REVIEWS. Introduction. FibroMax complete diagnosis of liver injury. Abbreviations
|
|
|
- Annis Clarke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 REVIEWS Noninvasive Biomarkers for the Screening of Fibrosis, Steatosis and Steatohepatitis in Patients with Metabolic Risk Factors: FibroTest-FibroMa Eperience Mona Munteanu, Vlad Ratziu 2, Rachel Morra, Djamila Messous 3, Francoise Imbert-Bismut 3, Thierry Poynard 2 ) Biopredictive, Paris, France; 2) Hepatology Department, Pitié Salpêtrière Hospital, Paris, France; 3) Biochemistry Department, Pitié Salpêtrière Hospital, Paris, France Introduction Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is characterized by hepatic steatosis occurring in those who do not consume high amounts of alcohol. The prevalence of NAFLD is high in the general population with metabolic risk factors and insulin resistance being mainly associated with overweight, diabetes, hyperlipidemia and hypertension [, 2]. Two histological patterns of NAFLD have been described: fatty liver alone and, in a minority of patients, necroinflammatory form of NAFLD known as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) that may progress to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma []. Although confirmation of the diagnosis of NAFLD can be achieved by imaging methods, they do not provide data on staging the disease (steatohepatitis and fibrosis), which until recently required a liver biopsy for confirmation. Due to the high prevalence of NAFLD in at risk populations [], the limitations of biopsy [3, 4] and the developing of reliable noninvasive blood tests [5-8], liver biopsy should no longer be considered mandatory as first-intention screening of liver lesions [9, 0]. FibroMa complete diagnosis of liver injury Three simple blood tests were developed to provide Abbreviations ALD: alcoholic liver disease; ALT: alanine-aminotrasnferase; AST: aspartate aminotransferase; AUROC: area under the ROC curve; BMI: body mass inde; GGT: gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase; HBV hepatitis B virus; HCV: hepatitis C virus; HIV: human immune-deficiency virus; HOMA-IR: homeostatic model assessment-estimated insulin resistance; NAFLD: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH: nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis June 2008 Vol.7 No 2, 87-9 Address for correspondence: Mona Munteanu Groupe Hospitalier Pitié Salpêtrière Service d Hépato-Gastroentérologie Bd de l Hôpital 7503 Paris, France mona.munteanu@biopredictive.com an estimate of liver fibrosis and of its aggravating factors, steatosis and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): FibroTest, SteatoTest and NashTest, respectively. FibroMa (Biopredictive, Paris, France) is the association of these three tests on the same result sheet and provides physicians with simultaneous and complete estimation of the liver injury associated with NAFLD []. All FibroMa s tests are patented algorithms owned by the French public health organization (Assistance Publique - Hôpitau de Paris, APHP) and all are provided with instructions for use, securing their interpretation. SteatoTest SteatoTest (score from 0 to, see Table I gives a quantitative estimation of steatosis of different origins: NAFLD (overweight, insulin resistance, hyperlipidemia or diabetes mellitus), chronic viral hepatitis and alcoholic liver disease (ALD) [7]. SteatoTest combines 0 blood components readily available in every laboratory (see Table II) with age, se and BMI and has several advantages over other proposed diagnostic tools, such as being cheaper than biopsy or magnetic resonance imaging. SteatoTest had a better value for the diagnosis of steatosis than classical markers of steatosis: AUROC (se) = 0.80 (0.02) for SteatoTest versus 0.66 (0.02) for GGT (p<0.000), 0.6 (0.02) for ALT (p<0.000), and 0.65 (0.03) for ultrasonography (p<0.00). Moreover, concordance with biopsy for steatosis detection was better for SteatoTest than for ultrasonography (kappa coefficient 0.44 versus 0.32, respectively, p=0.02) [7]. The better performance of SteatoTest than regular ultrasonography could be eplained by the quite low sensitivity, the observer variability and the low accuracy of ultrasonography, especially in patients with advanced fibrosis [2]. Moreover, one study with repeated SteatoTest and biopsy showed that SteatoTest is a sensitive marker for the followup of treated patients [7]. This first result was confirmed thereafter in a prospective trial in NAFLD patients with Advanced fibrosis was defined as portal fibrosis with few septa (F2), many septa (F3) or cirrhosis (F4).
2 88 Munteanu et al rosiglitazone versus placebo showing significant steatosis regression at the SteatoTest in the treated group versus placebo [3]. Recently, an original independent study used the SteatoTest as a reference noninvasive method instead of the biopsy, in order to validate a new imagistic method for liver steatosis quantification (the hepatorenal ultrasound inde, HRI) [4]. NashTest The NashTest is intended to detect probable NASH that associates necrosis and inflammation. NASH and fibrosis lesions may coeist with steatosis in a minority of NAFLD patients [8]. The utility of the NashTest may be to separate those patients with more severe injury from those with little injury for identifying patients at the greatest risk for disease progression. NashTest was constructed for the diagnosis of NASH in the three categories according to the histological NAS score of Kleiner [5]: NASH, Borderline NASH and No NASH (Table I and Table II). In the validation study on NAFLD patients (n=257), the value of NashTest for the diagnosis of NASH was fair (AUROC = 0.80) with no differences between the training and the validation group for the diagnosis of no NASH, Borderline NASH and NASH. An independent validation on a multicenter population found a similar value (AUROC = 0.83) for the diagnosis of NASH (de Ledinghen Victor, CYTOL study group, personal database). In a study with two concomitant percutaneous liver biopsies in NAFLD patients, authors demonstrated a high risk of misdiagnosis of NASH and staging inaccuracies of liver biopsy mainly because the histological lesions could be unevenly distributed throughout the liver parenchyma [4]. Because of biopsy limitations, NashTest together with SteatoTest and FibroTest were used in large scale studies to screen liver injury without biopsy, in at risk populations like hyperlipidemics, diabetics and morbidly obese [6-8]. FibroTest FibroTest (score from 0 to, see Table I and Table II) is a universal marker, fully validated to provide a quantitative estimation of fibrosis that occurs in the most frequent liver diseases: NAFLD, ALD and chronic viral hepatitis (HBV, HCV and HIV-coinfected) [6]. The last meta-analysis showed in NAFLD patients a mean standardized AUROC for advanced fibrosis of 0.84 (95% CI, ) without differences between the causes of liver disease. Moreover, the AUROC for the diagnosis of the intermediate adjacent stages F2 vs F did not differ from that of the etreme stages F3 vs F4 or F vs F0 [6]. The FibroTest was directly compared [9] to another The histological NASH score (NAS) is defined as the sum of the scores for steatosis (0 3), lobular inflammation (0 3), and ballooning (0 2); cases with scores of 0 to 2 were diagnosed as no NASH, cases with scores of 5 or greater were diagnosed as NASH and intermediate cases with scores of 3 or 4 were probable NASH (borderline) [5]. Table I. Conversion between FibroTest score and fibrosis stages (Panel A), SteatoTest score and steatosis grades (Panel B) and between NashTest score and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis categories (Panel C) in patients with non-alcoholic liver disease Panel A Fibro Test Fibrosis stage estimate* F F3-F F F F-F F F0-F F0 *According to METAVIR scoring system Panel B SteatoTest Estimate of steatosis percentage S2S3>32% S2 6-32% S -5% S0 0% Panel C NashTest Estimate of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis class 0.75 Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) 0.50 Borderline NASH 0.25 No NASH Table II. Biomarkers combined in FibroTest and FibroMa Biomarkers FibroTest FibroMa (for SteatoTest and NashTest) Age Gender Alpha 2 macroglobulin, g/l Haptoglobin, g/l Apolipoprotein A, g/l Total Bilirubin, µmol/l GGT, IU/l ALT, IU/l, AST, IU/l Total cholesterol, mmol/l Triglycerides, mmol/l Fasting glucose, mmol/l Weight, kg Height, m surrogate score of fibrosis in NAFLD: NAFLD fibrosis score (NFS) an independently validated non patented panel [20]. The FibroTest demonstrated a better value for the diagnosis of advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis in two different
3 FibroTest-FibroMa Eperience 89 retrospective analyses: AUROCs (95%CI): 0.89 ( ) for FibroTest vs ( ) for NFS (p=0.035) in the diagnostic cohort and 0.80 ( ) for FibroTest vs. NS 0.70 ( ) for NFS (p=0.0) in the therapeutic trial cohort [9]. Moreover, recently the FibroTest demonstrated its value for the long-term and short-term prediction of complications and death in chronic viral hepatitis [2-23]. For all these reasons, the FibroTest was widely used as a non invasive alternative to liver biopsy, with 300,000 tests ordered between September 2002 and May 2008 (Biopredictive data on file, Jean Marie Castille, personal communication). Large scale screening studies using FibroMa Several studies used FibroMa (FibroTest, SteatoTest and NashTest) to screen liver injury in identified at risk populations with one or several metabolically risk factors: hyperlipidemics, diabetics and morbidly obese patients. Hyperlipidemic patients screening for fibrosis, steatosis and NASH Hyperlipidemic patients have multiple risk factors of insulin resistance and abnormal serum levels of hepatic enzymes are frequent and often associated with elevated blood pressure, body mass inde, fasting glucose and uric acid [24]. A study using FibroMa was the first to assess prevalence and factors associated with liver injury in a large number of hyperlipidemic patients (n=909) followed prospectively in a lipid centre (all sera were analyzed retrospectively) [6]. Advanced fibrosis was identified by FibroTest in 2.8%, advanced steatosis by SteatoTest in 30.% and NASH by NashTest in 7% hyperlipidemic patients. Age, male gender, waist circumference, triglycerides increase and HDL-cholesterol decrease were the most significant clinical characteristics associated with presumed fibrosis. The highest prevalence of advanced steatosis was observed among diabetic hyperlipidemics and those with a high HOMA-IR and central obesity. The NASH prevalence in hyperlipidemics with metabolic syndrome was 0-fold higher in patients with the metabolic syndrome compared with those without (P < 0.000) [6]. The study found a highly significant association between the number of metabolic syndrome 2 factors and liver disease prevalence the highest being for hyperlipidemics with type 2 diabetes. This study stressed that the biomarkers could be useful when two metabolic syndrome factors or more are present because a clear increase of risk of liver injury. Hyperlipidemic patients were referred when they presented with either plasma low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholesterol levels. above 60 mg/dl or triglyceride levels above 50 mg/dl. 2 The definition of the metabolic syndrome was based on the ATPIII classification [25]. Diabetic patients screening for fibrosis, steatosis and NASH Patients with type 2 diabetes present a known risk for NAFLD leading to advanced fibrosis, cirrhosis and liver cancer [26-27]. A recent study estimated the efficacy to detect fibrosis with a noninvasive fibrosis biomarker (FibroTest) of a screening of diabetic patients without a history or clinical signs of liver disease, seen prospectively in a tertiary center (n=3 cases) [7]. All patients with presumed advanced fibrosis were reinvestigated by a hepatologist using elastography (FibroScan, Echosens, France) and, if necessary, ultrasonography, endoscopy, or liver biopsy. The prevalence of confirmed advanced fibrosis was 2.8% with 5 cases of cirrhosis, 4 cases of hepatocellular carcinoma and one cholangiocarcinoma. In the population with type 2 diabetes 45 years or older, the prevalence of confirmed advanced fibrosis was higher (4.3%) and of hepatocellular carcinoma was 5.7 of 000 [7]. The prevalence of steatosis at the SteatoTest and of NASH at the NashTest was higher in diabetics with confirmed advanced fibrosis (86% and 38%, respectively) compared to diabetics with no or minimal fibrosis (4% and 6%, respectively, all p <0.000). Among the confirmed advanced fibrosis diabetic patients, one quarter had normal GGT (false-negatives), and twothirds had normal ALT (false-negatives) confirming the low sensitivity to detect fibrosis of transaminases and GGT compared to combinations of biomarkers like FibroTest. The study strongly suggested the need for screening of advanced fibrosis, using validated biomarkers such as FibroTest, in type 2 diabetic patients aged 45 years or older in order to prevent liver-related mortality. Morbidly obese patients screening for fibrosis, steatosis and NASH Obesity is a major health issue worldwide since studies suggest it is associated with overall increased morbidity and mortality [28]. BMI seems correlated with NAFLD prevalence [29] with obesity being the most frequent risk factor associated with histological NAFLD at autopsy [30]. A review of available studies in severely obese patients submitted to bariatric surgery found that the prevalence of liver steatosis and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) ranged from 85% to 98% and from 24 to 98%, respectively, with unepected cirrhosis in % to 7% [3]. A recent study proposed to estimate the diagnostic value of biomarkers of liver injury in morbidly obese (MO) patients addressed to bariatric surgery for BMI 40kg/m² or higher, or for BMI 30kg/m² or higher and at least one risk factor [8]. MO patients (n=94) had peroperatory biopsy and concomitant biomarkers (FibroMa) and were compared to a nonmorbidly obese group (nonmo) with NAFLD (n=234) that had had percutaneous biopsy and biomarkers. The FibroTest value for the diagnosis of advanced fibrosis was not different in MO patients to that in nonmo [AUROCs 0.76 (0.07) vs (0.03), respectively, p=ns]; similar results were obtained for NASH diagnosis at the NashTest
4 90 Munteanu et al [AUROCs 0.72 (0.09) vs (0.06), respectively, p=ns] and for severe steatosis at the SteatoTest [AUROCs 0.8 (0.06) vs (0.05), respectively, p=ns] after adjustment of etreme BMI. The estimated prevalence of advanced fibrosis, steatosis and NASH with biomarkers in MO patients was 3%, 54% and %, respectively. These preliminary results suggest that biomarkers could be useful for the screening of liver injury in MO patients, a population difficult to investigate and for which the peroperatory biopsy demonstrates major limitations [32]. Limitations of biomarkers and precautions of use FibroMa biomarkers have several limitations related to the non-interpretability of results in about 5% of cases. One study identified the causes of failure of the FibroTest [33]. The most frequent cause leading to false negative result was high haptoglobin in acute inflammation or sepsis. The most frequent cause of false positive results was etremely low haptoglobin associated with intravascular hemolysis and high bilirubin in hemolysis and Gilbert disease. The biomarkers had to be deferred for: acute hemolysis, acute hepatitis, acute inflammation or etra hepatic cholestasis. Results are provided with security algorithms identifying situations of failure and isolated etreme values of one of the components; presence of warnings on the result sheet should lead to caution in interpreting the results. The reliability of results depends also on compliance of laboratories with the preanalytical and analytical conditions recommended by the quality chart of BioPredictive [34] Several studies have validated these analytical and preanalytical recommendations [35, 36]. According to a prospective study, fasting is not mandatory for the FibroTest dosage but is mandatory for FibroMa (SteatoTest and NashTest) [37]. Advantages of non invasive markers in trials Recently a trial with rosiglitazone versus placebo in patients with NASH, tested the impact on liver injury (steatosis and fibrosis) assessed concomitantly with biomarkers and biopsy at baseline and after one year of treatment [3]. Results showed more improved steatosis between baseline and end-of- treatment in the treated group compared to placebo at biopsy (47% vs. 6%, p=0.04) and at biomarkers (mean SteatoTest 0.7 vs. 0.64, p=0.04 in the treated group). There was no observed fibrosis histological improvement at biopsy in the treated group; meanwhile FibroTest score improved significantly in the treated group (0.44 vs. 0.34, p=0.04) compared to placebo (p=ns). These preliminary results suggest that biomarkers may be a more sensitive method than biopsy for detecting early histological changes. Recently, an original study assessed the hepatorenal ultrasound inde (HRI) for quantification of liver steatosis taking the SteatoTest as a standard instead of the biopsy [4]. This noninvasive approach was justified knowing that biopsy in NAFLD showed sampling variability for steatosis, with discordance in 22% of patients [4]. Several advantages of biomarkers in trials could be that they are at least as accurate as a 5 mm biopsy fragment, have no observer variability and no severe adverse events, being cheaper and repeatable and leading to less missing data, refusal and bias. Conclusion In France, according to a nationwide survey, the majority of hepatologists have changed their practice using noninvasive biomarker (FibroTest) and elastography instead of liver biopsy in chronic hepatitis C management. The French health authorities officially have agreed with this noninvasive practice [38, 39]. The screening for significant liver injury in patients with NAFLD will be an important medical challenge in the years to come, due to the epidemics of obesity and diabetes. A large-scale prospective screening with FibroTest- FibroMa on the general population is ongoing in France and preliminary data showed impaired fasting glucose as being one of the major risk factors associated with advanced fibrosis (Thierry Poynard personal database). From a practical point of view, the screening of liver injury could be recommended in patients with at least two metabolic syndrome factors and in type 2 diabetics aged 45 years or more. Transaminases or GGT should not be used as screening tests for the diagnosis of liver injury. The use of biomarkers should help the clinician to reassure patients with only steatosis and to identify among patients with steatosis, those with severe injuries such as advanced fibrosis and NASH in order to prevent liver-related mortality. The FibroTest and FibroMa have proven their efficacy as noninvasive biomarkers in large scale studies, being readily available in more than 50 countries and easy to perform in any routine analysis laboratory [34]. Conflicts of interest TP is the inventor of FibroTest and is a consultant and has a capital interest in Biopredictive, the company marketing FibroTest. RM and MM are Biopredictive employees. Acknowledgement We thank all the medical staff of the Diabetology Unit, Anti-fibrosis Hepatology Unit and Biomarkers Unit (Biochemistry and Biopredictive). References. Sanyl AJ. AGA technical review on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2002;23: Angulo P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Rev Gastroenterol Me 2005;70: Bedossa P, Dargère D, Paradis V. Sampling variability of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003;38:
5 FibroTest-FibroMa Eperience 9 4. Ratziu V, Charlotte F, Heurtier A, et al. LIDO Study Group. Sampling variability of liver biopsy in noalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2005;28: Ratziu V, Massard J, Charlotte F, et al. Diagnostic value of biochemical markers (FibroTest-FibroSURE) for the prediction of liver fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Gastroenterol 2006;6:6. 6. Poynard T, Morra R, Halfon P, et al. Meta-analyses of FibroTest diagnostic value in chronic liver disease. BMC Gastroenterol 2007;7: Poynard T, Ratziu V, Naveau S, et al. The diagnostic value of biomarkers (SteatoTest) for the prediction of liver steatosis. Comp Hepatol 2005;4:0. 8. Poynard T, Ratziu V, Charlotte F, et al. Diagnostic value of biochemical markers (NashTest) for the prediction of non alcoholosteatohepatitis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Gastroenterol 2006;6: Sebastiani G, Alberti A. Non invasive fibrosis biomarkers reduce but not substitute the need for liver biopsy. World J Gastroenterol 2006:2: Poynard T, Ratziu V, Benhamou Y, Thabut D, Moussalli J. Biomarkers as a first-line estimate of liver injury in chronic liver diseases: time for a moratorium on liver biopsy? Gastroenterology 2005;28: Morra R, Munteanu M, Imbert-Bismut F, Messous D, Ratziu V, Poynard T. FibroMa : Towards a new universal biomarker of liver disease? Epert Rev Mol Diagn 2007;7: Yao W, Zhao B, Zhao Y, Wang W, Qian G. Ultrasonographic teture analysis of parenchymatous organs by the four-neighborhood- piels algorithm: clinical eperiment. J Ultrasound Med 200;20: Poynard T, Charlotte F, Jacqueminet S, et al. Utility of a combination of non-invasive biomarkers (FibroMa) in assessing the efficacy of rosiglitazone in a one year randomized, double-blind trial in non alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol 2007; S298 (Abstr.). 4. Zelber-Sagi S, Webb M, Ratziu V, et al. Comparison between SteatoTest and a computerized Hepatorenal inde for ultrasonographic quantification of liver steatosis. J Hepatol 2008; 48: S368 (Abstr) 5. Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005;4: Ratziu V, Giral P, Munteanu M, et al. Screening for liver disease using non-invasive biomarkers (FibroTest, SteatoTest and NashTest) in patients with hyperlipidaemia. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2007; 25: Jacqueminet S, Lebray P, Morra R, et al. Screening for liver fibrosis by using a noninvasive biomarker in patients with diabetes. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008, in press. 8. Diaz E, Callafe R, Hollebecque A, et al. Diagnostic value of biomarkers: FibroTest, SteatoTest and NashTest for the prediction of liver injury in morbidly obese patients. Gastroenterol Clin et Biol 2007; 30 (Abstr.). 9. Munteanu M, Charlotte F, Ratziu V, et al. Direct comparison of two non invasive biomarkers for the diagnosis of advanced fibrosis in patients with non alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): NAFLD score and FibroTest. Hepatology 2007; 46:748A (Abstr.). 20. Angulo P, Hui JM, Marchesini G, et al. The NAFLD fibrosis score: a noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology. 2007;45: Ngo Y, Munteanu M, Messous D, et al. A prospective analysis of the prognostic value of biomarkers (FibroTest) in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Clin Chem 2006; 52: Ngo Y, Benhamou Y, Munteanu M, et al. FibroTest and ActiTest accurately predict risk of liver decompensation and death in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB). Hepatology 2007;46:637A (Abstr.) 23. Thabut D, Lebrec D, Oberti F, et al. Prognostic value of algorithms combining FibroTest-FibroSURE (FT) and AshTest (HT) in comparison with MELD and PUGH prognostic indees in patients with severe cirrhosis. Hepatology 2007;46:594 A (Abstr.) 24. Bruckert E, Giral P, Ratziu V, et al. A constellation of cardiovascular risk factors is associated with hepatic enzyme elevation in hyperlipidemic patients. Metabolism 2002; 5: Epert Panel on Detection Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Eecutive summary of the third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) epert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 200; 285: Ekstedt M, Franzen LE, Mathiesen UL, et al. Long-term follow-up of patients with NAFLD and elevated liver enzymes. Hepatology 2006; 44: El-Serag HB, Hampel H, Javadi F. The association between diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review of epidemiologic evidence. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006;4: Olshansky SJ, Passaro DJ, Hershow RC, et al. A potential decline in life epectancy in the United States in the 2st century. N Engl J Med 2005;352: Ruhl CE, Everhart JE. Determinants of the association of overweight with elevated serum alanine aminotransferase activity in the United States. Gastroenterology 2003; 24: Wanless IR, Lentz JS. Fatty liver hepatitis (steatohepatitis) and obesity: an autopsy study with analysis of risk factors. Hepatology 990;2: Machado M, Marques-Vidal Pedro, Cortez-Pinto H. Hepatic histology in obese patients undergoing bariatric surgery. J Hepatol 2006;45: Padoin AV, Mottin CC, Moretto M, et al. A comparison of wedge and needle hepatic biopsy in open bariatric surgery. Obes Surg 2006;6: Poynard T, Munteanu M, Imbert-Bismut F, et al. Prospective analysis of discordant results between biochemical markers and biopsy in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Clin Chem 2004; 50: www. biopredictive.com 35. Halfon P, Imbert-Bismut F, Messous D, et al. A prospective assessment of the inter-laboratory variability of biochemical markers of fibrosis (FibroTest) and activity (ActiTest) in patients with chronic liver disease. Comp Hepatol 2002; : Imbert-Bismut F, Messous D, Thibault V, et al. Intra-laboratory analytical variability of biochemical markers of fibrosis (Fibrotest) and activity (Actitest) and reference ranges in healthy blood donors. Clin Chem Lab Med 2004;42: Munteanu M, Messous D, Thabut D, et al. Intra-individual fasting versus postprandial variation of biochemical markers of liver fibrosis (FibroTest) and activity (ActiTest). Comp Hepatol 2004;3:3 38. Castera L, Denis J, Babany G, et al. Evolving practices of noninvasive markers of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C in France: time for new guidelines? J. Hepatol. 2007;46:S528-S529 (Abstr.) 39. La Haute Autorité de Santé (HAS) in France. The HAS recommendations for the management of the chronic hepatitis C using non-invasive biomarkers. Available at: fr/portail/display.jsp?id_c_
Alternatives to Liver Biopsy for Assessing Liver Disease
 Alternatives to Liver Biopsy for Assessing Liver Disease a report by Thierry Poynard Professor of Medicine, University of Paris The consensus conference statements recommend liver biopsy in the management
Alternatives to Liver Biopsy for Assessing Liver Disease a report by Thierry Poynard Professor of Medicine, University of Paris The consensus conference statements recommend liver biopsy in the management
An Accurate Definition of the Status of Inactive Hepatitis B Virus Carrier by a Combination of Biomarkers (FibroTest-ActiTest) and Viral Load
 An Accurate Definition of the Status of Inactive Hepatitis B Virus Carrier by a Combination of Biomarkers (FibroTest-ActiTest) and Viral Load Yen Ngo 1, Yves Benhamou 1, Vincent Thibault 2, Patrick Ingiliz
An Accurate Definition of the Status of Inactive Hepatitis B Virus Carrier by a Combination of Biomarkers (FibroTest-ActiTest) and Viral Load Yen Ngo 1, Yves Benhamou 1, Vincent Thibault 2, Patrick Ingiliz
MP Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease
 Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.04.41 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 9.01.502 Experimental / Investigational Services DISCLAIMER Our medical policies
Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.04.41 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 9.01.502 Experimental / Investigational Services DISCLAIMER Our medical policies
Bio Predictive. FibroTest/FibroSure Scientific Publications. Houot 2015 FibroTest, TE, FIB-4, APRI Meta-analysis
 AASLD 2015 /FibroSure Scientific Publications Section 1 - compared to APRI, FIB-4 and transient elastography Houot 2015, TE, FIB-4, APRI Meta-analysis is superior to TE by Fibroscan, APRI and Fib-4 using
AASLD 2015 /FibroSure Scientific Publications Section 1 - compared to APRI, FIB-4 and transient elastography Houot 2015, TE, FIB-4, APRI Meta-analysis is superior to TE by Fibroscan, APRI and Fib-4 using
Section: Laboratory Last Reviewed Date: June Policy No: 47 Effective Date: August 1, 2013
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Multianalyte Assays with Algorithmic Analysis for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Date of Origin: June 2013 Section: Laboratory Last Reviewed
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Multianalyte Assays with Algorithmic Analysis for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Date of Origin: June 2013 Section: Laboratory Last Reviewed
Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease
 Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease Policy Number: 2.04.41 Last Review: 2/2019 Origination: 2/2017 Next Review: 2/2020 Policy Blue Cross and
Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease Policy Number: 2.04.41 Last Review: 2/2019 Origination: 2/2017 Next Review: 2/2020 Policy Blue Cross and
Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease
 Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease Policy Number: 2.04.41 Last Review: 2/2018 Origination: 2/2017 Next Review: 2/2019 Policy Blue Cross and
Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease Policy Number: 2.04.41 Last Review: 2/2018 Origination: 2/2017 Next Review: 2/2019 Policy Blue Cross and
In Search of New Biomarkers for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
 REVIEW In Search of New Biomarkers for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ting-Ting Chan, M.R.C.P., and Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, M.D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) affects 15% to 40% of the general
REVIEW In Search of New Biomarkers for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ting-Ting Chan, M.R.C.P., and Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, M.D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) affects 15% to 40% of the general
Multianalyte assays with algorithmic analyses are considered investigational for the diagnosis or monitoring of patients with chronic liver disease.
 2.04.41 Multianalyte Assays with Algorithmic Analysis for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Section 2.0 Medicine Subsection 2.04 Pathology/Laboratory Effective Date September
2.04.41 Multianalyte Assays with Algorithmic Analysis for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Section 2.0 Medicine Subsection 2.04 Pathology/Laboratory Effective Date September
Bio Predictive. FibroTest Scientific Publications. Ratziu 2016 FibroMax NASH. Friedman 2016 FibroTest NASH EASL Key Publications for 2017
 EASL 2017 Scientific Publications Ratziu 2016 NASH Friedman 2016 NASH SteatoTest and sensitive markers of improvement in NASH trial using Elafibranor Elafibranor, an agonist of the peroxisome proliferator
EASL 2017 Scientific Publications Ratziu 2016 NASH Friedman 2016 NASH SteatoTest and sensitive markers of improvement in NASH trial using Elafibranor Elafibranor, an agonist of the peroxisome proliferator
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Page 1 of 38 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation
Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Page 1 of 38 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation
NASH : Diagnosis and investigation. VII Workshop international, Curitiba, Brazil 29/08/2014
 NASH : Diagnosis and investigation VII Workshop international, Curitiba, Brazil 29/08/2014 Vlad Ratziu, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Hôpital Pitié Salpêtrière, Paris, France Usual diagnostic circumstances
NASH : Diagnosis and investigation VII Workshop international, Curitiba, Brazil 29/08/2014 Vlad Ratziu, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Hôpital Pitié Salpêtrière, Paris, France Usual diagnostic circumstances
The role of non-invasivemethods in evaluating liver fibrosis of patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
 The role of non-invasivemethods in evaluating liver fibrosis of patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis Objectives: Liver biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosing the extent of fibrosis in NAFLD/NASH;
The role of non-invasivemethods in evaluating liver fibrosis of patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis Objectives: Liver biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosing the extent of fibrosis in NAFLD/NASH;
Section: Laboratory Last Reviewed Date: May Policy No: 47 Effective Date: August 1, 2014
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Multianalyte Assays with Algorithmic Analysis for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Date of Origin: June 2013 Section: Laboratory Last Reviewed
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Multianalyte Assays with Algorithmic Analysis for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Date of Origin: June 2013 Section: Laboratory Last Reviewed
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Page 1 of 34 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Professional
Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Page 1 of 34 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Professional
PROGRESSION TO FIBROSIS IN PATIENTS WITH NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE (NAFLD) THE VALUE OF NONINVASIVE MARKERS
 Supplement 1/2015, 4 th ISAA PROGRESSION TO FIBROSIS IN PATIENTS WITH NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE (NAFLD) THE VALUE OF NONINVASIVE MARKERS Denisa DOBRIN 1, Tiberiu Ioan NANEA 2, Cristian Mihai POMOHACI
Supplement 1/2015, 4 th ISAA PROGRESSION TO FIBROSIS IN PATIENTS WITH NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE (NAFLD) THE VALUE OF NONINVASIVE MARKERS Denisa DOBRIN 1, Tiberiu Ioan NANEA 2, Cristian Mihai POMOHACI
Simple non-invasive fibrosis scoring systems can reliably exclude advanced fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
 1 Liver Unit, Newcastle Upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Trust, Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK 2 Institute of Cellular Medicine, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Newcastle University, Newcastle Upon Tyne,
1 Liver Unit, Newcastle Upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Trust, Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK 2 Institute of Cellular Medicine, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Newcastle University, Newcastle Upon Tyne,
Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis. Patricia Slev, PhD University of Utah Department of Pathology
 Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis Patricia Slev, PhD University of Utah Department of Pathology Disclosure Patricia Slev has no relevant financial relationships to disclose. 2 Chronic Liver Disease
Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis Patricia Slev, PhD University of Utah Department of Pathology Disclosure Patricia Slev has no relevant financial relationships to disclose. 2 Chronic Liver Disease
Noninvasive Markers of Hepatic Fibrosis in Chronic Hepatitis B
 Curr Hepatitis Rep (2011) 10:87 97 DOI 10.1007/s11901-011-0096-0 Noninvasive Markers of Hepatic Fibrosis in Chronic Hepatitis B Thierry Poynard & Yen Ngo & Mona Munteanu & Dominique Thabut & Vlad Ratziu
Curr Hepatitis Rep (2011) 10:87 97 DOI 10.1007/s11901-011-0096-0 Noninvasive Markers of Hepatic Fibrosis in Chronic Hepatitis B Thierry Poynard & Yen Ngo & Mona Munteanu & Dominique Thabut & Vlad Ratziu
Transient elastography in chronic liver diseases of other etiologies
 4 Post Meeting A.I.S.F. Unmet Clinical Needs in Hepatology: New and upcoming diagnostic tools" Transient elastography in chronic liver diseases of other etiologies Dr. Vincenza Calvaruso Gastroenterologia
4 Post Meeting A.I.S.F. Unmet Clinical Needs in Hepatology: New and upcoming diagnostic tools" Transient elastography in chronic liver diseases of other etiologies Dr. Vincenza Calvaruso Gastroenterologia
Invasive. Sampling error. Interobserver variability. Nondynamic evaluation of
 How to assess liver fibrosis Serum markers or FibroScan vs. liver biopsy? Laurent CASTERA & Pierre BEDOSSA Hôpital Beaujon, AP-HP, Clichy Université Paris-VII France 4 th Paris Hepatitis Conference, Paris,
How to assess liver fibrosis Serum markers or FibroScan vs. liver biopsy? Laurent CASTERA & Pierre BEDOSSA Hôpital Beaujon, AP-HP, Clichy Université Paris-VII France 4 th Paris Hepatitis Conference, Paris,
Multianalyte Assays with Algorithmic Analysis for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease
 Medical Policy Manual Laboratory, Policy No. 47 Multianalyte Assays with Algorithmic Analysis for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Next Review: May 2018 Last Review:
Medical Policy Manual Laboratory, Policy No. 47 Multianalyte Assays with Algorithmic Analysis for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Next Review: May 2018 Last Review:
National Horizon Scanning Centre. Enhanced Liver Fibrosis Test (ELF) for evaluating liver fibrosis. June 2008
 Enhanced Liver Fibrosis Test (ELF) for evaluating liver fibrosis June 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended
Enhanced Liver Fibrosis Test (ELF) for evaluating liver fibrosis June 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended
Page: 1 of 19. Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease
 and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Page: 1 of 19 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Description Options for noninvasive monitoring of liver fibrosis
and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Page: 1 of 19 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Description Options for noninvasive monitoring of liver fibrosis
Awareness of the severity of liver disease re-examined using softwarecombined biomarkers of liver fibrosis and necroinflammatory activity
 Open Access To cite: Poynard T, Deckmyn O, Munteanu M, et al. Awareness of the severity of liver disease reexamined using softwarecombined biomarkers of liver fibrosis and necroinflammatory activity. BMJ
Open Access To cite: Poynard T, Deckmyn O, Munteanu M, et al. Awareness of the severity of liver disease reexamined using softwarecombined biomarkers of liver fibrosis and necroinflammatory activity. BMJ
IS LIVER BIOPSY NECESSARY IN PATIENTS WITH NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE?
 Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2016 vol. 120, no. 3 INTERNAL MEDICINE - PEDIATRICS UPDATES IS LIVER BIOPSY NECESSARY IN PATIENTS WITH NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE? R. S. Gavril 1, Laura Mihalache
Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2016 vol. 120, no. 3 INTERNAL MEDICINE - PEDIATRICS UPDATES IS LIVER BIOPSY NECESSARY IN PATIENTS WITH NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE? R. S. Gavril 1, Laura Mihalache
Update on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Timothy R. Morgan, MD Chief, Hepatology, VA Long Beach Professor of Medicine, UCI
 Update on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Timothy R. Morgan, MD Chief, Hepatology, VA Long Beach Professor of Medicine, UCI February 3, 2018 Disclosure Clinical trials: Genfit Speaker s Bureau: none
Update on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Timothy R. Morgan, MD Chief, Hepatology, VA Long Beach Professor of Medicine, UCI February 3, 2018 Disclosure Clinical trials: Genfit Speaker s Bureau: none
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2008;6:1249 1254 Cytokeratin 18 Fragment Levels as a Noninvasive Biomarker for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Bariatric Surgery Patients DIMA L. DIAB,* LISA YERIAN,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2008;6:1249 1254 Cytokeratin 18 Fragment Levels as a Noninvasive Biomarker for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Bariatric Surgery Patients DIMA L. DIAB,* LISA YERIAN,
Prognosis of NASH VII Workshop Intenracional de Actualizaçao em Hepatologia, Aug 29th 2014
 Prognosis of NASH VII Workshop Intenracional de Actualizaçao em Hepatologia, Aug 29th 2014 Vlad Ratziu, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Hôpital Pitié Salpêtrière, Paris, France NASH : a severe hepatic
Prognosis of NASH VII Workshop Intenracional de Actualizaçao em Hepatologia, Aug 29th 2014 Vlad Ratziu, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Hôpital Pitié Salpêtrière, Paris, France NASH : a severe hepatic
tage Percent Total & over Total & over Men Women Men Women
 Paul Angulo, MD, FACG, AGAF Professor of Medicine, Section Chief of Hepatology Division i i of Digestive i Diseases and Nutrition i University of Kentucky Medical Center Lexington, KY Paul Angulo, MD University
Paul Angulo, MD, FACG, AGAF Professor of Medicine, Section Chief of Hepatology Division i i of Digestive i Diseases and Nutrition i University of Kentucky Medical Center Lexington, KY Paul Angulo, MD University
HEP DART 2017, Kona, Hawaii
 HEP DART 2017, Kona, Hawaii Rong Yu 1, Ke Xu 1, Jing Li 1, Tong Sun 1, Shengjiang Zhang 2, Jinhua Shao 2, Jin Sun 2, Qiong He 3, Jianwen Luo 3, Cheng Wang 4, Yudong Wang 4, Jing Chen 4, Vanessa Wu 4, George
HEP DART 2017, Kona, Hawaii Rong Yu 1, Ke Xu 1, Jing Li 1, Tong Sun 1, Shengjiang Zhang 2, Jinhua Shao 2, Jin Sun 2, Qiong He 3, Jianwen Luo 3, Cheng Wang 4, Yudong Wang 4, Jing Chen 4, Vanessa Wu 4, George
/ FIB4 Index , simple steatosis. FIB4 Index. FIB4 Index. FIB4 Index FIB4 Index. Sterling FIB4 Index. FIB4 Index AST AST ALT
 原 著 29 34-41, 2014 FIB4 Index 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 FIB4 Index FIB4 Index cut off 2.67 2.67 12,059 FIB4 IndexFIB4 Index 2.67 / FIB4 Index AST ALT FIB4 Index 2.67 161 1.3% FIB4 Index 5 FIB4 Index 1.1 5 1.6 FIB4
原 著 29 34-41, 2014 FIB4 Index 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 FIB4 Index FIB4 Index cut off 2.67 2.67 12,059 FIB4 IndexFIB4 Index 2.67 / FIB4 Index AST ALT FIB4 Index 2.67 161 1.3% FIB4 Index 5 FIB4 Index 1.1 5 1.6 FIB4
Standardization of ROC Curve Areas for Diagnostic Evaluation of Liver Fibrosis Markers Based on Prevalences of Fibrosis Stages
 Clinical Chemistry 53:9 1615 1622 (2007) Evidence-Based Laboratory Medicine and Test Utilization Standardization of ROC Curve Areas for Diagnostic Evaluation of Liver Fibrosis Markers Based on Prevalences
Clinical Chemistry 53:9 1615 1622 (2007) Evidence-Based Laboratory Medicine and Test Utilization Standardization of ROC Curve Areas for Diagnostic Evaluation of Liver Fibrosis Markers Based on Prevalences
The evaluation of liver fibrosis is a key step to manage
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2011;140:1970 1979 CLINICAL LIVER, BILIARY TRACT Noninvasive Tests for Fibrosis and Liver Stiffness Predict 5-Year Outcomes of Patients With Chronic Hepatitis C JULIEN VERGNIOL,* JULIETTE
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2011;140:1970 1979 CLINICAL LIVER, BILIARY TRACT Noninvasive Tests for Fibrosis and Liver Stiffness Predict 5-Year Outcomes of Patients With Chronic Hepatitis C JULIEN VERGNIOL,* JULIETTE
*APHP: Hôpital Beaujon Professor P Bedossa, Dr F Degos, Professor P Marcellin, Professor
 APPENDIX 1 LIST OF COINVESTIGATORS *APHP: Hôpital Beaujon Professor P Bedossa, Dr F Degos, Professor P Marcellin, Professor M Vidaud; Hôpital Cochin-Necker: Professor S Pol, Professor Ph Sogni, Professor
APPENDIX 1 LIST OF COINVESTIGATORS *APHP: Hôpital Beaujon Professor P Bedossa, Dr F Degos, Professor P Marcellin, Professor M Vidaud; Hôpital Cochin-Necker: Professor S Pol, Professor Ph Sogni, Professor
Diagnostic Challenges of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/ Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
 REVIEW Diagnostic Challenges of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/ Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Erin Cleveland, M.D.,* Andrew Bandy, M.D., and Lisa B. VanWagner, M.D., M.Sc. *, Nonalcoholic fatty liver
REVIEW Diagnostic Challenges of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/ Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Erin Cleveland, M.D.,* Andrew Bandy, M.D., and Lisa B. VanWagner, M.D., M.Sc. *, Nonalcoholic fatty liver
The classical metabolic work-up, approved by the Ethics Committee of the Antwerp
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS METHODS Metabolic work-up The classical metabolic work-up, approved by the Ethics Committee of the Antwerp University Hospital and requiring written informed consent, included a
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS METHODS Metabolic work-up The classical metabolic work-up, approved by the Ethics Committee of the Antwerp University Hospital and requiring written informed consent, included a
Original article On-treatment monitoring of liver fibrosis with transient elastography in chronic hepatitis B patients
 Antiviral Therapy 2011; 16:165 172 (doi: 10.3851/IMP1726) Original article On-treatment monitoring of liver fibrosis with transient elastography in chronic hepatitis B patients Grace Lai-Hung Wong 1,2,
Antiviral Therapy 2011; 16:165 172 (doi: 10.3851/IMP1726) Original article On-treatment monitoring of liver fibrosis with transient elastography in chronic hepatitis B patients Grace Lai-Hung Wong 1,2,
Clinical Policy Title: Serum biomarkers for liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis
 Clinical Policy Title: Serum biomarkers for liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis Clinical Policy Number: 01.01.01 Effective Date: June 1, 2014 Initial Review Date: December 18, 2013 Most Recent Review Date:
Clinical Policy Title: Serum biomarkers for liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis Clinical Policy Number: 01.01.01 Effective Date: June 1, 2014 Initial Review Date: December 18, 2013 Most Recent Review Date:
Prise en charge actuelle de l'hépatite C et nouvelles approches thérapeutiques
 Prise en charge actuelle de l'hépatite C et nouvelles approches thérapeutiques Future Complications of Darius Moradpour Service de Gastro-entérologie et d'hépatologie Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois
Prise en charge actuelle de l'hépatite C et nouvelles approches thérapeutiques Future Complications of Darius Moradpour Service de Gastro-entérologie et d'hépatologie Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois
CDHNF & NASPGHAN A Partnership for Research and Education for Children s Digestive and Nutritional Health
 CDHNF & NASPGHAN A Partnership for Research and Education for Children s Digestive and Nutritional Health Obesity and NAFLD Definitions: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and nonalcoholic fatty liver
CDHNF & NASPGHAN A Partnership for Research and Education for Children s Digestive and Nutritional Health Obesity and NAFLD Definitions: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and nonalcoholic fatty liver
At Least 1 in 5 Patients in Your Practice Have Fatty Liver
 At Least 1 in 5 Patients in Your Practice Have Fatty Liver What Can You Tell Your Patients Magnus McLeod MD FRCPC Assistant Professor Dalhousie University 30-NOV-2017 NAFLD Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
At Least 1 in 5 Patients in Your Practice Have Fatty Liver What Can You Tell Your Patients Magnus McLeod MD FRCPC Assistant Professor Dalhousie University 30-NOV-2017 NAFLD Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
NONINVASIVE TECHNIQUES FOR EVALUATION AND MONITORING OF CHRONIC LIVER DISEASE
 LIVER DISEASE Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are
LIVER DISEASE Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are
Clinical Policy Title: Serum biomarkers for liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis
 Clinical Policy Title: Serum biomarkers for liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis Clinical Policy Number: 01.01.01 Effective Date: June 1, 2014 Initial Review Date: December 18, 2013 Most Recent Review Date:
Clinical Policy Title: Serum biomarkers for liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis Clinical Policy Number: 01.01.01 Effective Date: June 1, 2014 Initial Review Date: December 18, 2013 Most Recent Review Date:
Non-Invasive Testing for Liver Fibrosis
 NORTHWEST AIDS EDUCATION AND TRAINING CENTER Non-Invasive Testing for Liver Fibrosis John Scott, MD, MSc Associate Professor, University of Washington Associate Clinic Director, Hep/Liver Clinic, Harborview
NORTHWEST AIDS EDUCATION AND TRAINING CENTER Non-Invasive Testing for Liver Fibrosis John Scott, MD, MSc Associate Professor, University of Washington Associate Clinic Director, Hep/Liver Clinic, Harborview
Bio Predictive. FibroTest/FibroSure Scientific Publications. Perazzo 2014 FibroMax Prognosis Metabolic. Park 2014 FibroTest HBV Prognostic
 AASLD 2014 /FibroSure Scientific Publications Perazzo 2014 FibroMax Prognosis Metabolic Park 2014 Prognostic Bonnard 2014 HCV Genotype 4 Schistosomiasis Prognostic value of liver fibrosis and steatosis
AASLD 2014 /FibroSure Scientific Publications Perazzo 2014 FibroMax Prognosis Metabolic Park 2014 Prognostic Bonnard 2014 HCV Genotype 4 Schistosomiasis Prognostic value of liver fibrosis and steatosis
When to Treat: Staging Liver Disease David L. Thomas, MD, MPH
 When to Treat: Staging Liver Disease David L. Thomas, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Disclosures Received royalties from UpToDate, Inc. Staging refers to the assessment
When to Treat: Staging Liver Disease David L. Thomas, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Disclosures Received royalties from UpToDate, Inc. Staging refers to the assessment
Research Article. Introduction
 Validation of liver fibrosis biomarker (FibroTest) for assessing liver fibrosis progression: Proof of concept and first application in a large population Thierry Poynard 1,, Mona Munteanu 2, Olivier Deckmyn
Validation of liver fibrosis biomarker (FibroTest) for assessing liver fibrosis progression: Proof of concept and first application in a large population Thierry Poynard 1,, Mona Munteanu 2, Olivier Deckmyn
The Absence of Obstructive Sleep Apnea May Protect against Non- Alcoholic Fatty Liver in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery
 The Absence of Obstructive Sleep Apnea May Protect against Non- Alcoholic Fatty Liver in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share
The Absence of Obstructive Sleep Apnea May Protect against Non- Alcoholic Fatty Liver in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share
Non invasive assessment of liver fi brosis ONLY. liver diseases liver biopsy liver fibrosis biomarkers fibrotest fibroscan
 Ann Transplant, 2008; 13(2): 5-11 Received: 2008.04.15 Accepted: 2008.04.29 Published: 2008.06.17 Key words Full-text PDF: Word count: 1979 Tables: 1 Figures: 2 References: 50 Author s address: Non invasive
Ann Transplant, 2008; 13(2): 5-11 Received: 2008.04.15 Accepted: 2008.04.29 Published: 2008.06.17 Key words Full-text PDF: Word count: 1979 Tables: 1 Figures: 2 References: 50 Author s address: Non invasive
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International licence
 Munteanu M, Tiniakos D, Anstee Q, Charlotte F, Marchesini G, Bugianesi E, Trauner M, Romero Gomez M, Oliveira C, Day C, Dufour JF, Bellentani S, Ngo Y, Traussnig S, Perazzo H, Deckmyn O, Bedossa P, Ratziu
Munteanu M, Tiniakos D, Anstee Q, Charlotte F, Marchesini G, Bugianesi E, Trauner M, Romero Gomez M, Oliveira C, Day C, Dufour JF, Bellentani S, Ngo Y, Traussnig S, Perazzo H, Deckmyn O, Bedossa P, Ratziu
The role of ARFI and APRI in diagnosis of liver fibrosis on patients with common chronic liver diseases
 RESEARCH ARTICLE The role of ARFI and APRI in diagnosis of liver fibrosis on patients with common chronic liver diseases Objective: This study aimed to investigate the value of liver fibrosis assessment
RESEARCH ARTICLE The role of ARFI and APRI in diagnosis of liver fibrosis on patients with common chronic liver diseases Objective: This study aimed to investigate the value of liver fibrosis assessment
What is NAFLD?.NASH? Presenter Disclosure Information. Learning Objectives. Case 1: Rob. Questions Pertinent to Rob
 Presenter Disclosure Information 5 6pm Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Another Obesity-Related Epidemic SPEAKER Elliot Tapper, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation:
Presenter Disclosure Information 5 6pm Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Another Obesity-Related Epidemic SPEAKER Elliot Tapper, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation:
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic. Noninvasive Assessment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Obese or Overweight Patients
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:1162 1168 Noninvasive Assessment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Obese or Overweight Patients SVEN M. A. FRANCQUE,* AN VERRIJKEN, ILSE MERTENS, GUY
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:1162 1168 Noninvasive Assessment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Obese or Overweight Patients SVEN M. A. FRANCQUE,* AN VERRIJKEN, ILSE MERTENS, GUY
Faculty Disclosure. Objectives. Cirrhosis Management for the Family Physician 18/11/2014
 Cirrhosis Management for the Family Physician Mang Ma, MD, FRCP Professor University of Alberta Faculty: Mang Ma Faculty Disclosure Relationships with commercial interests: Advisory Board: Merck, Gilead
Cirrhosis Management for the Family Physician Mang Ma, MD, FRCP Professor University of Alberta Faculty: Mang Ma Faculty Disclosure Relationships with commercial interests: Advisory Board: Merck, Gilead
The place of bariatric surgery in NASH: can we extend the indications? - No
 The place of bariatric surgery in NASH: can we extend the indications? - No Nicolas Goossens Service de Gastroentérologie & Hépatologie Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Genève, Suisse How to extend the
The place of bariatric surgery in NASH: can we extend the indications? - No Nicolas Goossens Service de Gastroentérologie & Hépatologie Hôpitaux Universitaires de Genève Genève, Suisse How to extend the
Transient elastography in chronic viral liver diseases
 4 th AISF POST-MEETING COURSE Roma, 26 Febbraio 2011 Transient elastography in chronic viral liver diseases CRISTINA RIGAMONTI, M.D., Ph.D. Transient elastography (TE): a rapid, non-invasive technique
4 th AISF POST-MEETING COURSE Roma, 26 Febbraio 2011 Transient elastography in chronic viral liver diseases CRISTINA RIGAMONTI, M.D., Ph.D. Transient elastography (TE): a rapid, non-invasive technique
We don t need a liver biopsy. We have non-invasive tests
 We don t need a liver biopsy We have non-invasive tests Laurent CASTERA, MD PhD Department of Hepatology, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy Université Paris Diderot, France PHC 2018 www.aphc.info Liver biopsy: an
We don t need a liver biopsy We have non-invasive tests Laurent CASTERA, MD PhD Department of Hepatology, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy Université Paris Diderot, France PHC 2018 www.aphc.info Liver biopsy: an
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
 HEPATO-PANCREATO-BILIARY STOMACH CANCER PROGRAM Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Steatosis and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Management Recommendations UCSF Fresno Department of Surgery
HEPATO-PANCREATO-BILIARY STOMACH CANCER PROGRAM Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Steatosis and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Management Recommendations UCSF Fresno Department of Surgery
Downloaded from zjrms.ir at 3: on Monday February 25th 2019 NAFLD BMI. Kg/m2 NAFLD
 logistic regression Student s t-test P< BMI BMI P< ALT AST P< Email:mkhoshbaten@yahoo.com Kg/m2 NASH RUQ B C II Case-Control II Logistic Regression Chi-Square T-test P< Grade Model 1- A diffuse hyper echoic
logistic regression Student s t-test P< BMI BMI P< ALT AST P< Email:mkhoshbaten@yahoo.com Kg/m2 NASH RUQ B C II Case-Control II Logistic Regression Chi-Square T-test P< Grade Model 1- A diffuse hyper echoic
Challenges in the Diagnosis of Steatohepatitis
 The Bugaboos of Fatty Liver Disease: Ballooning and Fibrosis Hans Popper Hepatopathology Society Companion Meeting San Antonio, Tx March, 2017 David Kleiner, M.D., Ph.D. NCI/Laboratory of Pathology Challenges
The Bugaboos of Fatty Liver Disease: Ballooning and Fibrosis Hans Popper Hepatopathology Society Companion Meeting San Antonio, Tx March, 2017 David Kleiner, M.D., Ph.D. NCI/Laboratory of Pathology Challenges
Hepatology for the Nonhepatologist
 Hepatology for the Nonhepatologist Kenneth E. Sherman, MD, PhD Gould Professor of Medicine Director, Division of Digestive Diseases University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Cincinnati, Ohio Learning
Hepatology for the Nonhepatologist Kenneth E. Sherman, MD, PhD Gould Professor of Medicine Director, Division of Digestive Diseases University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Cincinnati, Ohio Learning
M30 Apoptosense ELISA. A biomarker assay for detection and screening of NASH
 M30 Apoptosense ELISA A biomarker assay for detection and screening of NASH NASH A Global Disease In the Western countries, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disease, strongly
M30 Apoptosense ELISA A biomarker assay for detection and screening of NASH NASH A Global Disease In the Western countries, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disease, strongly
Liver biopsy as the gold standard for diagnosis. Pierre BEDOSSA
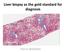 Liver biopsy as the gold standard for diagnosis Pierre BEDOSSA 1 PATHOLOGY OF NAFLD CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Grants and funding from Genfit, Intercept, Allergan, Inventiva, OWL, Echosens CEO and funding of
Liver biopsy as the gold standard for diagnosis Pierre BEDOSSA 1 PATHOLOGY OF NAFLD CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Grants and funding from Genfit, Intercept, Allergan, Inventiva, OWL, Echosens CEO and funding of
ALT and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels were measured using the α-ketoglutarate reaction (Roche,
 Supplemental Methods Analytical determinations ALT and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels were measured using the α-ketoglutarate reaction (Roche, Basel, Switzerland). Glucose, triglyceride, total
Supplemental Methods Analytical determinations ALT and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels were measured using the α-ketoglutarate reaction (Roche, Basel, Switzerland). Glucose, triglyceride, total
Module 1 Introduction of hepatitis
 Module 1 Introduction of hepatitis 1 Training Objectives At the end of the module, trainees will be able to ; Demonstrate improved knowledge of the global epidemiology of the viral hepatitis Understand
Module 1 Introduction of hepatitis 1 Training Objectives At the end of the module, trainees will be able to ; Demonstrate improved knowledge of the global epidemiology of the viral hepatitis Understand
First European NAFLD-NASH Summit European Parliament, Brussels, May 31 st NAFLD/NASH : an expanding burden on liver health
 First European NAFLD-NASH Summit European Parliament, Brussels, May 31 st 2017 NAFLD/NASH : an expanding burden on liver health Vlad Ratziu, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Hôpital Pitié Salpêtrière,
First European NAFLD-NASH Summit European Parliament, Brussels, May 31 st 2017 NAFLD/NASH : an expanding burden on liver health Vlad Ratziu, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Hôpital Pitié Salpêtrière,
PHC, Paris, 30th Jan 2017 PATHOLOGY OF NAFLD. Pierre Bedossa. Departement of Pathology Hôpital Beaujon University Paris-Diderot Paris - FRANCE
 PHC, Paris, 30th Jan 2017 PATHOLOGY OF NAFLD Pierre Bedossa Departement of Pathology Hôpital Beaujon University Paris-Diderot Paris - FRANCE 1 PATHOLOGY OF NAFLD NAFLD: a chronic liver disease with a wide
PHC, Paris, 30th Jan 2017 PATHOLOGY OF NAFLD Pierre Bedossa Departement of Pathology Hôpital Beaujon University Paris-Diderot Paris - FRANCE 1 PATHOLOGY OF NAFLD NAFLD: a chronic liver disease with a wide
Internal and Emergency Medicine Official Journal of the Italian Society of Internal Medicine. ISSN Volume 8 Number 3
 Hepatic Steatosis Index and Lipid Accumulation Product as middle-term predictors of incident metabolic syndrome in a large population sample: data from the Brisighella Heart Study Arrigo F. G. Cicero,
Hepatic Steatosis Index and Lipid Accumulation Product as middle-term predictors of incident metabolic syndrome in a large population sample: data from the Brisighella Heart Study Arrigo F. G. Cicero,
The effect of aerobic exercise on serum level of liver enzymes and liver echogenicity in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
 Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench. 2013 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effect of aerobic exercise on serum level of liver enzymes
Gastroenterology and Hepatology From Bed to Bench. 2013 RIGLD, Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effect of aerobic exercise on serum level of liver enzymes
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Harris R, Harman DJ, Card TR, Aithal GP, Guha
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Harris R, Harman DJ, Card TR, Aithal GP, Guha
Prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in a tertiary care hospital of Bihar
 Original Research Article Prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in a tertiary care hospital of Bihar Naresh Kumar 1, Jyoti Kumar Dinkar 2*, Chandrakishore
Original Research Article Prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in a tertiary care hospital of Bihar Naresh Kumar 1, Jyoti Kumar Dinkar 2*, Chandrakishore
Clinical Policy Title: Liver elastography
 Clinical Policy Title: Liver elastography Clinical Policy Number: CCP.1118 Effective Date: October 1, 2014 Initial Review Date: June 18, 2014 Most Recent Review Date: August 7, 2018 Next Review Date: August
Clinical Policy Title: Liver elastography Clinical Policy Number: CCP.1118 Effective Date: October 1, 2014 Initial Review Date: June 18, 2014 Most Recent Review Date: August 7, 2018 Next Review Date: August
American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology
 American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology e - ISSN - XXXX-XXXX ISSN - 2394-7721 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajomr PREVALENCE OF NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE AMONG TYPE 2 DIABETIC POPULATION
American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology e - ISSN - XXXX-XXXX ISSN - 2394-7721 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajomr PREVALENCE OF NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE AMONG TYPE 2 DIABETIC POPULATION
NAFLD: evidence-based management. Curso de residentes AEEH Salvador Augustin, MD Liver Unit Vall d Hebron Hospital Barcelona, Spain
 NAFLD: evidence-based management Curso de residentes AEEH 2017 Salvador Augustin, MD Liver Unit Vall d Hebron Hospital Barcelona, Spain Clinical case - 55 yo female - Sent for incidental steatosis at abdominal
NAFLD: evidence-based management Curso de residentes AEEH 2017 Salvador Augustin, MD Liver Unit Vall d Hebron Hospital Barcelona, Spain Clinical case - 55 yo female - Sent for incidental steatosis at abdominal
LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:1028 1033 LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT Prevalence and Indicators of Portal Hypertension in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease FLAVIA D.
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:1028 1033 LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT Prevalence and Indicators of Portal Hypertension in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease FLAVIA D.
CLINICAL STUDIES. Liver International ISSN
 Liver International ISSN 1478-3223 CLINICAL STUDIES Biochemical and biophysical assessment of MTX-induced liver brosis in psoriasis patients: predicts the presence and Fibroscan s predicts the absence
Liver International ISSN 1478-3223 CLINICAL STUDIES Biochemical and biophysical assessment of MTX-induced liver brosis in psoriasis patients: predicts the presence and Fibroscan s predicts the absence
DIAGNOSIS OF CIRRHOSIS BY TRANSIENT ELASTOGRAPHY (FIBROSCAN ): A PROSPECTIVE STUDY.
 Gut Online First, published on July 14, 2005 as 10.1136/gut.2005.069153 DIAGNOSIS OF CIRRHOSIS BY TRANSIENT ELASTOGRAPHY (FIBROSCAN ): A PROSPECTIVE STUDY. Juliette Foucher (1), Elise Chanteloup (1), Julien
Gut Online First, published on July 14, 2005 as 10.1136/gut.2005.069153 DIAGNOSIS OF CIRRHOSIS BY TRANSIENT ELASTOGRAPHY (FIBROSCAN ): A PROSPECTIVE STUDY. Juliette Foucher (1), Elise Chanteloup (1), Julien
FibroTest/FibroSure Scientific Publications Posters for AASLD 2012
 AASLD Survival Tuesday, Nov. 13 Poster 1733 /FibroSure Scientific Publications Posters for AASLD Long term survival of liver fibrosis after virological cure (SVR) in patients with chronic hepatitis C (CHC):
AASLD Survival Tuesday, Nov. 13 Poster 1733 /FibroSure Scientific Publications Posters for AASLD Long term survival of liver fibrosis after virological cure (SVR) in patients with chronic hepatitis C (CHC):
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Definitions, Risk Factors, and Workup
 REVIEW REVIEW Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Definitions, Risk Factors, and Workup Puneet Puri, M.B.B.S., M.D. and Arun J. Sanyal, M.B.B.S., M.D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is defined
REVIEW REVIEW Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Definitions, Risk Factors, and Workup Puneet Puri, M.B.B.S., M.D. and Arun J. Sanyal, M.B.B.S., M.D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is defined
Worldwide Causes of HCC
 Approach to HCV Treatment in Patients with HCC JORGE L. HERRERA, MD, MACG UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA COLLEGE OF MEDICINE Worldwide Causes of HCC 60% 50% 40% 54% 30% 20% 10% 31% 15% 0% Hepatitis B Hepatitis
Approach to HCV Treatment in Patients with HCC JORGE L. HERRERA, MD, MACG UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA COLLEGE OF MEDICINE Worldwide Causes of HCC 60% 50% 40% 54% 30% 20% 10% 31% 15% 0% Hepatitis B Hepatitis
National Horizon Scanning Centre. Transient elastography (FibroScan) for evaluating liver fibrosis. April 2008
 Transient elastography (FibroScan) for evaluating liver fibrosis April 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not
Transient elastography (FibroScan) for evaluating liver fibrosis April 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not
Management of autoimmune hepatitis. Pierre-Emmanuel RAUTOU Inserm U970, Paris Service d hépatologie, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy, France
 Management of autoimmune hepatitis Pierre-Emmanuel RAUTOU Inserm U970, PARCC@HEGP, Paris Service d hépatologie, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy, France Case 1 52 year-old woman, referred for liver blood tests
Management of autoimmune hepatitis Pierre-Emmanuel RAUTOU Inserm U970, PARCC@HEGP, Paris Service d hépatologie, Hôpital Beaujon, Clichy, France Case 1 52 year-old woman, referred for liver blood tests
NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE (NAFLD) AND NON- ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS (NASH) IN ASIAN-PACIFIC REGION
 SL 2-1 NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE (NAFLD) AND NON- ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS (NASH) IN ASIAN-PACIFIC REGION Mikio KAJIHARA 1,3, Yoshinori HORIE 2,3, Hiromasa ISHII 3 1 Tokyu Hospital, 2 Eiju General
SL 2-1 NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE (NAFLD) AND NON- ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS (NASH) IN ASIAN-PACIFIC REGION Mikio KAJIHARA 1,3, Yoshinori HORIE 2,3, Hiromasa ISHII 3 1 Tokyu Hospital, 2 Eiju General
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Both these authors contributed equally to this study. Liver International ISSN
 Liver International ISSN 1478-3223 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The combination of liver stiffness measurement and NAFLD fibrosis score improves the noninvasive diagnostic accuracy for severe liver fibrosis in patients
Liver International ISSN 1478-3223 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The combination of liver stiffness measurement and NAFLD fibrosis score improves the noninvasive diagnostic accuracy for severe liver fibrosis in patients
FDA Introductory Remarks Stephanie O. Omokaro, MD
 FDA Introductory Remarks Stephanie O. Omokaro, MD Division of Gastroenterology & Inborn Errors Products (DGIEP) Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Office of New Drugs Office of Drug Evaluation III
FDA Introductory Remarks Stephanie O. Omokaro, MD Division of Gastroenterology & Inborn Errors Products (DGIEP) Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Office of New Drugs Office of Drug Evaluation III
Noninvasive Diagnosis and Staging of Liver Disease. Naveen Gara, MD
 Noninvasive Diagnosis and Staging of Liver Disease Naveen Gara, MD Outline Brief overview of the anatomy of liver Liver-related lab tests Chronic liver disease progression Estimation of liver fibrosis
Noninvasive Diagnosis and Staging of Liver Disease Naveen Gara, MD Outline Brief overview of the anatomy of liver Liver-related lab tests Chronic liver disease progression Estimation of liver fibrosis
Original Article. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in severely obese individuals: The influence of bariatric surgery. Introduction
 364 Annals of Annals Hepatology of Hepatology 2008; 7(4): 7(4) October-December: 2008: 364-368 364-368 medigraphic Artemisa en línea Original Article Annals of Hepatology Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
364 Annals of Annals Hepatology of Hepatology 2008; 7(4): 7(4) October-December: 2008: 364-368 364-368 medigraphic Artemisa en línea Original Article Annals of Hepatology Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Worldwide Causes of HCC
 Approach to HCV Treatment in Patients with HCC Mark W. Russo, MD, MPH, FACG Carolinas HealthCare System Charlotte Worldwide Causes of HCC 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 54% 31% 15% Hepatitis B Hepatitis C
Approach to HCV Treatment in Patients with HCC Mark W. Russo, MD, MPH, FACG Carolinas HealthCare System Charlotte Worldwide Causes of HCC 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 54% 31% 15% Hepatitis B Hepatitis C
Steatotic liver disease
 Steatotic liver disease Fatty liver disease Prof. Dr. ANNE HOORENS Non-Neoplastic Liver Pathology December 8th 2018 Working Group of Digestive Pathology Belgian Society of Pathology OUTLINE NAFLD = Non-Alcoholic
Steatotic liver disease Fatty liver disease Prof. Dr. ANNE HOORENS Non-Neoplastic Liver Pathology December 8th 2018 Working Group of Digestive Pathology Belgian Society of Pathology OUTLINE NAFLD = Non-Alcoholic
Practical Diagnosis and Staging of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Narrative Review
 Practical Diagnosis and Staging of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Narrative Review Authors: Jennifer Gallacher, 1 *Stuart McPherson 1,2 1. Liver Unit, Newcastle Upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Trust, Freeman
Practical Diagnosis and Staging of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Narrative Review Authors: Jennifer Gallacher, 1 *Stuart McPherson 1,2 1. Liver Unit, Newcastle Upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Trust, Freeman
Abstract. Introduction
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, September: 185-194, 2014 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Performance of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging in Staging Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis in
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, September: 185-194, 2014 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Performance of Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging in Staging Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis in
NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE:
 NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE: ROLE OF THE PRIMARY PROVIDER Archita P. Desai, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Arizona 25 th Annual Southwestern Conference on Medicine Outline Pathophysiology
NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE: ROLE OF THE PRIMARY PROVIDER Archita P. Desai, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Arizona 25 th Annual Southwestern Conference on Medicine Outline Pathophysiology
Original Article. Significance of Hepatic Steatosis in Chronic Hepatitis B Infection INTRODUCTION
 Original Article Bhanthumkomol P, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2013 Vol. 14 No. 1 Jan. - Apr. 2013 29 Bhanthumkomol P 1 Charatcharoenwitthaya P 1 Pongpaiboon A 2 ABSTRACT Background: Significance of liver
Original Article Bhanthumkomol P, et al. THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2013 Vol. 14 No. 1 Jan. - Apr. 2013 29 Bhanthumkomol P 1 Charatcharoenwitthaya P 1 Pongpaiboon A 2 ABSTRACT Background: Significance of liver
Bio Predictive. FibroTest/FibroSure Scientific Publications Posters for AASLD 2013 #999! FibroTest HBV. Sun, Nov 03 8:00 AM AASLD
 AASLD #999 HBV Sun, Nov 03 FibroTest/FibroSure Scientific Publications Posters for AASLD 2-years impact of entecavir (ETV) on liver fibrosis and activity as assessed by the non-invasive methods of FibroTest-ActiTest
AASLD #999 HBV Sun, Nov 03 FibroTest/FibroSure Scientific Publications Posters for AASLD 2-years impact of entecavir (ETV) on liver fibrosis and activity as assessed by the non-invasive methods of FibroTest-ActiTest
Effect of lifetime alcohol consumption on the histological severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
 Liver International ISSN 1478-3223 METABOLIC AND STEATOHEPATITIS Effect of lifetime alcohol consumption on the histological severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Hellan K. Kwon 1, Joel K. Greenson
Liver International ISSN 1478-3223 METABOLIC AND STEATOHEPATITIS Effect of lifetime alcohol consumption on the histological severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Hellan K. Kwon 1, Joel K. Greenson
Assessment of Liver Stiffness by Transient Elastography in Diabetics with Fatty Liver A Single Center Cross Sectional observational Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. IV (June. 2017), PP 49-53 www.iosrjournals.org Assessment of Liver Stiffness by Transient
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. IV (June. 2017), PP 49-53 www.iosrjournals.org Assessment of Liver Stiffness by Transient
How to manage patients with NASH? Dr Raluca Pais Institute of Cardiometabolisme and Nutrition (ICAN) Hôpital Pitie Salpetrière, Paris
 How to manage patients with NASH? Dr Raluca Pais Institute of Cardiometabolisme and Nutrition (ICAN) Hôpital Pitie Salpetrière, Paris CLINICAL CASE 1996. 54 years old female Department of Primary CV Prevention
How to manage patients with NASH? Dr Raluca Pais Institute of Cardiometabolisme and Nutrition (ICAN) Hôpital Pitie Salpetrière, Paris CLINICAL CASE 1996. 54 years old female Department of Primary CV Prevention
NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE (NAFLD) NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS (NASH) ADDRESSING A GROWING SILENT EPIDEMIC
 NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE () & NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS () ADDRESSING A GROWING SILENT EPIDEMIC PREVALENCE OF / USA Prevalence in Middle Age Patients San Antonio, Texas (Williams et al., Gastroenterology
NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE () & NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS () ADDRESSING A GROWING SILENT EPIDEMIC PREVALENCE OF / USA Prevalence in Middle Age Patients San Antonio, Texas (Williams et al., Gastroenterology
