The evaluation of analgesic effects of simvastatin, pravastatin and atorvastatin in hot plate test
|
|
|
- Hannah Austin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences The evaluation of analgesic effects of simvastatin, pravastatin and atorvastatin in hot plate test M. KESIM, M. KADIOGLU, M. OKUYAN*, E. MUCI, I. ERKOSEOGLU, N.I. KALYONCU, E. YARIS 2012; 16: Department of Pharmacology and *Department of Physiology, Karadeniz Technical University, School of Medicine, Trabzon (Turkey) Abstract. Objectives: Simvastatin, pravastatin and atorvastatin have been evaluated whether to have analgesic effects in mice in hot plate test. Materials and Methods: Simvastatin (5, 10, 30 mg/kg), pravastatin (5, 10, 30 mg/kg) and atorvastatin (5, 10, 30 mg/kg) were administered acute and chronically by oral gavage in mice. Control (pretreatment value) and posttreatment (after drugs application) values in 60 th and 120 th minutes were measured in hot-plate test. Results: All three drugs at 10, 30 mg/kg doses produced analgesic effects compared with their control values in 60 th and 120 th minutes on acute and chronic application in mice. The analgesic effects of drugs were evaluated after the application of L-nitro arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) (10 mg/kg) or naloxone (0.5 mg/ kg). L-NAME (10 mg/kg) has no effect compared to the control value on both minutes. The analgesic effects of both atorvastatin (30 mg/kg) and simvastatin (30 mg/kg) in the presence of L-NAME (10 mg/kg) were not inhibited. However, the analgesic effect of pravastatin (30 mg/kg) in the presence of L- NAME (10 mg/kg) was inhibited significantly on both minutes (p < 0.05). Naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) has no effect compared to the control value on both minutes. The analgesic effect of atorvastatin (30 mg/kg) in the presence of naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) was partially (43%) but significantly inhibited only on 60 th minute (p < 0.05). The analgesic effect of pravastatin (30 mg/kg) in the presence of naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) was partially (48-40%) but significantly inhibited on both minutes (p < 0.05). However, the analgesic effect of simvastatin (30 mg/kg) in the presence of naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) was inhibited significantly on both minutes (p < 0.05). Conclusions: These finding indicated that the analgesic effect of pravastatin was related to nitrergic systems and partially opioidergic system; analgesic effect of simvastatin was related to opiodergic system in hot plate test. However, the analgesic effect of atorvastatin was not directly related to both system. Key Words: Simvastatin, Pravastatin, Atorvastatin, Analgesia, Hot plate test. Introduction The pain is an unpleasant sensory and an emotional experience occurs as a result of mechanical, thermal and chemical nociceptive stimuli induced tissue injury. Cytokines which are released from the damaged tissue cause the release of hyperalgesic neuromediators (such as prostaglandins, serotonine) and lead to pain and inflammation 1,2. In the meantime, nitric oxide and opioid peptides, released from the damaged tissues, contribute to the anti-inflammatory and analgesic process 3,4. It has been shown that as a result of reducing mast cell degranulation in the inflammatory tissues, nitric oxide causes antiinflammatory effects 3. Also, opioid peptides that are released from the damaged tissue generate an analgesic effect via the opioidergic receptors located on peripheral nociceptors 4-6. Statins, 3-hydroxy-3 methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase enzyme inhibitors, are lipid-lowering drugs, often used in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases (hyperlipidemia, atherosclerosis). It has been shown that statins have antiinflammatory effects independent of their lipid-lowering effects and these antiinflammatory effects inhibit the inflammation and pain process in the inflammatory diseases (such as rheumatoid arthritis) 7,8. The inhibition of releasing of cytokines is shown to play a role in anti-inflammatory effects of statins 9,10. In this study, we aimed to investigate the possible analgesic effects of three statins, two Corresponding Author: Murat Kesim, MD; muratkesim@gmail.com 789
2 M. Kesim, M. Kadioglu, M. Okuyan, E. Muci, I. Erkoseoglu, N.I. Kalyoncu, E. Yaris lipophilic (atorvastatin, simvastatin) and one hydrophilic (pravastatin), in hot-plate test in mice by oral gavage. Material and Methods Study was held on in the Karadeniz Technical University, School of Medicine, Behavioral Pharmacology Laboratory of Department of Pharmacology. Balb/c mice of either sex weighting g were randomly used in the experiments. All of the animals were housed in cages with free access to food and water. The cages were placed in a quiet and temperature-humidity controlled room (22 ± 2 C and 60 ± 5%, respectively) in which a 12:12-h light-dark cycle was maintained. Experiments were conducted between 9:00 and 17:00 h to minimize the diurnal variation. The experimental protocol was approved by the Local Ethics Committee of School of Medicine, Karadeniz Technical University. Hot plate test were used to analgesic method. Hot-Plate Test The temperature of the hot plate was set to 55 ± 0.5 C. The time of latency was defined as the time period between the zero point when the animal was placed on the hot plate surface and the time when the animal licked its back paw or jumped off to avoid thermal pain. Baseline latency (pretreatment value) was determined before drug application for each mouse. Post treatment latencies were determined after 60 th and 120 th minutes. Values were compared with pretreatment values. The cut-off time was set to 30 seconds in order to minimize skin injury. Drugs Simvastatin (Merck Sharp & Dohme, Istanbul, Turkey) and atorvastatin (Pfizer, Istanbul, Turkey) were dissolved in phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Pravastatin (Bristol-Myers Squibb, Istanbul, Turkey) and L-NAME (L-nitro arginine methyl ester; nitric oxide synthase inhibitor) (Sigma: Saint Louis, MO, USA) were dissolved in saline. Naloxone (opioidergic receptor antagonist) (Abbott Laboratories, Abbott Park, IL, USA) was used in the form they are manufactured. Simvastatin, atorvastatin and pravastatin were administrated by oral gavage. L-NAME and naloxone were administrated intraperitoneally (i.p.) in a dose volume of no more than 10 ml/kg. Experimental protocols Mice were divided into the following experimental groups: Group 1 (Acute application groups) Vehicle group (PBS) (n= 6) Atorvastatin (5 mg/kg) group [A(5)] (n= 6) Atorvastatin (10 mg/kg) group [A(10)] (n= 6) Atorvastatin (30 mg/kg) group [A(30)] (n= 6) Simvastatin (5 mg/kg) group [S(5) ](n= 6) Simvastatin (10 mg/kg) group [S(10)] (n= 6) Simvastatin (30 mg/kg) group [S(30)] (n= 6) Pravastatin (5 mg/kg) group [P(5)] (n= 6) Pravastatin (10 mg/kg) group [P(10)] (n= 6) Pravastatin (30 mg/kg) group [P(30)] (n = 6) Group 2 (Chronical application groups) Atorvastatin (5 mg/kg) group [A(5)] (n= 6) Atorvastatin (10 mg/kg) group [A(10)] (n= 6) Atorvastatin (30 mg/kg) group [A(30)] (n= 6) Simvastatin (5 mg/kg) group [S(5) ](n= 6) Simvastatin (10 mg/kg) group [S(10)] (n= 6) Simvastatin (30 mg/kg) group [S(30)] (n= 6) Pravastatin (5 mg/kg) group [P(5)] (n= 6) Pravastatin (10 mg/kg) group [P(10)] (n= 6) Pravastatin (30 mg/kg) group [P(30)] (n = 6) Group 3 (Investigation of mechanism groups) Naloxone (0,5 mg kg) group [N] (n= 6) L-NAME (10 mg/kg) group [L-NAME] (n= 6) Atorvastatin (30 mg/kg) +Naloxone (0.5 mg /kg) group [A(30)+N] (n= 6) Simvastatin (30 mg/kg) + Naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) group [S(30)+N)] (n= 6) Pravastatin (30 mg/kg) +Naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) group [P(30)+N) (n= 6) Atorvastatin (30 mg/kg) + L-NAME (10 mg/kg) group [A(30)+L-NAME] (n= 6) Simvastatin (30 mg/kg) + L-NAME (10 mg/kg) group [S(30)+L-NAME] (n= 6) Pravastatin (30 mg/kg) + L-NAME (10 mg/kg) group [P(30)+L-NAME] (n= 6) Group 1 (Acute application groups) Statins and vehicle were administered by oral gavage in mice. Control (preatreatment value) and post treatment (after drugs application) values in 60 th and 120 th minutes were measured in hot-plate test. Group 2 (Chronical application groups) Statins were administered by oral gavage once daily for 3 days in mice. At the end of 3 days, 790
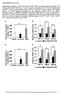
3 The evaluation of analgesic effects of simvastatin, pravastatin and atorvastatin in hot plate test control (preatreatment value) and post treatment (after drugs application) values in 60 th and 120 th minutes were measured in hot-plate test. Group 3 (Investigation of the mechanism groups) Firstly, L-NAME or naloxone have been evaluated whether to have an effect in hot plate test. In this context, naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) or L- NAME (10 mg/kg) was administered by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection in mice. Control (pretreatment value) and post treatment values in 60 th and 120 th minutes after naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) or L-NAME (10 mg/kg) application were measured in hot-plate test. Secondly, the analgesic effects of statins have been evaluated in the presence of L-NAME or naloxone. Before treatment with statins, pretreatment values were measured. Afterwards, statins were administered orally by gavage. After 30 minutes of statins application, naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) or L-NAME (10 mg/kg) was applied intraperitoneally (ip). Post treatment values in 60 th and 120 th minutes after statins application were measured in hot-plate test. Statistical Analysis The data were expressed as the mean ± S.E.M. Statistical analysis were carried out using Mann- Whitney U test. The level of significance was set at p < Results Atorvastatin (10, 30 mg/kg), simvastatin (10, 30 mg/kg) and pravastatin (10, 30 mg/kg) produced a statistically significant analgesic effect compared to their control values on 60 th and 120 th minutes in mice in group 1 (Figure 1) (p < 0.05). However, atorvastatin (5 mg/kg), simvastatin (5 mg/kg) and pravastatin (5 mg/kg) did not produce anyone statistically significant analgesic effect compared to their controls on 60 th and 120 th minutes in mice in group 1 (Figure 1) (p > 0.05). Vehicle group did not produce a statistically significant effect compared to the control (p > 0.05). Atorvastatin (10, 30 mg/kg), simvastatin (30 mg/kg) and pravastatin (10, 30 mg/kg) produced a statistically significant analgesic effect compared to their control values on 60 th and 120 th minutes in mice in group 2 (Figure 2) (p < 0.05). However, simvastatin (10 mg/kg) did not produce a statistically significant analgesic effect compared to their control on 120 th minutes in mice in group 2 (Figure 2) (p > 0.05). At doses of 5 Figure 1. Analgesic effect of atorvastatin, simvastatin and pravastatin after acute aplication in 60 th and 120 th minutes in hotplate test. {Atorvastatin (5 mg/kg) group [A(5)], Atorvastatin (10 mg/kg) group [A(10)], Atorvastatin (30 mg/kg) group [A(30)], Simvastatin (5 mg/kg) group [S(5)], Simvastatin (10 mg/kg) group [S(10)], Simvastatin (30 mg/kg) group [S(30)], Pravastatin (5 mg/kg) group [P(5)], Pravastatin (10 mg/kg) group [P(10)], Pravastatin (30 mg/kg) group [P(30)]}. *Compared with its own control value (p < 0.05). 791
4 M. Kesim, M. Kadioglu, M. Okuyan, E. Muci, I. Erkoseoglu, N.I. Kalyoncu, E. Yaris Figure 2. Analgesic effect of atorvastatin, simvastatin and pravastatin after chronically aplication in 60 th and 120 th minutes in hot-plate test. {Atorvastatin (5 mg/kg) group [A(5)], Atorvastatin (10 mg/kg) group [A(10)], Atorvastatin (30 mg/kg) group [A(30)], Simvastatin (5 mg/kg) group [S(5)], Simvastatin (10 mg/kg) group [S(10)], Simvastatin (30 mg/kg) group [S(30)], Pravastatin (5 mg/kg) group [P(5)], Pravastatin (10 mg/kg) group [P(10)], Pravastatin (30 mg/kg) group [P(30)]}. *Compared with its own control value (p < 0.05). mg/kg in atorvastatin, simvastatin and pravastatin did not produce a statistically significant analgesic effect compared to their control values on 60 th and 120 th minutes in mice in group 2 (Figure 2) (p > 0.05). L-NAME (10 mg/kg) has no effect compared to the control value on both minutes. The analgesic effects of both atorvastatin (30 mg/kg) and simvastatin (30 mg/kg) in the presence of L- NAME (10 mg/kg) were not inhibited (Figures 3 and 4). However, the analgesic effect of pravastatin (30 mg/kg) in the presence of L-NAME (10 mg/kg) was inhibited significantly on both minutes (Figure 5) (p < 0.05). Naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) has no effect compared to the control value on both minutes. The anal- Figure 3. Effect of L-NAME (10 mg/kg) on the analgesia induced by atorvastatin (30 mg/kg) in hot plate test. {Atorvastatin (30 mg/kg) group [A(30)], L-NAME (10 mg/kg) group [L-NAME], Atorvastatin (30 mg/kg) + L-NAME (10 mg/kg) group [A(30)+L-NAME]}. *Compared with its own control value (p < 0.05), 792
5 The evaluation of analgesic effects of simvastatin, pravastatin and atorvastatin in hot plate test Figure 4. Effect of L-NAME (10 mg/kg) on the analgesia induced by simvastatin (30 mg/kg) in hot plate test. {Simvastatin (30 mg/kg) group [S(30)], L-NAME (10 mg/kg) group [L-NAME], Simvastatin (30 mg/kg) + L-NAME (10 mg/kg) group [S(30)+L-NAME]}. *Compared with its own control value (p < 0.05). gesic effect of atorvastatin (30 mg/kg) in the presence of naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) was partially (43%) but significantly inhibited only on 60 th minute (Figure 6) (p < 0.05). The analgesic effect of pravastatin (30 mg/kg) in the presence of naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) was partially (48-40%) but significantly inhibited on both minutes (Figure 7) (p < 0.05). However, the analgesic effect of simvastatin (30 mg/kg) in the presence of naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) was inhibited significantly on both minutes (Figure 8) (p < 0.05). Discussion Statins are widely used for the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Recent studies have focused on the antiinflamatory effects on the inflammatory disease. It has been shown that atorvastatin produced antiinflammatory and analgesic effects by preventing the release of inflammatory cytokines (such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6) in arthritis models in rats There are clinical studies showing that simvastatin and atorvastatin Figure 5. Effect of L-NAME (10 mg/kg) on the analgesia induced by pravastatin (30 mg/kg) in hot plate test. {Pravastatin (30 mg/kg) group [A(30)], L-NAME (10 mg/kg) group [L-NAME], Pravastatin (30 mg/kg) + L-NAME (10 mg/kg) group [P(30)+L-NAME]}. *Compared with its own control value (p < 0.05). 793
6 M. Kesim, M. Kadioglu, M. Okuyan, E. Muci, I. Erkoseoglu, N.I. Kalyoncu, E. Yaris Figure 6. Effect of naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) on the analgesia induced by atorvastatin (30 mg/kg) in hot plate test {Atorvastatin (30 mg/kg) group [A(30)], Naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) group [N], Atorvastatin (30 mg/kg + Naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) group [A(30)+N]}. *Compared with its own control value (p < 0.05); Compared with the % inhibition in its own corresponding value (p < 0.05). prevented the release of proinflamatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8) and reduced the level of C-reactive proteins (CRP) and on this way contributed to the antiinflammatory process in inflammatory diseases (RA, SLE, osteoporosis) 8,14. Although there are several studies reporting the antiinflamatory effect of statins, there are not enough data related to their analgesic effects. We have studied the analgesic effects of three statins, two lipophilic (atorvastatin, simvastatin) and one hydrophilic (pravastatin), in hot-plate test in mice. In our study, atorvastatin, simvastatin and pravastatin produced analgesic effects on acute and chronically application in the hot-plate test. The role of cytokines in pain is clearly known. Cytokines which are released from damaged tissue lead to pain and inflammation 1,2. It is thought that statins produced antiinflammatory and analgesic effects by inhibiting the release of inflammatory cytokines. Also, nitric oxide and opioid peptides are released from damaged tissues and they contribute to anti-inflammatory and analgesic process 3,4. Santodomingo-Garzón T et al 10 Figure 7. Effect of naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) on the analgesia induced by pravastatin (30 mg/kg) in hot plate test {Pravastatin (30 mg/kg) group [P(30)], Naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) group [N], Pravastatin (30 mg/kg) + Naloxone (0.5 mg(kg) group [P(30)+N)]}. *Compared with its own control value (p < 0,05); Compared with the% inhibition in its own corresponding value (p < 0.05). 794
7 The evaluation of analgesic effects of simvastatin, pravastatin and atorvastatin in hot plate test Figure 8. Effect of naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) on the analgesia induced by simvastatin (30 mg/kg) in hot plate test [Simvastatin (30 mg/kg) group (S30), Naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) group (N), Simvastatin (30 mg/kg) + Naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) group (S30+N)]. *Compared with its own preatreatment value (p < 0.05). showed the analgesic and antiinflammatory effects of atorvastatin and the role of inhibition of cytokine release from tissues and the stimulation of the production of NO in rats in these effects. In our investigation, while L-NAME inhibited the analgesic effect of pravastatin completely, it had no effect on the analgesic effects of atorvastatin and simvastatin. As a result of the findings related with the studies done by L-NAME, it can be said that the analgesic effects of pravastatin might be related with the stimulation of NO production. There are studies reporting that pravastatin increased the NO release and produced antiinflammatory effects However, the analgesic effects of simvastatin and atorvastatin were not inhibited by L-NAME, so other factors in inflammation and pain process may have contributory role in the analgesic effects of simvastatin and atorvastatin. Many investigations have shown that the peripheral opioid receptors underwent an expression during the tissue damage by thermal, mechanical or chemical stimulus and the stimulation of these receptors produced an analgesic effect 4-6,18,19. In our study, naloxone (0.5 mg/kg) inhibited the analgesic effects of atorvastatin and pravastatin partially. However, it inhibited the analgesic effect of simvastatin completely. These findings showed that the opioidergic system has a role in the analgesic effect of simvastatin but not of atorvastatin and pravastatin. Atorvastatin and simvastatin used in this research have lipophilic characters; whereas pravastatin has hydrophilic character 20. When our findings are evaluated with these properties of statins, it could be said that there is a role of central and peripheral mechanisms in the analgesic effects of atorvastatin or simvastatin and only peripheral mechanisms in the analgesic effect of pravastatin. In conclusion, it can be thougth that there is a contribution of opioidergic system in the analgesic effect of simvastatin and pravastatin; contribution of nitrergic system in analgesic effect of pravastatin. However, in the analgesic effect of atorvastatin there can be other systems contributing to this effect in addition to opioidergic system rather than nitrergic system. Acknowledgements This study was supported by Karadeniz Technical University Research Fund (Grant No: ). References 1) CUNHA TM, VERRI WA JR, SILVA JS, POOLE S, CUNHA FQ, FERREIRA SH. A cascade of cytokines mediates mechanical inflammatory hypernociception in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: ) VERRI WA JR, CUNHA TM, PARADA CA, POOLE S, CUN- HA FQ, FERREIRA SH. Hypernociceptive role of cytokines and chemokines: targets for analgesic 795
8 M. Kesim, M. Kadioglu, M. Okuyan, E. Muci, I. Erkoseoglu, N.I. Kalyoncu, E. Yaris drug development? Pharmacol Ther 2006; 112: ) ABRAMSON SB, AMIN AR, CLANCY RM, ATTUR M. The role of nitric oxide in tissue destruction. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2001; 15: ) BUSCH-DIENSTFERTIG M, STEIN C. Opioid receptors and opioid peptide-producing leukocytes in inflammatory pain--basic and therapeutic aspects. Brain Behav Immunol 2010; 24: ) JOSEPH EK, LEVINE JD. Mu and delta opioid receptors on nociceptors attenuate mechanical hyperalgesia in rat. Neuroscience 2010; 171: ) KIVELL B, PRISINZANO TE. Kappa opioids and the modulation of pain. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2010; 210: ) MCINNES IB, MCCAREY DW, SATTAR N. Do statins offer therapeutic potential in inflammatory arthritis? Ann Rheum Dis 2004; 63: ) BIELINSKA A, GLUSZKO P. Statins are they potentially useful in rheumatology? Pol Arch Med Wewn 2007; 117: ) TAWFIK MK, GHATTAS MH, ABO-ELMATTY DM, ABDEL-AZ- IZ NA. Atorvastatin restores the balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory mediators in rats with acute myocardial infarction. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2010; 14: ) SANTODOMINGO-GARZÓN T, CUNHA TM, VERRI WA JR, VALÉRIO DA, PARADA CA, POOLE S, FERREIRA SH, CUN- HA FQ. Atorvastatin inhibits inflammatory hypernociception. Br J Pharmacol 2006; 149: ) BARSANTE MM, ROFFÊ E, YOKORO CM, TAFURI WL, SOUZA DG, PINHO V, CASTRO MS, TEIXEIRA MM. Antiinflammatory and analgesic effects of atorvastatin in a rat model of adjuvant-induced arthritis. Eur J Pharmacol 2005; 516: ) WAHANE VD, KUMAR VL. Atorvastatin ameliorates inflammator y hyperalgesia in rat model of monoarticular arthritis. Pharmacol Res 2010; 61: ) KUMAR VL, GURUPRASAD B, WAHANE VD. Atorvastatin exhibits anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties in adjuvant-induced monoarthritis. Inflammopharmacology 2010; 18: ) BLAKE GJ, RIDKER PM. Are statins anti-inflammatory? Curr Control Trials Cardiovasc Med 2000; 1: ) NAPOLI C, IGNARRO LJ. Nitric oxide-releasing drugs. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2003; 43: ) ONGINI E, IMPAGNATIELLO F, BONAZZI A, GUZZETTA M, GOVONI M, MONOPOLI A, DEL SOLDATO P, IGNARRO LJ. Nitric oxide (NO)-releasing statin derivatives, a class of drugs showing enhanced antiproliferative and antiinflammatory properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2004; 101: ) AMORUSO A, BARDELLI C, FRESU LG, POLETTI E, PALMA A, CANOVA DF, ZENG HW, ONGINI E, BRUNELLESCHI S. The nitric oxide-donating pravastatin, NCX 6550, inhibits cytokine release and NF-κB activation while enhancing PPARγ expression in human monocyte/macrophages. Pharmacol Res 2010; 62: ) SCHÄFER M. Peripheral opioid analgesia: from experimental to clinical studies. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 1999; 12: ) STEIN C, LANG LJ. Peripheral mechanisms of opioid analgesia. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2009; 9: ) Bellosta S, Paoletti R, Corsini A. Safety of statins: focus on clinical pharmacokinetics and drug interactions. Circulation 2004; 109(23 Suppl 1): III50- III
Analgesic Activity of Sathikkai Podi- a Siddha Drug
 Research Article Analgesic Activity of Sathikkai Podi- a Siddha Drug K. Kanagavalli 1, P. Kavitha 2, J. Anbu 3, P. Sathiya Rajeswaran 4 and P. Parthiban 5 1 UG Maruthuvam Department. 2 PG Scholar final
Research Article Analgesic Activity of Sathikkai Podi- a Siddha Drug K. Kanagavalli 1, P. Kavitha 2, J. Anbu 3, P. Sathiya Rajeswaran 4 and P. Parthiban 5 1 UG Maruthuvam Department. 2 PG Scholar final
Atorvastatin inhibits inflammatory hypernociception
 British Journal of Pharmacology (2006) 149, 14 22 & 2006 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 1188/06 $30.00 www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPER Atorvastatin inhibits inflammatory hypernociception
British Journal of Pharmacology (2006) 149, 14 22 & 2006 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 1188/06 $30.00 www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPER Atorvastatin inhibits inflammatory hypernociception
Graduate School of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Meiji University of Oriental Medicine , Japan
 The American Journal of Chinese Medicine, Vol. 32, No. 2, 269 279 2004 World Scientific Publishing Company Institute for Advanced Research in Asian Science and Medicine Corticotropin-Releasing Factor and
The American Journal of Chinese Medicine, Vol. 32, No. 2, 269 279 2004 World Scientific Publishing Company Institute for Advanced Research in Asian Science and Medicine Corticotropin-Releasing Factor and
TRAMADOL, A CENTRALLY ACTING OPIOID : ANTICONVULSANT EFFECT AGAINST MAXIMAL ELECTROSHOCK SEIZURE IN MICE
 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 1998; 42 (3) : 407-411 TRAMADOL, A CENTRALLY ACTING OPIOID : ANTICONVULSANT EFFECT AGAINST MAXIMAL ELECTROSHOCK SEIZURE IN MICE ANSHU MANOCHA, KRISHNA K. SHARMA* AND PRAMOD K.
Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 1998; 42 (3) : 407-411 TRAMADOL, A CENTRALLY ACTING OPIOID : ANTICONVULSANT EFFECT AGAINST MAXIMAL ELECTROSHOCK SEIZURE IN MICE ANSHU MANOCHA, KRISHNA K. SHARMA* AND PRAMOD K.
SHORT COMMUNICATION EFFECT OF SILDENAFIL ON ANXIETY IN THE PLUS-MAZE TEST IN MICE
 Copyright 2004 by Institute of Pharmacology Polish Academy of Sciences Polish Journal of Pharmacology Pol. J. Pharmacol., 2004, 56, 353 357 ISSN 1230-6002 SHORT COMMUNICATION EFFECT OF SILDENAFIL ON ANXIETY
Copyright 2004 by Institute of Pharmacology Polish Academy of Sciences Polish Journal of Pharmacology Pol. J. Pharmacol., 2004, 56, 353 357 ISSN 1230-6002 SHORT COMMUNICATION EFFECT OF SILDENAFIL ON ANXIETY
Original paper. Abstract. Abdullah S. Asia 1*, Al-Mahdi A. Modar 2, Hadi M. Ali 3
 Original paper Frequency Of Potential Adverse Effects Of A Semisynthetic Statin (Simvastatin) Compared To A Synthetic Statin (Atorvastatin) Used To Reduce Cardiovascular Risk For Patients In Basra 1*,
Original paper Frequency Of Potential Adverse Effects Of A Semisynthetic Statin (Simvastatin) Compared To A Synthetic Statin (Atorvastatin) Used To Reduce Cardiovascular Risk For Patients In Basra 1*,
Anti-nerve growth factor antibody attenuates chronic morphine treatmentinduced tolerance in the rat
 Cheppudira et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2016) 16:73 DOI 10.1186/s12871-016-0242-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Anti-nerve growth factor antibody attenuates chronic morphine treatmentinduced tolerance in
Cheppudira et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2016) 16:73 DOI 10.1186/s12871-016-0242-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Anti-nerve growth factor antibody attenuates chronic morphine treatmentinduced tolerance in
EFFECTS OF CHLOROGENIC ACID ON LEARNING AND MEMORY IN RATS
 Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 12, Suppl. 1, pp 132-136, 2014 Copyright 2014 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1313-7050 (print) ISSN 1313-3551 (online) EFFECTS OF CHLOROGENIC
Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 12, Suppl. 1, pp 132-136, 2014 Copyright 2014 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1313-7050 (print) ISSN 1313-3551 (online) EFFECTS OF CHLOROGENIC
In vivo effect of anti-inflammatory compounds on HIV-1 gp120 -mediated brain inflammation
 In vivo effect of anti-inflammatory compounds on HIV-1 gp120 -mediated brain inflammation Tamima Ashraf, PhD candidate Supervisor: Dr. Reina Bendayan University of Toronto, Leslie Dan Faculty of Pharmacy,
In vivo effect of anti-inflammatory compounds on HIV-1 gp120 -mediated brain inflammation Tamima Ashraf, PhD candidate Supervisor: Dr. Reina Bendayan University of Toronto, Leslie Dan Faculty of Pharmacy,
Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded
 BY Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded Pediatric Cardiology Unit, Mansoura Universty Children Hospital, Mansoura, Egypt Co-authors: Dina S El-Agamy and Mohamed A Elkablawy Background Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline
BY Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded Pediatric Cardiology Unit, Mansoura Universty Children Hospital, Mansoura, Egypt Co-authors: Dina S El-Agamy and Mohamed A Elkablawy Background Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline
International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics
 International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics ISSN Print: 2278-2648 IJRPP Vol.5 Issue 3 July - Sep - 2016 ISSN Online: 2278-2656 Journal Home page: Research article Open Access
International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics ISSN Print: 2278-2648 IJRPP Vol.5 Issue 3 July - Sep - 2016 ISSN Online: 2278-2656 Journal Home page: Research article Open Access
Nitric oxide (NO) and central dopamine (DA) D3 receptor reactivity to quinpirole in rats
 Nitric oxide (NO) and central dopamine (DA) D3 receptor reactivity to quinpirole in rats Ryszard ~rusl, Ryszard szkilnik1 and Richard M. ~ostrzewa~ '~e~artment of Pharmacology, Silesian Academy of Medicine,
Nitric oxide (NO) and central dopamine (DA) D3 receptor reactivity to quinpirole in rats Ryszard ~rusl, Ryszard szkilnik1 and Richard M. ~ostrzewa~ '~e~artment of Pharmacology, Silesian Academy of Medicine,
EVALUATION OF SELECTED BIOCHEMICAL PARAMETERS OF OXIDATIVE STRESS IN RATS PRETREATED WITH ROSUVASTATIN AND FLUOXETINE
 Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 72 No. 2 pp. 261ñ265, 2015 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society EVALUATION OF SELECTED BIOCHEMICAL PARAMETERS OF OXIDATIVE STRESS IN RATS PRETREATED
Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 72 No. 2 pp. 261ñ265, 2015 ISSN 0001-6837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society EVALUATION OF SELECTED BIOCHEMICAL PARAMETERS OF OXIDATIVE STRESS IN RATS PRETREATED
LETTER TO THE EDITOR. Statins alone are ineffective in cerebral malaria but potentiate artesunate ACCEPTED
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 8 September 2008 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00513-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 8 September 2008 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00513-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions.
Analgesic roles of peripheral intrinsic met-enkephalin and dynorphin A in long-lasting inflammatory pain induced by complete Freund's adjuvant in rats
 2344 Analgesic roles of peripheral intrinsic met-enkephalin and dynorphin A in long-lasting inflammatory pain induced by complete Freund's adjuvant in rats YONG LIANG JIANG, XIAO FEN HE, YA FANG SHEN,
2344 Analgesic roles of peripheral intrinsic met-enkephalin and dynorphin A in long-lasting inflammatory pain induced by complete Freund's adjuvant in rats YONG LIANG JIANG, XIAO FEN HE, YA FANG SHEN,
Jose L. Barboza Jr, Pharm.D. Candidate INSIDE THIS ISSUE: UPDATE ON STATINS: FOCUS ON UNAPPROVED USES. Table 1. Currently Marketed Statins
 Jose L. Barboza Jr, Pharm.D. Candidate O ver two decades ago, the first HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor (statin) was approved to treat hypercholesterolemia, a major modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular
Jose L. Barboza Jr, Pharm.D. Candidate O ver two decades ago, the first HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor (statin) was approved to treat hypercholesterolemia, a major modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular
ANTI-EDEMATOUS AND ANTIHYPERALGESIC ACTIVITIES OF ROSUVASTATIN IN INFLAMMATORY PAIN MODEL IN RATS
 IJPSR (2018), Volume 9, Issue 9 (Research Article) Received on 10 December, 2017; received in revised form, 13 February, 2018; accepted, 18 February, 2018; published 01 September, 2018 ANTI-EDEMATOUS AND
IJPSR (2018), Volume 9, Issue 9 (Research Article) Received on 10 December, 2017; received in revised form, 13 February, 2018; accepted, 18 February, 2018; published 01 September, 2018 ANTI-EDEMATOUS AND
Atorvastatin route of administration
 Atorvastatin route of administration 8-3-2017 Atorvastatin Calcium. Atorvastatin Calcium Combinations; Routes.. Petrella G et al. Effects of simvastatin and atorvastatin administration on. 1-3-2017 Atorvastatin
Atorvastatin route of administration 8-3-2017 Atorvastatin Calcium. Atorvastatin Calcium Combinations; Routes.. Petrella G et al. Effects of simvastatin and atorvastatin administration on. 1-3-2017 Atorvastatin
NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions as Related to Analgesia and Tolerance
 Vol. 19 No. 1(Suppl.) January 2000 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management S7 Proceedings Supplement NDMA-Receptor Antagonists: Evolving Role in Analgesia NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions
Vol. 19 No. 1(Suppl.) January 2000 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management S7 Proceedings Supplement NDMA-Receptor Antagonists: Evolving Role in Analgesia NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions
Statins and control of MHC2TA gene transcription
 Statins and CIITA 4 4 Statins and control of MHC2TA gene transcription 4 Hedwich F. Kuipers and Peter J. van den Elsen Nature Medicine, 2005, 11: 365-366 Statins and control of MHC2TA gene transcription
Statins and CIITA 4 4 Statins and control of MHC2TA gene transcription 4 Hedwich F. Kuipers and Peter J. van den Elsen Nature Medicine, 2005, 11: 365-366 Statins and control of MHC2TA gene transcription
A. Correct! Nociceptors are pain receptors stimulated by harmful stimuli, resulting in the sensation of pain.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 19: Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Drugs No. 1 of 10 1. are pain receptors stimulated by harmful stimuli, resulting in the sensation of pain. #01 (A) Nociceptors (B) Histamines
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 19: Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Drugs No. 1 of 10 1. are pain receptors stimulated by harmful stimuli, resulting in the sensation of pain. #01 (A) Nociceptors (B) Histamines
Ó Journal of Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences University 45
 ISSN 2231-4261 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Antinociceptive Effect of Ondansetron in Albino Mice Using Acetic Acid Induced Writhing Model 1 2* 1 1 1 Abhay Purohit, Sunil S. Gidamudi, Chitra C. Khanwelkar, Vandana
ISSN 2231-4261 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Antinociceptive Effect of Ondansetron in Albino Mice Using Acetic Acid Induced Writhing Model 1 2* 1 1 1 Abhay Purohit, Sunil S. Gidamudi, Chitra C. Khanwelkar, Vandana
Adolescent Prozac Exposure Enhances Sensitivity to Cocaine in Adulthood INTRODUCTION
 INTRODUCTION Epidemiologic reports indicate that mood disorders in children and adolescents are quite common, with up to 70% of depressed children and adolescents experiencing a recurrence within 5 years
INTRODUCTION Epidemiologic reports indicate that mood disorders in children and adolescents are quite common, with up to 70% of depressed children and adolescents experiencing a recurrence within 5 years
Participation of Placental Opioid-Enhancing Factor in Opioid-Modulated... Parturition
 1 of 9 6/11/2008 12:18 PM INABIS '98 Home Page Your Symposium Related Symposia & Posters Scientific Program Exhibitors' Foyer Personal Itinerary New Search Participation of Placental Opioid-Enhancing Factor
1 of 9 6/11/2008 12:18 PM INABIS '98 Home Page Your Symposium Related Symposia & Posters Scientific Program Exhibitors' Foyer Personal Itinerary New Search Participation of Placental Opioid-Enhancing Factor
THE CARDIOVASCULAR INFLAMMATORY CONTINUUM DR AB MAHARAJ
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR INFLAMMATORY CONTINUUM DR AB MAHARAJ Disclosures: On National Advisory Boards of: (1) Pfizer Pharmaceuticals (2) MSD (3) Roche Pharmaceuticals (4) Abbott International: AfME Rheumatology
THE CARDIOVASCULAR INFLAMMATORY CONTINUUM DR AB MAHARAJ Disclosures: On National Advisory Boards of: (1) Pfizer Pharmaceuticals (2) MSD (3) Roche Pharmaceuticals (4) Abbott International: AfME Rheumatology
Supplementary Figure 1. H-PGDS deficiency does not affect GI tract functions and anaphylactic reaction. (a) Representative pictures of H&E-stained
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. H-PGDS deficiency does not affect GI tract functions and anaphylactic reaction. (a) Representative pictures of H&E-stained jejunum sections ( 200 magnification;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. H-PGDS deficiency does not affect GI tract functions and anaphylactic reaction. (a) Representative pictures of H&E-stained jejunum sections ( 200 magnification;
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation
 Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Pain. Types of Pain. Types of Pain 8/21/2013
 Pain 1 Types of Pain Acute Pain Complex combination of sensory, perceptual, & emotional experiences as a result of a noxious stimulus Mediated by rapidly conducting nerve pathways & associated with increased
Pain 1 Types of Pain Acute Pain Complex combination of sensory, perceptual, & emotional experiences as a result of a noxious stimulus Mediated by rapidly conducting nerve pathways & associated with increased
Rhodiola rosea L- Standardized Extract on Passive
 Research Article ISSN: 0976-5700 Rhodiola rosea L- Standardized Extract on Passive Avoidance in Rats Liliya Vl Vasileva 1,2,3*, Damyanka P Getova 3 1Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology,
Research Article ISSN: 0976-5700 Rhodiola rosea L- Standardized Extract on Passive Avoidance in Rats Liliya Vl Vasileva 1,2,3*, Damyanka P Getova 3 1Department of Pharmacology and Clinical Pharmacology,
Dr. Hayam Gad Associate Professor of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University
 Dr. Hayam Gad Associate Professor of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University INTRODUCTION Diabetic nephropathy (DN) DN is defined as the appearance of persistent clinical albuminuria in an
Dr. Hayam Gad Associate Professor of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University INTRODUCTION Diabetic nephropathy (DN) DN is defined as the appearance of persistent clinical albuminuria in an
IL-17 in health and disease. March 2014 PSO13-C051n
 IL-17 in health and disease March 2014 PSO13-C051n Originally Researchers Suggested That IL-12 and IL-4 drove Th Cell Differentiation Naïve CD4 + T cell Question: Which of these cell types is responsible
IL-17 in health and disease March 2014 PSO13-C051n Originally Researchers Suggested That IL-12 and IL-4 drove Th Cell Differentiation Naïve CD4 + T cell Question: Which of these cell types is responsible
TRP modulators based on glycine and mono-, bicyclic terpenoids synthesis and pharmacological properties
 TRP modulators based on glycine and mono-, bicyclic terpenoids synthesis and pharmacological properties Mariia Nesterkina*and Iryna Kravchenko I.I. Mechnikov dessa National University, 2 Dvorjanskaya st.,
TRP modulators based on glycine and mono-, bicyclic terpenoids synthesis and pharmacological properties Mariia Nesterkina*and Iryna Kravchenko I.I. Mechnikov dessa National University, 2 Dvorjanskaya st.,
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
 72..83 British Journal of Pharmacology DOI:1.1111/j.1476-5381.21.895.x www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPERbph_895 Cooperative role of tumour necrosis factor-a, interleukin-1b and neutrophils in a novel
72..83 British Journal of Pharmacology DOI:1.1111/j.1476-5381.21.895.x www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPERbph_895 Cooperative role of tumour necrosis factor-a, interleukin-1b and neutrophils in a novel
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(5):468-472 Study on the anticonvulsant activity of Pentazocine
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(5):468-472 Study on the anticonvulsant activity of Pentazocine
Novel Markers of Arterial Dysfunction
 혈관연구회창립심포지움, 3 월 3 일, 2005 Novel Markers of Arterial Dysfunction Kwang Kon Koh, MD, FACC, FAHA Cardiology Gachon Medical School Incheon, Korea Atherosclerosis: A progressive process PHASE I: Initiation
혈관연구회창립심포지움, 3 월 3 일, 2005 Novel Markers of Arterial Dysfunction Kwang Kon Koh, MD, FACC, FAHA Cardiology Gachon Medical School Incheon, Korea Atherosclerosis: A progressive process PHASE I: Initiation
Morphine analgesic tolerance in 129P3/J and 129S6/SvEv mice
 Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior 85 (2006) 769 779 www.elsevier.com/locate/pharmbiochembeh Morphine analgesic tolerance in 129P3/J and 129S6/SvEv mice Camron D. Bryant a,b,c,, Kristofer W. Roberts
Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior 85 (2006) 769 779 www.elsevier.com/locate/pharmbiochembeh Morphine analgesic tolerance in 129P3/J and 129S6/SvEv mice Camron D. Bryant a,b,c,, Kristofer W. Roberts
Introduction SHORT COMMUNICATION. Irma V. Belozertseva Anton Yu. Bespalov
 Naunyn-Schmiedeberg s Arch Pharmacol (1998) 358:270 274 Springer-Verlag 1998 SHORT COMMUNICATION Irma V. Belozertseva Anton Yu. Bespalov Effects of NMDA receptor channel blockers, dizocilpine and memantine,
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg s Arch Pharmacol (1998) 358:270 274 Springer-Verlag 1998 SHORT COMMUNICATION Irma V. Belozertseva Anton Yu. Bespalov Effects of NMDA receptor channel blockers, dizocilpine and memantine,
Autoimmune Diseases. Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic
 Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
Pharmacologyonline 1: (2009)
 ANTINOCICEPTIVE ACTIVITY OF TADALAFIL AND ADRENERGIC AGENTS IN THE WRITHING TEST IN MICE Patel S 1, Shah J 1, Mistry K 1, Contractor R 1, Nagda C 1, Patel V 2 1 Indukaka Ipcowala College of Pharmacy, Beyond
ANTINOCICEPTIVE ACTIVITY OF TADALAFIL AND ADRENERGIC AGENTS IN THE WRITHING TEST IN MICE Patel S 1, Shah J 1, Mistry K 1, Contractor R 1, Nagda C 1, Patel V 2 1 Indukaka Ipcowala College of Pharmacy, Beyond
IK01400: non-opioid preclinical drug candidate for pain treatment
 IK01400: non-opioid preclinical drug candidate for pain treatment Introduction Bio-Link presents a valuable licensing opportunity for the development of novel nonopioid drug candidates to manage acute
IK01400: non-opioid preclinical drug candidate for pain treatment Introduction Bio-Link presents a valuable licensing opportunity for the development of novel nonopioid drug candidates to manage acute
American Journal of Human Genetics. American Journal of Hypertension. American Journal of Neuroradiology
 A) Acta Neurochir AJNR Am J Neuroradiol Am Coll Rheumatol Am J Cardiol Am J Hum Genet Am J Hypertens Am J Neuroradiol AJNR Am J Physiol Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol Am J Physiol Heart Circ physiol
A) Acta Neurochir AJNR Am J Neuroradiol Am Coll Rheumatol Am J Cardiol Am J Hum Genet Am J Hypertens Am J Neuroradiol AJNR Am J Physiol Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol Am J Physiol Heart Circ physiol
Heart Online First, published on March 29, 2005 as /hrt SCIENTIFIC LETTER
 Heart Online First, published on March 29, 2005 as 10.1136/hrt.2004.056523 Manuscript ID: HEARTJNL/2004/056523 March 18, 2005 SCIENTIFIC LETTER Effects of HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibition on Endothelial Function
Heart Online First, published on March 29, 2005 as 10.1136/hrt.2004.056523 Manuscript ID: HEARTJNL/2004/056523 March 18, 2005 SCIENTIFIC LETTER Effects of HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibition on Endothelial Function
Cholesterol Management Roy Gandolfi, MD
 Cholesterol Management 2017 Roy Gandolfi, MD Goals Interpreting cholesterol guidelines Cholesterol treatment in diabetics Statin use and side effects therapy Reporting- Comparison data among physicians
Cholesterol Management 2017 Roy Gandolfi, MD Goals Interpreting cholesterol guidelines Cholesterol treatment in diabetics Statin use and side effects therapy Reporting- Comparison data among physicians
Pharmacological Evidence for the Role of Nitric Oxide-cGMP in Antinociception
 Pharmacological Evidence for the Role of Nitric Oxide-cGMP in Antinociception Ehab S. EL Desoky, MD, PhD* Ihab A. Fouad, PhD *Pharmacology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Assiut University, Assiut, Egypt
Pharmacological Evidence for the Role of Nitric Oxide-cGMP in Antinociception Ehab S. EL Desoky, MD, PhD* Ihab A. Fouad, PhD *Pharmacology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Assiut University, Assiut, Egypt
Potential Role of Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in the. Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Potential Role of Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis COMMENTARY for Zhao, C., Fernandes, M.J., Turgeon, M., Tancrede, S., Di Battista, J., Poubelle, P.E. and Bourgoin,
Potential Role of Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis COMMENTARY for Zhao, C., Fernandes, M.J., Turgeon, M., Tancrede, S., Di Battista, J., Poubelle, P.E. and Bourgoin,
Atropine and ODQ antagonize tetanic fade induced by L-arginine in cats
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1277-1283 Antagonism of tetanic fade induced by NO ISSN 0-879X 1277 Atropine and ODQ antagonize tetanic fade induced by L-arginine in cats
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1277-1283 Antagonism of tetanic fade induced by NO ISSN 0-879X 1277 Atropine and ODQ antagonize tetanic fade induced by L-arginine in cats
Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases
 Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases Prof. Dr. med. Z. Fahmy Chief Consulting Rheumatologist Augusta Clinic for Rheumatic Diseases And Rehabilitation Bad Kreuznach Germany Rheumatoid arthritis
Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases Prof. Dr. med. Z. Fahmy Chief Consulting Rheumatologist Augusta Clinic for Rheumatic Diseases And Rehabilitation Bad Kreuznach Germany Rheumatoid arthritis
Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators
 Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators Introduction about chemical mediators in inflammation Mediators may be Cellular mediators cell-produced or cell-secreted derived from circulating inactive precursors,
Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators Introduction about chemical mediators in inflammation Mediators may be Cellular mediators cell-produced or cell-secreted derived from circulating inactive precursors,
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
The inhibition of CETP: From simply raising HDL-c to promoting cholesterol efflux and lowering of atherogenic lipoproteins Prof Dr J Wouter Jukema
 The inhibition of CETP: From simply raising HDL-c to promoting cholesterol efflux and lowering of atherogenic lipoproteins Prof Dr J Wouter Jukema Dept Cardiology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden,
The inhibition of CETP: From simply raising HDL-c to promoting cholesterol efflux and lowering of atherogenic lipoproteins Prof Dr J Wouter Jukema Dept Cardiology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden,
Leaky Gut Syndrome: Cannabinoids and the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) as a therapeutic target.
 Leaky Gut Syndrome: Cannabinoids and the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) as a therapeutic target. By Kyle Boyar What is Leaky Gut Syndrome and how is it diagnosed? Leaky Gut Syndrome (LGS) is an ailment characterized
Leaky Gut Syndrome: Cannabinoids and the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) as a therapeutic target. By Kyle Boyar What is Leaky Gut Syndrome and how is it diagnosed? Leaky Gut Syndrome (LGS) is an ailment characterized
Ultra-low-dose naltrexone suppresses rewarding effects of opiates and aversive effects of opiate withdrawal in rats
 Psychopharmacology (2005) 181: 576 581 DOI 10.1007/s00213-005-0022-7 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Mary C. Olmstead. Lindsay H. Burns Ultra-low-dose naltrexone suppresses rewarding effects of opiates and aversive
Psychopharmacology (2005) 181: 576 581 DOI 10.1007/s00213-005-0022-7 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Mary C. Olmstead. Lindsay H. Burns Ultra-low-dose naltrexone suppresses rewarding effects of opiates and aversive
Local administration of 9 -tetrahydrocannabinol attenuates capsaicin-induced thermal nociception in rhesus monkeys: a peripheral cannabinoid action
 Psychopharmacology (1999) 143:322 326 Springer-Verlag 1999 RAPID COMMUNICATION Mei-Chuan Ko James H. Woods Local administration of 9 -tetrahydrocannabinol attenuates capsaicin-induced thermal nociception
Psychopharmacology (1999) 143:322 326 Springer-Verlag 1999 RAPID COMMUNICATION Mei-Chuan Ko James H. Woods Local administration of 9 -tetrahydrocannabinol attenuates capsaicin-induced thermal nociception
Impact of Chronic Pain
 BURDEN OF ILLNESS Overview Impact of Chronic Pain Healthcare costs 6 Sleep disturbances 2 Depression 2 Presenteeism and absenteeism 4,5 Chronic pain 1 Anxiety 2 Disability 4 Decreased quality of life 3
BURDEN OF ILLNESS Overview Impact of Chronic Pain Healthcare costs 6 Sleep disturbances 2 Depression 2 Presenteeism and absenteeism 4,5 Chronic pain 1 Anxiety 2 Disability 4 Decreased quality of life 3
The Framingham Coronary Heart Disease Risk Score
 Plasma Concentration of C-Reactive Protein and the Calculated Framingham Coronary Heart Disease Risk Score Michelle A. Albert, MD, MPH; Robert J. Glynn, PhD; Paul M Ridker, MD, MPH Background Although
Plasma Concentration of C-Reactive Protein and the Calculated Framingham Coronary Heart Disease Risk Score Michelle A. Albert, MD, MPH; Robert J. Glynn, PhD; Paul M Ridker, MD, MPH Background Although
STATIN UTILIZATION MANAGEMENT CRITERIA
 STATIN UTILIZATION MANAGEMENT CRITERIA DRUG CLASS: HMG Co-A Reductase Inhibitors & Combinations Agents which require prior review: Advicor (niacin extended-release/lovastatin) Crestor (rosuvastatin)(5mg,10mg,
STATIN UTILIZATION MANAGEMENT CRITERIA DRUG CLASS: HMG Co-A Reductase Inhibitors & Combinations Agents which require prior review: Advicor (niacin extended-release/lovastatin) Crestor (rosuvastatin)(5mg,10mg,
Nitric Oxide in the Penis: Scientific Discoveries and Clinical Applications
 Nitric Oxide in the Penis: Scientific Discoveries and Clinical Applications Arthur L. (Bud) Burnett, M.D., M.B.A., F.A.C.S. Patrick C. Walsh Professor of Urology The James Buchanan Brady Urological Institute
Nitric Oxide in the Penis: Scientific Discoveries and Clinical Applications Arthur L. (Bud) Burnett, M.D., M.B.A., F.A.C.S. Patrick C. Walsh Professor of Urology The James Buchanan Brady Urological Institute
Continuous Wound Infusion and Postoperative Pain Current status?
 Continuous Wound Infusion and Postoperative Pain Current status? Pr Patricia Lavand homme Department of Anesthesiology St Luc Hospital University Catholic of Louvain Medical School Brussels, Belgium Severe
Continuous Wound Infusion and Postoperative Pain Current status? Pr Patricia Lavand homme Department of Anesthesiology St Luc Hospital University Catholic of Louvain Medical School Brussels, Belgium Severe
Effects of the angiotensin II type-1 receptor antagonist telmisartan on endothelial activation induced by advanced glycation endproducts
 Effects of the angiotensin II type-1 receptor antagonist telmisartan on endothelial activation induced by advanced glycation endproducts Serena Del Turco, Teresa Navarra, Giuseppina Basta, Raffaele De
Effects of the angiotensin II type-1 receptor antagonist telmisartan on endothelial activation induced by advanced glycation endproducts Serena Del Turco, Teresa Navarra, Giuseppina Basta, Raffaele De
This PDF is available for free download from a site hosted by Medknow Publications
 Research Paper www.ijpsonline.com Antinociceptive Activity of Certain Dihydroxy Flavones S. UMAMAHESWARI*, S. VISWANATHAN 1, B. W. C. SATHIYASEKARAN, S. PARVATHAVARTHINI AND S. RAMASWAMY 2 Sri Ramachandra
Research Paper www.ijpsonline.com Antinociceptive Activity of Certain Dihydroxy Flavones S. UMAMAHESWARI*, S. VISWANATHAN 1, B. W. C. SATHIYASEKARAN, S. PARVATHAVARTHINI AND S. RAMASWAMY 2 Sri Ramachandra
Hypoalgesic responses resulting from paired or separate exposures to naloxone and a heat stressor: Evidence from the tail-flick radiant heat test
 Psychobiology 1997,25 (4), 338-35/ Hypoalgesic responses resulting from paired or separate exposures to naloxone and a heat stressor: Evidence from the tail-flick radiant heat test H.FOO Northern Territory
Psychobiology 1997,25 (4), 338-35/ Hypoalgesic responses resulting from paired or separate exposures to naloxone and a heat stressor: Evidence from the tail-flick radiant heat test H.FOO Northern Territory
Managed Care Trends in Statin Usage GARY R. BAZALO, MS, MBA
 PHARMACY UTILIZATION Managed Care Trends in Statin Usage GARY R. BAZALO, MS, MBA ABSTRACT Purpose HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors ( statins ) have become the drug class of choice for the treatment of hyperlipidemia.
PHARMACY UTILIZATION Managed Care Trends in Statin Usage GARY R. BAZALO, MS, MBA ABSTRACT Purpose HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors ( statins ) have become the drug class of choice for the treatment of hyperlipidemia.
JAMA. 2011;305(24): Nora A. Kalagi, MSc
 JAMA. 2011;305(24):2556-2564 By Nora A. Kalagi, MSc Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the number one cause of mortality and morbidity world wide Reducing high blood cholesterol which is a risk factor for
JAMA. 2011;305(24):2556-2564 By Nora A. Kalagi, MSc Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the number one cause of mortality and morbidity world wide Reducing high blood cholesterol which is a risk factor for
Pain Pathways. Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH
 Pain Pathways Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH Objective To give you a simplistic and basic concepts of pain pathways to help understand the complex issue of pain Pain
Pain Pathways Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH Objective To give you a simplistic and basic concepts of pain pathways to help understand the complex issue of pain Pain
It is the policy of health plans affiliated with PA Health & Wellness that Vytorin is medically necessary when the following criteria are met:
 Clinical Policy: Ezetimibe and Simvastatin (Vytorin) Reference Number: PA.CP.PMN.77 Effective Date: 02.01.17 Last Review Date: 07.18 Revision Log Description Ezetimibe/simvastatin (Vytorin ) contains ezetimibe,
Clinical Policy: Ezetimibe and Simvastatin (Vytorin) Reference Number: PA.CP.PMN.77 Effective Date: 02.01.17 Last Review Date: 07.18 Revision Log Description Ezetimibe/simvastatin (Vytorin ) contains ezetimibe,
Respiratory Effects of IV CR845 - A Peripherally Acting, Selective Kappa Opioid Receptor Agonist
 Respiratory Effects of IV CR845 - A Peripherally Acting, Selective Kappa Opioid Receptor Agonist Eugene R. Viscusi, 1 Marc C. Torjman, 1 Joseph W. Stauffer, 2 Catherine L. Munera, 2 Beatrice S. Setnik,
Respiratory Effects of IV CR845 - A Peripherally Acting, Selective Kappa Opioid Receptor Agonist Eugene R. Viscusi, 1 Marc C. Torjman, 1 Joseph W. Stauffer, 2 Catherine L. Munera, 2 Beatrice S. Setnik,
EXPERIENCE IN THE USE OF ATORVASTATIN IN PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS AND HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA
 EXPERIENCE IN THE USE OF ATORVASTATIN IN PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS AND HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA N.S. Komendantova, Post Graduate Student Y.V. Kulakov, Prof. P.A. Lukyanov, Prof. A.A. Sinenko, Associate
EXPERIENCE IN THE USE OF ATORVASTATIN IN PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS AND HYPERCHOLESTEROLEMIA N.S. Komendantova, Post Graduate Student Y.V. Kulakov, Prof. P.A. Lukyanov, Prof. A.A. Sinenko, Associate
D. Nishizawa 1, N. Gajya 2 and K. Ikeda 1, * Global Research & Development, Nagoya Laboratories, Pfizer Japan Inc, Nagoya, Japan
 Current Neuropharmacology, 2011, 9, 113-117 113 Identification of Selective Agonists and Antagonists to G Protein-Activated Inwardly Rectifying Potassium Channels: Candidate Medicines for Drug Dependence
Current Neuropharmacology, 2011, 9, 113-117 113 Identification of Selective Agonists and Antagonists to G Protein-Activated Inwardly Rectifying Potassium Channels: Candidate Medicines for Drug Dependence
Μηχανισµός της απώλειας της καρδιοπροστατευτικής δράσης της µετισχαιµικής προστασίας (postconditioning) στην αθηρωµάτωση Iωάννα Ανδρεάδου
 Μηχανισµός της απώλειας της καρδιοπροστατευτικής δράσης της µετισχαιµικής προστασίας (postconditioning) στην αθηρωµάτωση Iωάννα Ανδρεάδου School of Pharmacy, University of Athens, Greece Definitions Preconditioning:
Μηχανισµός της απώλειας της καρδιοπροστατευτικής δράσης της µετισχαιµικής προστασίας (postconditioning) στην αθηρωµάτωση Iωάννα Ανδρεάδου School of Pharmacy, University of Athens, Greece Definitions Preconditioning:
Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and. widespread hyperalgesia
 Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and widespread hyperalgesia N. Sugimura 1, M. Ikeuchi 1 *, M. Izumi 1, T. Kawano 2, K. Aso 1, T. Kato 1, T. Ushida 3,
Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and widespread hyperalgesia N. Sugimura 1, M. Ikeuchi 1 *, M. Izumi 1, T. Kawano 2, K. Aso 1, T. Kato 1, T. Ushida 3,
Patowary S Assistant Professor, Department of Clinical Pharmacology, College of Medical Sciences, Bharatpur, Nepal
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2007), Vol. 5, No. 2, Issue 18, 199-203 Original Article A study on the modification of anti-inflammatory and analgesic action of aspirin by nifedipine Patowary S
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2007), Vol. 5, No. 2, Issue 18, 199-203 Original Article A study on the modification of anti-inflammatory and analgesic action of aspirin by nifedipine Patowary S
Recent Advances in Energy, Environment, Biology and Ecology
 Acute and long-term effects elicited by psychoactive drugs on 50-kHz ultrasonic vocalizations in rats: development of a new experimental tool for the study of drug-mediated reward NICOLA SIMOLA Department
Acute and long-term effects elicited by psychoactive drugs on 50-kHz ultrasonic vocalizations in rats: development of a new experimental tool for the study of drug-mediated reward NICOLA SIMOLA Department
Role of complement C5a in mechanical inflammatory hypernociception: potential use of C5a receptor antagonists to control inflammatory pain
 British Journal of Pharmacology (2008) 153, 1043 1053 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 1188/08 $30.00 www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPER Role of complement C5a in mechanical inflammatory
British Journal of Pharmacology (2008) 153, 1043 1053 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 1188/08 $30.00 www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPER Role of complement C5a in mechanical inflammatory
Reducing low-density lipoprotein cholesterol treating to target and meeting new European goals
 European Heart Journal Supplements (2004) 6 (Supplement A), A12 A18 Reducing low-density lipoprotein cholesterol treating to target and meeting new European goals University of Sydney, Sydney, NSW, Australia
European Heart Journal Supplements (2004) 6 (Supplement A), A12 A18 Reducing low-density lipoprotein cholesterol treating to target and meeting new European goals University of Sydney, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models. From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Hippocampal Pyramidal Neuron of Mice and Rats Figure 1 Open Field Apparatus Open Field Behavior
Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Hippocampal Pyramidal Neuron of Mice and Rats Figure 1 Open Field Apparatus Open Field Behavior
Streptozotocin-induced mechanical hypernociception is not dependent on hyperglycemia
 Brazilian STZ-induced Journal hypernociception of Medical and does Biological not depend Research on hyperglycemia (2009) 42: 197-206 ISSN 0100-879X 197 Streptozotocin-induced mechanical hypernociception
Brazilian STZ-induced Journal hypernociception of Medical and does Biological not depend Research on hyperglycemia (2009) 42: 197-206 ISSN 0100-879X 197 Streptozotocin-induced mechanical hypernociception
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. FGF21 does not exert direct effects on hepatic glucose production. The liver explants from C57BL/6J mice (A, B) or primary rat hepatocytes (C, D) were incubated with rmfgf21 (2
Supplementary Figure 1. FGF21 does not exert direct effects on hepatic glucose production. The liver explants from C57BL/6J mice (A, B) or primary rat hepatocytes (C, D) were incubated with rmfgf21 (2
Farmacologia di genere. Prof. Alberto Corsini Università degli Studi di Milano
 Farmacologia di genere Prof. Alberto Corsini Università degli Studi di Milano Women have been less enrolled in clinical trials A gender-specific analysis usually is not included in the evaluation of results
Farmacologia di genere Prof. Alberto Corsini Università degli Studi di Milano Women have been less enrolled in clinical trials A gender-specific analysis usually is not included in the evaluation of results
Innate Immunity. Chapter 3. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
The Journal of American Science, 4(1), 2008, ISSN ,
 Pravastatin Preserves Vasomotor Response in Atherosclerotic Arteries After Balloon Angioplasty Ma Hongbao Brooklyn, New York, USA mahongbao2007@yahoo.com Abstract: Background: Vasodilation response to
Pravastatin Preserves Vasomotor Response in Atherosclerotic Arteries After Balloon Angioplasty Ma Hongbao Brooklyn, New York, USA mahongbao2007@yahoo.com Abstract: Background: Vasodilation response to
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
 Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
Science & Technologies COMPARISON THE EFFECTS OF TACRINE AND GALANTAMINE ON ACTIVE AVOIDANCE TEST IN RATS WITH DIAZEPAM-AMNESIA MODEL
 COMPARISON THE EFFECTS OF TACRINE AND GALANTAMINE ON ACTIVE AVOIDANCE TEST IN RATS WITH DIAZEPAM-AMNESIA MODEL Darinka Dimitrova, Damianka Getova Medical University Plovdiv, Medical Faculty, 4002 Plovdiv,
COMPARISON THE EFFECTS OF TACRINE AND GALANTAMINE ON ACTIVE AVOIDANCE TEST IN RATS WITH DIAZEPAM-AMNESIA MODEL Darinka Dimitrova, Damianka Getova Medical University Plovdiv, Medical Faculty, 4002 Plovdiv,
Zinc and water intake in rats: investigation of adrenergic and opiatergic central mechanisms
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1217-1222 Opioid and zinc interplay in isoproterenol-induced drinking ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 1217 Zinc and water intake in rats:
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1217-1222 Opioid and zinc interplay in isoproterenol-induced drinking ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 1217 Zinc and water intake in rats:
Changes in Rats by Captopril
 Inhibition of Vascular Permeability Changes in Rats by Captopril J. C. FANTONE, D. SCHRIER, and B. WEINGARTEN, Department of Pathology, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109
Inhibition of Vascular Permeability Changes in Rats by Captopril J. C. FANTONE, D. SCHRIER, and B. WEINGARTEN, Department of Pathology, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48109
Rosuvastatin: An Effective Lipid Lowering Drug against Hypercholesterolemia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Cardiovascular Research Volume 3 Number 1 Rosuvastatin: An Effective Lipid Lowering Drug against Hypercholesterolemia V Save, N Patil, G Rajadhyaksha Citation V Save,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Cardiovascular Research Volume 3 Number 1 Rosuvastatin: An Effective Lipid Lowering Drug against Hypercholesterolemia V Save, N Patil, G Rajadhyaksha Citation V Save,
Seung-Hwan Lee, M.D., Ph.D.
 2015.10.16. ICDM, DMJ session Statin discontinuation after achieving a target low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level in type 2 diabetic patients without cardiovascular disease: a randomized controlled
2015.10.16. ICDM, DMJ session Statin discontinuation after achieving a target low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level in type 2 diabetic patients without cardiovascular disease: a randomized controlled
The Use of Analgesics in Rodents and Rabbits Deborah M. Mook, DVM
 The Use of Analgesics in Rodents and Rabbits Deborah M. Mook, DVM (Last updated August, 2005) Rationale. Well-established studies have shown repeatedly that effective analgesia enhances locomotion, increases
The Use of Analgesics in Rodents and Rabbits Deborah M. Mook, DVM (Last updated August, 2005) Rationale. Well-established studies have shown repeatedly that effective analgesia enhances locomotion, increases
Management of Pandemic Influenza In Have Not Countries
 1 10th Beijing/Hong Kong Medical Exchange Update on Respiratory Medicine 8-9 November 2008 Management of Pandemic Influenza In Have Not Countries David S. Fedson, MD Sergy Haut, France dfedson@wanadoo.fr
1 10th Beijing/Hong Kong Medical Exchange Update on Respiratory Medicine 8-9 November 2008 Management of Pandemic Influenza In Have Not Countries David S. Fedson, MD Sergy Haut, France dfedson@wanadoo.fr
Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological. findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL EN-12-2276 Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of adipocytokines in adipose tissue.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL EN-12-2276 Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of adipocytokines in adipose tissue.
Primary Results Citation 2
 Table S1. Adalimumab clinical trials 1 ClinicalTrials.gov Rheumatoid Arthritis 3 NCT00195663 Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, et al. The PREMIER study. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical
Table S1. Adalimumab clinical trials 1 ClinicalTrials.gov Rheumatoid Arthritis 3 NCT00195663 Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, et al. The PREMIER study. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical
OPIOID ANTINOCICEPTION AND ANTIHYPERALGESIA IN COMBINATION WITH METABOTROPIC GLUTAMATE RECEPTOR ANTAGONISM. Dana Elaine Daugherty
 OPIOID ANTINOCICEPTION AND ANTIHYPERALGESIA IN COMBINATION WITH METABOTROPIC GLUTAMATE RECEPTOR ANTAGONISM Dana Elaine Daugherty A thesis submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at
OPIOID ANTINOCICEPTION AND ANTIHYPERALGESIA IN COMBINATION WITH METABOTROPIC GLUTAMATE RECEPTOR ANTAGONISM Dana Elaine Daugherty A thesis submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at
Farmaci innovativi in ambito cardiovascolare: considerazioni di Farmacologia. Prof. Alberto Corsini University of Milan, Italy
 Farmaci innovativi in ambito cardiovascolare: considerazioni di Farmacologia Prof. Alberto Corsini University of Milan, Italy Outline of the presentation State of the art on statin therapy Explore unmet
Farmaci innovativi in ambito cardiovascolare: considerazioni di Farmacologia Prof. Alberto Corsini University of Milan, Italy Outline of the presentation State of the art on statin therapy Explore unmet
Potentiation of antinociceptive effect of NSAIDs by a specific lipooxygenase inhibitor, acetyl 11-keto-beta boswellic acid
 Indian Journal of Experimental Biology Vol. 44, February 2006, pp. 128-132 Potentiation of antinociceptive effect of NSAIDs by a specific lipooxygenase inhibitor, acetyl 11-keto-beta boswellic acid Mahendra
Indian Journal of Experimental Biology Vol. 44, February 2006, pp. 128-132 Potentiation of antinociceptive effect of NSAIDs by a specific lipooxygenase inhibitor, acetyl 11-keto-beta boswellic acid Mahendra
THE PHARMA INNOVATION - JOURNAL Immune Corrective Role of Statin Therapy in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Metabolic Syndrome
 Received: 19-07-2013 Accepted: 18-08-2013 ISSN: 2277-7695 CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: 2663038-2 IC Journal No: 7725 Vol. 2 No. 8 2013 Online Available at www.thepharmajournal.com THE PHARMA INNOVATION
Received: 19-07-2013 Accepted: 18-08-2013 ISSN: 2277-7695 CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: 2663038-2 IC Journal No: 7725 Vol. 2 No. 8 2013 Online Available at www.thepharmajournal.com THE PHARMA INNOVATION
Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of Annona squamosa Linn bark
 2014; 3 (1): 60-64 Available online at: www.jsirjournal.com Research Article ISSN 2320-4818 JSIR 2014; 3(1): 60-64 2014, All rights reserved Received: 24-11-2013 Accepted: 26-01-2014 Tej Pratap Singh Rakesh
2014; 3 (1): 60-64 Available online at: www.jsirjournal.com Research Article ISSN 2320-4818 JSIR 2014; 3(1): 60-64 2014, All rights reserved Received: 24-11-2013 Accepted: 26-01-2014 Tej Pratap Singh Rakesh
GMI-1070: A Novel Potential Study Treatment During Sickle Cell Crisis. September 17, 2011
 GMI-1070: A Novel Potential Study Treatment During Sickle Cell Crisis September 17, 2011 Current Available Treatment for Vaso-Occlusive Crisis (VOC) VOC results in life-threatening complications and reduced
GMI-1070: A Novel Potential Study Treatment During Sickle Cell Crisis September 17, 2011 Current Available Treatment for Vaso-Occlusive Crisis (VOC) VOC results in life-threatening complications and reduced
EFFECT OF SIMVASTATIN ON THE PHARMACOKINETICS OF SITAGLIPTIN
 Effect of EFFECT OF SIMVASTATIN ON THE PHARMACOKINETICS OF SITAGLIPTIN Michael Cerra, Wen-Lin Luo, Susie (Xiujiang) Li, Catherine Matthews, Edward A O'Neill, John A Wagner, S Aubrey Stoch, Matt S Anderson
Effect of EFFECT OF SIMVASTATIN ON THE PHARMACOKINETICS OF SITAGLIPTIN Michael Cerra, Wen-Lin Luo, Susie (Xiujiang) Li, Catherine Matthews, Edward A O'Neill, John A Wagner, S Aubrey Stoch, Matt S Anderson
Inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis and cardiovascular disease
 Inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis and cardiovascular disease Yvette Meißner, Pharmacoepidemiology, German Rheumatism Research Centre www. chronische-entzuendung.org Outline I. Cardiovascular disease II.
Inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis and cardiovascular disease Yvette Meißner, Pharmacoepidemiology, German Rheumatism Research Centre www. chronische-entzuendung.org Outline I. Cardiovascular disease II.
Insulin Attenuates Formalin-Induced Nociceptive Response in Mice through a Mechanism that Is Deranged by Diabetes Mellitus
 0022-3565/97/2811-0315$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 281, No. 1 Copyright 1997 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
0022-3565/97/2811-0315$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 281, No. 1 Copyright 1997 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
INFLUENCE OF METHYLDOPA ON CENTRAL EFFECTS OF RESERPINE
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1964), 22, 366-370. INFLUENCE OF METHYLDOPA ON CENTRAL EFFECTS OF RESERPINE BY B. G. BENFEY AND D. R. VARMA From the Department of Pharmacology, McGill University, Montreal, Canada
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1964), 22, 366-370. INFLUENCE OF METHYLDOPA ON CENTRAL EFFECTS OF RESERPINE BY B. G. BENFEY AND D. R. VARMA From the Department of Pharmacology, McGill University, Montreal, Canada
