZURE: A temporary dysfunction of the brain resulting from a self-limited abnormal
Epilepsy DOJ Lecture - 2005 Masud Seyal, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurology University of California, Davis Epilepsy SEIZURE: A temporary dysfunction of the brain resulting from a self-limited abnormal
Neurological Assessment
 Neurological Assessment Name: Age: Gender: Date: History Review of history related to neurological system YES/NO If YES, provide details: General Neurological Mental Illness Neurological disease Severe
Neurological Assessment Name: Age: Gender: Date: History Review of history related to neurological system YES/NO If YES, provide details: General Neurological Mental Illness Neurological disease Severe
Interactive seminar - neurosciences. 1_of 40+
 Interactive seminar - neurosciences 1_of 40+ Q1/1 EMG myopathies versus neuropathies Interactive seminar - neurosciences 2_of 40+ Q1/2 Neuropathies versus myopathies Clinical findings Muscle weakness Loss
Interactive seminar - neurosciences 1_of 40+ Q1/1 EMG myopathies versus neuropathies Interactive seminar - neurosciences 2_of 40+ Q1/2 Neuropathies versus myopathies Clinical findings Muscle weakness Loss
Diagnostic Grouping: Traumatic Brain Disorders
 Diagnostic Grouping: Traumatic Brain Disorders Brittany Livengood and Emily Lineberger Specific Type Names of disorders in this category Traumatic Brain Disorders Closed : This happens when the head thrusts
Diagnostic Grouping: Traumatic Brain Disorders Brittany Livengood and Emily Lineberger Specific Type Names of disorders in this category Traumatic Brain Disorders Closed : This happens when the head thrusts
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms
 III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
Peripheral Nerve Disorders
 Helping people affected by Guillain-Barré syndrome, CIDP & associated inflammatory neuropathies Peripheral Nerve Disorders Helpline: 0800 374803 (UK) 1800 806152 (ROI) Peripheral Nerve Disorders - Page
Helping people affected by Guillain-Barré syndrome, CIDP & associated inflammatory neuropathies Peripheral Nerve Disorders Helpline: 0800 374803 (UK) 1800 806152 (ROI) Peripheral Nerve Disorders - Page
Pain Management Questionnaire
 In order to make the most of your visit, we require this form to be completed to the best of your ability and sent to the Pain Management Clinic a copy should be shared with your Primary Care Provider
In order to make the most of your visit, we require this form to be completed to the best of your ability and sent to the Pain Management Clinic a copy should be shared with your Primary Care Provider
International Brain Bee Syllabus 2012 Department of Neurosciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia
 BRAIN DEVELOPMENT The cells of the nervous system connect with one another in trillions of remarkably specific patterns that form and change over the course of an organism s life. These connections develop
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT The cells of the nervous system connect with one another in trillions of remarkably specific patterns that form and change over the course of an organism s life. These connections develop
WILLIAM K MONTGOMERY, MD
 WILLIAM K MONTGOMERY, MD Knee and Hip Joint Replacement Specialist New Patient Questionnaire NAME: DOB: / / AGE: Your Primary Care Physician: Phone Number: Referring Physician: Phone Number: Are you a
WILLIAM K MONTGOMERY, MD Knee and Hip Joint Replacement Specialist New Patient Questionnaire NAME: DOB: / / AGE: Your Primary Care Physician: Phone Number: Referring Physician: Phone Number: Are you a
The High-Yield Neurologic Examination
 The High-Yield Neurologic Examination S. Andrew Josephson MD Carmen Castro Franceschi and Gladyne K. Mitchell Neurohospitalist Distinguished Professor Chair, Department of Neurology Director, Neurohospitalist
The High-Yield Neurologic Examination S. Andrew Josephson MD Carmen Castro Franceschi and Gladyne K. Mitchell Neurohospitalist Distinguished Professor Chair, Department of Neurology Director, Neurohospitalist
